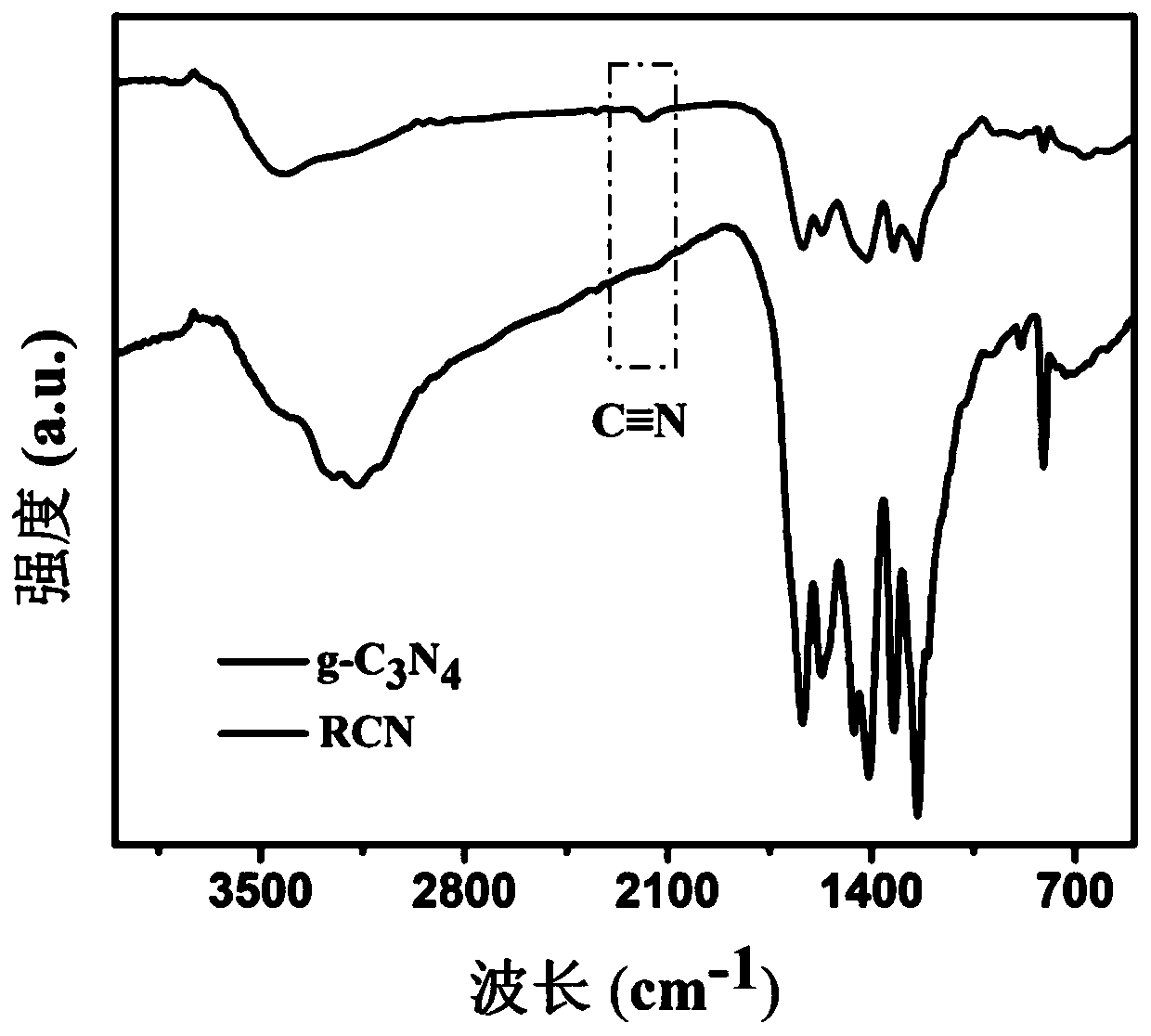
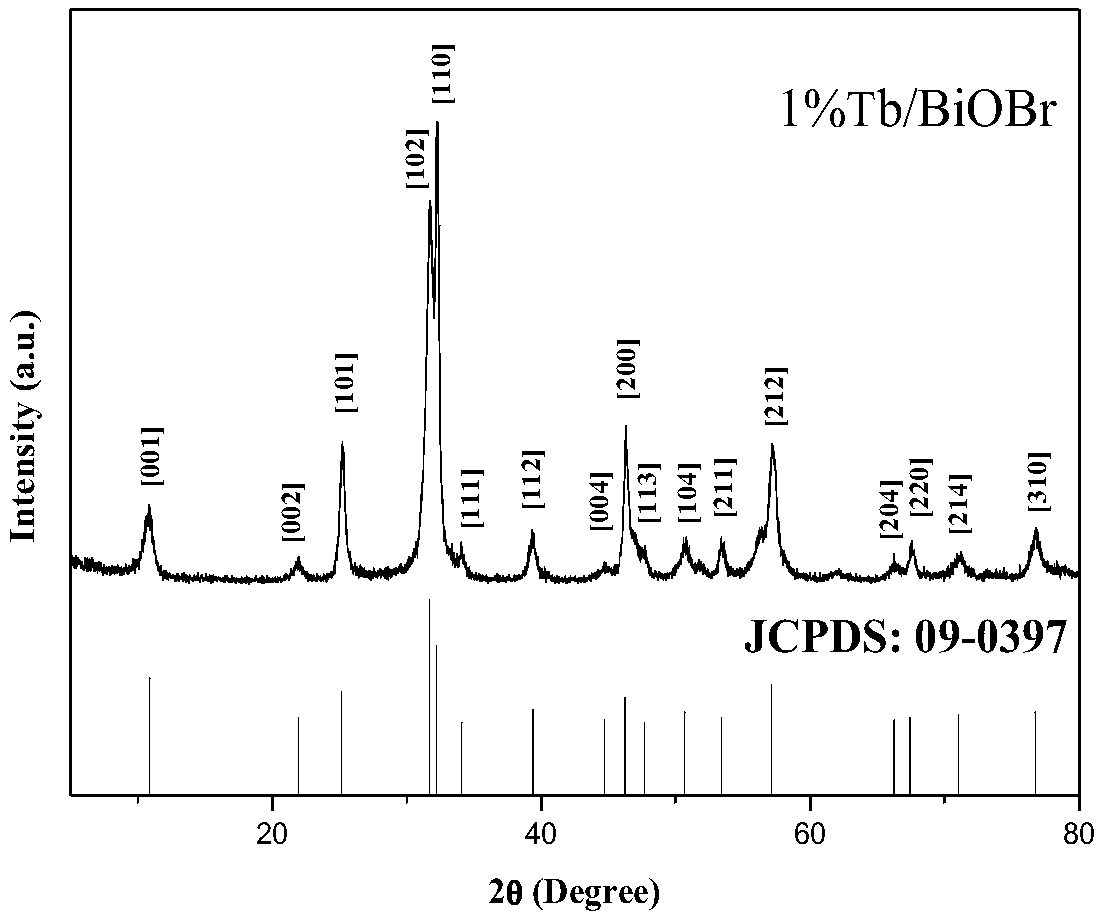
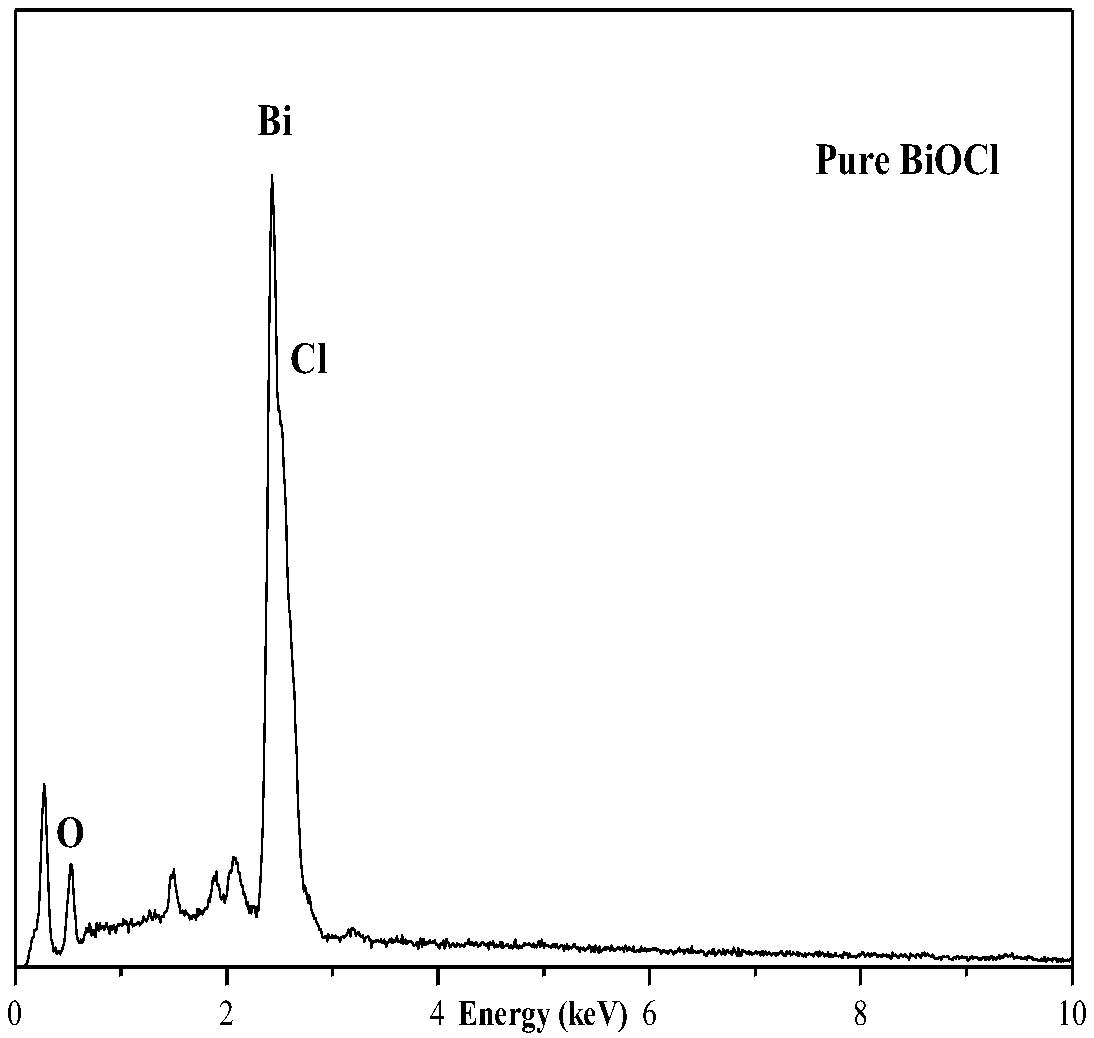
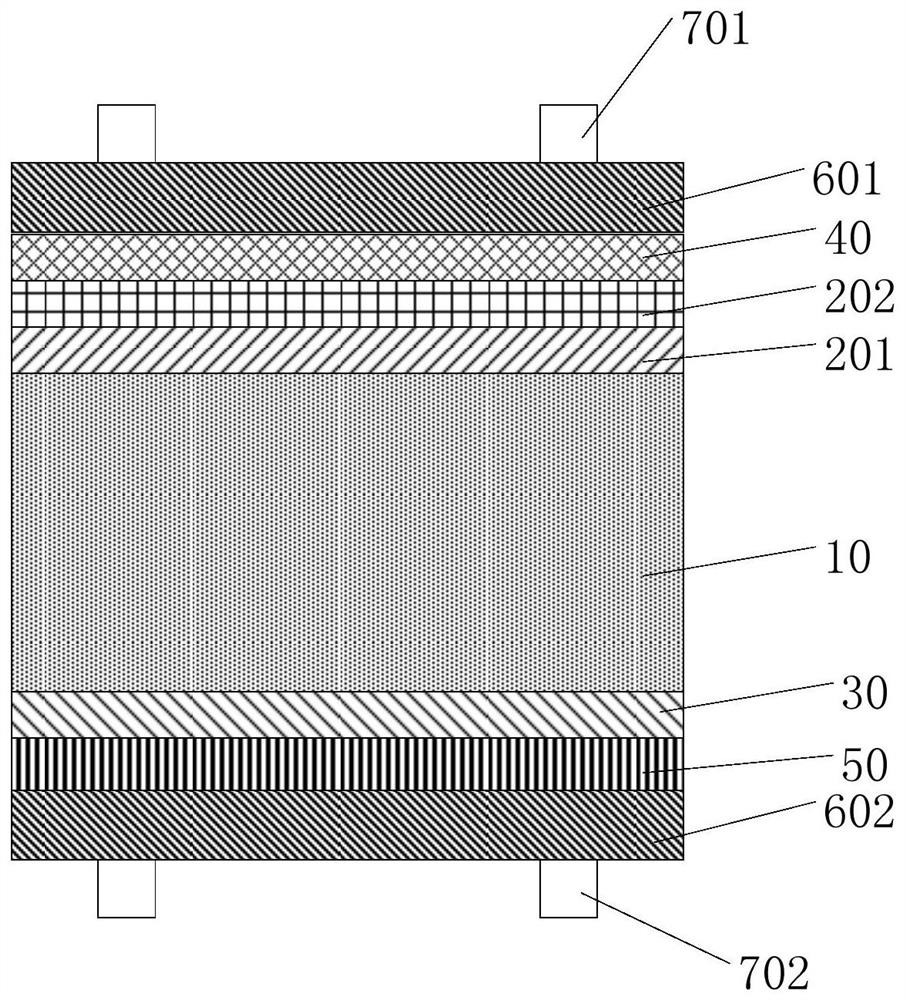
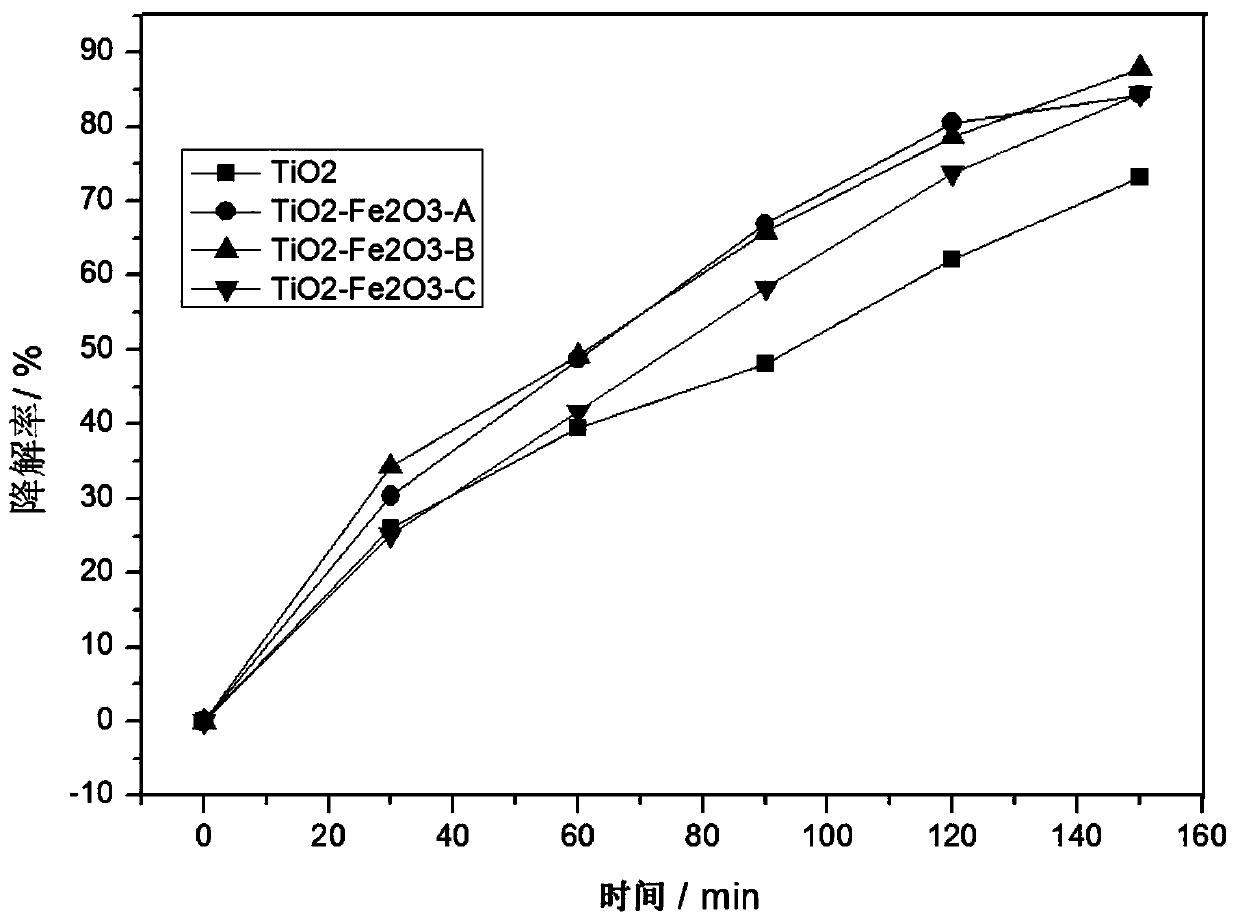
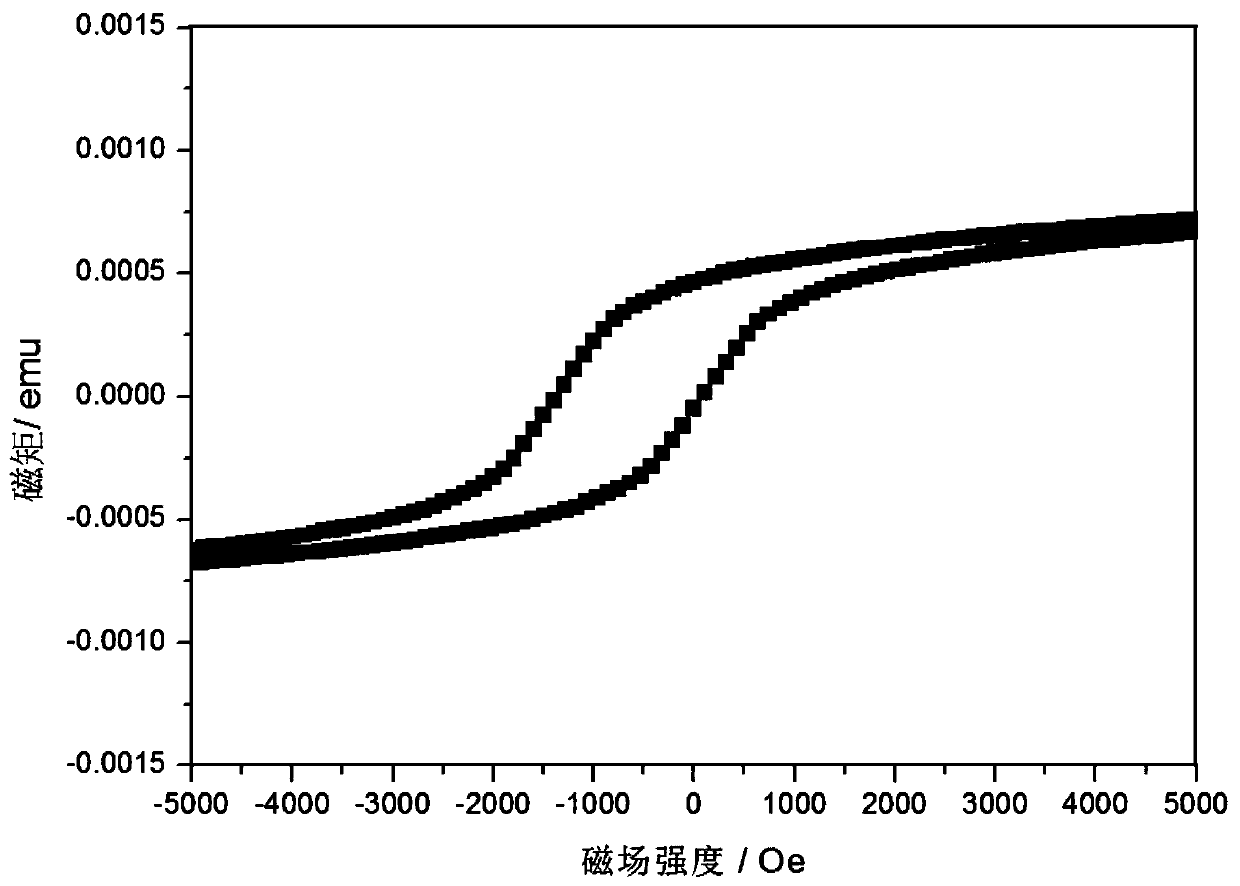
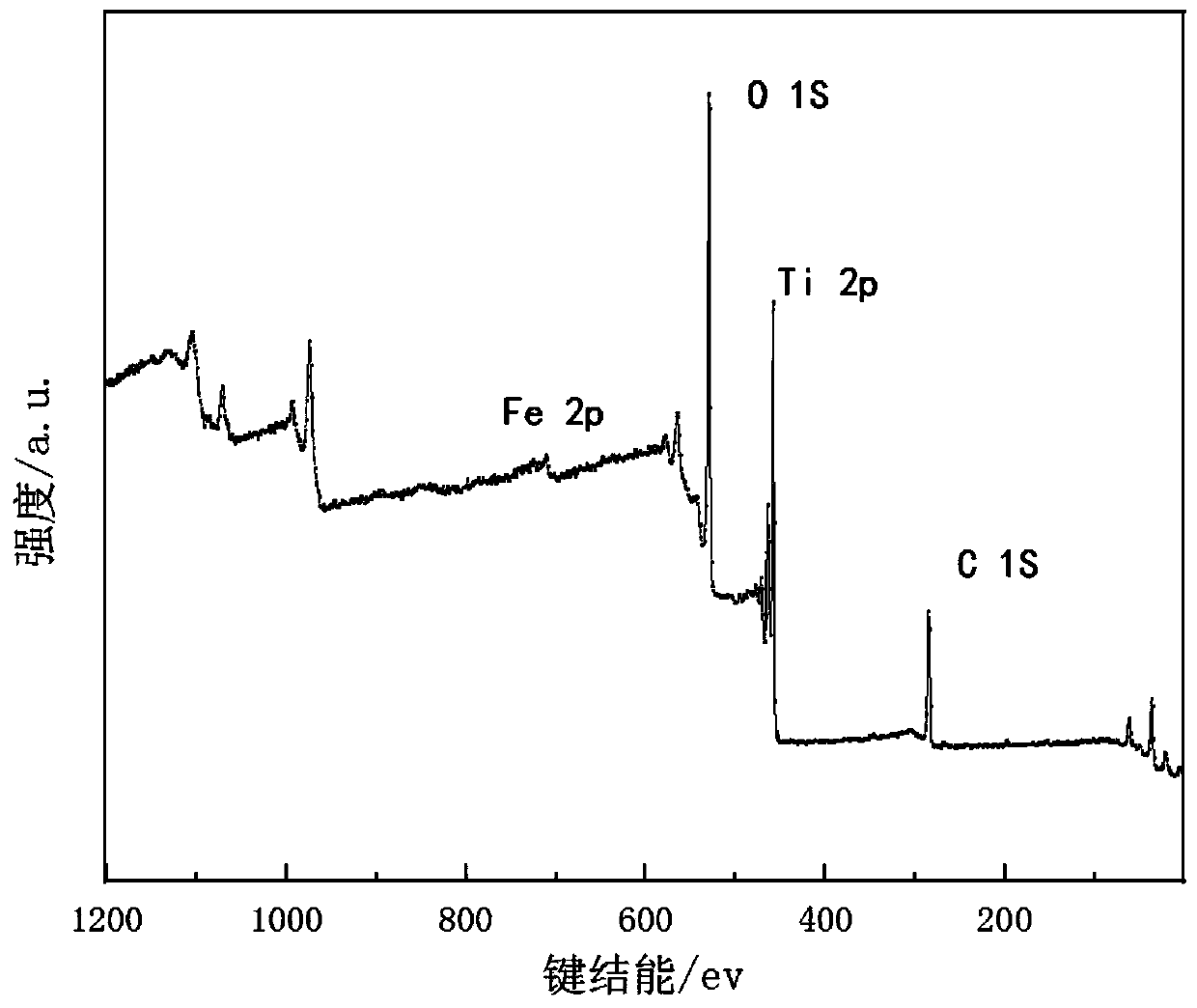
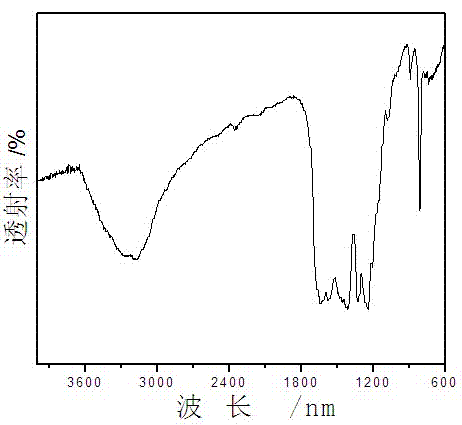
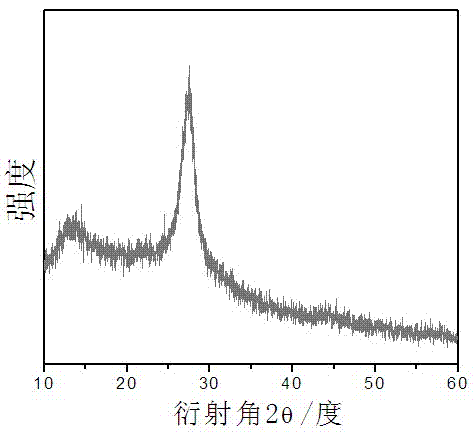
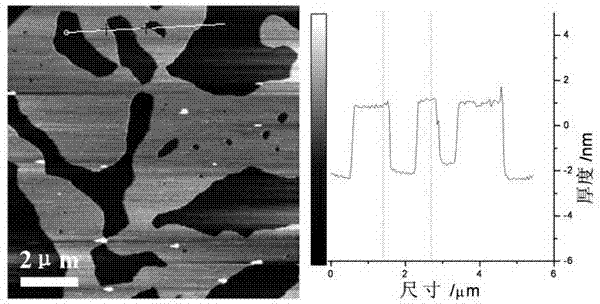
Patents
Literature
70results about How to "Reduced bandgap width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Condensed-ring compound and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN110698387AReduced bandgap widthPrevent backflowGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolid-state devicesOrganic electroluminescenceMaterials science
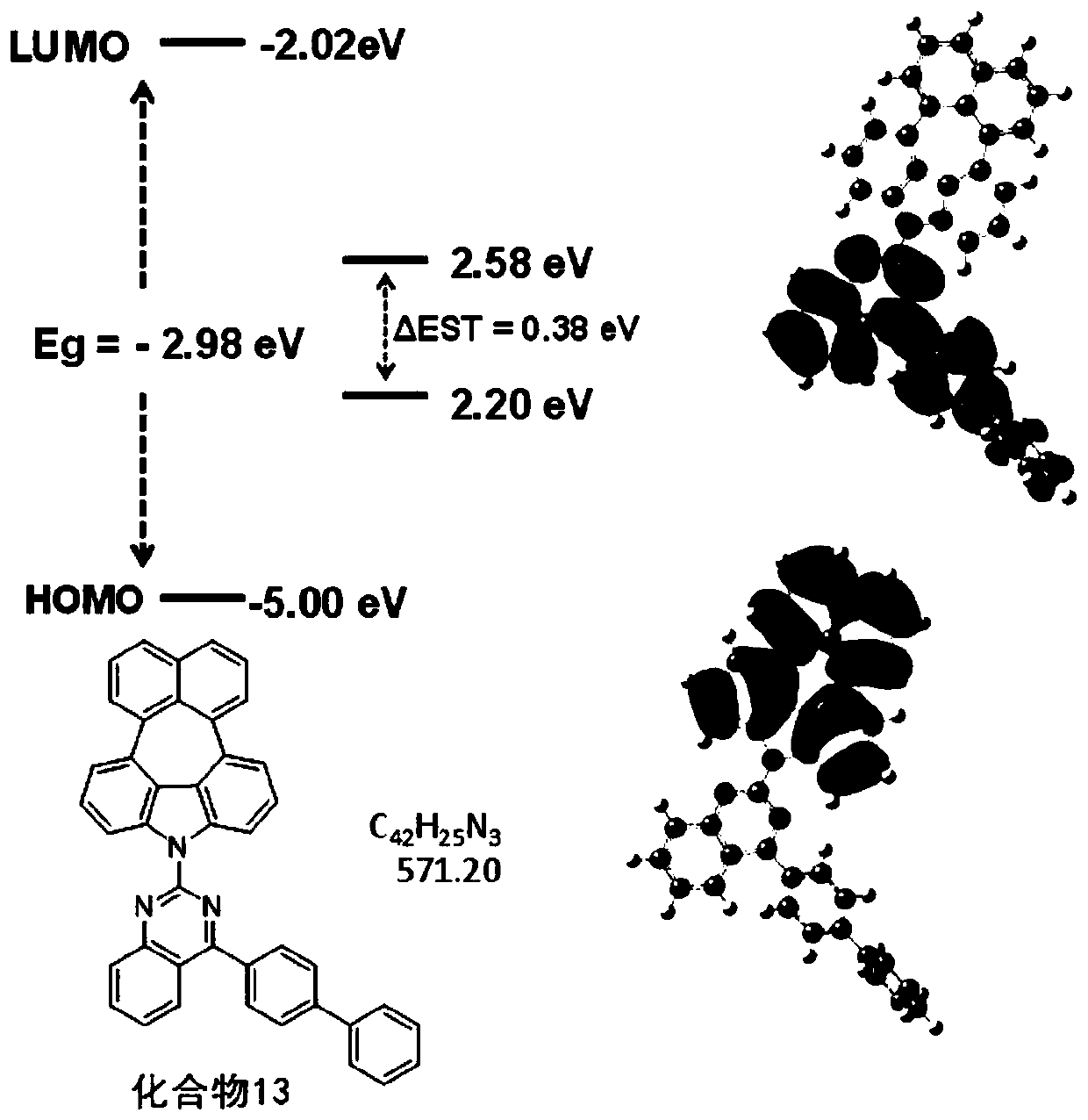
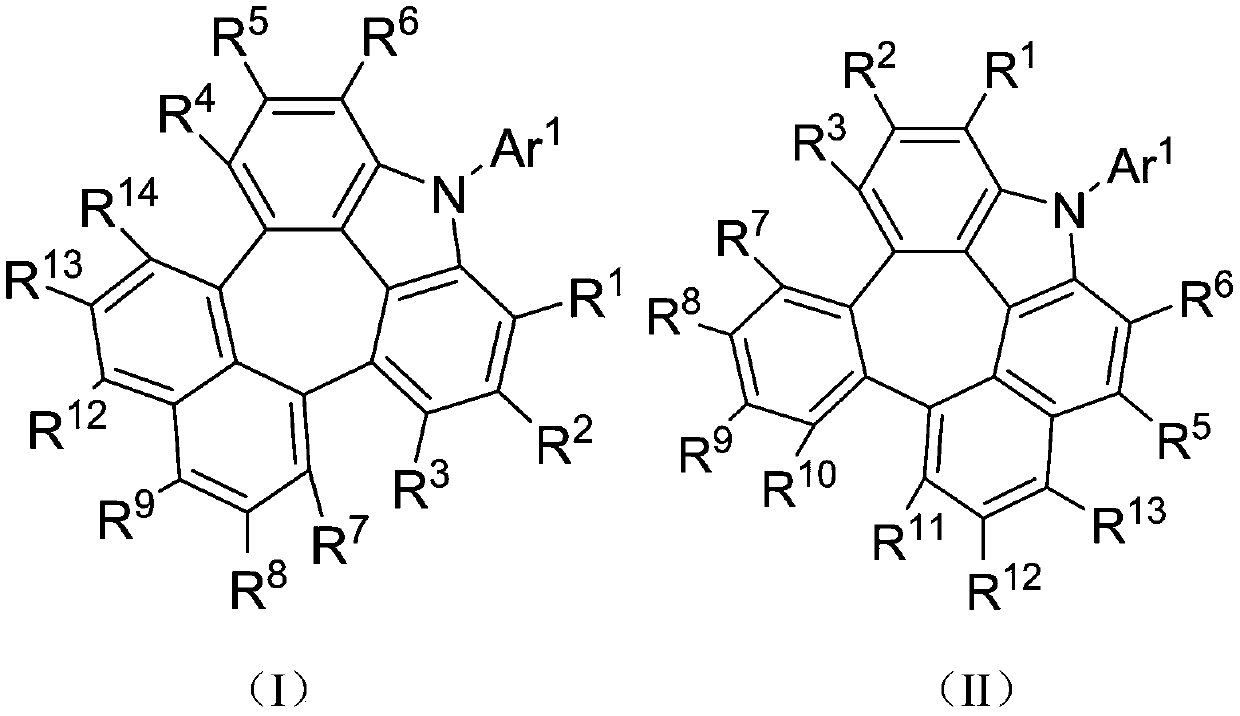
The invention discloses a condensed-ring compound and a preparation method and an application thereof. The condensed-ring compound has a structure represented by formula (I) or formula (II). The HOMOand LUMO energy levels of the fused-ring compound are completely separated, so that the energy gap width of the material is reduced, the three-wire energy level is improved, and the energy backflow from the object material to the main material is avoided to reduce the luminous efficiency; HOMO and LUMO energy levels are matched with adjacent materials, and the driving