Patents
Literature
62 results about "Dendrite (crystal)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A crystal dendrite is a crystal that develops with a typical multi-branching tree-like form. Dendritic crystal growth is very common and illustrated by snowflake formation and frost patterns on a window. Dendritic crystallization forms a natural fractal pattern. Dendritic crystals can grow into a supercooled pure liquid or form from growth instabilities that occur when the growth rate is limited by the rate of diffusion of solute atoms to the interface. In the latter case, there must be a concentration gradient from the supersaturated value in the solution to the concentration in equilibrium with the crystal at the surface. Any protuberance that develops is accompanied by a steeper concentration gradients at its tip. This increases the diffusion rate to the tip. In opposition to this is the action of the surface tension tending to flatten the protuberance and setting up a flux of solute atoms from the protuberance out to the sides. However, overall, the protuberance becomes amplified. This process occurs again and again until a dendrite is produced.
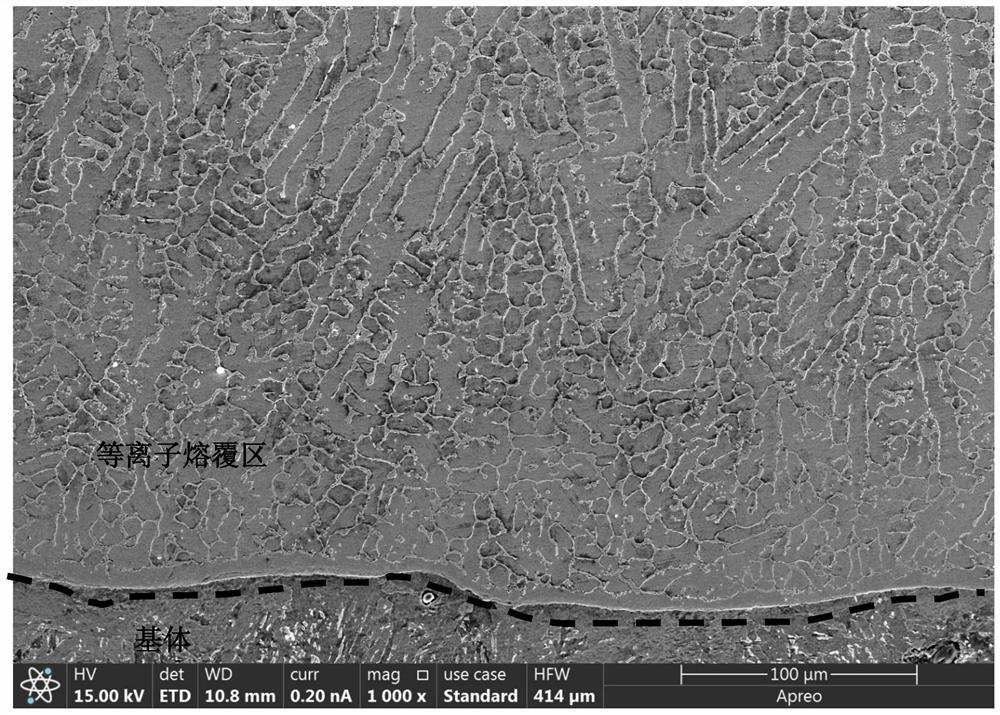
Corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant coating with gradient composite structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113122841ASmall plasticityGood plasticityMetallic material coating processesHigh entropy alloysEquiaxed crystals
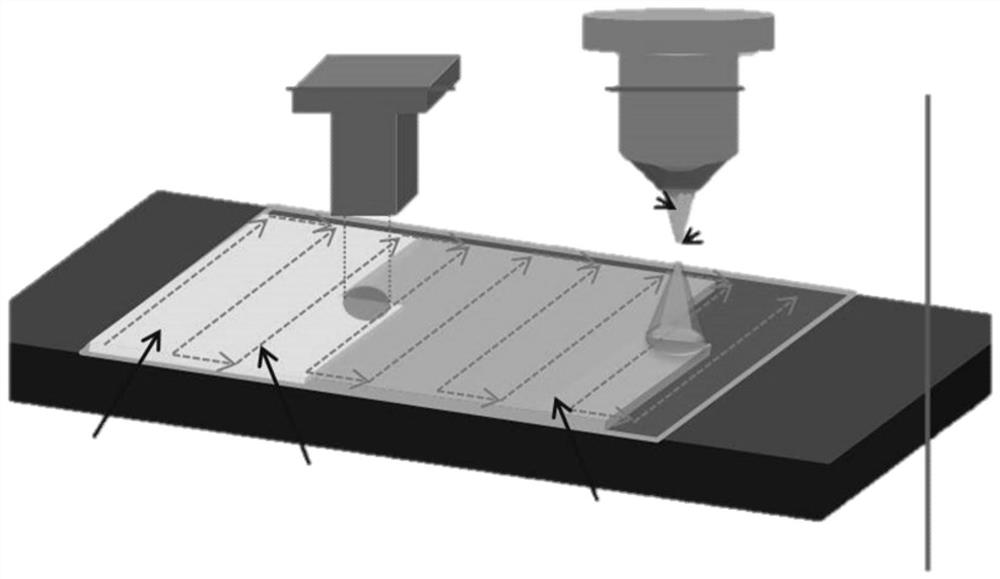
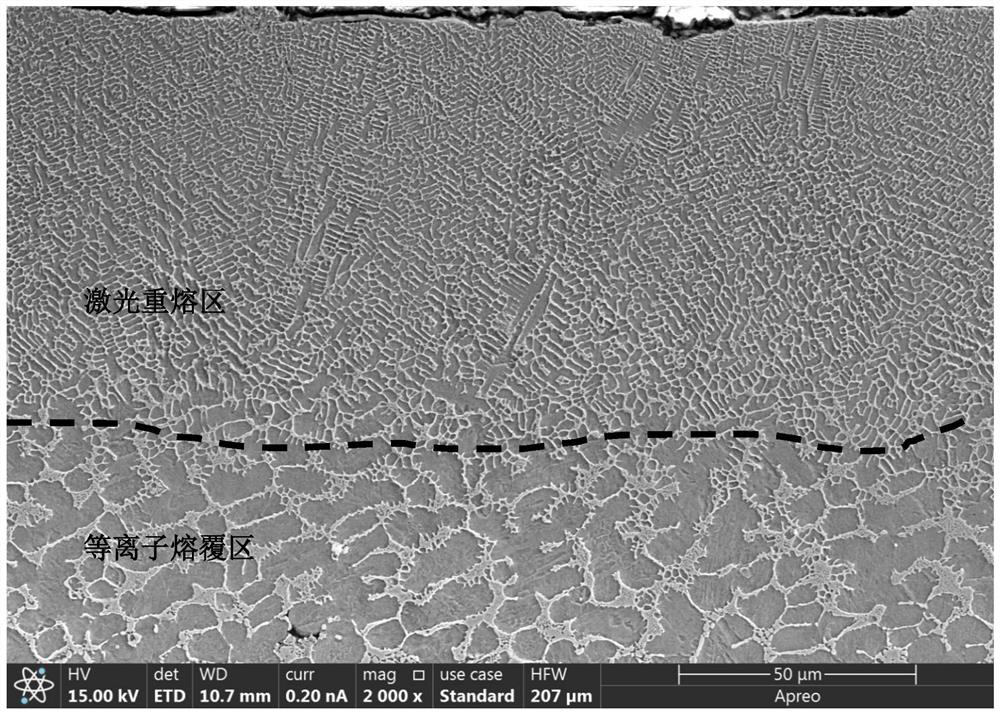
The invention discloses a corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant coating with a gradient composite structure and a preparation method thereof. According to the corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant coating, by cladding alloy powder on the surface of a pretreated matrix through a plasma cladding method to obtain an alloy layer with a large-thickness dendritic structure, and then re-melting and fusing growth of thick dendrites on the surface of the alloy layer through non-powder-feeding laser, so that a fine equiaxed crystal structure is obtained. According to the preparation method, a thick dendrite structure is formed after plasma cladding, dendrites have a nail pile effect on a matrix and have a supporting effect on a subsequent laser high-speed cladding layer, it is guaranteed that a large-thickness coating is obtained, combination with the matrix is strengthened, and the molten high-entropy alloy powder is fully and evenly mixed; and through subsequent laser remelting, thick dendrites can be fused, fine and compact isometric crystals are obtained, propagation of a corrosive medium is blocked, and corrosion resistance is improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
