Patents
Literature
41results about How to "Increase resistance to poisoning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
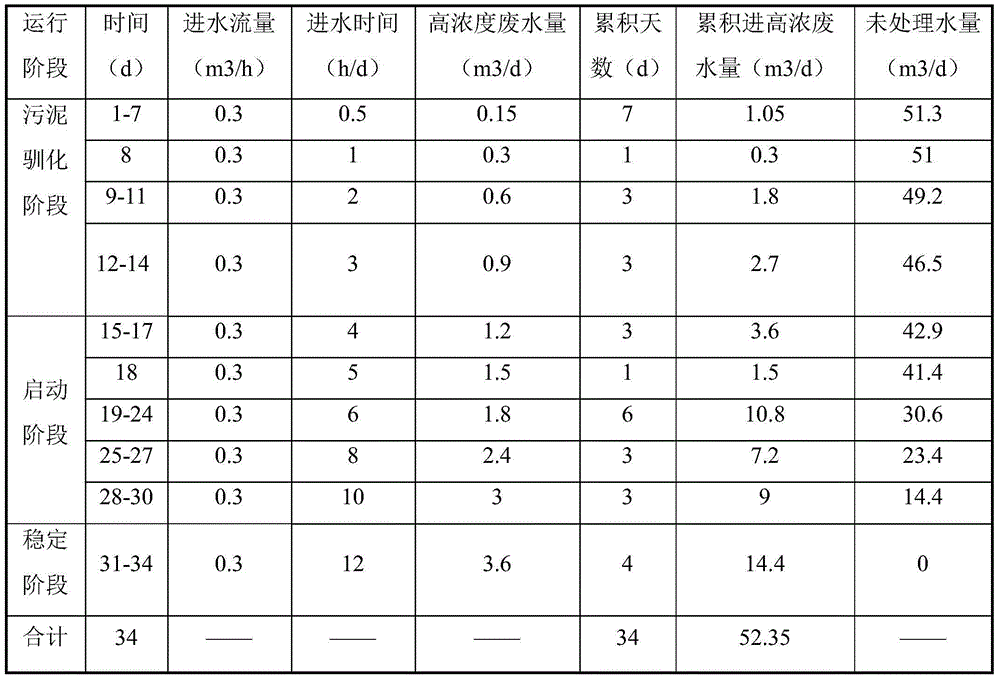
Organic waste water treatment process
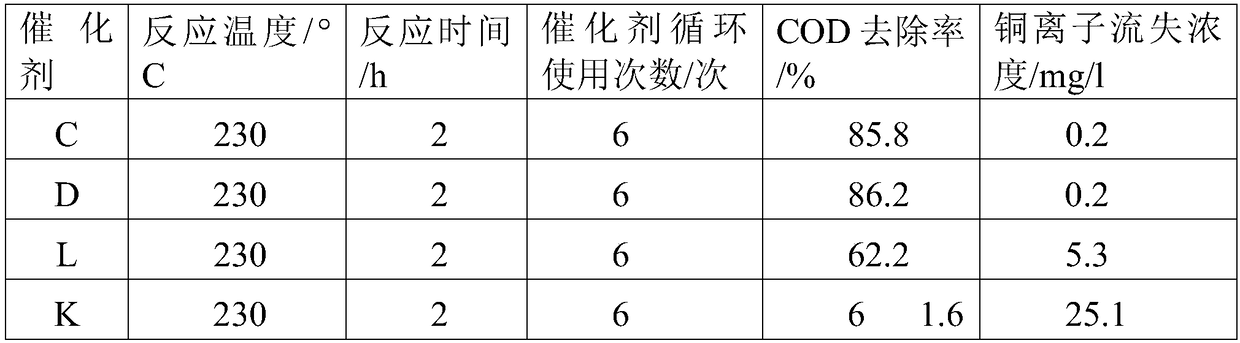
InactiveCN1631818AAvoid toxicityHigh removal rateMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh densityElectrolysis
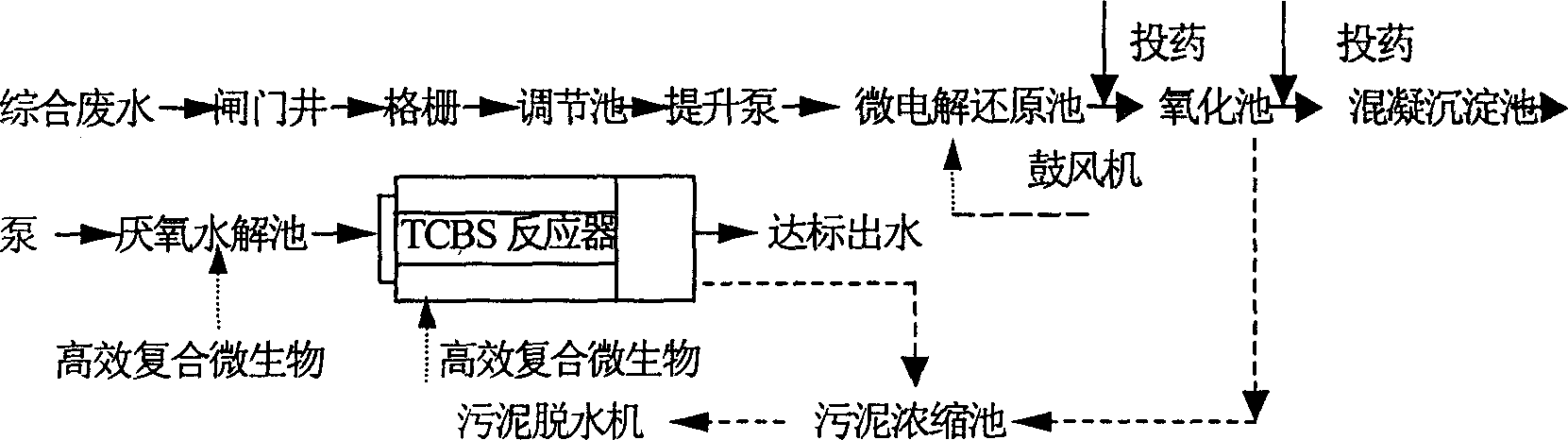
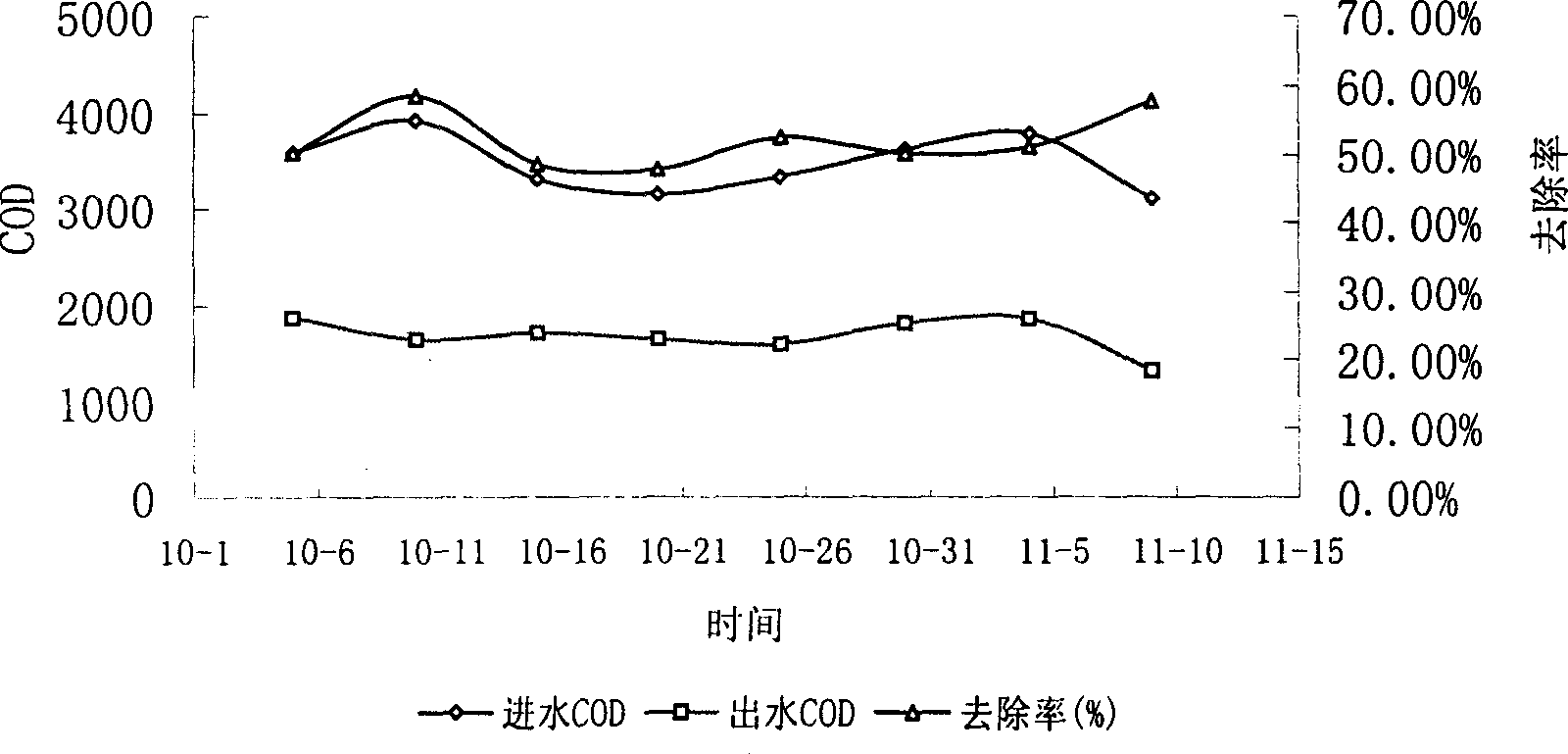
Disclosed is a technique for processing organic waste water, including the following steps: (a) preprocession: pour the waste water into the micro electrolytic reducing pool where the iron-carbon micro electrolytic reaction occurs under the agtatering effect, add hydrogen peroxide into it to have. Fento oxidation, then the water enters into coagulation pool into which add NaOH and PAM; (b) anaerobe hydrolysis oxidation procession: power the organic waste water preprocessed into high effective anaerobe hydrolysis oxidation pool in which add into the TCBS reactor in which add into high effective compound microbe, making the water mix with the flowing-back mud with high density after denitrification. The invention can increase the biochemical of organic waste water, strengthen its resistance to poison and impact as well as the biological denitrification funcation, and making the waste water reach the national environment protection requirement by reducing the polluting load by steps.
Owner:何义亮 +1
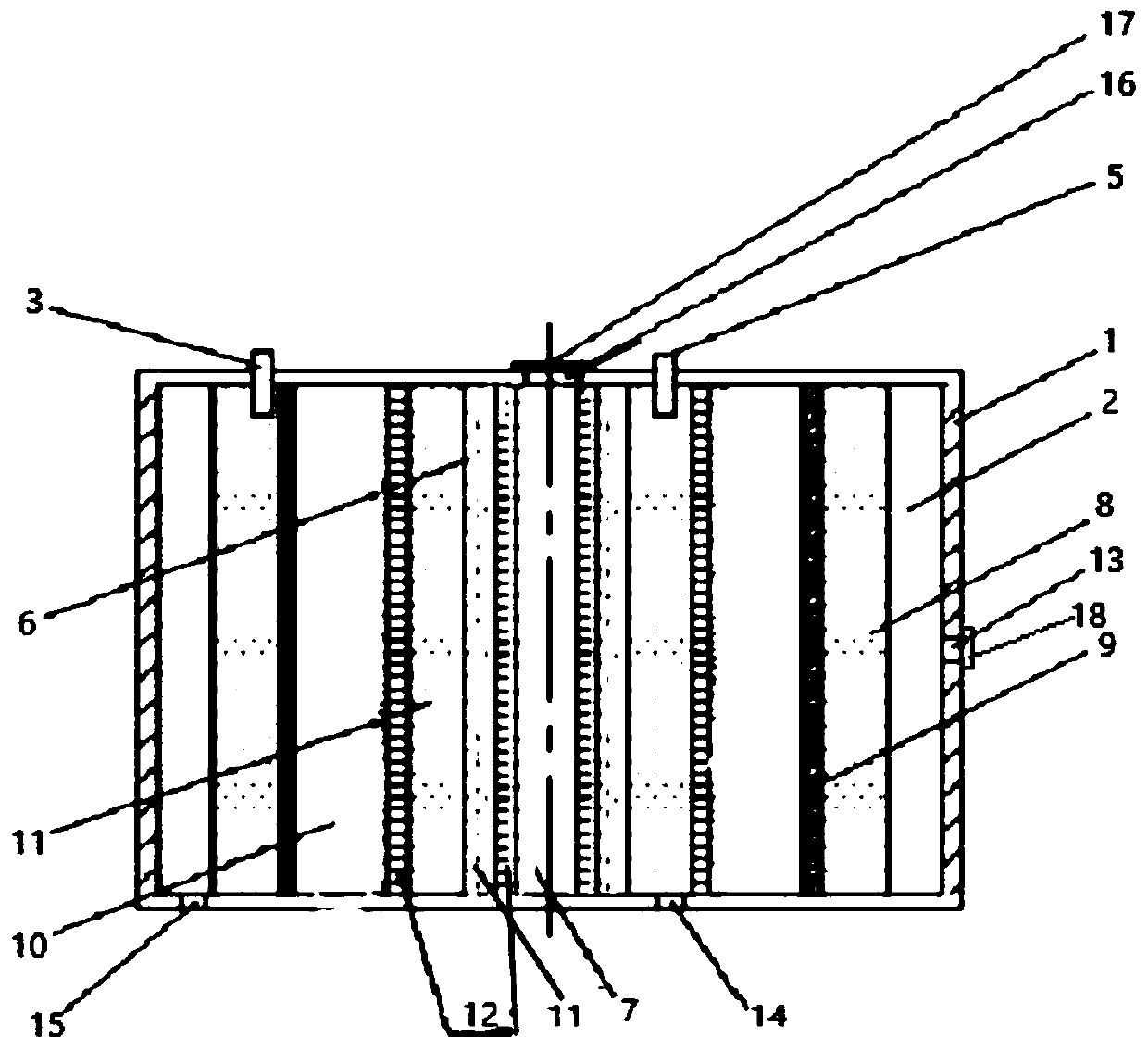
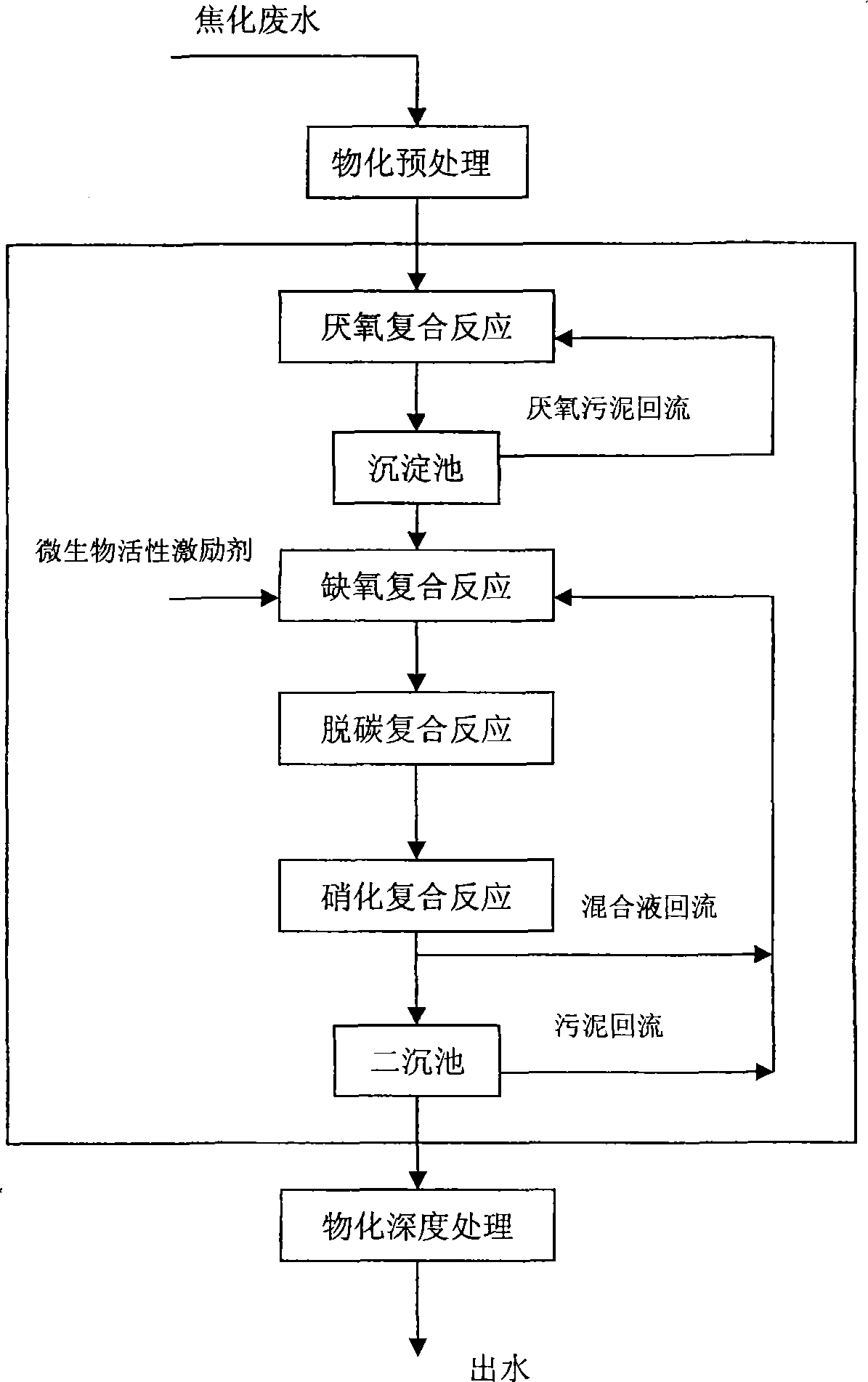
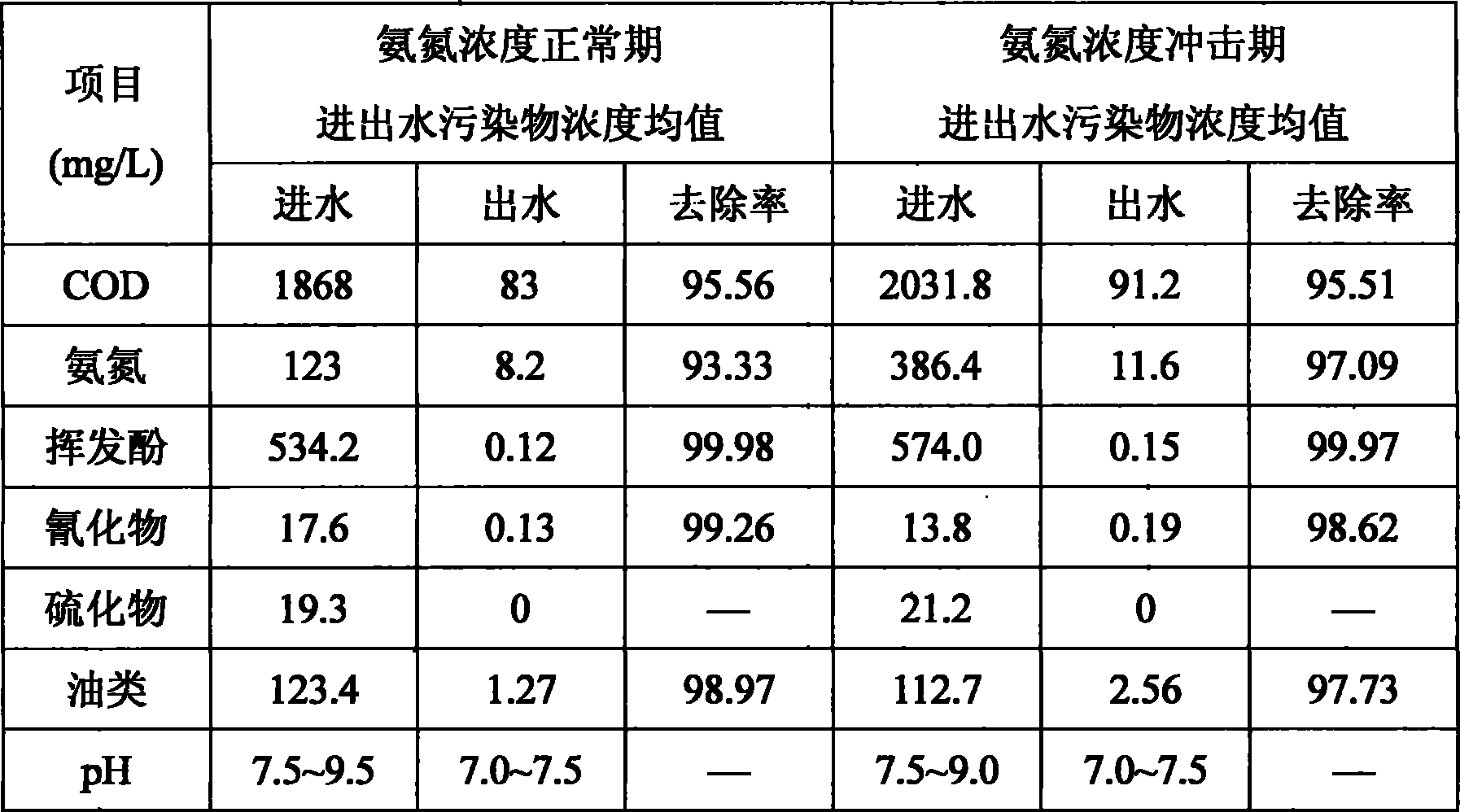
Impact-resistant multiplication combined type coking waste water treatment process
InactiveCN101113065AOptimize material compositionImprove biodegradabilityTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater treatmentWater quality
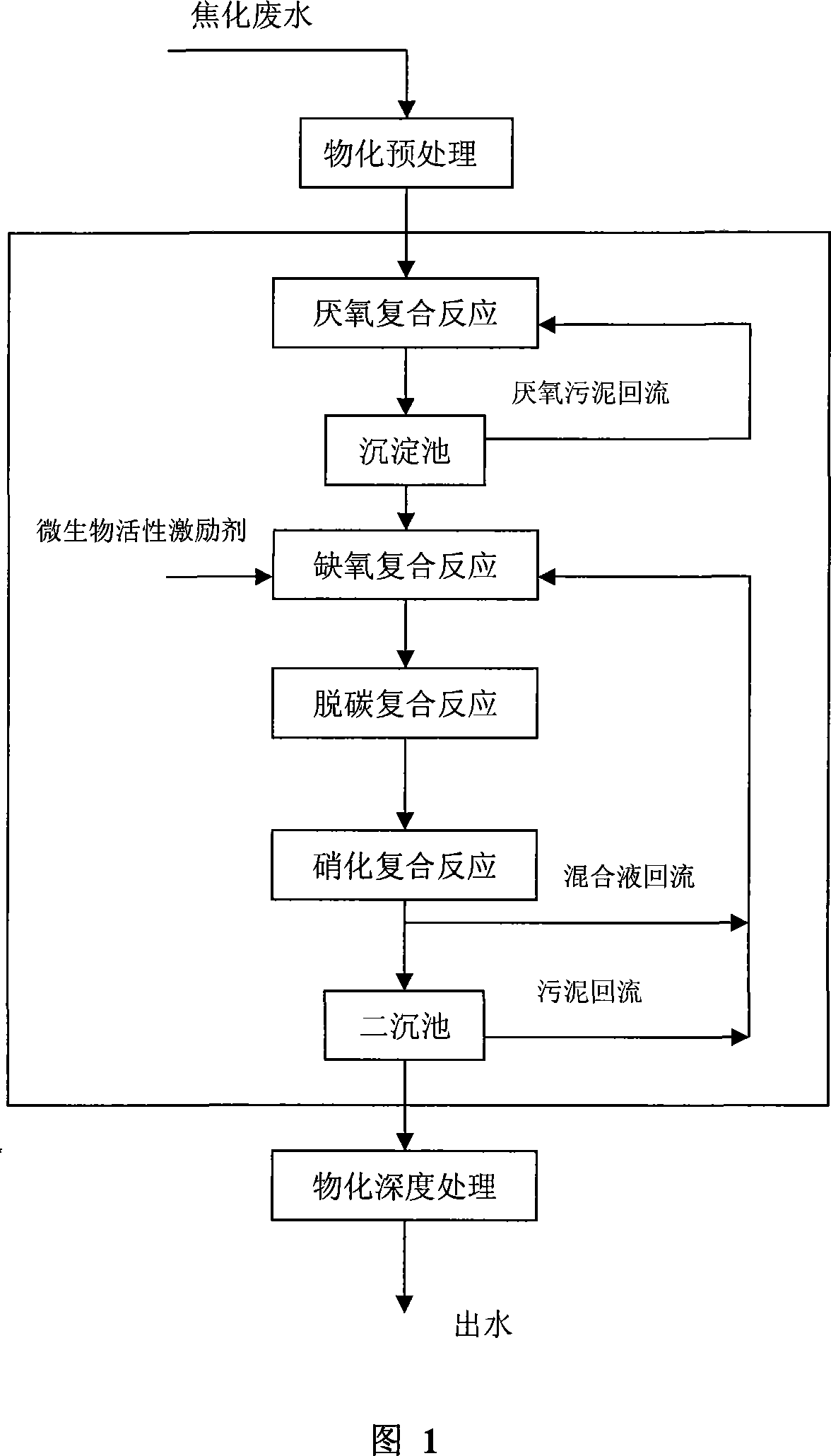
An anti-impact multiplying combination coking wastewater treatment technique relates to a treatment method of coking wastewater. The coking wastewater is first qualified by a physical-chemical pretreatment to improve biodegradable property of wastewater; the composite technology of a biological carrier of active sludge is adopted to do anaerobic / hypoxia / aerobic decarbonization / aerobic nitrification biochemical combination treatment; suspended or floating folding ball-shaped fillings are arranged in biochemical reactors and when micro organism traits are abnormal or a great amount of foams existing in the reactor, micro organism active incentive agents are added to the reactor in interval to improve active sludge traits and organism film quantity; finally the water is treated by a physical-chemical advanced treatment to reach a top grade standard. The invention not only strengthens the removal of COD, ammonia-nitrogen, volatile phenol and other pollutants in the coking wastewater by biochemical treatment but also resists serious water quality impact and has the advantages of quick system startup, less foams in an aeration tank, small occupying space, low operation cost and stable and effective treatment to coking wastewater.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
Method for processing nitrobenzene and aniline waste water
InactiveCN101279808AImproved poison resistanceThe treatment effect is stableWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAluminiumToxin
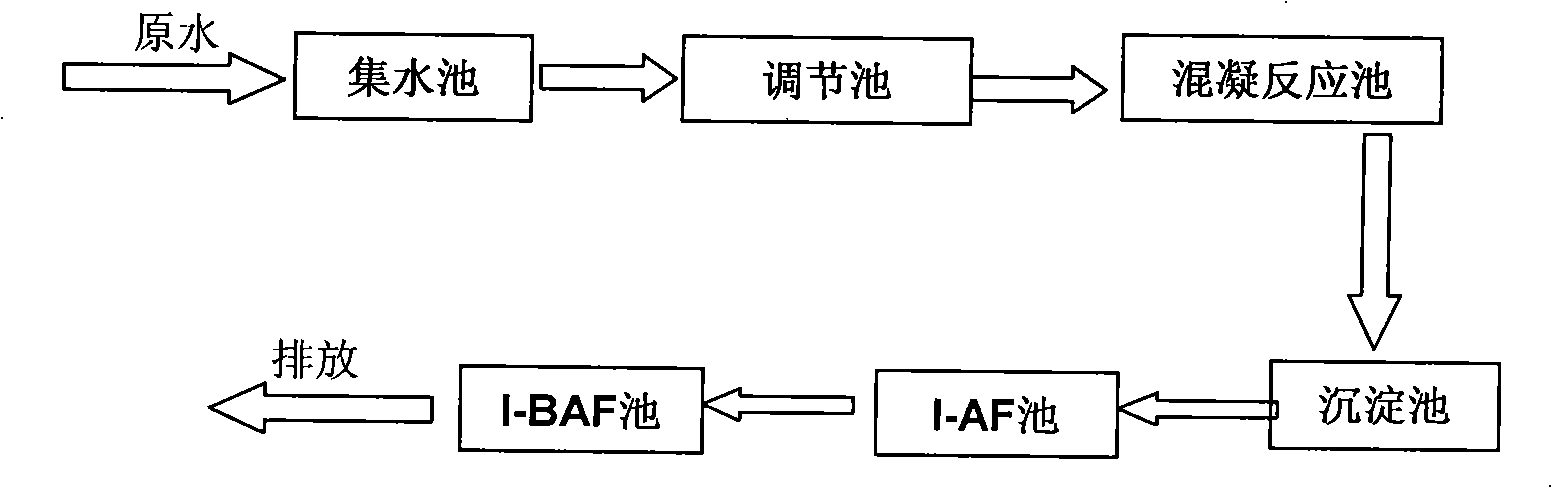
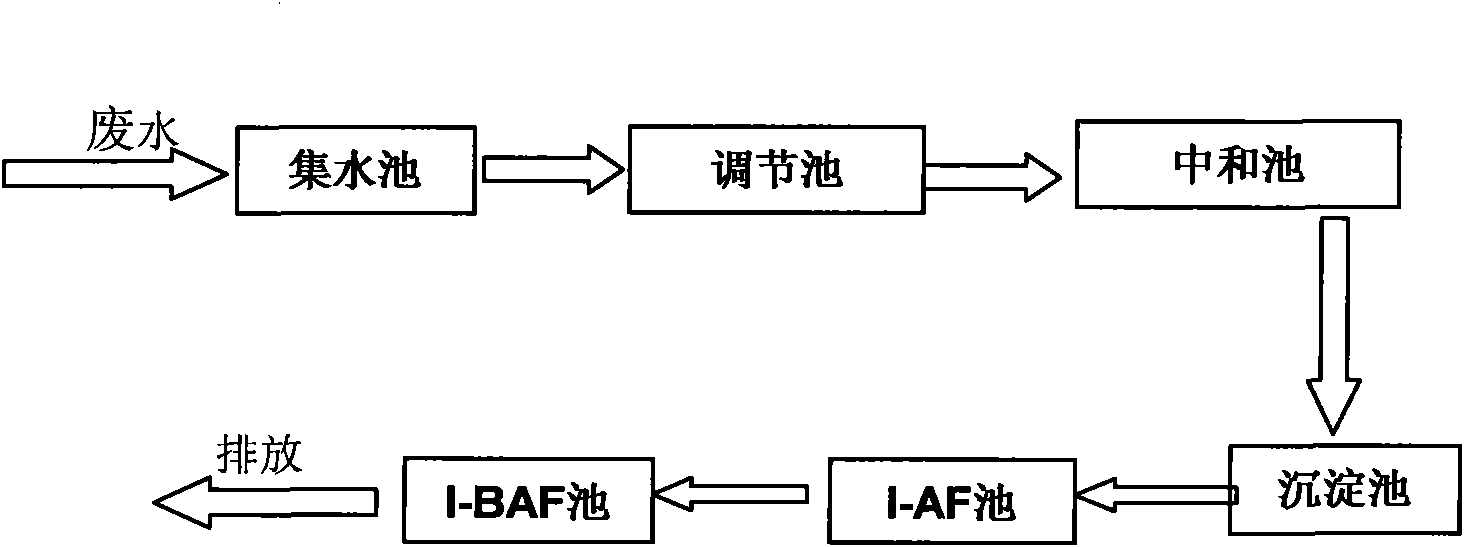
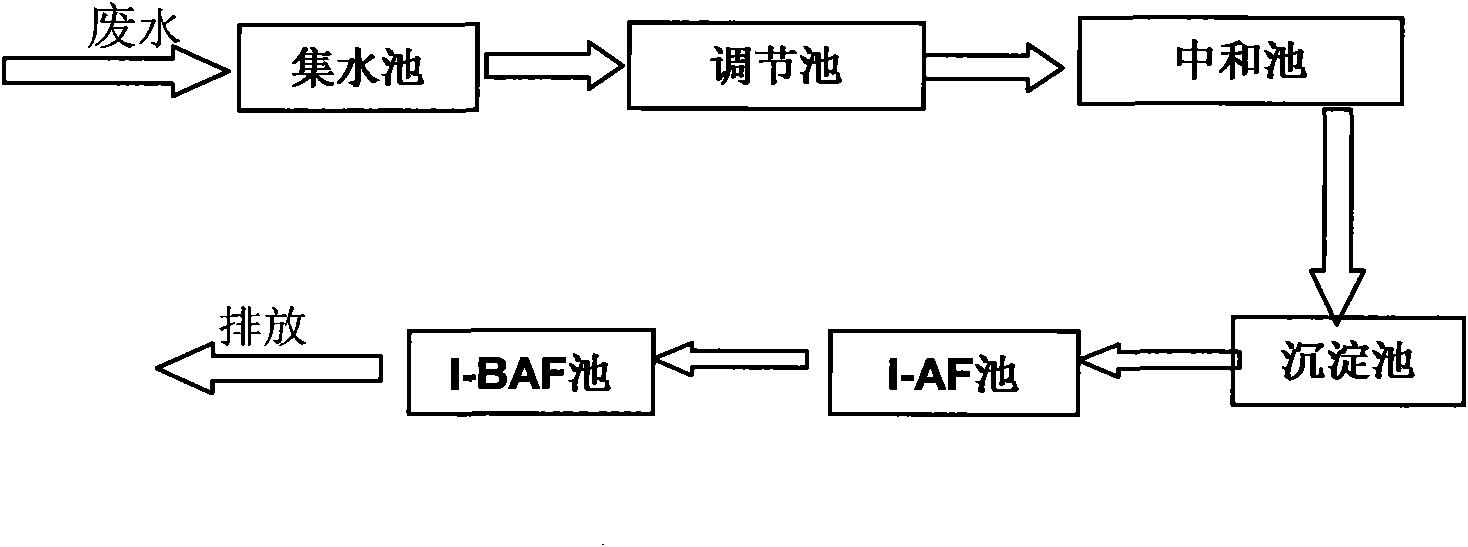
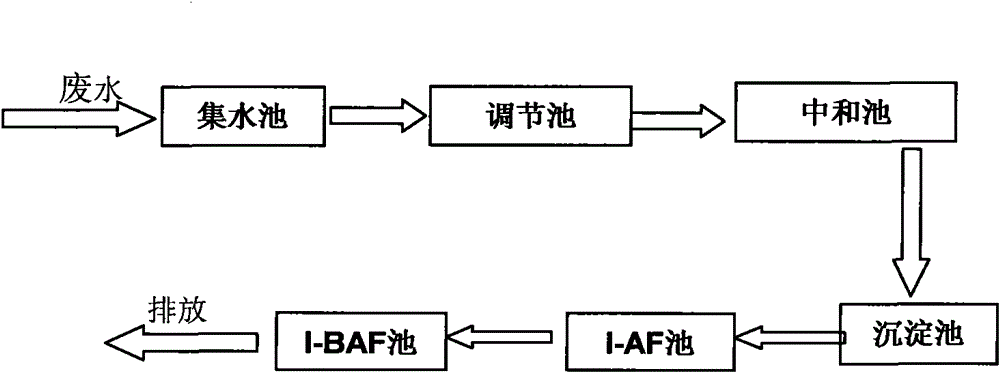
