Patents
Literature
36results about How to "Realize value-added utilization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
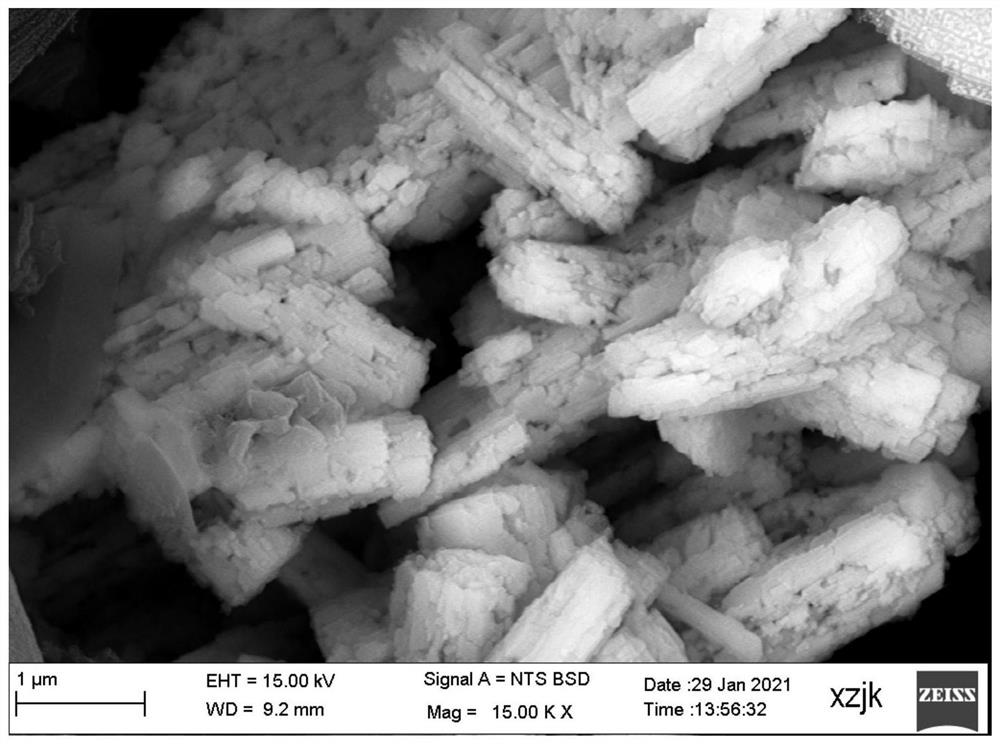
Treatment method of wet method zinc smelting by-products
InactiveCN101824541AAchieve separationSimple post-processingProcess efficiency improvementCadmium sulfateOrganic solvent
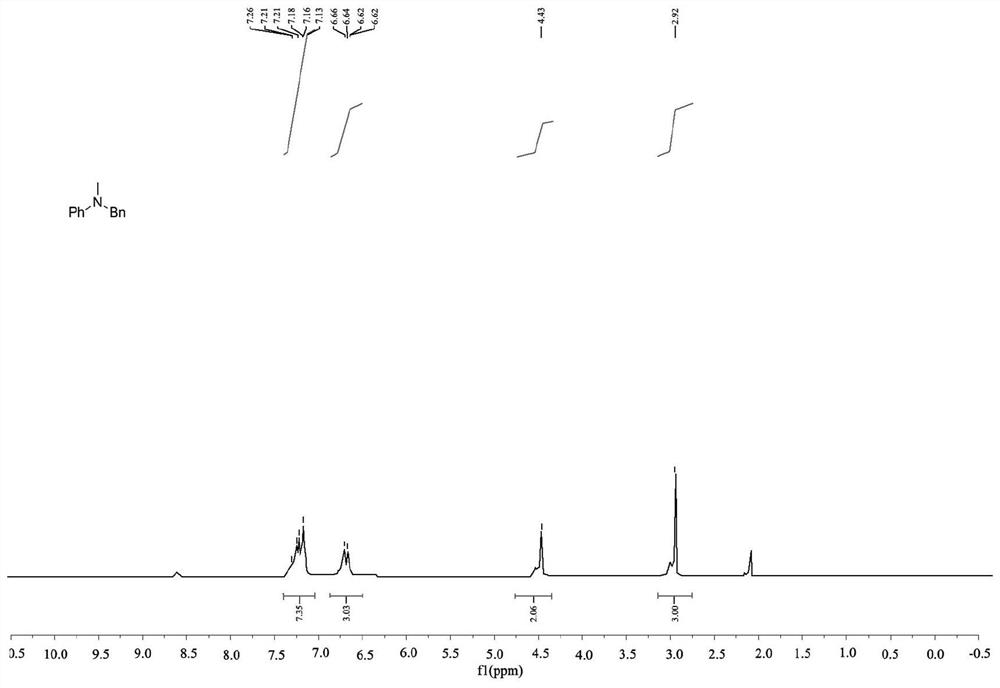
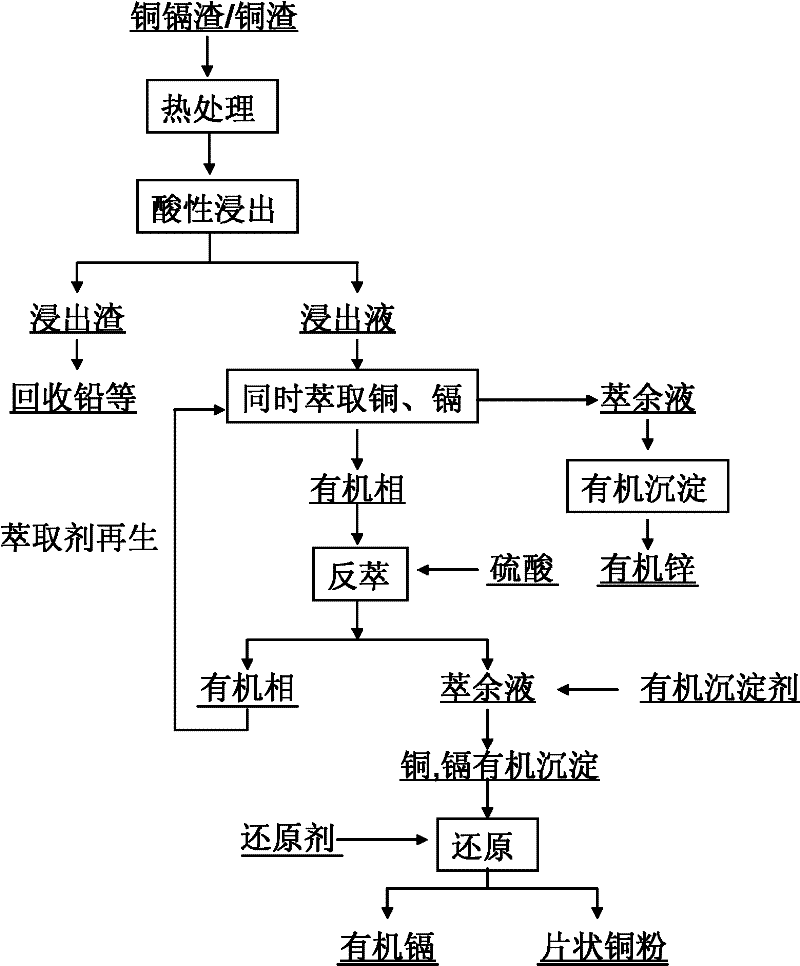
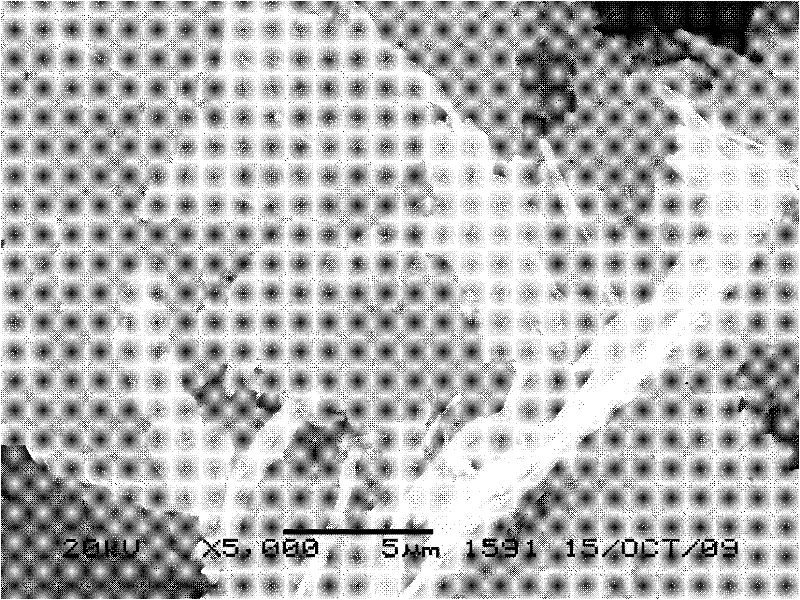
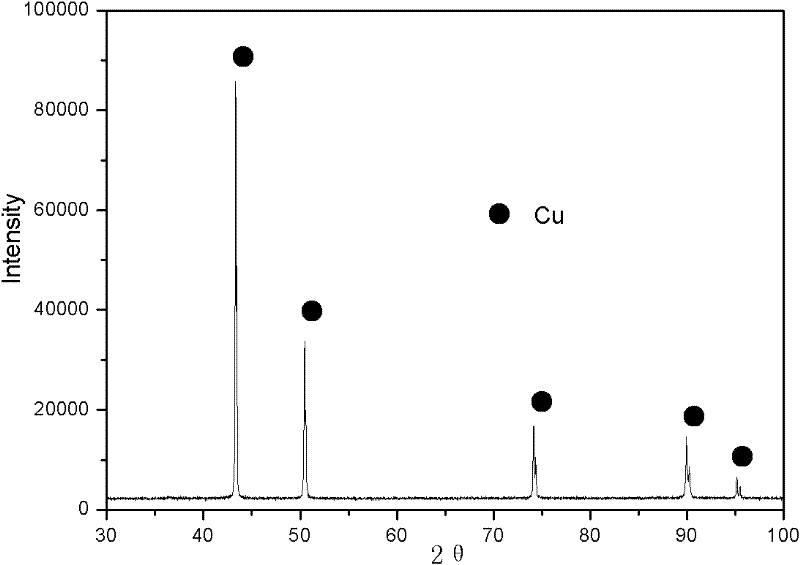
The invention discloses a treatment method of wet method zinc smelting by-products, which comprises the following steps: firstly, using a sulfuric acid solution for leaching heat treated copper-cadmium slag or copper-rich slag; then, using an organic solvent extraction method for extracting copper and cadmium at the same time from leach liquor to obtain copper-cadmium-rich organic phase zinc-sulfate-containing faffinate; using sulphuric acid for carrying out back extraction on the copper-cadmium-rich organic phase to obtain a mixed solution of copper sulfate and cadmium sulfate; then, adding a proper amount of organic precipitant into the mixed solution to obtain a mixture of organic precipitates of the copper and the cadmium; separating and washing the copper and cadmium precipitates; and adding a reducing agent solution for carrying out reduction reaction to respectively obtain sheet type copper powder and organic cadmium products. The invention realizes the value adding utilization of wet method zinc smelting by-products, reduces the treatment cost of the zinc smelting by-products, and reaches the goals of discharge reduction and yield improvement.