A samarium cobalt sintered permanent magnet material and its preparation method
ActiveCN104637642BSpeed up coolingIntegrity guaranteedInorganic material magnetismCobaltCritical magnetic field
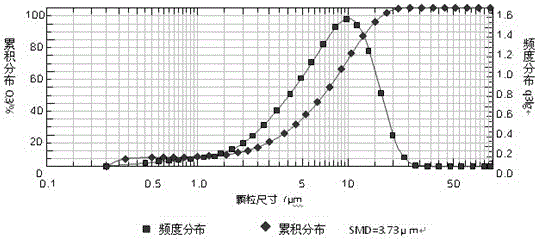
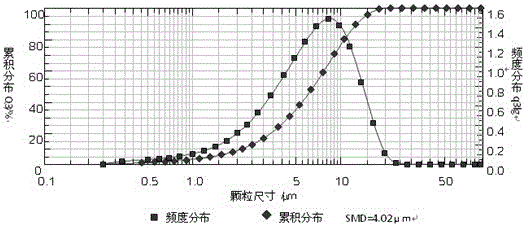
A samarium and cobalt sintered permanent magnet material comprises, in weight percent, 25-27%wt of samarium, 49-51%wt of cobalt, 5-6.5%wt of copper, 3-3.5%wt of zirconium and 15-18%wt of iron. A preparation method includes the steps: smelting; casting an ingot; absorbing hydrogen for the cast ingot; making powder; performing orientation forming and sintering. In the smelting process, the thickness of a casting mould cavity is decreased, cooling water is filled into the wall of the mould cavity, cooling of the cast ingot is accelerated, element composition segregation is decreased, the production process is stabilized, a dendrite crystal is restrained by adding a zirconium element, hydrogen absorbing is performed for the cast ingot in the smelting process, production steps are saved, and energy consumption is reduced. In the subsequent milling process, the cast ingot absorbed hydrogen is crystallized into particles, the particles fracture along crystal boundaries in the milling process of airflow, the integrality of crystal particles is ensured, the anisotropy of the crystal particles is improved, magnetic powder particles are obtained, particle size distribution is concentrated with the range of 3.5-4.5 micrometers, the sintering temperature needed by the magnetic powder particle of each point of a blank is the same in the later sintering process, the sizes of the sintered crystal particles are the same and uniform, and the performances, particularly, such as residual magnetism Br, maximum magnetic energy product (BH) max and critical magnetic field Hk of a sintered permanent magnet are improved.
Owner:NINGBO NINGGANG PERMANENT MAGNETIC MATERIALS
Method for inhibiting zinc dendritic crystal growth by using polydopamine film
PendingCN112349893AEffective control of thicknessPolymerization reaction conditions are easy to controlCell electrodesSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceMedicineDendrite (metal)
