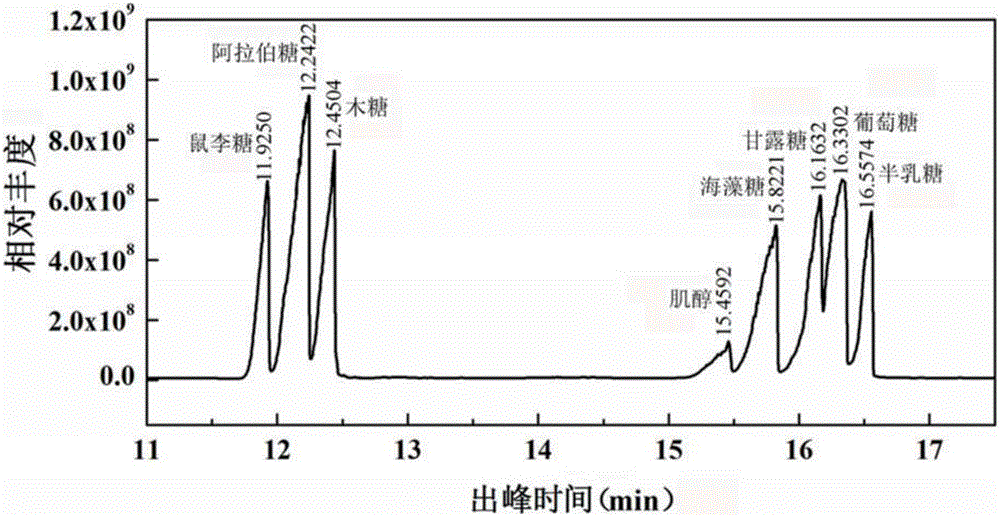
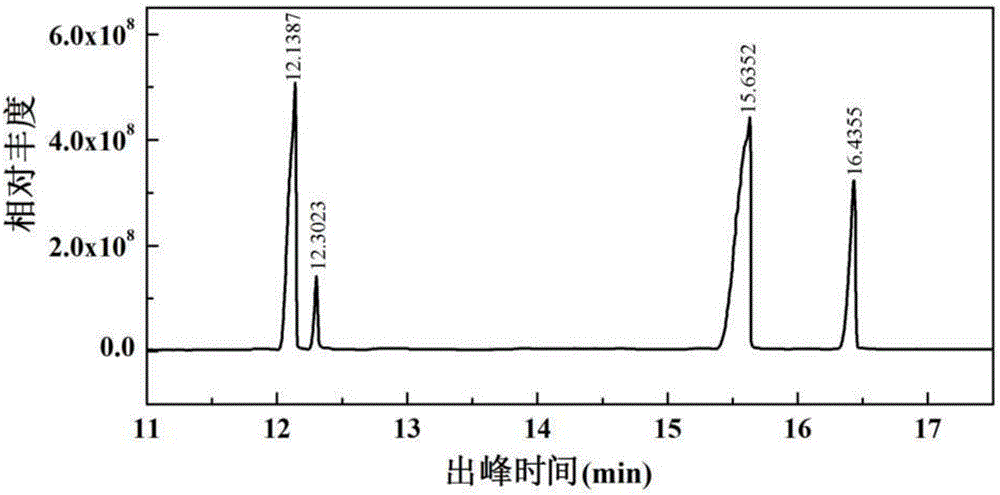
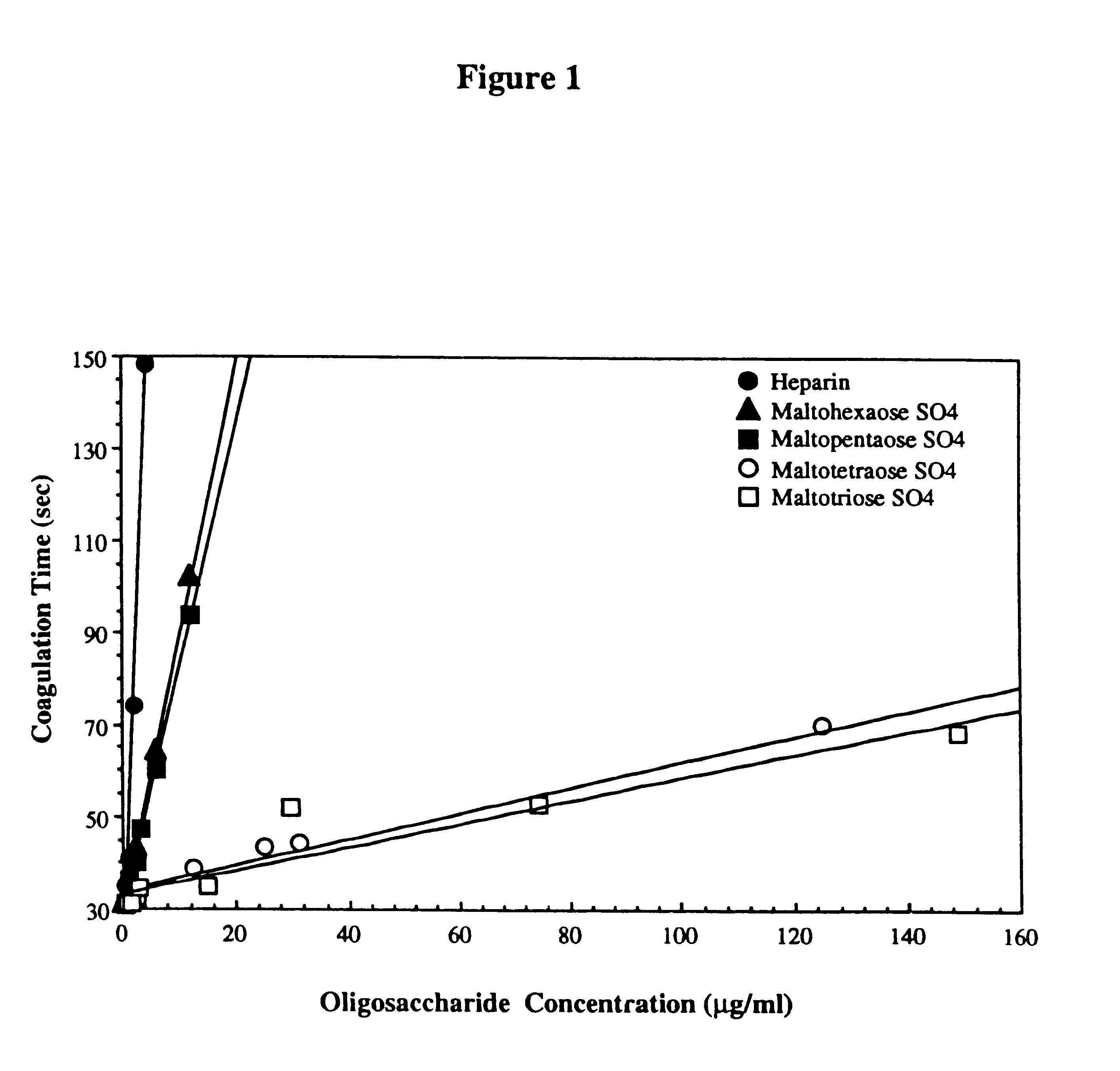
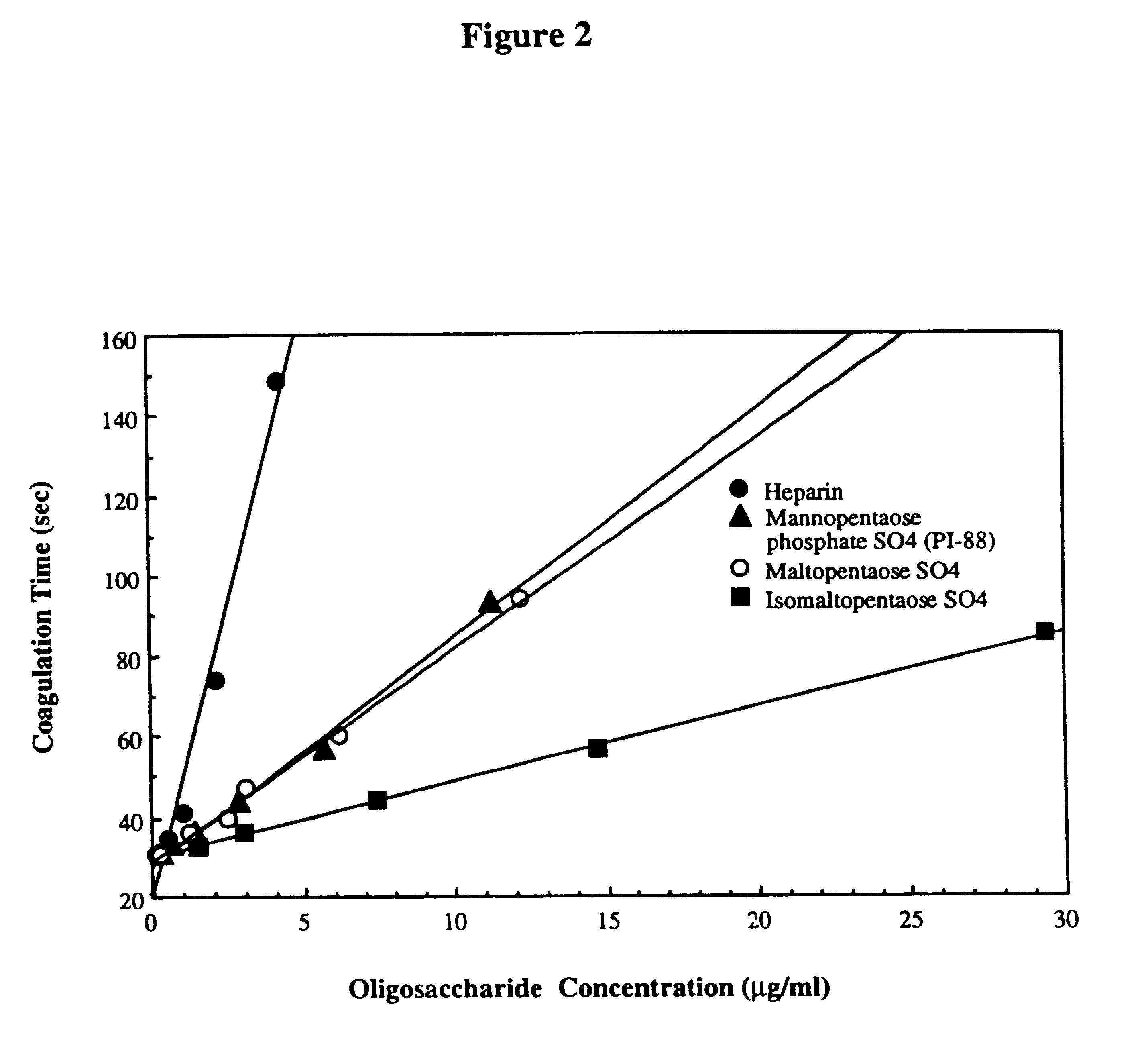
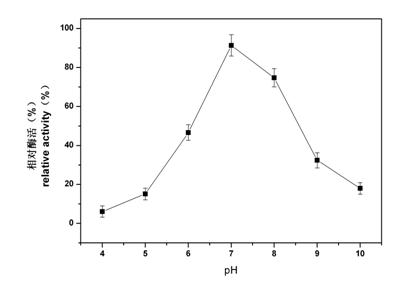
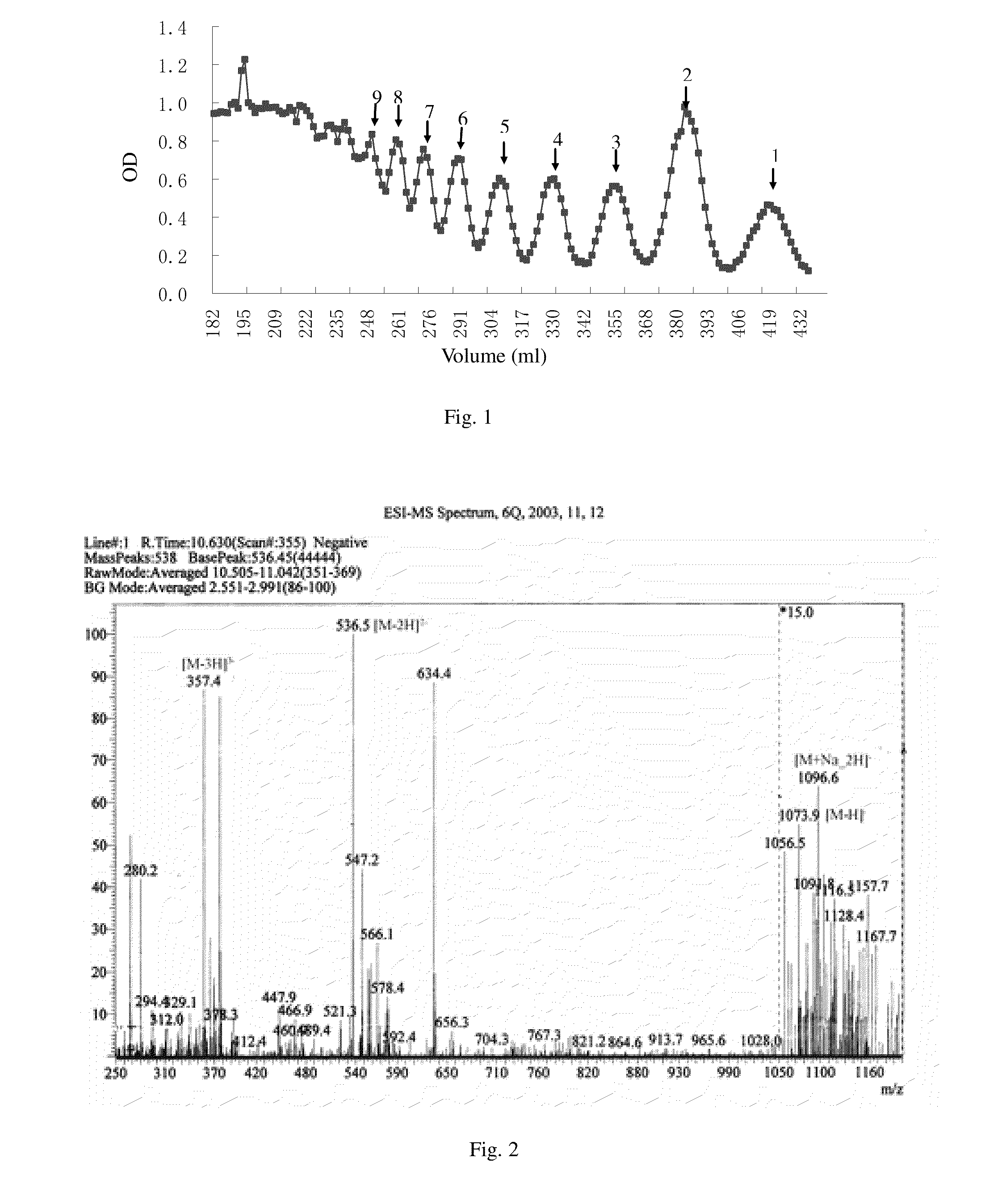
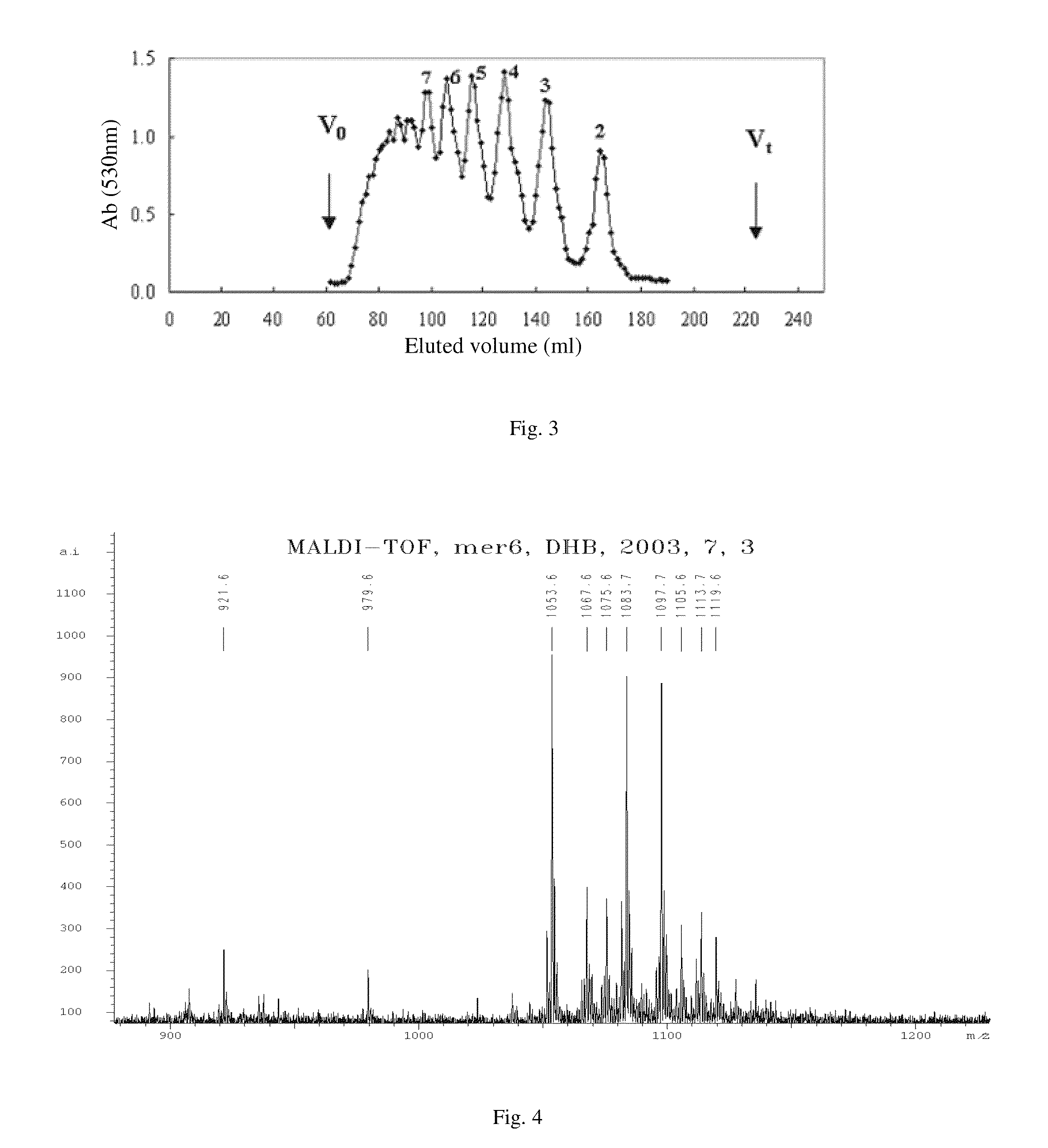
