Patents
Literature
471 results about "Metalorganics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
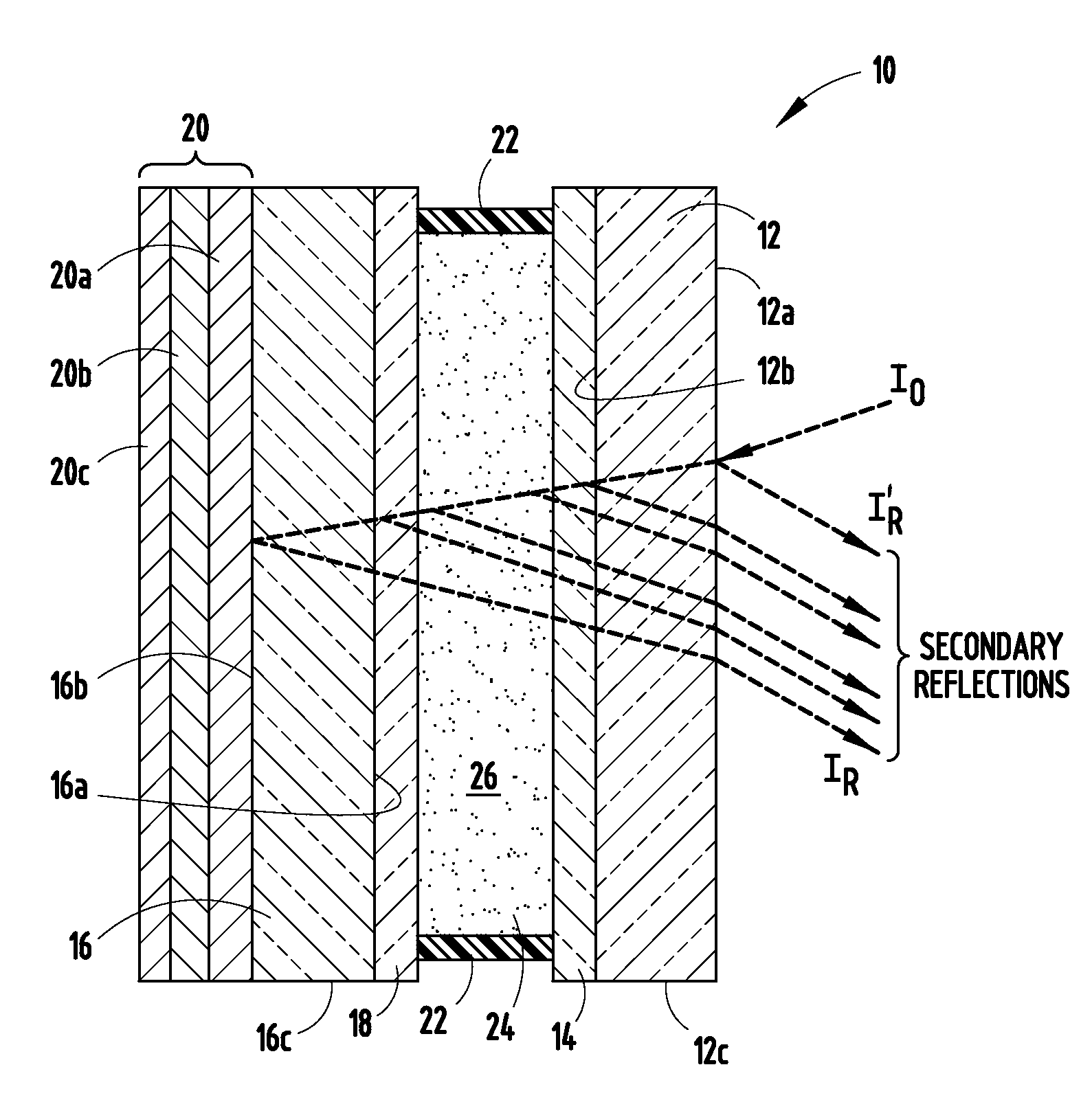
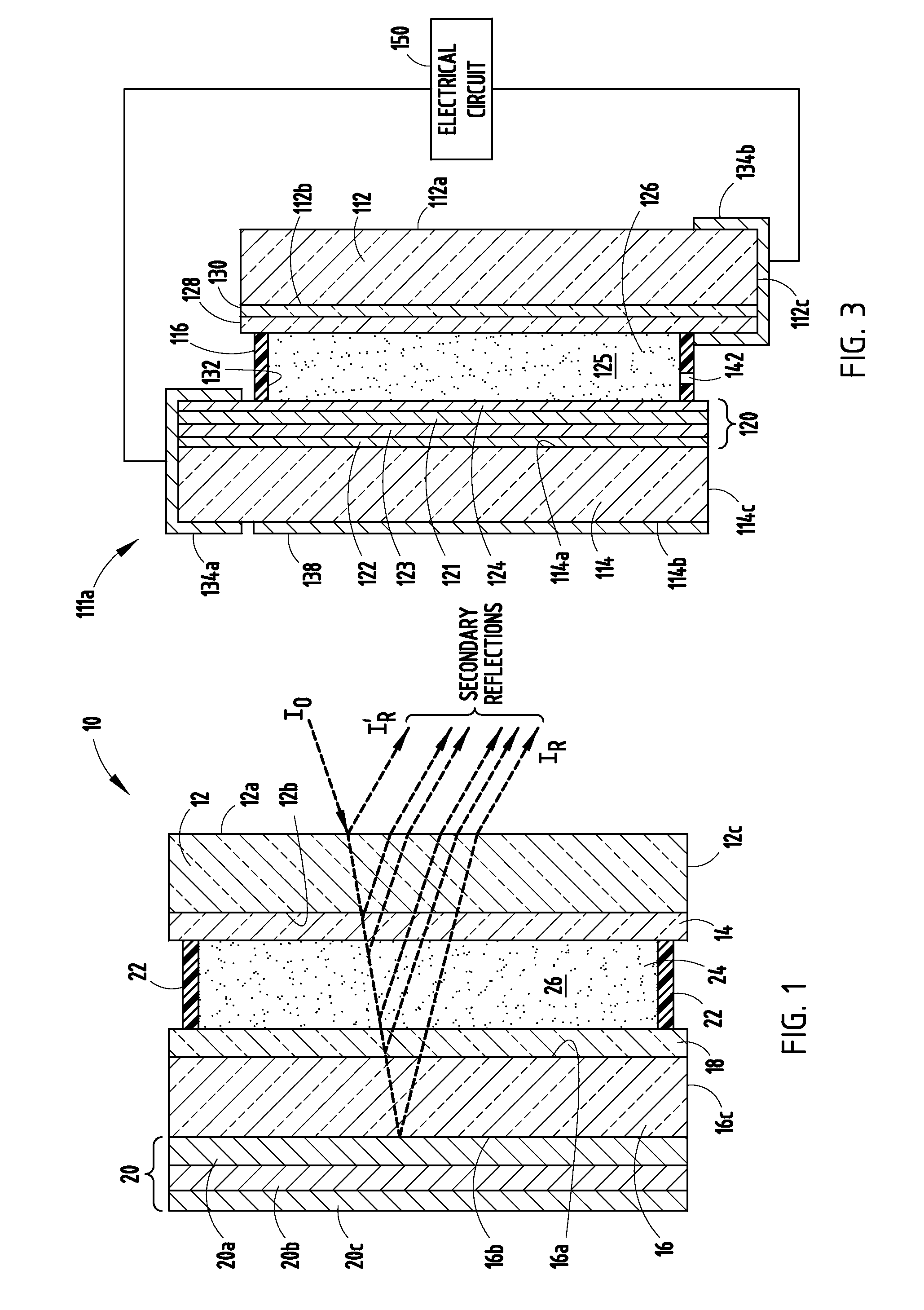
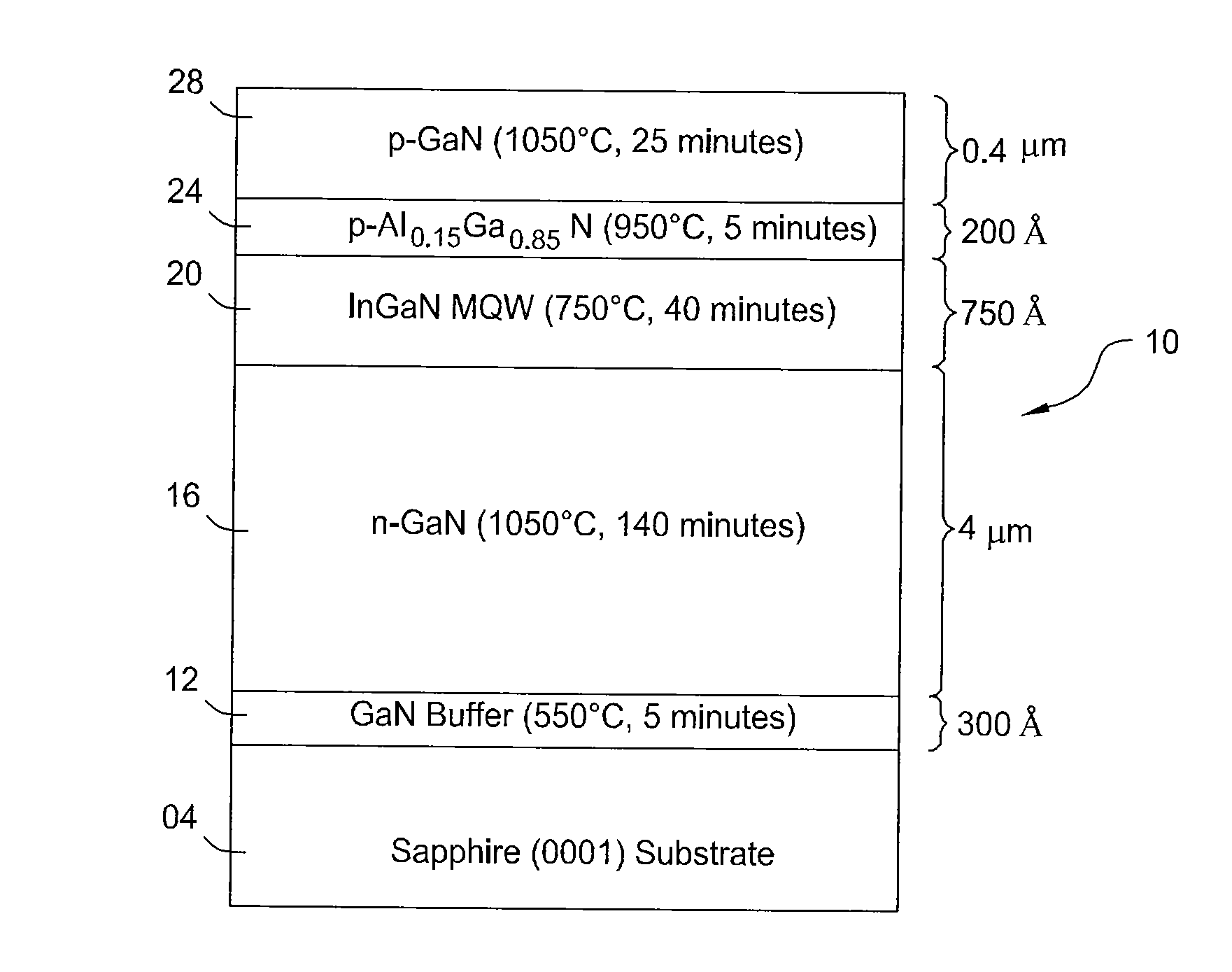
Metal-organic compounds (jargon: metalorganics, metallo-organics) are a class of chemical compounds that contain metals and organic ligands, which confer solubility in organic solvents or volatility. Compounds with these properties find applications in materials science for metal organic vapor deposition (MOCVD) or sol-gel processing. The distinct term "metal organic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. Precise definitions may vary, however the term may describe...
Electrical conductors formed from mixtures of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition compounds
The present invention relates to a thick film formed of a mixture of metal powders and metallo-organic decomposition (MOD) compounds in an organic liquid vehicle and a process for advantageously applying them to a substrate by silk screening or other printing technology. The mixtures preferably contain metal flake with a ratio of the maximum dimension to the minimum dimension of between 5 and 50. The vehicle may include a colloidal metal powder with a diameter of about 10 to about 40 nanometers. The concentration of the colloidal metal in the suspension can range from about 10 to about 50% by weight. The MOD compound begins to decompose at a temperature of approximately about 200 DEG C. to promote consolidation of the metal constituents and bonding to the substrate which is complete at temperatures less than 450 DEG C. in a time less than six minutes. The mixtures can be applied by silk screening, stencilling, gravure or lithography to a polymer-based circuit board substrate for producing rigid and flexible printed wiring boards in a single operation with negligible generation of hazardous wastes. The same mixtures can be used in place of solder to assemble circuits by bonding electrical components to conductors as well as to make the conductors themselves.
Owner:PARELEC
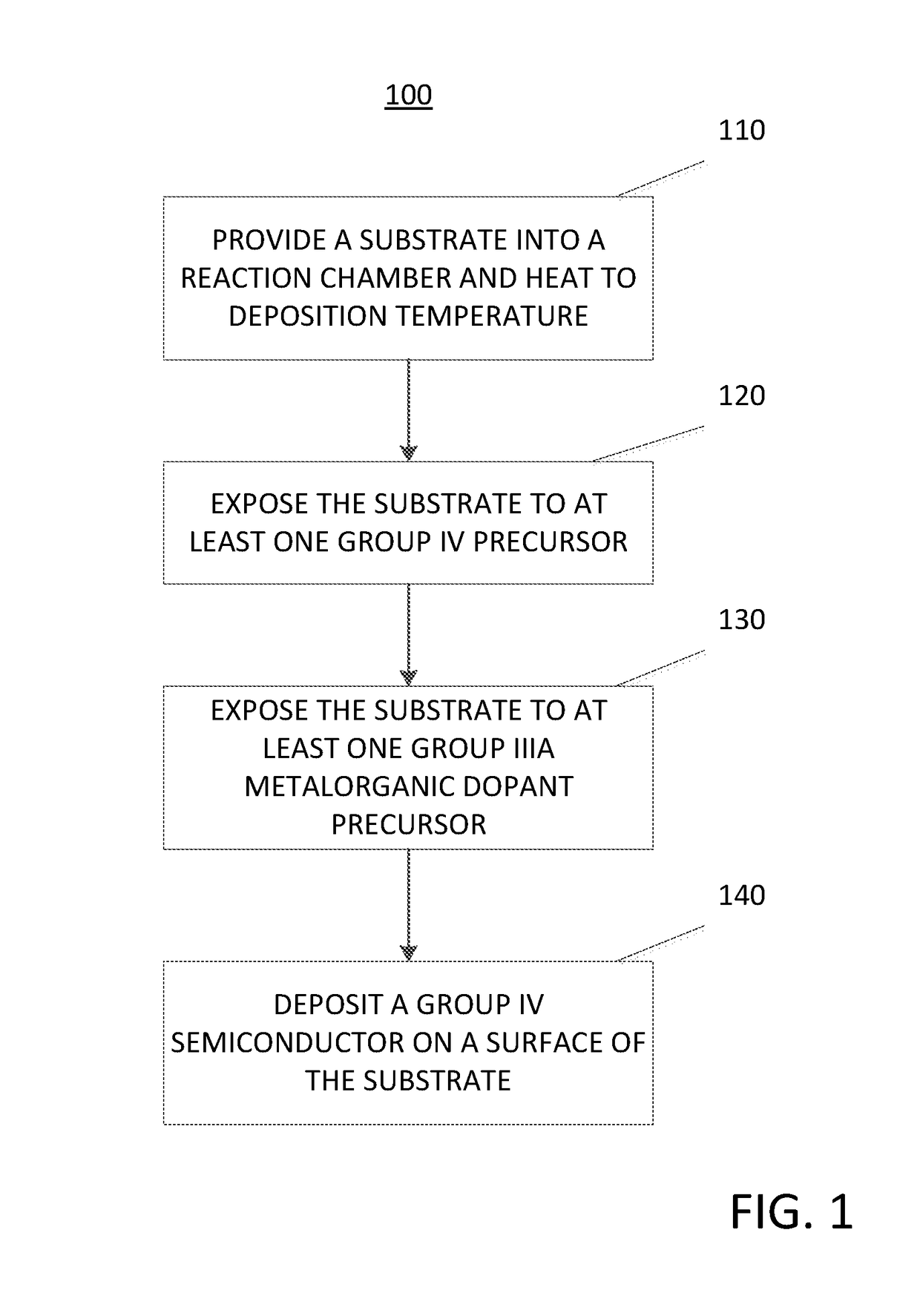
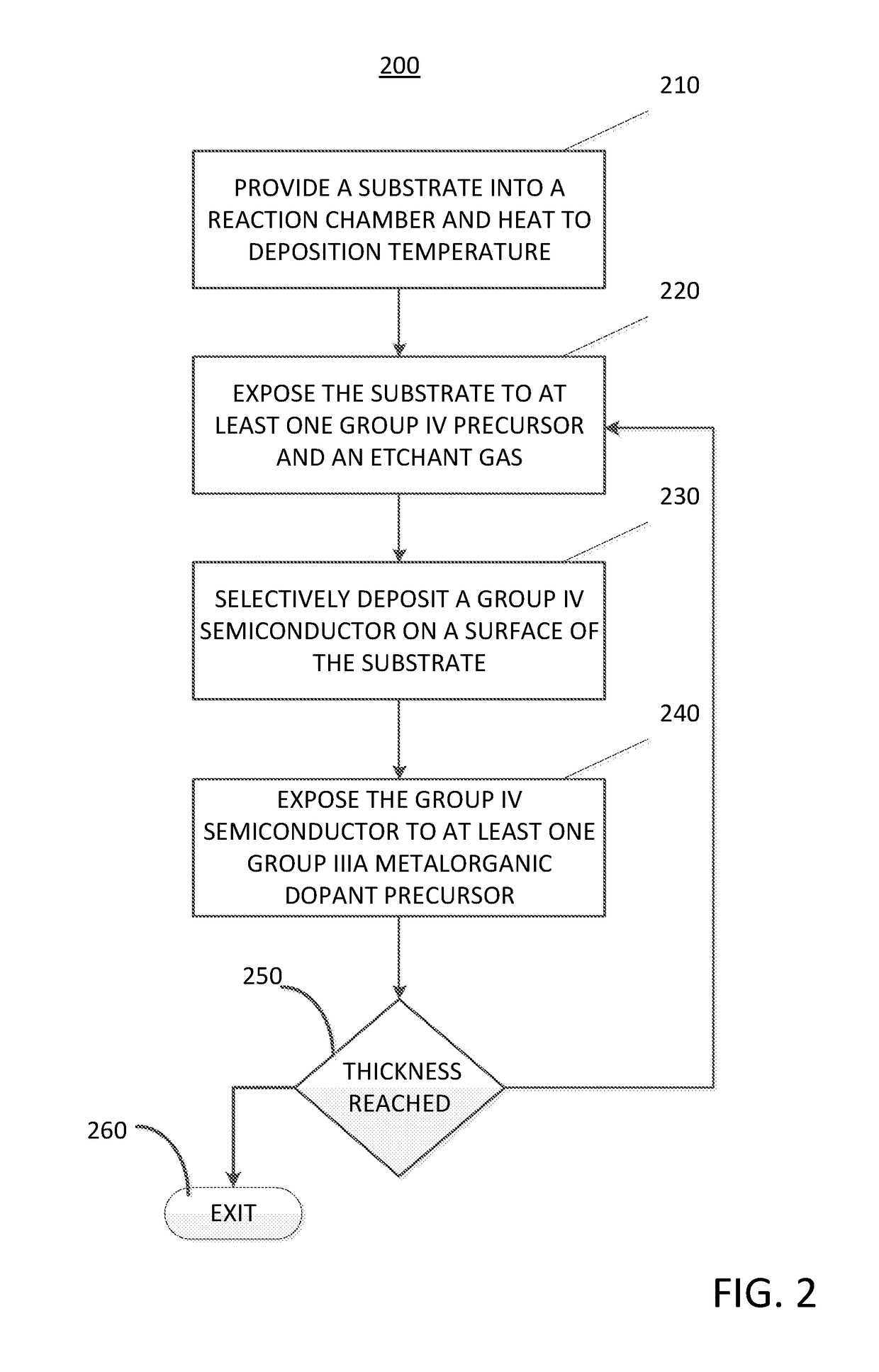
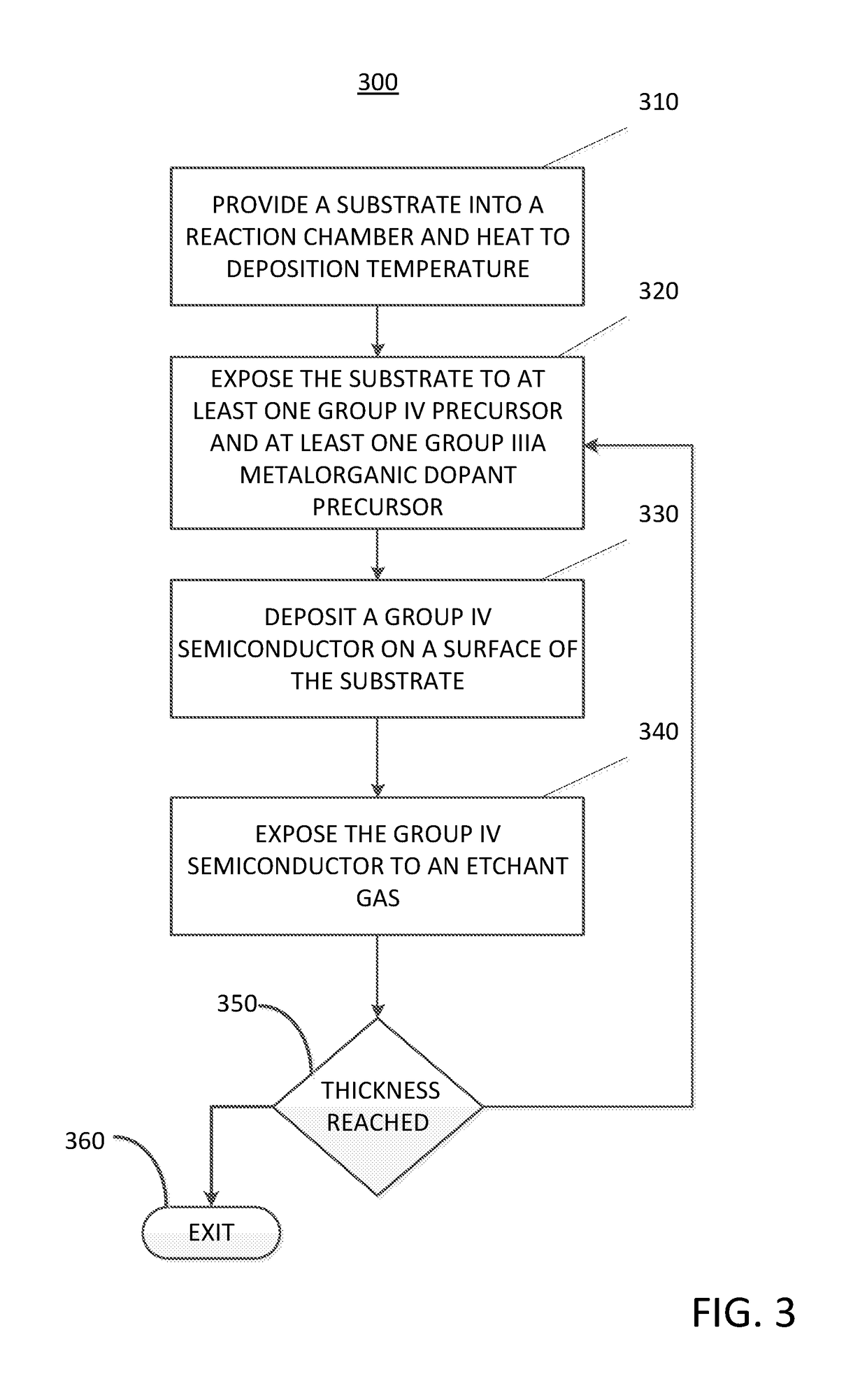
Method for depositing a group iv semiconductor and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20190027583A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDopantDeposition temperature
A method for depositing a Group IV semiconductor is disclosed. The method may include, providing a substrate within a reaction chamber and heating the substrate to a deposition temperature. The methods may further include, exposing the substrate to at least one Group IV precursor and exposing the substrate to at least one Group IIIA metalorganic dopant precursor. The methods may further include depositing a Group IV semiconductor on a surface of the substrate. Semiconductor device structures including a Group IV semiconductor deposited by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
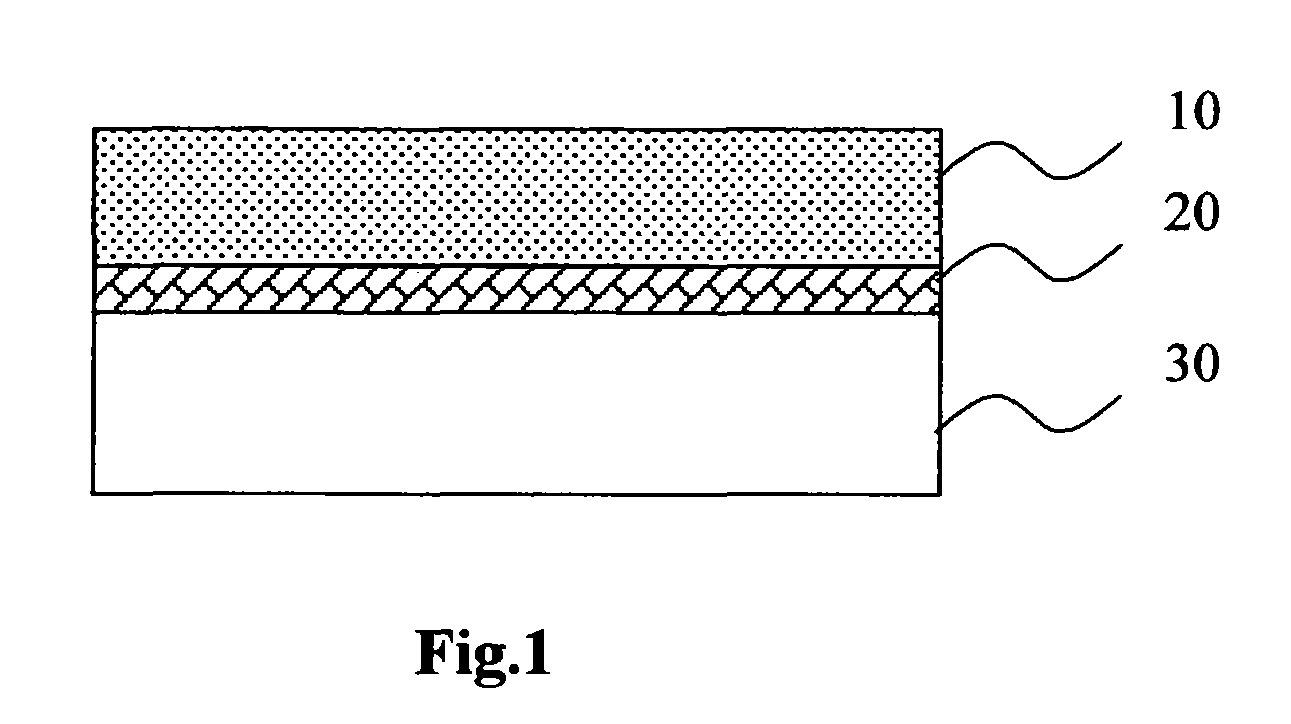
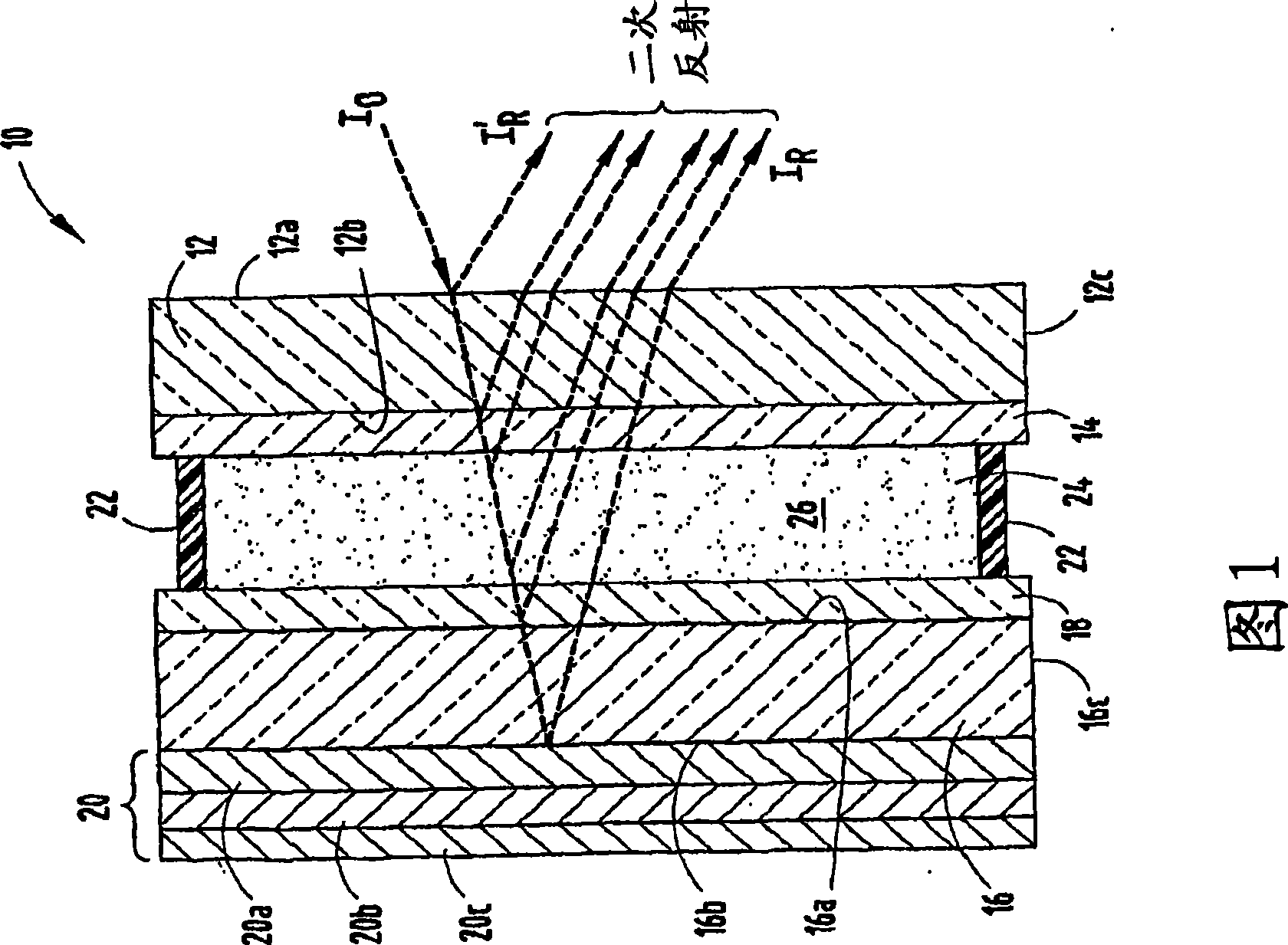
Electro-Optical Element Including Metallic Films and Methods For Applying The Same
A method for manufacturing an electrochromic element comprises providing a first substrate having first and second surfaces and a first edge surface, providing a second substrate having third and fourth surfaces and a second edge surface, the third surfaces facing the second surface, providing an electrochromic medium located between the first and second substrates, the medium having a light transmittance that is variable upon application of electric field thereto, applying a conductive layer on a portion of at least one of the surfaces, wherein applying the layer is accomplished at substantially atmospheric pressure, and applying at least one of metallic particles, an organometallic, a metallo-organic, and combinations thereof, wherein the conductive layer has a bulk resistivity of greater than or equal to 150 μΩ·cm. The conductive layer may be applied via ink jetting, ultrasonic spraying, auger or jet pumping.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Electro-optical element including metallic films and methods for applying the same
