Patents
Literature
312 results about "Crystal Clear" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Crystal Clear is a member of the Crystal family of methodologies as described by Alistair Cockburn and is considered an example of an agile or lightweight methodology. Crystal Clear can be applied to teams of up to 6 or 8 co-located developers working on systems that are not life-critical. The Crystal family of methodologies focus on efficiency and habitability as components of project safety. Crystal Clear focuses on people, not processes or artifacts. Crystal Clear requires the following properties: Frequent delivery of usable code to users Reflective improvement Osmotic communication preferably by being co-located Crystal Clear additionally includes these optional properties: Personal safety Focus Easy access to expert users Automated tests, configuration management, and frequent integration
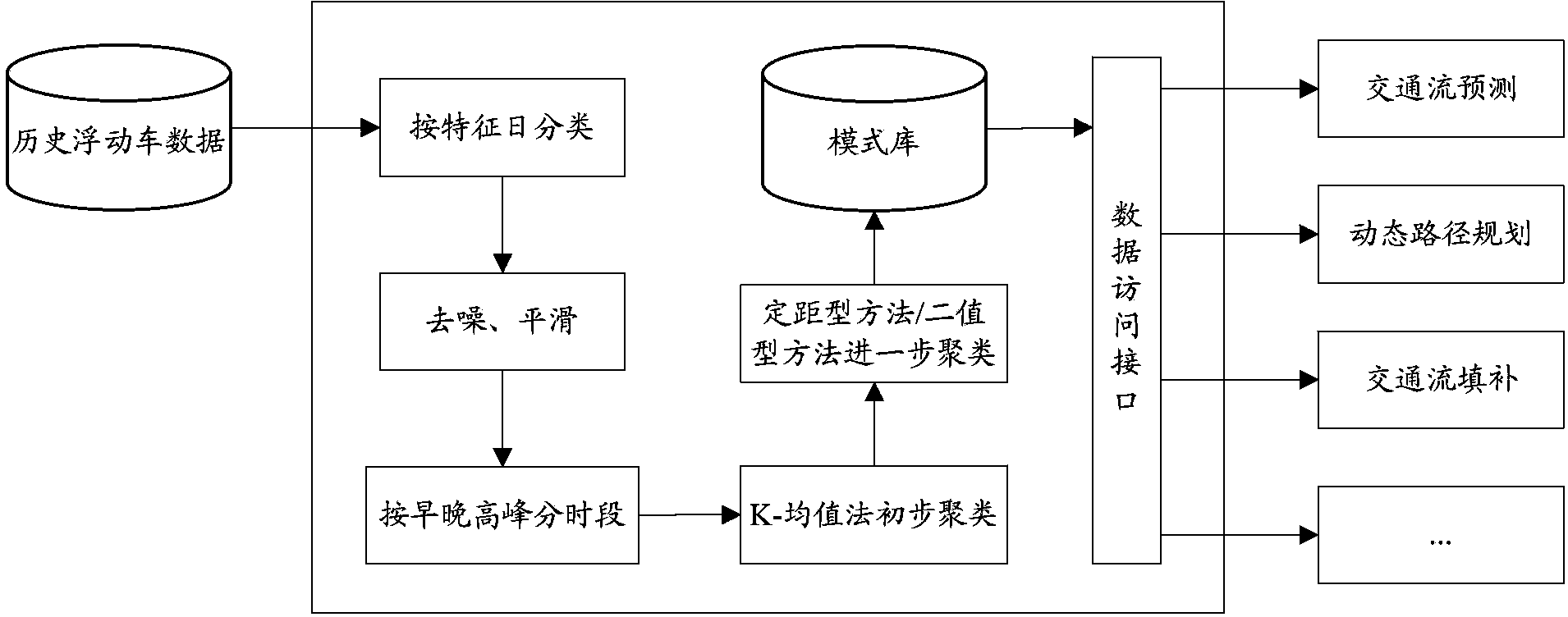
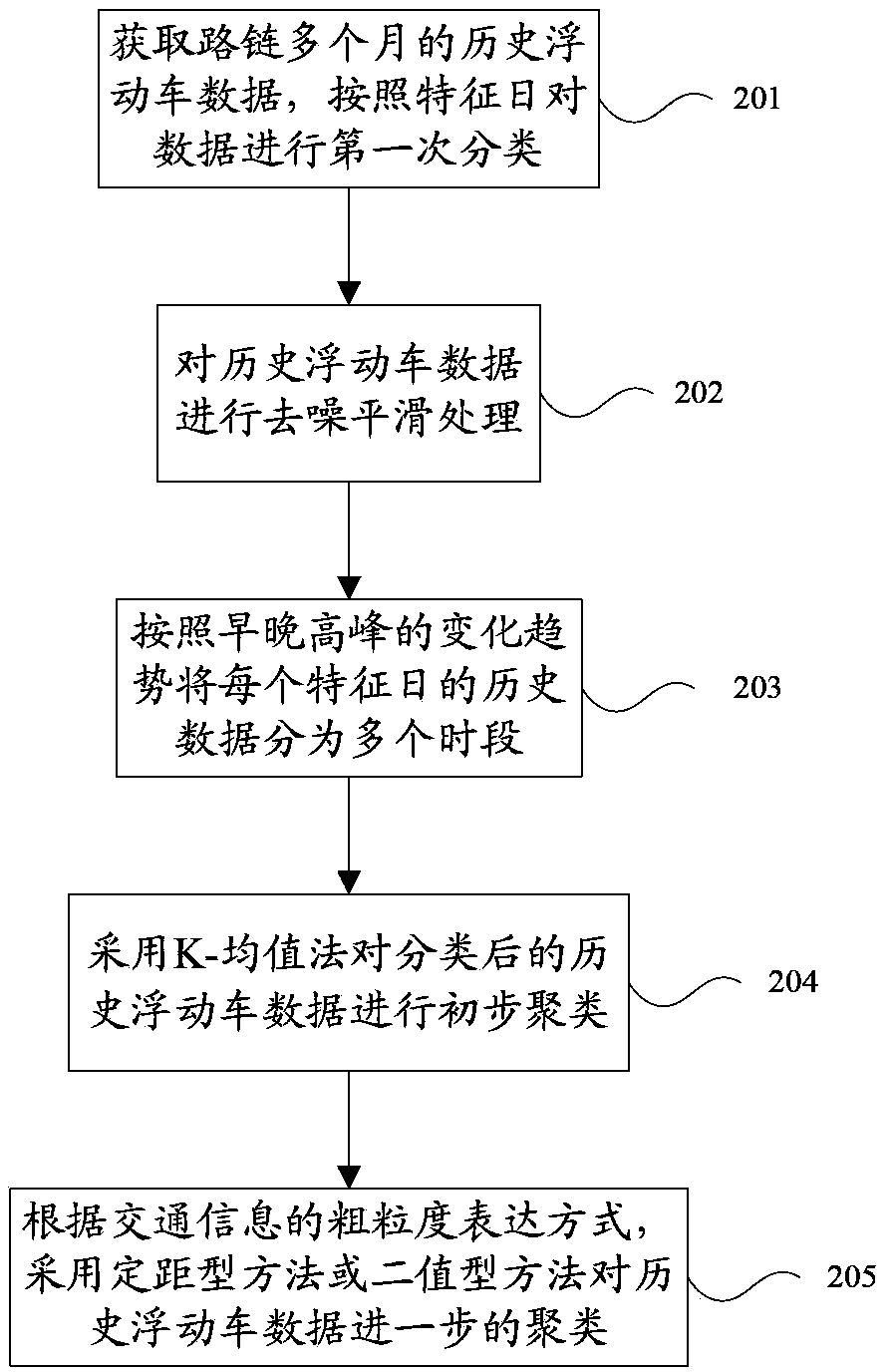
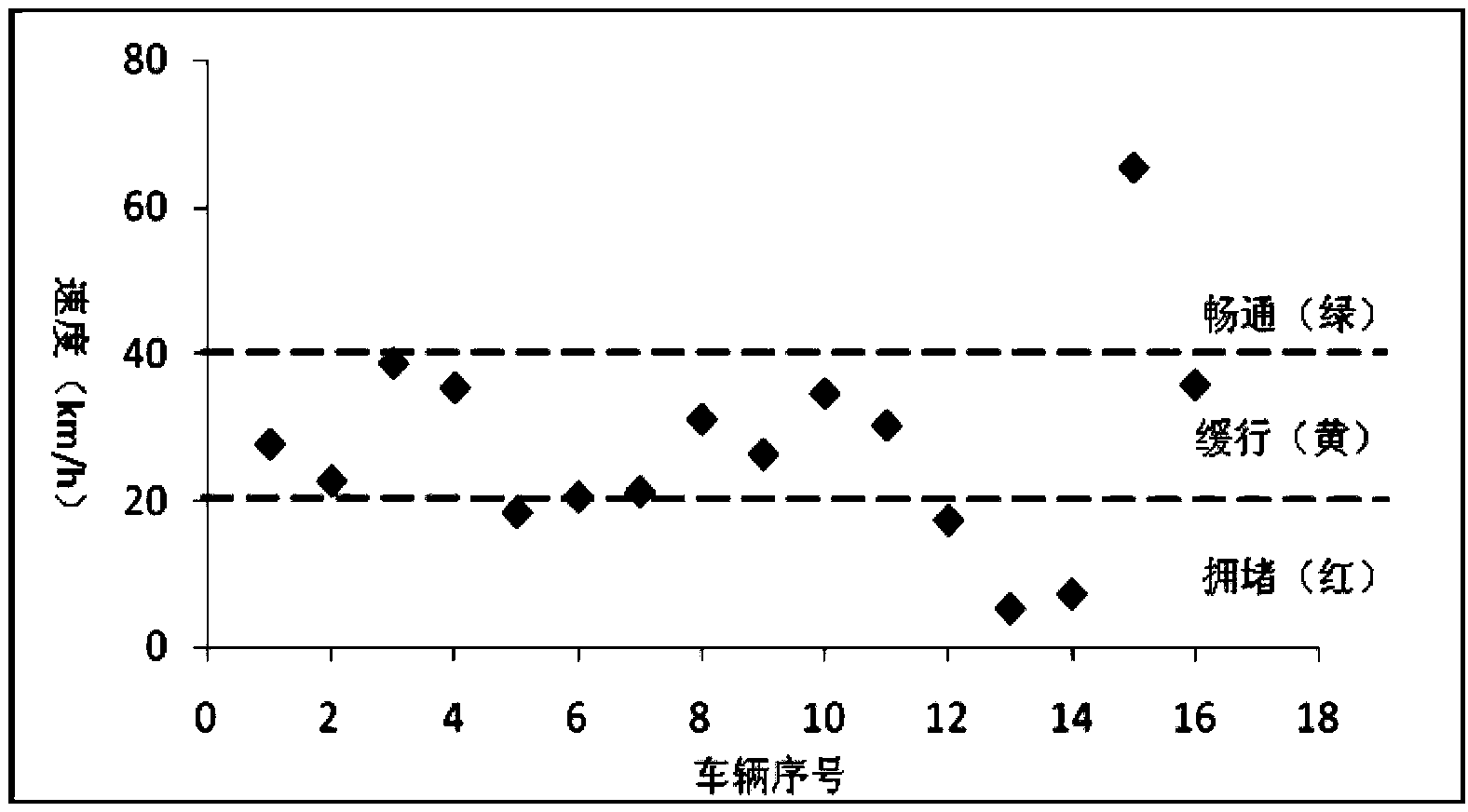
Traffic flow change trend extraction method based on floating car data
ActiveCN103810849AThe changing trend of traffic flow is highlightedClear referencesDetection of traffic movementSpecial data processing applicationsInterval methodGranularity
The invention discloses a traffic flow change trend extraction method based on floating car data and belongs to the technical field of intelligent transportation. The traffic flow change trend extraction method based on the floating car data comprises obtaining historical floating car data of at least three mouths of a road chain and classifying the data according to feature days; performing denoising and smoothing on the historical floating car data; dividing the historical floating car data of every feature days into at least one time frame according to the change trend of a morning peak and an evening peak; performing preliminary clustering on the classified historical floating car data through a K-means clustering method; further clustering the historical floating car data through a controlled interval method or a two-value method according to a coarse granularity expression of traffic information. The traffic flow change trend extraction method based on the floating car data combines the coarse granularity expression of the traffic information, further merges the traffic flow trends on the basis of a K-means clustering method, enables the traffic flow change trend to be more salient, thereby providing more crystal clear references for traffic flow prediction, route planning and induction, route planning and the like.
Owner:北京千方城市信息科技有限公司
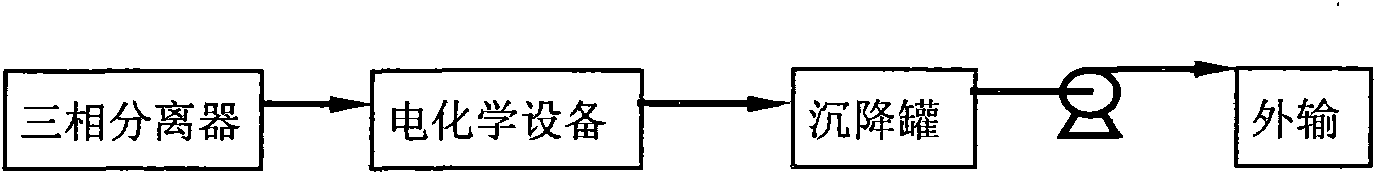
Electrochemical method of oil removal of wastewater produced in oil extraction by polymer flooding displacement
InactiveCN101602531AEasy to separateSave construction investmentWater/sewage treatment by flotationElectrolysisWater quality
The invention discloses an electrochemical method of oil removal by polymer flooding oil recovery wastewater, which comprises the following steps of: 1, electrolysis; 2, sedimentation. In the process of the electrolysis, tiny oil droplets in the wastewater lose electrons due to discharge on the surface of an anode, charges on the surface of the oil droplets are reduced, and electric potential of interface xi is decreased; and residual polymer pieces in the wastewater after the electrolysis are oxidized and degraded, viscosity of the wastewater is decreased, and water film intensity on the interface of oil / water