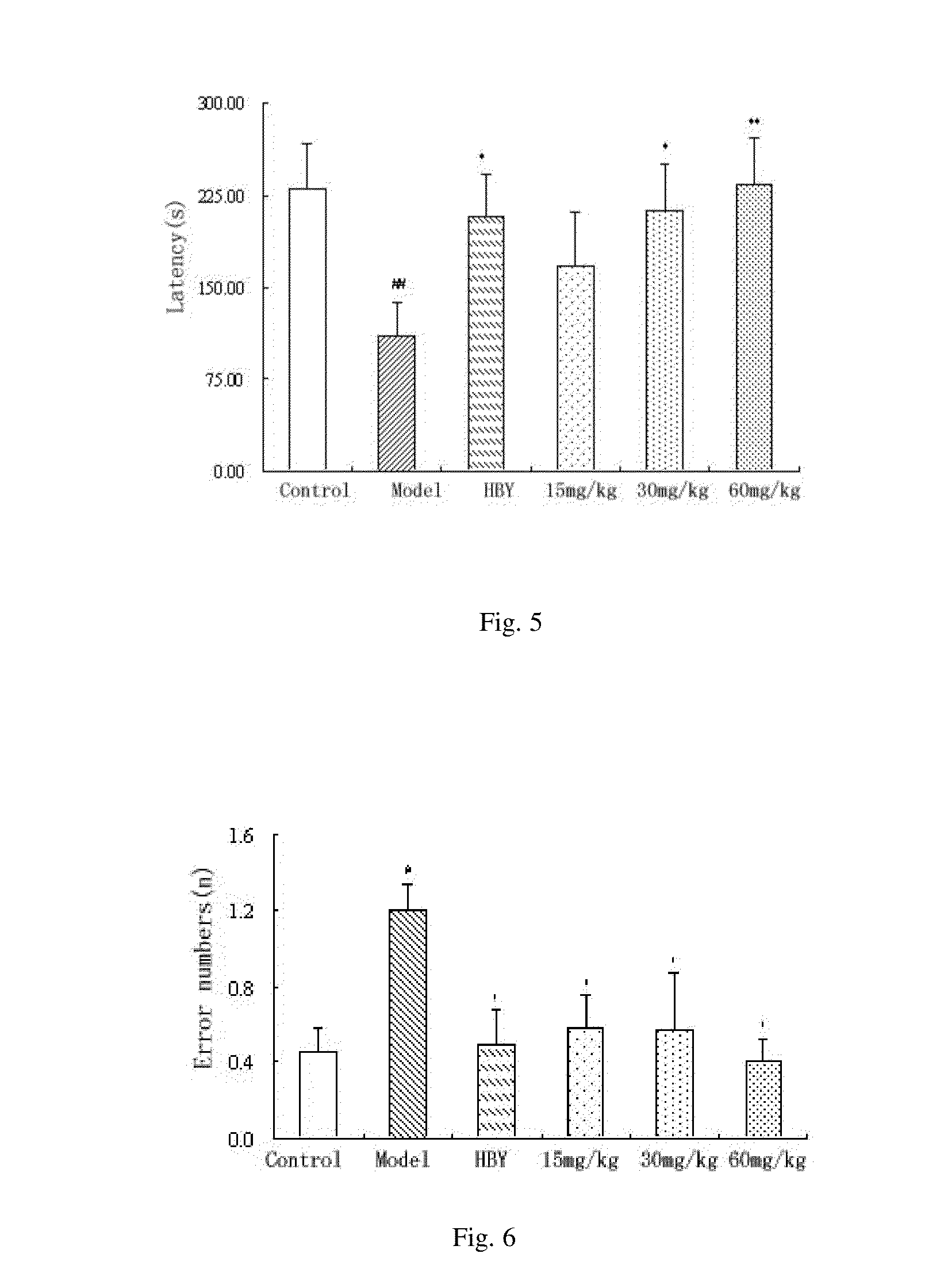
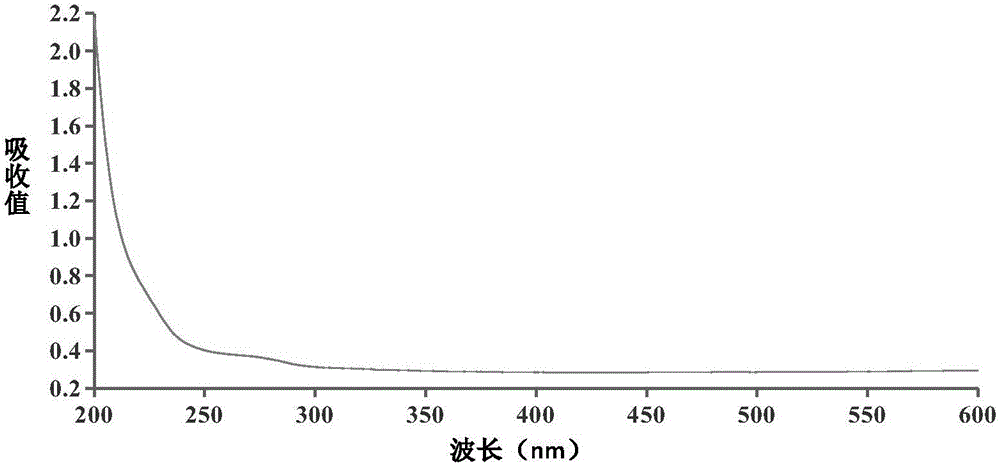
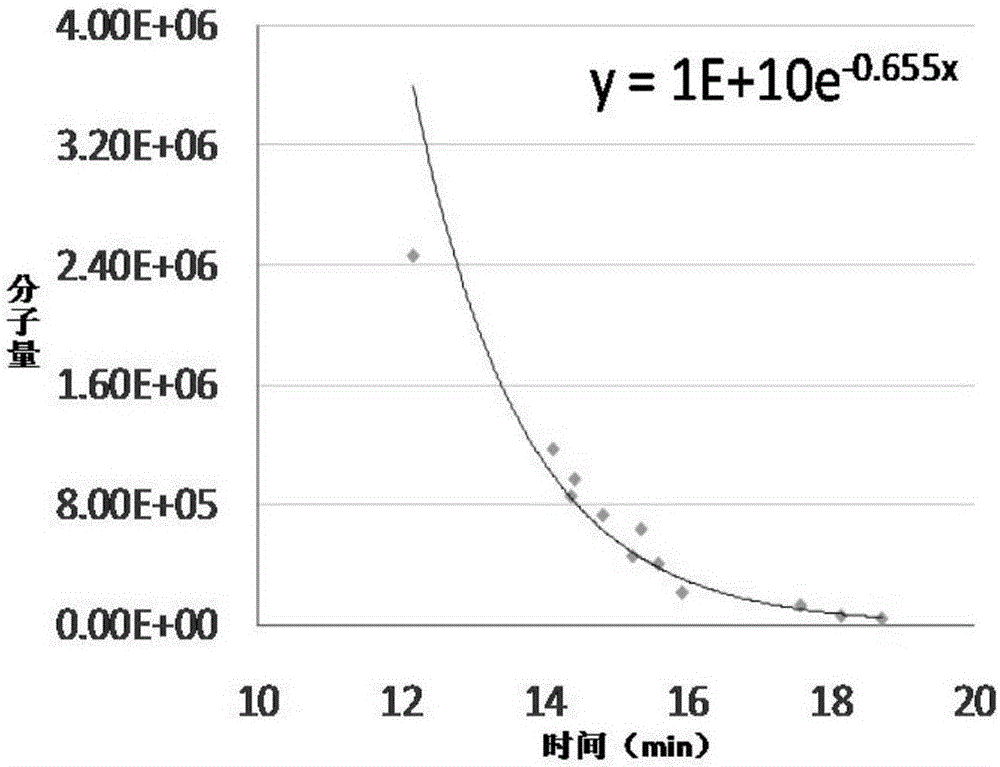
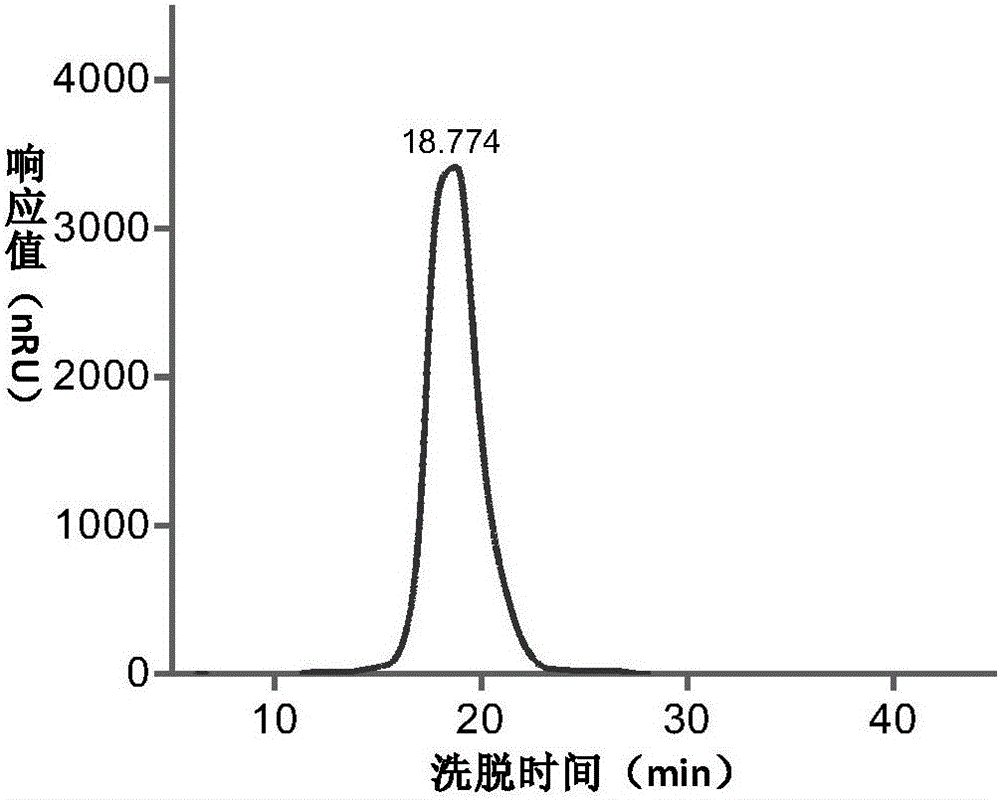
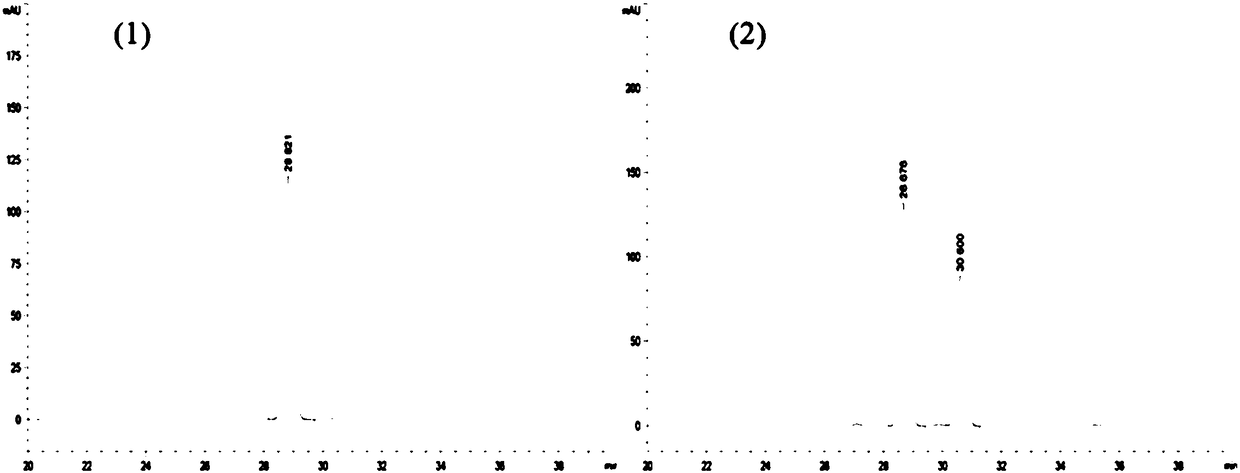
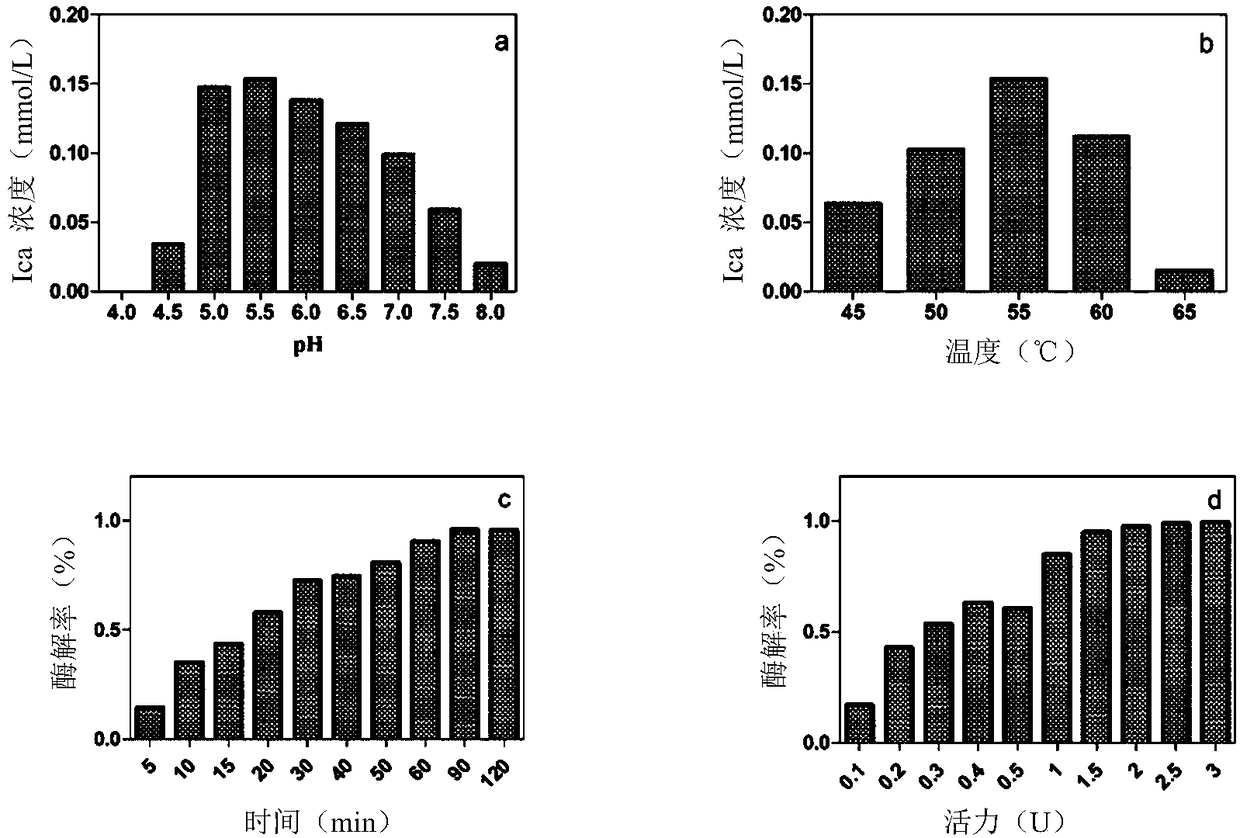
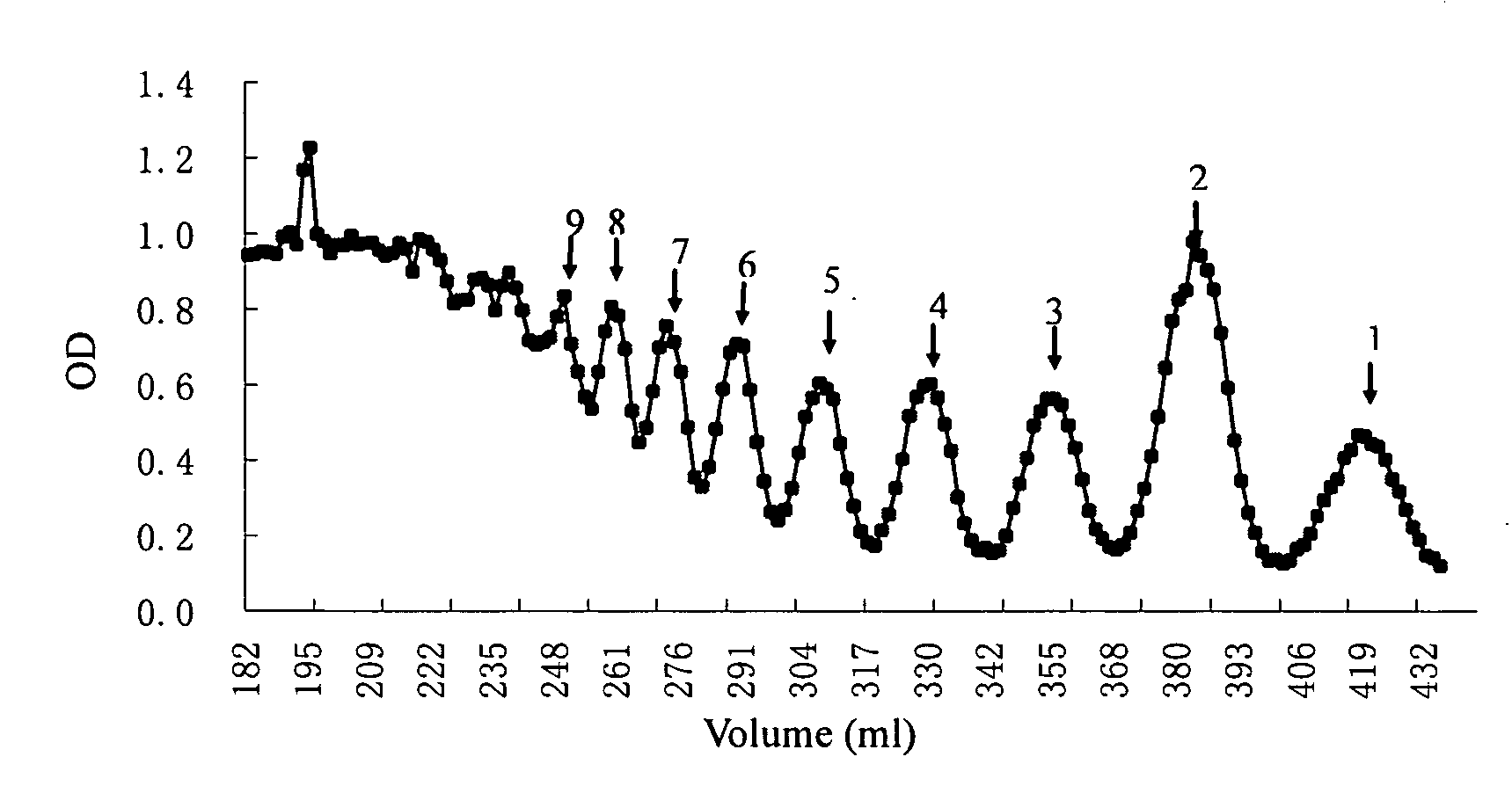