The invention provides a method for treating nitrobenzene and aniline waste water. The invention treats waste water mainly through immobilized microorganisms - an anaerobic biofilter (I-AF) and immobilized microorganisms - a biological aerated filter (I-BAF); wherein: the waste water is homogenized through a regulating tank and then enters a sedimentation tank to remove suspended substances (SS) in the waste water by putting into polymeric iron or polymeric aluminum for coagulation reaction; and the yielding water reach the up-to-standard discharge after entering a three-grade I-AF reactor and a four-grade I-BAF reactor for the further treatment. For detailed method and steps, please see the description. The method has advantages that the biological treatment improves the toxin immunity of microorganisms by adopting the immobilized microorganism technique, thereby realizing the high efficient biologic removal to poisonous harmful substances such as high concentration nitrobenzene and aniline, reducing the treatment costs and realizing the up-to-standard discharge of waste water. The purposes of the invention are applied to the treatment of wastewater containing nitrobenzene and aniline, as well as the treatment to high concentration organic waste water and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for treating 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene waste water and application thereof
ActiveCN101830606AAvoid inhibitionAvoid side effectsWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiotechnologyHazardous substance
The invention provides a method for treating 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT for short) waste water. In the invention, waste water is mainly treated by immobilized microorganisms, an anaerobic biological filter (I-AF) and immobilized microorganisms and a biological aerated filter (I-BAF), wherein the waste water enters a collecting tank, is lifted by a pump to enter a regulating tank and enters a setting tank after being homogenized and neutralized by the regulating tank so as to remove suspended substances (SS) in the waste water; the effluent is discharged after reaching standards after enteringthree-stage I-AF and five-stage I-BAF for further treatment. The specific steps of the method are shown in the specification. The invention has the advantages that biological treatment adopts an immobilized microorganism technology, which improves the poison resistance of the microorganisms, realizes the high-efficiency removal on toxic and harmful substances of nitrobenzene and the like, reducesthe treatment cost and realizes the standard-reaching discharge of the waste water. The application of the invention is not only suitable for treating the TNT waste water but also is applied to treating nitrobenzene and aniline contained pollutants and organic waste water thereof.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Catalyst for synthesis of methyl methacrylate by formaldehyde and methyl propionate and preparation method of catalyst