A method for manufacturing an electrochromic element comprises providing a first substrate having first and second surfaces opposite one another and a first edge surface, providing a second substrate having third and fourth surfaces opposite one another and a second edge surface, wherein the third surfaces faces the second surface, and providing an electrochromic medium located between the first and second substrates, wherein the electrochromic medium has a light transmittance that is variable upon the application of electric field thereto. The method further complies applying a conductive layer on at least a portion of at least a select one of a first, second, third, and fourth surfaces and the first and second edge surfaces, wherein applying the conductive layer is accomplished at substantially atmospheric pressure and including applying at least a select one of metallic particles, an organometallic, a metallo-organic, and combinations thereof, and wherein the conductive layer has a bulk resistivity of less than or equal to 150 μΩ·cm. Other aspects of this invention comprise applying the conductive layer via ink jetting, ultrasonic spraying, auger pumping and jet pumping.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Cluster tool for leds
ActiveUS20100261340A1Polycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenChemical vapor deposition
The present invention generally provides apparatus and methods for forming LED structures. One embodiment of the present invention provides a method for fabricating a compound nitride structure comprising forming a first layer comprising a first group-III element and nitrogen on substrates in a first processing chamber by a hydride vapor phase epitaxial (HVPE) process or a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) process, forming a second layer comprising a second group-III element and nitrogen over the first layer in a second processing chamber by a MOCVD process, and forming a third layer comprising a third group-III element and nitrogen over the second layer by a MOCVD process.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
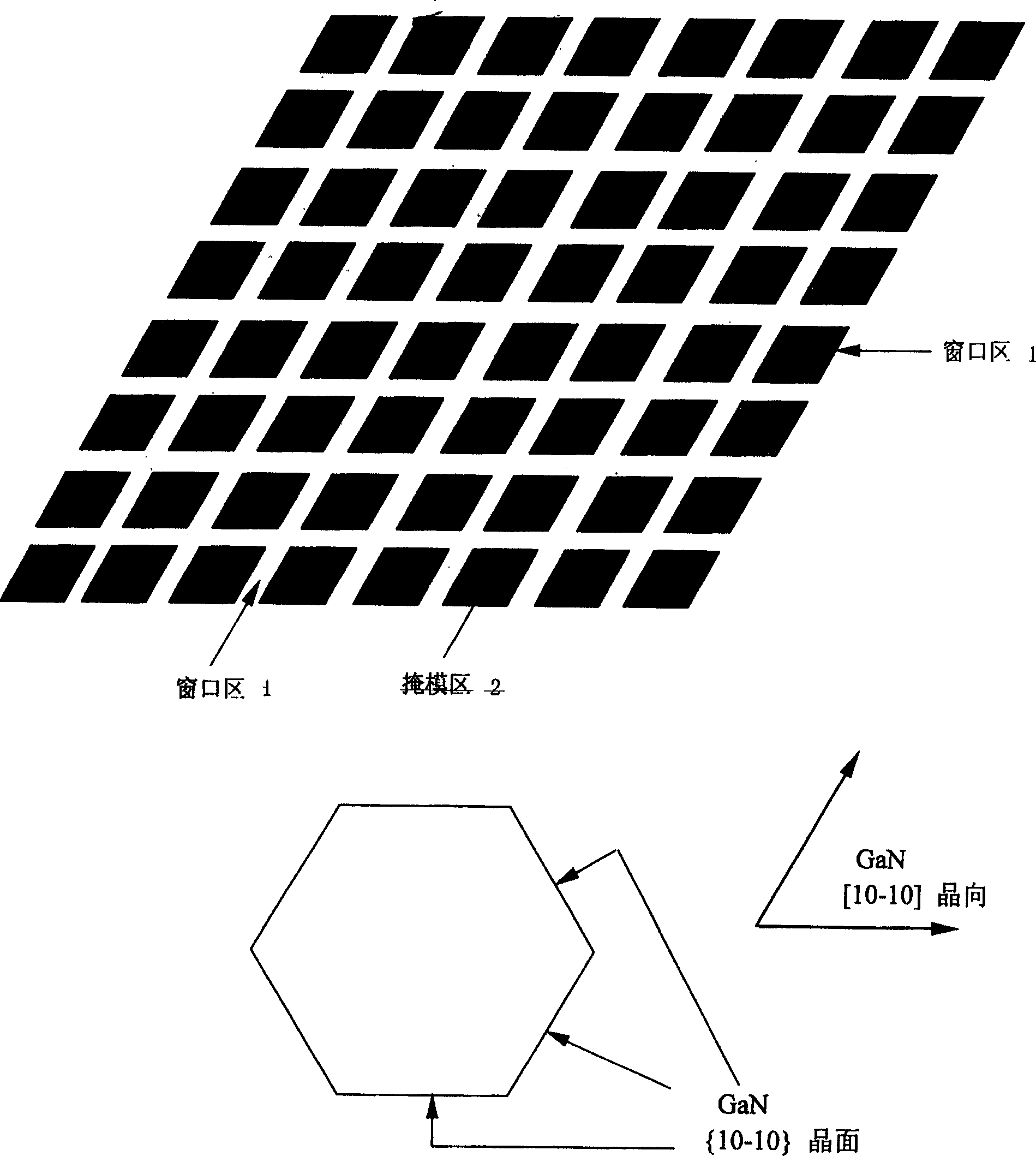
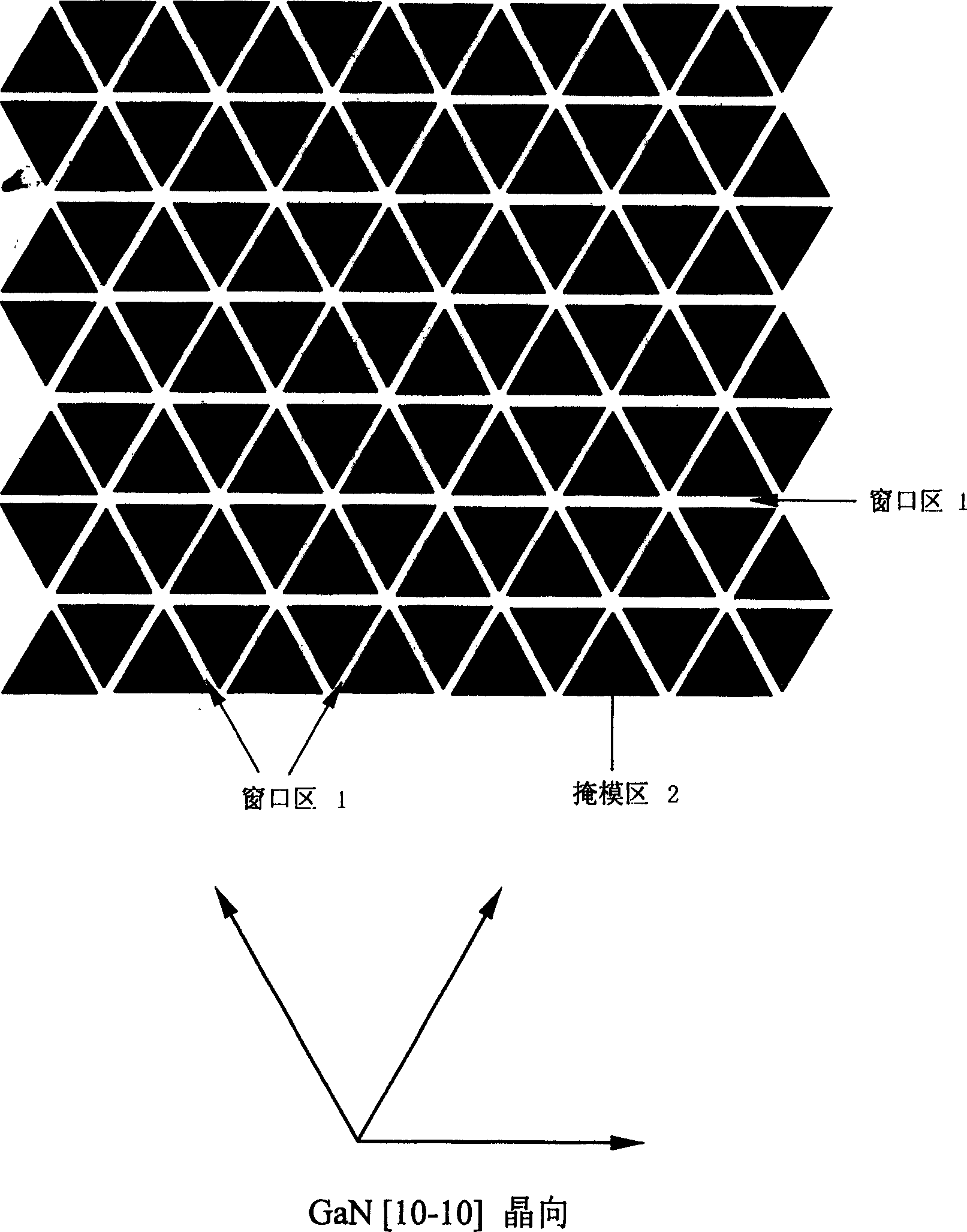
Horizontal epitaxial growth of gallium nitride and its compound semiconductor
InactiveCN1490844AOvercome MisorientationQuick mergeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseGallium nitride
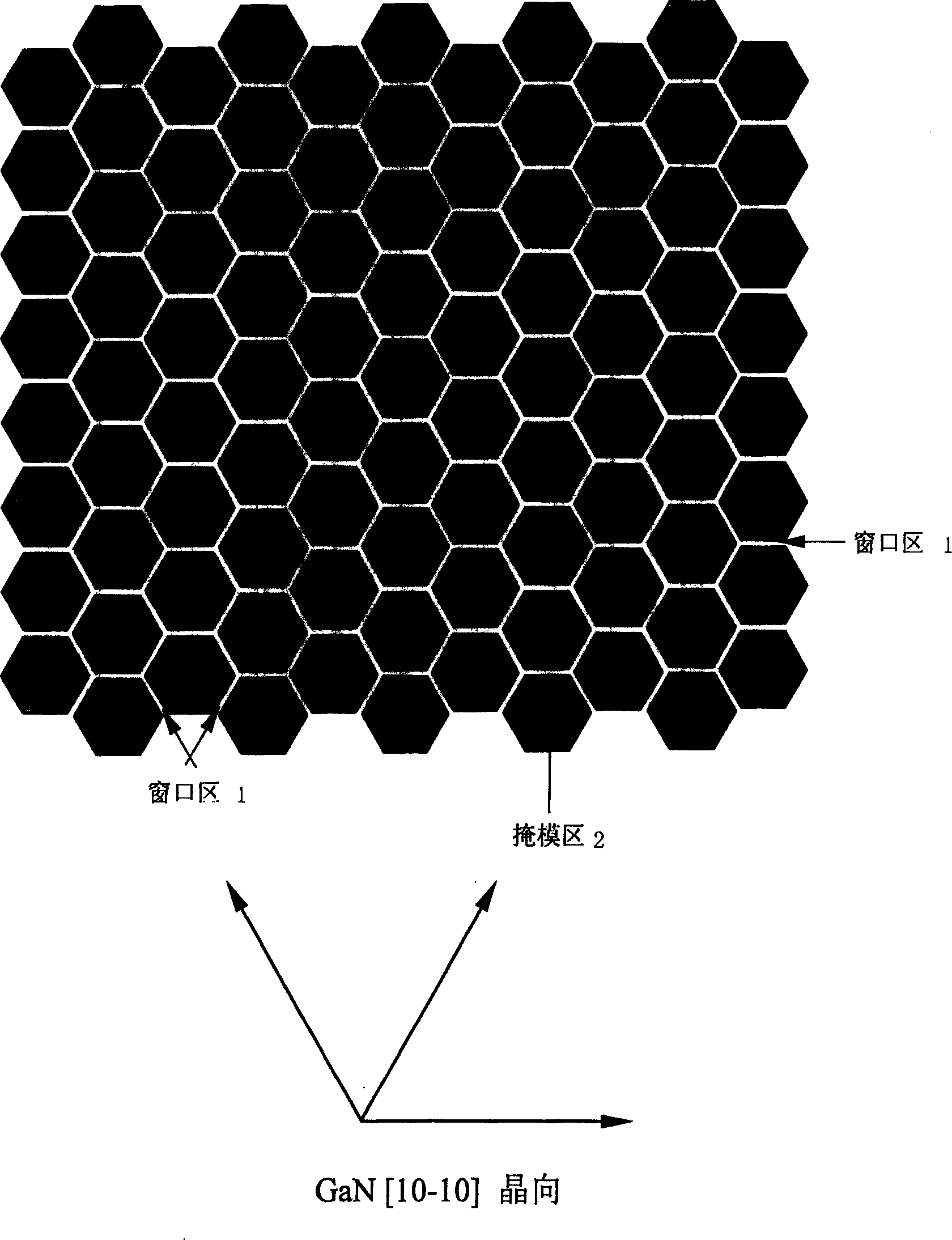
The present invention provides a method for growing a lateral epitaxy of the gallium nitride and its compound semiconductors, comprising the following steps: growing an intrinsic gallium nitride on the ( 0001 ) crystal face of sapphire or the ( 111 ) of silicon or the ( 0001 ) of silicon carbide using the metal organic chemical vapor deposition or the molecule beam epitaxy or the hydride vapor epitaxy; then depositing on it a layer of silicon nitride or silicon dioxide or silicon nitride-oxide as the mask area; patterning the mask area using the photolithography and wet or dry etch techniques, the pattern of the mask area being designed into the pattern structure of the triangle or parallelogram or rhombus or hexagon with the included angles of 60 or 120 degrees or the combination of above shapes which are constituted of the [ 10 - 10 ] crystal direction of gallium nitride on the edge of the adjacent windows; and finally growing the secondary epitaxy, that is, lateral epitaxy of gallium nitride and its compound using the metal organic vapor deposition or the molecule beam epitaxy or the hydride vapor epitaxy.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
In situ polymerization preparing method for carbon nano tube and polytene composite material
InactiveCN1640923AExcellent ElectricalImprove mechanical propertiesIn situ polymerizationCarbon nanotube
