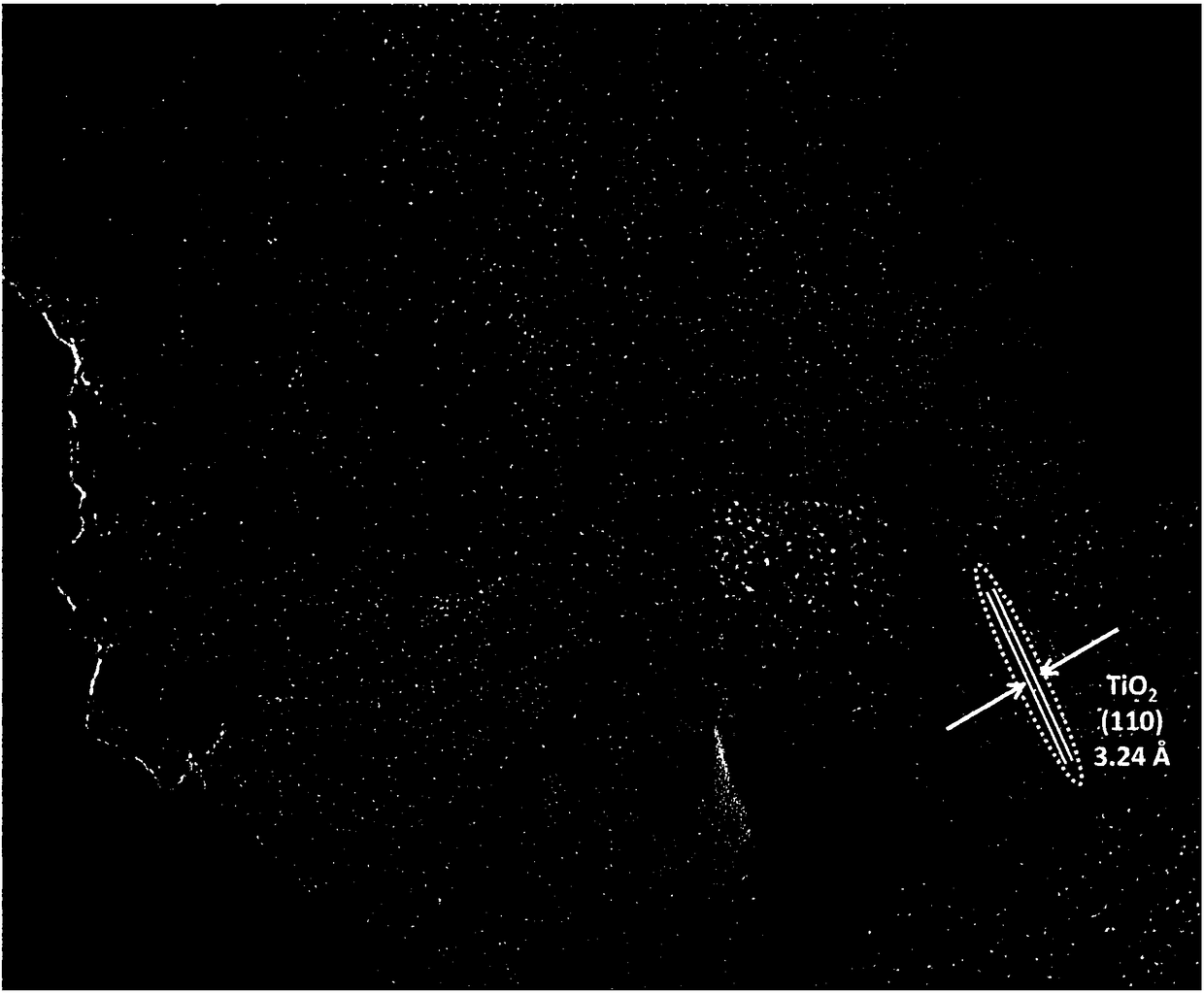
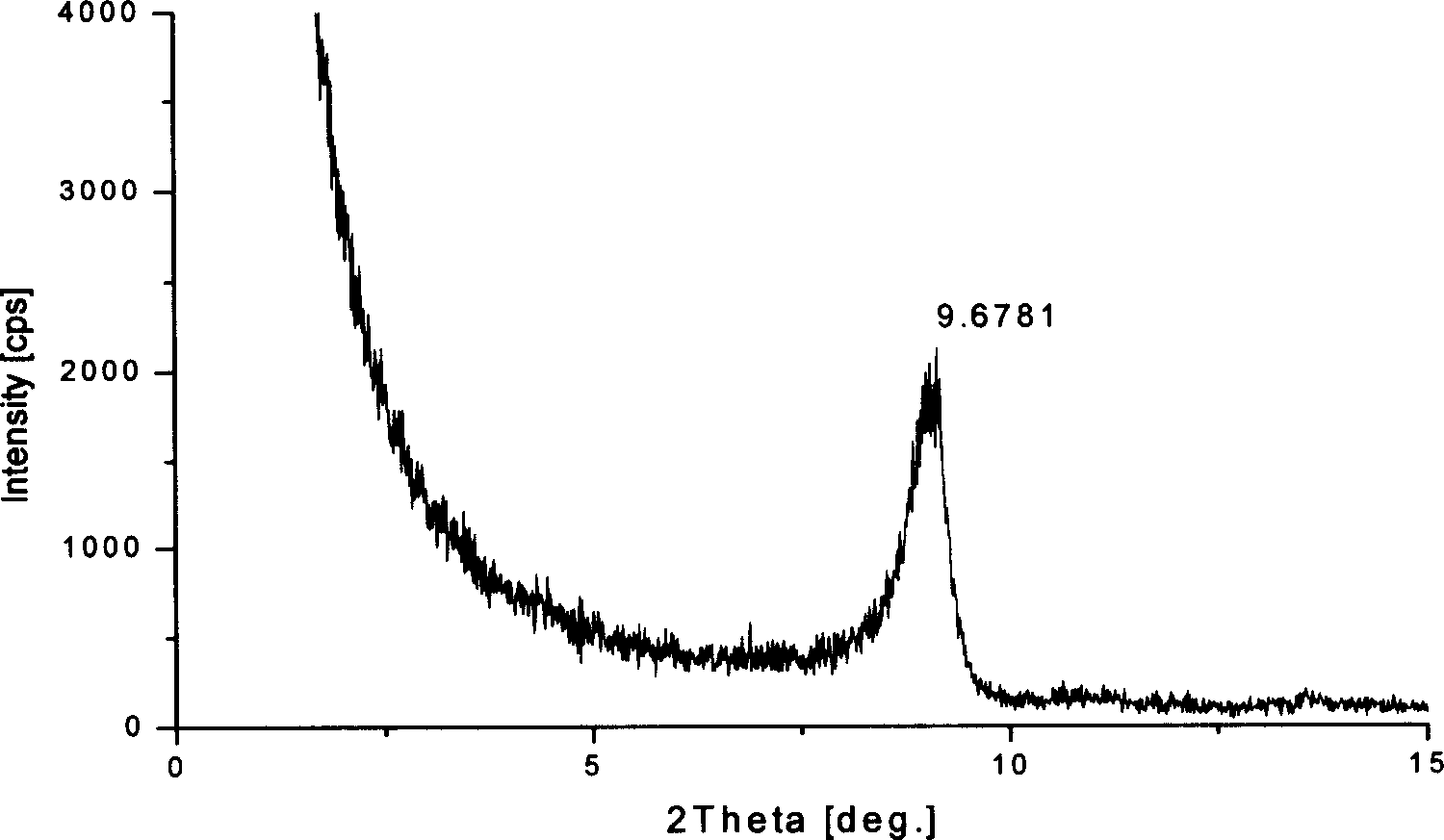
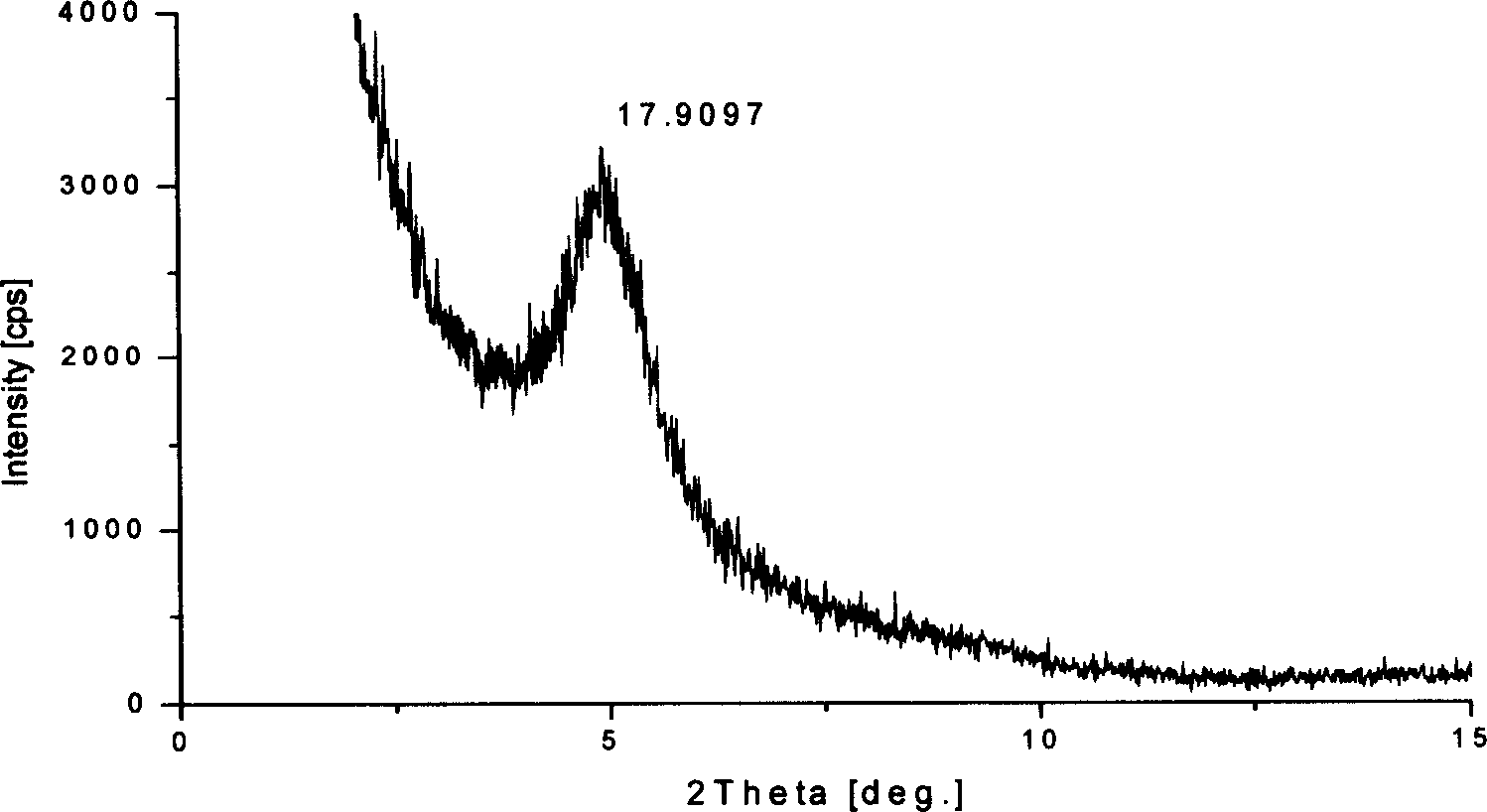
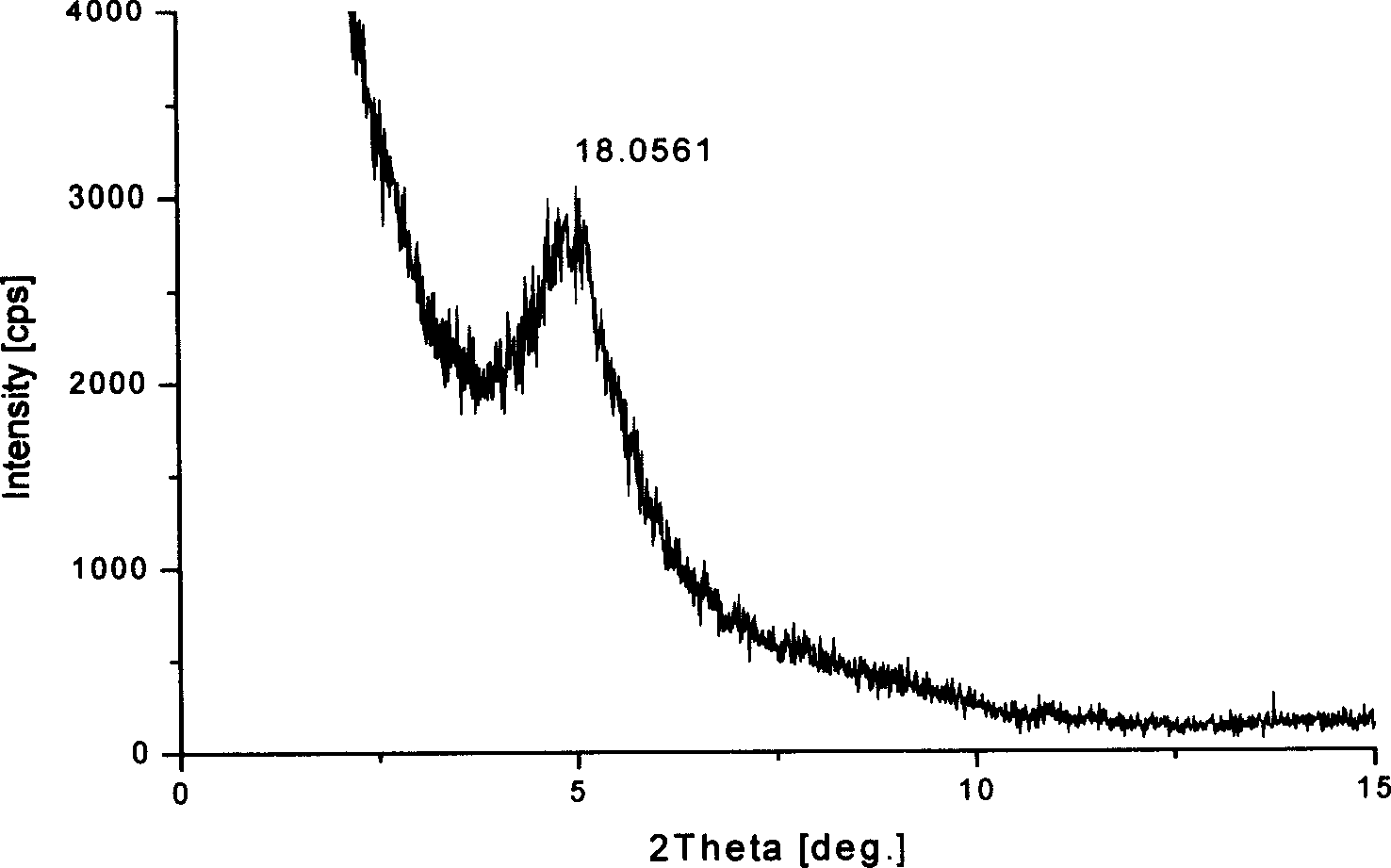
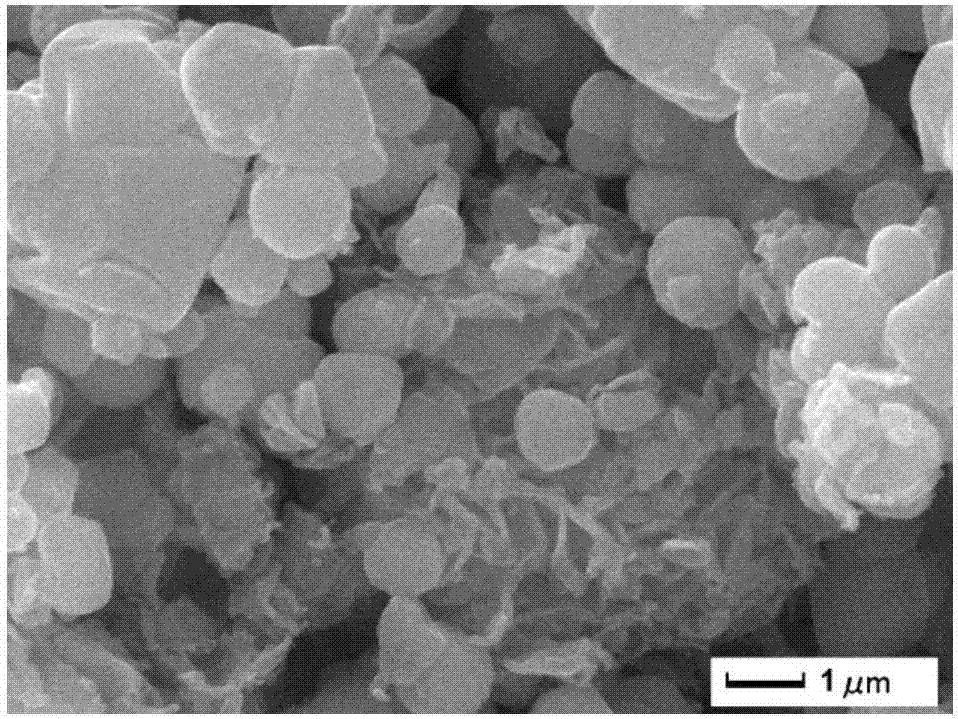
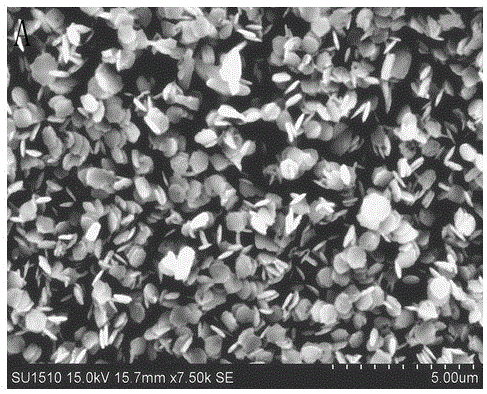
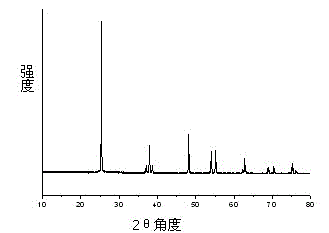
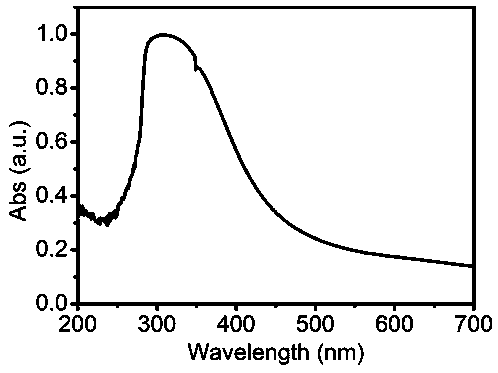
Patents
Literature
58results about How to "Efficient photocatalytic performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Micronano-structured and silver phosphate based composite visible light catalytic material and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN103480399AVisible light response range is wideImprove light energy utilizationPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFiltrationPhosphate
The invention relates to the technical field of photocatalysis, particularly to a micronano-structured and silver phosphate based composite visible light catalytic material and a preparing method thereof. The method includes the following steps: dissolving oxidized graphene in water, and performing ultrasonic treatment to obtain an oxidized graphene dispersion liquid; ultrasonically dispersing silver nitrate and zinc oxide in deionized water to obtain a mixed solution, stirring and dropwise adding the solution into the oxidized graphene dispersion liquid, so as to obtain a mixed precursor; slowly and dropwise adding a prepared phosphate solution in the mixed precursor of the oxidized graphene, the silver nitrate and the zinc oxide, and continuously stirring, performing suction filtration on the product, then repeatedly washing the product by the deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol, and obtaining a composite after vacuum drying. The invention has the advantages that the preparing technology is simple, the required raw materials are abundant, the performance of the product is superior, and motivated by visible light, the catalytic material has stronger degradation activity to organic dyestuff rhodamine B.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Hexagonal boron nitride modified graphitized carbon nitride composite optical catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106732727AOptimized areaBoost ratePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationElectron holeHexagonal boron nitride
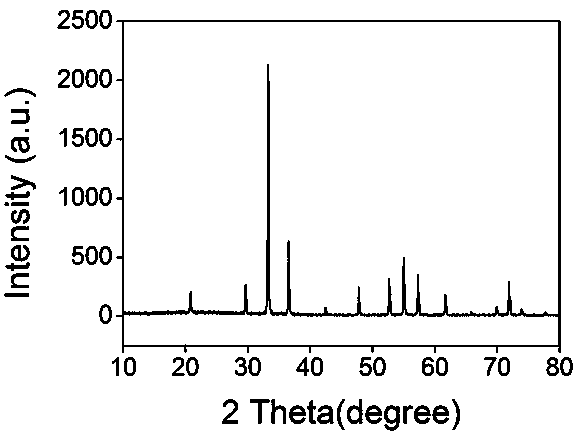
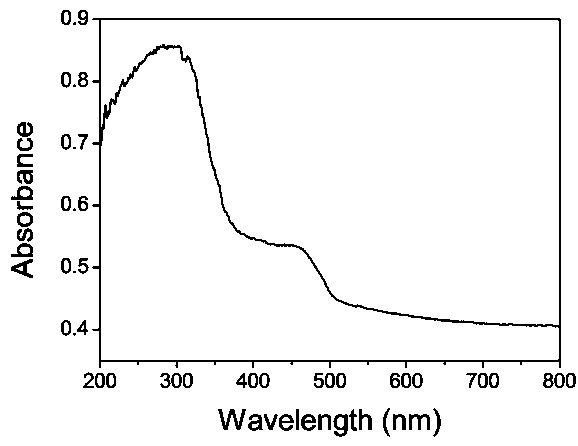
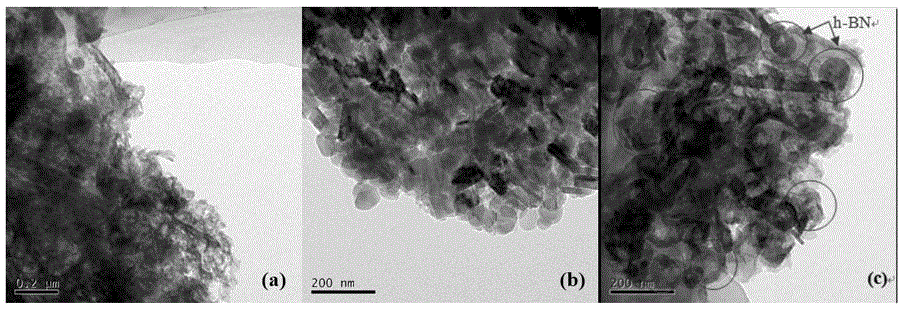
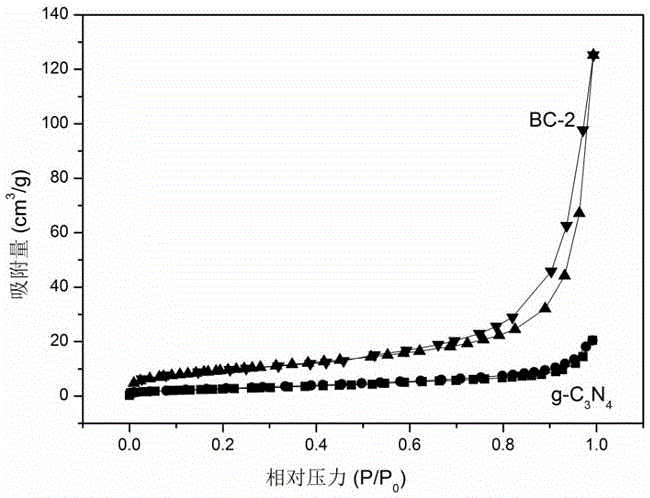
The invention discloses a hexagonal boron nitride modified graphitized carbon nitride composite optical catalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the composite optical catalyst, by taking graphitized carbon nitride as a carrier, laminated hexagonal boron nitride modifies the graphitized carbon nitride carrier. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing the hexagonal boron nitride with a graphitized carbon nitride precursor; and calcining the mixed precursor to obtain the hexagonal boron nitride modified graphitized carbon nitride composite optical catalyst. The hexagonal boron nitride modified graphitized carbon nitride composite optical catalyst disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being environmentally friendly, fully free of metal doping, large in specific surface area, high in photoproduction electron-hole separating efficiency, high in optical catalytic activity, good in stability, corrosion-resistant and the like. The preparation method has the advantages of being simple, low in cost of raw materials, less in energy consumption, easy to control conditions and the like. The composite optical catalyst disclosed by the invention is used for degrading dye wastewater and has the advantages of being simple in application method, stable in optical catalytic performance, high in corrosion resistance, high in dye wastewater degrading efficiency.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Inorganic clay compound material, its preparation and use