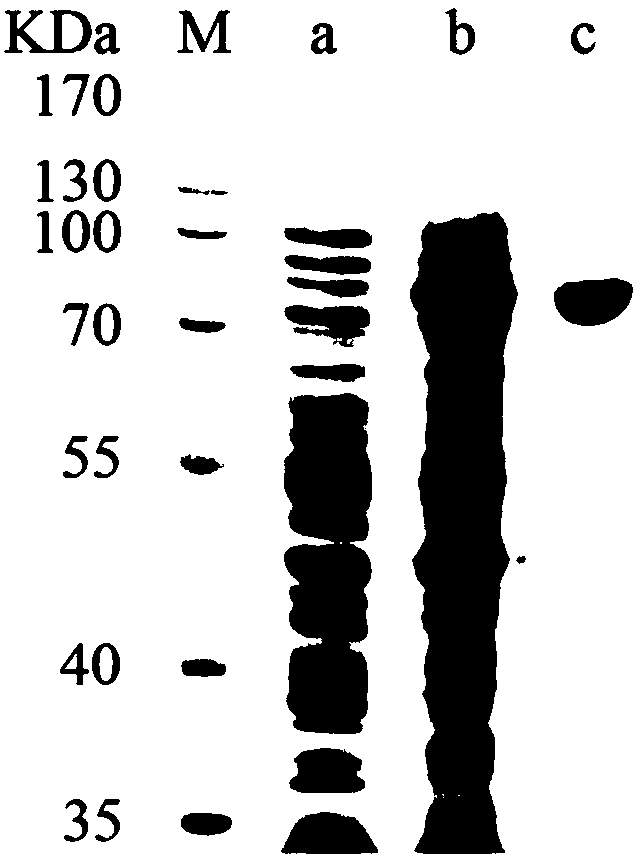Patents
Literature
368 results about "Carbohydrate Linkage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, a glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate. Formation of ethyl glucoside: Glucose and ethanol combine to form ethyl glucoside and water.
