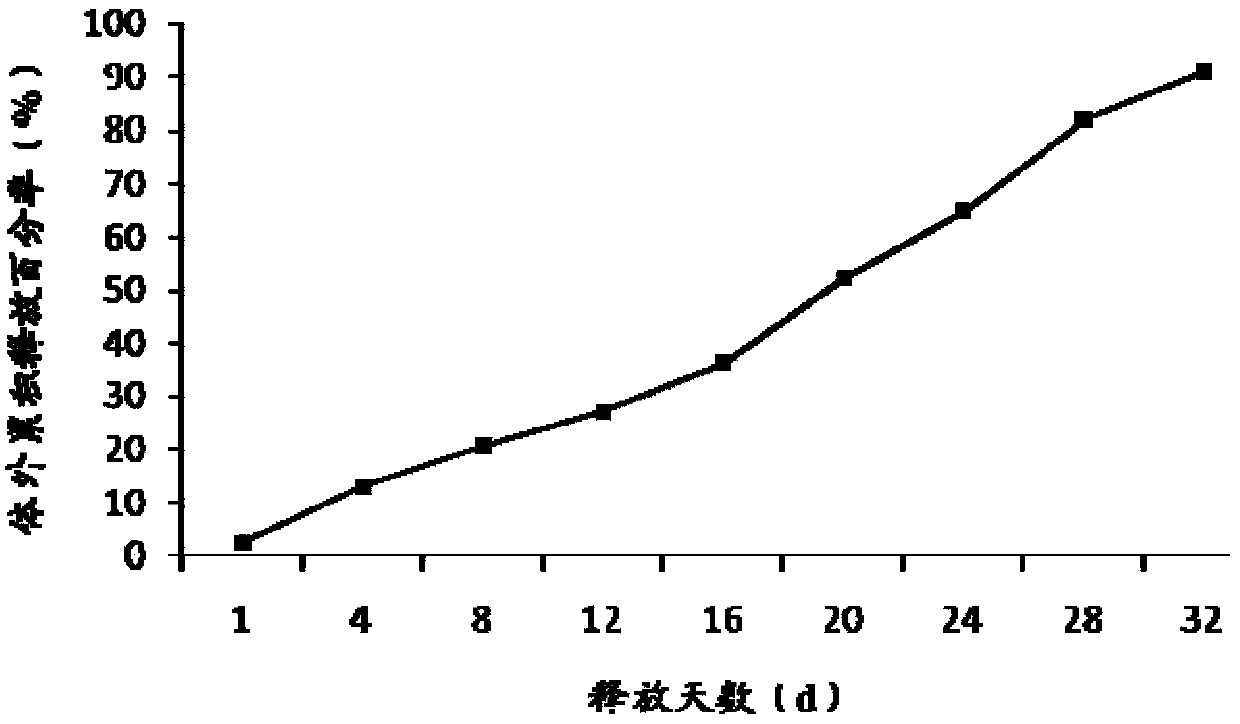
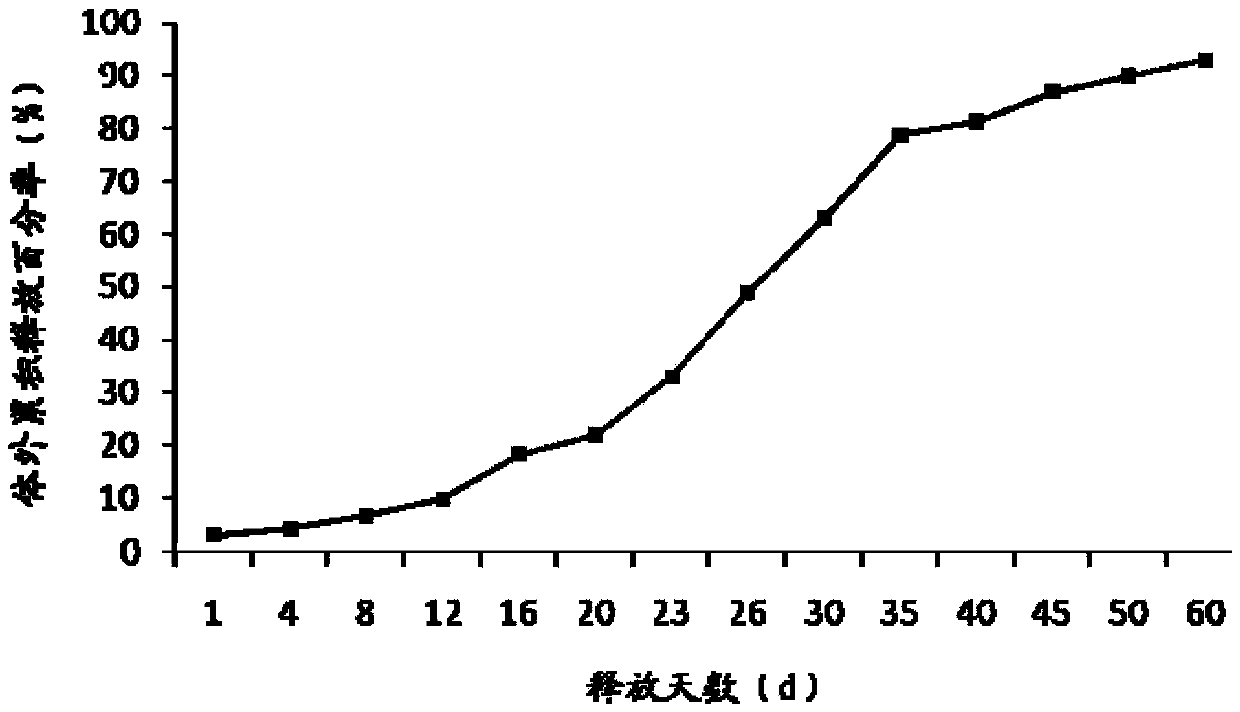
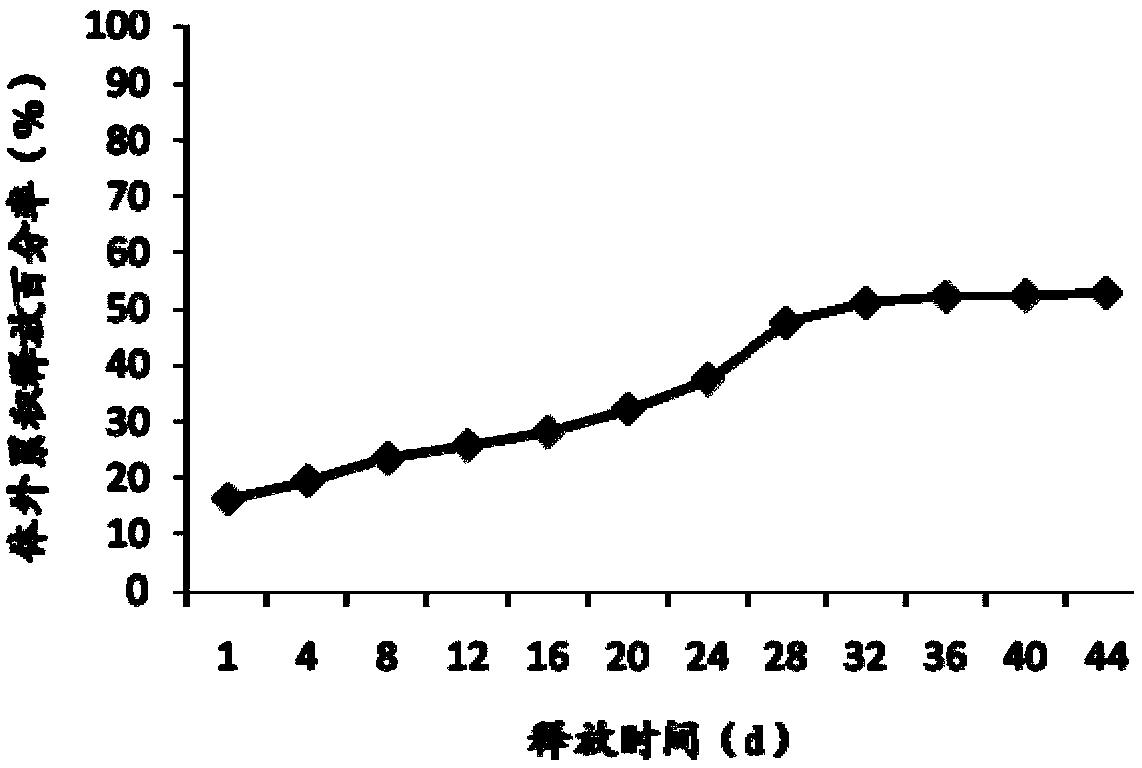
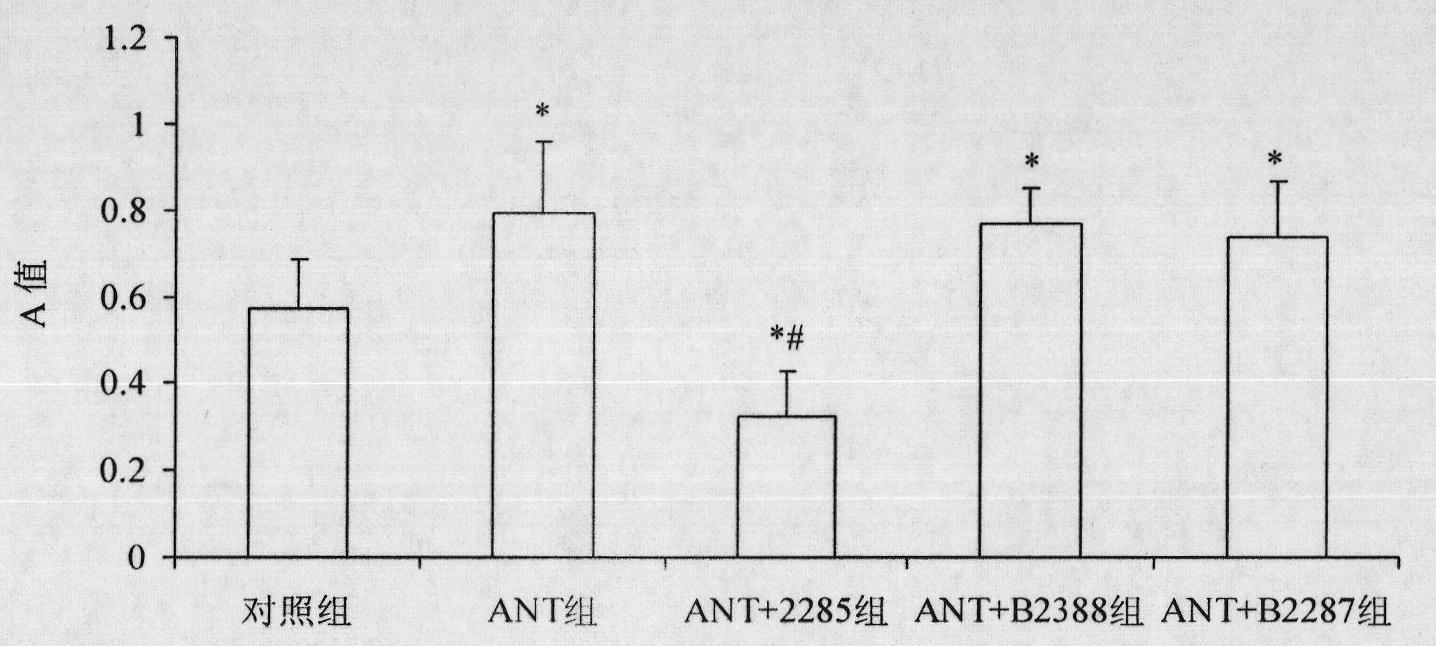
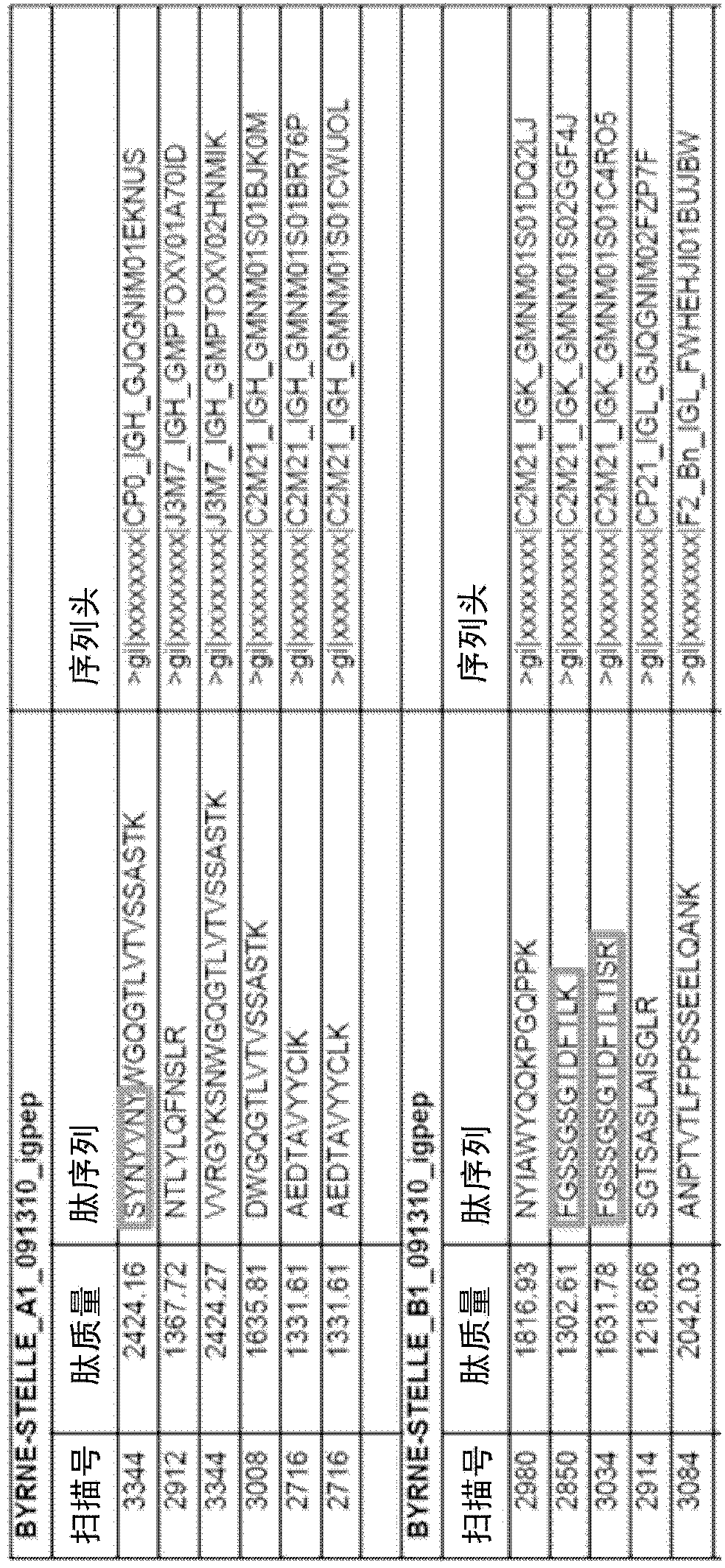
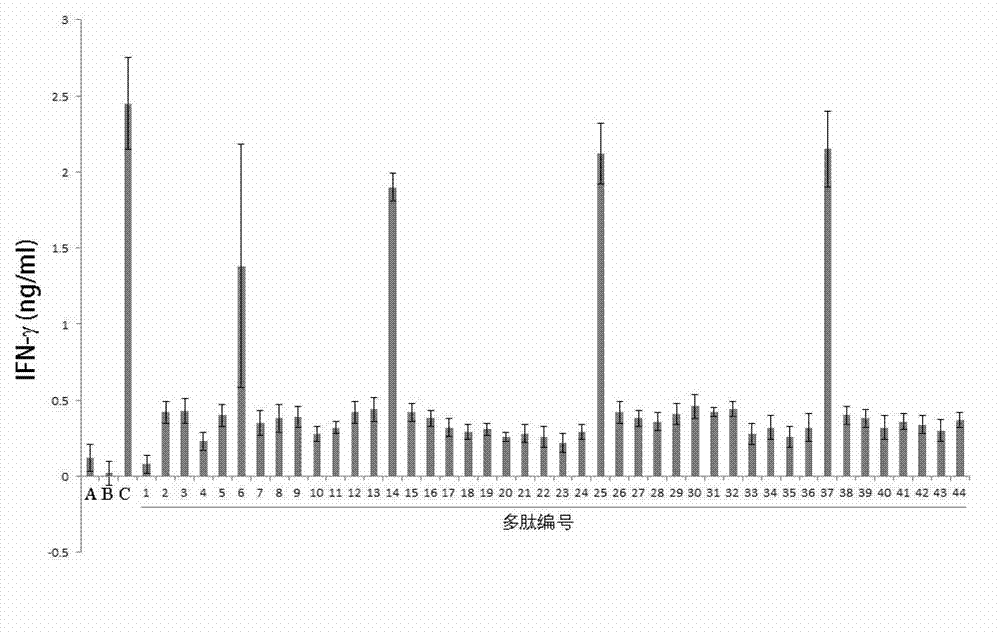
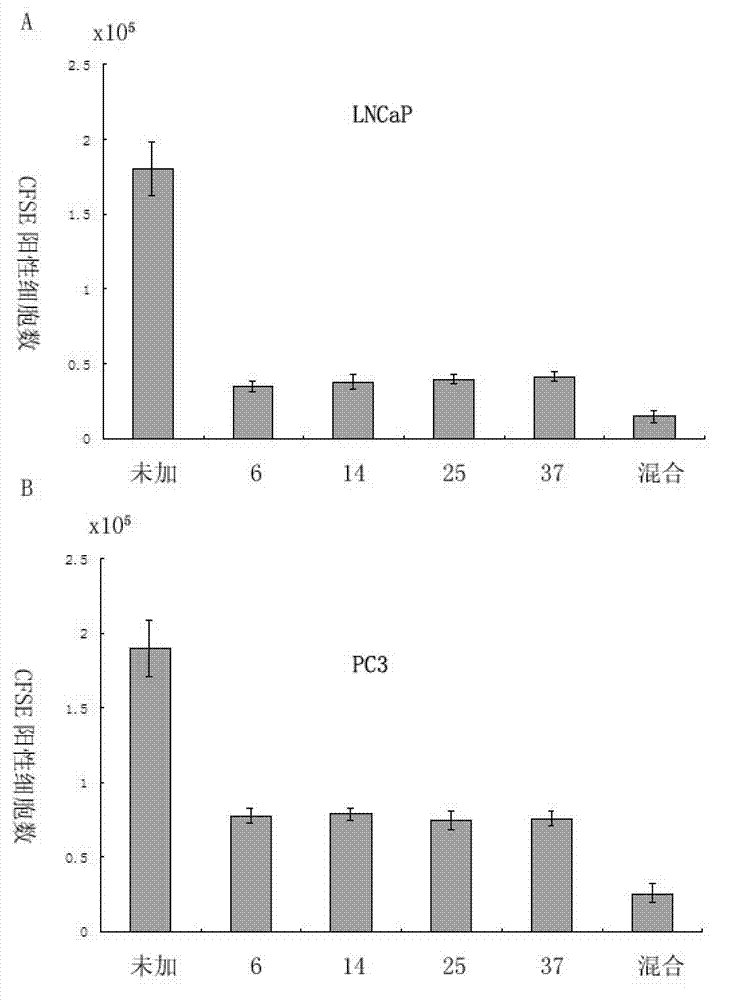
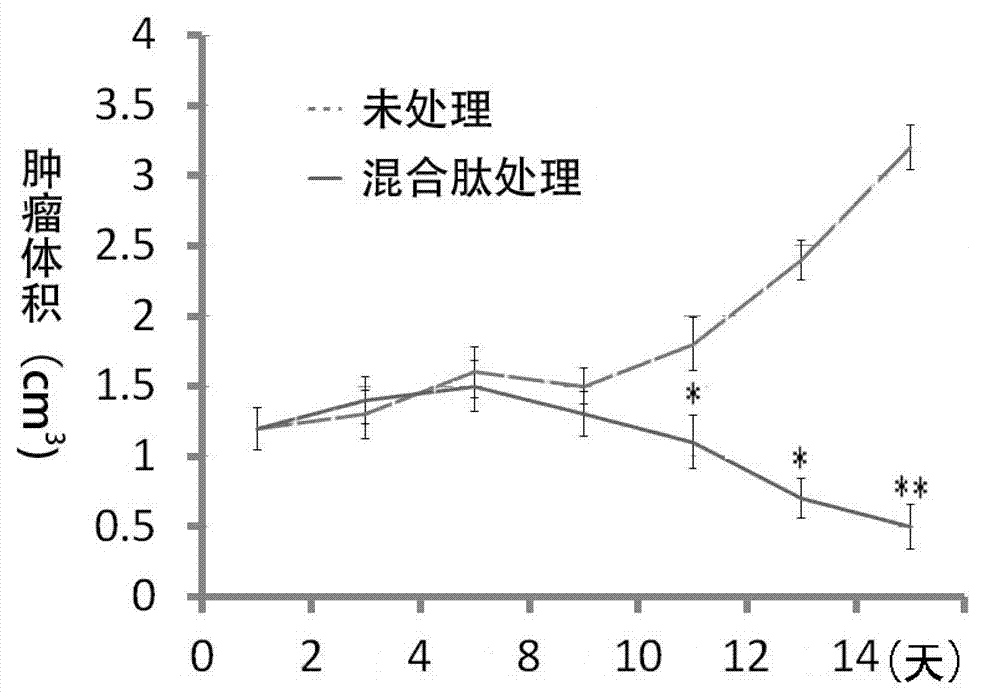
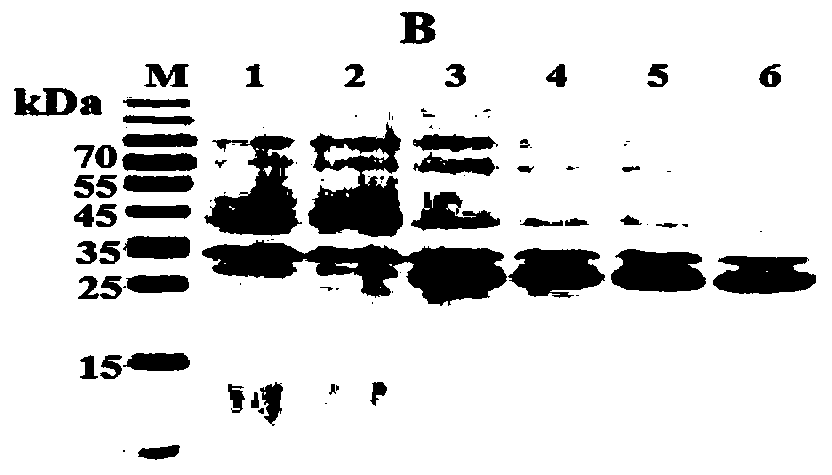Patents
Literature
44results about How to "Avoid immunogenicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
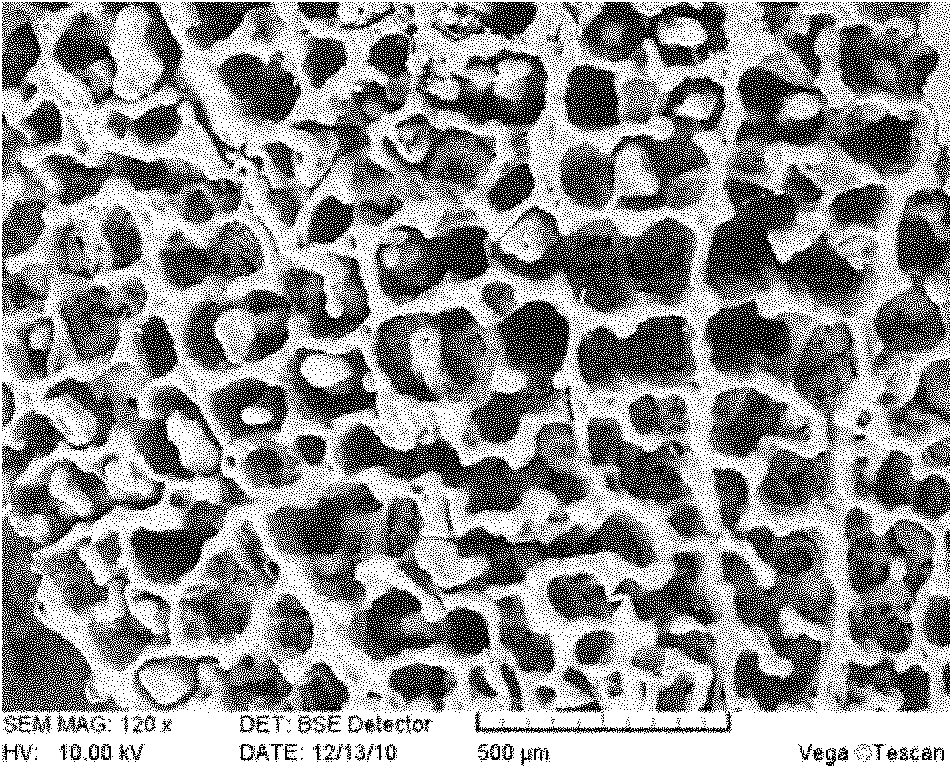
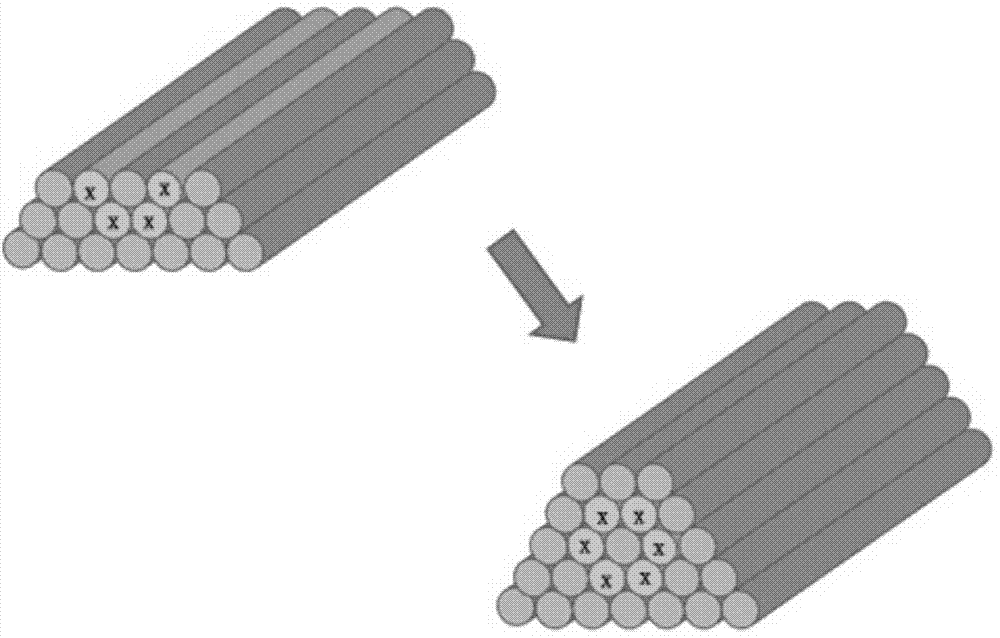
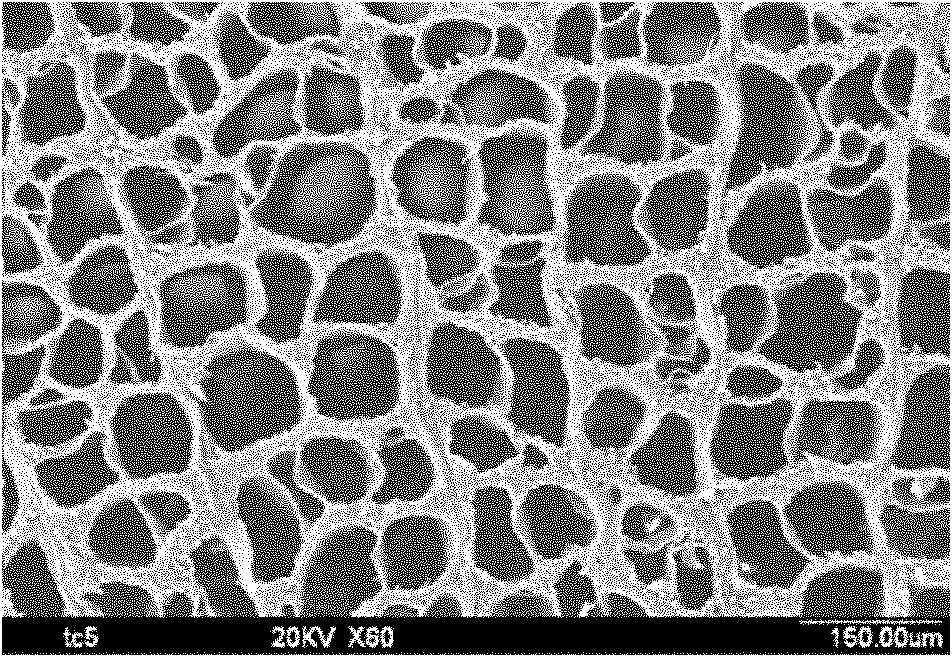
Cellular silk fibroin porous scaffold, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102430155AGood biocompatibilityGood mechanical propertiesProsthesisFreeze-dryingBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a cellular silk fibroin porous scaffold, and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: degumming silkworm cocoon serving as a raw material, dissolving, dialyzing, and freeze-drying to obtain silk fibroin; and immersing a negative norm sodium chloride porous body which has a plant tissue structure and serves as a template in a silk fibroin solution, vacuum-drying at room temperature, performing beta treatment, and desalting to obtain the silk fibroin porous scaffold which has a bionic plant tissue cellular pore structure. The porosity of the prepared cellar silk fibroin porous scaffold is more than 80 percent, and the apertures of cellular pores are 50 to 300 mu m; and the cellular silk fibroin porous scaffold is high in biocompatibility, and matter permeability, and good in mechanical property and degradation property and the like. The scaffold is particularly suitable for a tissue engineering technology of peripheral nerve, tendon, ligament and the like which have longitudinal structural tissues, and can be widely applied to in-vitro three-dimension cell culture.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing tissue engineering blood vessel based on 3D bioprinting technology
ActiveCN104490489AGood biocompatibilityStrong mechanical propertiesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture supports/coatingDiseaseThrombus
The invention provides a method for preparing a tissue engineering blood vessel based on a 3D (3-Dimensional) bioprinting technology. The method comprises the following steps:alternately printing a blood vessel shape by virtue of a high-polymer material and a human renascent skin fiber cell column, and removing the high-polymer material after fusion to structure a tissue engineering blood vessel; filling late-outgrowth endothelial progenitor cells into the blood vessel, and performing in-vitro dynamic culturing for 7 days in a bioreactor to obtain a differentiated tissue engineering blood vessel, wherein the high-polymer material is one of pluronic F127, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), methyl cellulose and sodium alginate. The blood vessel obtained by the method is high in biocompatibility and higher in mechanical property, thrombus formation resistant and platelet adhesion resistance, and can be used for repairing and replacing a damaged or disease blood vessel.
Owner:江苏知聚知识产权服务有限公司