InactiveCN1736586AEfficient photocatalytic performanceWide wavelength response rangeCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRare-earth elementAlcohol
The invention relates to inorganic clay composite and the method for preparation and the utility, belonging to the catalyst art. The material comprises rare-earth element, titanium oxide and clay, the rare-earth element being one or two from Ce, La, Nd, Pr, Yt, Eu and Er, the clay being montmorillonite, the mass ratio of every component being: montmorillonite 54- 90%, titanium oxide 8- 45%, and rare-earth oxide 0.1- 4.0%; and the technique contains the following steps: the mass ratio of material being: titanate 0.6- 1.8%, absolute ethyl alcohol 45- 90%, rare-earth salt 0.013- 0.08% clay 0.8- 1.8%, deionized water 3- 30% and glycerin 4- 35%, using titanate, absolute ethyl alcohol and glycerin solution to prepare titanium oxide sol, using rare-earth salt and absolute ethyl alcohol to prepare rare-earth solution, adding said sol and solution separately into the suspension of clay- absolute alcohol, mixing, aging, filter-pressing, drying in 60- 80Deg. C, and at last roasting 4- 10 hours to prepare the product. The material is added into coating as an additive. And the material has a high catalysis property and a short preparation process.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of Z-configuration visible light catalytic decomposing water composite material
InactiveCN106994360AShape is easy to controlGood size controlPhysical/chemical process catalystsPhotocatalytic water splittingPhotocatalytic reaction
The invention relates to a photocatalytic water splitting material, and particularly relates to a Z-configuration visible light catalytic decomposing water composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of dropwise adding a silver nitrate solution into flower-like molybdenum disulfide dispersion liquid under stirring, and stirring to obtain a mixed precursor solution; weighing and dissolving phosphate into deionized water to obtain a phosphate solution; under stirring, adding a sodium phosphate solution into the prepared mixed precursor solution, enabling the solution to gradually generate greyish-green sediments along with the adding of sodium phosphate, continuously stirring the mixed solution for 3h after dropwise adding, finally washing the reaction sediments with deionized water and ethyl alcohol respectively for three times and vacuum drying. The bent basal plane formed by flower-like molybdenum disulfide can become the main active site of a light-catalyzed reaction, and is stronger than a molybdenum disulfide nanosheet within the absorption range of visible light, and the performance of the composite photocatalyst can be further improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
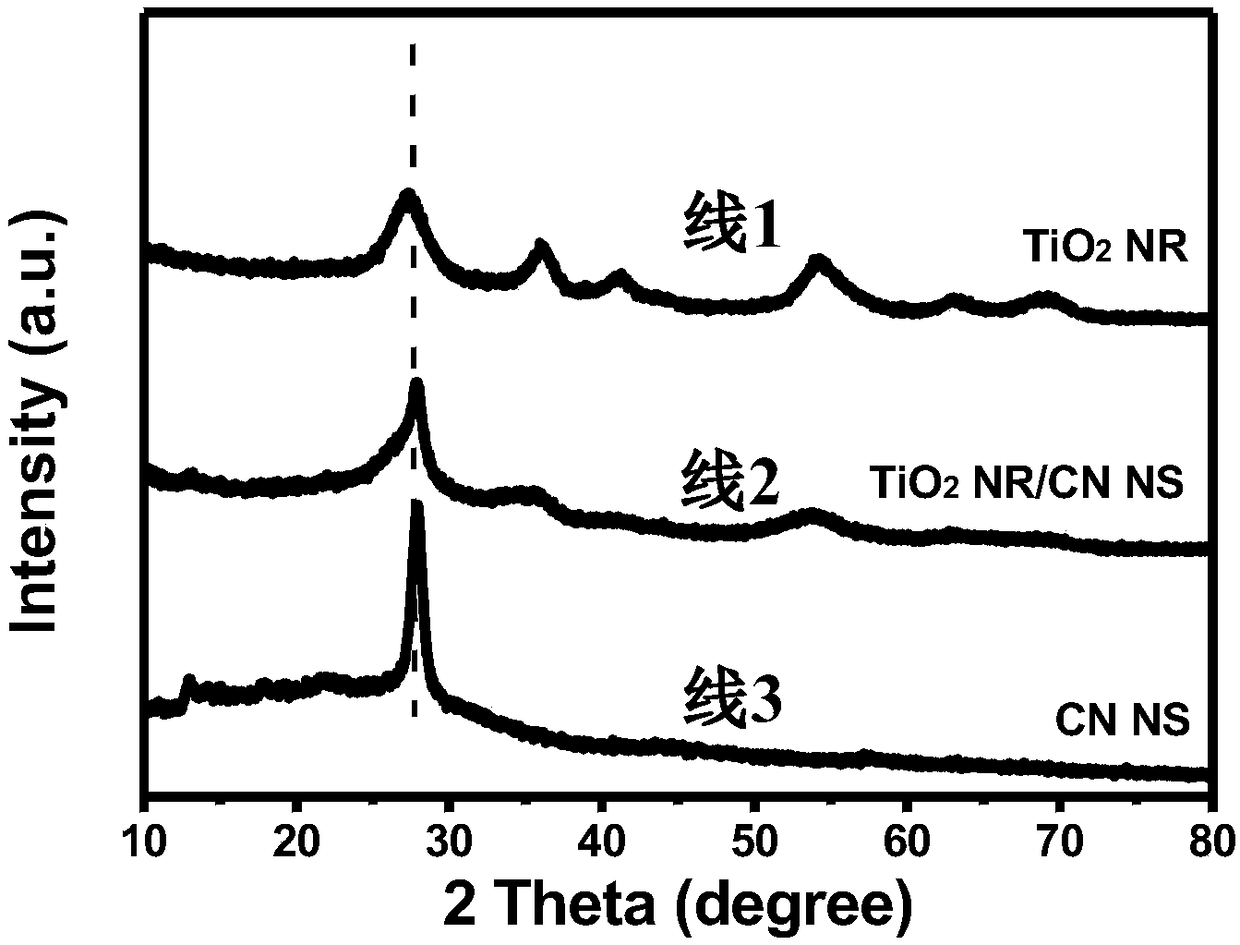
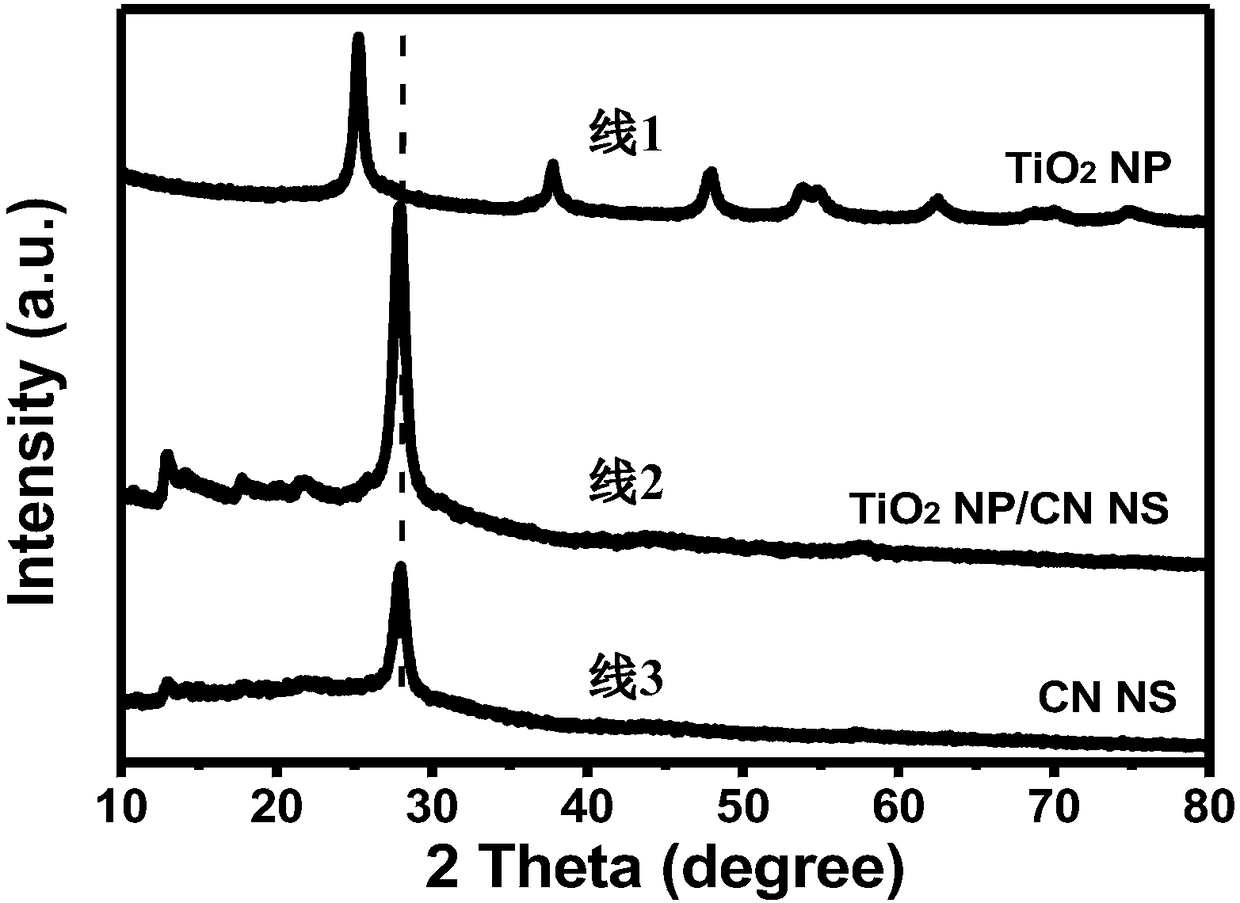
Preparation for high-efficiency ultrafine TiO2 nanoparticle/graphite phase carbon nitride nanosheet composite photocatalyst
InactiveCN108355693AEfficient photocatalytic performanceAchieve purificationPhysical/chemical process catalystsAir cleaningMaterials science
The invention provides preparation for a high-efficiency ultrafine TiO2 nanoparticle / graphite phase carbon nitride nanosheet composite photocatalyst, and belongs to the technical field of photocatalytic materials. The preparation uses TiCl3 as a titanium source, a graphite phase carbon nitride nanosheet as a carrier and an alcohol as a solvent, a hydrothermal reaction is performed for 1-12 h in ahydrothermal kettle at the temperature of 70-180 DEG C, the obtained ultrafine TiO2 nanoparticles are uniformly supported at the surface of the graphite phase carbon nitride nanosheet, and therefore the composite photocatalyst is formed. The composite photocatalyst provided by the invention has a higher specific surface area and higher photocatalytic activity; and when the photocatalyst is dispersed in sewage or coats a substrate, pollutants in water and air are effectively removed under sunlight, so that the photocatalyst can be used for buildings, indoor walls, vehicle surfaces, glass windows and other carrier surfaces to be used as a self-cleaning coating layer, has better effects on pollutant elimination, indoor air purification and outdoor air purification, and has better antibacterial and sterilized effects.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