Owner:河池市津泰资源再生有限公司
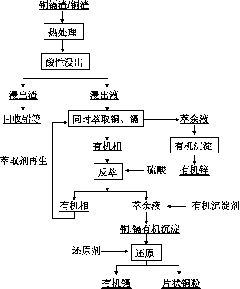
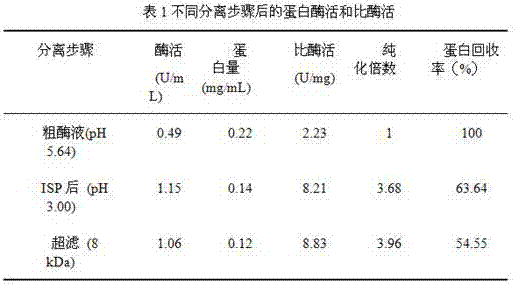
Method of quickly purifying protease of viscera of sleeve-fish and application
The invention provides a method of quickly purifying protease of viscera of sleeve-fish. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: 1) pre-treatment; 2) preparation of a crude enzyme liquid; (3) purification by an IPS method; 4) membrane separation and purification; and 5) drying. The method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that the protease of viscera of the sleeve-fish can be quickly purified; compared with the crude enzyme liquid, the protease of viscera of the sleeve-fish is purified by 3.68 times, the specific enzyme activity reaches 8.21 U / mg, and the protein recovery rate is 63.64% through ISP treatment; and through ultra-filtration, the protease is purified by 3.96 times, the specific enzyme activity reaches 8.83 U / mg, and the protein recovery rate is 54.55%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
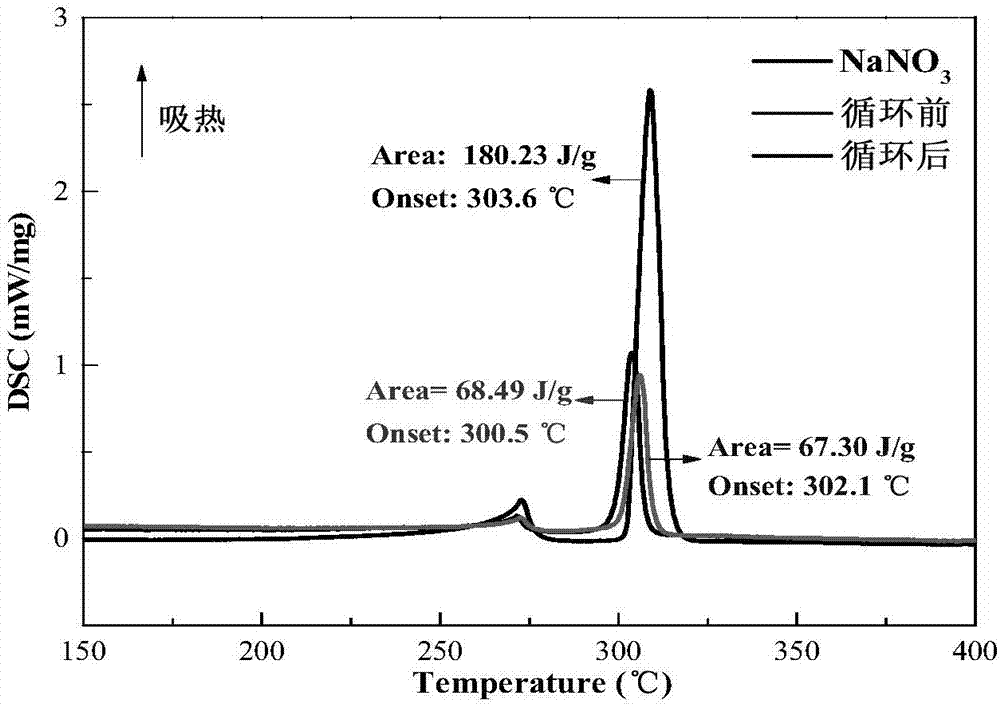
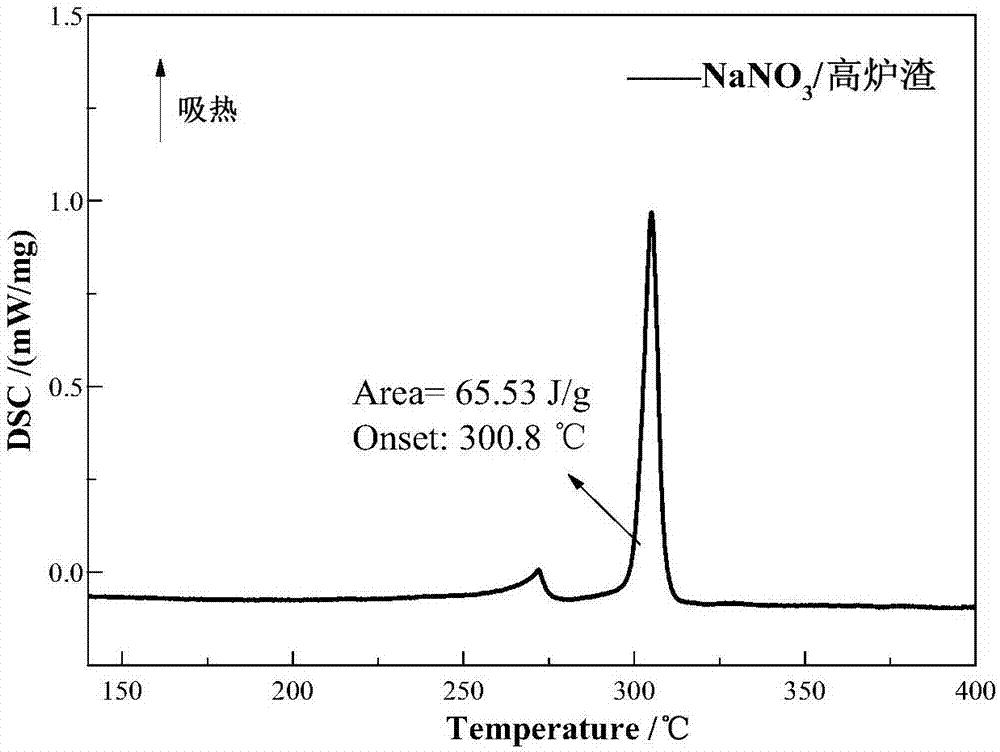
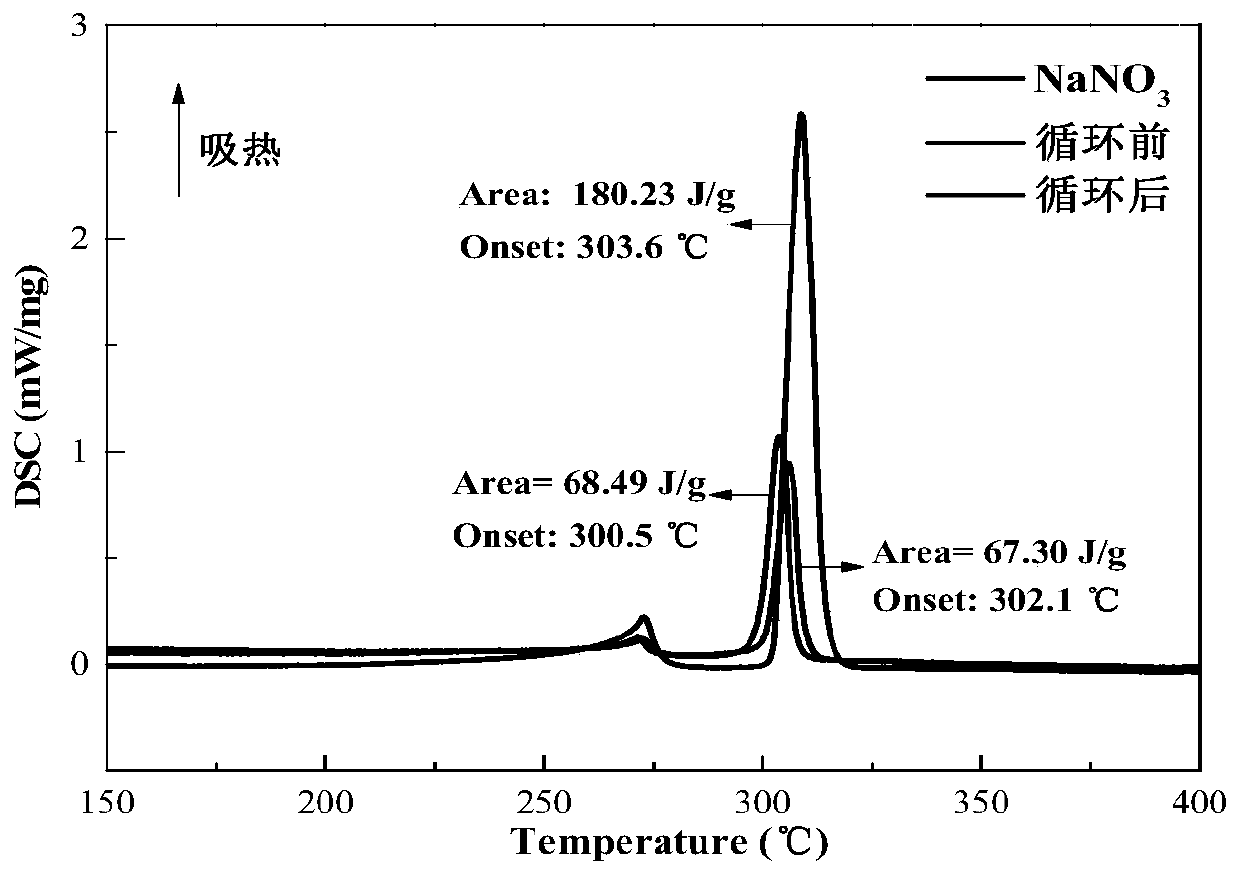
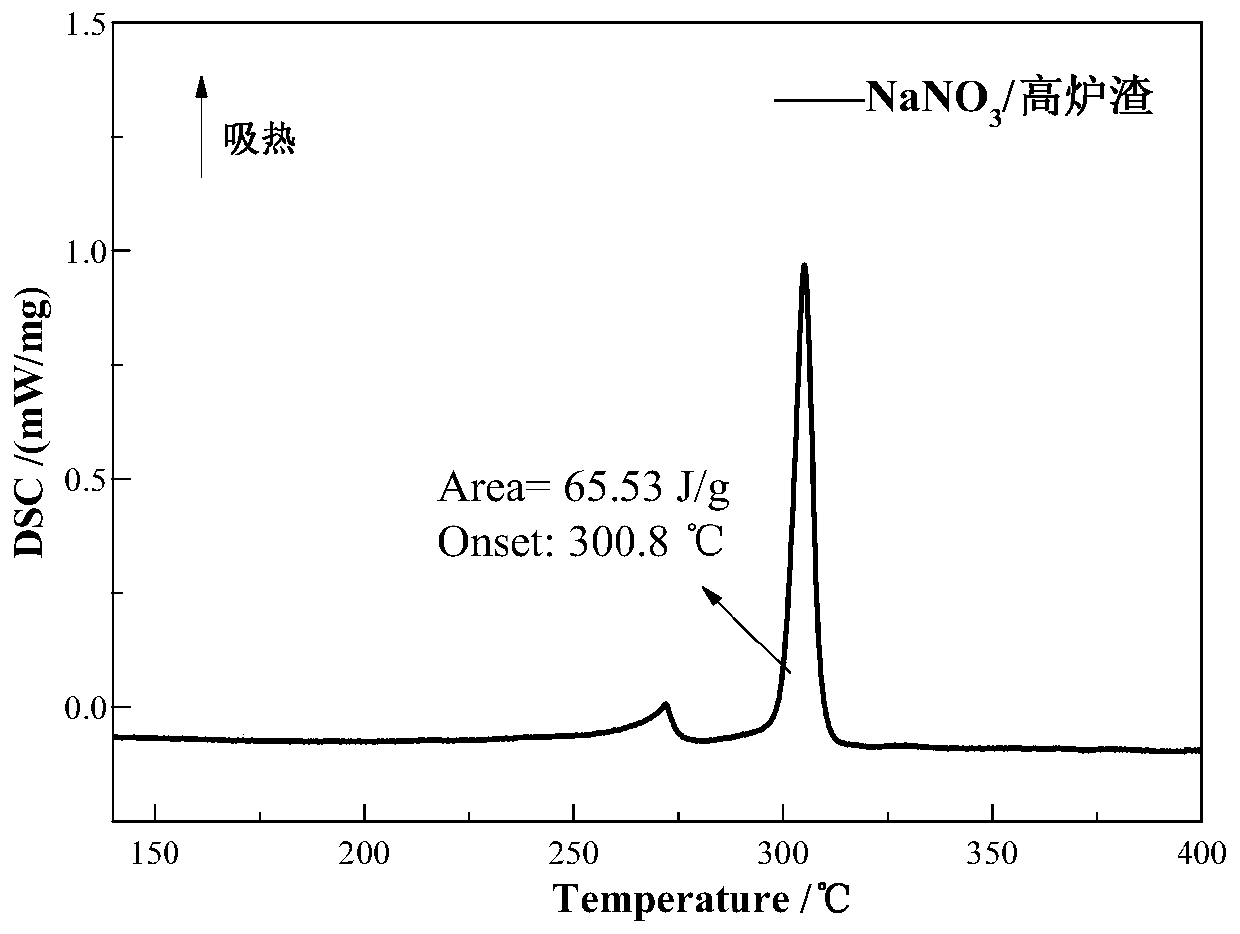
Preparation method of blast furnace slag-based composite phase-change heat storage material
ActiveCN107099275ARealize value-added utilizationReduce manufacturing costHeat-exchange elementsAir atmosphereSlag
The invention discloses a preparation method of a blast furnace slag-based composite phase-change heat storage material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing ball-milling pretreatment to a blast furnace slag raw material, uniformly mixing with an inorganic salt phase-change material and an adhesive, and pressing into a blank; sintering the blank in an air atmosphere to obtain the blast furnace slag-based composite phase-change heat storage material. The blast furnace slag has an excellent porous characteristic and can sufficiently adsorb the phase-change material, so that the formed composite phase-change heat storage material is uniform in appearance and stable in shape, does not seep out the phase-change material in the phase change process and can maintain the original outer shape; after multiple thermal cycles, the composite phase-change heat storage material still has good thermal stability, phase change latent heat and phase change temperature stability; the working temperature range of the composite phase-change heat storage material can be extended to a temperature of 300-850 DEG C according to different types of phase-change materials.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Fly ash aerated concrete blocks with sinter-dried desulfurization ash and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106316443ARealize value-added utilizationReduce the amount addedSolid waste managementCeramicwareFly ashMaterials science
The invention relates to fly ash aerated concrete blocks with sinter-dried desulfurization ash and a preparation method thereof. The fly ash aerated concrete blocks with the sinter-dried desulfurization ash solves the technical problems of unstable performance and high manufacturing cost of the existing fly ash aerated concrete blocks with sinter-dried desulfurization ash. The technical scheme of the fly ash aerated concrete blocks with the sinter-dried desulfurization ash is characterized by being composed of the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 6-9% of sinter-dried desulfurization ash, 62-68% of fly ash, 15-20% of un-slaked lime, 8-12% of cement and 1-2% of aluminum powder; and the total percentage of the raw materials is 100%. The fly ash aerated concrete blocks with the sinter-dried desulfurization ash disclosed by the invention is good in compactibility, stable in performance, good in insulation effects, simple in manufacturing processes and low in production cost, and realizes value-added utilization of the sinter-dried desulfurization ash.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
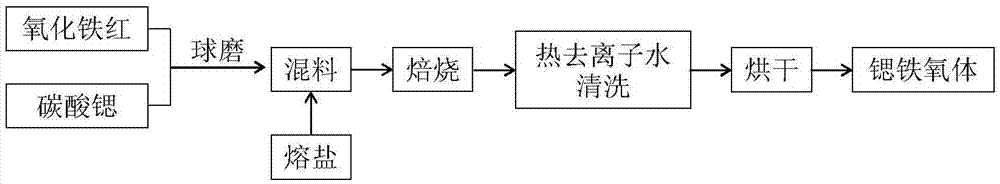
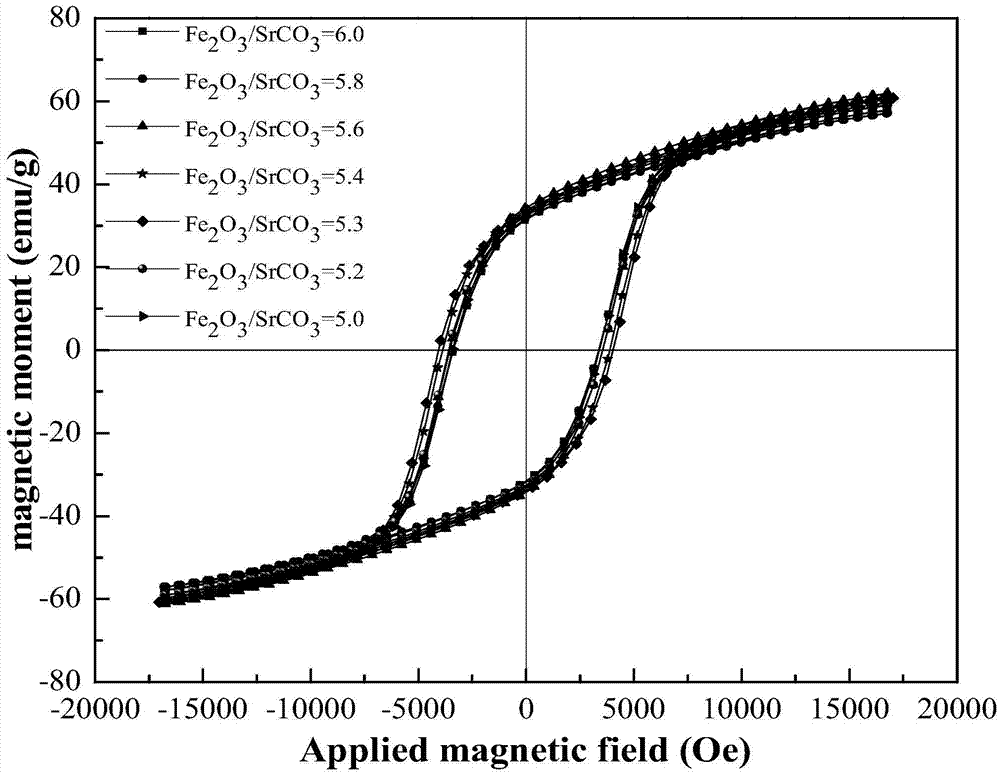
Method for preparing permanent magnet strontium ferrite by utilizing iron oxide red
InactiveCN105439208ASmall granularityUniform compositionIron compoundsStrontium carbonateGranularity
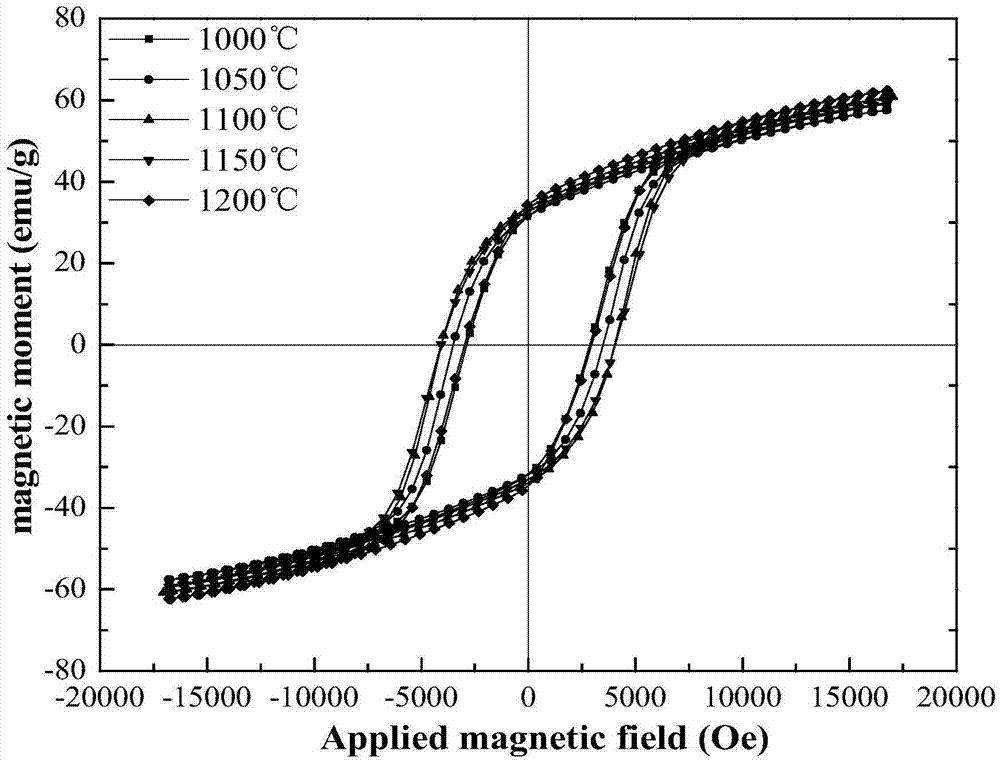