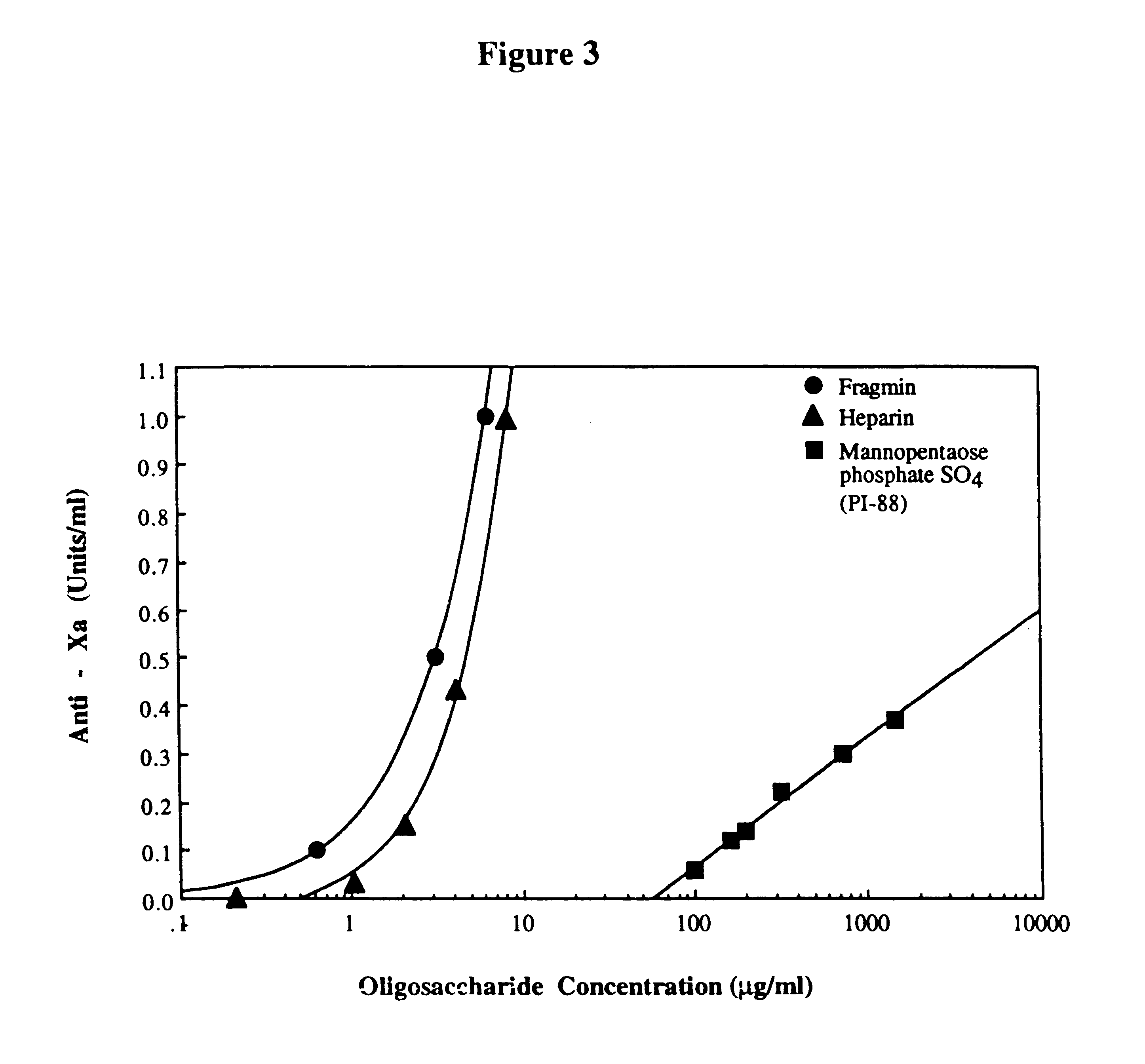
Preparation and use of sulfated oligosaccharides
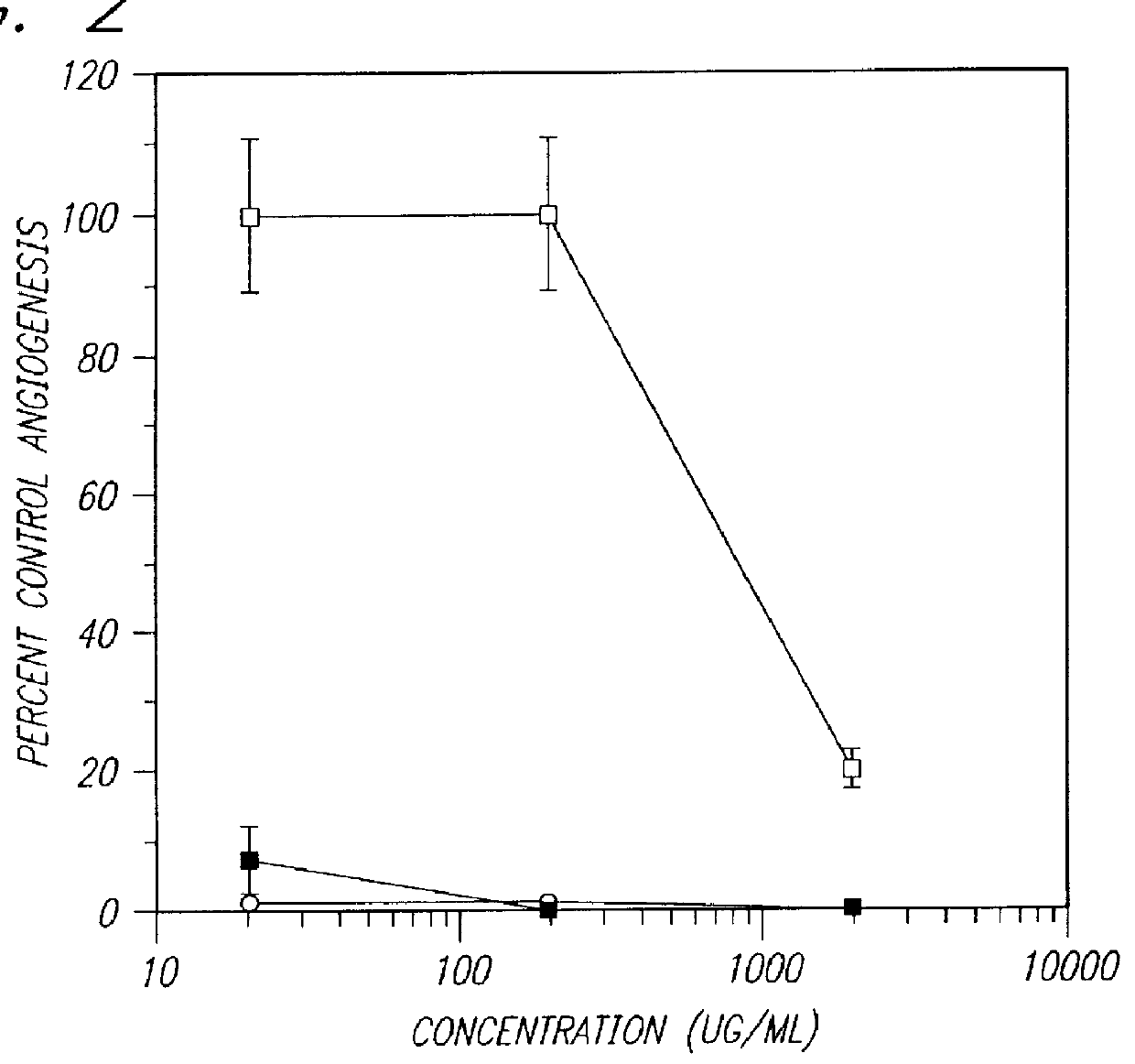
PCT No. PCT / AU96 / 00238 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 28, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 28, 1997 PCT Filed Apr. 24, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 33726 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 31, 1996Sulfated oligosaccharides, wherein the oligosaccharide has the general formula I:R1-(Rx)n-R2(I)wherein R1 and R2 and each Rx represents a monosaccharide unit, all of which may be the same or different, adjacent monosaccharide units being linked by 1->2, 1->3, 1->4 and / or 1->6 glycosidic bonds and n is an integer of from 1 to 6, and use thereof as anti-angiogenic, anti-metastatic and / or anti-inflammatory agents.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
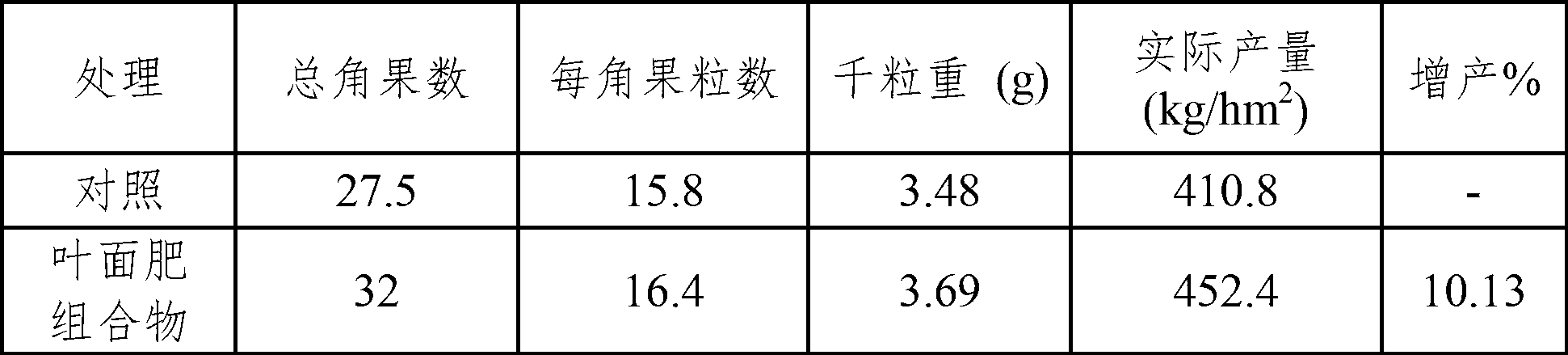
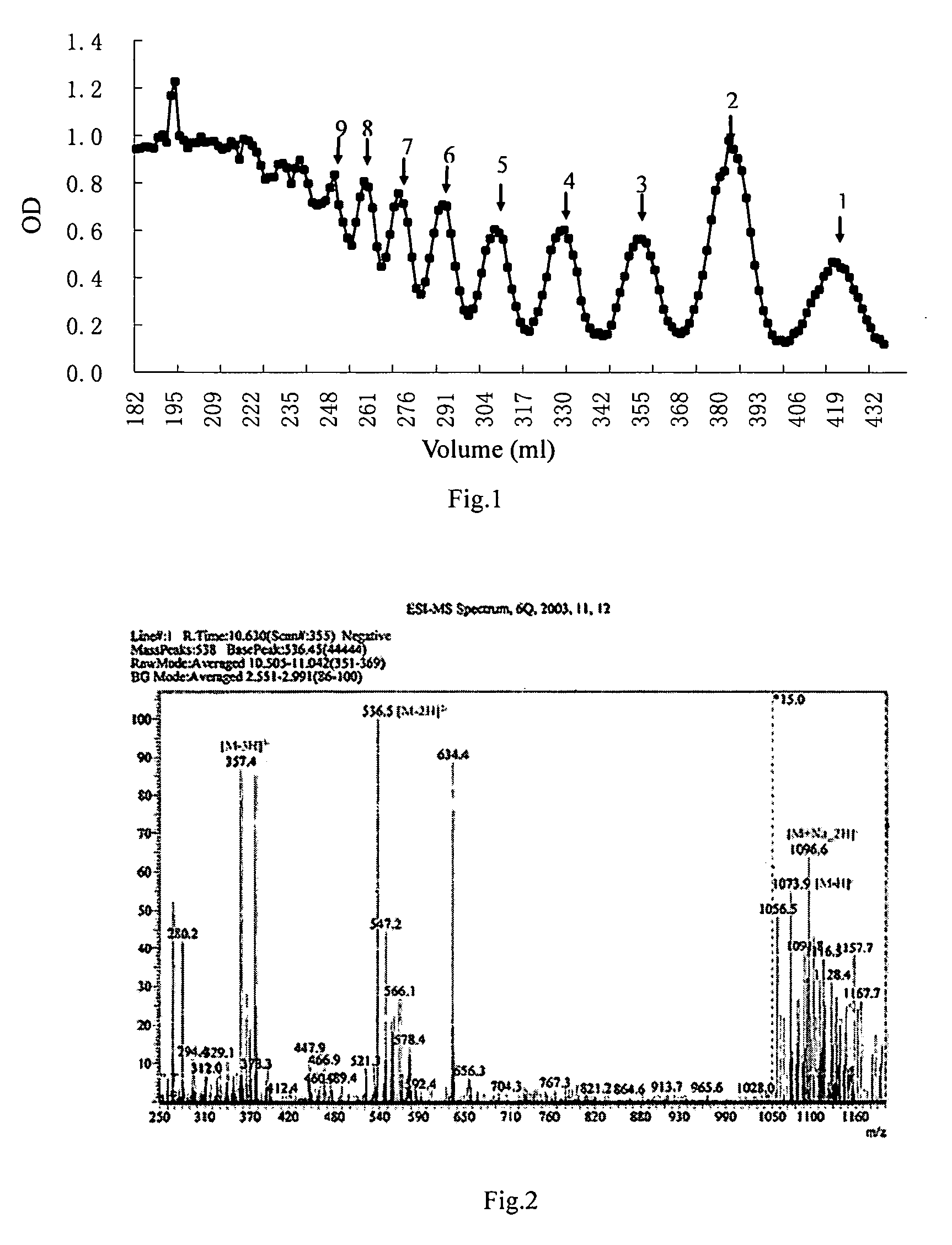
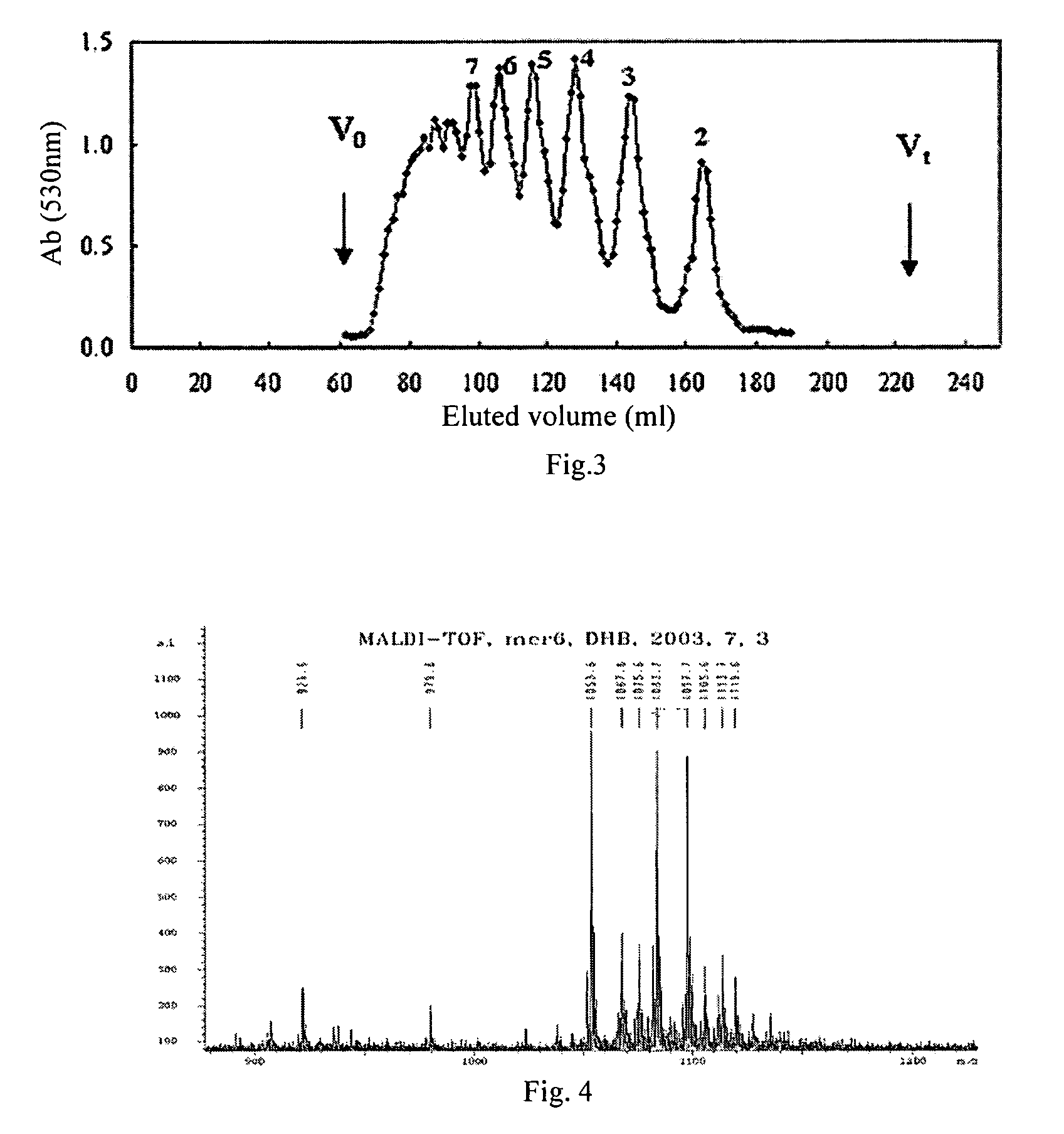
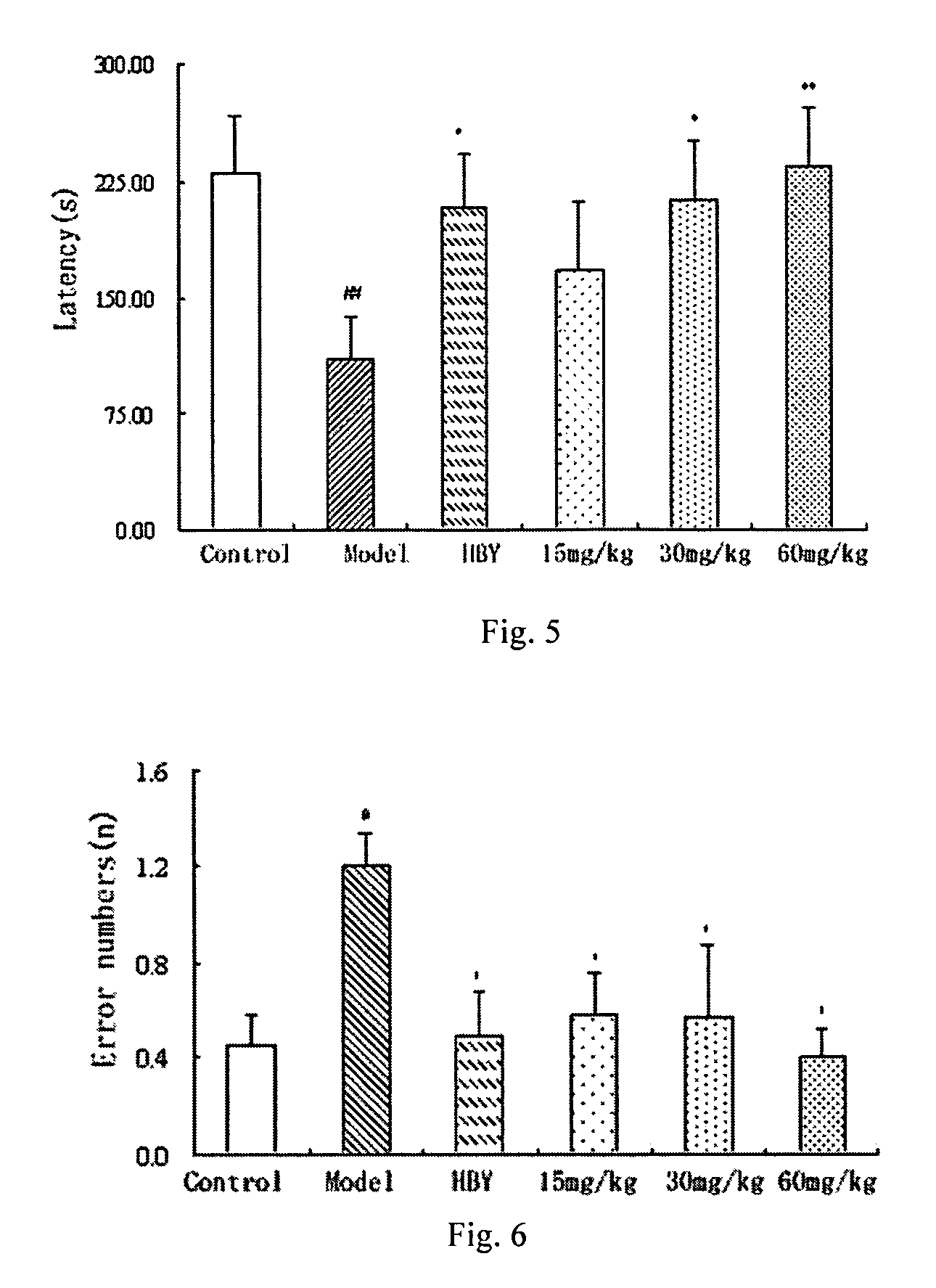
Leaf fertilizer composition comprising sodium alginate oligosaccharide and application of leaf fertilizer composition
ActiveCN103011968AWide variety of sourcesLow priceOrganic fertilisersLiquid fertilisersManganeseUronic acid
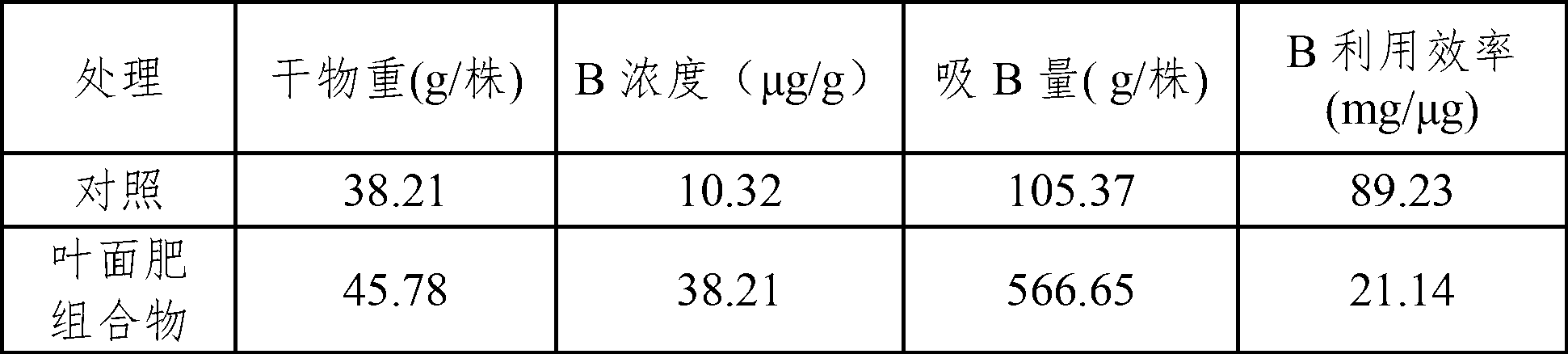
The invention discloses a leaf fertilizer composition comprising sodium alginate oligosaccharide, which is characterized in that the composition comprises sodium alginate oligosaccharide, amino acid and microelements that can promote plant growth significantly, wherein sodium alginate oligosaccharide is also known as sodium alginate, sea-tangle glue and algin, is natural polysaccharide carbohydrate extracted from sea tangle, and is a copolymer comprising a-L-mannuronic acid (M), b-D-guluronic acid (G) connected with a-L-mannuronic acid (M) by 1,4-glycosidic bond, and different GGGMMM fragments; a molecular formula is (C6H7O6Na)n; the degree of polymerization is 2-10; the uronic acid constitution M / G is equal to 7:3; the uronic acid content is greater than 90%, and is 2-3% of the total content; the content of a microelement leaf fertilizer is 2-20%; and the microelement leaf fertilizer comprises at least two of sulfur, boron, ferrum, manganese, copper, zinc and molybdenum. The composition is mainly applicable to industrial crops, fruit and vegetable crops, grain crops, economic trees, flowers, lawns and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Algin oligosaccharides and the derivatives thereof as well as the manufacture and the use of the same
The present invention provides an alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives with the degree of polymerization ranging from 2 to 22. The alginate oligosaccharide is composed of β-D-mannuronic acid linked by 1,4 glycosidic bonds. The derivatives with the reduced terminal in position 1 of carboxyl radical can be prepared by oxidative degradation. The present invention also provides a process for preparing the alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives, which includes the procedures that an alginate solution is reacted for 2 to 6 h in an autoclave at pH 2-6 and the temperature of 100-120° C., and pH is adjusted to 7 after the reaction is stopped, after which the resultant oligosaccharide is oxidized in the presence of an oxidant to obtain an oxidative degradation product. The alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives of the invention can be used in the manufacture of a medicament for the prophylaxis and treatment of AD and diabetes.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Algin oligose and derivative thereof and producing method and use thereof
ActiveCN100508985CAvoid difficultiesOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGlycosideDiabetes mellitus
The present invention provides algin oligosaccharides having polymerized degree of 2-22 and the derivatives thereof, such algin oligosaccharides are made of mannuronic acid bonded by [proportional to]-1,4 glycosidic bond. The derivatives which the reduced terminal in position-1 is carboxyl radical can be obtained by oxidation. The invention also provides the manufacture of algin oligosaccharides and the derivatives thereof, which includes the alginate solution in water reacts in the reactor under the condition of high press, 100-120 DEG C, pH2-6, for 2-6 hours, after the reaction completed, its pH value was adjusted to 7. The result oligosaccharides are oxidated in presence of the oxidant, and then produces the oxidated products. The algin oligosaccharides and the derivatives thereof of the invention can be used in the manufacture of medicaments for preventing Alzheimer's dementia and diabetes.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Extraction process and application of peach gum polysaccharide
ActiveCN105061617AHigh purityThe preparation method is fineMetabolism disorderGlucose degradationPrecipitation
The invention discloses an extraction process and application of peach gum polysaccharide (PGPSD). The process includes: water extraction and alcohol precipitation, protein removal by a Sevage reagent, dialysis, passing of a column with DEAE cellulose as the filler and other steps, thus obtaining finer polysaccharide (PGPSD). The PGPSD can be dissolved in water at room temperature, and is formed by connection of arabinose, mannose and galactose through a glycosidic bond. The peach gum polysaccharide (PGPSD) prepared by the process provided by the invention can reinforce the expression of insulin related transcription factors and glucose degradation key enzyme, has no toxicity to mice, and can significantly lower the blood glucose of diabetic mice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Preparation method for soluble dietary fiber with apple pomace as raw material
