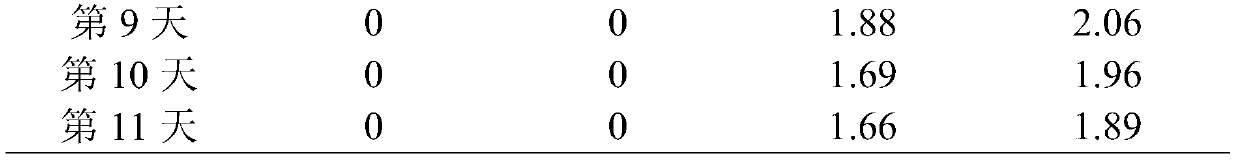Patents
Literature
44 results about "Venerupis philippinarum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ruditapes philippinarum (syn. Venerupis phlippinarum) is an edible species of saltwater clam in the family Veneridae, the Venus clams. Common names for the species include Manila clam, Japanese littleneck clam, Japanese cockle and Japanese carpet shell.
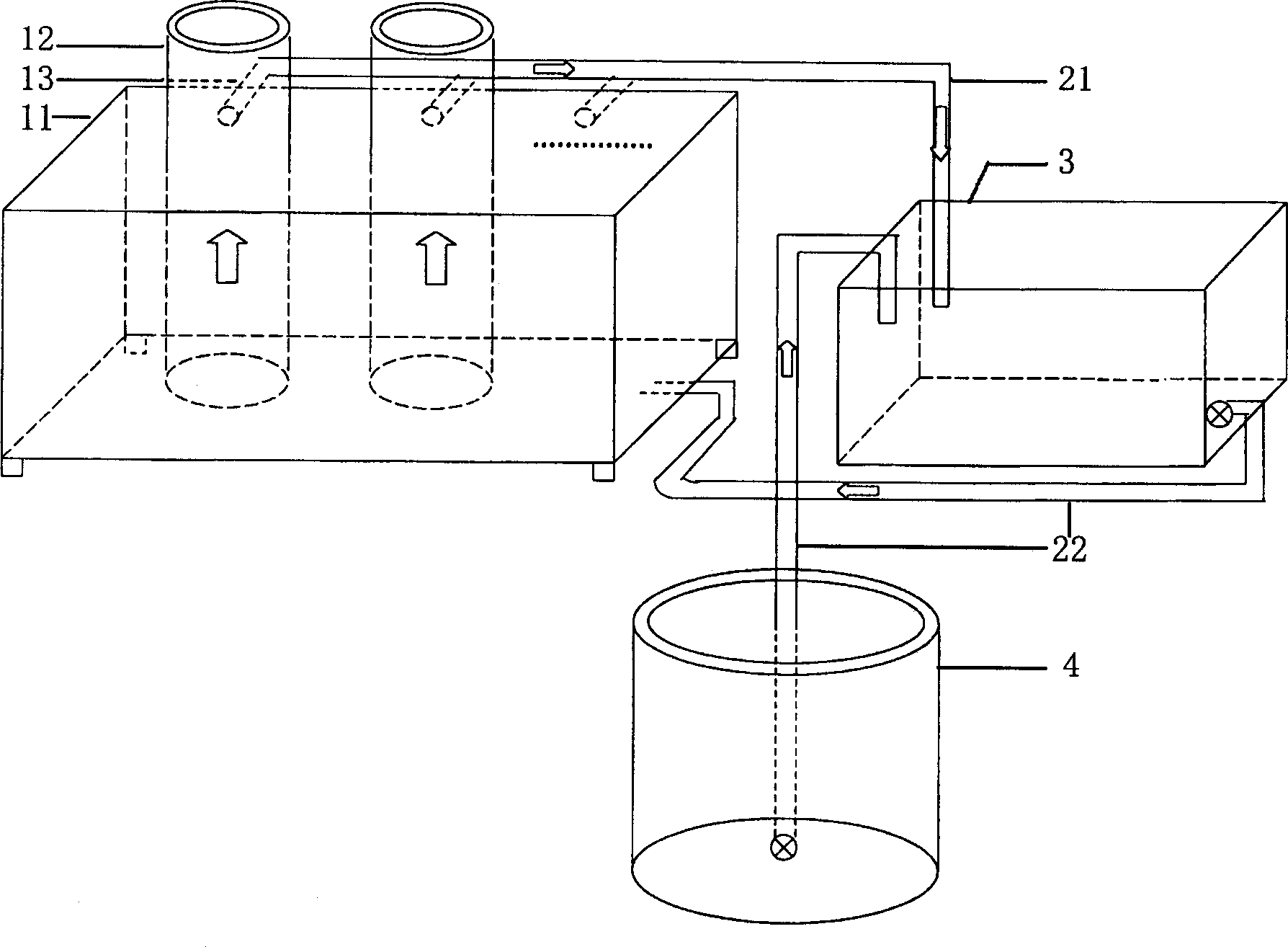
Intermediate breeding method suitable for mudflat shellfish and its used intermediate breading equipment
InactiveCN1478384AEnsure water qualityImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaObserved SurvivalSeawater
An intermediate breeding method for mudflat shellfish, especially the philippine clam, features use of a lifting-flow circulating facility which is composed of young clam suspending and nursing unit, seawater circulating unit, depositing and cleaning unit and feed culturing unit. Its advantages are high efficiency and high growth speed and survival rate.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Venerupis philippinarum compound feed
ActiveCN104799124AReduce fatImprove use valueFood processingClimate change adaptationFeed conversion ratioAquatic animal
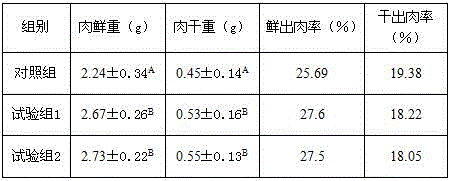
The invention relates to the technical field of aquatic animal feeds, in particular to a venerupis philippinarum compound feed. The compound feed consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of expanded soybean meal, 20-30 parts of corn flour, 15-25 parts of rapeseed meal, 3-5 parts of yeast powder, 8-15 parts of scallop powder, 0.2-0.3 part of compound vitamin, 0.2-0.3 part of choline chloride and 0.2-0.3 part of tangerine powder. During preparation, the materials are crushed respectively, are screened through a 120-mesh sieve and are uniformly mixed to obtain the feed. The venerupis philippinarum compound feed has good palatability, is convenient to use, has high feed conversion rate, causes low pollution to a water body, and can make up the problem of low venerupis philippinarum culture yield caused by insufficient natural bait in the existing venerupis philippinarum cultural water, the breeding density and the breeding number can be obviously improved, the nutrition level of the venerupis philippinarum can be obviously improved, and the venerupis philippinarum growth speed and the fresh meat rate are improved.