The present invention relates to the preparation process of one kind of composite carbon nanotube / polyethylene material. Single or multiple wall carbon nanotube is treated with oxidant to obtain functional carbon nanotube with hydroxyl, carbonyl and carboxyl groups on the surface; and further reacted with alkyl metallizing compound in inert atmosphere to connect metal organic matter component capable of catalyzing ethylene polymerization to obtain carbon nanotube supporting olefin polymerization catalyst. In the presence of alkyl metallizing compound as catalyst assistant, the prepared carbon nanotube supporting olefin polymerization catalyst catalyzes ethylene polymerization to obtain the composite carbon nanotube / polyethylene material. The composite material has two components homogeneously dispersed, electric and mechanical performance higher than other polyethylene material.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Preparation method of supporting type film bulk acoustic wave resonator
ActiveCN109309483APrecise thickness controlPromote growthImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorEtching
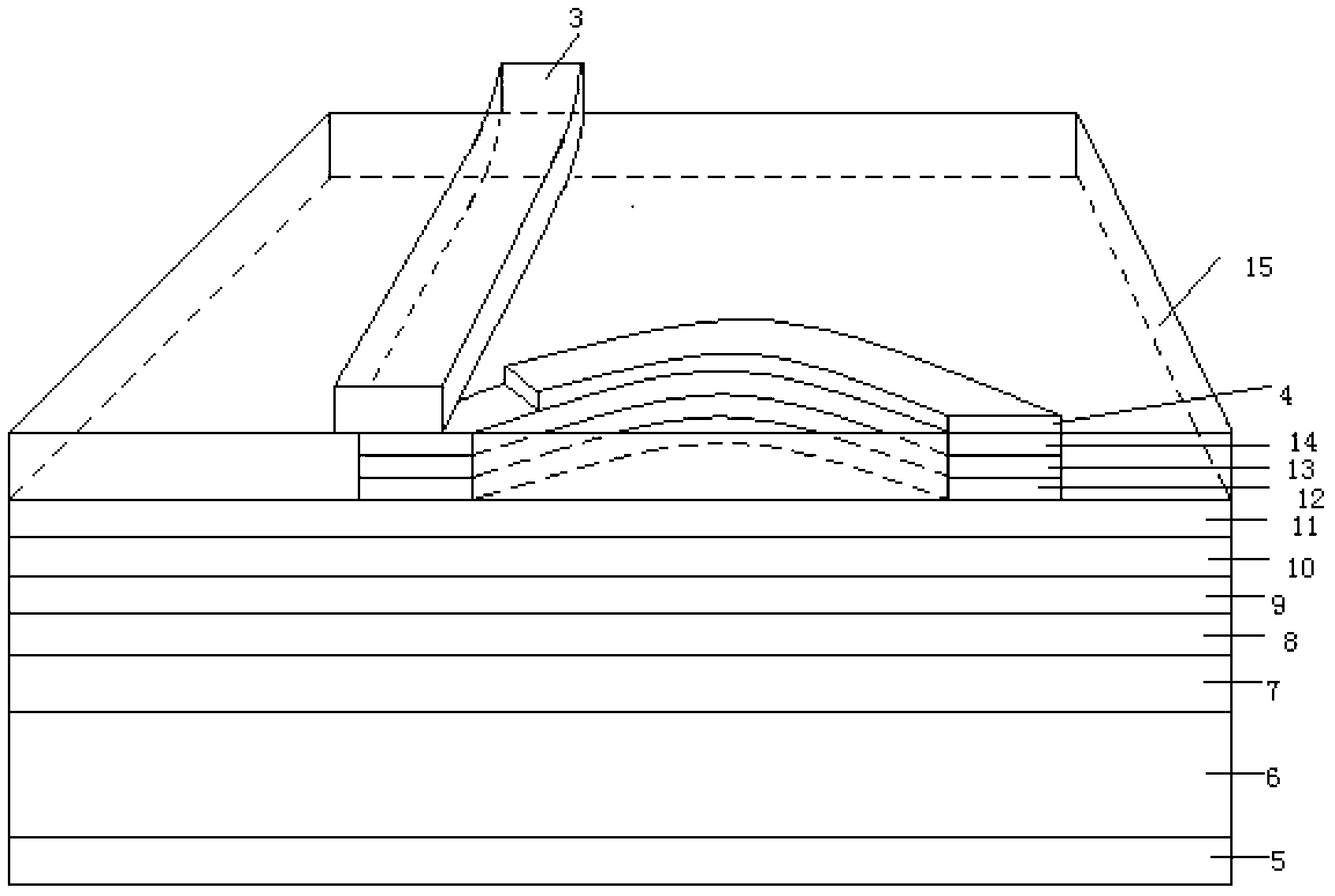
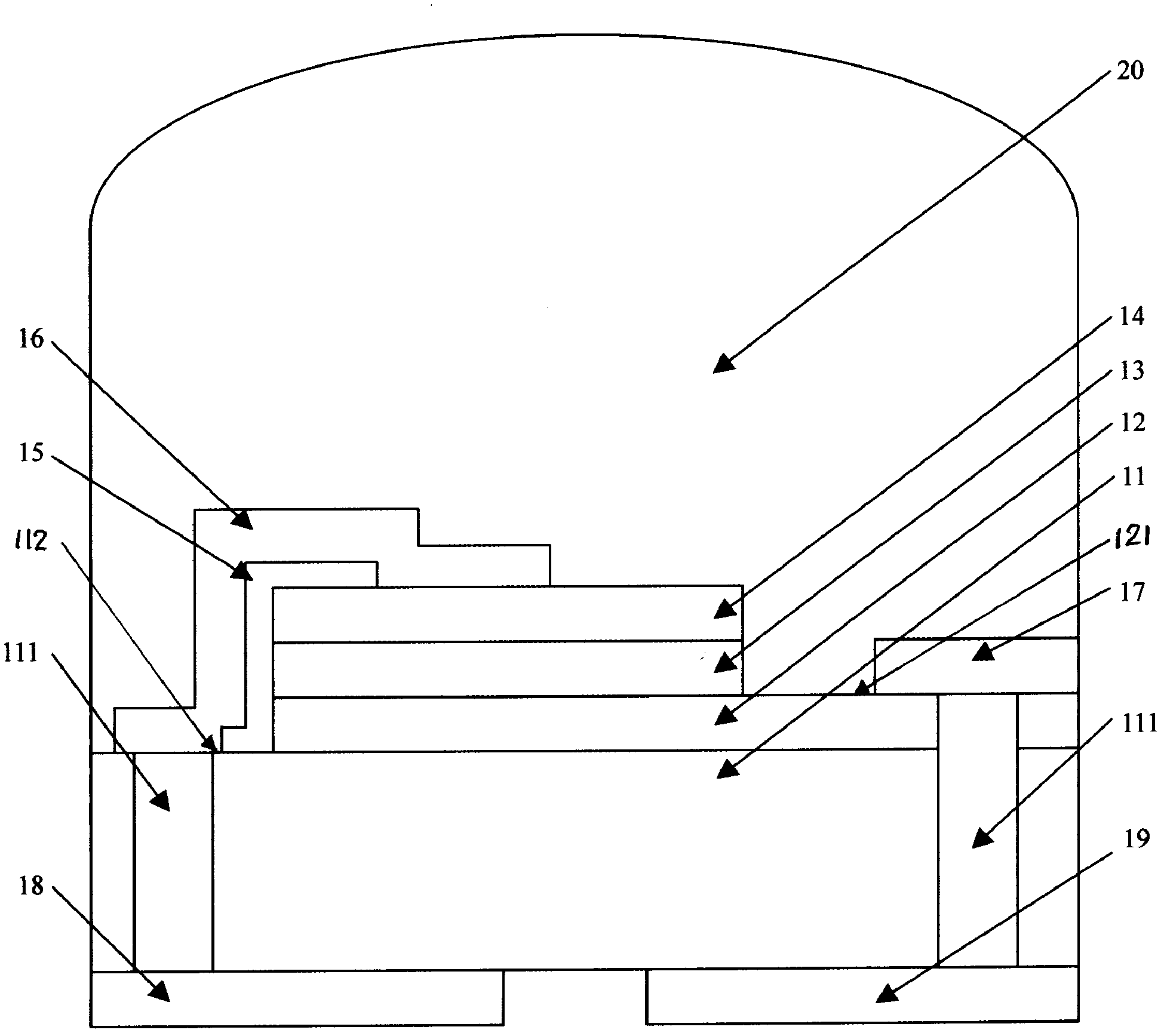
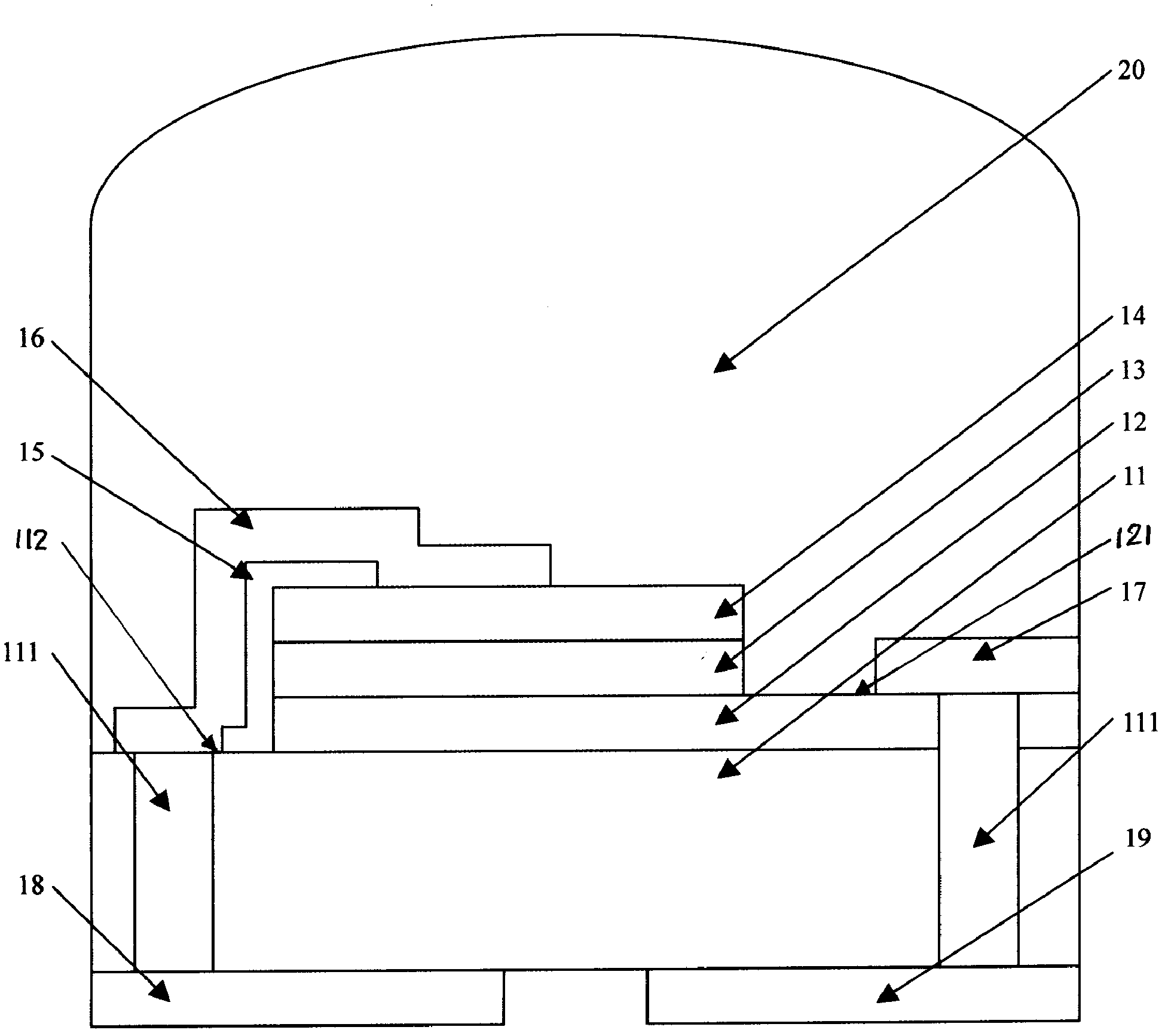
The invention discloses a preparation method of a supporting type film bulk acoustic wave resonator. The method comprises the following steps: growing a metal insertion layer on a (111) surface Si substrate, and continuing to grow a single crystal AIN film on the (111) surface Si substrate through a metal-organic chemical vapor deposition method, and finally depositing a metal electrode and a supporting layer on the single crystal AIN film. By means of film transfer, peeling, top electrode etching and other processes, a sandwich piezoelectric stacking structure of the film bulk acoustic wave resonator is formed at last. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, by importing the metal insertion layer, the mismatch phenomenon between the AlN epitaxial and the growth substrate is reduced, and the yield and the figure of merit of the device are improved on one hand; and on the other hand, a top electrode pattern can be directly etched after the film transfer and peeling procedures, so that the preparation procedures are simplified.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing doped, alloyed, and mixed-phase magnesium boride films
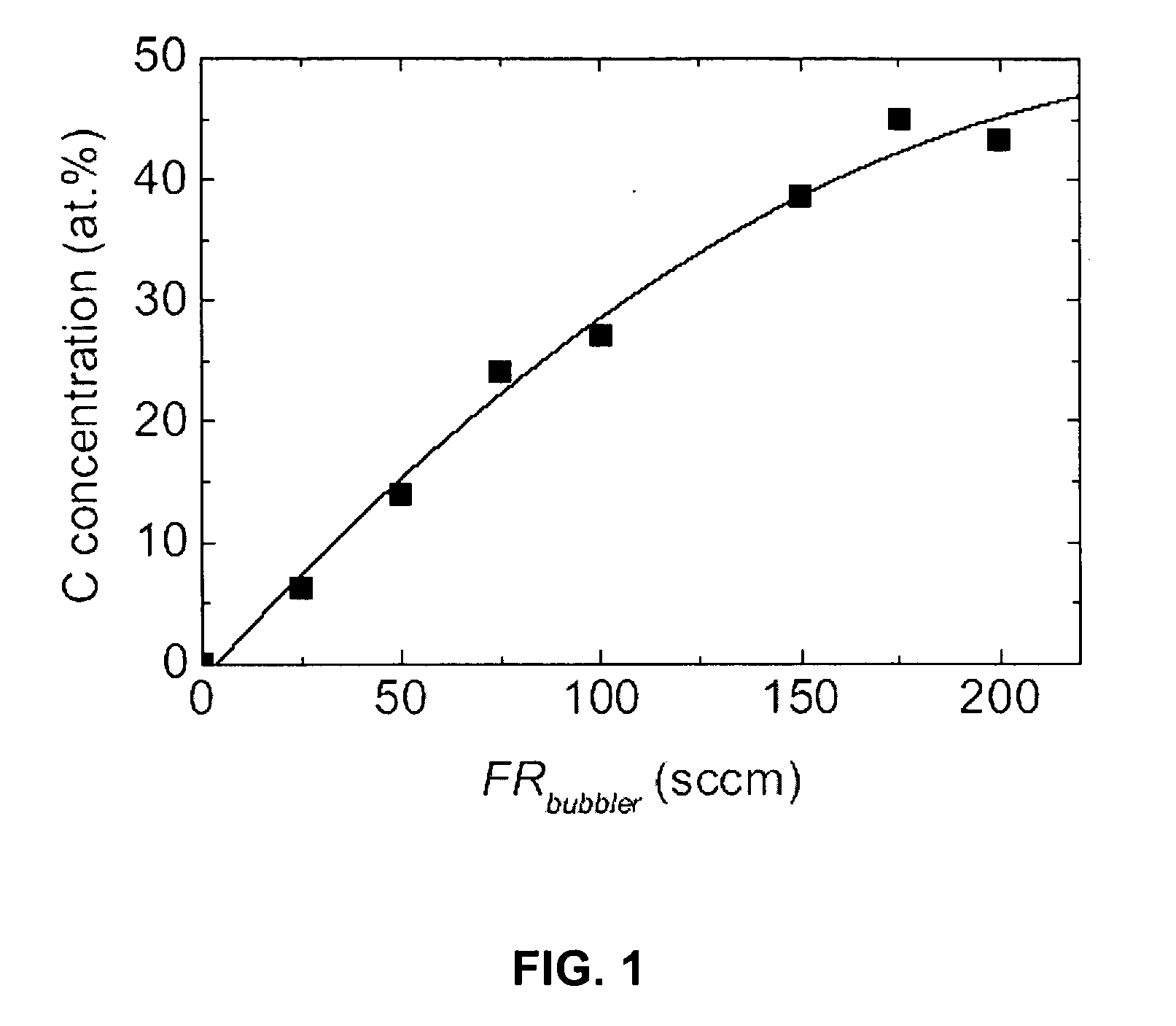
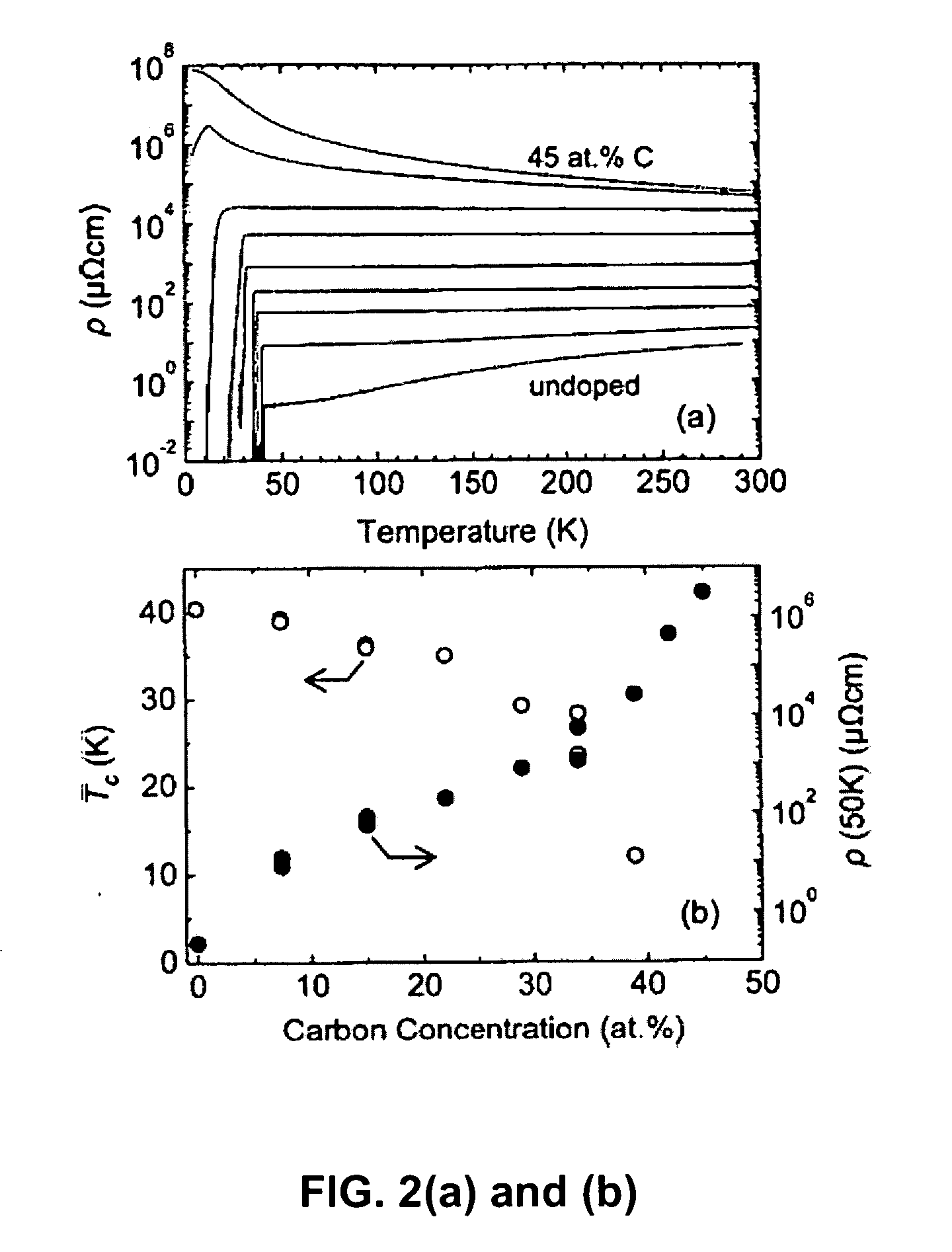
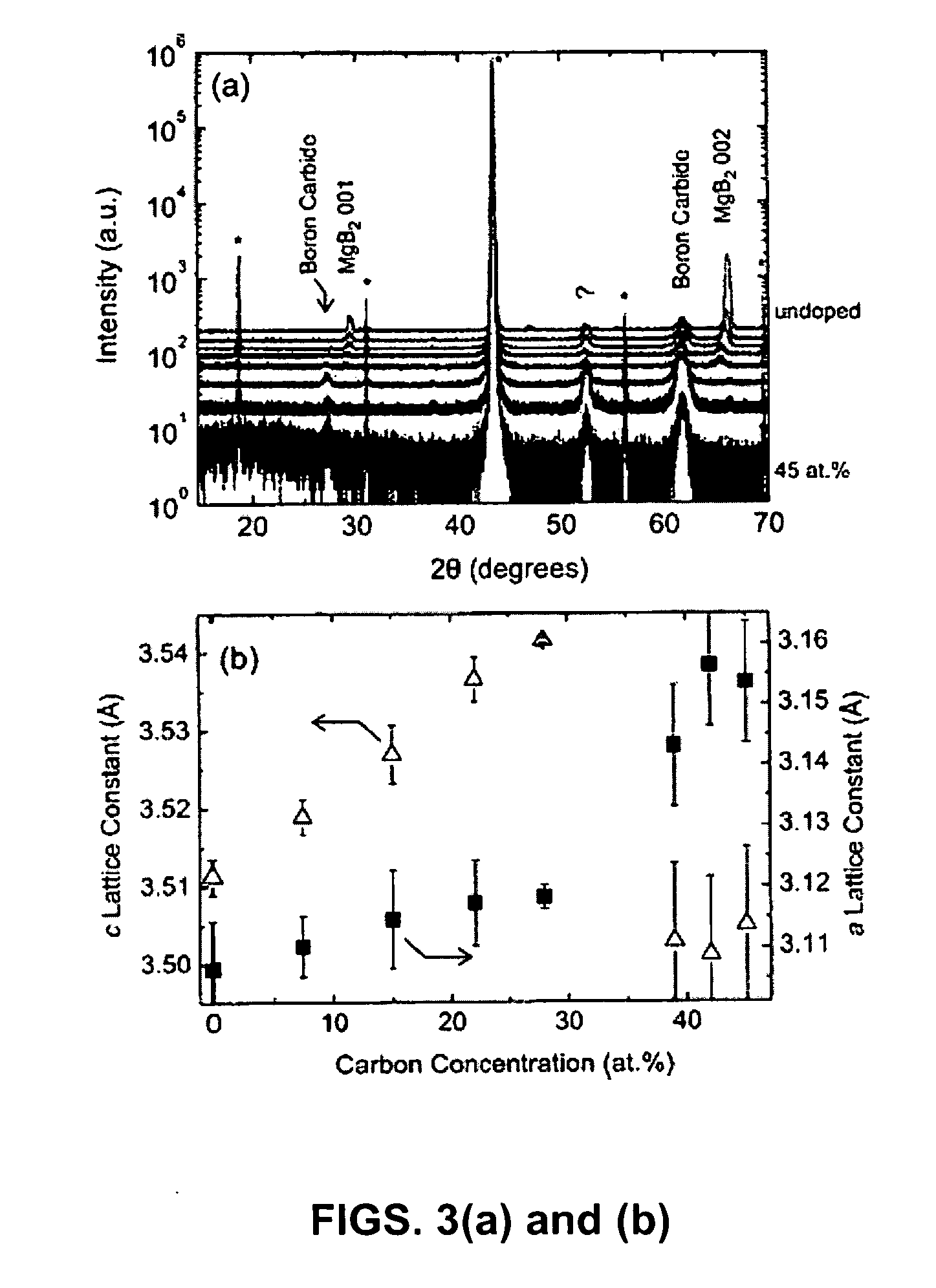
Conducting and superconducting doped, magnesium boride materials are formed by a process which combines physical vapor deposition with chemical vapor deposition by physically generating magnesium vapor in a deposition chamber and introducing a boron containing precursor and a dopant into the chamber which combines with the magnesium vapor to form the material. Embodiments include forming carbon-doped magnesium diboride film and powder with hybrid physical-chemical vapor deposition (HPCVD) by adding a carbon-containing metalorganic magnesium precursor, bis(methylcyclopentadienyl)magnesium, with a hydrogen carrier gas together with a borane precursor in a chamber having a source of magnesium vapor.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
High-efficiency thin-film solar cell provided with up-conversion fluorescent material film and film preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101794834AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyIncrease and improve photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationRare-earth elementUltraviolet lights
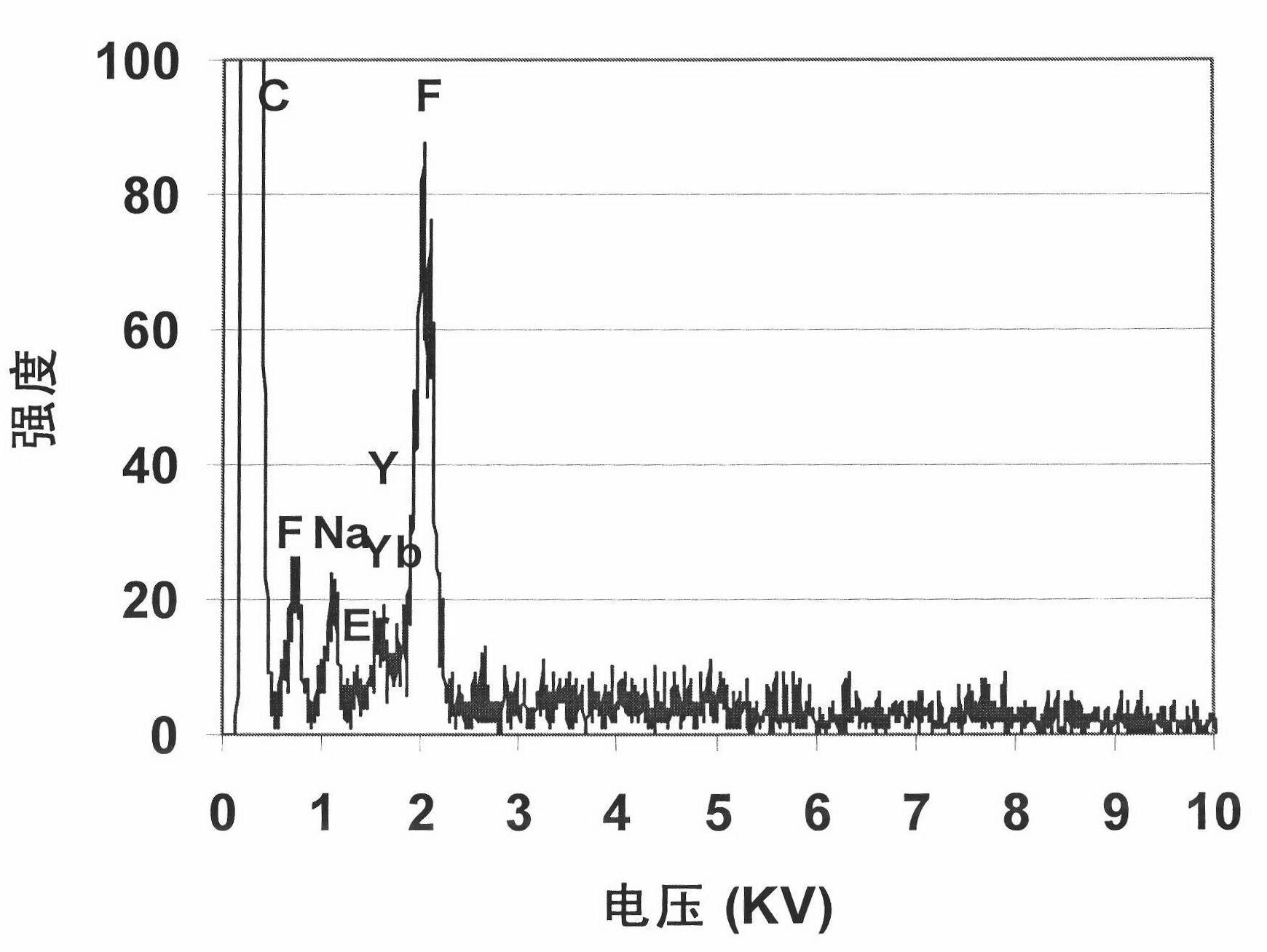
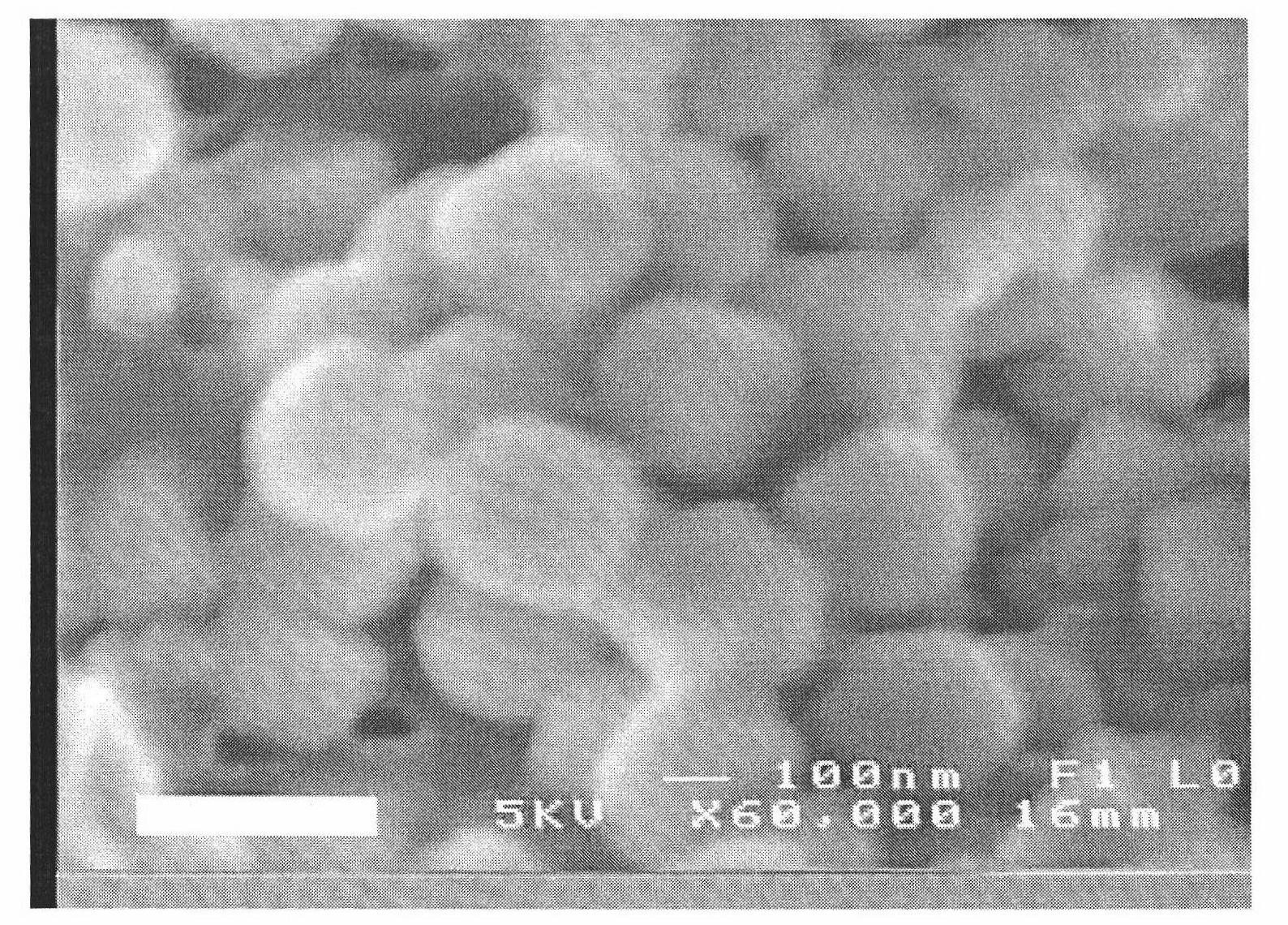
The up-conversion fluorescent powder is prepared by adopting a liquid-phase co-precipitation method and a thermal reaction method, and the up-conversion fluorescent material film is deposited by using a suspension coating film method or metal organic chemical vapor deposition. By adjusting the doping amount of Yb, Er, Tm and other rare-earth elements, the up-conversion fluorescent material can absorb near-infrared light with the wavelength between 800 and 2,000nm and emit visible light, and also can absorb ultraviolet light with the wavelength between 200 and 350nm and emit the visible light. The up-conversion fluorescent material film is applied to silicon-based thin-film solar cells, and the spectral absorption range of the silicon-based thin-film solar cells is widened. The silicon-based thin-film solar cells have the maximum photoelectric conversion efficiency in the visible light range, so the photoelectric conversion efficiency and the stability of the silicon-based thin-film solar cells can be improved by applying the up-conversion fluorescent material.