The invention discloses a preparation method for a soluble dietary fiber with apple pomace as a raw material. According to the method, an expanding method and an enzymatic hydrolysis method are combined. By the application of an expansion process, the structures of cellulose molecules become loose, and partial glycosidic bonds are broken, so that partial insoluble dietary fibers are transformed into soluble ones. After separation of the insoluble dietary fibers and the soluble dietary fibers, the expanded insoluble dietary fibers, which have the loose molecular structures, are hydrolyzed by utilizing a cellulase; and then the insoluble dietary fibers are further transformed into soluble dietary fibers. According to the invention, the modification of the insoluble dietary fibers in the apple pomace enables the insoluble dietary fibers to become high-quality soluble dietary fibers, so that an achievement rate of the soluble dietary fibers can substantially be enhanced as well as water binding capacity and expansibility of dietary fibers can also be improved. According to the test, the achieve rate of the soluble dietary fibers can reach 21.2%; the water binding capacity and expansibility can be enhanced by 110.3% and 7.0% respectively.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
Sulfated oligosaccharides having anticoagulant/antithrombotic activity
A method for the anticoagulant and / or antithrombotic treatment of a human or other warm-blooded animal patient in need of such treatment, comprises administration to the patient of an effective amount of at least one sulfated oligosaccharide, wherein the oligosaccharide has the general formula I:wherein R1 and R2 and each Rx represents a monosaccharide unit, all of which may be the same or different, adjacent monosaccharide units being linked by 1->2, 1->3, 1->4 and / or 1->6 glycosidic bonds andn is an integer of from 1 to 6.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Microorganisms or/and biological enzyme extracting method for plant anthocyanin
InactiveCN101760497AEfficient use ofMake full use ofOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyIntestinal microorganisms
The invention relates to a Microorganisms or / and biological enzyme extracting method for plant anthocyanin, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: classifying plants containing anthocyanin for smashing, adsorbing water, freezing the plants, heating the plants for thawing, pressing the plants, filtering for making juice, cracking and degrading the anthocyanin by the microorganisms or / and the biological enzyme cracking anthocyanin glycosidic bond, utilizing an anion active agent for precipitation reaction, degrading the precipitate by the microorganisms, and carrying out precipitation separation and evaporation concentration. Cation anthocyanin with the real content of more than 95%, namely color primitive but not the anthocyanin can be obtained by the technology of the invention. The cation anthocyanin made by the invention does not need human intestinal microorganisms for degrading, and is directly adsorbed and utilizedby a human body or directly goes into human blood. The medical care value of the plant anthocyanin is much higher than that of the anthocyanin.
Owner:安徽天紫花青素科技有限公司
Process for the preparation of homopolysaccharides
ActiveUS20110151517A1High specific viscosityReduce contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMembranesHomopolysaccharideGlycoside formation
A process for the preparation of aqueous solutions of glucans having a β-1,3-glycosidically-linked main chain and side groups having a β-1,6-glycosidic bond by fermentation of fungal strains. The fungal strains secrete the glucans into the fermentation broth, in an aqueous culture medium, and the separation of the glucans from the fermentation broth is effected using asymmetrical filter membranes.
Owner:WINTERSHALL HLDG
Method for hydrolytic preparing biological tangeritin by enzyme
InactiveCN101089187AControl the hydrolysis processEasy to separate and purifyFermentationNaringinCitrus Bioflavonoids
In the invented method, citrus bioflavonoid and corresponding enzyme are used as raw materials, being dissolved in organic solvent, adding glucoside solution at concentration of 1-100g / L, under pH value of 3.0-7.0 and temperature of 20-65 deg.C for 20-60 min. After separation and purification, obtained is citrus bioflavonoid monoglycoside. With this invention, naringoside enzymolysis and cirmtim enzymolysis method for production of naringen in monoglycoside and hesperetin monoglycoside, compared with chemical method, has advantages of:easily to be controlled of enzymolysis, mild reaction, less by-products and easy to be separated of products. By using this invented method, the enzymolysis of naringoside and cirmtim for production of naringenin monocoside and hesperetin monoglycoside can be effectively controlled, and only the first glycosidic bond is broken, so obtained is highest yield of naringenin monoglycoside, hesperetin monoglycoside and rhamnose.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Probiotics and prebiotic compound preparation
PendingCN106617091ARapid stimulation of reproductionIncrease vitalityFood ingredient functionsOligosaccharide food ingredientsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHENGDANGNIAN BIO TECH CO LTD
Carbon-based solid acid, catalyst comprising the solid acid, and reaction using the solid acid as catalyst
InactiveUS8013130B2High total acid contentMinimizationOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCarbonizationSolid acid
