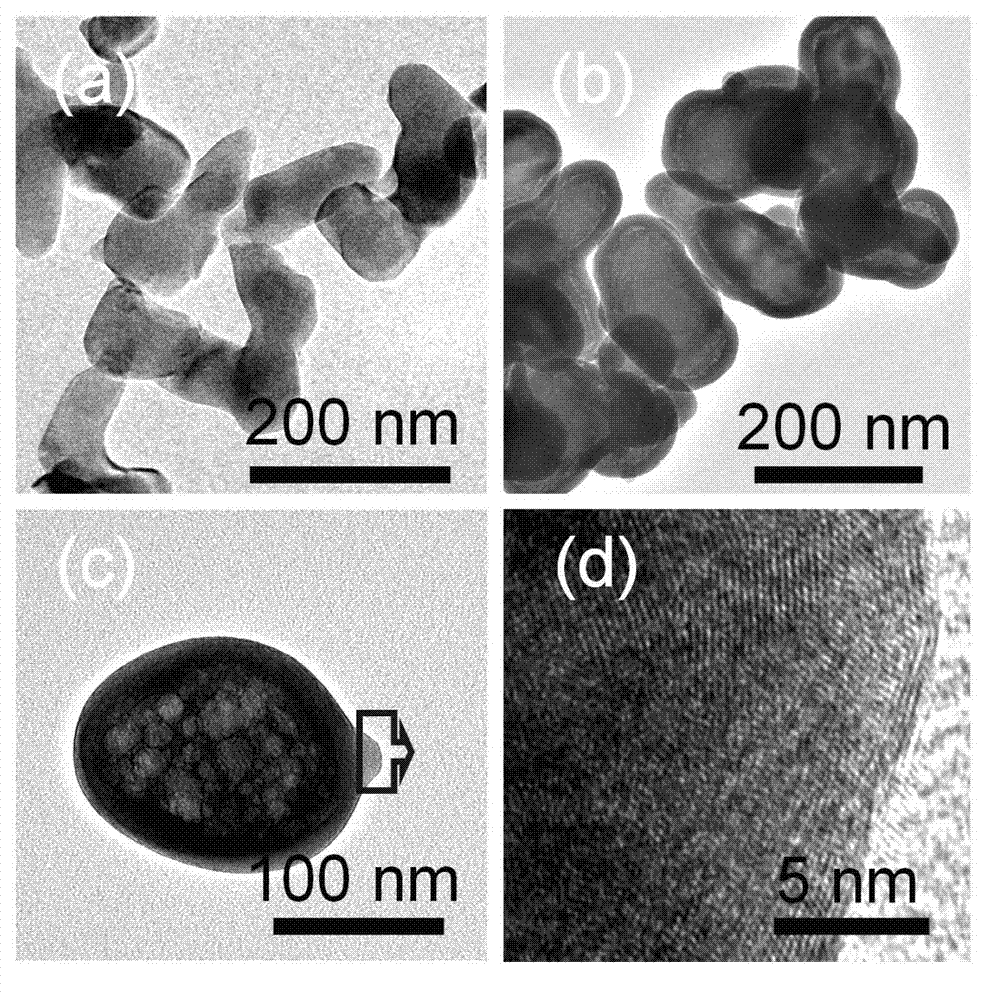
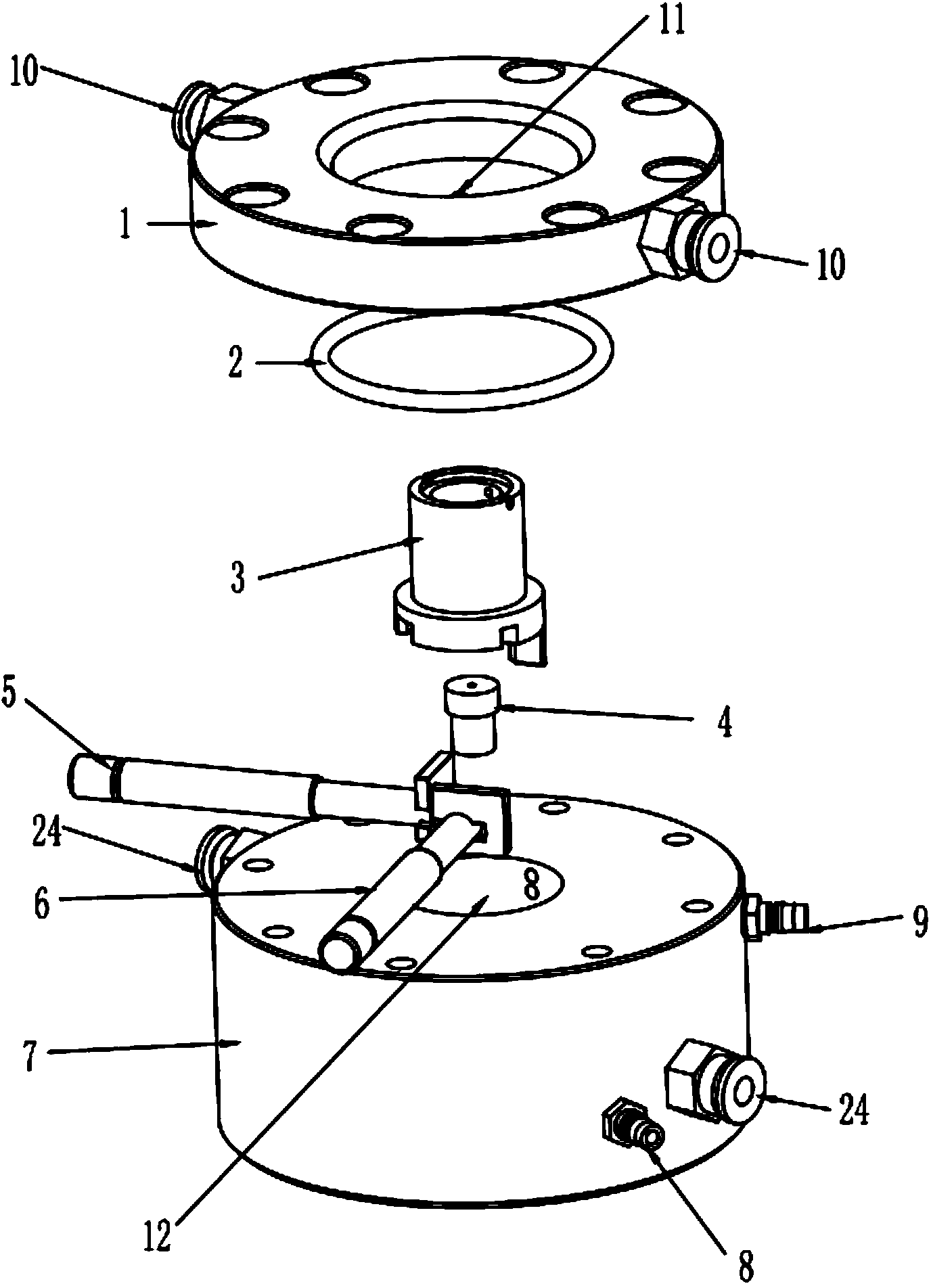
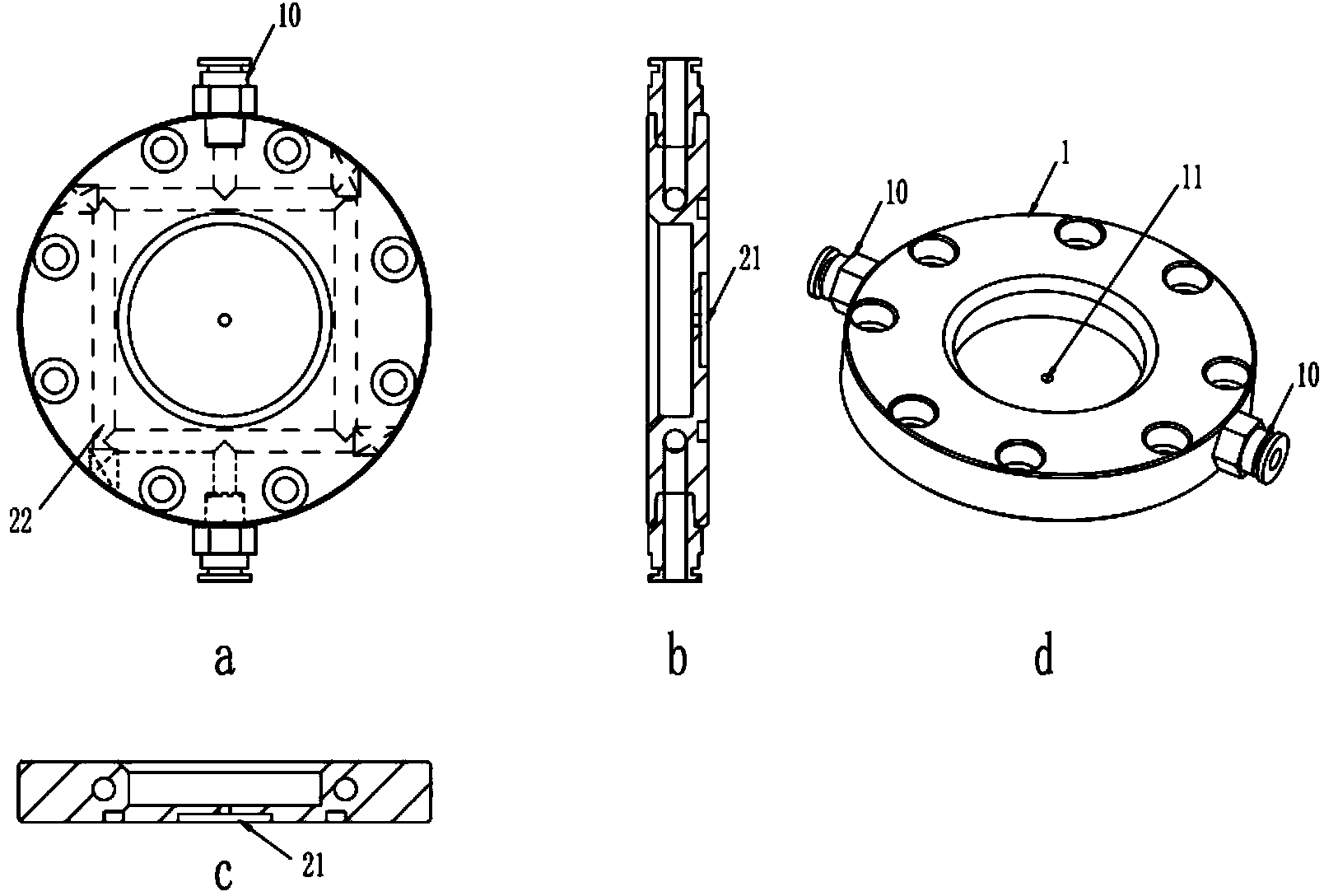
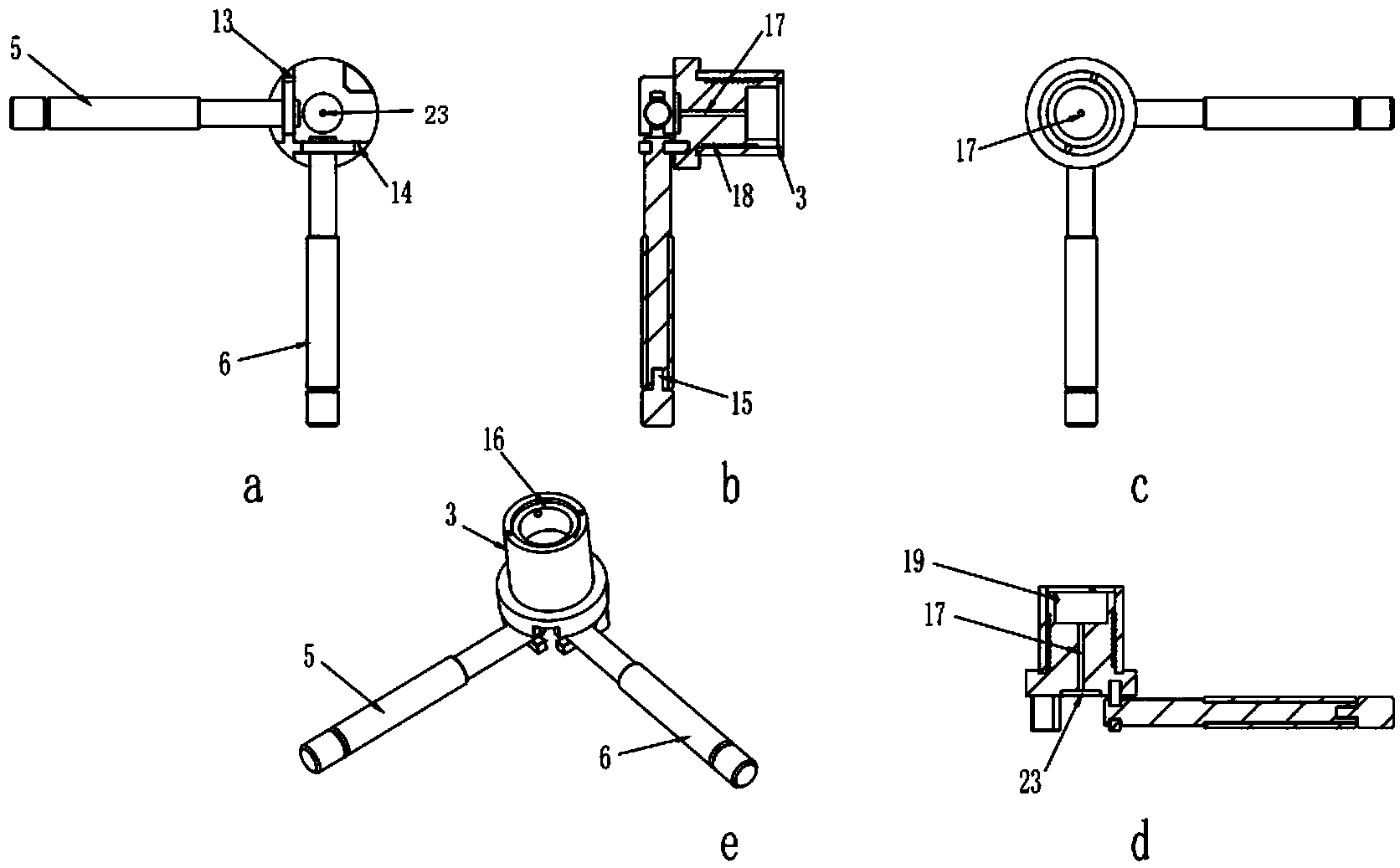
Patents
Literature
47 results about "Dry media reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A dry media reaction or solid-state reaction or solventless reaction is a chemical reaction system in the absence of a solvent.