Owner:湖南共创光伏科技有限公司
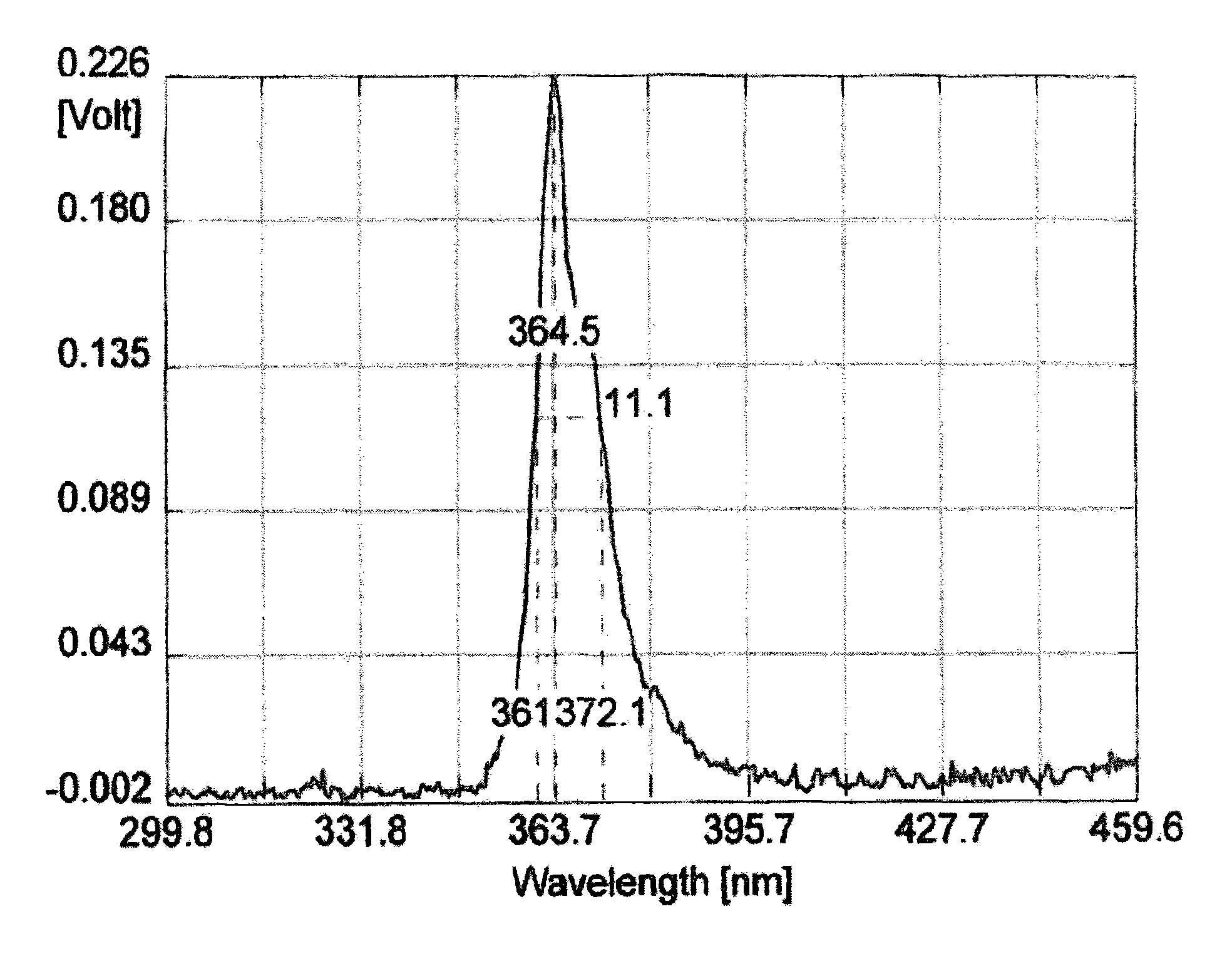
Method for measuring membrane temperature in metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) equipment in real time and measuring device
ActiveCN102455222AEnables growth temperature measurementEliminate errorsRadiation pyrometryMeasurement deviceGas phase
The invention discloses a method for measuring a membrane temperature in metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) equipment in real time and a measuring device. The method comprises the following steps of: monitoring radiant light of heat radiation of an epitaxial wafer through a spray hole in a vapor phase deposition technical process; and performing filtering separation on the radiant light to detect two or more types of membrane radiant light energy of different wavelengths. The measuring device disclosed by the invention comprises a light splitting mechanism, an optical detector and a data acquisition system. According to the method and the measuring device, a step for firstly measuring the surface emissivity of a membrane by adopting a single-wavelength optical temperature measuring technology in the conventional online measurement is omitted, an error caused by the change of the three-dimensional receiving angle of a receiving detector and the change of the distance between the detector and a measured object is eliminated, and the serviceable range and the measuring accuracy of an MOCVD online temperature measuring device are increased greatly. Due to the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention to processing, more accurate membrane temperatures are obtained.
Owner:甘志银
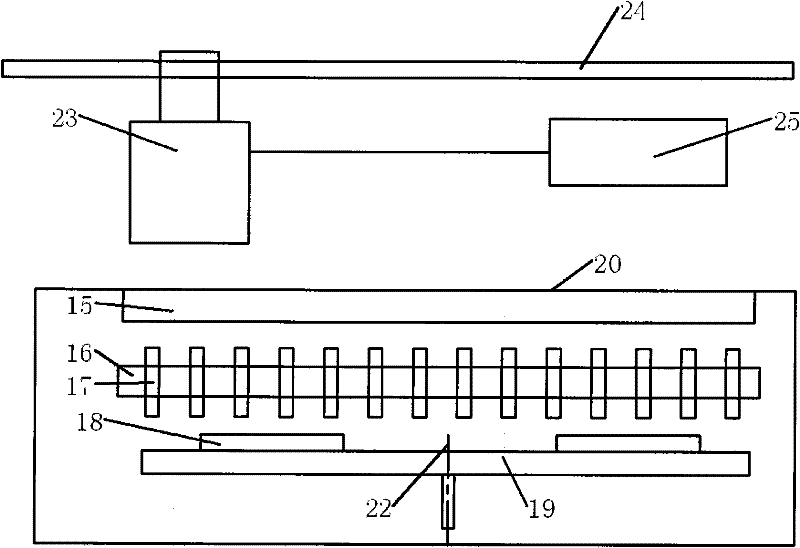
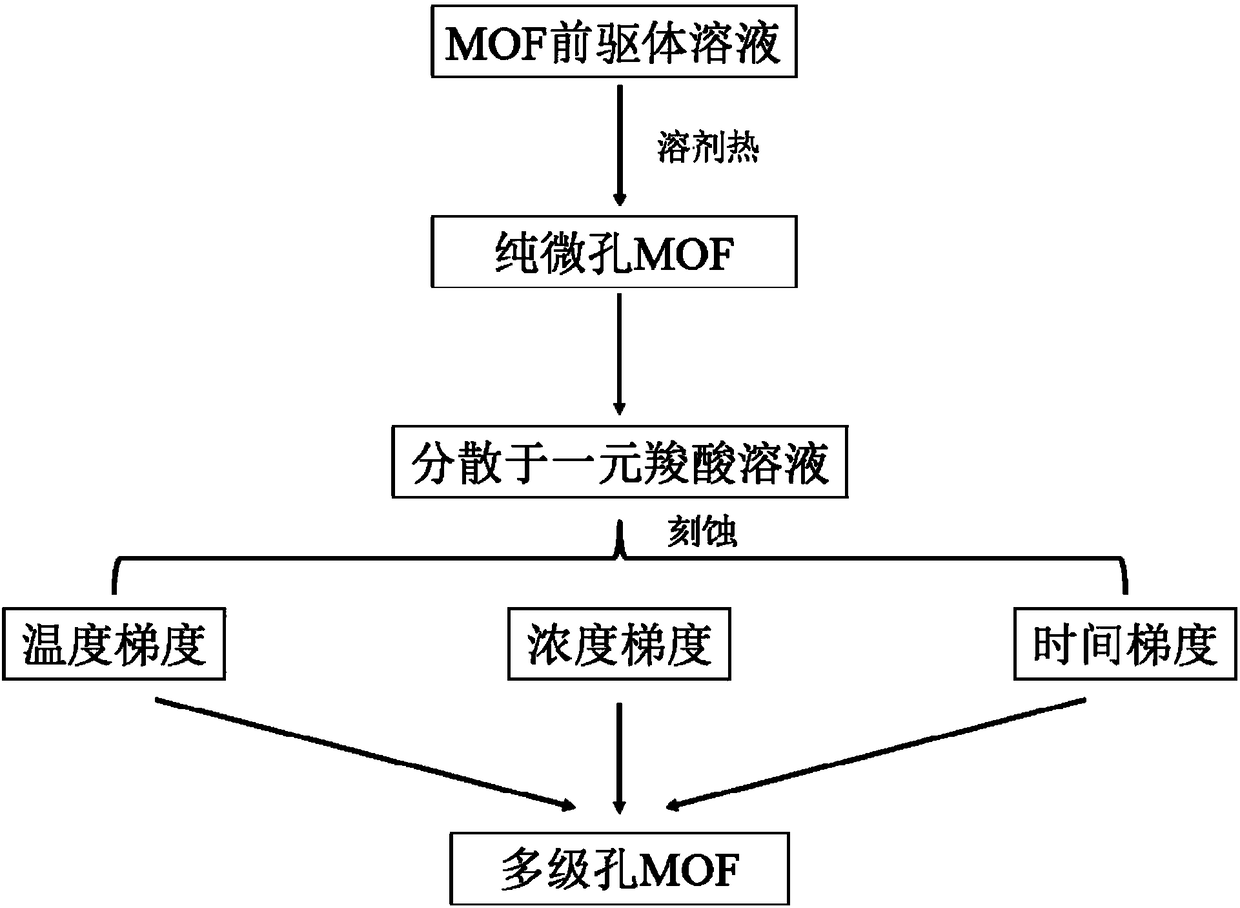
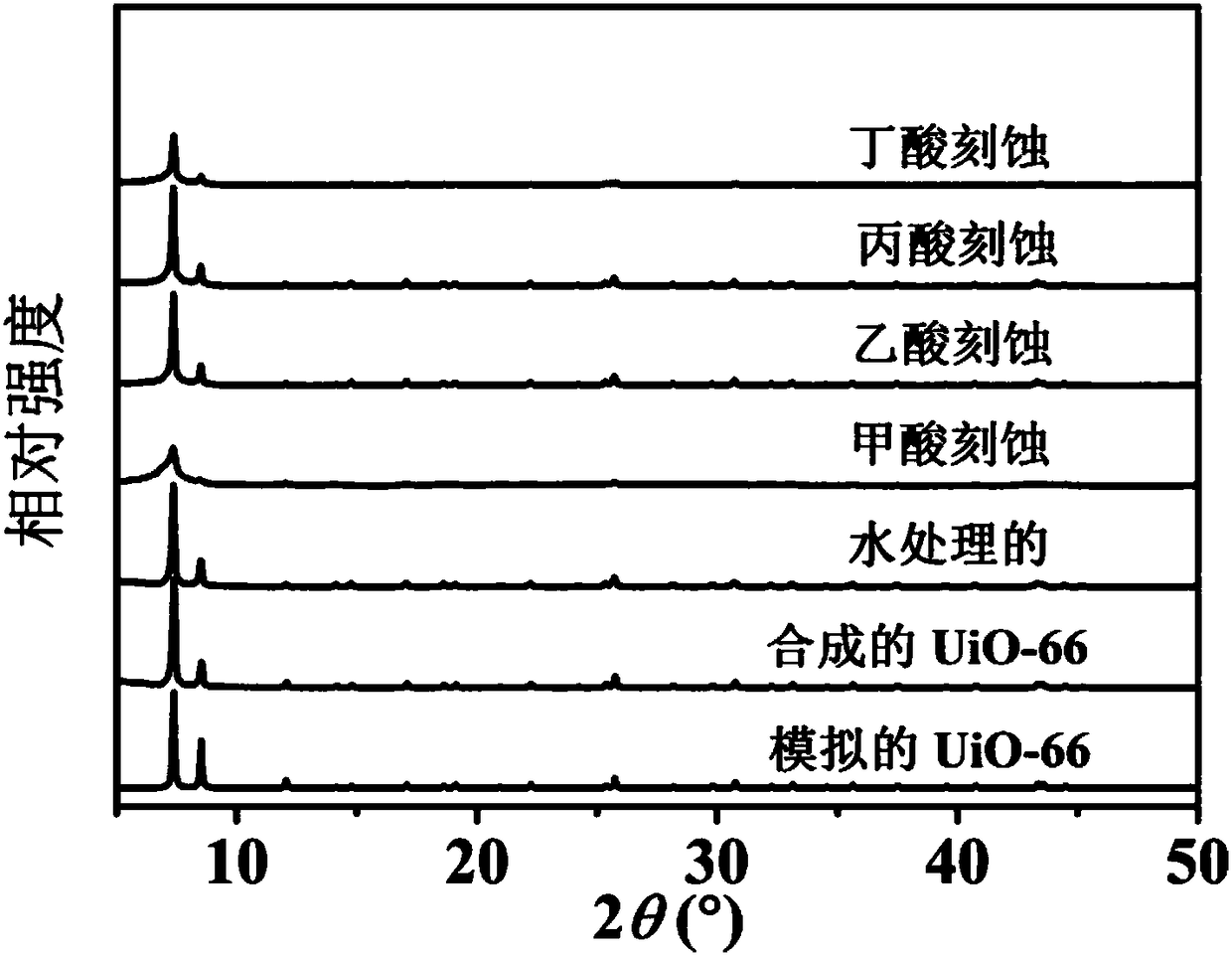
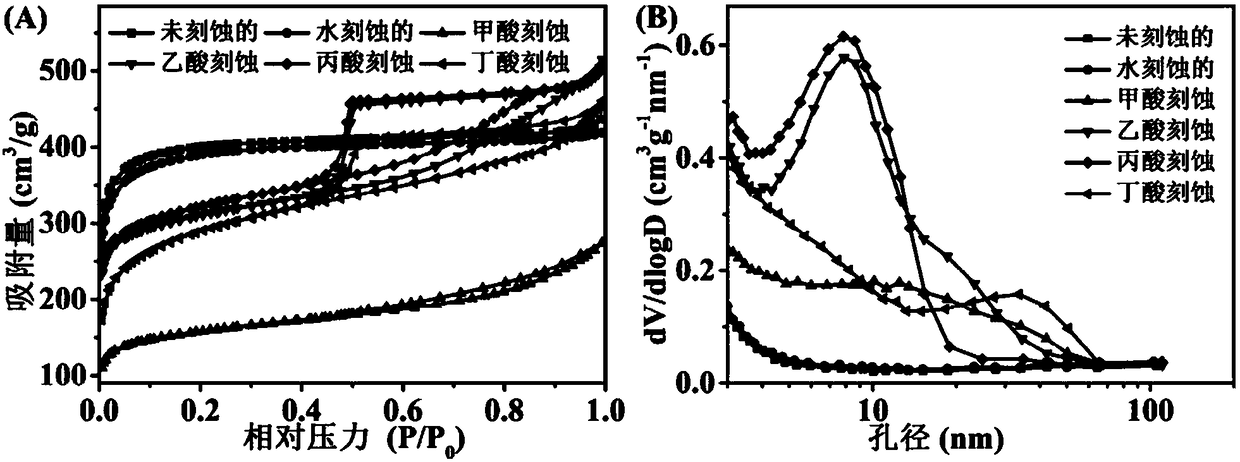
Preparation method of bore diameter adjustable hierarchical pore metal organic skeleton nanometer material, as well as obtained nanometer material and application thereof
ActiveCN108114699AImprove adsorption capacityEffective immobilizationOther chemical processesOxidoreductasesHeat stabilityMetal-organic framework
The invention relates to a preparation method of a bore diameter adjustable hierarchical pore metal organic skeleton nanometer material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing terephthalic acid with a zircon salt at the existence of a conditioning agent through a solvent thermal method to form a micropore zirconium-based metal organic skeleton; activating the microporezirconium-based metal organic skeleton with a low boiling point solvent and then drying to obtain an activated micropore zirconium-based metal organic skeleton; and dispersing the activated microporezirconium-based metal organic skeleton into 0.8 to 5.6 mol / L of monocarboxylic acid at the temperature of 25 to 180 DEG C for etching so as to obtain the hierarchical pore metal organic skeleton nanometer material. The invention also relates to the obtained bore diameter adjustable hierarchical pore metal organic skeleton nanometer material and application thereof. In short, according to the preparation method in the invention, a part of micropores is retained in the process that hierarchical pores are formed through etching of monocarboxylic acid, so that the obtained hierarchical pore metalorganic skeleton has chemical stability and heat stability similar to those of an original micropore skeleton.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Manufacturing method for distributed-feedback semiconductor laser with bar-shaped burying
ActiveCN102368591ALower the thresholdLower resistanceLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingGas phase
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a distributed-feedback semiconductor laser with bar-shaped burying. According to the method, primary epitaxy is carried out to form a primary epitaxial wafer; a single-beam spherical light mode is utilized to manufacture a distributed-feedback bragg grating with a gradient wavelength; a metal-organic chemical vapor deposition technology is utilized to carry out grating burying; a mode of combination of reactive ion etching and a two-step wet etching is used to manufacture a ridged bar; the metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOVCD) technology is used to carry out high-temperature meltback and then bar-shaped burying is carried out by a rapid growth mode; a SiO2 buried bar and a InGaAsP protective layer are removed and P type InP cover coat and a P+ In GaAs contact layer is grown; a large dual-channel structure is manufactured, a SiO2 insulated dielectric film is deposited, a P side electrode is manufactured, a substrate is thinned, an N side electrode is manufactured, an optical film is evaporated and plated on an end surface, and a laser chip is manufactured finally. According to the manufacturing method provided in the invention, the manufactured laser has characteristics of low threshold, low resistance, wide and stable working temperature range, high reliability and high yield and the like.