A carbon-based solid acid which has high activity and high thermal stability and is useful as an acid catalyst for various reactions such as hydration of olefins.The carbon-based solid acid for use as a catalyst is obtained by carbonization and sulfonation of an organic substance, which has a reduction rate of 10 mol % or less of acid content as measured by immersing the solid acid in hot water at 120° C. for 2 hours, is used as the acid catalyst.The organic substance to be used as the raw material for preparing the solid acid is preferably a saccharide having β1-4 glycosidic bond (e.g. cellulose) or lignin. Amylose is also suitable as the raw material. Examples of the reaction for which the solid catalyst can be used include hydration of olefins, etherification of olefins, and acid / alcohol esterification.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP +1
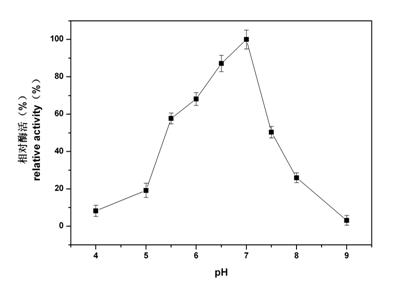
Exoinulinase Z2-5 with low-temperature activity and gene of exoinulinase Z2-5
The invention relates to exoinulinase Z2-5 with low-temperature activity and a gene of the exoinulinase Z2-5. An amino acid sequence of the exoinulinase Z2-5 from sphingobacterium sp. is shown as SEQIDNO.1. The invention provides the gene Z2-5 encoded with the exoinulinase, and a recombinant vector and a recombinant strain of the exoinulinase gene Z2-5. The exoinulinase has the properties that the optimum pH value is 7; after the exoinulinase is treated by a 0.1 M buffer solution of which the pH value is 9.0 at room temperature for 1 hour, the activity of the exoinulinase also can be kept at over 30 percent; the optimum temperature is 40 DEG C, the enzyme activity of the exoinulinase is about 40 percent at the temperature of 10 DEG C and 50 DEG C, and the enzyme activity of the exoinulinase is about 10 percent at the temperature of below 0 DEG C; after the exoinulinase is treated at the temperature of 50 DEG C for 1 hour, the enzyme activity of exoinulinase also can be kept at over 30percent; and substrates of cane sugar, fructosan and the like can be hydrolyzed, so the exoinulinase belongs to the reaction selectivity of the hydrolysis of a fructose glycosidic bond. By the exoinulinase Z2-5, synanthrin can be hydrolyzed to prepare high fructose corn syrup, so the exoinulinase Z2-5 is used for food industry.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Algin oligosaccharides and the derivatives thereof as well as the manufacture and the use of the same
The invention provides an alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives with the degree of polymerization ranging from 2 to 22. The alginate oligosaccharide is composed of β-D-mannuronic acid linked by 1,4 glycosidic bonds. The derivatives with the reduced terminal in position 1 of carboxyl radical can be prepared by oxidative degradation. The invention also provides a process for preparing the alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives, which includes the procedure that an alginate solution is reacted for 2 to 6 h in an autoclave at pH 2˜6 and the temperature of 100˜120° C., and adjusted pH to 7 after the reaction is stopped, after which the resultant oligosaccharide is oxidized in the presence of an oxidant to obtain an oxidative product. The alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives of the invention can be used in the manufacture of a medicament for the prophylaxis and treatment of AD and diabetes.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Sea lettuce polysaccharide, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101328227ANo side effectsHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderAntithrombotic AgentIon exchange
The invention relates to Monostroma nitidum polysaccharide, which is characterized in that: sugar chains of the Monostroma nitidum polysaccharide contain rhamnose groups, xylose groups, glucose groups, galactose groups, mannose groups and glucuronic acid groups, and the rhamnose group polysaccharide is a linear long chain molecule which is connected by alpha-1, 2-glycosidic bonds and alpha-1, 3-glycosidic bonds. Under the condition of preparation, algae frond is immersed into water for homogenate, and then heated and extracted, and a clear solution is separated, concentrated and desalinated; the desalinated solution is concentrated and deproteinized; the deproteinized solution is concentrated, alcohol deposited, dried, dissolved and then separated through an ion exchange chromatographic column and a gel chromatographic column in turn; the collected solution is concentrated and desalinated; and the desalinated solution is concentrated, alcohol deposited, cleaned, dried and crushed. The Monostroma nitidum polysaccharide can be used for preparing a novel anticoagulant or antithrombotic reagent.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Carbon-Based Solid Acid, Catalyst Comprising the Solid Acid, and Reaction Using the Solid Acid as Catalyst
InactiveUS20090099345A1Easy to reuseEasy to separateOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationSolid acidCarbonization
A carbon-based solid acid which has high activity and high thermal stability and is useful as an acid catalyst for various reactions such as hydration of olefins.The carbon-based solid acid for use as a catalyst is obtained by carbonization and sulfonation of an organic substance, which has a reduction rate of 10 mol % or less of acid content as measured by immersing the solid acid in hot water at 120° C. for 2 hours, is used as the acid catalyst.The organic substance to be used as the raw material for preparing the solid acid is preferably a saccharide having β1-4 glycosidic bond (e.g. cellulose) or lignin. Amylose is also suitable as the raw material. Examples of the reaction for which the solid catalyst can be used include hydration of olefins, etherification of olefins, and acid / alcohol esterification.