is reduced. Therefore, the tiny oil droplets after the electrolysis are liable to be converged into large oil droplets and are rapidly separated from the wastewater under the action of cathode hydrogen. As treated by the method, crude oil in wastewater produced in oil extraction by polymer flooding displacement is quite easy for removal with no need for large use of sedimentation tanks, thus saving construction fund for oilfield; the invention has simple process, requires no drug, saves resource and cost and conforms to green chemistry process, quality of the wastewater after the oil removal is obviously crystal-clear; in addition, the device is convenient and safe in operation, easy to control and realize automation, extensively adapted to the amount of water, and convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Hot tinting method on copper surface
InactiveCN101109079AImprove aestheticsImprove expressivenessMetallic material coating processesCrystal ClearHeating time
The invention relates to a hot tinting approach on the surface of bronze. By applying different chemistry raw material formulas and according to thinking of designers, the approach applies various chemistry materials to generate the chemical change on the heated copper surface with different copper content at the different temperature; the needy colors showed by the copper surface are controlled depending on the heating time and form various patterns. The clear color blocking material is used to block the colored copper surface. The color and the pattern are bleeded from the inside of the metal, thus, being sparkling and crystal-clear, jade-like, rich and natural in color and strong in teansparency. Therefore, the expressive force, attractiveness and collection value of the copper works or copper sculpture are greatly improved.
Owner:黄炜棠
A vine tea mask capsule and a method of preparing the same
InactiveCN102552092ABacteriostaticWith whiteningCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsIrritationToxin
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Manufacturing method of underglaze white double crystal fancy glaze
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of an underglaze white double crystal fancy glaze. The method comprises the steps of preparing materials according to a formula, manufacturing a frit, sieving by using a ball mill and modulating, wherein the frit is made from borax, potash feldspar and quartz; a ground glaze is made from potash feldspar, zinc oxide, calcite, quartz and frit; and an overglaze is made from frit, barium carbonate, iron red, potash feldspar, titanium oxide, zinc oxide, bentonite, quartz, iron oxide red and zirconium silicate; dry grinding frit materials, burning the frit materials at 1250 DEG C, and cooling fast to obtain the frit; sieving ground glaze and overglaze materials by using the ball mill; wet ball milling, and sieving by using a 250 mesh sieve; modulating the ground glaze and the overglaze: mixing the crushed frit respectively with the ground glaze and overglaze materials which are sieved and wet ball milling mixtures so as to modulate the mixtures into slurries at 45-50 baume degree; burning: spraying glaze on a green body, wherein the thickness of the ground glaze is 0.4-0.7mm, the thickness of the overglaze is 0.3 mm, and feeding the green body into a roller way to be burnt into the underglaze white double crystal fancy glaze in an oxidizing atmosphere; after burning, natural, smooth and crystal clear decorative patterns can be generated.