ActiveCN102962062ALarge specific surface areaImprove physicsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a catalyst for synthesis of methyl methacrylate by formaldehyde and methyl propionate and a preparation method of the catalyst. The catalyst mainly comprises a main active component, an activated auxiliary and a carrier, wherein the main active component is Cs, the activated auxiliary is selected from one or more of Sb, Nb and Ag, and the carrier is a nanometer SiO2 / Al2O3-ZrO2 composite carrier; and metered by oxides and according to mass percentage, the main active component Cs accounts for 5%-20%, the activated auxiliary accounts for 1%-5%, and the balance is the carrier. Simultaneously, the invention discloses a preparation method of the catalyst. The catalyst provided by the invention is good in activity, selectivity and stability, simple in manufacture technology, suitable for large-scale industrialized application and environment-friendly.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
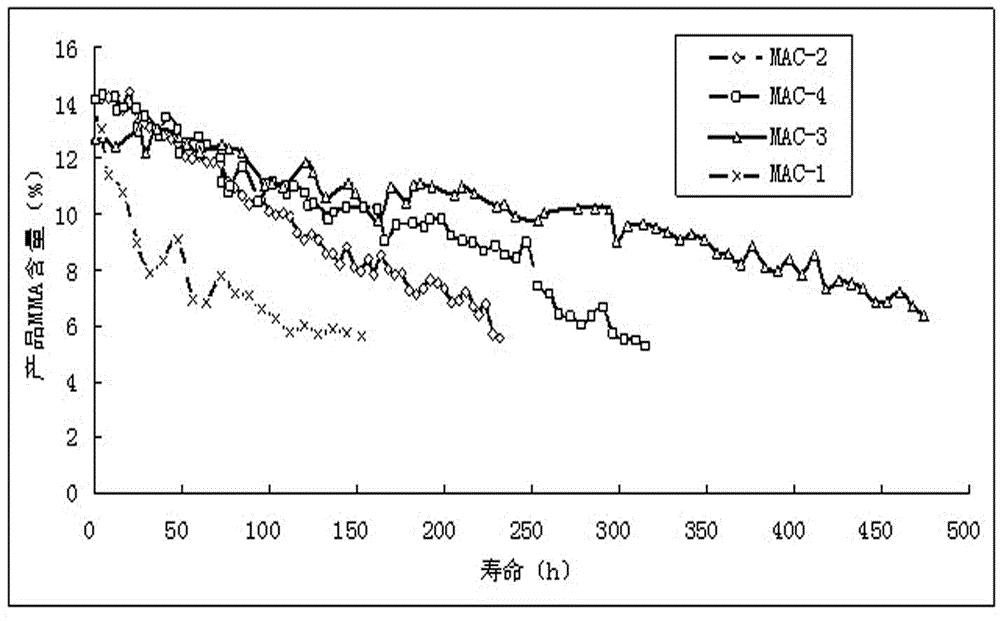
Water resistant catalyst for aldol condensation as well as preparation method and application thereof
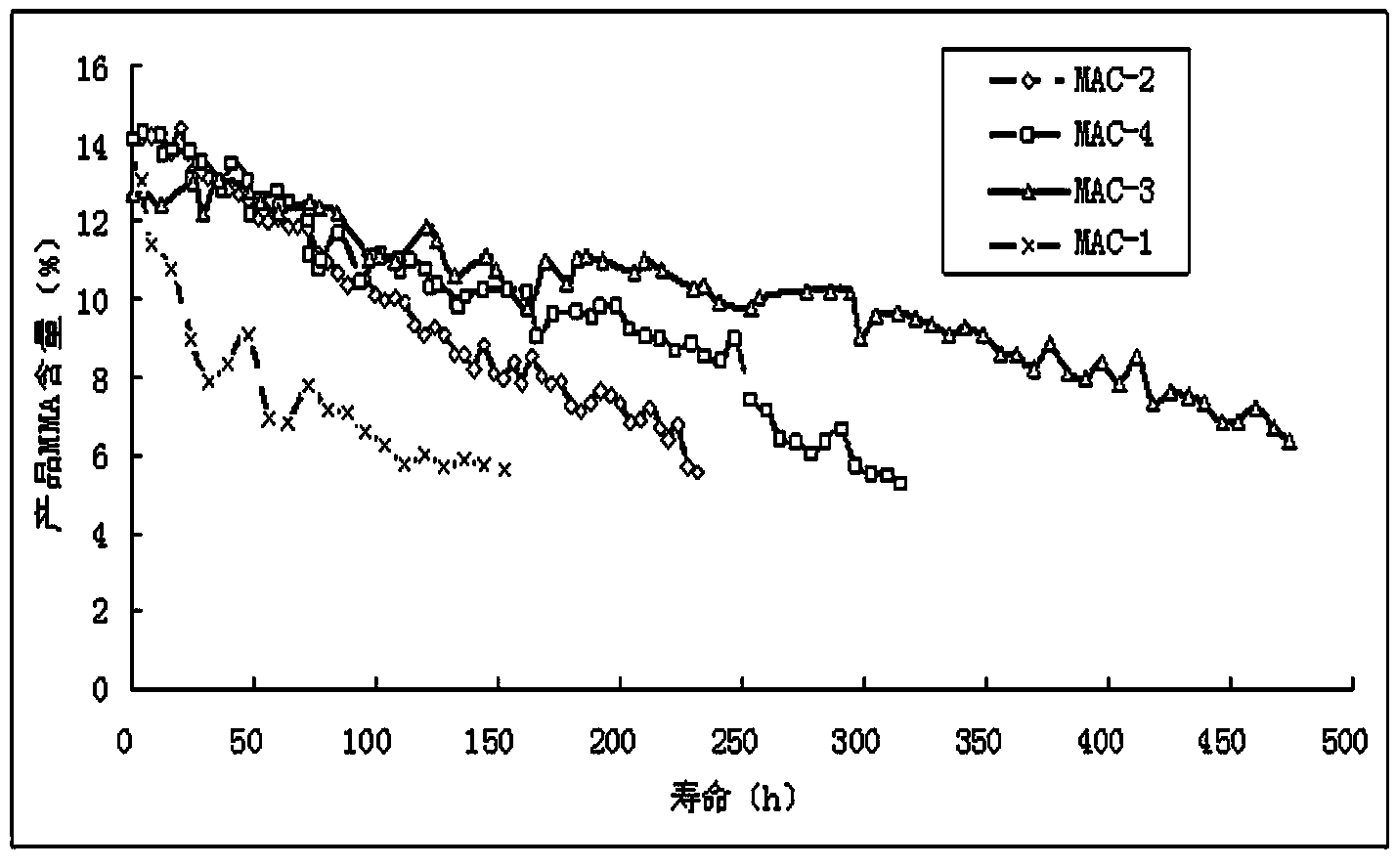
ActiveCN103551148AGood physical and mechanical propertiesIncrease resistance to poisoningOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPtru catalystPropanoic acid
The invention discloses a water resistant catalyst for aldol condensation. The water resistant catalyst comprises a main active ingredient, an active agent and a carrier, wherein the main active ingredient is one or more selected from oxides or salts of Cs; the active agent is one or more selected from oxides or salts of Sb, Nb, Ag, Al and Zr; the carrier comprises SiO2 and a carrier aid; the carrier aid is one or more selected from Al2O3, ZrO2, diatomite and kaolin; the SiO2 is hydrophobic nano SiO2; or (2) the catalyst is subjected to water-resistant treatment. The water resistant catalyst is used for aldol condensation, has the characteristics of high activity, high selectivity and long service life, is especially used for synthesizing methyl methacrylate through formaldehyde and methyl propionate. With calculation of methyl propionate, the selectivity of methyl methacrylate is 94 percent, and the single service life of the catalyst is over 400 hours. The catalyst is simple in preparation method and is suitable for industrial application.
Owner:HAO HUA CHENGDU TECH
Method of treating high-concentration metaformaldehyde waste water into reuse water
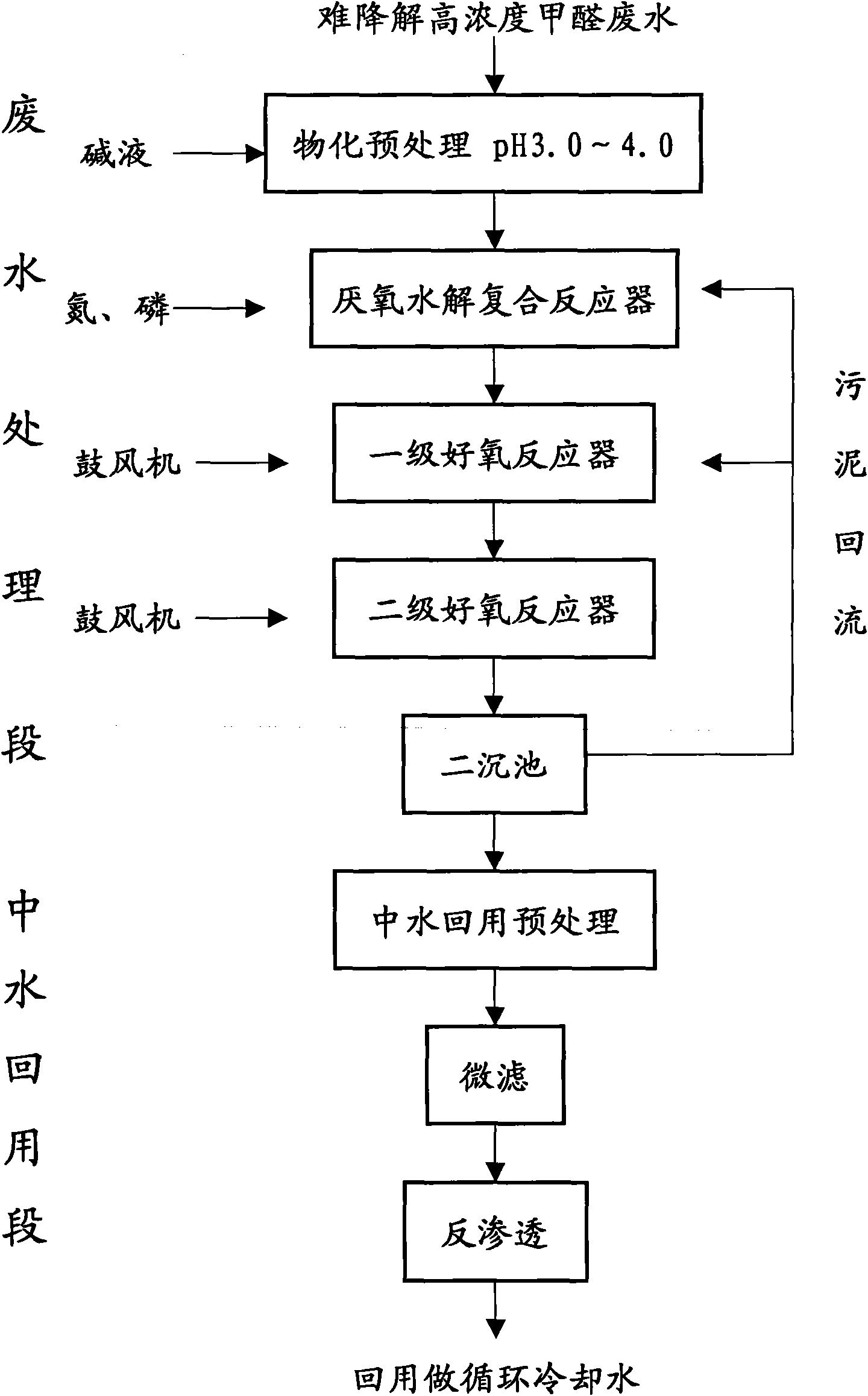
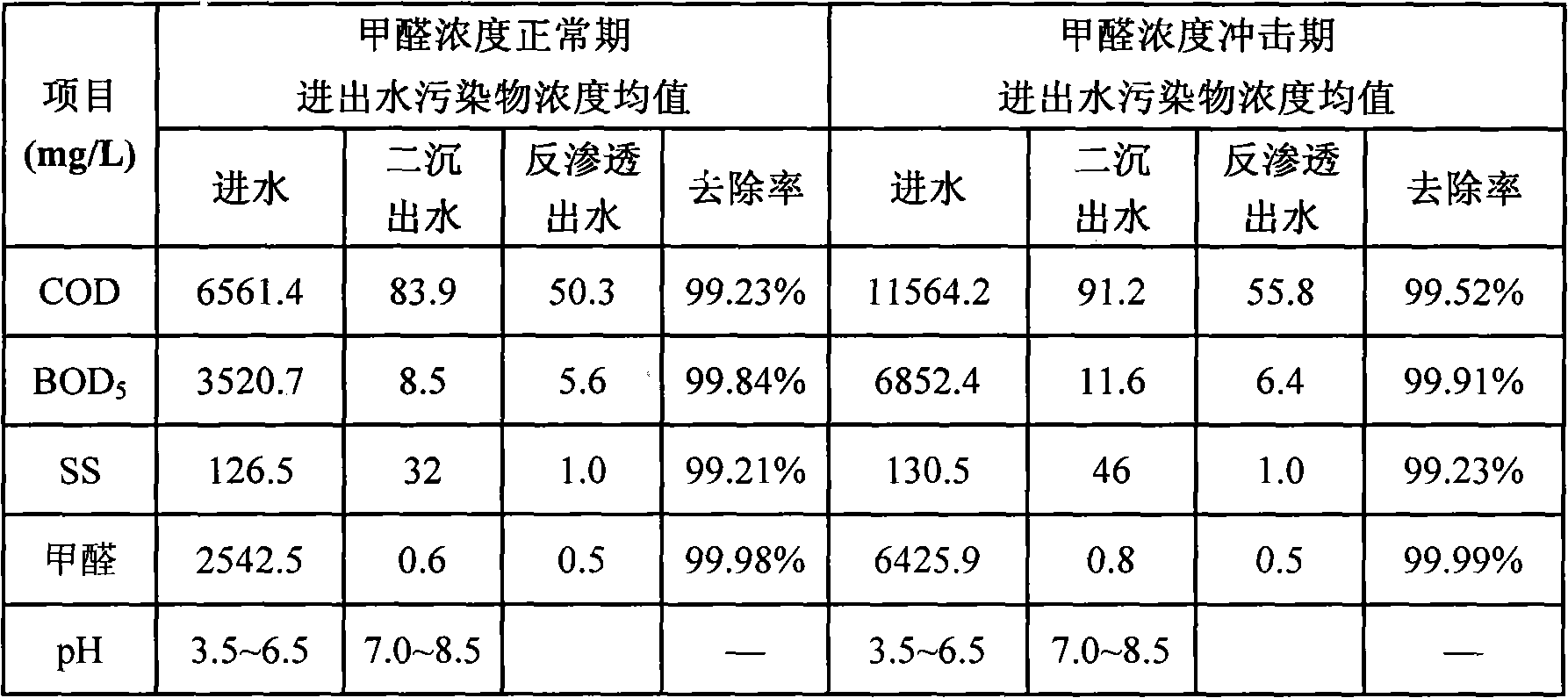
InactiveCN101671098AIncrease the amount of waterImprove impact resistanceGeneral water supply conservationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisActivated sludgeHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method of treating high-concentration metaformaldehyde waste water into reuse water, relating to a treatment technology of high-concentration metaformaldehyde waste water. The pH of metaformaldehyde waste water of which the formaldehyde content is 4000mg / L into 3.0-4.0, then metaformaldehyde waste water is sent into an anaerobic hydrolysis composite reactor combining activated sludge with biomembrane and an aerobic composite reactor; at last, a double-membrane method is adopted to treat to ensure that effluent reaches the standard of urban wastewater recycling industrial water quality, thus serving as recirculated cooling water. The invention strengthens removal of high-concentration formaldehyde, COD, trioxymethylene, divinylene oxide and other pollutants in high-concentration metaformaldehyde waste water by biological treatment, can effectively resist impact from violent water yield and water quality, and has the advantages of high system starting speed, small foam of the aerobic composite reactor, low operation cost, stable and effective treatment and zero discharge of waste water.
