Patents
Literature
189 results about "Phosphate anion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
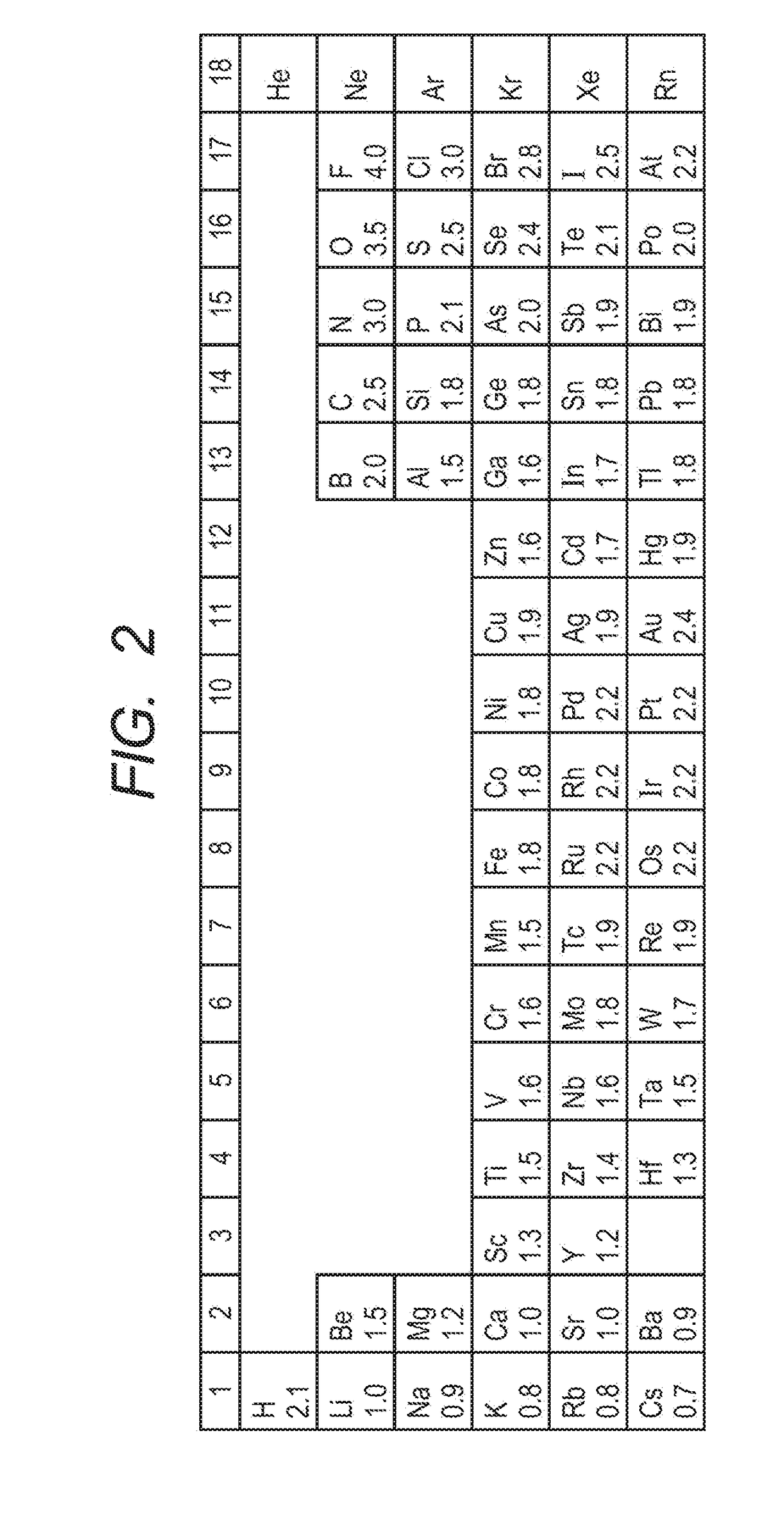
The phosphate anion is actually a polyatomic ion made up of one phosphorus atom and four oxygen atoms. The chemical formula of the anion is "PO"_4^(3-). Now, are always neutral. This means that you must balance the 3- charge on the anion by using three potassium cations.
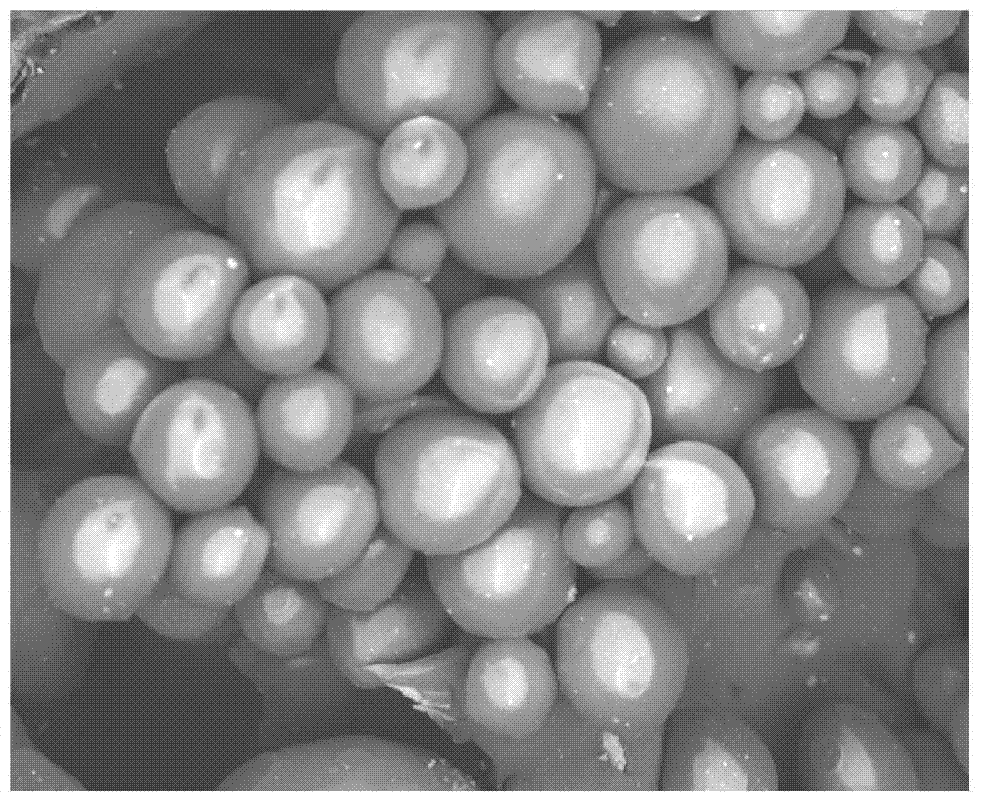
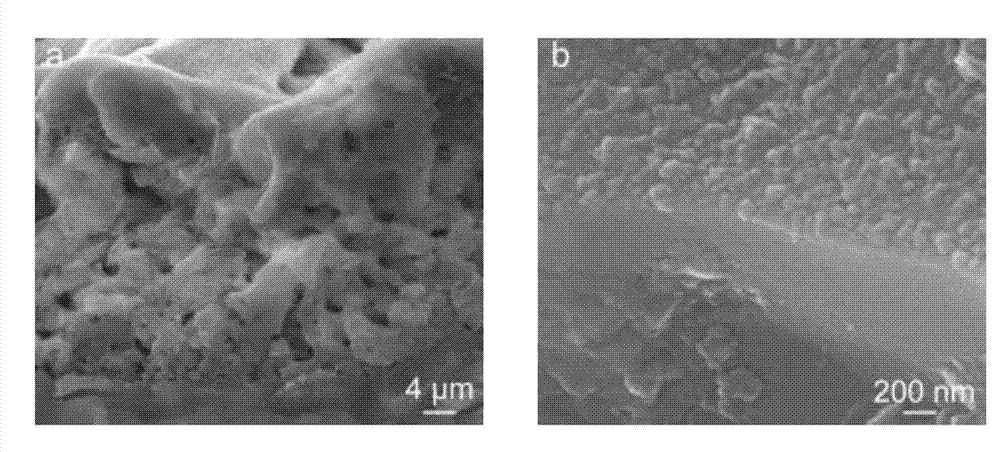
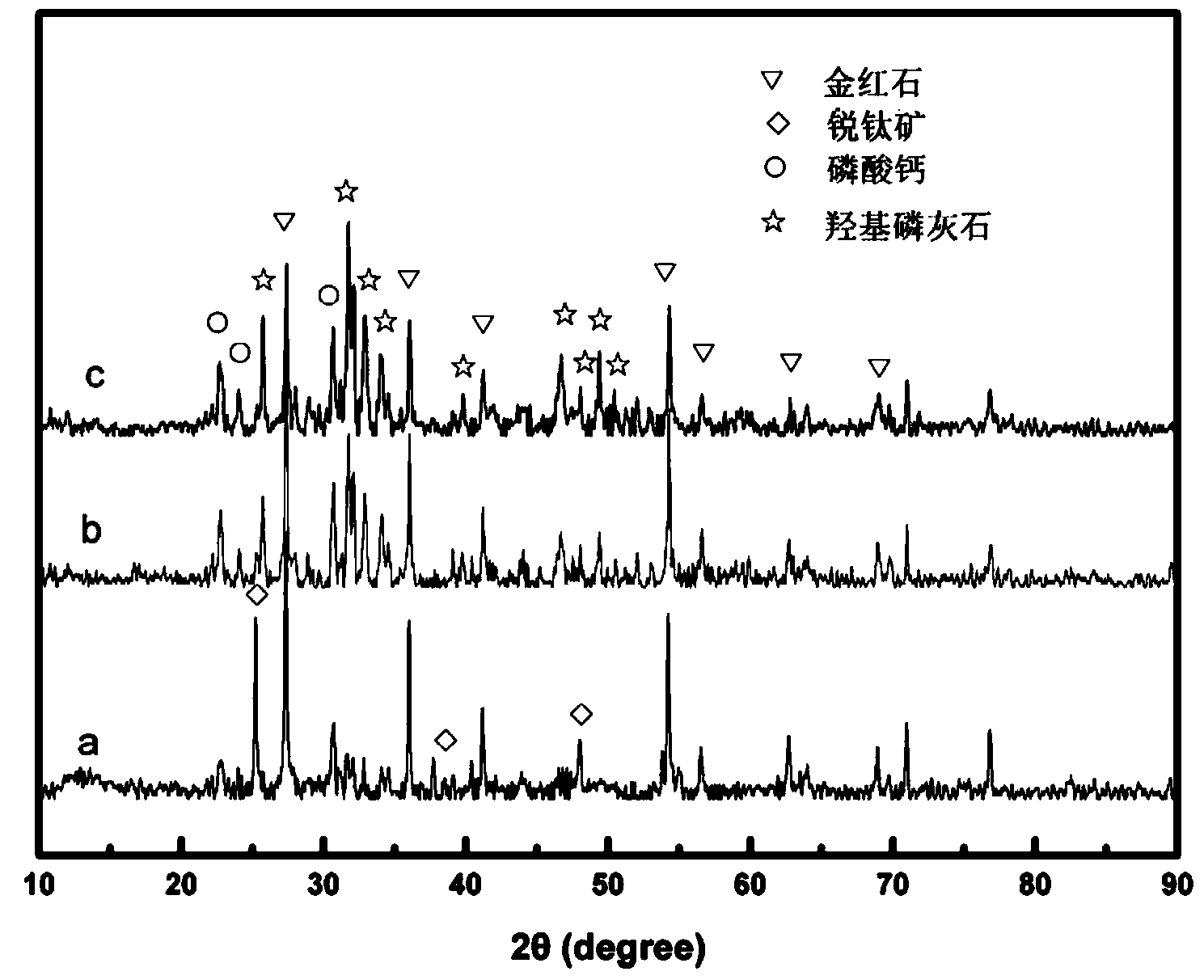
Preparation method of grapheme/hydroxyapatite composite material
InactiveCN103420364AGood biocompatibilityHigh activityCarbon compoundsPhosphorus compoundsApatitePhosphate ion
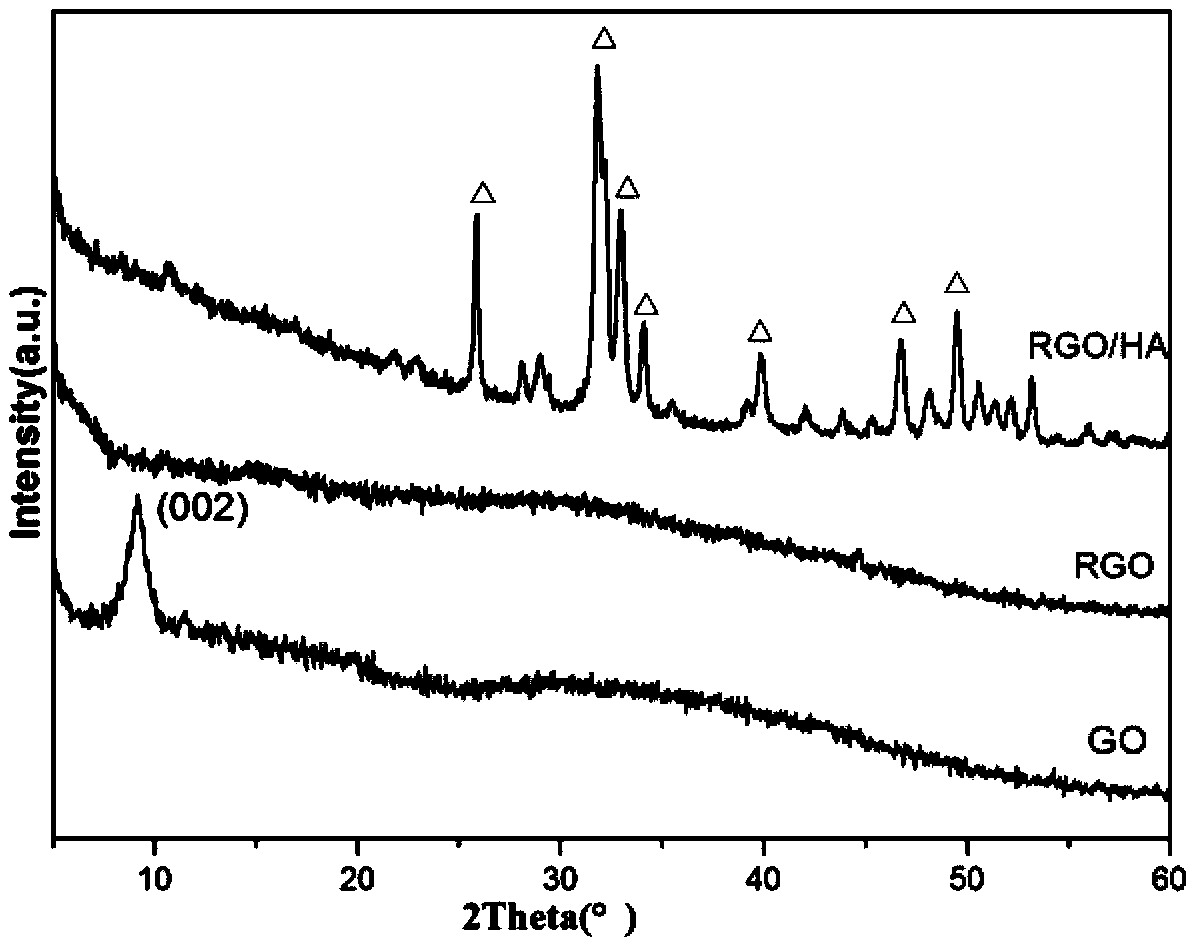
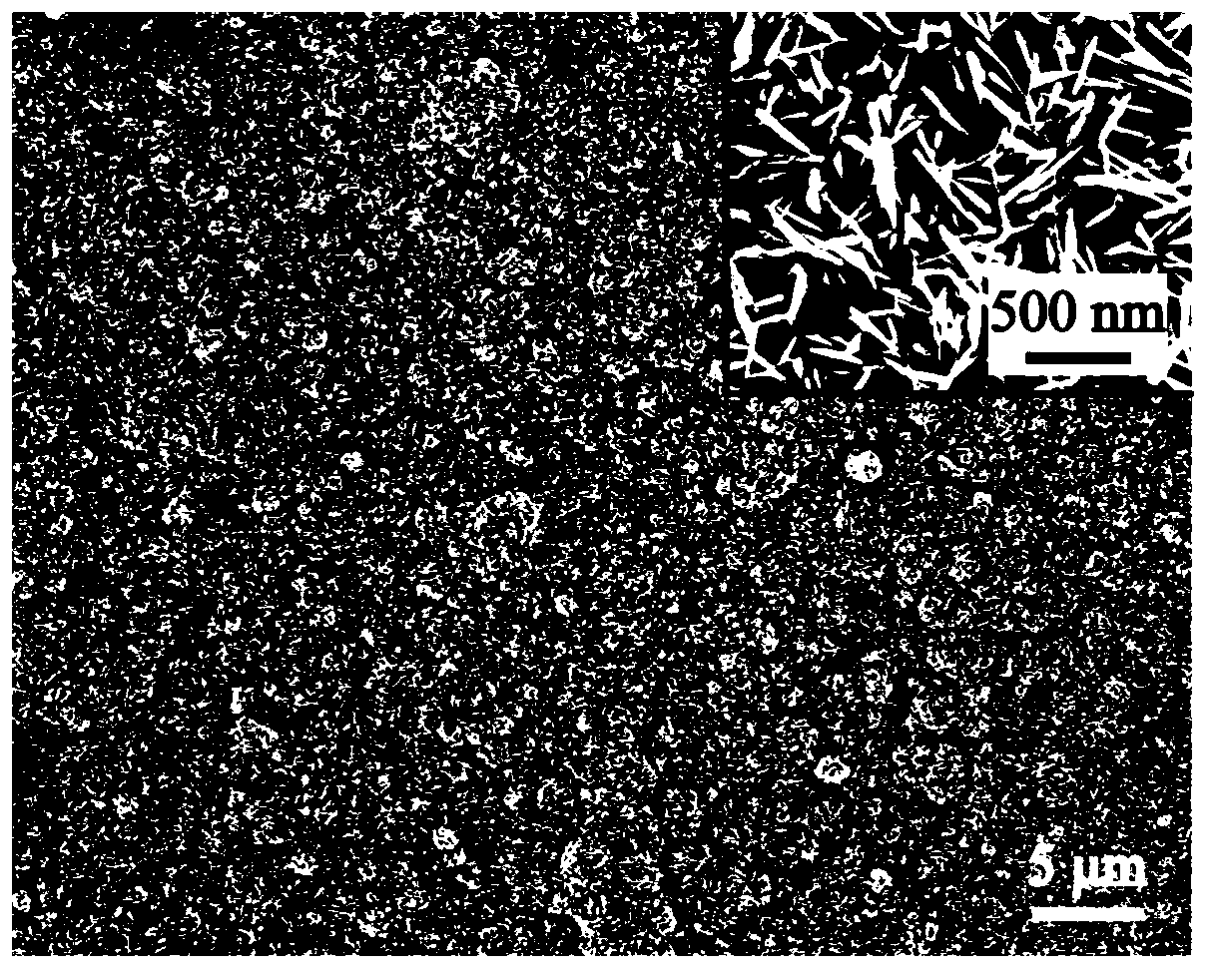
A preparation method of a grapheme / hydroxyapatite composite material comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing oxidized grapheme with the concentration of 0.5-5 mg / ml and a solution or a turbid liquid with the calcium ion concentration of 0.01-3.0 mol / L to obtain a first mixed solution; adding a solution I with the phosphate anion concentration of 0.01-2.0 mol / L to the first mixed solution according to the molar ratio of calcium to phosphorus is (1.5-2.0) to 1, and uniformly mixing the solution I and the first mixed solution under the action of magnetic mixing; adjusting the pH to be 8-14 through a pH adjusting agent to obtain a second mixed solution; transferring the second mixed solution to a reaction kettle; carrying out hydro-thermal treatment for 1-12 hours at the temperature of 160-240 DEG C; cooling the second mixed solution until the temperature of the second mixed solution is the room temperature; cleaning, freezing and drying to obtain the grapheme / hydroxyapatite composite material. The preparation method is environment-friendly, simple and beneficial to large-scale production. The prepared grapheme / hydroxyapatite composite material has the advantages of good mechanical property as well as high electrical conductivity, adsorbability, biocompatibility and osteogenic activity.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
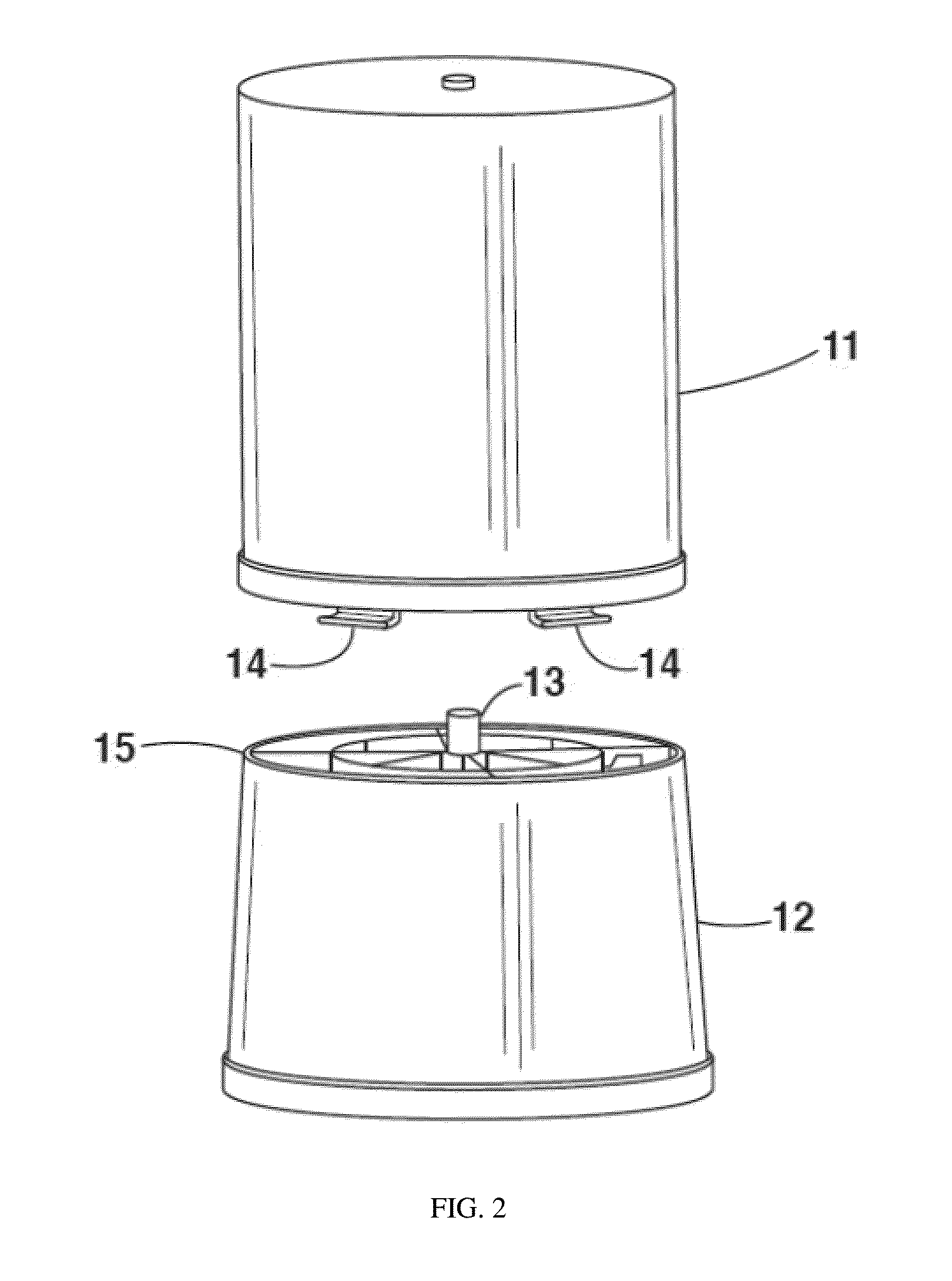
Multi-use sorbent cartridge
