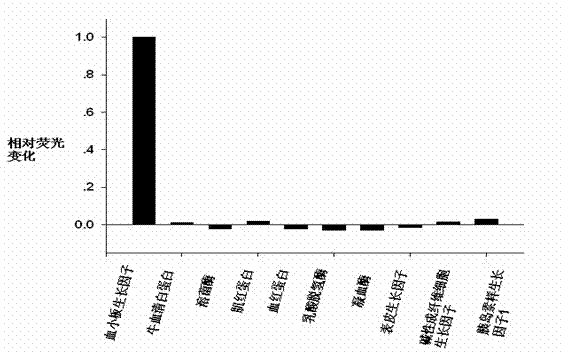
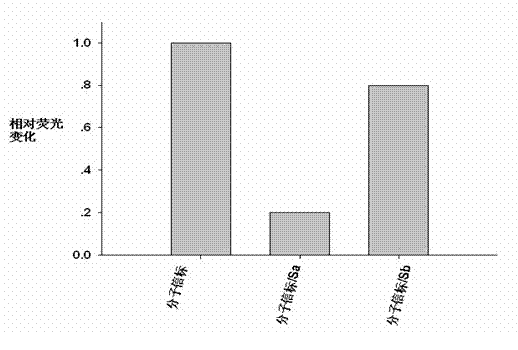
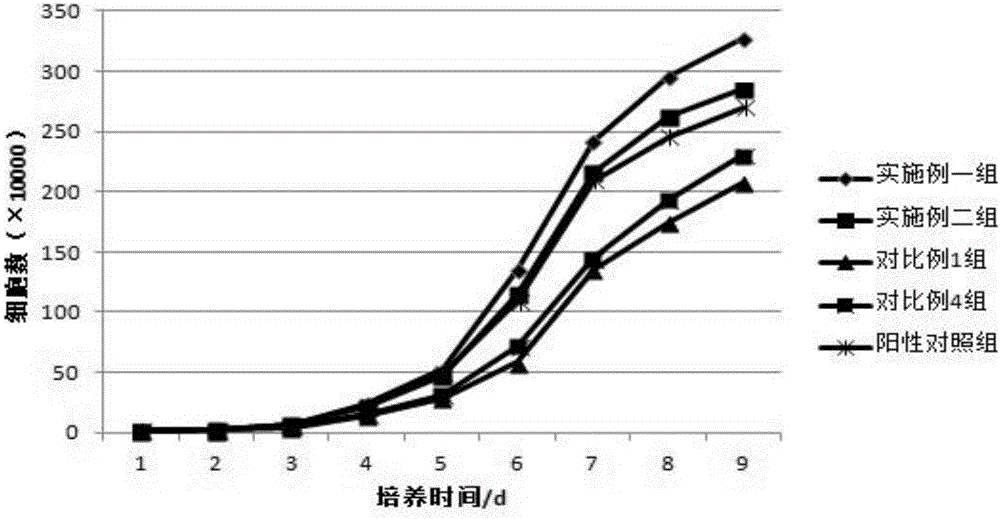
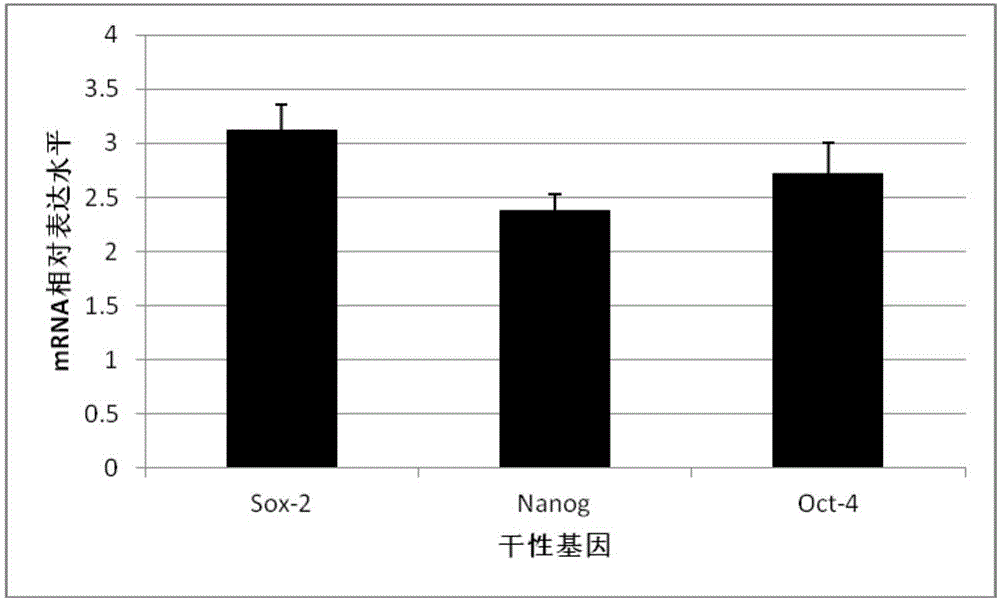
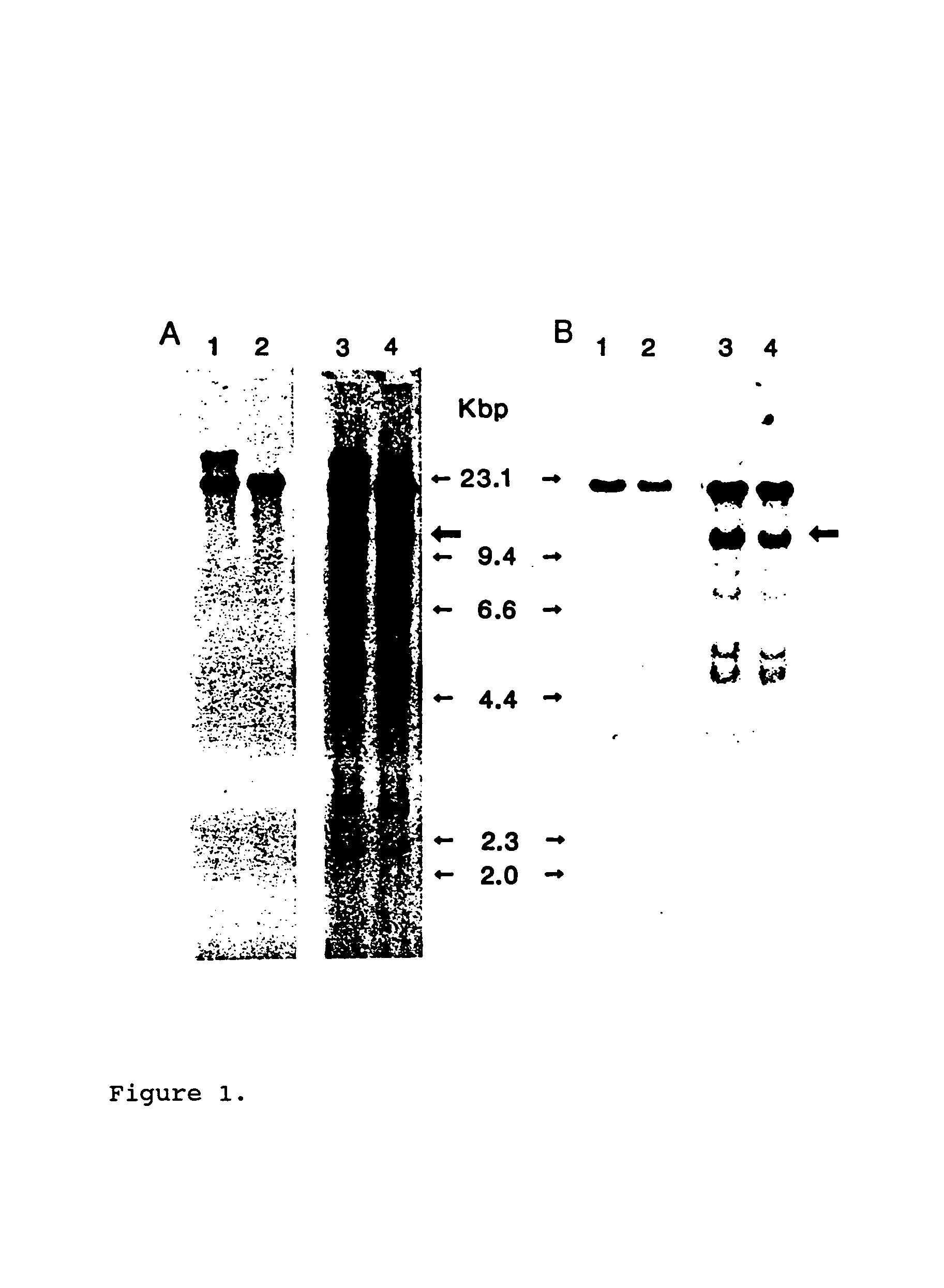
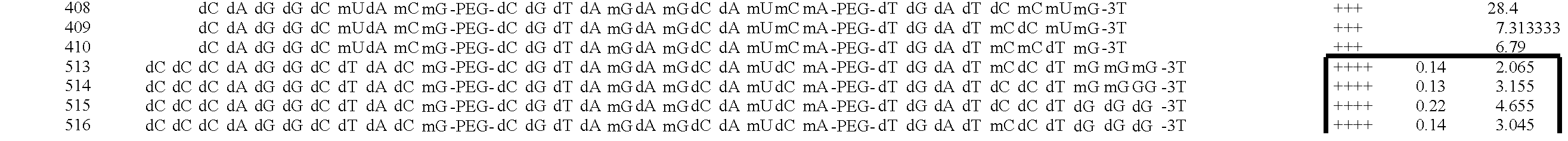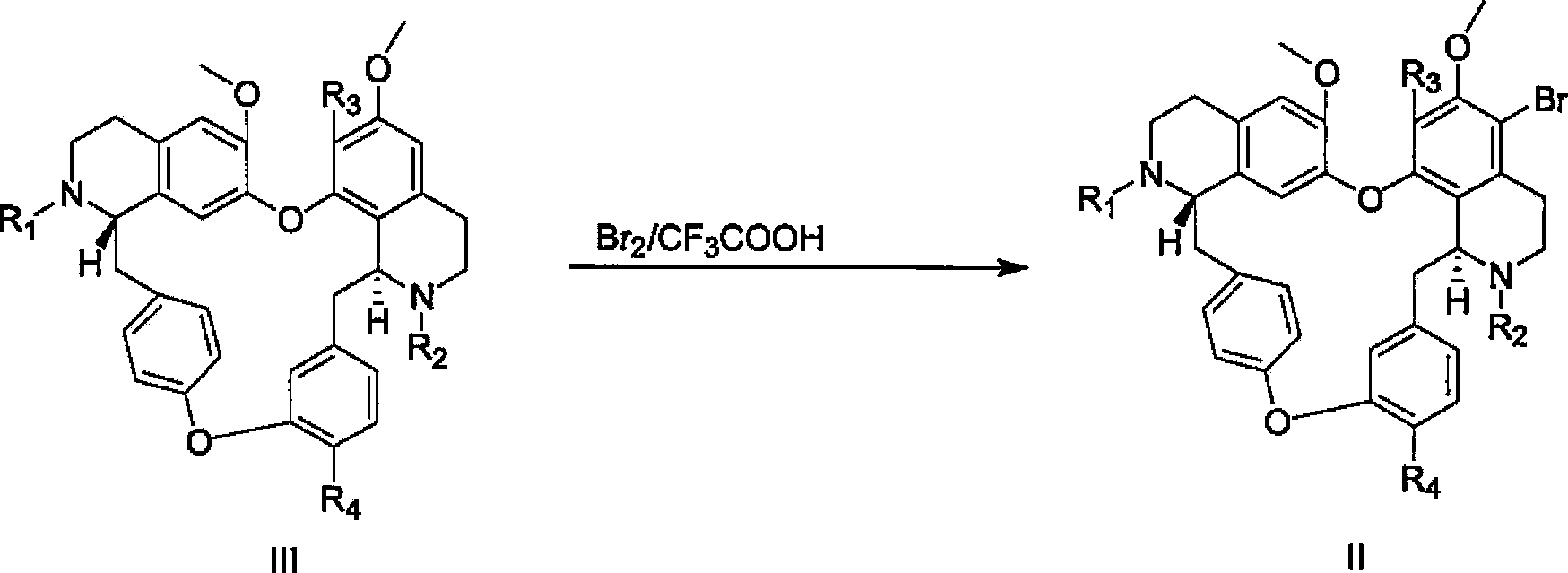Patents
Literature
98 results about "Platlet-Derived Growth Factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
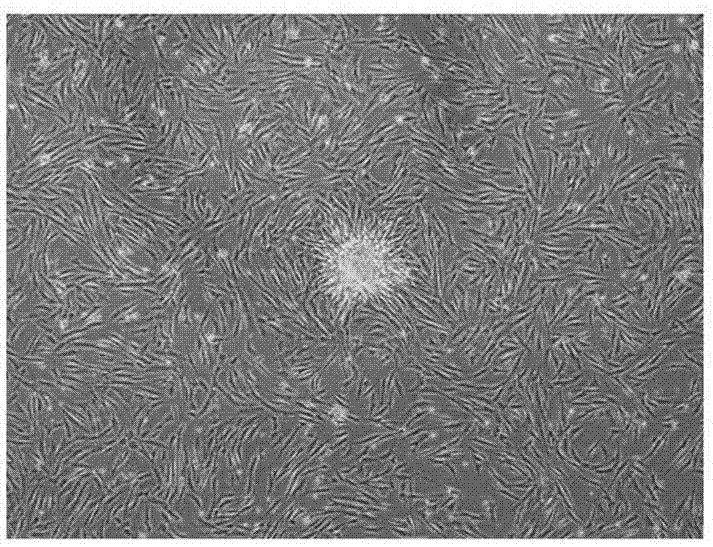
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is one of numerous growth factors that regulate cell growth and division.
