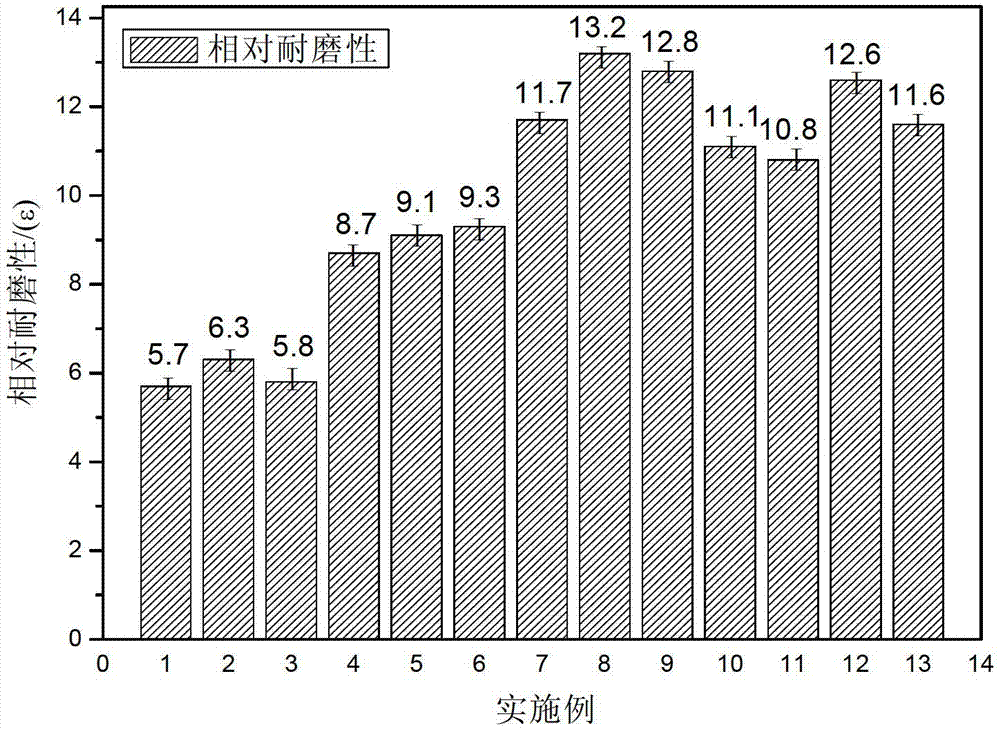
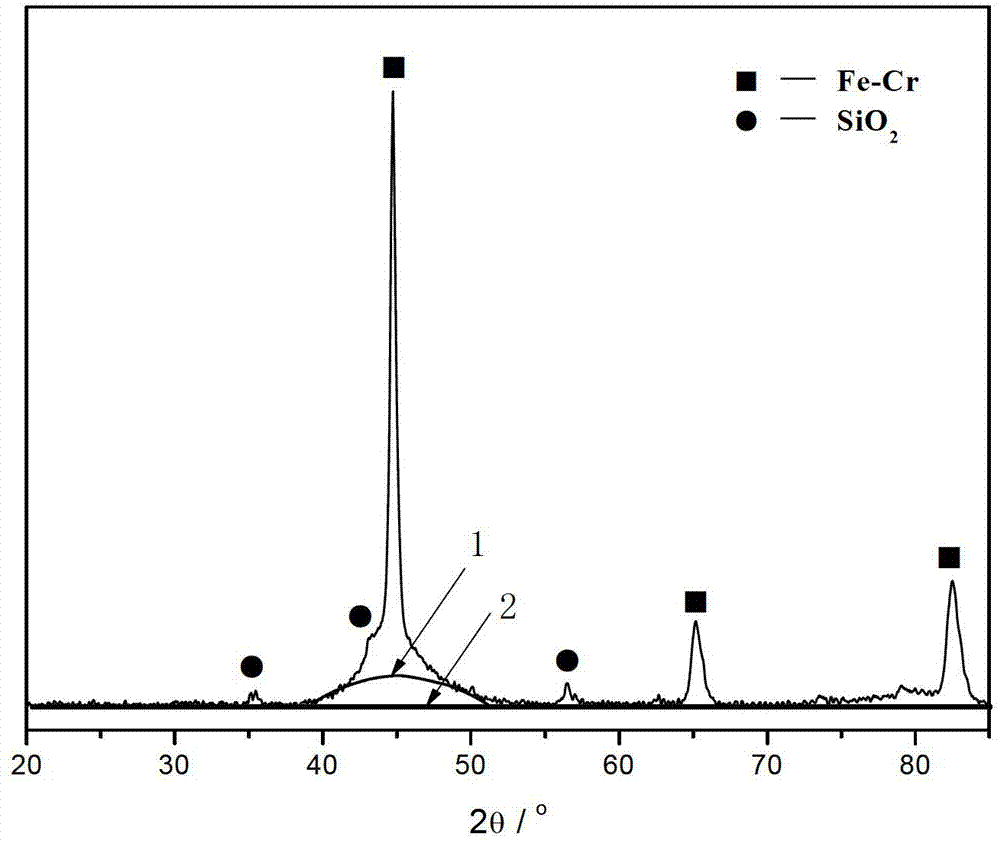
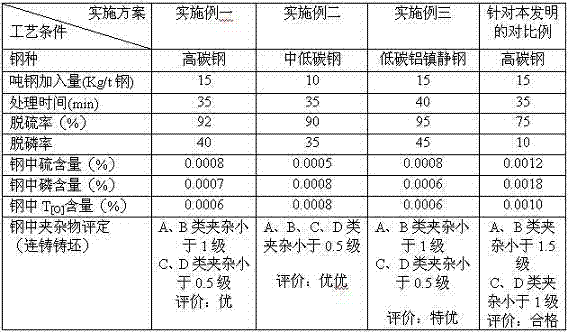
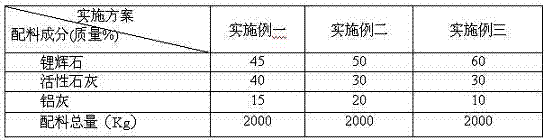
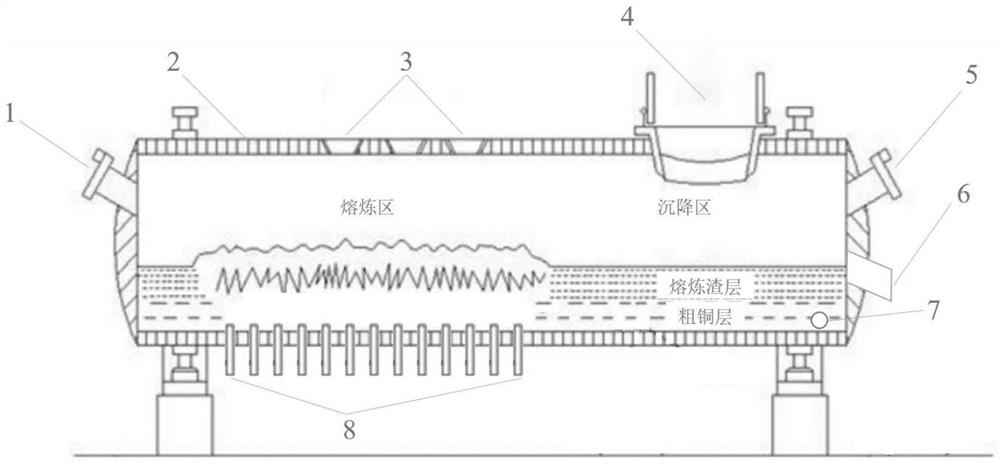
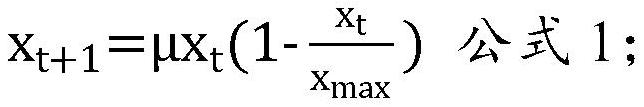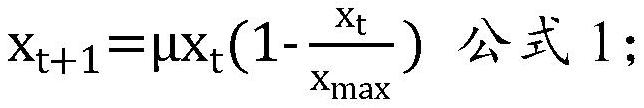Patents
Literature
35 results about "Flux (metallurgy)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In metallurgy, a flux (derived from Latin fluxus meaning "flow") is a chemical cleaning agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time. They are used in both extractive metallurgy and metal joining.