Owner:湖南泉湘陶瓷有限公司
Anti-oxidation moisturizing sleeping mask containing peony seed oil and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105769683AImprove antioxidant capacityEasy to useCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsIrritationNatural substance
The invention discloses an anti-oxidation moisturizing sleeping mask containing peony seed oil and a preparation method thereof.The sleeping mask is prepared from, by mass, 0.5%-20% of peony seed oil, 0.1%-5% of oil-soluble vitamin E, 0.1%-5% of an emulsifier, 1%-10% of rose hydrosol, 0.5%-20% of chamomile extract, 1%-10% of glycerin, 0.5%-3% of lower-molecular hyaluronic acid, 5%-15% of aloe gel, 0.05%-5% of an antibacterial agent and the balance deionized water.After peony seed oil, rose hydrosol, chamomile extract, aloe gel, lower-molecular hyaluronic acid and other substances are mixed, the sleeping mask suitable for modern women is formed; the sleeping mask has the advantage of being free of washing, and thus use is quite convenient.With natural substances serving as main raw materials, the mask has the advantages of being mild without irritation and easy to absorb and is high in moisturizing performance and good in anti-oxidation effect; after the mask is used, the skin is smooth and fine, moist and compact, crystal clear and full of vitality.
Owner:WUHAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Process for the Production of Partially Polymerized Antimicrobial Silanol Quaternary Ammonium Compounds
This invention is a process for the manufacture of water stable, partially polymerized antimicrobial alkoxysilyl quaternary ammonium compounds and their trisilanol, polysiloxanol and water soluble polysiloxane derivatives thereof (SQACs). Partial polymerization is accomplished by allowing the aqueous SQAC product solution to polymerize at conditions that will substantially convert all the chlorosilanol monomer to a copolymer of the SQAC, thus reducing the toxicity of the solution greatly. A stabilizing agent is added either before or after the partial polymerization. The stabilizing agent is selected from a list of antimicrobial, naturally occurring, renewable phytochemical essential oils and extracts that easily form crystal clear microemulsions when water is added to the concentrated SQAC / essential oil mixture. These non-foaming oil in water microemulsions have excellent long term storage stability, are freeze / thaw stable, remain very low in viscosity and do not phase separate or precipitate for many months. Many of the essential oils found to be useful in this process are non-toxic food additives and have pleasant scents, have low flammability yet are volatile enough to evaporate upon cure down of the SQAC, thereby resulting in a higher concentration of SQAC in the cured, antimicrobial film. Economically shippable concentrations of the low toxicity, partially polymerized, stabilized SQACs can be further diluted with water to application concentrations without loosing any of their stabilizing properties and remain storage stable at these lower concentrations indefinitely. In particular, the invention relates to the use of such aqueous dilutions cured as durable antimicrobial coatings on both manufactured and natural substrates and for human or animal skin that covalently bond to the skin, remain active through many washings and reduce or eliminate bacteria, viruses and fungi for days.
Owner:NOVALENT LTD
Rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze with antimicrobial function and preparation method of rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze
The invention relates to a rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze with an antimicrobial function and a preparation method of the rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze, which belong to the technical field of ceramic glazes. The rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze disclosed by the invention is composed of the following components: montmorillonite, kaolinite, quartz, talcum, potassium feldspar, glaze stone, wollastonite, dolomite, sodium carboxymethyl starch, zinc oxide and barium carbonate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: after the raw materials are prepared, carrying out ball milling and sieving the obtained object, pouring a glaze on a ceramic blank engraved with rice-pattern decorated holes, carrying out unglazed firing on the obtained product, and carrying out high-temperature firing, so that a rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze with an antimicrobial function is obtained. In the rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze disclosed by the invention, wollastonite is adopted for replacing traditional glaze ash, so that the prepared rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze product is full bodied, rich and crystal clear, and has a deeper dark green color and better transparency; by using the strong property of the added montmorillonite component, the rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze product has a fixation and inhibition effect on viruses and bacteria as well as toxins produced by the viruses and bacteria in the air, and therefore, the rice-pattern decorated ceramic glaze has the function of inhibiting bacterial growth, and can be used as a mildew preventive.
Owner:MEIZHOU FENGLIAN CERAMICS
Salting method of sugar-vinegar garlic
InactiveCN102342465ADeliciousFor long-term storageClimate change adaptationFood preparationFood additivePreservative
The invention belongs to the technical field of food processing, and particularly relates to a salting method of sugar-vinegar garlic. The salting method of sugar-vinegar garlic of the invention comprises salting for two times, wherein during the first salting, the garlic is salted by brine, and is preserved in a cellar; after the garlic is preserved in the cellar for 5-6 months, the second salting is performed with sugar-vinegar water for 2-6 months, and the product is packaged to obtain the finished product of sugar-vinegar garlic. The salting method of sugar-vinegar garlic of the inventiondoes not add any preservative or food additive, and the salted sugar-vinegar garlic has delicious taste, is sparking and crystal-clear, and especially can be preserved for a long time without deterioration.
Owner:聂中良
Rice flour convenient for fresh eating
The invention discloses rice flour convenient for fresh eating, which has the advantages of reasonable making process, simplicity and more convenience in manufacturing, and easiness of large-scale industrial automatic production. The rice flour convenient for fresh eating disclosed by the invention keeps the nutrition and the special flavor in rice flour production, and has the advantages of optimal taste, crystal clear appearance, and attractive scent and color. The rice flour convenient for fresh eating disclosed by the invention is not retrograded, can be eaten just by opening a package, and further can be eaten after being heated by about 1-5 minutes, so that the rice flour convenient for fresh eating is convenient for fast eating, is full of nutrients and is safe; and the quality of the product has no bad variation within a quality guarantee period due to the treatment of the most advanced retrograding technology, the biological sterilization treatment and the deoxidization refreshment vacuum package, so that the longer self period (more than 12 months) can be obtained in a normal temperature condition.
Owner:沈哲明
Preparation method of vacuum freeze drying roses
ActiveCN103461016AEasy to shapeMaintain nutrientsDead plant preservationFloral handlingFreeze-dryingAdditive ingredient
The invention belongs to the field of health-care food processing and particularly relates to a technical method of vacuum freeze drying roses. A reparation method of the vacuum freeze drying roses is mainly characterized by comprising the following steps of a, picking roses; c, performing vacuum freeze drying on the roses, i.e. vacuumizing until the pressure is 15 to 25kPa, meanwhile, starting refrigeration, reducing the cold trap temperature of a vacuum freeze drier to 40 DEG C below zero to 65 DEG C below zero within 2 to 4 hours, keeping for 0.5 to 2 hours, and raising the temperature of the roses to 0 to 15 DEG C within 9 to 30 hours to dry the roses. The original bright-colored color of the roses is kept, and the nutritional ingredients and the health-care effect of the roses are kept to the greatest degree. The method has the advantages that the damage to the effective components for bioactivity of the dried roses is very low, the appearance of the dried roses is well kept, the nutritional ingredients and the active substances of the roses are kept, the moisture content is low, sugar content is high, and the roses are reddish and bright in color and luster, crystal clear and convenient to convey and store for a long time.
Owner:GANSU INSPECTION & QUARANTINE SCI & TECH RES INST
Light-emitting painted pottery glaze composition
The invention relates to a light-emitting painted pottery glaze composition which is characterized in that the glaze material is prepared from the components of, by weight, 45-55 parts of nano-silica, 25-35 parts of electronic-grade red lead, 0.4-0.6 part of graphene, 0.4-0.6 part of glyceryl behenate, 0.4-0.6 part of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin, 0.4-0.6 part of modified corn starch, 4-6 parts of copper oxide, 1-2 parts of polyethylene wax, 0.1-0.3 part of iron oxide, 1-3 parts of potassium feldspar micro-powder, 0.4-0.6 part of silver nitrate, and 1-3 parts of sea mud. The painted pottery fired with the glaze composition has a crystal clear, bright and smooth glaze, and an excellent decorative effect. With the modified sea mud, the glaze never peels from a finished product, and the product can be preserved permanently.