Owner:上海中耀环保实业有限公司
Graphene/molecular sieve/metal oxide composite catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106475132AHas catalytic propertiesHas electrocatalytic propertiesElectrolysis componentsMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveCatalytic oxidation
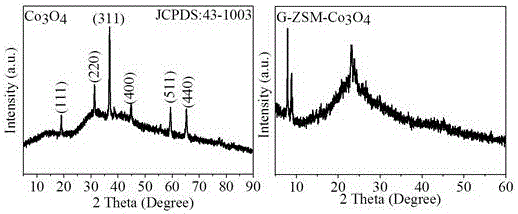
The invention discloses a graphene / molecular sieve / metal oxide composite catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst comprises graphene, molecular sieve and metal oxide. The weight ratio of the three materials is 3-38% of the graphene, 40-91% of molecular sieve and 4-37% of metal oxide. The prepared composite material has quasi -2D laminated structure. The metal oxide particle size is 10-20 nanometers. The preparation method comprises the steps of 1, mixing the graphene, silicon source, aluminum source and surface active agent, separating the part containing graphene, conducting crystallization, at last conducting purification and removing the surface active agent to acquire the graphene / molecular sieve composite material, 2, loading the metal oxide on the graphene / molecular sieve. The three element composite material can be used for the methanol electro-catalysis and oxidation, oxygen reduction (ORR), OER, CO2 electro-catalysis reduction, and exert very good catalytic activity. The stability and the poison resistance are enormously elevated, thus having promising application prospect.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
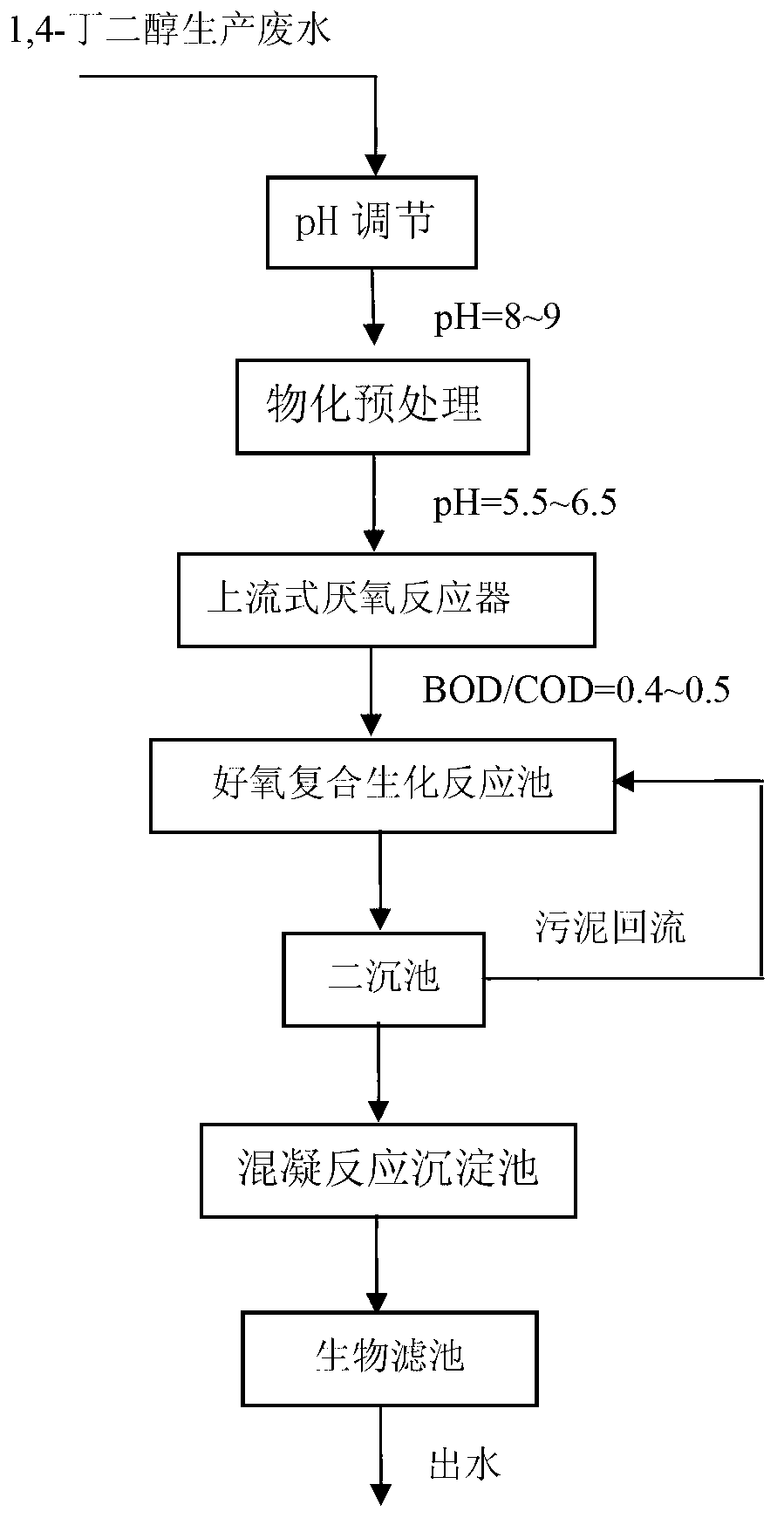
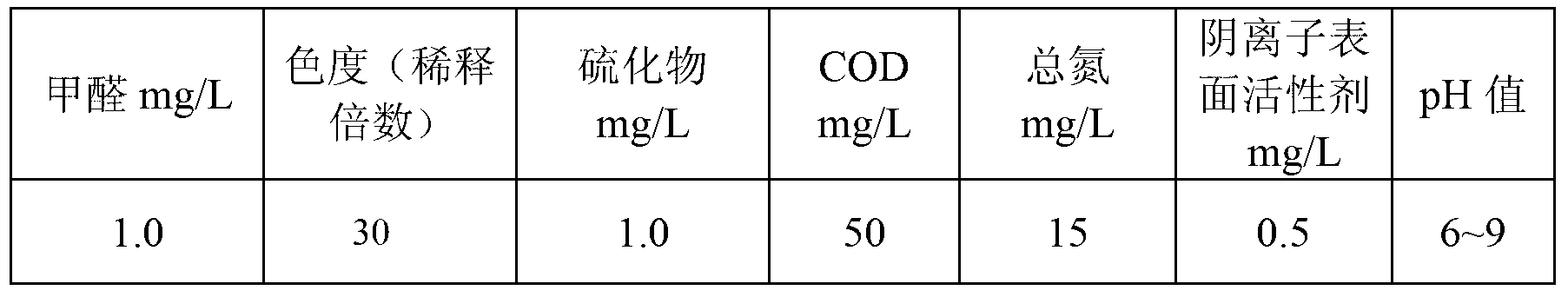
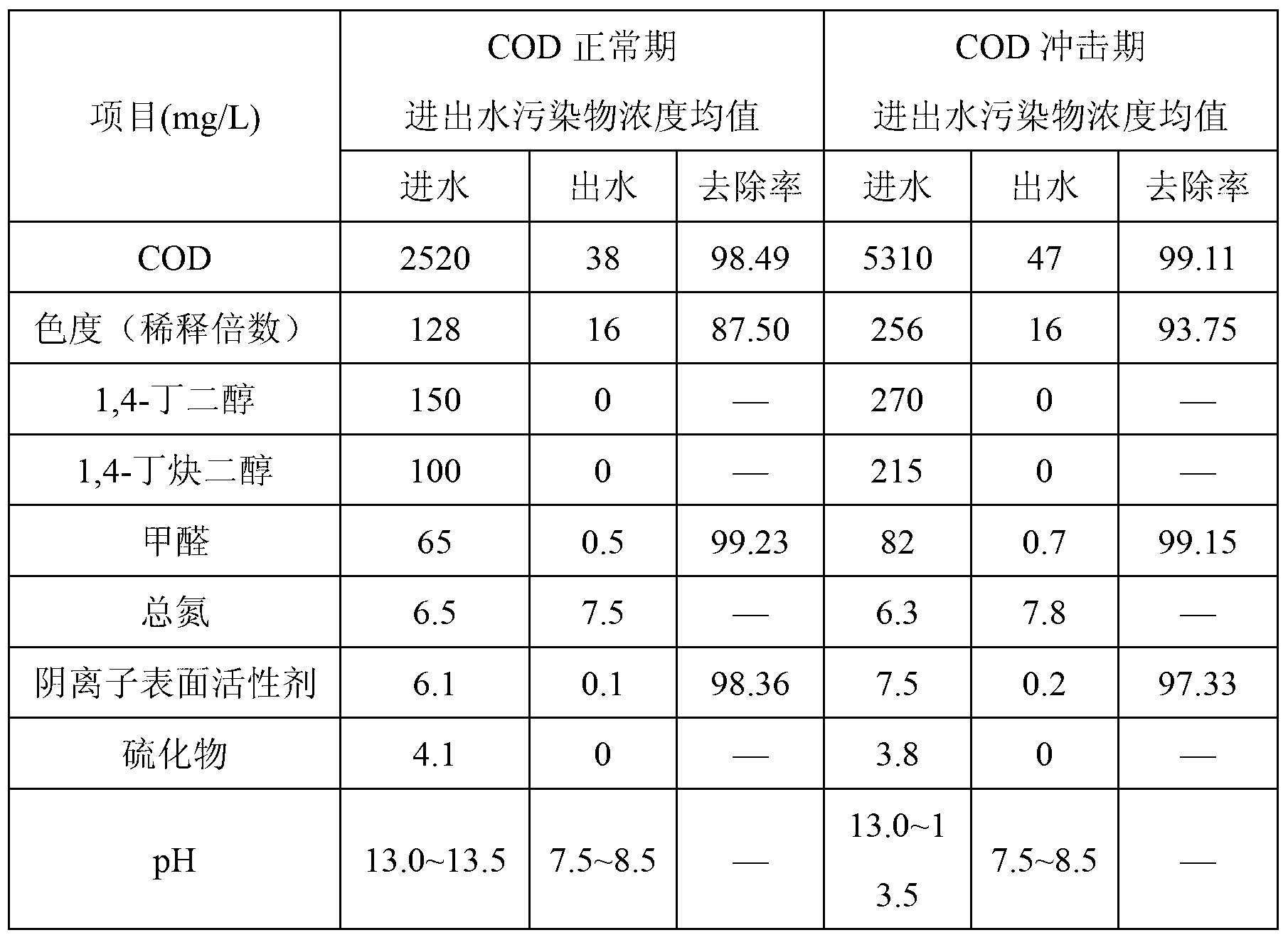
Combined treatment method of 1,4-butanediol production wastewater
InactiveCN103253827AReduce acidityWeak acidMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterHigh concentrationChemical oxygen demand
The invention relates to a combined treatment method of 1,4-butanediol production wastewater, which comprises the following steps: carrying out physical and chemical pretreatment on wastewater firstly so as to obtain pre-optimized wastewater; improving the biodegradability of the wastewater and further reducing the COD (chemical oxygen demand) concentration of the wastewater through an upflow anaerobic reactor and an aerobic combined biochemical reaction tank; and after the muddy water separation of the wastewater is realized through a secondary sedimentation tank, sequentially feeding the wastewater into a coagu-flocculation reaction settling pond and a biological filter, carrying out deep treatment on the wastewater, removing substances such as tiny suspended solids and colloids and the like in the wastewater through coagu-flocculation reaction and precipitation, and enabling discharged water to meet the requirements of one-class A standards in the Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant (GB18918-2002) through the synergistic effect of adsorption and biodegradation of the biological filter. The method disclosed by the invention not only has a stable removal effect on COD in 1,4-butanediol production wastewater, but also can effectively resist violent water impacts; and the method has the characteristics of rapid system startup and the like. The method disclosed by the invention also can be applied to the treatment of other high-concentration toxic degradation-resistant organic wastewater with a water quality similar to that of 1,4-butanediol production wastewater.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
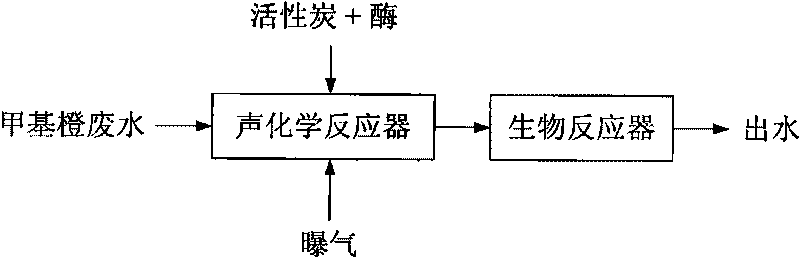
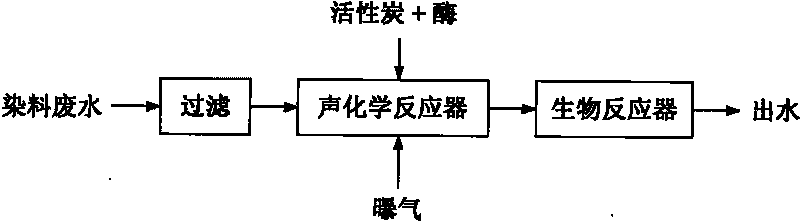
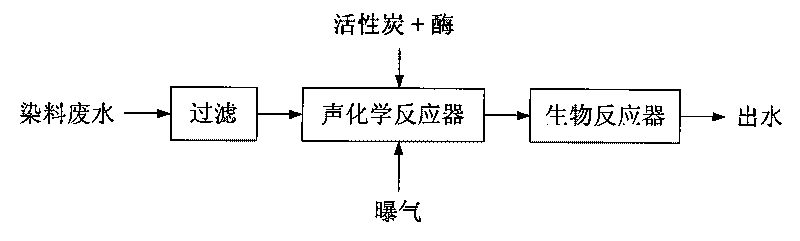
Method for treating dye wastewater with high concentration by using technology combining ultrasound wave with enzyme
InactiveCN101734803APromote degradationEfficient and stable degradation abilityWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsWater/sewage treatment by sorptionHigh concentrationPretreatment method
The invention relates to a method for treating dye wastewater with high concentration by using a technology combining ultrasound wave with enzyme, comprising the following steps of: feeding the treated active carbon in a sonochemical reactor; attaching enzyme to the surface of the active carbon and holes; filtering and removing large-particle suspended substances in the dye wastewater; introducing the large-particle suspended substances into the sonochemical reactor; under the aeration condition, radiating the fluidized state active carbon to which the enzyme is attached by using ultrasound wave with the frequency 40kHz and the power of 40W; generating a hydroxyl free radical with extremely-strong oxidation capacity and adsorption and decolorization reaction of the active carbon by using the coupling action of ultrasound-enzyme technology, thereby improving the biochemical property of the wastewater; and enabling the treated dye wastewater flowing out of the sonochemical reactor and then entering a bioreactor for further degrading. The invention has remarkable decolorization effect of the wastewater and greatly improves the biochemical property when being used as a pretreatment method of the dye wastewater with high concentration.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Nitrogen-doped graphene hollow microsphere (NGHM) preparation method
InactiveCN105236399AUnique hollow structureImprove conductivityCell electrodesDoped graphenePtru catalyst
The invention relates to a nitrogen-doped graphene hollow microsphere (NGHM) preparation method. Polystyrene microspheres as templates, graphene as a carbon source and melamine as a nitrogen source are calcined to form NGHM. The prepared NGHM has good oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalytic performances. Compared with the commercial Pt / C catalyst, the NGHM has slightly lower OPP onset potential and the same ORR limiting current density. Compared with Pt / C, the NGHM has higher stability and toxicity resistance and has a lower cost. The prepared NGHM can completely replace the commercial Pt / C.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Efficient and deep treatment process for high-concentration waste water in natural gas industry
ActiveCN102923910AReduce the amount of sedimentGood precipitation effectMultistage water/sewage treatmentPre treatmentSewage
The invention discloses an efficient and deep treatment process for high-concentration waste water in a natural gas industry. High-concentration industrial wastewater is subjected to physicochemical pretreatment to improve the biodegradability of the wastewater, and toxic and harmful substances in the wastewater are eliminated simultaneously, medium and low-concentration gas-field wastewater and domestic wastewater are mixed, and biochemical treatment is performed, accordingly, the biochemical treatment efficiency is improved, poison and impact resistances of a system are enhanced, and the denitrification function is strengthened. The technological process is simple, the operation is stable, the removal rate is high, investments and operation costs are saved, the process can be fully applied to treat industrial wastewater of various gas fields, and discharged water can achieve environment friendly emission standards required by the country.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Dehalogenation and degradation method for halogenated aromatic compound
InactiveCN105288927AImprove securityHigh selectivityPreparation by dehalogenationOrganic compound preparationAlcoholActive component
The invention relates to a dehalogenation and degradation method for a halogenated aromatic compound. The method includes the steps that the halogenated aromatic compound is used as raw materials, alcohol is used as a hydrogen source, and water is used as a solvent; under the action of a supported catalyst, a reaction is performed for 5-50 h at the temperature being 30-260 DEG C under the pressure ranging from 1 MPa to 10 MPa, and the halogenated aromatic compound is subjected to water-phase hydrogen production in-situ dehalogenation and degradation, wherein a benzene ring of the halogenated aromatic compound at least contains one F or Cl or Br or I substituent group, the supported catalyst is formed by active components and a carrier, the active components are composed of mixtures of transitional metal and other metal, the transitional metal is one of Rh, Pd, Pt and Ni, the other metal includes one of Se, Ca, Ba, La and Ce, and the carrier is one of active carbon, kieselguhr, zeolite, gamma-Al2O3, AlF3 and MgO. Active hydrogen is prepared to directly participate in the reaction through in-situ catalysis instead of directly using H2 as a reducing agent. Thus, the dehalogenation and degradation method has the beneficial effects of being high in reaction activity, selectivity and security, environment-friendly and the like, and having the good application prospect.