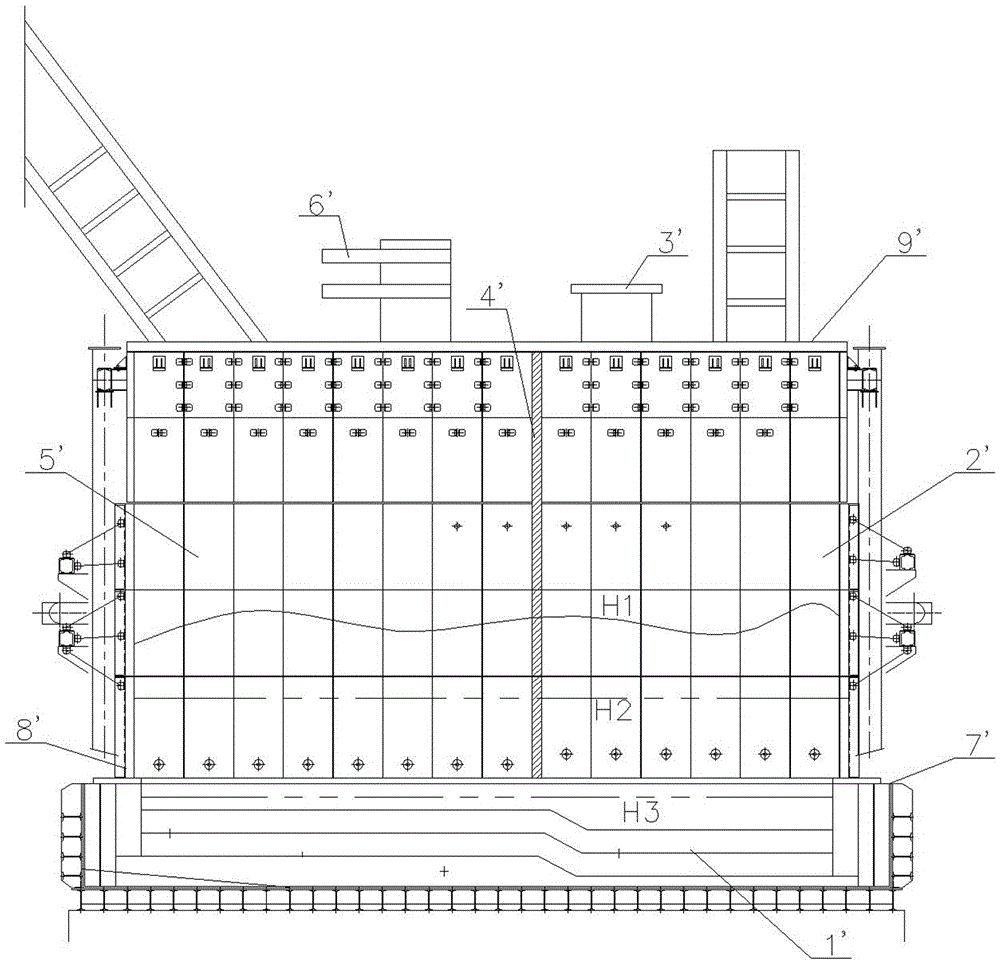
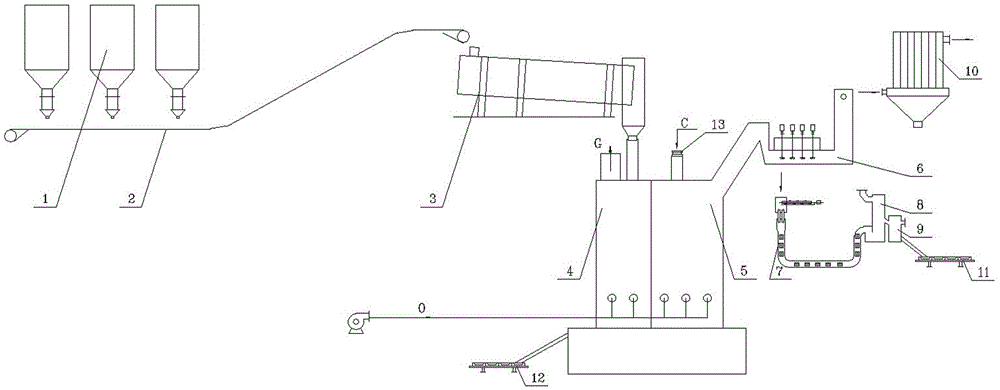
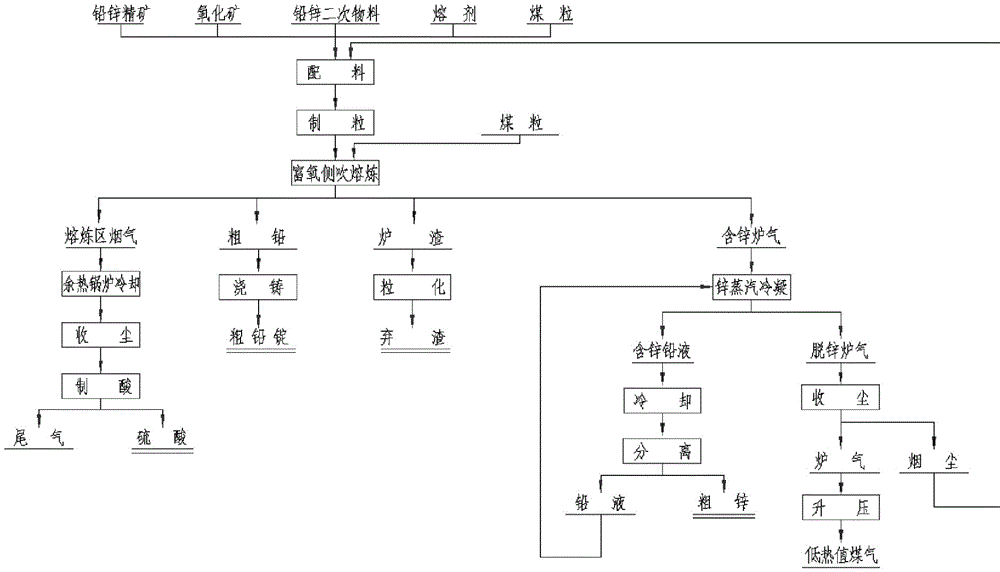
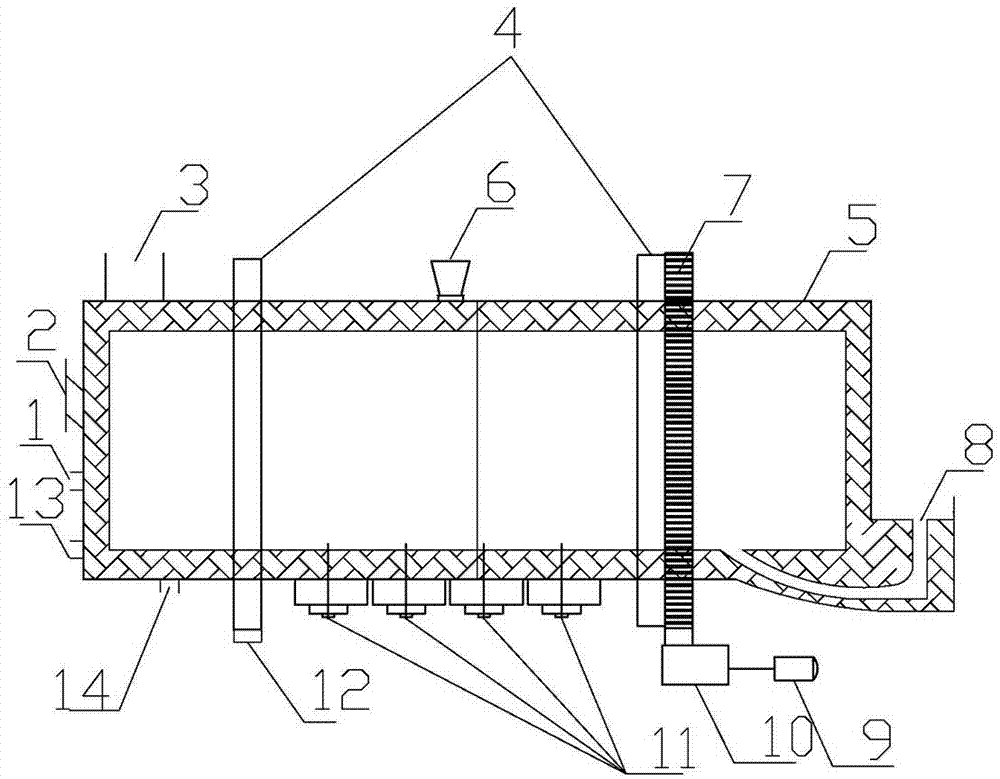
Direct smelting method and system for producing metallic lead and zinc at the same time
InactiveCN105671314AExpand sourceImprove protectionProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyReducing atmosphere
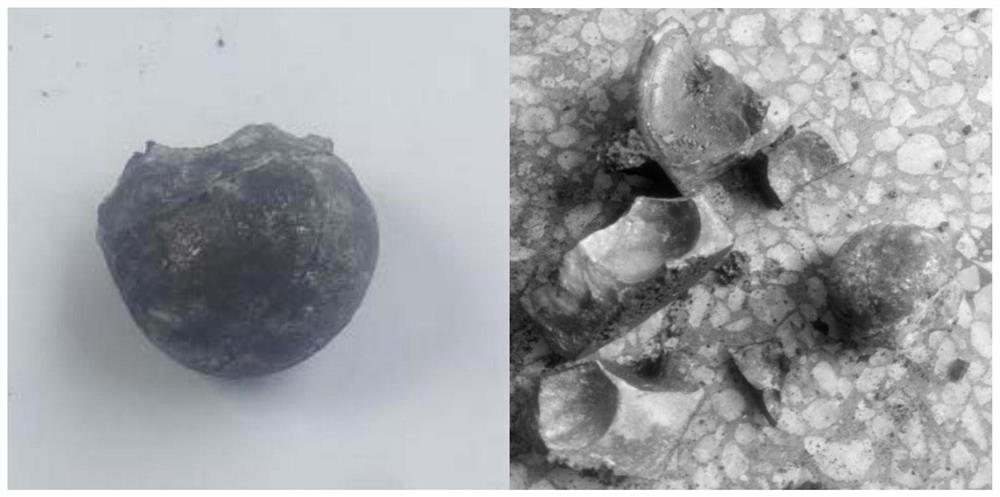
The invention relates to a direct smelting method and system for producing metallic lead and zinc at the same time. The method includes the steps that lead and zinc concentrate, lead and zinc oxidized ore and / or lead and zinc containing secondary materials and flux are mixed and pelleted; the pelleted furnace charges are added to a smelting zone of a dual-zone oxygen-enriched side-blowing furnace, oxygen-enriched air is blown, the weakly-reducing atmosphere is controlled for smelting, a lead phase and a slag phase are formed, coarse lead is discharged through a syphonic mouth, and high-zinc furnace slag enters a fuming zone of the oxygen-enriched side-blowing furnace; coal needed for zinc reducing is added to the fuming zone, the oxygen-enriched air is blown, and the fuming zone is controlled to be in a strongly-reducing atmosphere; zinc obtained after reducing forms zinc steam which enters a steam condenser along with furnace gas, zinc containing lead liquid is formed, cooled zinc liquid is separated from the lead liquid, and coarse zinc is obtained. By means of the method, the raw materials do not need to be sintered or calcined, and technological processes are greatly shortened; raw materials with a low lead and zinc grade can be smelted, especially zinc leached residues can be treated, and the environmental protection purpose is achieved for zinc hydrometallurgy; the coal can replace coke, and therefore production cost is reduced.
Owner:CINF ENG CO LTD
Method for producing compound filter of multi-layer metal meshes and metal powder
ActiveCN102059340ASmall filter resistanceLarge filtration fluxFiltration separationMetal filamentMetal powder
The invention relates to a method for producing compound filter of multi-layer metal meshes and metal powder, which comprises the steps of weaving metal wires to obtain metal meshes with different mesh numbers; laminating the metal meshes with different mesh numbers to obtain a laminated layer structure, wherein the mesh numbers of the laminated layers from one side to the other side increase continuously and the number of laminated layers is 2-6; then placing the laminated layer structure in a vacuum furnace and sintering at 1000-1600 DEG C to obtain a multiple support layers; then cooling and taking out of the support layers, manufacturing a metal compound layer of 100-600 meshes on one side of the support layer of high mesh by means of electrostatic spraying and curtain coating, controlling the thickness of the compound layer with 0.1-0.5mm and then sintering at 1000-1600 DEG C, cooling and taking out of the compound layer to obtain the compound filter of multi-layer metal meshes and metal powder. The compound filter has the advantages of low filtering resistance, large filter flux and strong bearing capacity and can be widely applied to industrial fields of chemical engineering, medicine, power generation,metallurgy, food and the like.
