Patents
Literature
99results about How to "Process parameters are reasonable" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
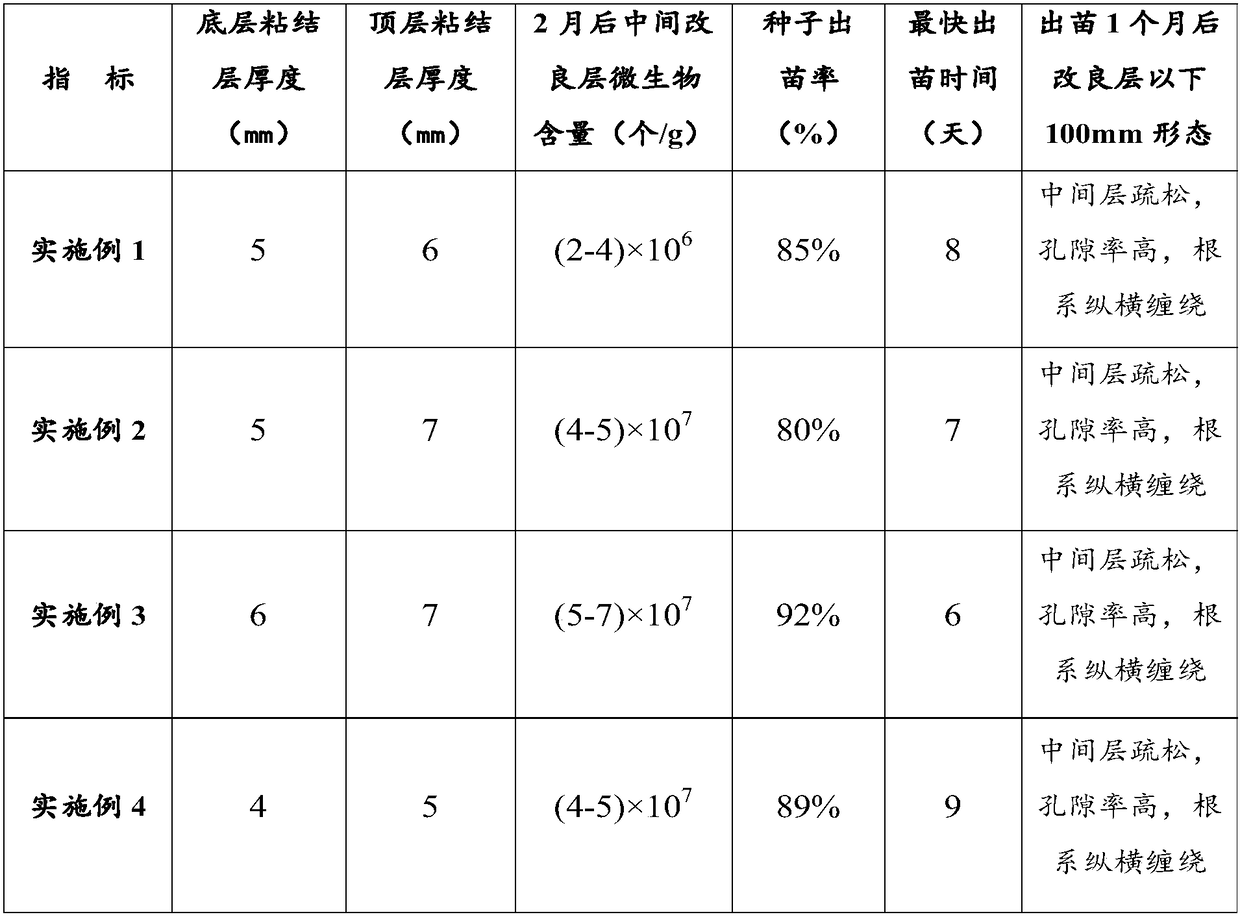
Soil improver for desert and desert soil improvement method
PendingCN108949184APromote germinationPromote pest controlBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSodium BentonitePeat
The invention provides a soil improver for desert and a desert soil improvement method, and belongs to the field of desert treatment. According to the weight parts, the soil improver for desert comprises the raw material components: diatomite, fly ash, bentonite, kaolin, peat, plant straw powder, an algae-containing carrier, an organic fertilizer, coated grass seeds, humus, zeolite powder, glass micro-beads, silica powder, a microbial liquid and the like. The soil improver for desert is composed of sand-fixing components and nutrient components with specific compatibility relation; a final product contains both solid and liquid components, also has the effects of sand fixing and soil (quality) improvement, and is a novel product for treating both roots cause and symptoms in the field of desertification control.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
A kind of preparation method of porous foamed iron-chromium-aluminum alloy material
The invention is a preparation method of porous foamed iron-chromium-aluminum alloy material, which is characterized in that: the steps include: select porous material, soak water-based polymer adhesive at normal temperature; mix chromium powder and high-activity aluminum The powder is evenly sprayed on the surface of the porous material impregnated with the water-based polymer adhesive; drying; the excess chromium powder and aluminum powder are separated from the porous material matrix; the chrome-aluminum porous material is dip-coated with conductive adhesive; Electrodeposition of iron after warm curing treatment; redox treatment; secondary diffusion treatment of chromium and aluminum to obtain porous foamed iron-chromium-aluminum alloy material. Its preparation method is scientific, the selected process parameters are reasonable, the quality is easy to control, the cost is low, and it can be prepared with light weight, large specific surface area, ultra-thickness, thickness is 5-100mm, high porosity 96-99.9%, high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance. Excellent, able to meet the requirements of high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and other harsh working conditions. It is especially suitable as high-temperature filtration, chemical catalysis, carrier, burner gas distribution and high-temperature flame-retardant materials.
Owner:JILIN ZHUOER TECH
Process for heat treatment of tube body of drill rod
InactiveCN101781702AImprove impact performanceSimple heat treatment stepsFurnace typesQuenching agentsRoom temperatureFree cooling
The invention discloses a process for heat treatment of the tube body of a drill rod, which comprises quenching and tempering heat treatment. The process comprises the following steps with the following process parameters: (1) quenching: a, conveying the tube body of the drill rod to a stepping quenching furnace with the temperature rising to be 880-930 DEG C, and keeping the temperature for 40-60 minutes; b, taking the tube body of the drill rod out of the furnace and placing the tube body of the drill rod into quenching solution with the temperature being 10-30 DEG C within 15 seconds, wherein the quenching time is no less than 30 seconds; and (2) tempering: conveying the tube body of the drill rod to a stepping tempering furnace with the temperature rising to be 560-590 DEG C, keeping the temperature for 60-85 minutes, taking the tube body of the drill rod out of the furnace, and naturally cooling the tube body of the drill rod to the room temperature. When the invention is applied, the impact performance of the drill rod is good and is 30 percent above the V150 steel grade standard; the strength, elongation rate and other mechanical indicators of the tube body of the drill rod after heat treatment meet the V150 steel grade requirements, and the qualification rate is higher than 98 percent; and the operating steps and process parameters of the heat treatment of the invention are reasonable.
Owner:CNPC BOHAI EQUIP MFG +1
Heat treatment process for joint of petroleum drill rod
InactiveCN1603429AProcess parameters are reasonableProcess parameter specificationFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCouplingHardness
One kind of petroleum drilling rod coupling heat treatment craft, after the main characteristic is installs the petroleum drilling rod coupling the frame to put in the elevation of temperature to in the 850deg.C~~900deg.C hardening furnace, keeps warm the 45~~95 minute, meets fast is entering after stirs, the temperature is in the 34deg.C~~38deg.C hardening liquid, at least cools 5 minutes, again loads the elevation of temperature to in the 560deg.C~~670deg.C tempering furnace, catches a chill, keeps warm the 120~~180 minute, latter draws a charge cooling to the normal temperature. The invention uses in petroleum drilling rod coupling quenching, the tempering heat treatment, solves in the present domestic petroleum drilling rod coupling production because the heat treatment craft not to be mature, causes the product qualified rate is only 60%~70% technical question, provides a kind to be reasonable, the standard, is advantageous for the operation heat treatment craft, caused the drilling rod coupling the degree of hardness, the intensity, the elongation ratio, the impact merit and so on completely to conform to the technical requirement, the qualified rate reaches above 99%.