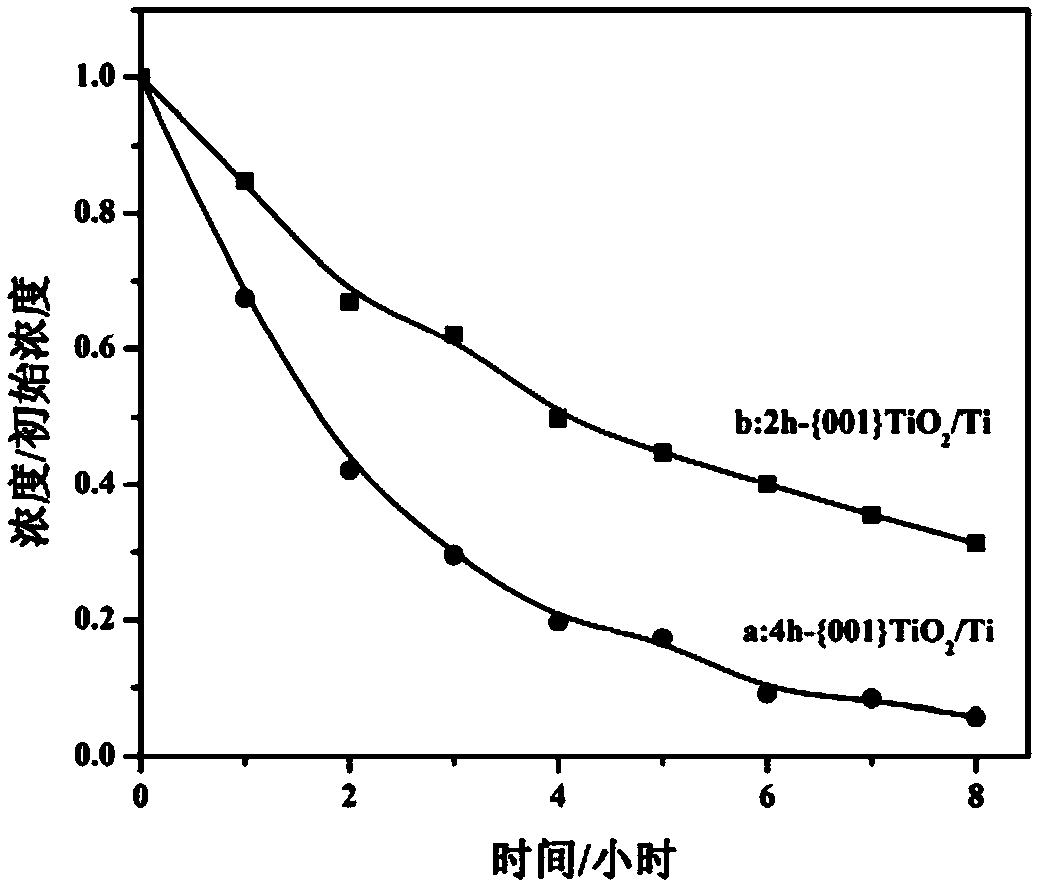
Preparation and applications of {001} crystal face controllable exposed titanium dioxide photoelectrode
ActiveCN108911056ASolve the problems that are difficult to recycle and reuseImprove the disadvantage of poor conductivityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsMicrosphereCatalytic oxidation
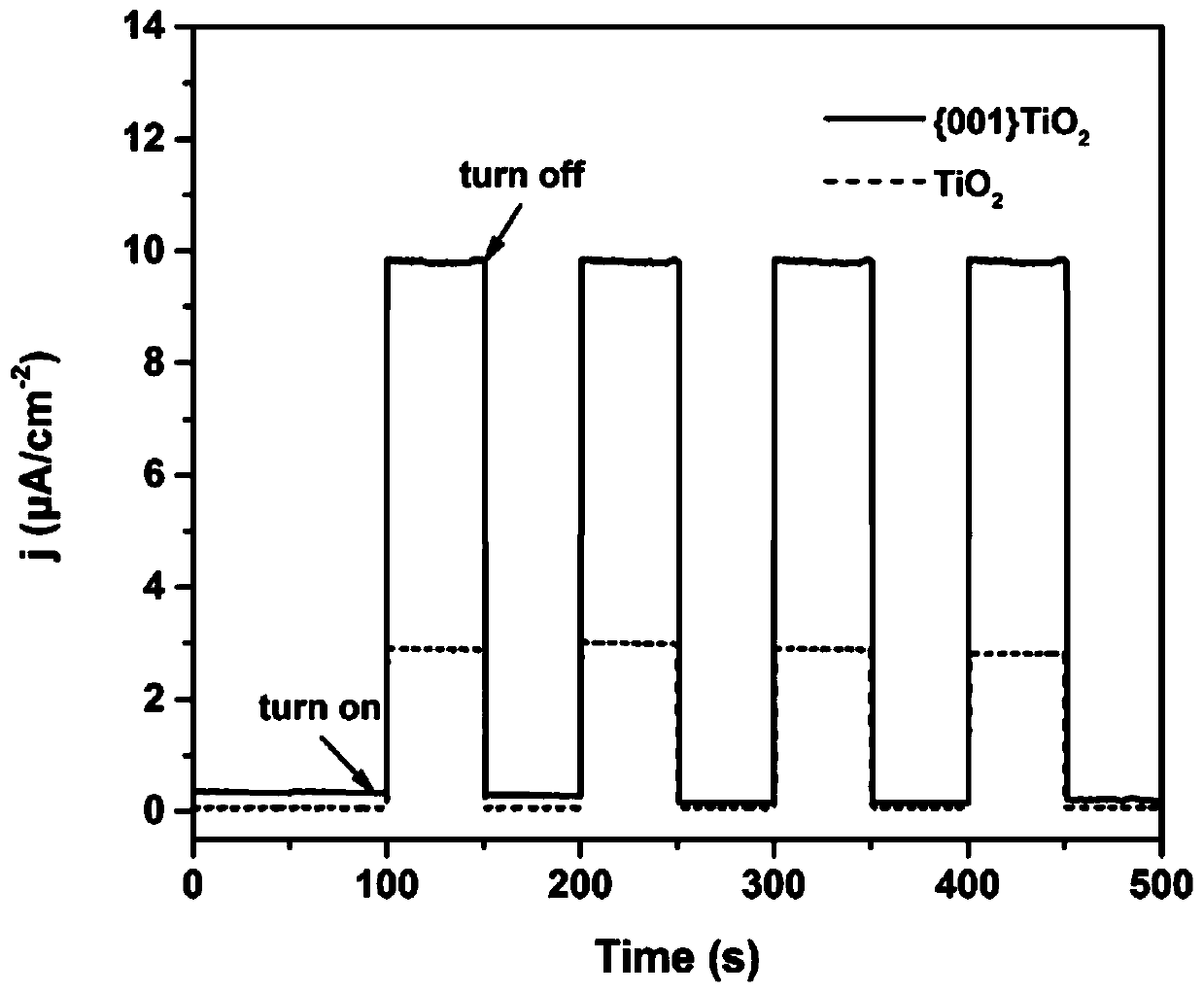
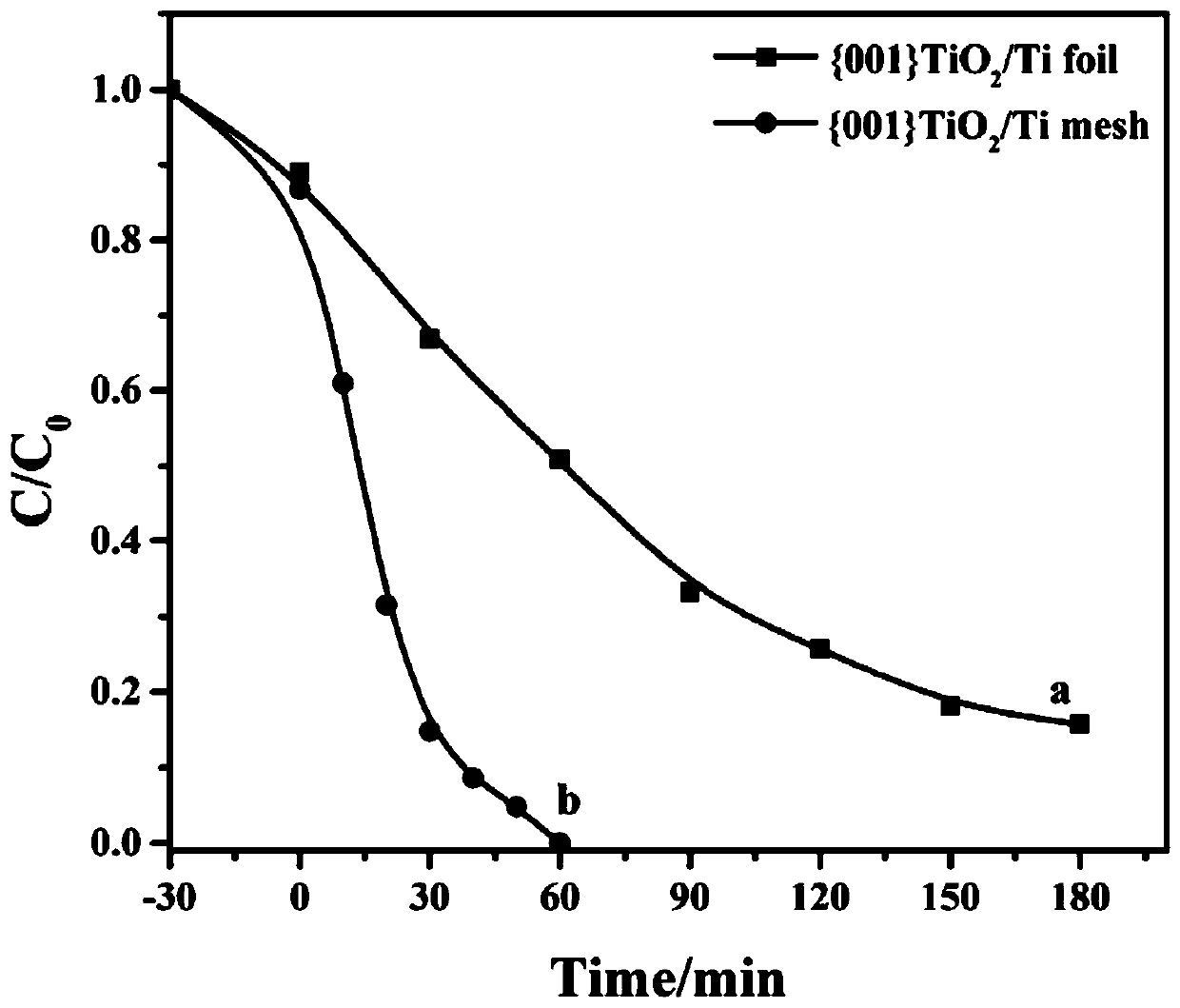
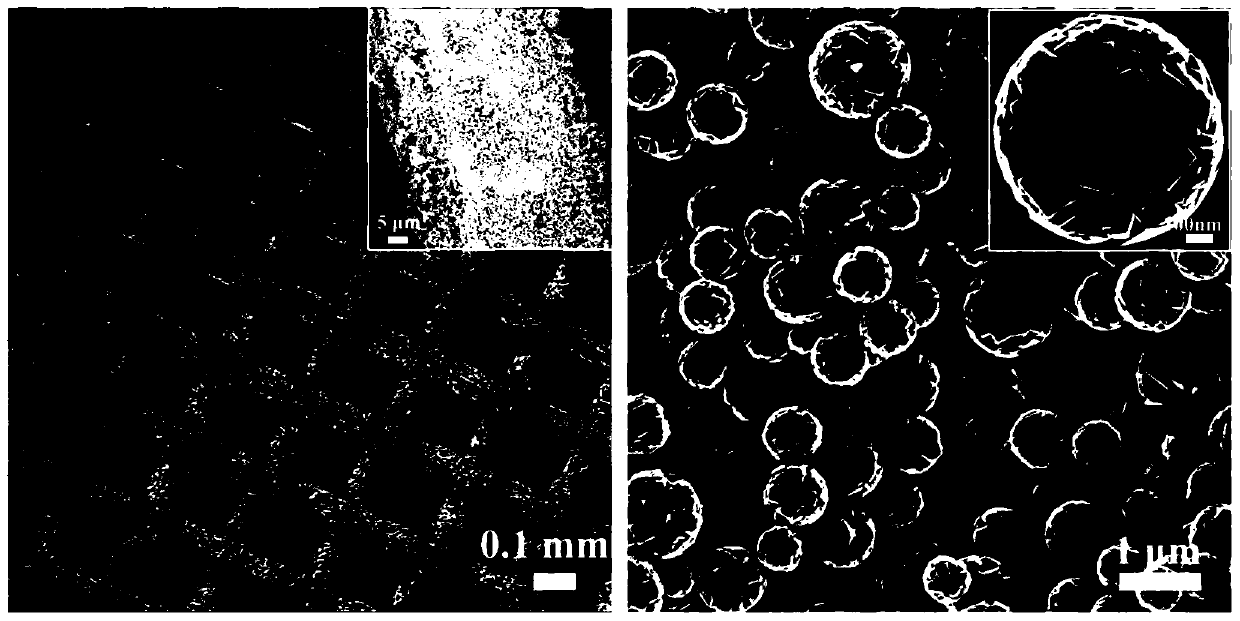
The invention relates to preparation and applications of a {001} crystal face controllable exposed titanium dioxide photoelectrode. According to the preparation, a titanium plate is taken as a titanium source, hydrofluoric acid is taken as an end-capping reagent, hydro-thermal method is adopted for in-suit growth of TiO2 flower-shaped microsphere structures on the titanium base plate, the {001} crystal face exposure ratio ranges from 0 to 100%, the obtained {001} TiO2 / Ti photoelectrode can be applied in dimethyl phthalate waste water photoelectric catalytic oxidation degradation. Compared withthe prior art, the advantages are that: the {001} crystal face controllable exposed {001} TiO2 / Ti photoelectrode is high in photoelectrocatalysis performance (the highest photocurrent density is 0.74mA / cm<2>), the removing rate on 5mg / L dimethyl phthalate in 8h is as high as 94.3%. The electrode material and the technology are suitable to be used in the field of phthalate pollutant photoelectrocatalysis degradation.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Synthesis method of high-activity TiO2 nanodisk photocatalyst
ActiveCN103331153AControlled hydrolysisNovel Crystal MorphologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsAcetic acidPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a synthesis method of a high-activity TiO2 nanodisk photocatalyst. The method is simple and easy to implement, and has the advantages of favorable repeatability and high stability; and the prepared {001}-surface-exposed TiO2 nanodisk photocatalyst has the advantages of novel structure and high photocatalytic activity. The method comprises the following steps: 1) mixing water with glacial acetic acid and hydrofluoric acid; 2) after adding tetrabutyl titanate, mechanically stirring for 10 minutes; 3) putting the solution into a reaction kettle, and carrying out hydrothermal treatment at 180 DEG C for 24 hours; and 4) separating, precipitating, carrying out centrifuge washing on the precipitate with water 3 times, drying at 60 DEG C, calcining at 600 DEG C for 2 hours, and naturally cooling to room temperature, wherein the tetrabutyl titanate:water:glacial acetic acid:HF mol ratio is 1:(50-100):100:2.
Owner:徐州大晶新材料科技集团有限公司
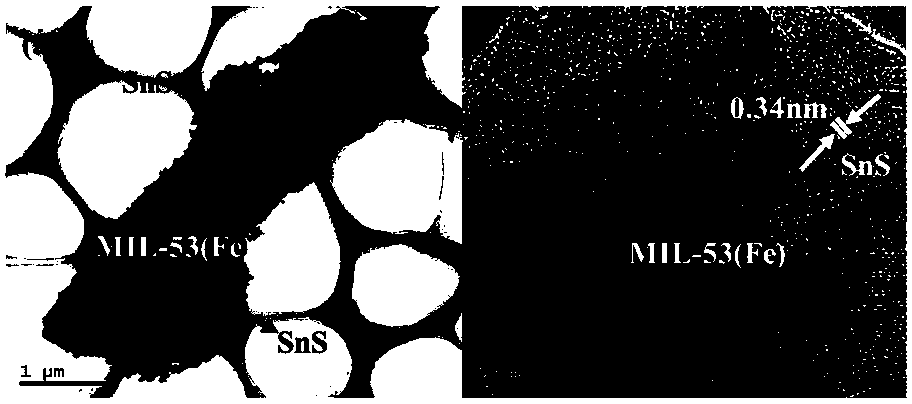
Metal organic framework modified stannous sulfide composite photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107913675ALarge specific surface areaIncreased toxicityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesMetal-organic frameworkWastewater