A sorbent cartridge comprising one or more detachable modules. The sorbent cartridge can have one or more modules contained therein having connectors connecting each of the modules. One or more of the modules can be reusable and the sorbent materials therein recharged. The sorbent cartridge can include a module containing an anion exchange resin, such as zirconium oxide, downstream of zirconium phosphate in the sorbent cartridge to recapture phosphate anions that leach out of the zirconium phosphate.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Phosphate selective resin and related methods
A crosslinked polymer for binding phosphate anions is provided, the polymer comprises a polyvalent cation attached to the polymer through at least one covalently bound anionic functional group, and wherein the anionic group is selected from a group consisting of sulfonate, carboxylate, phosphonate and mixtures thereof and wherein the cation is selected from a group consisting of aluminum, calcium, magnesium, molybdenum, manganese, titanium, barium, strontium, zirconium, vanadium, scandium, lanthanum, yttrium, cerium, nickel, iron, copper, cobalt, chromium, zinc and mixtures thereof.
Owner:ALBRIGHT ROBERT L
Phosphate selective resin and related methods
A crosslinked polymer for binding phosphate anions is provided, the polymer comprises a polyvalent cation attached to the polymer through at least one covalently bound anionic functional group, and wherein the anionic group is selected from a group consisting of sulfonate, carboxylate, phosphonate and mixtures thereof and wherein the cation is selected from a group consisting of aluminum, calcium, magnesium, molybdenum, manganese, titanium, barium, strontium, zirconium, vanadium, scandium, lanthanum, yttrium, cerium, nickel, iron, copper, cobalt, chromium, zinc and mixtures thereof.
Owner:ALBRIGHT ROBERT L
Method for preparing antibacterial active titanium oxide nanotube array composite coating material
InactiveCN103110981AAvoid dissociationLong-term antimicrobial stabilitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingTio2 nanotubeElectrolysis
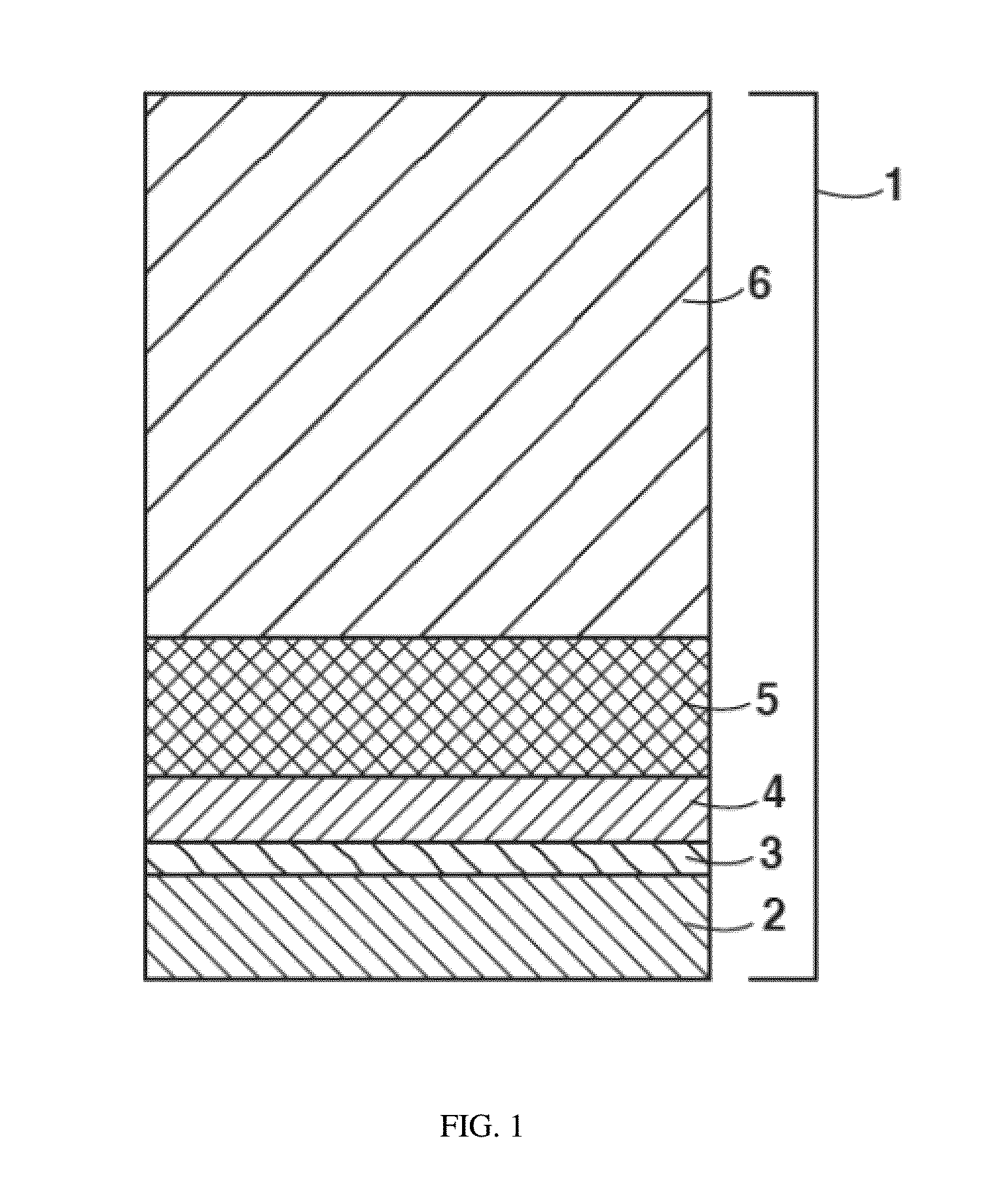
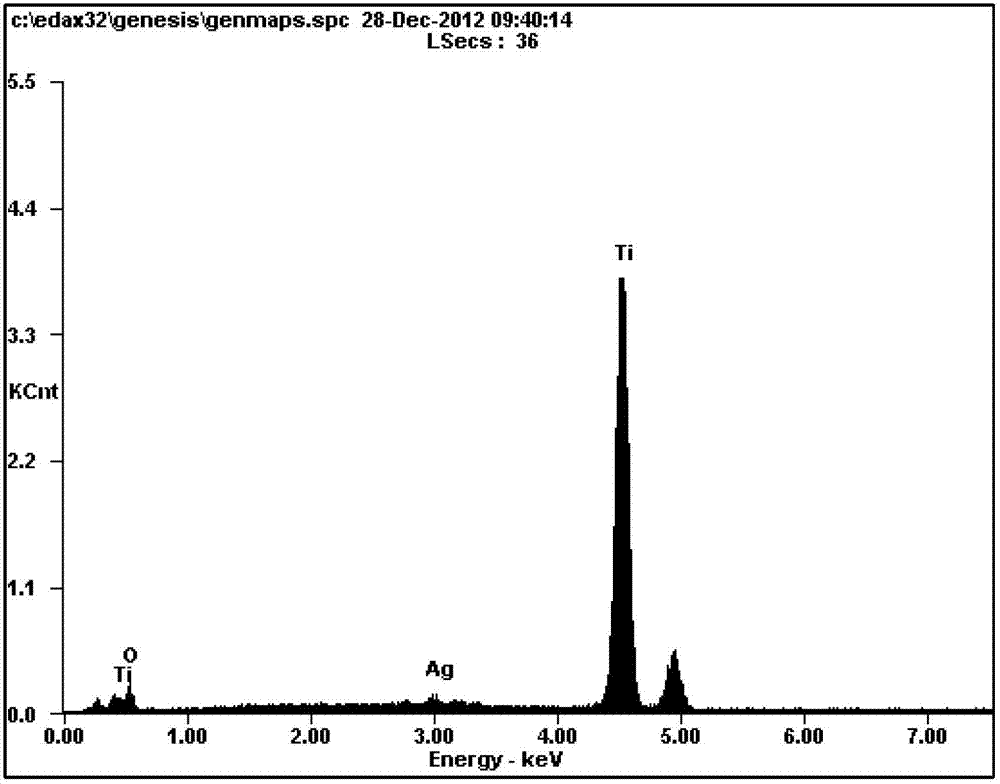
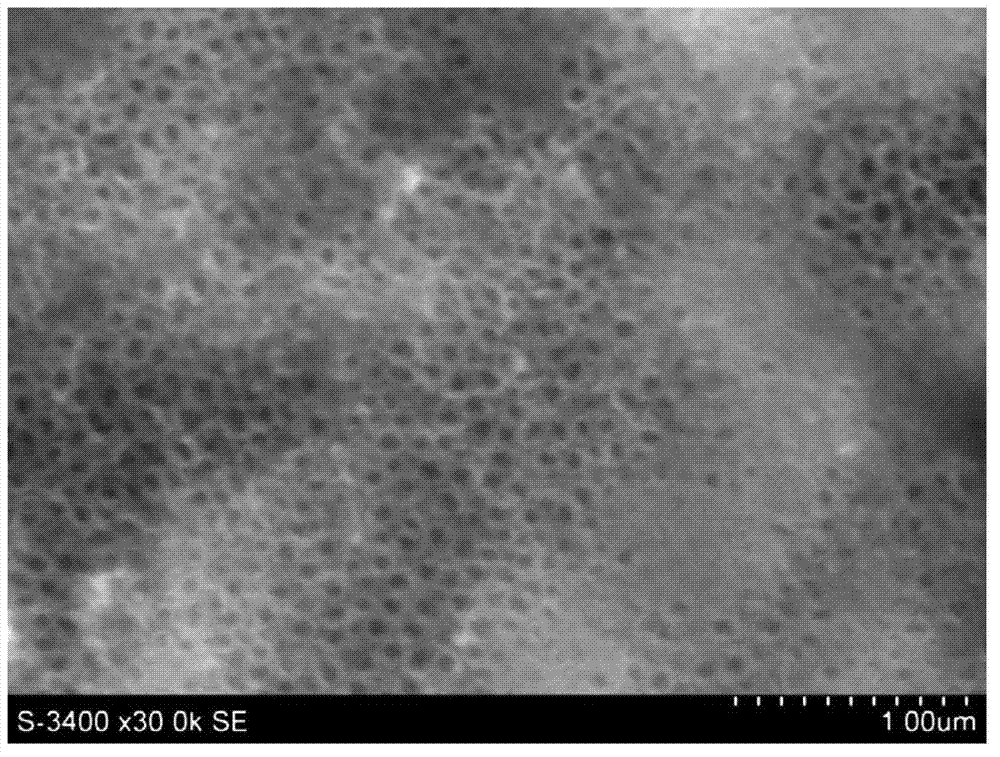