Owner:江苏曙光石油钻具有限公司
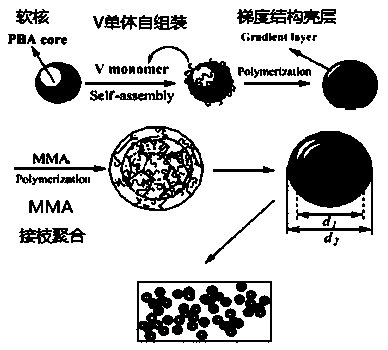
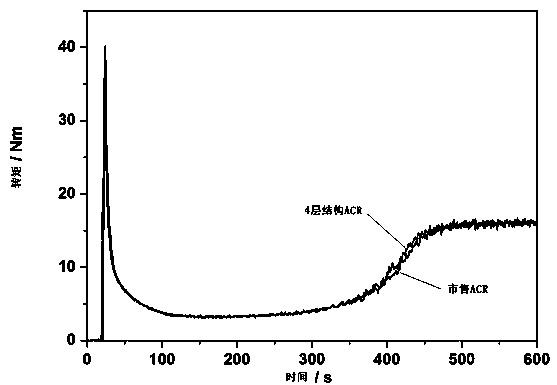
Preparation method of acrylic ester type processing aid with multilayer gradient core-shell structure
ActiveCN103467663AProcess parameters are reasonableReduce material and process costsEmulsionSolubility
The invention relates to a preparation method of an acrylic ester type processing aid with a multilayer gradient core-shell structure, belonging to the field of modification of functional macromolecular materials. The preparation method comprises the following process steps: (1) under the condition of stirring at 30 DEG C, adding deionized water, an initiator A, an emulsifier, a co-emulsifier, a dispersant, a soft monomer and a crosslinking agent into a reaction kettle, and performing pre-emulsification to obtain a pre-emulsion; (2) heating the pre-emulsion to a temperature less than or equal to 90 DEG C, and performing a thermal reaction to obtain a soft monomer core layer emulsion; and (3) adding an initiator B, alpha olefin and a monomer which has a solubility parameter similar to that of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) into the soft monomer core layer emulsion, and sequentially polymerizing 1-5 layers of rigid polymer shells with a solubility parameter similar to that of polyvinyl chloride to obtain the acrylic ester type processing aid. The obtained PVC processing aid has the advantages of low price, good effect of promoting plasticization, excellent weathering resistance, capability of improving impact properties of a product and the like, and can be widely applied to the fields of PVC building door and window profiles, pipes, wires, cables, small-scale household appliances and the like.
Owner:乌鲁木齐市华泰隆化学助剂有限公司
Manufacturing method for nickel composite board end sockets
The invention relates to a metal material machining technology and manufacturing method, in particular to a manufacturing method for nickel composite board end sockets. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of designing a die; calculating the diameter of an upper die pressure head, the diameter of an outlet of a lower die pull ring, the gap between an upper die and a lower die and the circular bead of the lower die pull ring; splicing composite boards; carrying out penetrant flaw detection; carrying out ultrasonic detection; polishing and cleaning the die; carrying out earlier stage processing of blanks; carrying out heating through a natural gas furnace; carrying out stamping forming, wherein three-time forming is adopted for the forming technology; carrying out spinning forming; cutting grooves; carrying out acid dipping; carrying out polishing; carrying out penetrant flaw detection and ultrasonic detection; stacking the end sockets. By means of the method, the stamping process is stable, transformation is even and smooth, a determined hot working system is feasible, the technology parameters are reasonable, control over the dimension of workpieces is good, metal streamline distribution is reasonable, and performance is stable.
Owner:无锡市前洲西塘锻压有限公司
Method for producing high-strength high-modules carbon fibre and special equipment thereof
InactiveCN1385567AStable output powerReaction temperature control sensitiveFibre chemical featuresMicrowave heatingTemperature controlCarbon fibers
The present invention relates to a high-strength high-modules carbon fibre and its special equipment. It is characterized by that its high-frequency heating reaction pipe is formed from deoxygenationsection. cracking section, graphitizing section air-cooling section and water-cooding section. The carbon fibre can be continuously passed through said sectional reactino pipe, the reaction temp. of the graphitizing section is controlled at 2500-2650 deg.C, under the action of catalyst the graphitizing process of carbon fibre is completed. The drafting equipment is equipped with a drafting force display device, the drafting force can be controlled in the optimum state, it also has an optical temp.-measuring device, and the output power is controlled and regulated by computer. The strength of said fibre of greater than 3.5 GPa, and its modules is greater than GPa.
Owner:张蓬洲
Water-based stearic acid amide emulsion and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103388285AAchieve micronizationGood compatibilityDefoamers additionPaper/cardboardWater basedSuspending Agents
The invention provides a water-based stearic acid amide emulsion. The water-based stearic acid amide emulsion comprises, by weight, 60-70 parts of deionized water, 30-40 parts of stearic acid amide, 3-7 parts of a wetting dispersant, 1-3 parts of an emulsifier, 0.5-1.5 parts of a crosslinking agent, 1-3 parts of a water-based defoaming agent, 0.6-1 part of a suspending agent and 1-1.4 parts of a bactericide. A preparation method of the water-based stearic acid amide emulsion comprises the steps of adding the deionized water in a dispersion pot; heating and stirring; adding the wetting dispersant, the emulsifier, the crosslinking agent, the bactericide and the suspending agent; dispersing and emulsifying the above materials; adding the water-based defoaming agent; adding stearic acid amide; grinding into particles with the particle size of 0.5-1 micrometer after stearic acid amide is completely emulsified; and discharging and packaging the materials. The method provided by the invention is simple in process, reasonable in process parameters and low in preparation cost, and realizes micro-particulation of stearic acid amide. The solid content of stearic acid amide particles in the emulsion is high. The emulsion is low in viscosity and uniform, has ideal enhancing and lubricating effects, can be stored for a long time without changing quality, does not appear phenomena of flocculation stratification, has no foam during the production, and is ideal in product quality.
Owner:杨福敬
Long thick wall petroleum drilling and mining steel pipe heat treatment technique
InactiveCN101168794AReasonable heat treatment operation stepsProcess parameters are reasonableDrilling rodsFurnace typesIntermediate frequencyThick wall
The invention provides a heat treatment technology for a long-thick wall petroleum drilling steel pipe. The invention comprises quenching and a tempering heat treatment technology. Firstly, the surface of the petroleum drilling steel pipe is cleaned, and oil stain can not exist on the surface; then quenching is performed under the intermediate frequency to be below 200 Hz, the quenching hardness reaches more than HRC48, and the tempering is performed on the petroleum drilling steel pipe within 4 hours after being quenched; during tempering, the intermediate frequency power source frequency is adjusted at 100 Hz. The adoption of the technical proposal ensures that the heat treatment operation steps and the technology parameters are reasonable and normative, the product satisfies the mechanical property requests such as hardness degree, the strength, the extensibility degree, the contraction percentage and the impact energy to a drilling rod connector issued by the department of the petroleum industry, and the qualified rate reaches more than 95 percent.