Owner:WUHAN HUAGONG GENUINE OPTICS TECH
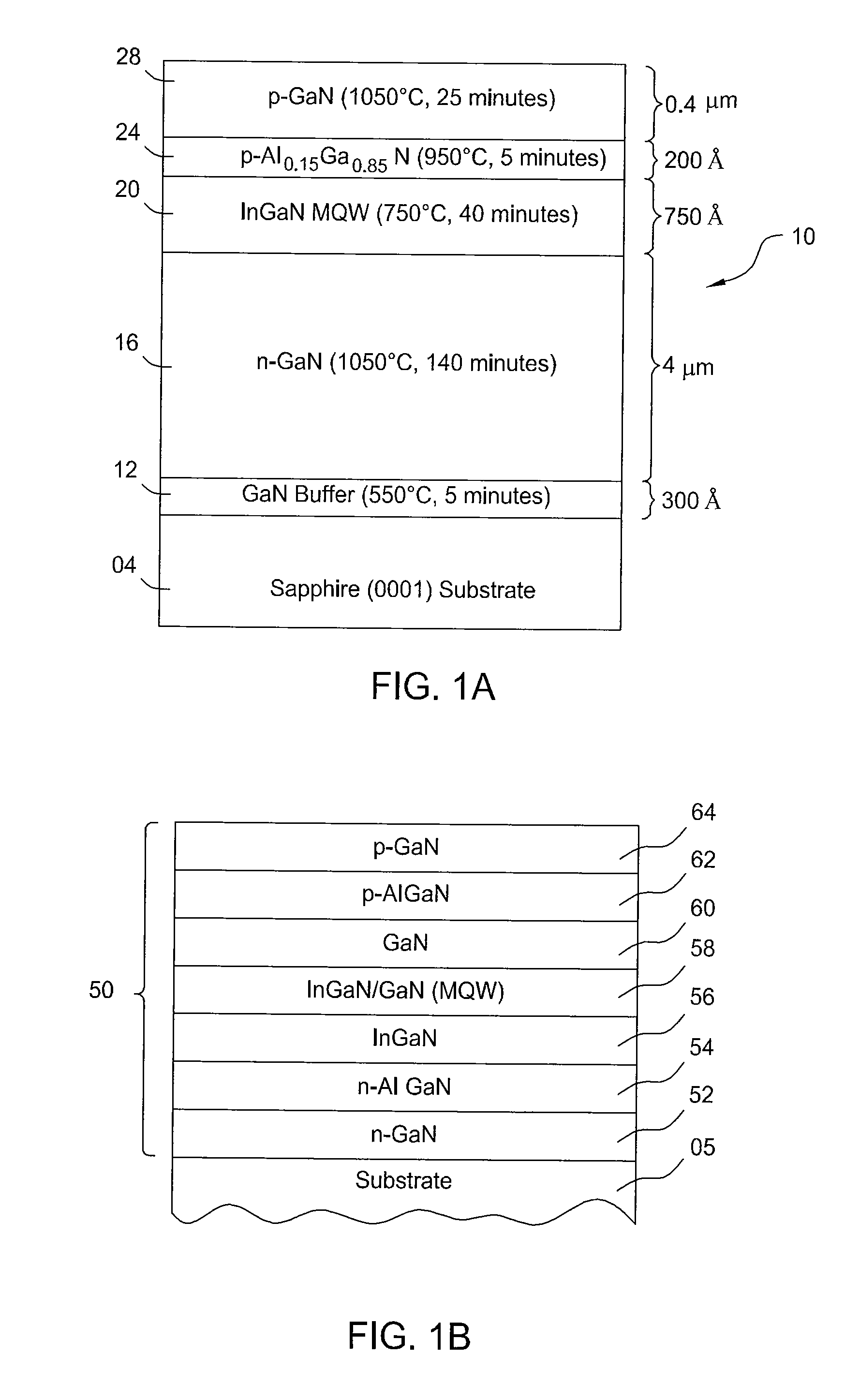
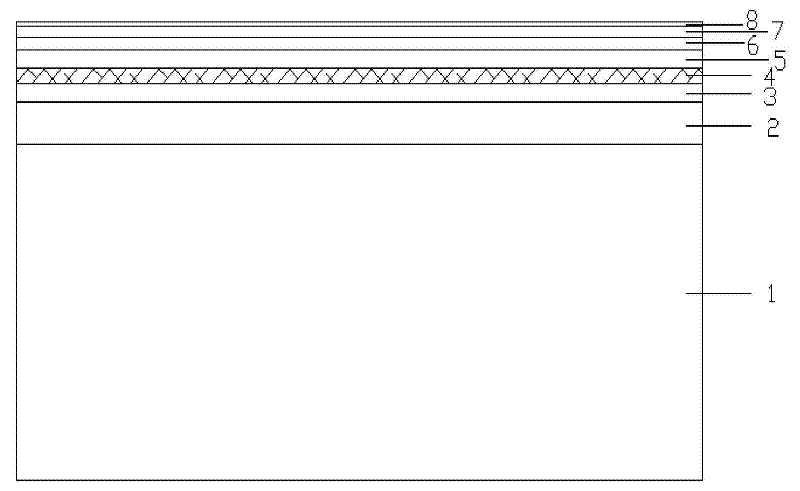
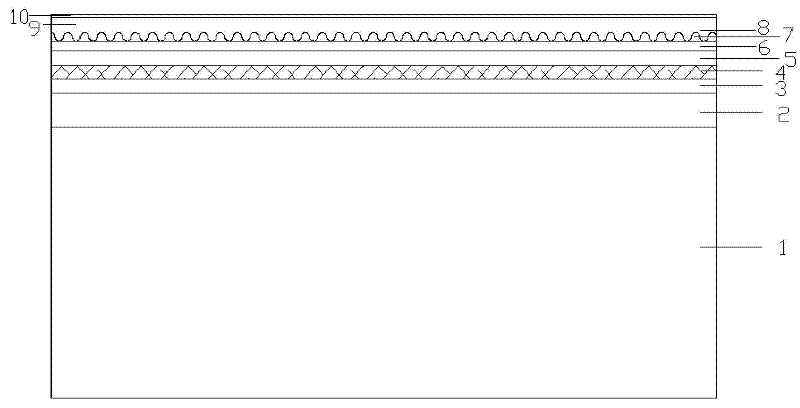
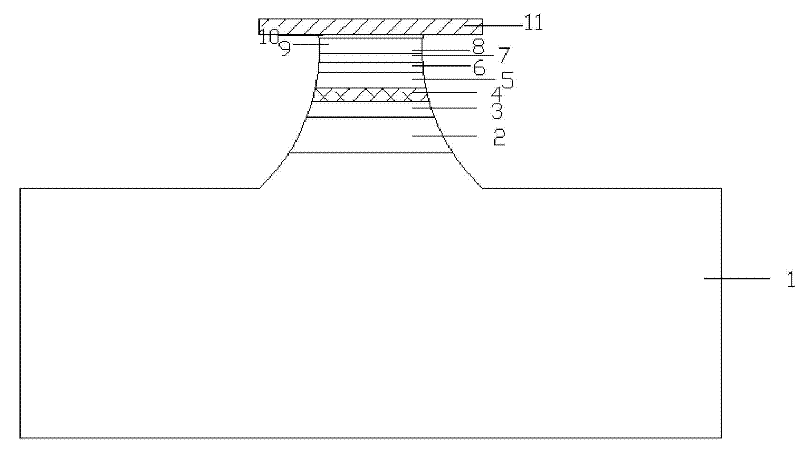
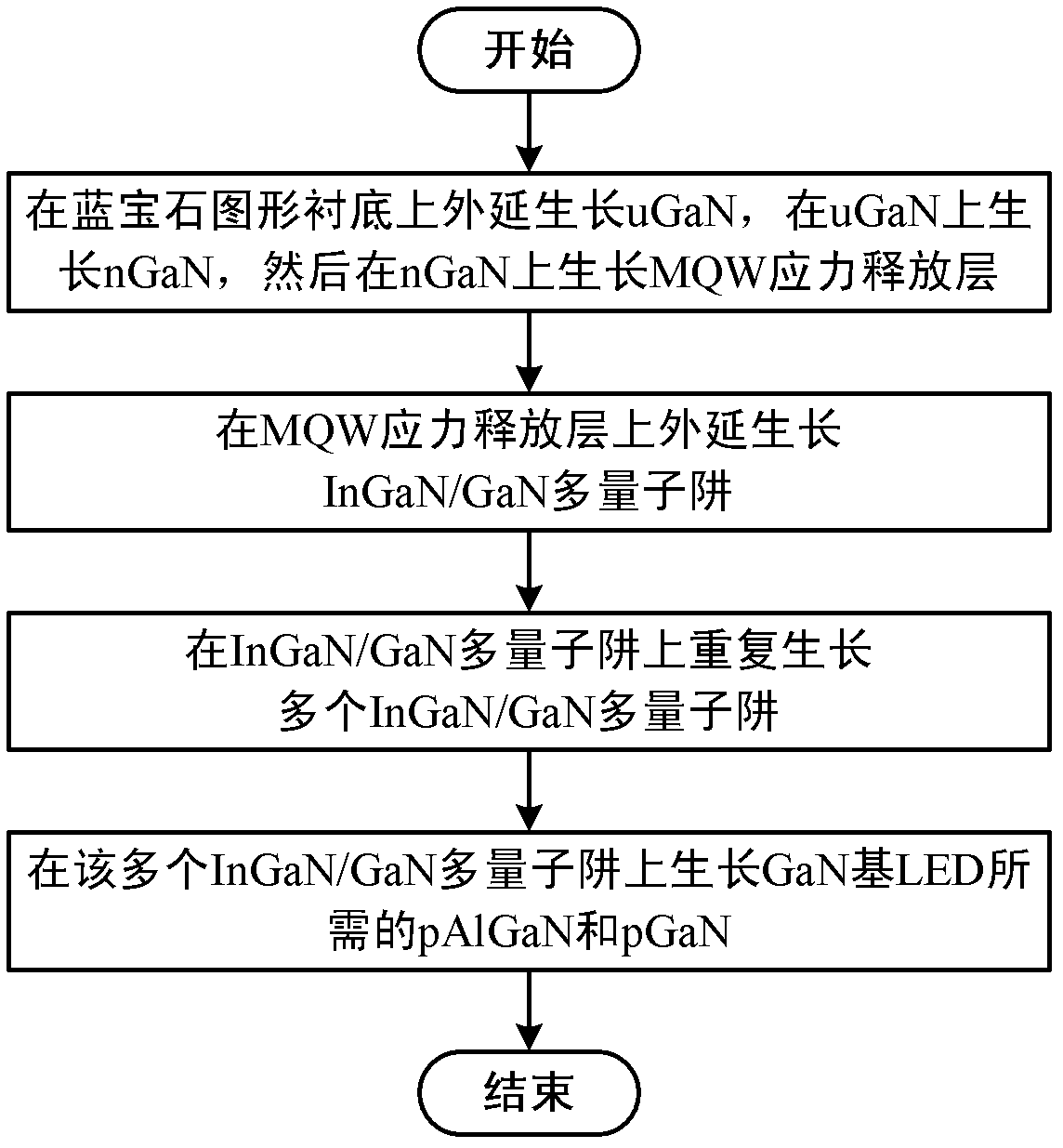
Method for uninterrupted growth of high-quality InGaN/GaN multi-quantum well (MQW)
ActiveCN102637787AQuality improvementShorten the timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellPatterned substrate
The invention discloses a method for uninterrupted growth of a high-quality InGaN / GaN multi-quantum well (MQW). The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out uGaN epitaxial growth on a sapphire-patterned substrate, growing nGaN on uGaN, and then, growing an MQW stress release layer on nGaN; carrying out InGaN / GaN MQW epitaxial growth on the MQW stress release layer; repeatedly growing a plurality of InGaN / GaN MQWs on the InGaN / GaN MQW; and growing pAlGaN and pGaN needed by a GaN-based LED (Light Emitting Diode) on the InGaN / GaN MQWs. According to the method for the uninterrupted growth of the high-quality InGaN / GaN MQW, a metal organic chemical vapor deposition method is adopted, and the growth of the GaN is kept during the process of switching growing conditions for quantum wells and quantum barriers, namely the uninterrupted growth of the quantum wells, so that the time required for the growth of the MQW is shortened, the production efficiency is greatly increased, and meanwhile, an LED epitaxial wafer with the high-quality InGaN / GaN MQW is obtained.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Annular semiconductor laser of vertical coupling structure and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN103259190AVersatileSimple structureOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsGas phaseRefractive index
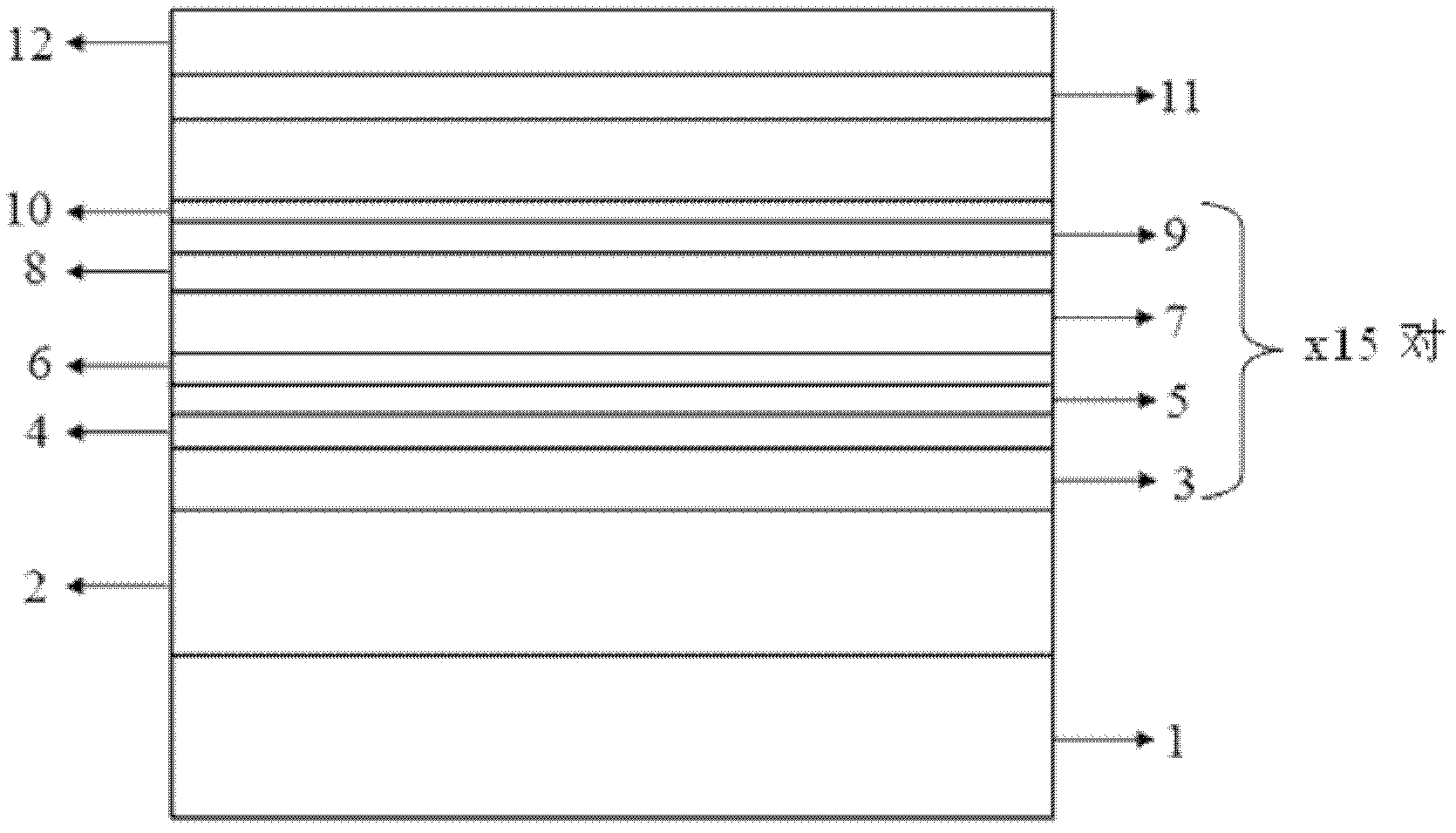
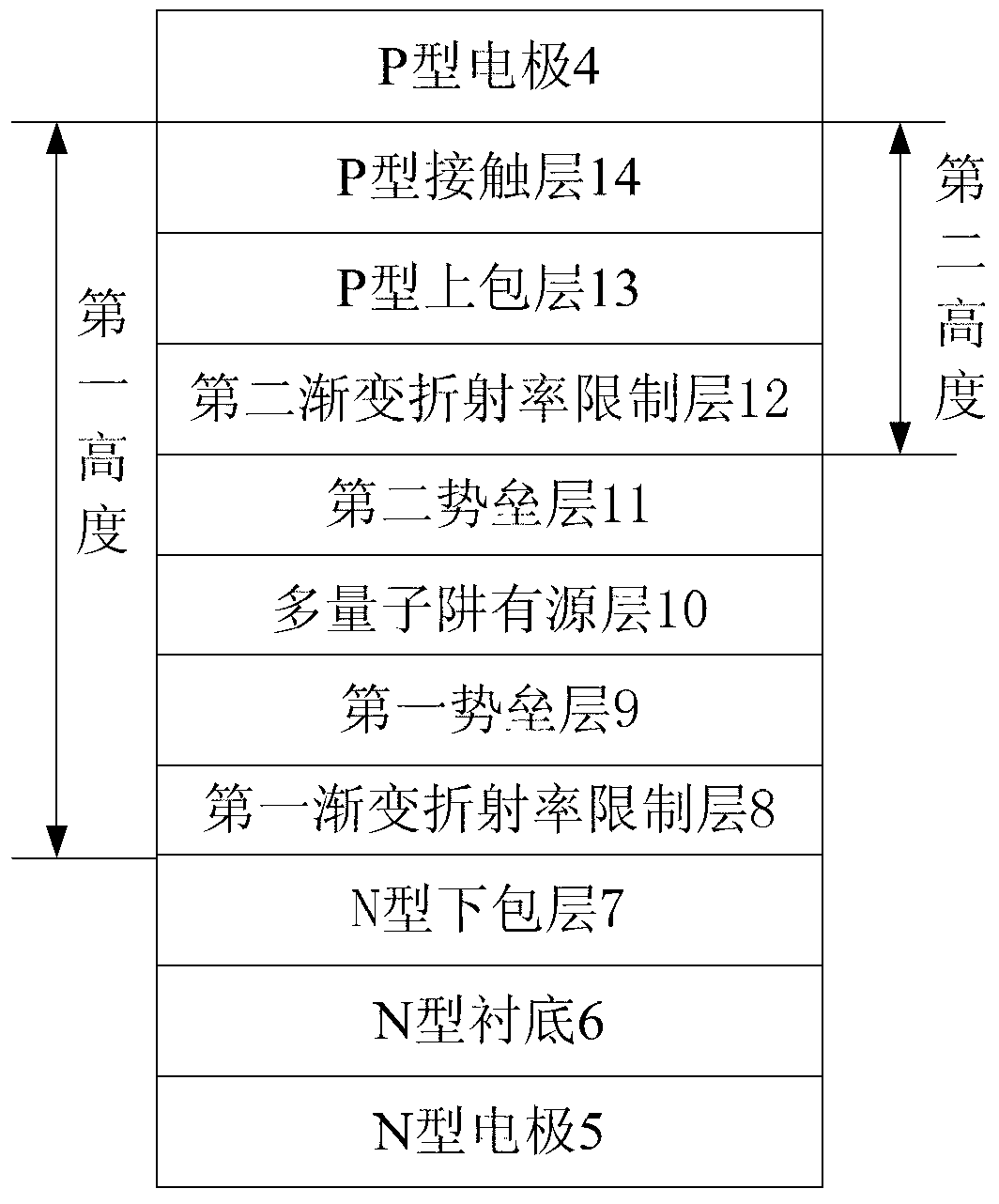
The invention discloses an annular semiconductor laser of a vertical coupling structure and a preparing method thereof. An annular active resonator cavity is any one closed loop composed of ridge type waveguide and strip type waveguide, a P type electrode and an N type electrode are arranged on the annular active resonator cavity, laser light in the annular active resonator cavity is coupled to strip type straight waveguide through a vertical coupler, and the strip type straight waveguide outputs the laser light. An N type lower wrapping layer, a first gradual-change refractive index limiting layer, a first barrier layer, a multiple quantum well active layer, a second barrier layer, a second gradual-change refractive index limiting layer, a P type upper wrapping layer and a P type contacting layer which have preset thicknesses and concentration are successively formed by means of a metal organism chemical vapor deposition or molecular beam epitaxy method. A plurality of epitaxial layers are etched by using a SiO2 image as a mask, the etching depth is less than or equal to a first height and greater than or equal to a second height, and the annular active resonator cavity is transferred to a chip. The obtained annular semiconductor laser has the advantages of being simple in process, low in cost, stable in performance of parts, high in reliability and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Silica-based gallium nitride growing method based on graphene and magnetron sputtering aluminum nitride
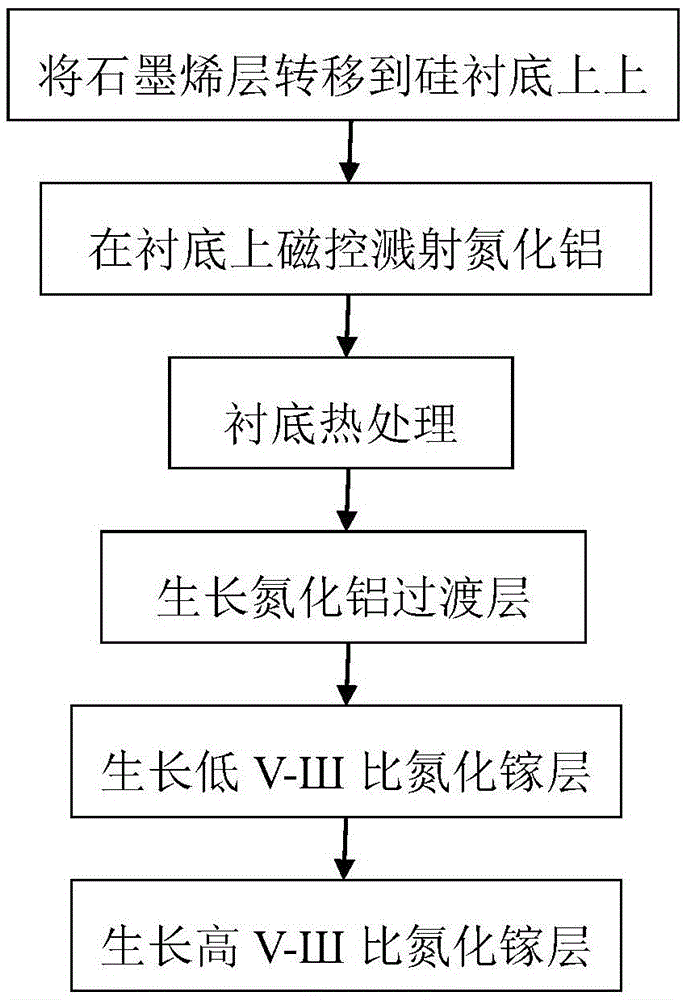
ActiveCN105655238AOvercome growth difficulties and poor qualityNucleation is easyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGas phaseSingle layer graphene