Owner:柳培健
Jelly and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103719648ADeliciousUniform tasteFood ingredient as thickening agentFood ingredient as flavour affecting agentSugarCrystal Clear
The invention provides a jelly and a preparation method thereof. The jelly is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5-10 parts of lotus seed, 1-30 parts of honey, 2-10 parts of chufa extractive, 5-15 parts of aloe juice, 10-20 parts of edible flower, 15-30 parts of bean, 20-30 parts of white granulated sugar and 5-8 parts of a thickening agent. The invention further provides the method for preparing the jelly. The preparation method is simple and feasible; through adding lotus seeds, honey, chufa and aloe juice, the prepared jelly is crystal clear, tastes delicious, tender and unique, and is balanced in nutrition.
Owner:江苏维尼食品有限公司
Housing with display—and/or operating-element
InactiveUS7875797B2Reduce manufacturing costPLC for automation/industrial process controlDigital data processing detailsDisplay deviceElectron
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Preparation method of fish skin collagen jelly
The invention discloses a preparation method of fish skin collagen jelly. The preparation method of the fish skin collagen jelly mainly comprises the steps that after unfreezing and pretreatment are conducted on fish skin, water, seasoning and spices are added for decoction, a compound of transglutaminase and sodium caseinate, hydrophilic colloid and preservative are added for blending, obtained skin frozen liquid is filled into jelly cups, and after vacuum sealing, high temperature sterilization and cooling shaping are conducted sequentially, products are obtained. According to the preparation method of the fish skin collagen jelly, the prepared fish jelly is long in quality guarantee period and can be preserved for six months at normal temperature; the nutritive value is high, the gel mouthfeel and elasticity are enhanced, and the shaped jelly is crystal clear, standardization control of the production technology is convenient, novel jelly cups are adopted for packing, and eating is convenient.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Powder coating for polypropylene sanitary product, preparation method and application
InactiveCN104861826ALow curing temperatureFast curingPowdery paintsEpoxy resin coatingsSolventPolypropylene