Honeycomb polymer-based bionic porous scaffold material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a honeycomb polymer-based bionic porous scaffold material and a preparation method thereof. Natural plant tissues are used as templates. The method comprises the following steps of: performing vacuum carbonation, melting, permeating in water-soluble salt, performing oxidation and carbon removal on the templates to obtain template carrying porous salt, and finally performing the processes of vacuum / pressure biological macromolecular solution soaking, vacuum drying, desalting treatment and the like to prepare the honeycomb polymer-based bionic porous scaffold material. The prepared bionic porous scaffold material has a honeycomb porous structure based on the plant tissues, the porosity is 70 to 95 percent, and the aperture is 10 to 160 microns. The preparation methodis widely applied to water-insoluble biological macromolecular materials, and is easy to realize regulation and control of physicochemical, mechanical and biological properties of porous scaffolds. The honeycomb polymer-based bionic porous scaffold material and the preparation method thereof have special significance for realizing regenerative repair of defective tissues of peripheral nerves, muscle tendons, ligaments and the like with longitudinal morphology by using tissue engineering technology, and have broad practical application prospect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
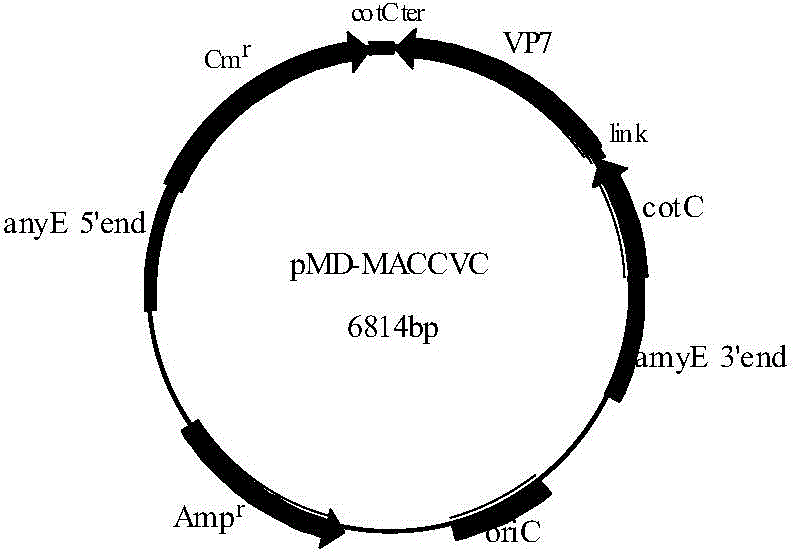
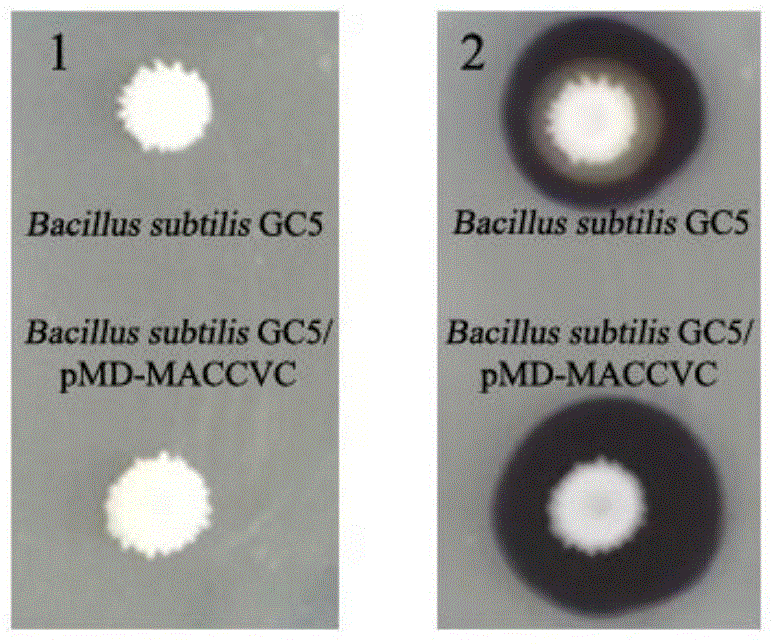
Recombinant bacillus displaying GCRV VP7 proteins on surface of bacillus subtilis GC5 and preparation method
ActiveCN104560860AAvoid immunogenicityAvoid security issuesBacteriaVirus peptidesBiotechnologyAntigen
The invention discloses a recombinant bacillus displaying GCRV VP7 proteins on the surface of bacillus subtilis GC5 and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a present epidemic strain type-II GCRV VP7 nucleotide sequence; (2) separating wide bacillus from the body of a grass carp, determining the wide bacillus to be bacillus subtilis, and naming the wide bacillus as Bacillus subtilis GC5, CCTCC NO: M2014654; (3) constructing a fusion expression recombinant integrated carrier, wherein a vp7 sequence in recombinant plasmids is the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1; (4) preparing and authenticating recombinant bacillus subtilis, CCTCC NO: M2014655; (5) inducing and authenticating the recombinant bacillus displaying VP7 on the surface. The generation rate of spores is up to 100%, and the recombinant bacillus is simple and convenient to produce, low in cost, and capable of being used as a feed additive; the recombinant bacillus has an intestinal customization capacity, as well as is beneficial to regulating the intestinal bacterial colony balances of animals, improving the body immunocompetence of the animals, and enhancing the nutrition metabolism functions of the animals. The spores are high in stress resistance and easy for large-scale production, as well as solve the problem of instability of GCRV VP7 proteins used as immunizing antigens in extreme environments.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