The invention relates to a silica-based gallium nitride growing method based on graphene and magnetron sputtering aluminum nitride. The method includes the following steps that 1, single-layer graphene is transferred to a silicon substrate through a transferring technology of graphene on a copper substrate; 2, an aluminum nitride film grows on the silicon substrate covered by the graphene layer through magnetron sputtering; 3, heat treatment is conducted; 4, an aluminum nitride film is formed in an epitaxy mode through a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) method; 5, a sample is put into MOCVD, and a low-V / III-ratio GaN epitaxial layer and a high V / III ratio GaN epitaxial layer are sequentially formed in an epitaxy mode. The good-quality gallium nitride epitaxial layer covering the silicon substrate of the graphene layer is obtained easily through the method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
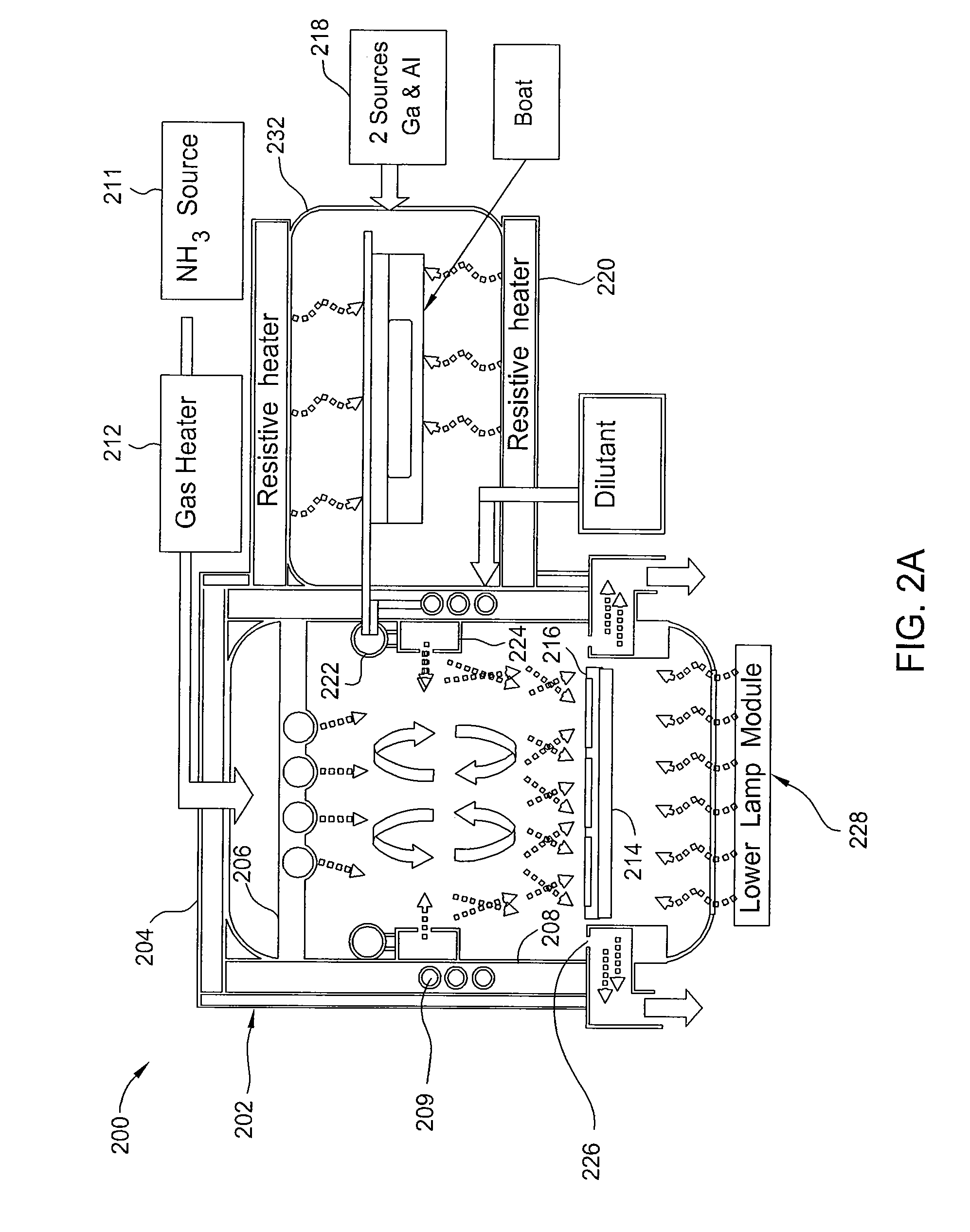
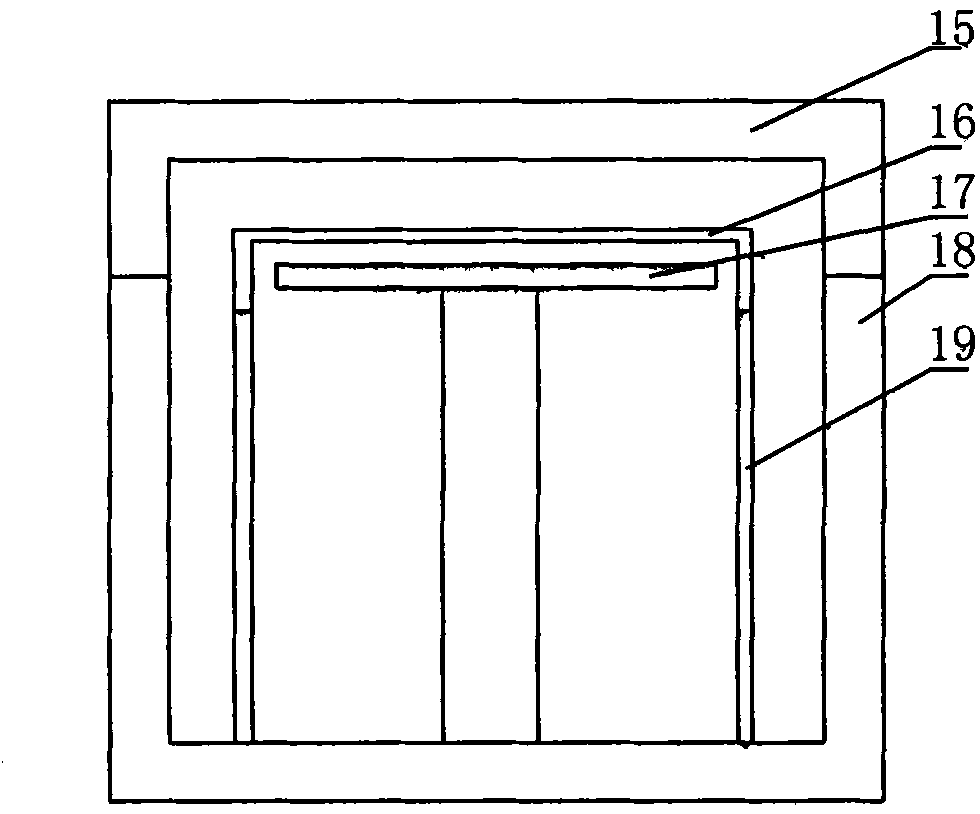
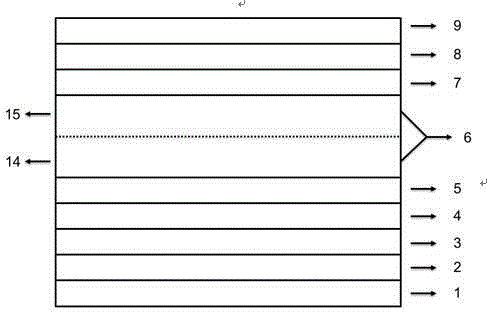
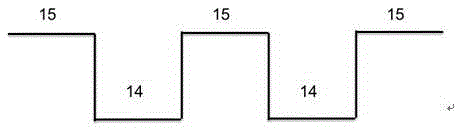
Large-area pectinate spraying head used for metal organic chemical gas phase deposition device
InactiveCN101122012AAchieve mutual isolationGuarantee mutual isolationSpray nozzlesChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseEngineering
A large area comb-shaped sprinkler head for metal-organic chemical vapor deposition equipment is provided with two sets of comb-shaped sprinkler heads; the first set of comb-shaped sprinkler head consists of a gas A main pipe provided with a gas inlet and a plurality of gas A ventilation branch pipes which are lined in parallel; one end of each gas A ventilation branch pipe is communicated with the gas A main pipe and the other end is sealed; the second set of comb-shaped sprinkler head is provided with a gas B main pipe with the gas inlet and a plurality of gas B ventilation branch pipes which are lined in parallel; one end of each gas B ventilation branch pipe is communicated with the gas B main pipe and the other end is sealed; the gas A ventilation branch pipes and the gas B ventilation branch pipes are alternatively lined and connected into an integral structure; the gas A main pipe and the gas B main pipe are respectively arranged on the corresponding two sides of the integral structure; all gas A ventilation branch pipe and gas B ventilation branch pipes are opened with a plurality of sprinkler holes. The invention effectively feeds two source gases and separates them before they are sprayed into the reaction chamber, so as to evenly mix them before they reach above the substrate and react.
Owner:48TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Method of growing single crystal Gallium Nitride on silicon substrate
InactiveUS7014710B2Break the bottleneckPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing cost reductionEtching
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
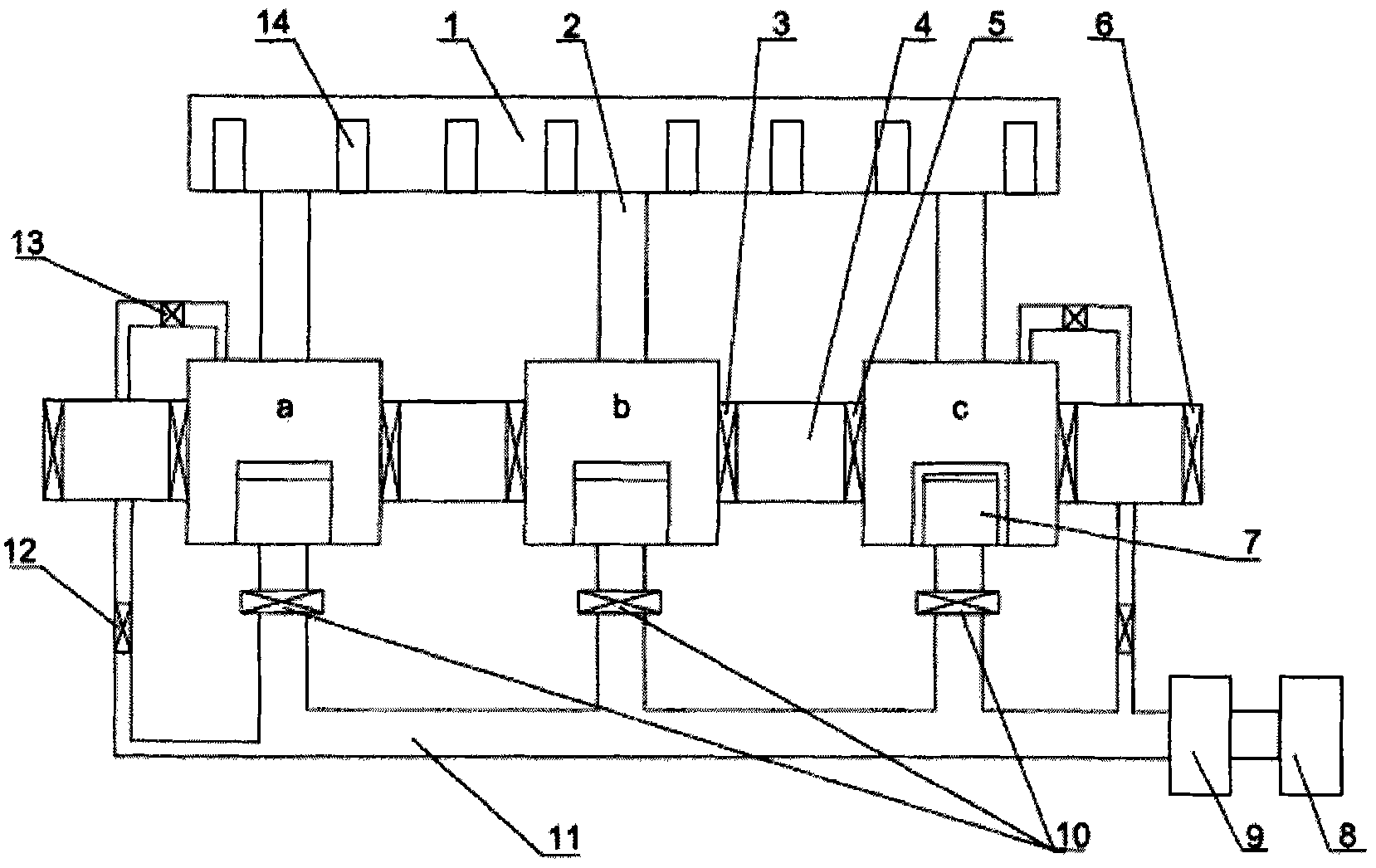
Multiple-reaction cavity metallorganic chemical vapor deposition equipment
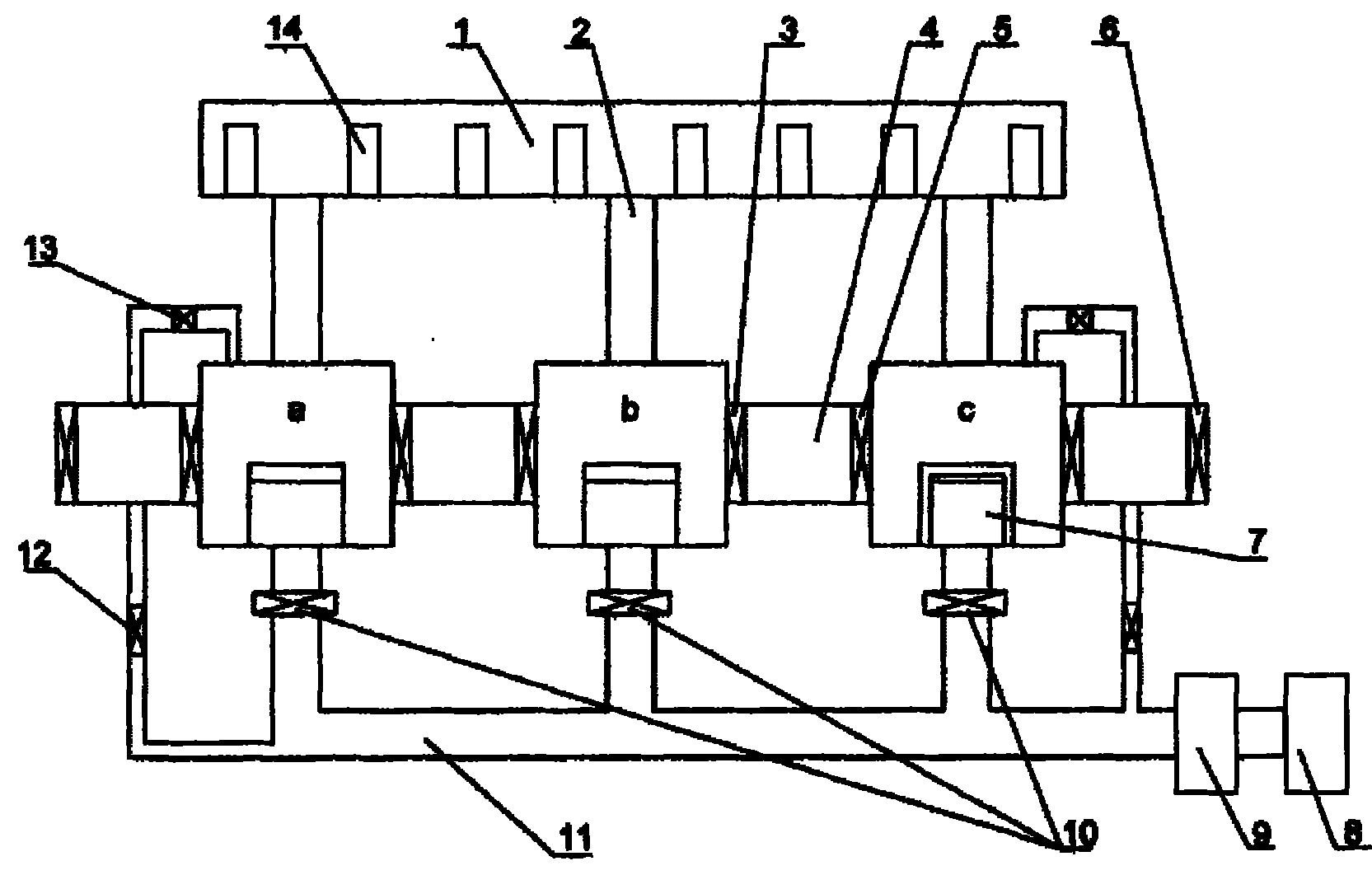
ActiveCN101921999AShorten the timeSave energyChemical vapor deposition coatingTransport systemProduct gas
The invention relates to multiple-reaction cavity metallorganic chemical vapor deposition equipment comprising a gas transport system, reaction cavities, a tail gas treatment system, heaters and a wafer fetch and transport mechanism. The equipment is characterized by comprising two or more than two reaction cavities; the reaction cavities are mutually connected by the gas transport system; the equipment is provided with the tail gas treatment system; each reaction cavity is connected with the tail gas treatment device; a control valve is arranged in a pipeline; the reaction cavities are arranged in glove boxes; the wafer fetch and transport mechanism is arranged among the glove boxes; both ends of the wafer fetch and transport mechanism are respectively provided with a valve; and each cavity is provided with one heater. The invention has the advantages that the equipment is provided with a plurality of reaction cavities, can complete various process manufactures in one step and switches to another growth process after one growth process is ended, and thereby, the processing time and the energy sources are saved, the efficiency is improved, the cost is reduced and the product quality is improved.