The invention relates to a special powder coating for a polypropylene sanitary product. The special powder coating for the polypropylene sanitary product comprises, by weight, 540-850 parts of special resin, 90-250 parts of special curing agents, 120-280 parts of packing, 40-90 parts of pigment, 10-20 parts of adhesion promoters and 30-50 parts of additives. The powder coating is low in curing temperature, high in curing speed and high in crosslinking density, and has excellent solvent resistance, scratch resistance and decorative performance, the problem that a polypropylene / calcium carbonate material is poor in decorative performance and chemical resistance is solved, the value of a coated object is improved, the high decorative performance is achieved, the coating effect is good, the coated object, like ceramics, is sparkling, crystal clear and lustrous, and the powder coating is quite suitable for coating of the sanitary product.
Owner:TIANJIN XIANGSHENG NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
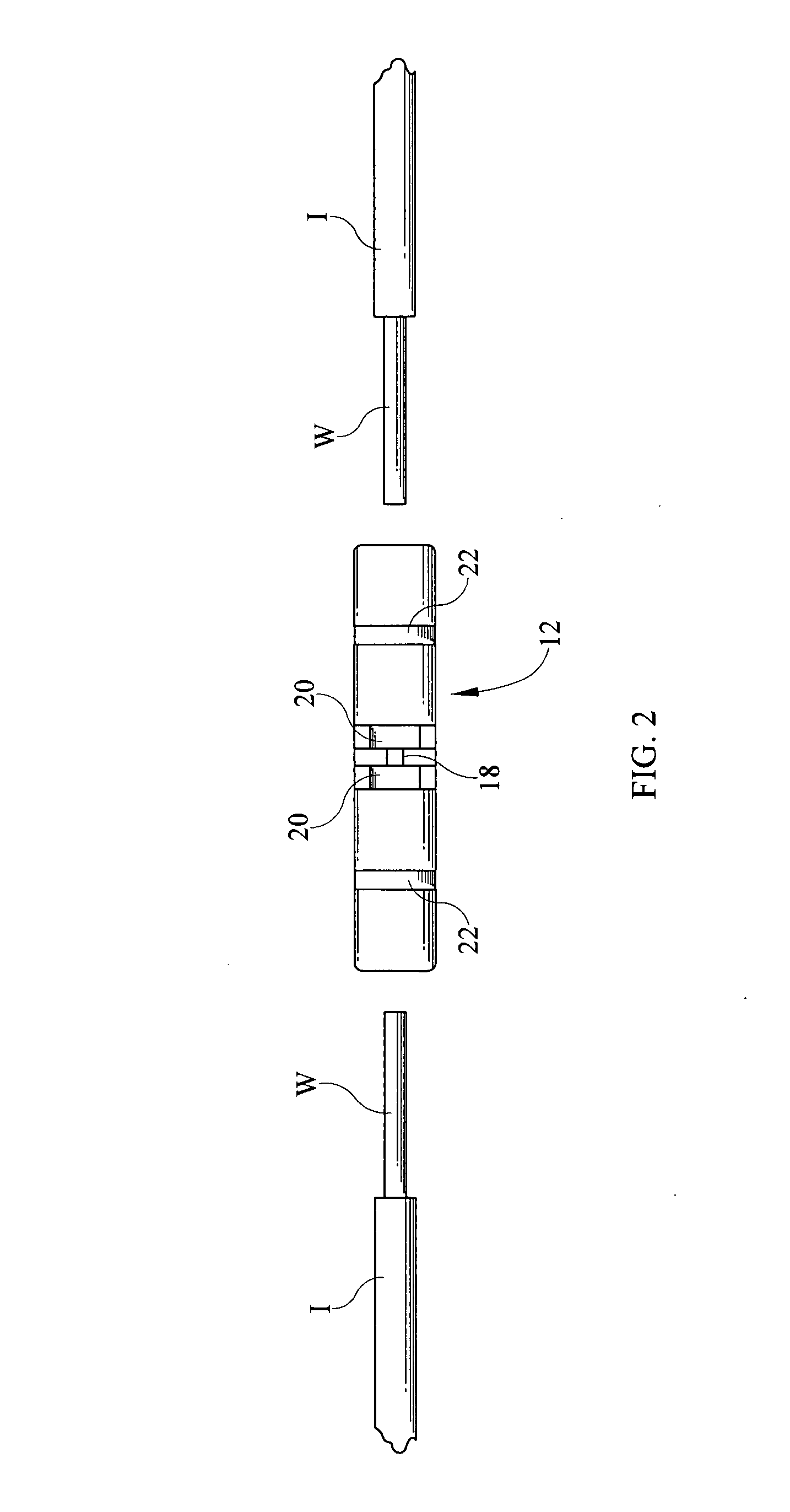
Crimpable insulated electrical connector
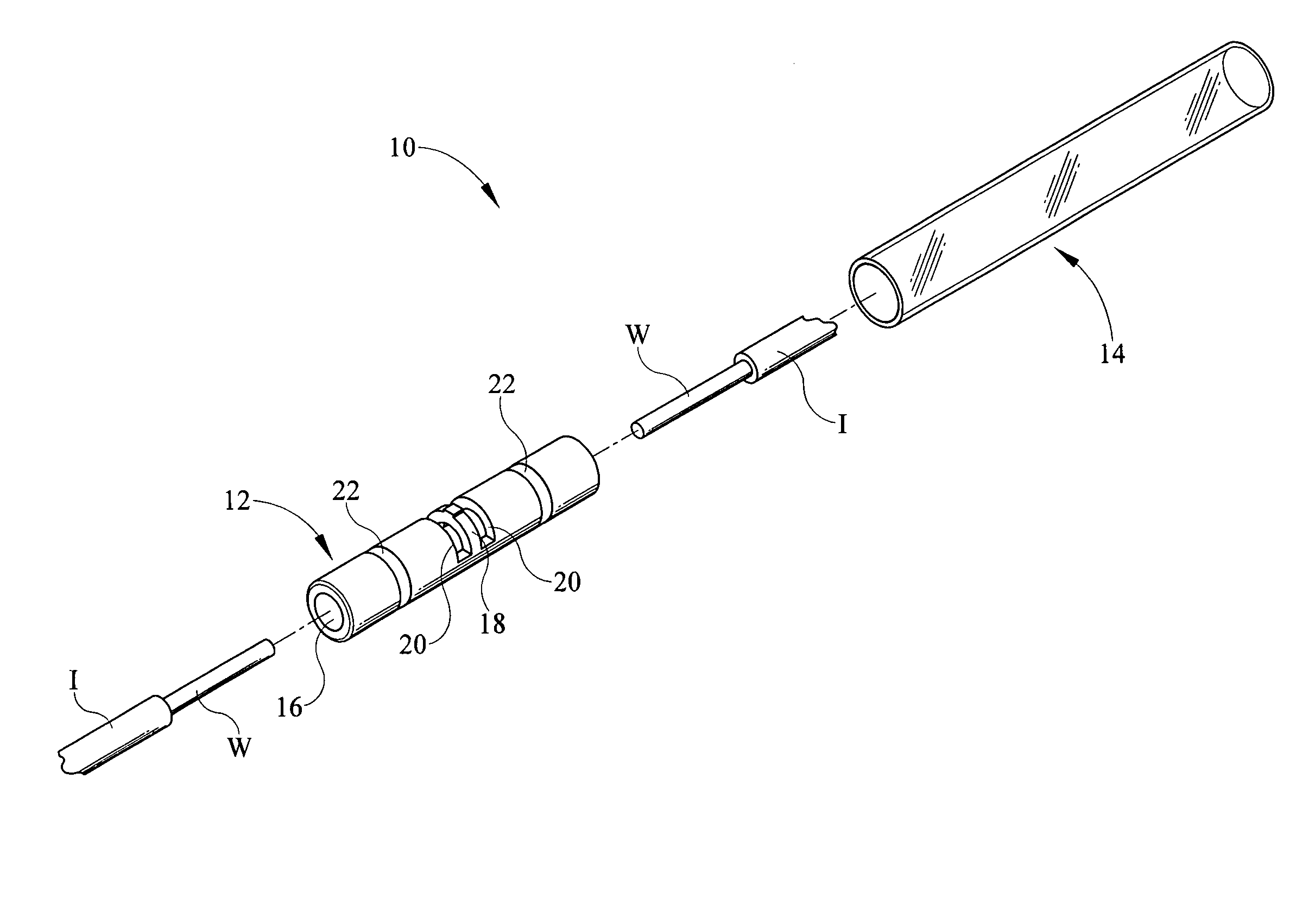
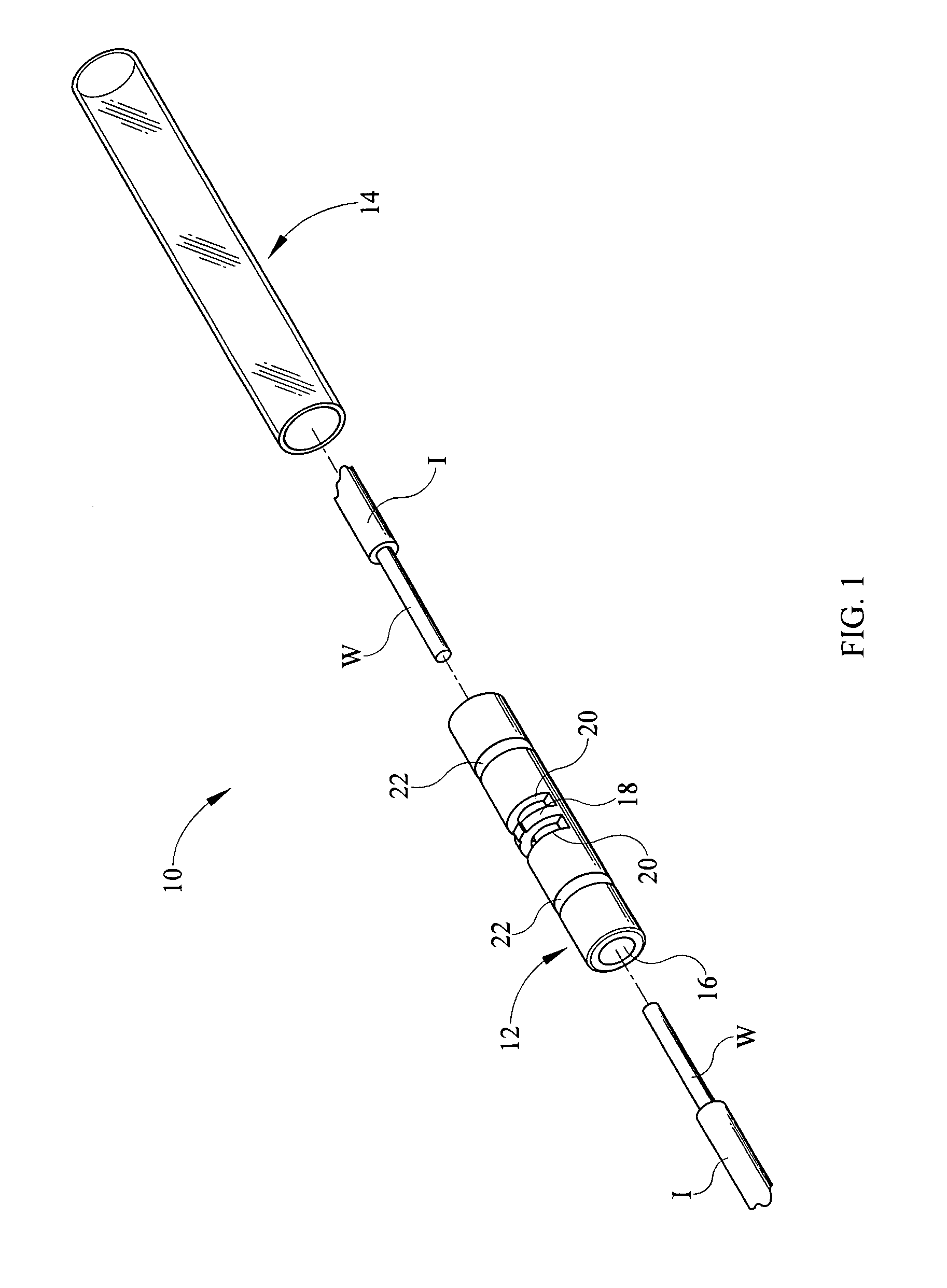
InactiveUS9184517B1Quick and easy visual inspectionElectric connection structural associationsConnections effected by permanent deformationHeat-shrinkable sleeveElectrical conductor
An electrical connector electrically connects two or more conductors in end to end orientation such that a bared end of each conductor is positioned within a hollow crimp barrel and crimped therein. The crimp barrel is held within a heat shrinkable sleeve that is crystal clear. Openings on either side of a stop within the crimp barrel allow for visual access into the central channel within the crimp barrel to assure proper placement and subsequent crimping of the conductors.
Owner:ENDACOTT JOHN E
Distiller's yeast and preparation method thereof as well as method for making wine by virtue of distiller's yeast
ActiveCN104194999ARaw materials are easy to getLow costAlcoholic beverage preparationBiotechnologyYeast
The invention relates to the wine making field and particularly relates to distiller's yeast and a preparation method thereof as well as a method for making wine by virtue of the distiller's yeast. The distiller's yeast comprises the following components in parts by weight: 80-100 parts of wheat meal, 0.1-0.3 part of flaccid knotweed herb and 40-50 parts of water. Compared with the distiller's yeast in the prior art, the distiller's yeast provided by the invention adopts pure natural wheat and flaccid knotweed herb as raw materials to ferment, and is free of any chemical additive; and moreover, the raw materials are easy to get, the cost is low, the long-term storage is easy and the use is convenient. The wine made by virtue of the distiller's yeast provided by the invention is fragrant, crystal clear in color and luster, refreshing and cool in mouthfeel during drinking, and capable of being lasting in scent while being placed in a container.