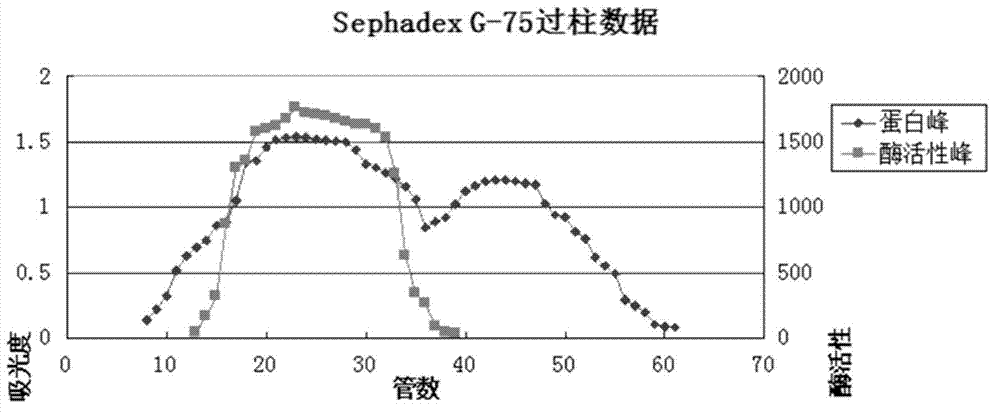
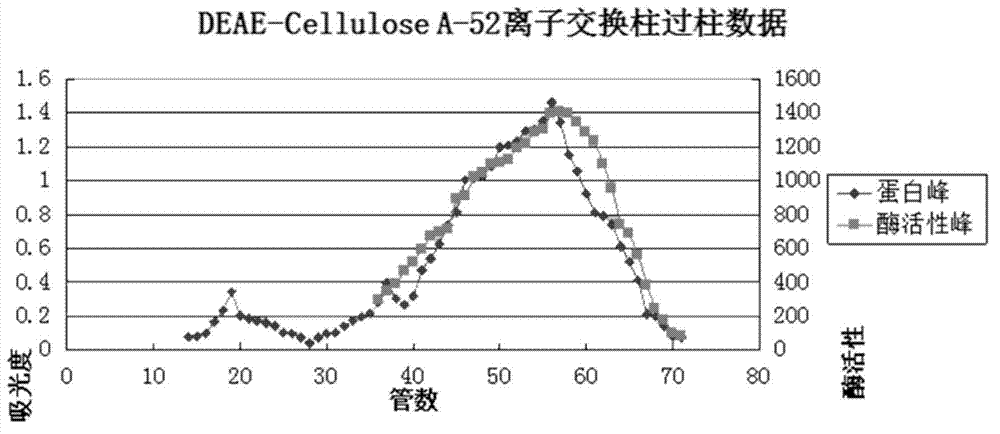
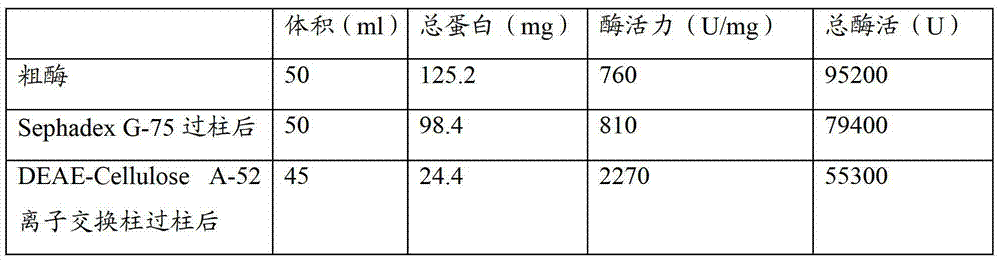
A preparation method for lyophilized powder of earthworm fibrinolytic enzymes
The present invention discloses a preparation method for lyophilized powder of earthworm fibrinolytic enzymes. The preparation method comprises the steps of the preparation of earthworm meal, the preparation of a crude enzyme solution, the purification of crude enzymes, the modification of the earthworm fibrinolytic enzymes, and the preparation of lyophilized powder of the earthworm fibrinolytic enzymes. According to the preparation method for lyophilized powder of earthworm fibrinolytic enzymes of the present invention, on the basis of isolated and purified pure enzymes, activated polyethylene glycol is employed for modifying the earthworm fibrinolytic enzymes, so that the earthworm fibrinolytic enzymes have no direct contact with body fluids and the free amino groups are cleared, thus extending the half-life and eliminating immunogenicity of the earthworm fibrinolytic enzymes in the body.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RAINHOME PHARM&TECH CO LTD
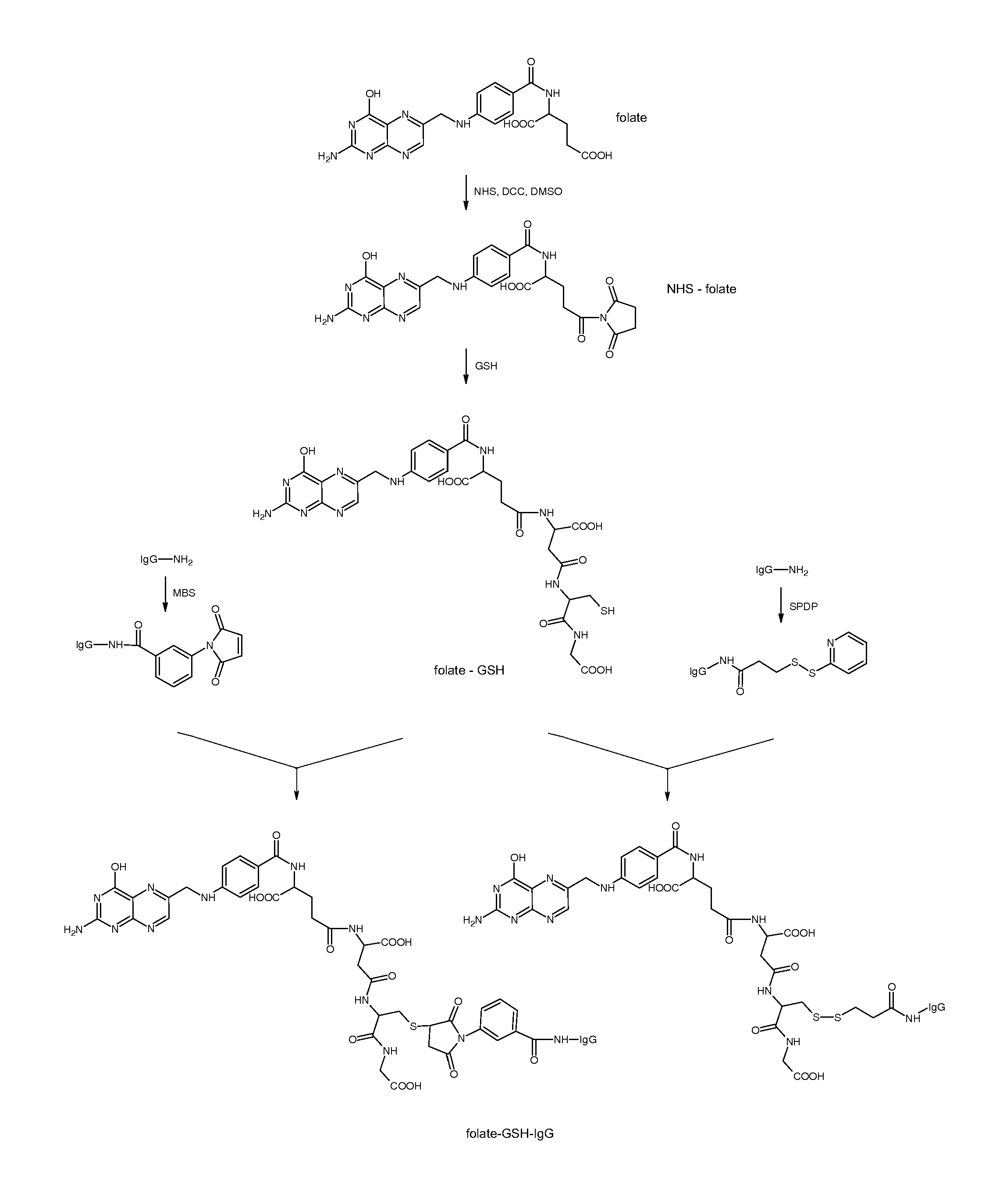
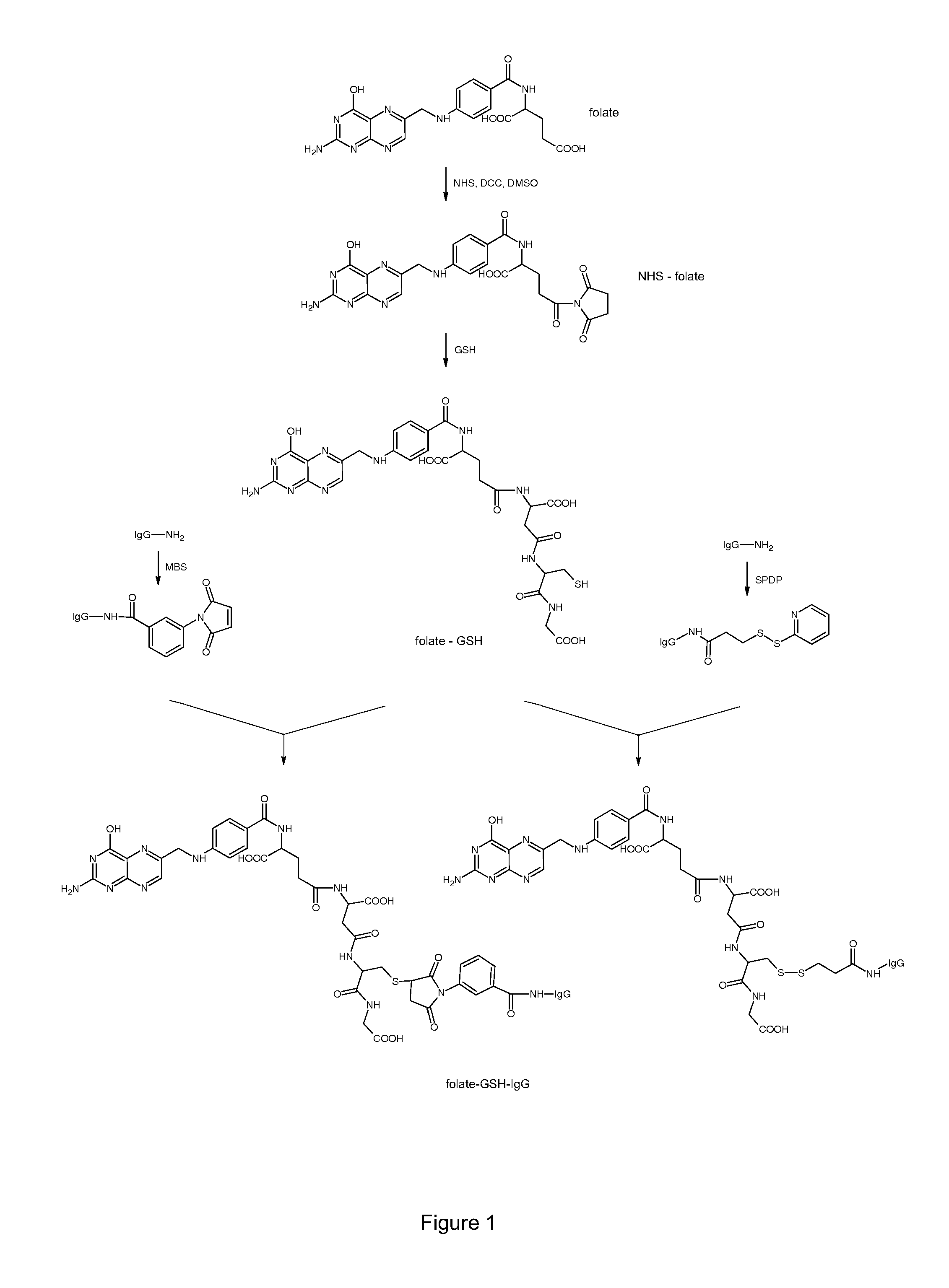
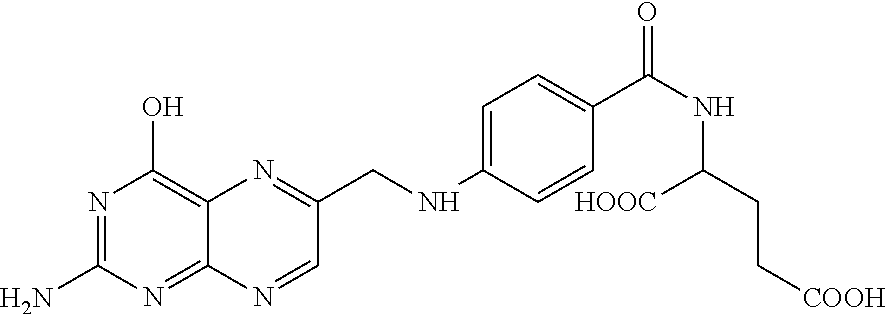
Conjugate of Folate and Antibody Preparation Method and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20130259882A1Function increaseInducing effectAntipyreticDigestive systemCysteamineAutoimmune disease
Anti-tumor conjugates, which consists of foliate or analogues thereof, linkers, an antibodies such as immunoglobulin G. The linker comprises glutathione, cysteamine or cysteine residue, and further comprises N-hydroxysuccinimide. The Conjugates target folate-receptor-positive tumor cells. Also provided are preparation methods and anti-tumor and anti-autoimmune disease uses of the conjugates.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIANFENG HANSHENG BIOSCI
Cryopreservation method for adipose tissues
InactiveCN109497041AReduce application concentrationLow toxicityDead animal preservationLiquid nitrogenRefrigeration
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a cryopreservation method for adipose tissues. The cryopreservation method includes the steps of preparing adipose tissue cryopreservation protection liquid, treating lipoaspirate, cryopreserving the adipose tissues, performing refrigeration according to a pre-controlled freezing curve after a cryopreservation tube containing the adipose tissues is balanced at the temperature of 4 DEG C, and storing the adipose tissues in a liquid nitrogen tank at the temperature of minus 196 DEG C for a long time. According to the characteristics and application features of the adipose tissues, the activity of the cryopreserved adipose tissues is further improved by reducing the damage of the thermal stress to the adipose tissues, controlling the freezing rate and optimizing cryoprotectants in the cryopreservation process of the adipose tissues; the cryopreservation method has the advantages of stable preservation effect, capability ofeffectively improving the activity of the adipose tissues after re-thawing, and ideal transplantation effect.