voltage is small. The devicehas large molecular structure size and good intramolecular conjugation, so it has good thermal stability, can avoid thermal decomposition of materials during film formation or use, avoids loss of material layer function, and improves luminous efficiency and luminous performance of the device. The invention also provides a preparation method of the fused-ring compound and its application as an organic electroluminescent material.
Owner:NINGBO LUMILAN NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Modified graphite phase carbon nitride photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108940344AHigh specific surface areaEasy transferPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationElectron holeReactive site
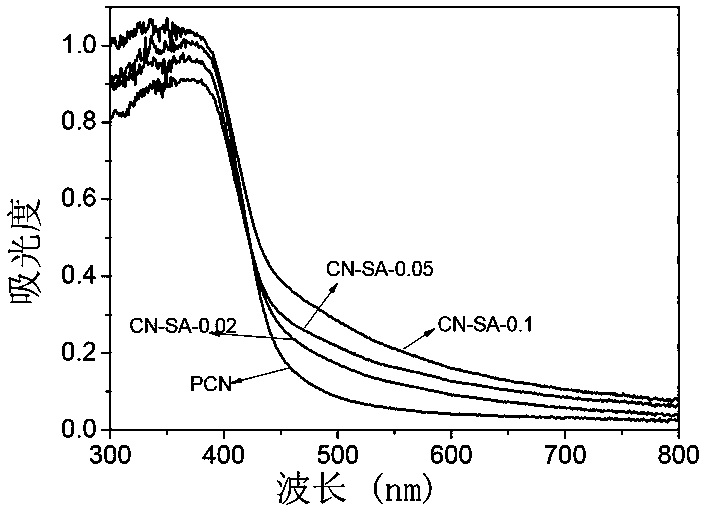
The invention discloses a modified graphite phase carbon nitride photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The modified graphite phase carbon nitride photocatalyst is prepared from urea and salicylic acid serving as raw materials by virtue of calcination, wherein a mass ratio of urea to salicylic acid is 1:(0.002-0.02). The modified graphite phase carbon nitride photocatalyst disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being high in specific surface area, wide in light absorption range, low in electron-hole pair recombination rate, excellent in photocatalyticperformance and the like, and has multiple reactive sites, excellent application value and application prospects. The preparation method has the advantages of being simple in process, wide in raw material source, low in cost, high in preparation efficiency, high in yield and the like, is suitable for large-scale preparation and is favorable for industrial production. The modified graphite phase carbon nitride photocatalyst disclosed by the invention can be used for degrading organic pollutants, has the advantages of being simple in process, convenient to operate, low in cost, high in treatmentefficiency, excellent in degradation effect and the like, and has excellent effects of degrading the various organic pollutants.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Preparation method of graphene/TiO2 composite material
InactiveCN107011783AWide variety of sourcesControl activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsAntifouling/underwater paintsGrapheneAntibacterial property
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene / TiO2 composite material. The method comprises the steps of preparation of graphene oxide, preparation of nano TiO2 and preparation of graphene / TiO2 composite material. The prepared composite material has the antibacterial property, and is capable of improving the antibacterial property and the environmental protection performance of a paint when being applied to the paint.