The invention relates to a method for preparing a permanent magnet strontium ferrite by utilizing iron oxide red and belongs to the fields of comprehensive utilization of resources and material synthesis. The method for preparing the permanent magnet strontium ferrite by utilizing the iron oxide red comprises the following steps: (1) mixing the iron oxide red obtained by rolling steel scale and strontium carbonate, and then carrying out ball milling; (2) mixing the material obtained through the ball milling with fused salt, and then calcining; and (3) cleaning the materials obtained after reaction, and drying, so that the permanent magnet strontium ferrite product is obtained. The method for preparing the permanent magnet strontium ferrite by utilizing the iron oxide red has the advantages that the synthetic permanent magnet strontium ferrite is small in granularity and uniform in composition, large-scale production can be realized, and the fused salt can be recycled; value-added exploration of a secondary resource, namely the iron oxide red obtained by rolling the steel scale, is realized, and the energy is saved; the prepared permanent magnet strontium ferrite is uniform in granularity distribution, and the grain size is 0.5-3mu m; and the coercive force value is 2687-4043Oe, the residual magnetism is 32.92-35.37emu / g, the saturated magnetic intensity is 59.57-62.29emu / g, and the maximum magnetic energy product is 0.42-0.61MG.Oe.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for preparing high-purity magnesium oxide from titanium sponge byproduct fused magnesium chloride
ActiveCN102139895AImprove reaction efficiencyRealize value-added utilizationEnergy inputMagnesiaGas liquid reactionDistillation
The invention relates to the technical field of comprehensive utilization of secondary resources, in particular relates to a method for preparing high-purity magnesium oxide from titanium sponge byproduct fused magnesium chloride. The method comprises the following steps: in the process of titanium sponge production, leading the fused magnesium chloride generated in a distillation process section and oxygen into an in-situ pyrolytic reaction device in a molar ratio of (1:0.5)-(1:10); and carrying out pyrolytic reaction for 1-60 minutes by utilizing waste heat of the fused magnesium chloride while stirring at the reaction temperature of 600-1000 DEG C so as to obtain a solid product containing magnesium oxide and a byproduct chlorine. In the in-situ pyrolytic reaction, oxygen bubbles are micronized and dispersed through stirring, thereby improving the efficiency of a gas-liquid reaction; based on the byproduct generated by titanium sponge as the raw material, the high-purity magnesium oxide and the chlorine product are simultaneously obtained through the in-situ pyrolysis, thereby achieving the value-added utilization of the secondary resources; and the waste heat of the fused magnesium chloride is utilized as a heat source, thereby greatly reducing energy consumption in the production process.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Protease extracted by using squid viscera as raw materials and extraction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102392010BRealize value-added utilizationIncrease the added value of fishery productionHydrolasesProtein foodstuffs working-upBiotechnologyProtease preparation
The invention discloses protease extracted by using squid viscera as raw materials and an extraction method and an application thereof. According to the invention, fresh or freezed squid viscera are used as raw materials; the squid viscera are crushed, and extracted by water or a table salt solution; the concentration of the table salt solution, the solid-liquid ratio, the temperature, and the extraction time are controlled during the extraction so as to obtain a high protease recovery rate; then protein is removed by methods of isoelectric point precipitation and flocculant addition precipitation so as to increase the protease purity; finally a liquid squid viscera protease enzyme preparation is obtained by concentration, stabilizer and preservative addition, and the like; or a solid squid viscera protease preparation is obtained by filler addition, drying and crushing. The invention realizes the application of squid viscera with increased value, increases the added value of fishery production, and reduces environment pollution caused by squid product production; the prepared squid protease can be used as an enzyme preparation for hydrolyzing various food protein; and the varietyof commercial protease is increased.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for preparing high-yield hydrothermal carbon microspheres through slurrying pre-hydrolysis liquid
InactiveCN109806837AReduce pollution loadGood spherical shapeOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesMicrosphereHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-yield hydrothermal carbon microspheres through slurrying pre-hydrolysis liquid. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a certain amount of inorganic acid is added into the slurrying pre-hydrolysis liquid to enable the acid concentration of the pre-hydrolysis liquid to be within the appropriate range; (2) a certain amount of acrylic acid isadded to serve as a functional agent, a hydrothermal reaction is conducted at a certain temperature and certain time, filtering, washing and drying are conducted, and hydrothermal carbon microspheresare obtained; and (3) the hydrothermal carbon microsphere are dispersed in an alkali solution to be stirred and activated for certain time, and the high-yield functional hydrothermal carbon microspheres are obtained. Carbohydrate and lignin in the slurrying pre-hydrolysis liquid are utilized as a carbon source, and through the hydrothermal carbonization reaction, the high-yield hydrothermal carbon microspheres are prepared; and the prepared hydrothermal carbon microspheres are high in yield and good in spherical morphology, the surfaces of the hydrothermal carbon microspheres contain a largenumber of oxygen-containing active sites, the carbohydrate and lignin resources in the pre-hydrolysis liquid are utilized, and the problem of pollution of wastewater of paper making enterprises to theenvironment is further relieved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of multifunctional feedstuff additive
InactiveCN1568748ARealize value-added utilizationImprove protectionAnimal feeding stuffIon exchangeDistilled water
The invention provides the preparation method of multifunctional feedstuff additive by using shell manufacturing leftover bits and pieces as the raw material, wherein two products of fresh flavor agent and feed addictive can be prepared, the process comprises the steps of excorticating, fragmenting biological tissue, extracting through water boiling, removing alkaline protein with hydrochloric acid and NaOH solution deposition, liquid-solid separating, adjusting pH to be 4-5, disintegrating through ion exchange process and enriching, distilled water eluting, collecting the effluent liquid, drying and disintegrating the solid body.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of alkali-activated fly ash-converted carbon nanotube/leucite porous ceramic composite material
ActiveCN113773110AAchieve compositeRealize value-added utilizationCeramic materials productionCeramicwareCeramic compositeLeucite
The invention provides a preparation method of an alkali-activated fly ash-converted carbon nanotube / leucite porous ceramic composite material, belonging to the technical field of green preparation of waste residue porous materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: pretreatment of fly ash and carbon nanotubes; preparation of an alkaline silica sol activation solution; mixing of the carbon nanotubes and the alkaline silica sol activation solution; pore forming of mixed slurry; low-temperature curing molding of a porous precursor; and high-temperature sintering ceramization. According to the invention, the porous ceramic material is prepared by taking the fly ash as a raw material, allowing the fly ash to participate in room-temperature synthesis of an alkaline inorganic precursor and synchronous and uniform dispersion of the carbon nanotubes and combining room-temperature pore-forming and subsequent high-temperature calcination treatment, so problems in resource utilization of the fly ash, green preparation of porous ceramic, strength and the like are solved, the carbon nanotube / leucite porous ceramic composite material is obtained, the mechanical strength and porosity of the porous material are improved, and recycling of fly ash and preparation of a low-cost nanometer reinforced porous material are realized.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
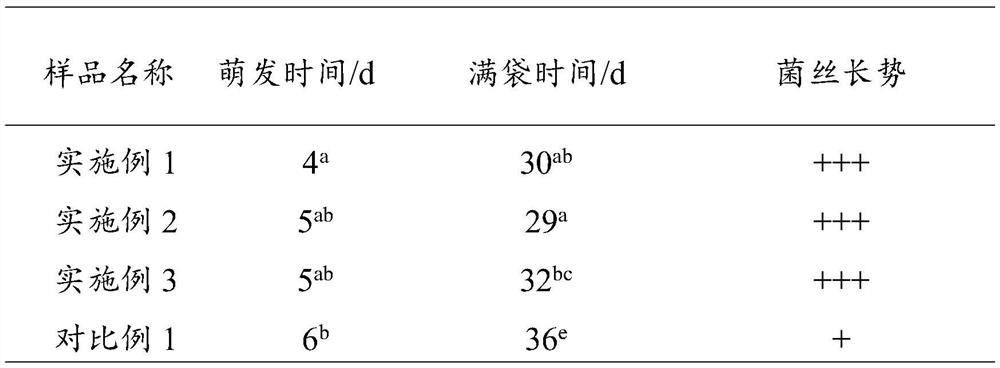
Edible mushroom bag based on walnut shell/dregs and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108419609ARealize value-added utilizationEfficient conversionCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationPhosphoric acidUrea
The invention discloses an edible mushroom bag based on a walnut shell / dreg and a preparation method and application thereof. The mushroom bag is prepared from the following components in parts by mass: 100 parts of walnut shell / dreg complex, 0.1 to 0.5 part of urea, 0.1 to 1 part of superphosphate, 1 to 2 parts of gypsum and 150 to 160 parts of water; the walnut shell / dreg complex is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 30% to 50% of walnut shell, 30% to 50% of walnut dreg, and 10% to 20% of maize straw, and the total mass percentage of the components is 100%. The walnut shell and the walnut dreg, which are by-products in production of walnut milk, are used for comprehensively developing a novel edible mushroom bag, so that the value-added exploitation of the by-products is realized, and the resources are efficiently converted; moreover, the novel mushroom bag is better in substrate nutrition and permeability, thereby facilitating mycelial growth, increasing the fruiting rate, shortening fruiting time, and significantly shortening the production cycle.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Multi-mixing method product information classification and coding method
InactiveCN106021475AQuality improvementHigh precisionRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsTerra firmaInformation resource