Owner:XIANYANG HENGTONG DRILLING EQUIP MFG
Physical treatment method for ginseng seeds
ActiveCN102487626APromote riftPromote germinationSeed and root treatmentPlant cellBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a plant seed treatment method, namely a physical treatment method for ginseng seeds. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) stratification pretreatment: soaking the picked ginseng seeds into normal-temperature clean water for 24 hours, filling the ginseng seeds into a bag, putting the bag into an ultrasonic container with set parameters, performing ultrasonic treatment under the condition that the ultrasonic frequency is 30 to 100kHz, the ultrasonic treatment temperature is 15 to 60 DEG C, the ultrasonic treatment power is 200 to 700W and the ultrasonic treatment time is 10 to 40 minutes, standing for 1 to 5 days after the treatment and performing conventional stratification treatment; and (2) sowing pretreatment: performing treatment according to the ultrasonic method in the (1) before sowing, and sowing. By the method, wall breakage or deformation of plant cell tissues can be promoted, so that cracking and germination of the seeds are promoted, the cracking rate and the germination rate are effectively improved, and physiological after-ripening, growth, development and matter accumulation of ginseng are facilitated.
Owner:JILIN JIAN YISHENG PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Precise near-net forming technology and device for bevel gear shaft
The invention discloses a precise near-net forming technology and device for a bevel gear shaft. The technology comprises the following steps of (a) precise saw cutting of a bar; (b) annealing treatment; (c) blank lubrication by adopting a high polymer lubricant; (d) conical blank preforming through cold heading: preliminarily preforming the blank according to a bevel angle of the bevel gear shaft and the shape of a shaft step and laying a foundation for next near-net forming of a bevel gear and a step shaft; (e) molybdenum disulfide lubrication: mixing molybdenum disulfide powder and engine oil at a ratio of (30-40wt%):(60-70wt%), coating the surface of the preformed blank with the prepared molybdenum disulfide and directly putting the preformed blank into a near-net forming die for molding; (f) precise near-net forming: forming the bevel gear shaft on a precise near-net forming device; (g) machining according to the requirements; and (h) forming of a product. The forming device comprises four parts, such as a set of combined bevel gear die, a set of combined step shaft die, a reinforcing plate and an ejector stopper.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU RES INST OF MECHANICAL ENG CO LTD
Metal wheel hub injection molding technology
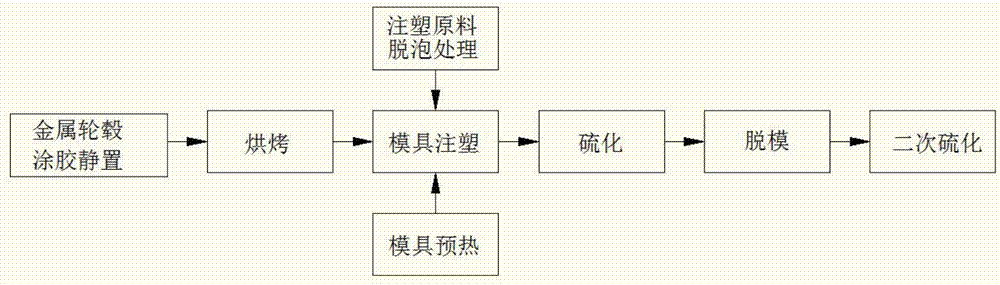
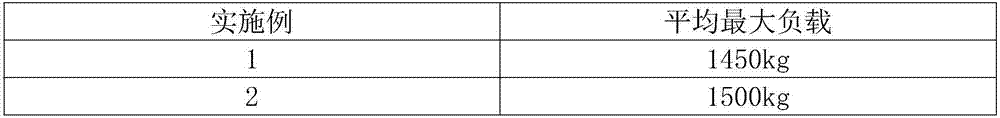
InactiveCN107263797AAvoid crackingGuaranteed adhesionTyresDomestic articlesSurface finishingInjection molding process
The invention relates to the field of wheel manufacturing, and discloses a metal wheel hub injection molding technology. The metal wheel hub injection molding technology comprises the following steps of: carrying out rubber coating on the surface of a metal wheel hub, keeping the metal wheel hub still, preheating, roasting, carrying out injection molding by using a mold, carrying out vulcanization mold release and carrying out secondary vulcanization. Good technical effects are achieved by technological parameters such as specific temperature, time and pressure through correlative creative technological design of all working procedures. The metal wheel hub injection molding technology has the technical advantages of reasonable technological parameters, simple actual operation, stable product quality and high production efficiency and solves the problems that polyurethane wheels in the prior art have unstable quality, polyurethane on the surface of adherence of a wheel hub easily cracks, falls off, drops in blocks, strips and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU TAICHUANG IND