Owner:四川嘉宝莉涂料有限公司
Copolymerization-modified graphite-phase carbon nitride hollow ball visible light-driven photocatalyst
InactiveCN103861630ALarge specific surface areaReduced bandgap widthPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrogen productionOrganic moleculesPhoto catalysis
The invention discloses a copolymerization-modified graphite-phase carbon nitride hollow ball visible-light-driven photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and an application thereof and belongs to the technical fields of material preparation and photocatalysis. A carbon nitride hollow ball is synthetized by taking cyanamide and a small organic molecule monomer as precursors, a mesoporous silicon dioxide ball as a template and through the steps of thermal polymerization and template removing. The copolymerization-modified graphite-phase carbon nitride prepared by adopting the method disclosed by the invention is shaped like a hollow ball and is uniform in grain size and proper in band gap; compared with traditional-phase carbon nitride, the graphite-phase carbon nitride is capable of effectively increasing the specific surface area and increasing the utilization rate of sunlight and has the efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation performance in visible light. The visible-light-driven photocatalyst disclosed by the invention is simple in synthetic process, low in cost and high in catalytic efficiency, meets the actual production requirements and has the broad application prospect in the photocatalysis field.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of metastable phase bismuth oxide and application thereof in photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants
ActiveCN107029770AEasy to separateQuick migrationPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationPhotocatalytic degradationLight response
The invention discloses a preparation method of metastable phase bismuth oxide and application thereof in photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out hydrothermal reaction on an aqueous solution which contains ammonium bismuth citrate, urea and hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide to obtain bismuthyl carbonate microflowers; and calcining the bismuthyl carbonate microflowers in an air environment to obtain the metastable phase bismuth oxide beta-Bi2O3 / Bi2O2.33@Bi2O2CO3. The preparation method is simple and controllable to operate, and is environmentally friendly. The synthesized metastable phase bismuth oxide has the advantages of visible-light response, large specific surface area, high catalytic activity and the like, has the characteristics of rapidness and high efficiency in a process of visible-light catalytic degradation of the organic pollutants, and can be widely applied to the technical field of treatment of the organic pollutants.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Composite film, its preparation method and composite material
ActiveCN102898035AImprove self-cleaning abilityImprove anti-reflection effectComposite filmTransmittance
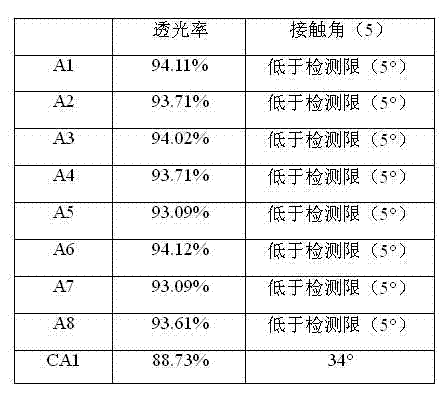
The invention provides a composite film containing titanium dioxide and silicon dioxide, wherein the titanium dioxide is nitrogen doped titanium dioxide. In terms of the total mole number of the film, the titanium dioxide accounts for 9.8-49.8 mole percent, the silicon dioxide accounts for 44.8-88.2 mole percent, and the nitrogen element accounts for 0.4-2 mole percent. Being spherical, the silicon dioxide has an average particle size of 80-100nm. The invention also provides a preparation method of the thin film and a composite material containing the film. The film provided in the invention has high light transmittance and a strong self-cleaning ability.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Method for treating organic pollutants and photocatalytic sterilization by using modified carbon quantum dot loaded hollow tubular carbon nitride photocatalyst
ActiveCN109603882AEfficient degradationSimple processPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationModified carbonWastewater
The invention discloses a method for treating organic pollutants and photocatalytic sterilization by using a modified carbon quantum dot loaded hollow tubular carbon nitride photocatalyst, which comprises the following steps: the modified carbon quantum dot loaded hollow tubular carbon nitride photocatalyst and organic pollutant wastewater or bacteria solution are mixed for photocatalytic treatment to finish the treatment of the organic pollutant or bacteria, the modified carbon quantum dot loaded hollow tubular carbon nitride photocatalyst is prepared by taking hollow tubular carbon nitride as a carrier and the carrier is loaded with modified carbon quantum dots, wherein the hollow tubular carbon nitride is prepared from urea and melamine in a molar ratio of 1-5:1 and melamine through hydrothermal treatment and calcination. The method has the advantages of simple process, convenient operation, simple equipment, low cost, high treatment efficiency / photocatalysis efficiency, good removal effect / sterilization effect, cleanness, no pollution and the like, and has high application value and commercial value.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Preparation method for bismuth ferrate nano fibers
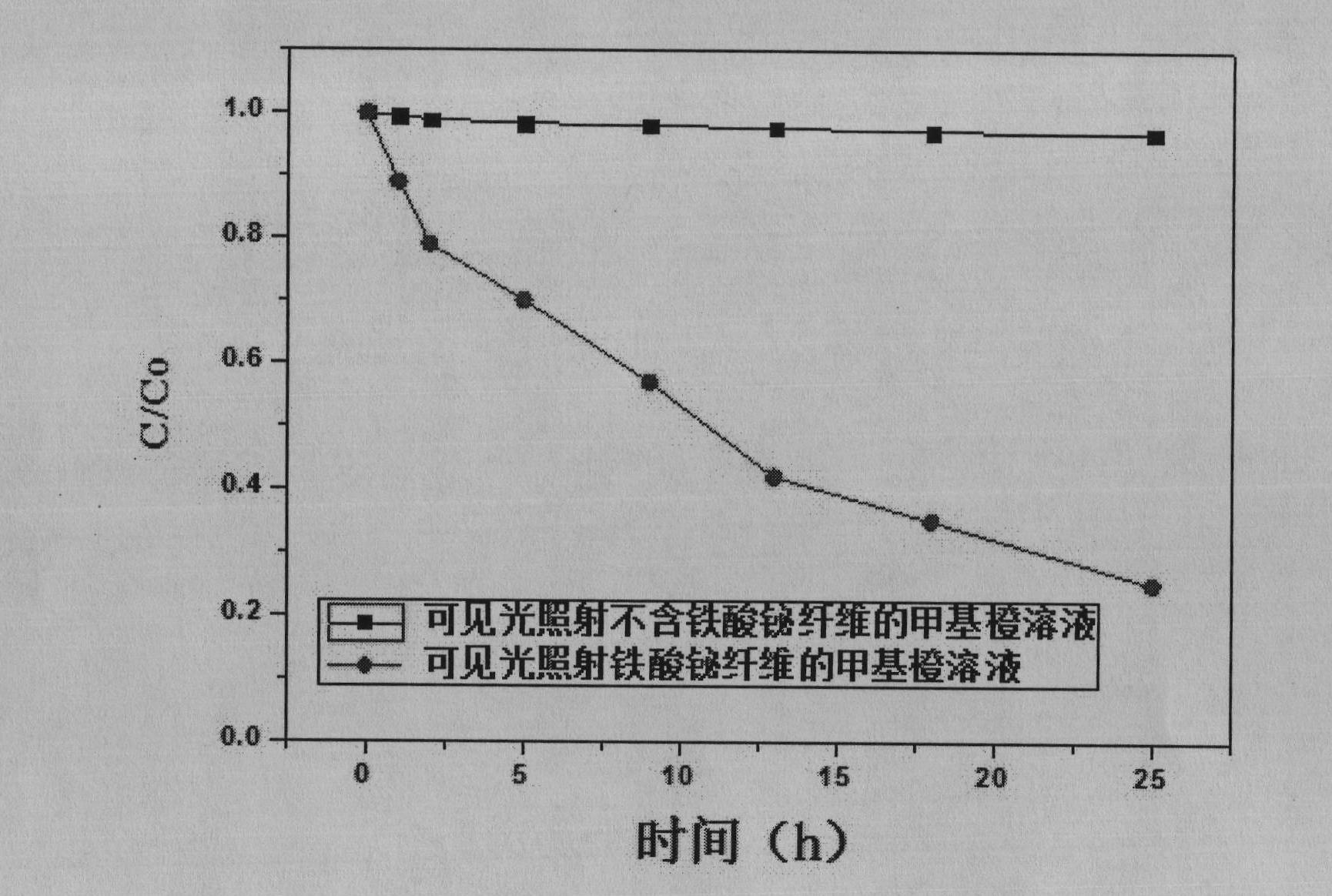
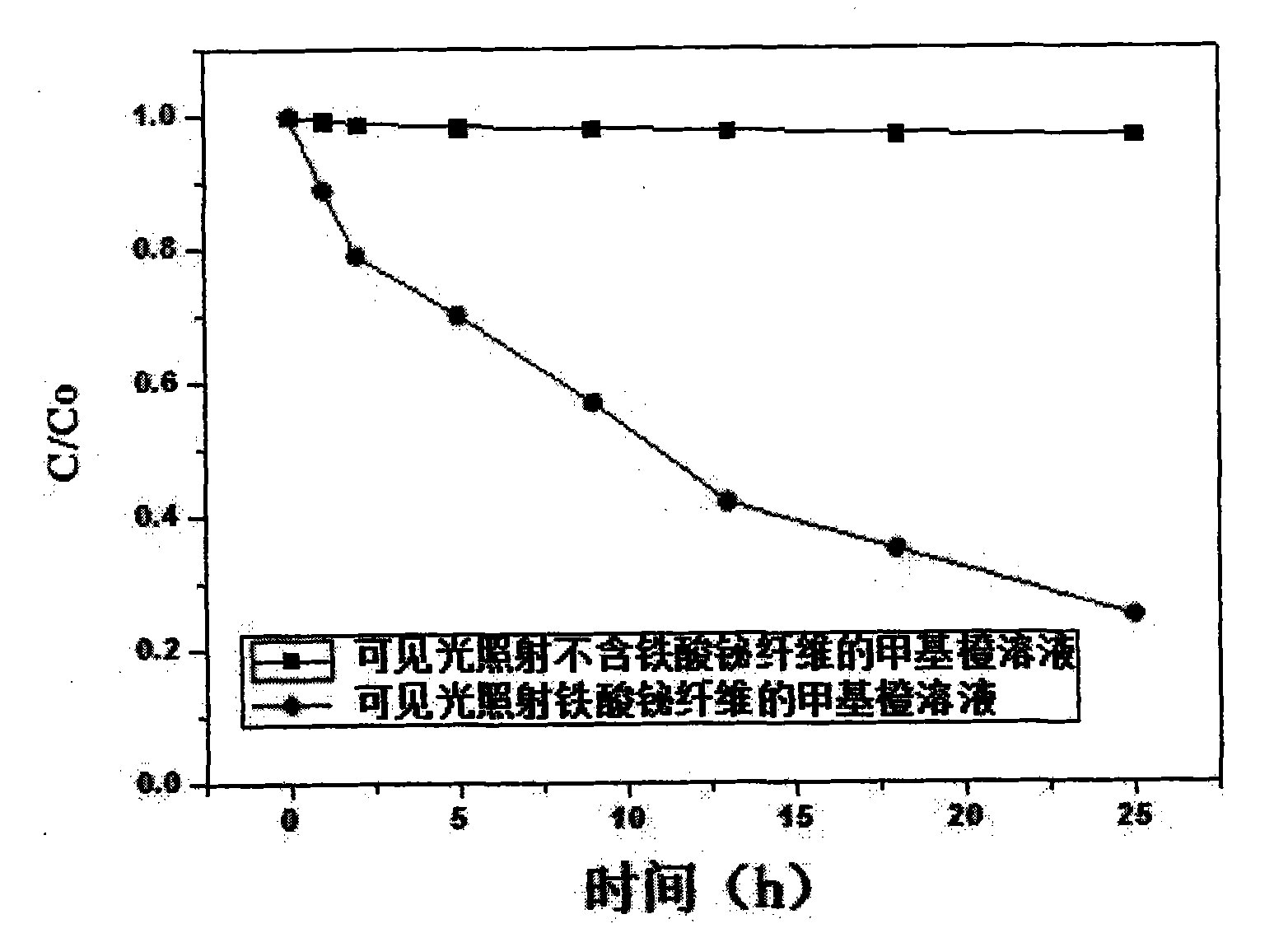
InactiveCN102583566AGuaranteed concentrationReduced bandgap widthNanotechnologyIron compoundsFiberWater baths
The invention discloses a preparation method for bismuth ferrate nano fibers and aims to solve the technical problem that the traditional photocatalytic material has a wide band gap. The invention adopts the technical scheme which comprises the following steps of: dissolving citric acid in deionized water to form a citric acid solution; adding ferric nitrate and bismuth nitrate into the citric acid solution, stirring the mixture until the mixture is clear and transparent, after standing the solution, heating and stirring the solution in a water-bath pot, adding polyvinylpyrrolidone into the solution, continuously stirring until the polyvinylpyrrolidone is completely dissolved, keeping the concentration of the polyvinylpyrrolidone, performing electrostatic spinning by using an injection pump and a high-pressure power supply, and collecting the fibers by using a monocrystalline wafer; and after drying the collected fibers in a drying box, calcining the fibers at consistent temperature in a muffle furnace to obtain the bismuth ferrate nano fibers. The band gap of the bismuth ferrate nano fibers prepared by the preparation method is reduced from 3.2 to 3.4ev in the background technology to below 2.1ev.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Modified carbon quantum dot loaded hollow tubular carbon nitride photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109603881ALarge specific surface areaMany holesPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationAbsorption capacityModified carbon