Owner:NIPPON OIL CORP +1
Lactobacillus plantarum exopolysaccharide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105821093AHigh purityHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationCross-linkPurification methods
The invention provides a lactobacillus plantarum exopolysaccharide. According to the exopolysaccharide, sugar units in the molecular structure are only xylose and galactose, the galactose accounts for 98%, and the exopolysaccharide belongs to a lactobacillus plantarum exopolysaccharide of a brand new structure. Meanwhile, the invention provides a method for preparing the exopolysaccharide. The method comprises the following steps: precipitating polysaccharides in lactobacillus plantarum fermentation solution by ethanol, dialyzing to remove small molecules, removing nucleic acid and protein impurities by the enzymolysis methods; precipitating impurity proteins by trichloroacetic acid, performing solid-liquid separation, taking the supernatant, and performing dialysis, thereby obtaining the purified target polysaccharide. According to the method, due to the property of the target polysaccharide and impurity component design process parameters of lactobacillus plantarum fermentation solution, the temperature and pH conditions are mild, purification methods capable of possibly breaking polysaccharide cross-linked bonds such as ultrafiltration are avoided, and integrity of polysaccharide glycosidic bonds and secondary structures is effectively guaranteed. The polysaccharide prepared by the method is high in purity and yield and lays a foundation for subsequent performance analysis and industrial application.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Activated anti-swelling shrinkage agent and application thereof
InactiveCN103820093AImprove surface activityExcellent anti-expansion and shrinkage effectDrilling compositionAlkaneHydrogen
The invention provides an activated anti-swelling shrinkage agent and application thereof. The structural formula of the activated anti-swelling shrinkage agent is as follows: R1R2R3N<+>Y1N<+>R4R5R6.X<2->, R1R2R3N<+>Y2N<+>(R7)(R8)Y3N<+>R4R5R6X<3->, wherein R1 to R8 refer to hydrogen, alkane radical, aromatic alkane radical, polyoxyethylene radical, polyoxypropylene radical, polyoxyethylene / propylene segmented copolymer, poly-glycosidic bond and various substituent groups thereof respectively and independently; X<-> is Cl<->, Br<->, I<->, RCO3<->, COO<->, RSO3<->, RSO4<->, and RPO4<-> atoms, and R is H, alkyl or substituent alkyl independently; Y1 to Y3 are -(CH2)n- (n=1-10), -(CH2)n-CH=CH-(CH2)m- (n+m=8), -(Ph)n- (n=1-4), -(CH2)mO(CH2)n- (m+n<10), -(CH2)n-O-(EO)m- (m+n<10), -(CH2)n-O-(PO)m- (m+n<10) and various substituent groups. The activated anti-swelling shrinkage agent is used for protection of sensitive reservoir with high clay content, can be used independently, and can also be used as an additive to be used in oil-water well work.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method and application of graphene oxide derivative
InactiveCN103483466AAchieve specific targetingGood biocompatibilityOrganic chemistryAerosol deliverySolubilityNon target
The invention relates to a preparation and application method of a graphene oxide derivative, which can effectively solve the problem of non-targeting in the traditional photothermal therapy and chemotherapy technologies. The method comprises the following step: performing covalent connection on an azo aromatic compound and graphene oxide by taking an azo aromatic bond as a connecting arm, or performing covalent connection on a polysaccharide compound and the graphene oxide by taking a glycosidic bond as a connecting arm, wherein the weight ratio of the azo aromatic compound or polysaccharide compound to the graphene oxide is (5:1)-(17:4); the height of the graphene oxide is 0.8-1.2 nm, and the dimension is 0.1-50 mu m; and the azo aromatic compound is one of 4,4'-azodiphenylamine, 4,4'-dimethylacrylamide azobenzene, 4,4'-di(N-methylacryloyl-6-aminohexanamide)azobenzene, 3,3',5,5'-tetrabromo-4,4,4,4'-tetra(methacrylamide)azobenzene and 4-(methylacryloyl)azobenzene. The graphene oxide derivative has fine biocompatibility water solubility and stability, can realize specific tumor targeting and is an innovation of medicaments for tumor therapy.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Alpha--L-rhamnosidase and application thereof
PendingCN108467858ASpecific degradation and high efficiencyEfficient degradationBacteriaHydrolasesGlycosideAlpha-L-rhamnosidase
The invention relates to alpha-L-rhamnosidase and application thereof. The amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The alpha-L-rhamnosidase BtRha capable of specifically degrading alpha-1,2 glycosidic bonds is cloned and recombinantly expressed for the first time, and a blank of the alpha-L-rhamnosidase for hydrolyzing the alpha-1,2 glycosidic bonds between rhamnose is filled up. The alpha-L-rhamnosidase can efficiently and specifically degrade epmedin C and convert the epmedin C into icariin, and the molar conversion rate of 1 g / L of the epmedin C hydrolyzed by 1.5 U / mL of the alpha-L-rhamnosidase is as high as 90.5% or above under the conditions that the pH is 5.5 and the temperature is 55 DEG C.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Algin Oligosaccharides and the Derivatives thereof as Well as the Manufacture and the Use of the Same
The present invention provides an alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives with the degree of polymerization ranging from 2 to 22. The alginate oligosaccharide is composed of β-D-mannuronic acid linked by 1,4 glycosidic bonds. The derivatives with the reduced terminal in position 1 of carboxyl radical can be prepared by oxidative degradation. The present invention also provides a process for preparing the alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives, which includes the procedures that an alginate solution is reacted for 2 to 6 h in an autoclave at pH 2-6 and the temperature of 100-120° C., and pH is adjusted to 7 after the reaction is stopped, after which the resultant oligosaccharide is oxidized in the presence of an oxidant to obtain an oxidative degradation product. The alginate oligosaccharide and its derivatives of the invention can be used in the manufacture of a medicament for the prophylaxis and treatment of AD and diabetes.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Novel technology for extracting tea polyphenol in tea leaves
InactiveCN105616709AReduce consumptionStrong specific adsorption capacityFood preservationPlant ingredientsCelluloseCavitation
Owner:BAOZHIHUI BIOLOGICAL TECH TIANJIN CO LTD
Extraction method of cationic anthocyanidin aglycone
InactiveCN103834702AAvoid pollutionProtect healthFermentationWater insolubleIntestinal microorganisms
The invention relates to an extraction method of natural anthocyanidin active aglycone, and belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. The method comprises the following steps: classifying and grinding of the anthocyanidin-containing plants, water absorption, freezing, heating for unfreezing, squeezing and filtering to obtain juice, cracking and degradation of anthocyanidin with the bio-enzyme for cracking the glycosidic bond of anthocyanidin, a combination reaction with an anionic surfactant for precipitation or suspension, a replacement reaction with hydrochloric acid, separation of water insoluble matters, and freezing and drying of anthocyanidin aqueous solution. By adopting the technology, the method provided by the invention can obtain cationic anthocyanidin active aglycone with true content of 67% rather than anthocyanidin. The prepared cationic anthocyanidin does not need to be degraded by the intestinal microorganisms of human body and is directly absorbed and utilized by a human body or directly enters the blood of human body. The value in health care is much higher than that of anthocyanidin.
Owner:耿兆翔
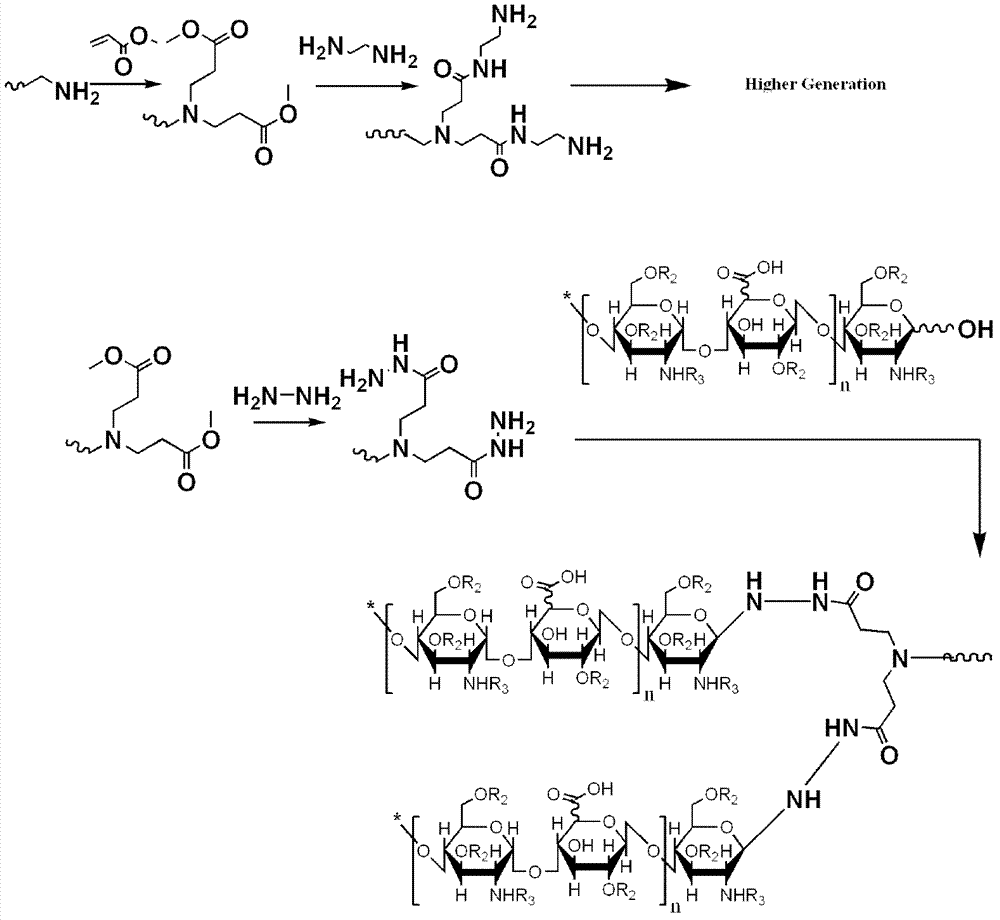
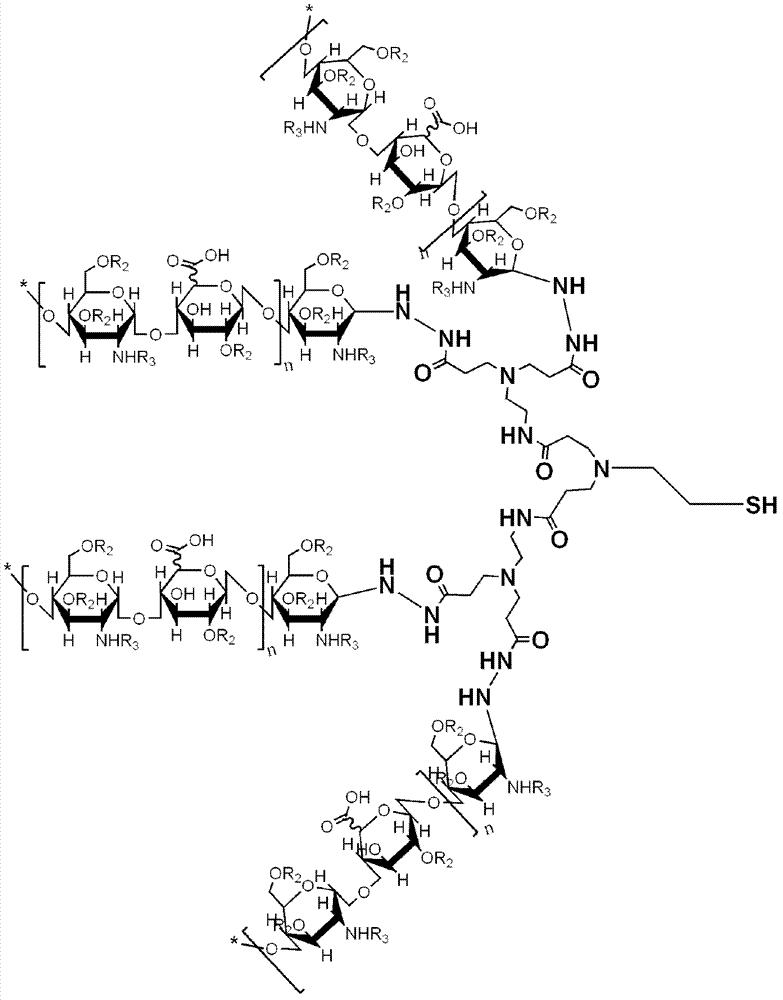
Dentritic heparin nano-material modified biological type artificial blood vessel
ActiveCN103087219ARetain natural propertiesInhibitory propertiesPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingDendrimerEnd-group