Particulate acellular tissue matrix
A method of processing an acellular tissue matrix to give a particulate acellular tissue matrix includes: cutting sheets of dry acellular tissue matrix into strips; cryofracturing the dry acellular tissue matrix strips at cryogenic temperatures; separating the resulting particles by size at cryogenic temperatures; and freeze drying the fraction of particles desired size to remove any moisture that may have been absorbed to give a dry particulate acellular tissue matrix. Rehydration of the dry particulate acellular tissue matrix may take place just prior to use. The particulate acellular tissue may be applied to a recipient site, by way of injection, spraying, layering, packing, in-casing or combinations thereof. The particulate acellular tissue may further include growth and stimulating agents selected from epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, nerve growth factor, keratinocyte growth factor, platelet derived growth factor, vasoactive intestinal peptide, stem cell factor, bone morphogetic proteins, chondrocyte growth factor and combinations thereof. Other pharmaceutically active compounds may be combined with the rehydrated particulate material including: analgesic drugs; hemostatic drugs; antibiotic drugs; local anesthetics and the like to enhance the acceptance of the implanted particulate material. The particulate material product may also be combined with stem cells selected from mesenchymal stem cells, epidermal stem cells, cartilage stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells and combinations thereof.
Owner:LIFECELL
Serum-free culture medium for mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN102827807AAvoid instabilityClear chemical compositionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell phenotypeSodium bicarbonate
The invention relates to the field of biology, and discloses a serum-free culture medium which essentially comprises an IMDM (Iscove Modified Dulbecco Medium), L-glutamine, sodium bicarbonate, Hepes, recombinant human insulin, recombinant human transferrin, recombinant human albumin, 2-mercaptoethanol, protocatechuic acid, lipid, amino acid, vitamins, trace elements, Pluronic F-68, hydrocortisone, vitamin C, bonding amine or recombinant human fibronectin, progesterone, putrescine, heparin, serotonin, epidermal growth factors (EGFs), b-fibroblast growth factors (FGF), platelet derive growth factor (PDGF)-BB and insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I. The serum-free culture medium is clear in chemical components, free from animal sources and serum and safe and ideal in cell cultivation and avoids the doped animal components and unstable batches, and the results of the cultured mesenchymal stem cells show that the total cellular score, the cell phenotype and the secretory cell factors are normal, so that the serum-free culture medium has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:内蒙古干细胞医学工程技术研究中心
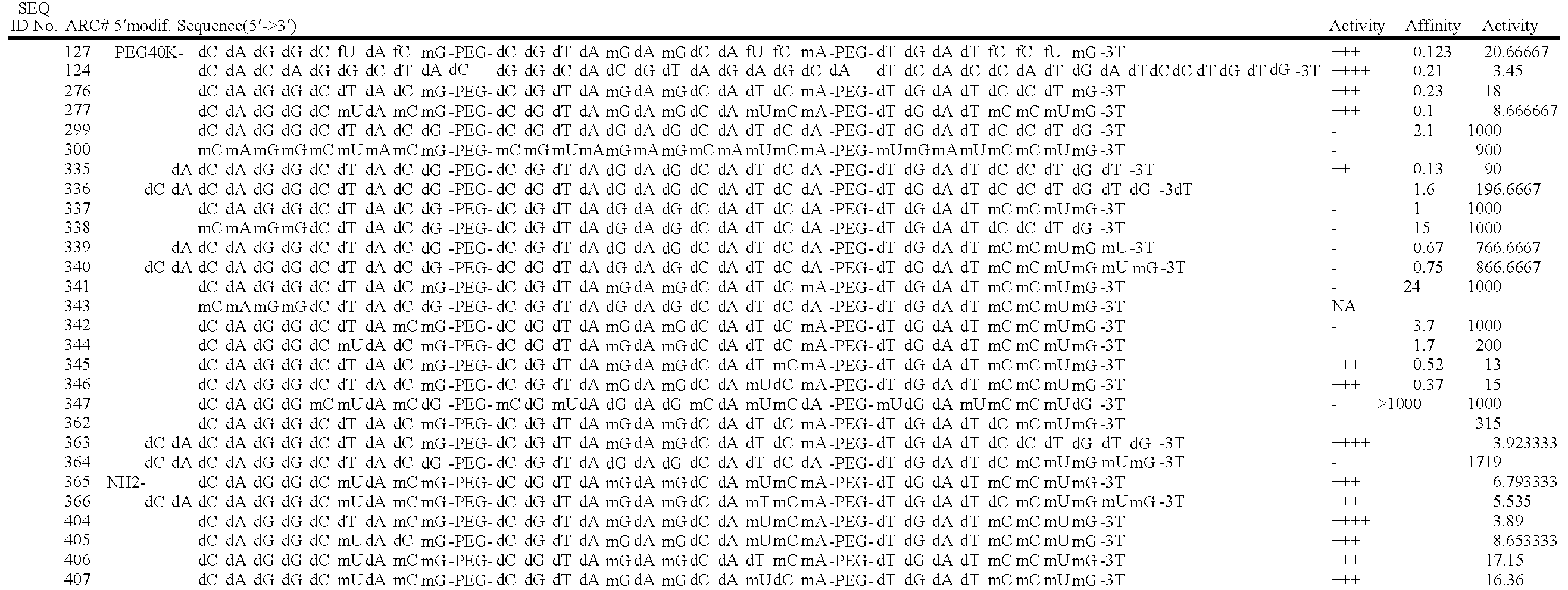
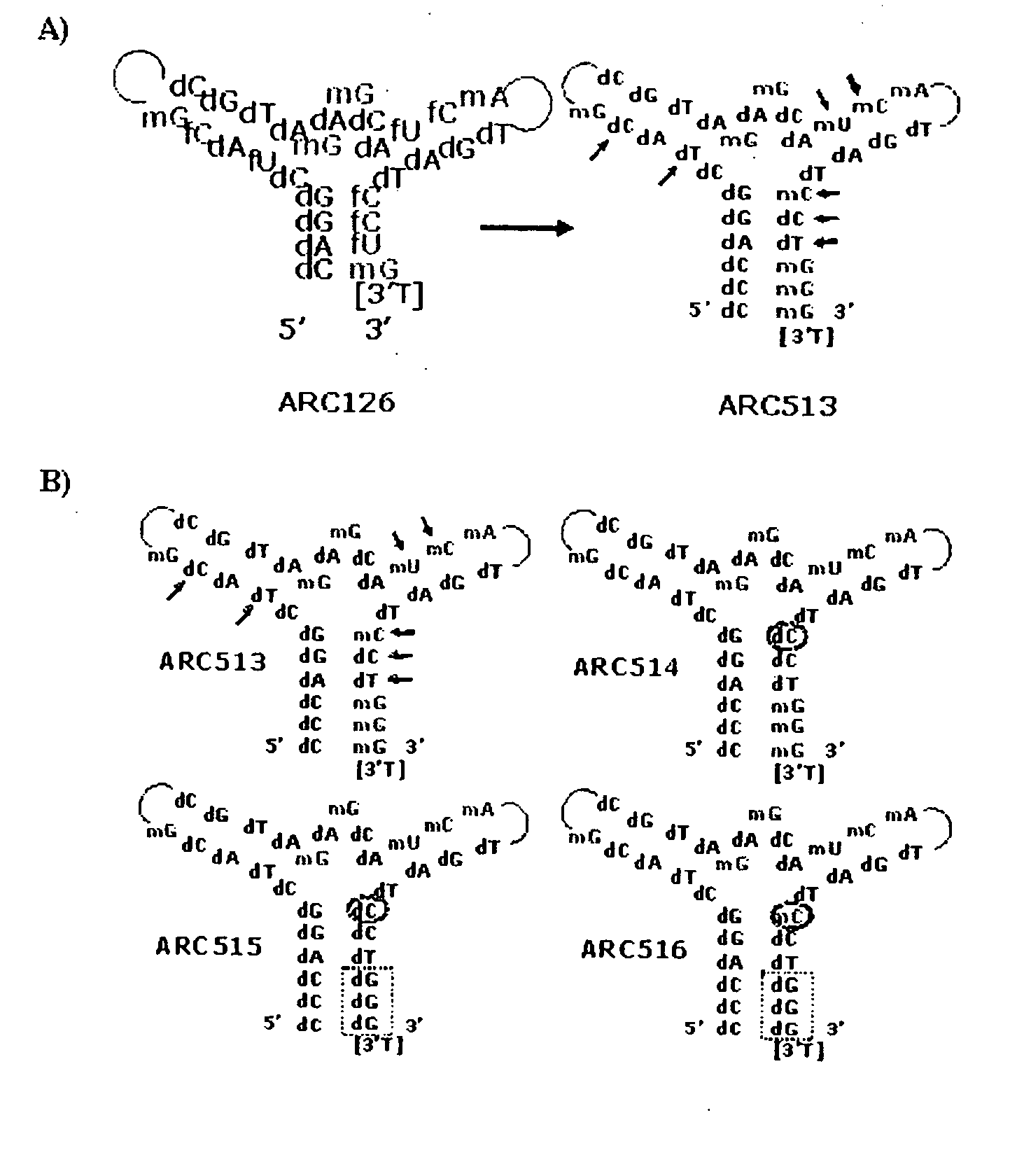
Stabilized aptamers to platelet derived growth factor and their use as oncology therapeutics
Materials and methods are provided for producing and using aptamers useful as oncology therapeutics capable of binding to PDGF, PDGF isoforms, PDGF receptor, VEGF, and VEGF receptor or any combination thereof with great affinity and specificity. The compositions of the present invention are particularly useful in solid tumor therapy and can be used alone or in combination with known cytotoxic agents for the treatment of solid tumors. Also disclosed are aptamers having one or more CpG motifs embedded therein or appended thereto.
Owner:ARCHEMIX CORP
Bifunctional novel periodontal guided tissue regeneration membrane with sandwich structure and preparation method thereof and application
InactiveCN107456607AGood biocompatibilityImprove biological activityTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberMicrosphere
The invention relates to a bifunctional novel periodontal guided tissue regeneration membrane with a sandwich structure and a preparation method thereof and application. The bifunctional novel periodontal guided tissue regeneration membrane comprises an inner layer, an intermediate layer and an outer layer. The inner layer is a polycaprolactone / silk fibroin / mesoporous bioactive glass microsphere fiber membrane; the intermediate layer is a polycaprolactone / silk fibroin fiber membrane; and the outer layer is a polycaprolactone / silk fibroin fiber membrane loading platelet-derived growth factors. The bifunctional novel periodontal guided tissue regeneration membrane is of a three-layer-membrane structure and can promote periodontal soft tissue regeneration and have functions of periodontal hard tissue and soft tissue dual regeneration and repair; the bifunctional novel periodontal guided tissue regeneration membrane can also effectively prevent the invasion of gingival epithelial cells to a bone defect area and provide a space for regeneration and reconstruction of bone tissues. In addition, the periodontal guided tissue regeneration membrane also has good biocompatibility, biodegradability and biological activity.