The invention relates to the technical field of information classification, in particular to a multi-mixing method product information classification and coding method used for classifying product information on a website or system platform. Firstly, according to product or information attributes, a linear classification method or a surface classification method is selected to use, and the product information is classified according to subjects with the linear classification method; when the linear classification method or the surface classification method is insufficient to express an integral structure or a hierarchical relationship, the linear classification method and the surface classification method are fused; since the simple linear classification method is insufficient to integrally express product structure information, the product information is expanded according to different fields and dimensions; and in the linear classification method, one-dimensional linear classification is fused to form multidimensional classification, i.e., surface-shaped classification, so as to improve data retrieval quality and accuracy, reduce redundancy, realize the value added utilization of public information resources and lay a solid foundation for constructing a steady and integrated data model.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHENTENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
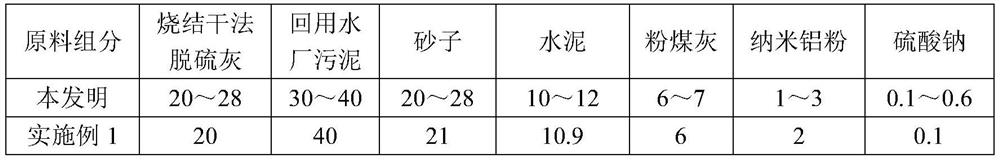
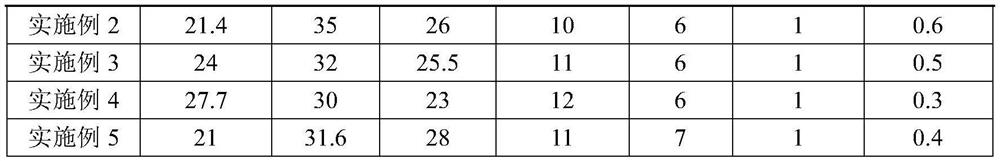
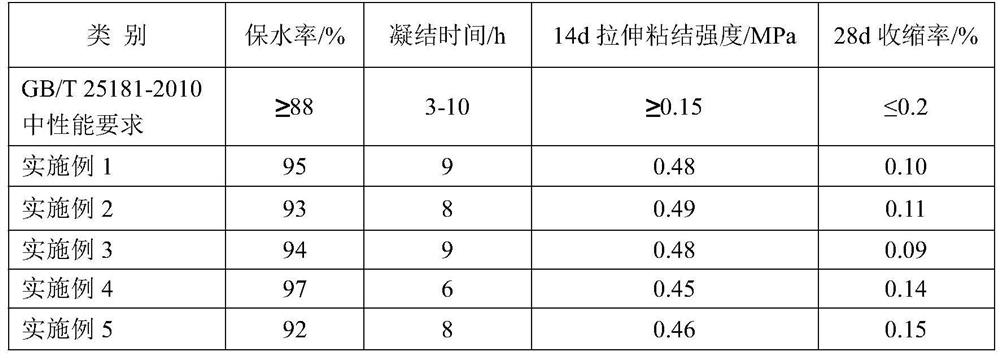
Dry-mixed mortar containing sintering dry desulfurization ash and recycled water plant sludge
The invention discloses a dry-mixed mortar containing sintered dry desulfurization ash and recycled water plant sludge and a preparation method thereof, and solves the technical problem of high manufacturing cost of the existing dry-mixed mortar. According to the technical scheme, the dry-mixed mortar containing sintering dry desulfurization ash and recycled water plant sludge comprises the following raw material components in percentage by mass: 20 to 28 percent of sintering dry desulfurization ash, 30 to 40 percent of recycled water plant sludge, 20 to 28 percent of sand, 10 to 12 percent ofcement, 6 to 7 percent of fly ash, 1 to 3 percent of nano aluminum powder and 0.1 to 0.6 percent of sodium sulfate, wherein the sum of the mass percentages of all the raw material components is 100 percent. The dry-mixed mortar provided by the invention is simple in preparation process and low in production cost, so that the invention achieves value-added utilization of sintered dry-process desulfurized ash, recycled water plant sludge and fly ash.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Roof greening cultivation system based on biomass utilization and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113924885AReduce complexityRealize value-added utilizationRoof improvementClimate change adaptationAgricultural scienceAgriculture
The invention relates to the technical field of landscaping facilities, in particular to a roof greening cultivation system based on biomass utilization and a preparation method thereof. The roof greening cultivation system based on biomass utilization comprises a protective shell, a seedling raising layer and a planting layer, wherein the seedling raising layer is a product obtained through fermentation of a first biological raw material, and the planting layer is a product obtained through mixed fermentation of a second biological raw material, livestock and poultry manure and wood vinegar; the protective shell is composed of biomass ash extracted by wood vinegar, cement and a third biological raw material; and the first biological raw material and the biomass ash are pretreated by wood vinegar. A traditional complex roof greening cultivation system is compressed and integrated into a three-layer multifunctional composite system, and biomass pyrolysis waste is combined to treat agricultural waste so as to regulate and control the comprehensive performance of the system, so that the system is better in stability, more complete in function and suitable for mechanical transplanting operation, the raw material cost, the maintenance cost and the construction cost of the roof greening cultivation system can be reduced to a high degree.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Preparation method of methylamine
ActiveCN112010767ASimple post-processingRich sourcesAmino compound purification/separationAmino preparation from aminesDodecanePtru catalyst
The invention provides a preparation method of methylamine. The preparation method comprises the following step: preparing methylamine by utilizing an amine methylation reaction, wherein in the aminemethylation reaction, the catalyst is dodecyldimethylamine caprolactone. According to the invention, additives required by the reaction are effectively reduced, and the post-treatment process after the reaction is finished is simplified.