Owner:QUZHOU UNIV
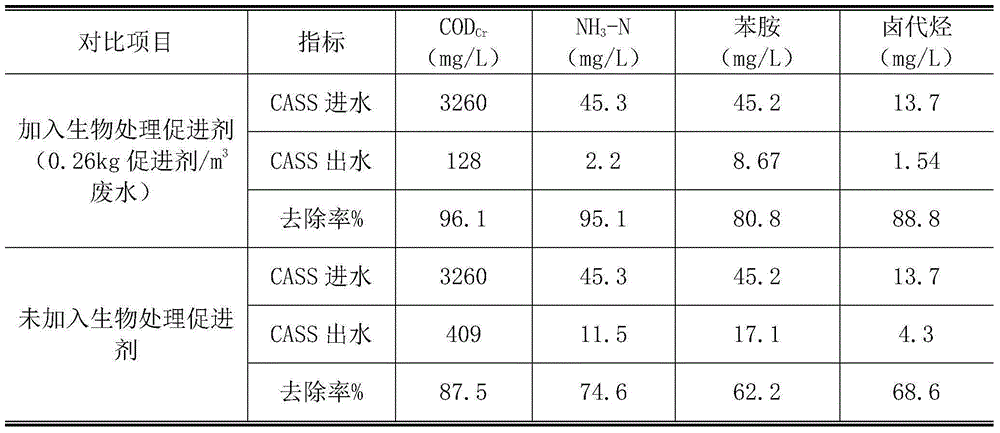
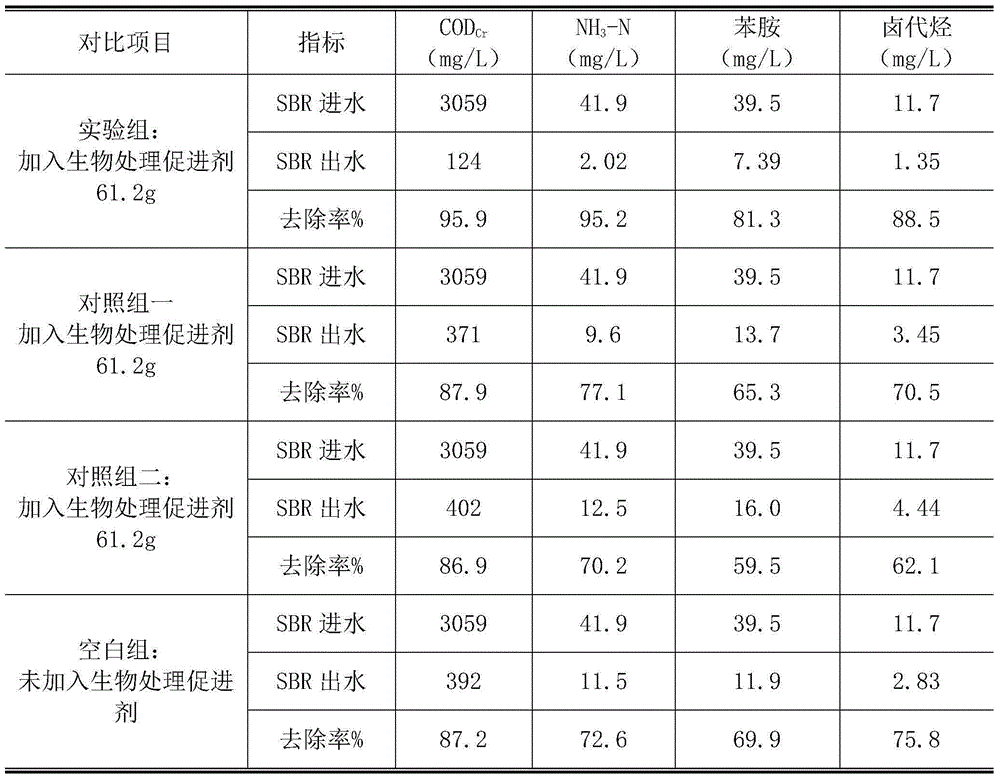
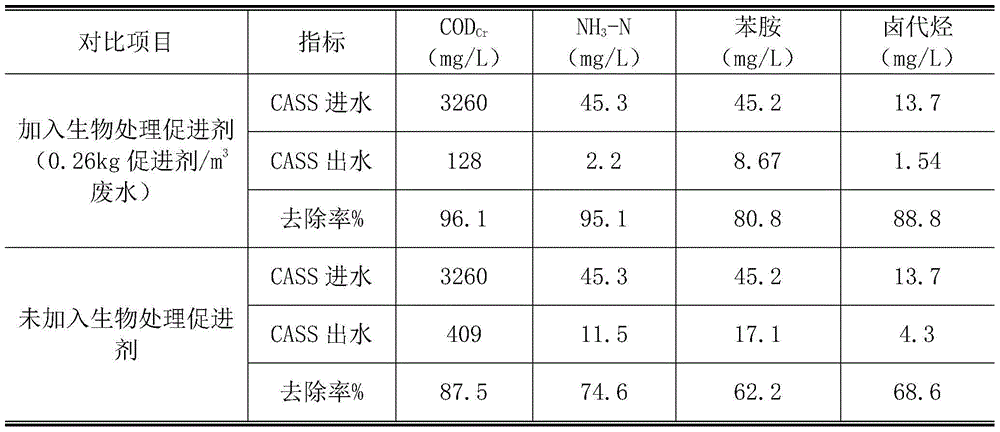
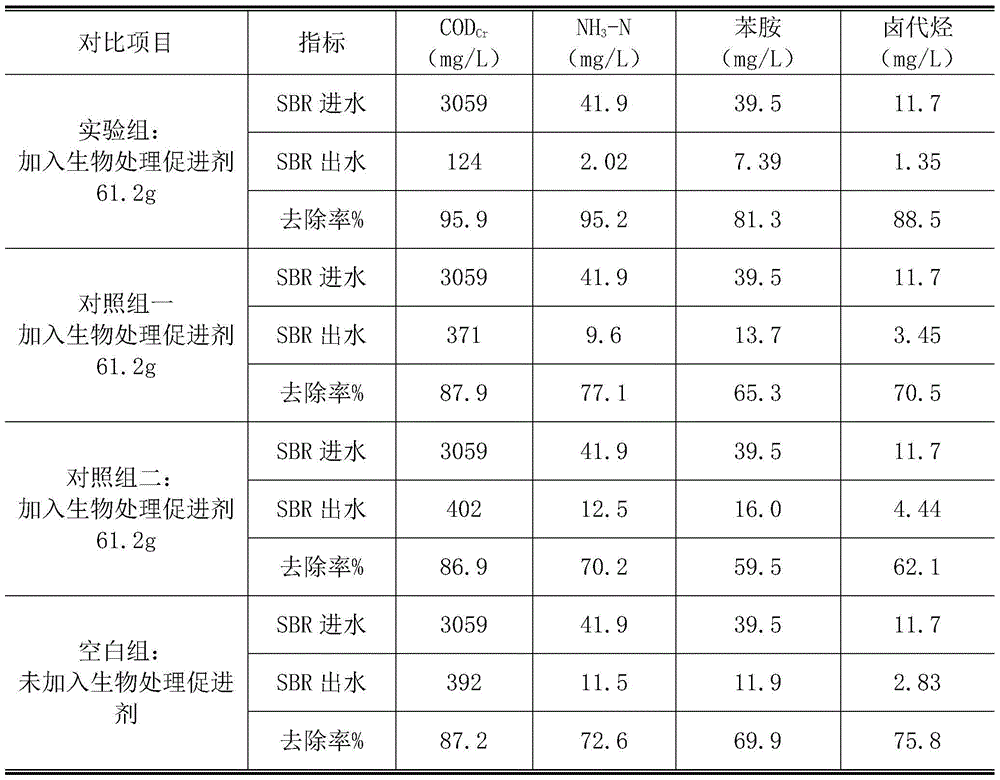
Medical intermediate biological waste water treatment accelerant and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN105152357APromote growthPromote growth and reproductionBiological water/sewage treatmentWater qualityVitamin B12
The invention discloses a medical intermediate biological waste water treatment accelerant and a preparing method and application thereof and belongs to the field of waste water treatment. The accelerant is prepared by matching glucose, ammonium phosphate, ethyl alcohol, phenol, calcium chloride, zinc chloride, magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate, vitamin B1 and vitamin B12. The accelerant can promote growth of microorganism, start a cometabolism action of the microorganism and improve the toxicity resistance of the microorganism to the medical intermediate by adding the accelerant into a medical intermediate waste water disposal system, thus effectively stably treating the medical intermediate waste water; the accelerant is wide in raw material resource, simple to prepare, convenient to use and suitable for the water quality of the medical intermediate waste water, and has a broad application prospect.