A method for inhibiting zinc dendritic crystal growth by using a polydopamine film comprises the steps: a zinc foil is soaked in a dopamine solution, and a polydopamine film layer is formed on the surface of zinc by adjusting the concentration of dopamine, the pH value of the solution, the polymerization time and the reaction temperature; the dopamine-modified zinc foil is used as the negative electrode of the secondary battery, and structural characterization after charge-discharge circulation shows that the surface of the electrode is smooth, and no obvious dendritic crystal is generated; and the polydopamine has strong metallophilicity, a stable protective layer is formed on the surface of the zinc foil, and the deposition of zinc is limited in a limited space, so that the growth of zinc dendrites is effectively inhibited, and the cycle life of the zinc negative electrode is prolonged. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, easy in reaction condition control, environment-friendly and beneficial to performance optimization and practical application of the zinc negative electrode.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
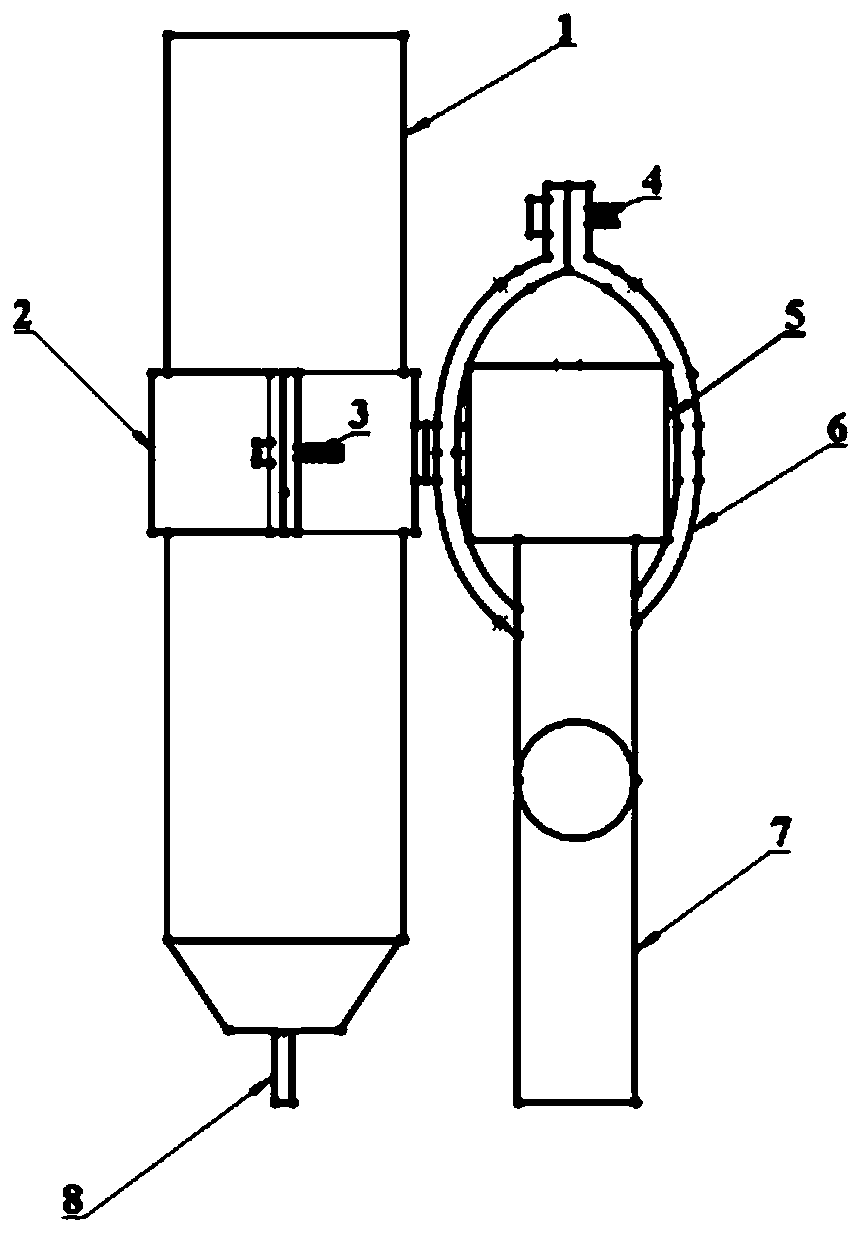
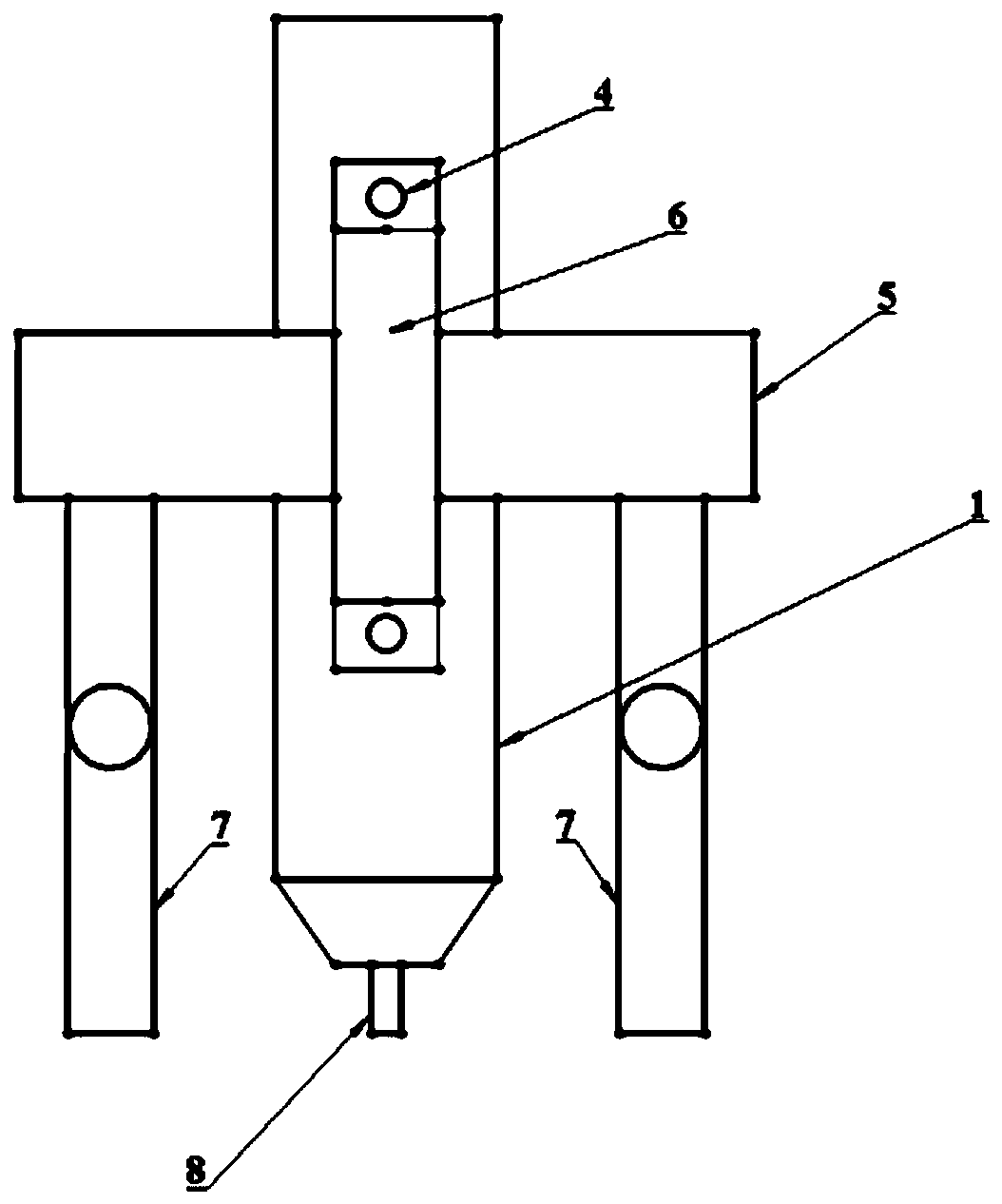
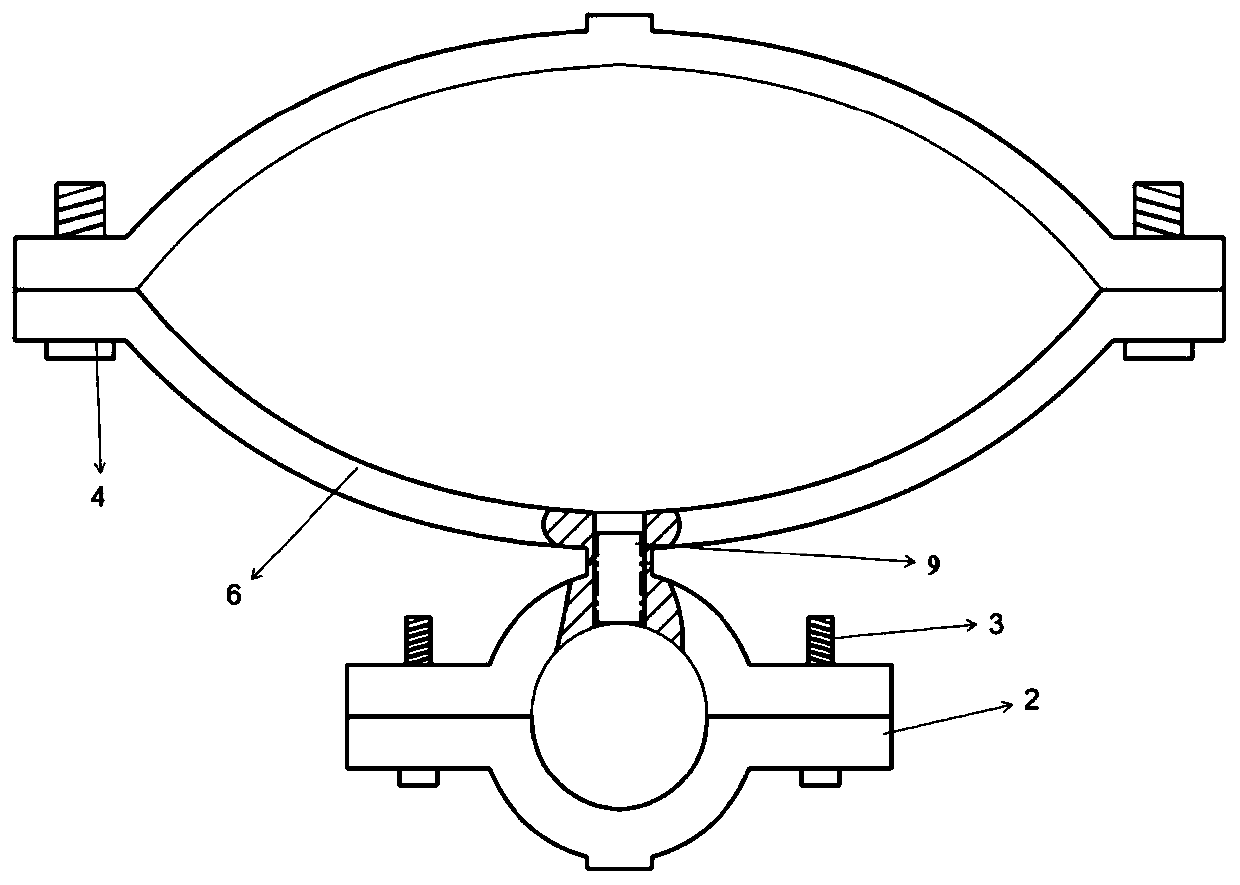
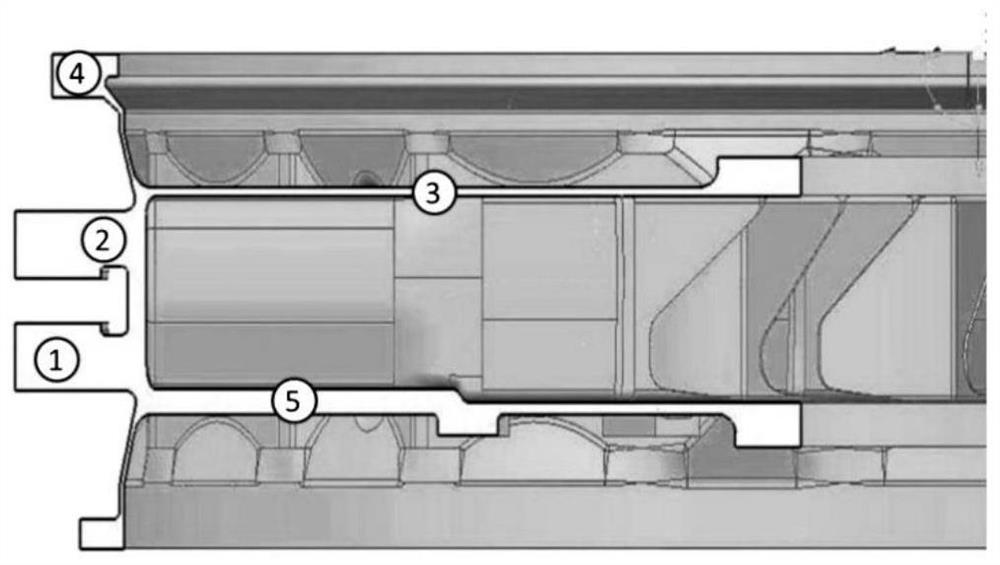
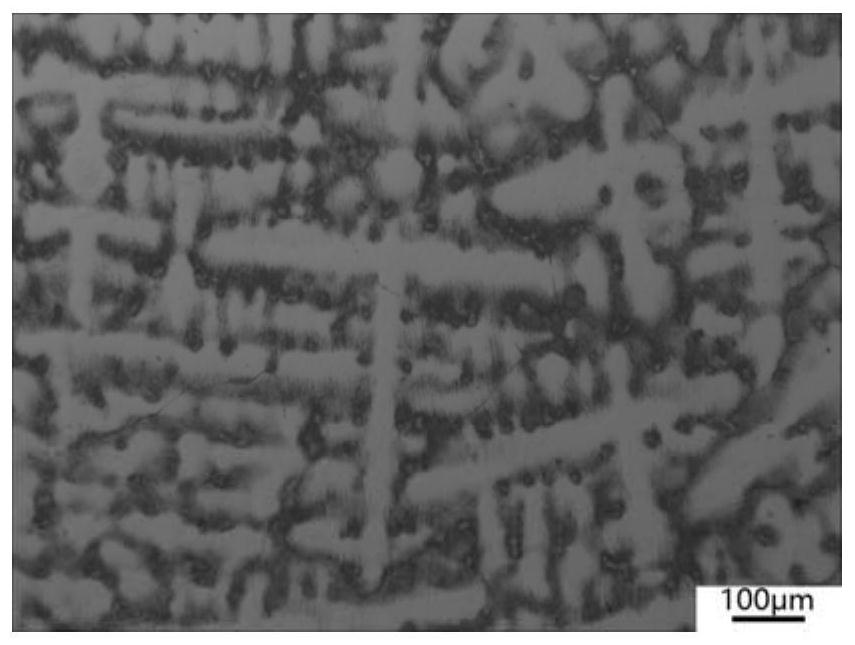
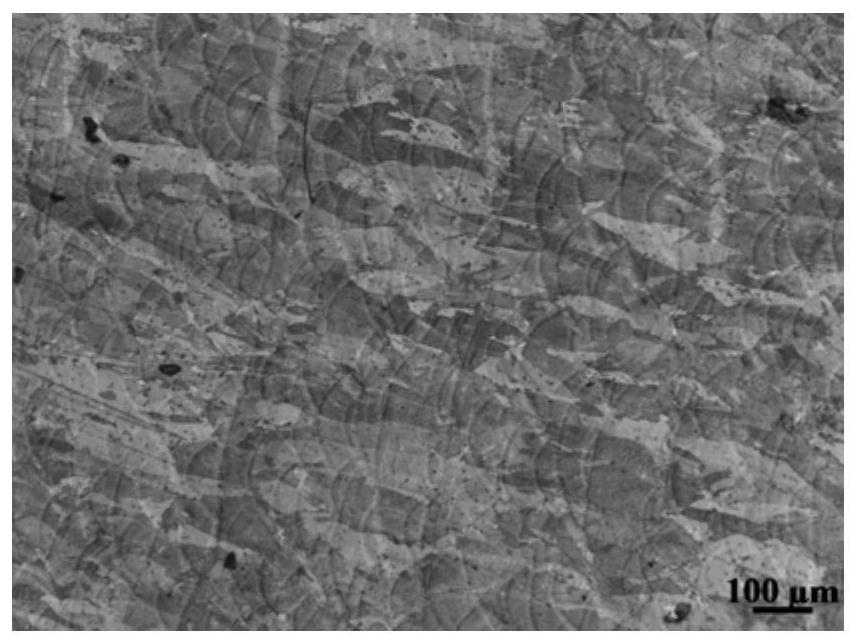
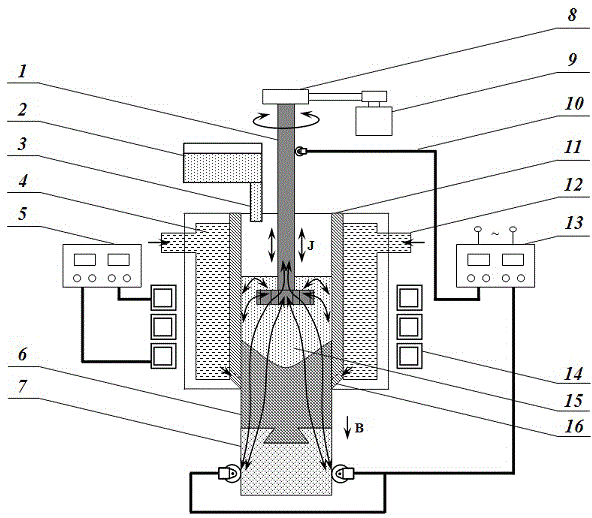
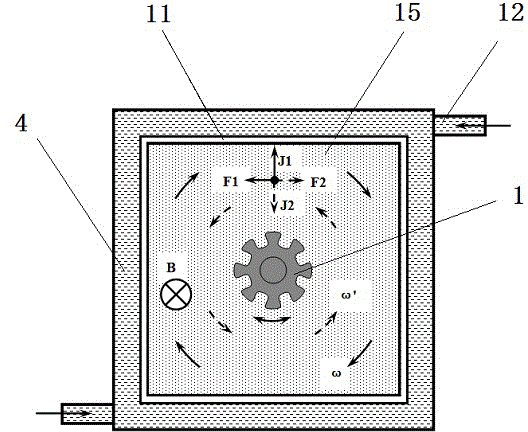
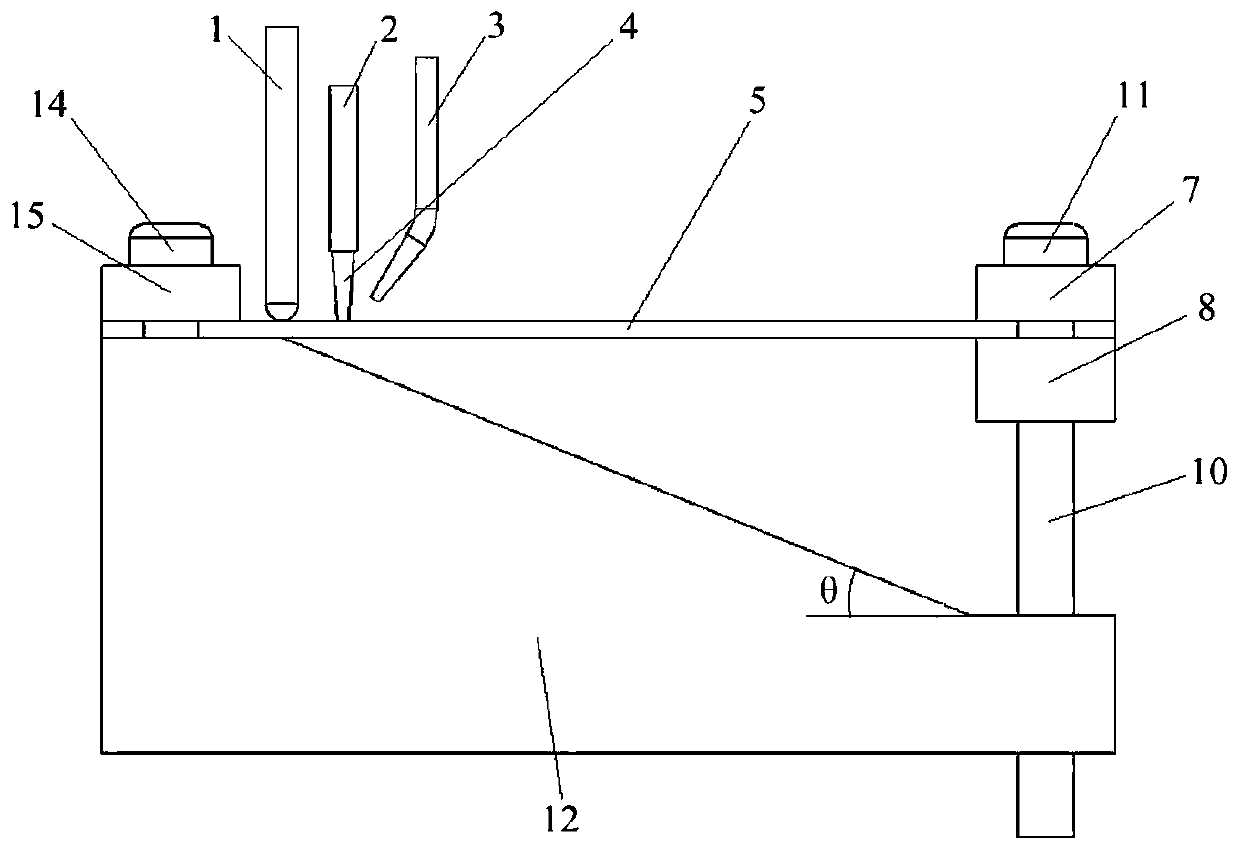
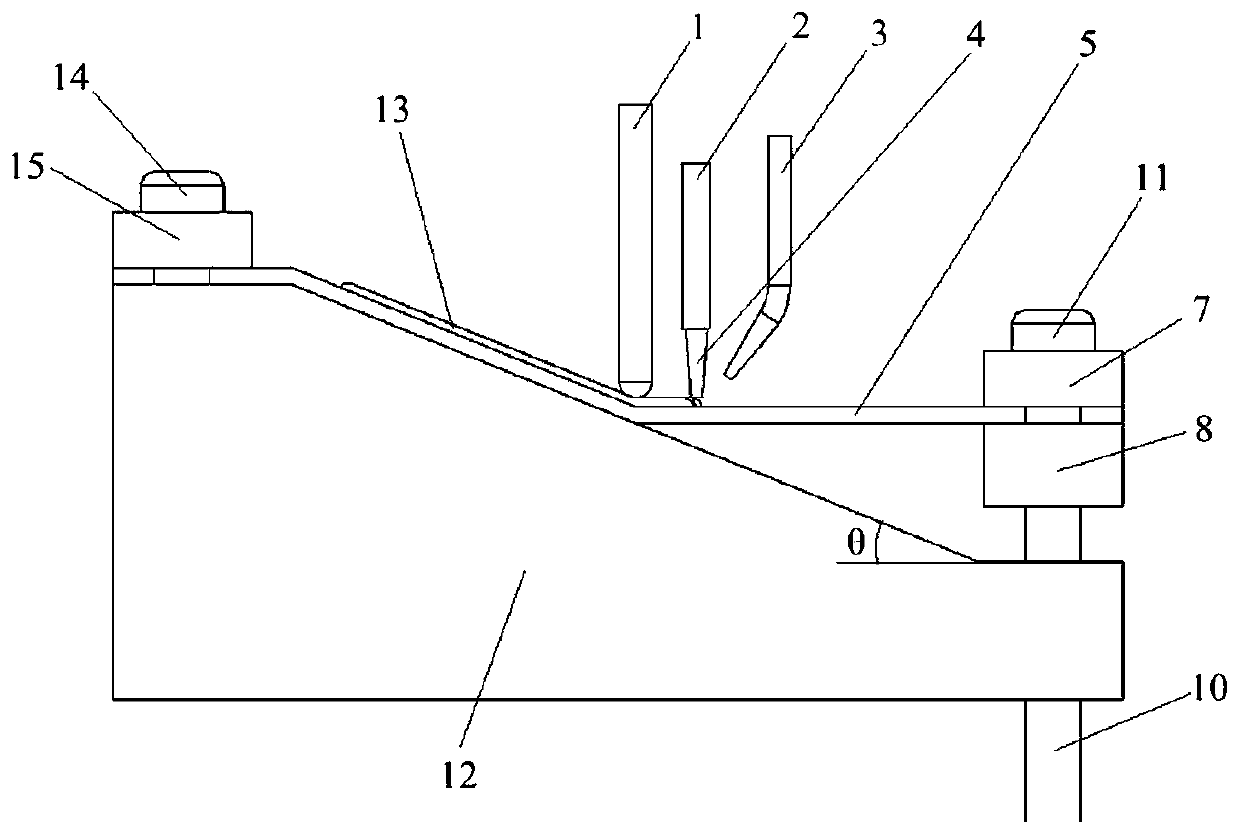
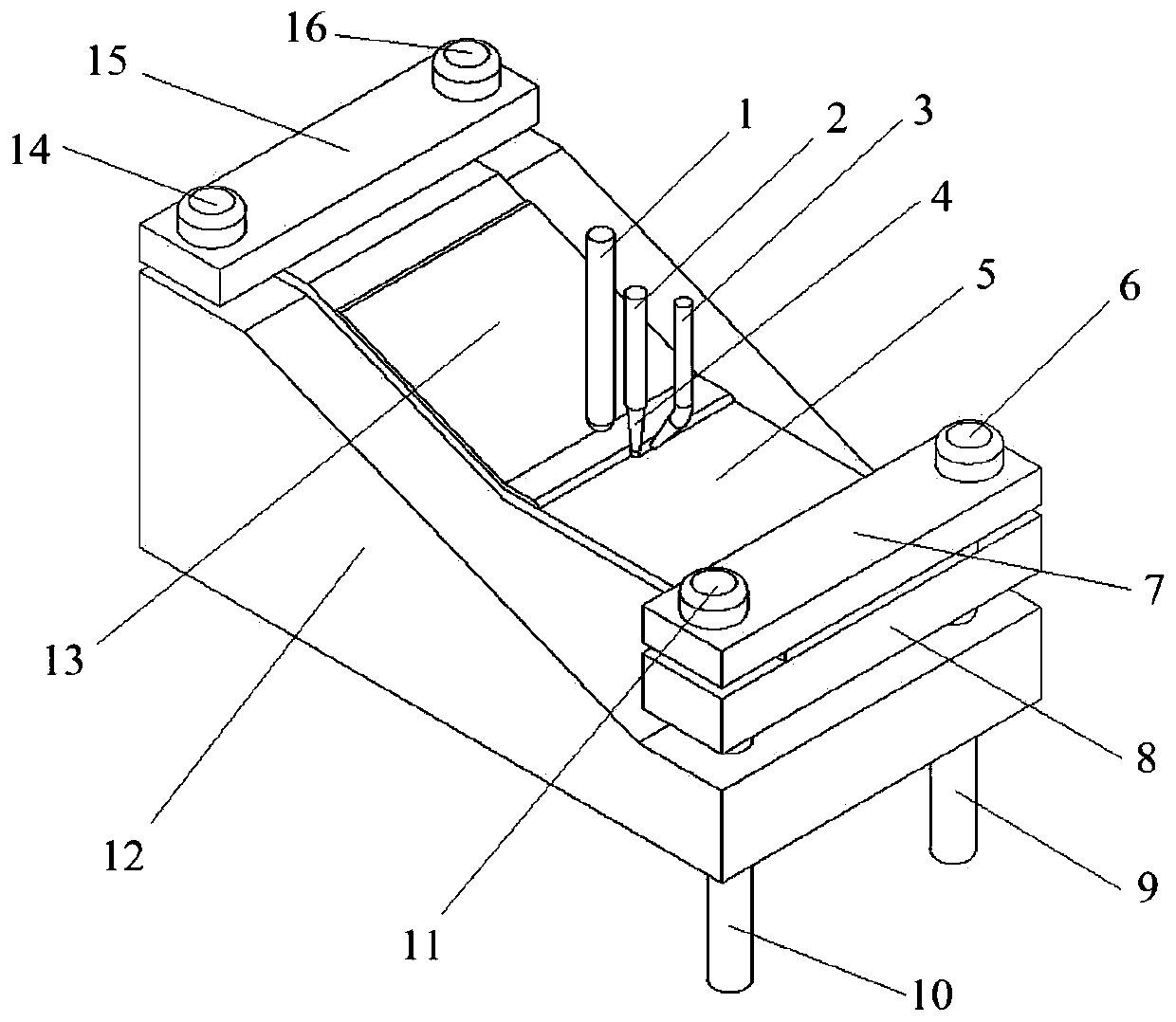
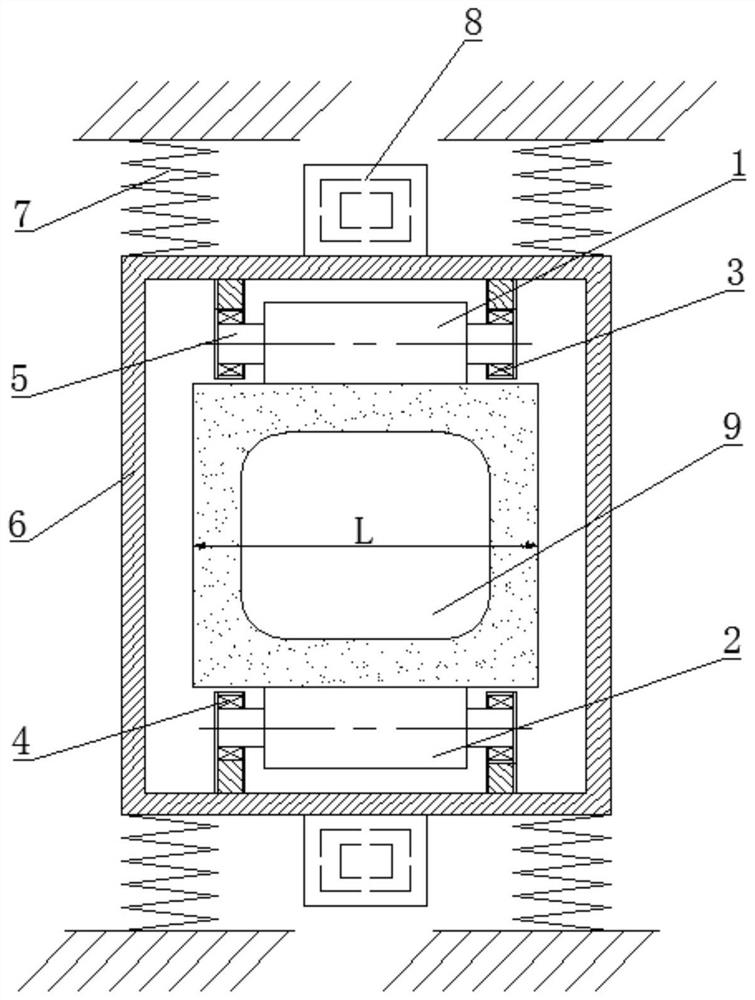
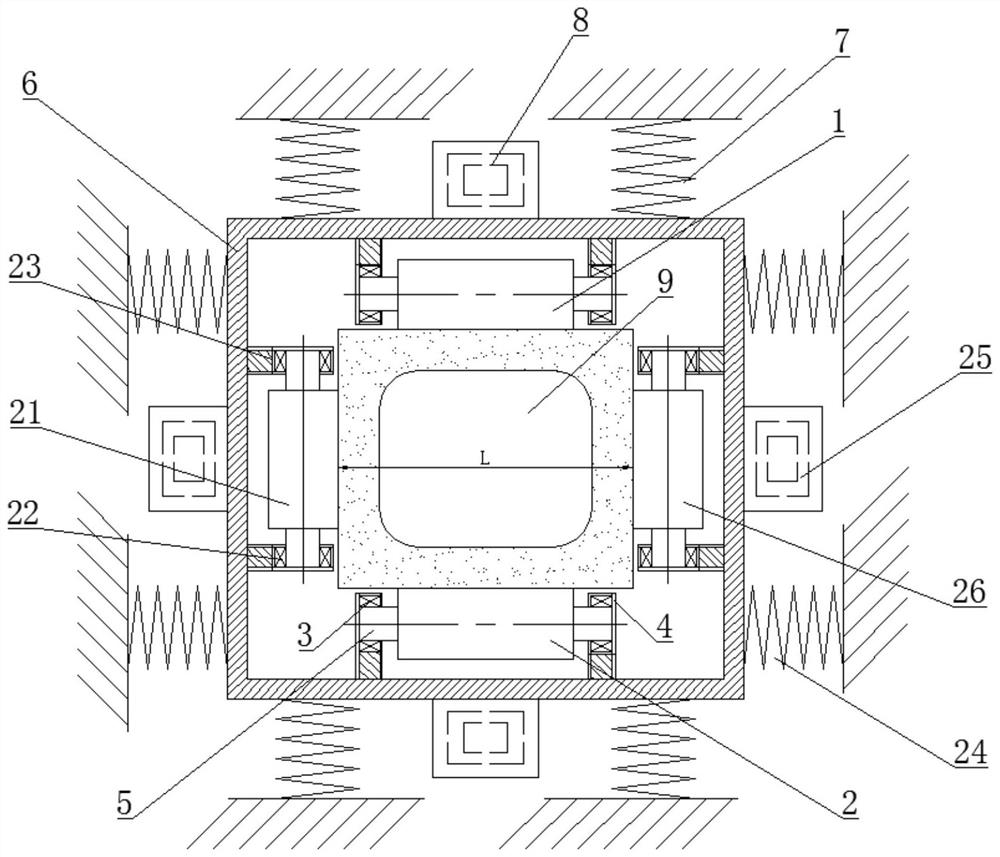
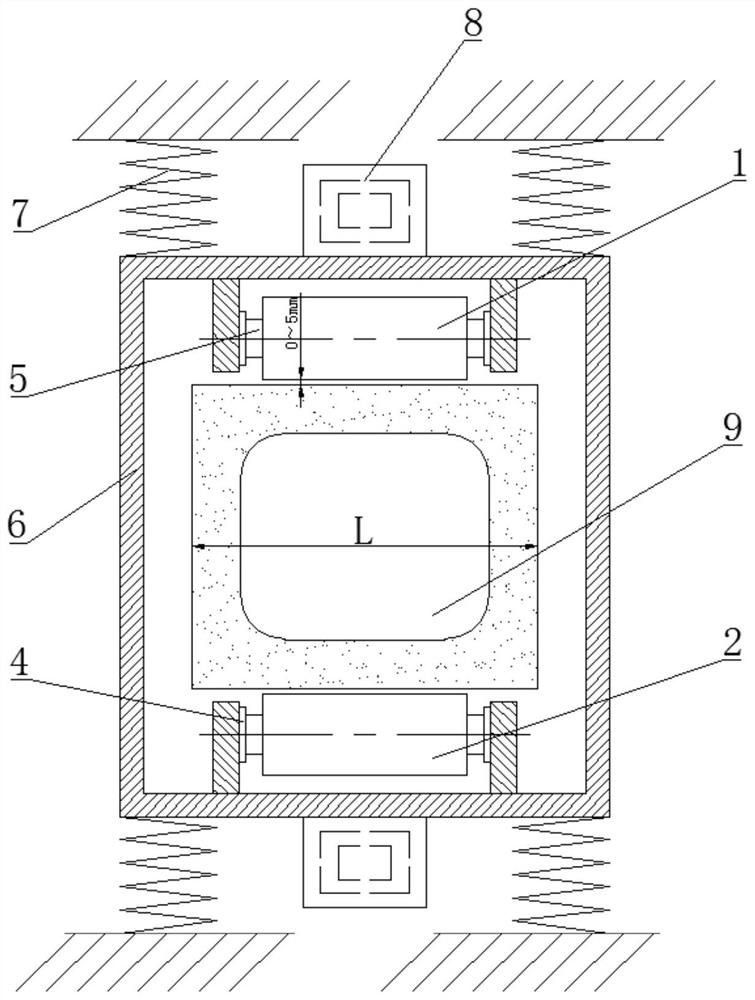
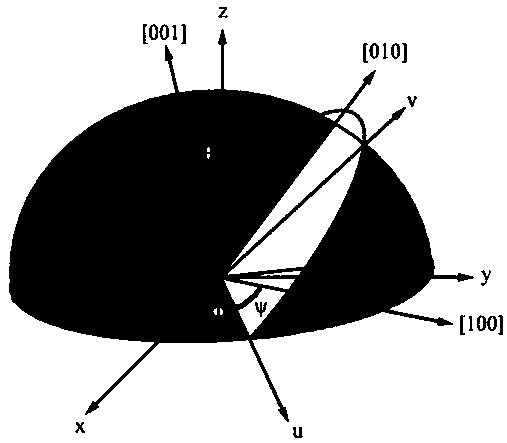
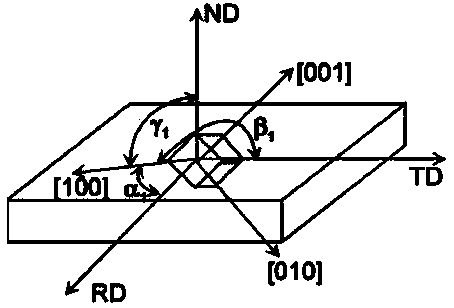
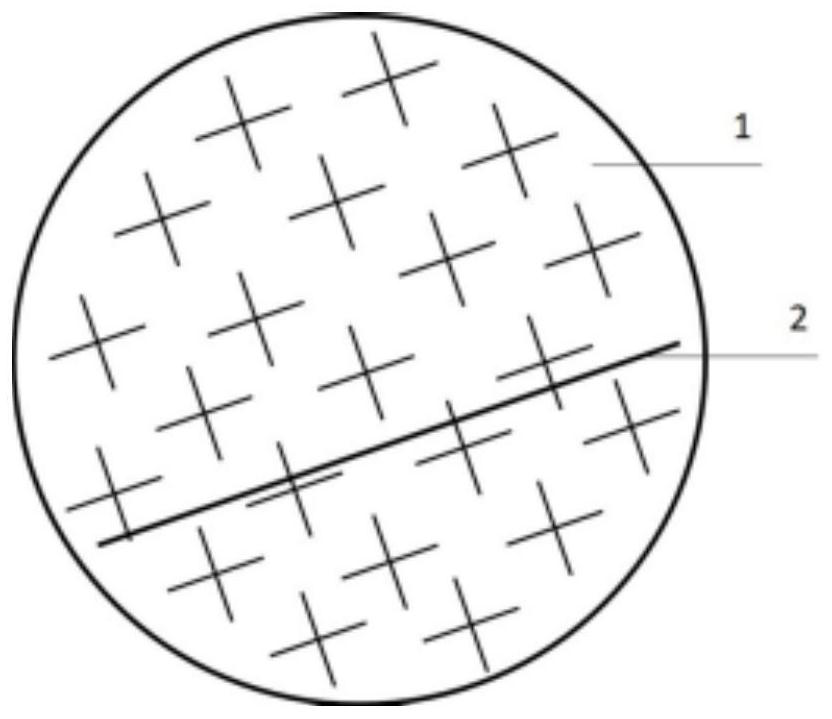
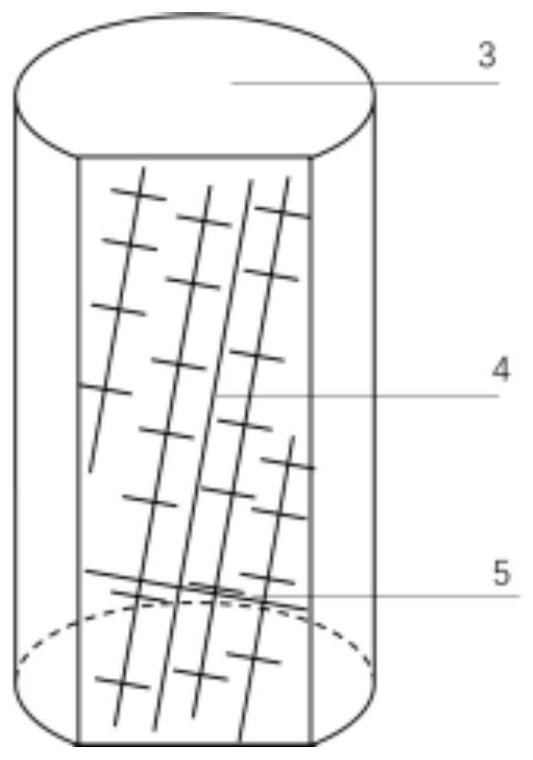
Mold shell and method for preparing [011] or [111] oriented single crystal high-temperature alloy
ActiveCN112695377AImprove mechanical propertiesPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsHeat flowSingle crystal superalloy
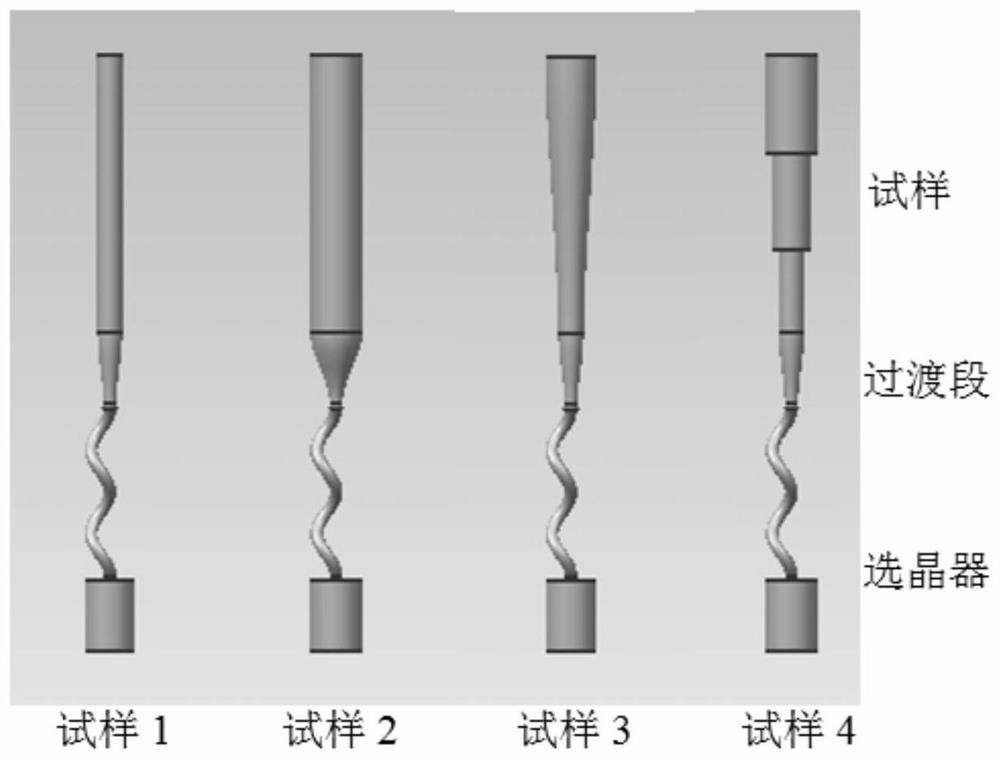
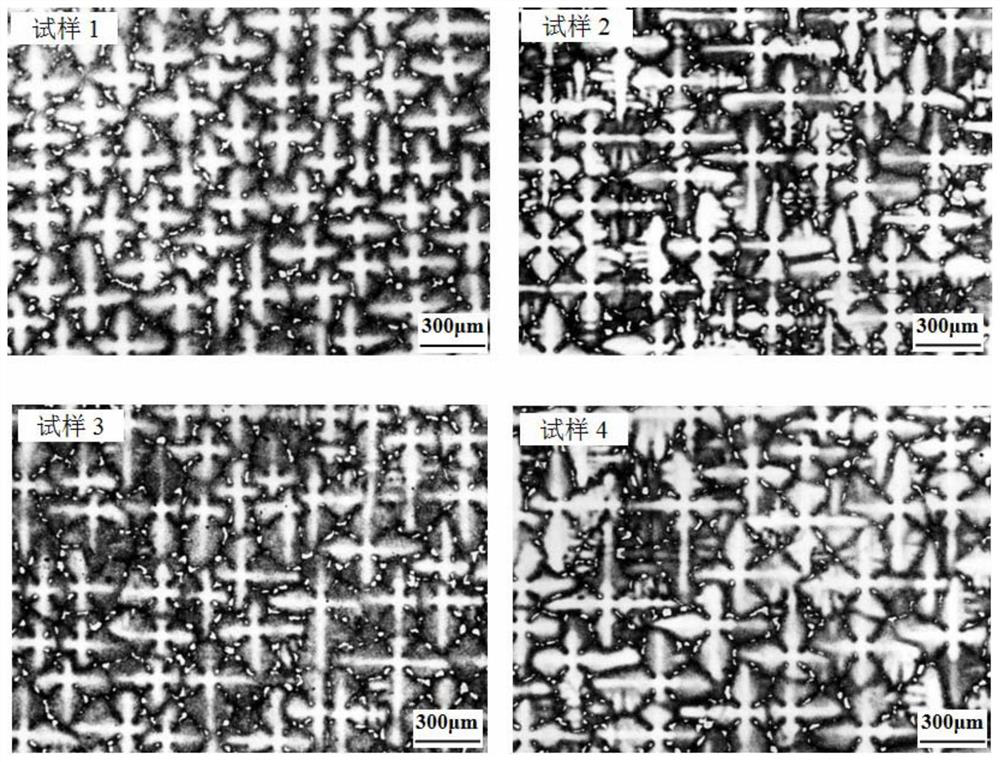
The invention provides a mold shell and method for preparing [011] or [111] oriented single crystal superalloy, and belongs to the technical field of single crystal superalloy preparation. The mold shell provided by the invention comprises an amplifier, a seed crystal, an angle regulator and a casting, wherein the angle regulator realizes axial direction regulation of the casting; and the axial direction of the casting is consistent with the [011] direction or the [111] direction of the seed crystal. According to the invention, the mold shell can enable the growth direction of dendrites in the casting to be consistent with the heat flow direction, can effectively avoid intersection among the dendrites, enables elements to be uniformly distributed, eliminates a weak region generated by asymmetric growth of the dendrites, and improves the mechanical properties of the single crystal superalloy.