Owner:甘志银
GaN thin film upgrowth method based on Al3O2 substrate
InactiveCN101140867AReduce tensile stressIncrease critical thicknessLaser detailsFinal product manufactureMaserGas phase
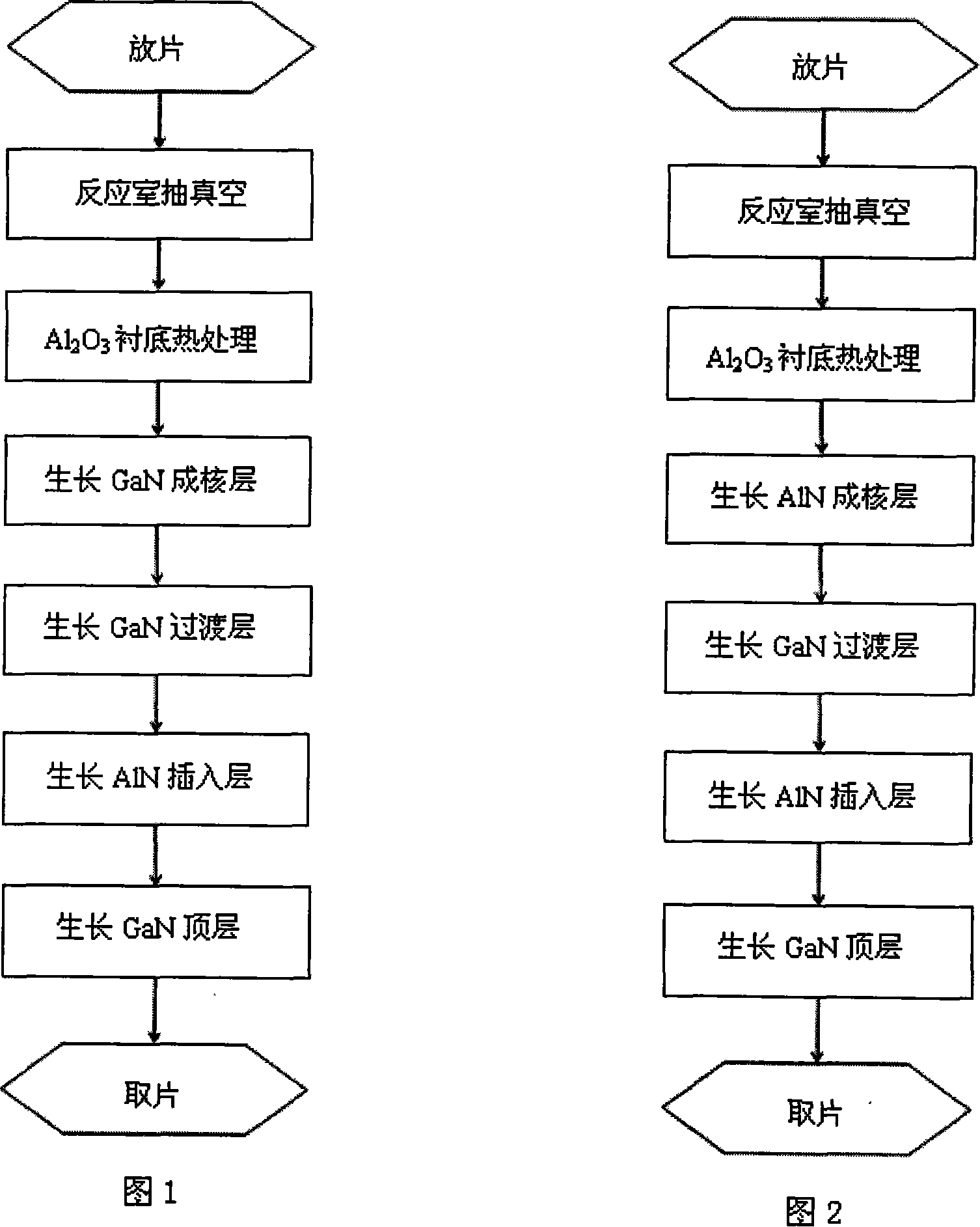
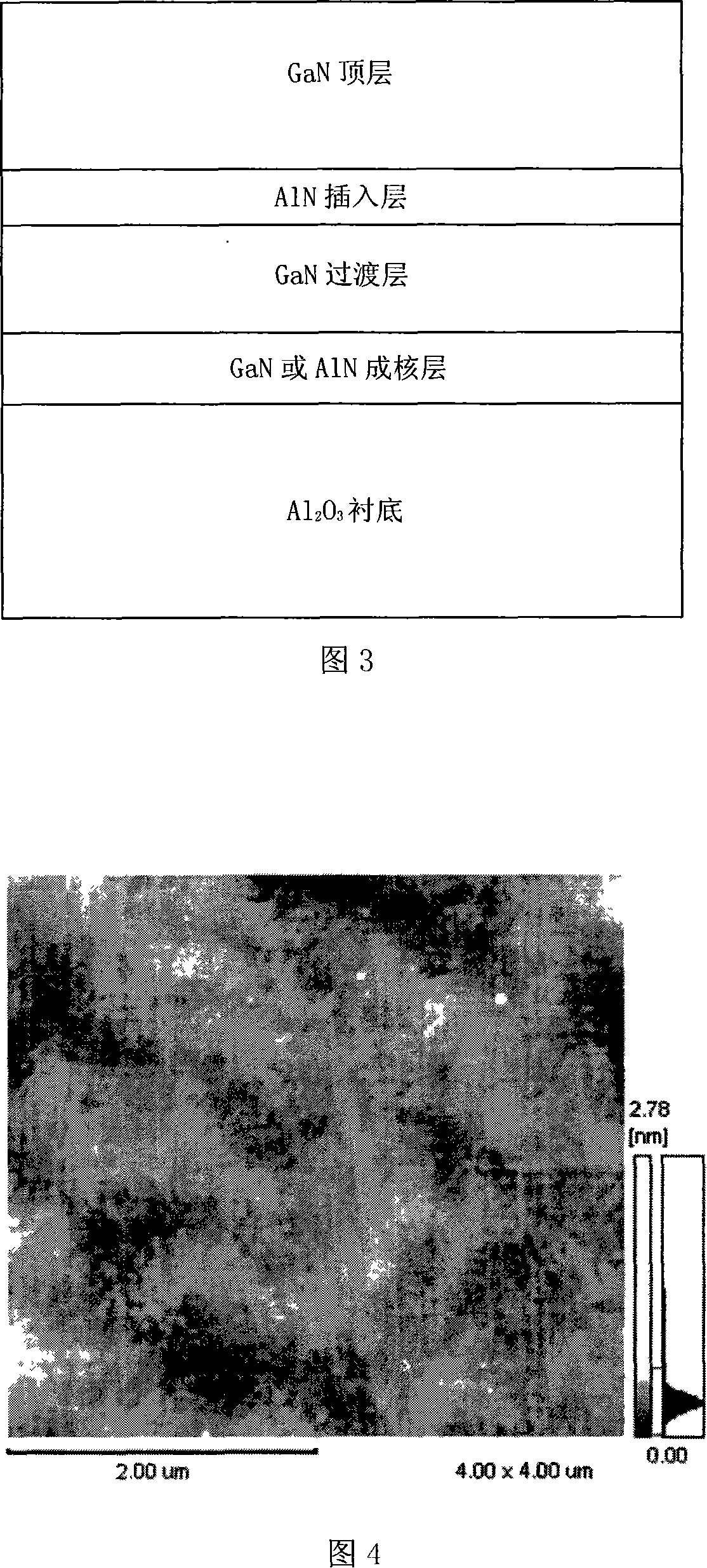
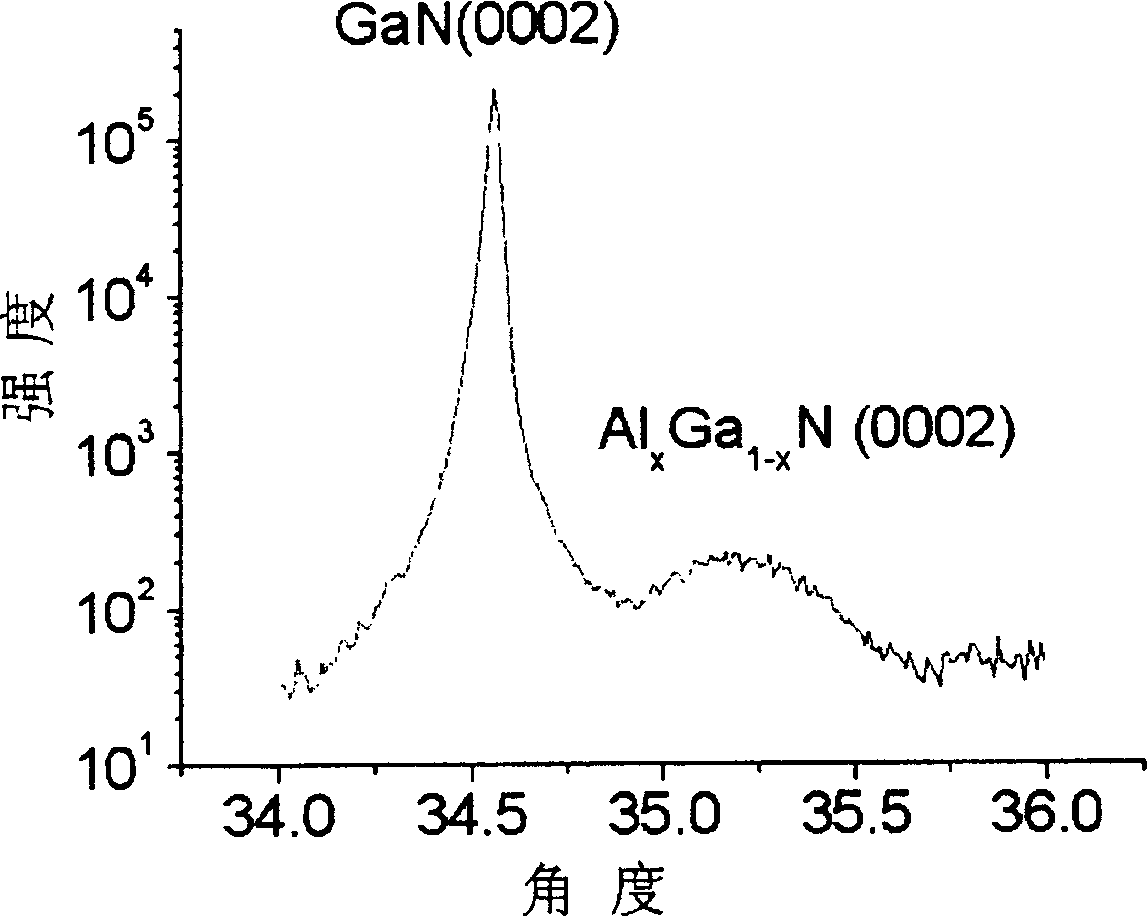
The invention discloses a growing direction for GaN thin film based on Al2O3 underlay, which aims to solve the problem of generating excessive heat stress during the growing of AIN layer inserted under low temperature in prior art. The growing process of the Gan thin film is that: put the underlay of Al2O3 in the MOCVD reaction chamber where the chemical vapor deposition of metallorganics occurs; inflate the hydrogen or mixed gas of hydrogen and alkaline air to the reaction chamber and make heat treatment to the underlay chip; grow the GaN orAIN nucleating layer on the heat-processed underlay; grown the GaN top layer on the AIN interposed layer. The technological conditions of AIN interposed layer growing under high temperature is: 20 to 760 Torr in growing pressure, 900 to 1,100 degrees centrigrade in temperature, 120 mu mol / min in flow rate of aluminium resources and 1000 to 5000 sccm in flow rate of alkaline air. The GaN epitaxial layer grown by the method provided in the invention is applicable to making micro wave high power transistor based on GaN, LED and optical maser.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
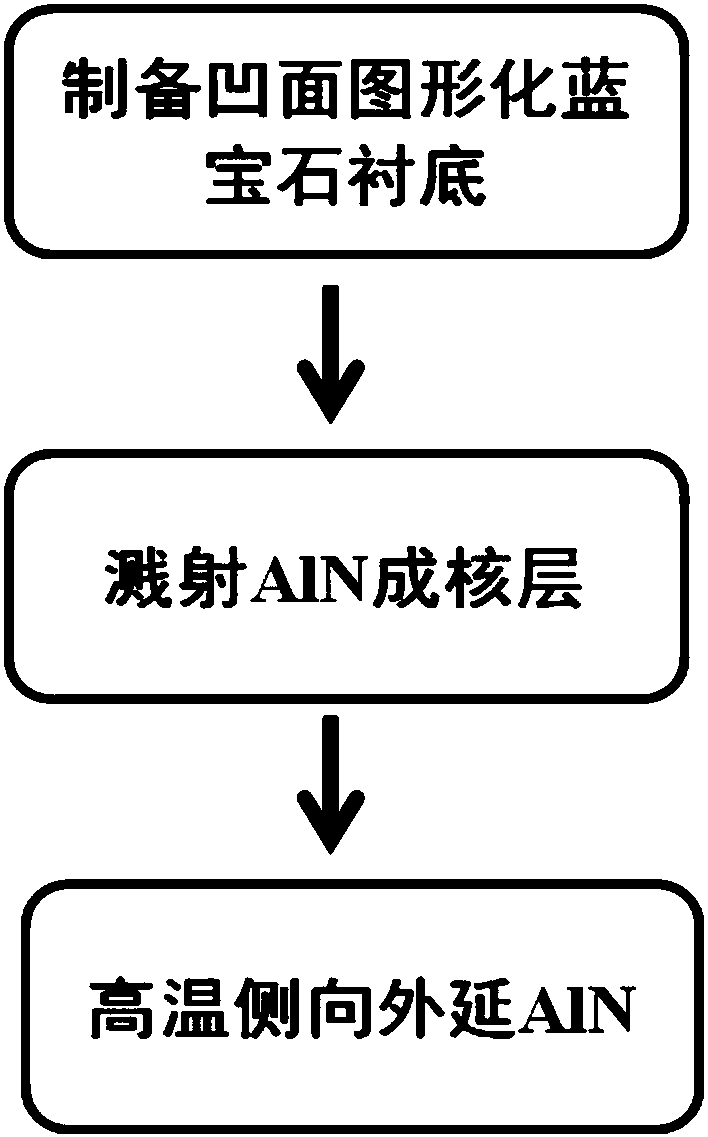
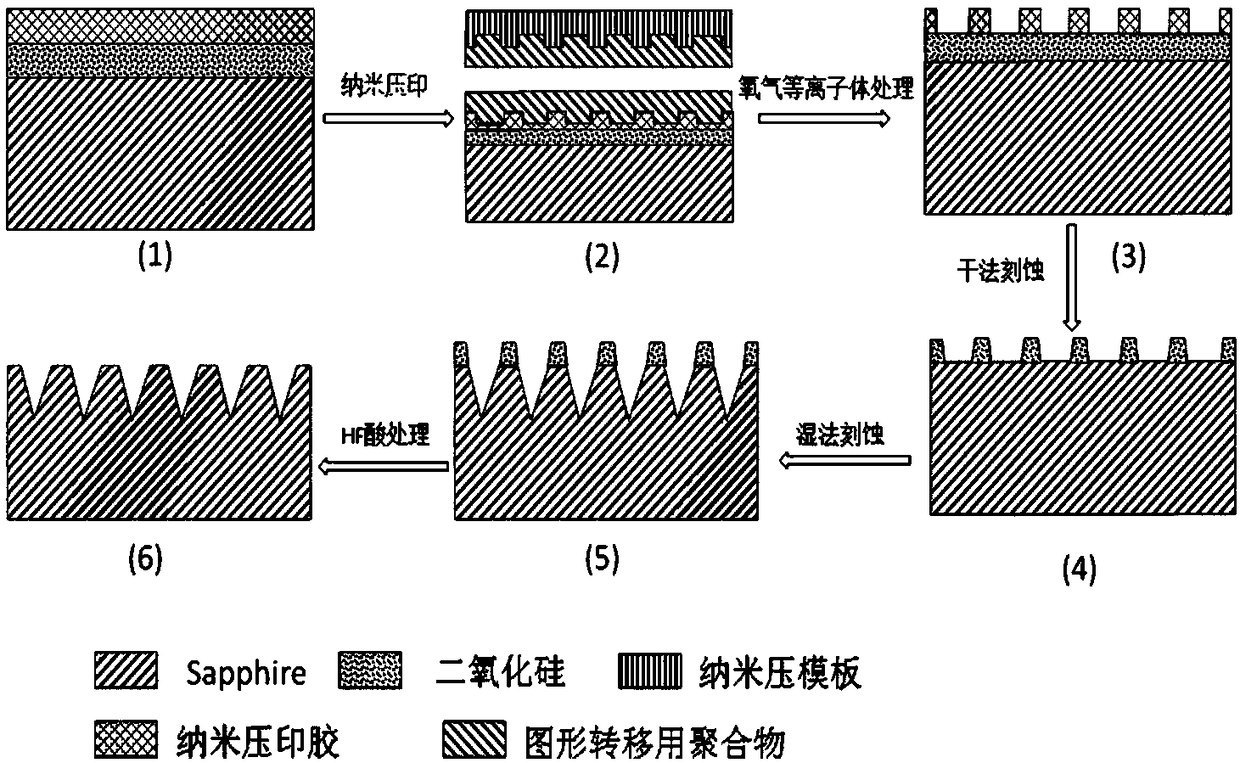
AlN film preparation method based on patterned sapphire substrate and pre-sputtering technology
The invention belongs to the field of III-family nitride semiconductor preparation technology, and relates to preparation of a low-dislocation-density AlN epitaxial film. The method of the invention is combined with two core key links of a patterned sapphire substrate and a pre-sputtering AlN nucleation layer. Based on the two core key links, a lateral epitaxial process is realized through metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD), thereby obtaining the AlN film with smooth surface and low dislocation density.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
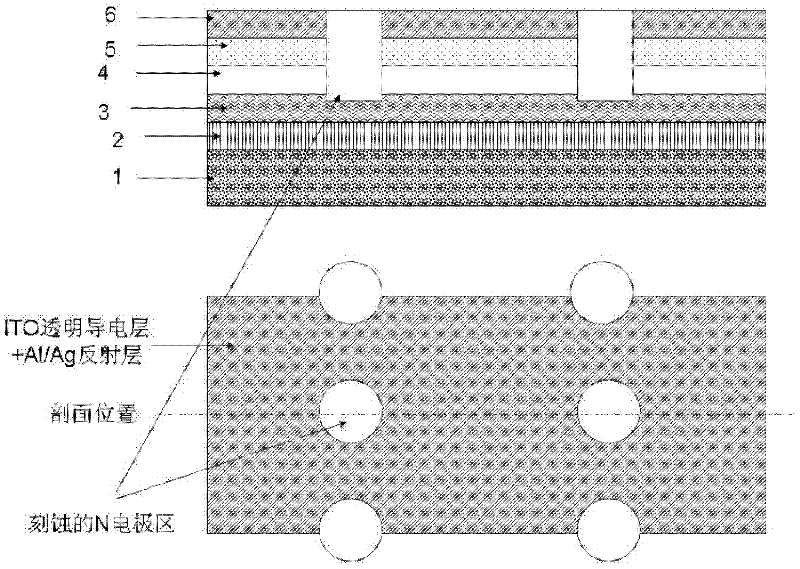
GaN (gallium nitride)-based LED (light-emitting diode) with N-type electrodes in dotted distribution and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to a GaN (gallium nitride)-based flip-chip LED (light-emitting diode) with N-type electrodes in dotted distribution and a manufacturing method thereof. The LED comprises a GaN-based chip and a flip-chip-bonding substrate which is bonded with the GaN-based chip by a flip chip bonding method. In the manufacturing method, a metallorganic chemical vapor deposition growth technology is adopted to grow a multilayer material structure of the GaN-based LED on a heterogeneous material or sapphire substrate, and the main manufacturing processes of the device such as photoetching, deposition, etching, evaporation, sputtering and peeling are carried out to realize P-type reflecting layer electrodes and N-type electrodes of the flip-chip-bonding chip. In the method, multiple N-type electrodes in dotted distribution is adopted, and the flip-chip-bonding substrate is utilized to be connected with the N-type electrodes, thus the P-type region area is increased and the process complexity is lowered at the same time, the reliability is improved, and the luminous efficiency of the flip-chip-bonding LED chip is improved greatly.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for fabricating transistor of aluminum-gallium-nitrogen/gallium nitride with high electron mobility
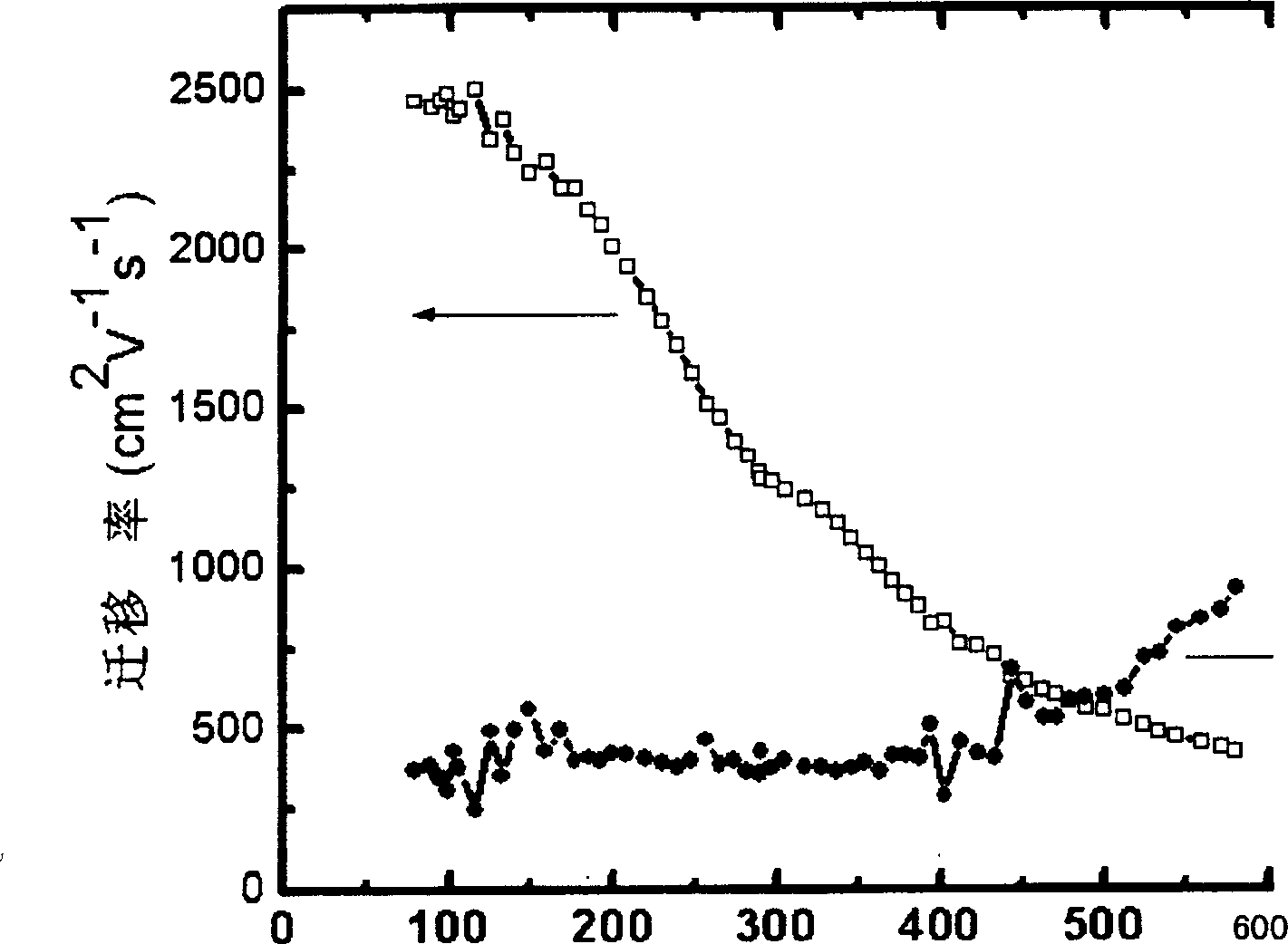
InactiveCN1728349AIncrease concentrationImprove crystal qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGas phaseGallium nitride
The method includes steps: (1) using method of metallorganics chemical vapor deposition or method of molecular beam epitaxy or method of gas phase epitaxy for hydride develops a thin layer of nucleation layer of aluminum nitride on crystal face of sapphire (0001) substrate or silicon carbide (0001) substrate or silicon (111) substrate; (2) developing a thicker buffer layer of semi insulating gallium nitride in high impedance; (3) developing aluminum-gallium-nitrogen barrier layer in high aluminum content including spatial isolation layer without aluminum-gallium-nitrogen doped, carrier supplying layer with aluminum-gallium-nitrogen doped; (4) developing a covering cap in thin layer of gallium nitride.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
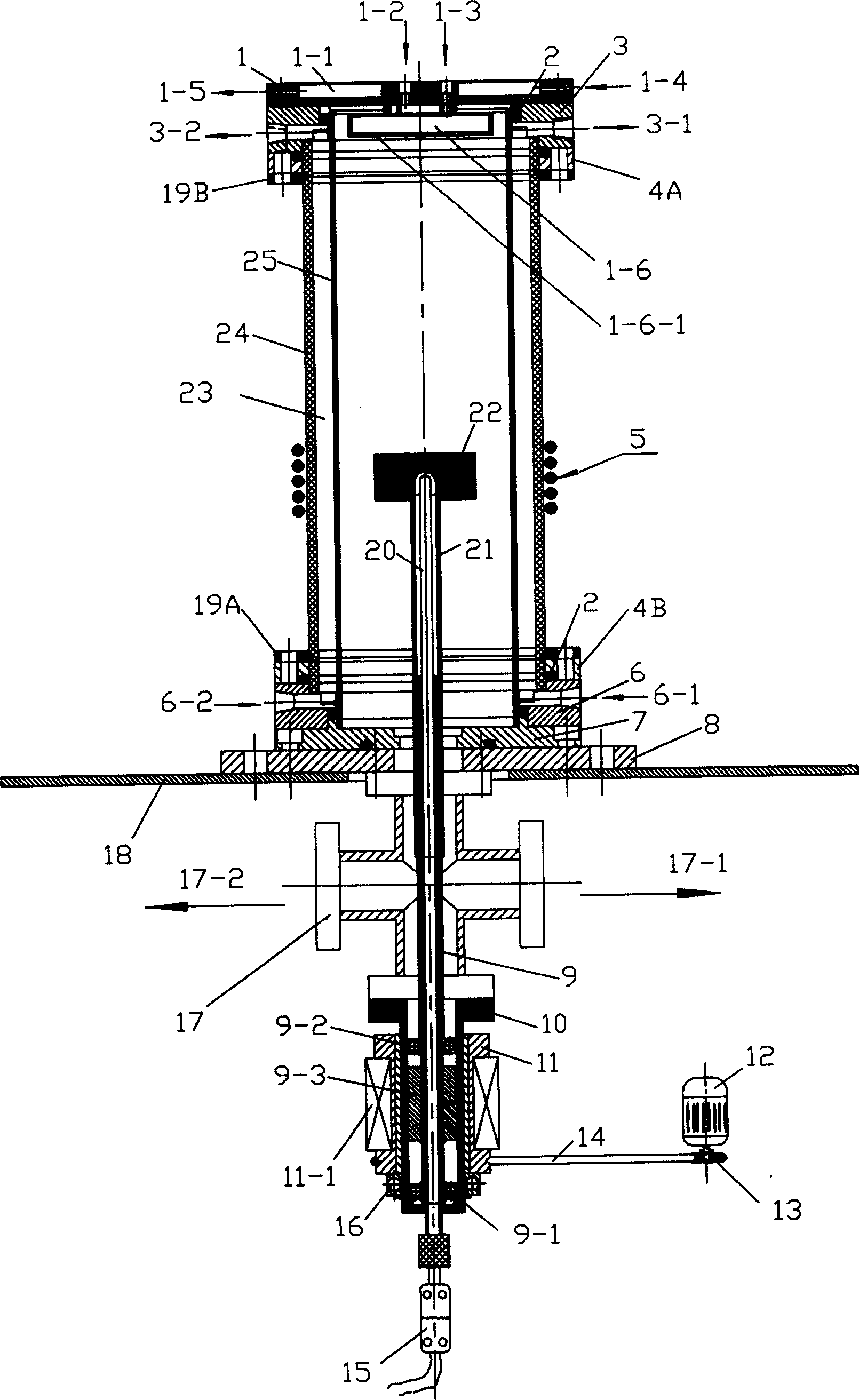
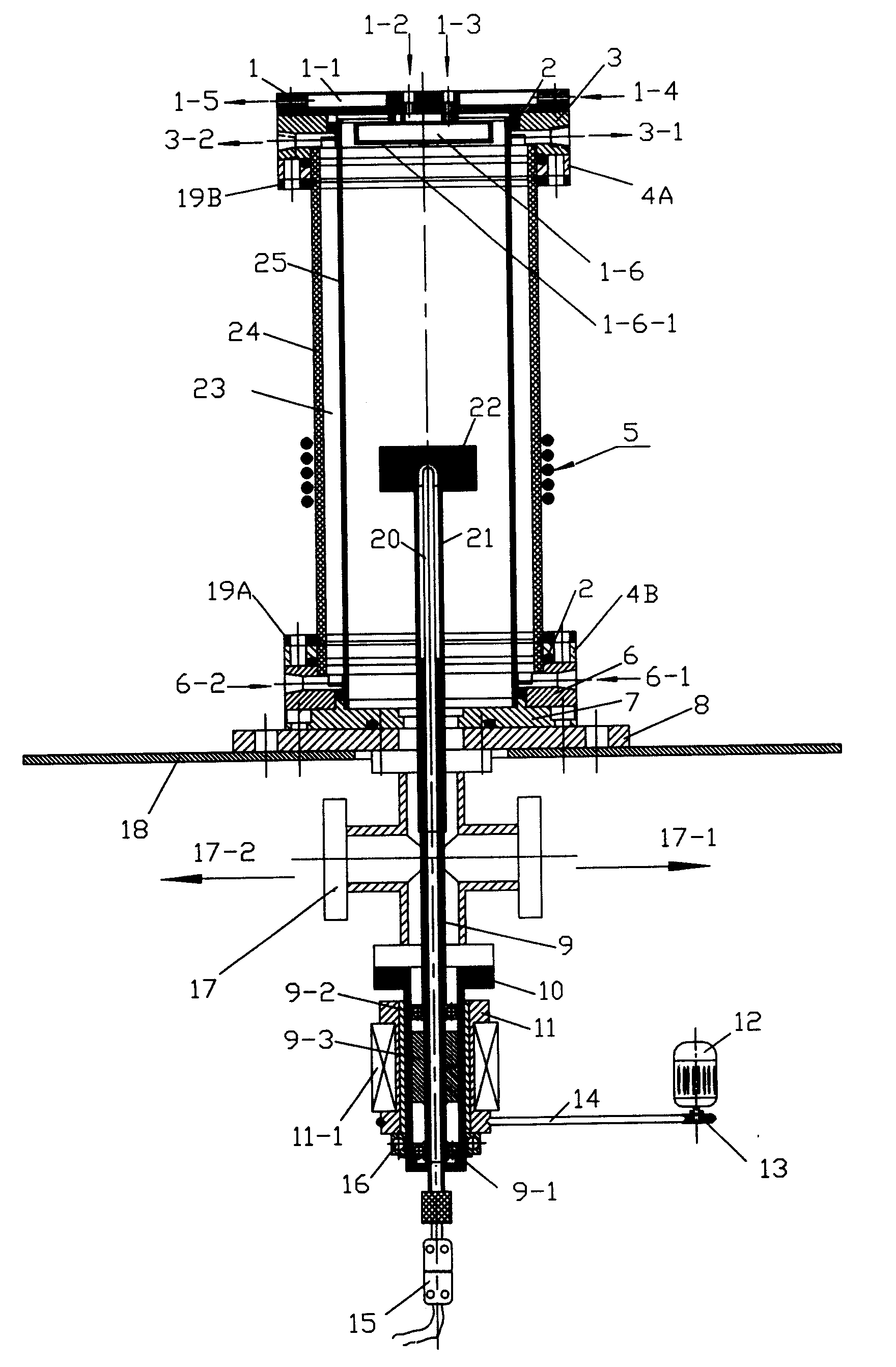
Revolution and rotation arrangement in reaction chamber of metallorganics chemical vapor deposition device
InactiveCN1865495ALower growth costsSave raw materialsChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseGraphite
The invention discloses a substrate base rotary structure in the metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) equipment, which is characterized by the following: (1) the big graphite boat in the reacting chamber revolves one public fixing point; the small graphite boat rotates each center point; (2) the motor anchors substrate base (big graphite boat) to revolve; (3) the motor anchors the substrate base (small graphite boat) rotates; (4) the high-temperature region (substrate base) and low-temperature region (rotary dynamic structure) are separated by heat-durability material, which transmits the rotary dynamics.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electro-optical element including metallic films and methods for applying the same
A method for manufacturing electrochromism element comprises: providing a first base plate having a first and second surface and a first edge surface; providing a second base plate having a third and fourth surface and a second edge surface with the third surface facing to the second surface; providing an electrochromism medium, which has a variable light transmittance while applied with a electric field, between the first and the second base plate; coating conductive layer at least a part of one of the surfaces under basic atmospheric pressure applying at least one of metal particulate, organic metal, metallorganics and their combination, in which, the conductive layer has a volume resistivity not less than 150 gemmbo.cm. The conductive layer can be coated by spray painting, ultrasonic spray painting, screw pump spray painting or jet pump spray painting.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
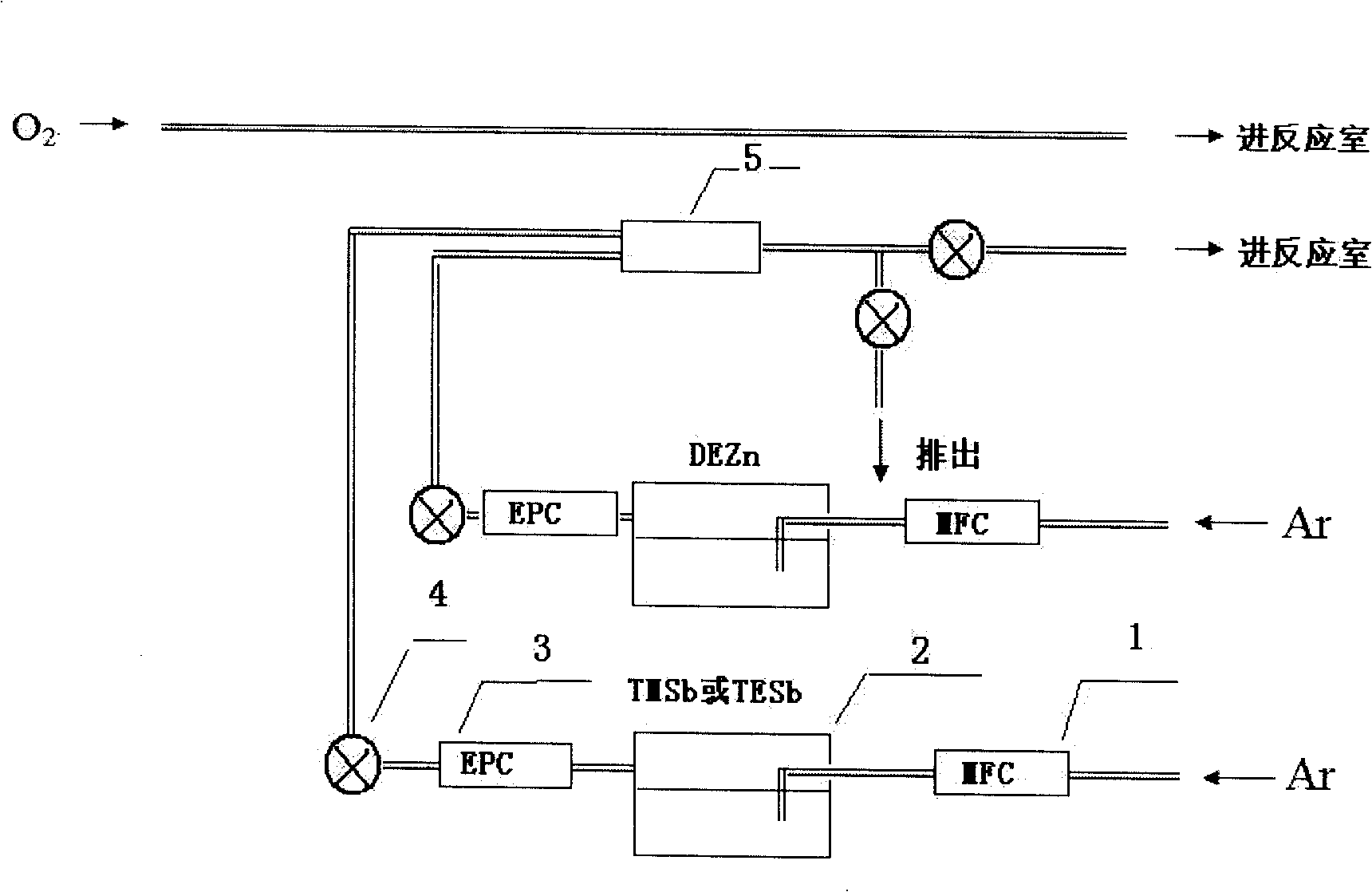
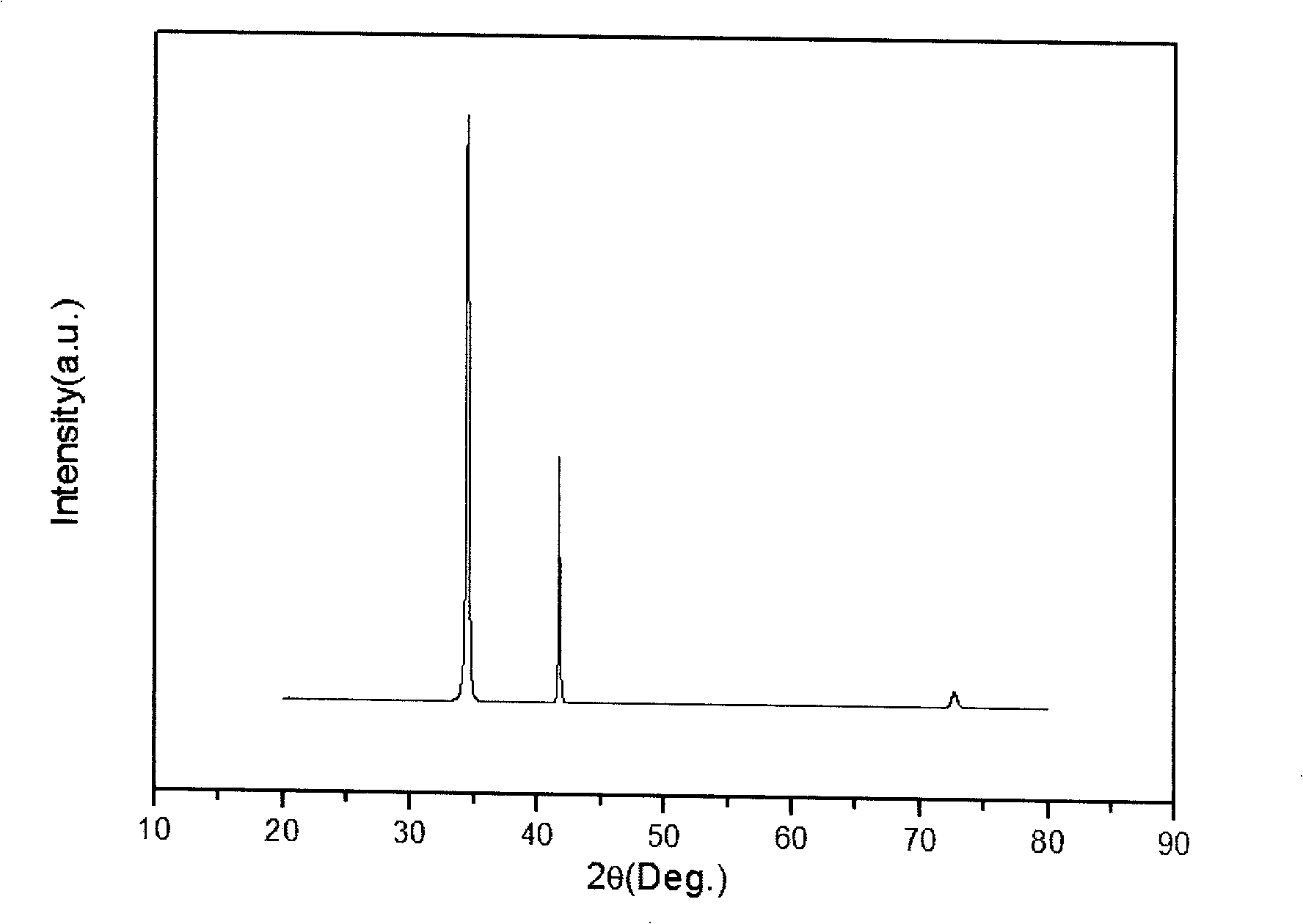
Method for preparing p-type ZnO film by doping Sb
InactiveCN101255550AOvercome preparation difficultiesAvoid craft methodsChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseP–n junction