Owner:STOMATOLOGY AFFILIATED STOMATOLOGY HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Serum-free media and their uses for chondrocyte expansion
InactiveUS20070292949A1Enhance cell attachmentIncreased proliferationCulture processSkeletal disorderInterleukin 6Lipid formation
The present invention provides defined serum-free cell culture media useful in culturing fibroblasts, especially articular chondrocytes, that avoid problems inherent in the use of serum-containing media. The defined media comprise platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), chemically defined lipids, oncostatin M (OSM), interleukin-6 (IL-6), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), or combinations of these compounds. In another aspect, the present invention also provides tissue culture methods that comprise incubating chondrocytes in the defined serum-free media. The methods enhance attachment and proliferative expansion of chondrocytes seeded at low density while maintaining their redifferentiation potential.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
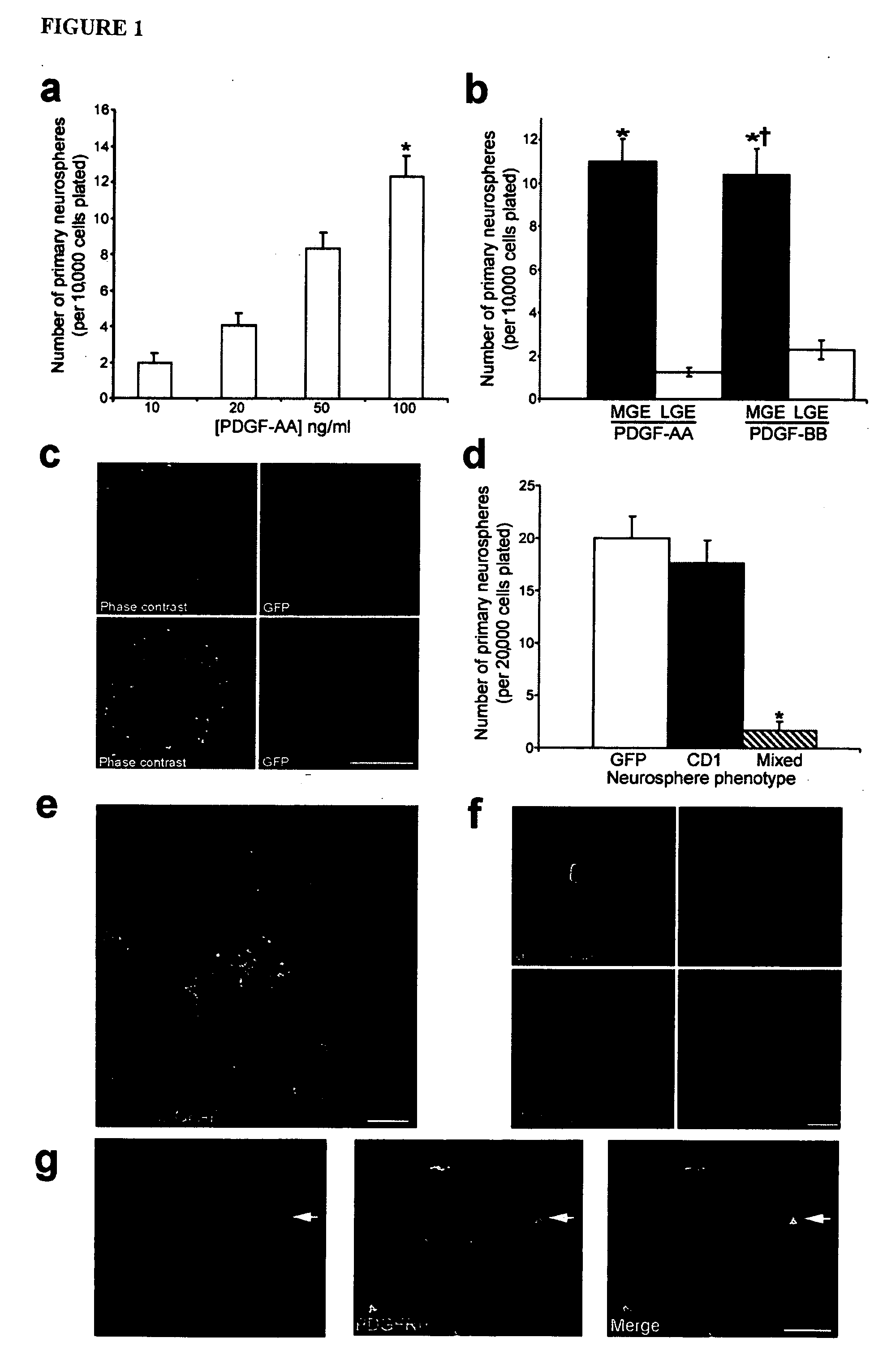
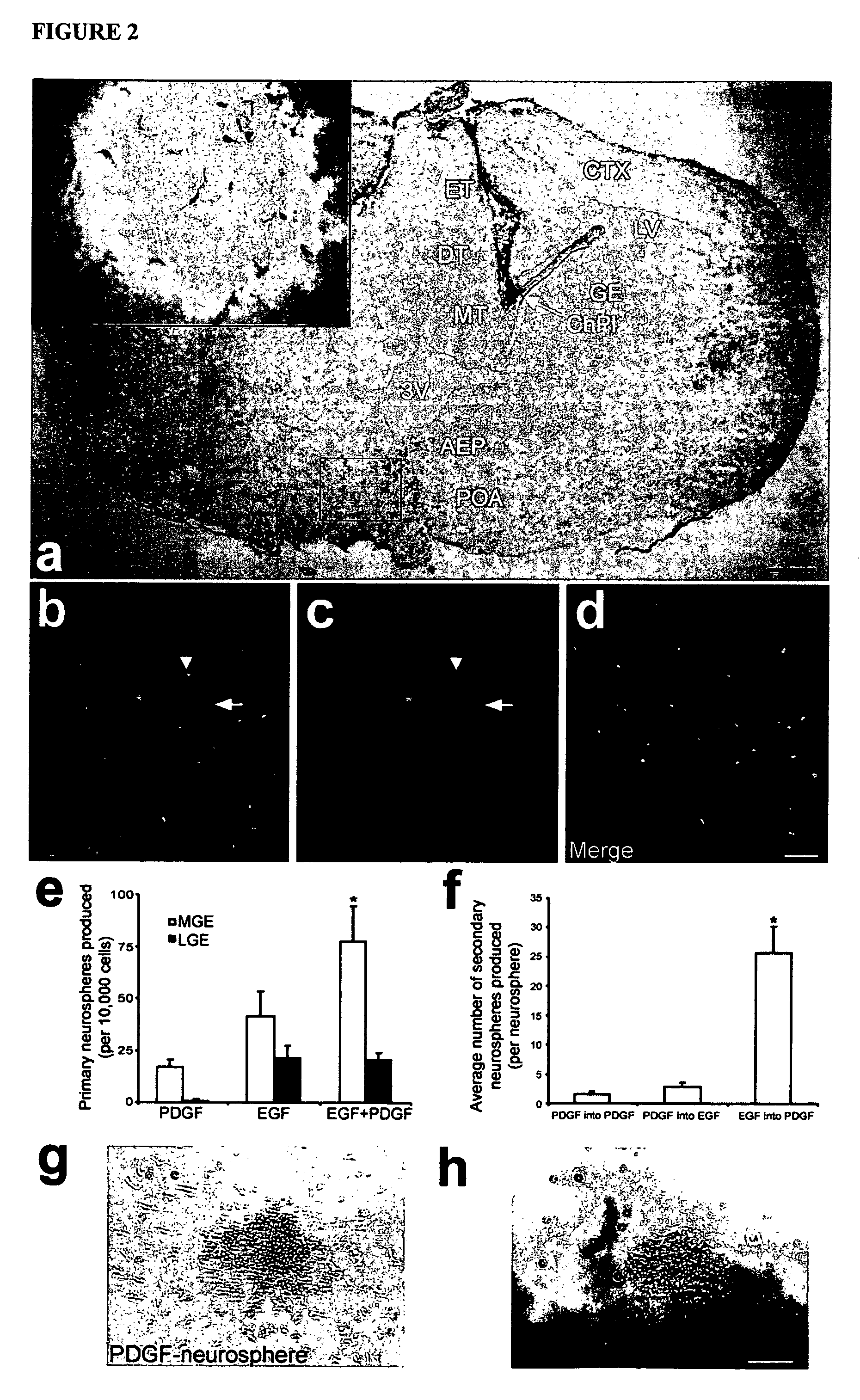
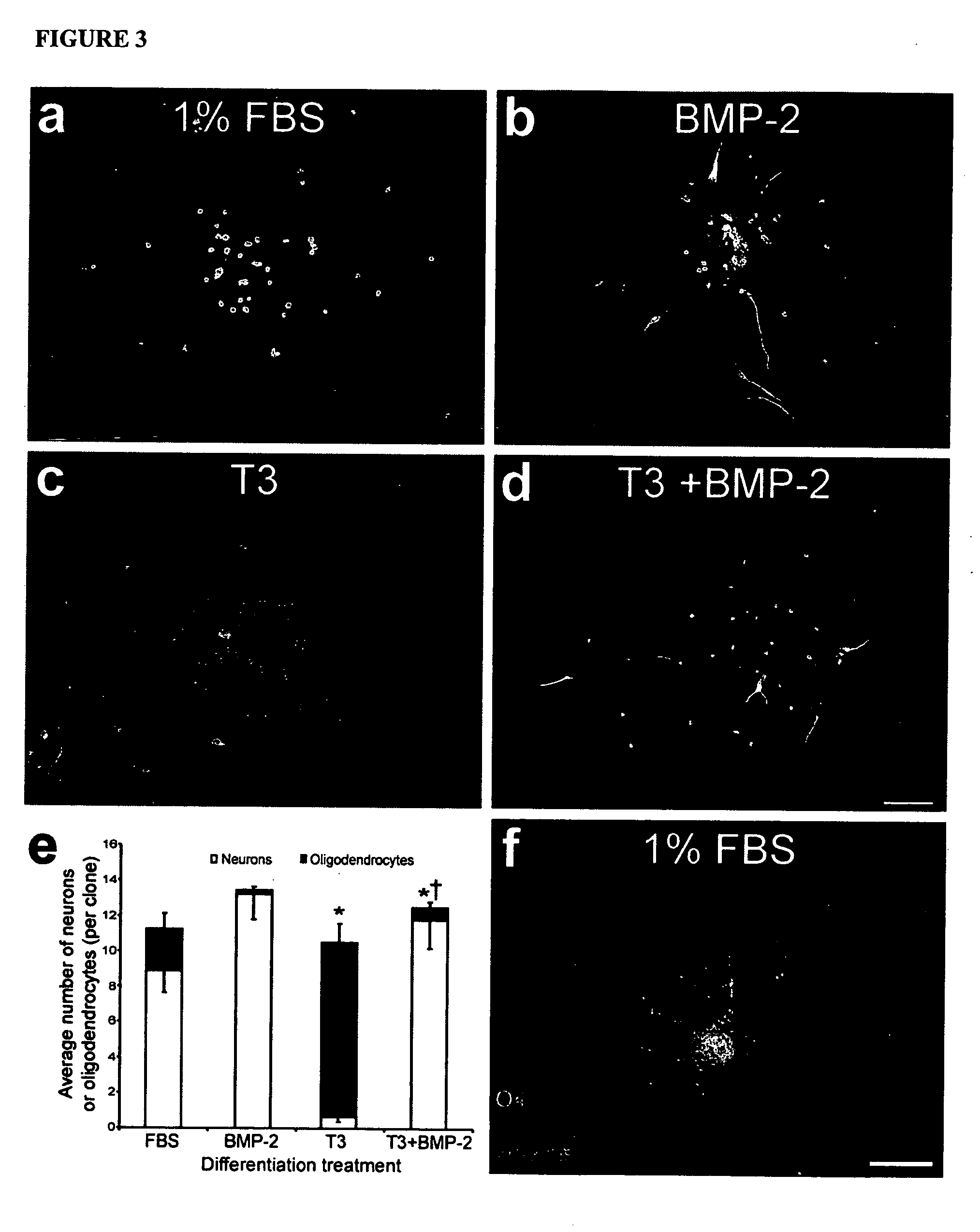
Platelet-derived growth factor-responsive neural precursor cells and progeny thereof
This invention provides platelet-derived growth factor-responsive neural precursor (PRP) cells and methods of producing such cells in vivo or in vitro. These cells can further be used to generate neurons, oligodendrocytes and / or astrocytes.
Owner:STEM CELL THERAPEUTICS
Serum-free culture medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106635978AExcellent adhesionIncrease speedSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAdipogenesisStem cell culture
The invention provides a serum-free culture medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. The serum-free culture medium is characterized by comprising a DMEM low-sugar culture medium, transferrin, serum albumin, insulin, platelet-derived growth factors, epidermal growth factors, transforming growth factors, beta-mercaptoethanol, dihydromyricetin and catechin. The invention belongs to the technical field of stem cell culture. The serum-free culture medium for umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, provided by the invention, can obviously promote the adherence performance and multiplication rate of the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, is beneficial to the multiplication of the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and the maintenance of features of the stem cells, is excellent in adipogenesis and osteogenic induction differentiation potential, is relatively simple in component of the culture medium and is relatively low in cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG COOWAY BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Platelet-derived growth factor compositions and methods for the treatment of osteochondral defects
InactiveUS20130122095A1Promote growthIncrease the number ofPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor iiPlatelet
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating an osteochondral defect. In one embodiment, provided is a composition for treating an osteochondral defect comprising a biphasic biocompatible matrix and platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), wherein the biphasic biocompatible matrix comprises a scaffolding material and wherein the scaffolding material forms a porous structure comprising an osseous phase and a cartilage phase. In another embodiment, also provided is a method for treating an osteochondral defect in an individual comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a composition comprising a biphasic biocompatible matrix and PDGF to at least one site of the osteochondral defect, wherein the biphasic biocompatible matrix comprises a scaffolding material and wherein the scaffolding material forms a porous structure comprising an osseous phase and a cartilage phase.