The invention discloses a modified carbon quantum dot loaded hollow tubular carbon nitride photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The photocatalyst takes hollow tubular carbon nitride as a carrier and is loaded with modified carbon quantum dots; urea and melamine with a mole ratio of 1-5:1 are used to prepare the hollow tubular carbon nitride through hydrothermal and calcination. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing hollow tubular carbon nitride, water and modified carbon quantum dot solution, and drying to obtain the photocatalyst. The photocatalyst has the advantages of large specific surface area, large number of pores, multiple active sites, high speed of separation and migration of photo-generated carriers, strong light absorption capacity, high photocatalytic activity, high stability, high photocatalytic efficiency and the like; the preparation method of the photocatalyst has the advantages of convenience in synthesis, simplicity in operation,no secondary pollution to the environment and the like. The photocatalyst can be widely used for treating organic pollutants in the environment and killing harmful microorganisms in the environment,and has good application value and application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
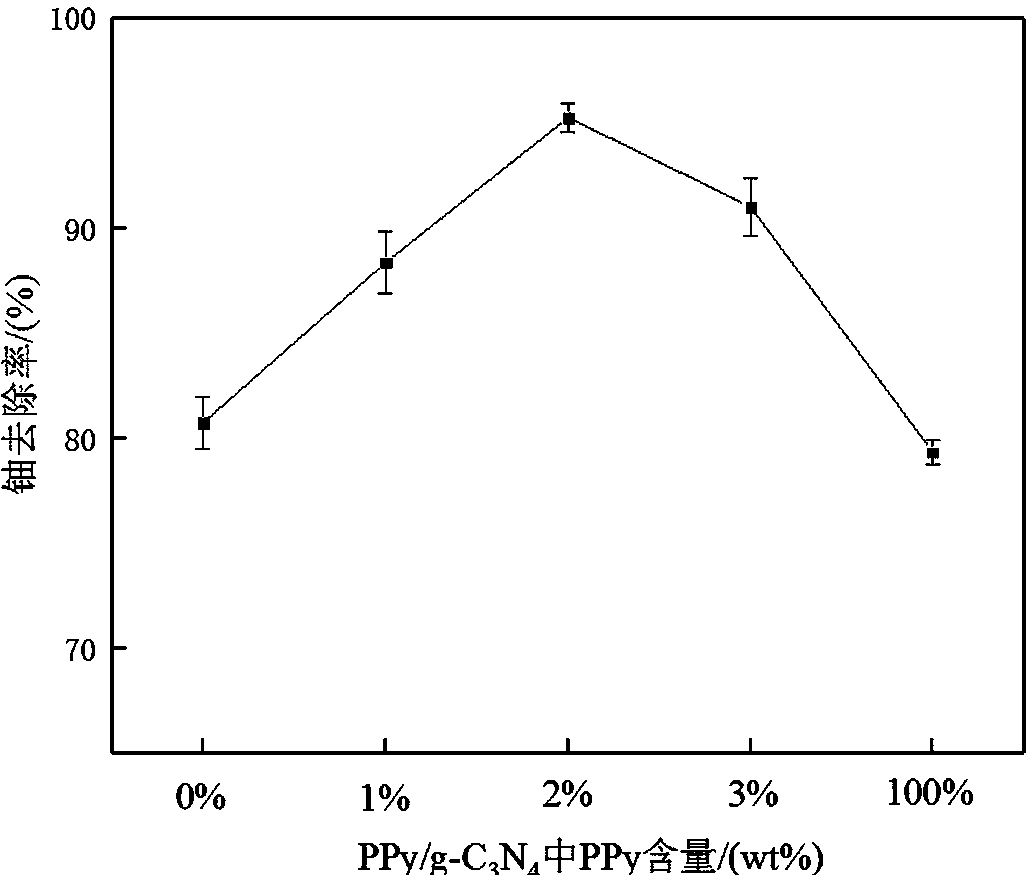
Preparation method of polypyrrole graphite-phase carbon nitride composite material for treating uranium-containing wastewater through photocatalytic reduction and application thereof
InactiveCN111018041AGood dispersionReduced bandgap widthWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolypyrroleAdsorption effect
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polypyrrole graphite-phase carbon nitride composite material for treating uranium-containing wastewater through photocatalytic reduction and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: calcining melamine to obtain graphite phase carbon nitride, mixing and oscillating the graphite phase carbon nitride and sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, adding pyrrole with different mass ratios, filtering, washing with water, and drying to obtain the polypyrrole=graphite phase carbon nitride composite material; adjusting the pH value of the uranium-containing wastewater to 4-7, adding the composite material as a uranium removal agent into the uranium-containing wastewater, placing the uranium-containing wastewater in a dark box environment, introducing nitrogen, stirring, irradiating the stirred solid-liquid mixture with a xenon lamp, filtering the irradiated hexavalent uranium-containing wastewater, taking the filtered clear liquid, and calculating the removal rate of uranium in the uranium-containing wastewater. The polypyrrole-graphite-phase carbon nitride composite material prepared by the method is good in catalytic activity in a visible light region, low in cost, simple to operate, relatively high in uranium-containing wastewater removal rate, remarkable in adsorption effect and relatively good in economic benefit.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
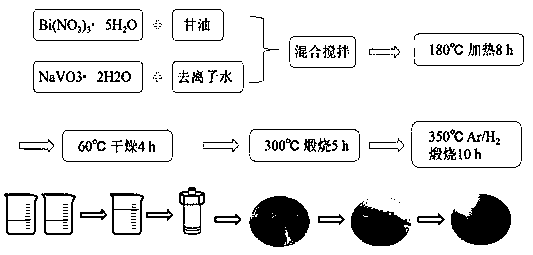
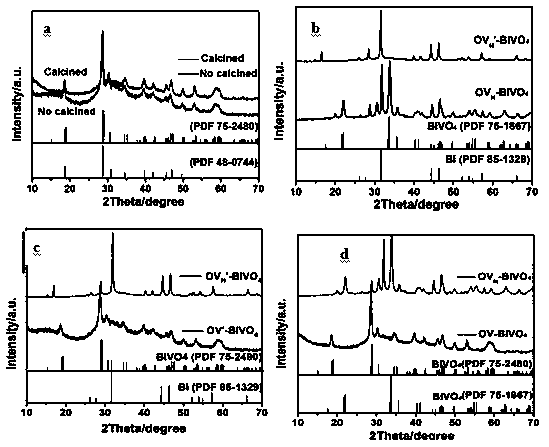
H-occupied BiVO4-OVs photocatalytic material and production method and application thereof
ActiveCN109985618ABroaden the range of light absorptionWide light absorption rangeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsSolventHigh pressure
The invention discloses a method for producing an H-occupied BiVO4-OVs photocatalytic material and application of the H-occupied BiVO4-OVs photocatalytic material. The production method comprises thesteps of dissolving a certain molar weight of Bi(NO3)3.5 H2O in glycerin; dissolving a certain molar weight of NaVO3.2 H2O in deionized water; mixing solutions; transferring a mixed solution into a teflon-lined high-pressure kettle, and maintaining 180 DEG C for 8 h; conducting 10000-rpm centrifugal separation on a solvothermal synthesis product, washing the solvothermal synthesis product subjected to 10000-rpm centrifugal separation with deionized water and ethyl alcohol, and drying the washed solvothermal synthesis product subjected to 10000-rpm centrifugal separation at 60 DEG C for 4 h; calcining the solvothermal synthesis product, which is thoroughly washed, in a muffle furnace at 300 DEG C for 5 h; and conducting annealing on a calcined product in an Ar / H2 atmosphere at 350 DEG C for10 h to obtain the H-occupied BiVO4-OVs photocatalytic material. The H-occupied BiVO4-OVs photocatalytic material has the advantages that a photoresponse range is wide, the catalytic activity is high, the degradation rate is high, and the hydrolysis ability is high; and solar energy can be fully and effectively used.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing flaky TiO2/g-C3N4 heterojunction by one-step method
InactiveCN110124716ASmall diameterThe method is simple and fastWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsHeterojunctionAir atmosphere
The invention relates to a method for preparing a flaky TiO2 / g-C3N4 heterojunction by a one-step method, the method comprises the following steps: (1) sequentially adding acetylacetone and tetrabutyltitanate into absolute ethyl alcohol to obtain a solution A; (2) adding polyvinyl pyrrolidone into the solution A to obtain a solution B after complete dissolution; (3) adding a proper amount of melamine powder into the solution B to obtain a solution C after complete dissolution; (4) filling the mixed solution C into a syringe, performing electrostatic spinning under certain conditions, and collecting a spinning product by using a stainless steel disc; and (5) after the spinning product is dried, roasting the spinning product for 4 hours at 550 DEG C in an air atmosphere. The method has the characteristics of simple and quick method, low cost, small product fiber diameter and large specific surface area, and is widely applied to photocatalytic hydrogen production and pollutant degradation.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for treating chromium-containing wastewater by using straw cellulose-cerium oxide composite through photocatalytic reduction
ActiveCN106378124AGood dispersionReduced bandgap widthWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsCelluloseFiltration
The invention relates to a method for treating chromium-containing wastewater by using a straw cellulose-cerium oxide composite through photocatalytic reduction. The method comprises the following steps: dispersing straw pulp in tetramethyl piperidine nitrogen oxide and sodium bromide, dropwise adding an alkaline sodium hypochlorite solution; reacting for several hours while vigorously stirring, and regulating pH of the solution by using sodium hydroxide; carrying out suction filtration, washing and drying to obtain nano straw cellulose; dissolving a proper amount of straw cellulose and a proper amount of cerium nitrate hexahydrate in a mixed solution of deionized water and ethyl alcohol and uniformly stirring, transferring a mixture into a high-pressure reactor for reacting; centrifugally separating the mixture and then washing the mixture with the ethyl alcohol and the deionized water; drying the mixture to obtain a finished straw cellulose-cerium oxide product; adding the finished straw cellulose-cerium oxide product into wastewater containing hexavalent chromium in an initial concentration of 3-10mg / L, uniformly stirring and then irradiating for 30 minutes or longer by using a xenon lamp, and measuring the concentration of the hexavalent chromium in the treated wastewater and calculating the removal rate of the hexavalent chromium. The method for treating the chromium-containing wastewater by using the straw cellulose-cerium oxide composite is high in removal rate of the hexavalent chromium and low in treatment cost, and is environmental-friendly.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Reducing carbon nitride photocatalyst, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110961129APromote absorptionReduced bandgap widthWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