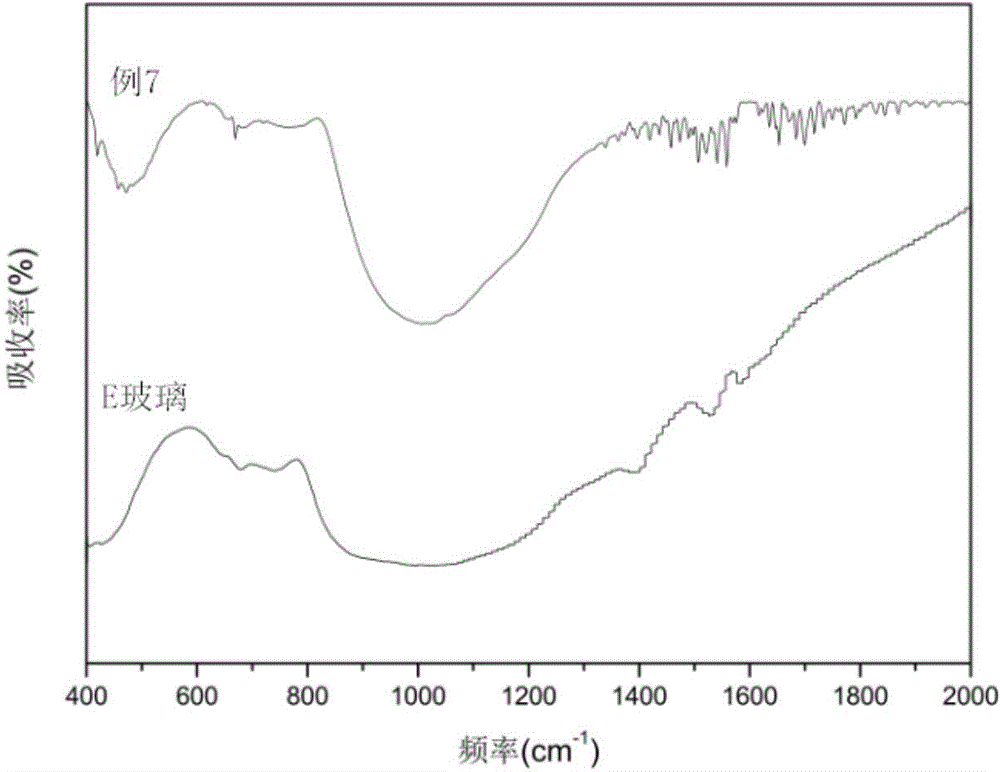
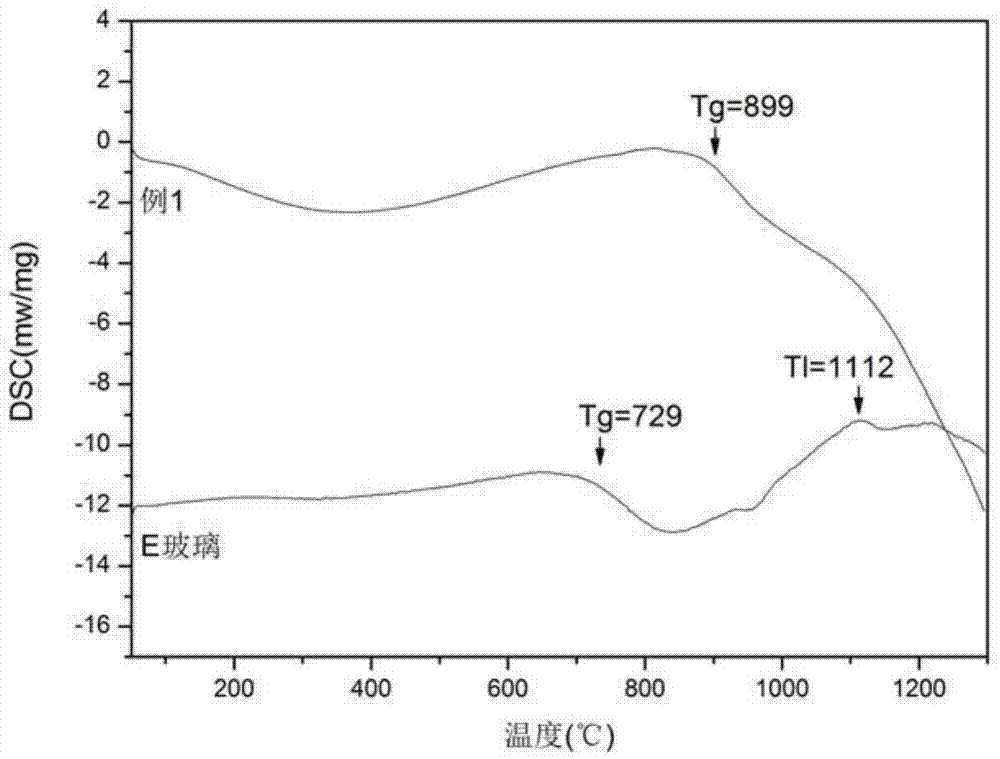
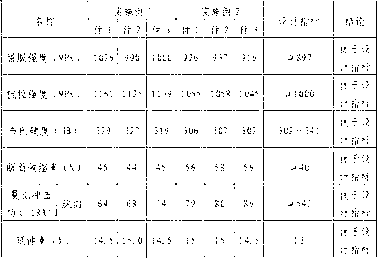
Boron-free high-performance glass fiber and preparation method thereof
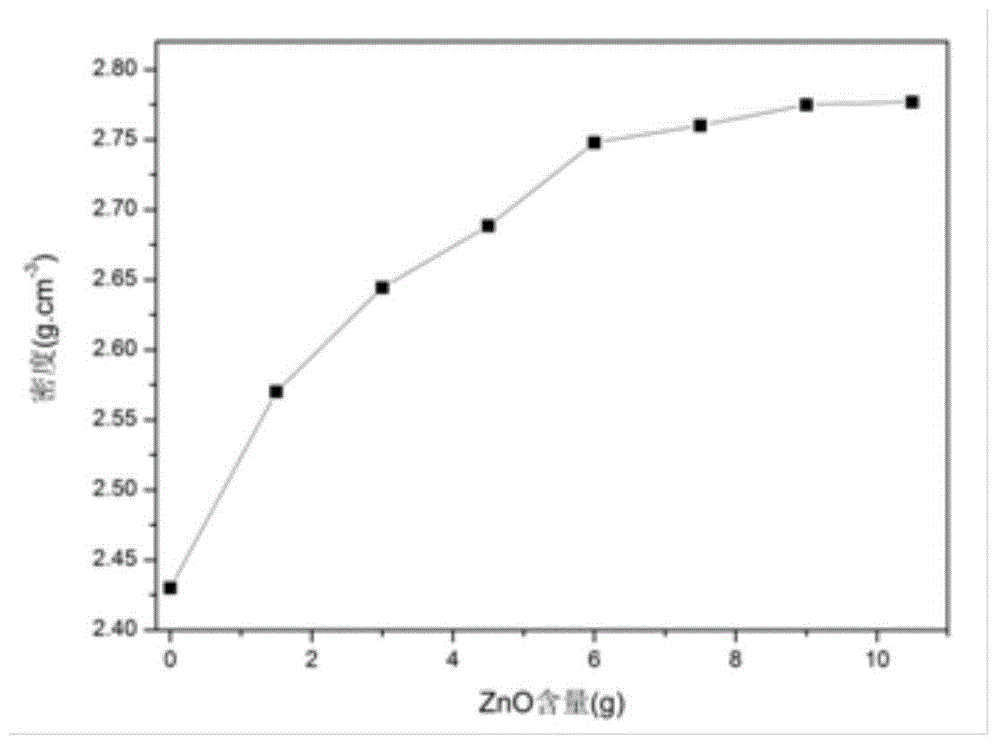
The invention discloses a boron-free high-performance glass fiber and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of materials. The boron-free high-performance glass fiber is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 30-55% of blast furnace slag, 1-15% of fly ash, 42-50% of quartz sand, 0-15% of zinc oxide, 0-2% of magnesium oxide and 0-3.5% of calcium oxide. According to the boron-free high-performance glass fiber, the adversely effects of the volatilization of boron on a kiln, the environment and the production cost are avoided, and the boron-free high-performance glass fiber has the advantages of excellent performance, reasonable process parameters, low production cost and environmental friendliness and furthermore, the raw materials can directly adopt industrial-grade raw materials and the effect is not affected.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Preparation method of flame-retardant, impact-resistant and high-fluidity chloroethylene-based special resin
The invention relates to a preparation method of flame-retardant, impact-resistant and high-fluidity chloroethylene-based special resin, and belongs to the field of modification of functional polymer materials. The preparation method comprises the following process steps of (1) adding deionized water, an initiator A, an emulsifier, a co-emulsifier, a dispersing agent, a soft monomer and a crosslinking agent into a reaction kettle at 30 DEG C while stirring, pre-emulsifying the resulting solution to obtain a pre-emulsified solution; (2) increasing the temperature of the pre-emulsified solution to be not greater than 90 DEG C, and carrying out reaction while keeping the temperature to obtain a soft monomer kernel emulsion; and (3) adding a chloroethylene-based monomer, styrene, the soft monomer kernel emulsion, an initiator B, the deionized water, and the dispersing agent into the reaction kettle and carrying out reaction while keeping the temperature at 30-70 DEG C to obtain the special resin. Compared with acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS), the chloroethylene-based special resin has the advantages of low price, self flame retardance, high toughness and the like, and can be used for completely replacing ABS and the flame-retardant ABS to be widely applied to the fields of airplanes, cars, ships, household appliances, building materials and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU HONGDING WATER
Production technique of tea wine by fermentation
InactiveCN104726266AGreat tasteHigh nutritional valueAlcoholic beverage preparationYeastNutritive values
The invention discloses a production technique of tea wine by fermentation, which comprises the following steps: adding sucrose into tea liquor, wherein the ratio of the sucrose to the tea liquor is 1.5:10; adding a citric acid solution to regulate the pH value of the tea liquor to 4-5; adding 180-220g of dried yeast to every liter of tea liquor, and fermenting at 28 DEG C while intermittently shaking the fermentation bottle; after the fermentation is finished, adding 300 mg / L chitosan into the fermentation liquid as a clarifier while stirring, stirring uniformly, standing for 7 days, carrying out clarification filtration on the supernate, and finally, sterilizing to obtain the tea wine. The production technique is simple, has the advantage of reasonable technological parameters, and maintains good taste of the tea wine. The tea wine has higher nutritive value.