Owner:BIOMIMETIC THERAPEUTICS INC
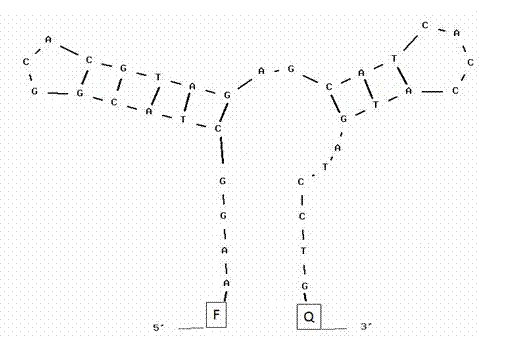
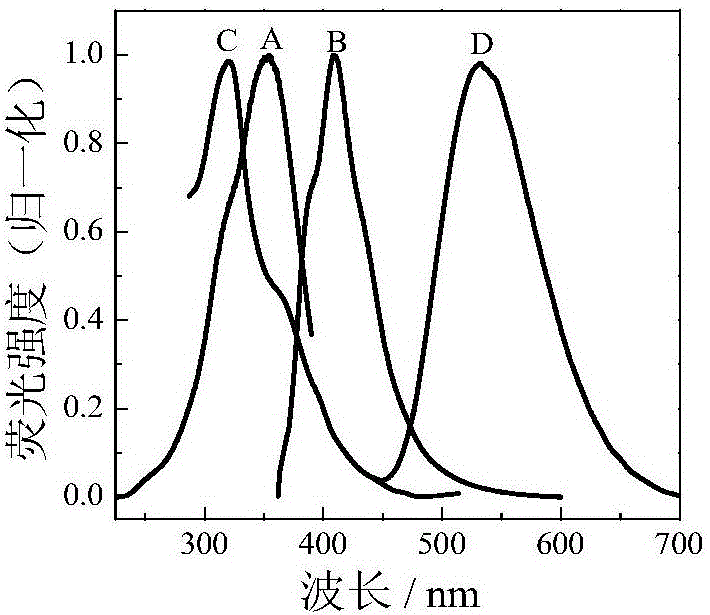
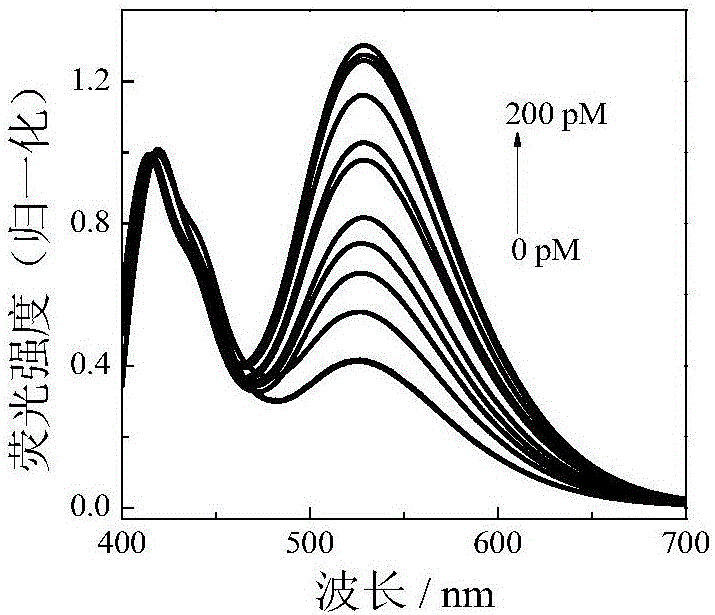
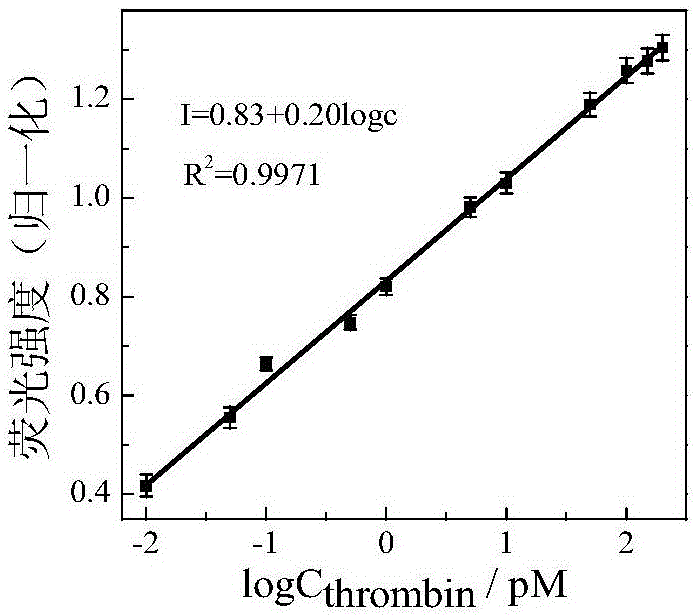
Nucleic acid aptamer molecular beacon probe for detection of platelet-derived growth factor
InactiveCN102735669AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerProtein target
The invention discloses a nucleic acid aptamer molecular beacon probe for the detection of platelet-derived growth factor. The nucleic acid aptamer molecular beacon probe comprises a PDGF-BB nucleic acid aptamer, a fluorescent group which connects to the 5' end of the PDGF-BB nucleic acid aptamer and a quenching group which connects to the 3' end of the PDGF-BB nucleic acid aptamer. According to the invention, high specificity and high affinity of the nucleic acid aptamer probe to the target protein and high sensitivity type conversion mechanism are subtly utilized, and fluorescence quenching mechanism is also utilized. The nucleic acid aptamer molecular beacon probe provided by the invention has a high sensitivity and a good selectivity. The detection process by the use of the nucleic acid aptamer molecular beacon probe provided by the invention is simple to operate with only one step, and the operation cost can be reduced.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Chondrocyte culture medium and chondrocyte culture method
The invention relates to a chondrocyte culture medium and a chondrocyte culture method. The chondrocyte culture medium can reduce dedifferentiation of the chondrocyte and improve the multiplication capacity of the chondrocyte. The chondrocyte culture medium provided by the embodiment of the invention comprises a basal culture medium, serum with a concentration of 5-20%, a platelet-derived growth factor with a concentration of 1-20 ng / ml, and beta-mercaptoethanol with a concentration of (1-5)*10<-5> M / L.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Stabilized Aptamers to Platelet Derived Growth Factor and their Use as Oncology Therapeutics
InactiveUS20090053138A1Increase edematous fluid contentIncrease oxygen contentOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesVEGF receptorsTumor therapy
Materials and methods are provided for producing and using aptamers as oncology therapeutics capable of binding to PDGF, PDGF isoforms, PDGF receptor, VEGF, and / or VEGF receptor or any combination thereof with affinity and specificity. The compositions of the present invention are particularly useful in solid tumor therapy and can be used alone or in combination with known cytotoxic agents for the treatment of solid tumors. Also disclosed are aptamers having one or more CpG motifs embedded therein or appended thereto.
Owner:ARCHEMIX CORP
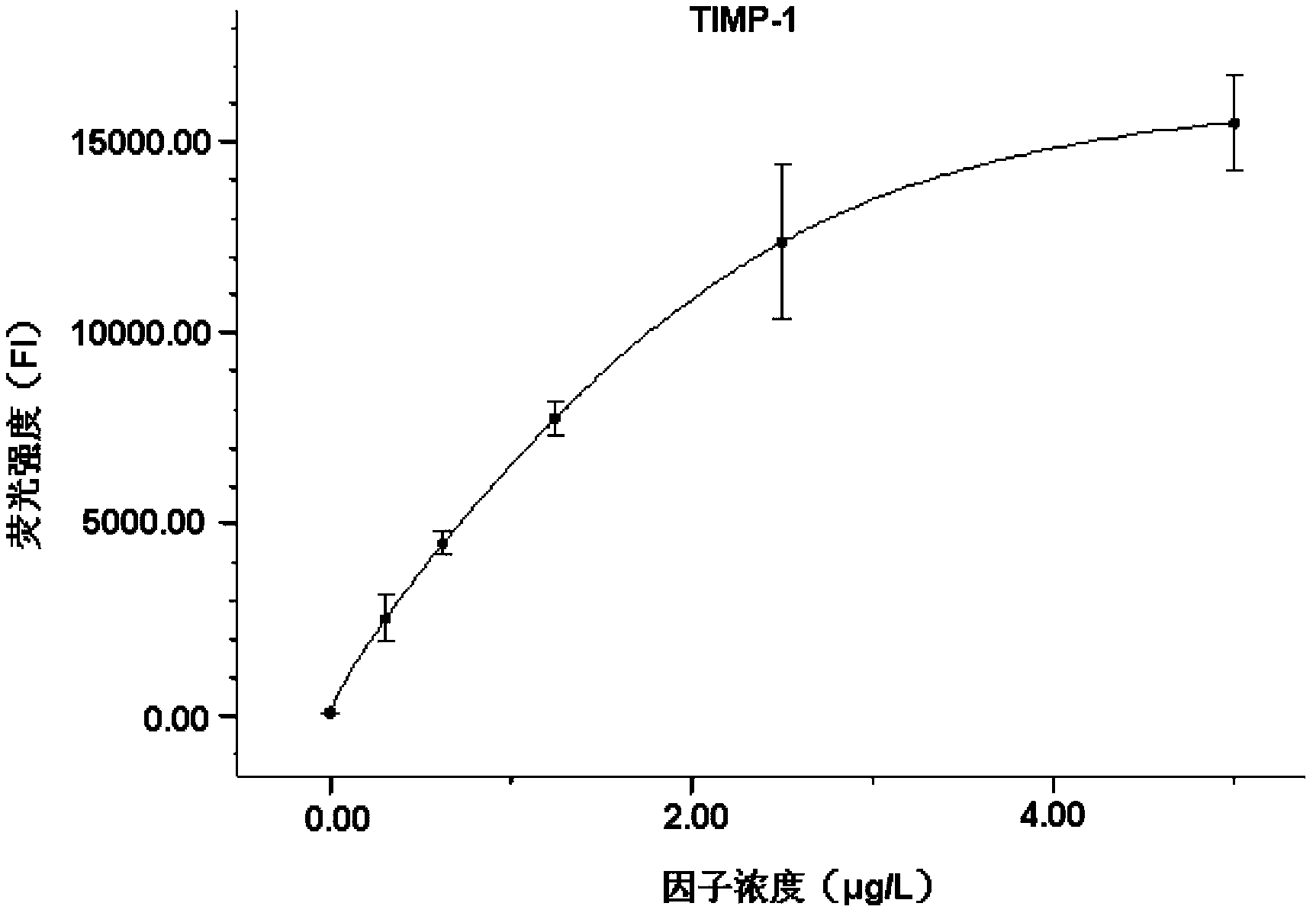
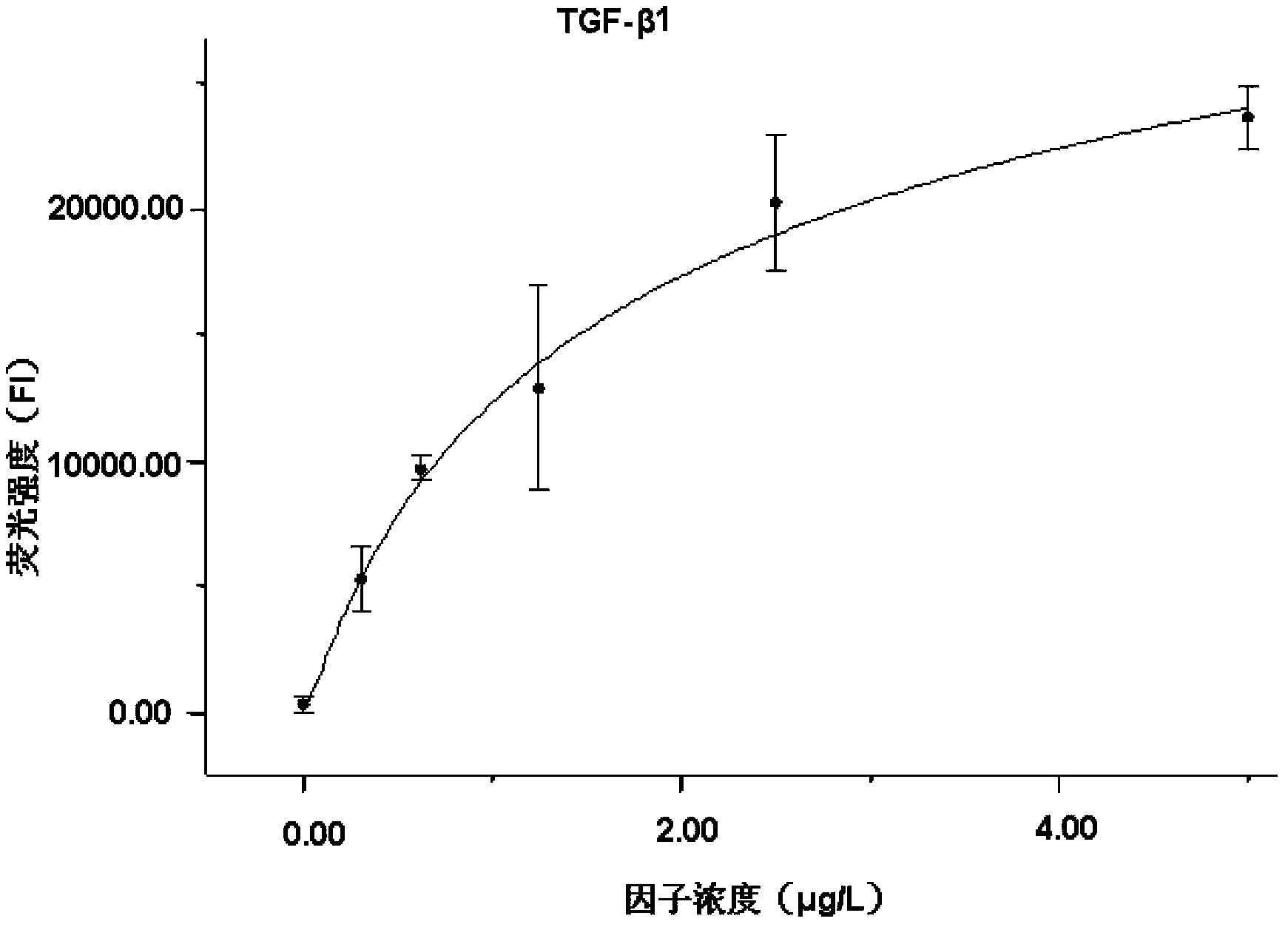
Liquid protein chip kit for detecting liver fibrosis degree
InactiveCN103399158AShorten detection timeSerum sample volume is smallBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceTumor necrosis factor alphaPlatlet-Derived Growth Factor
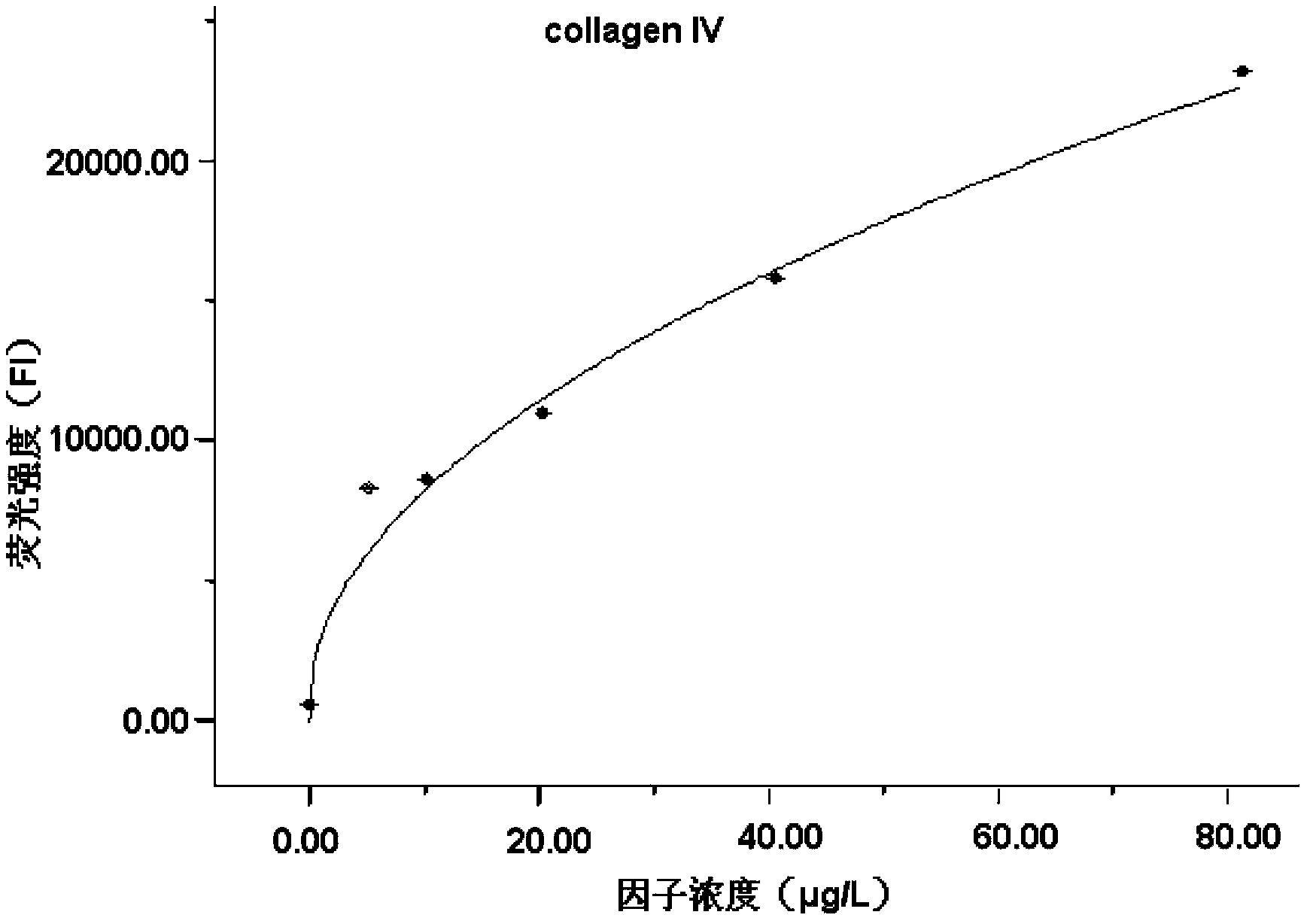
The invention provides a liquid protein chip kit for detecting a liver fibrosis degree. In the liquid protein chip kit, coupling antibody microspheres comprise 1, fluorescent microspheres coupling with procollagen peptide III and / or a metalloprotease tissue inhibitor factor-1 capture antibody, 2, one or more of fluorescent microspheres coupling with collagen peptide IV, fibronectin, a transforming growth factor-beta 1, a platelet-derived growth factor, a tumor necrosis factor alpha capture antibody, and an angiotensin II capture antibody, and 3, fluorescent microspheres coupling with a serum hyaluronic acid capture antibody and / or a laminin capture antibody. The liquid protein chip kit can realize combined detection of a plurality of liver fibrosis-related markers for reflection of different liver fibrosis stages, can shorten detection time to more than ten minutes from a few hours, can finish detection of a plurality of markers only by 1 microliter of a serum sample, can be operated simply and has a low diagnosis cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide inhibitor as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103333227ASmall molecular weightImprove stabilityPeptide preparation methodsCyclic peptide ingredientsCyclic peptideCell membrane