The invention discloses a metal organic framework modified stannous sulfide composite photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite photocatalyst takes a metal organic framework MIL-53(Fe) as a carrier and is loaded with stannous sulfide. The preparation method of the composite photocatalyst comprises the following steps: mixing MIL-53(Fe) with stannous sulfide, adding solution containing S<2->, and carrying out precipitation reaction, so that the metal organic framework modified stannous sulfide composite photocatalyst is obtained. The composite photocatalyst disclosed by the invention has the advantages of environment friendliness, large specific surface area, many reaction sites, high photogenerated electron-hole utilization rate, high photocatalytic activity, good stability and corrosion resistance, and the preparation method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low raw material cost, low energy consumption, short consumed time and easy-to-control conditions. The composite photocatalyst disclosed by the invention can be used for degrading hexavalent chromium wastewater, has the advantages of high degradation efficiency, simple application method, low cost and no secondary pollution and has a good practical application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Photocatalyst and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN103736506AEfficient PhotocatalyticLarge specific surface areaPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationChemistryEthanol
The invention relates to a photocatalyst and a preparation method and use thereof. The preparation method of the photocatalyst comprises the following steps: dissolving a bismuth source in a dilute nitric acid solution of which the pH is 5.0 to form a clear solution A; ultrasonically dispersing CTAB (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide), PVP (polyvinyl pyrrolidone) and a spherical Ni elementary substance in 10mL of ethyl alcohol to form a mixed system B; mixing the clear solution A and the mixed system B, and standing at room temperature to obtain a white precipitate; washing and drying the white precipitate to constant weight. The obtained nano material can be used for degrading toxic and non-degradable organic pollutants, which are discharged from a factory, into non-toxic carbon dioxide and water. The photocatalyst can be repeatedly used, the activity of the photocatalytic performance of the photocatalyst cannot be reduced along with the increase of use frequency, visible light is unique energy needed in a photocatalytic process, and in conclusion, the photocatalyst has a high economic benefit. Therefore, the photocatalyst has potential application prospects in the fields of environmental management and protection so as to have high economic and social benefits.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
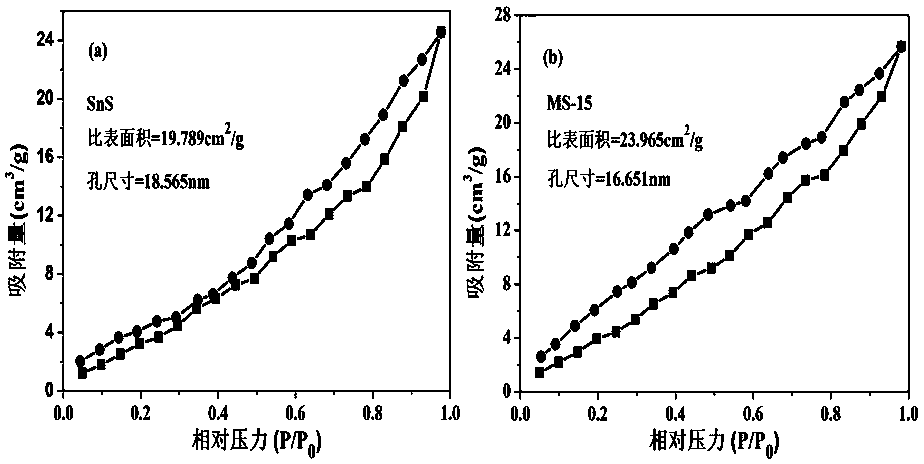
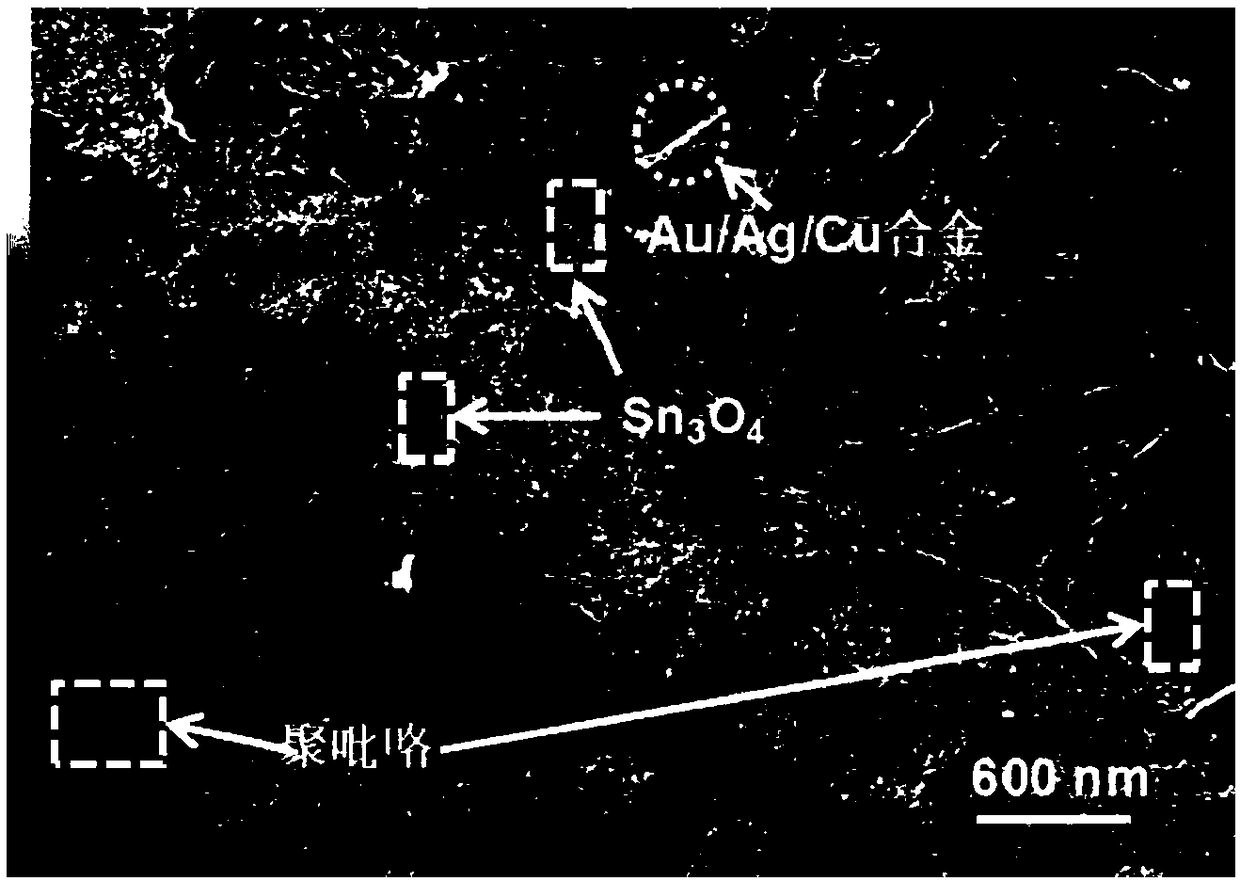
Preparation method of polypyrrole/metal-modified Sn3O4 nano composite photocatalytic material
InactiveCN109107614AEnhanced Broad Spectrum Light AbsorptionImprove photocatalytic performanceGas treatmentOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHeterojunctionPhotocatalytic reaction
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polypyrrole / metal-modified Sn3O4 nano composite photocatalytic material. The nano composite material is a composite photocatalyst material obtained byloading and dispersing metal-modified Sn3O4 semiconductor heterojunction on polypyrrole in a chemical bond complexing form; and the metal-modified Sn3O4 is obtained by separately loading metal nano particles of a single-component metal or multi-component alloy of Pt, Au, Ag, Cu and the like having a plasma resonant effect onto Sn3O4. The photo-induced electron-hole separation rate in the photocatalytic reaction can be sufficiently improved by utilizing the visible light photocatalytic oxidation and reduction characteristics of Sn3O4, the plasma resonant effect of metal nano particles, photo conduction and conductivity of polypyrrole as well as the chemical bond heterojunction structure among different components, so that the performance for degrading pollutants in a photocatalytic oxidation and reduction manner and generating hydrogen by photocatalytic and decomposition of water can be improved. The easy-to-mold characteristic of polypyrrole can effectively avoid the recycling difficulty of the powder material.