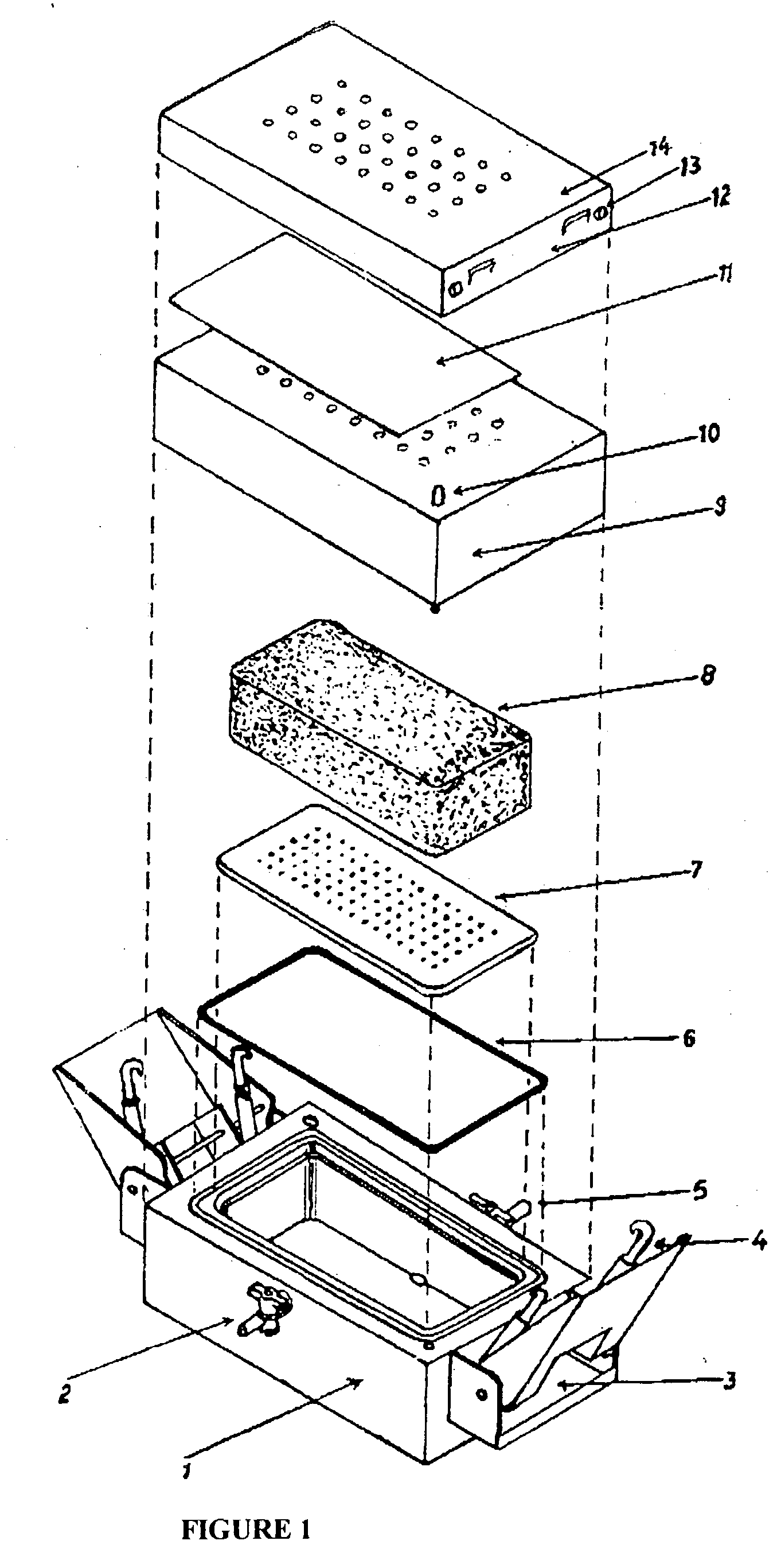
Solid phase reaction system for oxidation
InactiveUS20100113807A1High yieldComplicated operationOrganic oxidationOrganic compound preparationOrganic solventSolid reaction
A solid phase reaction system for oxidation of an organic compound,having high industrial value in which an organic solvent exerting a reverse influence on earth environments is not necessary, reuse of a catalyst is possible, and high yield can be attained, comprisinga mixture of a powdery dispersion medium and a powder of a solid catalyst for the above-described oxidation reaction, and the above-described organic compound and aqueous hydrogen peroxide,wherein the above-described organic compound, the above-described solid catalyst and the above-described aqueous hydrogen peroxide are dispersed in the above-described mixture so that they get into contact mutually.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
High throughput solid phase chemical synthesis utilizing thin cylindrical reaction vessels useable for biological assay
InactiveUSRE37194E1Reduce deliveryFacilitate detailed study of chemical structureSequential/parallel process reactionsElectrolysis componentsChemical synthesisChemical structure
A high throughput chemical synthesis system utilizing cylindrical reaction vessels is disclosed. Reaction vessels are utilized which include a tubular member adapted for placement of electronically readable identifying indicia thereon. The identifying indicia are representative of reaction conditions within the tubular member and of one or more reagents utilized in a reaction within the tubular members. A method of performing chemical synthesis on solid phase reactive material within a plurality of reaction vessels using a plurality of reaction stages resulting in final products and employing identifying indicia representing the reaction stages is also disclosed. The method includes reading the identifying indicia located on the reaction vessels, reacting one or more reagents within the reaction vessels under particular reaction conditions which may be determined by reading the identifying indicia, thereby synthesizing chemical compounds within the reaction vessels. The method allows chemical synthesis to occur according to a predetermined set of reactions and also allows for combinatorial chemistry to be performed utilizing random mix and split techniques. The final synthesized products may be tested for chemical or biological activity. The chemical structures of desired end products may be obtained by reading recorded information wherein the reaction conditions and reagents of reaction steps have been recorded, preferably in conjunction with the identifying indicia.
Owner:PHARMACOPEIA DRUG DISCOVERY
Method for preparing bismuth oxychloride by solid-phase reaction at room temperature
The invention provides a method for preparing bismuth oxychloride by solid-phase reaction at room temperature. The method is characterized in that oxygen-containing bismuth salt and sodium chloride are taken as raw materials, and comprises the following steps: mixing and grinding or carrying out ball-milling on the oxygen-containing bismuth salt and the sodium chloride, removing soluble by-products by rinsing, and drying to obtain the bismuth oxychloride. The method has the advantages of simple process, high efficiency and low cost, and is easy to amplify; especially, in the whole preparation method, acid and alkali as well as organic additives are not used, and heating is not required; and the method has the advantages of energy conservation and environmental friendliness. The bismuth oxychloride prepared by the method has wide market prospects in the fields, such as coatings, inorganic pigment, high-quality cosmetics, pearly jewelries and the like.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
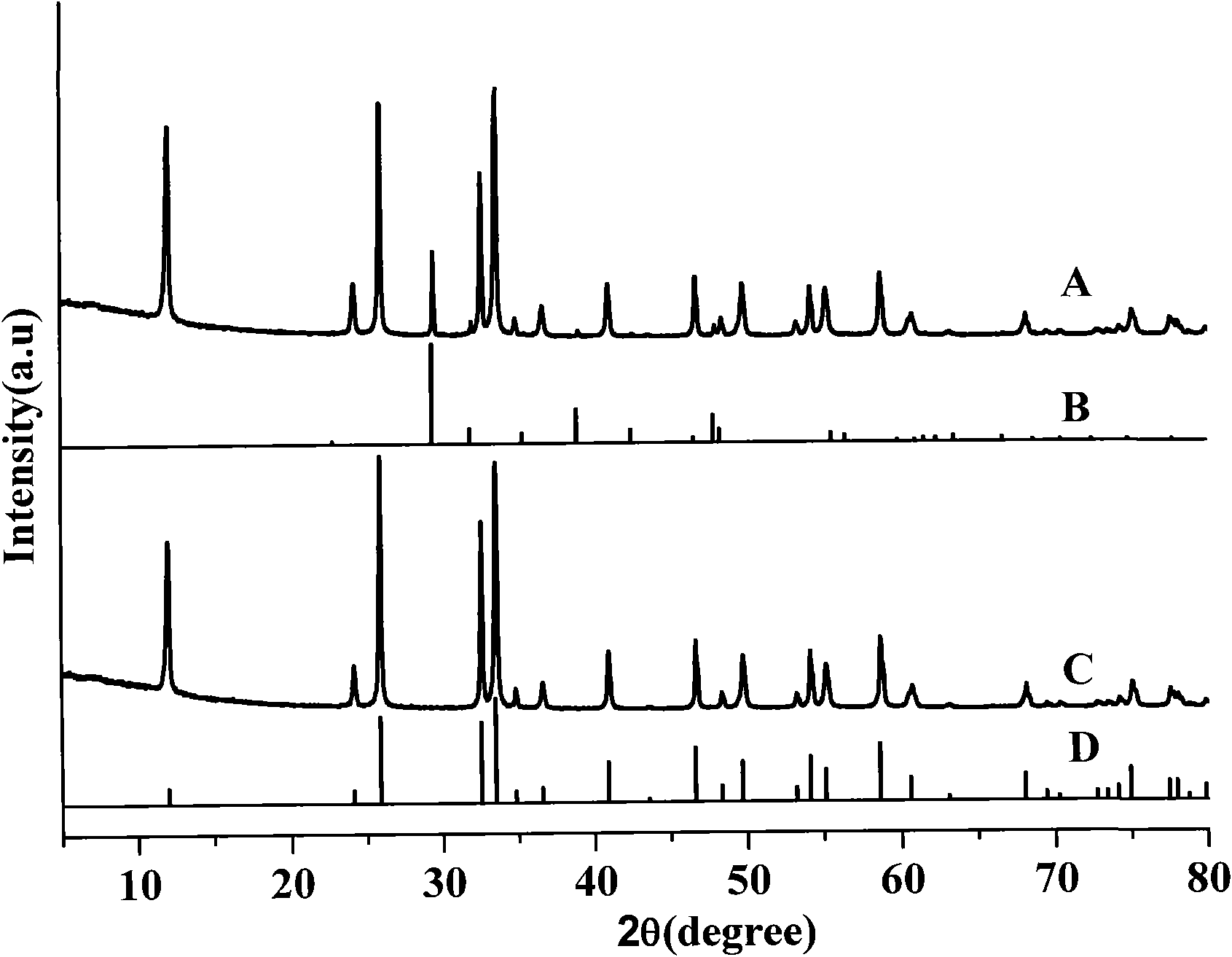
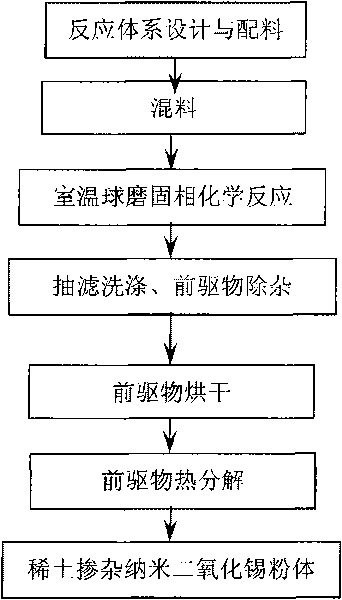
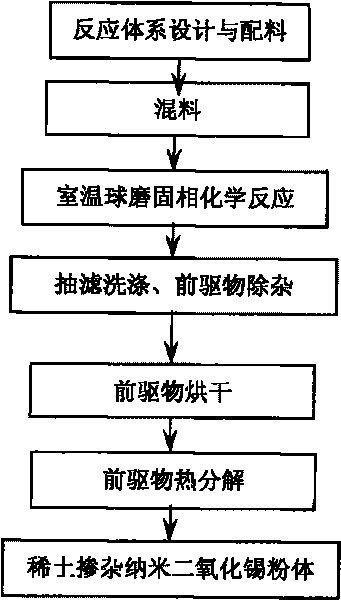
Preparation method of room-temperature ball-milling solid phase chemical reaction of rare earth mixing with nano stannic oxide
InactiveCN101746812ALarge specific surface areaIncrease the speed of diffusionTin oxidesChemical reactionReaction rate
The invention discloses a preparation method of room-temperature ball-milling solid phase chemical reaction of rare earth mixing with nano stannic oxide, relates to a preparation technology of the rare earth mixing with the nano stannic oxide, which can be applied for antistatic coating, plastics, fibre and other fields. Inorganic salts containing stannum and rare earth are taken as reactants, oxalic acid, ammonium carbonate, ammonium bicarbonate, sodium oxalate or sodium carbonate is taken as a ligand, the processing steps are sequentially dosing, mixing and preparing precursors of the room-temperature ball-milling solid phase chemical reaction, and the targeted product can be obtained after impurity removing, drying and thermal decomposition. The preparation method is characterized in that the reaction process does not use water, the stannum ion can be prevented from hydrolysis, uniform mixing can be realized, a solid phase reaction system is broken by utilizing the shearing force and the impact force generated during the ball milling process, the specific surface area of the reactant is increased, the reaction rate is increased, micro-fine and uniform precursors can be prepared, then the processes of cleaning, drying and controlling the thermolysis temperature and time are carried out, and thereby the rare earth mixing with nano stannic oxide powder, the particle size distribution of which is 30 to 80nm and has controllable morphology, can be obtained.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