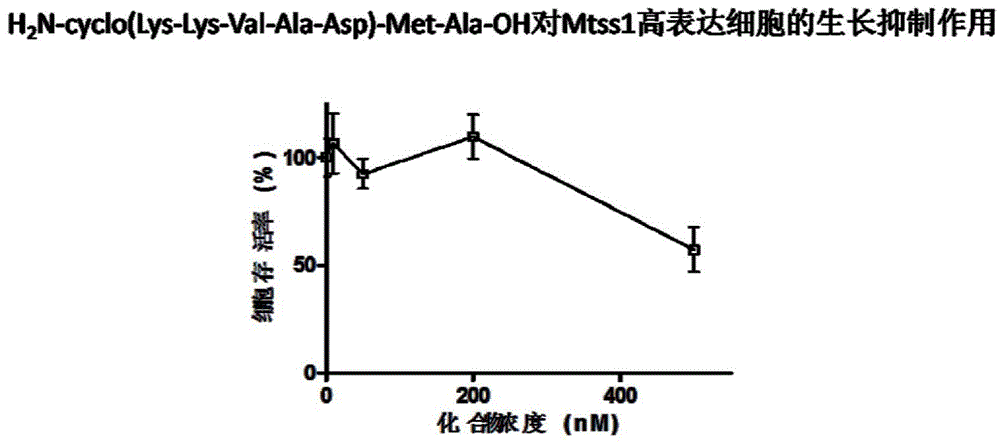
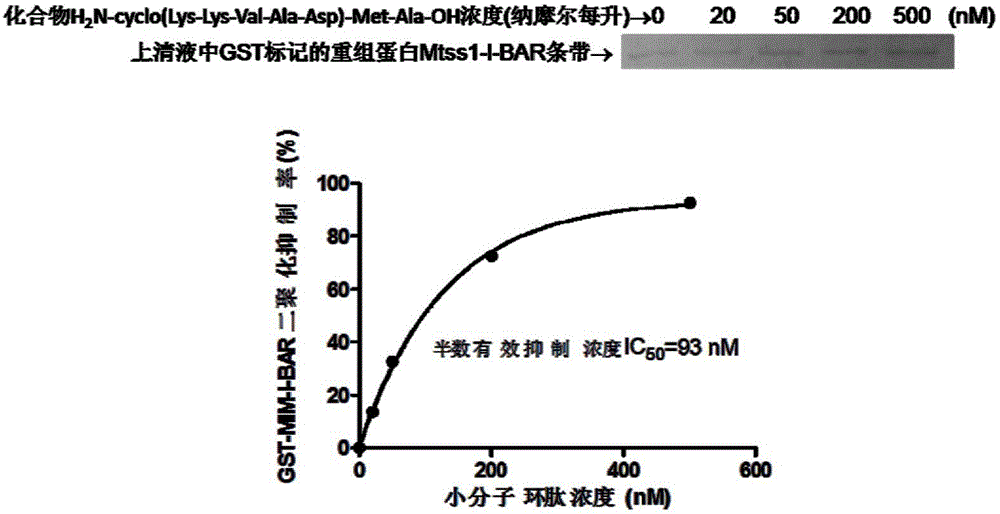
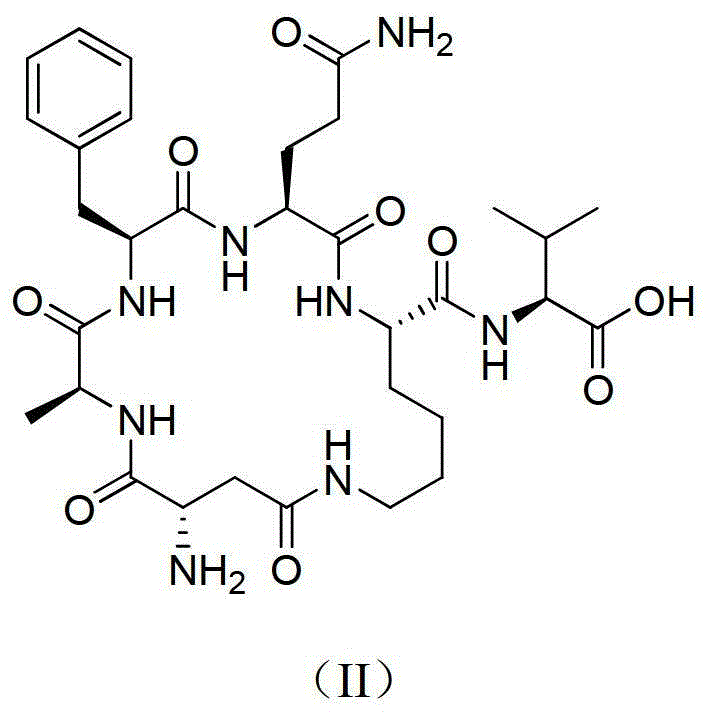
The invention provides metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide, derivatives or salts thereof, a preparation method for the metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide, the derivatives or salts thereof and an application of the metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide, the derivatives or salts thereof in preparation of antitumor medicaments. The metastatic tumor deletion protein small-molecule cyclopeptide is low in molecular weight, high in stability and very low in toxicity and can enter cells through cell membranes to inhibit endocytosis of tumor cells and interfere morphologic change of the cell membranes and conduction of relevant antitumor signals by inhibiting dimerization of Mtss1 protein, so that cell proliferation and growth caused by tumor stimulating factors such as epidermal growth factors EGF, platelet derived growth factor PDGF or sonic hedgehog (shh) factors are weakened, wherein the in-vitro inhibition activity of nanomole-scale inhibitor-protein can remarkably inhibit the endocytosis of the cells after the inhibitor-protein is directly added into cell culture fluid without being transfected or packaged by lipidosome.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Composition with anti-aging function and preparation thereof
ActiveCN104922658AImprove anti-aging effectRich in nutrientsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCuticleBlood vessel
The invention belongs to the field of medical cosmetology, and particularly relates to composition with an anti-aging function and preparation thereof. The composition comprises, by weight, 0.03-4 parts of stem cell growth factors, 1-30 parts of honeysuckle extracts, 50-300 parts of honey and 0.1*10<-3>-1*10<-3> parts of hyaluronic acid. The stem cell growth factors comprise at least two of epidermal growth factors, fiber cell growth factors, platelet-derived growth factors and vascular endothelial growth factors. According to the composition with the anti-aging function and the preparation, multiple stem cell growth factors are added into the composition, the multiplication capacity of epidermis cells is improved remarkably, meanwhile the composition formula is optimized, and the effects of all components in the composition are played effectively, so that the composition has rich nutritional ingredients, the good moisturizing effect and the antioxidant effect, and the composition presents excellent anti-aging effect.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method of generating mesenchymal stem cells and uses thereof
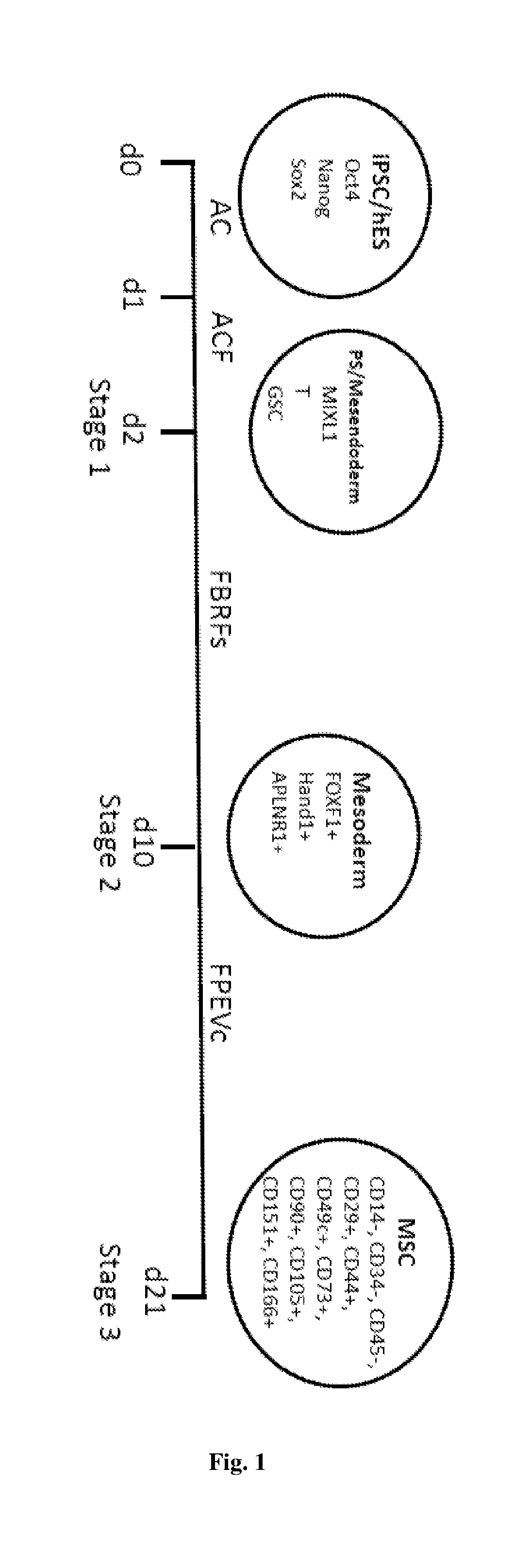
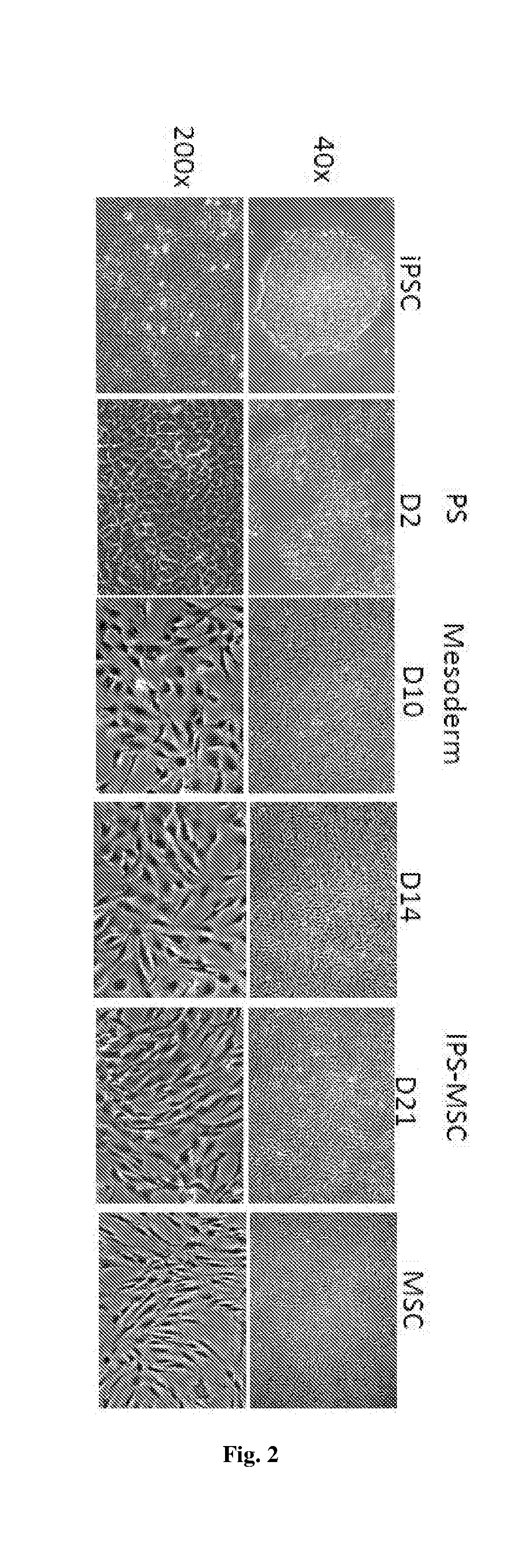
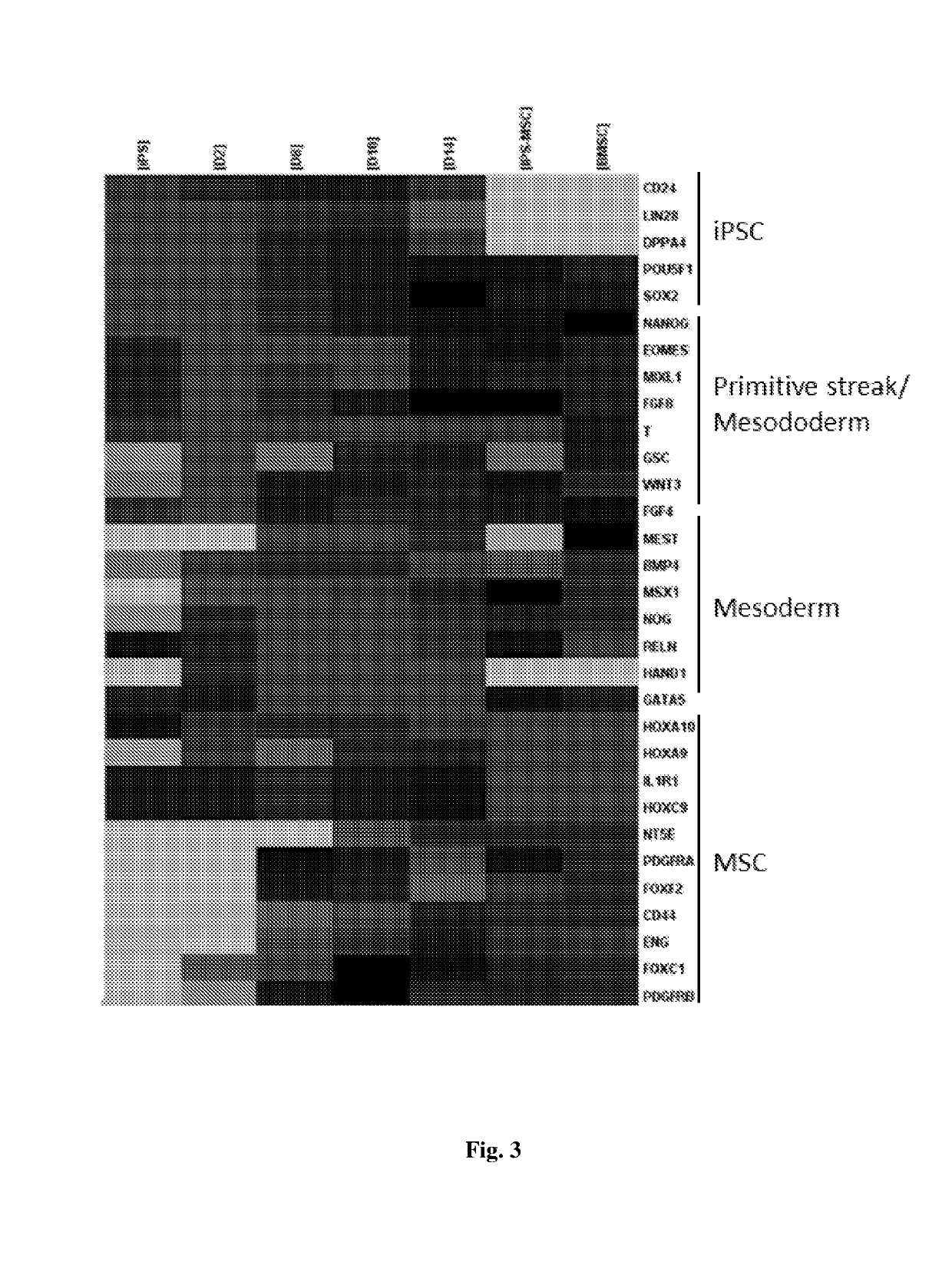
The present disclosure provides a method of generating mature mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) from lateral plate mesoderm comprising culturing the lateral plate mesoderm cells on an extracellular matrix in a MSC cell culture media comprising (i) fibroblast growth factor; (ii) platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF); (iii) epidermal growth factor (EGF) and (iv) ascorbic acid. Also claimed are MSCs obtained by said culture method and a method of treating cartilage and bone disease in a patient using said cells. In addition, a culture medium for deriving primitive streak mesendoderm cells from pluripotent stem cells comprising (a) activin; (b) WNT-signalling activator; and / or (c) fibroblast growth factor and a culture medium for deriving lateral plate mesoderm cells from primitive streak mesendoderm cells comprising (1) fibroblast growth factor; (2) bone morphogenetic protein; (3) follistatin; and optionally Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor are claimed.