The present invention discloses a method for preparing p type ZnO film by Sb doping, belonging to the field of semiconductor doping technology. The invention relates to a p type Zno doping technology, particularly to a doping technology by metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) technology, which uses organic source as the p type doping agent of ZnO. The method is characterized in: with antimony metallorganic as the doping source of p type ZnO, antimony doping p type ZnO film is prepared by metal organic chemical vapor deposition. When the temperature of a substrate is 250 DEG to 650 DEG C, the proportion of antimony doping to ZnO is controlled by adjusting the carrier gas flow rate of antimony metallorganic and zinc metallorganic to grow p type ZnO. The effect and benefit of the invention lies in a high-quality high-controllability p type ZnO growing technology is provided, which is an industrial production transplantable metal organic chemical vapor deposition technology, the difficulty of p type ZnO doping is overcome, thus to realize p-n junction type optoelectronic devices of ZnO.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Gallium nitride base film epitaxial growth apparatus by metal organic chemical vapor deposition
InactiveCN1528948AControlling Epitaxial Growth TemperatureGuaranteed uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseEngineering
The invention is a extension growing device for metal organic chemical gas phase deposition kalium nitride base film, it includes reactor, whose character lies in: the reacting room is tube type double layer structure, and it is made up interior tube and exterior tube, the interior tube cavity is reacting cavity, the interior and exterior are inserted in the upper and subjacent fixing device, there is cooling water cavity between the interior and the exterior, the outer wall of exterior tube is winded with conduction heating coil, there sets a black lead base in the interior tube, the black lead is set on a ceramic tube, the ceramic tube connects with gearing part. The reactor has water cooling system, in order to maintain the low temperature within reactor, especially the part above crystal piece and gas mixing room; it can prevent the occurrence of pre-reaction.
Owner:QINGDAO JASON ELECTRIC
Quantum well composite LED epitaxial structure with high luminous efficiency and preparation method thereof
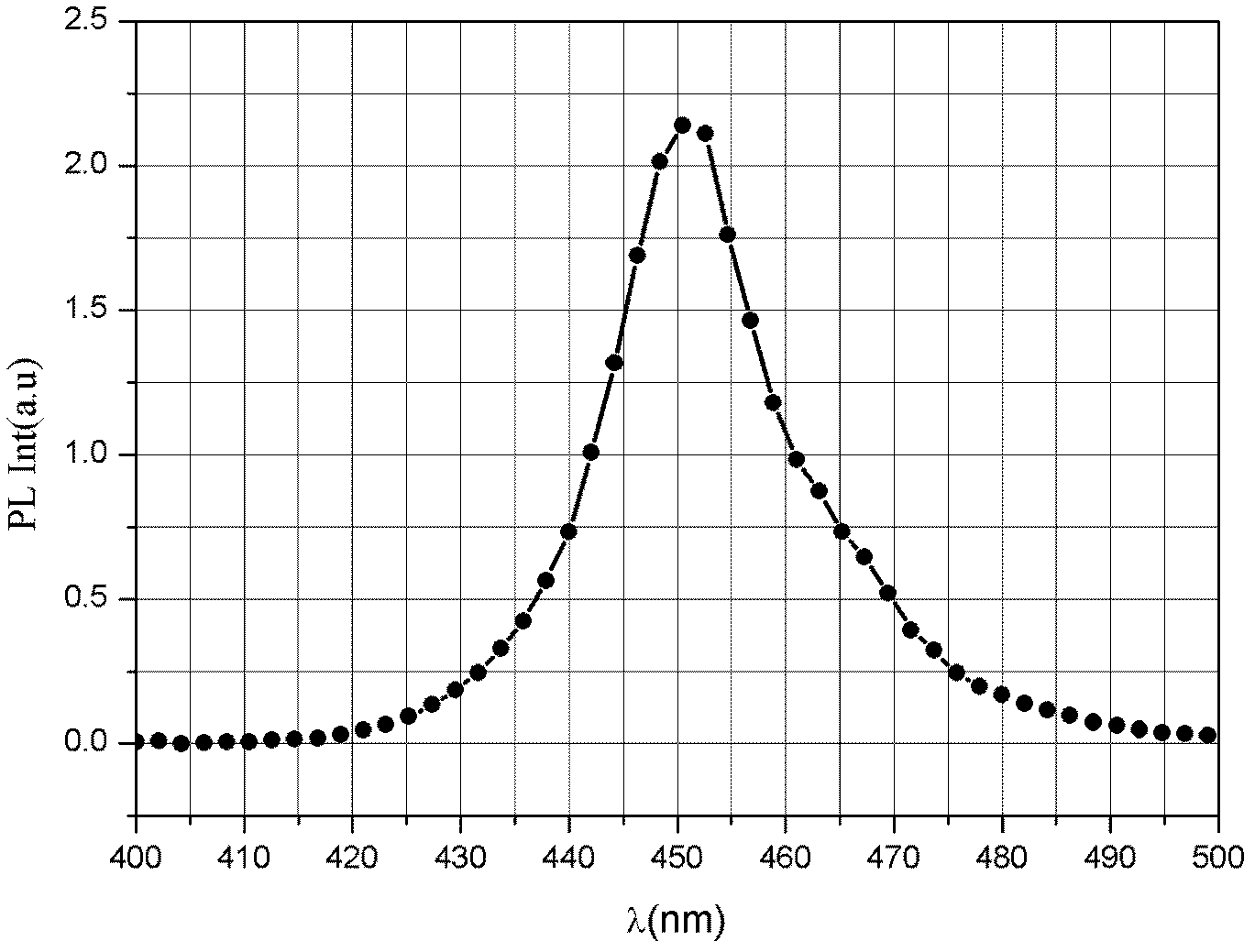
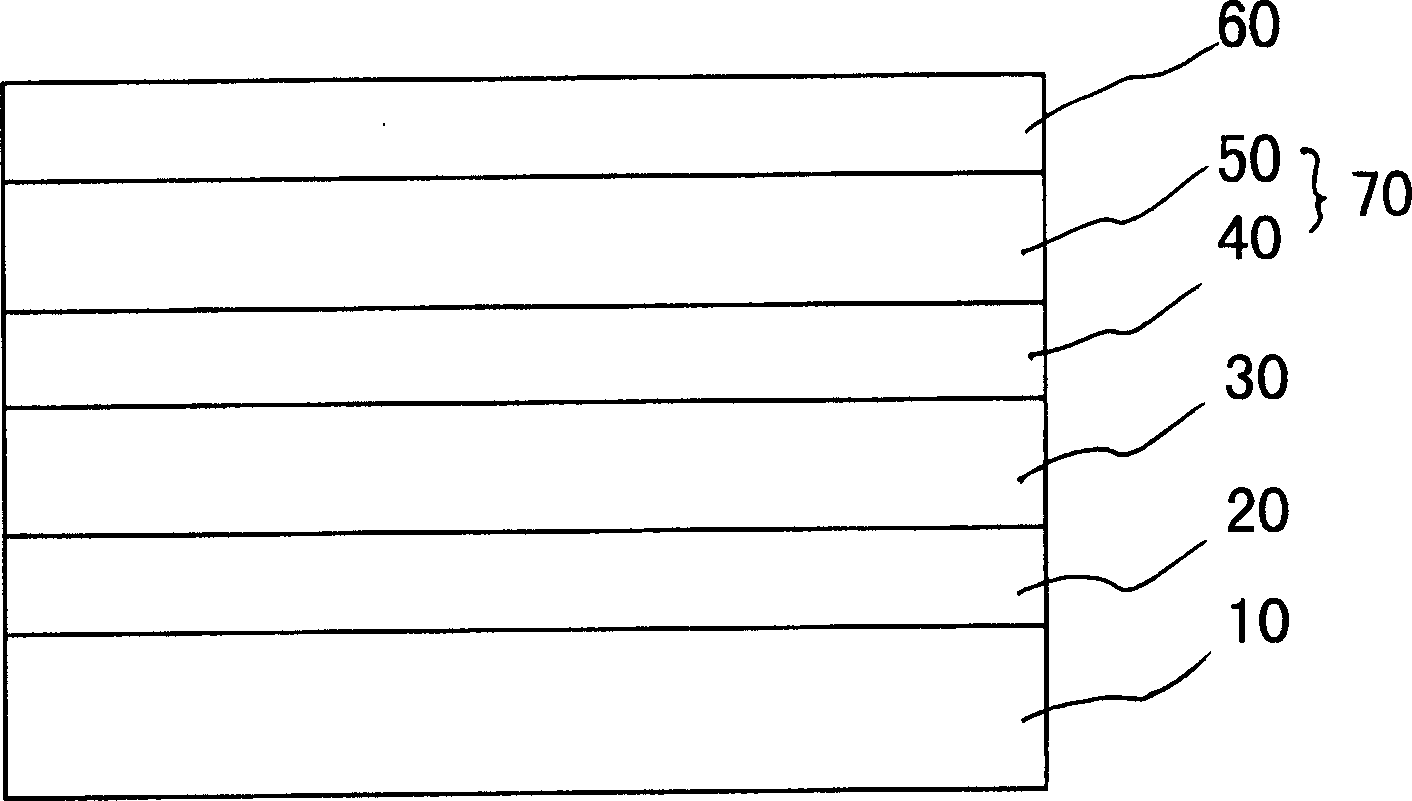
The invention relates to a quantum well composite LED epitaxial structure with high luminous efficiency and a preparation method thereof. The epitaxial structure is sequentially provided with a substrate, a buffer layer, an undoped GaN layer, an n-type AlGaN layer, an n-type GaN layer, an active layer, a P-type AlGaN layer, a P-type GaN layer and a P-type InGaN contact layer from the bottom up, wherein the active layer comprises a lower layer multi-quantum well structure, a constant temperature multi-quantum well structure and an upper layer multi-quantum well structure, the lower layer multi-quantum well structure is formed by periodically overlying an InGaN potential well layer and a GaN barrier layer, the constant temperature multi-quantum well structure is formed by periodically overlying a constant temperature InGaN potential well layer and a constant temperature GaN barrier layer, and the upper layer multi-quantum well structure is formed by periodically overlying the InGaN potential well layer and the GaN barrier layer. The preparation method is that the layers are sequentially prepared from the bottom up in a reaction chamber of metal organic chemical vapor deposition equipment. The epitaxial structure and the preparation method thereof can effectively reduce stress between well barrier interfaces, relieve bending of an energy band, and improve the efficiency of hole injection and electron injection to an active region and the radiative recombination efficiency.
Owner:SHANDONG INSPUR HUAGUANG OPTOELECTRONICS
Light-emitting diode package structure manufacturing method
ActiveCN102231421AThe process path is simpleReduce package sizeSemiconductor devicesActive layerLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses a light-emitting diode package structure manufacturing method, which comprises the following steps of: sequentially growing an n-type layer, an active layer and a p-type layer on an insulating substrate by utilizing a metal organic vapor phase epitaxial method; downwards photoetching one side of the upper surface of the p-type layer with the photoetching depth of reaching the surface of the n-type layer to form a first tabletop, downwards etching the other side with the etching depth of reaching the surface of the insulating substrate to form a second tabletop; manufacturing conductive through holes on the first and second tabletops, and filling conductive metals; manufacturing an insulating layer partially covering the upper surface of the p-type layer on the sideclose to the second tabletop; manufacturing a p electrode covering the insulating layer on the insulating layer; manufacturing an n electrode on the conductive through hole on the first tabletop; thinning the insulating substrate; manufacturing a first back electrode and a second back electrode on the two sides of the back of the insulating substrate to form a substrate of a device; packaging an optical element on the substrate of the device to finish manufacturing the device on the substrate; and cutting the device on the substrate into independent devices in a mechanical way.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Growth method for improving quality of AlN thin film crystal
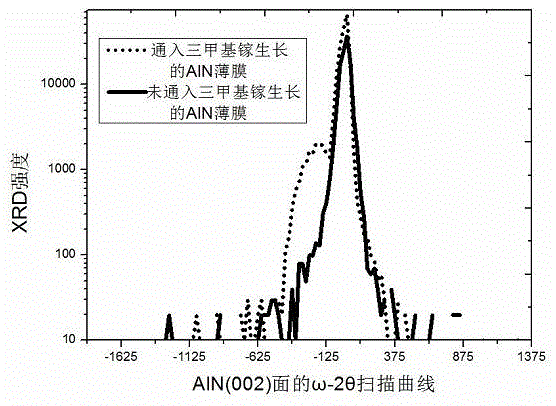
ActiveCN105543969AQuality improvementImprove surface topographyPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesTwo stepChemical vapor deposition
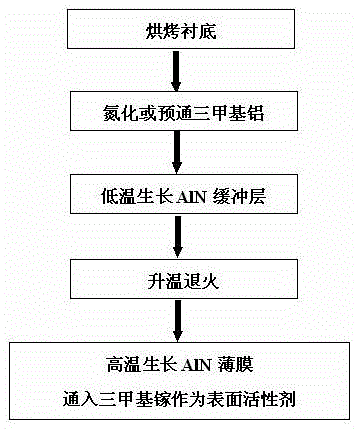
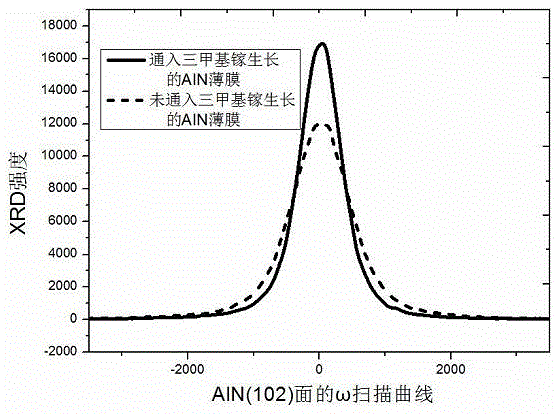
The invention provides a growth method for improving the quality of an AlN thin film crystal and relates to the technical field of metalorganic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) growth of III-group nitrides. An AlN thin film grows through a two-step method includes the following steps that firstly, a roasting substrate is cleaned; secondly, trimethylaluminum is nitridized or introduced in advance; thirdly, an AlN buffering layer grows at low temperature; fourthly, heating and annealing are conducted; fifthly, the AlN thin film grows at high temperature, and trimethyl gallium needs to be introduced as a surfactant at least in one of the third step and the fifth step. Compared with the prior art, the AlN thin film prepared through the method has the advantages of being small in dislocation density and good in surface smoothness.
Owner:NANTONG TONGFANG SEMICON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com