Owner:北航(四川)西部国际创新港科技有限公司
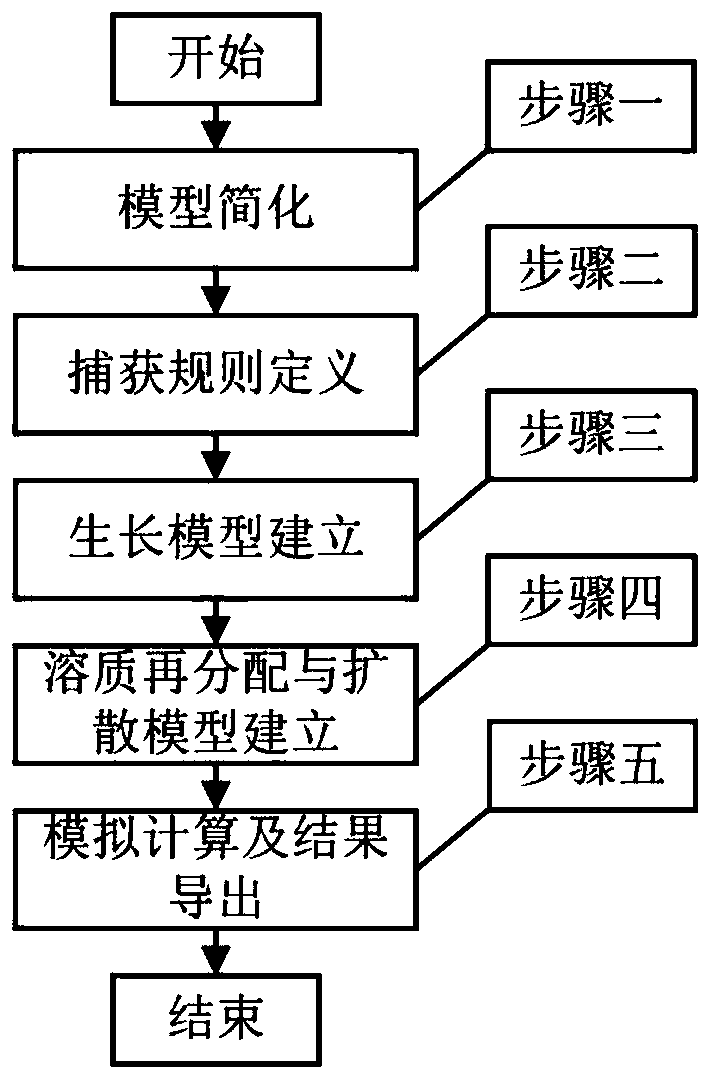
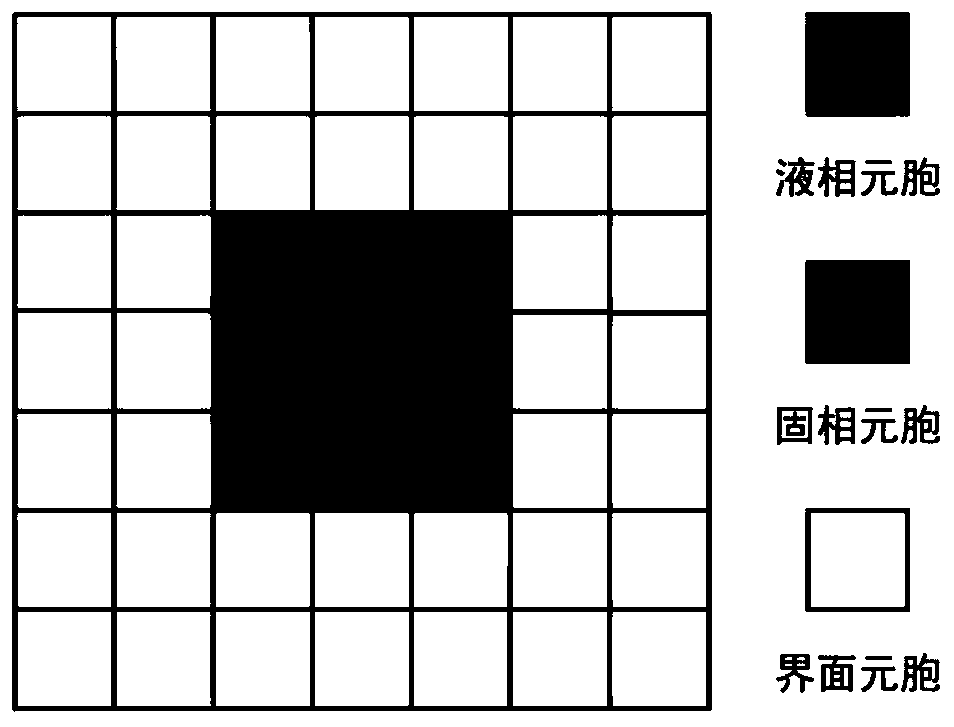
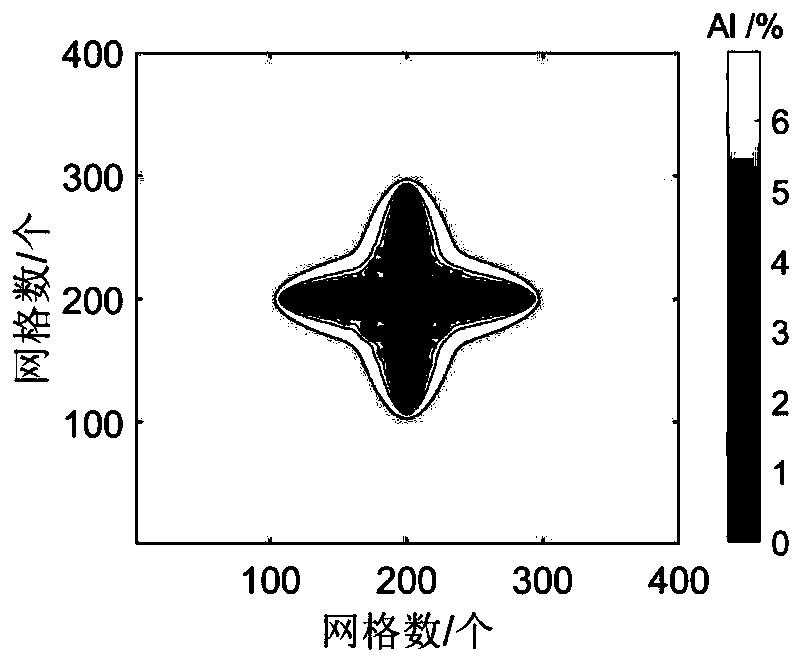
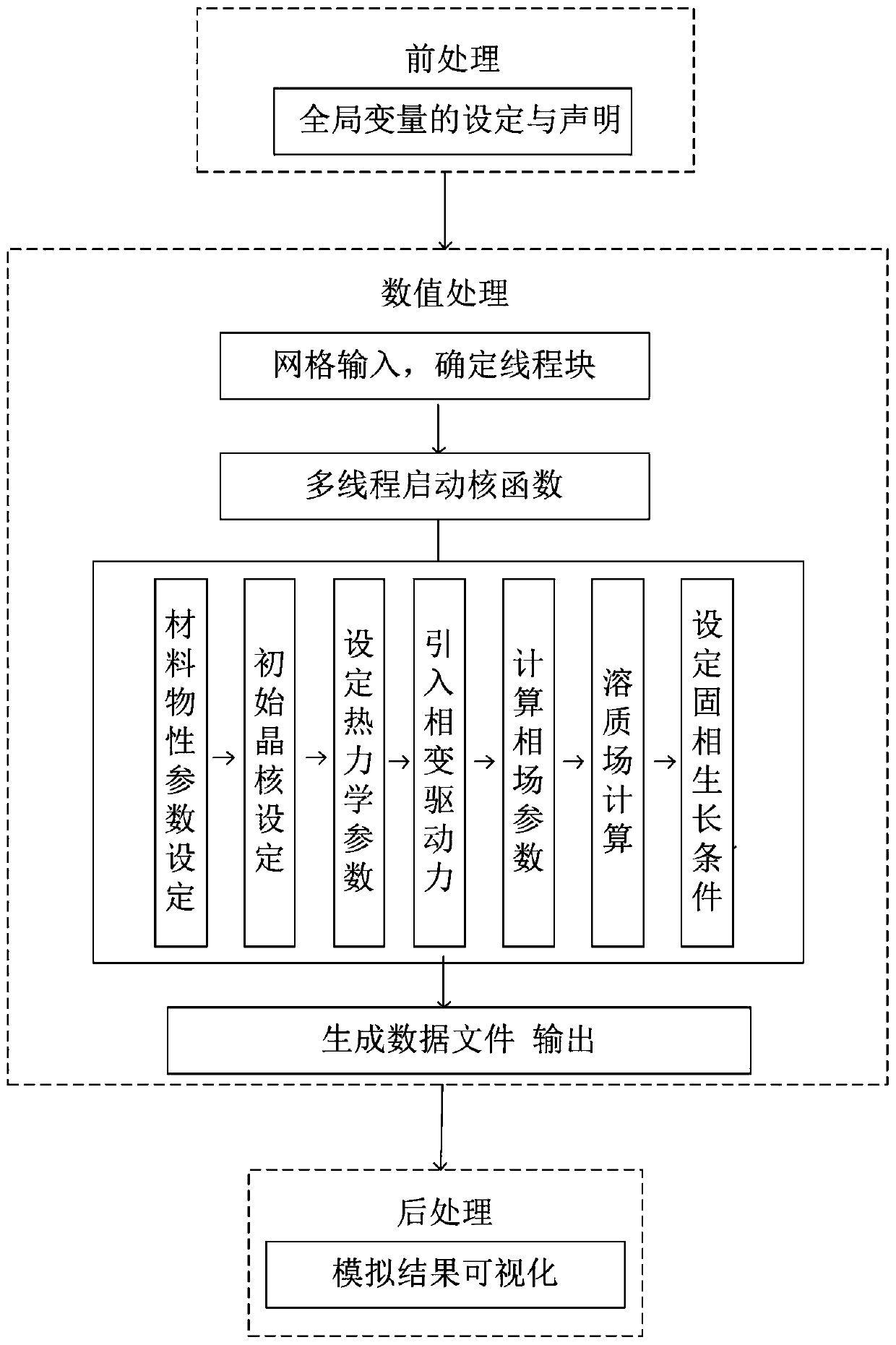
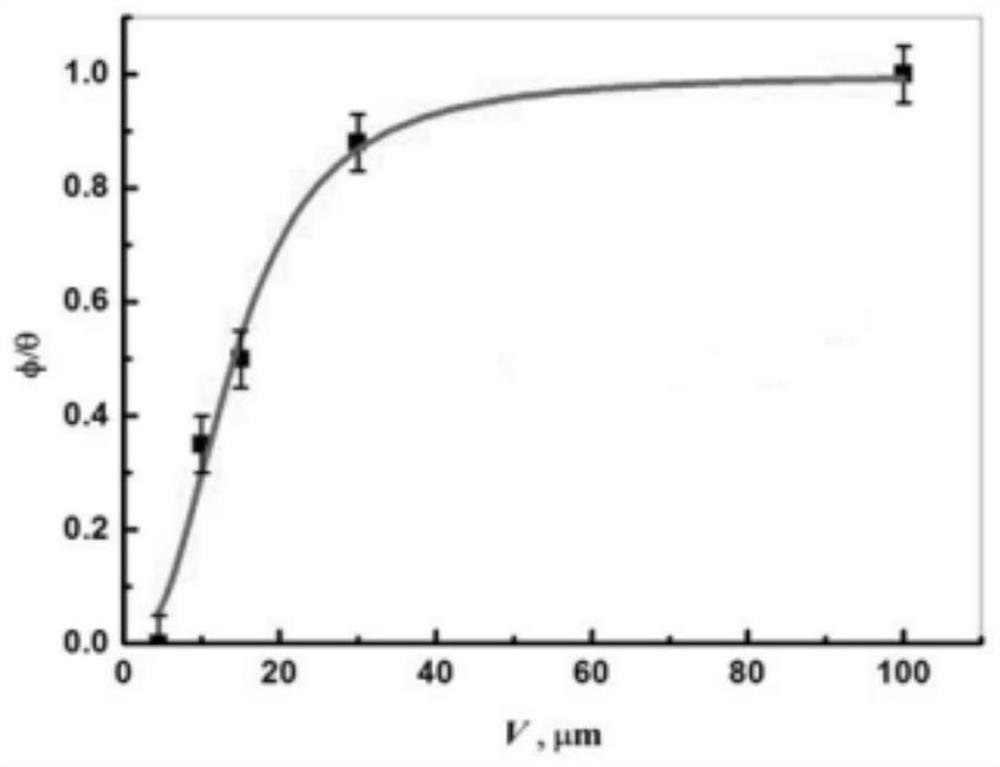
Method for simulating single dendritic crystal growth numerical value in ternary alloy solidification process
ActiveCN110321604APlay a guiding roleDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiffusionDendrite
The invention discloses a method for simulating a single dendritic crystal growth numerical value in a ternary alloy solidification process. The method comprises the following specific steps: simplifying solidification conditions, establishing a dendritic crystal growth model and a solute redistribution and diffusion model, writing a computer program based on the established models, importing simulation software for calculation, and finally obtaining a simulation result of dendritic crystal growth in the solidification process. According to the invention, the growth morphology of dendrites andthe distribution state of solute components in the solidification process of the ternary alloy can be simulated, and the influence of factors such as supercooling degree, disturbance amplitude, anisotropic strength and the like on the solidification process can also be simulated, thereby playing a guiding role in practical engineering application.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Adjustable magnetic field cooperation electric arc additive system and additive method
ActiveCN111185651AHigh aspect ratioImprove mechanical propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectrode holder supportersMagnetic tension forceMagnetic poles
The invention belongs to the field of additive manufacturing, and particularly relates to an adjustable magnetic field cooperation electric arc additive system and additive method. The system comprises an arc deposition device and a magnetic field generating device, wherein the arc deposition device comprises a welding gun; the magnetic field generating device is used for generating an adjustablemagnetic field and comprises a magnetic flaw detector; the magnetic flaw detector comprises two magnetic poles; and the two magnetic poles are rotationally connected with a main body of the magnetic flaw detector and are arranged on two sides of the welding gun. Through the magnetic field generating device provided by the invention, an external magnetic field in more than one direction can be generated, when a transverse magnetic field is applied, molten metal and heat can be conveyed to the rear of a molten pool and the crystal face of the molten pool can be washed directly, so that the temperature gradient and the solute concentration at the front end of a dendrite crystal are reduced, and the component supercooling at the front end of the dendrite crystal is increased, thereby being beneficial to refining crystal grains; when a longitudinal magnetic field is applied, the aspect ratio of a single weld bead can be improved, so that the lapping precision and the surface quality of a deposited layer are improved; and in theory, the system can meet the need to generate magnetic fields in any direction.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
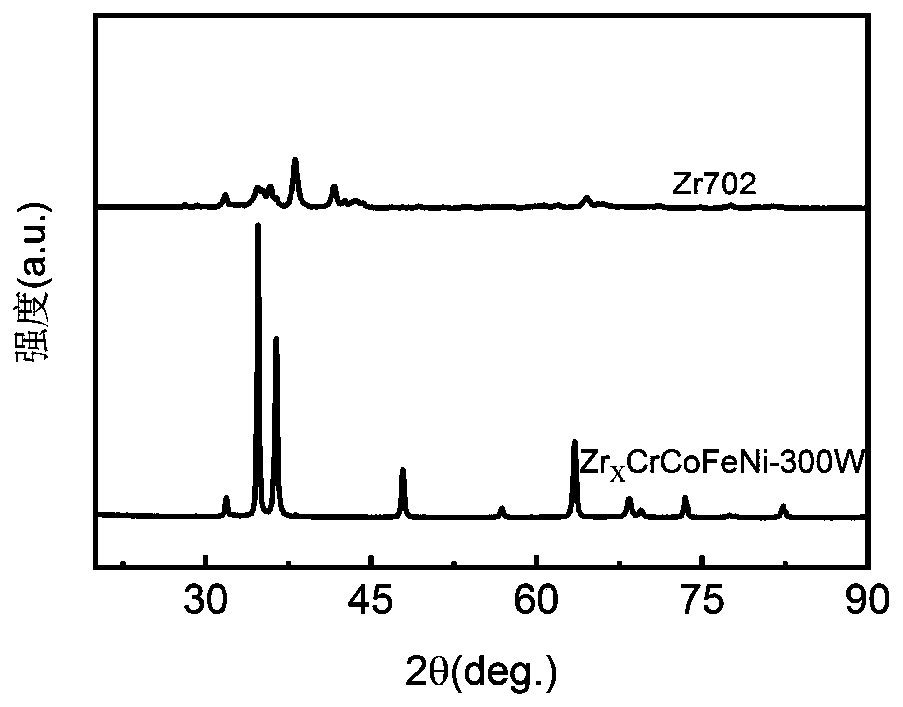
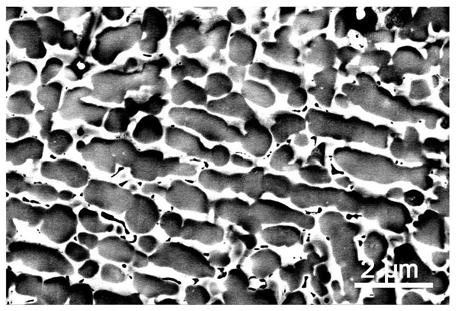
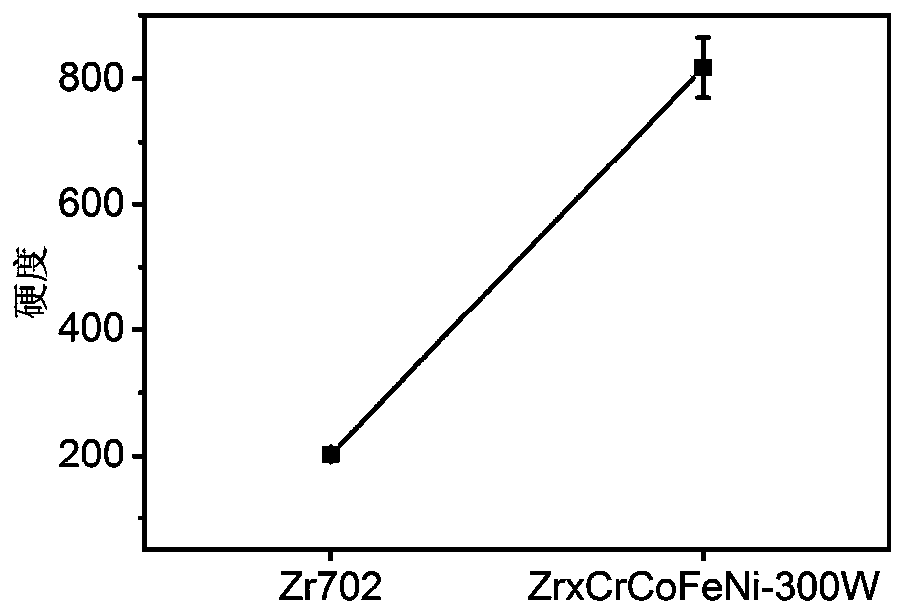
Method for preparing superhard ZrxCrCoFeNi high-entropy alloy coating on surface of zirconium alloy
ActiveCN111139471AImprove wear resistanceHigh hardnessMetallic material coating processesOrganic solventHigh entropy alloys
The invention discloses a method for preparing a superhard ZrxCrCoFeNi high-entropy alloy coating on the surface of zirconium alloy. The method comprises the following steps that (1), a zirconium alloy workpiece is polished to be bright, cleaned and dried; (2), Co, Cr, Fe and Ni metal powder with the same mole fractions are mixed into paste through an organic solvent, and the paste is smeared on the surface of the workpiece and then dried; (3), the workpiece obtained after coating preset treatment is subjected to laser surface fusion covering treatment; and (4), the workpiece subjected to laser surface fusion covering treatment is taken out, and the workpiece with the surface with the ZrxCrCoFeNi high-entropy alloy coating is obtained. The high-entropy alloy coating prepared through the method has a dendrite crystal texture structure, the chemical properties such as the surface microhardness and the strength of the obtained workpiece are remarkably improved, and the depth and texture of the hardened layer are slighter and more uniform; and in addition, the technical process is easy and convenient to implement, equipment is simple, economical performance and practicability are achieved, the technology is reliable, the efficiency is high, the quality is stable, and good economic benefits can be achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
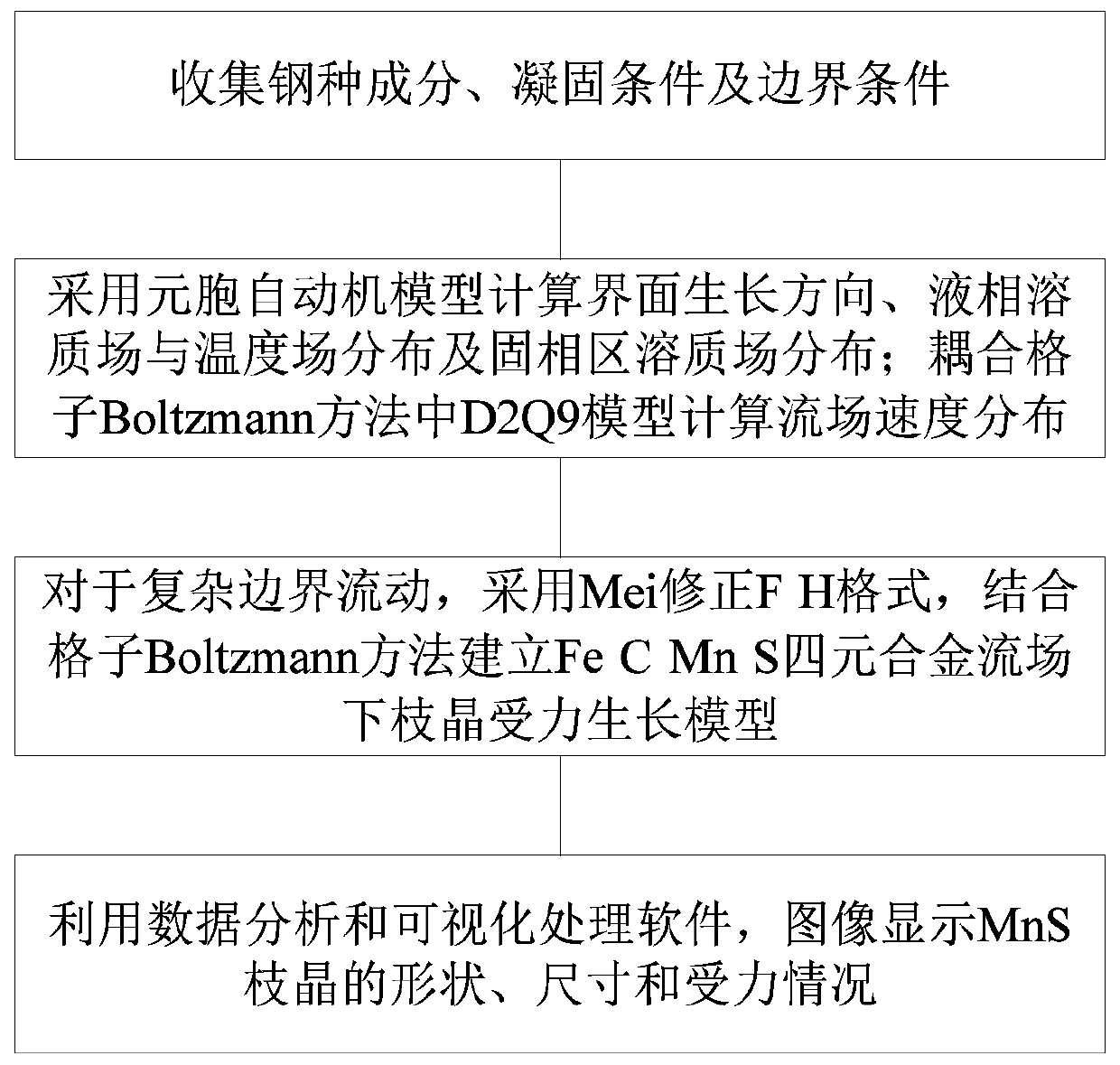
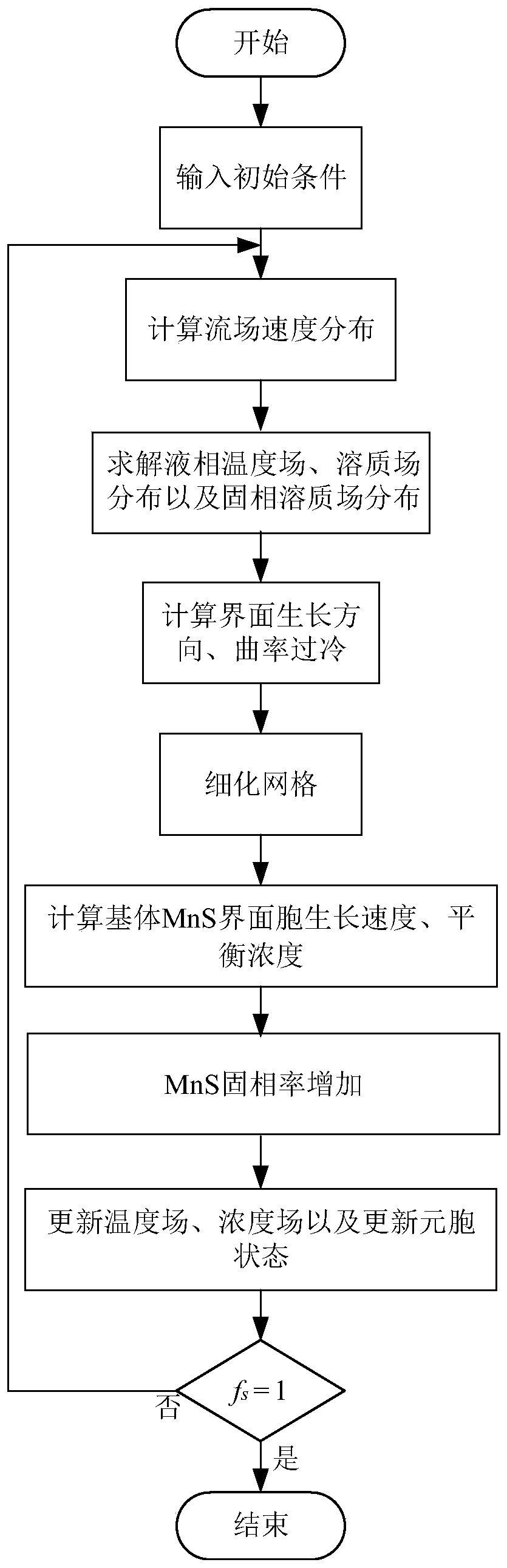
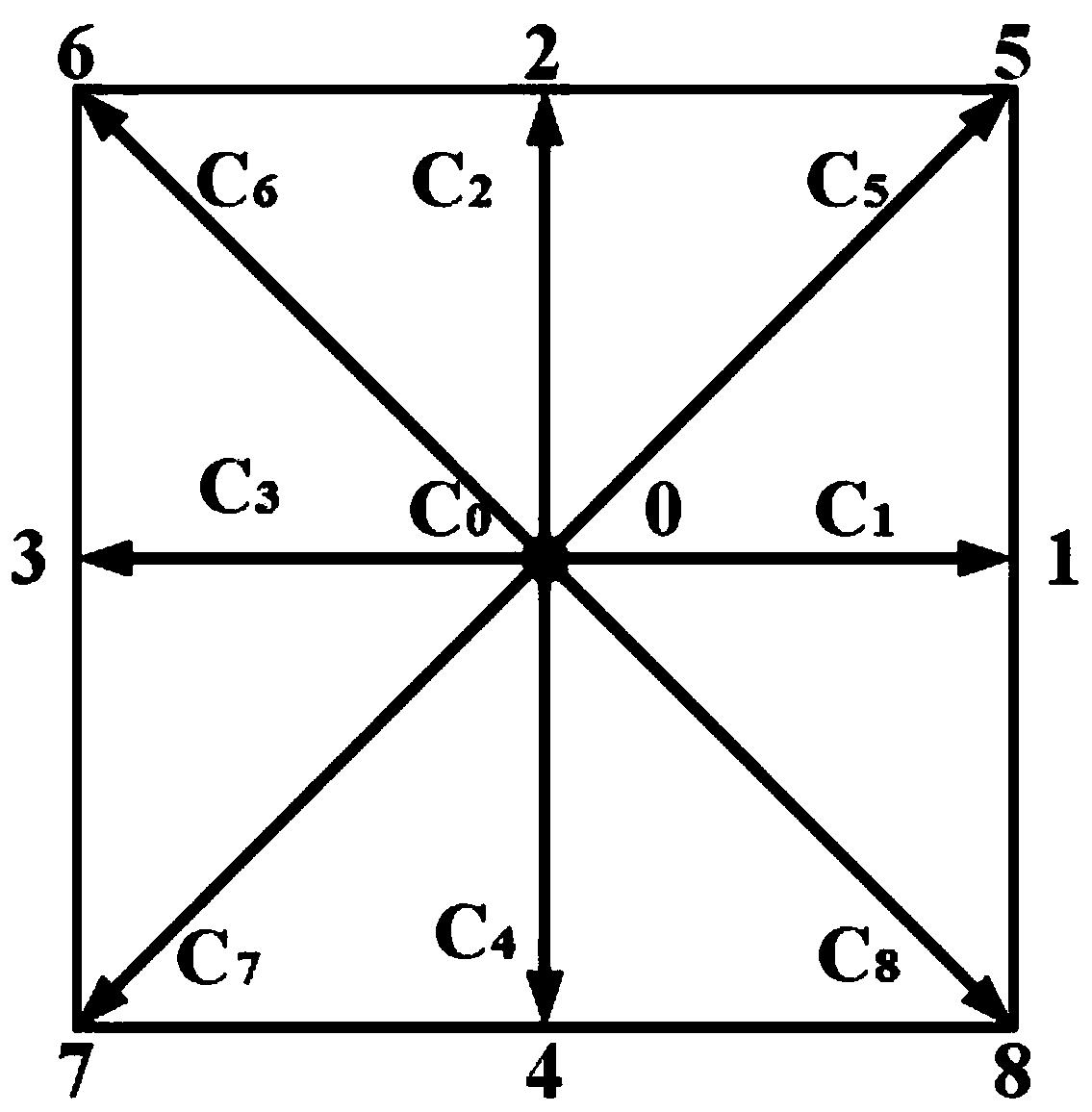
Method for calculating MnS dendritic crystal stress caused by forced convection in molten steel solidification process
ActiveCN110908973AImprove calculation accuracyImprove billet qualityComputational theoretical chemistryStructured data retrievalEngineeringForced convection
The invention discloses a method for calculating MnS dendritic crystal stress caused by forced convection in the molten steel solidification process. The method comprises the steps that 1, steel gradecomponents, solidification conditions and boundary conditions are collected; 2, an interface growth direction, liquid-phase solute field and temperature field distribution and solid-phase region solute field distribution are calculated by adopting a cellular automaton model; meanwhile, a classic model D2Q9 in a lattice Boltzmann method is coupled to calculate flow field speed distribution; 3, forcomplex boundary flow, a Mei correction F-H format is adopted, the speed is increased in the X direction, free boundary conditions are added to the right side, and a dendritic crystal stress growth model under the Fe-C-Mn-S quaternary alloy flow field is established in combination with a lattice Boltzmann method; and 4, the shape, the size and the stress condition of the MnS dendritic crystal inan image manner are displayed by utilizing data analysis and visual processing software. According to the method, the solidification technology is optimized, stress analysis of dendrites under forcedconvection is predicted, and theoretical guidance is provided for improving the casting blank quality.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
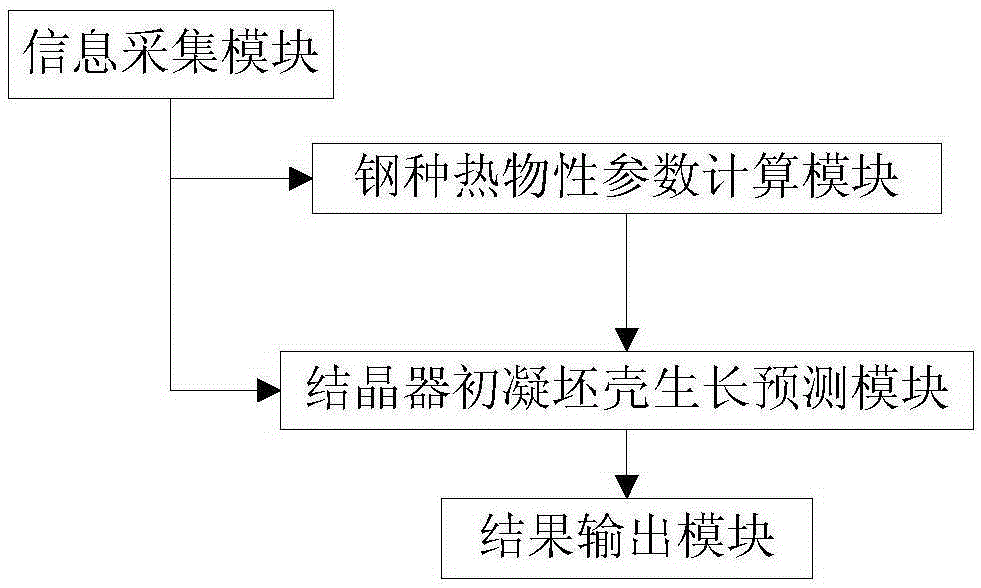
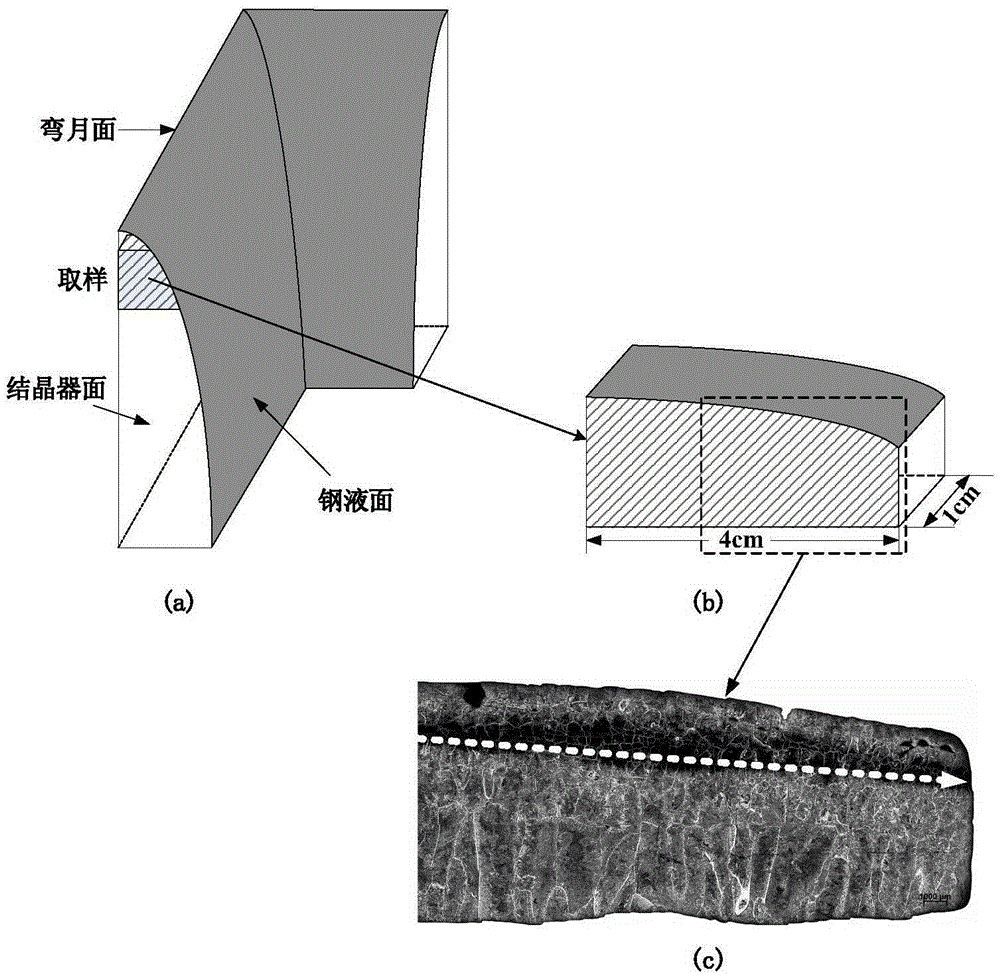
A system and method for predicting the thickness of the initial solidified billet shell in a steel continuous casting crystallizer
ActiveCN104384469BPredict growth behaviorPredicting Microscopic Solidification BehaviorMolten steelPrediction system