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Composition with cell repairing function and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103405751AGood effectImplement the repair functionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyDisease
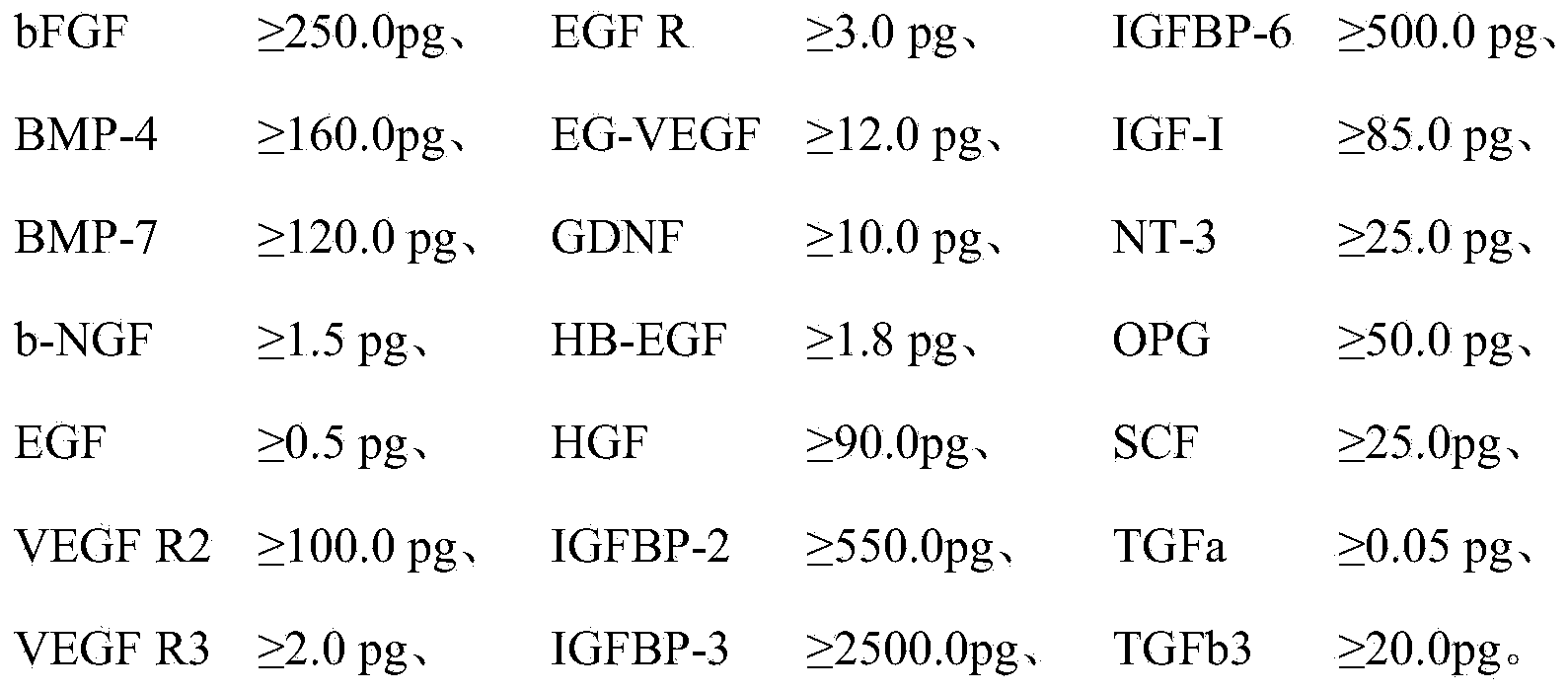
The invention provides a composition with a cell repairing function. The composition per milliliter comprises the following components: (1) a growth factor group which comprises platelet-derived growth factors PDGF greater than 600pg, vascular endothelial growth factors VEGF greater than or equal to 3300pg and stem cell factor receptors SCF R greater than or equal to 750pg; (2) a protein group with the repairing function, wherein the protein group is 0.3-0.8mg based on nitrogen content; and (3) polypeptides and amino acids, wherein the polypeptides and amino acids are 0.5-1.0mg based on nitrogen content. The composition provided by the invention has the excellent cell repairing function and has good preventing and repairing effects on series of diseases or wounds caused by cellular damage. The invention further provides a preparation method and an application of the composition.
Owner:珠海安肽生物医药技术开发有限公司
Culture medium for adipose derived stem cells
InactiveCN106222136AKeep aliveReduce apoptosis rateCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCholesterolVascular endothelium
The invention discloses a culture medium for adipose derived stem cells. The culture medium for the adipose derived stem cells comprises RPMI-1640 medium, and further comprises 2 to 2.5g / L of D-glucose, 30 to 45mg / L of cholesterol, 0.5 to 0.8g / L of potassium chloride, 0.1 to 0.3 mu g / L of sodium selenite, 8 to 10 mu g / L of taurine, 10 to 20 mu g / L of heparin calcium, 2.2 to 2.5g / L of human serum albumin, 20 to 50mg / L of vascular endothelial growth factors, 3 to 6mg / L of fibroblast growth factors, 40 to 80mg / L of platelet-derived growth factors, 20 to 40mg / L of glutathione, 50 to 100mg / L of vitamins, and 100 to 200mg / L of plant extracts. The culture medium for the adipose derived stem cells disclosed by the invention is free of components of animal origin, has no residues or pollution, has good cell anchorage dependence and high proliferation rate, improves the pathogenic microorganism resistance of the culture medium, and further lowers the cost of the culture medium.
Owner:ANHUI HUIEN BIOTECH
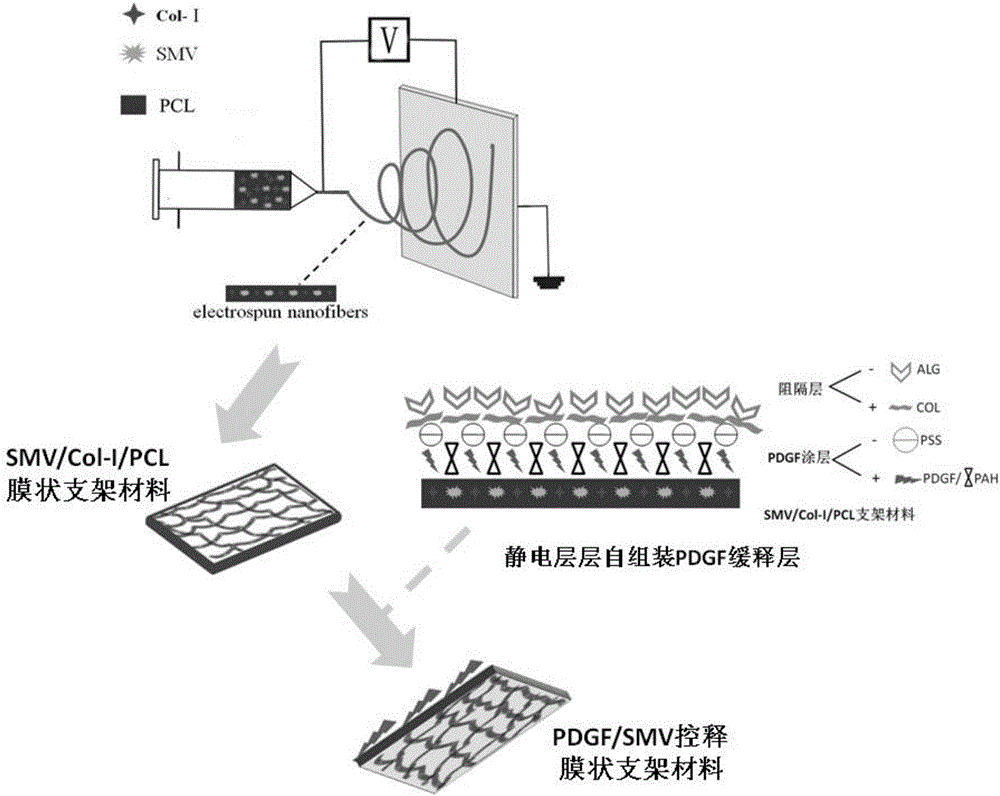
Drug/factor control-released thin film scaffold and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106492275AImprove hydrophilicityImprove adhesionCoatingsProsthesisEngineering researchSurface layer
The invention provides a drug / factor control-released thin film scaffold. The drug / factor control-released thin film scaffold is characterized by comprising a film-like bionic scaffold, a PDGF (Platelet Derived Growth Factor) coating layer and a slow release layer which are sequentially arranged. According to a scaffold material, i.e, a film-like scaffold material on the surface layer of a factor / the core layer of a drug, for clinic periodontal treatment, provided by the invention, controlled release of active factors and drugs is realized, and cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation are promoted, so that three elements of seed cells, a scaffold material and regulatory factors in tissue regeneration are organically combined, periodontal repairing is promoted, and a facilitation function for periodontal tissue engineering research is obtained.