The invention discloses a method for preparing an antibacterial active titanium oxide nanotube array composite coating material. The method comprises the following steps of: performing electrolytic oxidation to prepare a titanium oxide nanotube array with biological activity by taking titanium and an alloy thereof as an anode, taking an electrolyte solution containing phosphate anion and fluorinion as electrolyte; soaking the titanium oxide nanotube array with biological activity in the solution of silver nitrate and polyethylene glycol which are taken as a soaking solution, taking the titanium oxide nanotube array out, inducing the light in the active titanium oxide nanotube array to deposit silver particles through UV-irradiation, and obtaining the titanium oxide nanotube array composite coating material with the antibacterial property and biological activity. According to the material prepared by the method, the silver particles enter the titanium alloy or a titanium alloy matrix, and the material has long-term antibacterial stability; the thickness of the active titanium oxide nanotube array can be controlled in a range from 100 to 1000nm, and bone cell growth and nutrition transfer are promoted; the active titanium oxide generated through anodic oxidation can prevent release of titanium ion in the matrix, and the corrosion resistance of the matrix is improved; and moreover, the coating material has obvious biological activity and can induce bone apatite formation.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA METAL MATERIAL RES INST
Chitosan and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt composite magnetic microsphere and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104258822AImprove adsorption capacityStrong pH adaptabilityOther chemical processesAnion exchangersPhosphate ionMicrosphere
The invention discloses a chitosan and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt composite magnetic microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of preparing a water phase, stirring and dissolving chitosan, chitosan quaternary ammonium salt and a pore-foaming agent PEG or PVP according to a ratio in an acetic acid aqueous solution, and adding magnetic particles for stirring and ultrasonic treatment; preparing an oil phase, and stirring liquid paraffin and Span80 to obtain the oil phase; gradually adding the water phase into the oil phase drop by drop while stirring is carried out to obtain a liquid mixture; adding a sodium polyphosphate aqueous solution into the liquid mixture drop by drop, carrying out stirring, and adding a glutaraldehyde aqueous