Owner:PINGDINGSHAN UNIVERSITY
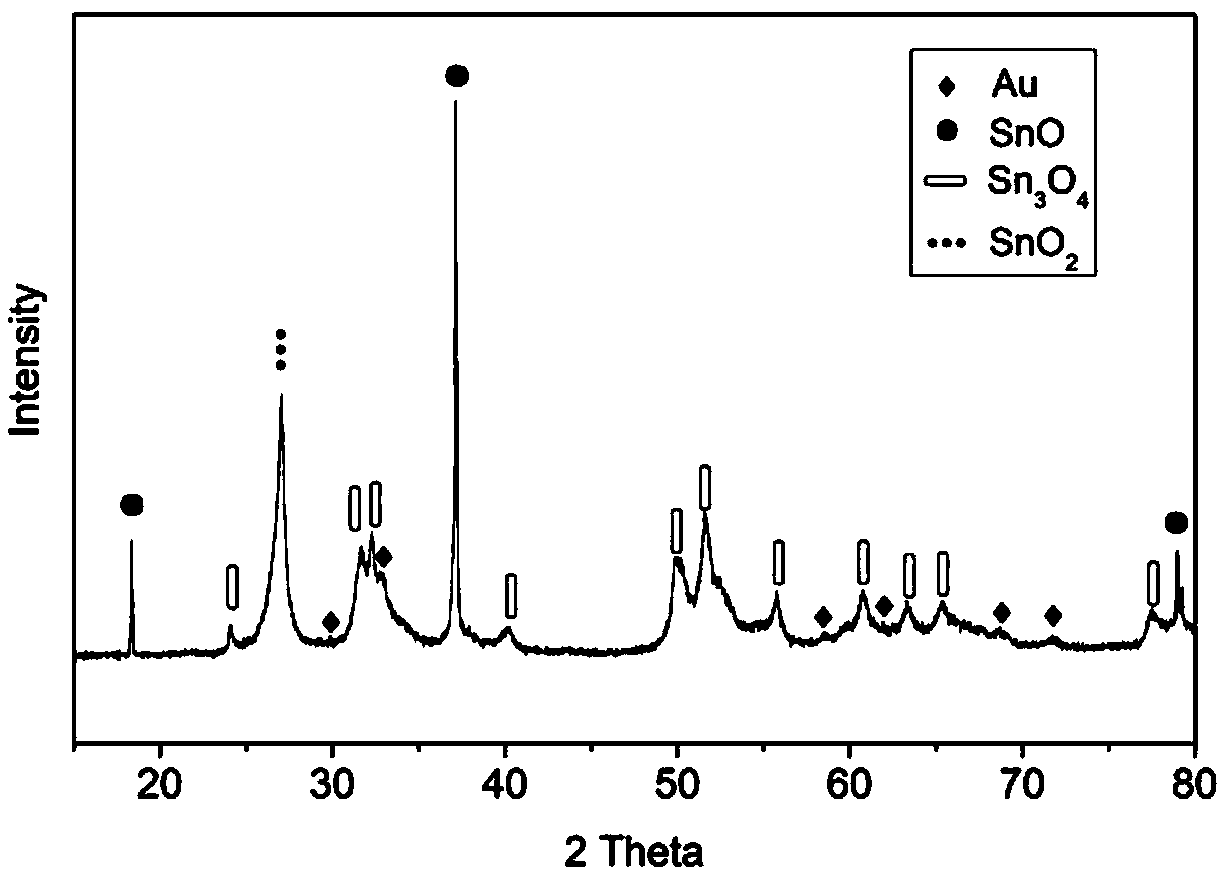
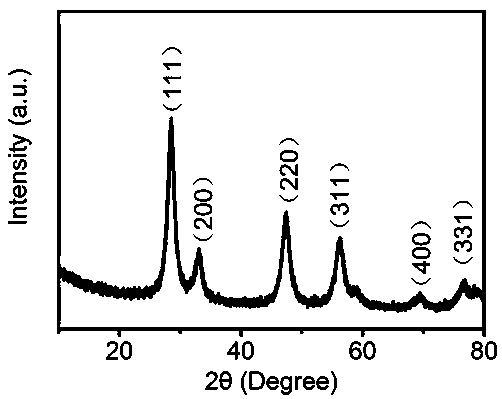
Preparation method of Au modified SnO/Sn3O4/SnO2 nano composite photocatalytic material
InactiveCN109092307AEnhanced light absorptionEasy to separateHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionHeterojunctionPhotocatalytic water splitting
The invention relates to a preparation method of an Au modified SnO / Sn3O4 / SnO2 nano composite photocatalytic material. The nano composite material is obtained by placing chloroauric acid and a tin source into a solvent, a surfactant and a reducing agent and forming chemical bond complexing among composite ingredients of the materials according to an ice salt bath and solvent combined hot wet chemical in-situ synthesis method. The composite material prepared by the invention utilizes a plasma resonance effect of Au metal nanoparticles, an excellent energy level matching heterojunction structureamong composite components of a tin oxide material and excellent electron conduction of Au metal nanoparticles, and implements rapid electron-hole separation in the process of cooperating photocatalytic oxidation and reduction degradation of pollutants with photocatalytic water splitting hydrogen production, thereby improving efficiency of photocatalytic water splitting and photocatalytic rhodamine B degradation of the Au modified SnO / Sn3O4 / SnO2 nano composite photocatalytic material.
Owner:PINGDINGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of high-activity cerium dioxide photocatalyst
InactiveCN109046313AGood adsorption performanceEasy to prepareRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologySolventChemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a high-activity cerium dioxide photocatalyst and belongs to the technical field of synthesis of cerium dioxide photocatalysts. Accordingto the technical scheme, the preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: dissolving trivalent cerium salt into an alcohol solvent to obtain a uniform solution; adding hydrogen peroxide into the uniform solution; reacting at room temperature for 0.5 to 2h to obtain a mixed solution; adding a sedimentation agent into the mixed solution; regulating the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) of a mixing system to be 7 to 12; continually stirring and reacting for 0.5 to 2h; carrying out centrifugal separation on sediment in a reaction solution and washing with de-ionized water; drying sediment at 40 to 300 DEG C for 0.5 to 12h to obtain a high-activity cerium dioxide nano-material. The photocatalytic material prepared by the invention has efficient photocatalytic performance, can be used for effectively degrading organic pollutants under sunlight or visible light irradiation and hopefully has good social and economic benefits in the field of environment management.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
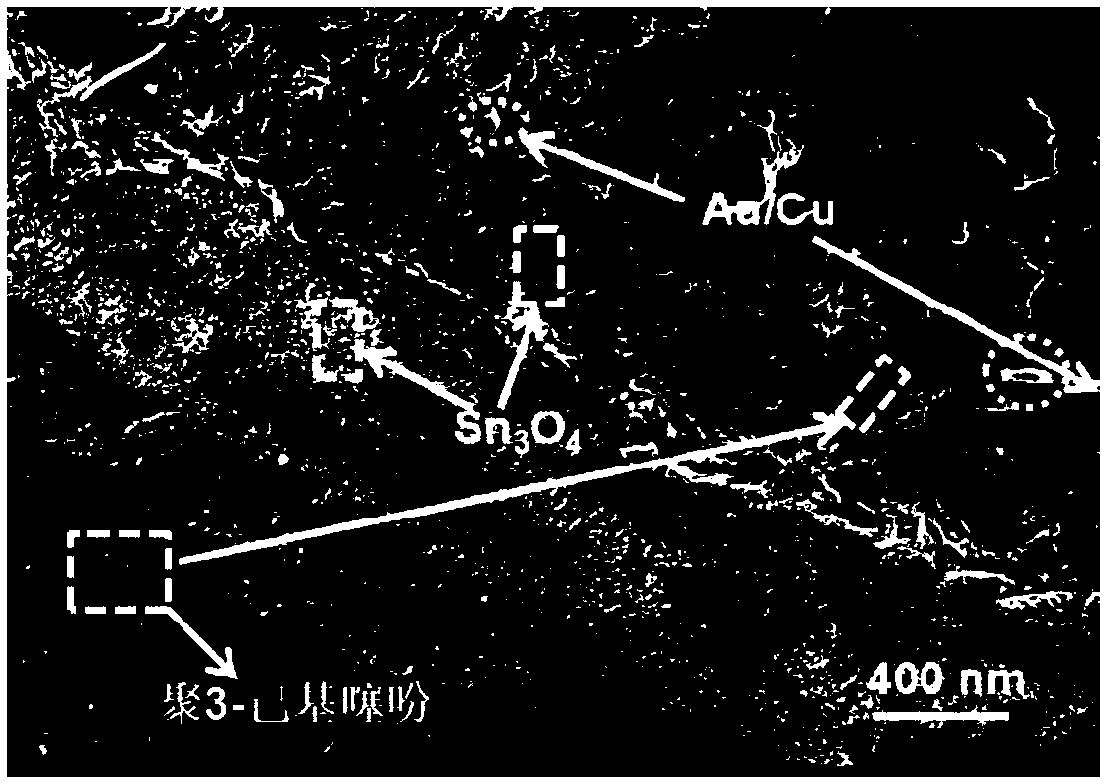
Preparation method of poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT)/metal-modified Sn3O4 nano composite photocatalytic material
InactiveCN109092369AImprove stabilityGood dispersionGas treatmentOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHeterojunctionPhotocatalytic reaction
The invention discloses a preparation method of a poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT) / metal-modified Sn3O4 nano composite photocatalytic material. According to the method, a composite photocatalyst materialis obtained by loading and dispersing a metal-modified Sn3O4 semiconductor heterojunction in poly(3-hexylthiophene) in the form of chemical bond complexation; wherein the metal-modified Sn3O4 is prepared by loading Sn3O4 with metal nanoparticles of a one-component mental or a multi-component alloy with a plasmon resonance effect such as Pt, Au, Ag, Cu and the like, respectively. According to theinvention, the visible light photocatalytic redox properties of Sn3O4, the plasmon resonance effect of metal nanoparticles, the electrical conductivity of poly(3-hexylthiophene) and a heterojunction structure with chemical bonding among the three components are utilized to fully enhance the photo-generated electrons-hole separation rate of the nano composite photocatalytic material in a photocatalytic reaction, so that the improvements on the performance of photocatalytic redox degradation of pollutants and photocatalytic decomposition of hydrogen produced by water of the nano composite photocatalytic material are facilitated. At the same time, the characteristics of being easy to be molded of poly(3-hexylthiophene) can effectively avoid the problem of difficulty in recovery of powder materials.
Owner:PINGDINGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Fresh air purifying photocatalysis technology for fresh air system
InactiveCN106031867AHas a mesoporous structureEfficient photocatalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsDispersed particle separationFiltrationFresh air
The invention relates to a photocatalyst for removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) contained in fresh air which is inhaled into indoor by a fresh air system. A hydrothermal synthesis method is used for preparing a TiO2 material with a mesoporous structure and a high photocatalytic activity, and a photocatalyst prepared by the method has the mesoporous structure and high photocatalysis efficiency for removing formaldehyde. The invention is characterized in that a preparation method comprises the following steps: a certain amount of titanium alkoxide is dissolved into absolute ethyl alcohol, and a solution A is prepared; a template whose mass percentage is 15-35% and a chelating agent whose mass percentage is 10-25% (the mass percentages are calculated based on the titanium alkoxide raw material) are dissolved into deionized water, and a solution B is prepared; the solution A and the solution B are mixed in order to prepare suspension liquid; the suspension liquid is transferred to a crystallization reaction vessel whose inner liner is made from polytetrafluoroethylene, a reaction is carried out at 150-220 DEG C for 6-24 hours, the reaction vessel is cooled to a room temperature, centrifugation is carried out for reaction products in order to obtain precipitation, deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol are used for cleaning for 5-10 times, pumping filtration is carried out in order to obtain a sample, and the sample is dried in a baking oven at 100-120 DEG C for 12-24 hours in order to obtain powder; the powder is placed in a muffle furnace, the muffle furnace is heated at a speed of 1-5 DEG C / min to 450-650 DEG C, calcination is carried out for 3-5 hours, and the TiO2 photocatalyst with the mesoporous structure is obtained.