A system and method for predicting the initial solidification shell thickness in a steel continuous casting mold. The system includes an information collection module, a steel type thermophysical parameter calculation module, a crystallizer initial solidification shell growth prediction module and a result output module; the method Including: detection of the microscopic solidification structure of the billet shell; collecting initial information: calculating the solute segregation and solidification path between dendrites during the solidification process of the molten steel to obtain the thermal physical parameters of the steel; solving the molten steel flow field and crystallizer temperature field of the mold and the solute field of the crystallizer, and coupled the macroscopic transport process in the crystallizer with the evolution behavior of the microscopic solidification structure in the crystallizer to further predict the shell growth behavior during the solidification process of high-temperature molten steel inside the continuous casting mold; the predicted solidification in the crystallizer The structure morphology and the thickness of the initially solidified shell at different positions in the crystallizer are output and displayed, as well as the comparison results with the actual thickness of the initially solidified shell. The invention can accurately predict the microscopic solidification behavior of the initial solidification shell in the crystallizer.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
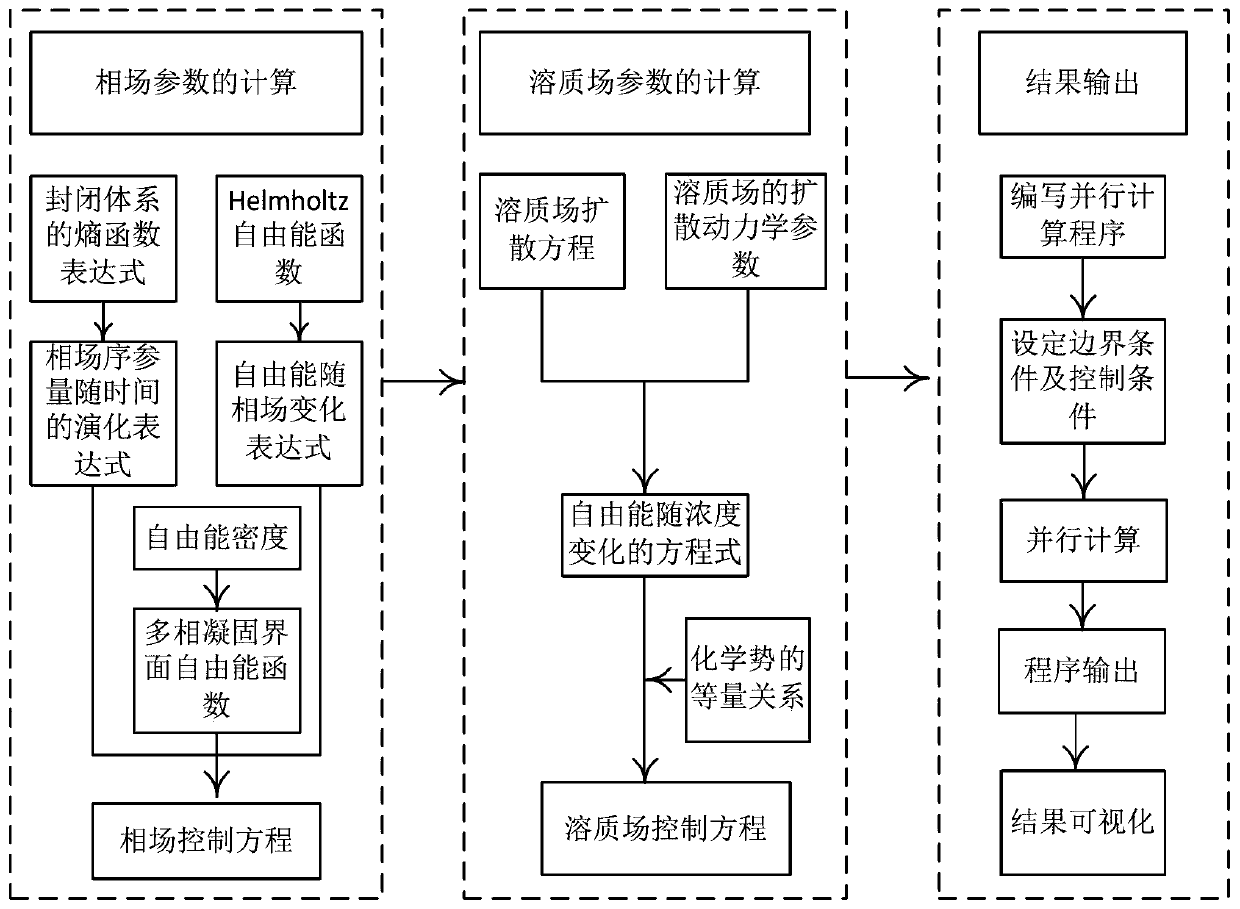
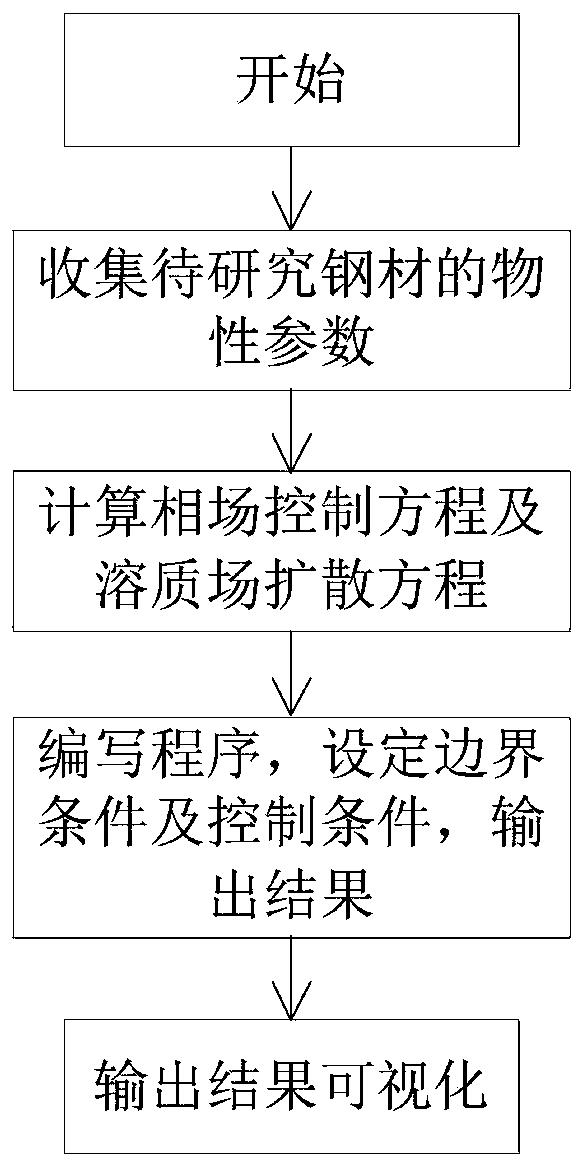
Prediction method for dendritic crystal growth in static molten steel based on parallel computing
PendingCN110993038AHigh precisionHigh cost of solutionResource allocationForecastingConcurrent computationMaterials science
The invention relates to the technical field of metallurgy continuous casting, and provides a prediction method for dendritic crystal growth in static molten steel based on parallel computing. The method comprises the following steps: collecting physical property parameters of to-be-studied steel and proportion data of each component; calculating a control equation of a phase field and a solute field according to the collected physical property parameter data and a phase field method model: writing multi-thread program codes based on parallel calculation, distributing a phase field variable and a concentration calculation process of an i-th node to an i-th thread, and setting a boundary condition and a control condition; enabling the n threads to execute the multi-thread program codes based on parallel computing at the same time, and enabling the i-th thread to output the phase field variable and concentration of the i-th node to an (n + 1)-th thread; and enabling the (n + 1)-th threadto convert the phase field variables and concentrations of the n nodes into an image form to obtain the growth process of dendrites in the static molten steel. According to the method, the growth process of the dendritic crystal in the static molten steel can be reproduced, and the dendritic crystal growth prediction accuracy and calculation efficiency are improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
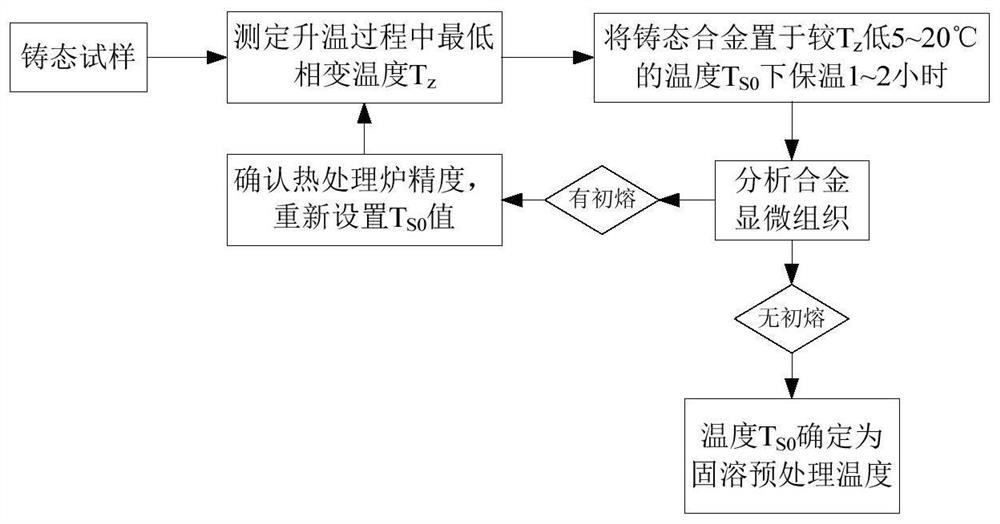
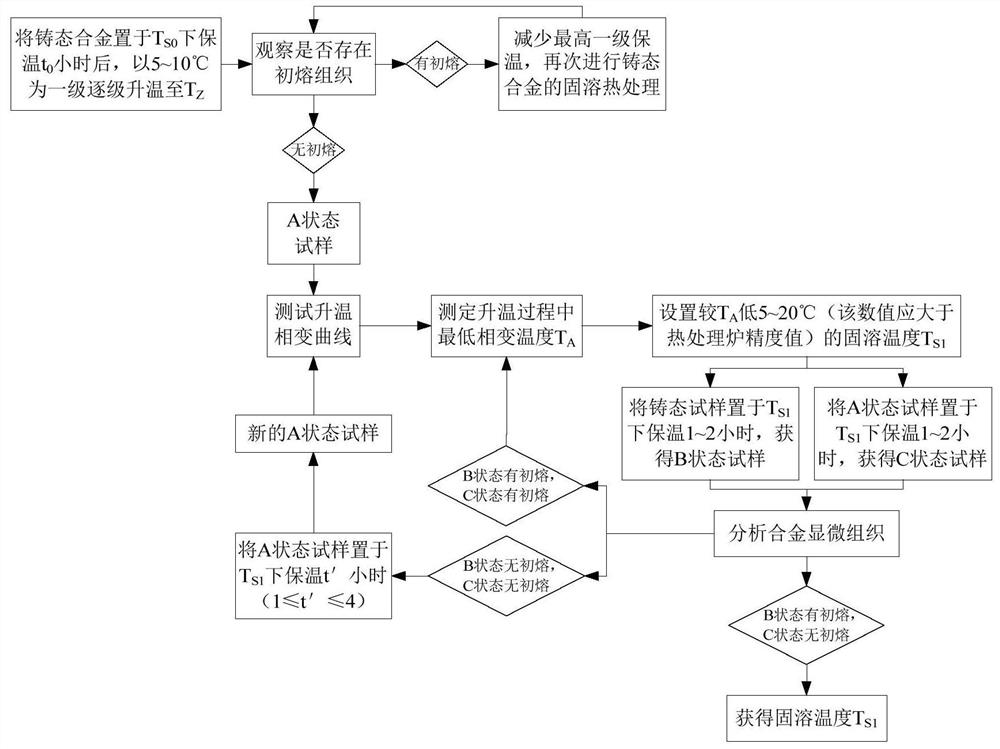
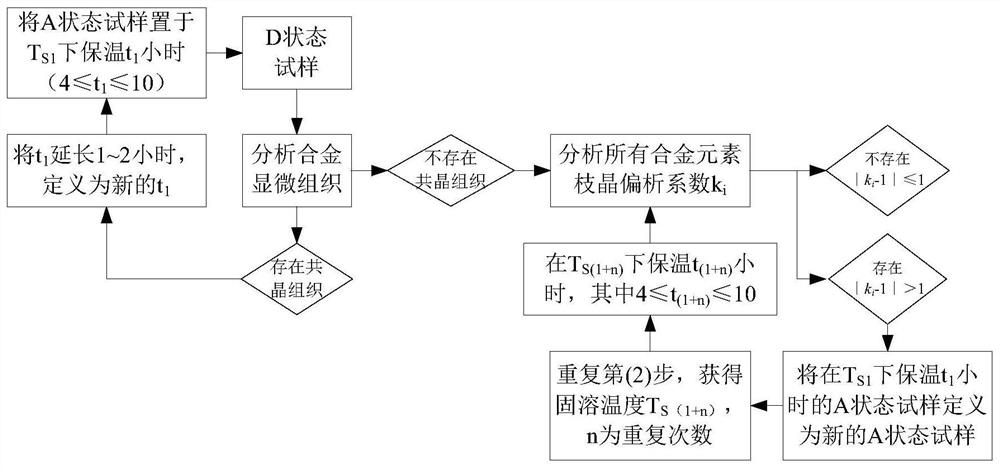
Method for Determining Homogenization/Solution Heat Treatment System of Nickel-based Single Crystal Superalloy
ActiveCN111763897BImprove diffusion efficiencyGood homogenization effectPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsSingle crystal superalloySingle crystal
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Simulation method for predicting solidification process of vacuum consumable melting cast ingot
PendingCN114091248AUniform compositionSolve liquidity problemsDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsMetallurgyMathematical model
The invention discloses a simulation method for predicting the solidification process of a vacuum consumable melting cast ingot, and relates to the technical field of vacuum consumable arc melting. The simulation method comprises the following steps: establishing a mathematical model related to an electromagnetic field and a flow field, carrying out mesh generation on a geometric model, adopting an Eulerian-Eulerian method, setting three phases: molten metal, equiaxed dendrites and columnar crystals, and obtaining related material attributes; setting relevant boundary conditions and relevant dynamic grid parameters, and simulating flowing and solidification of molten metal in the vacuum consumable arc melting process and distribution of an electromagnetic field and a solidification structure. According to the method, the rising process of the molten pool and the solidification process of the cast ingot in the vacuum self-consuming arc melting process are simulated, the flowing form of the molten metal in the solidification process is obtained, the capacity of predicting macrosegregation of the cast ingot is achieved, and the method plays an important guiding role in optimizing the vacuum self-consuming arc melting process to obtain the cast ingot with uniform components; and the method is of great significance to actual production.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
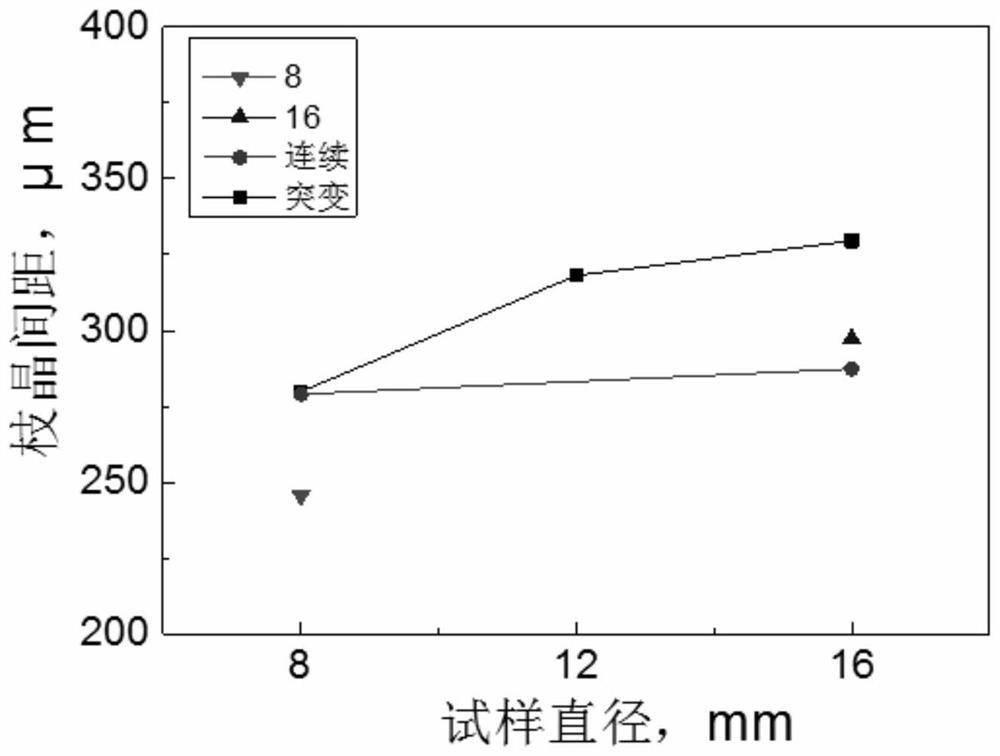
Method for measuring dendritic crystal spacing of chalcogenide free-cutting steel continuous casting billet
ActiveCN111024741AAccurate measurementDetermination method is simpleMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUsing wave/particle radiation meansStatistical analysisMetallic materials
The invention discloses a method for measuring dendritic crystal spacing of a chalcogenide free-cutting steel continuous casting billet, and belongs to the technical field of metal material detection.The method comprises the following specific steps and parameters: firstly, cleaning, grinding and polishing a sample, and then putting into an electron microscope for analysis; then carrying out automatic statistical analysis on the non-metallic inclusions; adjusting the current of the probe to enable the dead time of the free-cutting steel sample under the electron beam to reach 20-30%; and thelike; carrying out closed operation image processing to obtain an inclusion distribution diagram spliced by all fields of view, screening according to elements and content information of the inclusiondistribution diagram, and judging the inclusion with the S content of more than or equal to 0.1 percent and the Mn content of more than or equal to 0.1 percent as manganese sulfide inclusion; obtaining a manganese sulfide inclusion distribution diagram; and finally, averaging more than or equal to 10 positions to obtain a final measurement value of the secondary dendrite spacing. The method has the advantages that the method is simple and convenient, the measured dendrite spacing value is accurate, the analysis scanning areas can be continuously spliced, and the measurement area is more than100mm < 2 >.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
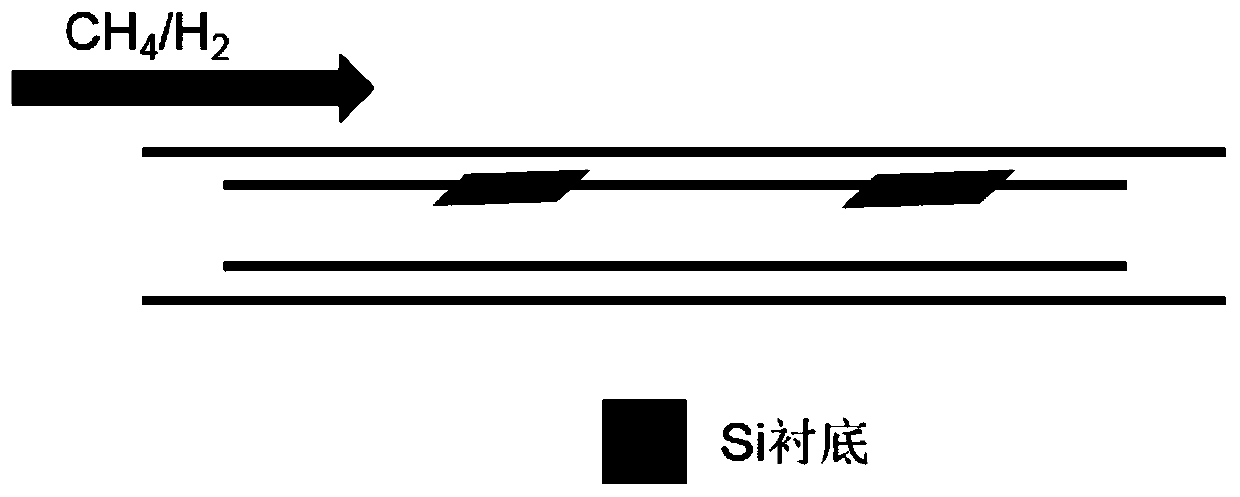
A method for preparing graphene dendrites on an insulating substrate