Owner:西安九州医学中心有限公司
Exenatide slow release sustained release microsphere, and preparation method and preparation thereof
ActiveCN103417957AMaintain biological activityOptimize drug release profilePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderArginineMicrosphere
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine and particularly relates to an exenatide slow release sustained release microsphere, and a preparation method and a preparation thereof. The exenatide slow release sustained release microsphere comprises the following components in parts by mass: 0.5-10 parts of exenatide, 0.5-10 parts of protecting agent and 80-99 parts of polylactic glycollic acid copolymer, wherein the protecting agent is one of or the combination of more than two of glycine, lysine, arginine or histidine. The exenatide slow release sustained release microsphere adopts the alkali protecting agent which can neutralize local acidation caused by degradation of the polylactic glycollic acid copolymer during release in vitro and degradation in vivo of the microsphere, so that aggregation of polypeptide is reduced and the stability of exenatide is maintained.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
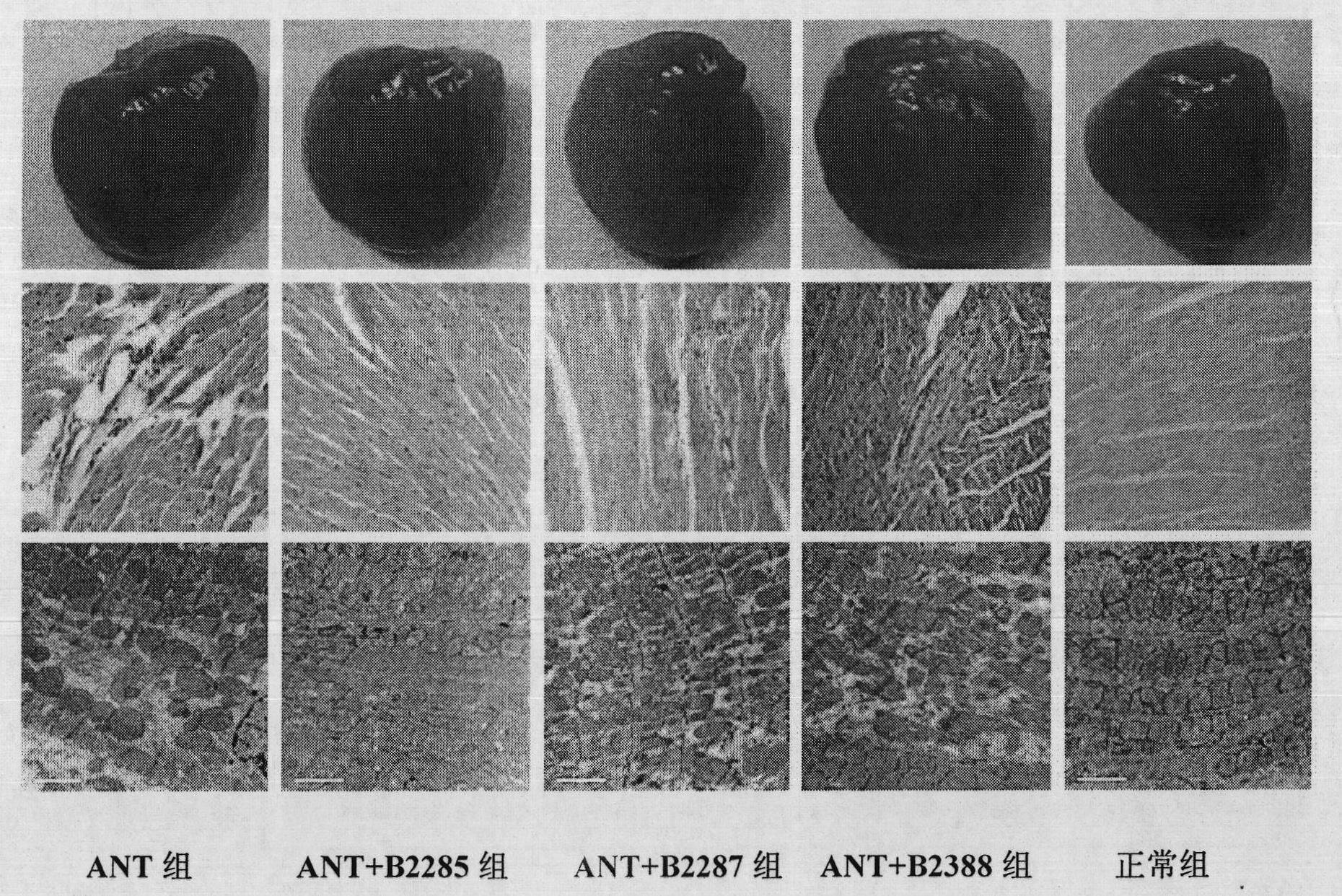
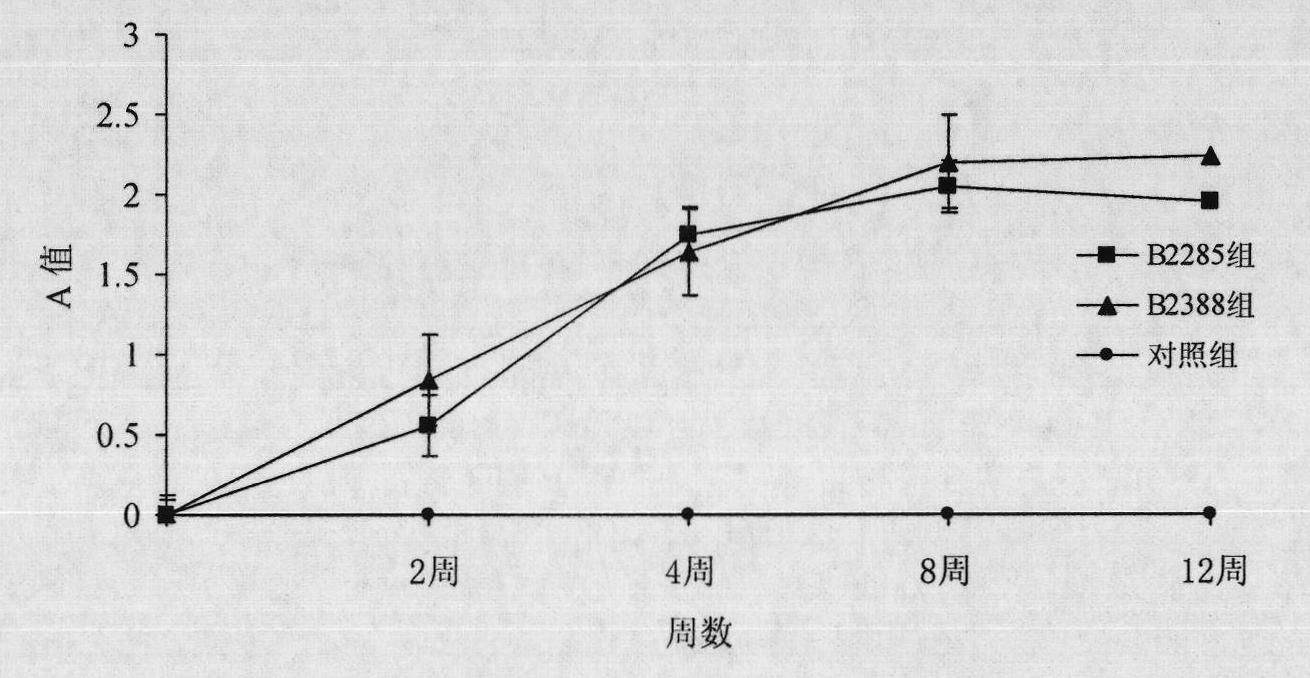
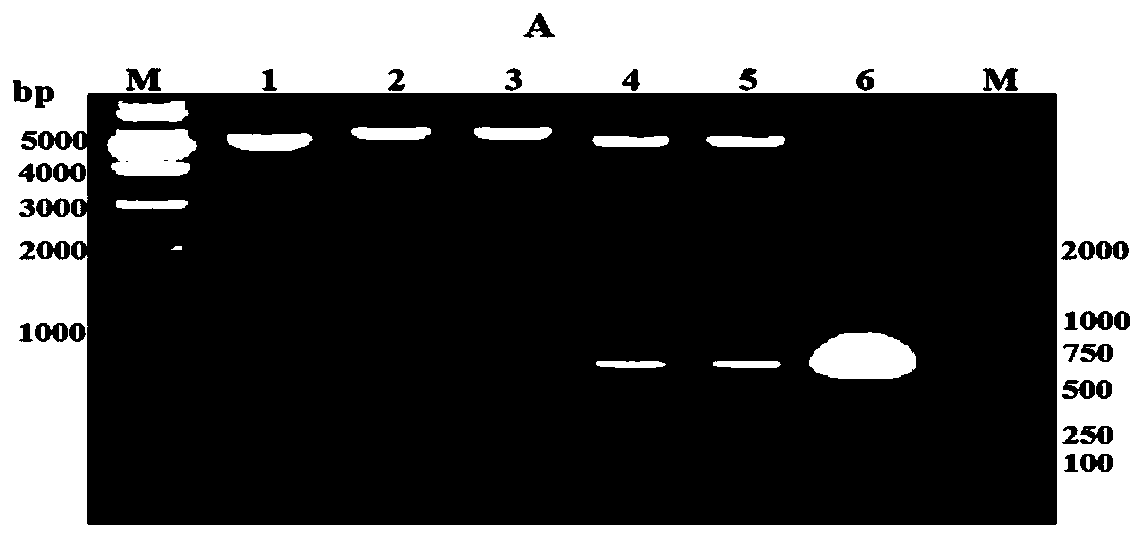
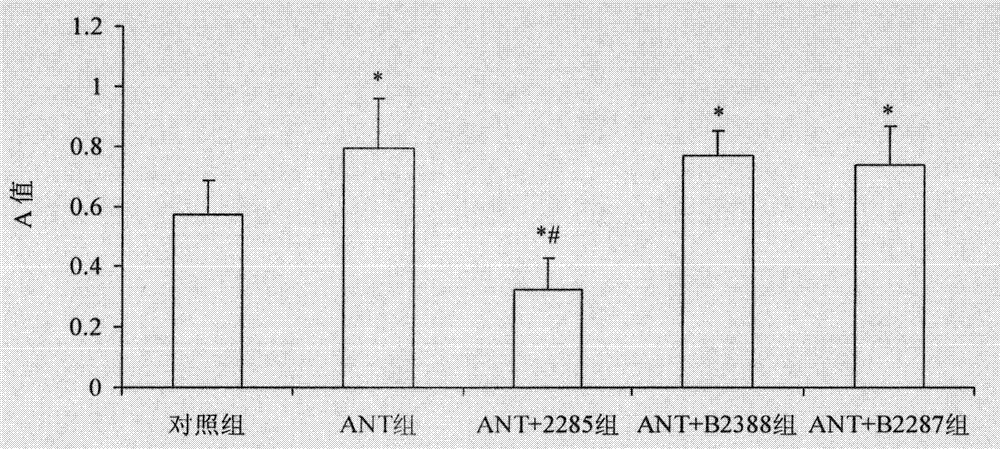
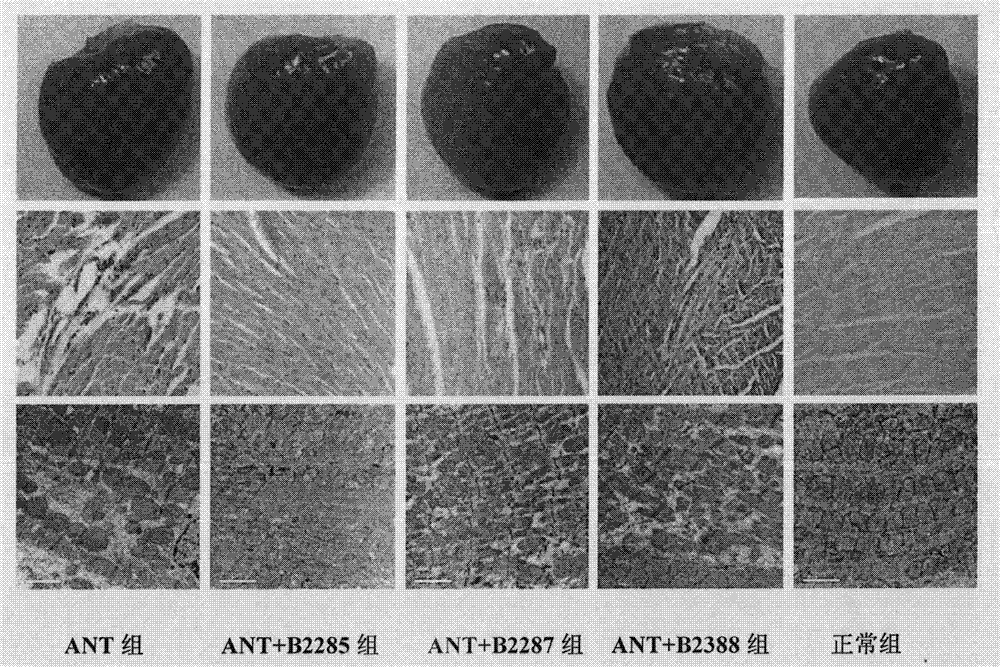
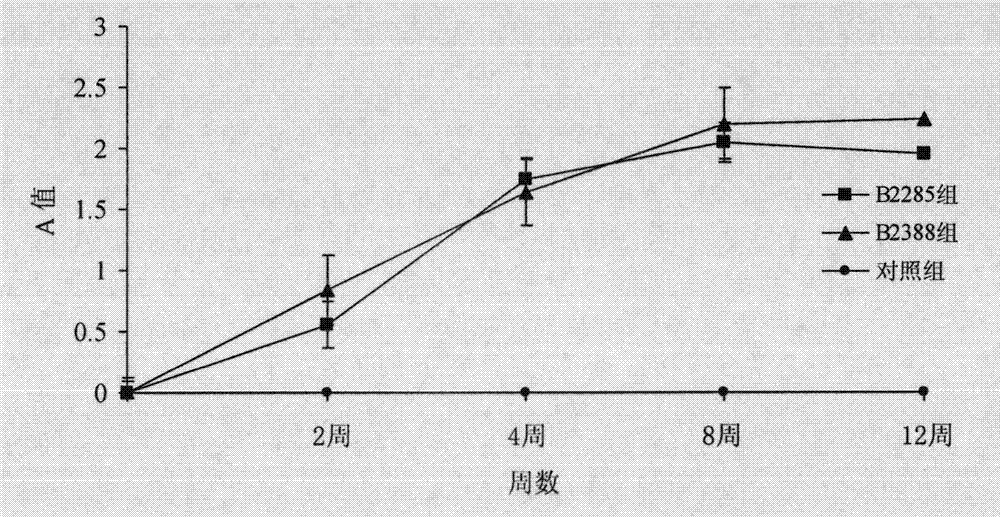
Preparation method for B cell CD 22 extracellular inhibitive peptide fragment B2285 vaccines
InactiveCN101897961AAvoid immunogenicityLess toxic side effectsPeptidesCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsDiseaseHigh homology
The invention provides a preparation method for B cell CD 22 extracellular peptide fragment B2285 vaccines. Sequential eight amino acids from the 85th to the 93rd starting at an amino terminal in a mice CD 22 molecule amino acid sequence, specifically in a sequence of Lys- Thr- Glu- Lys- Asp-Pro- Glu- Ser- Glu, are selected. The sequence is similar to the sequence of Lys- Asp- Gly- Lys- Val- Pro-Ser- Glu, having the sequential eight amino acids from the 81st to the 88th starting at the amino terminal in a human CD 22 molecular amino acid sequence, is located at the same functional region in a spatial structure, and has high homology. A prepared vaccine or a drug composite containing B2285 has the functions of inhibiting B cell proliferation, activating and generating antibody per se, canbe applicable to treating immunologic diseases involved or mediated B cells such as dilated cardiomyopathy testing positive in an anti-myocardial antibody, systemic lupus erythematosus with a positive antibody per se, and the like.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
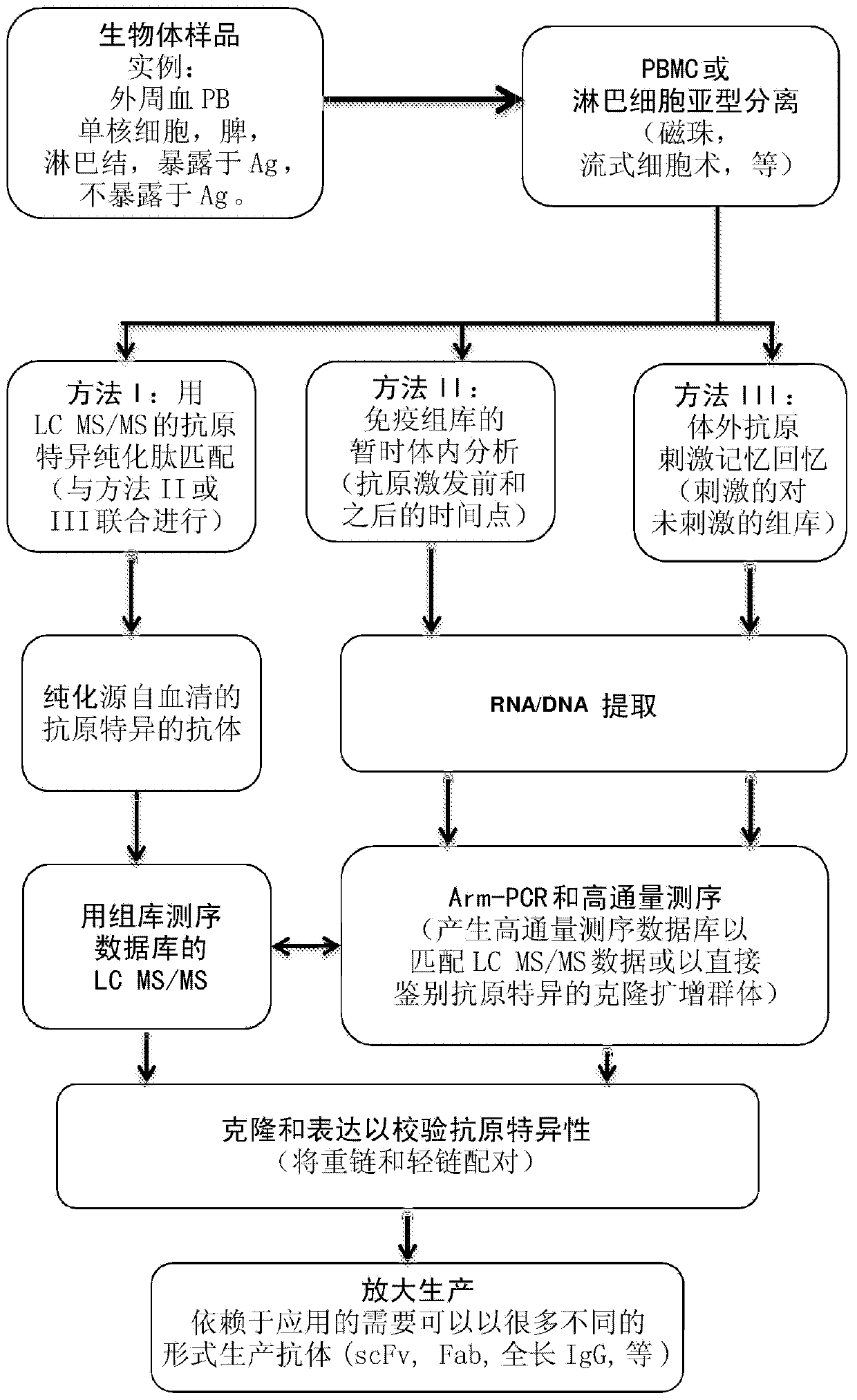
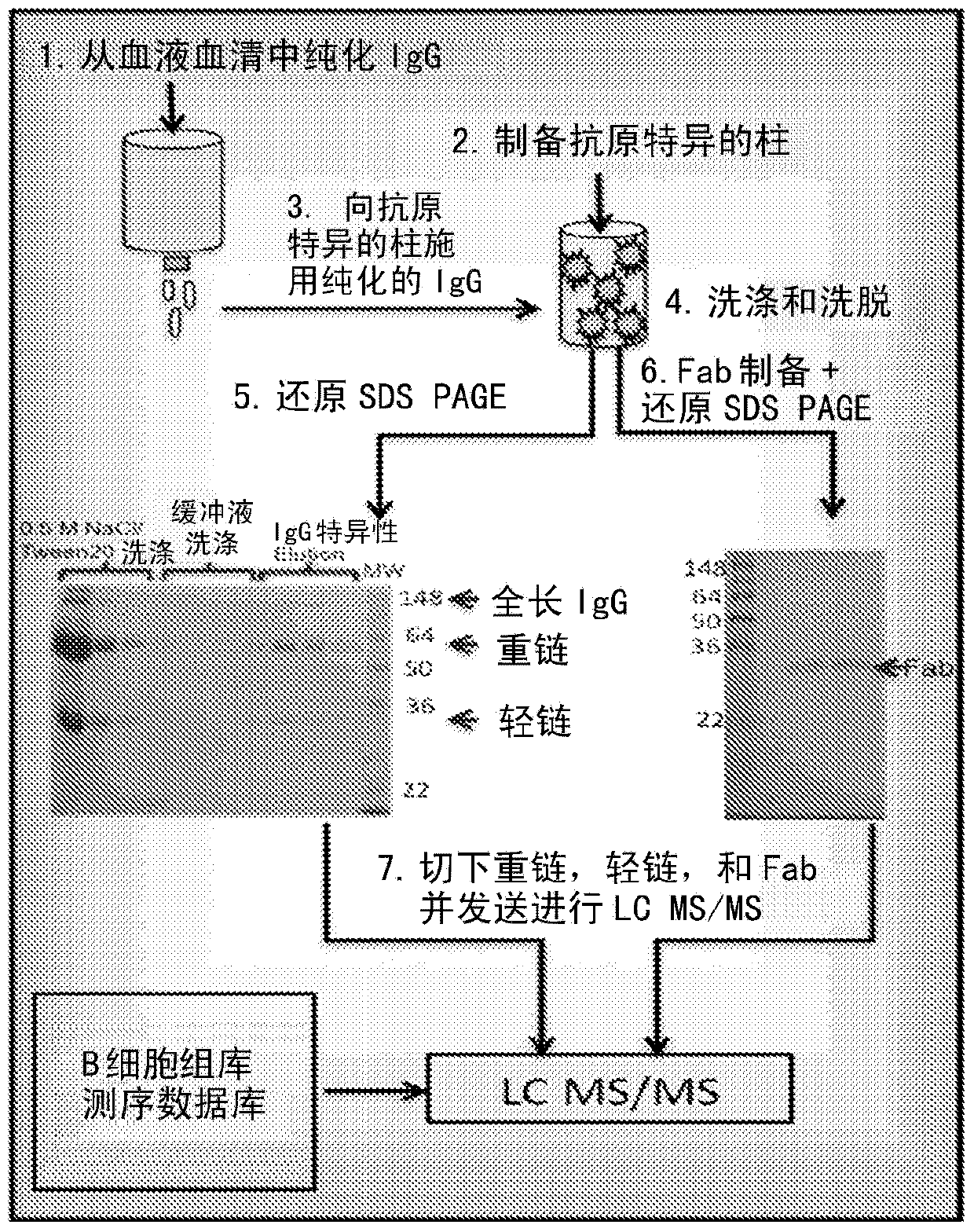
Identification of antigen-specific adaptive immune responses using Arm-PCR and high-throughput sequencing
InactiveCN103987853AAvoid immunogenicityAvoiding the need for murine hybridomasMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHeavy chainMonoclonal antibody
Disclosed is a method for correlating at least one amino acid sequence from an antibody isolated from human or animal blood with at least one DNA sequence corresponding to the antibody in the immunorepertoire of the human or animal. The method also provides a means for pairing heavy and light chains to produce synthesized monoclonal antibodies.