Owner:湖北省金谷药业有限公司
Extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101580550AHigh flocculation activityMicroorganism based processesSustainable biological treatmentBiotechnologyActivated sludge
The invention relates to an extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof. An aerobic strain ZHT4-13 is separated from adhesive sludge of wild Ruditapes philippinarums in the Bohai sea offshore of China and is identified as a Ruthia sp. The aerobic strain is treated by seed culture and amplification culture, and a fermentation broth of the aerobic strain is precipitated with ethanol and separated centrifugally to obtain the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13. The extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 is measured to have high flocculation activity, the FR value to kaolin reaches over 80 percent, and the removal rate to hexavalent chromium ions reaches 69.3 percent; the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 has high activity to decolorize high-concentration wastewater, and the decolorization ratios to methylene blue, ink blue, malachite green and crystal violet reach 86.11 percent, 99.49 percent and 97.84 percent; and the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 plays a role of obviously improving the performance and the structure of activated sludge. The extra-cellular polysaccharide has potential value of developing a novel microbial flocculant.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Jellyfish breeding method
ActiveCN104186393AIncrease the amount of feedingFeed amount increasedClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMixed cultureWater quality
The invention discloses a jellyfish breeding method including subjecting jellyfishes to mixed culture with ruditapes philippinarum, sinonovacula constrictas, penaeus chinensis, penaeus monodons and goby; controlling ecological breeding technologies including a stocking system based on breeding species and density, a feeding system based on a match between the species and number and a water quality control system based on a principle that firstly applying fertilizer into water, secondly maintaining fertilizer content and thirdly controlling the water quality. In this way, the jellyfishes and other species are rapid to grow and high in output and economic benefit. By the use of the jellyfish breeding method, the jellyfish output reaches 200-400kg / mu, the outputs of the ruditapes philippinarum and the sinonovacula constrictas reach 200-300kg / mu, and the outputs of the penaeus chinensis and the penaeus monodons reach 10-30kg / mu, and the goby output reaches 20-30kg / mu.
Owner:辽宁每日农业集团有限公司
Ruditapesphilippinarum seedling large scale cultivation method
ActiveCN105145413ALarge single-port seedling areaPromote growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAquatic productSeedling
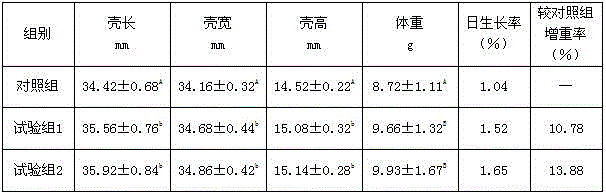
The invention discloses a Ruditapesphilippinarum seedling large scale cultivation method, belongs to the aquatic product cultivation field, and the method comprises the following steps: reclamation area sand blowing and disinfection, parent selection and spawning induction, planktonic larva cultivation, adhesion juvenile mollusk cultivation, and sand seedling harvesting; by using the method, 50,000,000-120,000,000 Ruditapesphilippinarum sand seedlings (shell length 1.5-4mm) can be grown in each mu; the method can be applied to coastal area in our nation, thus realizing Ruditapesphilippinarum seedling large scale and industrialization production, and providing seedling guarantee for developing Ruditapesphilippinarum cultivation industry; the method is simple in operation and easy in promotion.
Owner:FISHERIES RES INST OF FUJIAN +2
Feed for increasing crab feed intake
InactiveCN105935107AMeet growthHigh nutritional valueFood processingClimate change adaptationBacillus licheniformisPropolis
The invention discloses a feed for increasing crab feed intake; the feed comprises the raw materials: corn, fermented soybean meal, bran, a mussel powder, a sweet potato vine powder, dry venerupis philippinarum, a feather powder, an earthworm powder, a seashell powder, a dried small shrimp powder, a spirulina powder, dicalcium phosphate, choline chloride, a zeolite powder, elaeagnus angustifolia, radix astragali, radix paeoniae alba, poria cocos, albizia julibrissin, herba portulacae, wild chrysanthemum, pericarpium citri reticulatae, a compound amino acid, lactic acid bacteria, monascuspurpureus, bacillus licheniformis, a compound trace element, a compound vitamin, polysaccharides, octacosanol, L-carnitine, a propolis extract, marjoram essential oil, needle juniper essential oil, gamma-amino butyric acid, and malic acid. The feed for increasing the crab feed intake has the advantages of scientific formula, rich nutrition and good palatability, increases the crab feed intake, improves the appetite of crabs, also improves the immunity, and promotes the growth of the crabs.