solution for reaction; carrying out centrifugation and washing to obtain the chitosan and chitosan quaternary ammonium salt composite magnetic microsphere. The composite magnetic microsphere disclosed by the invention is higher in adsorption to electronegative materials such as humic acid, anionic dyes, arsenate ions, phosphate anions and nitrate ions, is higher in pH adaptability, magnetic separation property and regeneration performance, and is high in exchange capacity, high in adsorption speed and easy to separate.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Preparation method and application of modified charcoal adsorbent based on lanthanum ferrite
InactiveCN106362688AAvoid pollutionLow costOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesPhosphate ionSorbent
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a modified charcoal adsorbent based on lanthanum ferrite. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing charcoal; S2, performing modification treatment; and S3, performing finished product treatment. According to the method, low-cost and sufficient-source crop straws are adopted as a raw material; by virtue of a chemical coprecipitation method, the surface of the charcoal obtained by pyrolysis of the straws is modified with the lanthanum ferrite, so that the modified charcoal adsorbent has a favorable removal effect on pollution by phosphate anions in a water body, especially low-concentration phosphorus; furthermore, the adsorbent is favorable and stable in magnetism and convenient to recycle; in addition, the preparation method is simple to operate and high in preparation yield, and has potential application prospect in the field of inorganic wastewater treatment.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
MOFs materials for adsorbing phosphate anions
ActiveCN104707569ALarge specific surface areaReduce manufacturing costOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionIndustrial waste waterPhosphate ion
The invention relates to MOF materials for adsorbing phosphate anions. The MOF materials are taken as adsorbents to be applied to adsorption of the phosphate anions in a water solution, and have remarkable adsorptivity on the phosphate anions. Several MOFs materials are respectively added in phosphorous water of different concentrations and phosphorous water of different pH values