Owner:王东伟
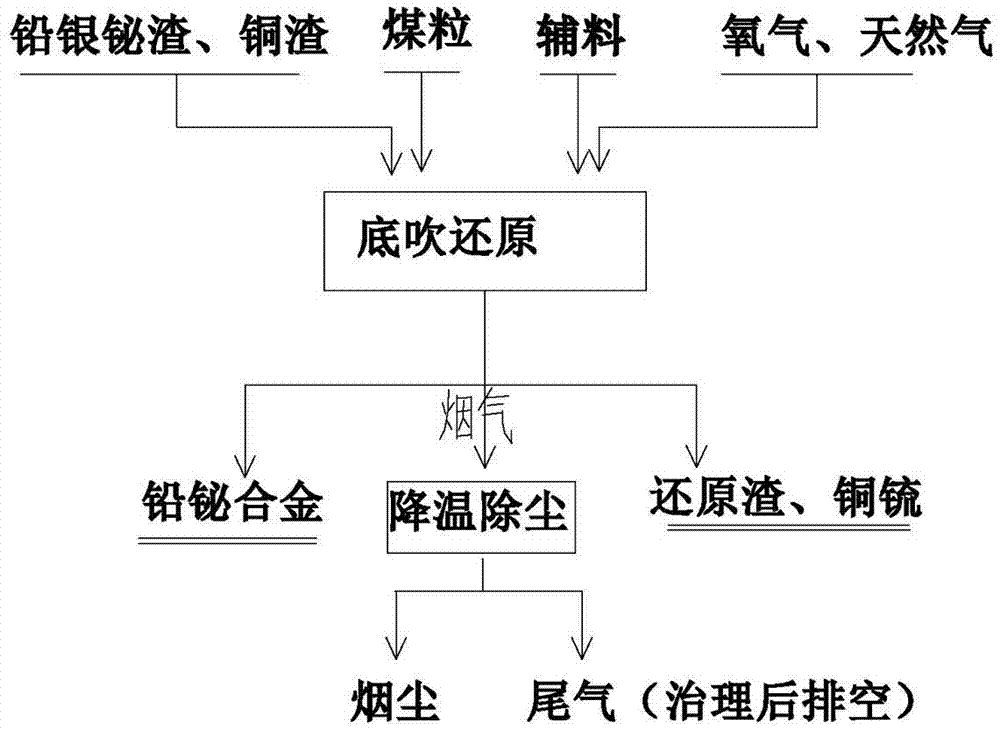
Method and device for recovering valuable elements from lead-silver-bismuth slag in copper smelting
ActiveCN103114206AImprove melt strengthImprove work efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementHigh pressureLead bismuth
The invention belongs to nonferrous metal metallurgy industry, and particularly relates to a method and device for recovering valuable elements (lead, gold, silver, bismuth, copper, arsenium and sulfur) from lead-silver-bismuth slag in copper smelting. The method comprises the following steps: adding lead-silver-bismuth slag, copper slag, reducer and slagging flux through a feed port at the upper part of a bottom-blowing alloying furnace, performing reduction reaction under high-temperature conditions to generate metal lead, metal bismuth and copper matte; under the stirring action of high-pressure gas supplied by a submerged combustion device at the bottom, continuously blowing and dispersing the molten lead deposited at the bottom to the molten mass at the upper part, and using the molten lead to continuously trap gold, silver and bismuth to obtain a lead-bismuth alloy which is rich in gold and silver; and under the action of iron chips and the reducer at high temperature, forming copper in the lead-silver-bismuth slag into copper matte, wherein the copper matte is enriched with arsenium. The method provided by the invention is high in smelting strength, high in operating efficiency, high in metal recovery rate, favorable in device sealing property, low in heat loss, low in energy consumption, high in automation level, low in labor intensity, favorable in stability and convenient to operate, and can realize converter tipping quickly.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG GOLD & LEAD
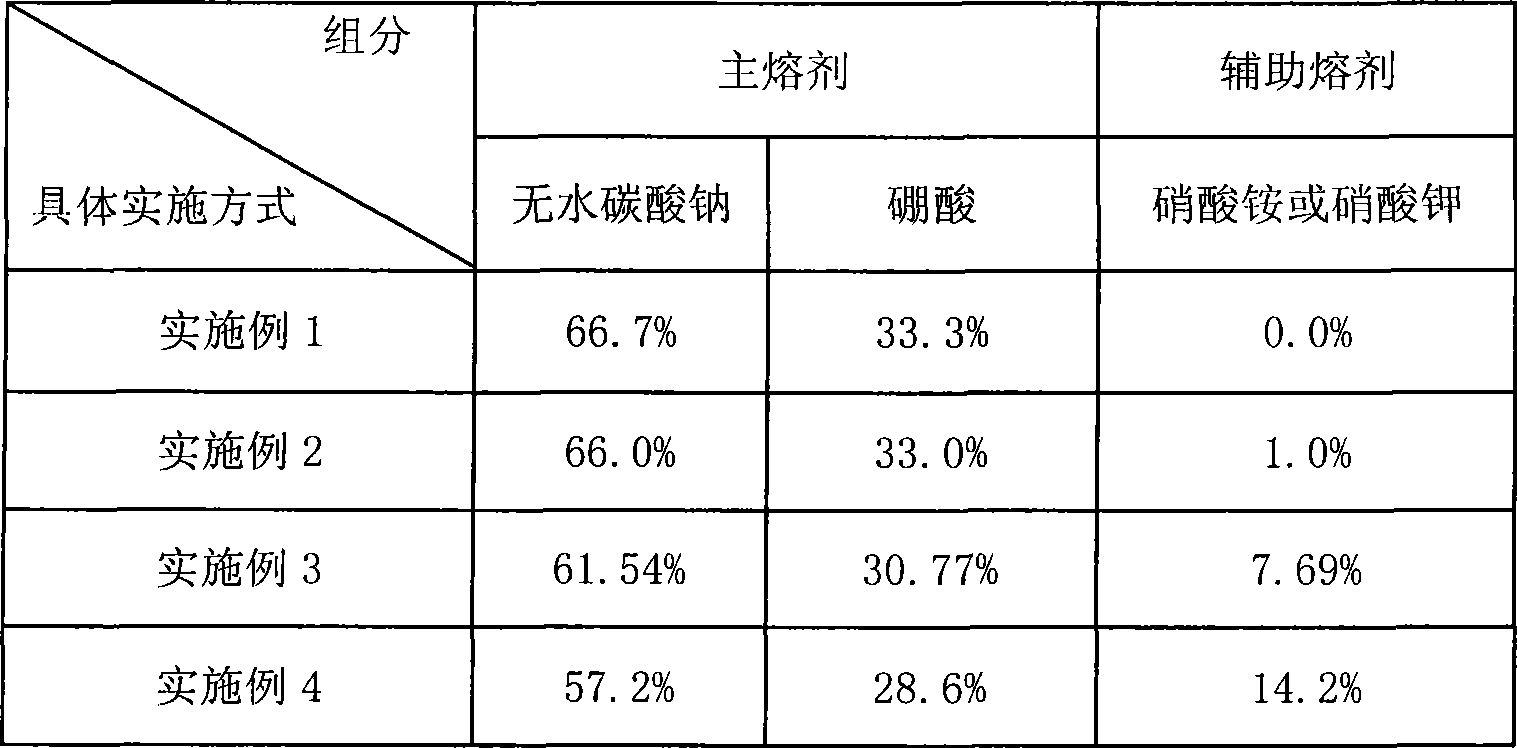
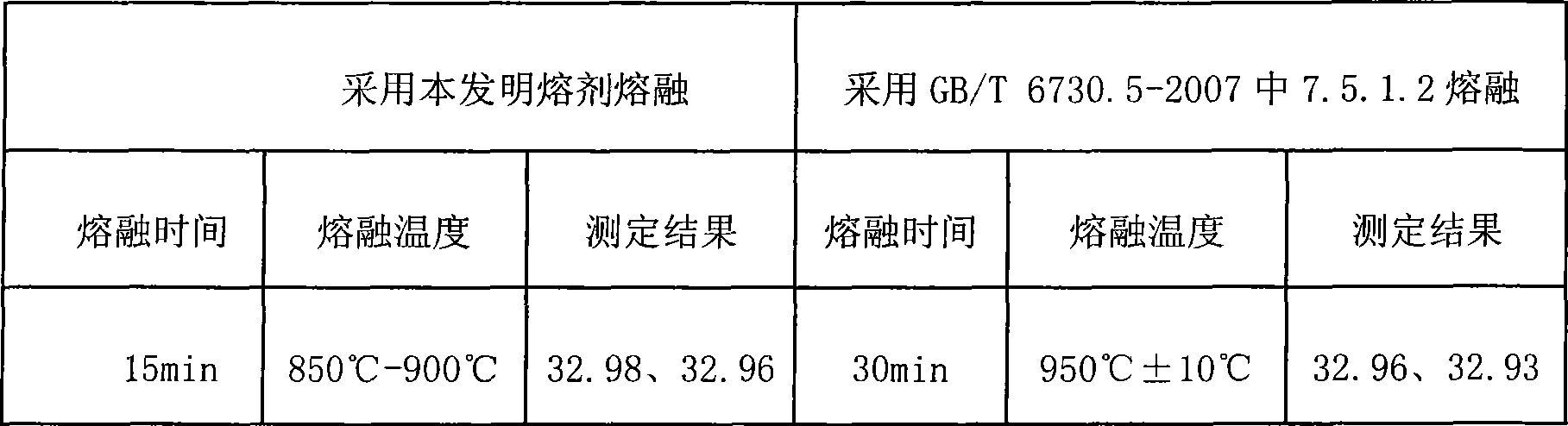
Fusion metallurgy sample analysis fusing agent and its preparation and use method
InactiveCN101368886ALess materialEasy to preparePreparing sample for investigationDecompositionMagnetite
The invention discloses an analysis fluxing agent for melting metallurgical samples, and a preparation and using method thereof; the analysis fluxing agent is prepared with a main fluxing agent and an auxiliary fluxing agent, wherein, the contents of anhydrous sodium carbonate and boric acid reach 85.80% to 100%; the content of the auxiliary flux agent nitrate ammonium or potassium nitrate is 0 to 14.20%; the invention can be used to melt and decompose vanadium-titanium magnetite, vanadium-titanium-bearing slag, high-titanium slag, metallurgical auxiliary material, refractory material, vanadium slag, non-ferrous metal ores and other metallurgical samples; the flux agent of the invention has the advantages of less material adoption, simple preparation method, low cost, simple operation, short melting time, as well as good melting and decomposition effect; the melted samples are of easy acid leaching and decomposition, wide application and convenient using.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +2
Equipment for preparing metal test piece and structural piece by using high-energy beam
ActiveCN113245562AAdditive manufacturing apparatusPreparing sample for investigationManufacturing technologyEngineering
The invention discloses equipment for preparing a metal test piece and a structural piece by using a high-energy beam. The equipment comprises a high-energy beam heat source, an atmosphere protection system, a powder feeding system and a dual-purpose cooling copper plate system for high-flux forming and specific structure forming. The dual-purpose cooling copper plate system for high-flux forming and specific structure forming comprises two cooling copper plates capable of being spliced in a turnover mode and a rail system used for rapidly turning over the cooling copper plates. A plurality of powder containing grooves used for high-flux forming are formed in the surface of one side of each cooling copper plate in a concave mode, and a plurality of positioning threaded holes are formed in the surface of the other side of each cooling copper plate. A passage for circulating a cooling medium is arranged in each cooling copper plate. According to the equipment for preparing the metal test piece and the structural piece by using the high-energy beam, and a method provided by the invention, on the basis of a new material laser metallurgy high-flux preparation technology and a complex structure additive manufacturing technology, laser serves as a heat source, so that on one hand, a large number of small samples with different components or process parameters can be designed and formed at a time, and on the other hand, a large number of samples with specific structures can be formed.