Owner:QUANJIAO TIANRUN ECOLOGICAL BREEDING PROFESSIONAL COOP
Extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101580550BHigh flocculation activityMicroorganism based processesSustainable biological treatmentBiotechnologyActivated sludge
The invention relates to an extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof. An aerobic strain ZHT4-13 is separated from adhesive sludge ofwild Ruditapes philippinarums in the Bohai sea offshore of China and is identified as a Ruthia sp. The aerobic strain is treated by seed culture and amplification culture, and a fermentation broth ofthe aerobic strain is precipitated with ethanol and separated centrifugally to obtain the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13. The extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 is measured to have high flocculation activity, the FR value to kaolin reaches over 80 percent, and the removal rate to hexavalent chromium ions reaches 69.3 percent; the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 has high activity to decolorize high-concentration wastewater, and the decolorization ratios to methylene blue, ink blue, malachite green and crystal violet reach 86.11 percent, 99.49 percent and 97.84 percent; and theextra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 plays a role of obviously improving the performance and the structure of activated sludge. The extra-cellular polysaccharide has potential value of developing a novel microbial flocculant.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of anti-oxidation Venerupis philippinarum enzymatic extract
InactiveCN102846665AImprove cleanlinessGood workmanshipAntinoxious agentsMolluscs material medical ingredientsVenerupis philippinarumChemistry
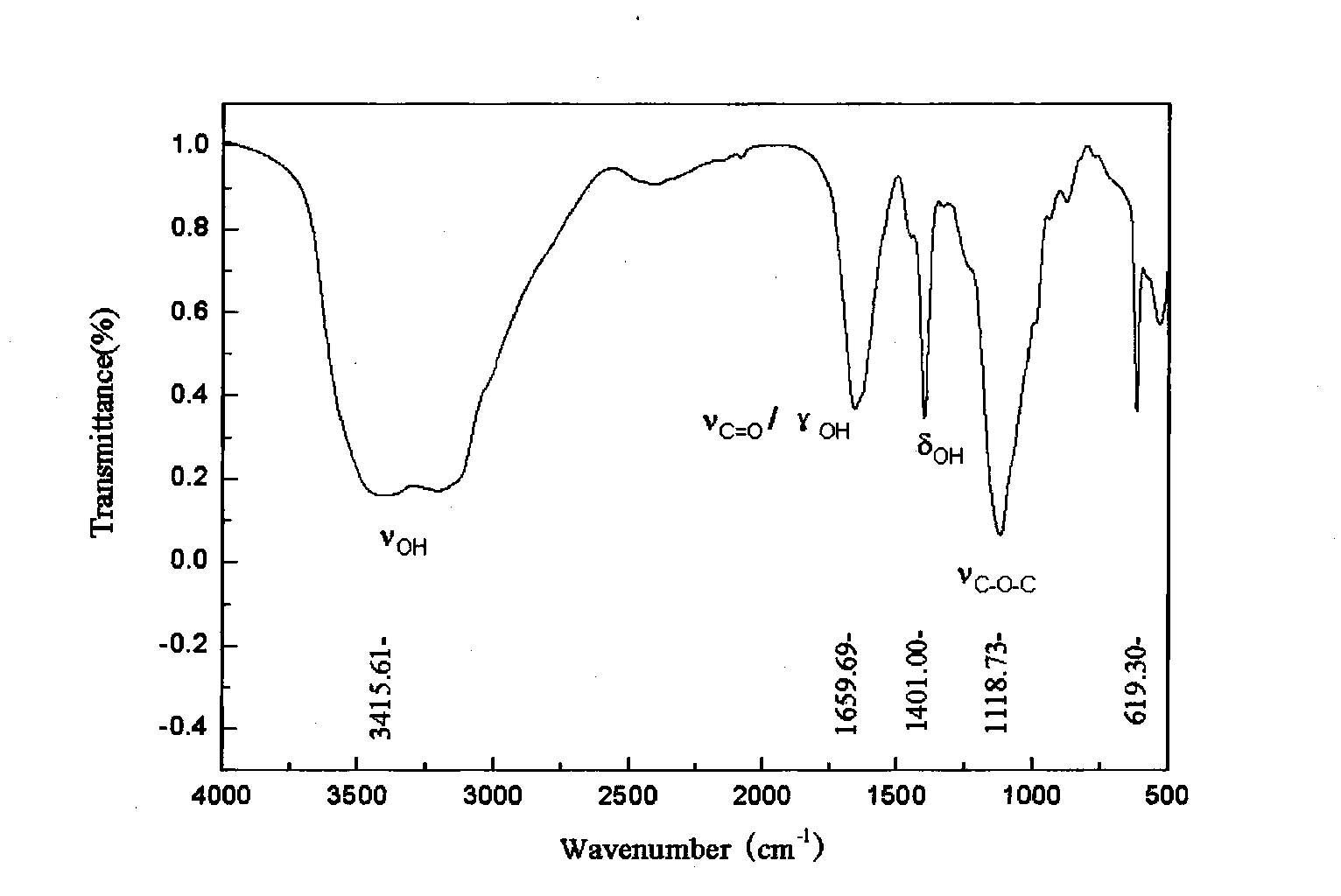
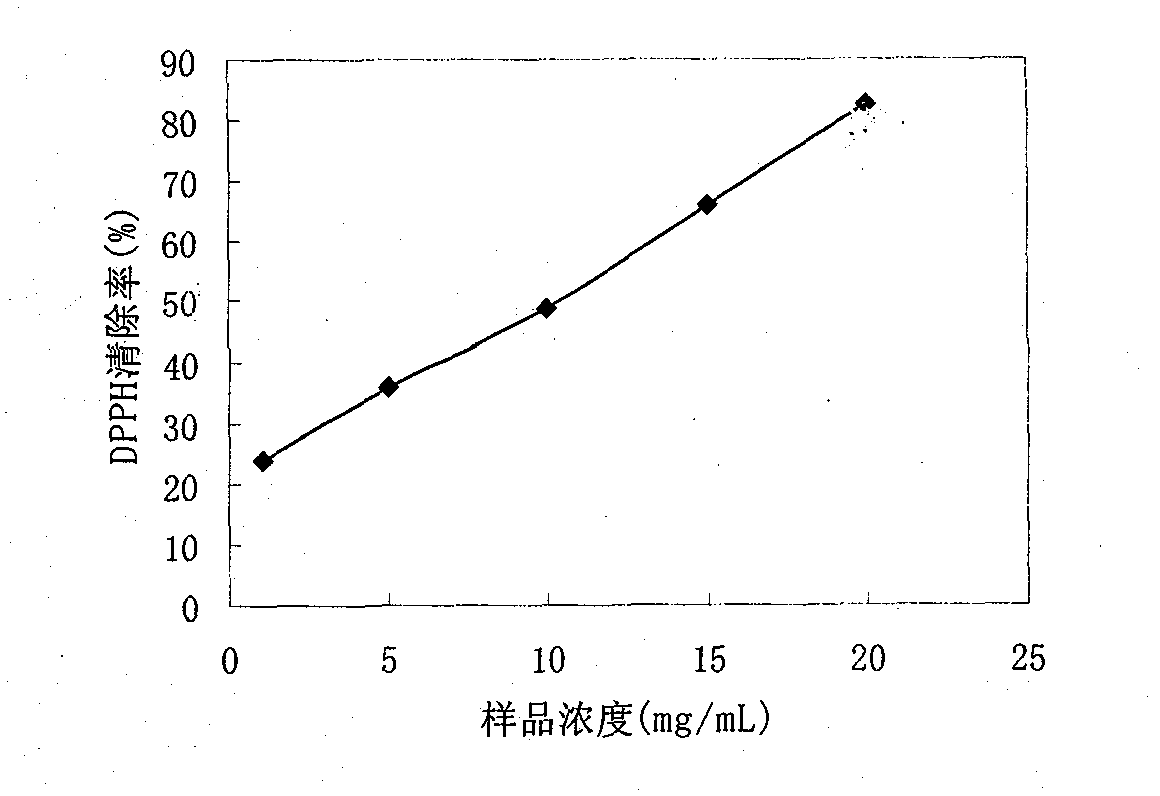
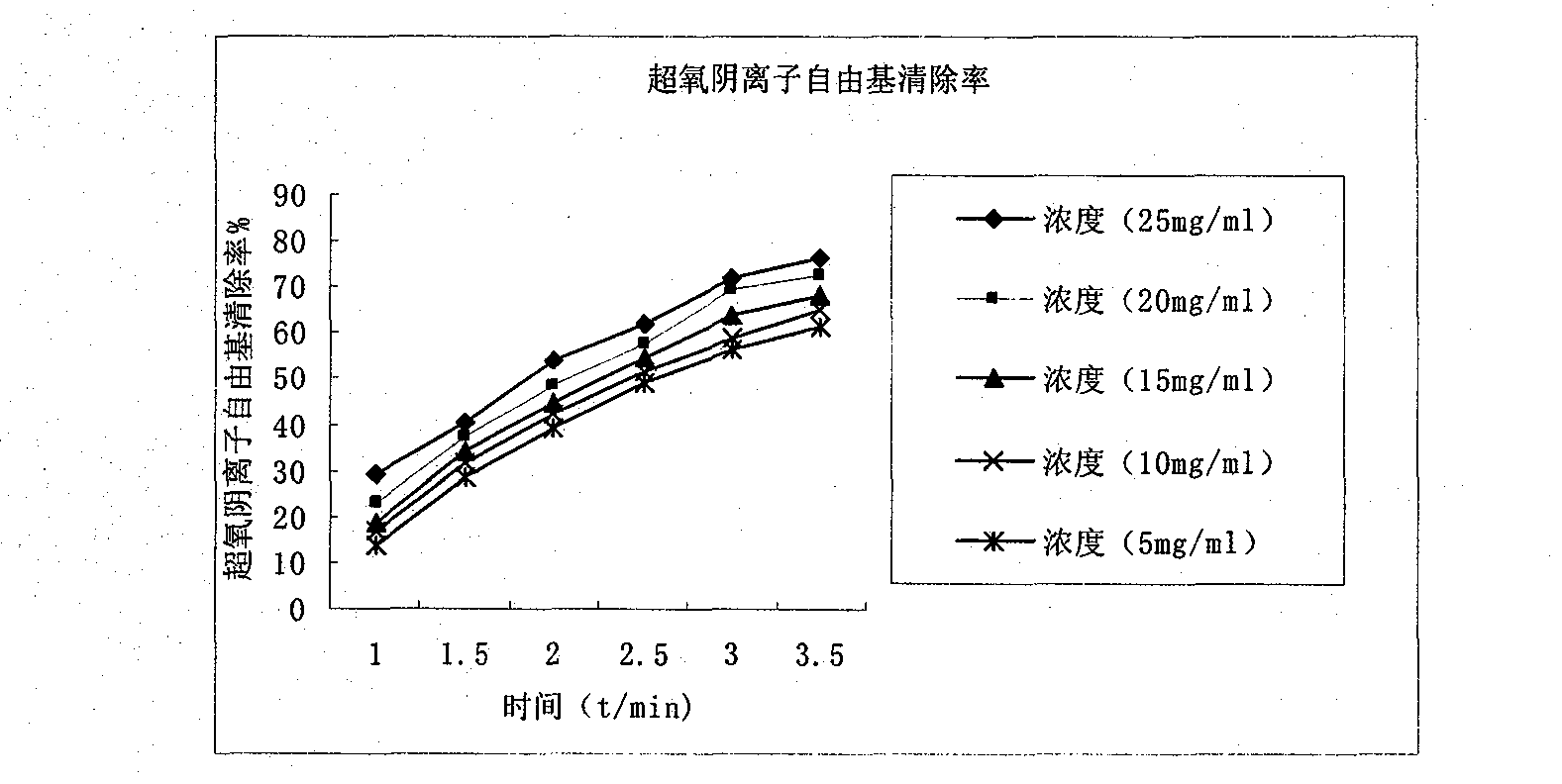
A preparation method of anti-oxidation Venerupis philippinarum enzymatic extract includes preparing sample by cleaning Venerupis philippinarum, shelling to obtain meat, homogenizing, and adding deionized water at the ratio of material to liquid of 1:2-1:3; and regulating pH to 6.8-7.3, adding papain 1500-2000 u / g, performing enzymolysis at 42-47 degrees for 2-4 h, inactivating