Owner:QINGDAO XIUXIAN FOODS
Boron-free high-performance glass fiber taking pulverized fuel ash and desalted river sand as raw materials, as well as preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a boron-free high-performance glass fiber taking pulverized fuel ash and desalted river sand as raw materials, as well as a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of materials. The boron-free high-performance glass fiber is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 30-55% of pulverized fuel ash, 0-15% of blast-furnace slag, 40-50% of desalted river sand, 0-12%of magnesium oxide, and 0-6% of calcium oxide. The high-performance glass fiber can be prepared in a common refractory material liner smelting furnace by pretreating the pulverized fuel ash and adding a less amount of blast furnace slag, magnesium oxide and calcium oxide through taking pulverized fuel ash and desalted river sand as raw materials, the strength and elastic modulus are obviously higher than those of the common E glass and ECR, Advantex boron-free glass and the like, the preparation processes are simple, the smelting temperature is at 1400-1420DEG C, a difference between the fiber forming temperature and liquid phase temperature is more than 70DEG C which is far higher than the lowest standard of the glass fiber industrial production being 50DEG C, the production cost is low, and the glass fiber industrial production standard can be met. The component glass has higher chemical corrosion resistance and high-temperature resistance properties compared with the traditional E glass.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Heat treatment process of welded type weighted drill rod joint
InactiveCN103233113AReduce crackingImprove organizational structureFurnace typesHeat treatment bathsWater channelOil temperature
The invention discloses a heat treatment process of a welded type weighted drill rod joint. The heat treatment process comprises the following steps of: sequentially placing workpieces into a box type quenching furnace, vertically placing in a large-space mode, heating the furnace to 860 to 890 DEG C, preserving heat for at least 60 minutes, and stirring quenching oil before discharging the workpieces out of the furnace, wherein the oil temperature is controlled to be 80+ / -1 DEG C; taking the workpieces out of the furnace, throwing the workpieces into the quenching oil at once, quenching, and cooling the workpieces in the quenching oil for at least 10 minutes; performing tempering treatment on the workpieces within 3.5 hours after the workpieces are quenched, heating a tempering furnace to 600 to 630 DEG C, preserving heat for at least 120 minutes, taking the workpieces out of the tempering furnace, throwing the workpieces into a water channel at once, and cooling to normal temperature. By adopting the heat treatment process, the quenching quality is improved mainly by taking a series of technology measures of reducing the quenching upper limit temperature, increasing the heat-preserving time and the like, so that the cracking phenomenon is avoided.
Owner:JIANGSU SHUGUANG OIL DRILLING EQUIP CO LTD
Processing method of ready-to-eat tuna slice
The invention provides a processing method of a ready-to-eat tuna slice. The method comprises the following steps: preprocessing raw materials; slicing; seasoning, namely adding 490 to 510g of tuna, 15 to 20g of white granulated sugar, 6 to 8g of table salt, and 10 to 15g of bean flour, then adding 5 to 8g of cinnamon, clove, ginger powder and aginomoto, finally adding 2 to 3g of a water activity water-retaining agent, and seasoning for 3 to 5 hours; uniformly spreading the seasoned slices; drying through an oven for 6 to 8 hours at the temperature of 40 to 45 DEG C until the water content reaches 20 to 25wt%; moving out the slices; baking through an infrared baking machine for 5 to 8 minutes at the temperature of 160 to 180 DEG C until the centers of the slices reach the temperature of 85 to 95 DEG C; drying, namely, drying to dewater the slices by hot air until the water content ranges from 15 to 17wt%; cooling the dried slices to reach room temperature; and introducing nitrogen and packing to obtain the finished product. The processing method is reasonable in preparation process and easy to operate; the processed ready-to-eat tuna slices are uniform in color, fresh and delicious in taste, and unique in flavor, and meets the demands of modern people on convenient, ready-to-eat, healthy and nutritional aquatic products; in addition, the expiration date of the product can be prolonged, and therefore, the commercial value of the tuna slice can be increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Method for extracting flavonoid compound from marigold residue
InactiveCN102516335AProcess parameters are reasonableSimple process routeSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationAqueous acetoneImpurity
The invention discloses a method for extracting a flavonoid compound from a marigold residue. The method comprises the steps of: (1) conducting extraction on the marigold residue with an acetone water solution so as to obtain a crude extraction solution; (2) concentrating the crude extraction solution so as to obtain a concentrated solution, which is then cooled to obtain a crude extract; and (3) eluting the crude extract with n-hexane so as to obtain a fat-soluble impurity removed crude extract, which is then eluted by a sodium hydrogen phosphate-citric acid buffer solution, thus obtaining a product. The method of the invention takes a marigold residue as the raw material, which is subjected to crushing, sieving, as well as rapid and effective extraction of a flavonoid substance by a water solution of the organic solvent. And through concentration, precipitation, drying, and purification, an obtained yellow substance has a flavonoid compound content of over 90g RE / 100g. The method provided in the invention has the advantages of reasonable technical parameters, simple technological path, simple and safe operation, high yield, low equipment and production cost, and great practical value as well as social and economic benefits.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
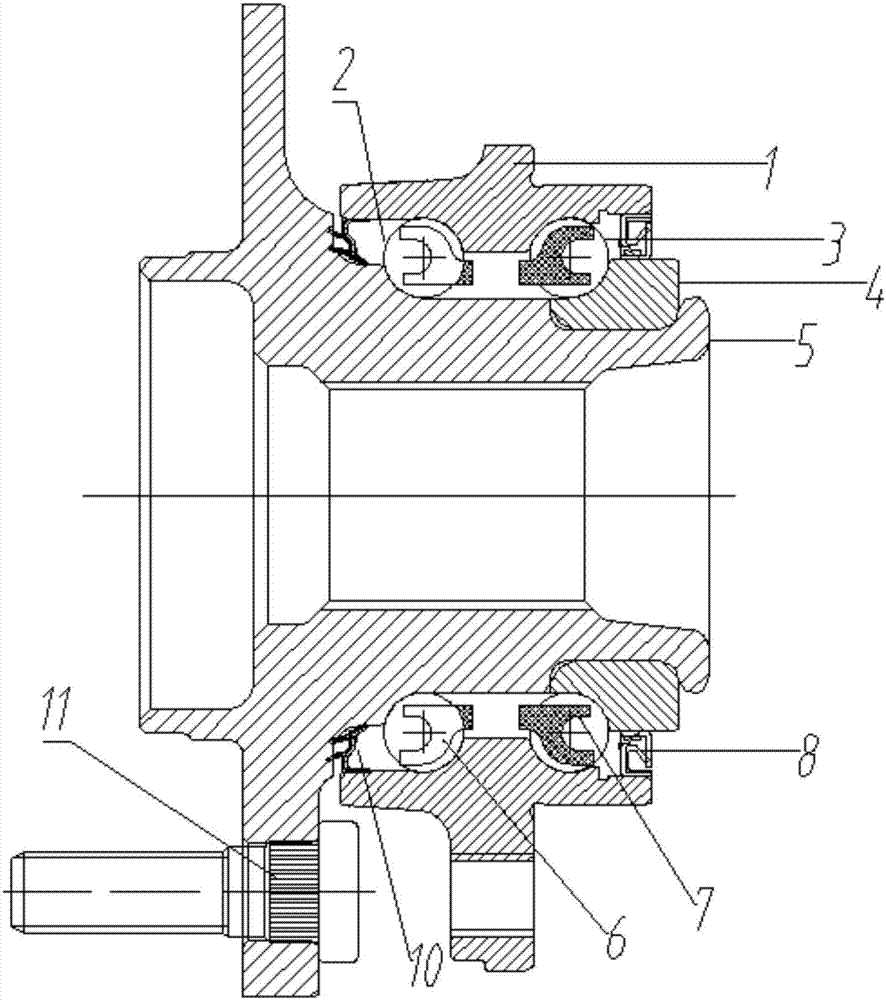
Drive hub bearing unit spin riveting pressure measurement system and measurement method
PendingCN107228725AReasonable structural designDetermination method is simpleForce measurementApparatus for force/torque/work measurementStrain gaugeAxial pressure
The invention belongs to the field of production of an automobile hub bearing unit and especially relates to a drive hub bearing unit spin riveting pressure measurement system and measurement method. The measurement system comprises an outer ring, an external steel ball, an internal steel ball, a flange plate, an external holder, an internal holder, a bolt and foil gauges. The system is reasonable in structure design and simple in measurement method, and can accurately measure axial pressure remaining on the hub bearing unit after the hub bearing unit finishes spin riveting process to determine axial pre-tightening effect under a bearing loading state, thereby preventing the problem of flange shaft rupture due to inner ring loosening and skid, and ensuring driving safety. The measurement can check reasonability of structure design of a spin riveting structure and select reasonable process parameters.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANXIANG PRECISION IND +1
A kind of preparation method of porous foamed iron-nickel-chromium alloy material
InactiveCN102277486APreparation method scienceProcess parameters are reasonablePorosityConductive paste
The present invention is a preparation method of a porous foamed iron-nickel-chromium alloy material, which is characterized in that: the steps include: selecting a porous material, immersing a water-based polymer adhesive at normal temperature; spraying nano-chromium powder evenly on the Immersion on the surface of porous material with water-based polymer adhesive; drying; separating excess chromium powder from porous material matrix; dip-coating conductive adhesive on chromium porous material; electrodepositing iron-nickel alloy after heating and curing treatment on chromium porous material ; Oxidation-reduction treatment; Carrying out secondary diffusion treatment of chromium to obtain porous foamed iron-nickel-chromium alloy material. Its preparation method is scientific, the selected process parameters are reasonable, the quality is easy to control, the cost is low, and it can be produced with light weight, large specific surface area, super thickness, thickness of 5-100mm, high porosity of 96-99.9%, high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance. Excellent, able to meet the requirements of high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance and other harsh working conditions. It is especially suitable as high-temperature filtration, chemical catalysis, carrier, burner gas distribution and high-temperature flame-retardant materials.