Owner:北京煜鼎增材制造研究院股份有限公司
Cored wire for preparing iron-based coating as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103088280AImprove corrosion resistanceCorrosion resistant barrierMolten spray coatingThermal sprayingFilling rate
The invention provides a cored wire for preparing an iron-based coating as well as a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of thermal spraying in material processing engineering. The flux composition comprises 15-35 at.% of Cr, 5-25 at.% of B, 5-25 at.% of Si, 2.5 to 5.5 at.% of C and the balance of Fe; a strip material for a sheath of the cored wire is a stainless steel band; and the filling rate of the cored wire is 33%. When electric-arc spraying is used for preparing an iron-based amorphous / nanocrystal coating containing ceramic phase SiO2, firstly a matrix is pretreated, and according to a spraying technology, the voltage is 28-34V, the electric current is 160-220A, the spraying distance is 190-210mm, and the compressed air pressure is 0.4-0.6Mpa. The coating can be widely applied to repair and protection of equipment parts in industries such as metallurgy, electricity and petroleum. The coating with the advantages of corrosion resistance, high hardness and high wearing resistance is obtained according to the preparation method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Ladle furnace refining fluoride-free pre-melted slags, preparation method and using method
InactiveCN102787214AImprove use valueIncrease profitProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingRefining (metallurgy)
The invention belongs to the field of the steel-making secondary refining ladle metallurgy, particularly relates to ladle furnace refining fluoride-free pre-melted slags, a preparation method and a using method and is suitable for the slagging refining process of the steel-making secondary refining in a steel ladle. The invention aims to provide the ladle furnace refining fluoride-free pre-melted slags, the preparation method and the using method by utilizing existing spodumene resources and adding a refining flux and a slag regulation component, solve the problems of defects of slag desulfurization, low dephosphorizing efficiency, large difficulty in rephosphorization control, poor slag melting performance, poor slag inclusion adsorption performance and the like of current ladle refining slagging materials, also reduce the ladle secondary refining slagging cost and implement the low-cost processing and utilization of a spodumene mineral. The ladle furnace refining fluoride-free pre-melted slags are characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 40 to 60 percent of spodumene powder, 30 to 50 percent of lime powder and 5 to 25 percent of aluminium ash powder.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for comprehensively and efficiently treating zinc leaching residues
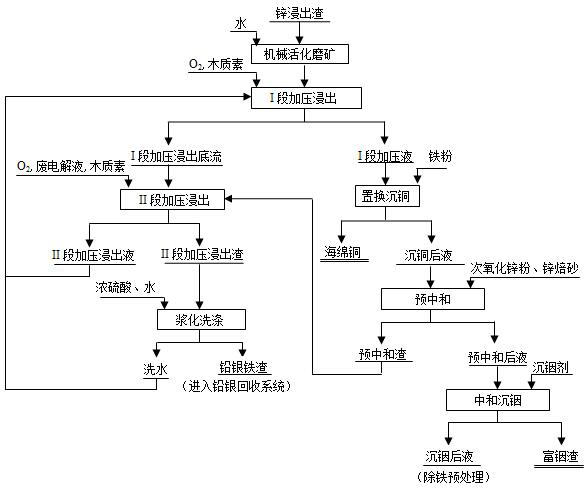
ActiveCN113897491AHigh recovery rateSimple recycling processProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionLead smelting
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively and efficiently treating zinc leaching residues, and belongs to the technical field of hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the following steps of 1) grinding of the zinc hydrometallurgy leaching residues; 2) first-stage pressure leaching; 3) second-stage pressure leaching; 4) slurrying washing of the leaching residues; 5) replacement copper precipitation; 6) pre-neutralization; and 7) neutralization indium precipitation. According to the method, efficient leaching of valuable metals such as zinc, indium, copper and silver and efficient synchronous precipitation of iron in the zinc hydrometallurgy leaching residues are achieved at the same time; the recovery rates