Belonging to the technical field of photocatalysis, the invention discloses a reducing carbon nitride photocatalyst, a preparation method and application thereof. The photocatalyst is prepared by thesteps of: heating melamine to 520-550DEG C, performing roasting, and conducting grinding to obtain g-C3N4 powder; mixing NaBH4 with g-C3N4 powder, and then performing heating to 570-600DEG C in a protective atmosphere; and performing cooling, then cleaning the product with deionized water and ethanol, and conducting drying. The reducing carbon nitride catalyst does not contain metal, and has the advantages of environmental protection, stability, low cost and the like. According to the invention, reducing carbon nitride is applied to photocatalytic degradation of diclofenac sodium for the firsttime, also shows excellent photocatalytic performance, and has good stability.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing composite nano Tb/BiOCl material
InactiveCN108043429AReduced band gapReduce chancePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMethyl orangeUltrasonic oscillation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a composite nano Tb / BiOCl material. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, putting potassium chloride into ethylene glycol so as to form a solution A; putting bismuth nitrate pentahydrate into ethylene glycol so as to form a solution B, and dropping the solution A into the solution B one droplet by one droplet till the ratio of n(Bi) to n(Cl) is 1:1; after dropping is completed, continuously stirring, adding terbium nitrate, and performing ultrasonic oscillation so as to obtain a mixed solution; transferring the mixed solution into a reaction kettle, sealing, and putting into an oven for reactions; after the reactions are completed, naturally cooling the reaction kettle to the room temperature, collecting solid precipitate, washing, and drying, thereby obtaining the composite nano Tb / BiOCl material. The composite nano Tb / BiOCl material prepared by using the method has relatively good catalytic degradation properties upon methylorange under visible light.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for treating hexavalent chromium-containing wastewater by photocatalytic reduction of nickel oxide-nickel cobaltate-black titanium dioxide compound
InactiveCN110918099AReduced bandgap widthLarge specific surface areaWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPyrrolidinonesPoly ethylene
The invention relates to a method for treating hexavalent chromium-containing wastewater by photocatalytic reduction of a nickel oxide-nickel cobaltate-black titanium dioxide compound. The method comprises the following steps: preparing black titanium dioxide, dissolving cobalt nitrate hexahydrate, nickel nitrate hexahydrate and the black titanium dioxide in a proper amount of deionized water, magnetically stirring to form a uniform solution, adding a proper amount of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP, K30) into the solution, and stirring the suspension with a magnetic stirrer for at least 1 hour; dispersing urea into the suspension, grinding powder, and calcining the powder in a tubular furnace in air at 500 DEG C for 2 hours to obtain the nickel oxide-nickel cobaltate-black titanium dioxide compound; adding the nickel oxide-nickel cobaltate-black titanium dioxide compound into the hexavalent chromium-containing wastewater; taking out the mixture at a certain time interval, immediately filtering, measuring the concentration of the treated hexavalent chromium at 540nm by using an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer according to a 1, 5-diphenylcarbazide method, and calculating the removalrate. The method has the advantages of high removal rate, low treatment cost, environmental friendliness and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
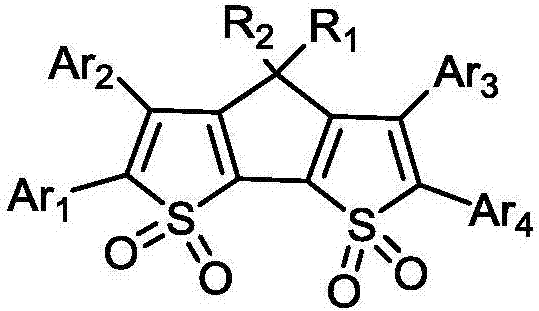
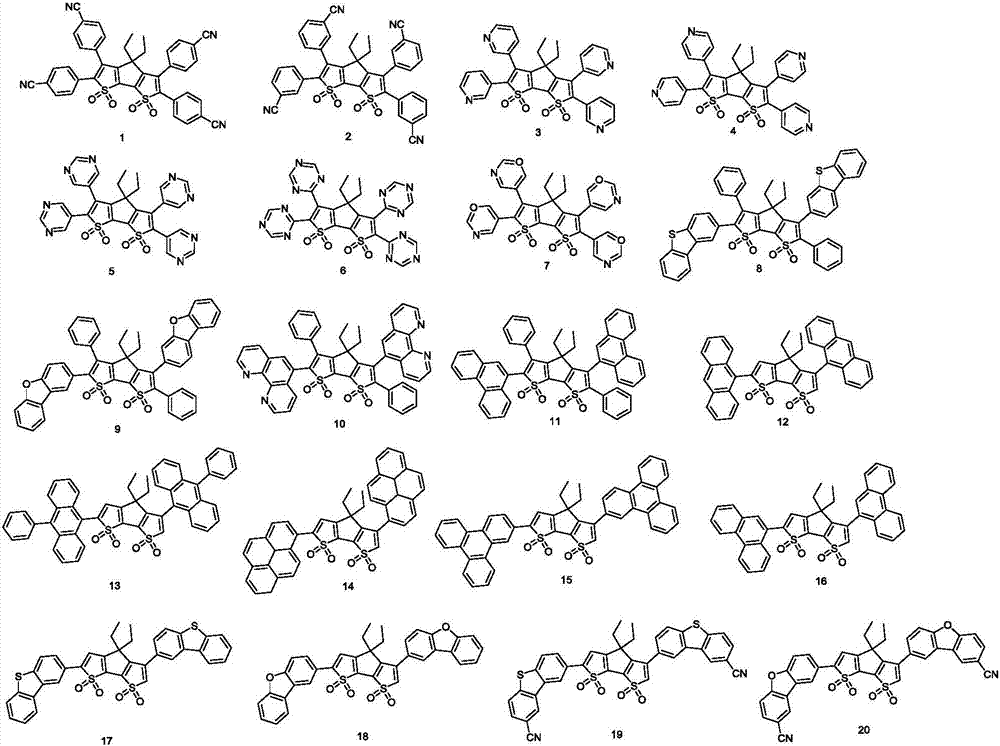
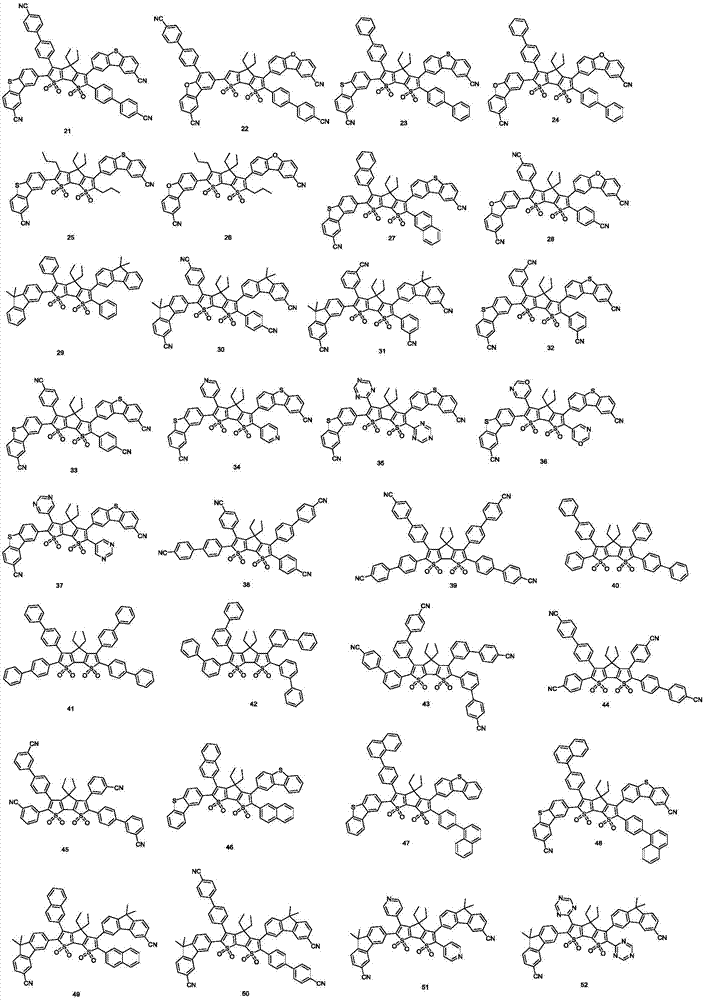
Organic light-emitting material with bithiophene pentalene derivative structure and organic light-emitting device of organic light-emitting material
InactiveCN107056804AReduced bandgap widthImprove luminous efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesTransfer capacityPentalene
The invention discloses an organic light-emitting material with a bithiophene pentalene derivative structure and an organic light-emitting device of the organic light-emitting material, and belongs to the technical field of organic photoelectric materials. According to the organic light-emitting material with the bithiophene pentalene derivative structure and the organic light-emitting device of the organic light-emitting material, 4-H-cyclopentadiene bithiophene-1,1,7,7-tetroxide is adopted as a body structure, and through connection of ligand genes with different polarities, the obtained derivative has strong eletrophilicity, charge transferring capacity and light-emitting performance. In the organic light-emitting device prepared through the bithiophene pentalene derivative, the light-emitting efficiency is high, the pohotochromism is uniform, and the organic light-emitting device has good film stability and thermal stability, and the problem that a unipolarity transmission material in the organic light-emitting device is unbalanced in current carrier can be effectively solved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN HYPERIONS TECH CO LTD
One-step method for preparing GQDs modified flaky TiO2/g-C3N4 heterojunction
InactiveCN110124715ASmall diameterThe method is simple and fastCatalyst activation/preparationHeterojunctionAir atmosphere
A one-step method for preparing a GQDs modified flaky TiO2 / g-C3N4 heterojunction composite material comprises the following steps: (1) sequentially adding acetylacetone and tetrabutyl titanate into absolute ethyl alcohol to obtain a solution A; (2) adding polyvinyl pyrrolidone into the solution A to obtain a solution B after complete dissolution; (3) adding a proper amount of melamine powder intothe solution B to obtain a solution C after complete dissolution; (4) adding graphene quantum dot powder into the solution C, and ultrasonically dispersing for 24 hours to obtain a mixed solution D; (5) filling the mixed solution D into a syringe, performing electrostatic spinning under certain conditions, and collecting a spinning product by using a stainless steel disc; AND (6) after the spinning product is dried, roasting the spinning product for 4 hours at 550 DEG C in an air atmosphere. The one-step method has the characteristics of simple and quick method, low cost, improved spectral response range, reduced photogenerated electron-hole recombination rate, large specific surface area and the like, and is widely applied to photocatalytic degradation of pollutants.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
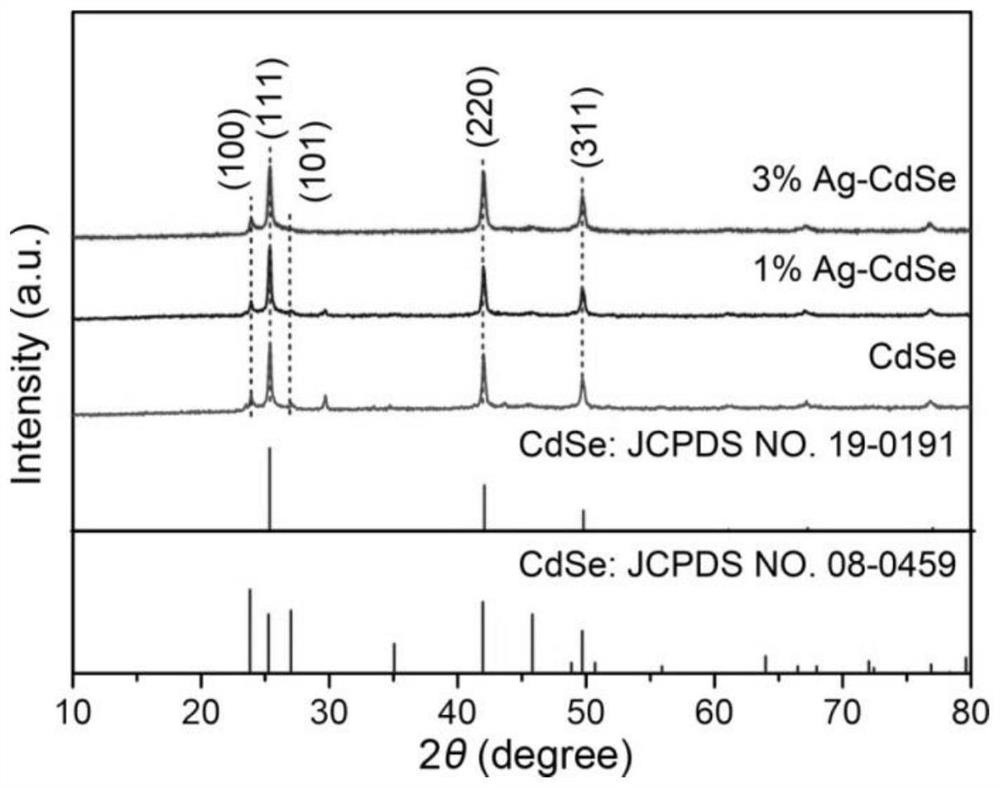
Preparation and application of Ag-doped CdSe nanosheet photocatalytic material for uranium reduction separation
PendingCN113499790ARaise the lead positionImprove light absorption abilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsPhoto catalysisMeth-