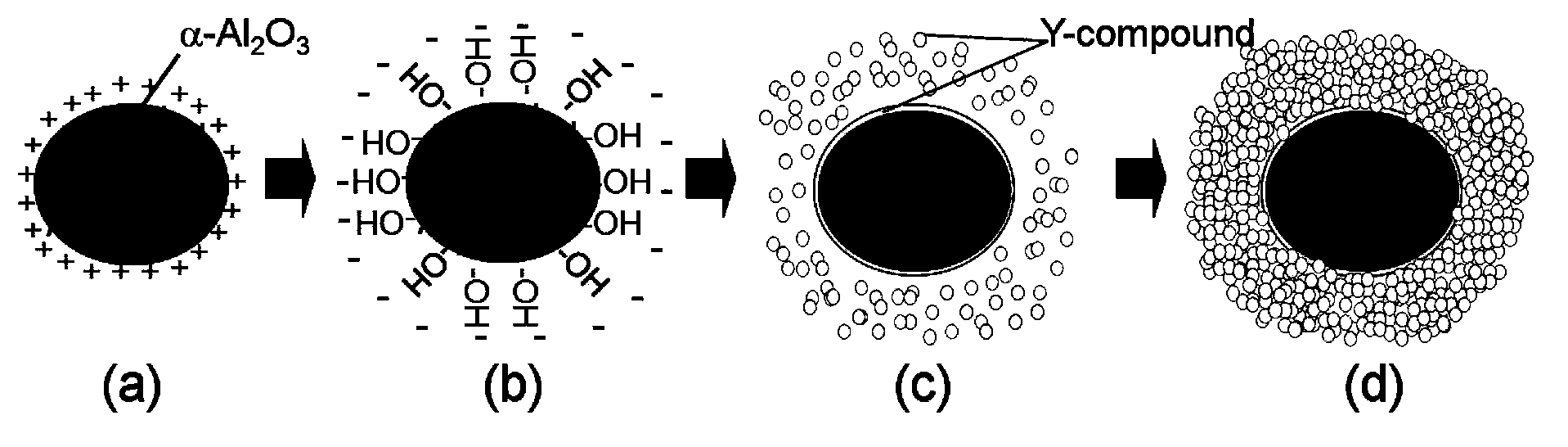
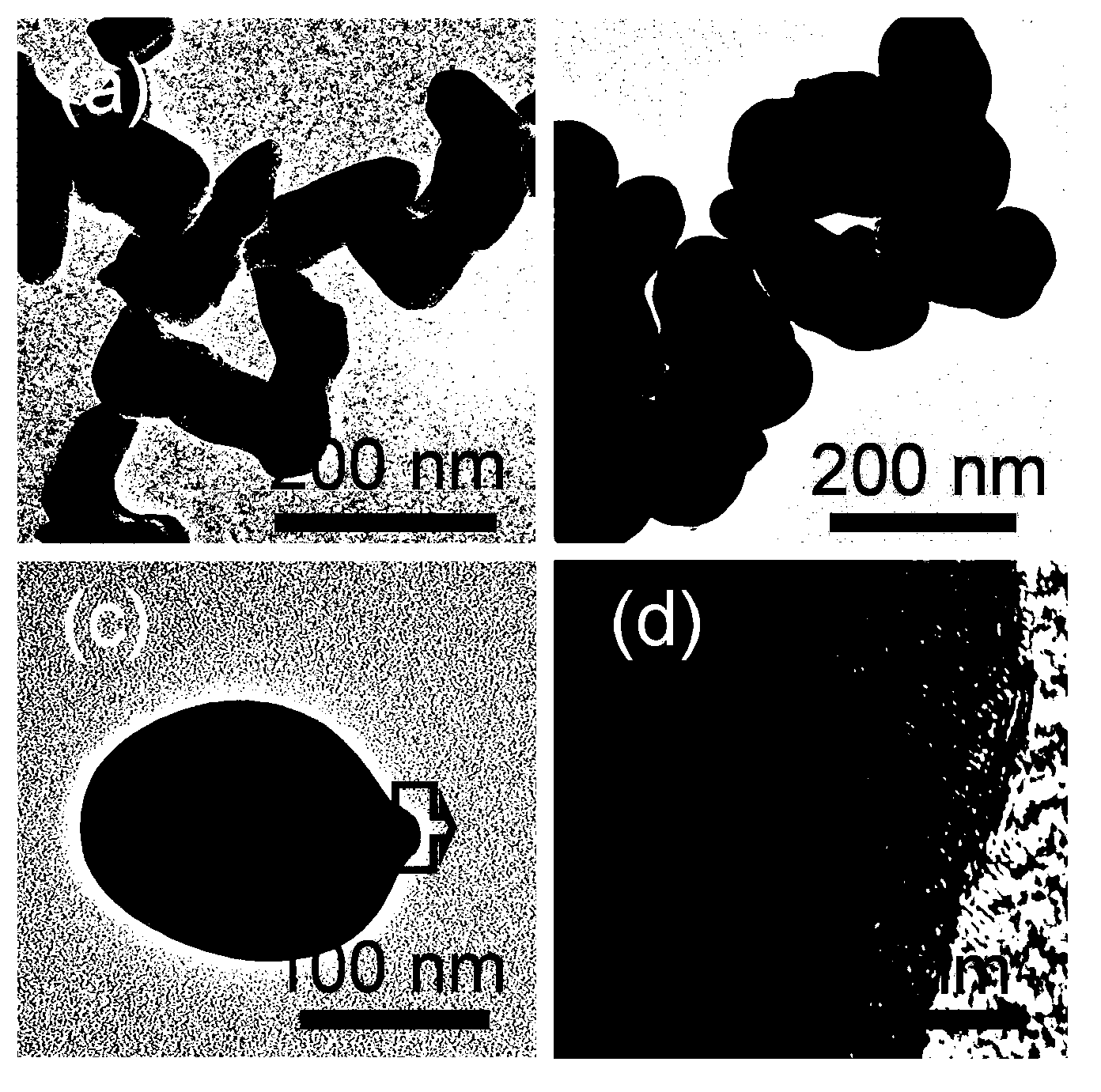
Method for preparing multibasic oxide nanometer particles based on core-shell structure three-dimensional micro-solid-phase reaction.
ActiveCN103242042AAchieving controllable equipmentAvoid Agglomeration FormationDecompositionCalcination
The invention discloses a method for preparing multibasic oxide nanometer particles based on a core-shell structure three-dimensional micro-solid-phase reaction. The method comprises the following steps of: with an oxide particle, which is one of prepared multibasic oxides and has easily controlled morphology, as a core, carrying out appropriate surface charge modification so that other element ions evenly wrap the oxide particle so as to form an oxide particle core-shell structure precursor; and during calcination, implementing low-temperature phase transformation and particle morphology control through the three-dimensional micro-solid-phase reaction between the shell made of the nanometer oxide or an amorphous part generated by decomposition and the wrapped nucleus, thereby obtaining the multibasic oxide nanometer particle and providing a raw material base for the preparation of corresponding ceramic.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
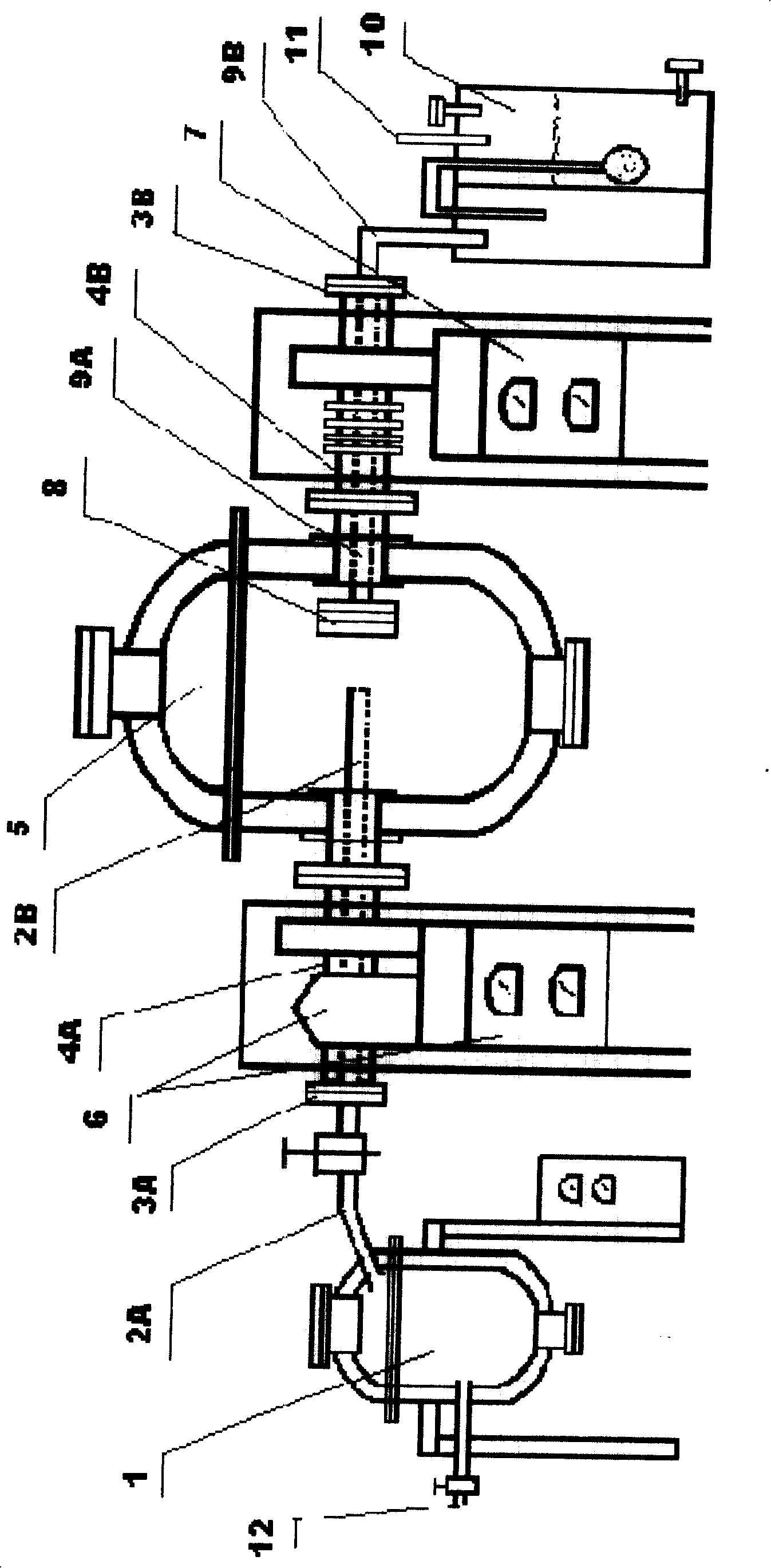
In-situ gas-solid phase reaction pool for measuring high-temperature high-pressure dynamic field spectrum in situ
The invention provides an in-situ gas-solid phase reaction pool for measuring high-temperature high-pressure dynamic field spectrum in situ. The reaction pool comprises a heating stage main body and an internal sample pool, wherein one side of the heating stage main body is provided with an air inlet passage, a reaction pool cover is arranged above the heating stage main body, and is provided with an unthreaded hole, and a window plate covers the unthreaded hole. The internal lower part of the heating stage main body is provided with a cabin body space for storing the sample pool, the bottom of the heating stage main body is provided with a horizontal adjusting transmission rod and is connected with the sample pool in the reaction pool cavity, the sample pool can move on the horizontal plane, a heating wire is wound at the periphery of the pool body, a thermocouple is inserted into the pool body, the bottom of the pool body is provided with an air outlet, and a cooling water passage is respectively arranged in each of the heating stage main body and the reaction pool cover. As a heating state adopts an internal adjusting way, the size of the unthreaded hole is reduced, the thickness of a quartz plate is reduced, the signal attenuation is reduced, a high space resolution requirement is met, and the structural variation of the sample can be monitored under the high-temperature high-pressure reaction condition.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
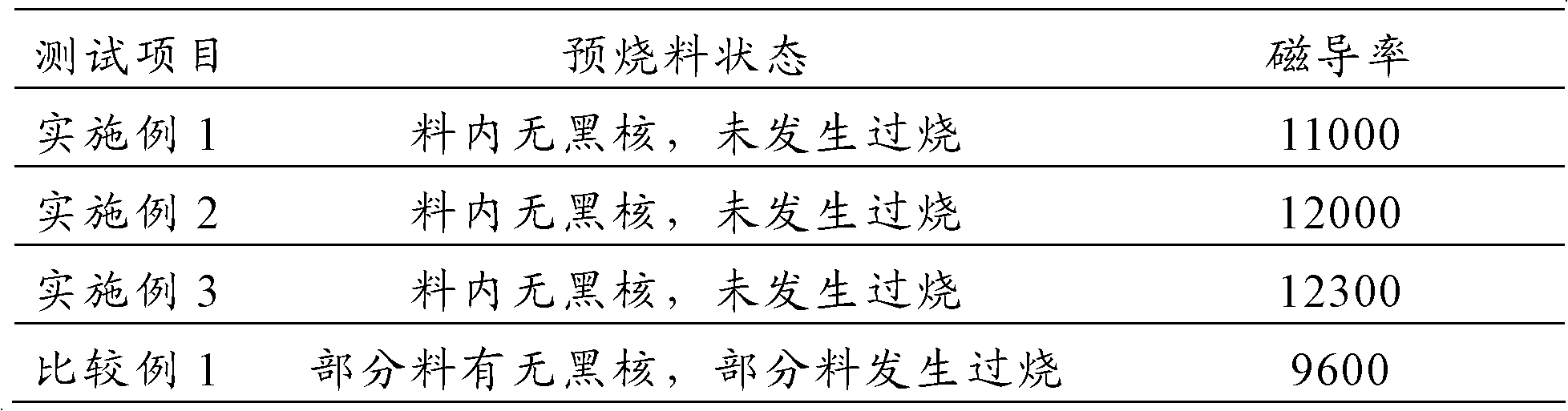
Method for pre-sintering soft magnetic manganese-zinc high-permeability powder in microwave kiln and preparation method of soft magnetic manganese-zinc high-permeability powder
The invention provides a method for pre-sintering and preparing manganese-zinc ferrite powder, and a preparation method of manganese-zinc ferrite material. The pre-sintering method comprises the following steps: delivering a manganese-zinc ferrite mixture in a microwave high-temperature kiln to perform the microwave sintering, wherein the microwave frequency of the microwave sintering is 2450 MHz and the sintering temperature is 700 DEG C-900 DEG C. In the process of pre-sintering, the mixture quickly absorbs the energy of the microwave from inside to outside under the action of the microwave, the entire material uniformly generates heat, is evenly heated and not easy to excessively sinter, so that the product quality is stable; and as the heating speed of the microwave is high, the time for raising the temperature of the mixture to the required temperature of solid phase reaction is shortened, the producing period is shortened and the energy consumption is also reduced. Therefore, the method for pre-sintering the manganese-zinc ferrite powder, provided by the invention, has the characteristics of high product quality stability and low energy consumption.