Owner:CB BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC +1
Polypeptide for enclosing TGF-beta acceptor or IL-10 acceptor, pharmaceutical composition and application
ActiveCN102898508AEnhance tumor killing activityGood tissue specificityFungiBacteriaProstate cancerT cell
The invention belongs to the immunobiology and biological medicine fields, and relates to a polypeptide for enclosing a TGF-beta acceptor or an IL-10 acceptor, a pharmaceutical composition and an application. Concretely, the invention relates to the polypeptide or a polypeptide combination, an amino acid sequence is one or more shown as the following (1)-(4), 1) the amino acid sequence shown in a SEQ ID NO: 6, 2) the amino acid sequence shown in a SEQ ID NO: 14, 3) the amino acid sequence shown in a SEQ ID NO: 25, and 4) the amino acid sequence shown in a SEQ ID NO: 37. The polypeptide can effectively enclose the TGF-beta acceptor or the IL-10 acceptor, thereby the tumor killing activity of the T cell (especially the antigenic specificity T cell) is enhanced, and the polypeptide has potential as a medicine for treating or assistantly treating prostate.
Owner:PEKING UNIV FIRST HOSPITAL
Method for preparing humanized camelidae single-domain antibody through transgenic rodent
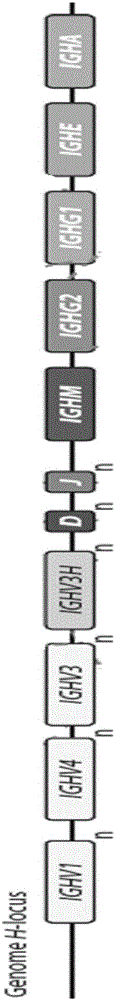
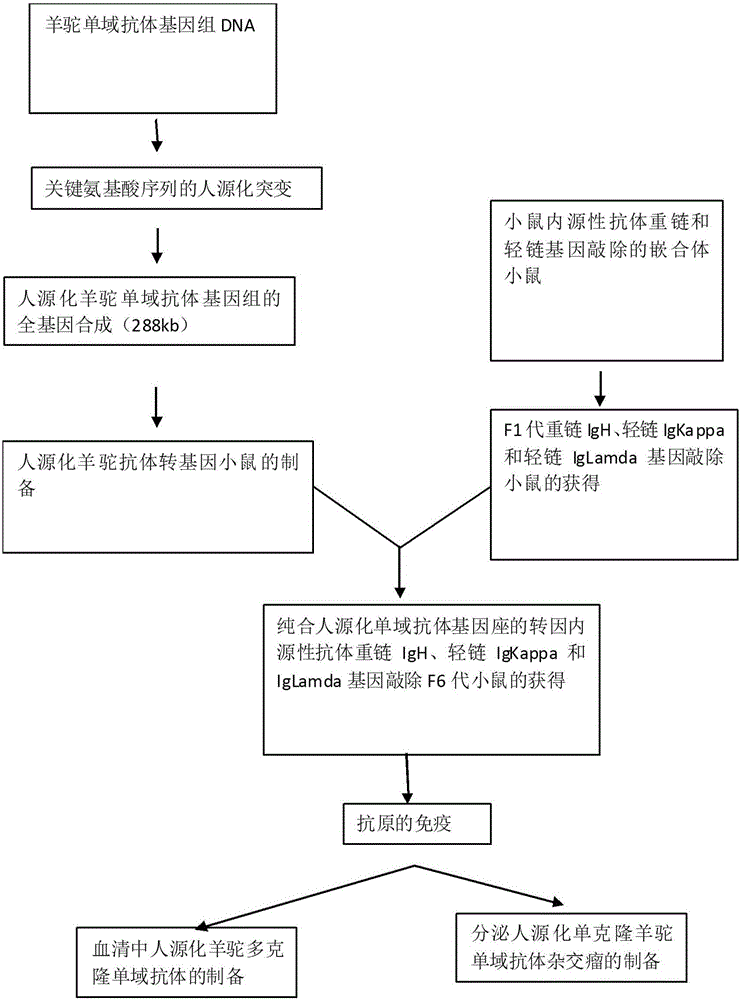
InactiveCN105777894AReduce usageImprove securityMicroinjection basedImmunoglobulinsGene clusterScreening method
The invention provides a method for preparing humanized camelidae single-domain antibody through a transgenic rodent. According to the method, a transgenic mouse can be prepared by constructing humanized alpaca single-domain antibody artificial chromosomes; meanwhile, endogenous antibodies, such as IgH, IgKappa and IgLamda gene clusters, of the mouse are subjected to knockout by adopting a homologous recombination method, and the transgenic mouse which only expresses the humanized alpaca single-domain antibody is obtained and is used for preparing a humanized monoclonal alpaca single-domain antibody. The humanized single-domain antibody can be directly obtained through a hybridoma or single cell PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) screening method, the obtained single-domain antibody is not required to be subjected to in-vitro mutation and humanized modification, and a gene bank is not required to be established for screening, so that the method has the advantages of high simplicity, convenience, and safety.
Owner:长春力太生物技术有限公司
Polypeptide, polypeptide nano drug-loading carrier and preparation method of polypeptide and polypeptide nano drug-loading carrier
InactiveCN110423266AEasy to synthesizeEasy to purifyPeptide preparation methodsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsStructural formulaHEPES
The invention discloses a polypeptide, a polypeptide nano drug-loading carrier and a preparation method of the polypeptide and the polypeptide nano drug-loading carrier. The polypeptide has a structural formula of Ac-LLLLLLKKKK-NH2. The preparation method of the polypeptide comprises the steps that various raw materials are added to a polypeptide solid phase synthesizer, and Ac-IIIIKK-NH2 is synthesized from a C-terminal to an N-terminal; and Ac-IIIIKK-NH2 is further prepared to obtain the requried polypeptide. The polypeptide nano drug-loading carrier is of a nanosphere structure capable of being ruptured in an acidic environment, and the nanosphere structure is used for embedding a fat-soluble drug. The preparation method of the polypeptide nano drug-loading carrier comprises the steps that the polypeptide is added to a Hepes solution, and the polypeptide is self-assembled to form the polypeptide nano drug-loading carrier embedding the fat-soluble drug.
Owner:WEIFANG MEDICAL UNIV
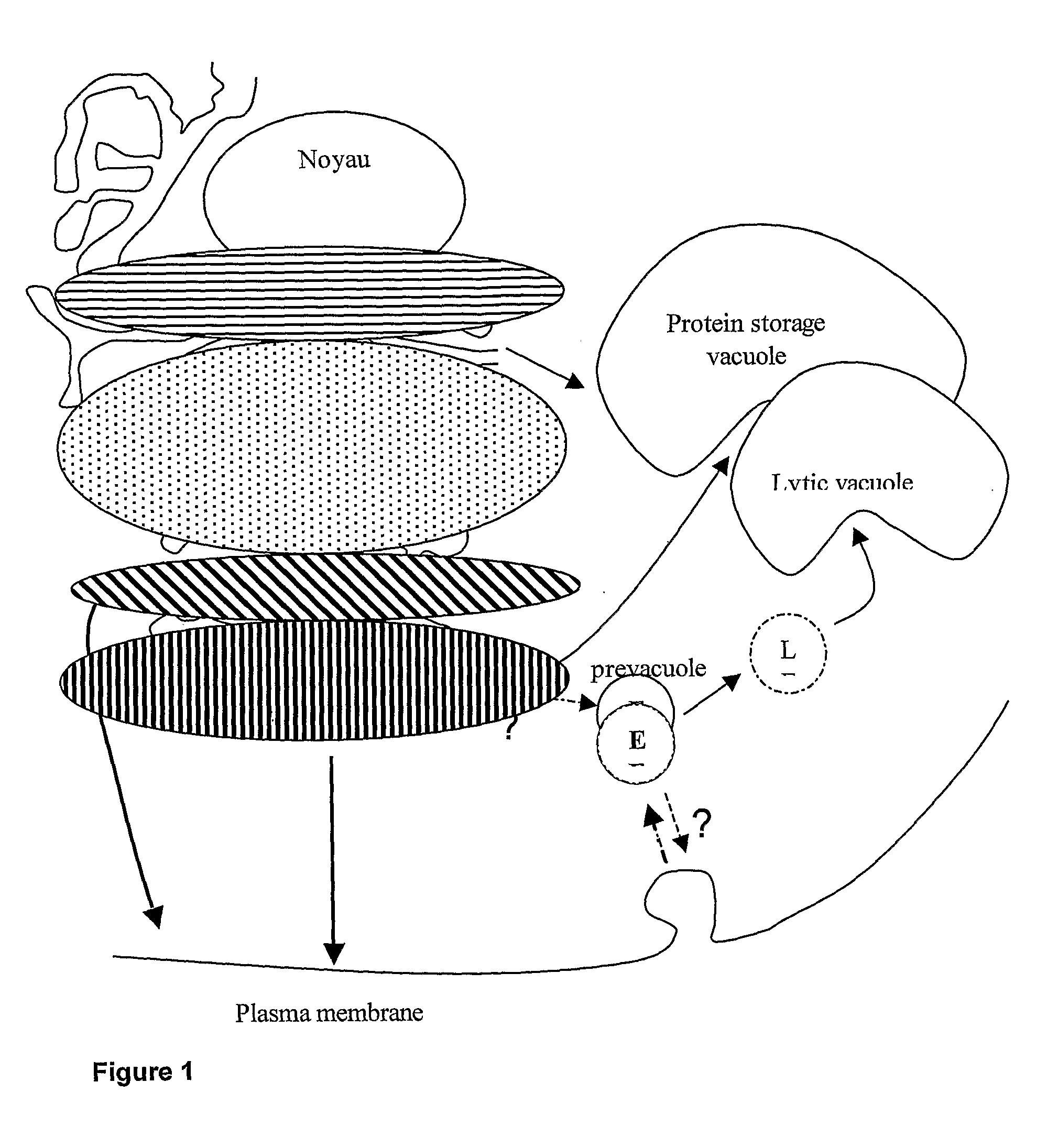
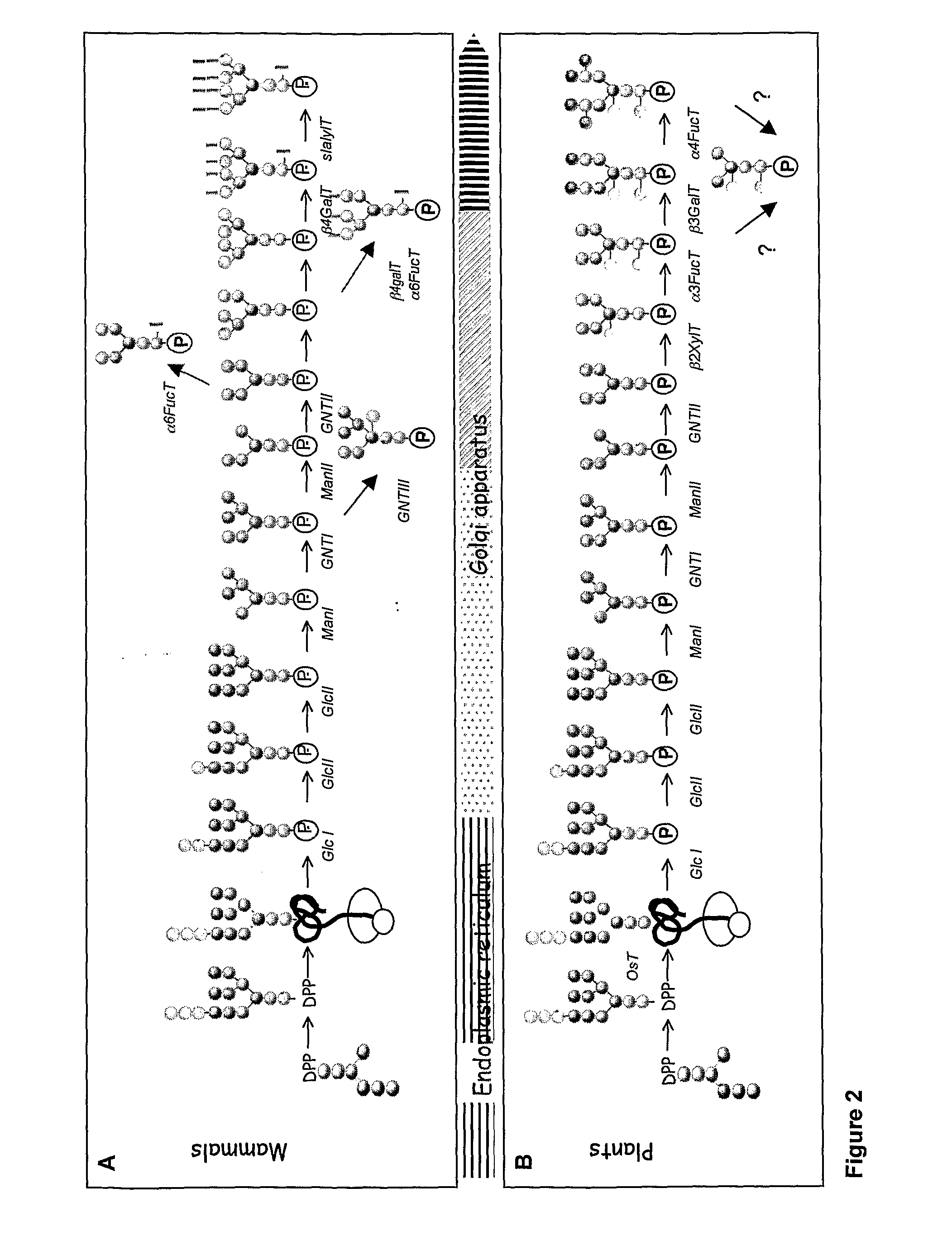
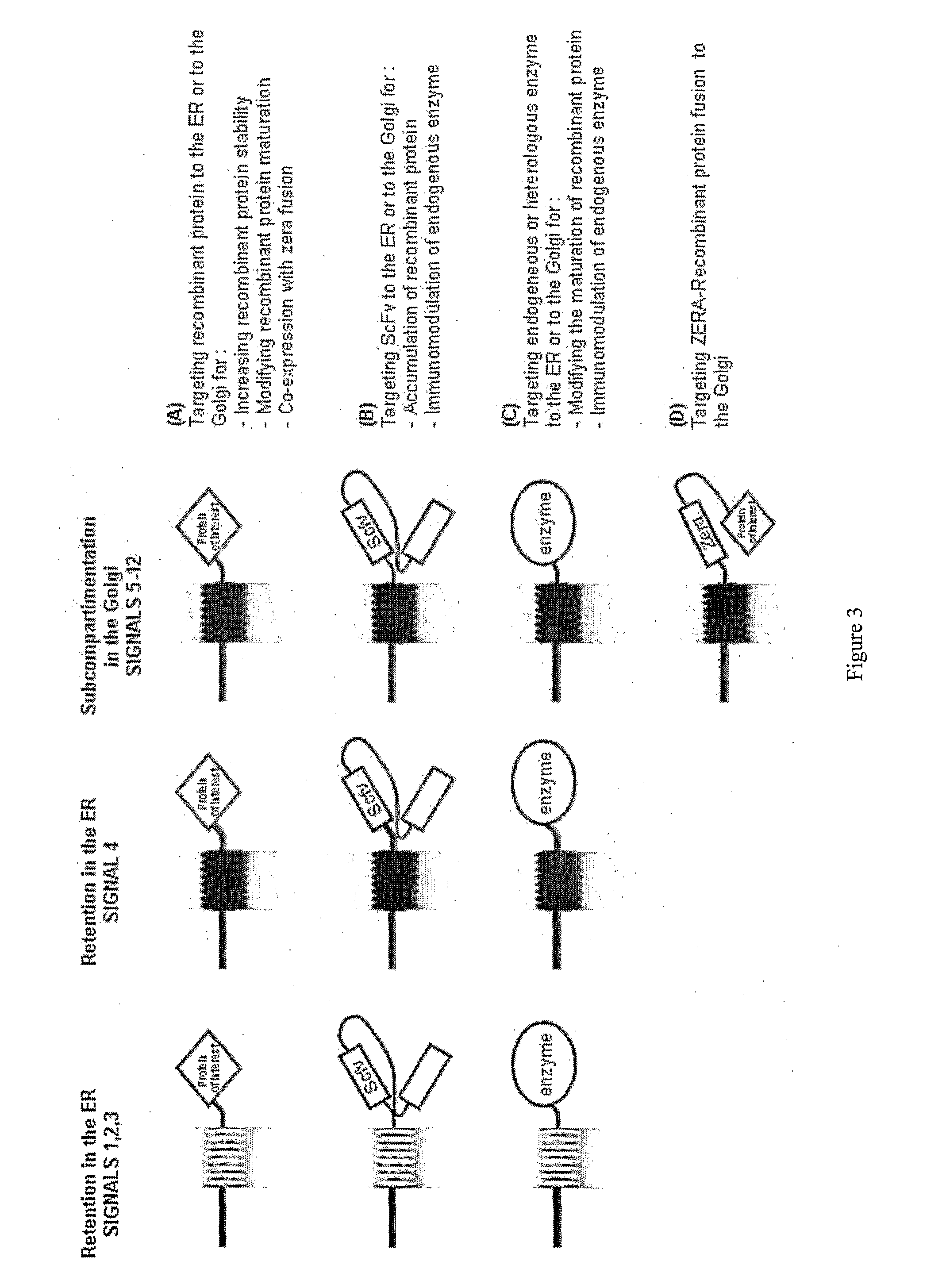
Set of sequences for targeting expression and control of the post-translational modification of a recombinant polypeptide
InactiveUS20110195452A1Improve stabilityImprove production yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsSequence signalPost translational
The present invention provides new tools useful for controlling the post-translational modifications of recombinant polypeptides. These tools are particular signal peptides allowing the targeting of recombinant polypeptides during their synthesis in a host cell to specific sub-cellular compartments and a specific designing of said recombinant polypeptides within said sub-cellular compartments. These signal peptides are SEQ ID no 1 to SEQ ID no 31 disclosed herein. The present invention relates therefore also to a process for producing a recombinant polypeptide, in particular to a post-translationally modified polypeptide comprising the steps of transfecting or transforming a cell with at least one numleic acid vector encoding a recombinant protein which is the polypeptide before being post-translationally modified or a recombinant protein different to said polypeptide, said recombinant protein comprising a peptide signal according to the present invention; growing the transfected cell; and harvesting the post-translationally modified polypeptide; wherein, when said recombinant protein is different to said polypeptide, the method also comprises a step of transfecting said cell with at least one vector encoding said polypeptide. The present invention allows advantageously, for example, to increase the yield of production of recombinant polypeptides, to prevent immunogenicity if recombinant polypeptides and to obtain therapeutically active recombinant polypeptides that are the exact copy of their natural counterpart. This invention relates particularly to the field of reorientation of plants made pharmaceuticals (PMP).