Owner:HAIMEN THE YELLOW SEA ENTREPRENEURSHIP PARK SERVICE CO LTD
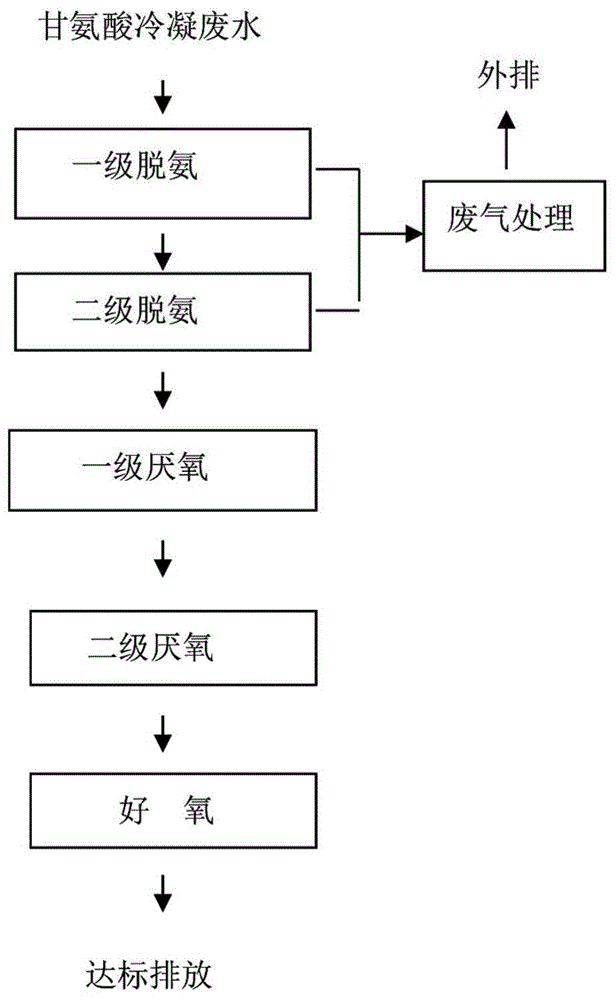
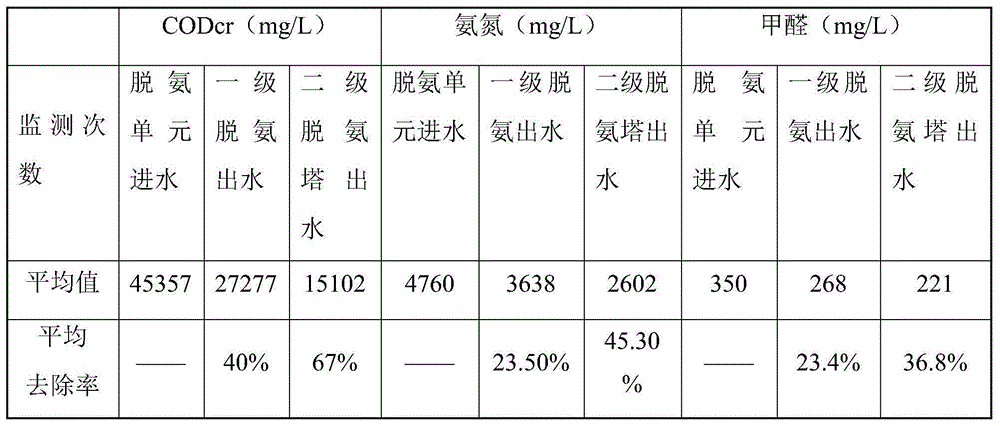
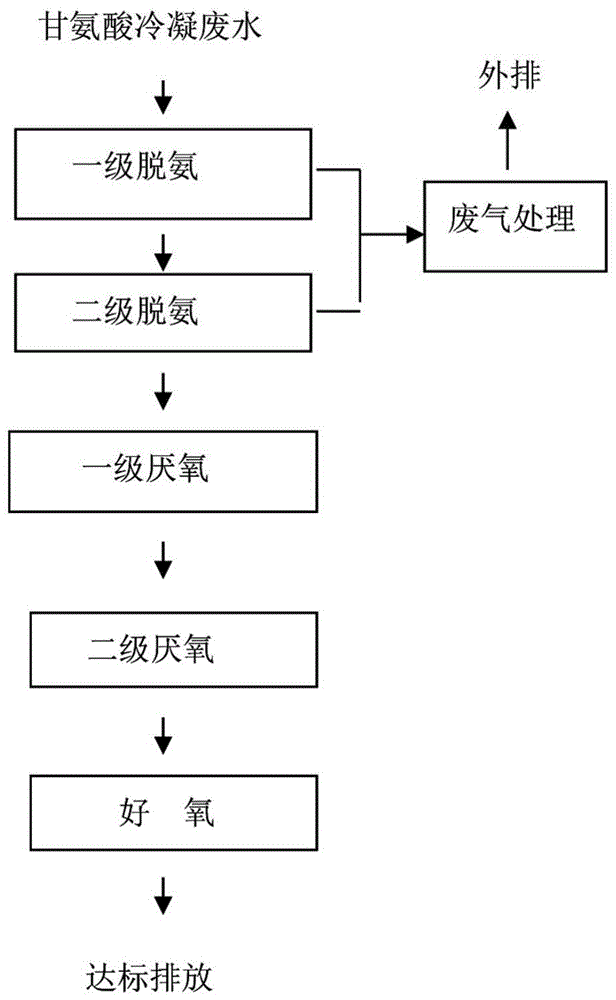
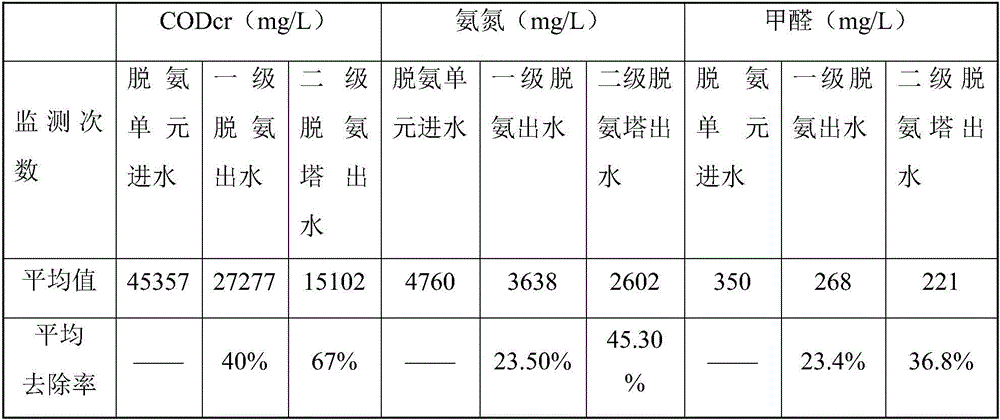
Treatment process of glycine condensation wastewater
ActiveCN104628224AImprove impact resistanceHigh activityMultistage water/sewage treatmentAmmonia compoundsHigh concentrationOxygen
The invention relates to a treatment process of glycine condensation wastewater, which specifically comprises the following steps: spraying the glycine condensation wastewater down from a first-level deamination tower; absorbing in air from the bottom of the first-level deamination tower in which the air is absorbed by sulfuric acid to generate ammonium sulfate, recycling the ammonium sulfate, conveying the rest wastewater to a second-level deamination tower by a second-level lift pump, and spraying the wastewater down from the second-level deamination tower to realize free flow; absorbing in air from the bottom of the second-level deamination tower in which the air is absorbed by sulfuric acid to generate ammonium sulfate, recycling the ammonium sulfate, and conveying the rest wastewater to a first-level EGSB anaerobic reactor by a first-level anaerobic lift pump; conveying the wastewater in a first-level anaerobic water collection tank to a second-level EGSB anaerobic reactor by a second-level anaerobic lift pump; and discharging the wastewater from the upper part of a second-level anaerobic sedimentation tank and conveying to an aerobic tank by an aerobic lift pump, wherein the bottom of the second-level anaerobic sedimentation tank is connected with an EGSB reflux pump. The total operation cost of the system is 3-4 yuan / m<3>, the high-concentration water can be diluted by 10-30 times through the three reflux systems, and the tolerance of an anaerobic system to the toxicity of high-concentration wastewater is improved to a relatively great degree.
Owner:HUBEI XINGFA CHEM GRP CO LTD
A kind of water-resistant catalyst for aldol condensation and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN103551148BGood physical and mechanical propertiesIncrease resistance to poisoningOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a water-resistant catalyst for aldol condensation, which comprises a main active component, a coagent and a carrier, the main active component is one or more of oxides or salts of Cs, and the coagent is One or more of oxides or salts of Sb, Nb, Ag, Al, Zr, the carrier includes SiO2 and a carrier additive, and the carrier additive is one or more of Al2O3, ZrO2, diatomaceous earth, kaolin ; Wherein: the SiO2 is hydrophobic nano-SiO2; or (2) the catalyst is treated with water resistance. The water-resistant catalyst of the present invention is used for the aldol condensation reaction and has the characteristics of high activity, good selectivity and long life, especially for the synthesis of methyl methacrylate from formaldehyde and methyl propionate, calculated as methyl propionate, The selectivity of methyl methacrylate is as high as 94%, and the single service life of the catalyst is more than 400h. The preparation method of the catalyst of the invention is simple and suitable for industrial application.
Owner:HAO HUA CHENGDU TECH
Dehalogenation degradation method for halogenated pyridine compound
InactiveCN105503706AImprove securityHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActivated carbonAlcohol
The invention provides a dehalogenation degradation method for a halogenated pyridine compound. The halogenated pyridine compound is adopted as a raw material, alcohol is adopted as a hydrogen source, water is adopted as a solvent, reacting is carried out for 3-10 h under normal pressure at the temperature of 20 DEG C to 120 DEG C under the action of a supported catalyst, and the halogenated pyridine compound is subjected to dehalogenation degradation in situ through water phase hydrogen production. A pyridine ring of the halogenated pyridine compound at least contains an F or Cl or Br or I substituent group. The supported catalyst is composed of an active component and a carrier, the active component is composed of a mixture of transition metal and other metal, the transition metal is one of Rh, Pd, Pt and Ni, and other metal is one of Se, Ca, Ba, La and Ce. The carrier is one of activated carbon, kieselguhr, zeolite, gamma-Al2O3, AlF3 and MgO. H2 is not directly used as a reduction agent, activated hydrogen is prepared through in-situ catalysis to directly participate in reacting, the advantages of being high in reaction activity, high in selectivity, high in safety, environmentally friendly and the like are achieved, and good application prospects are achieved.
Owner:QUZHOU UNIV
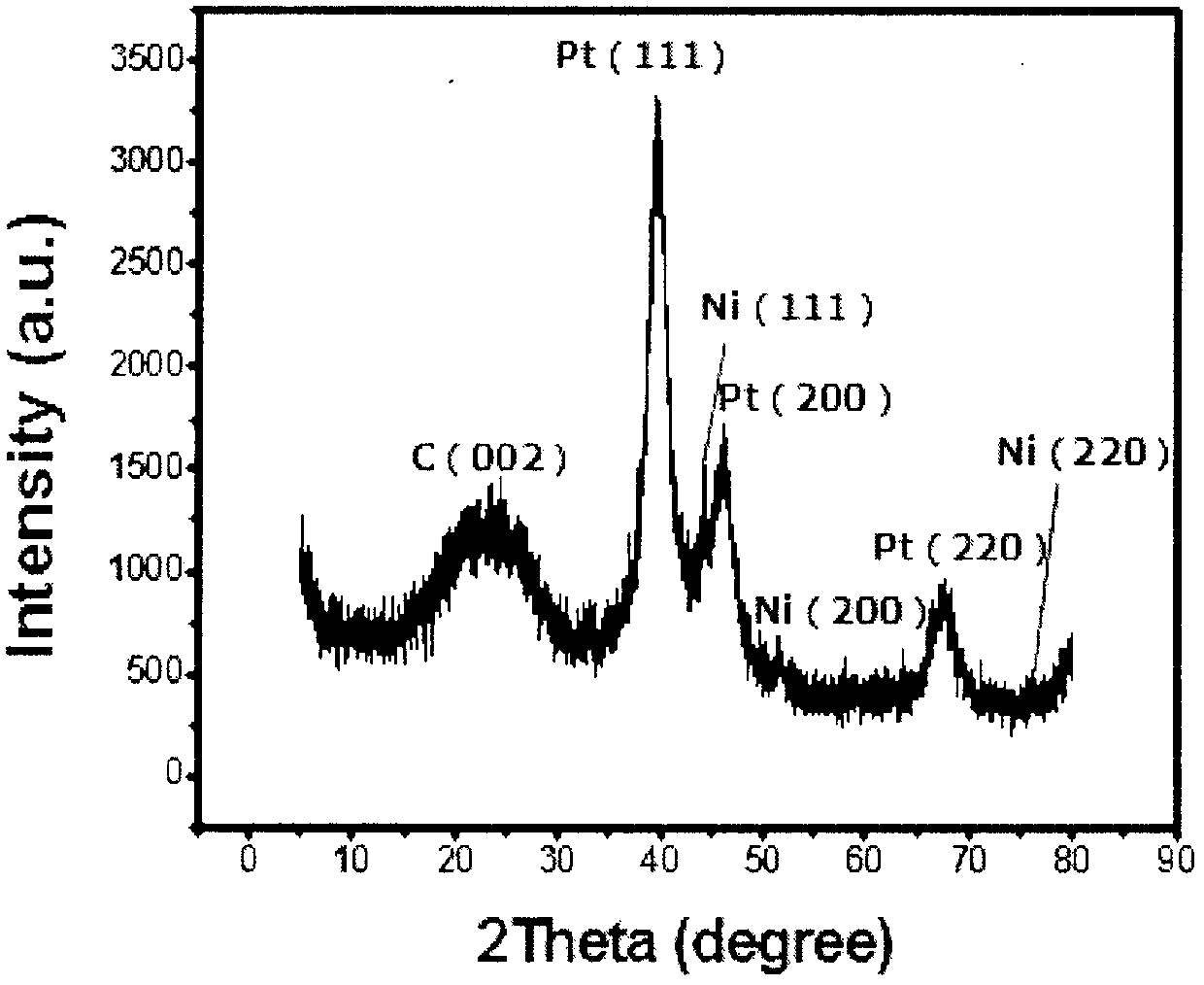
Preparation method of ethanol oxidation catalyst with high-efficient electron transporting structure
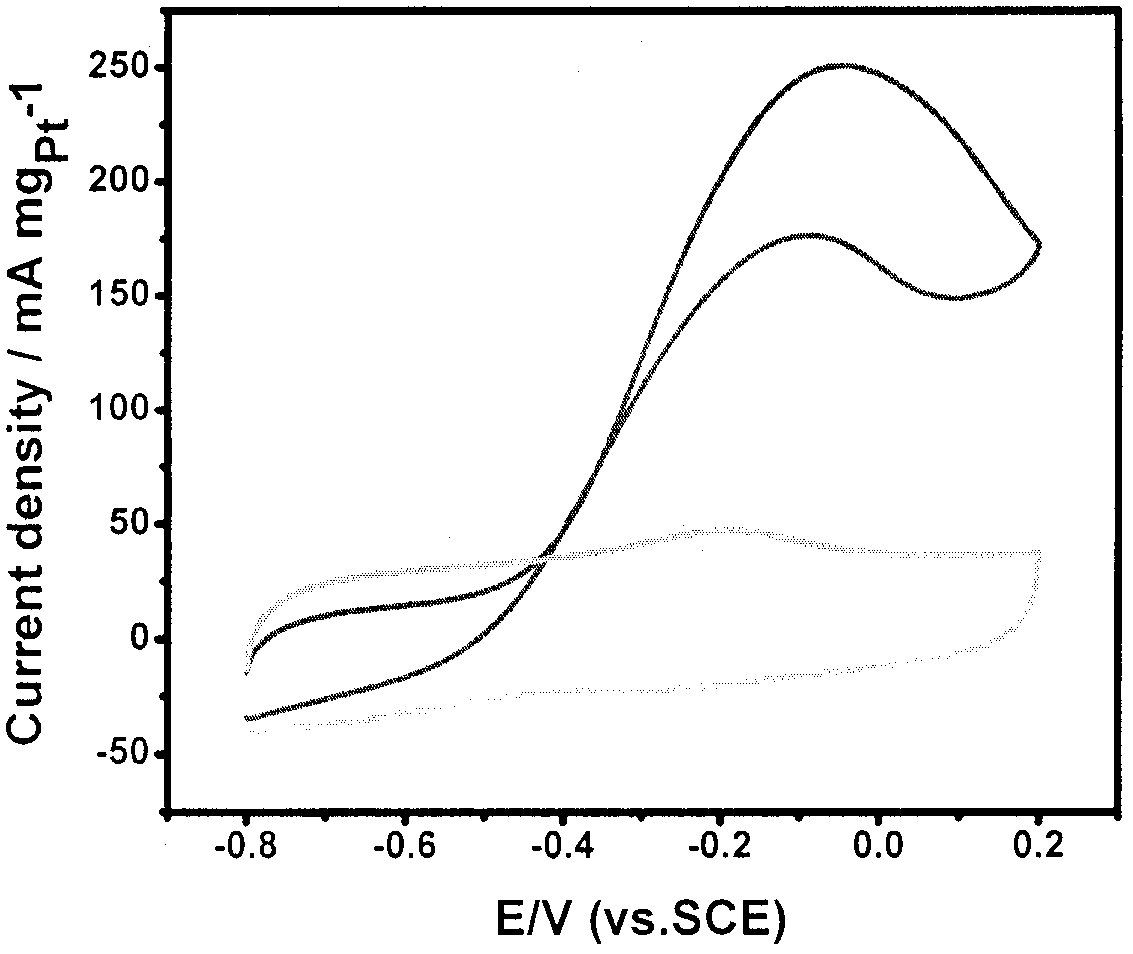
InactiveCN107732263AImprove stabilityIncrease resistance to poisoningMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesEvaporationNitrogen doped
The invention discloses a preparation method of an ethanol oxidation catalyst with a high-efficient electron transporting structure. The method concretely the following steps: 1. glucose, urea, nickelchloride are mixed in order to prepare an aqueous solution, evaporation to dryness, calcination, washing and drying are carried out, in order to obtain a nitrogen doped nickel / carbon solid sample. 2.the nitrogen doped nickel / carbon sample and a chloroplatinic acid solution are mixed in order to prepare an ethylene glycol solution, ultrasonic treatment, oil bath, centrifugal washing, and drying are carried out in order to obtain the nitrogen doped platinum-nickel / carbon catalyst. The nitrogen doped platinum-nickel / carbon catalyst has the high efficient electron transporting structure, and excellent electrocatalytic oxidation performance for ethanol.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for treating 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene waste water and application thereof
ActiveCN101830606BAvoid inhibitionAvoid side effectsWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentMicroorganismThree stage
The invention provides a method for treating 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT for short) waste water. In the invention, waste water is mainly treated by immobilized microorganisms, an anaerobic biological filter (I-AF) and immobilized microorganisms and a biological aerated filter (I-BAF), wherein the waste water enters a collecting tank, is lifted by a pump to enter a regulating tank and enters a setting tank after being homogenized and neutralized by the regulating tank so as to remove suspended substances (SS) in the waste water; the effluent is discharged after reaching standards after entering three-stage I-AF and five-stage I-BAF for further treatment. The specific steps of the method are shown in the specification. The invention has the advantages that biological treatment adopts an immobilized microorganism technology, which improves the poison resistance of the microorganisms, realizes the high-efficiency removal on toxic and harmful substances of nitrobenzene and the like, reduces the treatment cost and realizes the standard-reaching discharge of the waste water. The application of the invention is not only suitable for treating the TNT waste water but also is applied to treating nitrobenzene and aniline contained pollutants and organic waste water thereof.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Preparation method for wet oxidation catalyst