Owner:湖南阳东微波科技有限公司
Novel process for synthesizing povidone iodine by gas phase/ solid phase reaction
InactiveCN101161688AReduce manufacturing costSimple processSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsDermatological disorderGas phaseReaction temperature
The present invention discloses a novel process for synthesizing povidone iodine by gas phase and solid phase reaction. The process combines the iodine-subliming purification process and the synthesization process of povidone iodine by using periston and coarse iodine as raw materials, using a gas phase-solid phase reactor for synthesizing povidone iodine, heating the coarse iodine in the iodine sublimation kettle to make it to sublime to be purified, leading the iodine steam through the heat-preserving conduit into the gas phase-solid phase reactor containing the solid periston to perform gas phase and solid phase reaction directly; adding inert gases with a certain velocity of flow and volume of flow in iodine sublimation kettle to take and raise the flow of the iodine steam in to the gas phase-solid phase reactor; controlling gas phase-solid phase reactor to rotate clockwise and counter-clockwise in a predetermined cycle, and keeping a certain reaction temperature to make periston and iodine stream to be contacted, adsorbed and reacted adequately; exhausting after treatment of the exhaust gas which is connected to the collecting pot of the exhaust gas by the exhaust pipe; batching off when reacting the schedule time to obtain the povidone iodine meeting the pharmacopoeia standard.
Owner:BEIJING BEIDA MINGDE CHEM PHARMA
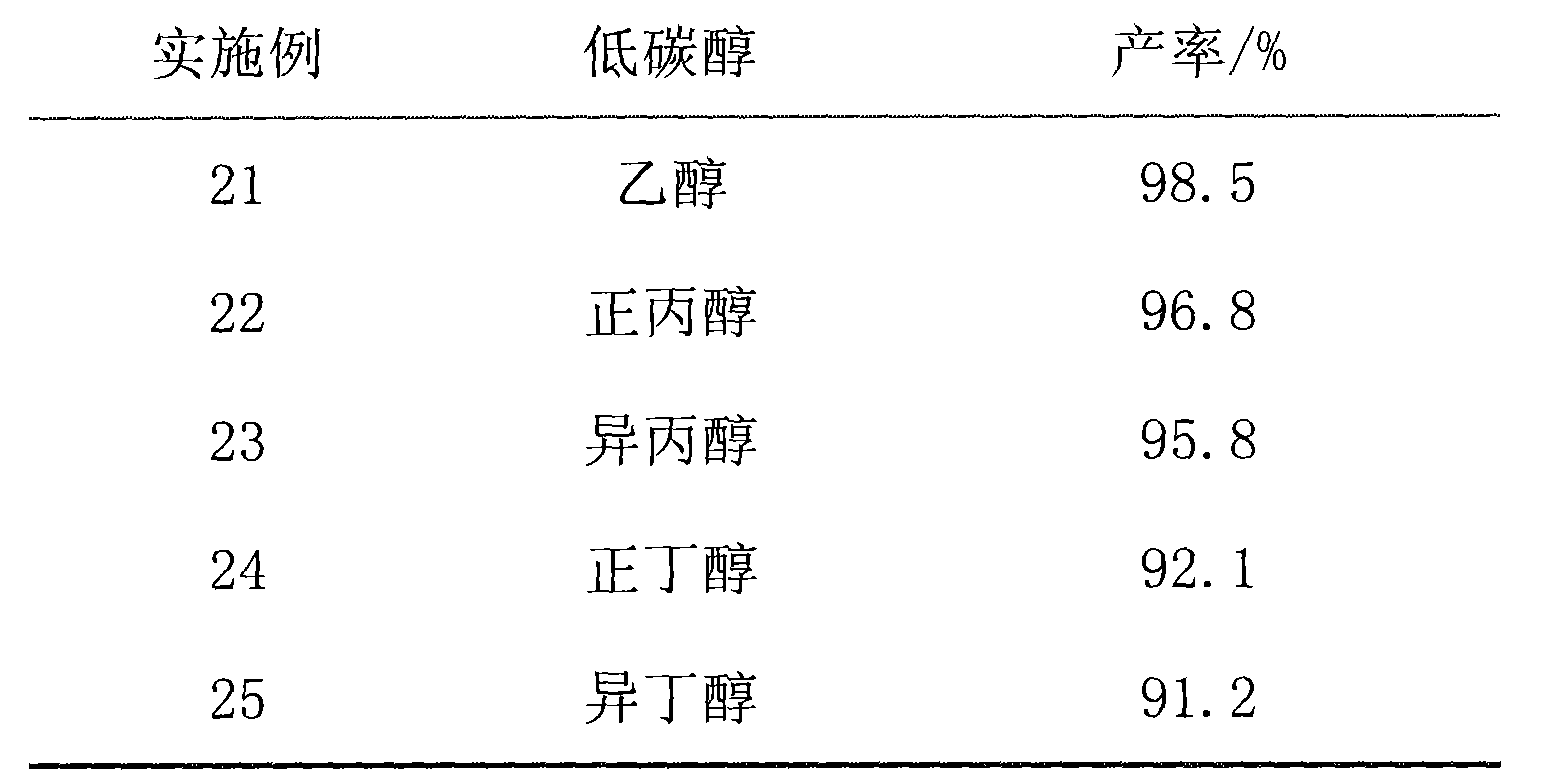
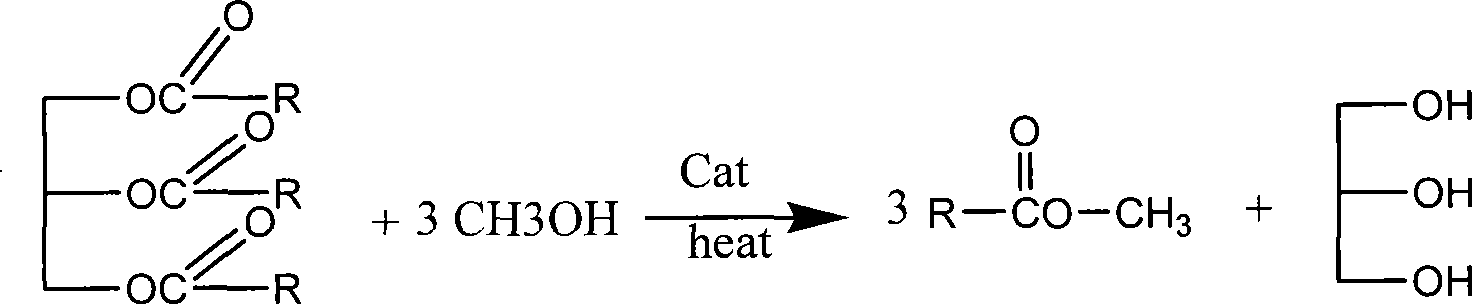
Solid base catalyst and applications of biological diesel oil synthesizing
InactiveCN101249453AActivity unchangedIncrease profitBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBiodieselAlcohol
The invention discloses a solid base catalyst and application thereof in biodiesel synthesis. The catalyst is prepared by allowing organic metal salt and alkali or alkali carbonate to a solid phase reaction and calcining at a high temperature. The biodiesel is synthesized by ester exchange, by adding grease, low carbon alcohol and the solid base catalyst into a three-necked container to heat for refluxing under stirring, filtering to obtain catalyst, demixing the filtrate to obtain lower layer glycerol and upper layer mixture, adding NaHCO3 solution to the upper layer mixture, washing until a neutral condition, drying with anhydrous MgSO4, and vacuum distilling. The catalyst for biodiesel synthesis has the advantages of high yield, cheap price, small consumption amount, mild reaction condition, short reaction time, repeated use of the catalyst, no environmental pollution and low requirement for raw material.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Solid-phase reacting synthesis of composite ceramic powder non-toxic gel
A non-toxic gel solid phase reacting synthesis of composite ceramic powder is carried out by proportioning, preparing sodium alginate solution, mixing, ball milling, adding catalyst, gelating, drying and calcining. Its advantages include low cost, simple operation, no pollution and higher powder quality.