Owner:JILIN ZHUOER TECH
Manufacturing method for nickel board end sockets
The invention relates to a metal material machining technology and manufacturing method, in particular to a manufacturing method for nickel board end sockets. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of designing a die; calculating the diameter of an upper die pressure head, the diameter of an outlet of a lower die pull ring, the gap between an upper die and a lower die and the circular bead of the lower die pull ring; splicing nickel boards; carrying out penetrant flaw detection; detecting the hardness; carrying out stress relief annealing processing on the nickel boards; polishing and cleaning the die; carrying out earlier stage processing of blanks; carrying out stamping forming, wherein three-time cold forming is adopted for the forming technology; cutting grooves; carrying out acid dipping; carrying out polishing; carrying out penetrant flaw detection; stacking the end sockets. By means of the method, the stamping process is stable, transformation is even and smooth, a determined hot working system is feasible, the technology parameters are reasonable, control over the dimension of workpieces is good, metal streamline distribution is reasonable, and performance is stable.
Owner:无锡市前洲西塘锻压有限公司
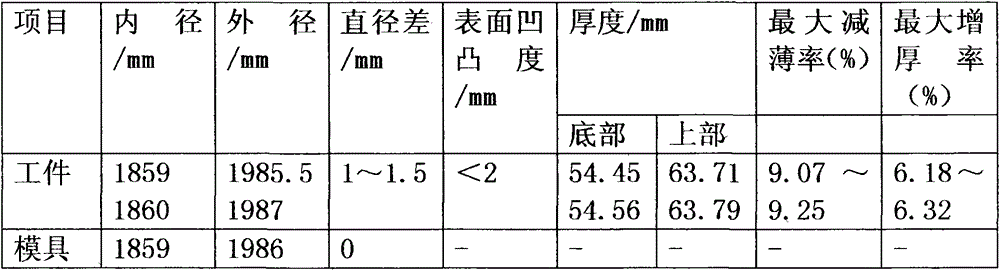
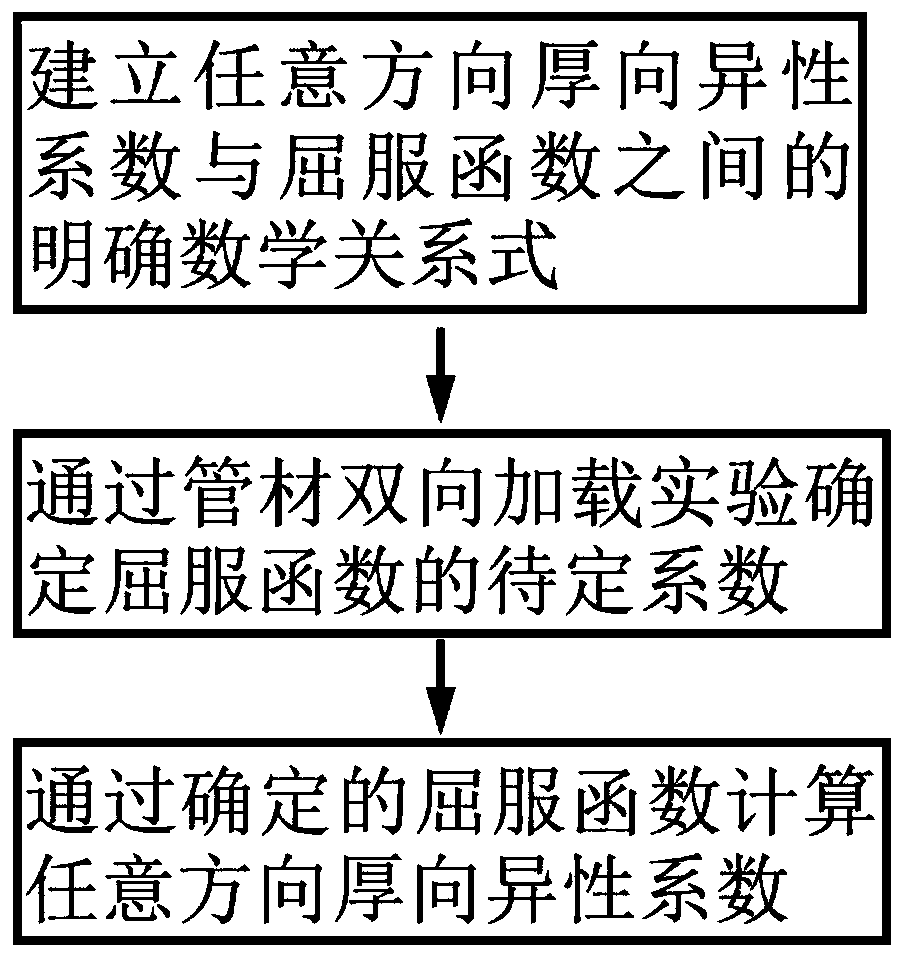
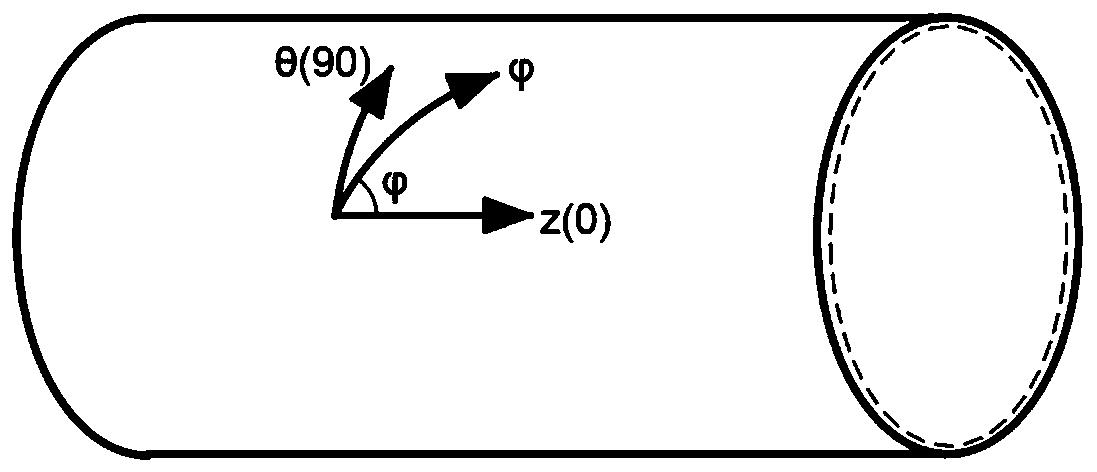
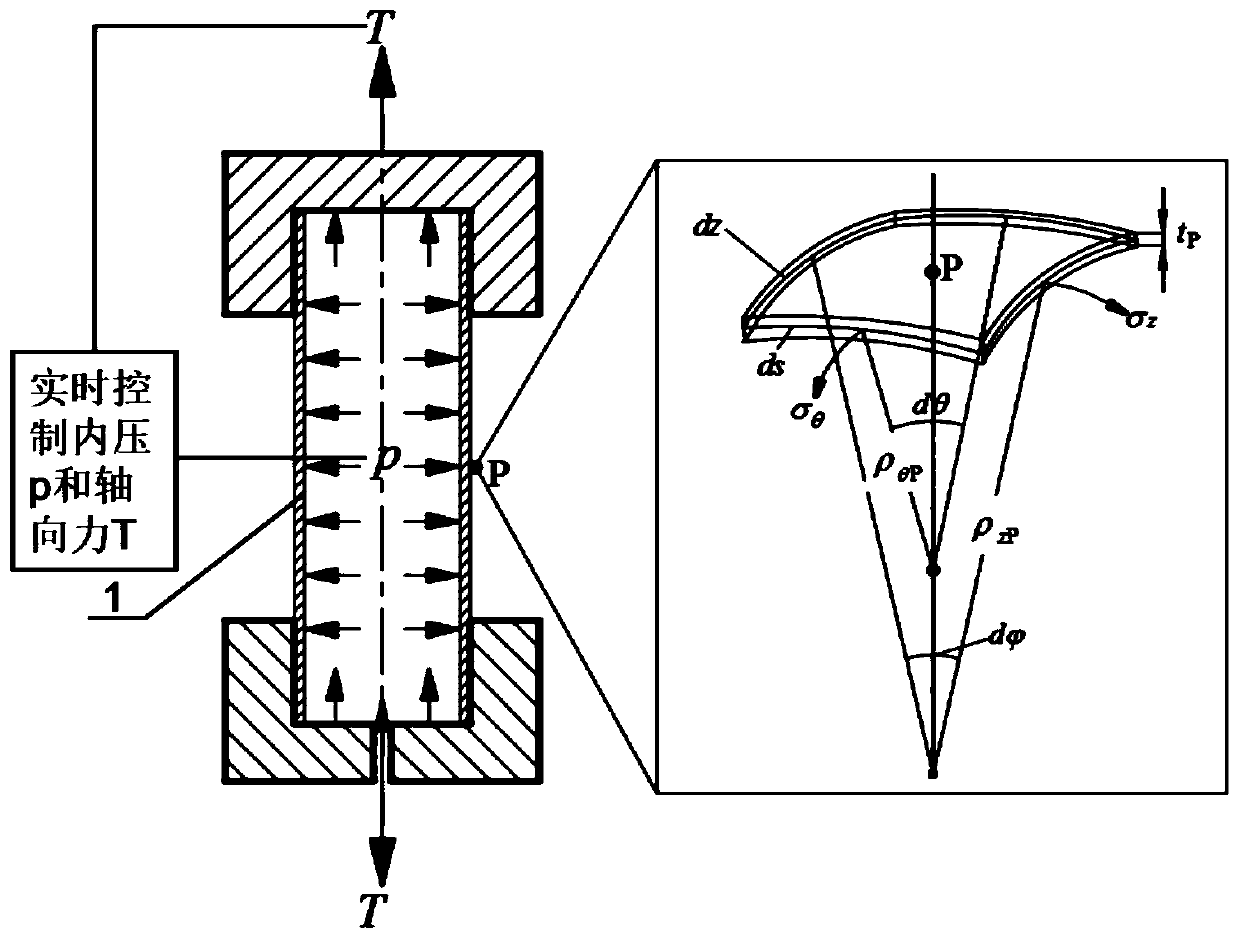
Determination method of normal anisotropy coefficient of pipe in any direction
ActiveCN110763568AAccurately reflect plastic propertiesFully reflect the plastic flow characteristicsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesExperimental methodsElement analysis
The invention discloses a determination method of a normal anisotropy coefficient of a pipe in any direction, and belongs to the field of pipe performance testing. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing a relational expression between the normal anisotropy in any direction and a yield function, determining an undetermined coefficient of the yield function through a pipe bidirectional loading experimental method, and then determining the normal anisotropy coefficient of the pipe in any direction by substituting the established relational expression. The method ensures the accuracy and reliability of the normal anisotropy coefficient from three aspects, 1) blanks of related experiments are original tube blanks, the shape of the tube cannot be damaged, pre-deformation cannot be introduced, and the obtained experiment result can accurately reflect the plasticity of the tube; 2) an advanced yield function can be selected, and experimental data under different loading paths can be introduced simultaneously, so that the plastic flow characteristic of the pipe can be reflected more comprehensively; and 3) characteristic experiments for obtaining the same deformation in different directions are designed, and the accuracy and reliability of the coefficients of the shearing components can be ensured by repeatedly iterating the finite element analysis and the characteristicexperiments, thereby establishing an accurate and reliable yield function.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Heating treatment technology for aluminum alloy castings
InactiveCN107620017ASufficient hardenabilityHigh mechanical strengthMechanical propertyMaterials science
The invention discloses a heating treatment technology for aluminum alloy castings, and relates to the technical field of metal casting. The heating treatment technology comprises the following stepsthat (1) vacuum homogenization preheating is carried out; (2) first-time normalizing is carried out; (3) second-time normalizing is carried out; (4) high-temperature tempering is carried out; (5) vacuum hardening is carried out; and (6) annealing is carried out. According to the heating treatment technology for the aluminum alloy castings, the heating temperature is appropriately improved for prolonging the soaking time, and therefore structural transformation of the aluminum alloy castings can be sufficient, the mechanical property and the impact toughness are effectively improved, and the heating treatment technology is suitable for application and popularization.
Owner:和县华顺铸造有限公司
Heat treatment technology for engine shield
ActiveCN107190130AHigh hardnessUniform grain refinementFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesRoom temperatureWater cooling