to be stirred for 1-120 min, the phosphorus removal rate can be up to 90-99%, and the processed MOFs materials have no phosphorus desorption phenomenon and secondary pollution on environment. The several MOFs materials have the advantages of being large in specific surface area, high in adsorption capacity, high in dephosphorization efficiency, small in usage amount, simplicity, safety, high efficiency and low cost. The invention relates to phosphorus removal application of industrial wastewater, lake water, tail water discharged by sewage treatment plants, and aquaculture wastewater.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
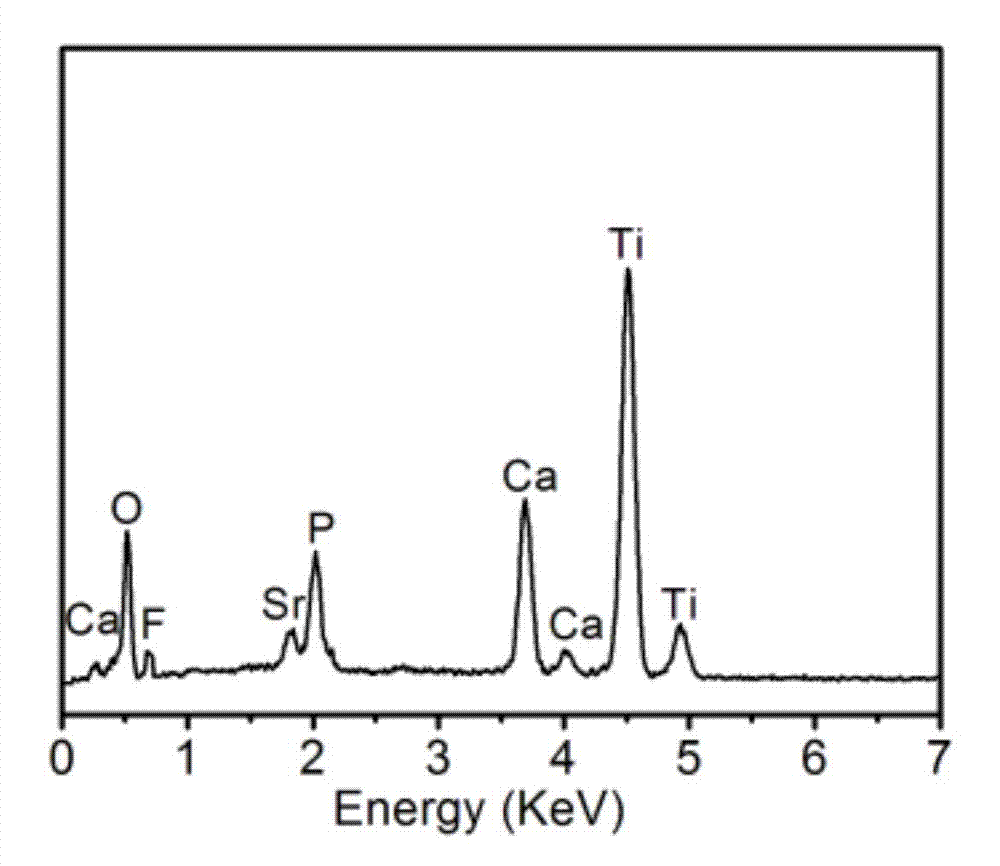
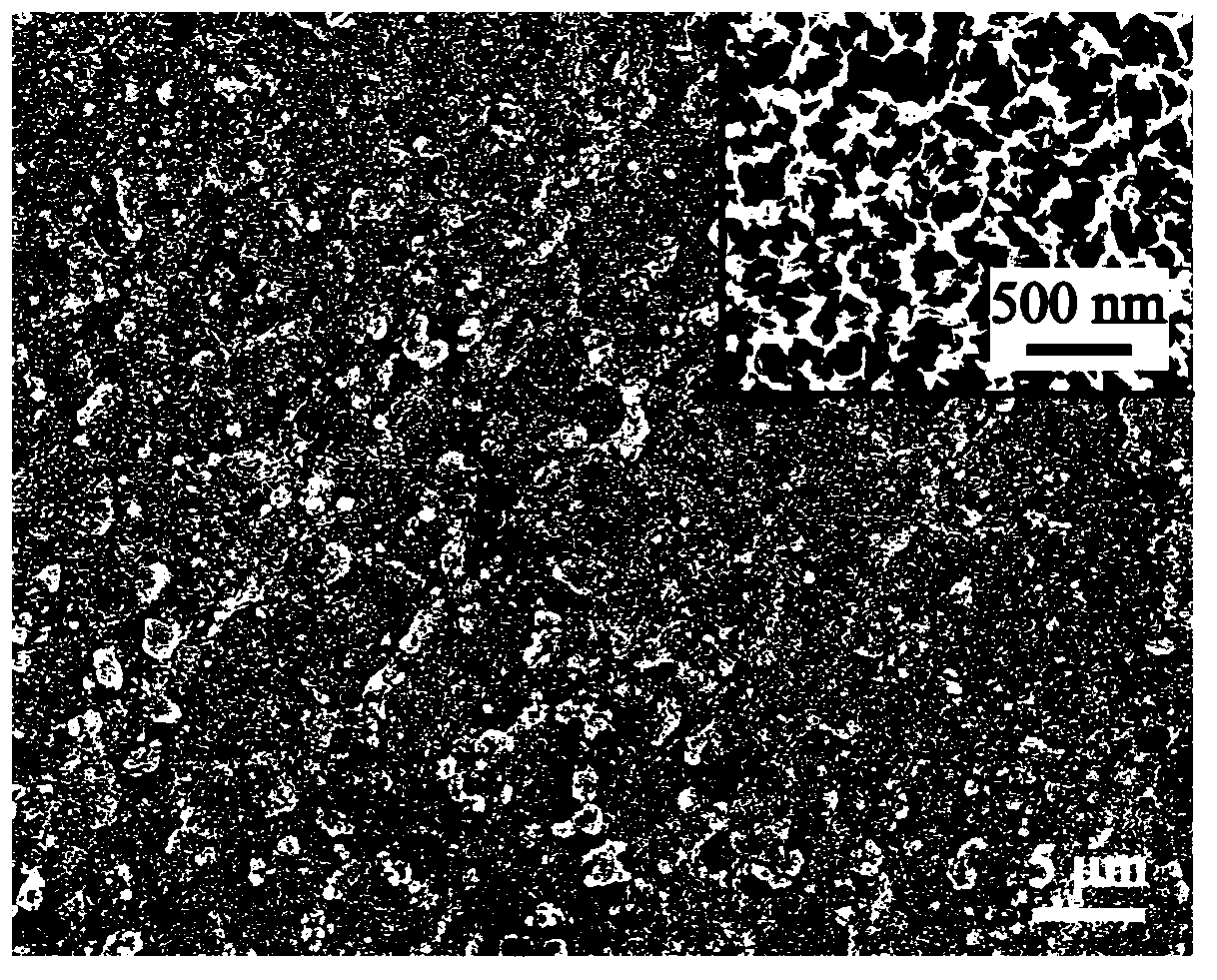
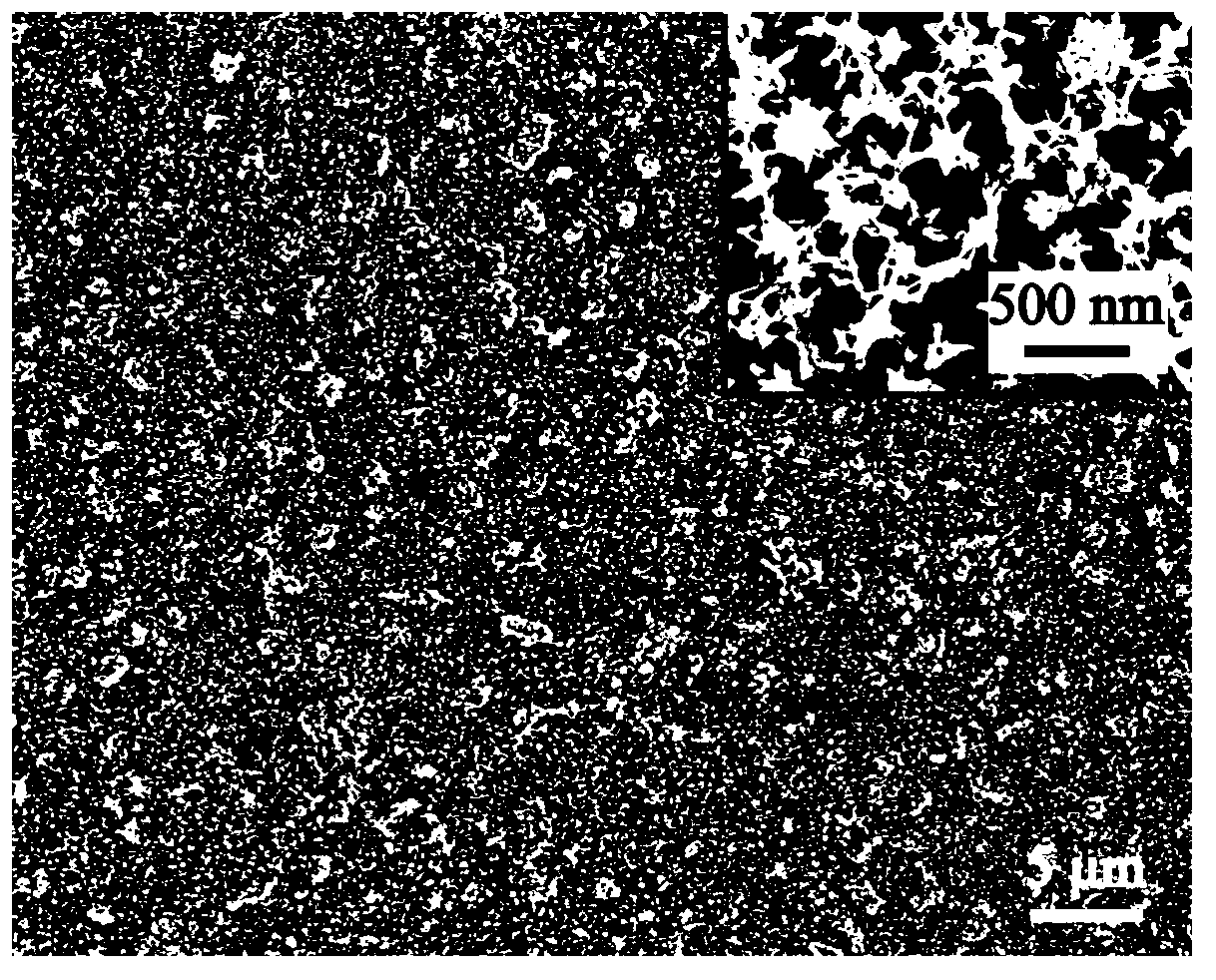
Titanium dioxide/strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104726921AEase of mass productionSimple and fast operationSurface reaction electrolytic coatingProsthesisSolubilityPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention provides a titanium dioxide / strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly preparing an electrolyte containing calcium ions, strontium ions, fluorine ions and phosphate anions; and then by taking titanium or a titanium alloy as an anode and stainless steel as a cathode, directly preparing the titanium dioxide / strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite bioactive nano-composite coating on the surface of a titanium or titanium alloy substrate by virtue of a micro-arc oxidation technology. The coating consists of an inner layer combined on the surface of the substrate and a surface layer combined on the surface of the inner layer, wherein the inner layer is a titanium dioxide layer in a form of a nano crystal and the surface layer is a nano-particle strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite layer. No non-continuous interfaces are available between the coating and the substrate and the coating has high combining strength and structural stable performance; the coating is relatively small in solubility in a simulated body fluid, so that the coating is effectively implanted and used; and the nano-particle strontium and fluorine-containing hydroxyapatite layer in the surface layer can remarkably promote the osteogenic function of the cells to form new bones and inhibit bacterial adhesion and growth.