Owner:BEIJING AVIATION MATERIAL INST NO 1 GRP CORP CHINA AVIATION IND
Preparation method for maleic anhydride modified hydrothermal bamboo charcoal adsorbent
InactiveCN108262028AIncrease contentImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSodium bicarbonateSorbent
The invention discloses a preparation method for a maleic anhydride modified hydrothermal bamboo charcoal adsorbent. The method is performed according to the following steps: (1) modifying hydrothermal bamboo charcoal by maleic anhydride: performing uniform mixing on the hydrothermal bamboo charcoal and the maleic anhydride, performing a reaction under the temperature condition of 120-140 DEG C for 2-6 h, performing natural cooling, placing the cooled material into distilled water, performing stirring, performing filtration, and performing washing by using distilled water to obtain a semi-finished product; and (2) performing treatment on the maleate modified semi-finished product: adding the semi-finished product into a saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, performing stirring, performingfiltration, performing washing until the obtained solution is neutral, and performing drying to obtain the finished product. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that a hydroxyl group on the surface of the hydrothermal bamboo charcoal and the maleic anhydride are subjected to an esterification reaction, the content of groups of a carboxylic acid, carbonyl, unsaturated bonds andthe like on the surface of the hydrothermal bamboo charcoal is improved, and therefore the adsorption capacity of the hydrothermal bamboo charcoal to pollutants such as cationic dyes and heavy metalions is increased; and the reaction is a solid phase reaction, does not require participation of organic solvents, and has no problems such as solvent recovery and treatment, and is a green syntheticmethod.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
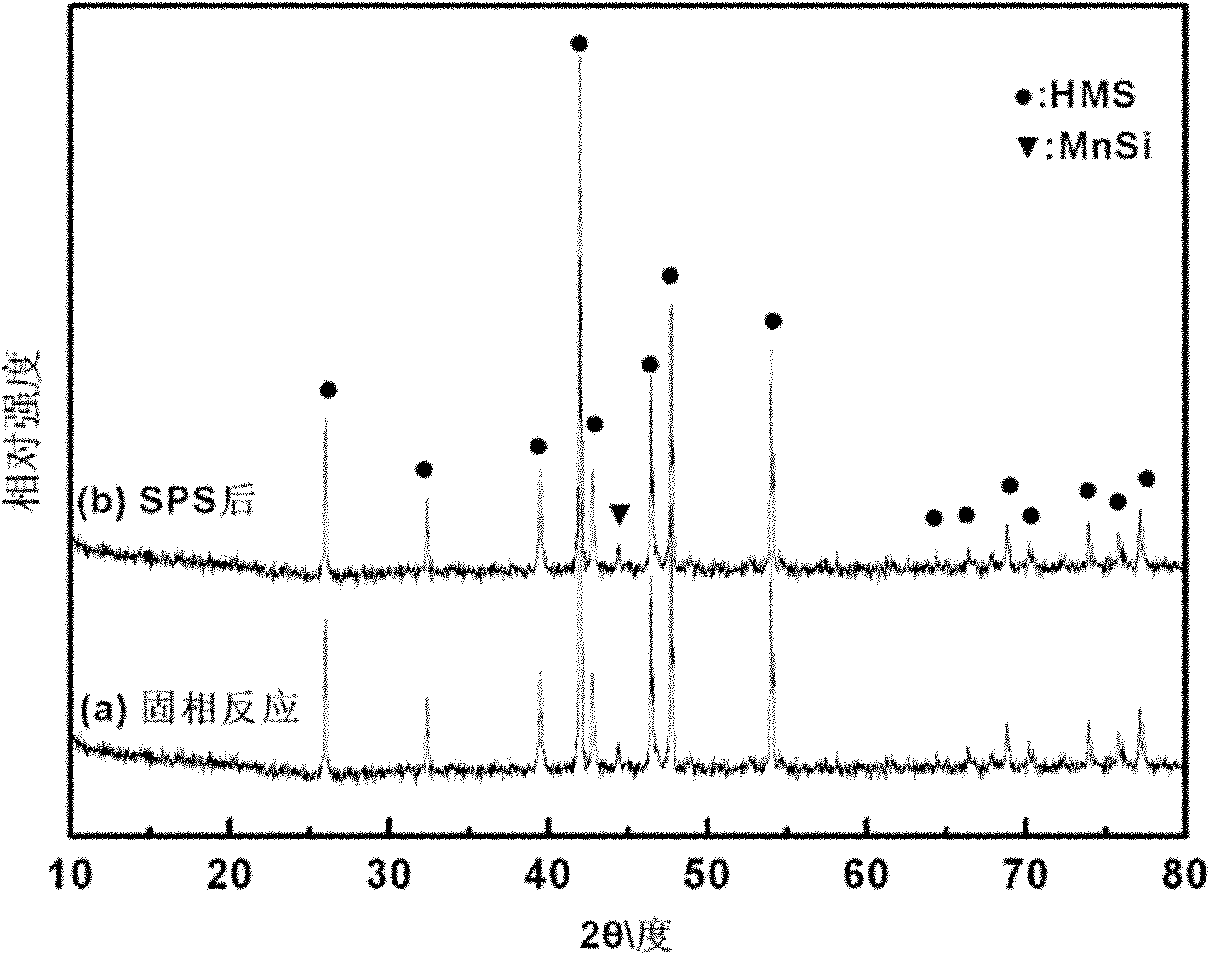
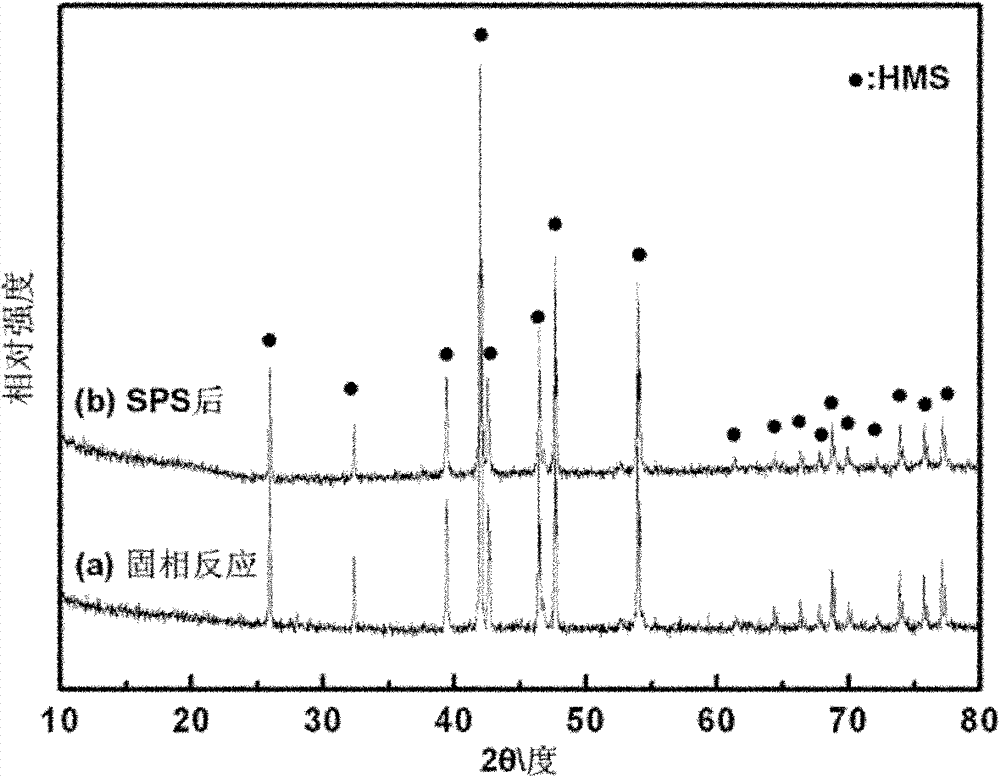
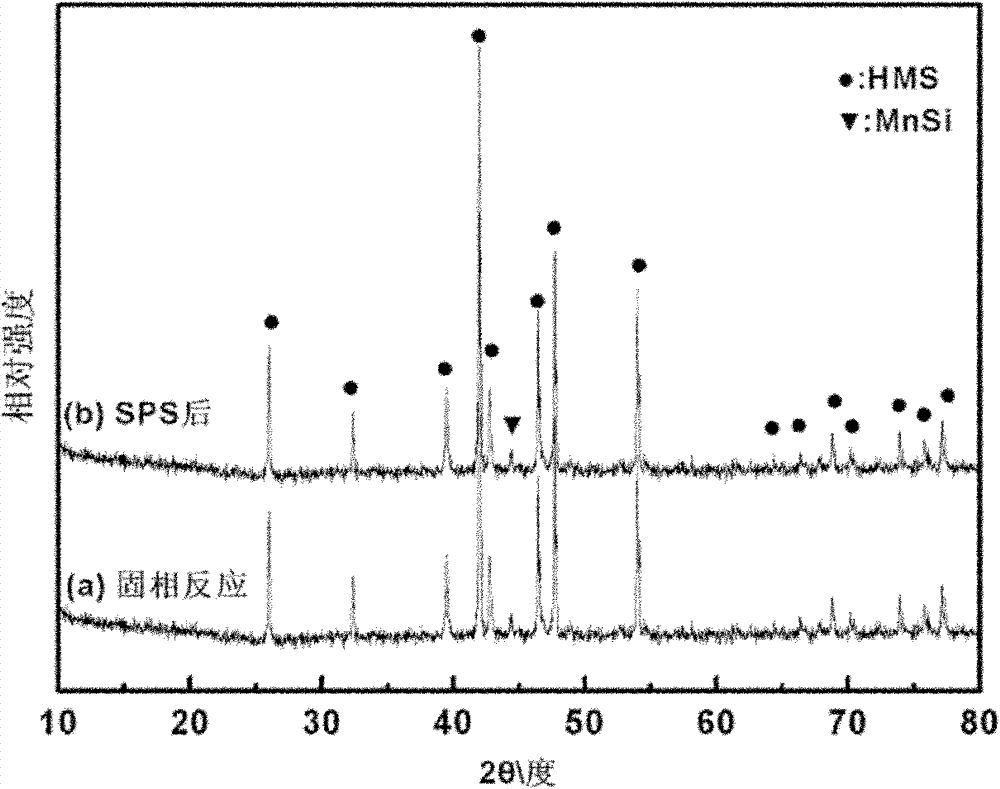
Solid-phase reaction preparation method for silicious manganese thermoelectric material
InactiveCN102174677ALow costLow priceThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric materialsElectric discharge
The invention belongs to the technical field of new energy materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method for a silicious manganese thermoelectric material. A solid-phase reaction preparation method for the silicious manganese thermoelectric material is characterized by comprising the steps as follows: (1) Si powder and Mn powder are taken as raw materials, weighed according to the molar ratio of (1.75-1.80):1, and mixed evenly to obtain evenly mixed powder; (2) the evenly mixed powder are put on a tabletting machine and pressed into a bulk, the bulk is placed into a quartz glasstube, the quartz glass tube is vacuumized and sealed and then is placed in a muffle furnace for 850-900 DEG C solid-phase reaction for 12-24 hours, and the product is obtained after heat preservationis finished and furnace cooling is carried out; (3) the product obtained in step (2) is ground into fine powder; and (4) the fine powder obtained in step (3) is subjected to electric discharge plasmasintering, and the compact silicious manganese thermoelectric material can be obtained. The method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, energy conservation, and low requirements for instruments and equipment, and is suitable for commercial manufacture.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Compound low-temperature pre-sintering method of ferrite monoliths structure materials
InactiveCN101700981AImprove electromagnetic performanceBroaden the technical scope of low temperature sintering processSolid reactionWarming process
The invention discloses a compound low-temperature pre-sintering method of ferrite monoliths structure materials, which comprises the steps of: 1. confirming reference indexes, and preparing raw materials; 2. compositely and previously sintering: previously sintering powder materials of the step 1 at least two times, wherein the first previous sintering leads the solid phase reaction to happened among the each raw material, so that all or some of the raw materials are changed into the ferrite to be taken as a base for the second previous sintering; detecting the powder materials after the first previous sintering, and confirming the technology condition of the second previous sintering according to a detecting result, wherein the second previous sintering leads the non-extensive quantity of the galvanomagnetic property in the raw materials to meet or exceeds the requirement of product performance; confirming the temperature and the technology of the nest previous sintering according to the formulation of the materials and the requirement of the product performance; and detecting the powder materials after the previous sintering, wherein if the product performance after the previous sintering can not meet the requirement of the product performance, sintering for several time, and if the product performance after the previous sintering can not meet the requirement of the product performance, granulating and shaping; 3. granulating and shaping; and 4. low-temperature sintering, the temperature of the low-temperature sintering is lower than the maximum temperature in the process of pre-sintering, and the compared with the normal process, the temperature is faster raised.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
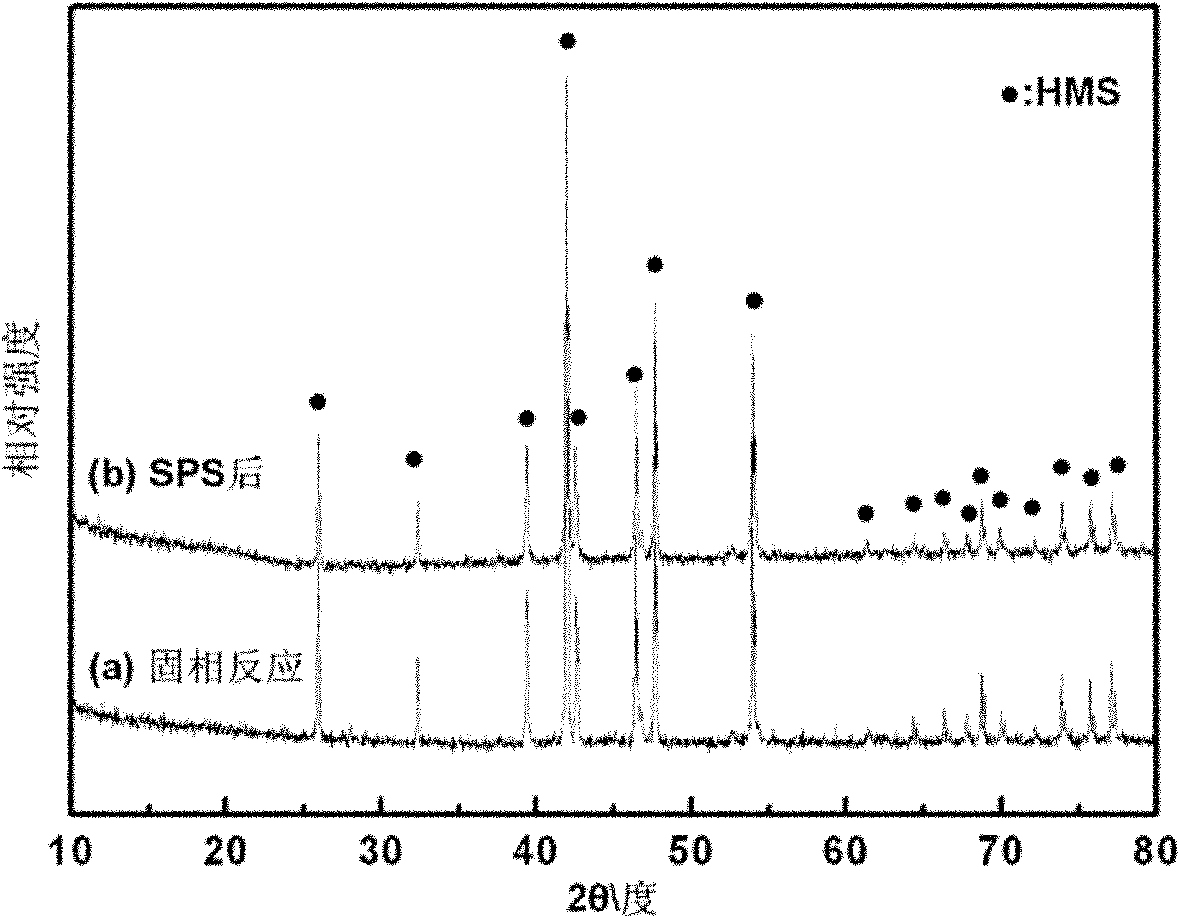
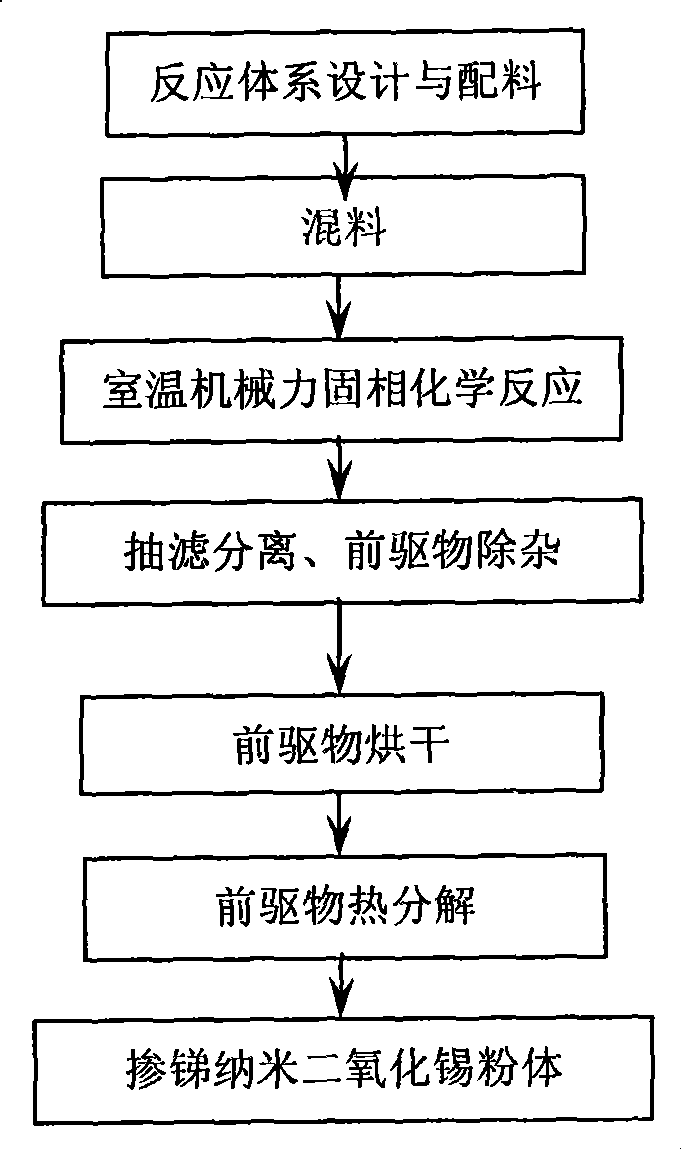
Room temperature mechanical force solid phase chemical reaction preparation of antimony-doped nano stannic oxide