at 90-95 degrees, centrifuging, and collecting supernatant to obtain enzymolysis product. The invention also discloses an application of enzymatic extract in oxidation resistance activity. Compared with prior art, the invention obtains a perfect process via control on pH value, enzyme amount, temperature and enzymolysis time, and has perfect effect of removing a plurality of free radicals.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Feed additive for spent hens
InactiveCN106819578AActivate egg productionRealize physiological regulationAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsFood additiveAnimal science
The invention relates to the technical field of poultry feeds, in particular to a feed additive for spent hens. Each part of feed additive is prepared from compounding the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3 to 5 parts of round cardamon seed, 1 to 1.5 parts of venerupis philippinarum leavening and 3 to 5 parts of lettuce enzymatic hydrolysate. The obtained feed additive is harmless to the hen bodies, and has the advantages of freeness from pollution and freeness from residues; when the feed additive is added into a spent hen feed in a weight ratio of 3 to 3.5 percent, physiological regulation of the hen bodies can be realized, and the internal secretion hormone level of the spent hens is increased, so that the laying performance of the hens is reactivated.
Owner:安徽省微科生物科技有限公司
Pickled cabbage venerupis philippinarum and making method thereof
InactiveCN102771833ARealize the standardization of raw materialsRealize the craftFood preparationCayenne pepperUmami
The invention discloses pickled cabbage venerupis philippinarum and a making method thereof. The pickled cabbage venerupis philippinarum is mainly made by proportioning 950-1050 parts of main material venerupis philippinarum, 245-255 parts of main material green pickled cabbage, 12-14 parts of dry cayenne pepper, 7-9 parts of chicken essence, 7-9 parts of table salt, 5-7 parts of white granulated sugar an 3-5 parts of Xianweiwang by weight. According to the invention, raw material standardization, product standardization and technology standardization of the pickled cabbage venerupis philippinarum can be realized.