Owner:宝鸡卡斯特医疗科技有限公司
Hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103272269AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove biological activityCoatingsProsthesisChitosan coatingPhosphate ion
The invention discloses a hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite coating and a preparation method thereof. The preparation process mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing liquor containing chitosan, calcium ions and phosphate anions; (2) based on biomedical metal as a matrix, preparing a chitosan coating containing calcium ions and phosphate anions by a dipping-pulling method; and (3) converting the chitosan coating containing calcium ions and phosphate anions to the hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite coating by a biomineralization method. The coating prepared by the invention adequately combines advantages of the biomedical metal matrix, hydroxyapatite and chitosan. With the biomedical metal matrix, the coating has stronger mechanical property. With a porous structured formed by sequentially arranging sheet hydroxyapatite, the coating has good biocompatibility. Chitosan organic matters are introduced, so that not only is the binding capacity of hydroxyapatite and the metal matrix remarkably improved, but also the coating material is endowed with the antibacterial performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Combined fertilizer synergist containing polyglutamic acid, phosphate solubilizing bacteria and potassium bacteria and preparation method and application of combined fertilizer synergist
ActiveCN104276882AStrong ability to decompose inorganic phosphorusImprove bioavailabilityFertilizer mixturesPhosphate ionPhosphate solubilizing bacteria
The invention discloses a combined fertilizer synergist containing polyglutamic acid, phosphate solubilizing bacteria and potassium bacteria. The combined fertilizer synergist comprises the following components in proportion: phosphate solubilizing bacteria, potassium bacteria and polyglutamic acid at the mass ratio of (0.1-1) to (0.1-1) to (0.001-0.1). The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the fertilizer synergist. The phosphate solubilizing bacteria disclosed by the invention are capable of effectively releasing phosphate anions (PO4<3+>) in soil or fertilizer; the potassium bacteria are capable of effectively releasing potassium ions (K<+>) in the soil or fertilizer; after being compounded with the phosphate solubilizing bacteria and the potassium bacteria, the polyglutamic acid not only can provide a good growth environment for survival of the phosphate solubilizing bacteria and the potassium bacteria, but also can fully chelate nutrient elements released by the phosphate solubilizing bacteria and the potassium bacteria; and due to the synergistic effect, the effect of solubilizing phosphate and potassium is relatively outstanding, therefore the combined fertilizer synergist can be cooperatively used together with fertilizers, the utilization rate of the fertilizer is increased, and the combined fertilizer synergist can also be directly fertilized as a bacterial manure.
Owner:轩凯生物科技(滁州)有限公司
Process for preparing graphite according to electrochemical method
The invention discloses a process for preparing graphite according to an electrochemical method. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, mixing lewis acid with protonic acid to obtain electrolyte; secondly, taking graphite paper as an anode, and completely immersing the graphite paper into the electrolyte for intercalating to obtain intercalated graphite paper with expanded volume; thirdly, using the intercalated graphite paper as an anode, immersing the intercalated graphite paper into a solution containing sulfate ions or phosphate anions, and applying voltage to enable the intercalated graphite paper to continuously expand, wherein the intercalated graphite paper gradually falls off to form expanded graphite paste; fourthly, repeatedly washing the graphite paste by using pure water, filtering, then uniformly mixing the graphite paste with the pure water to obtain dilute paste, and sequentially carrying out ultrasonic exfoliation, filtering and drying on the dilute paste to obtain graphene powder. According to the process disclosed by the invention, the problem that a strong acid, a strong oxidant or an expensive poisonous organic solvent is adopted for preparing graphene according to an existing electrochemical method is solved, a preparation process of the graphene is also simplified, and the preparation cost is reduced.
Owner:DEYANG CARBONENE TECH
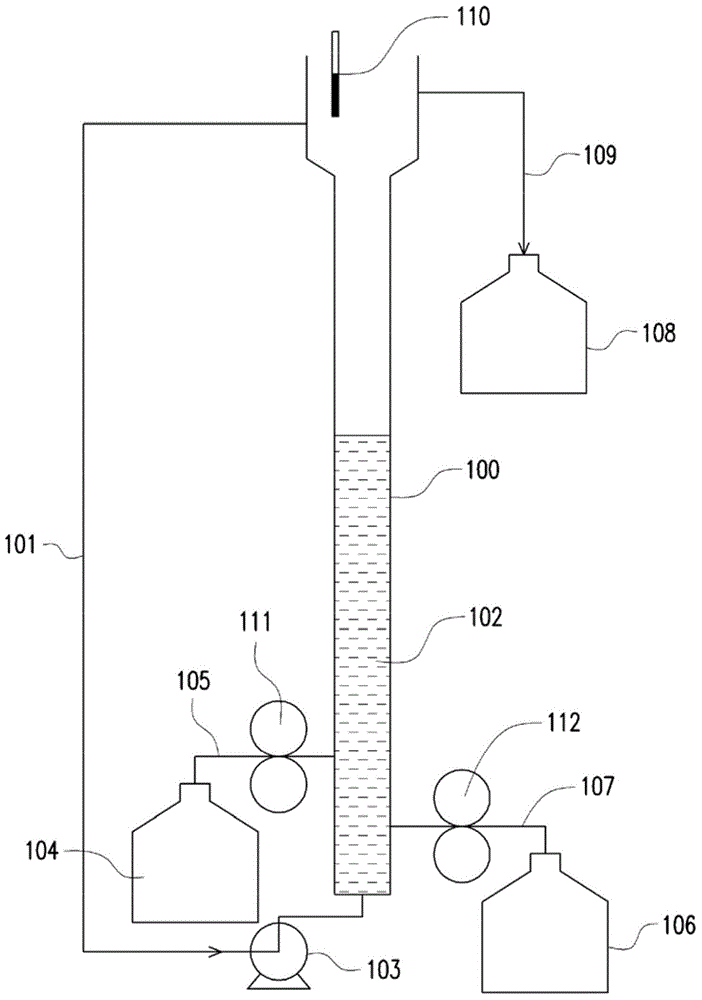
Phosphorus removing method from waste water and preparation method of ferrous phosphate
InactiveCN104445555AHigh purityIncrease crystallization rateWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsPhosphate ionFluidized bed
The invention provides a phosphorus removing method from waste water. The method includes following steps: providing a solution containing phosphate anion; mixing a solution containing ferrous ions and the solution containing the phosphate ion and performing fluidized bed crystallization to obtian a ferrous phosphate precipitation, wherein a pH value of the fluidized bed crystallization is 5-6 and a molar ratio of the ferrous ion to the phosphate ion is 1.5-2.5 and a volume ratio of the solution containing ferrous ions to the solution containing the phosphate ion is 10-20; and removing the ferrous phosphate precipitation. The invention also provides a preparation method of ferrous phosphate. By means of the phosphorus removing method, damage of the waste water to environment can be reduced and meanwhile economic benefit is achieved. By means of the preparation method of the ferrous phosphate, the ferrous phosphate being low in water content, being high in purity and being high in crystallization rate can be prepared.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP +1
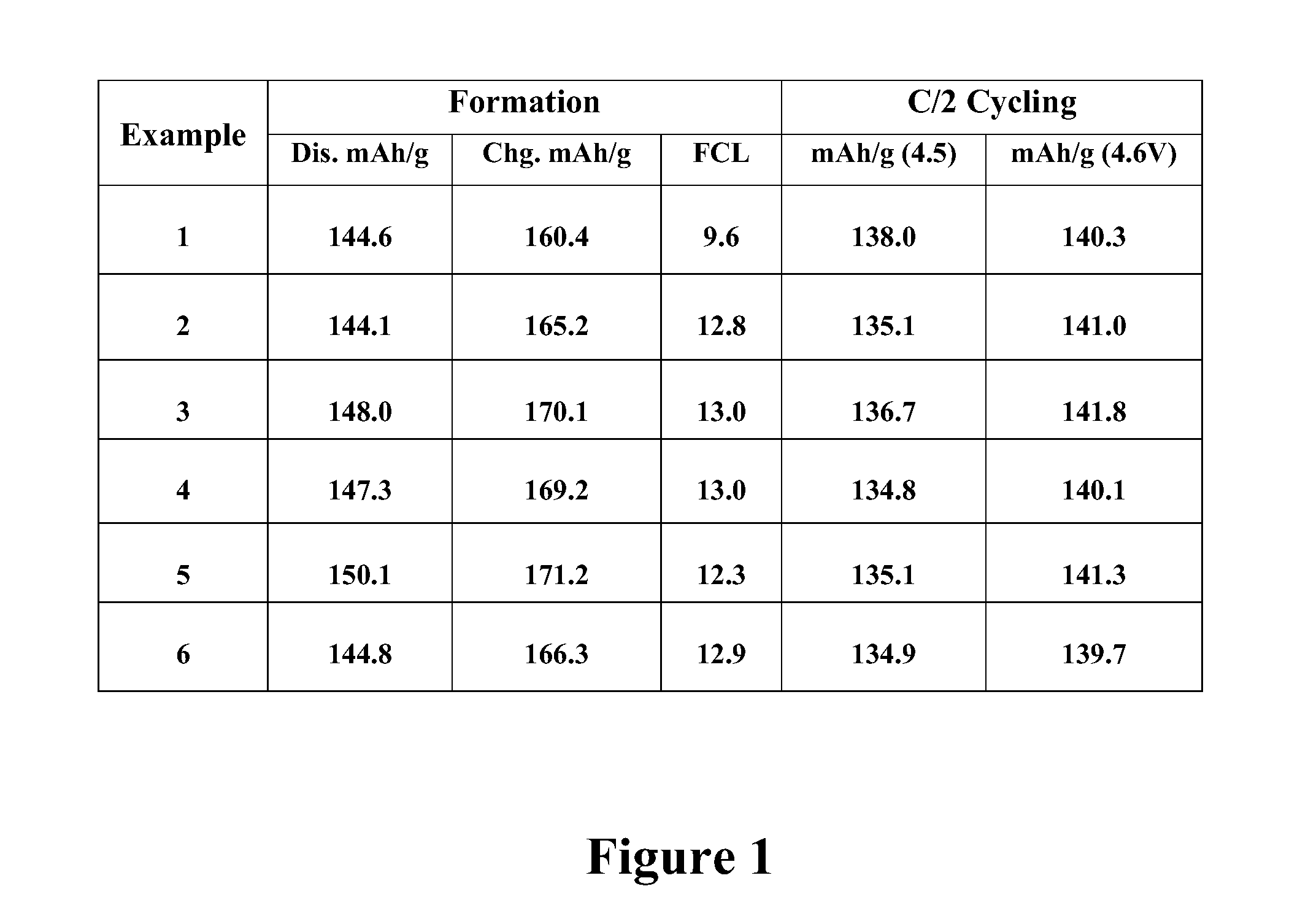
Synthesis of cathode active materials
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a lithium vanadium phosphate material comprising forming a aqueous slurry (in which some of the components are at least partially dissolved) comprising a polymeric material, an acidic phosphate anion source, a lithium compound, V2O5 and a source of carbon; wet blending said slurry, spray drying said slurry to form a precursor composition; and heating said precursor composition to produce a lithium vanadium phosphate. In one embodiment the present invention relates to a method for preparing a lithium vanadium phosphate which comprises reacting vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) with phosphoric acid (H3PO4) to form a partially dissolved slurry; then mixing with an aqueous solution containing lithium hydroxide; adding a polymeric material and a source of carbon to form a slurry; wet blending said slurry; spray drying said slurry to form a precursor composition; and heating said precursor composition for a time and at a temperature sufficient to produce a lithium vanadium phosphate compound. In an alternative embodiment the present invention relates to a method for preparing a lithium vanadium phosphate which comprises preparing an aqueous solution of lithium hydroxide; partially dissolving vanadium pentoxide in said aqueous solution; adding phosphoric acid to the aqueous solution; adding a polymeric material and a source of carbon to the solution containing vanadium pentoxide to form a slurry; spray drying said slurry to form a precursor composition; and heating said precursor composition for a time and at a temperature sufficient to form a lithium vanadium phosphate. The electrochemically active lithium vanadium phosphate so produced is useful in making electrodes and batteries.