of zinc, indium, copper and silver reach 98%, 88%, 96% and 99% or above respectively, and low-acid and low-iron leachate beneficial to selective separation of copper and indium is produced; and iron is enriched in lead-silver-iron slag together with lead and silver, iron in the lead-silver-iron slag can be used as a lead pyrometallurgy slagging flux and is finally stably solidified in furnace slag or kiln slag in the lead enrichment process, and the transformation from impurities to lead smelting raw materials is achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
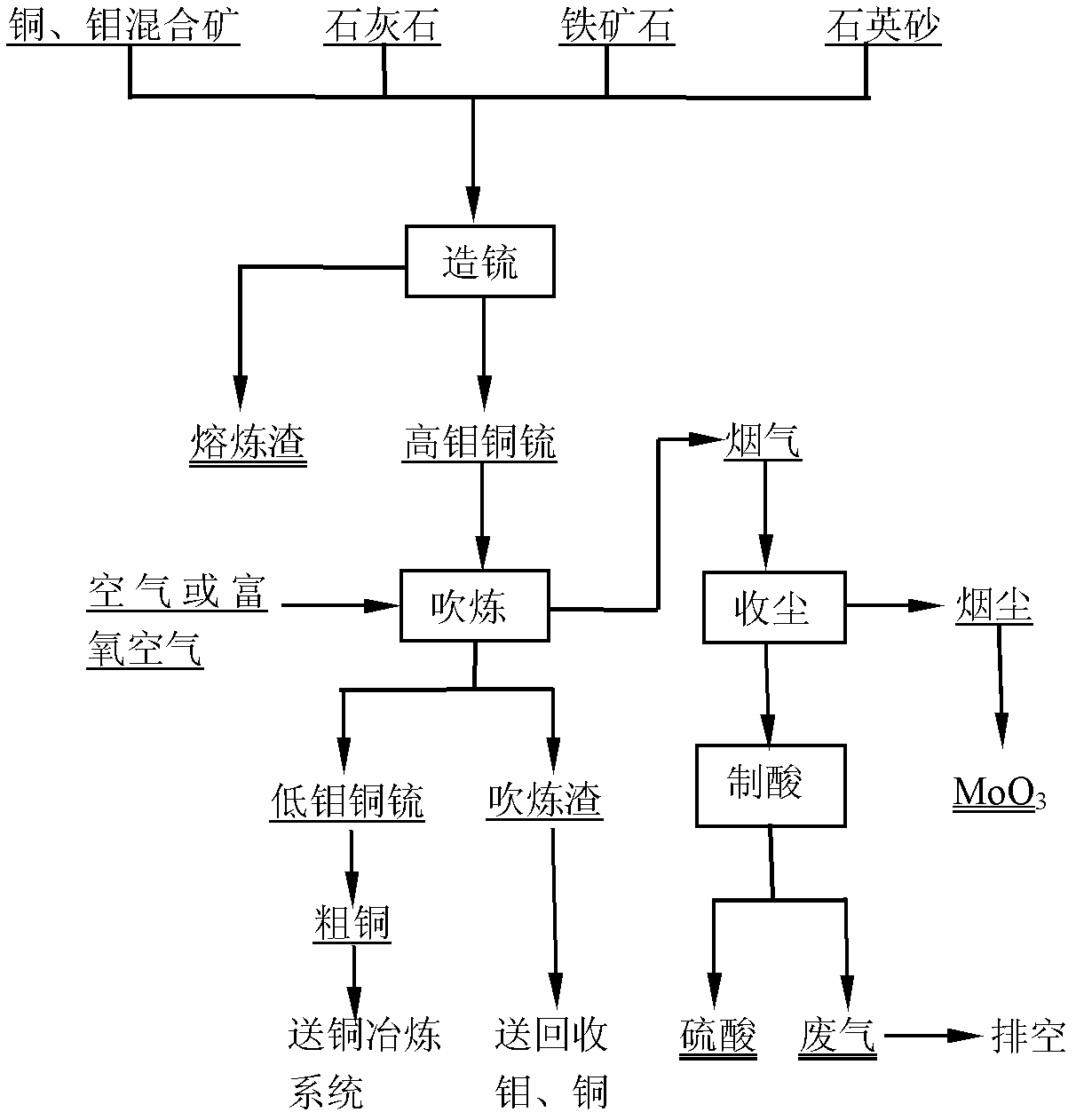
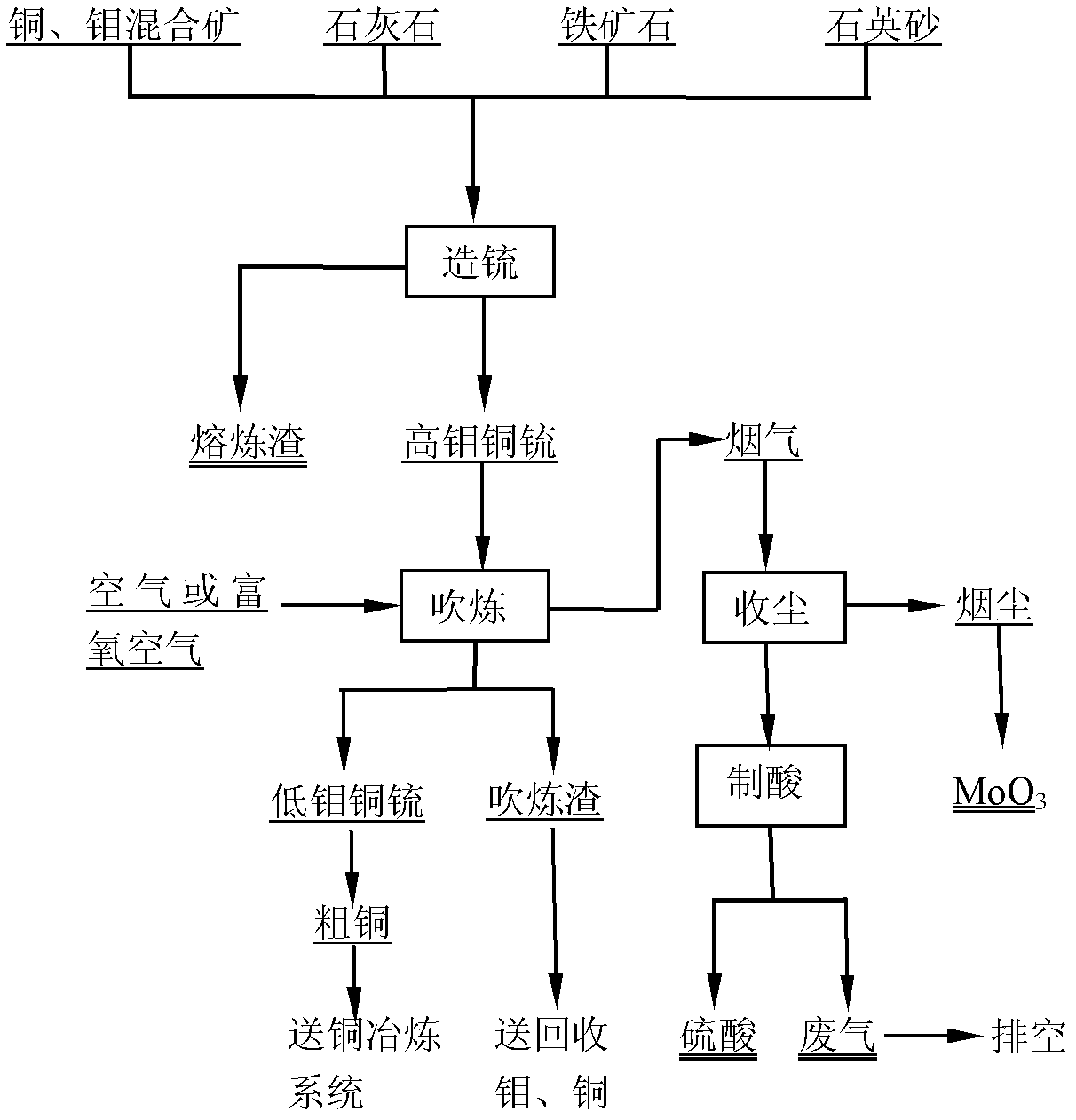
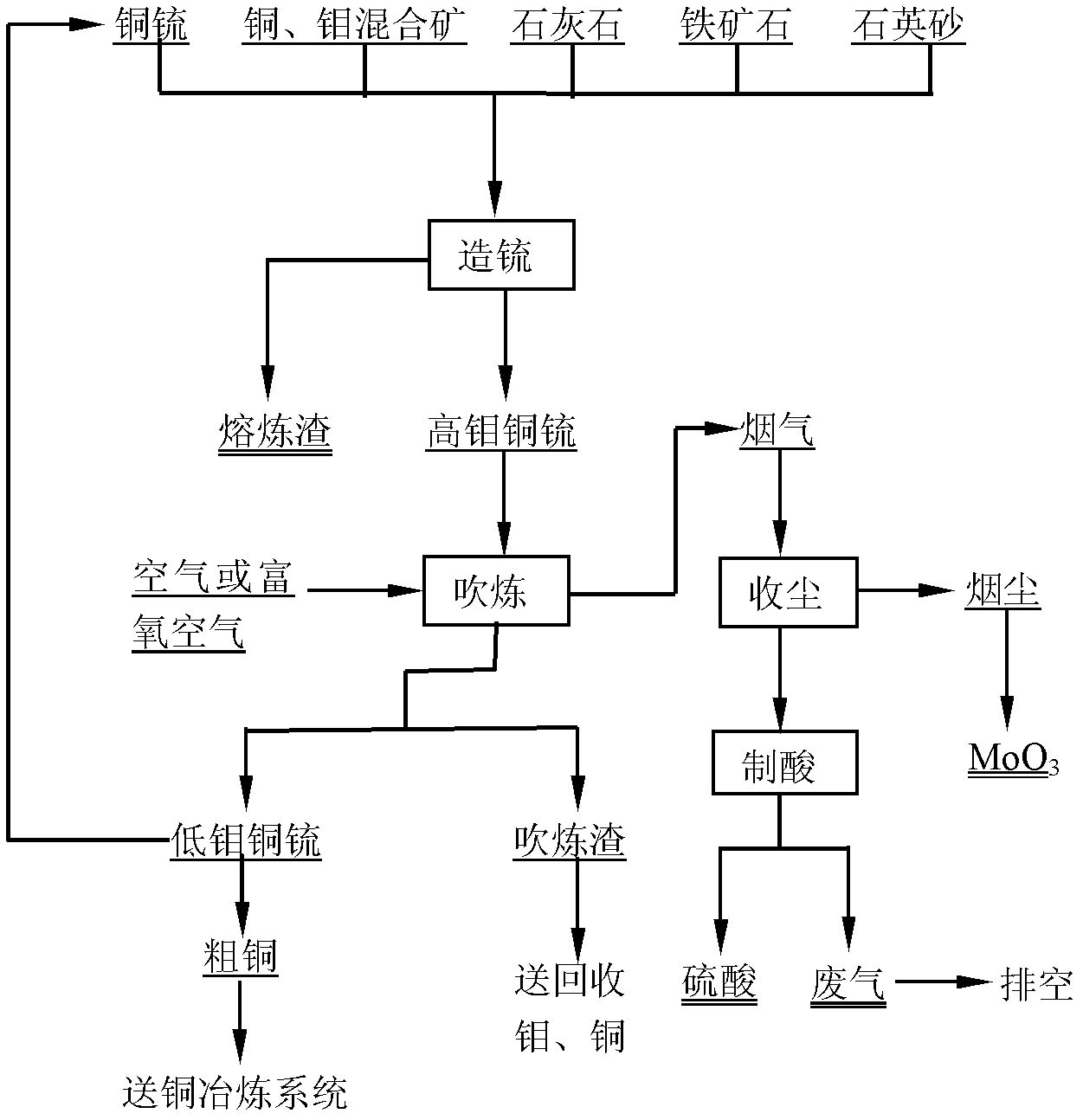
Method for treating copper-molybdenum mixed ores
The invention discloses a method for treating copper-molybdenum mixed ores, belonging to the field of molybdenum metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: directly heating the copper-molybdenum mixed ores to a molten state, or heating to a molten by using an assistant flux copper matte (matte) (for high-molybdenum low-copper mixed concentrate) to form copper molybdenum matte; introducing air or oxygen-enriched air into the copper molybdenum matte to carry out converting until molybdenum sulfide in the copper molybdenum matte is oxidated into MoO3 to be volatilized, recycling the MoO3 from smoke dust by dust collection, and sending the dedusted flue gas to the acid making process; and after finishing converting, returning the low-molybdenum copper matte to the next matte formation process or sending the low-molybdenum copper matte to a copper smelting system. The method has the advantages of short process, favorable mass-transfer heat-transfer conditions, high productivity, high heat utilization, high SO2 concentration in flue gas, strong adaptability to raw materials, and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
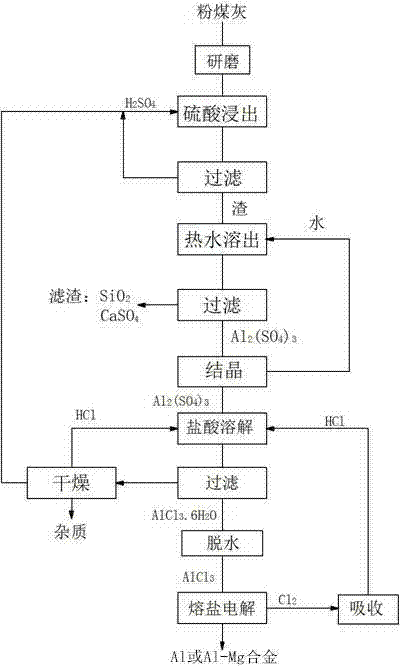
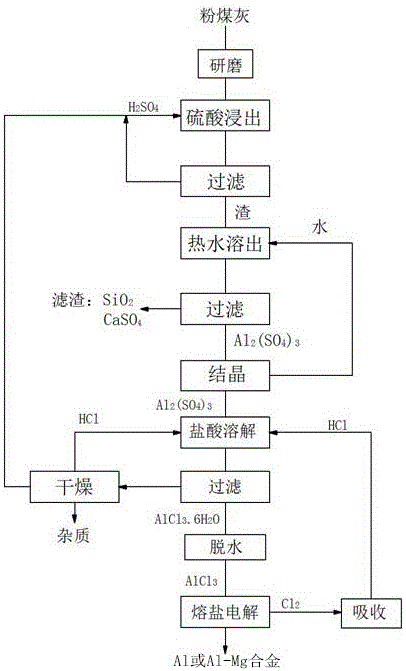
Method for preparing metallic aluminum or aluminum-magnesium alloy by utilizing pulverized fuel ash
ActiveCN104294314AWith green energy saving and environmental protectionReduce the temperatureAluminium chlorideMetallic aluminum
The invention belongs to the field of non-ferrous metallurgy and relates to a method for preparing metallic aluminum or an aluminum-magnesium alloy by utilizing pulverized fuel ash. According to the technical scheme of the invention, the method comprises the following steps: preparing aluminum chloride by adopting acid leaching of pulverized fuel ash, wherein the adopted electrolyte system consists of a flux, a solute and an additive, and the flux comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0-60 percent of NaCl, 25-75 percent of KCl and 0-66 percent of MgCl2; adding a solute AlCl3 which accounts for 5-50 percent of the mass of the flux, an additive LiCl which accounts for 0-5 percent of the mass of the flux, 0-5 percent of an additive KF, 0-5 percent of an additive MgF2 or 0-5 percent of an additive AlF3, wherein the solute AlCl3 is added from the bottom of the electrolytic cell, the interpolar voltage is controlled to be 2.3-3.3V, the cathode-current density is 0.5-1.5A / cm<2>, and the electrolysis temperature is 450-500 DEG C; and producing chlorine on one side of the anode in the electrolysis process, recycling chlorine, and depositing solid metallic aluminum or the aluminum-magnesium alloy on one side of the cathode. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the power consumption is saved, the electrolysis temperature is low, the production cost is low, the problems of aluminum chloride evaporation and generation of dendritic crystals during electrolysis are solved, the environmental pollution is avoided, and the equipment is easy to realize.