Owner:NANJING XIAOZHUANG UNIV
Method for improving protein solubility of rapeseed cakes
InactiveCN107788223AImprove protein solubilityImprove solubilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffEnzymatic hydrolysisRapeseed
The invention relates to the technical field of feed processing, and discloses a method for improving the protein solubility of rapeseed cakes; the method includes that the rapeseed cake raw materialis subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis, wherein enzymatic hydrolysis is carried out with the water content of the rapeseed cake raw material in a range of 20-60 wt%. Through the method for improving theprotein solubility of the rapeseed cakes, with the rapeseed cakes as the raw material, the product with high protein solubility can be prepared, and the rapeseed cakes are fully utilized in feed culture industries. The rapeseed cakes have high protein solubility, and are more conducive to absorption and utilization of proteins; the problem of low profits brought by excess production capacity in rapeseed processing industries is effectively solved, and the value-added utilization of the rapeseed cakes in the feed culture industries is realized.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
Treatment method of wet method zinc smelting by-products
InactiveCN101824541BAchieve separationSimple post-processingProcess efficiency improvementCadmium sulfateOrganic solvent
Owner:河池市津泰资源再生有限公司
Preparation method of a blast furnace slag-based composite phase change heat storage material
ActiveCN107099275BRealize value-added utilizationReduce manufacturing costHeat-exchange elementsAir atmosphereSlag
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
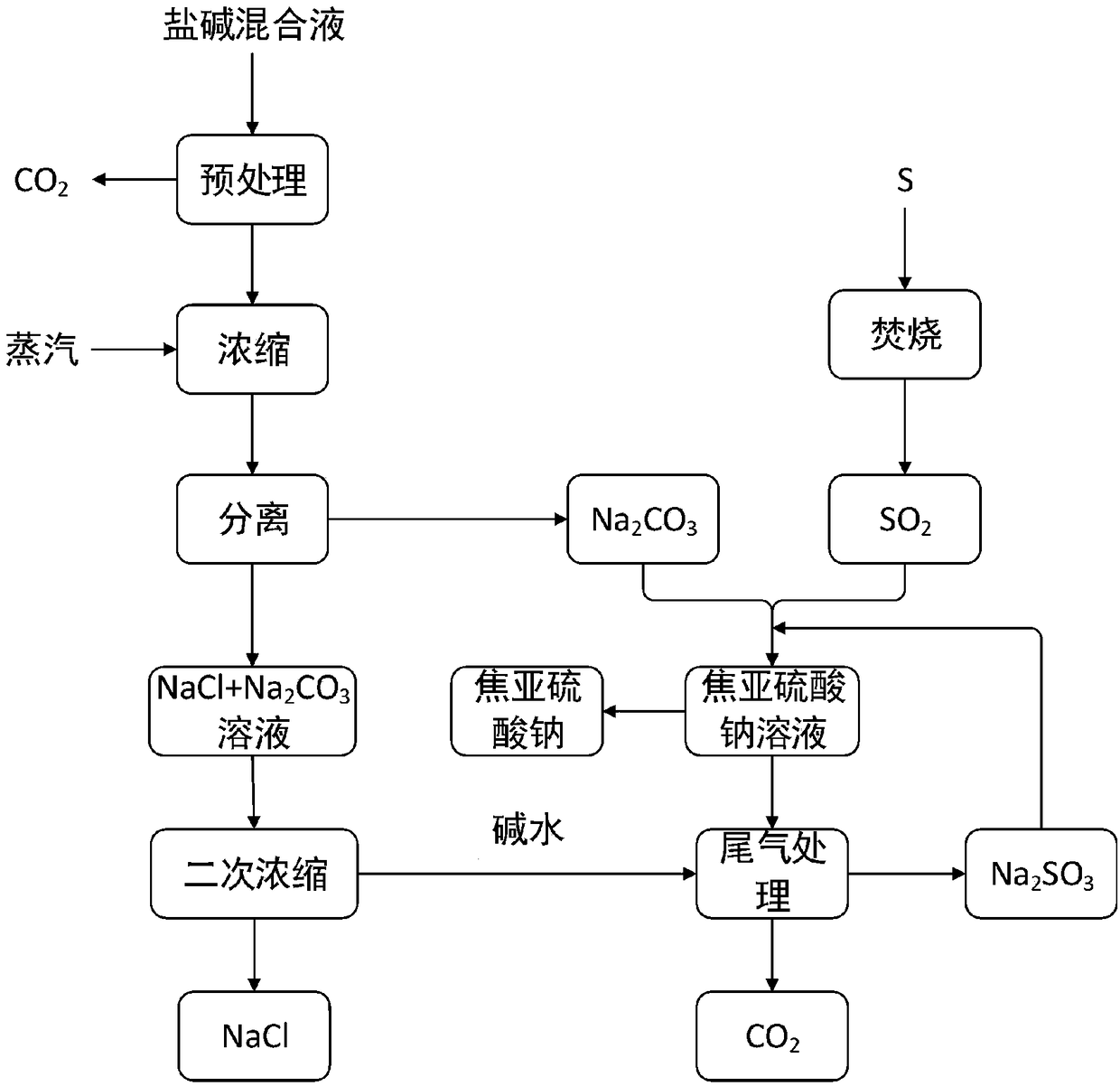
Cleaner production technology for producing sodium metabisulfite and sodium chloride through saline-alkaline mixed liquor
InactiveCN108715453ARealize resource utilizationRealize value-added utilizationAlkali metal sulfite preparationAlkali metal chloridesSodium metabisulfiteWastewater
The invention discloses a cleaner production technology for producing sodium metabisulfite and sodium chloride through saline-alkaline mixed liquor and belongs to the field of environmental resource protection in chemical production. According to the technology, the method for multistage salt separation and staged utilization is adopted in the production process, sodium carbonate and sodium chloride in the mixed waste liquor are converted into products such as sodium metabisulfite and sodium chloride, and resource-based value-added utilization of the waste liquor is realized. The method is high in product quality, low in equipment input, low in cost and zero in wastewater and waste residue emission, and belongs to the cleaner production technology.