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Cell protective agent containing metallothionein
InactiveCN102634479AAvoid immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsArtificial cell constructsDiseaseCritical illness
The invention discloses cell protective agent containing metallothionein, which aims to solve the problems that blood cells are damaged during blood perfusion, corresponding tissues and organs during growth are damaged after the cells are cultured and augmented in vitro and transplanted and survival rate is low and the like, and can be used for blood perfusion treatment method and cell treatment method including a method for protecting the corresponding tissues and organs after vitro-culturing, augmenting and transplanting of the cells. The cell protective containing metal sulfur protein can be widely used for protecting blood cells of human bodies with diseases such as uremia, critical illness, intoxication, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), severe hepatitis and the like during blood perfusion treatment, and protecting corresponding cultured and augmented cells or transplanted and hyperplasia cells of the corresponding tissues and organs in the cell treatment of diseases caused by severe damage or reduction of the cells.
Owner:汪志友
Preparation method of human nerve growth factor transgenic pig
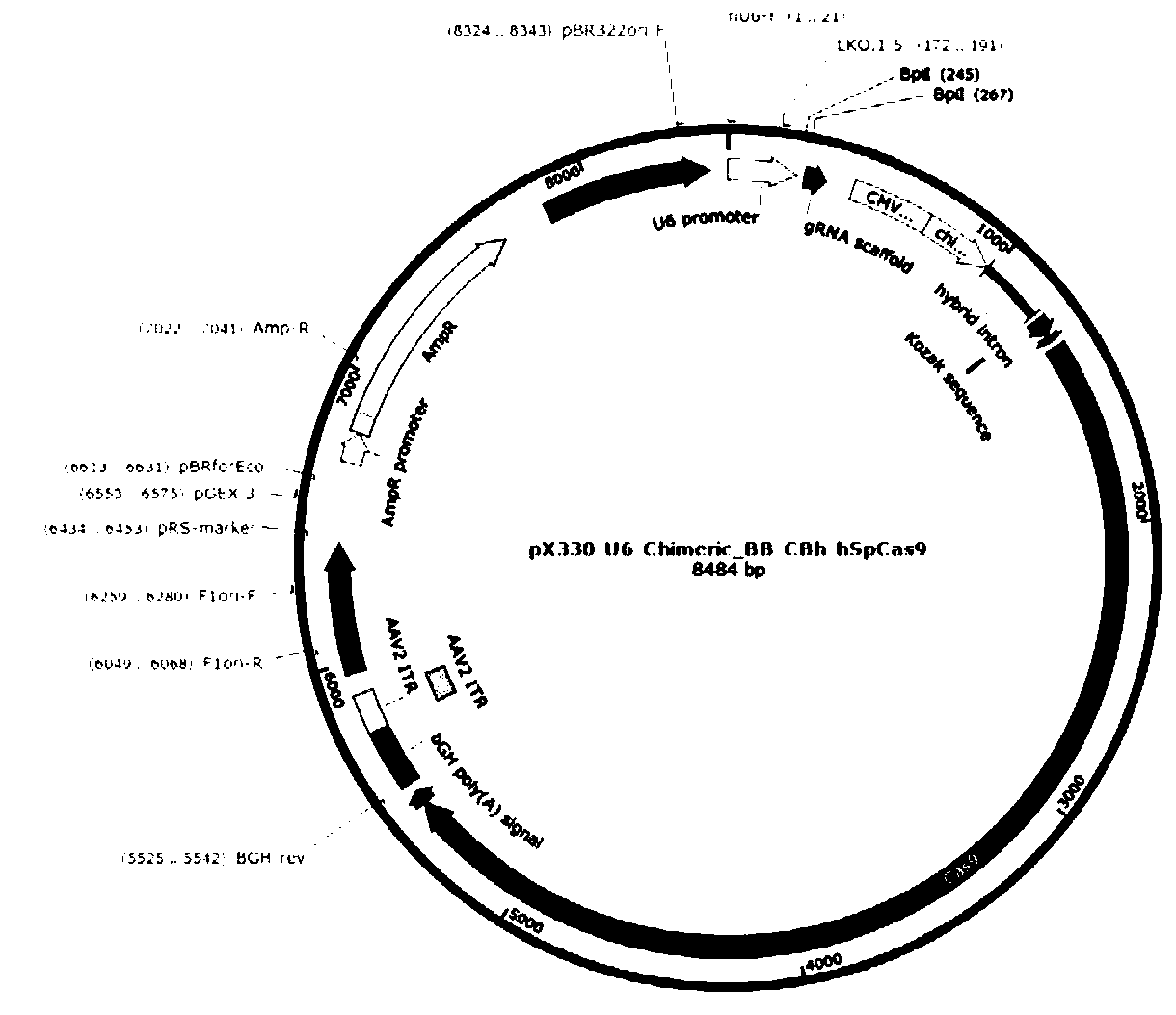
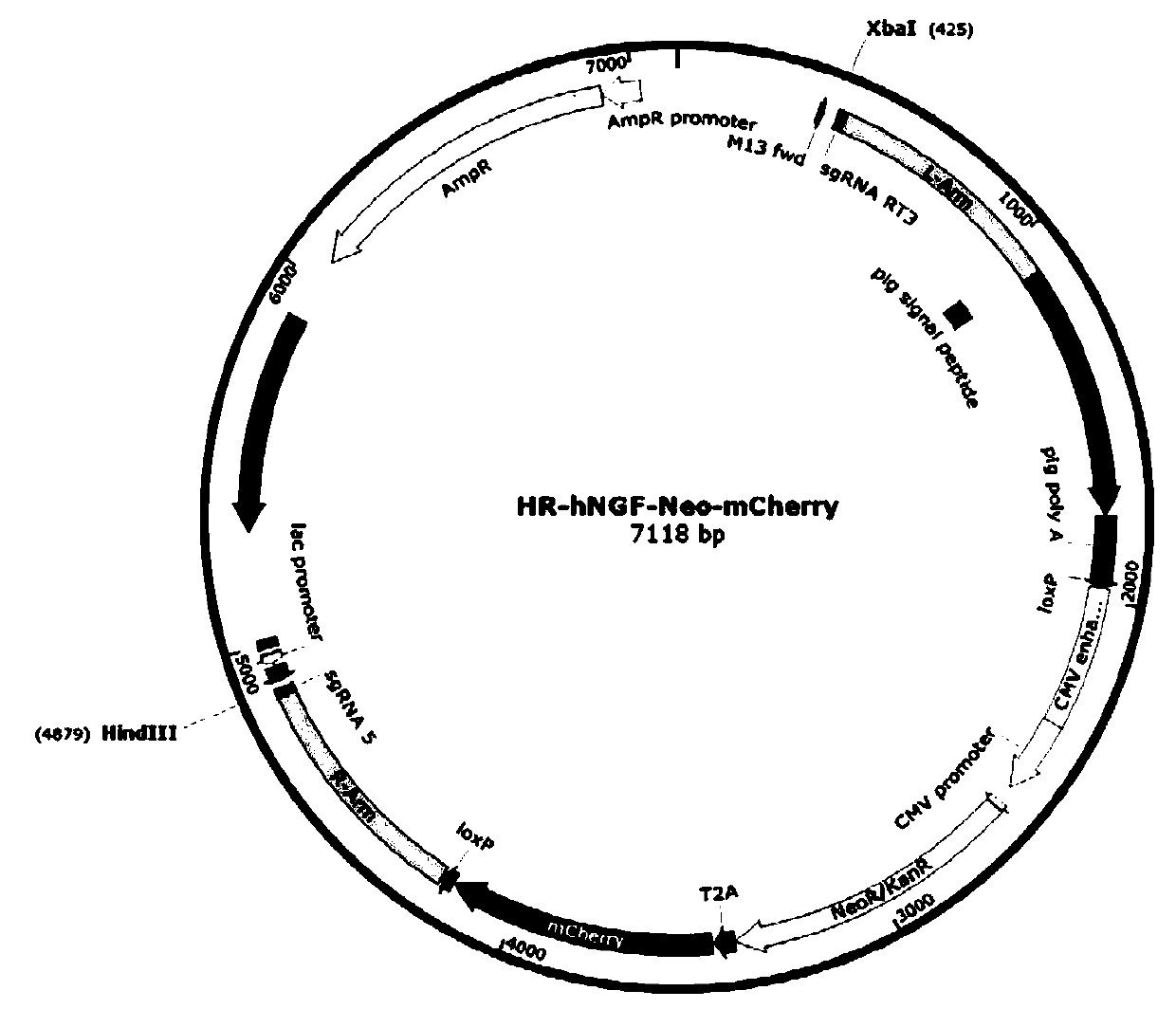
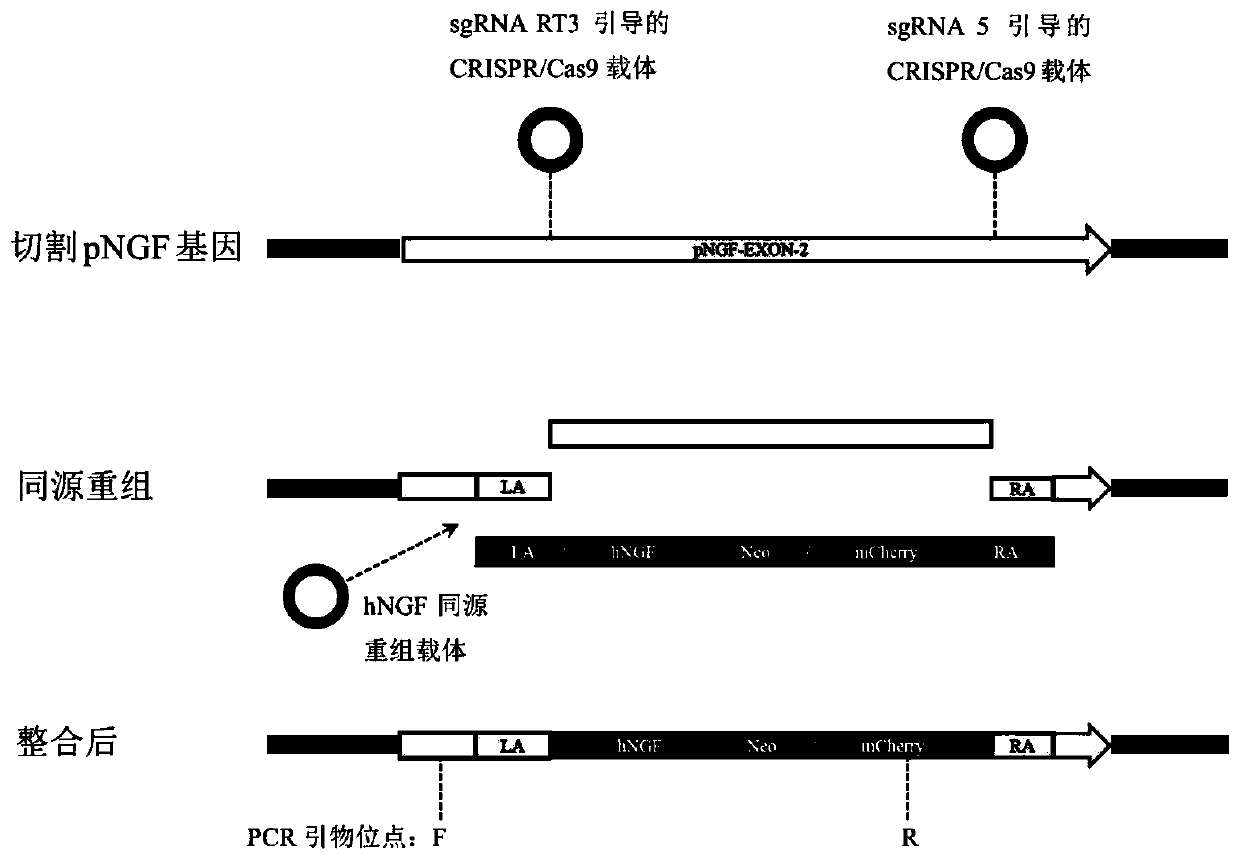
InactiveCN111500641AAvoiding Immunogenicity IssuesAvoid immunogenicityStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorSwine originMolecular biology
The invention discloses a preparation method of a human nerve growth factor transgenic pig. The method comprises the following steps: a, constructing a CRISPR / Cas9 system expression vector of a targeted pNGF gene exon, b, constructing a homologous recombinant vector for providing an hNGF gene, c, co-transfecting porcine ear fibroblasts with the CRISPR / Cas9 system expression vector and the homologous recombinant vector of the hNGF gene, and d, screening the transfected porcine ear fibroblasts to obtain a positive cell line, and cloning somatic cells to obtain the transgenic pig with the human nerve growth factor. According to the invention, by a fixed-point gene recombination mode, the hNGF gene is insert into a pig pNGF gene locus, therefore, the obtained transgenic pig with the human nerve growth factor can express the human nerve growth factor without expressing the pig nerve growth factor, so that the current situation that when the human NGF is collected in pig saliva, the human NGF is mixed in the pig saliva is avoided, the problem of immunogenicity when the pig is used for drug therapy is also avoided, and the transgenic pig is safer and more effective.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Novel use of multi-arm polyethylene glycol modifier and application of multi-arm polyethylene glycol modifier in l-asparaginasum modification
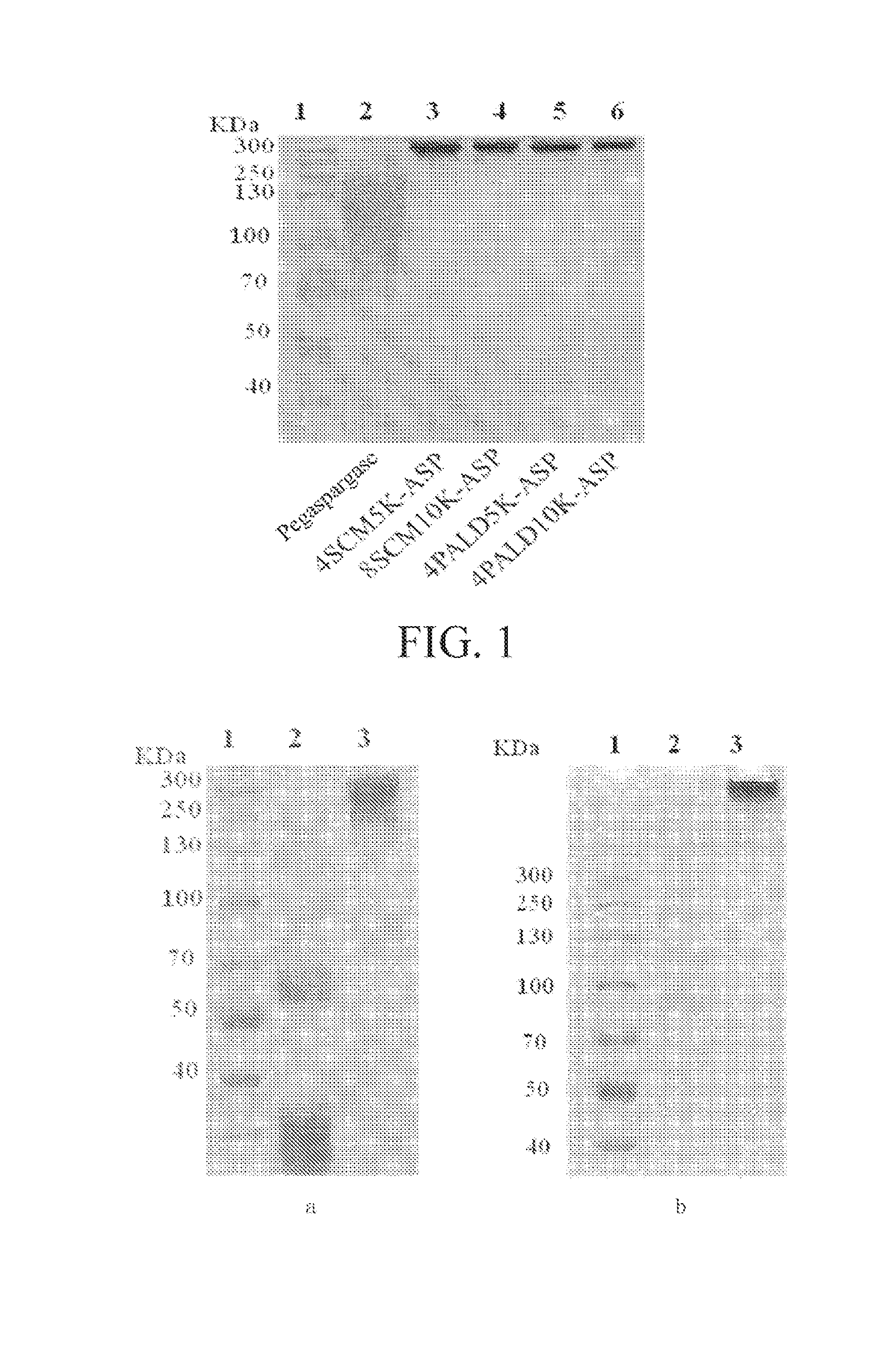
ActiveUS20170043028A1Improving immunogenicityInteractionPowder deliveryHydrolasesDepolymerizationBinding site
Methods for use of a multi-arm polyethylene glycol (PEG) modifier in modification of asparaginase. The described multi-arm PEG modifier enhances the subunit interaction of a multimeric protein to maintain the multimeric protein in a polymerized form, thereby improving the stability of the multimeric protein, maintaining the bioactivity of the multimeric protein, and reducing the probability of exposure of the antigen binding site after depolymerization of the subunits, so as to reduce the immunogenicity.