The invention discloses preparation and application of an Ag-doped CdSe nanosheet photocatalytic material for uranium reduction separation. The preparation method comprises the steps of mixing mixed powder of CdCl2. 5H2O and AgNO3 with a first mixed solvent of octylamine and oleylamine, carrying out heating reaction, and cooling to room temperature to obtain a reaction solution; mixing Se powder with a second mixed solvent of octylamine and oleylamine at room temperature to obtain a Se precursor solution; and adding the Se precursor solution into the reaction solution, carrying out heating reaction, cooling, cleaning the obtained precipitate with a trichloromethane solution for multiple times, uniformly mixing the precipitate with a cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution, and carrying out ultrasonic treatment, ethanol washing and drying to obtain the Ag-doped CdSe nanosheet photocatalytic material for uranium reduction separation. According to the Ag-doped CdSe nanosheet photocatalytic material disclosed by the invention, photocatalytic reduction of U (VI) is met while the light absorption capacity is improved, and generation and use of photon-generated carriers are facilitated.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
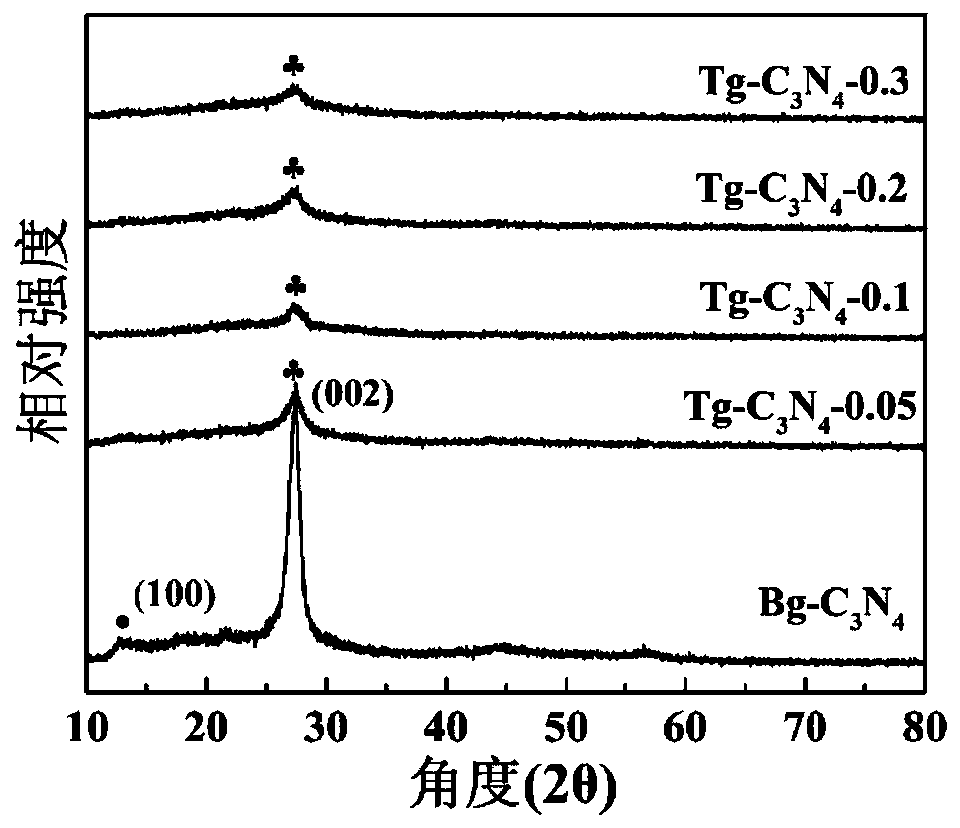
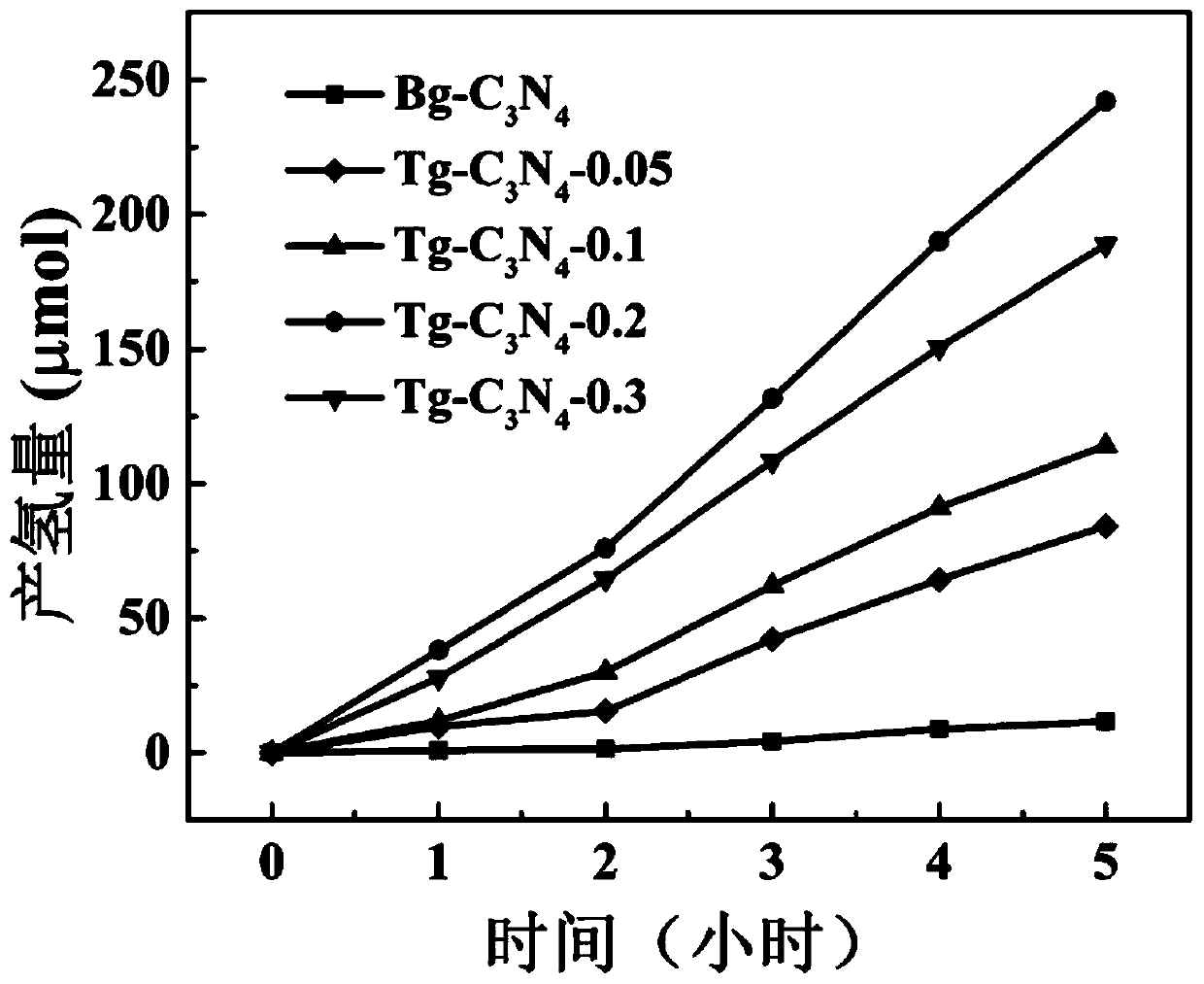
Preparation method of tubular g-C<3>N<4> with visible-light response function
InactiveCN110697667AMeets friendly requirementsSimple processPhysical/chemical process catalystsNitrogen and non-metal compoundsSemiconductor materialsNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a preparation method of tubular g-C<3>N<4> with a visible-light response function and belongs to the field of photocatalytic semiconductor material preparation technologies. The preparation method comprises the steps that (1) melamine and cyanuric acid are mixed and dissolved in ultrapure water according to an arbitrary proportion, magnetic stirring is performed, and a uniform mixed solution is formed; (2) then, the solution is transferred to a stainless steel autoclave for a reaction, and a precursor of a synthetic product is obtained; (3) the obtained precursor is dried after being washed with ultrapure water; and (4) after the dried precursor is calcined in nitrogen, the tubular g-C<3>N<4> with the visible-light response function is obtained. According to the preparation method, the one-dimensional tubular g-C<3>N<4> is prepared through high-temperature calcination, band gap width of the tubular g-C<3>N<4> is remarkably reduced, visible-light response of thetubular g-C<3>N<4> is improved, and the charge transport capability of the tubular g-C<3>N<4> is enhanced through a tube separation mode; and application of the tubular g-C<3>N<4> with the visible-light response function in the photocatalytic field comprises degradation, hydrogen production, nitrogen fixation, bacterial resistance and the like.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Silicon heterojunction solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN112002778AIncrease the open circuit voltageImprove fill factorFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionEngineering
The invention discloses a silicon heterojunction solar cell and a manufacturing method thereof, and relates to the technical field of solar cells. The invention aims to inhibit epitaxial growth of a silicon substrate interface by using an intrinsic amorphous silicon germanium layer and improve the passivation effect of the silicon substrate interface by using an intrinsic amorphous silicon layer.The silicon heterojunction solar cell comprises: an N-type silicon substrate; an intrinsic amorphous silicon germanium layer formed on one surface of the N-type silicon substrate; a first intrinsic amorphous silicon layer formed on the intrinsic amorphous silicon germanium layer; and a P-type doped amorphous silicon layer formed on the first intrinsic amorphous silicon layer. The manufacturing method of the silicon heterojunction solar cell is used for manufacturing the silicon heterojunction solar cell.
Owner:LONGI GREEN ENERGY TECH CO LTD
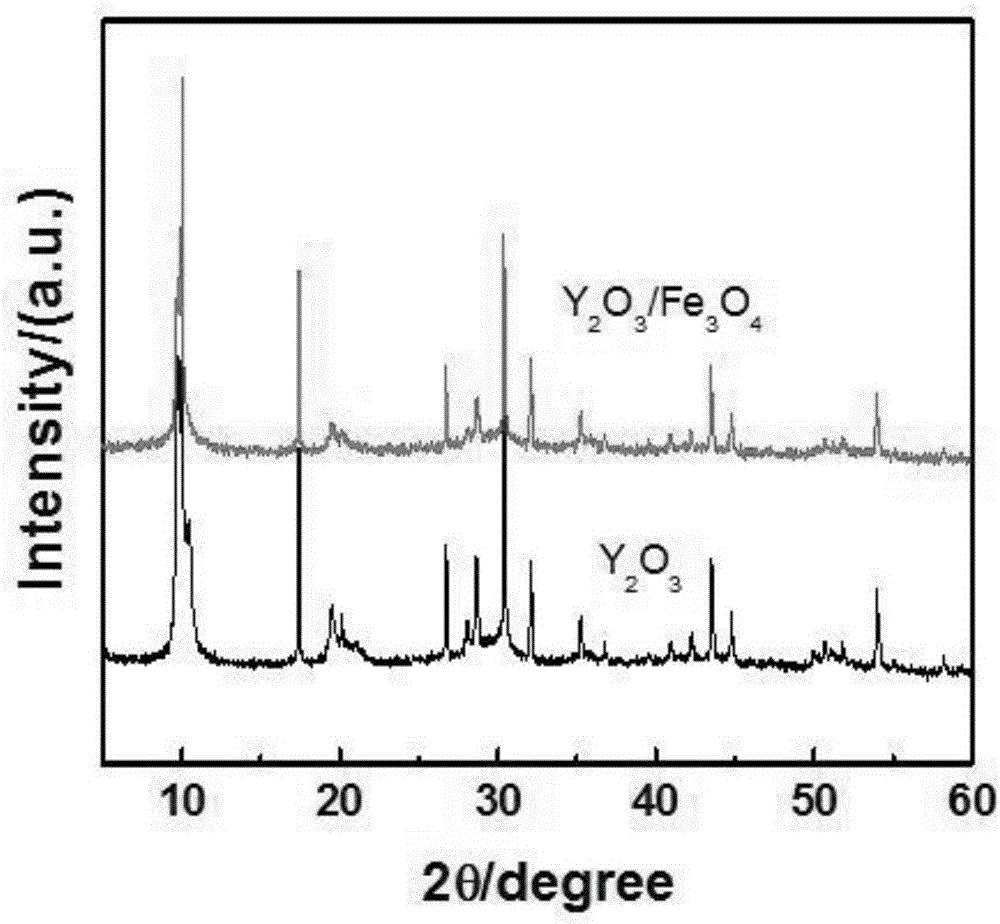
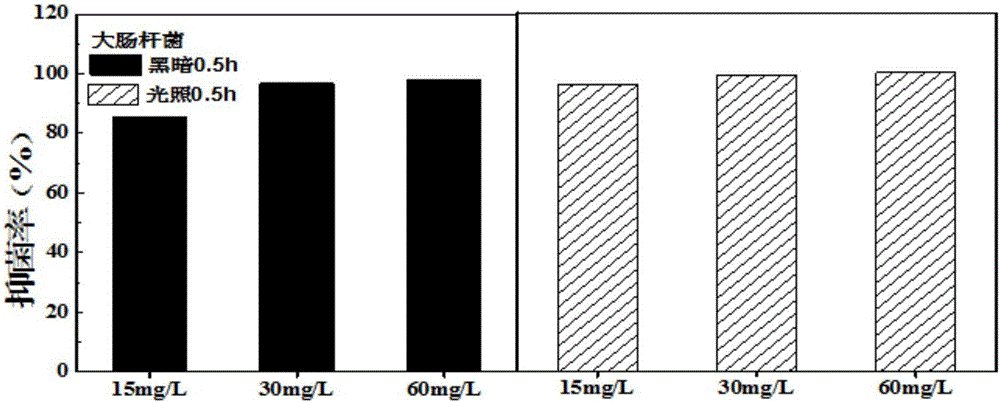
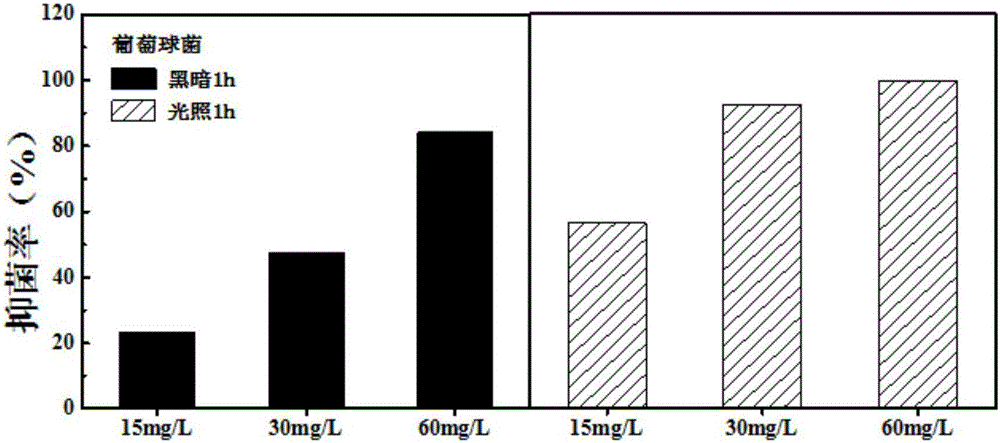
Yttrium oxide-ferric oxide composite nano antibacterial material
ActiveCN106719817AImprove antibacterial propertiesLow costBiocideDead animal preservationEscherichia coliOxide composite
The invention relates to an yttrium oxide-ferric oxide composite nano antibacterial material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly dispersing nano ferric oxide obtained by hydrothermal synthesis into a yttrium oxide synthetic system, carrying out reaction in a high-pressure reaction kettle, carrying out centrifugal separation to obtain a precipitate, and drying over night to obtain a yttrium oxide-ferric oxide composite; sterilizing the nano material by anhydrous ethanol, centrifugating, removing the supernate, adding water, and sufficiently mixing uniformly; adding the yttrium oxide-ferric oxide composite material with unequal concentrations into test tubes with a certain concentration of Escherichia coli and staphylococci, and respectively carrying out shake culture in the light and dark for some time; and analyzing the inhibition efficiency of the nano material for Gram-negative bacteria and Gram-positive bacteria by a plate counting process. The yttrium oxide-ferric oxide composite material has favorable inhibition effects on both Gram-negative bacteria and Gram-positive bacteria, and especially has very high inhibition efficiency for Gram-negative bacteria. The yttrium oxide-ferric oxide composite material is environment-friendly, and can not cause the problem of bacterial drug resistance and the like.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Photocatalytic material and preparation method and fabric thereof
InactiveCN109107558AImprove bindingImprove stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsBiochemical fibre treatmentReduction treatmentOxygen content
The invention relates to a photocatalytic material and a preparation method and a fabric thereof. The preparation method for the photocatalytic material comprises the following steps: a graphene oxidesolution is provided; thermal reduction treatment is carried out for the graphene oxide solution, so that a graphene solution is obtained, the concentration of graphene in the graphene solution is 10mg / mL to 20mg / mL, and the oxygen content of the graphene is 5 to 10 percentage by weight; the graphene solution is added with hydrated titanium dioxide and is subjected to homogenization treatment, sothat mixed liquid is obtained; and a spray dryer is adopted to carry out spray-drying for the mixed liquid, so that the photocatalytic material is obtained. The graphene and the titanium dioxide nanoparticles are combined to form the photocatalytic material, and voids exist between the graphene and the titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Because the photocatalytic material which is formed by combining the graphene and the titanium dioxide nanoparticles can be obtained by the preparation method, the photocatalytic effect of the titanium dioxide nanoparticles can be effectively improved, and thereby the photocatalytic material can effectively degrade polluting gas in the environment when being applied to fabrics.