Owner:JIANGSU HONGZHU ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH
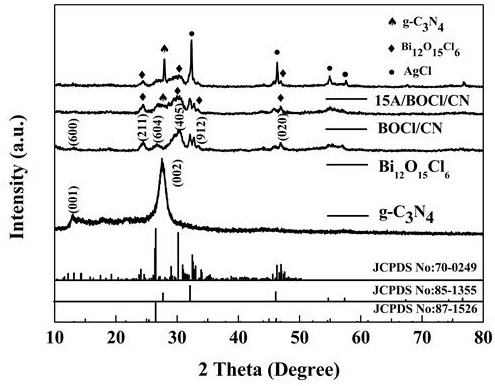
Ternary composite catalytic material for removing tetracycline in wastewater and preparation method of ternary composite catalytic material
PendingCN113731451AEasy to prepareEasy to operatePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPhoto catalysisSewage treatment
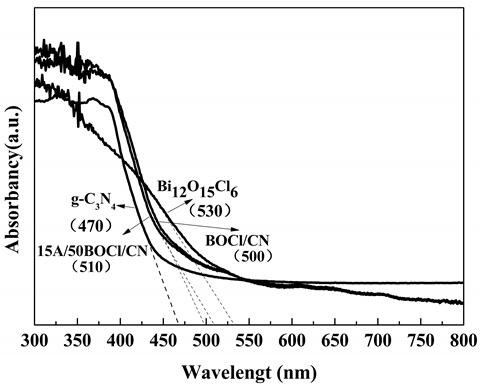
The invention discloses a ternary composite catalytic material for removing tetracycline in wastewater and a preparation method of the ternary composite catalytic material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing g-C3N4; (2) preparing Bi12O15Cl6 ; (3) preparing a Bi12O15Cl6 / g-C3N4 binary composite material; and (4) preparing the AgCl / Bi12O15Cl6 / g-C3N4 ternary composite catalytic material. The prepared ternary composite catalytic material can be used for degrading tetracycline under the visible light condition. The ternary photocatalyst is synthesized through a wet impregnation method, and the method has the advantages of being simple in operation method and easy to implement. AgCl and Bi12O15Cl6 are doped on g-C3N4, so that the utilization rate of g-C3N4 to visible light is effectively improved, the separation efficiency of photon-generated carriers is promoted, and the visible light catalysis efficiency is further improved; and the process flow is simple and convenient to operate, and has a great application prospect in the aspect of sewage treatment.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing Ti-Fe alloy oxide photonic crystal electrode with high periodicity
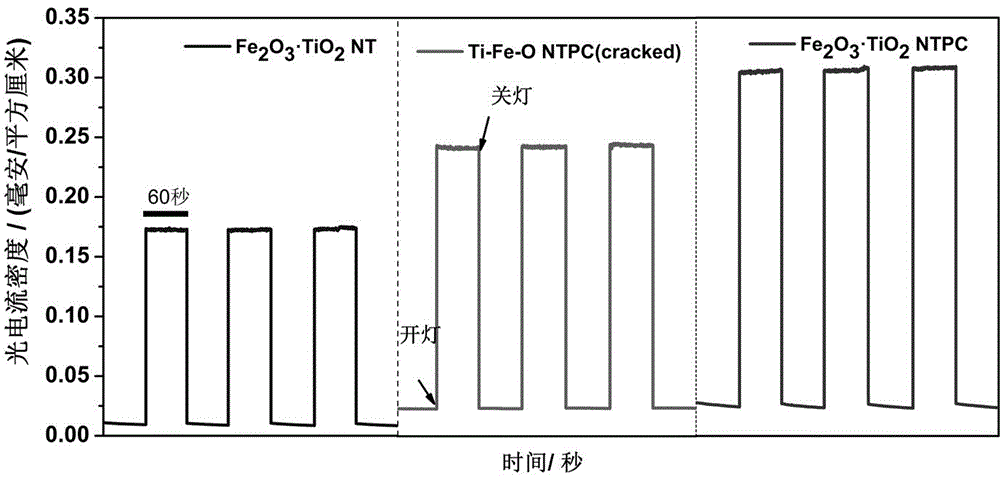
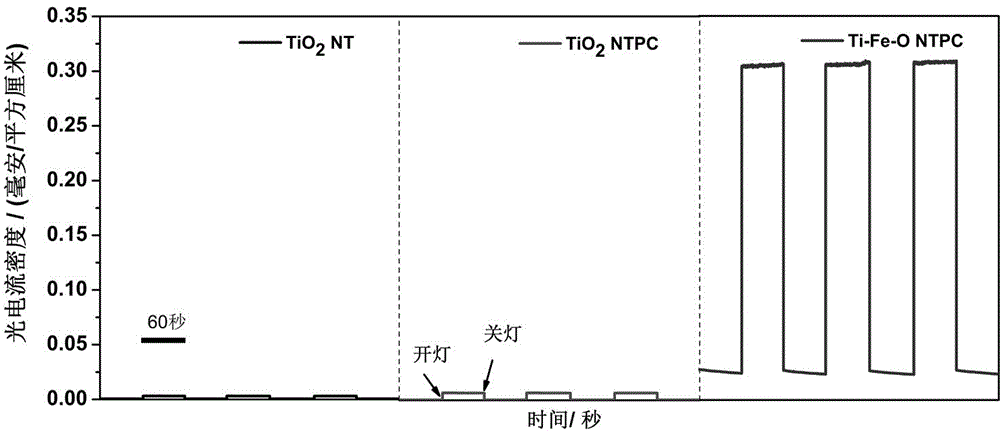
The invention relates to a method for preparing a three-dimensional layered Ti-Fe alloy oxide photonic crystal electrode (Ti-Fe-O NTPC) with a high periodicity. The photonic crystal electrode is prepared by using ferrotitanium as a substrate and using a three-step electrochemical anodizing method. Compared with a conventional nanotube structure and a layered titanium dioxide nanotube without doped ferrum, the Ti-Fe-O NTPC novel electrode has high-efficient visible photoelectrocatalysis performance because the Ti-Fe-O NTPC has a high-periodicity ordered nanometer net which can be used as photonic crystal layer to increase light absorption and the use of the alloy substrate guarantees uniform doping of Fe and Ti at an atom level so as to promote electron transmission. The electrode has potential application value in the field of photocatalysis, photoelectrocatalysis, and new energy preparation and analysis detection.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Preparation method of Au/Cu co-modified Sn3O4 nano composite photocatalytic material
InactiveCN109092327AGood dispersionNarrow dispersionHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionPhotocatalytic water splittingOxygen vacancy
The invention discloses a preparation method of a shape-controlled binary metal loaded Au / Cu co-modified Sn3O4 nano composite photocatalytic material. The nano composite material is the Au / Cu co-modified Sn3O4 nano composite material obtained by placing chloroauric acid, cupric nitrate and a tin source material into a solvent, a surfactant and a reducing agent and forming chemical bond complexingamong composite ingredients of the materials by an ice salt bath and solvent combined hot wet chemical in-situ synthesis method. The composite material prepared by the invention utilizes a plasma resonance effect of Au / Cu binary metal nanoparticles, an oxygen vacancy effect of an Sn3O4 material and excellent electron conduction of Au / Cu metal nanoparticles, and implements rapid electron-hole separation in the process of cooperating photocatalytic oxidation and reduction degradation of pollutants with photocatalytic water splitting hydrogen production, thereby improving efficiency of photocatalytic water splitting and photocatalytic rhodamine B degradation of the Au / Cu co-modified Sn3O4 nano composite photocatalytic material.
Owner:PINGDINGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of self-assembly silver phosphate based composite visible light catalytic material
InactiveCN103521247ARestricted nucleation growthMorphological structure controllablePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPhosphateOrganic dye
The invention relates to a photocatalytic material and in particular relates to a preparation method of a self-assembly silver phosphate based composite visible light catalytic material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving graphene oxide in water, performing ultrasonic treatment and obtaining a graphene oxide dispersion liquid; dripping a silver nitrate solution in the graphene oxide dispersion liquid under a stirring condition, stirring for a period of time and obtaining a mixed precursor solution A; slowly dripping a prepared titanium dioxide solution into the mixed precursor solution A and obtaining a mixed solution B; slowly dripping a prepared phosphate solution into the mixed solution B, continuously stirring for a period of time after celadon turbidity is generated in a reaction system, then centrifugally separating, washing and drying a product obtained by reaction, and obtaining the visible light catalytic material. The preparation method of the self-assembly silver phosphate based composite visible light catalytic material has the advantages that the preparation process is simple, the prepared material is regular in shape and structure and uniform in size, and is also capable of having strong degradation activity on an organic dye rhodamine B under the action of visible light irradiation.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Composite photocatalyst for degrading tetracycline and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110639620AGood redox abilityThe synthesis process is simpleWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPhoto catalysisMetal-organic framework
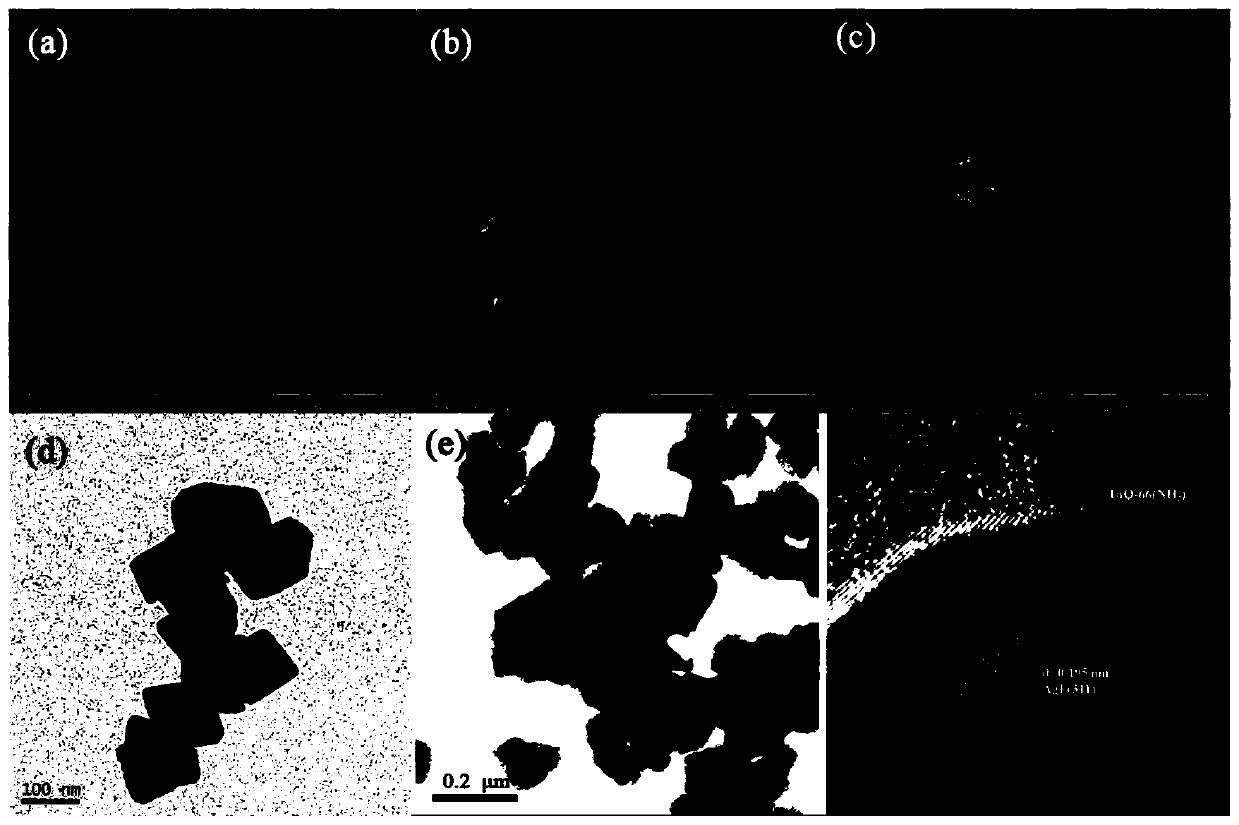