Owner:SUZHOU HAODELAI FOOD
Nutrition-balanced aquaculture feed for giant salamanders
InactiveCN105995222AAvoid distractionReduce the risk of diseaseFood processingClimate change adaptationMillipedeWheat Brans
The invention discloses a nutrition-balanced aquaculture feed for giant salamanders. The nutrition-balanced aquaculture feed for the giant salamanders comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3-25 parts of water fleas, 40-70 parts of earthworms, 3-20 parts of grasshoppers, 1-15 parts of slugs, 10-35 parts of tubificidaes, 8-25 parts of river snails, 5-25 parts of bean worms, 5-25 parts of millipedes, 3-20 parts of venerupis philippinarum, 3-20 parts of breams, 5-20 parts of krills, 10-35 parts of silver carps, 8-25 parts of pond crayfishes, 1-20 parts of perches, 35-65 parts of hornwort, 5-25 parts of wheat bran, 10-40 parts of skimmed milk powder, 60-90 parts of peanut meal, 5-20 parts of pomelo peel, 5-20 parts of egg white, 1-10 parts of locust bean gum and 1-15 parts of gelatin. Animal bait components and modern aquaculture feed components are combined in the nutrition-balanced aquaculture feed for the giant salamanders, so that the feed is reduced in cost; moreover, the feed is comprehensive, rich and balanced in nutrition, so that the feed is capable of decreasing disease rates of the giant salamanders; thus, the feed is suitable for daily application of the giant salamanders. The egg white, the locust bean gum and the gelatin are mutually cooperated in the nutrition-balanced aquaculture feed for the giant salamanders, so that the components in the feed are mutually condensed into masses or blocks so as to facilitate food intake of the giant salamanders; moreover, pollution to the living environment of the giant salamanders is avoided for excessive dispersion of the feed is prevented.
Owner:XINCHANG LAOWU AGRI PROD SPECIALIZED COOP
Building house coating material
The invention discloses a building house coating material which is characterized by comprising the following substances in parts by weight: 19-20 parts of isocyanate, 17-26 parts of urea resin, 18-23 parts of polytetrafluoroethylene vegetable glue, 0.5-2.5 parts of a bactericide, 11-16 parts of organic silicon modified epoxy resin, 3-6 parts of n-hexane, 2-6 parts of isopropanol, 1-4 parts of benzoic acid, 5-10 parts of carbon black, 4-9 parts of clam shell powder, 3-9 parts of venerupis philippinarum shell powder, 1-2 parts of white clam shell powder and 3-7 parts of azodicarbonamide. The coating material disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects of being difficult to age, waterproof, fireproof, heatproof, soundproof and applicable to heat insulation of light partition walls and pipelines of high-rise buildings.
Owner:QINGDAO XIANGHAI ELECTRONICS
Efficient cultivation method for ruditapes philippinarum northern indigenous group in huanghai and bohai sea intertidal zone mud flat
ActiveCN112075366AImprove survival rateImprove adaptabilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaIntertidal zoneSeedling
The invention provides an efficient cultivation method for a ruditapes philippinarum northern indigenous group in the huanghai and bohai sea intertidal zone mud flat, and belongs to the technical field of aquaculture. The efficient cultivation method for the ruditapes philippinarum northern indigenous group in the huanghai and bohai sea intertidal zone mud flat comprises the following steps that ruditapes philippinarum seedlings are cultivated in a pond to the north of the northern Jiangsu coastal region of the China until large-size ruditapes philippinarum seedlings with the shell length notsmaller than 2.5 cm and the total wet weight not smaller than 2.5 g are obtained; in September to October every year, the large-size ruditapes philippinarum seedlings are evenly sown on the huanghai and bohai sea intertidal zone mud flat; and in the culture period, harmful organisms of the ruditapes philippinarum are intensively removed in spring and summer, culture indexes of seawater are regularly detected, and the ruditapes philippinarum is harvested after being cultured for 7-10 months. The large-size ruditapes philippinarum is bred in a huanghai and bohai sea intertidal zone, the breedingsurvival rate is greatly increased, the breeding period is shortened, the waste mud flat is recovered and utilized, and the breeding benefit is improved.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Biofertilizer for tea tree planting
The invention discloses a biofertilizer for tea tree planting. The biofertilizer contains the following substances in parts by weight: 25-30 parts of chicken manure, 15-20 parts of potassium chloride, 15-20 parts of ammonium nitrate, 9-11 parts of diammonium phosphate, 8-14 parts of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 3-5 parts of calcium nitrate, 2-8 parts of potassium ore powder, 1-4 parts of mountain flour, 3-6 parts of turf powder, 2-8 parts of trumpet shell powder, 3-5 parts of white clamshell powder, 11-20 parts of venerupis philippinarum shell powder, 15-20 parts of veronica linariifolia straw powder, 25-30 parts of mustard stalk powder, 25-30 parts of flax straw powder, 0.0001 part of plant activating enzyme, 0.001-0.002 part of trichoderma strains, 0.003 part of bacillus subtilis and 11-16 parts of potassium sulfate. The biofertilizer has the beneficial effects that the quality of tea can be improved, the yield of the tea is increased, meanwhile, diseases and pests are reduced, and the intensity for manual labor is lowered; the problems that the tea trees are in lack of nutrition and grow slowly are solved effectively; the applicable range is wide, the use is convenient, and the supplies are abundant; the cost is low, and the biofertilizer has the characteristics of environmental friendliness and recyclability.
Owner:QINGDAO LAOXIANG TEA PROD
Crop straw organic fertilizer for tea tree planting
InactiveCN103708883AReduce diseaseGood fertilizer effectFertilizer mixturesPhosphoric acidPlant disease
The invention discloses a crop straw organic fertilizer for tea tree planting. The crop straw organic fertilizer is characterized by containing the following substances in parts by weight: 20-25 parts of rice hull ash, 25-30 parts of chicken manure, 15-20 parts of potassium chloride, 15-20 parts of ammonium nitrate, 9-11 parts of diammonium phosphate, 8-14 parts of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 3-5 parts of calcium nitrate, 2-8 parts of potassium ore powder, 1-4 parts of rock flour, 3-6 parts of grass carbon powder, 2-8 parts of conch shell powder, 3-5 parts of white clamshell powder, 11-20 parts of venerupis philippinarum shell powder, 10-13 parts of talcum powder, 25-30 parts of urea and 15-20 parts of calcium superphosphate. The organic fertilizer disclosed by the invention contains inorganic nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and the like, and is also provided with a large number of microelements and organic matters, so that the fertilizer effect is remarkable, the tea disease can be alleviated, the cost is low, the economic benefit is high, and then, the application prospect is huge.