The invention discloses a heat treatment technology for an engine shield. The heat treatment technology comprises the steps of 1) carrying out normalizing, specifically, carrying out secondary normalizing treatment on the cast-formed engine shield; 2) carrying out high-temperature tempering, specifically, carrying out heat preservation on the normalized shield in a furnace at 340-380 DEG C for 6-8 hours, carrying out high-temperature tempering to increase the temperature to 670-730 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation for 8-10 hours, gradually cooling the shield until the temperature is lower than 120 DEG C, and discharging the shield from the furnace; 3) carrying out quenching, specifically, raising the temperature of the shield to 680-720 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation for 2-3 hours, increasing the temperature to the quenching temperature of 820-880 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation for 4-5 hours, and then carrying out water cooling to the room temperature; and 4) carrying out annealing, specifically, the shield is finally heated to 380-420 DEG c, carrying out heat preservation for 8-10 hours, increasing the temperature to the annealing temperature of 660-720 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation for 10-12 hours, and carrying out air cooling to the room temperature. According to the heat treatment technology, the heating temperature is properly increased and the heat preservation time is prolonged, and therefore the structure of alloy steel of the engine shield can be fully converted, the mechanical property and the impact toughness of the engine shield can be effectively improved, and the good comprehensive mechanical property requirements of the automobile engine shield can be met.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHONGTUO NEW ENERGY CO LTD
A device for simulating the initial solidification of molten steel in a mold
A device for simulating the initial solidification of molten steel in a crystallizer. The inner surface of the heating furnace is covered with a refractory material layer. The inside of the refractory material layer is a molten steel cavity. A refractory material baffle is provided at the bottom of the molten steel cavity. The first lifting rod passes through The bottom of the heating furnace is firmly connected to the refractory material baffle; the water-cooled crystallizer is located on the upper part of the heating furnace and the two are sealed and connected through a sealing ring. The second lifting rod is vertically installed above the water-cooled crystallizer, and its lower end is connected to a thermocouple. The invention has the ability to directly obtain the initial solidified shell in the mold, and simulates the solidification behavior of the initially solidified shell in the mold by squeezing the molten steel for reverse movement, which can ensure the stability of the molten steel level and ensure the stability of the molten steel. The surface conditions are more consistent with the actual on-site continuous casting steel liquid level conditions; through the initial solidification of the continuous casting billet obtained, and then combining the macroscopic heat transfer solidification with the microstructure, more reasonable process parameters can be designed, thereby reducing the need for continuous casting. The occurrence of billet quality defects.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
A preparing method of an antibacterial reverse osmosis membrane support body
ActiveCN106917285AAssisted mixing fastHigh speedBiochemical fibre treatmentFibre typesFiberReverse osmosis
A preparing method of an antibacterial reverse osmosis membrane support body is provided. The method overcomes technical problems that present production processes are too simple, and require repeated manual operation, complex operation, and the like. The method includes a) a weaving step, namely a step of weaving dacron long fibers into a blank cloth through a warp knitting machine; b) a setting step, namely a step of subjecting the blank cloth to high-temperature setting through a setting device, with the setting temperature being 160-200 DEG C and a vehicle speed being 20-26 m / min; c) a finishing liquid padding and rolling step, namely a step of preparing a finishing liquid, putting the set blank cloth into a padding and rolling device and performing padding and rolling in the finishing liquid; and d) a finishing step, namely a step of firstly pre-drying the padded and rolled blank cloth at 95-105 DEG C for 5-8 min, then drying the blank cloth at 110-118 DEG C for 3-8 min, then washing the blank cloth with water and finally drying the blank cloth to obtain the support body. The method has an advantage of simple operation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LVLONG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Production technique of Chinese wolfberry/licorice health-care wine
InactiveCN104726297AProcess parameters are reasonableLow alcohol contentDigestive systemAlcoholic beverage preparationLycium chinenseCitric acid
The invention discloses a production technique of Chinese wolfberry / licorice health-care wine, which comprises the following steps: preparing a Chinese wolfberry juice and a licorice juice from Chinese wolfberry and licorice, stirring white wine, the Chinese wolfberry juice, the licorice juice, citric acid and deionized water in a ratio of 1:0.08:0.1:0.04:1.3 in a mixer, uniformly mixing to obtain unblended wine, storing the unblended wine under sealed conditions for 3-6 months, pouring into a barrel, pouring out wine lees, and sterilizing to obtain the finished product wine. The technique has the advantage of reasonable technological parameters. The health-care wine product has lower alcohol content, has peculiar aroma of the Chinese wolfberry and licorice, has the effects of removing fire and relieving cough, and has favorable health-care function.