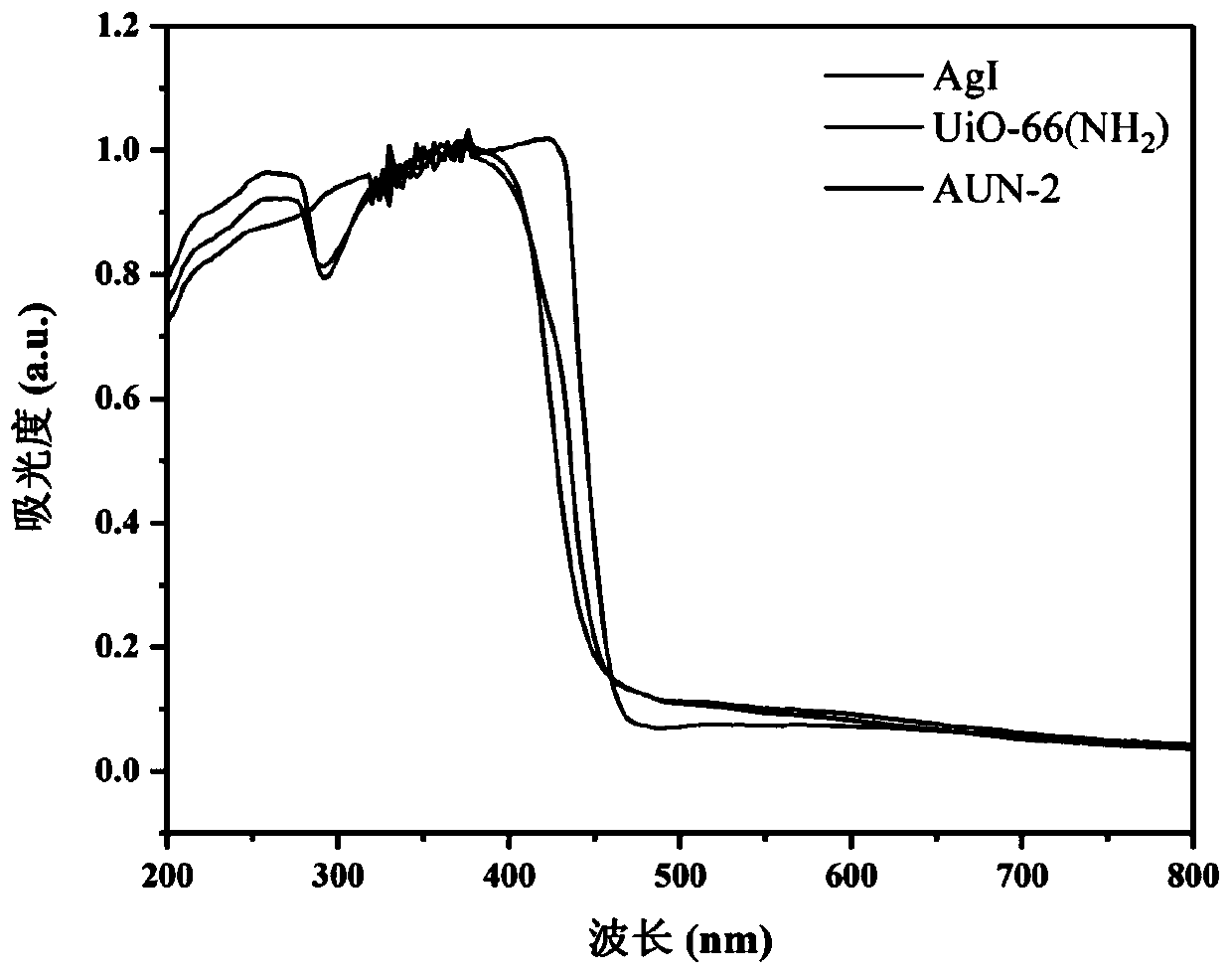
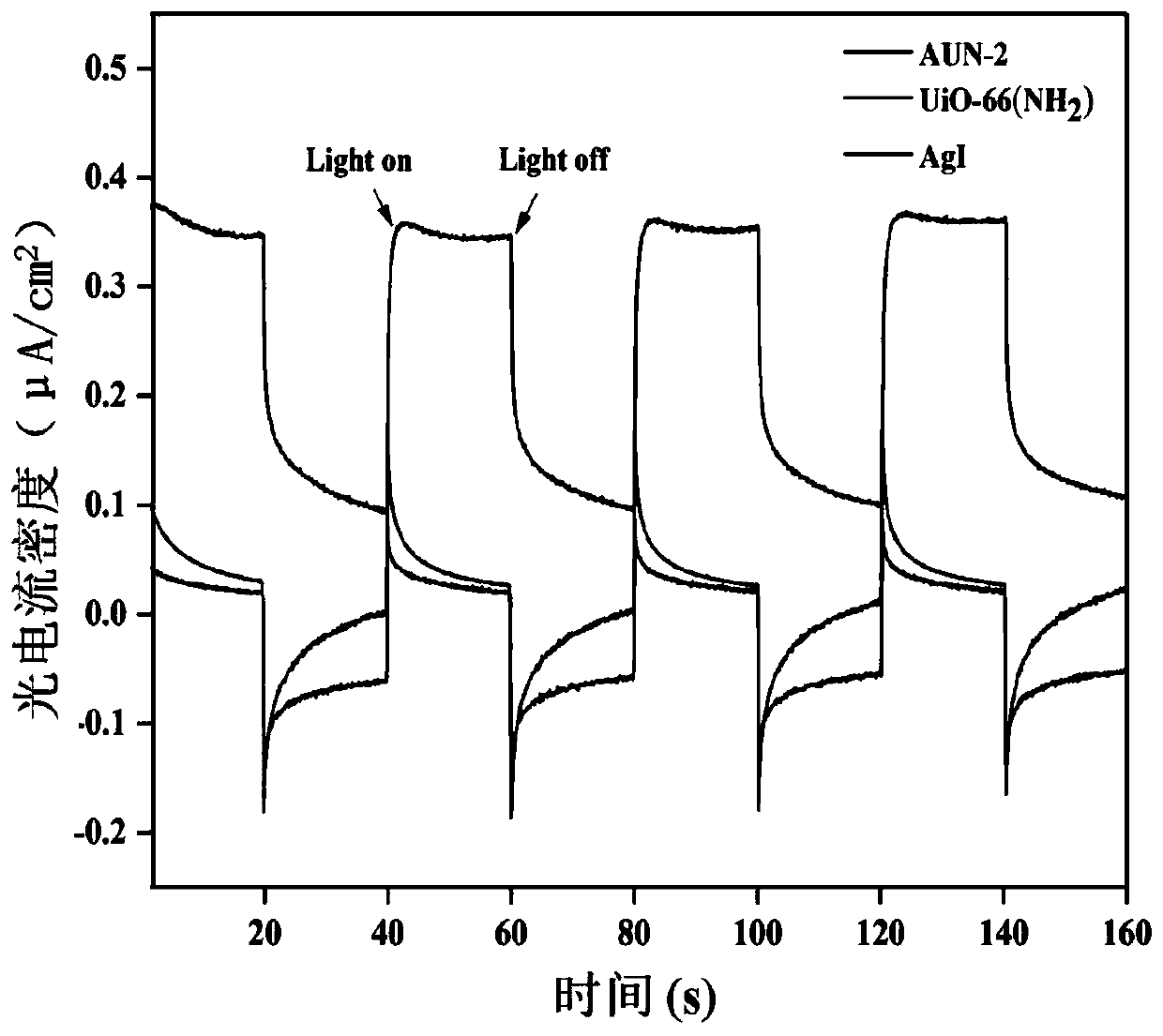
The invention discloses a composite photocatalyst for degrading tetracycline and a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the field of photocatalysis. The composite photocatalyst takes a metal organic framework UiO-66 (NH2) as a carrier, and the metal organic framework UiO-66 (NH2) is modified with granular silver iodide; the composite photocatalyst is a binary composite material AgI / UiO-66(NH2) with a Z-type heterojunction structure. The preparation method thereof comprises the following steps of mixing the metal organic framework UiO-66 (NHS) with a silver iodide precursor, and performing chemical precipitation on the obtained mixture to obtain silver iodide modified metal organic framework UiO-66 (NHS) binary composite photocatalyst. The silver iodide modified metalorganic framework UiO-66 (NH2) binary composite photocatalyst has the advantages of being environment-friendly, large in specific surface area, high in photoproduction electron-hole separation efficiency, high in photocatalytic activity, good in stability, light in corrosion resistance and the like, and the preparation method has the advantages of being simple, low in raw material cost, less in energy consumption, short in time consumption, easy to control conditions and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
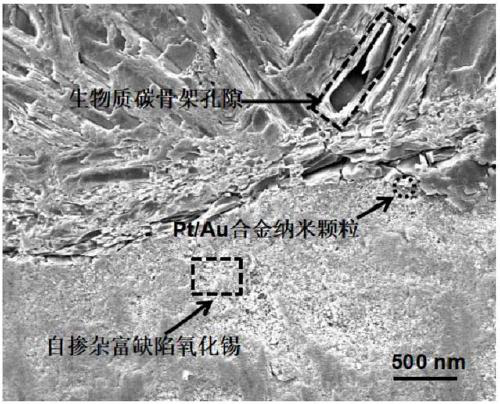
Method for preparing biomass carbon-based metal-modified self-doped vacancy-rich tin oxide nano-composite photocatalytic materials
InactiveCN109126821AImprove stabilityGood dispersionHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionOxygen vacancyElectron hole
The invention discloses a method for preparing biomass carbon-based metal-modified self-doped vacancy-rich tin oxide nano-composite materials. The method includes loading and dispersing metal-modifiedself-doped vacancy-rich tin oxide semiconductor heterojunctions in biomass carbon bases in chemical bond complexation forms to obtain composite photocatalyst materials. Self-doped vacancy-rich tin oxide is selected from Sn-doped nonstoichiometric or mixed valence state oxygen-vacancy-rich tin oxide; metal nano-particles with plasma resonance effects are loaded on self-doped vacancy-rich tin oxidenano-particles to obtain metal-modified self-doped vacancy-rich tin oxide. The method has the advantages that the photo-induced electron-hole separation rate of the biomass carbon-based metal-modified self-doped vacancy-rich tin oxide nano-composite materials can be sufficiently increased during photocatalytic reaction by the aid of the visible-light photocatalytic oxidation and reduction characteristics of the self-doped vacancy-rich tin oxide, the plasma resonance effects of the metal nano-particles, the electric conductivity of biomass carbon-based materials and chemical bonding heterojunction structures between three components, and accordingly the method is favorable for improving the photocatalytic oxidation and reduction pollutant degradation and photocatalytic water decompositionhydrogen production performance of the biomass carbon-based metal-modified self-doped vacancy-rich tin oxide nano-composite materials.
Owner:PINGDINGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of Au/Ag co-modified Sn3O4 nano composite photocatalytic material
InactiveCN109107573AFully developedImprove photocatalytic performanceHydrogen productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSource materialOxygen vacancy
The invention discloses a preparation method of an Au / Ag co-modified Sn3O4 nano composite photocatalytic material. The nano composite material is an Au / Ag co-modified Sn3O4 nano composite material which is obtained through forming chemical bonds among the composite ingredients of the nano composite material to complex by using a wet chemistry in-situ synthesis method, in which ice baths are combined with solvent heat, in the solvent, surface active agent and reducing agent of chloroauric acid, silver nitrate and a tin source material. The composite material prepared by the invention utilizes the plasma resonance effect of Au / Ag binary metal nanoparticles, the oxygen vacancy defect effect of a Sn3O4 material and the excellent electron conduction of Au / Ag metal nanoparticles to realize rapidelectron-hole separation in the process of reducing and degrading pollutants through photocatalytic oxidation to collaborate with photocatalytic decomposition of water to generate hydrogen, thereby improving the efficiency of the photocatalytic decomposition of the water and the photocatalytic decomposition of Rhodamine B.
Owner:PINGDINGSHAN UNIVERSITY
WXTiO2+3X/SiO2 aerogel compound photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104689813AImprove adsorption capacityHigh visible light photocatalytic performanceOther chemical processesSilicon compoundsAir purificationMole ratio
The invention relates to a WXTiO2+3X / SiO2 aerogel compound photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of adsorption / photocatalystic materials for environment purification. SiO2 aerogel acts as a carrier of the WXTiO2+3X / SiO2 aerogel compound photocatalyst; a duct and the surface of the SiO2 aerogel are loaded with anatase type WxTiO2+3x particles; the WXTiO2+3X / SiO2 aerogel compound photocatalyst has the specific surface area of 190-350m<2> / g, and has the pore volume of 0.6-1.50ml / g, wherein the mole ratio of SiO2 aerogel to WxTiO2+3x is (0.06:1) to (1.5:1), and x=0.005-0.15. The mesoporous WXTiO2+3X / SiO2 aerogel compound prepared by the invention not only has an efficient adsorption performance, but also has an excellent visible light catalysis performance; harmful pollutants in air and water can be effectively removed effectively via the synergism of adsorption and photocatalysis; the WXTiO2+3X / SiO2 aerogel compound photocatalyst and the preparation method thereof have wide application prospect in the fields of environment purification of air purification, water purification and the like.