Owner:杨崇凡
Method for manufacturing three-dimensional artistic glazed brick
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a three-dimensional artistic glazed brick, which comprises the following processes of: 1) selecting a white finished brick blank as a bottom brick; 2) designing various different patterns as required, and manufacturing the patterns into a silk screen for printing; 3) wiping the surface of the bottom brick, and printing patterns of different colors and patterns on the bottom brick by using an automatic printer; 4) covering a fusion cake layer of different patterns on the bottom brick printed with different colors and patterns; 5) sintering the bottom brick covered with the fusion cake layer in a kiln; 6) polishing the sintered brick through a polisher; and 7) obtaining a final product after sorting and packing. The surface of the product obtained by using the manufacturing method becomes crystal clear, the colors below the fusion cake layer are clear and rich, the whole product has strong third dimension, and dirt absorbing problem of many polished bricks is avoided.
Owner:章云树
Preparation method of EVOH (ethylene-vinyl alcohol) copolymer
InactiveCN106146719AHigh polymerization efficiencyImprove barrier propertiesCarvacryl acetateSolvent
A preparation method of an EVOH (ethylene-vinyl alcohol) copolymer comprises steps as follows: a solvent, vinyl acetate monomers, an initiator and vinyl monomers are used as raw materials, and the EVOH copolymer is prepared through steps including replacement in a kettle, initial addition, a polymerization reaction, blowing out of residual monomers and saponification; the step of oxygen removal of the raw materials is implemented before replacement in the kettle and is implemented as follows: the vinyl acetate monomers, the solvent and the initiator are added to a mixing tank to be stirred, nitrogen is introduced while stirring to be evenly mixed, replacement is performed, and the content of oxygen in a system is smaller than 1.0*10<-3> mol / L. With the preparation method, the efficiency of the polymerization reaction is high, the conversion ratio of the polymerization reaction is 60% or above and can reach 85%, and the reaction speed is controllable. The obtained EVOH product has the good quality as follows: the chromaticity ranges from 1.0 degree to 3.0 degrees, the transparency is good, and the product is crystal clear, has the high barrier property, has the oxygen permeability being 1.0-1.2 cm<3> / (m<2>.24h.0.1 Mpa) and the water vapor permeability being 3.0-3.2 g / (m<2>.24h) and has the good processability.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Method for making enhanced mulberry wine
InactiveCN108949444AGuaranteed contentGuaranteed qualityAlcoholic beverage preparationFruit juiceDistillation
The invention provides a method for making enhanced mulberry wine. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting raw materials; (2) low-temperature crushing; (3) fermenting; (4) separating the juice from flesh timely; (5) fermenting the fruit juice again; (6) removing wine lees, fining and clarifying; (7) performing semi-solid fermentation on the pulp; (8) performing primary distillation; (9) performing secondary distillation; and (10) blending wine base. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the alcoholic strength of the enhanced mulberry wine disclosed by the invention reaches 15-17% (v / v), the sugar degree reaches 3.0g / L or less, the acidity reaches 6.5-9.0g / L, and the volatile acid content is 0.5g / L or less. The wine made by the method disclosed by theinvention has a dark ruby red color and a beautiful purple red color, is clarified and transparent in wine body and crystal clear, has elegant mulberry aroma and wine aroma as well as elegant storagefragrance, and is capable of fusing various aromas; and the enhanced mulberry wine is mellow and fine in taste, pure, sweet in flavor, complete in wine body and strong and long-lasting in aftertaste.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Sewage treatment agent and preparation method thereof
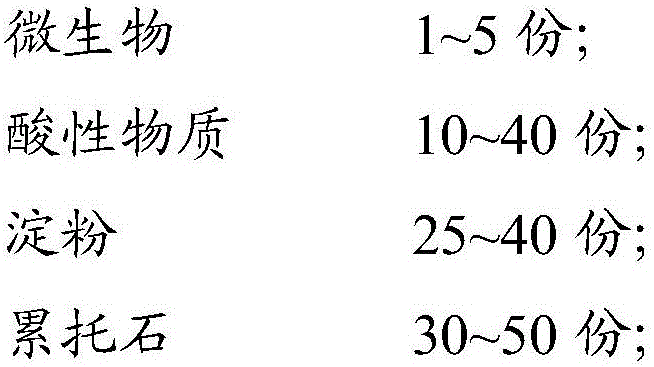
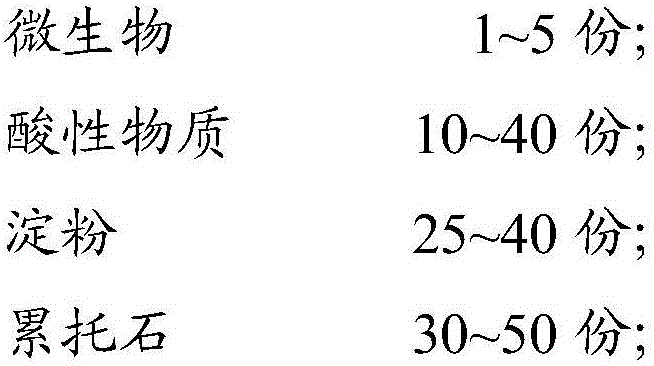
InactiveCN106007005AThere is no problem of secondary pollutionWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentMicroorganismWastewater
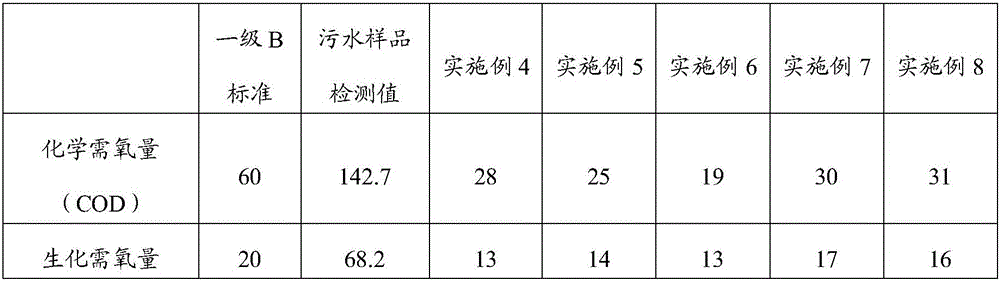
The invention discloses a sewage treatment agent, which comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1-5 parts by weight of microorganisms, 10-40 parts by weight of acidic substances, 25-40 parts by weight of starch and 30-50 parts by weight of pump Stolite; the microorganism is one or both of Rhodococcus erythropolis and Corynebacterium. The sewage treatment agent prepared by using microorganisms, acidic substances, starch, and rectorite in the present invention can produce clear, transparent, colorless and odorless water body, and its various indicators can meet GB18918‑2002 "Urban Sewage Treatment Plant Pollutant Discharge Standard" 》First-class B standard, some of the indicators can reach the first-class A standard, and there is no secondary pollution problem.