Owner:QINGDAO XIUXIAN FOODS
Preparation method of graphene solution
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphene solution. The method is as below: pouring sulfuric acid into a round bottom flask, adding natural flake graphite while stirring into an ice-water bath, mixing evenly, slowly adding NaNO3 and KMnO4 by batches, continuously stirring for 60 min, adding dilute sulphuric acid solution with mass fraction of 5 wt%, heating to 98 DEG C, stirring for 2 h, cooling the mixture to 60 DEG C, adding hydrogen peroxide with concentration of 30%, stirring for 2 h, filtering, washing the product with dilute hydrochloric acid and deionized water, diluting to needed concentration and stripping to obtain a graphene oxide solution; pouring the graphene oxide solution into a round bottom flask, adding hydrazine and ammonia solution, conducting magnetic stirring at the speed of 500 r / min, heating to 95 DEG C, reducing for 1 h, and filtering and centrifuging to obtain uniformly dispersed graphene solution. The method has the advantages of simpleness, easy operation and reasonable process parameters, and the prepared graphene solution is uniformly dispersed.
Owner:QINGDAO TAIHAODA CARBON MATERIAL
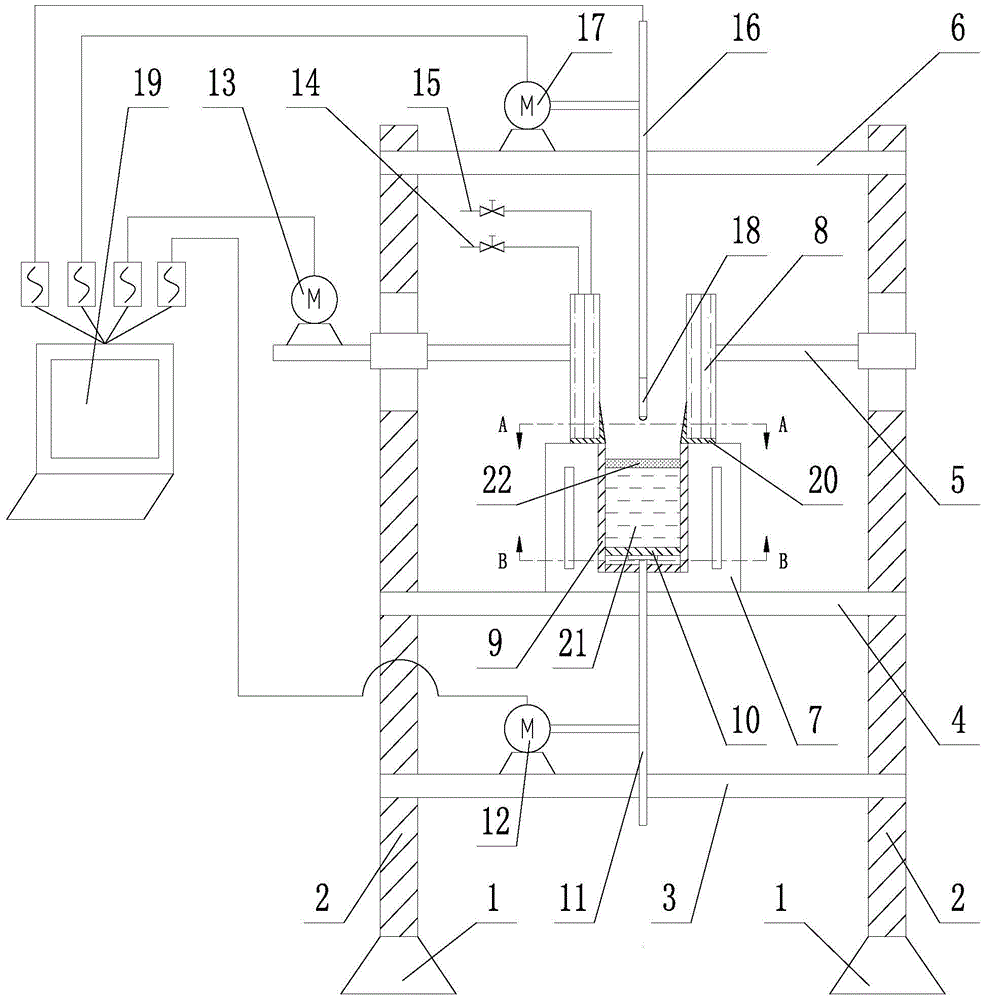
Device for simulating initial solidification of liquid steel in crystallizer
The invention discloses a device for simulating initial solidification of liquid steel in a crystallizer. The inner surface of a heating electric furnace is covered with a fireproofing layer. A liquid steel cavity is formed in the fireproofing layer. A fireproofing baffle is arranged at the bottom of the liquid steel cavity. A first lifting rod penetrates the bottom of the heating electric furnace and is fixedly connected with the fireproofing baffle. The water-cooling crystallizer is located on the heating electric furnace, and the water-cooling crystallizer and the heating electric furnace are in sealing connection through a sealing ring. A second lifting rod is vertically arranged on the water-cooling crystallizer. The lower end of the second lifting rod is connected with a thermocouple. The device has the capability of directly obtaining an initial solidification blank shell in the crystallizer, simulates the solidification behavior of the initial solidification blank shell in the crystallizer by extruding liquid steel to move reversely and can guarantee the stability of the liquid steel face, and the steel liquid face coincides with the actual site continuous casting liquid steel face better. By means of the obtained continuous casting blank initial solidification blank shell and combination of macroscopic heat transferring solidification and microstructure, more reasonable technical parameters can be designed, and then quality defects of the continuous casting blank are reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com