Owner:河南元亨精细化工有限公司
Application of an edible fungus bag based on walnut shell/meal in strain cultivation
ActiveCN108419609BRealize value-added utilizationEfficient conversionCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologyWalnut Nut
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Cleaning process for value adding utilization of nickel-contained pyrite burning slag
ActiveCN105734610ARealize value-added utilizationSolve heavy pollutionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementScrapPyrite
The invention discloses a cleaning process for value adding utilization of nickel-contained pyrite burning slag. The process firstly performs efficient leaching for the nickel-contained pyrite burning slag to obtain leaching liquid and leaching slag containing iron and nickel; and then, the sacrifice anode electric reinforcing reduction purification is performed for the leaching liquid, so that impurity elements in the leaching liquid are deeply reduced into reduction purification slag through an electric reinforcing reduction method. The process realizes the value adding utilization of the pyrite burning slag. A new technological process is a closed cycle, and a leaching agent can be recycled, so that the cleaning process preferably solves such problems as heavy pollution and low metal recovery rate generally generated in a traditional pyrite burning slag treatment process, is suitable for treating other various wastes containing iron and nickel, and has the prominent advantages of high adaptability to raw materials, simple technological process, high recovery rate of valuable elements, cleanness and environmental protection.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Non-combustible non-immersible steel ladle upper nozzle and preparation method thereof
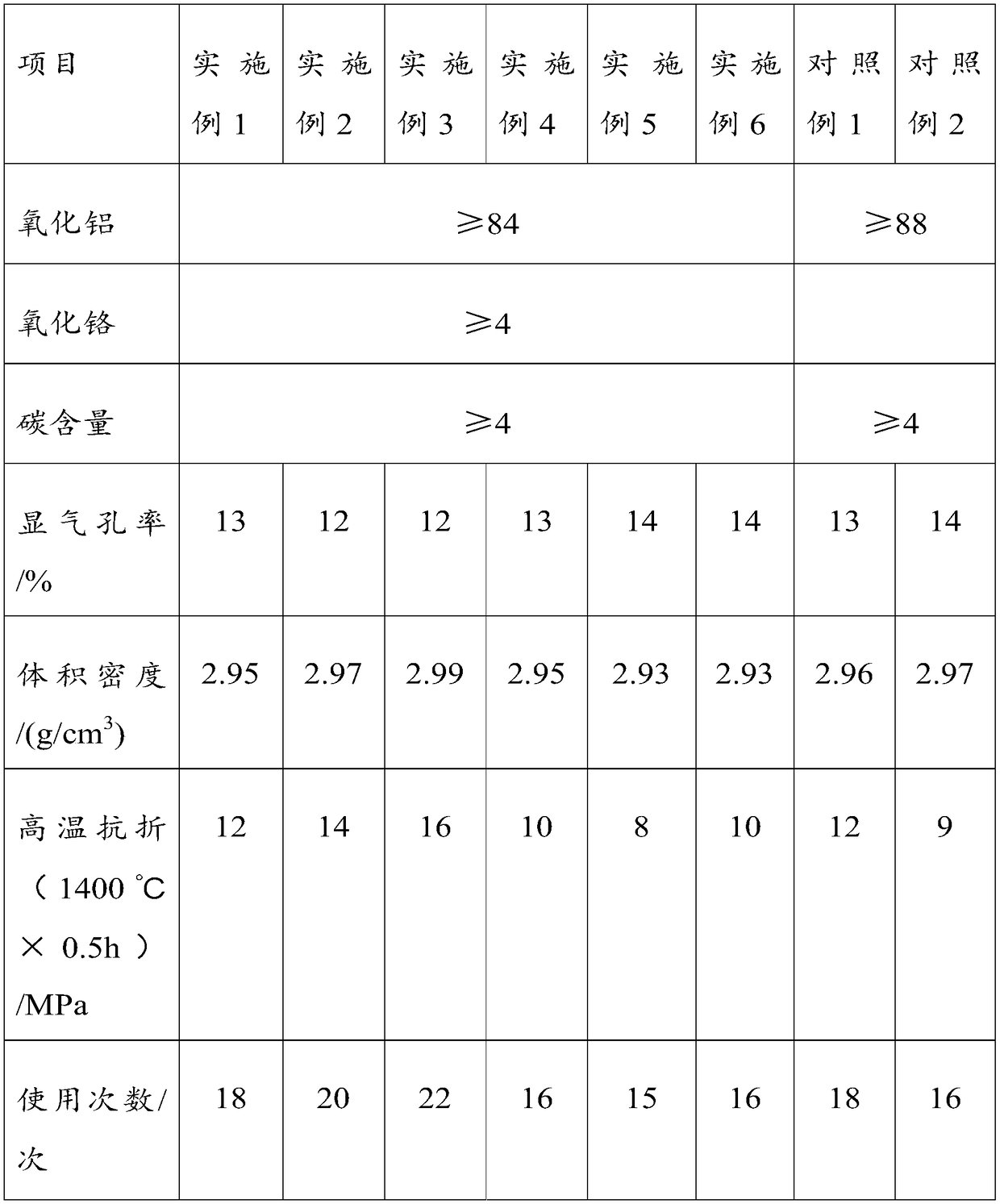
InactiveCN109437940AImproved thermal shock stabilityStrong resistance to molten steel corrosionMetallic aluminumSlag
The invention discloses a non-combustible non-immersible steel ladle upper nozzle and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of preparation of a steel ladle upper nozzle. Specifically, alumina-chrome slag is introduced into raw materials of the steel ladle upper nozzle and is used for replacing partial tabular corundum or white corundum, and metallic aluminum, metallic silicon and boron carbide are added, so that the pollution problem of alumina-chrome slag solid waste can be effectively solved, value-added utilization can be realized, and the cost of raw materials per tonnage can be reduced by 400 to 800 yuan; the prepared steel ladle upper nozzle has the advantages that the high-temperature strength is high, the thermal shock stability is good, and molten steelcorrosion resistance is strong, the steel ladle upper nozzle can be used on a continuous casting steel ladle upper nozzle which is 100 to 150 tonnage, and the using requirements of 15 to 20 times canbe achieved.
Owner:河南新拓耐火材料有限公司
A kind of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt-licl-dmf system prepares the method for microfiber corn stalk
ActiveCN107501571BEffective swellingReduce cohesionOther chemical processesWater contaminantsVacuum dryingHydroxy compound
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
A cleaning process for value-added utilization of pentlandite slag
ActiveCN105734610BAchieving Co-ElectrodepositionImprove solubilityPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSlagPollution
The invention discloses a cleaning process for value adding utilization of nickel-contained pyrite burning slag. The process firstly performs efficient leaching for the nickel-contained pyrite burning slag to obtain leaching liquid and leaching slag containing iron and nickel; and then, the sacrifice anode electric reinforcing reduction purification is performed for the leaching liquid, so that impurity elements in the leaching liquid are deeply reduced into reduction purification slag through an electric reinforcing reduction method. The process realizes the value adding utilization of the pyrite burning slag. A new technological process is a closed cycle, and a leaching agent can be recycled, so that the cleaning process preferably solves such problems as heavy pollution and low metal recovery rate generally generated in a traditional pyrite burning slag treatment process, is suitable for treating other various wastes containing iron and nickel, and has the prominent advantages of high adaptability to raw materials, simple technological process, high recovery rate of valuable elements, cleanness and environmental protection.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of preparation method of methylamine
ActiveCN112010767BSimple post-processingRich sourcesAmino compound purification/separationAmino preparation from aminesDodecanePtru catalyst
The invention provides a preparation method of methylamine, which is to prepare methylamine by amine methylation reaction; in the amine methylation reaction, the catalyst is dodecyldimethylamine caprolactone . The invention effectively reduces the additives required for the reaction, and is beneficial to simplify the post-processing process after the reaction is completed.
Owner:NANJING XIAOZHUANG UNIV
Method for preparing micro-fibre corn stalks by 1-butyl-3-methimidazole chloride-LiBr-DMF (dimethylformamide) system
ActiveCN107501572AEffective swellingReduce cohesionOther chemical processesWater contaminantsFiberChloride
The invention discloses a method for preparing micro-fibre corn stalks by a 1-butyl-3-methimidazole chloride-LiBr-DMF (dimethylformamide) system. The method comprises the following steps: crushing and drying corn stalks; performing high-shear sulphonating treatment at a certain temperature by taking a 1-butyl-3-methimidazole chloride-LiBr-DMF compound system as a solvent and adding a pyridine sulphur trioxide compound; filtering, washing and performing vacuum drying on a material which is subjected to the sulphonating treatment, so as to obtain the micro-fibre corn stalks with high sulphonation degree. According to the method, the corn stalk fibres can be effectively swelled and free hydroxyls can be released by combining 1-butyl-3-methimidazole chloride with LiBr, so that the cohesive force of a raw material is weakened, and the sulphonating modifying efficiency of sulphur trioxide-pyridine complex is improved. According to the method, the degradation of hemicellulose and lignin components of the corn stalks can be reduced remarkably; a modifying process is simple and feasible; the modified products of micro-fibres are high in yield and sulphonation degree and large in specific surface area; value-added utilization of agricultural waste is realized; moreover, a modifying liquid is easy to recycle and utilize.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
A kind of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride salt-libr-dmf system prepares the method for microfiber corn stalk
ActiveCN107501572BEffective swellingReduce cohesionOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSulfur trioxide pyridine complexChloride
The invention discloses a method for preparing micro-fibre corn stalks by a 1-butyl-3-methimidazole chloride-LiBr-DMF (dimethylformamide) system. The method comprises the following steps: crushing and drying corn stalks; performing high-shear sulphonating treatment at a certain temperature by taking a 1-butyl-3-methimidazole chloride-LiBr-DMF compound system as a solvent and adding a pyridine sulphur trioxide compound; filtering, washing and performing vacuum drying on a material which is subjected to the sulphonating treatment, so as to obtain the micro-fibre corn stalks with high sulphonation degree. According to the method, the corn stalk fibres can be effectively swelled and free hydroxyls can be released by combining 1-butyl-3-methimidazole chloride with LiBr, so that the cohesive force of a raw material is weakened, and the sulphonating modifying efficiency of sulphur trioxide-pyridine complex is improved. According to the method, the degradation of hemicellulose and lignin components of the corn stalks can be reduced remarkably; a modifying process is simple and feasible; the modified products of micro-fibres are high in yield and sulphonation degree and large in specific surface area; value-added utilization of agricultural waste is realized; moreover, a modifying liquid is easy to recycle and utilize.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of catfish visceral protease
A preparation method of catfish visceral protease includes extraction, salting out, dialysis and purification and has the beneficial effects: extracted protease has high purity and stable activity, can be used as an enzymatic hydrolysis agent for hydrolyzing a variety of food proteins, realizes the value-added use of catfish viscera, and improves the economic added value of catfishes. At the sametime, the high-purity protease extracted by the method can improve lymphocyte activity, thereby enhancing the body ability to prevent and resist diseases, and also having unexpected effect of scavenging free radicals in organisms.