Owner:佛山杰致信息科技有限公司
Preparation technology of dendrobium officinale kimura ex migo liquor rich in plant active substances
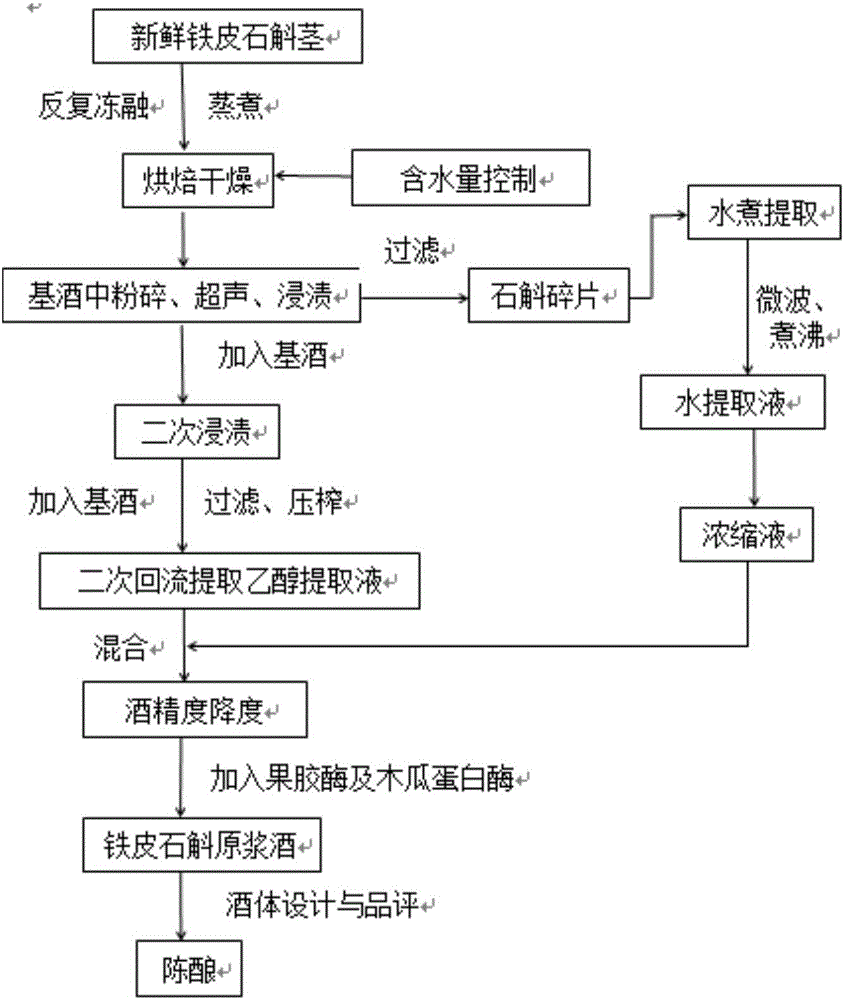
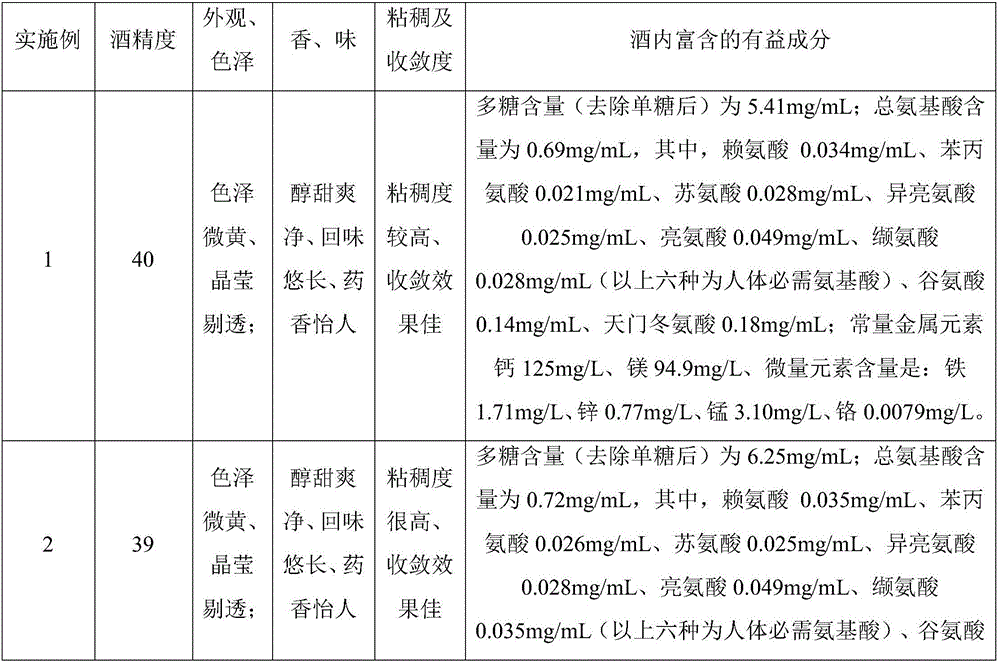
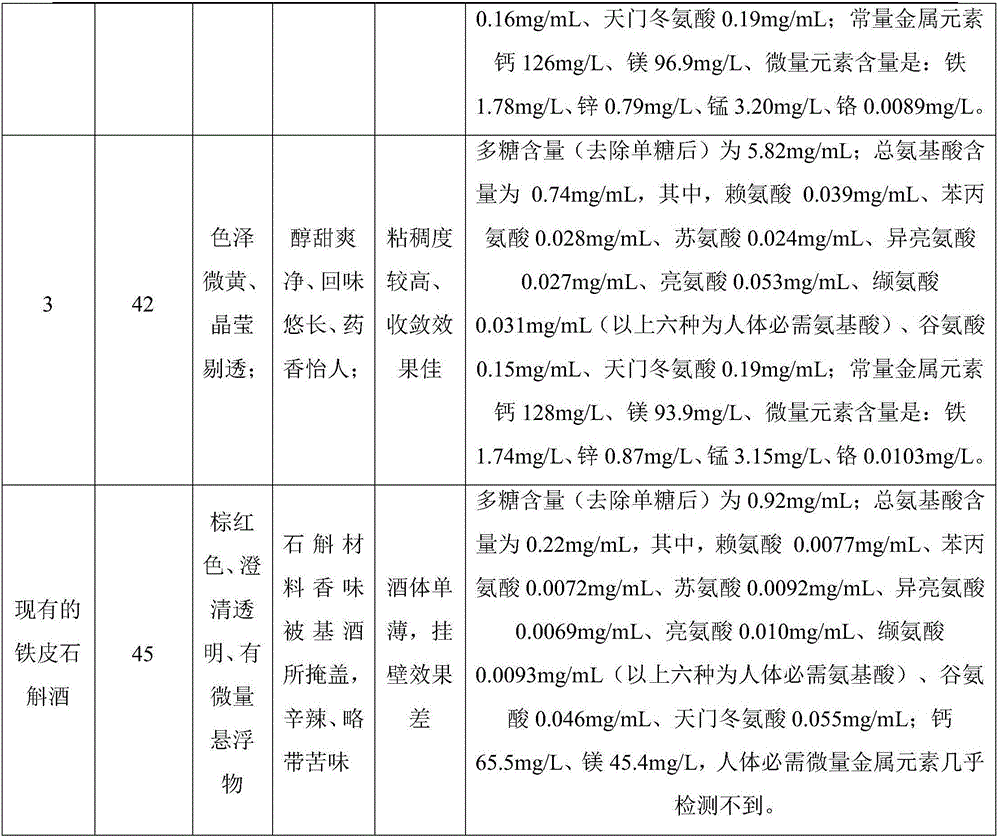
InactiveCN106754115AYellowish colorLong aftertasteAlcoholic beverage preparationFood additiveCrystal Clear
The invention provides a preparation technology of dendrobium officinale kimura ex migo liquor rich in plant active substances and belongs to the technical field of medical health foods. A novel preparation technology of the dendrobium officinale kimura ex migo liquor is provided through dendrobium officinale kimura ex migo raw material selection, raw material pretreatment, base liquor selection, active substance extraction, concentration for alcohol dropping, enzymatic clarification, production cycle and the like. By taking fresh stems of dendrobium officinale kimura ex migo as the only raw material, liquor as a carrier and extraction of the active substances from the dendrobium officinale kimura ex migo as means, the preparation technology improves the utilization efficiency of the raw material and lowers the cost. The prepared dendrobium officinale kimura ex migo liquor has the alcoholic strength of 38-42 degrees, is slight yellow in color, long in aftertaste, pleasant in medicine smell and lustre, is crystal clear, mellow, sweet, fresh and clear, is higher in viscosity, good in convergence effect and rich in active substances including polysaccharide as well as amino acid, trace elements and the like essential to a human body. The preparation technology is short in production cycle, high in raw material utilization ratio, mild in processing condition, simple and conventional in involved equipment and liable to operate and does not use any food additive.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
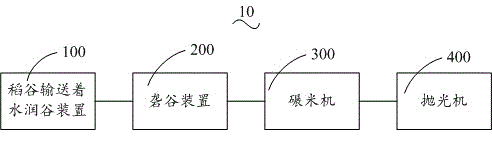
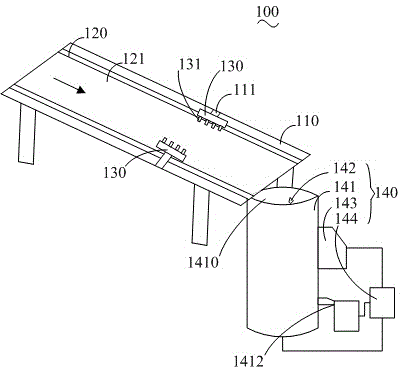
Rice processing system having reduced rate of broken rice
ActiveCN104437716AReduce breakage ratePenetrate fastGrain huskingGrain polishingBroken riceEngineering
A rice processing system having reduced rate of broken rice comprises a rice conveying and wetting device, a husking device, a rice mill and a polisher. The rice conveying and wetting device is used for wetting cleaned rice and allowing water attaching to the surface of rice to quickly permeate into husks and husked rice. The husking device is used for husking the wetted rice provided by the rice conveying and wetting device so as to husk the wetted rice and separate the husks from the husked rice. The rice mill is used for milling the husked rice conveyed by the husking device so as to obtain white rice. The polisher is used for polishing the white rice conveyed by the rice mill so as to obtain polished rice which is crystal clear and smooth.