Owner:上海市口腔病防治院
Adipose-derived stem cell serum-free culture medium and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106754675ASimple ingredientsLow costCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAdditive ingredientStem cell culture
The invention provides an adipose-derived stem cell serum-free culture medium which comprises a DMEM low-sugar culture medium and further comprises transferrin, serum albumin, a platelet-derived growth factor, an epidermal growth factor, a transforming growth factor, beta-mercaptoethanol, dihydroarbutin, and catechin. The adipose-derived stem cell serum-free culture medium belongs to the technical field of cell culture. The adipose-derived stem cell serum-free culture medium can remarkably improve the adherence performance and multiplication rate of adipose-derived stem cells and facilitates multiplication and property keeping of the adipose-derived stem cells, the ingredients of the culture medium are simpler, and the cost is lower.
Owner:广东省科玮智丽生物医药有限公司
Compositions of alpha platelet derived growth factor receptor nucleic acid and protein and method of making
ActiveUS7427671B1Increasing the amount of PDGF-R protein encodedPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHuman plateletADAMTS Proteins
A DNA sequence which encodes a human type α platelet derived growth factor receptor protein which preferentially binds to the AA homodimer and AB heterodimer forms of platelet derived growth factor and also binds the BB homodimer at high affinity, is described. Substantially pure human a platelet derived growth factor receptor protein and methods for recombinantly producing human α platelet derived growth factor receptor protein are also described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
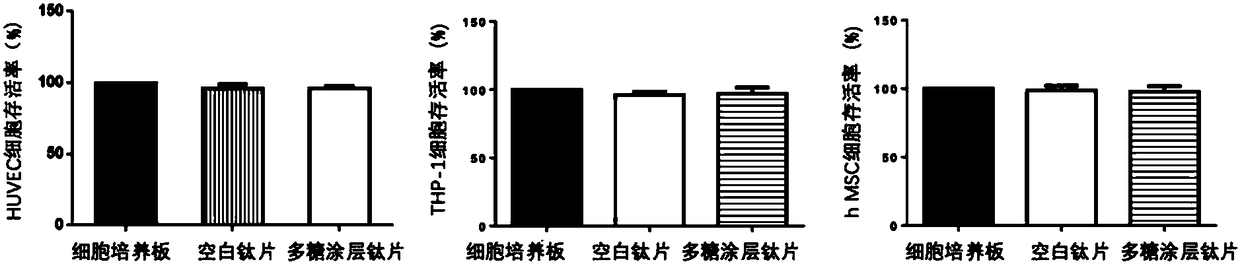
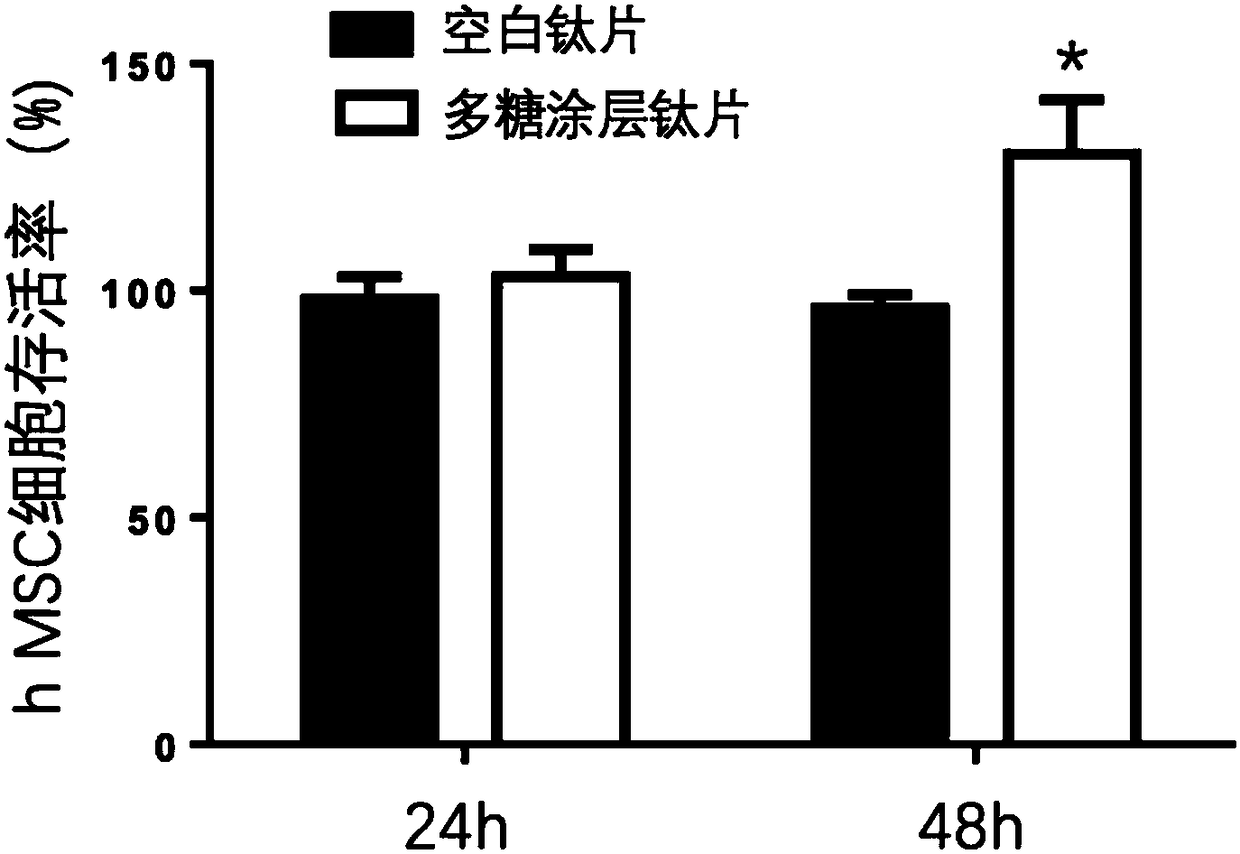
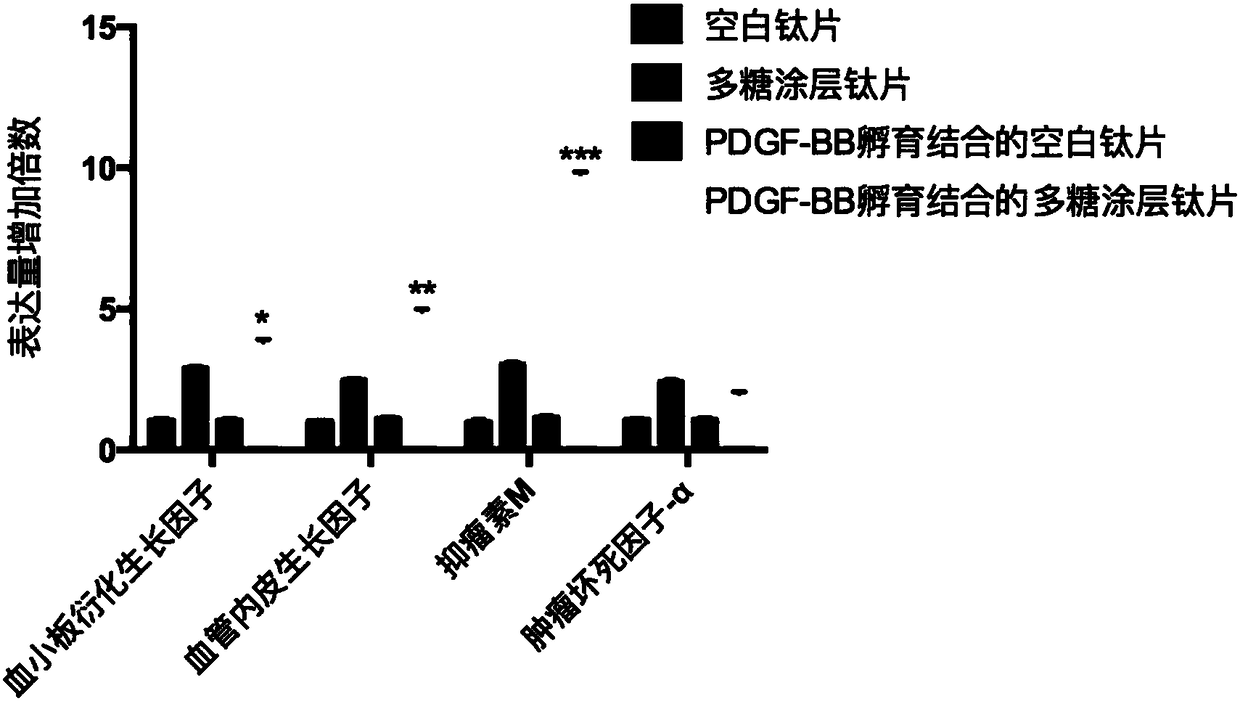
Implant containing polysaccharide coating capable of binding to growth factor, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108478298AExcellent osteogenic effectGood biocompatibilityDental implantsCrystallographyDerivatization
The invention relates to an implant containing a polysaccharide coating capable of binding to a platelet-derived growth factor, and a preparation method thereof. The implant containing the polysaccharide coating comprises an amino-anchored matrix, and the polysaccharide coating grafted onto the surface of the matrix and capable of binding to the growth factor.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
Bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cell culture medium and application thereof
ActiveCN110468099AHigh purityIncrease originalityCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHigh cellPenicillin
The invention provides a bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cell culture medium and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of stem cells as well as cell culture and amplification. The bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cell culture medium consists of the following ingredients at the following concentrations: 52-53% by volume of Dulbecco modified MEM medium, 38-42% by volume of MCDB medium, 1XITS cell culture additives, 8-12 microgram / milliliter of linoleic acid, 40-60 microgram / milliliter of human serum albumin, 1X penicillin and streptomycin, 75-125 micromoles of L-ascorbic acid, 1-3% by volume of fetal bovine serum, 10-15 micromoles of dexamethasone, 12-18 ng / mL of platelet-derived growth factors, and 8-12 ng / mL of growth promoting factors. Being adopted, the bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cell culture medium provided by the invention is capable of increasing success rate of clonal culture of bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells (bMSC); and moreover, the bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cell culture medium is capable of increasing passage times, ensuring relatively high cell purity and improving cell primitivity.