Owner:QINGDAO LAOXIANG TEA PROD
Instant ruditapes philippinarum leisure food processing process
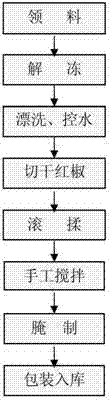
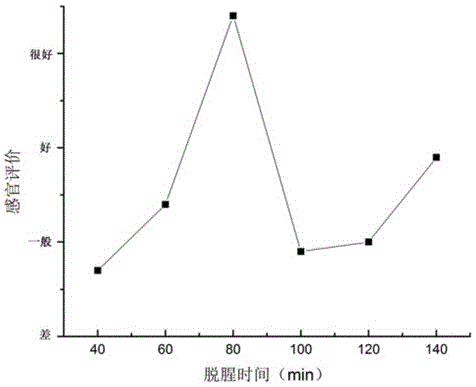
The invention discloses an instant ruditapes philippinarum leisure food processing process. The instant ruditapes philippinarum leisure food processing process comprises the following steps: temporarily culturing ruditapes philippinarum; opening shells and taking meat; deodorizing; pickling; protecting a colour; packaging and sterilizing; optimizing various steps; selecting a best optimized scheme through analysis and measurement. The prepared ruditapes philippinarum leisure food is loosened in texture and is not hard; clam meat is tasty, the flavour is better, and meanwhile, the chewiness and the taste are ensured.
Owner:FISHERIES RES INST OF FUJIAN
Buoyant raft culture method for Ruditapes philippinarum 'Zebra Clam 2'
ActiveCN112806288AReduce return rateHigh capture fragmentation rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRaft cultureZoology
The invention belongs to the technical field of shellfish culture, and particularly relates to a buoyant raft culture method for ruditapes philippinarum 'Zebra clam 2'. The buoyant raft culture method comprises the following steps of (1) selecting the ruditapes philippinarum with the specification of 240-400 ruditapes philippinarum / kg and the shell length of 2.2-2.9 cm as fries; and (2) putting the fries into a multi-layer net cage hung on a floating raft in a sea area to be bred, the number of layers of the multi-layer net cage is 18-25, and the density of the loaded fries is 150-200 fries per layer. According to the buoyant raft culture method, the ruditapes philippinarum is bred in a raft mode, and the specifications of the fries, the breeding density and the specifications of the multiple- layer the net cage are controlled, so that the problems that in the prior art, the ruditapes philippinarum breeding survival rate is low, the recapture rate is low, the capture breakage rate is high, and the ruditapes philippinarum is difficult to capture in winter are solved; the harvested Ruditapes philippinarum 'Zebra Clam 2' has the advantages of good quality, no sand, no near-shore heavy metal pollution, high fatness and the like.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Building wall decoration biological material
InactiveCN104058663AEnvironmental protection is goodImprove insulation effectSolid waste managementFiberThermal insulation
The invention discloses a building wall decoration biological material, which is characterized by including the following substances by weight: 35-45 parts of cement, 15-20 parts of Venerupis philippinarum shell powder, 14-20 parts of razor clam shell powder, 2-8 parts of quartz sand, 9-14 parts of potassium sulfate, 3-6 parts of anhydrous sodium sulfate, 1-4 parts of ammonia water, 9-15 parts of aluminum hydroxide, 4-6 parts of methyl fiber, 3-6 parts of maidenhair tree sawdust, 9-14 parts of ginkgo sawdust, 11-13 parts of fengqiao pine sawdust, 10-15 parts of a mixed solvent, and 3-9 parts of octanol. The building wall decoration biological material provided by the invention has the advantages of good environmental protection performance, no substance damaging human health, good thermal insulation performance, strong bonding performance, difficult shedding and cracking, long service life, and good sound insulation effect.
Owner:QINGDAO QIANXIANG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Communication base station protection coating material
InactiveCN104059423ALow thermal conductivityStable physical and chemical propertiesCoatingsCooking & bakingCalcite
The invention discloses a communication base station protection coating material, which comprises the following components by weight: 20-25 parts of plastic base material, 3-6 parts of oilseed straw powder, 1-3 parts of turnip straw powder, 11-14 parts of meerschaum, 1-3 parts of scallop shell powder, 2-6 parts of venerupis philippinarum, 3-6 parts of clam shell powder, 11-21 parts of ethane-acrylate, 14-16 parts of furfuryl alcohol resin, 10-13 parts of isocyanate, 10-15 parts of urea resin, 2-8 parts of calcite, 9-10 parts of pyridine, 3-6 parts of acetone and 10-18 parts of gypsum. The communication base station protection coating material has the beneficial effects of excellent insulation material, low thermal conductance coefficient, stable physical and chemical performances, no aging, high temperature resistance and no cracking, can be taken as a paint, and can be placed in a die for strickling, heating and baking to sheet materials.
Owner:QINGDAO XIANGHAI ELECTRONICS
Environment-friendly modified external wall thermal insulation material
The invention discloses an environment-friendly modified external wall thermal insulation material, which is characterized by including the following substances by weight: 30-40 parts of cement, 11-13 parts of oyster shell powder, 13-15 parts of Venerupis philippinarum powder, 2-6 parts of razor clam shell powder, 3-9 parts of a composite matrix material, 3-9 parts of an auxiliary agent, 3-9 parts of a binding agent, 12-14 parts of cedar sawdust, 3-6 parts of coffee sawdust, 2-9 parts of gardenia sawdust, 3-6 parts of polypropylene ester, 3-9 parts of oxidated polyethylene, 3-6 parts of hydrogen peroxide, 9-14 parts of zinc sulfate, 8-12 parts of magnesium sulfate, 3-6 parts of silver sulfate, and 3-8 parts of anatase titanium dioxide. The environment-friendly modified external wall thermal insulation material provided by the invention has the advantages of: high bonding strength, low coefficient of heat conductivity, long service life, and low production cost.