The invention relates to a method for preparing graphene dendritic crystals on an insulating substrate, and belongs to the technical field of microelectronic materials. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning an insulating substrate, and carrying out drying by blowing; placing the substrate into the outer wall of a quartz inner tube in a CVD tube furnace, vacuumizing the tubular furnace, carrying out heating to 200-300 DEG C, introducing hydrogen, and carrying out etching on the surface of the substrate when the temperature is raised to 800-900 DEG C; slowly carrying out heating to1050-1080 DEG C after the etching by hydrogen, keeping the temperature constant, introducing a carbon source and hydrogen, and carrying out graphene growth; stopping introducing gas after the growth is ended, carrying out cooling to 700-800 DEG C first, and then carrying out natural cooling to room temperature. The morphology of the graphene dendritic crystals is of a dendritic shape, and the graphene dendritic crystals are distributed at the top ends of branches. Through the control of the introduction amount of methane, the ratio of the methane to the hydrogen, and the like in the preparation method, the purpose that the graphene grows on the insulating substrate and form a dendritic crystal shape is realized. The dendritic crystal-like graphene has a better mechanical property and electrical property compared with reticulate graphene.
Owner:DEZHOU UNIV +1
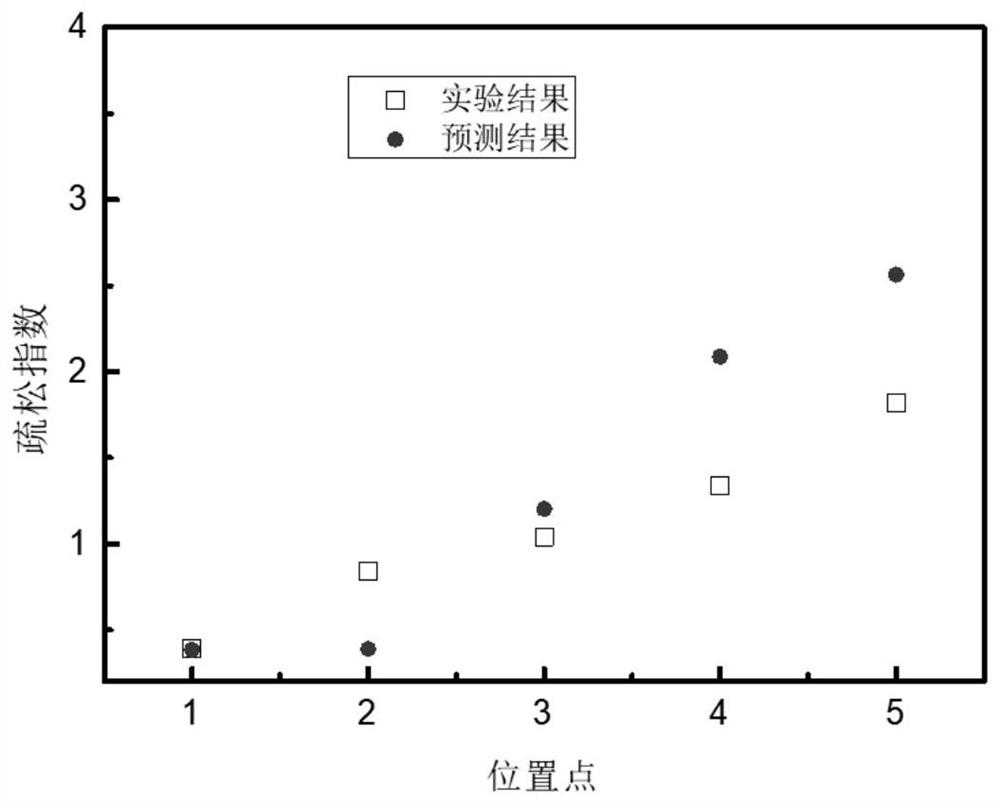
Quantitative prediction method for loosening defects of large complex thin-wall high-temperature alloy casting
ActiveCN112417583AThe formation mechanism of evasion porosity is complexFacilitate access to sensitive process parametersGeometric CADForecastingSuperalloyMaterials science
The invention provides a quantitative prediction method for loosening defects of large complex thin-wall high-temperature alloy casting, which comprises the following steps: analyzing the structure ofa large complex thin-wall casting, and calculating the thermal modulus of each part of the casting; calculating the crystallization temperature interval, density, specific heat capacity and shrinkagecoefficient parameters of the high-temperature alloy, importing the calculated parameters into ProCAST to carry out molding and solidification simulation on the casting, extracting the temperature gradient and cooling speed values, calculating the secondary dendritic crystal interval through a formula, and calculating the secondary dendritic crystal density of the high-temperature alloy; selecting the obtained thermal modulus, temperature gradient and secondary dendrite spacing as input parameters of the BP neural network and the porosity index as output parameters, constructing a BP neural network prediction model, training the BP neural network prediction model by adopting casting body anatomical data, and constructing a casting porosity quantitative prediction network after training, thereby realizing casting porosity defect quantitative prediction. The BP neural network is constructed to realize casting loose defect quantitative prediction, and loose defect sensitive process parameters can be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
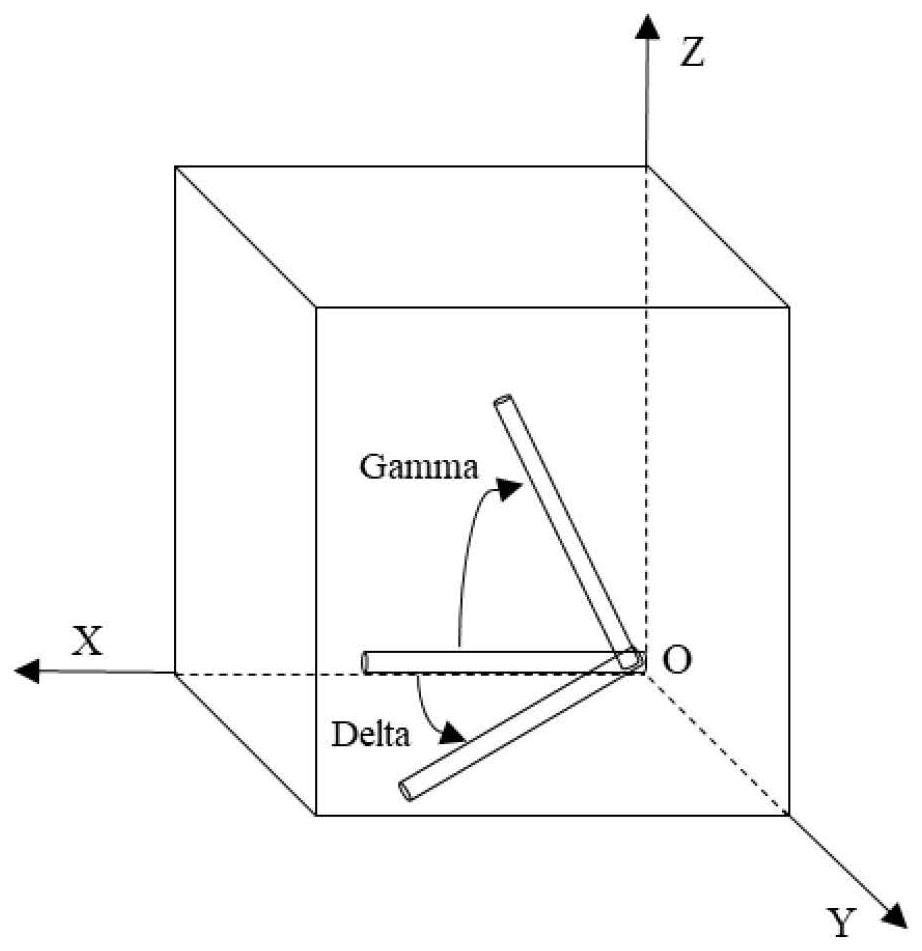
Seed cutting device and method for casting single crystal superalloys with different crystal orientations
ActiveCN113232176BImprove yieldEasy to cutWorking accessoriesFine working devicesSingle crystal superalloyDiffractometer
The invention discloses a seed crystal cutting device and a method for casting single crystal superalloys with different crystal orientations, belonging to the technical field of mechanical processing. The seed crystal cutting device consists of two parts: the bottom device that controls and corrects the Gamma angle of the primary dendrite direction and the top device that controls and corrects the Delta angle of the primary dendrite direction, the Alpha angle and the Beta angle of the secondary dendrite direction. X-ray diffractometer was used to measure the angles of the primary dendrite and the secondary dendrite, and the middle angle index of the top device was rotated to determine the corresponding angle for direction correction, and the angle index of the bottom device was rotated to the corresponding angle for direction correction; single crystals were obtained. After the direction of the test bar is accurately corrected, the seed crystal block is cut by the cutting machine, and the obtained seed crystal block is the seed crystal with the [001], [011] or [111] orientation. The seed crystal cutting device can easily and quickly cut single crystal sample seed crystals with different crystal orientations, and improves the yield of seed crystal cutting.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
GH4169 high-temperature alloy cast ingot forming method
PendingCN113996805ALow segregation coefficientSmall dendritesAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyIngotLayer thickness
The invention relates to a GH4169 high-temperature alloy cast ingot forming method, which is characterized in that a GH4169 alloy oversized cast ingot is prepared by a laser casting additive manufacturing method, and the GH4169 alloy oversized cast ingot comprises the following average chemical components in percentage by weight: 52.5% of Ni, 19.0% of Cr, 5.13% of Nb, 3.05% of Mo, 0.9% of Ti, 0.5% of Al, 0.05% of C, 18.87% of Fe. The forming laser power is 280-290 W, the scanning speed is 950-970 mm / s, the scanning interval is 79-81 [mu]m, the layer thickness is 39-41 [mu] m, and the interlayer rotation angle is 17-25 degrees. The alloy matrix is a gamma phase, no obvious precipitated phase exists in the crystal and on the crystal boundary, intracrystalline dendrites are fine, and dendritic segregation is mainly the Nb element. The GH4169 alloy cast ingot obtained through the additive manufacturing forming method is low in segregation coefficient, and compared with a traditional cast alloy, cogging can be directly conducted without homogenization heat treatment. The cogging deformation activation energy of the alloy is lower than that of a traditional cast GH4169 alloy, cracking is avoided in the cogging process, and the excellent cogging performance is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Metal continuous casting process and metal continuous casting device based on electromagnetic excitation combined with mechanical stirring
The invention discloses a metal continuous casting process of electromagnetic excitation combined mechanical stirring. When the alloy melt is solidified, the electromagnetic excited combined mechanical stirring technology is used to generate microscopic and macroscale strong shear flow to break dendrites. In this way, the goal of refining the solidification structure, fully equiaxed crystallization, and reducing the degree of solute segregation can be achieved, thereby improving the performance of the alloy. The invention also provides a metal continuous casting device, which is realized by a device composed of a main crystallizer, a rotor stirring paddle, a runner, a program-controlled motor, a magnetic field generator, a coil, and a voltage-regulated and frequency-regulated AC power supply. The present invention uses the microscopic flow generated by electromagnetic excitation and the macroscopic flow generated by mechanical stirring to form a very complex chaotic flow, forming a strong shear flow, breaking dendrites, promoting the proliferation of crystal nuclei, reducing the temperature gradient, and obtaining ultra-fine Fully equiaxed crystal structure, while significantly reducing or even completely inhibiting the segregation of alloy elements, the energy consumption of the present invention is significantly lower than that of conventional electromagnetic stirring, and the energy saving effect is remarkable.