The invention discloses a dentritic heparin nano-material and a modified biological type artificial blood vessel. The dentritic heparin nano-material provided by the invention has a terminal branch unit shown in formula I, and is obtained by a reaction between polyamidoaminedendrimers using hydrazide group as a terminal group and heparin, wherein the inner core of the polyamidoaminedendrimers is cystamine, and the dentritic frame of the polyamidoamine dendrimers is hydrazide modified polyamidoamine including -0.5, 0.5, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.5 and 7.5; and the connection between the heparin and polyamidoamine is a glycosidic bond formed a reaction between the hydrazide on the surface of the polyamidoamine and the heparin reducing terminal. The disulfide bond in the dentritic heparin nano-material is cut through a reducing agent to obtain a sulfydryl site which can react with an intravascular stent material; and the surface in a blood vessel can be activated through a coupling agent of a two-way functional group, and the heparin with a branch structure can be fixed on the inner surface of the blood vessel material through chemical bond covalence, so that a composite artificial blood vessel with an anticoagulation effect can be obtained.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
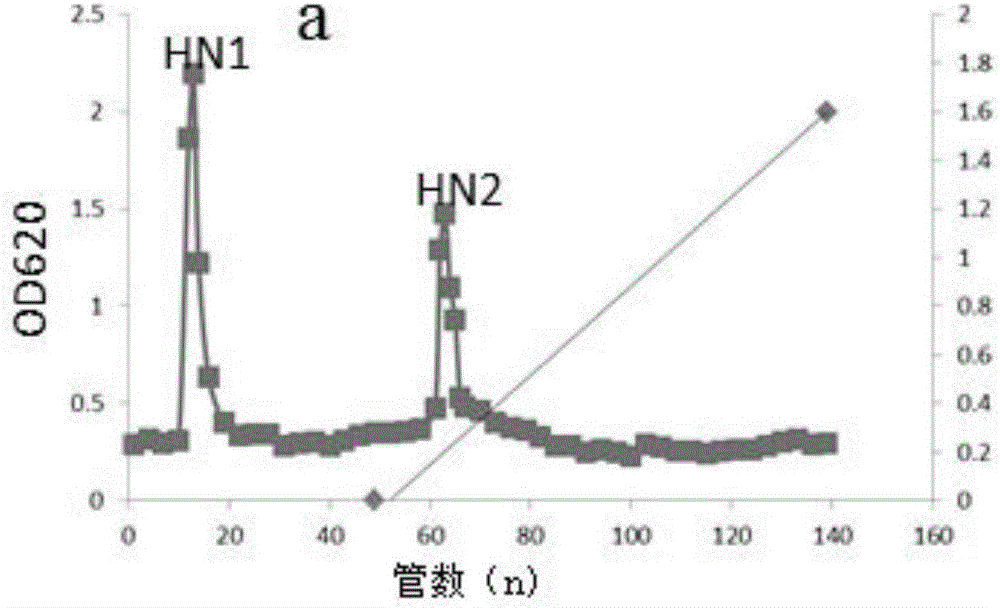
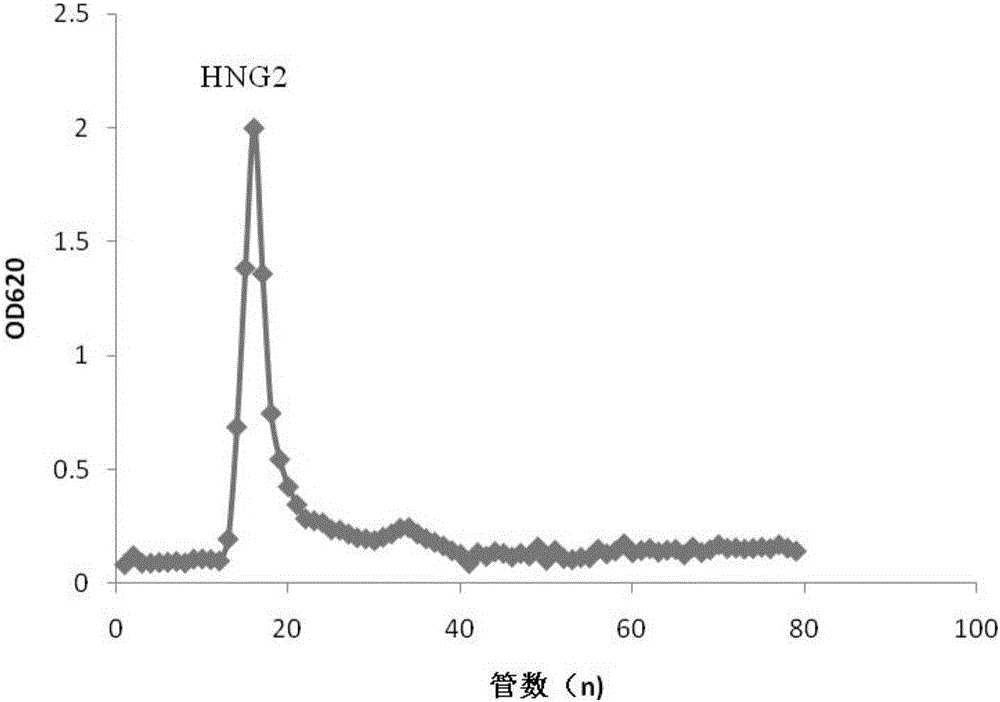
Anti-oxidation polysaccharide in boletus subsplendidus as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106317246AImprove antioxidant capacityEasy to makeOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsDPPHBoletus subsplendidus
The invention discloses an anti-oxidation polysaccharide in boletus subsplendidus as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The anti-oxidation polysaccharide is extracted from boletus subsplendidus and is named HNG2. The anti-oxidation polysaccharide is obtained by grinding boletus subsplendidus sporocarp into powder and then carrying out hot water extraction, ethanol precipitation, protein removal, dialysis, freeze-drying, ion exchange and molecular sieving. The HNG2 is yellowish powder, is a polysaccharide containing alpha- and beta-glycosidic bond configurations simultaneously, has a molecular weight of 177KDa, is easily soluble in hot water, and is insoluble in organic solvents, such as ethanol, ethyl ether and acetone. The anti-oxidation polysaccharide is composed of fucose, xylose, glucose, galactose and mannitose in a ratio of 0.36:0.8:30:2:1.6. The polysaccharide has a relatively strong effect on eliminating DPPH, superoxide anion and hydroxyl radical. The anti-oxidation polysaccharide in boletus subsplendidus is a natural extract and is simple in preparation method, relatively low in cost and high in purity.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Non-dairy contanining milk substitute products
Efficient, selective, and economical methods for producing non-dairy ready-to-use milk substitute cereal dispersions having intact beta-glucans, proteins, and natural sugars, while retaining the aroma and flavor of natural cereal. The methods include treating a cereal substrate suspension with an enzyme preparation that comprises at least one hydrolase having the ability to hydrolyze alpha-glycosidic bonds and having no glucanase and proteinase effect. The hydrolase may be selected from the group consisting of beta-amylase, alpha-amylase, amyloglucosidase and pullulanase, with the proviso that when the enzyme preparation comprises alpha-amylase or beta-amylase, there is always a mixture of at least one other of the alpha-glycosidic hydrolases. When beta-amylase and alpha-amylase are selected, they are used as a mixture, i.e., introduced simultaneously, to provide for accelerated enzymatic hydrolysis and for reduced amounts of the enzymes than otherwise needed if the enzymes were used separately. In addition to the above-identified hydrolases, the enzyme preparations of the present invention may further comprise an isomerase, such as glucose isomerase.
Owner:OATLY AB
Composition of starwort sulphonic acid or vitriolic acid polyoses ester total phenolic glycoside and method of preparing the same and antiviral application
The invention relates to a kind of natural medicine of broad spectrum antibiotic. At present, the broad spectrum antibiotic medicine with high effect and safety is at shortage all round the world. The invention is intended to extract laminarinsulphate or sulphonic acid sugar ester or sulphosalts from plant chickweed or other chickweed plant with two resin adsorption methods or a water extraction and alcohol precipition method. The spectrum antibiotic in the invention is distributed under 50,000 in the formula weight formed by carbon glycosidic bond and / or oxide glycosidic bond with phenol, especially the total flavones comprising apigenin. However, the invention mainly acts as total phenolic glycoside with the formula weight under 4,000. Besides, the invention can form brownish compound with the total flavones comprising apigenin and the glycosidic ingredients without sulfur element, so as to be applied as broad spectrum antibiotic drug. Therefore, the compound in the invention can be applied to cure ADIS virus, hepatitis virus, influenza virus and parainfluenza virus comprising SARS, adenovirus, verruca acuminate virus, enterovirus, mumps virus, herpes simplex virus, herpes zoster virus and varicella. No toxic effect has been found in the application. What is more, the invention can be made into 10 sorts of formulation, disinfector and health-improving products.
Owner:朱耕新
Process for the preparation of homopolysaccharides
ActiveUS8574873B2Reduce contentQuality improvementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHomopolysaccharideGlycoside
A process for the preparation of aqueous solutions of glucans having a β-1,3-glycosidically-linked main chain and side groups having a β-1,6-glycosidic bond by fermentation of fungal strains. The fungal strains secrete the glucans into the fermentation broth, in an aqueous culture medium, and the separation of the glucans from the fermentation broth is effected using asymmetrical filter membranes.
Owner:WINTERSHALL HLDG
Method for preparing chitin oligosaccharides, chitooligosaccharides and chitosan oligosaccharides
The invention belongs to the technical field of fine chemical industry and particularly relates to a method for preparing chitin oligosaccharides, chitooligosaccharides and chitosan oligosaccharides, of which the molecular weight is 50,000 or below. The method comprises the steps of firstly, dissolving chitin in a certain solvent, carrying out homogeneous degradation under acid catalysis so as to obtain the chitin oligosaccharides with certain molecular weight, and subjecting the chitin oligosaccharides to deacetylating treatment by a strong base, thereby preparing the chitooligosaccharides and the chitosan oligosaccharides. After the chitin oligosaccharides are subjected to deacetylating treatment by the strong base, the chitooligosaccharides or the chitosan oligosaccharides with the degree of deacetylation of 50% to 98% is obtained. Glycosidic bonds among acetylglucosamine are more easily degraded under the condition of acid catalysis, so that a chitin degradation reaction can be carried out under mild conditions, the yield is high, and the control on molecular weight is effectively achieved. According to the chitin oligosaccharides, chitooligosaccharides and chitosan oligosaccharides prepared by the method, the molecular weight can be continuously adjustable in the range of 1,000 to tens of thousands, the distribution of the molecular weight is relatively narrow, the product quality is high, and the production cost is reduced remarkably.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A novel glycosyltransferase derived from dolwoe and use thereof
Provided are a novel UDP-glycosyltransferase (uridine diphosphate glycosyltransferase) protein from Dolwoe (Gynostemma pentaphyllum) having glycosyltransfer activity for glucose linked by a glycosidic bond at the C-20 position of PPD (protopanaxadiol)-type or PPT (protopanaxatriol)-type ginsenoside, and use thereof.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com