Owner:QINGDAO QIANXIANG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Clam-flavor rice mixing condiment and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104366415AEasy to eatKeep fresh fragranceFood preparationMaillard reactionAdditive ingredient
The invention aims to provide a clam-flavor rice mixing condiment and a preparation method thereof, mainly in order to improve nutritional ingredients and unique flavor of the condiment and make the condiment to be a nutrient source in food. In order to achieve the purpose, the method specifically includes: selecting one or several of fresh meretrix, venerupis philippinarum and mactra veneriformis, subjecting the fresh clams to pretreatment such as sand removal and cleaning, opening shells for scraping meat, cooking the meat, subjecting a little of the clam meat to freeze drying, and then beating the rest meat into clam pulp; freezing and drying a little of the pulp, subjecting the rest clam pulp to biological enzymolysis prior to standing, precipitation and solid-liquid separation, and subjecting enzymolysis supernatant to concentration and freeze drying; subjecting the precipitate to Maillard reaction, performing centrifugation to obtain supernatant, and subjecting the supernatant to concentration and freeze drying, wherein the two become main base materials for making the clam-flavor rice mixing condiment. Since the biological enzymolysis and Maillard combined method is adopted, nutritional components contained in the clams can be retained, and flavor of the clam-flavor rice mixing condiment can be improved. For preparing the clam-flavor rice mixing condiment, a certain amount of sodium glutamate, salt, disodium succinate, I+G and minced clam meat have to be added to be mixed into the clam-flavor rice mixing condiment.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Energy-saving environmental-friendly biological material
InactiveCN104230232AWith anti-corrosion functionImprove insulation effectSolid waste managementThermal insulationStearic acid
The invention discloses an energy-saving environment-friendly biological material. The energy-saving environment-friendly biological material is characterized by comprising the following substances in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of sepiolite, 10-11 parts of diatomite, 5-8 parts of trumpet shell powder, 3-8 parts of razor clam shell powder, 2-8 parts of Venerupis philippinarum shell powder, 1-4 parts of oak tree sawdust, 3-8 parts of willow sawdust, 1-4 parts of goldenrain tree sawdust, 3-8 parts of scapharca subcrenata shell powder, 2-9 parts of hollow glass microballon, 11-26 parts of glass fibers, 3-9 parts of mica powder, 12-31 parts of wood flour, 9-16 parts of modified polypropylene, 3-15 parts of poly(4-methyl-1-pentene), 8-16 parts of active calcium, 9-13 parts of stearic acid, 30-50 parts of cement, 3-16 parts of a thickening agent, 3-8 parts of an antimony-based nano compound environment-friendly flame retardant and 5-9 parts of triisocyanurate. The energy-saving environment-friendly biological material has good thermal insulation performance, long service life, no aging, a corrosion prevention function, good nonflammable performance, high social benefits and economic benefits.
Owner:黄艳
Feed additive capable of improving flesh quality and flavor of venerupis philippinarum and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106615995AMeeting nutritional needsFast growthClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyFeed additive
The invention discloses a feed additive capable of improving flesh quality and flavor of venerupis philippinarum and a preparation method thereof. The feed additive is prepared from the following raw materials: root of twelve stamen melastoma, calystegia hederacea, eucommia ulmoides, lucid ganoderma, marshy betony herb, bambooleaf fig herb, the fruit of Chinese magnoliavine, menyanthes trifoliate, liquorice, denseflower bulbophyllum herb, fructus piperis longi, Chinese yam, plantain herb, youngia japonica, polygonum bistorta, capsella bursa-pastoris, radix pseudostellariae and oriental grape roots. The feed additive disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the feed additive not only can meet the nutritional requirements of venerupis philippinarum, but also can obviously improve the flesh microstructures, is less in water pollution, and is capable of promoting emission of harmful wastes and improving the growth speed, fresh flesh yield, palatability and delicious degree of venerupis philippinarum; raw materials are natural products, so that the feed additive has the advantages of high safety, no drug residue and toxic and side effects, and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG NEW HOPE LIUHE GROUP
Beer venerupis philippinarum nutrition seasoning and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104222960ADelicious meatFull of nutritionFood preparationNutritive valuesPleurotus tuber-regium
The invention discloses a beer venerupis philippinarum nutrition seasoning and a preparation method thereof. The beer venerupis philippinarum nutrition seasoning is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5-6 parts of table salt, 7-8 parts of white vinegar, 7-9 parts of oyster sauce, 15-18 parts of venerupis philippinarum meat, 8-10 parts of pleurotus tuber-regium, 5-6 parts of mint cakes, 4-5 parts of egg tarts, 6-8 parts of peanut skin powder, 5-7 parts of plum powder, 9-11 parts of pig blood, 8-10 parts of tomato juice, 15-17 parts of beer, 18-20 parts of hollow cucumber sections, 1-2 parts of atractylodes macrocephala, 1-2 parts of ligusticum wallichii, 1-2 parts of ginsengs, 1-2 parts of agropyron cristatum, 1-2 parts of gynostemma pentaphylla, a suitable amount of water and 15-20 parts of a nutritional addition agent. According to the beer venerupis philippinarum nutrition seasoning, the venerupis philippinarum is adopted, so that the beer venerupis philippinarum nutrition seasoning has delicious taste, abundant nutrition and high protein content; the specific composition and the ratios of amino acids are reasonable and the nutritive value is high; and the added traditional Chinese medicines have the effects of tonifying qi and tonifying spleen, preventing phlegm from forming and stopping coughing and clearing away heat and toxic materials.
Owner:汪宗永
A kind of method for large-scale cultivation of philippine clam seedlings
ActiveCN105145413BLarge single-port seedling areaPromote growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAquatic productSeedling
The invention discloses a Ruditapesphilippinarum seedling large scale cultivation method, belongs to the aquatic product cultivation field, and the method comprises the following steps: reclamation area sand blowing and disinfection, parent selection and spawning induction, planktonic larva cultivation, adhesion juvenile mollusk cultivation, and sand seedling harvesting; by using the method, 50,000,000-120,000,000 Ruditapesphilippinarum sand seedlings (shell length 1.5-4mm) can be grown in each mu; the method can be applied to coastal area in our nation, thus realizing Ruditapesphilippinarum seedling large scale and industrialization production, and providing seedling guarantee for developing Ruditapesphilippinarum cultivation industry; the method is simple in operation and easy in promotion.