Owner:宁波米瑞科技有限公司
Electrostatically spun defect-state TiO2/Fe3O4 composite nanofiber material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113546625AEfficient compositeNo shedding problemMaterial nanotechnologyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationFiberSpinning
The invention relates to a defect-state TiO2 / Fe3O4 composite nanofiber material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of materials. The preparation method of the material comprises the following steps: firstly, dispersing a titanium source, an iron source and a high-molecular polymer in a solvent to prepare a stable and uniform solution; then preparing the solution into a nanofiber membrane through an electrostatic spinning technology; and calcining the nanofiber membrane, grinding the calcined material and sodium borohydride, and reducing in a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain the defect-state TiO2 / Fe3O4 composite nanofiber material. The method is simple to operate, easy to control, environment-friendly and capable of realizing continuous production, and the obtained defect-state TiO2 / Fe3O4 composite nanofiber material has good crystallinity and photoresponsiveness and has excellent degradation performance on organic pollutants in a water environment.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation and application of yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide composite nanometer antibacterial material
ActiveCN106587291AImprove antibacterial propertiesLow costSpecific water treatment objectivesWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processEscherichia coliAntibiotic resistance
The invention relates to preparation and application of an yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide composite nanometer antibacterial material. Preparation of the yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide composite nanometer antibacterial material includes the following steps that nanometer iron oxide obtained through hydro-thermal synthesis is uniformly dispersed into an yttrium oxide synthesis system, a reaction is conducted in a high-pressure reaction kettle, precipitate is subjected to centrifugal separation and dried and stays overnight, and an yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide compound is obtained; a nanometer material is subjected to sterilization with absolute ethyl alcohol, then supernatant is removed through centrifugation, then water is added, and the mixture is fully and uniformly mixed; yttrium oxide-ferroferric oxide compound materials of different concentrations are added into a test tube of escherichia coli and staphylococcus of a certain concentration and subjected to shake cultivation under the light or in dark for certain time; and then inhabitation efficiency of the nanometer material to the gram-negative bacterium and the gram-positive bacterium is analyzed through a plate count method. The compound material has a good inhabitation effect on both the gram-negative bacterium and the gram-positive bacterium, particularly on the gram-negative bacterium, is environmentally friendly and cannot cause antibiotic resistance in bacteria and other problems.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
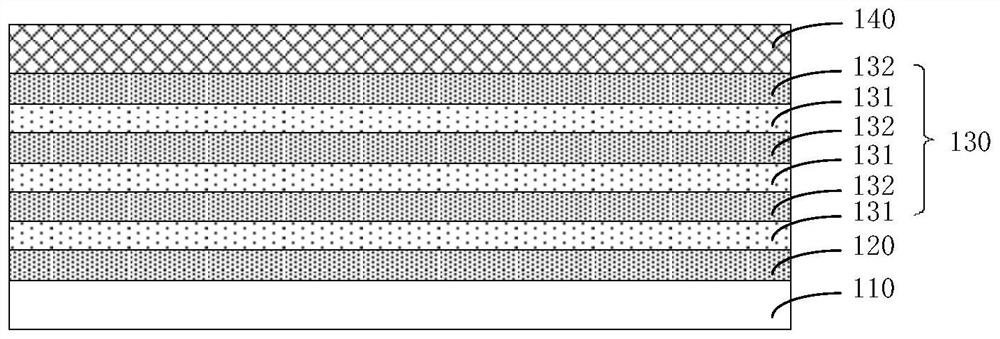
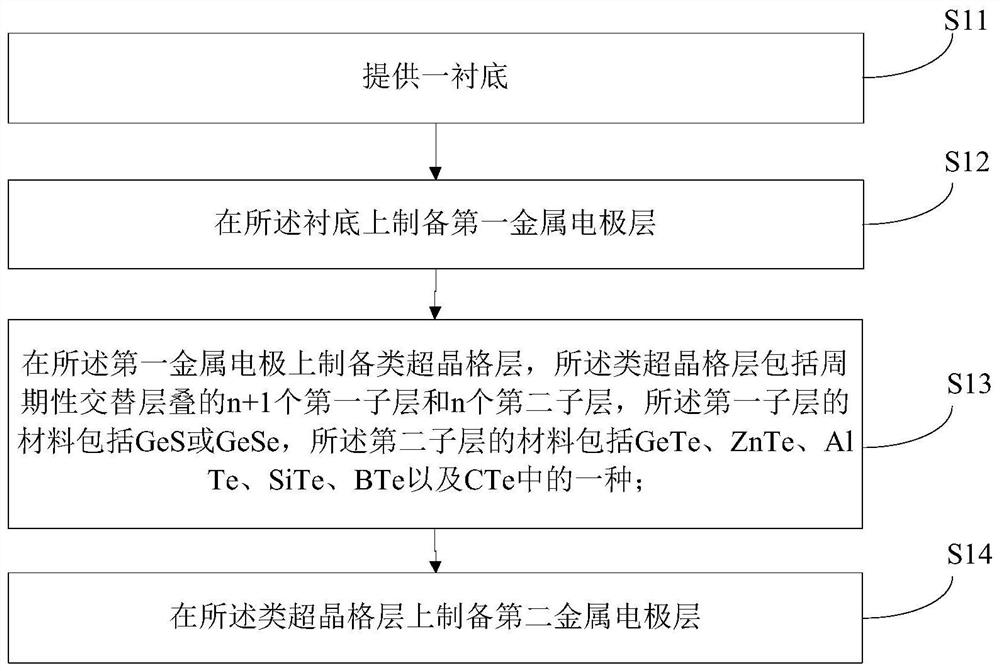
Gate tube with superlattice-like structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112242487AImprove thermal stabilityLower threshold voltageElectrical apparatusElectronicsSuperlattice
The invention discloses a gating tube with a superlattice-like structure and a preparation method of the gating tube, and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano electronics. The gate tube comprises a substrate, and a first metal electrode layer, a superlattice-like layer and a second metal electrode layer which are sequentially stacked on the substrate; the superlattice-like layer comprisesn + 1 first sub-layers and n second sub-layers which are periodically and alternately stacked, the material of the first sub-layers comprises GeS or GeSe, and the material of the second sub-layers comprises one of GeTe, ZnTe, AlTe, SiTe, BTe or CTe. Due to the fact that the GeS material and the GeSe material have high stability, diffusion separation of Te in the second sub-layer material caused byhigh temperature can be prevented. Meanwhile, each sub-layer of the superlattice-like structure is very thin, the coupling between adjacent wells is very strong, periodic quantum potential wells areformed in the superlattice-like layer, and the original discrete energy levels in the quantum wells are expanded into energy bands, so the band gap width can be reduced, the power consumption is reduced, and the superlattice-like structure can be better integrated with a memory device unit.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Photocatalyst spray for air purification
InactiveCN111686576AHigh activityReduced bandgap widthGas treatmentOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOxygen vacancyNew energy
The invention relates to the technical field of photocatalyst spray, and discloses photocatalyst spray for air purification, which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1 to10 parts of I-TiO2, 1 to 5 parts of nano titanium dioxide, 5 to 15 parts of polyethylene glycol, 5 to 20 parts of glycerol, 1 to 5 parts of tourmaline powder, 5 to 10 parts of nano silicon dioxide and 1 to 8 parts of nano silver. According to the photocatalyst spray, effects of the spray after iodine doping is superior to that of a pure TiO2 photocatalyst; the main reason is that on one hand, a new energy level can be introduced into a TiO2 energy band gap by an iodine element so that the band gap width of TiO2 is reduced and TiO2 surface properties and effects of enhancing photo-induced electron hole pair separation are achieved; on the other hand, impurity replacement is carried out after iodine enters TiO2 crystal lattices, so that oxygen vacancies and defects of photo-induced electroncenters capable of generating strong-oxidation active particles on the surface of TiO2 are increased, and the active effect of the photocatalyst is enhanced.
Owner:广东中检检测技术有限公司
High-In-composition InGaN/GaN quantum well structure solar cell based on self-supporting GaN substrate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105552149AAvoid mismatchReduced bandgap widthFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationFilm coatingFilm-coated tablet
The invention provides a high-In-composition InGaN / GaN quantum well structure solar cell based on a self-supporting GaN substrate and a preparation method thereof. The solar cell is composed of the self-supporting GaN substrate, a GaN buffer layer, an n-type doped GaN layer, a high-In-composition InGaN / GaN quantum well layer, a p-type doped GaN layer and a P-type electrode which are laminated in turn. An epitaxial layer is grown by adopting the self-supporting GaN substrate, and high In composition is adopted in the quantum well layer; an n-type doped GaN layer mesa is manufactured by adopting a dry etching method, and an N-type electrode is formed on the mesa; and the P-type electrode is formed on the p-type doped GaN layer by adopting the methods of photoetching and film coating. Performance of the solar cell can be greatly enhanced; and crystal lattice mismatching can be effectively reduced by adopting the self-supporting GaN substrate, and high-quality high-In-composition InGaN is grown by adopting an RF-MBE technology so that light absorption range of the solar cell can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:江苏第三代半导体研究院有限公司
Iron oxide doped mixed crystal form titanium dioxide nano-net photocatalytic composite material
PendingCN111229223AImprove utilization efficiencyImprove purification efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsElectrolytic agentMixed crystal
The invention provides an iron oxide doped mixed crystal form titanium dioxide nano-net photocatalytic composite material. A preparation method comprises the steps of placing a titanium mesh as an anode and a platinum sheet as a cathode in an electrolyte for an anodic oxidation reaction so that a titanium dioxide nano-mesh array of a titanium mesh substrate is obtained, placing the titanium dioxide nano-net array of the titanium net substrate in an ethanol solution dissolved with ferric chloride for dipping treatment, taking out the titanium dioxide nano-net array, drying the titanium dioxidenano-net array, and then carrying out heat treatment to obtain the ferric oxide doped mixed crystal form titanium dioxide nano-net photocatalytic composite material. An ethanol solution of ferric chloride is used as an iron source for doping, amorphous titanium dioxide does not fall off in ethanol, and ferric oxide is generated after a thermal reaction of ferric chloride. Iron oxide is deposited on the titanium dioxide nano-net, a part of crystal lattices are occupied, the band gap width of TiO2 can be changed, and the photocatalytic activity is improved, and meanwhile, the product is of a net-shaped thin film structure, so that the use is convenient and secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Copolymerization modified graphite-phase carbon nitride nanosheet visible-light-driven photocatalyst
ActiveCN103272639BEasy to separateImprove migration efficiencyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen productionCarbon nitrideGraphite
The invention discloses a copolymerization modified graphite-phase carbon nitride nanosheet visible-light-driven photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of material preparation and photocatalysis. The graphite-phase carbon nitride nanosheet visible-light-driven photocatalyst which adopts a nanosheet structure and synthesized with a copolymerization method is formed by taking urea and different small organic molecule monomers as precursors through the high-temperature copolymerization action. The prepared graphite-phase carbon nitride has a lower-dimension nanosheet microstructure and a proper band gap; compared with conventional bulk-phase carbon nitride, the graphite-phase carbon nitride effectively increases the specific surface area, enhances the utilization rate of sunlight, and has efficient photocatalysis hydrogen production performance in visible light. According to the copolymerization modified graphite-phase carbon nitride nanosheet visible-light-driven photocatalyst, the synthetic process is simple, the cost is low, the catalytic efficiency is high, the actual production requirements are met, and the photocatalyst has broad application prospects in the field of photocatalysis.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com