Owner:李景江
Low silver brazing and soldering alloy with In, Li, Zr and La and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107097017AReduced silver contentReduce dosageWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaIntermediate frequencyRare earth
The invention relates to the metal material and metallurgy field, in particular to low silver brazing and soldering alloy with In, Li, Zr and La and a preparation method and application thereof. The low silver brazing and soldering alloy with In, Li, Zr and La belongs to a medium-temperature soldering and brazing material and comprises, by weight, 3%-5% of Ag, 6%-8% of P, 0.05%-2.5% of In, 0.05%-2.5% of Li, 0.005%-0.1% of Zr, 0.005%-0.1% of La, and the balance Cu. Silver ingot, phosphori, electrolytic copper, metal In, metal Li, metal Zr and rare earth La, which are sold in the market, are used, matching is carried out according to the design composition, conventional intermediate-frequency smelting and pouring are adopted, a wire can be obtained through squeezing and drawing, and a flux-cored colder wire can be obtained by adding brazing flux. The brazing and soldering alloy has the characteristics of low silver content, a low melting point, good wettability and high strength, and can replace BCu75PAg with 20% of silver and BAg25CuZnSn brazing and soldering alloy with 25% of silver, and the BCu75PAg with 20% of silver and the BAg25CuZnSn brazing and soldering alloy with 25% of silver are widely used in the refrigeration industry.
Owner:江西金世纪特种焊接材料有限公司
Self-fluxing brazing filler metal and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104942476ALow costReduce dosageWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaAlloyAmmonium Hydrogen Carbonate
The invention relates to self-fluxing brazing filler metal and a preparation method thereof. The self-fluxing brazing filler metal comprises a porous body formed by sintering an alloy and a welding flux in the holes in the porous body. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing atomizing alloy powder; (2) uniformly mixing 93 to 97 weight parts of the atomizing alloy powder with 3 to 7 weight percent of ammonium hydrogen carbonate to obtain mixture, and processing the mixture into a blank piece; (3) sintering the blank piece to form the porous body with the holes; (4) placing the welding flux into the holes in the porous body; (5) placing the porous body obtained in the step (4) into a lukewarm water tank to remove excessive welding flux on the surface of the porous body, drying to remove moisture, and packaging. As the preparation method adopts powder metallurgy, and sintering is carried out after mechanical extrusion or pressing is conducted on alloy powder, the problem that moderate-temperature brazing filler metal is difficult to be processed into forms in the prior art is solved. Moreover, as the molten welding flux is soaked into a porous workpiece through dipping, an operator is prevented from being in touch with the welding flux, harm to the body of the operator is reduced, the labor intensity is greatly reduced, and convenience is brought for popularization.
Owner:徐鲁豫
Green body, sintered porous metal film and dust removal method
The invention discloses a green body, a sintered porous metal film and a dust removal method, and solves the technical problem that the sintered porous metal film with high strength and high gas flux is difficult to obtain in the prior art. The green body of the sintered porous metal film comprises a precursor layer, the precursor layer is provided with a first porous metal supporting layer and a coating attached to the surface of the first porous metal supporting layer, and the coating is provided with a metal powder raw material used for powder metallurgy; the reinforcing layer is provided with a second porous metal supporting layer, the strength and / or air flux of the second porous metal supporting layer are / is larger than those of the first porous metal supporting layer, and the reinforcing layer and the precursor layer are arranged in an overlapped mode.
Owner:CHENGDU INTERMENT TECH
Control method of corner cracks in yq450nqr1 B-shaped steel blooms
ActiveCN109317628BImprove cooling effectImproved uniformity control of solidification evolutionCrazingSlag
The present invention discloses a method for controlling cracks at the corners of YQ450NQR1 B-shaped steel billets in the field of iron and steel metallurgy. Special mold flux for continuous casting mold. The physical properties of the flux are: viscosity 0.99~1.00Pa.S, alkalinity 0.81~0.83, softening temperature 1127~1130℃, hemispherization temperature 1194~1198℃, flow temperature 1201 ~1203℃, slag consumption 0.61~0.65kg / t during application 钢 . The invention optimizes the cooling of the corners of the slab and improves the uniformity control of the solidification evolution at the corners of the slab by using a tubular crystallizer with a large cross-section, and cooperates with the special mold slag to effectively protect the YQ450NQR1 B-shaped steel bloom The corner quality of the slab, especially the control effect on the defect width of the slab corner crack caused by the shrinkage of the peritectic transformation line is remarkable, which solves the problem of rolling cracks caused by the microcracks at the corner of the slab.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Magnesium-neodymium intermediate alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a magnesium-neodymium intermediate alloy and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of metal materials and metallurgy. The magnesium-neodymium intermediate alloy comprises the following raw materials including, by weight, 10-15 parts of magnesium powder, 10-15 parts of neodymium powder and 0.1-0.15 part of a multi-element refining agent. The magnesium powder is added into a smelting furnace, a protective flux is added, slagging-off is conducted, the neodymium powder is added after slagging-off, the temperature is increased to 1050 DEG C after complete adding, the multi-element refining agent is added, the protective flux is added again after the temperature is increased to 1100 DEG C, secondary slagging-off is conducted, and a smelting material is prepared; brewing and boiling are carried out; ingot casting is carried out; testing is carried out; and carbon powder can serve as a pore-forming agent to decompose and release gas, on one hand, part of hydrogen in molten metal is taken away, on the other hand, nano-calcium-based powder is sintered at the temperature, a large number of porous structures are generated, the specific surface area of the nano-calcium-based powder is increased, the excellent adsorption performance is achieved, residual hydrogen and impurities in melt can be adsorbed, and the effects of refining and impurity removal are achieved.
Owner:LOUDI XINGXIN ALLOY
Novel flux-cored silver solder
InactiveCN110936065AGood moisture absorptionImprove liquidityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaDipotassium hydrogen phosphateTetrafluoroborate
The invention discloses a novel flux-cored silver solder, which belongs to a soldering material in the fields of metal materials and metallurgy. The novel flux-cored silver solder is prepared by coating soldering flux powder with a BAg18CuZnSn silver solder strip. And the BAg18CuZnSn silver solder strip is prepared from metal silver, copper, zinc and tin. The coating brazing flux powder is composed of potassium bifluoride (KHF2), potassium fluoride, boric acid, cesium carbonate, potassium carbonate, potassium silicate, sodium silicate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate and potassium tetrafluoroborate (KBF4). Soldering flux powder in the flux-cored silver solder has excellent flowability and moisture absorption resistance, in the tape winding and drawing process of the flux-cored silver solder, the flux-cored silver solder does not have the phenomenon of wire breakage, the soldering flux powder cannot adhere to a roller, and the drawing diameter of the flux-cored silver solder can be reduced to 0.4 mm or below so as to meet the requirement for precise soldering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YONGWANG WELDING MATERIALS CO LTD
Ladle furnace refining fluoride-free pre-melted slags, preparation method and using method
InactiveCN102787214BImprove use valueIncrease profitProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingRefining (metallurgy)
The invention belongs to the field of the steel-making secondary refining ladle metallurgy, particularly relates to ladle furnace refining fluoride-free pre-melted slags, a preparation method and a using method and is suitable for the slagging refining process of the steel-making secondary refining in a steel ladle. The invention aims to provide the ladle furnace refining fluoride-free pre-melted slags, the preparation method and the using method by utilizing existing spodumene resources and adding a refining flux and a slag regulation component, solve the problems of defects of slag desulfurization, low dephosphorizing efficiency, large difficulty in rephosphorization control, poor slag melting performance, poor slag inclusion adsorption performance and the like of current ladle refining slagging materials, also reduce the ladle secondary refining slagging cost and implement the low-cost processing and utilization of a spodumene mineral. The ladle furnace refining fluoride-free pre-melted slags are characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 40 to 60 percent of spodumene powder, 30 to 50 percent of lime powder and 5 to 25 percent of aluminium ash powder.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for producing compound filter of multi-layer metal meshes and metal powder
ActiveCN102059340BSmall filter resistanceLarge filtration fluxFiltration separationMetal filamentMetal powder
Owner:王东伟
Method for extracting metal lead and zinc through bottom blowing oxygen-enriched self-heating smelting-electric smelting direct reduction
PendingCN111996374AHigh recovery rateIncrease added valueProcess efficiency improvementSlagExhaust gas emissions
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy, and specifically relates to a method for extracting metal lead and zinc through bottom blowing oxygen-enriched self-heating smelting-electric smeltingdirect reduction. The method comprises the following steps of preparing a mixture from lead-zinc sulfide ore, lead-zinc oxidized ore, flux calcium oxide and silicon dioxide, feeding the mixture intoa bottom blowing oxidation furnace, introducing high-pressure oxygen at the temperature of 950-1200 DEG C in the furnace, and smelting to obtain SO2 flue gas, lead liquid and oxidized slag melt; feeding the oxidizing slag melt into an electric smelting reduction furnace, adding coal, silicon dioxide, calcium oxide and a cold material containing lead and zinc oxides, and heating and reducing to obtain lead liquid, reducing slag and zinc-containing flue gas; and introducing the zinc-containing flue gas into an efficient condenser, and condensing to obtain lead liquid, zinc liquid and CO gas. According to the method, metal zinc can be obtained while the metal lead product is obtained, the additional value of the product is increased, and the recovery rate of lead and zinc is increased. The method has the advantages that the raw material applicability is wide, the fuel consumption is reduced, and the waste gas emission is reduced.