Owner:海门生原干细胞科技有限公司
Method for preparing cartilage angiogenesis inhibiting factor for scalloped hammerhead shark
ActiveCN104894200AProduction suppressor activityAdvanced Extraction ProcessPeptide preparation methodsFermentationVascular endotheliumCell membrane
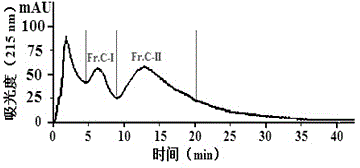
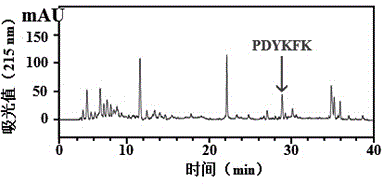
The invention relates to a method for preparing a cartilage angiogenesis inhibiting factor for a scalloped hammerhead shark. During preparation, Pro-Asp-Tyr-Lys-Phe-Lys is obtained through cartilage homogenate of the scalloped hammerhead shark, guanidine hydrochloride extraction, acetone precipitation and grading, enzymolysis, gel filtration chromatography, cell membrane chromatography purification and efficient liquid phase chromatography purification. The angiogenesis inhibiting factor can effectively inhibit angiogenesis of chick chorioallantoic membranes, and has an obvious inhibition function on expression of three angiogenesis promoting factors including the vascular endothelial cell growth factor, the basic fibroblast growth factor and the platelet-derived growth factor of lung cancer tissue of mice suffering from the Lewis lung cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Biological diagnosis marker for central nervous system demyelinating diseases
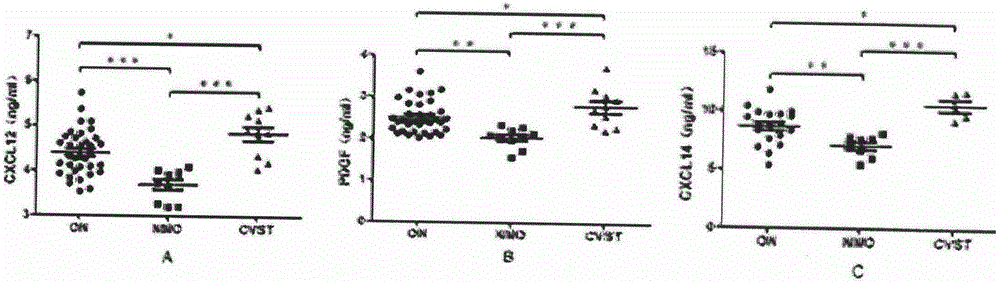
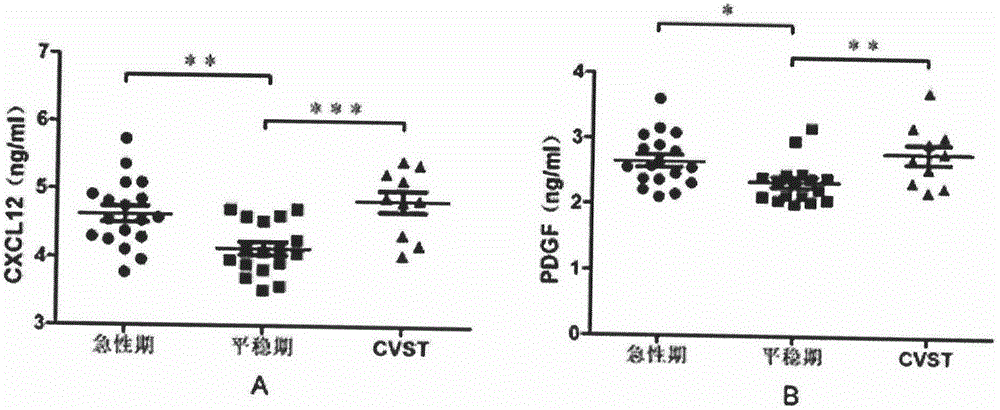
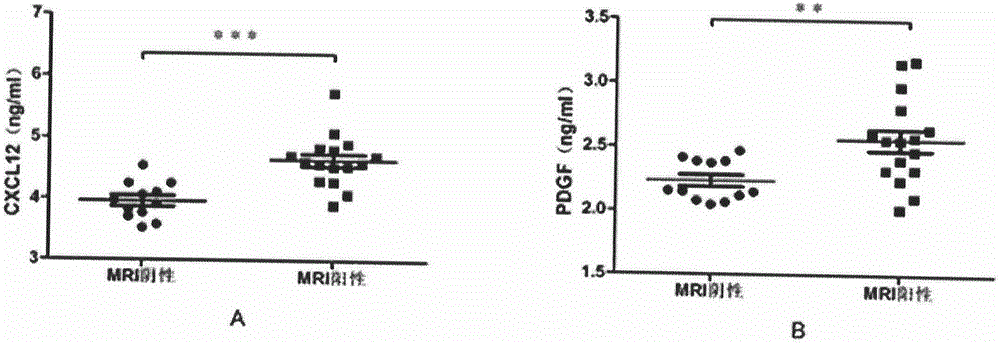
The invention discloses a biological diagnosis marker for central nervous system demyelinating diseases. The biological diagnosis marker refers to platelet-derived growth factors, chemotactic factors 12 and chemotactic factors 14 in cerebrospinal fluid. The central nervous system demyelinating diseases include optic neuritis (ON) and neuromyelitis optica (NMO); disease changes can be evaluated by monitoring the platelet-derived growth factor and the chemotactic factors in cerebrospinal fluid in different phases of the optic neuritis ON so as to judge recovering conditions. A new biological marker can be discovered by detecting levels and changes of platelet-derived growth factors, chemotactic factors 12 and chemotactic factors 14 in cerebrospinal fluids of ON and NMO patients, so that the medullar sheath regeneration capability can be estimated, an experimental basis is provided for the ON and NMO recovery and development, and a new idea is provided for treatment.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method for efficiently inducing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into Schwann-like cells
The invention belongs to the field of cytobiology and relates to a method for efficiently inducing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into Schwann-like cells. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) culturing the umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to a sub-fusion state, discarding the old culture solution, and adding culture solution comprising 1 mM of beta-mercaptoethanol to induce overnight; (2) discarding the induction solution, washing with a Dulbecco modified eagle medium (DMEM), and adding all-trans retinoic acid to induce for 60 to 84 hours; and (3) discarding the induction solution, washing with the DMEM, adding composition induction solution comprising 5 to 6 ng / ml of platelet-derived growth factors, 9 to 10 ng / ml of alkaline desmocyte growth factors, 13 to 15 uM of Forskolin and 250 to 260 ng / ml of gliocyte growth factors or 200 to 210 ng / ml of nerve growth factors to induce for 10 to 16 days, and change the solution for one time every other 72 hours. By the method, the inductivity can reach over 90 percent.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
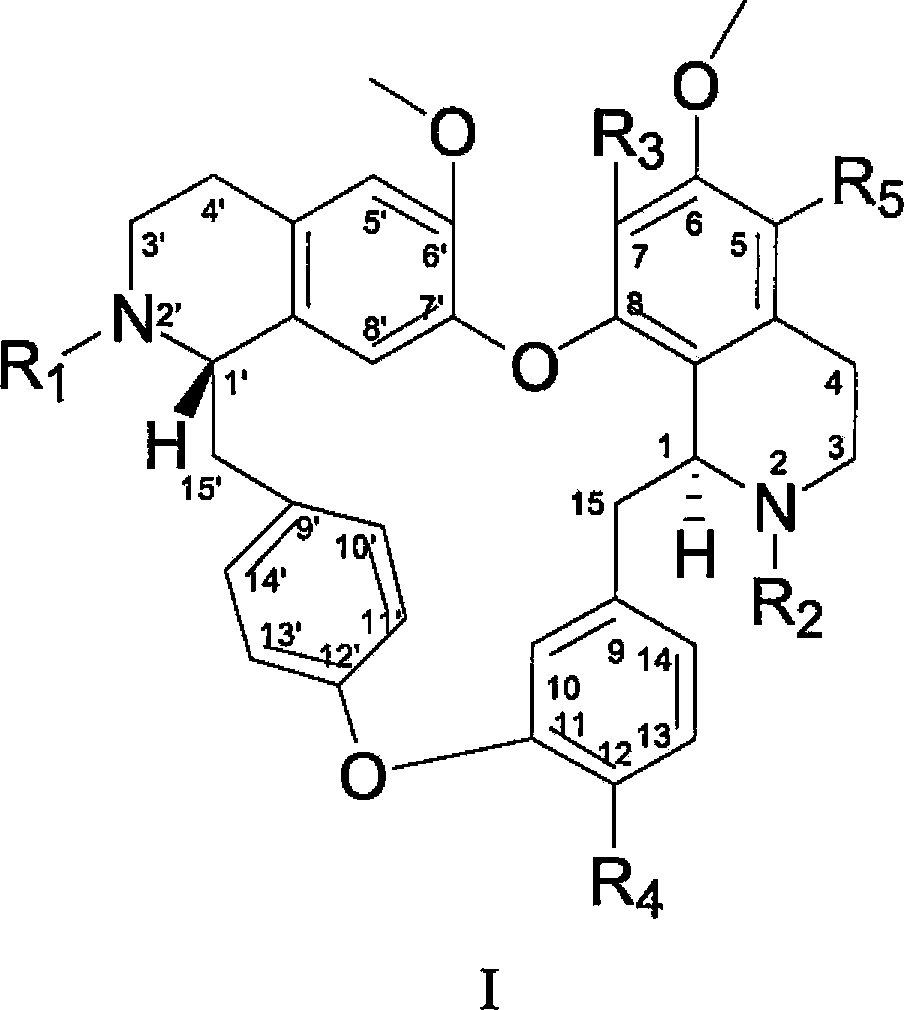
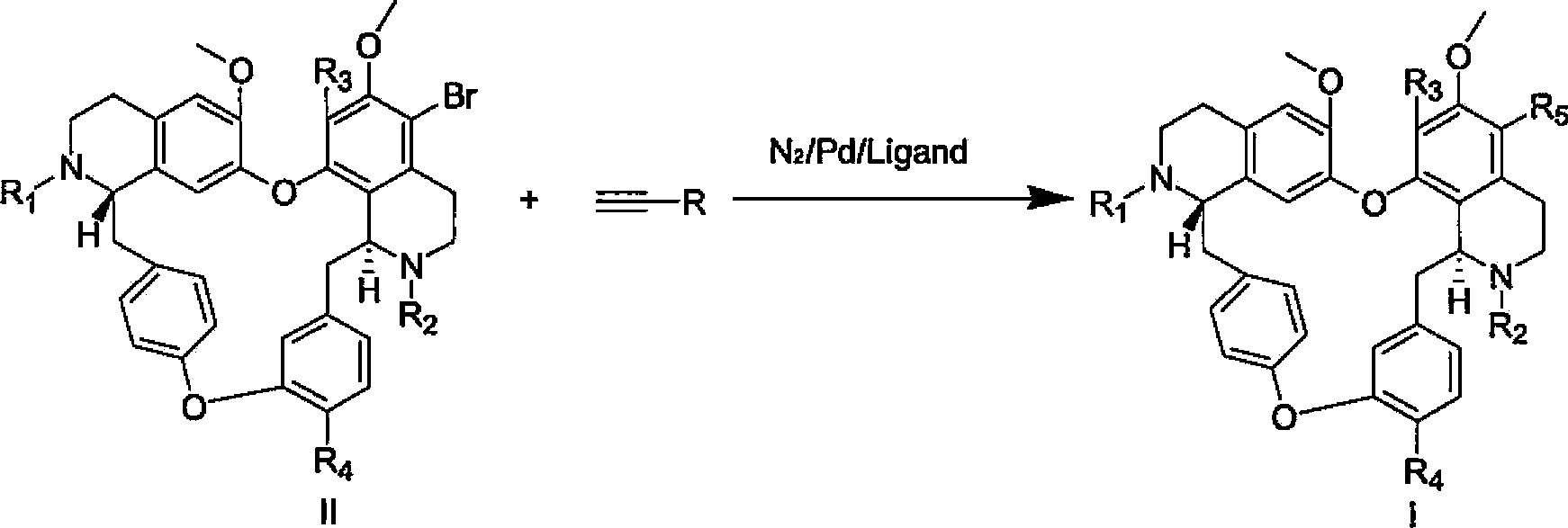
Dibenzyl tetrahydroisoquinoline derivative as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103772404AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHepatic fibrosisTetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives
The invention discloses a compound shown in the following formula I or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof. In the formula I, R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are defined in the specification. The invention further discloses a method for preparing the compound which is shown in the formula I. The compound shown in the formula I can be used for inhibiting hepatic stellate cells activated by PDGF (Platelet Derived Growth Factor) so as to reverse hepatic fibrosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Preparation method of fluorescent sensor system based on cationic conjugated polymer and iridium complex FRET effect and application thereof
ActiveCN106589321AHigh sensitivityAchieve improvementIndium organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceIridiumSensor system
The invention discloses a preparation method of fluorescent sensor system based on cationic conjugated polymer and iridium complex FRET effect and application thereof and is characterized in that it comprises the synthesis step of the iridium complex; the synthesis step of the cationic conjugated polymer;the cationic conjugated polymer and iridium complexes give rise to FRET and obtain the fluorescence sensor system steps based on the FRET effect of the cationic conjugated polymer and iridium complex; the fluorescence sensor system can be used to detect thrombin, adenosine triphosphate, platelet derived growth factor, cocaine and lysozyme . The invention has the advantages of good specificity, high sensitivity, accurate and reliable results, low cost, high speed and simple process.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Culture medium for culturing dental pulp stem cells and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106754658AClear ingredientsLow priceCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTaurineCulture mediums
The invention belongs to the technical field of cell culture, and specifically relates to a culture medium for culturing dental pulp stem cells and a preparation method thereof. The culture medium for culturing the dental pulp stem cells comprises the a basal culture medium and an additive added into the basal culture medium, wherein the additive is prepared from the following components in final concentrations: 3 to 5 micrograms / L of epidermal growth factors, 2 to 4 g / L of carboxymethyl chitosan, 5 to 8 mg / L of catalase, 0.14 to 0.18 mg / L of lipoic acid, 0.3 to 0.6 micro mol / L of coenzyme Q10, 15 to 25 micrograms / L of laminin, 2 to 5 micro mol / L of linolenic acid, 8 to 14 micro mol / L of nicotinamide, 2 to 4 mg / L of taurine, 2 to 6 micrograms / L of platelet-derived growth factors, 70 to 80 micro mol / L of choline chloride and 0.5 to 2 mg / L of diosgenin. The culture medium for culturing the dental pulp stem cells disclosed by the invention is relatively low in cost and high in safety, and the amplification speed of the dental pulp stem cells can be obviously increased.
Owner:JIANGXI YIXINTANG MEDICAL TECH
Tumor living tissue in-vitro culture system and culture method
ActiveCN103966168AExcellent SurvivalExcellent growth statusTumor/cancer cellsInsulin-like growth factorPenicillin
The invention relates to a tumor living tissue in-vitro culture system and a corresponding tumor living tissue in-vitro culture method. The tumor living tissue in-vitro culture system comprises a support system for simulating an in-vivo basilemma structure and a blood supply system of tumor, a tumor tissue specimen treatment liquid which is a RPMI1640 culture liquid containing 2mu g / ml of amphotericin, 1000U / ml of penicillin and 1000mu g / ml of streptomycin, and a special culture medium for tumor tissue culture, wherein the culture medium contains 20mu g / L of bFGF (Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor), 20mu g / L of EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor), 10mu g / L of PDGF (Platelet Derived Growth Factor), 10mu g / L of HGF (Hepatocyte Growth Factor), 10mu g / L of IGF (Insulin-like Growth Factor), 10mu g / L of NRG1, 10mu g / L of VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor), 5% of fetal calf serum as well as 500U / ml of penicillin and 500mu g / ml of streptomycin on the basis of a mixture solution containing 50 percent of DMEM (Dulbecco Modified Eagle Medium) and 50 percent of HamF 12. The invention provides a systematic solution scheme and an appropriate culture medium for the in-vitro culture of tumor tissue cells.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HANDY BIOTECH CO LTD
Culture medium for amplifying human mesenchymal stem cell and amplification method of culture medium
InactiveCN107119011AHigh speedImprove the purification effectCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPlateletMesenchymal stem cell
The invention discloses a serum-free medium for expanding human mesenchymal stem cells, which is based on the medium for culturing stem cells, adding linoleic acid, human AB type serum, and platelet-derived growth factors. The invention also discloses a culture method for human mesenchymal stem cells. The serum-free medium of the present invention uses multiple cytokines in combination reasonably, which not only improves the purification effect of mesenchymal stem cells, but also shows that the morphology of human mesenchymal stem cells is still uniform even after 30 passages, thus ensuring The safety of human mesenchymal stem cells improves the expansion speed of cells, reduces the expansion time and reduces the cost.
Owner:刘力伟
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com