ActiveCN108927166ATightly boundPacked tightlyCatalyst protectionWater contaminantsHigh concentrationSulfur
The invention discloses a preparation method for a wet oxidation catalyst. The preparation method includes the following steps: (1) processing active carbon by adopting carbohydrate, and performing pulping; (2) dissolving a copper source precursor into a solution; (2) dissolving a cerium source precursor into a solution; (4) mixing materials prepared by the step (1), (2) and (3), adjusting pH values to form deposition, and performing filtering, washing and drying, and roasting in an inert gas environment so that a powder material can be formed; and (5) mixing the powder material of the step (4) with a manganese source precursor solution into slurry, and adding a pore forming agent after stirring, performing seal standing to form the mixture into a clover shape through extruding after secondary stirring, coating nanometer zirconia after drying, and performing roasting in an inert gas environment to form a wet oxidation catalyst. The prepared wet oxidation catalyst can be used for high concentration organic wastewater, and has characteristics of large specific surface areas, strong sulfur tolerance and stable catalytic activity, etc.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
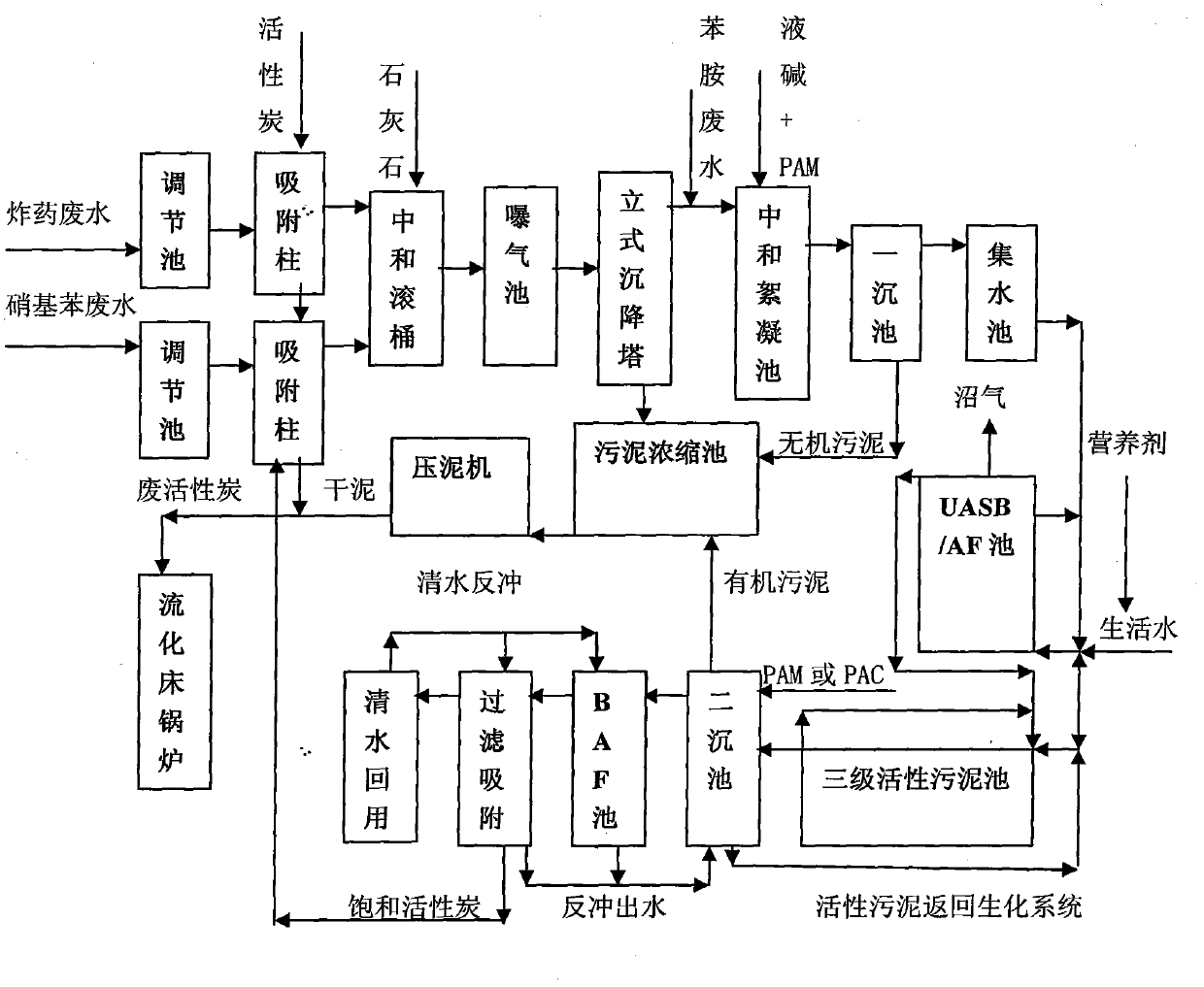
Mixed treatment method of explosive waste water and nitrobenzene and aniline waster water
ActiveCN102491584BAvoid inhibitionAvoid side effectsMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeFiltration
The invention belongs to the field of industrial waster water treatment, and more particularly relates to the technical field of waste water treatment of mixed waste water containing pollutant such as nitramines, nitrobenzenes and anilines and the like in the explosive and polyurethane industry by using pretreatment in combination with a biochemistry method. A mixed treatment method of explosive waste water and nitrobenzene and aniline waster water is characterized in that the waste water reaches the recycling standard after being subjected to procedures, such as activated carbon adsorption, neutralization with limestone and caustic soda liquid, flocculation settling, biochemical treatment with an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) / AF (Anaerobic filter) and activated sludge, processing with a ceramisite biological aerated filter (BAF), filtration and adsorption, waste activated carbon and sludge after-treatment. The mixed treatment method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of stable and reliable equipment operation, qualified effluent continuity, small excess sludge amount, low energy consumption, reasonable process, strong applicability and relatively good shock resistance and operability.
Owner:GANSU YINGUANG CHEM IND GRP CO LTD
A kind of treatment technology of glycine condensation wastewater
ActiveCN104628224BImprove impact resistanceHigh activityMultistage water/sewage treatmentAmmonia compoundsHigh concentrationOxygen
The invention relates to a treatment process of glycine condensation wastewater, which specifically comprises the following steps: spraying the glycine condensation wastewater down from a first-level deamination tower; absorbing in air from the bottom of the first-level deamination tower in which the air is absorbed by sulfuric acid to generate ammonium sulfate, recycling the ammonium sulfate, conveying the rest wastewater to a second-level deamination tower by a second-level lift pump, and spraying the wastewater down from the second-level deamination tower to realize free flow; absorbing in air from the bottom of the second-level deamination tower in which the air is absorbed by sulfuric acid to generate ammonium sulfate, recycling the ammonium sulfate, and conveying the rest wastewater to a first-level EGSB anaerobic reactor by a first-level anaerobic lift pump; conveying the wastewater in a first-level anaerobic water collection tank to a second-level EGSB anaerobic reactor by a second-level anaerobic lift pump; and discharging the wastewater from the upper part of a second-level anaerobic sedimentation tank and conveying to an aerobic tank by an aerobic lift pump, wherein the bottom of the second-level anaerobic sedimentation tank is connected with an EGSB reflux pump. The total operation cost of the system is 3-4 yuan / m<3>, the high-concentration water can be diluted by 10-30 times through the three reflux systems, and the tolerance of an anaerobic system to the toxicity of high-concentration wastewater is improved to a relatively great degree.
Owner:HUBEI XINGFA CHEM GRP CO LTD
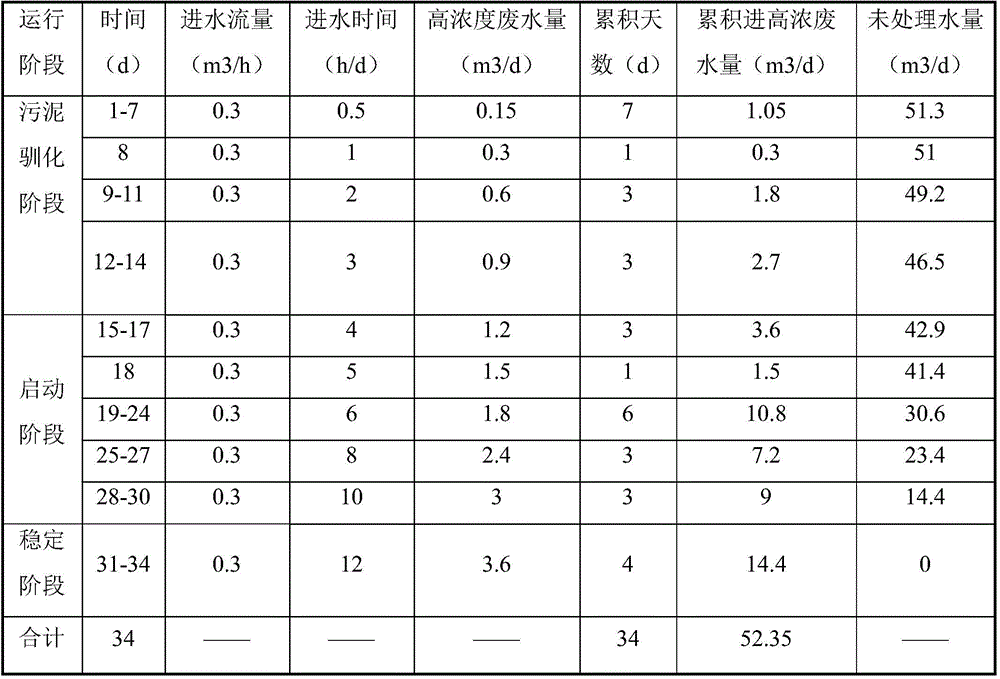
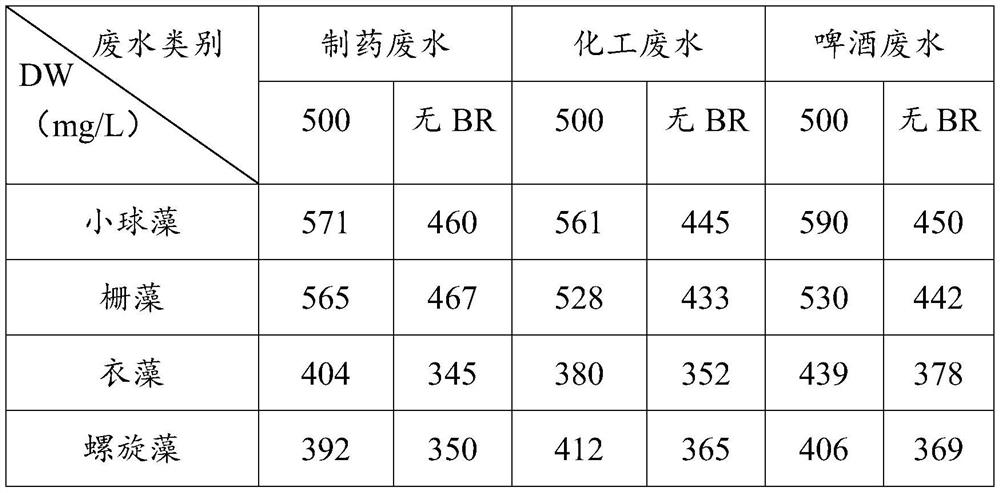
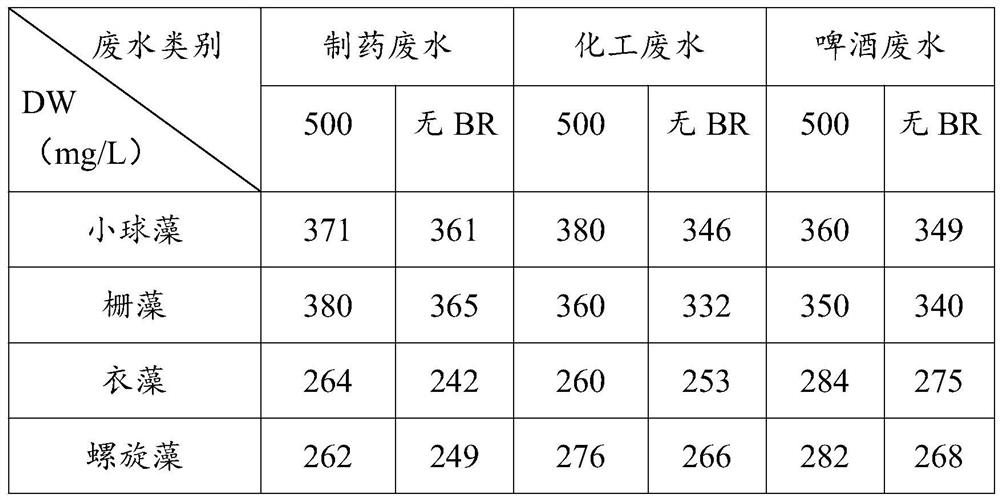
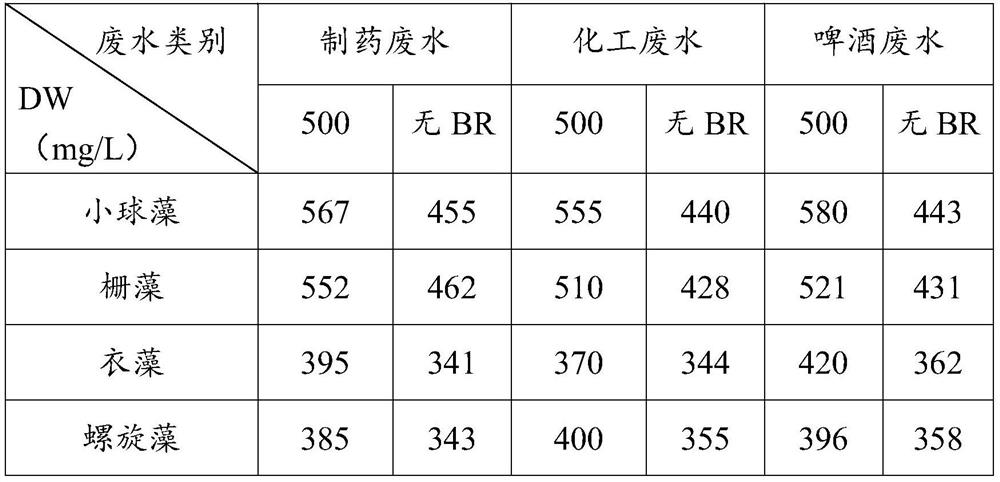
Method for improving toxicity resistance of microalgae in wastewater treatment process through brassinolide
ActiveCN111646576AIncrease productionIncrease resistance to poisoningUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBrassinolideEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of wastewater treatment, in particular to a method for improving the toxicity resistance of microalgae in the wastewater treatment process through brassinolide. According to the invention, a trace amount of brassinolide is added, so that the toxicity resistance of microalgae is improved, the metabolic activity of microalgae is optimized, the yield of microalgae biomass in a wastewater biological treatment and microalgae biomass energy coupling technology is increased, and the synthesis of high-value additional products is directionally adjusted.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
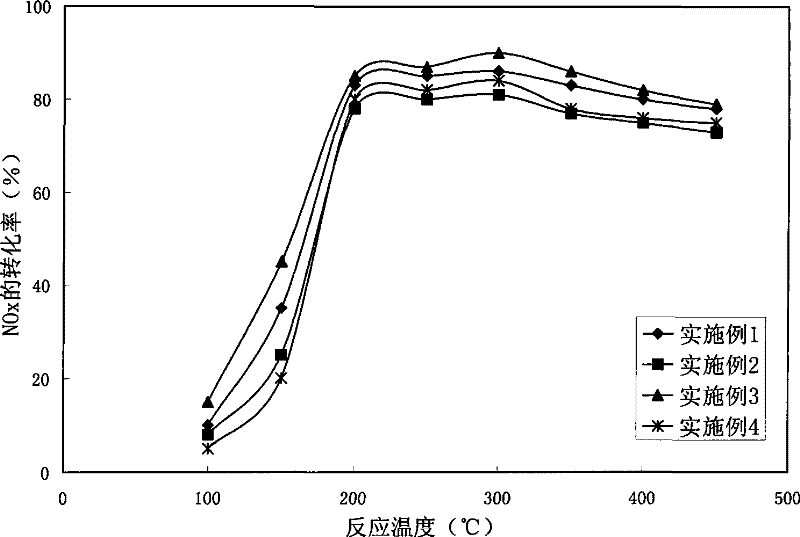
Method for preparing nitrous oxides selectivity reduction catalyst on metal alloy carrier
InactiveCN101249444BLow efficiencyIncrease resistance to poisoningDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCerium nitrateDip-coating
The invention belongs to a field of diesel-engined car tail gas cleaning and relates to a method for preparing a catalyst with optimized performance on metal alloy support for selectively reducing nitrogen oxide. The method includes preparing nickel nitrate solution, manganese nitrate solution, copper nitrate solution, cobalt nitrate solution, ferric nitrate solution, cerium nitrate solution and chromium nitrate solution with the distilled water as solvent; selecting 2-4 kinds of solutions from the solutions and mixing with silver nitrate solution or palladium nitrate of equivalent volume to prepare catalyst solution; dip-coating the catalyst solution on a glass ceramic coating of metal alloy support by; air-drying the coated metal carrier at room temperature; drying at 120-180 DEG C; repeating the coating and the drying for 5-8 times; and calcining at 600-1,000 DEG C for 1-5h to activate and mold. The method has the advantages of low cost, good initiation and catalytic characteristiceffect.