Owner:岷山环能高科股份公司
Tungsten copper and dissimilar metal welding structure and method
ActiveCN114406388AReliable weldingIncrease productivitySoldering apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesCopperFlux (metallurgy)
The invention provides a tungsten copper and dissimilar metal welding structure and method. A first weldment is provided with an assembly hole, and a second weldment is inserted into the assembly hole; the first weldment is formed by a mold in a powder metallurgy mode, and the mold comprises a mold body and an insert used for forming an assembly hole. The insert comprises an insert body, an insert body and a template, the insert body is detachably mounted between the insert body and the template, convex teeth are arranged on the outer wall of the template, the insert body and the template are made of ferromagnetic materials, and after the insert body is pulled out, the template is adsorbed by the insert body to be separated from the assembly hole, so that a tooth-shaped groove is formed in the inner wall of the assembly hole; the welding flux is melted in a welding seam between the second weldment and the assembly hole and fills the groove, so that the second weldment is meshed with the first weldment. Tungsten copper and dissimilar metal are reliably welded, and the process is easy and convenient to operate and high in efficiency.
Owner:无锡鑫巨宏智能科技有限公司
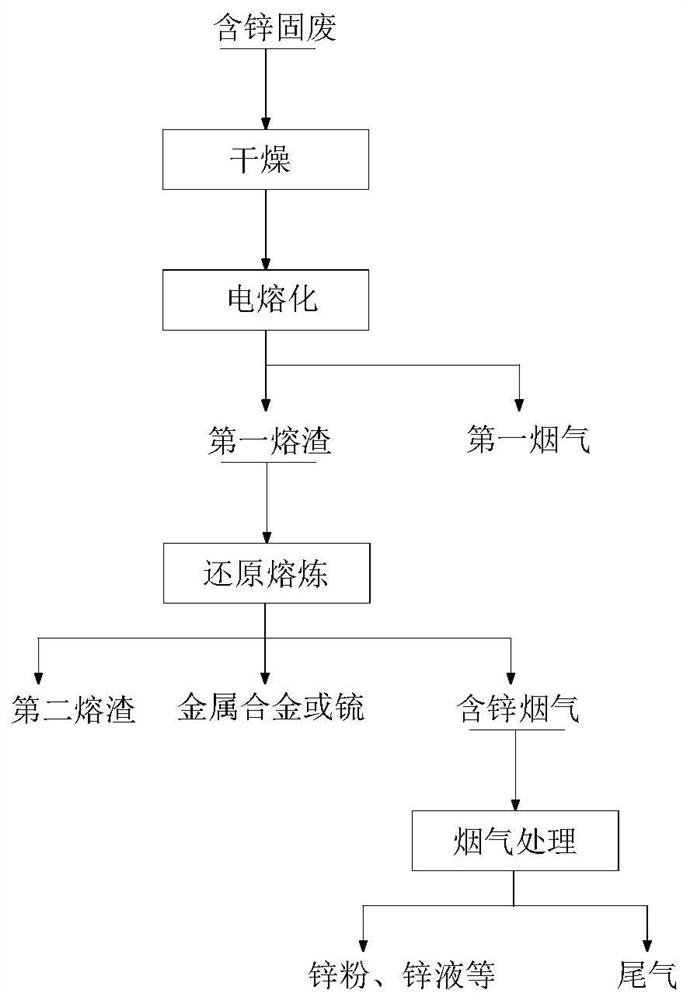
Zinc-containing solid waste treatment method and system
PendingCN113652557AReduce moisture contentProcess efficiency improvementNon-ferrous extractive metallurgySulfonium
The invention relates to the technical field of non-ferrous metal metallurgy, in particular to a zinc-containing solid waste treatment method and system. The treatment method comprises the following steps that zinc-containing solid waste, a flux and a reducing agent are dried, the dried zinc-containing solid waste, the flux and the reducing agent are molten, so that first molten slag and first flue gas are obtained, the first slag is subjected to reduction smelting in a reducing atmosphere, so that second slag and zinc-containing flue gas, or metal alloy and zinc-containing flue gas, or sulfonium and zinc-containing flue gas is obtained, the zinc-containing flue gas is subjected to cooling or oxidation treatment, so that a zinc-containing product is obtained, and the zinc-containing product comprises any one of zinc powder, zinc liquid or zinc oxide. The zinc-containing solid waste treatment method is short in technological process, less in related matching, small in occupied area and low in investment cost, reduces the use of a reducing agent and fuel, and reduces carbon emission and environmental pollution.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
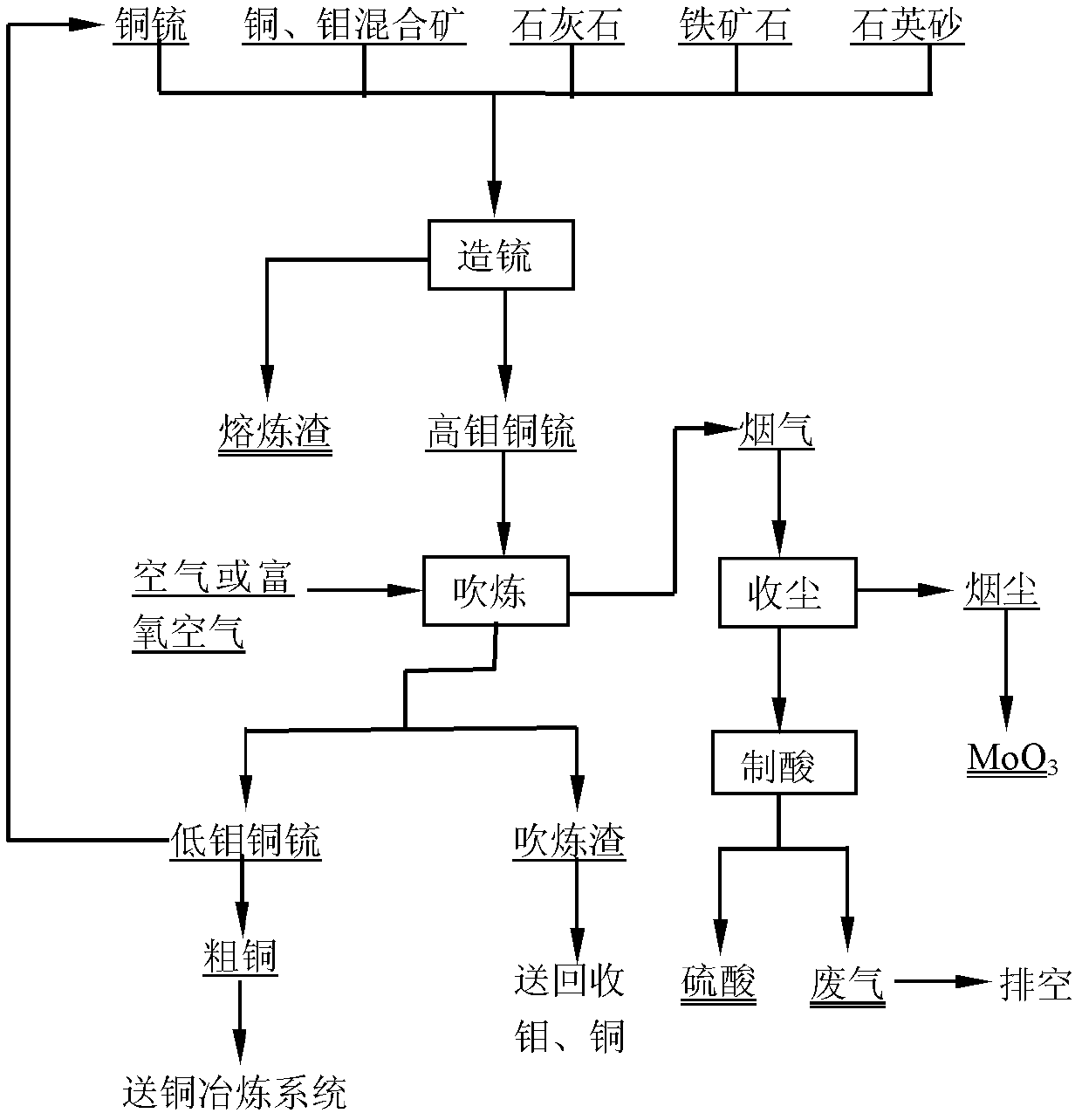
Method for treating copper-molybdenum mixed ores
The invention discloses a method for treating copper-molybdenum mixed ores, belonging to the field of molybdenum metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: directly heating the copper-molybdenum mixed ores to a molten state, or heating to a molten by using an assistant flux copper matte (matte) (for high-molybdenum low-copper mixed concentrate) to form copper molybdenum matte; introducing air or oxygen-enriched air into the copper molybdenum matte to carry out converting until molybdenum sulfide in the copper molybdenum matte is oxidated into MoO3 to be volatilized, recycling the MoO3 from smoke dust by dust collection, and sending the dedusted flue gas to the acid making process; and after finishing converting, returning the low-molybdenum copper matte to the next matte formation process or sending the low-molybdenum copper matte to a copper smelting system. The method has the advantages of short process, favorable mass-transfer heat-transfer conditions, high productivity, high heat utilization, high SO2 concentration in flue gas, strong adaptability to raw materials, and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A method for extracting lead-bismuth alloy from copper anode slime smelting waste residue
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy, and relates to a method for extracting a lead-bismuth alloy from copper anode slime smelting waste. The method includes the following stepsthat the copper anode slime smelting waste and a flux are mixed to be added into a Kaldo furnace for reduction smelting, a coarse lead-bismuth alloy is obtained by drossing after reduction smelting, and after the coarse lead-bismuth alloy melt is transferred to an intermediate frequency furnace, liguation decoppering, sulphurating denickeling and zincification silver separation are successively conducted to obtain the refined lead-bismuth alloy; and the flux includes coke, limestone and sodium carbonate, and the flux is prepared from the components in percentage by mass of the copper anode slime smelting waste: 5-6% of coke, 15-19% of limestone and 2-4% of sodium carbonate. According to the method for extracting the lead-bismuth alloy from the copper anode slime smelting waste, the obtained refined lead-bismuth alloy has high lead grade and few impurities, lead and bismuth can be recovered by direct lead electrolysis separation, gold and silver are recovered by furnace returning of silver-zinc crust, and efficient separation and recovery of lead, bismuth and gold and silver from the copper anode slime smelting waste are realized.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Reflection furnace fire refining method for high-arsenic and high-antimony crude copper
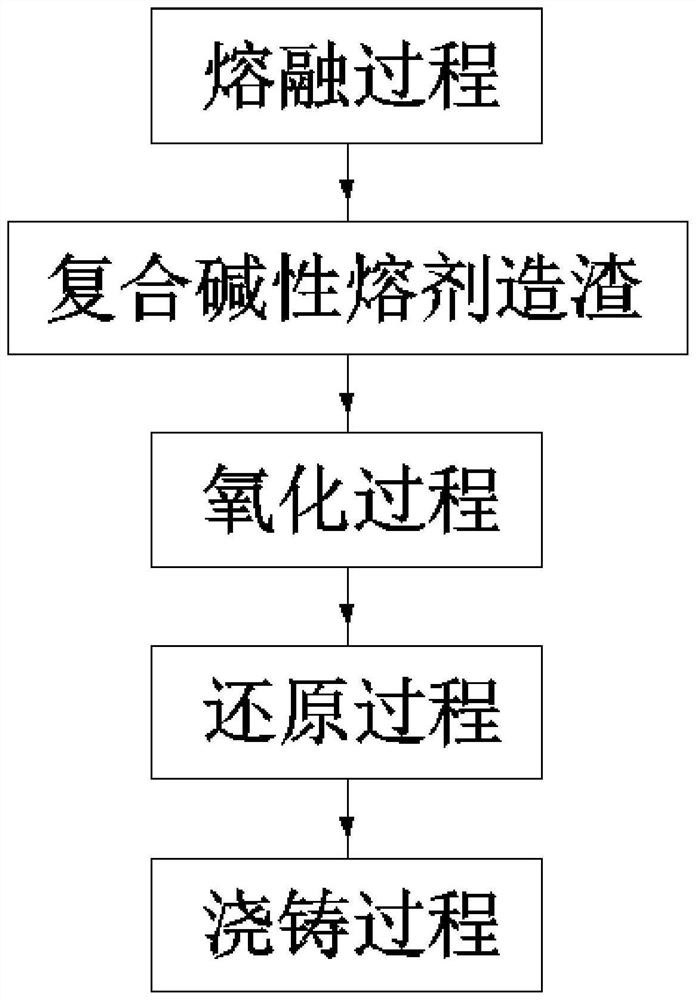
ActiveCN114350975AGood removal effectImprove refining effectReverberatory furnaceProcess efficiency improvementRefining (metallurgy)Slag
The invention discloses a reflecting furnace fire refining method for high-arsenic and high-antimony crude copper, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metallurgy, the refining method comprises the following steps: S1, a melting process: crude copper is fed from a feeding port in the top of a reflecting furnace, a burner is started for heating, and copper liquid is obtained; s2, slagging with a composite alkaline flux: adding the composite alkaline flux into the copper liquid for slagging and refining; s3, oxidation process; s4, a reduction process; s5, a casting process: feeding the copper liquid to a casting mold area for slow cooling, then returning the copper liquid to a copper ore blowing system, and finally casting in a copper mold of a disc casting machine to obtain an anode plate; in the step S1, the reverberatory furnace comprises a furnace body and a power mechanism, the furnace body is provided with a flue gas outlet, a feeding opening, a molten copper outlet and a slag discharging opening, the feeding opening is located in the top of the furnace body, the burner is rotationally connected to one side in the furnace body, and the power mechanism is used for driving the burner to rotate in the furnace body. According to the method, high-arsenic, antimony and other impurities difficult to remove in the crude copper can be effectively removed.
Owner:高诺(衡阳)新材料有限责任公司
A kind of method that uses fly ash to prepare aluminum-magnesium alloy
ActiveCN104294314BWith green energy saving and environmental protectionReduce the temperatureAluminium chlorideMaterials science