InactiveCN101412858ALarge specific surface areaIncrease the speed of diffusionPigmenting treatmentSodium bicarbonateTin dioxide
The invention discloses a room-temperature mechanical force solid-phase chemical reaction method for stibium-doped nanometer tin dioxide and relates to a technology for preparing the stibium-doped nanometer tin dioxide in anti-electrostatic painting, plastic, fibre and other fields. Stanniferous inorganic salt and antimonial inorganic salt are used as reactants; and oxalic acid, ammonium carbonate, ammonium hydrogen carbonate, sodium oxalate or sodium bicarbonate and the like are used as ligands. The method comprises the following process steps: the materials are matched, are mixed and are subjected to room-temperature mechanical force solid-phase chemical reaction to prepare a precursor; the precursor is subjected to impurity removal, drying and thermal decomposition to obtain the target product. The method is characterized in that water is not introduced in the reaction process to prevent the hydrolysis of tin ions and stibium ions so as to realize even doping; simultaneously, the method utilizes shearing force and impacting force produced in the ball milling process to crush a solid-phase reaction system, increases the specific surface areas of the reactants and increases the speed of reaction to prepare the superfine and even precursor; the precursor is washed and dried; and the temperature and the time for thermal decomposition are controlled, thereby obtaining the nanometer tin dioxide doped powder body which has distribution of particle diameter of between 30 and 80 nm and a controllable pattern.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for nanometer cupric oxide through two-step solid phase synthesis
InactiveCN101544393AAvoid reunionUniform responseNanostructure manufactureCopper oxides/halidesFeed additiveSolid-phase synthesis
The invention relates to a method for nanometer cupric oxide through two-step solid phase synthesis, which belongs to the technical field of nano materials and comprises the following steps: obtaining a nanometer cupric chloride precursor by a first step solid phase reaction; decreasing activation energy of a second step solid phase reaction; controlling nucleation rate; and realizing the control of the size of grain diameter of the nanometer cupric oxide, wherein the grain diameter of the nanometer cupric oxide is controlled to be below 30 nm; and the nanometer cupric oxide is dispersed uniformly. The synthetic process of the process has the advantages of environmental protection, less energy consumption, no discharge of three wastes, and no pollution; and by adding an inert carrier, the stability of the nanometer cupric oxide is improved, and the nanometer cupric oxide is dispersed uniformly. A final byproduct of the two-step solid phase synthesis is non-hazardous to human and animals, and a mixture needs not washing and separating so as to solve the problems of dispersion and aggressiveness of the nano materials in the process of washing and drying. The method provides technical support for fundamental research for promoting the nanometer cupric oxide as a feed additive, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for preparing pipeline material by utilization of recovered HDPE low-temperature solid-phase extrusion reaction
The invention relates to the material field and modification of a high-molecular material and discloses a method for preparing a pipeline material by the utilization of a recovered HDPE (high density polyethylene) low-temperature solid-phase extrusion reaction. Raw materials contain the following substances: by weight, 96.8%-99.7% of recovered HDPE, 0.1%-2% of a cross-linking agent and 0.1%-1.5% of an anti-oxidant. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) drying the raw materials except the recovered HDPE, uniformly mixing the dried raw materials at 40-50 DEG C, and adding the raw materials and the recovered HDPE together into an extruder; and (2) extruding the mixture by the use of the extruder at 110-140 DEG C and at the speed of 80-150 rpm. According to the invention, the low-temperature solid-phase extrusion reaction is adopted and the traditional concept of recycled material recycling is changed, physical modification and chemical modification are carried out in the extruder at the same time, and injection-moulding-grade plastic is modified into extrusion-grade plastic which can be used as a special pipeline material.
Owner:上海宝利纳材料科技有限公司
Preparation process of sulfonated solid particle
A process produces a sulfonated solid particle by burning sulfur to yield gaseous sulfur dioxide, subjecting the gaseous sulfur dioxide to catalytic oxidation to yield gaseous sulfur trioxide, and sulfonating a dry powdery or granular solid particle with the gaseous sulfur trioxide in a gas phase-solid phase reaction.
Owner:DAINICHISEIKA COLOR & CHEM MFG CO LTD
Gas/solid phase reaction
InactiveUS20090028783A1Reduce the temperatureContinuous productionHydrogen productionEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesChemical reactionHydrogen
The invention relates to a process and reactor for the quasi-continuous performance of a chemical reaction on the surface of a fixed reactant in a gas / solid phase reaction. In particular, the invention relates to a thermal process and a reactor for the continuous preparation of hydrogen from water vapor on the surface of a metal oxide in a gas / solid phase reaction.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV +1
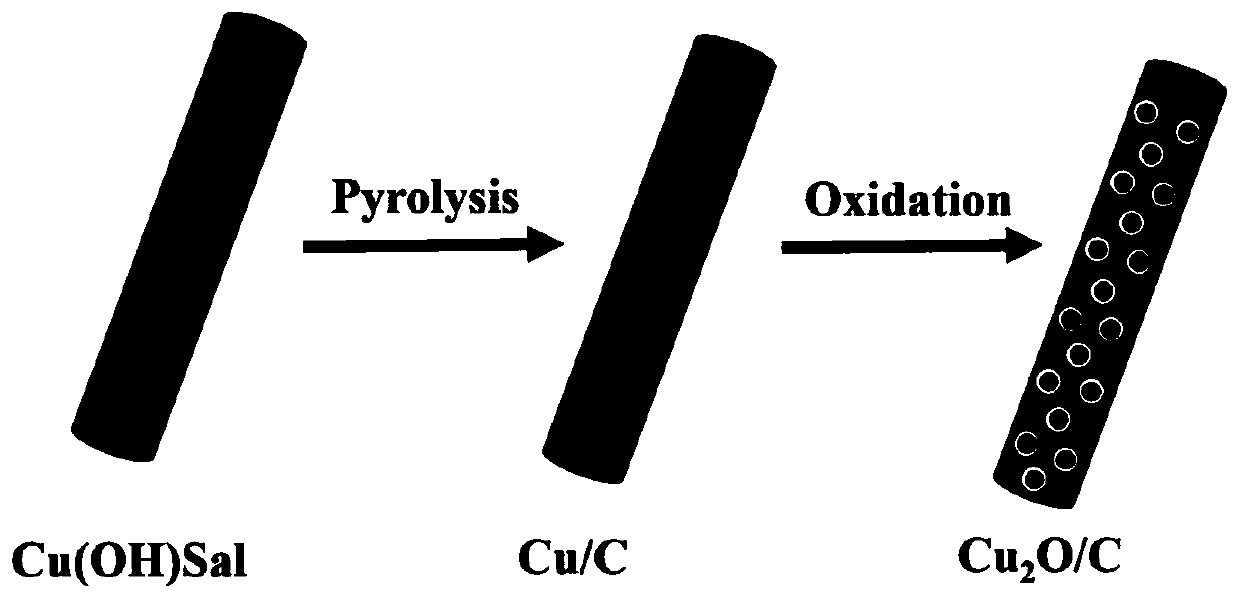
Method for preparing one-dimensional cuprous oxide/carbon nanocomposite catalyst and application
ActiveCN110152664AHigh crystallinityImprove catalytic performanceMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationCarbon nanocompositeCrystallinity