Owner:CHANGCHUN JLU KENUO TECH CO LTD
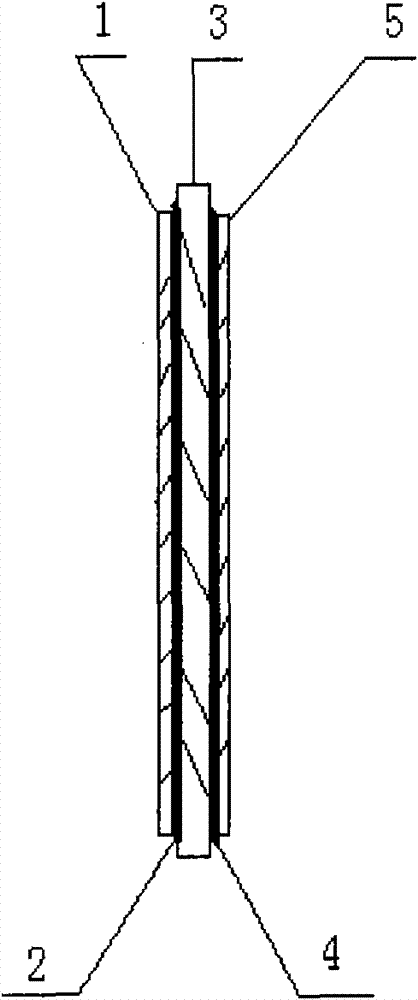
Membrane electrode for water electrolysis and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a membrane electrode for water electrolysis and a preparation method thereof. The membrane electrode sequentially comprises a cathode porous support layer, a cathode catalysis layer, an alkaline polymer electrolyte membrane, an anode catalysis layer and an anode porous support layer, wherein the cathode catalysis layer comprises non-noblemetal cathode hydrogen evolution catalyzer and alkaline polymer electrolyte, and the anode catalysis layer comprises a non-noblemetal anode oxygen evolution catalyzer and alkaline polymer electrolyte.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
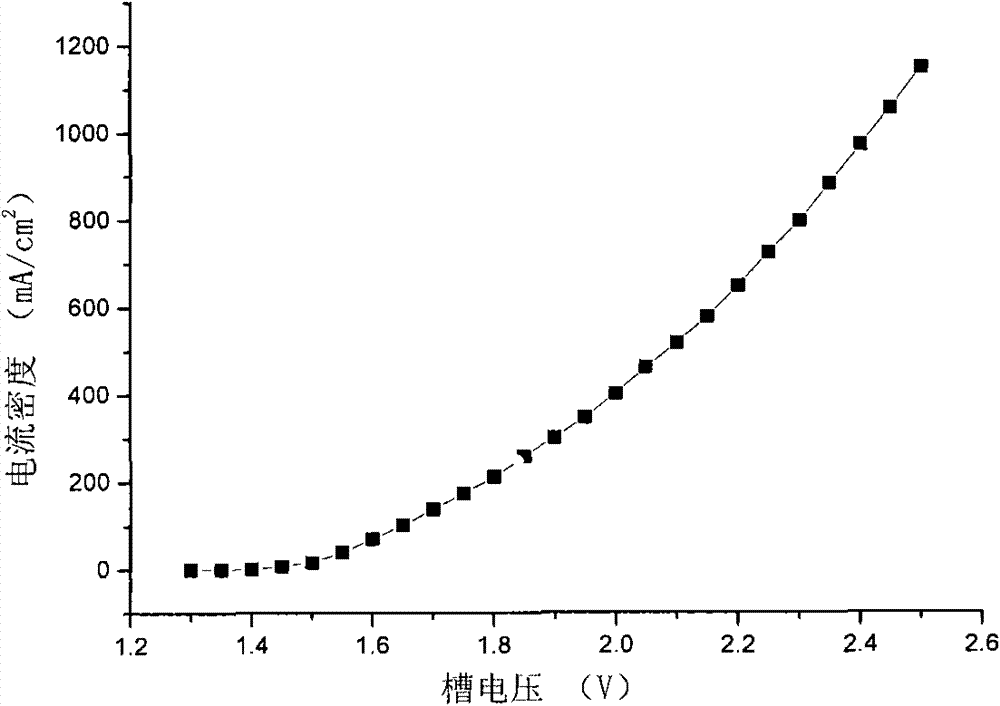
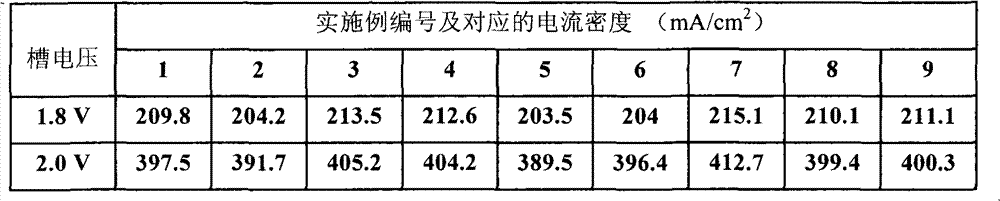
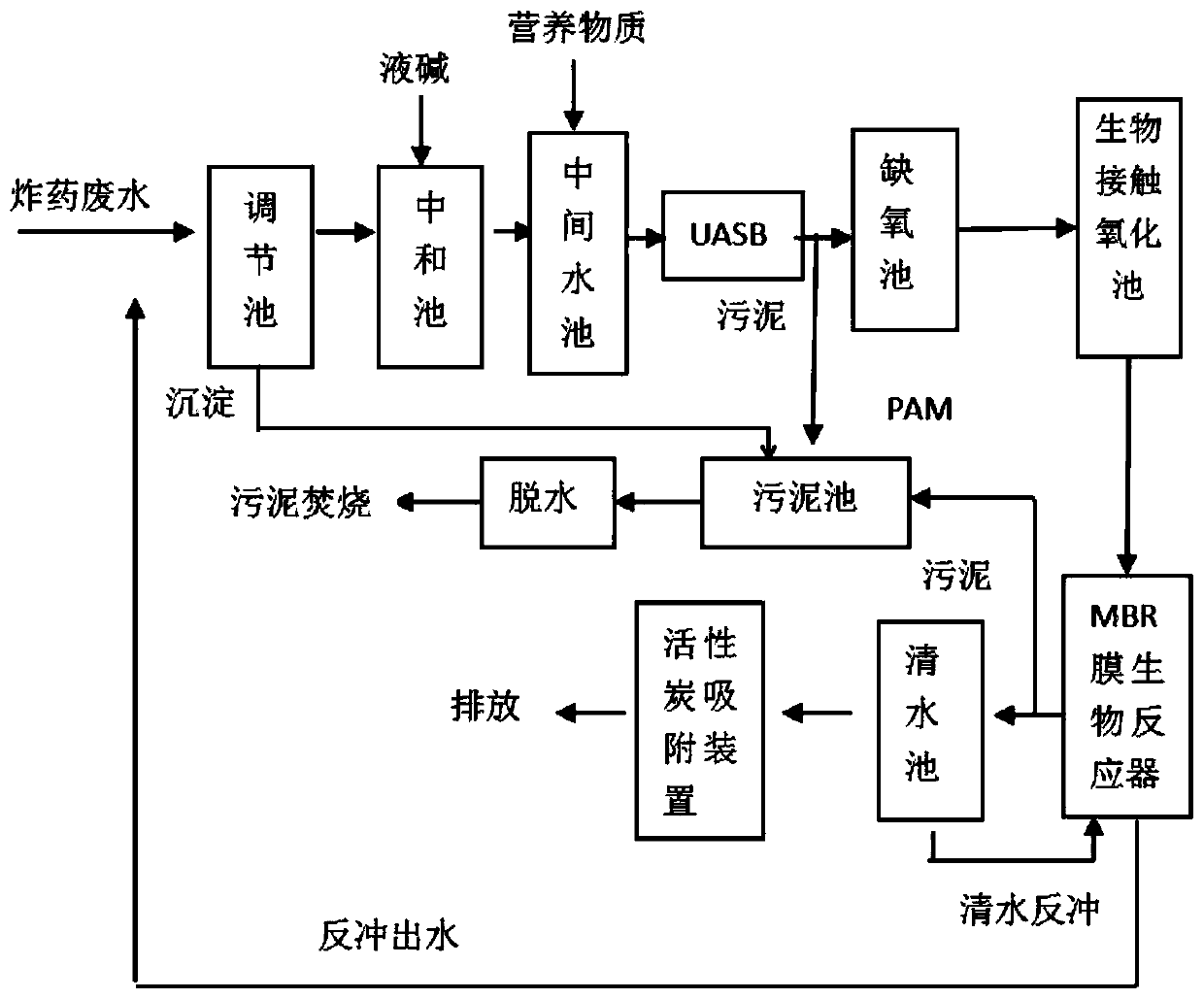
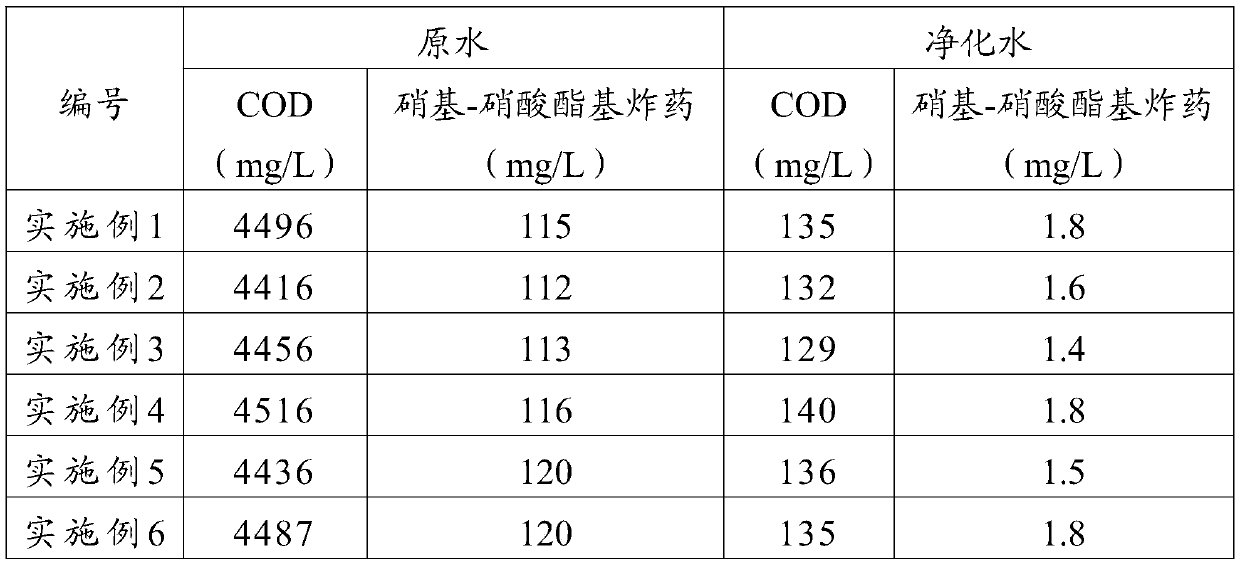
Treatment method of nitro-nitrate-based explosive wastewater
InactiveCN111056712AReduce ammonia nitrogen contentReduce CODExplosive contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated carbonExplosive Agents
The invention provides a treatment method of nitro-nitrate-based explosive wastewater, and belongs to the technical field of explosive wastewater treatment. The treatment method comprises the following steps: homogenizing and averaging the nitro-nitrate-based explosive wastewater, adjusting the pH value to 4-5, and then mixing with nutrient substances to obtain wastewater to be biochemically treated; sequentially carrying out anaerobic treatment, denitrifying treatment and aerobic treatment on the wastewater to be biochemically treated, and enabling the aerobically treated effluent to pass through an MBR (membrane bioreactor) to obtain biochemically treated wastewater; and precipitating the biochemical treatment wastewater, and performing activated carbon adsorption to obtain purified water. Physicochemical and biological treatment technologies are combined, the process is reasonable, the operation is safe, the operation cost is low, the impact resistance and the operability are good,and the problems of high COD concentration, high treatment difficulty, high operation cost and high operation labor intensity of the nitro-nitrate explosive wastewater are effectively solved.
Owner:SHANXI BEIHUA GUANLYU CHEM IND
A biological treatment accelerator for pharmaceutical intermediate waste water and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN105152357BPromote growthPromote growth and reproductionBiological water/sewage treatmentWater qualityVitamin B12
Owner:HAIMEN THE YELLOW SEA ENTREPRENEURSHIP PARK SERVICE CO LTD
Black phospho-TiO2 nanotube/Ti sensitive electrode hydrogen sulfide sensor
ActiveCN111141788AGood choiceHigh anti-poisoning and anti-interference abilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsHydrogen sensorCathode catalyst
The invention discloses a hydrogen sulfide sensor with a black phospho-TiO2 nanotube / Ti sensitive electrode. The sensor comprises a sensor shell and a membrane electrode arranged in the sensor shell,an air chamber is arranged between the sensor shell and the membrane electrode, a gas reaction chamber is arranged in the membrane electrode, and the membrane electrode comprises a cathode diffusion layer, a cathode catalyst layer, a Nafion membrane and a black phospho-TiO2 nanotube / Ti sensitive electrode from outside to inside; the cathode diffusion layer is connected with the sensor shell through a welding point to form a cathode output end, the black phospho-TiO2 nanotube / Ti sensitive electrode is connected with the sensor shell through a welding point to form an anode output end, and a gasfiltering cap with diffusion holes is arranged at a top end of the gas reaction chamber to allow hydrogen sulfide gas to be detected to pass through; an air circulation hole cover communicated with the air chamber is arranged on the sensor shell, a water discharge hole is formed in the bottom of the air chamber, and an SO2 discharge hole is formed in the bottom of the black phospho-TiO2 nanotube / Ti sensitive electrode. The sensor provided by the invention has good selectivity on hydrogen sulfide gas and strong anti-poisoning and anti-interference capabilities.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Impact-resistant multiplication combined type coking waste water treatment process
InactiveCN100503485COptimize material compositionPromote degradationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentVolatile phenolsSludge
An anti-impact multiplying combination coking wastewater treatment technique relates to a treatment method of coking wastewater. The coking wastewater is first qualified by a physical-chemical pretreatment to improve biodegradable property of wastewater; the composite technology of a biological carrier of active sludge is adopted to do anaerobic / hypoxia / aerobic decarbonization / aerobic nitrification biochemical combination treatment; suspended or floating folding ball-shaped fillings are arranged in biochemical reactors and when micro organism traits are abnormal or a great amount of foams existing in the reactor, micro organism active incentive agents are added to the reactor in interval to improve active sludge traits and organism film quantity; finally the water is treated by a physical-chemical advanced treatment to reach a top grade standard. The invention not only strengthens the removal of COD, ammonia-nitrogen, volatile phenol and other pollutants in the coking wastewater by biochemical treatment but also resists serious water quality impact and has the advantages of quick system startup, less foams in an aeration tank, small occupying space, low operation cost and stable and effective treatment to coking wastewater.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
Method for rapidly recovering efficiency of anaerobic treatment of wastewater generated in coal chemical industry
ActiveCN102910734AImprove adaptabilityPromote decompositionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesChemical industryWater quality
The invention discloses a method for rapidly recovering efficiency of anaerobic treatment of wastewater generated in the coal chemical industry. The method comprises the following steps of: stopping or reducing inflow when an anaerobic reactor suffers from the impact of water, and introducing air into the anaerobic reactor to control the concentration of dissolved oxygen; performing the procedures of aeration stopping, quiescent settling or inflow reduction and inflow recovery; and performing the procedures repeatedly until the concentration of toxic pollutants detained in the anaerobic reactor is reduced to or lower than a normal level, and then restoring a normal continuous inflow condition, so that the anaerobic reactor can reach or even exceed treatment efficiency in a stable running state in a short period of time. The method has the advantages of flexible operation, wide application range, low operation cost and good treatment effect.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com