Owner:新兴发展集团有限公司
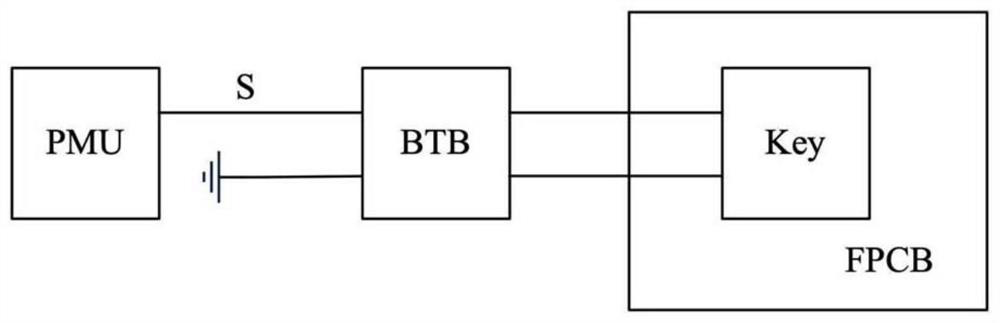
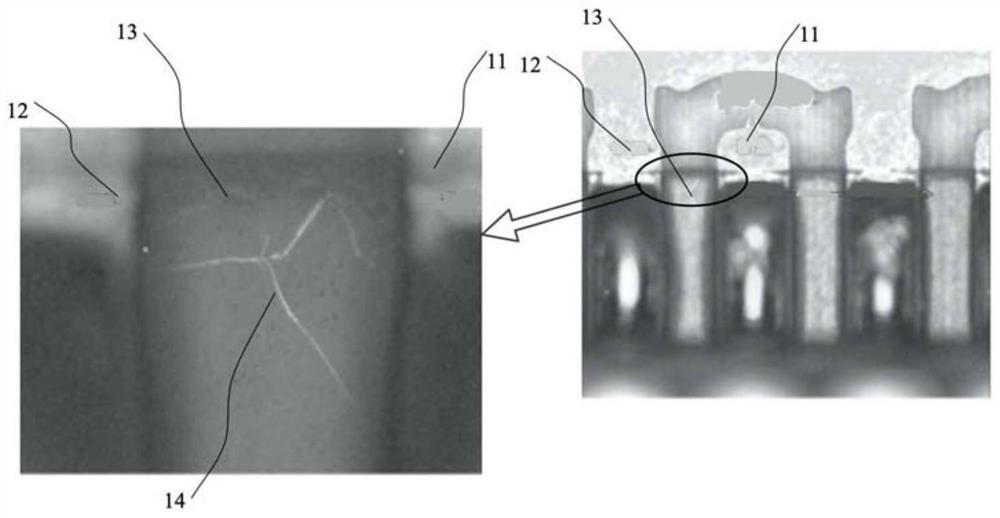
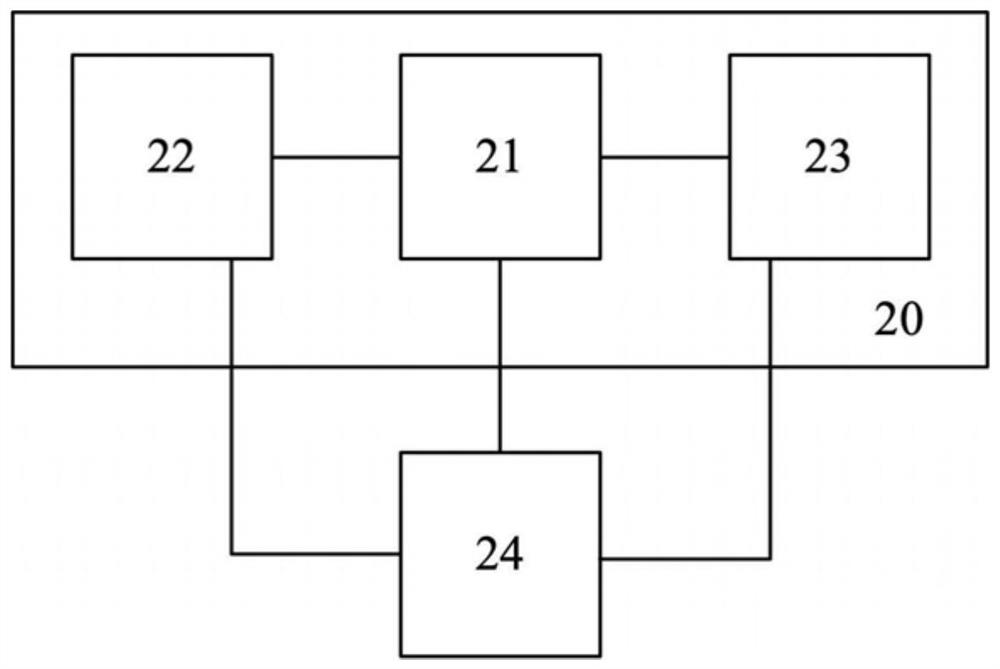
Repair circuit and method and electronic equipment
PendingCN112485634ARecovery functionElectronic circuit testingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionHemt circuitsComputer science
The invention discloses a repair circuit and method and electronic equipment. The repair circuit comprises a detection circuit, an isolation circuit and a fusing circuit, wherein the detection circuitis connected with the isolation circuit and the fusing circuit, and a target circuit is connected with the detection circuit, the isolation circuit and the fusing circuit. When the detection circuitdetects that there is a dendritic crystal fault in the target circuit, the detection circuit controls the isolation circuit to isolate the target circuit; and under the condition that the target circuit is isolated, the detection circuit controls the fusing circuit to output fusing current to the target circuit so as to fuse the dendrites in the target circuit.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
A preparation method of laser cladding wear-resistant plate based on synchronous progressive shear deformation
ActiveCN108950541BHigh strengthImprove wear resistanceMetallic material coating processesStructural engineeringShearing deformation
The invention belongs to the field of laser cladding remanufacturing, and particularly relates to a laser cladding abrasion-resistant plate preparation method based on synchronous progressive shear deformation. The method comprises the procedures of surface abrasive blasting, laser cladding, progressive shear deformation and heat treatment, wherein the progressive shear deformation process comprises the steps that to the two ends of a cladding substrate are fixed correspondingly, and one of the ends can move freely in the vertical direction; a ball end cutter moves gradually along a predetermined path, the cladding plate is forced to conduct progressive shear deformation and to attach to a supporting slope; by adjusting the angle of the supporting slope, the degree of shear deformation ofthe cladding plate can be controlled; and the progressive shear deformation process and the laser cladding process are conducted synchronously, and the ball end cutter conducts shear deformation treatment on a recently solidified alloy layer immediately along with a molten pool. According to the laser cladding abrasion-resistant plate prepared through the method, columnar crystals and dendrites which are grown in an oriented mode are broken, fine isometric crystal are fomred, the structure is uniformized, the dislocation density is high, the compactness is good, and the strength and abrasion resistance are high. Meanwhile, the strength of the substrate is improved through shear deformation, the defects of an interface between the laser cladding layer and the substrate are overcome, the bonding strength is improved, and compared with laser cladding wear plates prepared through traditional methods, the laser cladding abrasion-resistant plate has more excellent comprehensive mechanical properties.
Owner:江阴富朗特机械有限公司
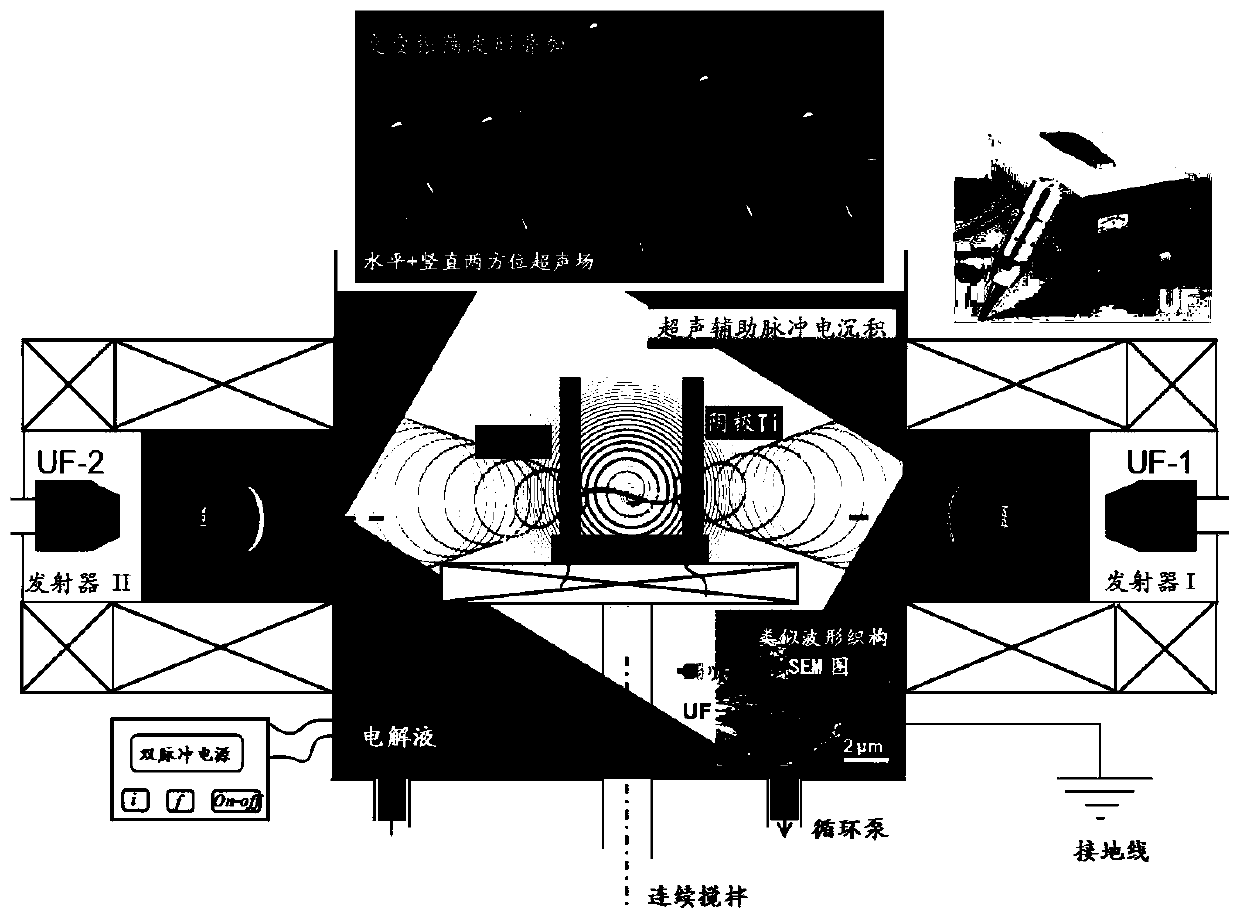
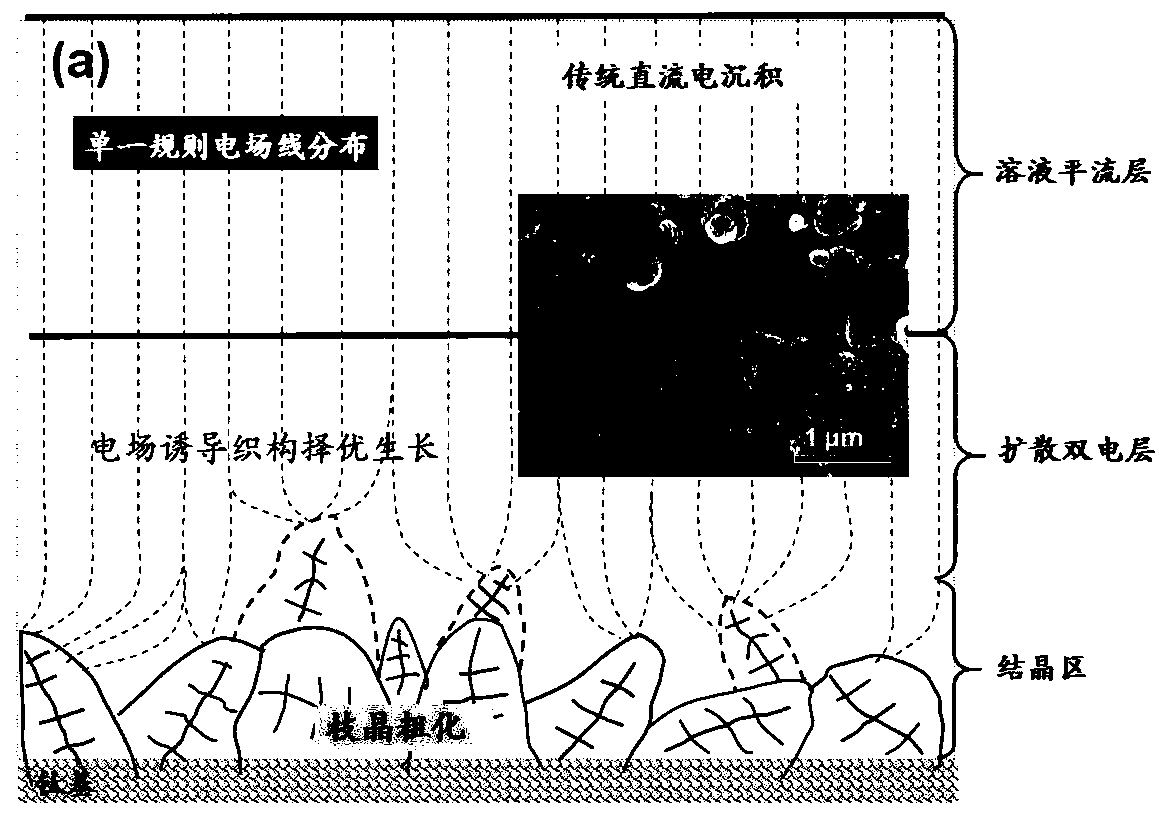
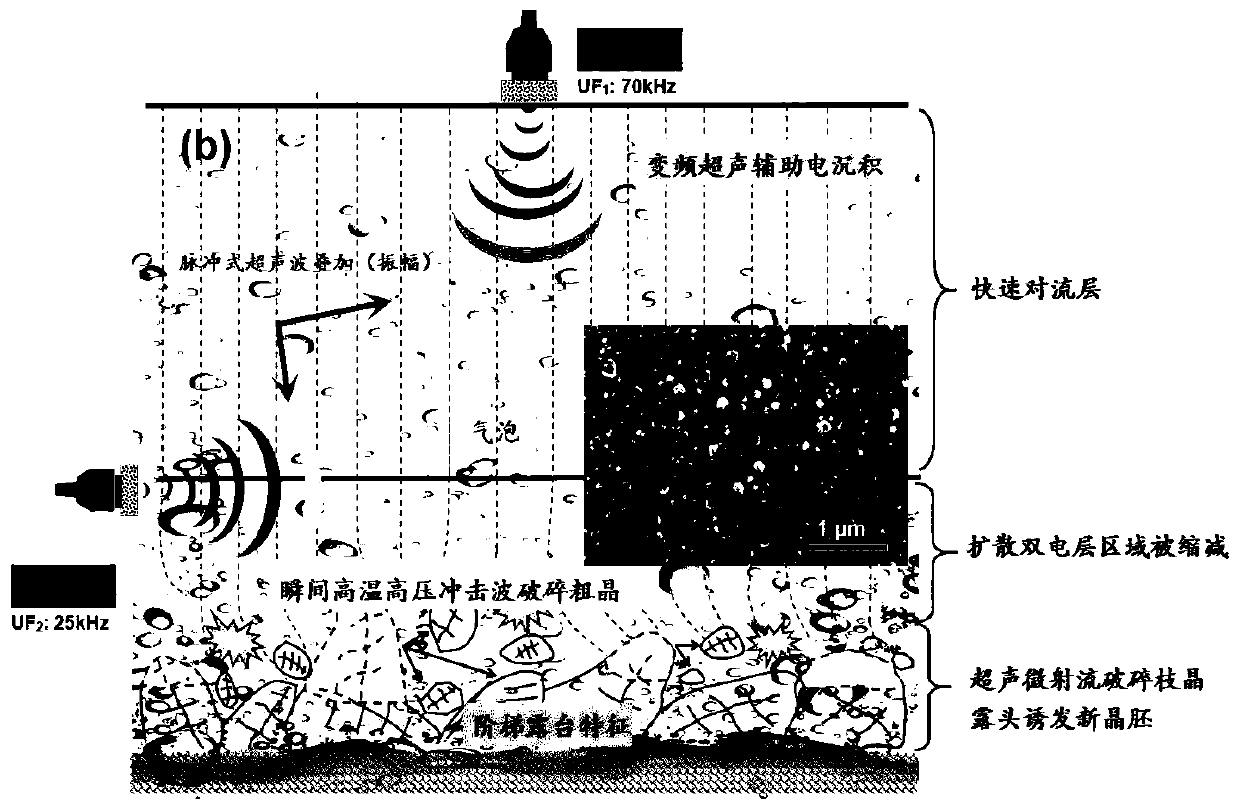
Method for regulating and controlling growth of nanocrystalline texture by means of alternating ultrasonic frequency
ActiveCN111101162AInhibition of selective growth trendsFlexible wiringSurface reaction electrolytic coatingYoung's modulusDeposition process
The invention discloses a method for regulating and controlling the growth of a nanocrystalline texture by means of an alternating ultrasonic frequency. The method includes the following steps that firstly, Pd-Sn sensitization pre-nucleation is performed on a substrate; secondly, the substrate is placed into nickel aminosulfonate system nickel plating liquid for electro-deposition, an ultrasonic generator I is arranged in the horizontal direction of electrodes in the electro-deposition process, and an ultrasonic generator II is arranged in the vertical direction; and (3) a sample where electro-deposition ends is subjected to aging stabilizing heat treatment in a protecting atmosphere. Due to the method, local undercooling of a micro area can be promoted in the dendrite growth process, andmore nucleation centers are triggered; dendrite fragmentation is performed so that the preferred growth tendency of the texture can be inhibited; the fragmentation dendrite becomes nucleation centersin other directions, and the defects of crystal whiskers and the like are avoided; Ni crystals grow randomly in various directions, the structure is compact, the Young modulus Er of the structure reaches 198 GPa, and the hardness reaches up to 914 HV<0.2>; and the process is simple, wiring of the ultrasonic generators is flexible, and operation is convenient.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Synchronous vibration back-up roll device with frame
The invention relates to a synchronous vibration back-up roll device with a frame. The device comprises at least one pair of vibration back-up rolls in contact with a casting blank, a back-up shaft penetrating through the vibration back-up rolls and at least two vibration sources, and further comprises the vibration frame arranged around the casting blank and the vibration back-up rolls. The vibration back-up rolls are symmetrically arranged on the inner side of the vibration frame, and the inner side of the vibration frame vibrates the casting blank through the vibration back-up rolls. The vibration sources are arranged on the outer side or the inner side of the vibration frame, the vibration sources are driven by external force, and vibration is applied to a blank shell of the casting blank through the vibration frame and the vibration back-up rolls. The device can realize synchronous vibration of inner and outer arcs and / or the width direction of the casting blank, so that a large number of dendrites at the solidification front edge of a primary green body shell are broken off to become a source of central solidification isometric crystals, thick central isometric crystals of the casting blank in the later solidification period can be uniformly broken, the solidification structure is refined, and the quality of the casting blank is effectively improved.