The invention discloses a method for preparing a one-dimensional cuprous oxide / carbon nanocomposite catalyst and application. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: by utilizing an intercalation assembly of salicylate and metal ions, preparing salicylate intercalation layered copper hydroxide having one-dimensional morphology; carrying out solid-state pyrolysis and low-temperature oxidation two-step solid-phase reactions, thereby obtaining the one-dimensional cuprous oxide / carbon nanocomposite catalyst. According to the method disclosed by the invention, cheap water soluble salts serve as reactants, any organic solvent, surfactant, extra carrier, template agent or reducing agent is not needed in the preparation process, the prepared catalyst particle is uniform in distribution, high in purity and high in crystallinity, and the Cu nanoparticles form Cu2O having a hollow structure by utilizing a Kirkendall effect. The catalyst synthesized in the invention has excellent catalytic performance and excellent cycling stability in a liquid phase hydrogenation reaction of p-nitrophenol.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Rapid Solid-State Reaction of Oxides with Ultraviolet Radiation
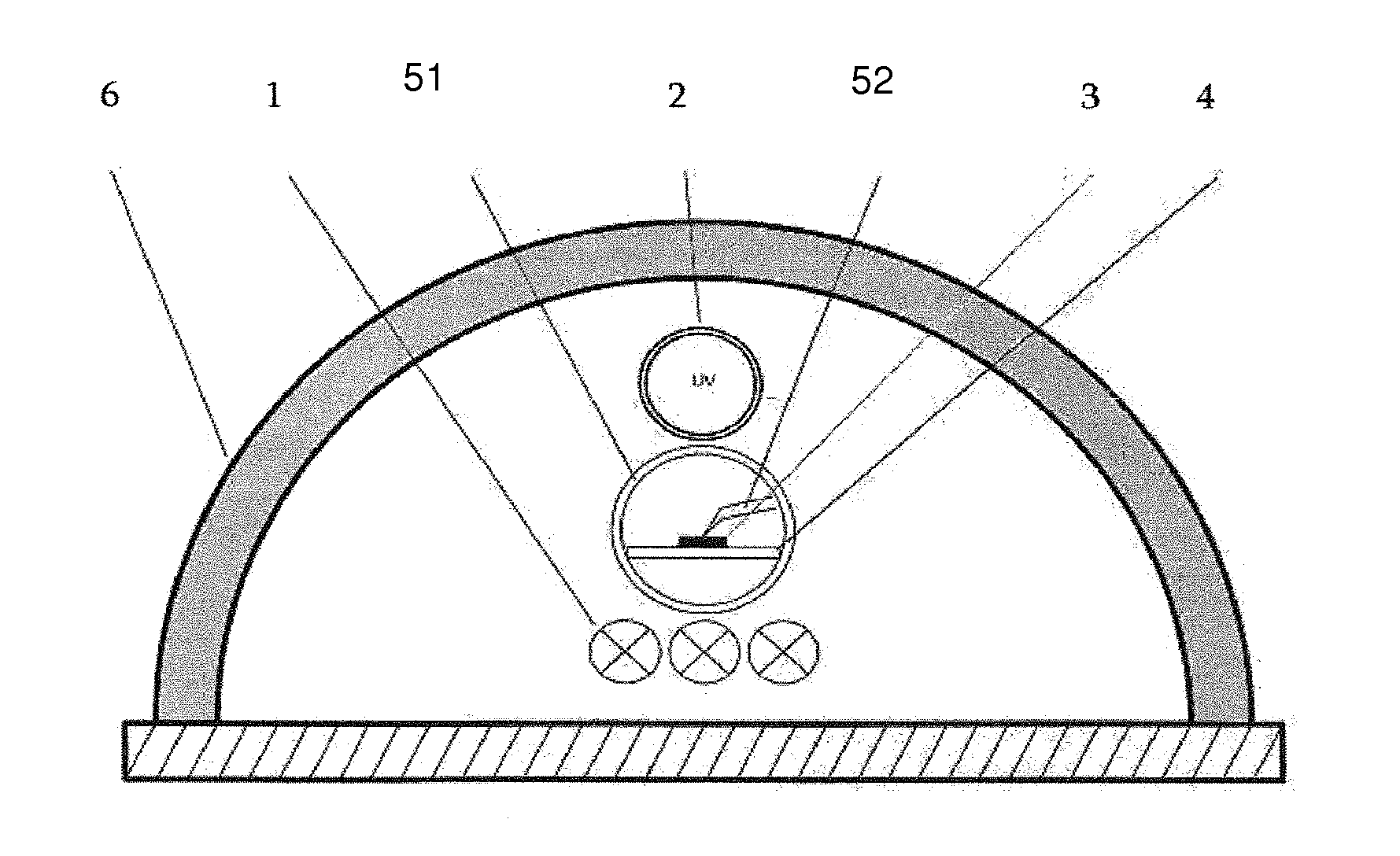
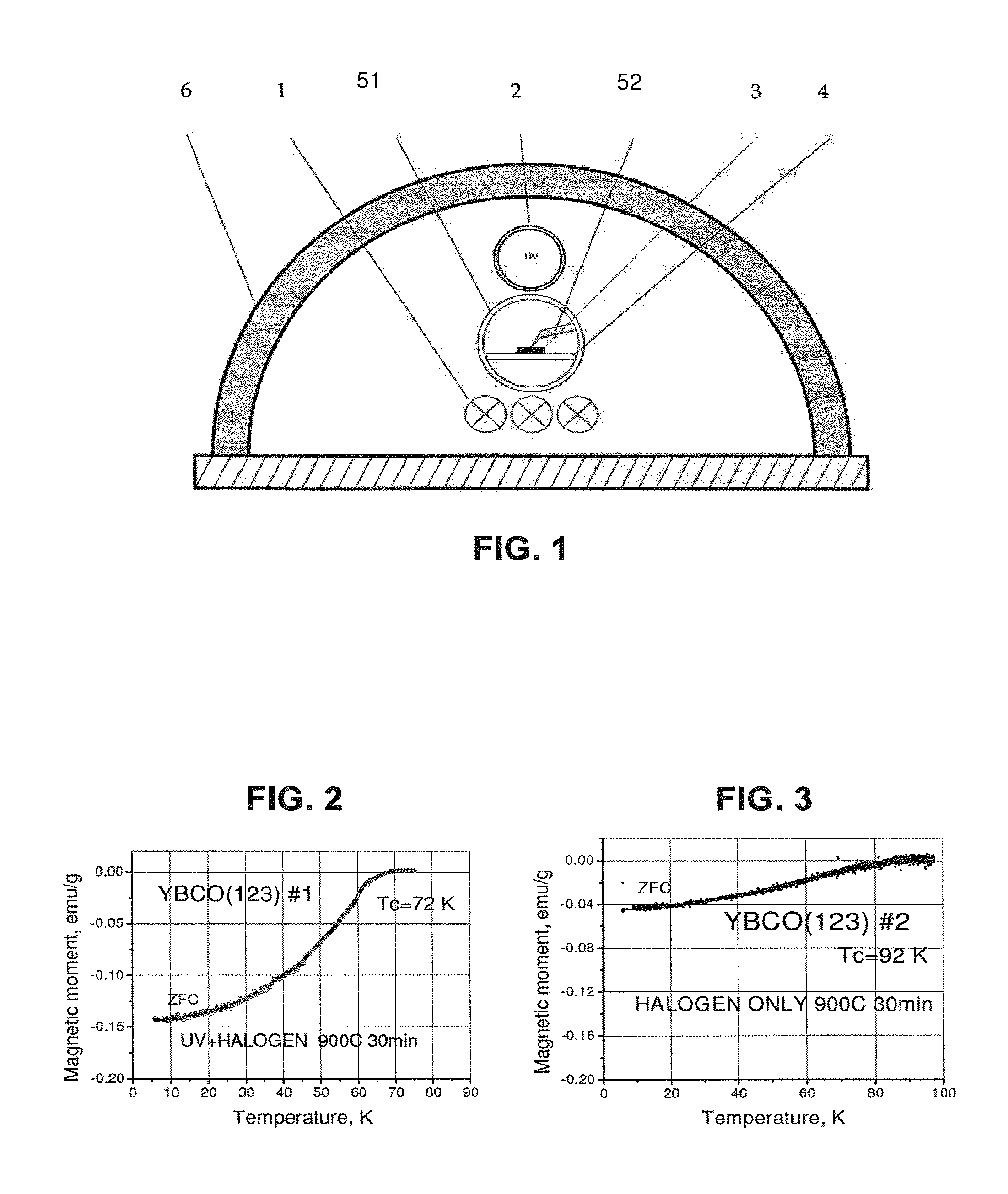
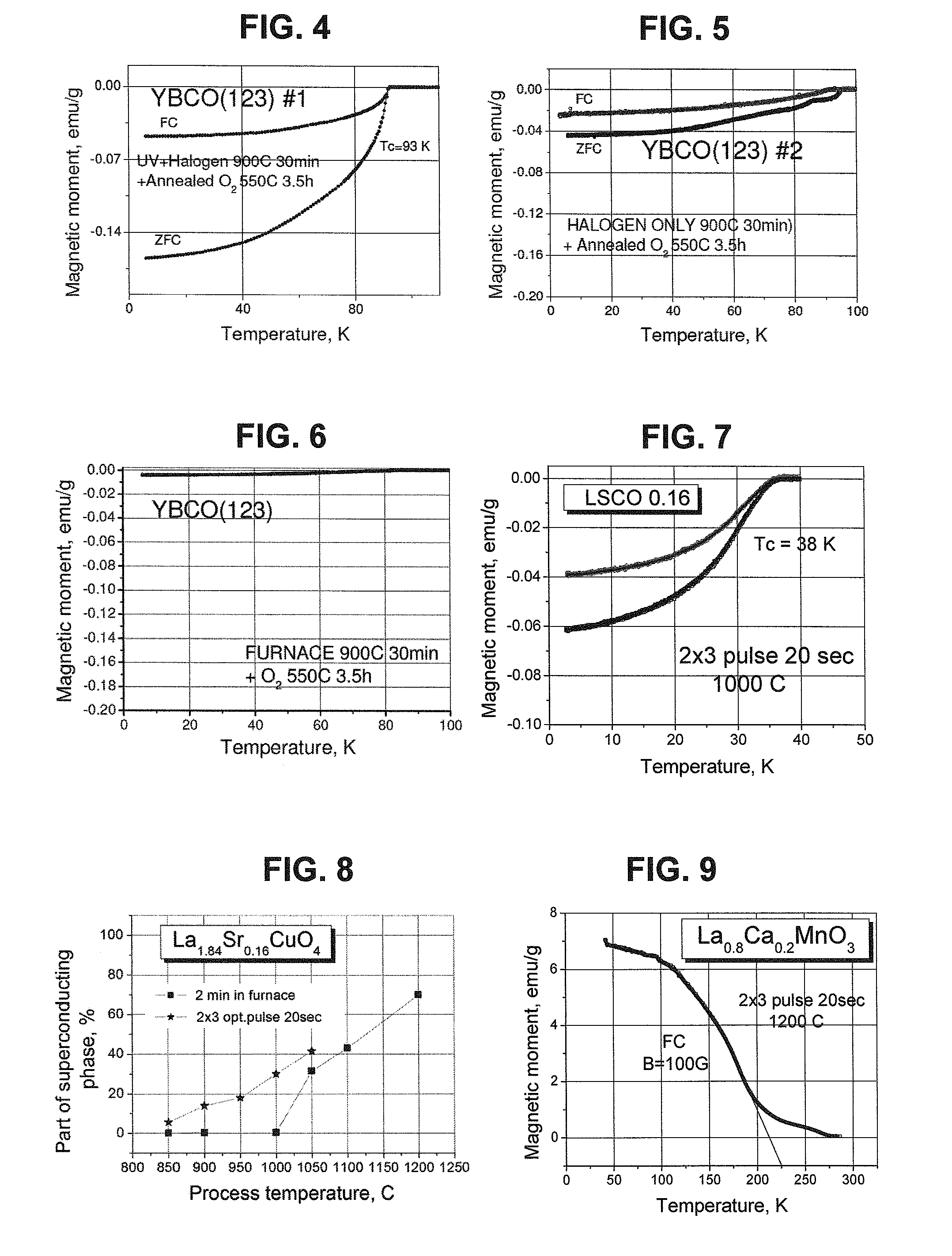
InactiveUS20150357549A1Increase synthesisShorten production timeSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsSolid reactionUltraviolet lights
The present invention relates to a method for solid-state synthesis of ceramic materials, in particular of oxide materials or cuprates, comprising or consisting of the step of providing starting material in amounts effective to produce the ceramic material and, thereafter, applying a treatment to said material by use of a solid-state reaction therein, said reaction being performed by irradiating said material from at least one light source with ultraviolet light. The present invention also relates to methods for producing thin films and to a use of the method for production of high-temperature superconductors.
Owner:MUELLER F +1
Microporous filtration based dot immunoassay device for method for screening of analytes and method of use
InactiveUS20040185577A1Efficient and effectiveFacilitated reaction kineticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteFiltration
The present invention is based on rapid displacement of solvents under mild vacuum in solution-solid phase reaction of immunocomplex [Ijsselmuiden et al., J. Immunol. Methods, 6 (1989): 35]. In the present invention, this is achieved by a microporous absorbing pad upon which a nitrocellulose transfer membrane is placed. The absorbing pad under mild vacuum generated / regulated by running tap effectively filters out the unbound ligand and rinsing solutions through transfer membrane, thus enhancing the reaction kinetics of immunocomplex. This mechanism, in turn reduces the incubation steps of antibody-antigen reaction from hours to few minutes, allowing total assay time in less than 20 minutes.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Room temperature solid phase preparation method for cuprous oxide/copper oxide nanocomposite
InactiveCN107352573AHigh yieldHigh catalytic activityMaterial nanotechnologyCopper oxides/halidesChemical reactionCopper oxide
The invention relates to a method for preparation of a nanoscale cuprous oxide / copper oxide compound by room temperature solid phase reaction. A cuprous salt and alkali are mixed in different ratios for room temperature solid phase chemical reaction to obtain a nano cuprous oxide / copper oxide compound and pure phase cuprous oxide. The obtained products are 20-50nm granular substances, and can show good catalytic activity when used for catalyzing carbon monoxide oxidation reaction. The method has the advantages of simple operation, mild conditions, environmental protection and no pollution, and cheap raw materials, thus being easy for mass production. The obtained cuprous oxide based nanomaterial is expected to show important application in catalysis, energy storage, environmental detection and repair and other fields.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Horizontal type self-cleaning pressure-bearing solid-phase reaction kettle
PendingCN107617406AIncrease productionWith self-cleaning functionCleaning using toolsChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsSolid reactionEngineering
The invention provides a horizontal type self-cleaning pressure-bearing solid-phase reaction kettle, aiming at solving the problems in the prior art that the heat transferring area is small and materials are easily stuck so as to influence the heat transferring efficiency. The reaction kettle comprises a reaction kettle barrel body which is horizontally arranged; the reaction kettle barrel body isinternally provided with at least two stirring shafts which extend along the length direction and are rotatable; two rows of stirring paddles, which are symmetrically distributed in the peripheral direction, on the stirring shafts; the stirring paddles are vector-shaped; the plane of the vector-shaped stirring paddles is vertical to the stirring shaft; an overlapping part formed between the stirring paddles of the adjacent stirring shafts in the axial direction. The horizontal type self-cleaning pressure-bearing solid-phase reaction kettle provided by the invention is convenient to use and has a certain self-cleaning function; caking, shaft covering and wall sticking phenomena of materials can be avoided; the horizontal type self-cleaning pressure-bearing solid-phase reaction kettle has high heat transferring efficiency and has very good practicability.