Owner:DALIAN DALICAP TECH CO LTD
Preparation and use methods of magnesium hydrate/reduced graphene oxide composite material
ActiveCN108295829AEfficient photocatalytic performanceEasy to separatePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOxide compositeSewage
The invention provides a preparation method of a magnesium hydrate / reduced graphene oxide composite material with efficient photocatalytic performance. Another aim of the invention is to provide efficient application of the material in photodegradation of organic pollutants in dyeing wastewater. The composite material is extremely strong in photocatalytic degradation effect and is still relativelyhigh in photocatalytic degradation capacity under a plurality of circulations. Furthermore, as magnesium hydrate has a relatively large density, the composite material is easy to be separated from sewage, thereby providing convenience for recycling of a catalyst.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
Three-dimensional TiO2 photoelectrode with efficient visible light response as well as construction and application thereof
InactiveCN110606526AEasy transferFacilitate transmissionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsHydrofluoric acidMicrosphere
The invention relates to a three-dimensional TiO2 photoelectrode with efficient visible light response as well as construction and application thereof. A preparation process of the photoelectrode comprises the following steps: firstly performing in-situ growing of {001}TiO2 microspheres with nearly 100% exposed {001} crystal faces on a titanium mesh through hydrothermal reaction, with the titaniummesh being adopted as a titanium source and hydrofluoric acid being adopted as an end-capping reagent; and loading CQDs on the surfaces of the {001}TiO2 microspheres through hydrothermal treatment toobtain a CQDs-{001}TiO2 / Ti photoelectrode with a three-dimensional structure, namely a target product. Compared with the prior art, the prepared three-dimensional TiO2 photoelectrode has efficient and very stable photoelectrocatalysis performance and the like under visible light.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
A kind of graphite phase nitrogen carbide nanosheet/cobalt trioxide nanosheet fish scale structure composite nanomaterial and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106622324BLarge specific surface areaMany sitesPhysical/chemical process catalystsHigh heatNanomaterials
The present invention aims to provide a method for synthesizing "fish scale-like" graphite phase nitrogen carbide nanosheets / cobalt tetroxide nanosheet composite materials, and belongs to the technical field of material preparation and catalysis. The composite material is made of functionalized graphite phase carbonized nitrogen and metal cobalt salt as raw materials, and is prepared by hydrothermal method at high temperature. The morphology of the fish scale-shaped two-dimensional nitrogen carbonate nanosheet / cobalt tetroxide nanosheet composite material prepared by the present invention is that the surface of the two-dimensional nitrogen carbide nanosheet is uniformly grown with scaly cobalt tetroxide nanosheet nanocomposite material, which is different from the traditional simple two-dimensional carbonic acid nanosheet nanocomposite material. Compared with other materials, it effectively improves the material's specific surface area and screening ability for catalytic substrates, and has more efficient photocatalytic performance. The invention has the advantages of simple process, low cost and high catalytic efficiency, and the prepared material has efficient carbon dioxide reduction ability. Therefore, it has good application prospects in photocatalytic fields such as environmental restoration and elimination of greenhouse gases.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
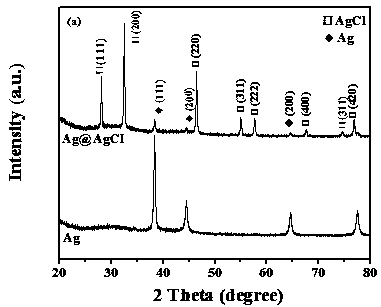
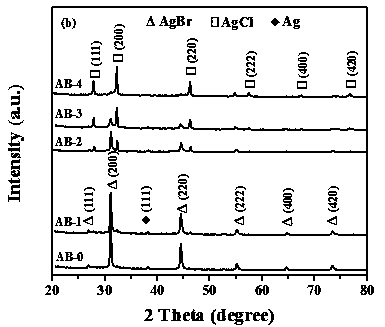
Preparation of one-dimensional nanotubular Ag/AgCl/AgBr composite heterojunction visible light catalyst and application thereof
InactiveCN108067268AImprove photocatalytic activityHigh photocatalytic stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHeterojunctionWater baths
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanocomposite photocatalysis, and particularly relates to preparation of a one-dimensional nanotubular Ag / AgCl / AgBr composite heterojunction visible light catalyst and application thereof. In the invention, a copper nanowire template is obtained by a water bath method, silver nitrate is introduced, a reaction is performed to obtain a one-dimensionalsilver nanotube carrier with relatively good uniformity, and then ferric chloride hexahydrate and a certain amount of potassium bromide are added to obtain the one-dimensional nanotubular Ag / AgCl / AgBrcomposite heterojunction visible light catalyst through an ion exchange reaction. The one-dimensional three-component composite heterojunction photocatalyst adopting a tubular structure contains an inner layer surface and an outer layer surface, so that reactive sites are increased; the presence of heterojunctions greatly reduces the composite rate of photoelectron-hole pairs; under the conditionof visible light irradiation, the photocatalytic activity and the stability are greatly improved; the one-dimensional nanotubular Ag / AgCl / AgBr composite heterojunction visible light catalyst can degrade dye macromolecules effectively, and has a very good practical value in environmental protection fields such as wastewater treatment. The preparation method of the one-dimensional nanotubular Ag / AgCl / AgBr composite heterojunction visible light catalyst is easy to operate, mild in reaction condition, short in cycle and environment-friendly.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing Fe3O4/polypyrrole/polyaniline/TiO2/ZnO composite material
PendingCN109731617AImprove magnetic recovery performanceImprove catalytic performanceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolypyrrolePotassium hydroxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of photocatalysis, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a Fe3O4 / polypyrrole / polyaniline / TiO2 / ZnO composite material. The preparation methodof the Fe3O4 / polypyrrole / polyaniline / TiO2 / ZnO composite material comprises the following steps: firstly, reacting ferrous chloride, potassium sulfite, polyvinylpyrrolidone and potassium hydroxide at constant temperature to prepare Fe3O4; then adding pyrrole, ethanol and concentrated hydrochloric acid into Fe3O4 dispersion respectively to obtain Fe3O4 / polypyrrole, adding an aniline monomer, hydrochloric acid and ammonium persulfate into Fe3O4 / polypyrrole dispersion to prepare Fe3O4 / polypyrrole / polyaniline, and coating the surface of the Fe3O4 / polypyrrole / polyaniline with TiO2 by a sol-gel mode;and finally, dispersing Fe3O4 / polypyrrole / polyaniline / TiO2 / ZnO in acetone, adding ammonia water, carrying out ultrasonic dispersion, adding zinc gluconate for reaction, and preparing the Fe3O4 / polypyrrole / polyaniline / TiO2 / ZnO composite material. The preparation method is simple, the composite material has high saturated magnetization and magnetic recovery rate, and the prepared Fe3O4 / polypyrrole / polyaniline / TiO2 / ZnO composite material has long-term and high-efficiency photocatalytic performance and magnetic recovery performance.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
Hexagonal boron nitride modified graphitized carbon nitride composite photocatalyst and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106732727BLarge specific surface areaMany reaction sitesPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationElectron holeHexagonal boron nitride
The invention discloses a hexagonal boron nitride modified graphitized carbon nitride composite photocatalyst and its preparation method and application. The composite photocatalyst uses graphitized carbon nitride as a carrier, and the graphitized carbon nitride carrier is decorated with layered Hexagonal boron nitride. The preparation method includes mixing hexagonal boron nitride and graphitized carbon nitride precursor, and calcining the resulting mixture precursor to obtain a hexagonal boron nitride modified graphitized carbon nitride composite photocatalyst. The hexagonal boron nitride modified graphitized carbon nitride composite photocatalyst of the present invention has the characteristics of green and environmental protection, complete no metal doping, large specific surface area, high photogenerated electron-hole separation efficiency, high photocatalytic activity, good stability, corrosion resistance, etc. Advantages: The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, low raw material cost, low energy consumption, short time consumption, and easy control of conditions. When the composite photocatalyst of the present invention is used to degrade dye wastewater, it has the advantages of simple application method, stable photocatalytic performance, strong corrosion resistance, and high efficiency in degrading dye wastewater.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Phosphorus-doped carbon nitride/carbon nitride homogeneous heterojunction photocatalyst and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108380233BImprove utilization efficiencyPromote absorptionPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHeterojunctionCharge separation
The invention discloses a phosphorus-doped carbon nitride / carbon nitride homojunction photocatalyst and its preparation method and application. The photocatalyst uses carbon nitride as a carrier, and the carbon nitride is modified with phosphorus-doped nitride. carbon. The preparation method includes: mixing phosphorus-doped carbon nitride and melamine, and calcining the resulting mixture precursor to obtain a phosphorus-doped carbon nitride / carbon nitride homo-heterojunction photocatalyst. The photocatalyst of the present invention has the advantages of being green and environmentally friendly, completely free of metal doping, strong visible light absorption ability, increased specific surface area, fast photogenerated charge separation rate, high photocatalytic activity, stable chemical properties, corrosion resistance, etc. Its preparation method has the following advantages: The process is simple, easy to control, the raw materials are easily available, the cost is low, and it is suitable for continuous large-scale batch production. The photocatalyst of the present invention can be used to degrade antibiotic wastewater, has the advantages of stable photocatalytic performance, strong corrosion resistance, and high degradation efficiency, and has good practical application prospects.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Photocatalytic material for degrading antibiotics as well as preparation method and application of photocatalytic material
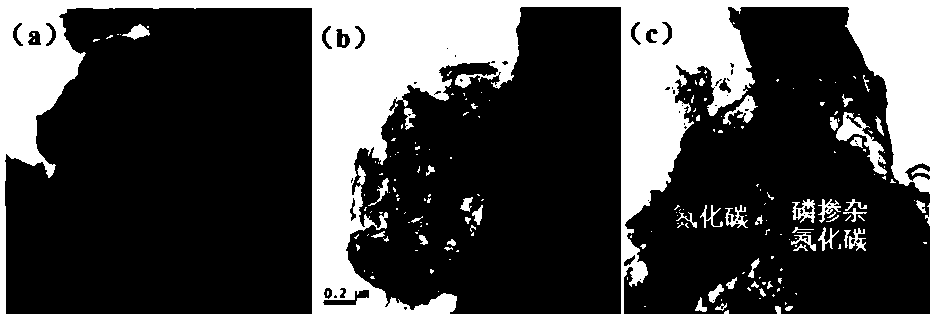
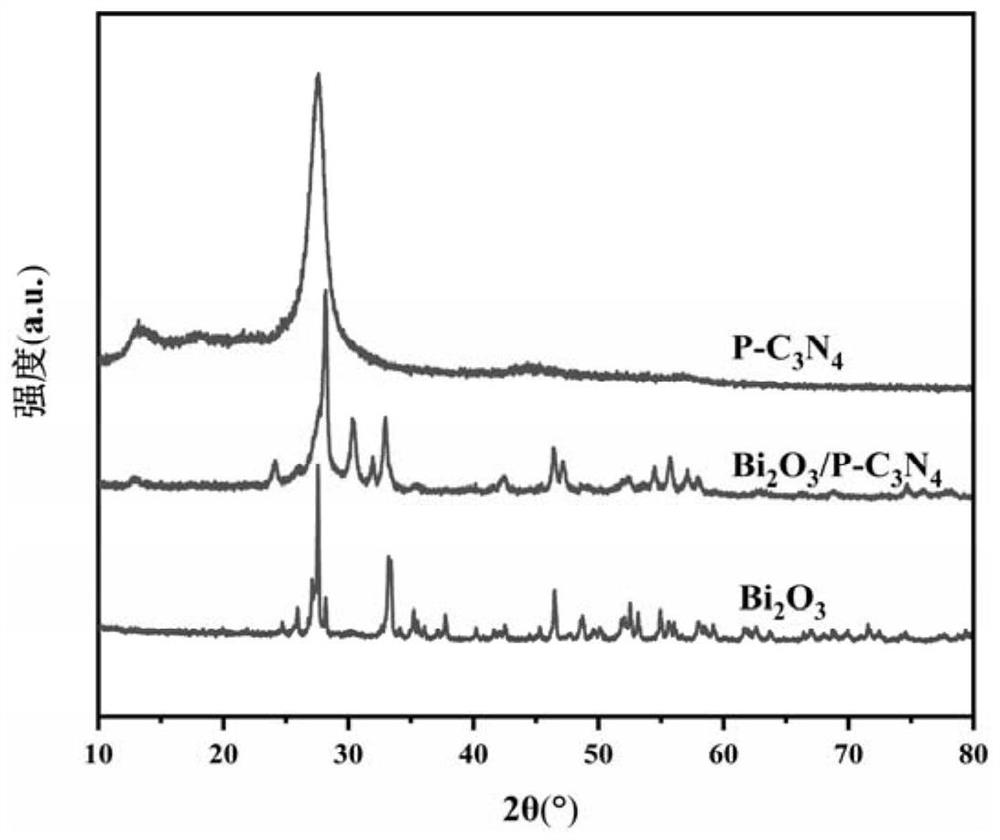
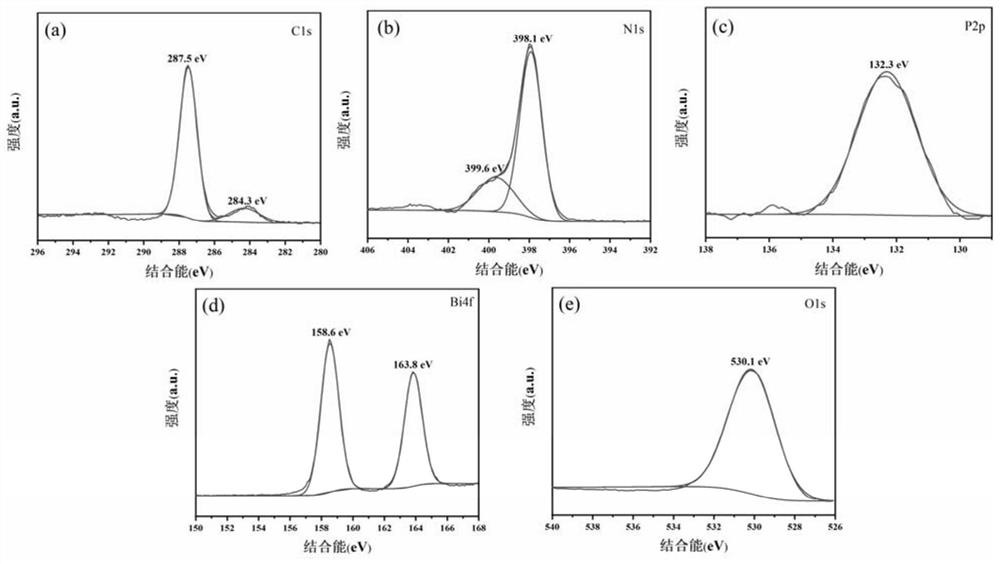
ActiveCN112774712AEfficient photocatalytic performanceImprove photocatalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPhysical chemistryLevofloxacin
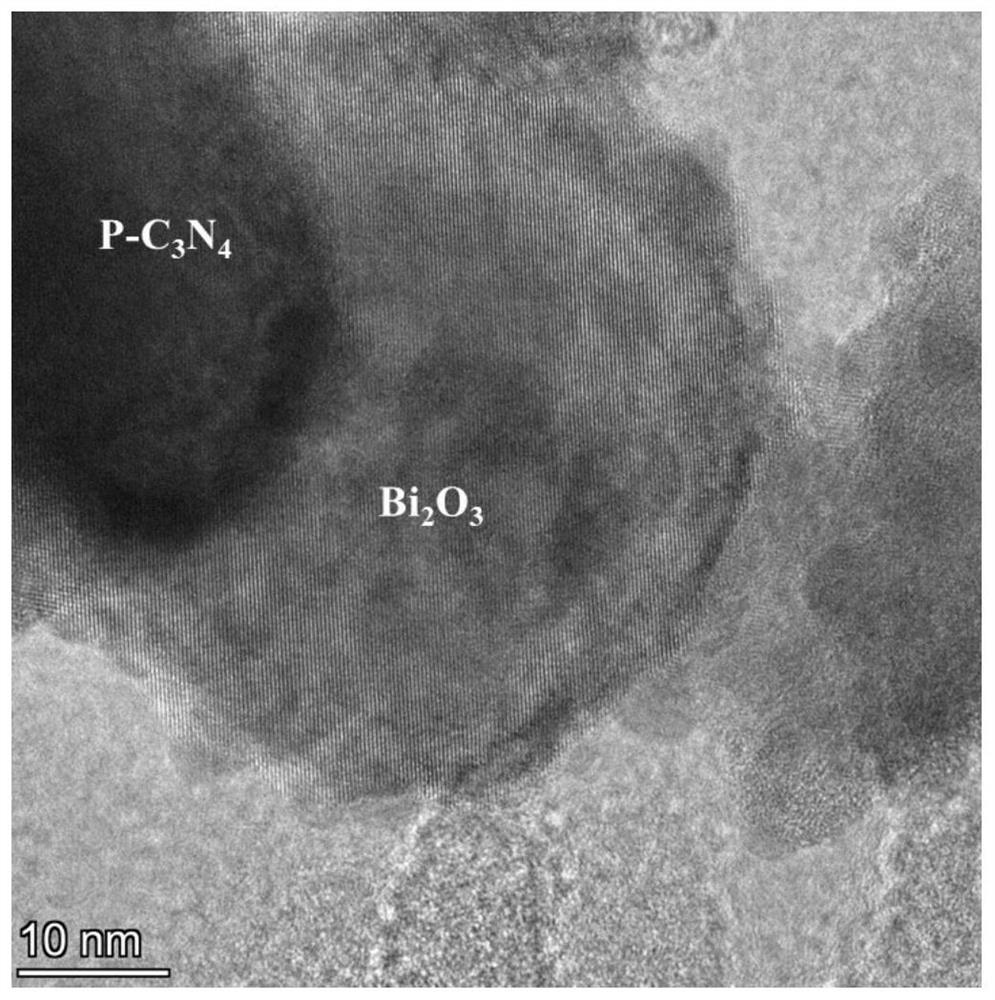
The invention provides a photocatalytic material for degrading antibiotics. The photocatalytic material is a Z-type photocatalytic material, and the active component of the photocatalytic material is a Z-type Bi2O3 / P-C3N4 heterojunction. Experiments prove that 89.2% of levofloxacin can be degraded within 75 minutes. After being recycled for four times, the photocatalytic material (Bi2O3 / P-C3N4) still shows efficient photocatalytic performance, and the degradation efficiency still reaches 80% after being recycled for four times, which shows that the photocatalytic material (Bi2O3 / P-C3N4) is stable in photocatalytic performance, high in corrosion resistance and high in levofloxacin degradation efficiency, and is a composite photocatalytic material high in degradation efficiency and good in reusability.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com