Owner:ZHONG NAT ENG & RES CENT
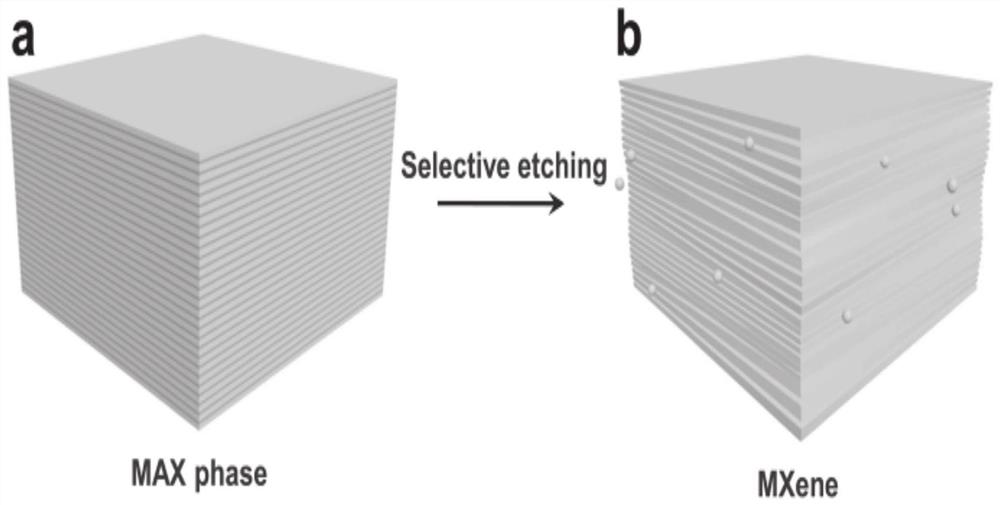
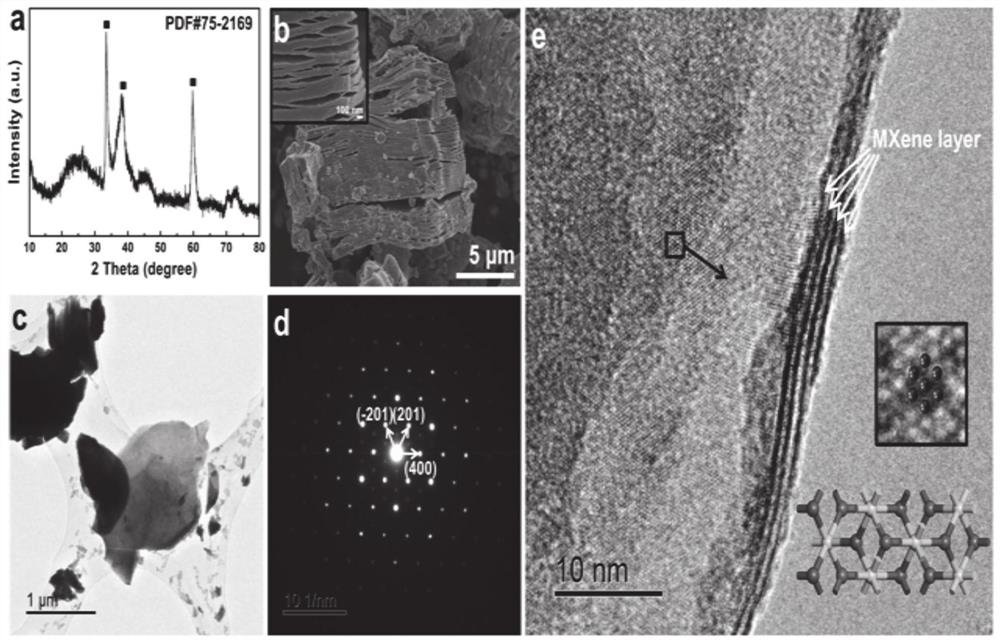
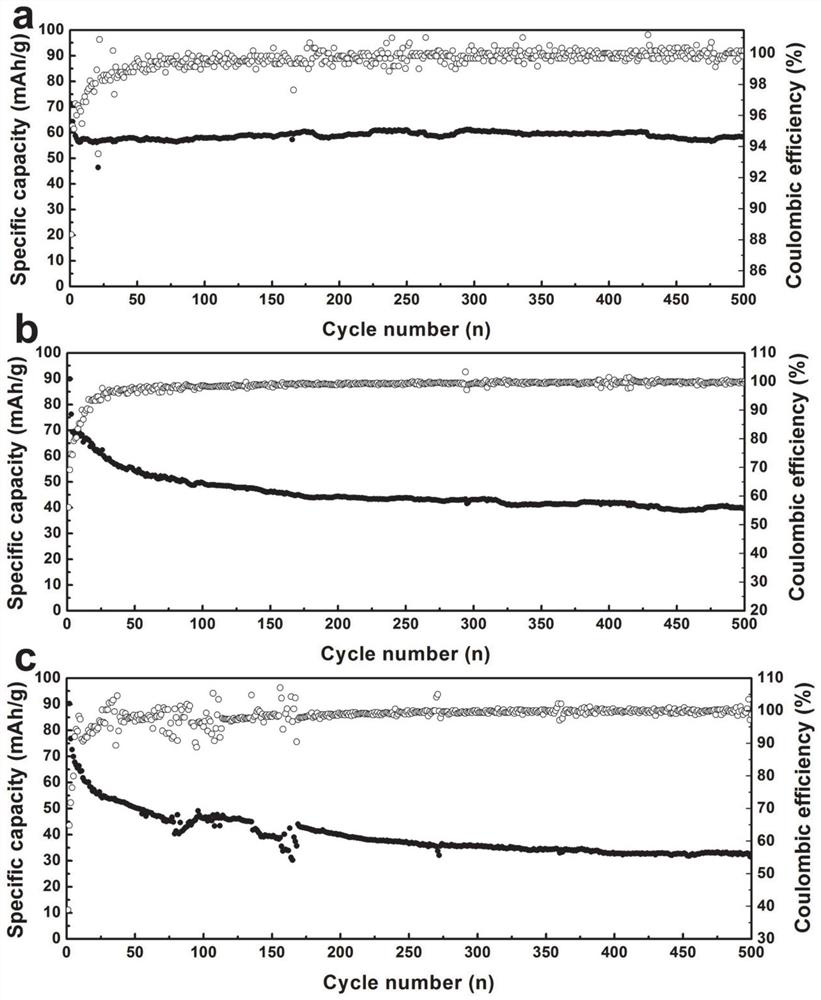
a nb 2 c MXene material and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112047341BLarge poresGrowth inhibitionCarbon compoundsSecondary cellsHexagonal crystal systemPotassium ions
The present disclosure relates to the field of battery electrodes, and specifically provides a Nb 2 C MXene materials and their preparation methods and applications. The material is macroscopically in the shape of an organ with sheets separated, and microscopically arranged in a hexagonal crystal system. The preparation method of the material comprises the following steps: preparing Nb 2 The AlC MAX phase is obtained by selectively etching it with HF to completely etch away the Al layer. It solves the problems in the prior art that metal sodium and potassium ions have relatively large radii, and dendrites are likely to be generated during the cycle process, which cannot replace the application of lithium batteries.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
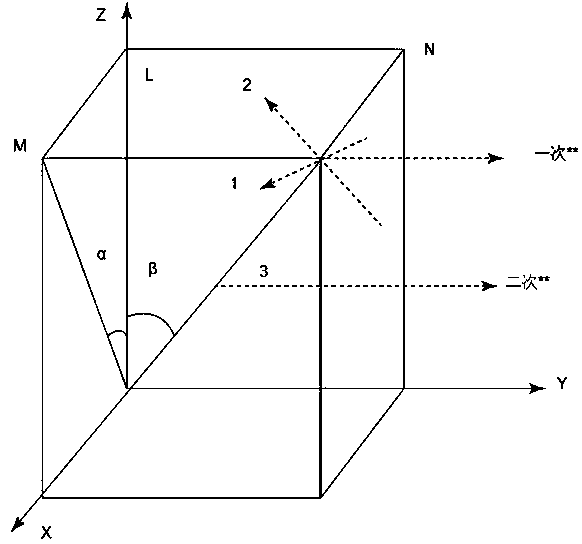
Detection method for 001 orientation optimization of single crystal blade prepared by two-dimensional crystal selection method
InactiveCN111308041AHigh precisionImprove qualityPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsRectangular coordinatesWire cutting
The invention belongs to the technical field of single crystal blade detection application, and particularly discloses a detection method for 001 orientation optimization of a single crystal blade prepared by a two-dimensional crystal selection method, which comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a space rectangular coordinate system according to the appearance direction of the crosssection of a two-dimensional crystal selector in the 001 direction; 2, calculating a direction vector of the primary dendritic crystal by utilizing projections of the primary dendritic crystal on twoside surfaces and included angles alpha and beta of the growth direction of the single crystal; 3, calculating a direction vector of the secondary dendrite by utilizing the included angles A and B between the projection of the secondary dendrite on the horizontal cross section and the horizontal axial direction; 4, a wire cutting machine is used for cutting a tangent plane parallel to the 001 direction of the two-dimensional crystal selector and a tangent plane horizontal to the 001 direction; and step 5, determining the same dendritic crystal of the two tangent planes and the angle of 001 toobtain the final orientation. The method has the advantages that the problems existing in an existing detection method are solved, the detection efficiency and the accuracy of detection data are improved, the production process is adjusted according to the detection result, and the product quality is improved.
Owner:江苏金瑞机械制造有限公司
Method for inhibiting growth of zinc dendrites in zinc ion battery
PendingCN114388902AGrowth inhibitionNo growthFinal product manufactureSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceZinc ionCross linker
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting dendritic crystal growth in a zinc battery by preparing an electrolyte with ultrafast self-repairing performance to construct an electrolyte / zinc negative electrode dynamic self-adaptive interface. According to the invention, a certain amount of guar gum is completely dissolved in a zinc salt solution to form a uniform colloid. Subsequently, glycerol is added to the prepared colloid to form a binary solvent system. And finally, adding a neutral organic boron cross-linking agent and curing the neutral organic boron cross-linking agent to obtain the gel with ultrafast self-repairing performance. When the gel is applied to an electrolyte in a quasi-solid-state battery, a dynamic and continuous electrolyte / zinc negative electrode interface can be constructed, dendritic crystal growth is inhibited, and the service life of a zinc battery is greatly prolonged. The method is low in price, simple in process, safe and environment-friendly, and has the potential of large-scale application.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
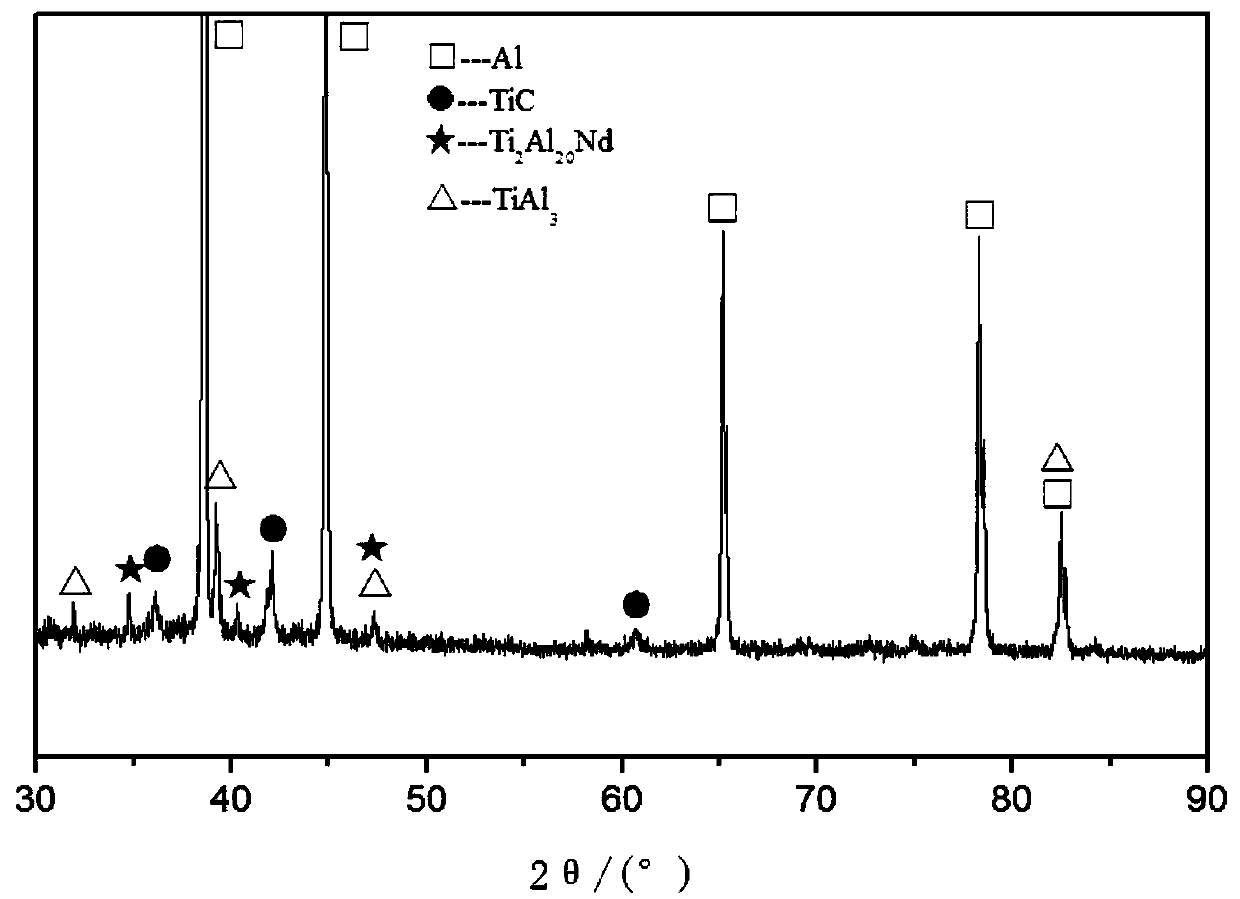
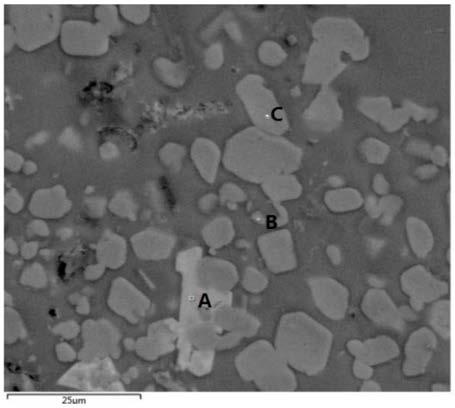
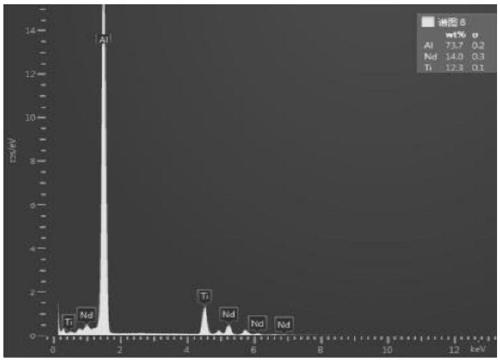
A kind of al-ti-c-nd master alloy and its preparation method and application
The invention provides an Al-Ti-C-Nb intermediate alloy as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The Al-Ti-C-Nb intermediate alloy provided by the invention comprises the following alloy elements in percentage by mass: 1.0-5.0% of Ti, 0.5-2.0% of C and 0.5-2.0% of Nd. By the addition of 0.5-2.0% of Nd, the forming effect of TiC is improved, so that the prepared Al-Ti-C-Nb intermediate alloy has an excellent refining effect. Experimental results prove that when the Al-Ti-C-Nb intermediate alloy provided by the invention is used for refining pure aluminum, a fine equiaxial crystal structure can be obtained by virtue of the addition amount of 0.2wt%, and the grain size is 150-180 microns; and when the intermediate alloy is used for refining hypoeutectic aluminum-silicon alloys, thick dendrite can be enabled to become a fine equiaxial crystal structure of 20-50 microns by virtue of the addition amount of 0.5wt%, and the eutectic silicon is changed from a thick strip form to a fine short-rod or granular structure of 5-10 microns.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Zinc-based electrode capable of delaying nucleation of zinc dendrites as well as preparation method and application of zinc-based electrode
PendingCN113764632AReduce failureAvoid potential side reactions such as galvanic corrosionElectrode rolling/calenderingFinal product manufactureElectrical batteryRechargeable cell
The invention discloses a zinc-based electrode material and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of adopting a polycrystalline metal zinc block (ingot) as an initial raw material, and preparing a zinc-based negative electrode with specific crystal face preferred orientation by using a machining method of mechanical plastic deformation and cold cutting, wherein the zinc-based negative electrode can be applied to the field of zinc-based rechargeable secondary energy storage devices. According to the method, the plastic deformation machining method is adopted to process a polycrystalline metal zinc material with crystal face orientation random distribution or weak texture to generate the polycrystalline metal zinc with specific crystal face preferred orientation and a composite negative electrode material of the polycrystalline metal zinc, and the polycrystalline metal zinc and the composite negative electrode material can be used as a negative active electrode material of a secondary rechargeable battery. The zinc-based negative electrode obtained through processing has the characteristic of specific crystal face preferred orientation, and compared with a zinc material with crystal face orientation random distribution or other crystal face preferred orientation, the nucleation time of dendritic crystals in the high-power charging process of the secondary battery and the like can be shortened, so that the generation of the dendritic crystals is delayed, and the service life of a rechargeable energy storage device is prolonged.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MATERIALS & PROCESSING
Dendrite etchant and corrosion method for large ingot modified in617 alloy
The invention relates to a dendritic crystal etchant of a large ingot type modified IN617 alloy and a corrosion method thereof, belongs to the technical field of metallographic sample preparation, andsolves the technical problem that the existing etchant cannot corrode a clear dendritic crystal structure of the ingot type modified IN617 alloy in the prior art. The dendritic corrosion agent of thelarge ingot type modified IN617 alloy comprises 80-120 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid, 9-15 ml of concentrated nitric acid, 100-130 ml of water and 10-20 ml of ethanol. The etchant provided bythe invention can rapidly and clearly corrode the dendritic structure in the as-cast state and the homogenized heat treatment state of the modified IN617 alloy, measure the dendritic spacing, measurethe components between dendrites and dendrite arms through energy spectrum, analyze the segregation degree of the dendrites, evaluate the elimination effect of the as-cast structure and the homogenized heat treatment of the modified IN617 alloy on the dendritic segregation, and provide an important basis for formulating the homogenization process before forging.
Owner:TIANJIN HEAVY EQUIP ENG RES +1
A control method of dendrite spacing during the growth process of Ni-based single crystal superalloy
ActiveCN107747120BIncrease horizontal widthIncreased dendrite spacingPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsMetallurgySingle crystal superalloy
The invention discloses a control method for dendritic crystal spacing in a growth process of a Ni-based single-crystal high-temperature alloy, and belongs to the technical field of single-crystal high-temperature alloys. The method aims to the Ni-based single-crystal high-temperature alloy, and achieves the purpose of controlling the dendritic crystal spacing through adjusting a dendritic crystalgrowth path in the process of directional solidification; and when dendritic crystals of a Ni-based single-crystal casting are coarsened, the method can adjust the dendritic crystal spacing through changing a single-crystal casting growth mode. The method provided by the invention achieves the purpose of controlling the dendritic crystal spacing through adjusting the dendritic crystal growth path, and lays a foundation for preparing single-crystal structural parts with variable cross-section characteristics in the future.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method of cutting and preparing cast single crystal superalloy seed crystal
A method for cutting and preparing cast single crystal superalloy seed crystals. Based on the strict correspondence between the growth direction of single crystals and crystal directions, the directions of primary dendrites and secondary dendrites are precisely cut and calibrated, and standard dendrites are constructed based on the dendrite directions. The FCC crystal structure can cut out the (001) crystal plane of the single crystal test rod, and then use the crystal plane angle formula of the FCC crystal to calculate the angle θ between the target crystal plane and the (001) crystal plane, and according to the FCC crystal structure Features Mark the intersection line between the target crystal plane and the (001) crystal plane on the (001) crystal plane, and cut out the target crystal plane along the intersection line with an angle of θ with the (001) crystal plane; cut perpendicular to the target crystal plane A seed crystal with the target orientation is obtained. The invention adopts metallographic observation and directional cutting to directly cut seed crystals with any crystal orientation on cast single crystal test rods, has simple equipment and operation steps, and the orientation deviation of cut out seed crystals is less than 5°.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![Mold shell and method for preparing [011] or [111] oriented single crystal high-temperature alloy Mold shell and method for preparing [011] or [111] oriented single crystal high-temperature alloy](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/977a1895-e162-426a-9deb-d0014ac87a6a/HDA0002829092580000011.png)
![Mold shell and method for preparing [011] or [111] oriented single crystal high-temperature alloy Mold shell and method for preparing [011] or [111] oriented single crystal high-temperature alloy](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/977a1895-e162-426a-9deb-d0014ac87a6a/HDA0002829092580000012.png)
![Mold shell and method for preparing [011] or [111] oriented single crystal high-temperature alloy Mold shell and method for preparing [011] or [111] oriented single crystal high-temperature alloy](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/977a1895-e162-426a-9deb-d0014ac87a6a/HDA0002829092580000021.png)