Owner:NINGXIA HAOWANG RICE IND GRP
Raw material for sculpture and production method thereof
InactiveCN102417322AEasy to manufactureEasy to produceCeramic shaping apparatusMoisture absorptionCobalt
The invention discloses a raw material for a sculpture, comprising the following ingredients: 350-600 weight portions of dustsalt with a particle size of 100-200 meshes, 120-240 weight portions of transparent resin, 0.5-4 weight portions of methylethyl ketone peroxide, and 0.5-2 weight portions of cobalt isooctoate. The production method of the raw material for the sculpture comprises the following steps: 1) putting 60-120 weight portions of transparent resin in a container; b) drying 350-600 weight portions of weight portions of dustsalt with a particle size of 100-200 meshes to reduce the water content to less than 1 %; c) pouring the dustsalt in the container, uniformly mixing the dustsalt with the transparent resin; d) adding 0.5-4 weight portions of methylethyl ketone peroxide and 0.5-2 weight portions of cobalt isooctoate and uniformly stirring; and e) pouring the mixture in a die for curing molding with a solidification time of more than 2 h. A carving handicraft produced by using the raw material disclosed herein has the special effects of crystal clear property, muddy white color, ecological property, moisture absorption and water given off. According to the invention, the disadvantages that salt products must not get damp, are easy to dissolve, can not be shaped, and can not be stored for a long time are solved.
Owner:夏一栋
Transparent composition containing oil droplets and application thereof
InactiveCN107661230AImprove stabilityEvenly suspendedCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsVolumetric Mass DensityTrehalose
The invention discloses a transparent composition containing oil droplets. The composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 80-90 parts of deionized water, 1-2 parts of diphenylsiloxypoly trimethylsiloxane, 0.5-1.5 parts of diphenyl polydimethylsiloxane, 0.05-0.15 part of xanthan gum, 0.03-0.08 part of gellan gum, 5-7 parts of glycerinum, 3-5 parts of 1,3-propylene glycol and 1-3 parts of trehalose. By employing a special suspended thickening stable system (xanthan gum plus gellan gum), a product at a very low thickness keeps a very strong suspending ability; by employing the special grease raw materials: diphenyl siloxypoly trimethylsiloxane and diphenyl polydimethylsiloxane (great in density and high in hydrophobicity), the stability of the grease suspension is improved by compounding; and grease is uniformly dispersed in water, so that the oil droplets are uniformly suspended in water to show a crystal clear appearance.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHEENCOLOR COSMETICS CO LTD
Housing and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103096653AGood chemical stabilityImprove acid and alkali corrosion resistanceGlass shaping apparatusThin material handlingFiberHardness
The invention provides a housing. The housing body is made of colored glaze materials, the colored glaze is silica glass with lead dioxide, and fibre is embedded in the housing. The colored glaze is used for preparing housing, the housing is good in chemical stability, resistant to acid and alkali corrosion, high in hardness and wearproof, and the whole housing is crystal clear and beautiful in color. In addition, by the fact that fibre is introduced to the colored glaze, not only is the intensity of the housing greatly improved, but also the competitiveness of the housing appearance is improved. The invention further provides a preparation method of the housing.
Owner:SHENZHEN FUTAIHONG PRECISION IND CO LTD
Rich-flavor mulberry fruit wine making method
InactiveCN108611231AGuaranteed contentGuaranteed qualityAlcoholic beverage preparationFruit juiceFood flavor
The invention provides a rich-flavor mulberry fruit wine making method. The method includes steps: (1) raw material selection; (2) low-temperature crushing; (3) fermentation; (4) juice, skin and pulpseparation in good time; (5) pulp squeezing treatment; (6) temperature-controlled fermentation; (7) wine lees removal and fining clarification treatment. The alcoholic strength reaches 12.0-13.0%(v / v), the residual sugar is lower than 3.0g / L, and the volatile acid is 0.5g / L or below. The rich-flavor mulberry fruit wine making method has advantages that in multiple process procedures, the volatileacid of mulberry fruit wine is controlled through key techniques, and problems of difficulty in mulberry fruit wine making and failure in wine making due to proneness to high volatile acid are solved.By adoption of the process, infectious bacterial growth can be controlled, volatile acid content increasing can be controlled, flavor substances such as pigments in mulberries can be extracted to a greatest extent, and fruit aroma and freshness of the fruit wine can be guaranteed. The fruit wine prepared according to the method is in deep ruby red and beautiful purple red and is crystal clear, and the fruit wine has a typical mulberry aroma and a harmonious balanced oak aroma, and lasting aftertaste fruit aroma and oak sweet aroma are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Peach gum slices and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103766903AAnti-wrinkle and skin rejuvenationMoisten the intestines and detoxifyFood ingredientsFood shapingCarrageenanSucrose
The invention discloses peach gum slices and a preparation method of the peach gum slices. The method comprises the steps of (1) cleaning impurities by pretreatment; (2) hydrolysis: putting 100 parts by weight of pretreated peach gum into 200-300 parts by weight of boiling water, adding 2-5 parts by weight of citric acid, and micro-boiling for 120-160min; (3) agitation: adding 20-30 parts by weight of acid-modified starch, 0.3-0.5 part by weight of carrageenan, 0.6-0.8 part of hydroxylated lecithin, 0.3-0.5 part by weigh of sucrose ester, 0-12 parts by weight of sucrose powder, 0.0-0.06 part by weight of meringue and 0.05-0.2 part of juicy peach essence, and stirring for 30-35 min; (4) injection molding; (5) demoulding: taking the mixture formed by injection molding out from a mould to obtain primary finished products; and (6) aftertreatment: slicing the primary finished products, and drying to obtain the finished products of the peach gum slices. The peach gum slices prepared by the method are light yellow and crystal clear, have the unique flavor of peach gum, are smooth in mouthfeel and pure in taste, and have chewiness.
Owner:WUHAN GOLD ORCHARD AGRI DEV
Durable Skin Sanitizers Containing Water Stable Antimicrobial Silanol Quaternary Ammonium Compounds
ActiveUS20160346193A1Lower levelCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsHigh concentrationFood additive
This invention is a method of eliminating the number of microorganisms on the surface of skin, hair or nails, by contacting these surfaces with a water stable, antimicrobial silanol quaternary ammonium compounds (SQACs) and the trisilanol, polysiloxanol and water soluble polysiloxane derivatives thereof. The stabilizing agent is selected from a list of volatile, antimicrobial, naturally occurring, renewable phytochemical essential oils and extracts that easily form crystal clear microemulsions when water is added to the concentrated SQAC / essential oil mixture. These non-foaming oil in water microemulsions have excellent long term storage stability, are freeze / thaw stable, remain very low in viscosity and do not phase separate or precipitate for many months. Many of the essential oils found to be useful in this process are non-toxic food additives and have pleasant scents, have low flammability yet are volatile enough to evaporate upon cure down of the SQAC, thereby resulting in a higher concentration of SQAC in the cured, antimicrobial film. Economically shippable concentrations of the stabilized SQACs can be further diluted with water to application concentrations without loosing any of their stabilizing properties and remain storage stable at these lower concentrations indefinitely. In particular, the invention relates to the use of such viscosity controlled aqueous dilutions cured as durable antimicrobial coatings for human or animal skin that covalently bond to the skin, remain active through many washings and reduce or eliminate bacteria, viruses and fungi for days.
Owner:NOVALENT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com