Owner:金华市川璞农业科技有限公司
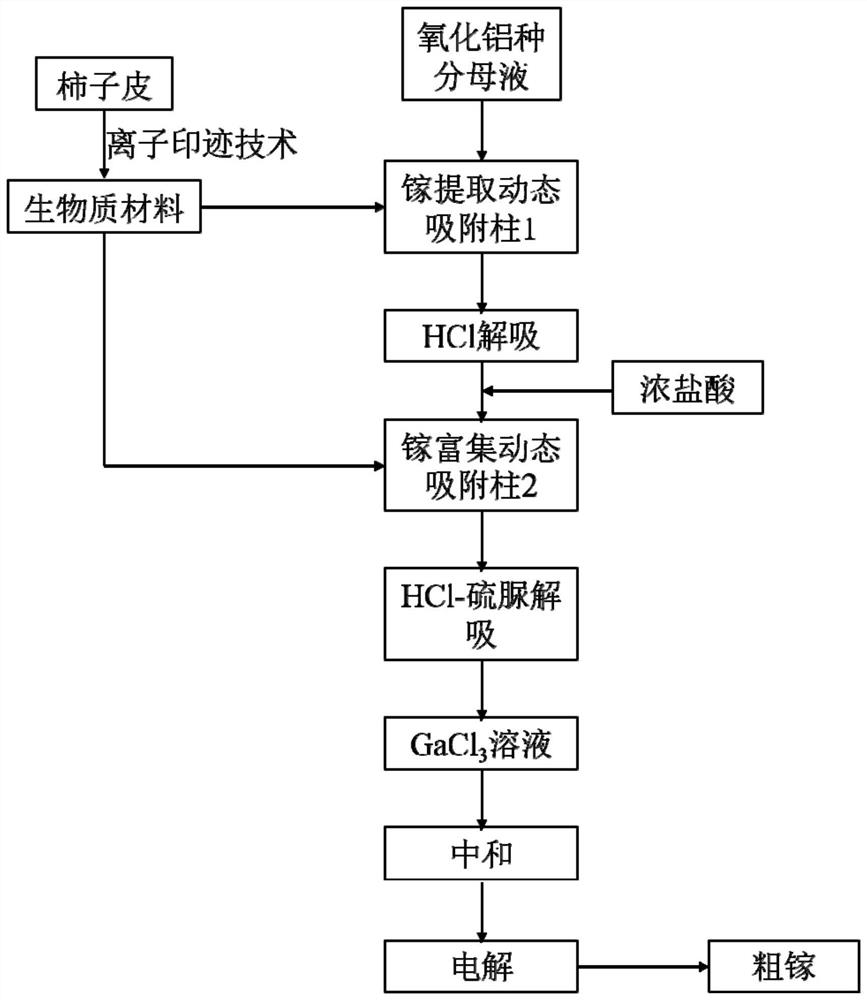
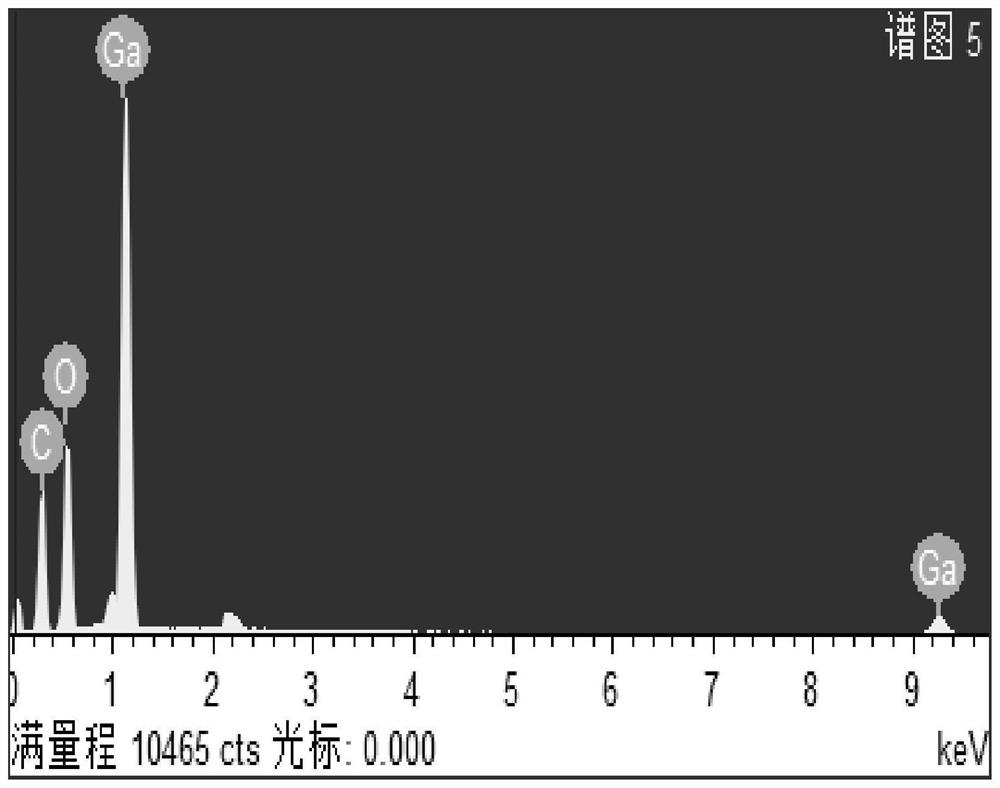
A method for enriching and extracting gallium from alumina seed separation mother liquor based on biomass materials
ActiveCN113249596BImplement selective extractionEfficient enrichmentPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementEnvironmental engineeringIon imprinted
The invention discloses a method for enriching and extracting gallium from alumina seed separation mother liquor based on biomass materials. The method includes: using biomass materials as adsorbents, and the biomass materials are persimmon skins modified by ion imprinting technology The obtained persimmon skin-based imprinted composite material; the persimmon skin-based imprinted composite material is loaded into a two-stage dynamic adsorption column, and the alumina seed separation mother liquor is extracted through the gallium-extracted dynamic adsorption column 1 and the gallium-enriched dynamic adsorption column 2 respectively. Gallium-rich electrolytic stock solution is obtained by selective adsorption and desorption of gallium. In the present invention, waste biomass persimmon skin is used as the material, and the adsorbent is obtained through surface ion imprinting modification, and the gallium ion-specific recognition sites on the surface of the adsorbent are used to realize the selective extraction of gallium in the mother liquor of alumina species, which has the advantages of Gallium enrichment has the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, and has good economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
Method for producing Bacillus mucilaginosus liquid microbial inoculant from lignocellulose
InactiveCN105567623AEfficient use ofImprove hydrolysis efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesInorganic saltsGeonoma congesta
The invention provides a method for producing a Bacillus mucilaginosus liquid microbial inoculant from lignocellulose. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pulverizing a lignocellulose raw material into 40-60-mesh particles, and carrying out hydrothermal treatment to obtain a suspension; (2) adding cellulase into the suspension obtained in the step (1), carrying out enzymolysis, and centrifugating to remove residues, thereby obtaining a glucose-containing enzymolysis solution; (3) adding culture medium components, inoculating Bacillus mucilaginosus, and culturing at 37 DEG C at the rate of 200 rpm under the pH value of 7.0 to obtain the Bacillus mucilaginosus cells; and (4) adding the Bacillus mucilaginosus cells obtained in the step (3) into an inorganic salt buffer system to obtain the Bacillus mucilaginosus liquid microbial inoculant. After the hydrothermal technique is adopted to pretreat the lignocellulose raw material, the degradation capacity of the cellulose is enhanced. The enzymolysis solution is utilized to perform the fermentation production of the Bacillus mucilaginosus microbial inoculant, thereby enhancing the viable count and implementing the value-added utilization of the lignocellulose.
Owner:北京中植科创生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com