Owner:VALENCE TECH INC
Coating Compositions With Anticorrosion Properties
InactiveUS20120091397A1Improve corrosion resistanceEasy to manufactureLiquid surface applicatorsOther chemical processesAlkaline earth metalNano size
Anticorrosive coating compositions as disclosed comprise a binding polymer and an aluminum phosphate corrosion inhibiting pigment dispersed therein. The coating composition comprises up to 25 percent by weight aluminum phosphate. The binding polymer can include solvent-borne polymers, water-borne polymers, solventless polymers, and combinations thereof. The aluminum phosphate is made by sol gel process of combining an aluminum salt with phosphoric acid and a base material. Aluminum phosphate colloidal particles are nanometer sized, and aggregate to form substantially spherical particles. The coating composition provides a controlled delivery of phosphate anions of 100 to 1,500 ppm, depending on post-formation treatment of the aluminum phosphate, and has a total solubles content of less than 1500 ppm, The amorphous aluminum phosphate is free of alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, and has a water adsorption potential of up to about 25 percent by weight water when present in a cured film.
Owner:BUNGE AMORPHIC SOLUTIONS
Stable, non-chrome, thin-film organic passivates
Storage-stable organic passivate formulations that are essentially chromium-free are provided comprising non-ionic or non-ionically stabilized organic film forming resin; at least one complex fluoride and optionally, dissolved phosphate anions, at least one component comprising vanadium, at least one inorganic oxide in dispersed form; and at least one wax in dispersed form.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Method of reducing staining of stannous in dentifrice compositions
InactiveUS7063833B2Reduce stainsImprove efficacyCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsStainingMedicine
Disclosed are methods for reducing the staining of dentifrice composition containing stannous comprising administering to a subject the dentifrice composition. The dentifrice composition is a dual phase dentifrice and is contained in physically separated compartments of a dentifrice dispenser. The first dentifrice composition comprises an effective amount of one or more linear polyphosphates having an average chain length of about 4 or more and has a total water content of up to about 20%. The second dentifrice composition comprises an effective amount of stannous ions. The molar ratio of polyphosphate anion to stannous ion is from about 0.2:1 to about 5:1 and the efficacy of the stannous ion in the dentifrice is not reduced by the polyphosphate. The dentifrice composition may alternatively be a single phase dentifrice. The single phase dentifrice will comprise an effective amount of one or more linear polyphosphates having an average chain length of about 4 or more and an effective amount of a stannous ion. The single phase dentifrice has a total water content of up to about 20%, the stannous ion is not delivered from stannous fluoride, a molar ratio of polyphosphate anion to stannous ion is from about 0.2:1 to about 5:1, and the efficacy of the stannous ion in the dentifrice is not reduced by the polyphosphate.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Preparation method for directly generating hydroxyapatite-containing biological ceramic membrane on surface of titanium
InactiveCN103451706AIncrease profitReduce solubilitySurface reaction electrolytic coatingSolubilityMicro arc oxidation
The invention discloses a preparation method for directly generating a hydroxyapatite-containing biological ceramic membrane on the surface of titanium, and aims to solve the practical problems that the prior art is complex in process, time-consuming, low in electrolyte utilization ratio, poor in membrane forming efficiency and the like. The preparation method adopts a basic method of micro-arc oxidation, and is characterized in that during the preparation of electrolyte, low-solubility calcium dihydrogen phosphate is used for providing phosphate anions and citric acid is used as a complexing agent. Compared with the prior art, although the solubility of the calcium dihydrogen phosphate used in the preparation method is low, the solubility of the calcium dihydrogen phosphate is improved after the calcium dihydrogen phosphate is complexed with the citric acid, calcium ions and phosphate anions are provided at the same time, the utilization ratio of the electrolyte is high, the reaction speed is high, the membrane forming efficiency is high, the preparation method is simple and easy to operate and low in cost, the hydroxyapatite-containing biological ceramic membrane prepared by the preparation method is stable in structure, uniform in distribution and high in effective matter content, and has a wide prospect in the fields of hard tissue implants, tooth planting and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Coating Compositions With Anticorrosion Properties
InactiveUS20120094128A1Improve corrosion resistanceEasy to manufactureOther chemical processesSynthetic resin layered productsAlkaline earth metalPhosphoric acid
Anticorrosive coating compositions comprise a binding polymer and an amorphous aluminum phosphate corrosion inhibiting pigment dispersed therein. The coating composition comprises 1 to 25 percent by weight aluminum phosphate. The binding polymer can include solvent-borne polymers, water-borne polymers, solventless polymers, and combinations thereof. The aluminum phosphate is made by combining an aluminum source with a phosphorous source to form an amorphous aluminum phosphate solid condensate. The coating composition is specially engineered to provide a controlled delivery of phosphate anions of 50 to 500 ppm, and has a total solubles content of less than 1500 ppm. The amorphous aluminum phosphate is preferably free of alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. The amorphous aluminum phosphate has an oil absorption of less than 50, and a surface area of less than about 20 m2 / g, The coating composition has a water adsorption potential of up to 25% by weight water.
Owner:BUNGE AMORPHIC SOLUTIONS
Method of quickly preparing calcium phosphate coating containing third-party beneficial ions
The invention provides a method of preparing a calcium phosphate coating containing third-party beneficial ions in a microwave-assisted manner within a short time. The method comprises the following steps: microwave heating a reaction solution containing phosphate anions and calcium ions to form the calcium phosphate coating; and adding the third-party beneficial ions into the reaction solution to prepare the calcium phosphate coating containing the third-party beneficial ions. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of efficiency, low energy consumption, low investment and easiness in control and can fully coat orthopaedical or dental implantation apparatuses and stents with complex structures and the like. The obtained calcium phosphate coating containing the third-party beneficial ions can be applied to the biomedical engineering field of hard tissue repair.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Synthesis of Cathode Active Materials
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a lithium vanadium phosphate material comprising forming a aqueous slurry (in which some of the components are at least partially dissolved) comprising a polymeric material, an acidic phosphate anion source, a lithium compound, V2O5 and a source of carbon; wet blending said slurry, spray drying said slurry to form a precursor composition; and heating said precursor composition to produce a lithium vanadium phosphate. In one embodiment the present invention relates to a method for preparing a lithium vanadium phosphate which comprises reacting vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) with phosphoric acid (H3PO4) to form a partially dissolved slurry; then mixing with an aqueous solution containing lithium hydroxide; adding a polymeric material and a source of carbon to form a slurry; wet blending said slurry; spray drying said slurry to form a precursor composition; and heating said precursor composition for a time and at a temperature sufficient to produce a lithium vanadium phosphate compound. In an alternative embodiment the present invention relates to a method for preparing a lithium vanadium phosphate which comprises preparing an aqueous solution of lithium hydroxide; partially dissolving vanadium pentoxide in said aqueous solution; adding phosphoric acid to the aqueous solution; adding a polymeric material and a source of carbon to the solution containing vanadium pentoxide to form a slurry; spray drying said slurry to form a precursor composition; and heating said precursor composition for a time and at a temperature sufficient to form a lithium vanadium phosphate. The electrochemically active lithium vanadium phosphate so produced is useful in making electrodes and batteries.