Owner:FISHERIES RES INST OF FUJIAN +2
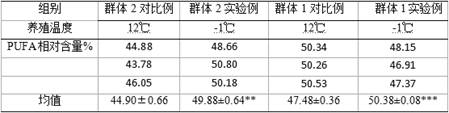
Method for increasing PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acid) relative content of soft parts of ruditapes philippinarum
ActiveCN113349118AIncrease contentImprove food valueClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaChlorella sp.Salinity
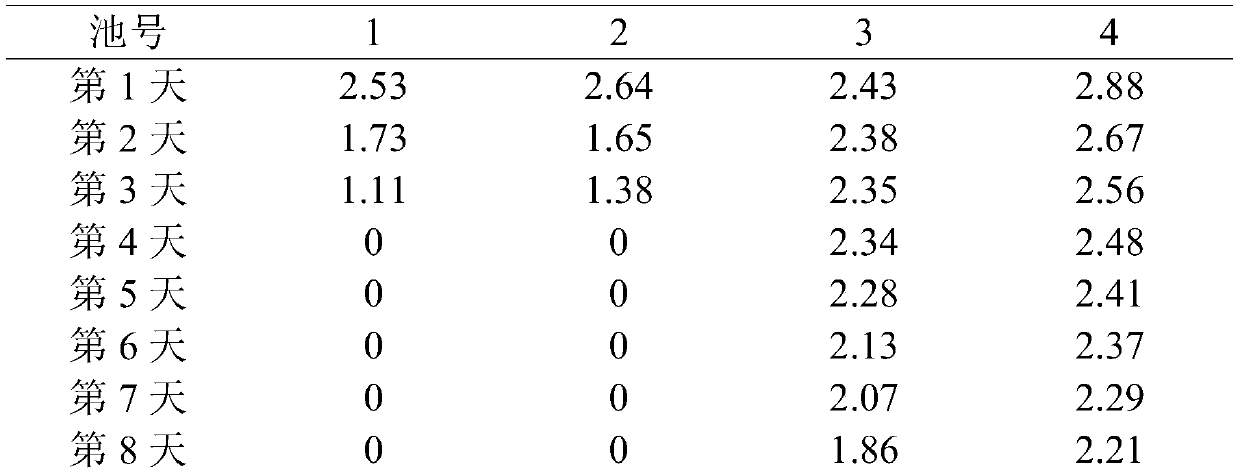
The invention discloses a method for increasing PUFA (polyunsaturated fatty acid) relative content of soft parts of ruditapes philippinarum. The method comprises the following steps: collecting ruditapes philippinarum with undamaged body surfaces and shell length of 2.5-4.5 cm, transferring the ruditapes philippinarum into a room for room-temperature temporary rearing in temporary rearing seawater with salinity being 26-32 and pH value being 7.8-8.3, changing the total amount of water once every day in the temporary rearing period, feeding twice every day, performing continuous oxygenating, setting the culture capacity to be 20-30 kg / m<3>, after one week of temporary rearing, putting the ruditapes philippinarum into a temperature-controllable water circulation tank, carrying out gradient low-temperature treatment on the ruditapes philippinarum, reducing the culture temperature at the speed of 2-3 DEG C / d by taking the seawater temperature at room temperature as the initial temperature, when the water body temperature is 4 DEG C or above, feeding the ruditapes philippinarum with unicellular algae or chlorella algae paste every day with the feeding amount of 80-120 g / m<3>, and meanwhile, changing the total amount of water once every day; when the temperature of the water body is reduced to 4 DEG C or below, stopping feeding, meanwhile, performing continuous oxygenating, picking out dead individuals in time, changing water once every 3-5 days, when the temperature of the water body is reduced to 0 DEG C, stopping cooling, maintaining the temperature of 0 DEG C for one week or more, and changing water once a week.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
A kind of artificial seedling raising method of philippine clams in high-temperature season in high-salt sea area
ActiveCN106900614BGuaranteed normal abnormal attachmentRealize normal artificial breedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFresh waterSalinity
The invention relates to a method for achieving industrial breeding of ruditapes philippinarum by adjusting the salinity of water under a high temperature condition of a high-salt sea area. Particularly, the invention provides a method for adjusting the salinity of water into a certain range by adding fresh water or seawater separately in a spawning incubation phase, a floating stage and an attachment stage of the ruditapes philippinarum, thereby achieving smooth abnormal attachment of planktonic larvae and effectively promoting fast growth of juvenile mollusk.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-efficiency culture method of Philippine clams in the intertidal tidal flats of the Yellow and Bohai Seas
ActiveCN112075366BImprove survival rateImprove adaptabilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTidal flatZoology
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Green self-regulation energy-conservation paint
InactiveCN104059537ALow water absorptionThe construction method is simple and fastFireproof paintsConjugated diene hydrocarbon coatingsThermal insulationOyster
The invention discloses a green self-regulation energy-conservation paint, which is characterized by comprising the following components by weight: 3-5 parts of redispersible latex powder, 14-19 parts of mactra veneriformis shell powder, 6-11 parts of oyster shell powder, 9-11 parts of venerupis philippinarum shell powder, 1-6 parts of mineral insulation material, 5-9 parts of film forming auxiliary agent, 1-2 parts of cosolvent, 3-6 parts of camellia wood chip, 2-5 parts of fringed hibiscus wood chip, 3-6 parts of Chinese rose wood chip, 3-5 parts of perlite, 11-16 parts of polyisoprene rubber, 14-16 parts of alcohol-soluble resin, 9-13 parts of resorcinol, 3-6 parts of paraformaldehyde and 9-13 parts of acid anhydrides. The green self-regulation energy-conservation paint has the beneficial effects of heat insulation, fire resistance, high temperature resistance, aging resistance, less water absorption; simple and fast construction method with manual plasterer, and good heat insulation effect; can be widely used as a thermal insulation layer for any building such as metope and roof.
Owner:QINGDAO XIANGHAI ELECTRONICS
A strain of marine cryobacteria and method for preparing flocculant by using it
ActiveCN107619802BImprove flocculation abilityAccelerated settlementBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBiology
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to psychrobacter aquimaris and a method for preparing a flocculating agent by the psychrobacter aquimaris. The psychrobacter aquimaris Psychrobacter sp. GHF2 is separated and purified from sludge liquor spit by ruditapes philippinarum, a strain of the psychrobacter aquimaris is subjected to enlarging cultivation to prepare strain liquid, the strain liquid is fermented and cultivated to prepare fermented liquid, a flocculating carrier is added into the fermented liquid in a fermentation late period, and the flocculating carrier and added ethyl alcohol are mutually reinforced, so that extracellular polysaccharide in the fermented liquid is safely settled. The extracellular polysaccharide secreted by the screened psychrobacter aquimaris Psychrobacter sp. GHF2 has strong flocculating effects, the flocculating carrier is added in the fermentation late period, so that bacterial cells are clumped on the flocculating carrier, settling of the extracellular polysaccharide is promoted, use of the ethyl alcohol is reduced, and the obtained flocculating agent is strong in flocculating capacity and stable in performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com