Owner:ZONHON BIOPHARMA INST +1
Method for preparing ephrin-B2 peripheral nerve injury repair promotion stent
The invention discloses a method for preparing a peripheral nerve injury repair promotion stent containing ephrin-B2 protein, which comprises the steps of using the autologous skin of a patient as a material for a neural stent and utilizing nerves at the injured position of autologous peripheral nerves of the patient to obtain Schwann cells used as a material for preparing the neural stent, wherein the material selection mode can control the function damage caused by material selection operation on the patient at a minimum level. The stent has the effect of effective guide on axonal regeneration, and can repair nerve defect with longer distance compared with the prior art. Compared with the repair of ruptured nerves, through the method, the stent is connected between broken ends to promote the repair of missing parts of peripheral nerves based on missing nerves between the broken ends after the peripheral nerves rupture, and the stent is higher in difficulty and clinical application value.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Method and device for assisting in gene transfer by utilizing electroporation
ActiveCN101955973AOptimal Electrical Pulse Stimulation ConditionsImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceElectroporation
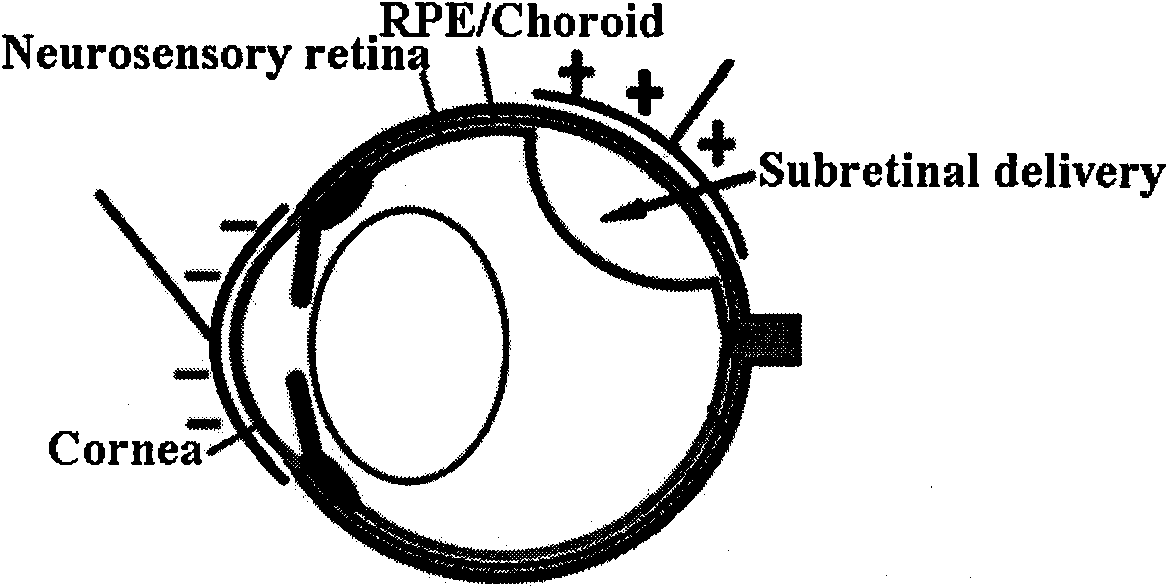
The invention belongs to the technical field of ophthalmology, and relates to a method and a device for assisting in gene transfer by utilizing electroporation. In the method and the device, a double-spoon electrode device is adopted, proper electric stimulation pulse conditions are determined, and green fluorescence protein-containing plasmids are transfected by a retinal pigment epithelial cell layer. The method of the invention has the advantages of directionally controlling the intraocular transfection of genes by using an electric field, simultaneously avoiding the shortcomings of cellular immunogenicity, potential pathogenicity, tumorigenicity and the like caused by viral gene transfer, reducing side injuries to eyeballs by adopting the double-spoon electrode device, simultaneously realizing the transfection of a plurality of plasmids, and compensating for the shortcomings of conventional methods, along with convenient operation, high efficiency, capability of being used as a reference for the gene transfer in ophthalmic researches, and the like.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
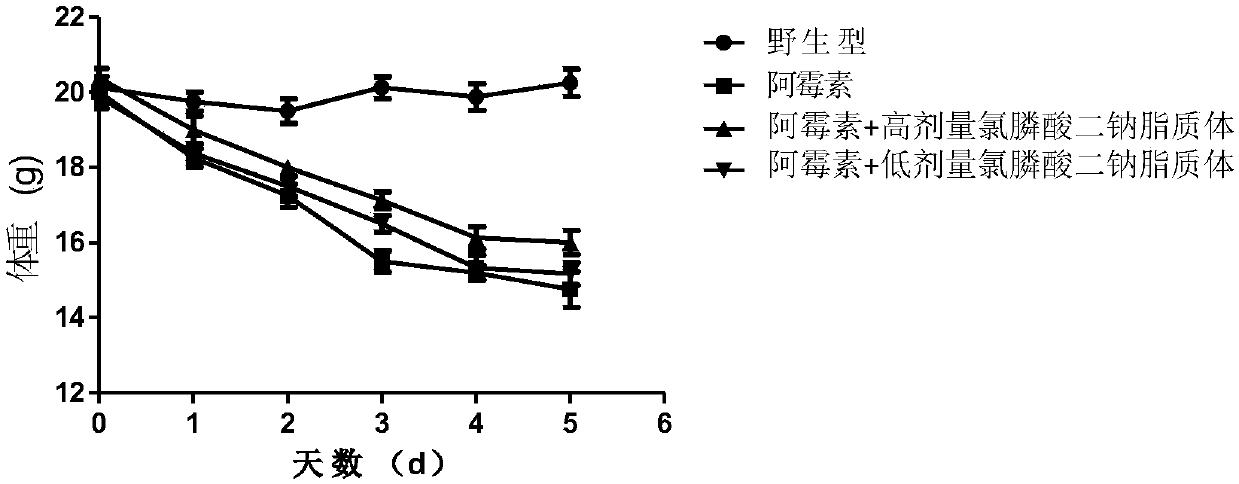
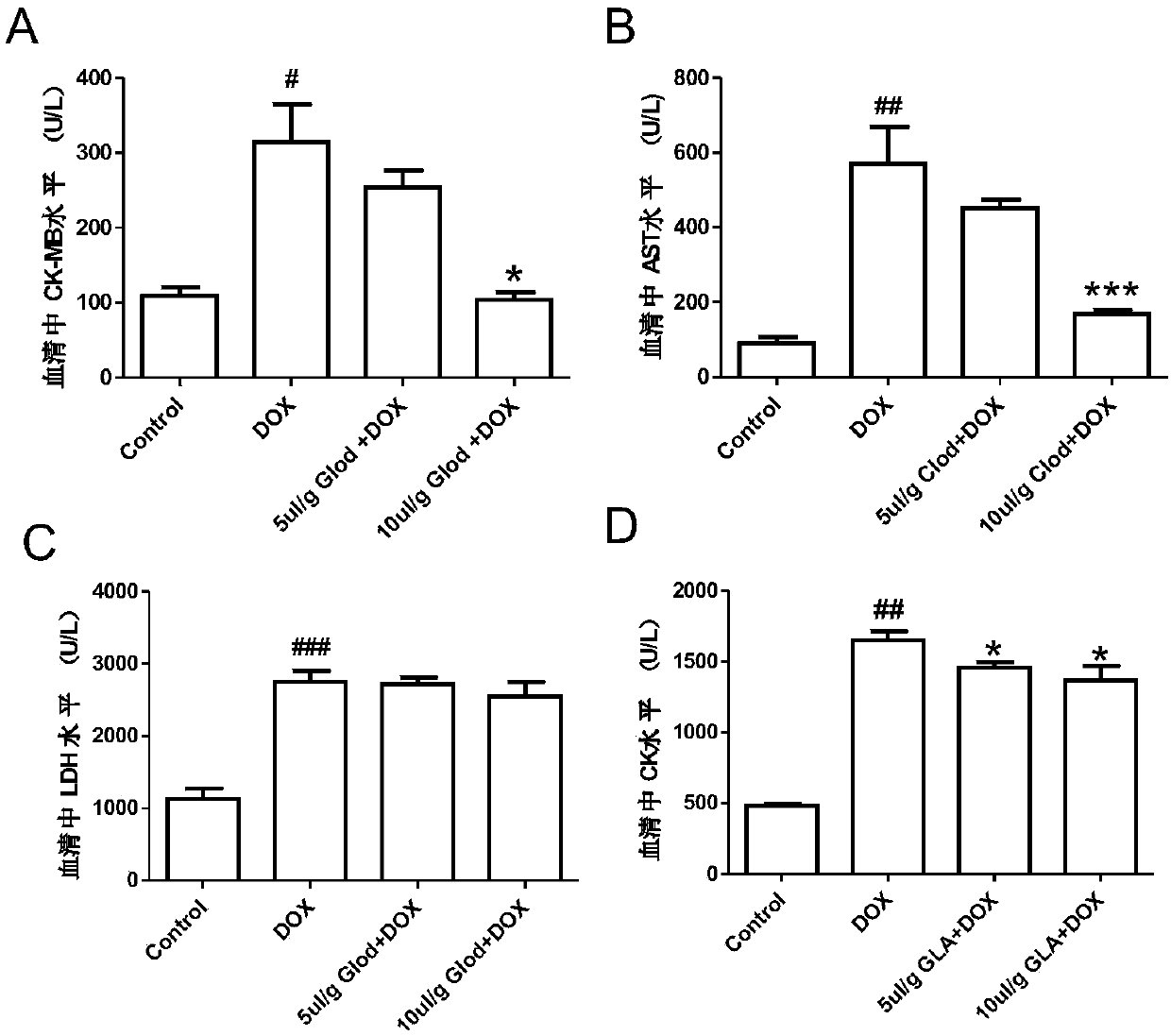
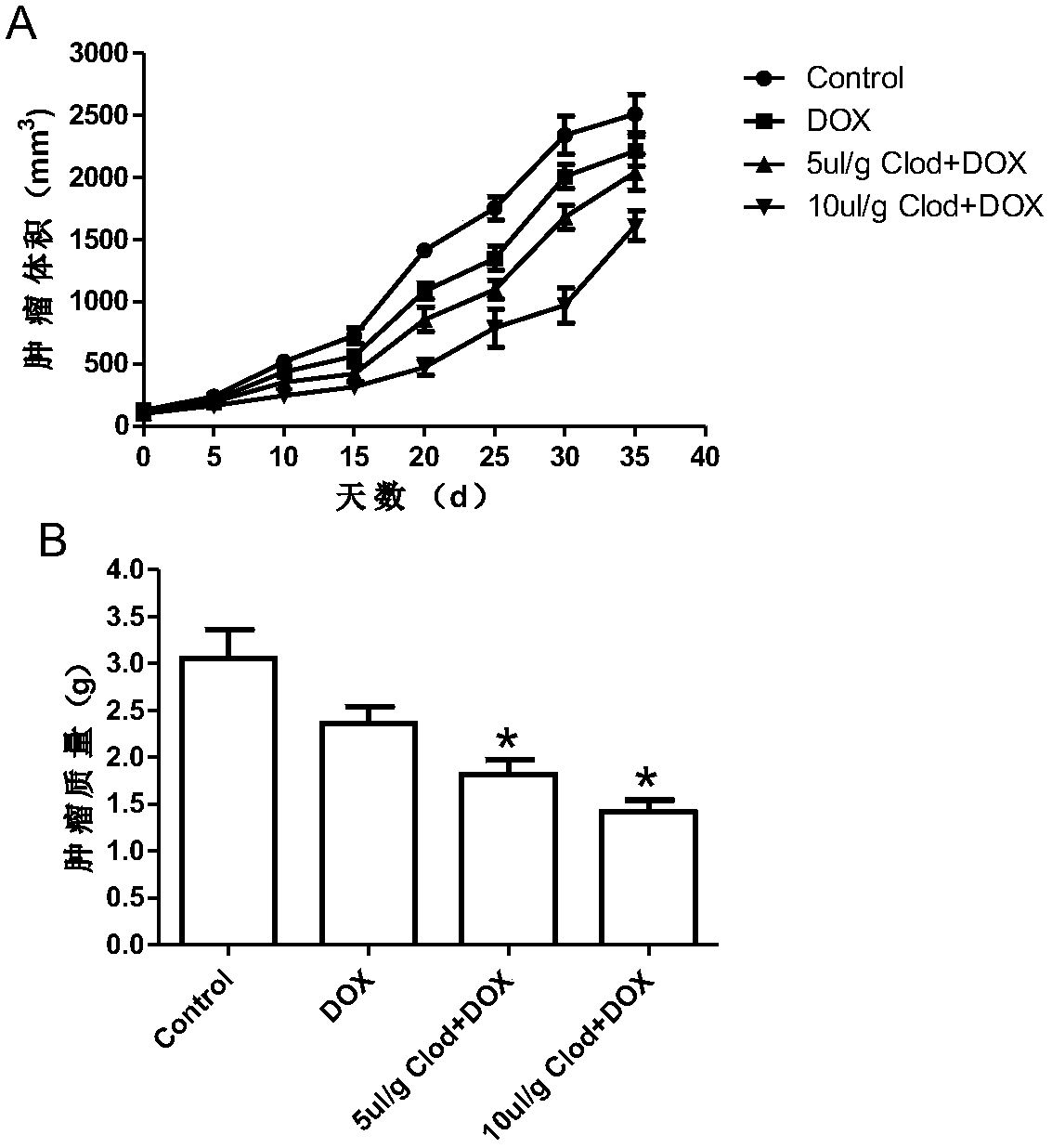
Application of liposomal clodronate on adjuvant treatment aspect of tumor doxorubicin chemotherapy
InactiveCN107854489AMature and reliable technologyQuality improvementOrganic active ingredientsInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsLipid filmCholesterol
The invention discloses application of liposomal clodronate on the adjuvant treatment aspect of tumor doxorubicin chemotherapy. After an appropriate amount of cholesterol and lecithin are mixed, a chloroform-methyl alcohol mixed solution is added, a rotary thin-film evaporation method is adopted to prepare a uniform dry lipid film, and then a phosphate buffer solution of disodium clodronate is added. The liposomal clodronate has the advantages that it is found that the prepared stable and efficient liposomal clodronate can reduce cardiotoxicity caused by doxorubicin and improve the breast cancer treatment effect of the doxorubicin.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
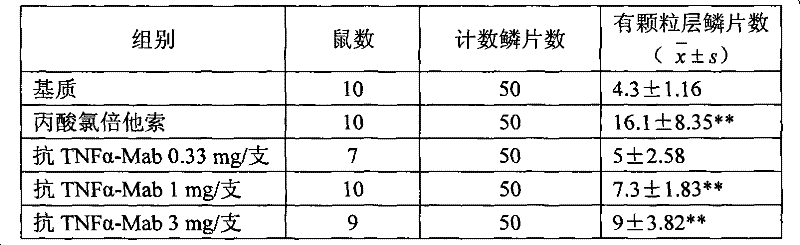
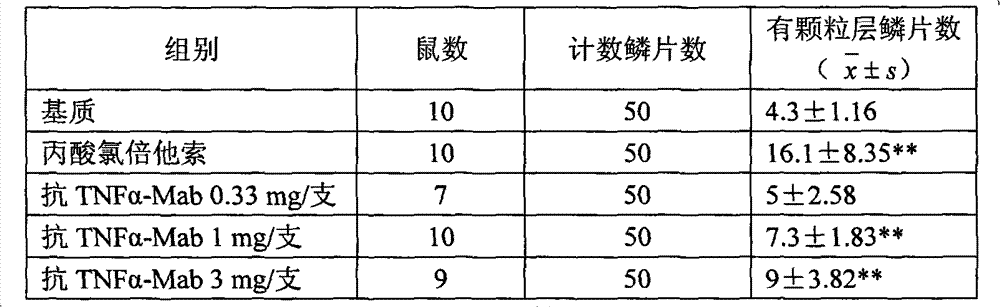
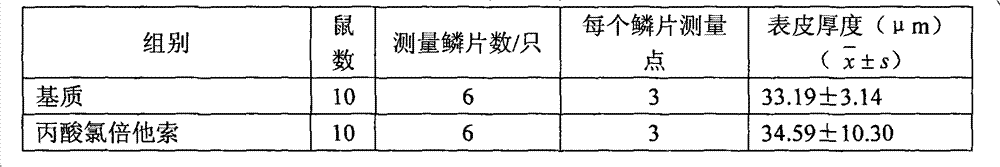
A kind of ointment for treating psoriasis based on anti-tnf-alpha monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN102274165AGood treatment effectAvoid immunogenicityAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryWhole bodyAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses an ointment based on an anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody used for treating psoriasis, and the ointment comprises the following ingredients by weight: 0.33-0.5 part of anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody, 1.5-2.5 parts of acryloyl dimethyl taurine ammonium / VP copolymer (AVC), 4-6 parts of polyethylene glycol4000, 4-6 parts of glycerol, 0.02-0.04 part of preservative and 85.127-89.98 parts of water. The ointment based on anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody used for treating psoriasis enables the therapeutic effect without adverse reaction caused by using the anti-TNF-alpha antibody by whole body.
Owner:赵宁
Alliin antigen and rabbit alliin antibody acquired through immune response of alliin antigen
ActiveCN108948185AAvoid immunogenicityImmunogenicSerum immunoglobulinsOvalbuminAdjuvantEuropean rabbit
The invention discloses a rabbit alliin antibody acquired through the immune response of the alliin antigen in the technical field of biological preparations. The rabbit alliin antibody contains the alliin antigen and a Freund's complete adjuvant, the alliin antigen and the Freund's complete adjuvant with equal amount are mixed to obtain an adjuvant antigen, the alliin antigen is injected into thebody of a rabbit, and the alliin antibody is obtained after the immune response. According to the alliin antigen and the rabbit alliin antibody, the immunogenicity of alliin is solved, the antibody is acquired through the immunization of the rabbit, and the alliin antibody can be applied to research of the concentration detection, in-vivo distribution and pharmacological action mechanisms of alliin and has important application values in the foundation and clinical researches of alliin.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
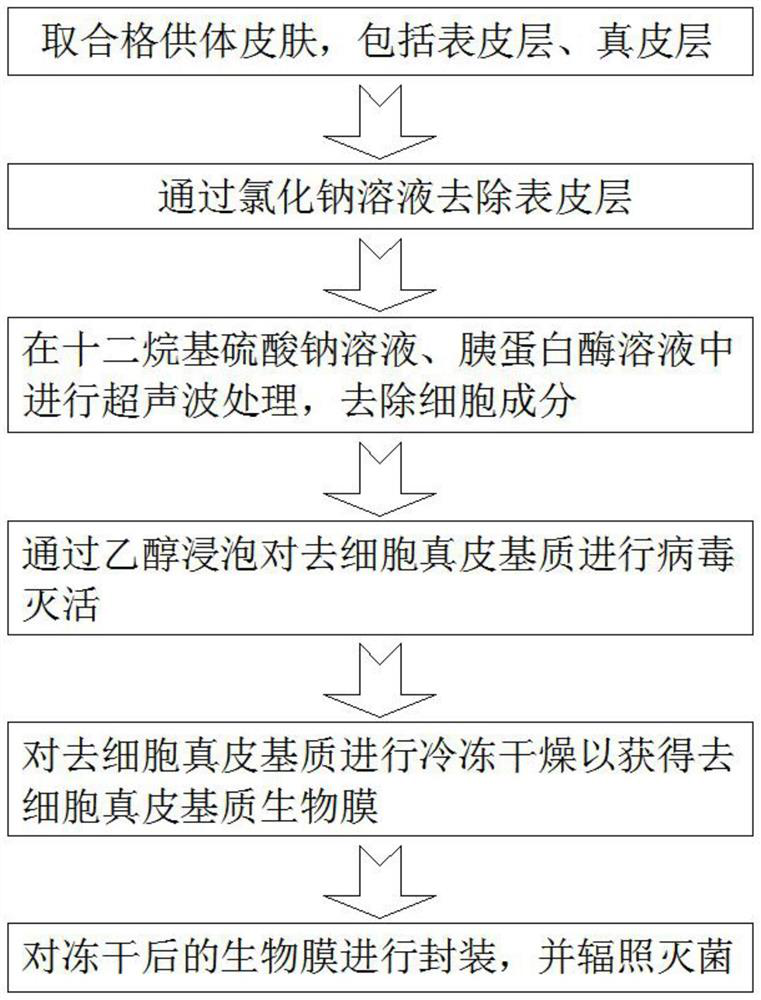
Preparation method of biological membrane for dental implantation
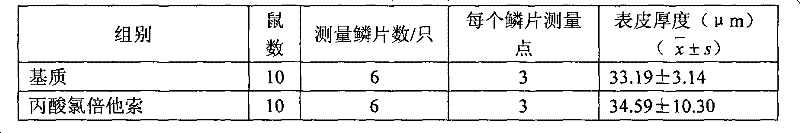
The invention discloses a preparation method of a biological membrane for dental implantation, which comprises the following steps: taking qualified donor skin as a raw material, removing subcutaneous tissues, and taking a faulted skin graft with a certain thickness; treating the faulted skin graft in a sodium chloride solution, and removing an epidermal layer to obtain a dermal matrix; performing ultrasonic treatment on the dermal matrix in a sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) solution and a trypsin solution, crushing and removing cell components; taking the acellular dermal matrix, and soaking the acellular dermal matrix in ethanol to carry out virus inactivation; performing freeze drying to obtain an acellular dermal matrix biological membrane; and packaging the freeze-dried biological membrane, and carrying out irradiation sterilization. According to the invention, an extracellular matrix repairing material can be obtained, the immunogenicity of a heterogeneous material and the degradability of a synthetic collagen membrane are overcome, and an extracellular matrix biological material is provided for dental implantation.