Owner:青岛量子元基环保科技有限公司
Preparation method of silver-loaded molecular sieve efficient antibacterial agent by solid-solid ion exchange
InactiveCN106538519AIncrease silver loadingQuick in and outBiocideFungicidesMass ratioMinimum inhibitory concentration
The invention relates to a preparation method of silver-loaded molecular sieve efficient antibacterial agent by a solid-solid ion exchange. The method includes steps of applying NaA molecular sieve with grain diameter of 200-300 nm as an antibacterial agent carrier, dosing and fully mixing NaA molecular sieve and ammonium salt according to n (Na+): n(NH4+)=1: 6-1:10, and reacting the mixture for 0.5-1.5 h in a high temperature stove at 150-250 DEG C; obtaining ammonium type molecular sieve after sufficiently cleaning the mixture by distilled water. The prepared ammonium type molecular sieve and silver nitrate are dosed and fixedly mixed according to n (NH4+): n(AgNO3)=1: 2-1:6, and performed with solid phase reaction in the high temperature stove for 1.5-5 hours at 330-460 DEG C; after fully washing the mixture, the silver-loaded molecular sieve efficient antibacterial agent is obtained. The silver load of the silver-loaded molecular sieve efficient antibacterial agent prepared in the invention is 28.15%-41.08% (mass ratio); the minimum inhibitory concentration is 9.38 ppm; the method improves the silver load and the antibacterial ability of the of silver-loaded molecular sieve efficient antibacterial agent.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Low-heat solid-phase synthesis method of heparin quaternary ammonium salt
The invention discloses a low-heat solid-phase synthesis method of a heparin quaternary ammonium salt. In the method, the heparin quaternary ammonium salt is prepared by a low-heat solid-phase reaction by using heparin sodium and benzethonium chloride as raw materials, using sodium chloride and ferric oxide as mineralizers and using inert gas as a protective agent. The method has the advantages of thorough reaction, high yield, low energy consumption and less pollution, and is applicable to industrial production, thereby being a promising preparation method.
Owner:石河子市郁茏生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing hydrogen fluoride and silicon tetrafluoride by using waste materials containing calcium fluoride
ActiveCN107188129AIncrease productivitySimple processHydrogen fluorideFluosilicic acidCalcium silicateSilicon tetrafluoride
The invention provides a method for preparing hydrogen fluoride and silicon tetrafluoride by using waste materials containing calcium fluoride. The method comprises the steps that firstly, the waste materials containing the calcium fluoride is reacted with fluosilicic acid to generate calcium fluosilicate and hydrofluoric acid, and the hydrofluoric acid reacts with silicon dioxide in the waste materials containing calcium fluoride to generate fluosilicic acid; secondly, the material in the first step is subjected to solid-liquid separation, and the fluosilicic acid is reused in the first step; thirdly, the calcium fluosilicate obtained through the separation in the second step is reacted with concentrated sulfuric acid, and hydrogen fluoride gas, silicon tetrafluoride gas and calcium sulfate solid are generated. In the method, process steps are continuous and cyclic, and a continuous production line can be formed; the fluosilicic acid is reacted with the calcium fluoride to generate an intermediate product, namely the calcium fluosilicate, so that the concentrated sulfuric acid and the calcium fluosilicate are subjected to a dry-media reaction to generate the silicon tetrafluoride gas and the hydrogen fluoride gas. By means of the method, the aims that environmental pollutions are reduced, the waste materials are changed into things of value and the economic efficiency is improved can be achieved.
Owner:衢州市鼎盛化工科技有限公司
Method for preparing multibasic oxide nanometer particles based on core-shell structure three-dimensional micro-solid-phase reaction.
ActiveCN103242042BAchieving controllable equipmentAvoid Agglomeration FormationDecompositionCalcination
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
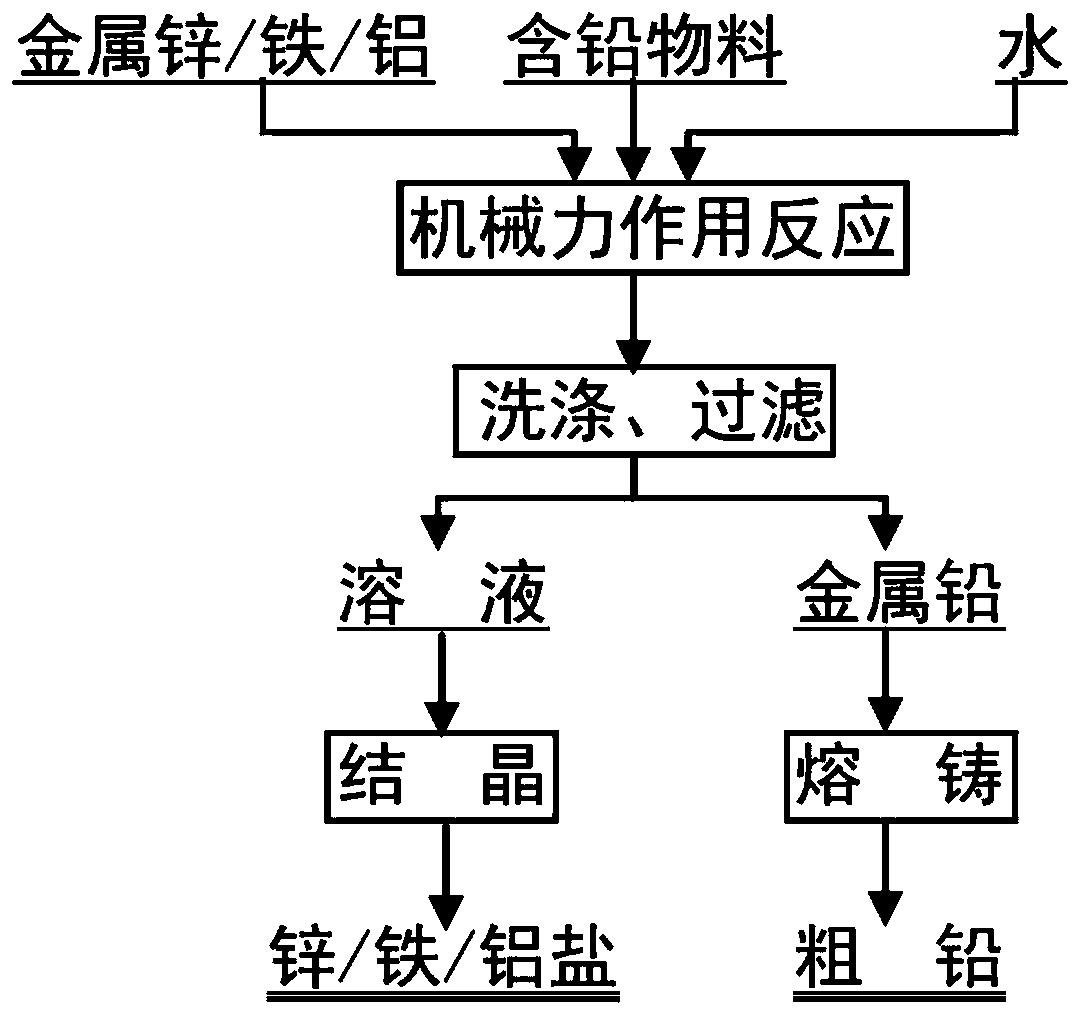
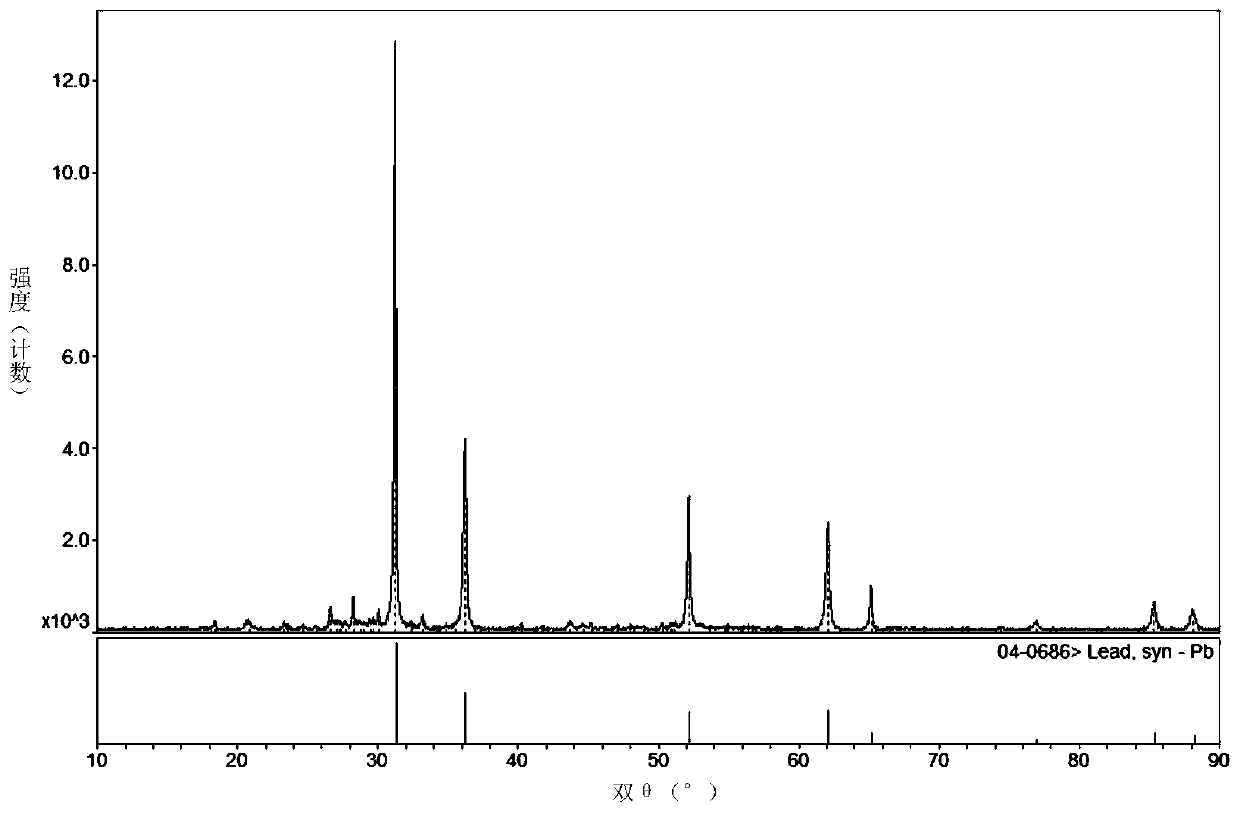
Method for directly preparing metal lead from lead-containing material through solid phase reaction
The invention provides a method for directly preparing metal lead from a lead-containing material through solid phase reaction. The method comprises the following steps: 1, adding the lead-containingmaterial to be treated into a grinding machine, adding a metal substance and water into the grinding machine, and directly carrying out solid-phase reaction on the lead-containing material and the metal substance by using the grinding machine under the action of mechanical force to obtain a reaction product, specifically, the activity of the metal substance is greater than that of lead; 2, washingand filtering the reaction product to obtain metal lead and a metal salt solution corresponding to the metal substance; and 3, carrying out fusion casting on the metal lead to obtain coarse lead, andcrystallizing the metal salt solution to obtain the metal salt corresponding to the metal substance. Compared with the existing processes for treating lead-containing materials by a fire method and awet method, the method for preparing the metal lead has the characteristics of short flow, few procedures, large treatment capacity, low energy consumption cost and the like, and can meet the environmental protection requirements of clean production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for synthesizing nanometer bismuth oxycarbonate through room-temperature solid phase chemical reaction
ActiveCN108178193AReduce reunionEasy to makeMaterial nanotechnologyBismuth compoundsChemical reactionSolvent
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing nanometer bismuth oxycarbonate through a room-temperature solid phase chemical reaction. The method comprises the following steps: mixing solid phaseraw materials sodium bismuthate dihydrate and oxalic acid dehydrate according to a certain molar ratio, then performing a ball-milling solid phase reaction, and washing, centrifuging and drying the obtained product to obtain the target product nanometer bismuth oxycarbonate. Solid mixing and the raw material room-temperature ball-milling solid phase reaction are adopted, so the preparation processis simple, and the agglomeration of product particles is easily controlled and greatly reduced; and addition of a redox agent, a template and a solvent is avoided, so the purity of the product is improved, green synthesis requirements of the above material are met, and the method is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:BENGBU COLLEGE
Solid-phase reaction preparation method for silicious manganese thermoelectric material
InactiveCN102174677BLow costLow priceThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric materialsElectric discharge
The invention belongs to the technical field of new energy materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method for a silicious manganese thermoelectric material. A solid-phase reaction preparation method for the silicious manganese thermoelectric material is characterized by comprising the steps as follows: (1) Si powder and Mn powder are taken as raw materials, weighed according to the molar ratio of (1.75-1.80):1, and mixed evenly to obtain evenly mixed powder; (2) the evenly mixed powder are put on a tabletting machine and pressed into a bulk, the bulk is placed into a quartz glasstube, the quartz glass tube is vacuumized and sealed and then is placed in a muffle furnace for 850-900 DEG C solid-phase reaction for 12-24 hours, and the product is obtained after heat preservationis finished and furnace cooling is carried out; (3) the product obtained in step (2) is ground into fine powder; and (4) the fine powder obtained in step (3) is subjected to electric discharge plasmasintering, and the compact silicious manganese thermoelectric material can be obtained. The method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, energy conservation, and low requirements for instruments and equipment, and is suitable for commercial manufacture.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com