Owner:SWOYER JEFFREY +2
Developing member, method of producing the same, process cartridge and electrophotographic image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20170139336A1Good effectReduction durability of can preventedElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersOxalateArsenate
A developing member that can prevent bleed under a high temperature and high humidity and prevent charge up of the developing member under a low temperature and low humidity is provided. A developing member including an electro-conductive substrate and an elastic layer disposed on the electro-conductive substrate; the elastic layer including a binder resin, an anion and a particle containing a metal, oxide; the binder resin including a resin having a cationic organic group in the polymer chain; the anion being at least one selected from the group consisting of a fluorinated sulfonate anion, a fluorinated carboxylate anion, a fluorinated sulfonylimide anion, a fluorinated sulfonylmethide anion, a dicyanamide anion, a fluorinated alkylfluoroborate anion, a fluorinated phosphate anion, a fluorinated antimonate anion, a fluorinated arsenate anion and a bis(oxalate)borate anion; the metal oxide including an oxide of a metal having an electronegativity of 11.0 or less as a metal ion.
Owner:CANON KK
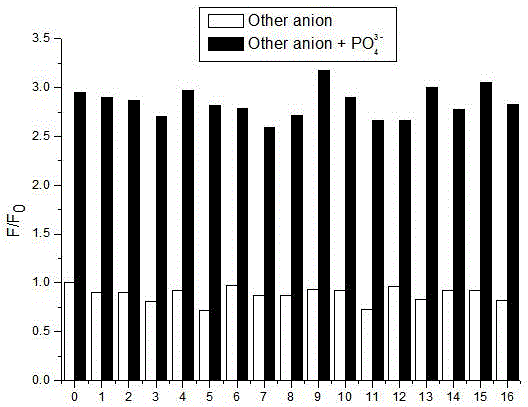
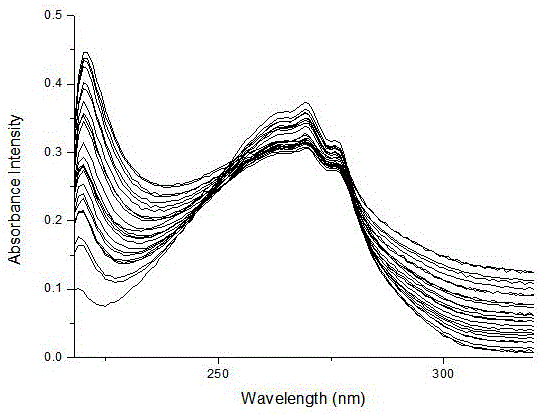
Method for detecting phosphate ions based on dual-emission europium metal organic framework material
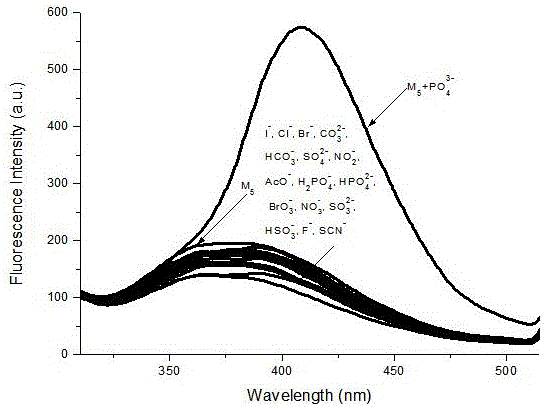
InactiveCN108535231AUnique Dual Fluorescent Emission PropertiesHigh selectivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsPhosphate ionTricarboxylic acid
The invention relates to a method for detecting phosphate ions based on a dual-emission europium metal organic framework material. The dual-emission lanthanide europium metal organic framework material is used as a ratio-type fluorescence probe for being applied to high-selectivity high-sensibility detection of the phosphate ions. The chemical general formula of the adopted dual-emission lanthanide europium metal organic framework material is [Eu2(L)2(H20)2(DMF)2], wherein a Eu2O2 cluster is used as an inorganic node, a rigid asymmetric tricarboxylic acid ligand terphenyl-3,4'',5-tricarboxylicacid (H3L) is used as an organic bridging ligand, and preparation is successfully conducted by means of a simple and convenient one-pot solvothermal technology. The invention further discloses application of the metal organic framework material in the aspect of selectively detecting phosphate anions. In a detecting process, along with increase of the content of the added phosphate anions, obviouscolor change from pink to purple which is easily observed with naked eyes is presented under radiation of an ultraviolet lamp, and thus the detecting process becomes more convenient and practical.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method of reducing staining of stannous in dentifrice compositions
InactiveUS6667027B2Reduce stainsImprove efficacyCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsStainingChain length
Disclosed are methods for reducing the staining of dentifrice composition containing stannous comprising administering to a subject the dentifrice composition. The dentifrice composition is a dual phase dentifrice and is contained in physically separated compartments of a dentifrice dispenser. The first dentifrice composition comprises an effective amount of one or more linear polyphosphates having an average chain length of about 4 or more and has a total water content of up to about 20%. The second dentifrice composition comprises an effective amount of stannous ions. The molar ratio of polyphosphate anion to stannous ion is from about 0.2:1 to about 5:1 and the efficacy of the stannous ion in the dentifrice is not reduced by the polyphosphate. The dentifrice composition may alternatively be a single phase dentifrice. The single phase dentifrice will comprise an effective amount of one or more linear polyphosphates having an average chain length of about 4 or more and an effective amount of a stannous anion. The single phase dentifrice has a total water content of up to about 20%, the stannous ion is not delivered from stannous fluoride, a molar ratio of polyphosphate anion to stannous ion is from about 0.2:1 to about 5:1, and the efficacy of the stannous ion in the dentifrice is not reduced by the polyphosphate.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate by using whole cell biocatalysis
ActiveCN101805770AIncrease chemical potentialConformational stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphate ionBacterial strain
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Method for removing cobalt from polycrystalline diamond clad sheet
InactiveCN105603428AHigh removal rateImprove extraction efficiencyPhosphate ionPolycrystalline diamond
The invention provides a method for removing cobalt from a polycrystalline diamond clad sheet. The method comprises the steps that acid liquor is provided and includes phosphoric acid and hydrogen peroxide; a polycrystalline diamond layer of the polycrystalline diamond clad sheet is soaked in the acid liquor to obtain a clad sheet without cobalt. According to the method, phosphoric acid is used for removing the cobalt phase in polycrystalline diamond, phosphate anions and cobalt ions can form stable soluble coordination ions, and therefore cobalt is promoted to continuously enter the solution to be removed from the clad sheet; moreover, hydrogen peroxide is added, so that the removal rate of cobalt is further increased. As a result, through the method for removing cobalt from the polycrystalline diamond clad sheet, the amount of volatilized irritant gas is small, corrosion to a seal of equipment and the clad sheet is small, damage to a base body seal is small, and harm to the working environment is small; meanwhile, a high cobalt removal rate is achieved, cost is lowered, and large-scale application is easy to realize.
Owner:CHANGSHA DIAT NEW MATERIAL SCI & TECH
Method for leaching nickel and molybdenum from nickel-molybdenum ore
InactiveCN105506278AImprove solubilityImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementSolubilityPhosphate ion
The invention relates to a method for leaching nickel and molybdenum from nickel-molybdenum ore, in particular to a method for decomposing the nickel-molybdenum ore with molybdophosphate heteropoly acid. According to the invention, P in phosphate anion is used as a central atom to form the molybdophosphate heteropoly acid with molybdenum in an acid solution, so as to increase the solubility in an acid solution, and improve the leaching rate of nickel and molybdenum of the nickel-molybdenum ore during acid leaching. The method has the advantages of being high in nickel and molybdenum leaching rate, short in technological process, simple in equipment, simple and convenient to operate, low in production cost, environment-friendly and the like, and is convenient for large-scale industrial application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Benzimidazole derivative phosphate anion fluorescence probe synthesis and application method
ActiveCN106349167ASimple detection operationSimple and convenient detection operationOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceBenzimidazole derivativePhosphate ion
The invention discloses a method for synthesis of a benzimidazole derivative phosphate anion fluorescence probe and an application method thereof, and relates to the field of synthesis and application of the fluorescence probe. The synthesis of the benzimidazole derivative phosphate anion fluorescence probe can solve the problem that the florescence probes used for detecting PO43- are very scarce in kinds, that the identification of PO43- can be easily influenced by H2PO4- and HPO42-, and that the florescence probes can not directly carry out identification independently. The Benzimidazole derivative phosphate anion fluorescence probe is 1,4 phenyl double (carbamoyl methyl) N e alkylbenzimidazole ammonium chloride], which is obtained under quaterisation between Dichloro acetyl para-phenylene diamine and N-E alkyl benzene and imidazole. The fluorescence probe dissolves in HEPES buffered solution prepared by deionized water, and then test change in the absorbance value and fluorescence intensity to adjust the existence of PO43-. The Benzimidazole derivative phosphate anion fluorescence probe can be used to directly detect the po43- in water and blood.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Method for extracting exosomes and exosome proteins
ActiveCN110343664AHighly Specific ExtractionHigh recovery ratePeptide preparation methodsBiological testingHuman bodyPhosphate ion
The invention discloses a method for extracting exosomes and exosome proteins from human body fluid or culture medium. The method for extracting exosomes and exosome proteins provided by the inventionincludes: extraction materials are added to to-be-extracted solution containing the exosomes, and carrying out extraction to obtain the exosomes; the extraction materials are metallic oxides or function materials modified with the metallic oxides; the metallic oxides and phosphate anions can occur double coordination; and the to-be-extracted solution is body fluid from the human body, diluent ofthe body fluid or cell culture products. Experiment shows that the exosome extraction method of the invention can realize highly-efficient extraction of the exosomes from the human body fluid or the cell culture medium, the extraction time is short, the purity of the obtained exosomes is high, complete exosomes can be obtained by eluent elution, and the used extraction materials can be recycled and reused; in addition, extracting the exosome proteins can reveal that the obtained exosome proteins are more in types and more closely related to exosome functions.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Stable, non-chrome, thin-film organic passivates
InactiveUS20060169363A1Trend downGood molding effectPretreated surfacesSolid state diffusion coatingWaxOrganic film
Storage-stable organic passivate formulations that are essentially chromium-free are provided comprising non-ionic or non-ionically stabilized organic film forming resin; at least one complex fluoride and optionally, dissolved phosphate anions, at least one component comprising vanadium, at least one inorganic oxide in dispersed form; and at least one wax in dispersed form.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com