Owner:山西奥瑞生物材料有限公司
Method for preparing tissue-engineered blood vessels based on 3D bioprinting technology
ActiveCN104490489BGood biocompatibilityStrong mechanical propertiesCell culture supports/coatingSkeletal/connective tissue cellsDiseaseThrombus
The invention provides a method for preparing a tissue engineering blood vessel based on a 3D (3-Dimensional) bioprinting technology. The method comprises the following steps:alternately printing a blood vessel shape by virtue of a high-polymer material and a human renascent skin fiber cell column, and removing the high-polymer material after fusion to structure a tissue engineering blood vessel; filling late-outgrowth endothelial progenitor cells into the blood vessel, and performing in-vitro dynamic culturing for 7 days in a bioreactor to obtain a differentiated tissue engineering blood vessel, wherein the high-polymer material is one of pluronic F127, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), methyl cellulose and sodium alginate. The blood vessel obtained by the method is high in biocompatibility and higher in mechanical property, thrombus formation resistant and platelet adhesion resistance, and can be used for repairing and replacing a damaged or disease blood vessel.
Owner:江苏知聚知识产权服务有限公司
Ointment based on anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody used for treating psoriasis
ActiveCN102274165BGood treatment effectAvoid immunogenicityAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryWhole bodyPreservative
The invention discloses an ointment based on an anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody used for treating psoriasis, and the ointment comprises the following ingredients by weight: 0.33-0.5 part of anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody, 1.5-2.5 parts of acryloyl dimethyl taurine ammonium / VP copolymer (AVC), 4-6 parts of polyethylene glycol4000, 4-6 parts of glycerol, 0.02-0.04 part of preservative and 85.127-89.98 parts of water. The ointment based on anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody used for treating psoriasis enables the therapeutic effect without adverse reaction caused by using the anti-TNF-alpha antibody by whole body.
Owner:赵宁
Affinity toxin targeting molecule of HPV16E7 affinity loaded granzyme B and application thereof
PendingCN110862459AAvoid immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsHeterologousPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses an affinity toxin targeting molecule of HPV16E7 affinity body loaded granzyme B and an application thereof, the granzyme B loaded by the affinity toxin targeting molecule belongs to endogenous protein, the immunogenicity problem caused by heterologous protein is avoided, and the affinity toxin targeting molecule has a wider application prospect; in addition, the invention also provides the application of the affinity toxin targeting molecule as a drug and the like.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method for B cell CD 22 extracellular inhibitive peptide fragment B2285 vaccines
InactiveCN101897961BAvoid immunogenicityLess toxic side effectsPeptidesCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsImmunologic disordersAutoantibody
The invention provides a preparation method for B cell CD 22 extracellular peptide fragment B2285 vaccines. Sequential eight amino acids from the 85th to the 93rd starting at an amino terminal in a mice CD 22 molecule amino acid sequence, specifically in a sequence of Lys- Thr- Glu- Lys- Asp-Pro- Glu- Ser- Glu, are selected. The sequence is similar to the sequence of Lys- Asp- Gly- Lys- Val- Pro- Ser- Glu, having the sequential eight amino acids from the 81st to the 88th starting at the amino terminal in a human CD 22 molecular amino acid sequence, is located at the same functional region in a spatial structure, and has high homology. A prepared vaccine or a drug composite containing B2285 has the functions of inhibiting B cell proliferation, activating and generating antibody per se, can be applicable to treating immunologic diseases involved or mediated B cells such as dilated cardiomyopathy testing positive in an anti-myocardial antibody, systemic lupus erythematosus with a positive antibody per se, and the like.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
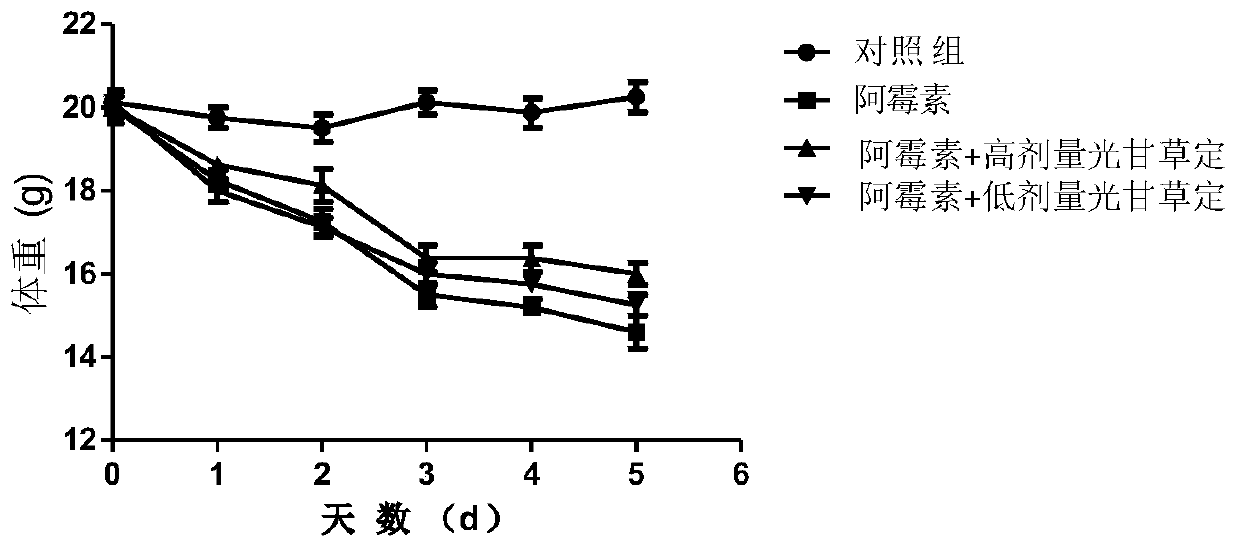
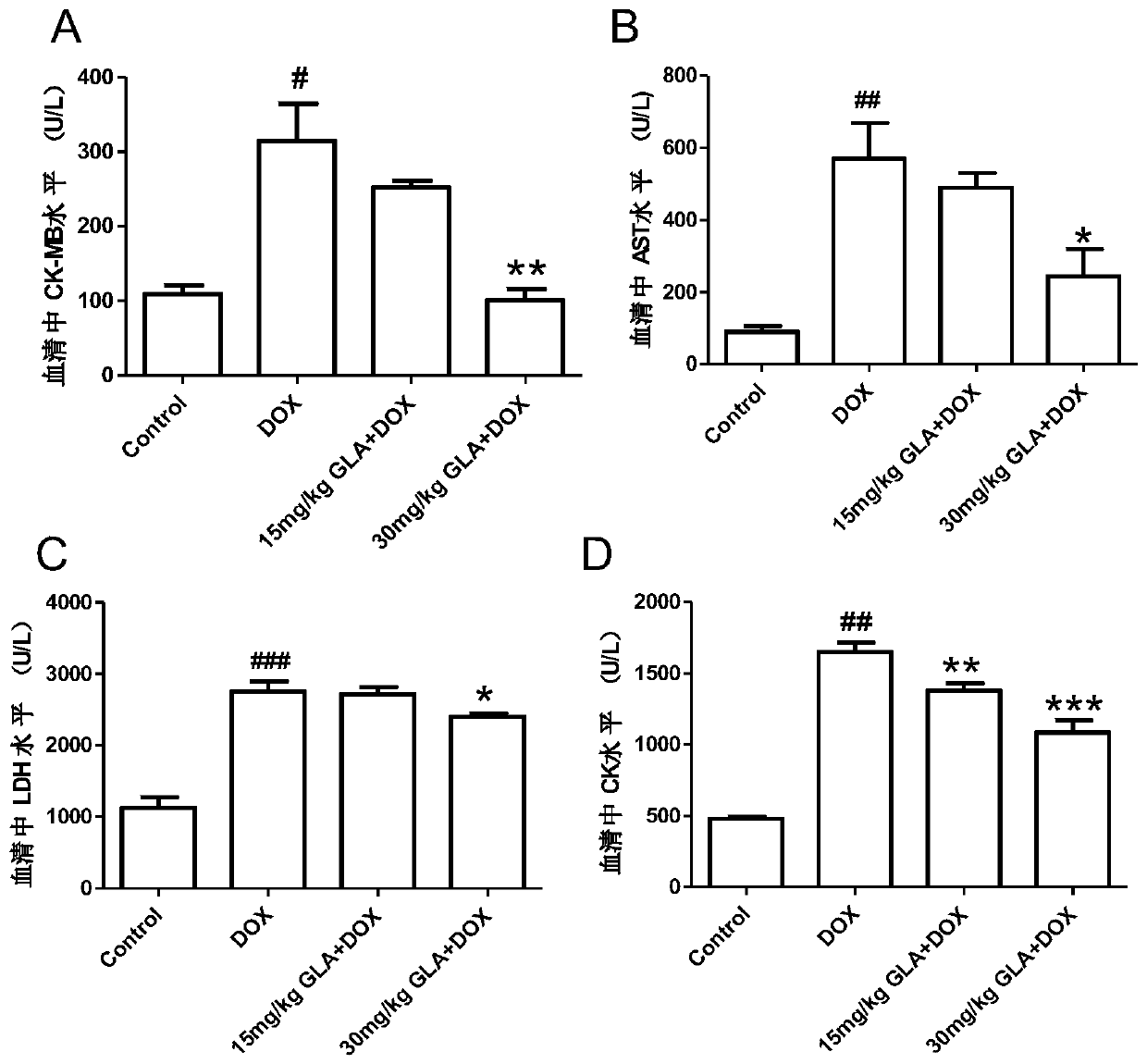
Application of glabridin liposomes in the preparation of drugs for the treatment of acute (chronic) cardiotoxicity induced by doxorubicin
InactiveCN107898780BMature and reliable technologyQuality improvementOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLipid filmCholesterol
The invention discloses an application of glabridin lipidosome in preparing a drug for treating acute (chronic) cardiotoxicity induced by adriamycin. An appropriate amount of cholesterol, lecithin andglabridin are mixed, a chloroform-methanol mixed solution is added, a uniform lipid dry membrane is prepared by adopting a rotary film evaporation method, then a phosphoric acid buffer salt solutionwith a PH of 7 is added, the lipid membrane is sufficiently swelled and hydrated and is ultrasonically dispersed for 5 min under ultrasonic power of 400 W, and the glabridin lipdosome is obtained. Byvirtue of pretreatment of glabridin lipidosome for C57BL / 6 mice, then the mice are injected with adriamycin, and a myocardial enzyme level is reduced; and the weight loss of the mice is gradually reduced, which proves that the glabricin can alleviate the cardiotoxicity induced by the adriamycin and is safe and low in toxicity to normal cells of the human body.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
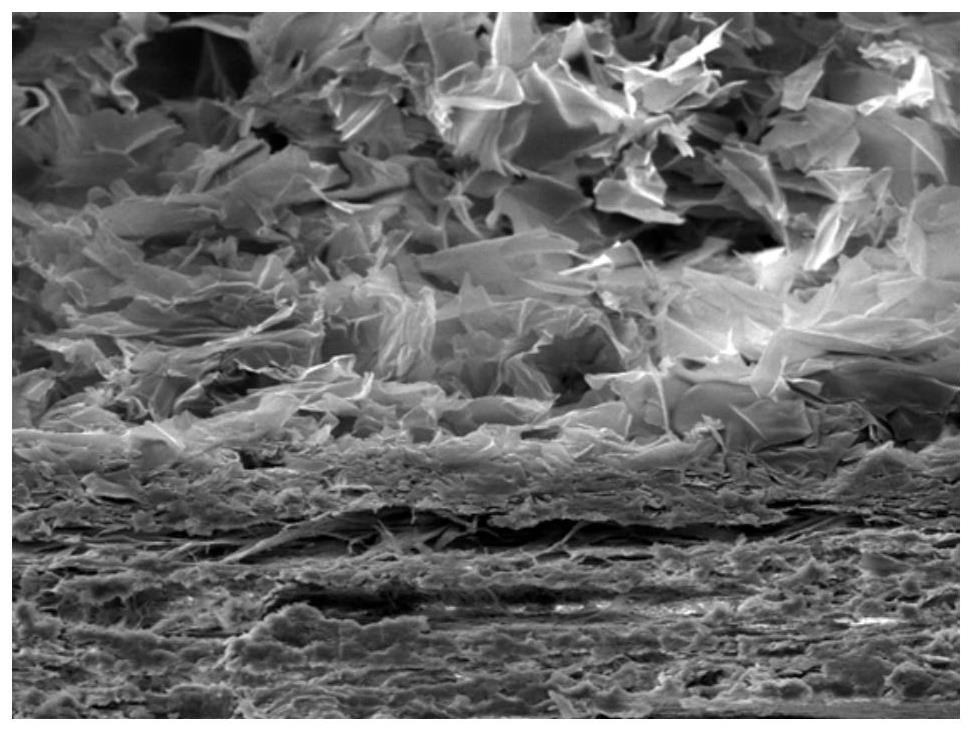
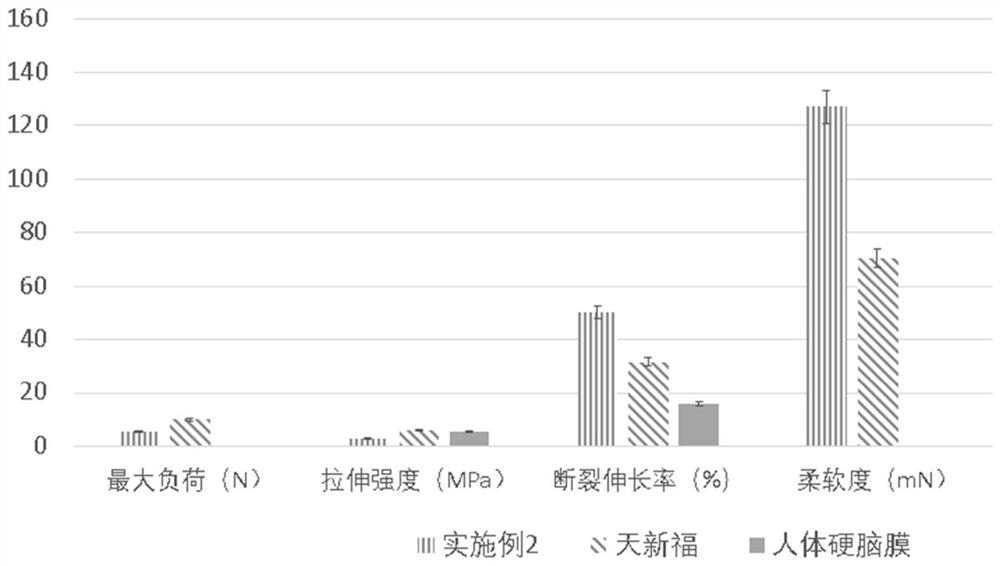
Degradable artificial dura mater with double-layer structure and preparation method of degradable artificial dura mater
The invention relates to a degradable artificial dura mater with a double-layer structure and a preparation method of the degradable artificial dura mater, and relates to the technical field of biomedical materials. The degradable artificial dura mater with the double-layer structure comprises a stent layer and a bonding layer, the thickness of the artificial dura mater is 0.5-1.0 mm, the stent layer is made of recombinant human-like collagen, and the bonding layer is made of mussel mucin. According to the degradable artificial dura mater with the double-layer structure, the recombinant human-like collagen and the mussel mucin serve as main raw materials, and the artificial dura mater is a non-animal-derived material, so that the immunogenicity problem can be avoided; the artificial dura mater disclosed by the invention has a double-layer structure, degradability, good flexibility, adhesion, mechanical property and biocompatibility; meanwhile, according to the preparation method of the artificial dura mater, recombinant human-like collagen and mussel mucin serve as main raw materials, the degradable artificial dura mater of the double-layer structure is prepared through the processes of dissolution, crosslinking, dialysis, mixing, coating, drying and the like, the process operation is simple, and the method is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:西安臻研生物科技有限公司
Alliin antibody prepared through immunization of guinea pigs
ActiveCN108948192AAvoid immunogenicityImmunogenicSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against plantsPharmacological actionClinical research
The invention discloses an alliin antibody prepared through the immunization of guinea pigs. The alliin antibody contains an alliin antigen and a Freund's complete adjuvant, the alliin antigen and theFreund's complete adjuvant with equal amount are mixed to obtain an adjuvant antigen, the alliin antigen is injected into the body of a guinea pig, and the alliin antibody is obtained after the immune response. According to the alliin antibody, the immunogenicity of alliin is solved, the antibody is acquired through the immunization of the guinea pigs, and the alliin antibody can be applied to research of the concentration detection, in-vivo distribution and pharmacological action mechanisms of alliin and has important application values in the foundation and clinical researches of alliin.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com