The invention belongs to the field of nonferrous metallurgy and relates to a method for preparing aluminum-magnesium alloys with fly ash. The technical solution of the present invention is to first adopt fly ash acid leaching to produce aluminum chloride, and then the electrolyte system used is composed of flux, melt and additives, wherein the composition of the flux is: NaCl: 0-60%, KCl : 25-75%, MgCl2: 0-66%, then add the melt AlCl3 that accounts for 5-50% of the flux quality, the additive LiCl, 0-5% additive KF, 0-5% additive that account for 0-5% of the flux quality MgF2 or 0-5% additive AlF3, in which molten AlCl3 is added from the bottom of the electrolytic cell, the inter-electrode voltage is controlled at 2.3-3.3V, the cathode current density is 0.5-1.5A / cm2, the electrolysis temperature is 450-500°C, during the electrolysis process Chlorine gas is generated on the anode side, which is recycled and reused, and solidified aluminum-magnesium alloy is deposited on the cathode side. The method of the invention has low power consumption, low electrolysis temperature, and low production cost, solves the problems of aluminum chloride evaporation and dendrite generation by electrolysis, has no environmental pollution, and is easy to implement.
Owner:李景江
Oxygen-enriched bottom blowing one-step copper smelting method
PendingCN114703376AReduce generationLow viscosityRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesThermodynamicsSmelting process
The invention belongs to the technical field of nonferrous metallurgy, and provides an oxygen-enriched bottom blowing one-step copper smelting method. The method comprises the following steps: mixing copper concentrate, a flux and fuel, and carrying out melt chaotic stirring smelting by adopting oxygen-enriched variable-frequency bottom blowing; the gas of the oxygen-enriched variable-frequency bottom blowing is oxygen-enriched air; the flow of the oxygen-enriched air is a variable-frequency regulation flow; the variable-frequency regulation and control flow accords with a formula 1: in the formula 1, mu is equal to 4, xt is instantaneous flow, and xmax is maximum flow; the flow fluctuation of the oxygen-enriched air ranges from-20% to 20%. According to the method, oxygen-enriched variable-frequency bottom blowing is adopted for carrying out melt chaotic stirring smelting, generation of Fe3O4 can be reduced, the viscosity of smelting slag is reduced, and generation of foamed slag is reduced; meanwhile, oxygen-enriched variable-frequency bottom blowing achieves chaos stirring of the melt, enhances the heat and mass transfer effect in the smelting process, improves the smelting efficiency and prevents foaming slag from being generated.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of preparation method of nano W-xcu alloy, nano W-xcu alloy
InactiveCN108927527BEvenly distributedFine and uniform particlesMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingTungstateCopper oxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano-W-xCu alloy and a nano-W-xCu alloy, belonging to the technical field of preparing composite materials by powder metallurgy. The method is to put copper tungstate and a certain amount of copper oxide into a high-pressure hydrothermal kettle for hydrothermal reaction, then cool the obtained hydrothermal product, filter and clean it, and finally dry it to obtain nano-sized tungsten copper. Precursor powder, followed by two-stage hydrogen reduction to obtain the final product nano-W‑xCu alloy powder. The method uses hydrothermal reaction to prepare tungsten-copper alloy powder, which has the advantages of high efficiency, low consumption, and easy operation. The prepared nano W-xCu alloy powder is spherical, the particle size reaches nanometer level, and the particles are fine and uniform. Tungsten copper is evenly distributed.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for smelting titanium-silicon-aluminum intermediate alloy by reducing titanium-containing blast furnace slag with aluminum under atmosphere protection
InactiveCN111809061AHigh titanium contentLess impuritiesRecycling and recovery technologiesProcess efficiency improvementAl powderSlag
The invention relates to a method for smelting a titanium-silicon-aluminum intermediate alloy by reducing a titanium-containing blast furnace slag with aluminum under atmosphere protection, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. The method for smelting the titanium-silicon-aluminum intermediate alloy by reducing the titanium-containing blast furnace slag with the aluminum under atmosphere protection comprises the following steps: A. Mixing the titanium-containing blast furnace slag, aluminum powder, lime, and flux according to a mass ratio100:30-50:20-28:0-10, and reacting under Arprotection or vacuum protection of 1-1000Pa at a temperature of 1500-1700 DEG C; and B. After the reaction is completed, cooling a reaction product through isolating from air and cooling to a room temperature, then crushing and deslagging to obtain titanium-containing titanium-silicon-aluminum intermediate alloy. An alloy phase prepared by the method of the invention has high titanium content, lowsilicon and iron content, and can realize economical titanium extraction, so the waste of titanium resources is reduced greatly.
Owner:PANZHIHUA UNIV
Metal pipeline butt-welding type welding device for metallurgy
ActiveCN114453717APrevent splashPlay a protective effectResistance welding apparatusFlux (metallurgy)Materials science
The invention relates to a welding device, in particular to a metallurgical metal pipeline butt-welding type welding device. The invention aims to provide the butt-welding type welding device for the metallurgical metal pipeline, which can be automatically lifted and has a protection effect. According to the technical scheme, the butt-welding type welding device for the metallurgical metal pipeline comprises a bottom plate; the shell is mounted at the top of the bottom plate; the two placing frames are symmetrically and fixedly connected to the middle of the top of the bottom plate, and the placing frames are located on the inner side of the shell; the welding mechanism is mounted between the bottom plate and the middle part of the shell; the number of the butt-welding devices is two, and the butt-welding devices are both installed on the welding mechanism. When the butt-welding device is used for welding a pipeline, welding flux is inevitably splashed out and easily hurts people, and under the action of the shell, when the pipeline is welded, the welding flux is prevented from being splashed out, the protection effect is achieved, and the working efficiency of people is improved.
Owner:乳山市创新新能源科技有限公司
sn-ag-cu lead-free solder with nd, se and ga
ActiveCN102896436BImprove wettabilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMetallic materialsElectronic industry
The invention relates to a Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder containing Nd, Se and Ga, and belongs to a brazing material in the fields of metal materials and metallurgy. The Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.01 to 0.5 percent of Ag, 0.02 to 1.0 percent of Cu, 0.001 to 0.5 percent of Nd, 0.001 to 0.5 percent of Se, 0.003 to 1.5 percent of Ga and the balance of Sn. Noble metal silver which belongs to a strategic resource can be saved; silver content can be reduced to be ultralow, and the wettability of the solder can be improved; when the Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder is matched with a commercially available RMA brazing flux, the mechanical property of a brazing seam is 75 to 85MPa, and the tensile strength is 76 to 88MPa, so that the Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder can be suitable for wave soldering, reflow soldering and manual welding in electronic industry; and environment-friendly, lead-free and cadmium-free requirements in manufacturing industry can be met.
Owner:CHANGSHU HUAYIN FILLER METALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com