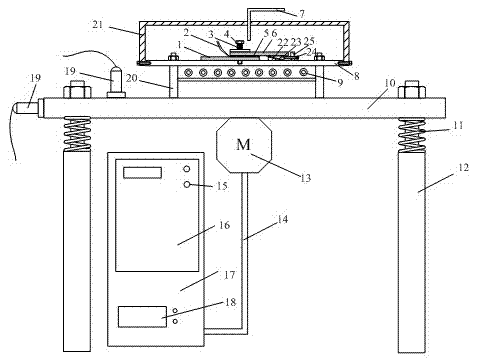
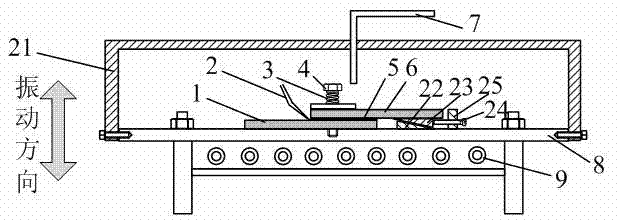
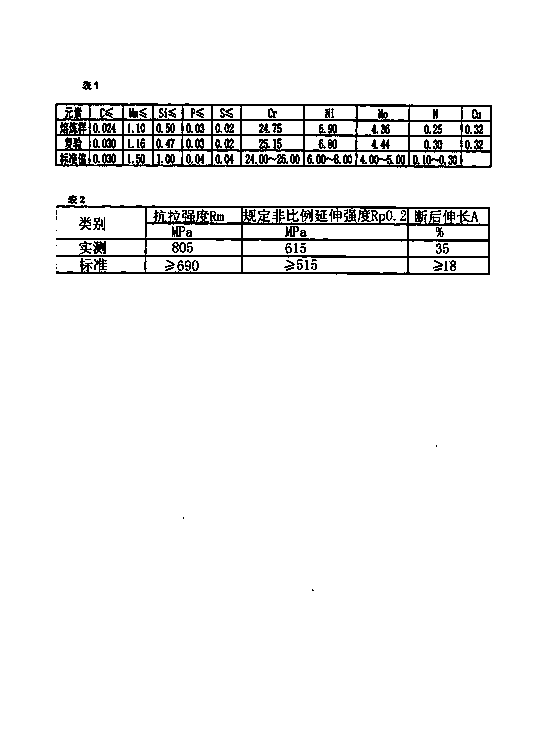
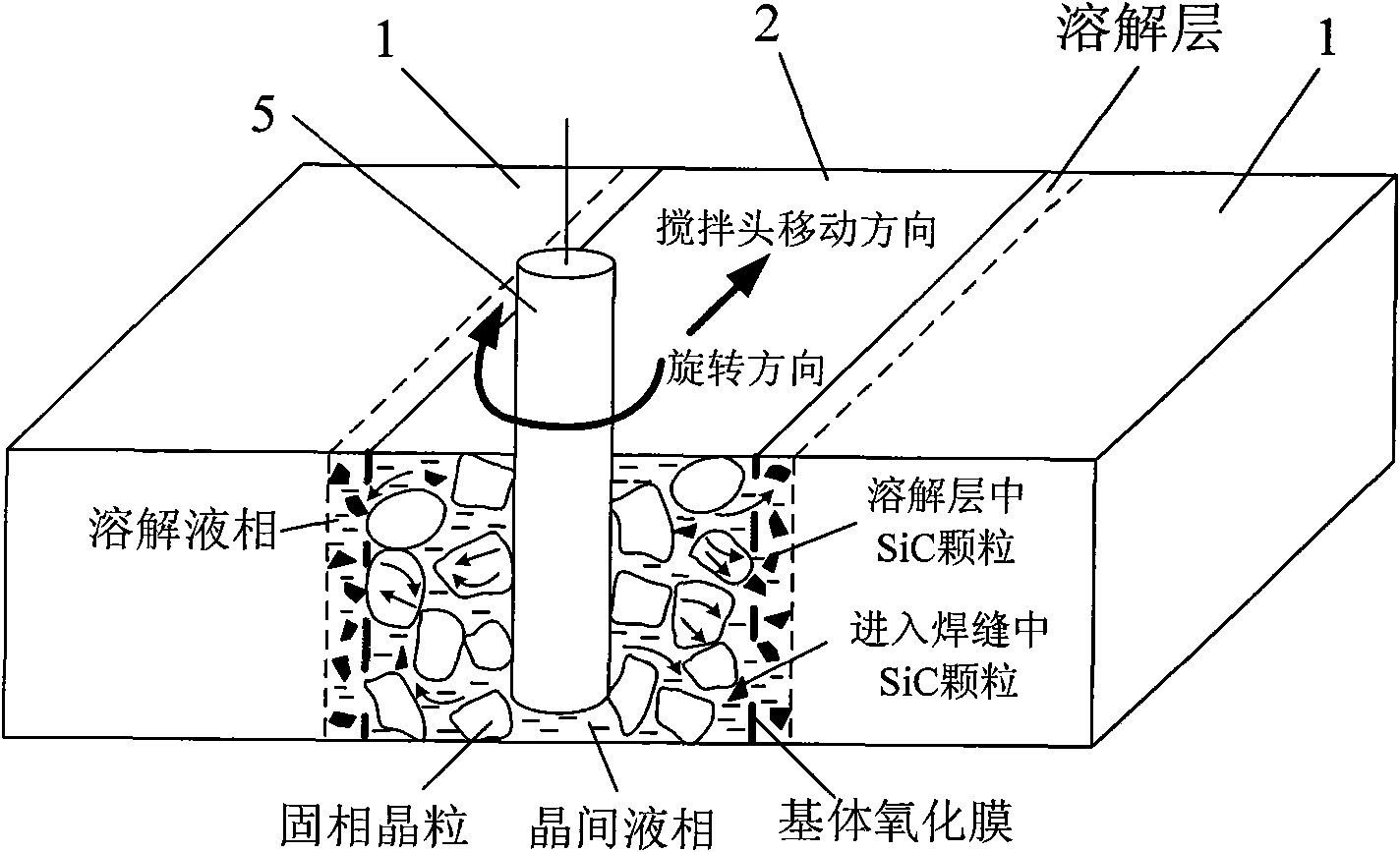
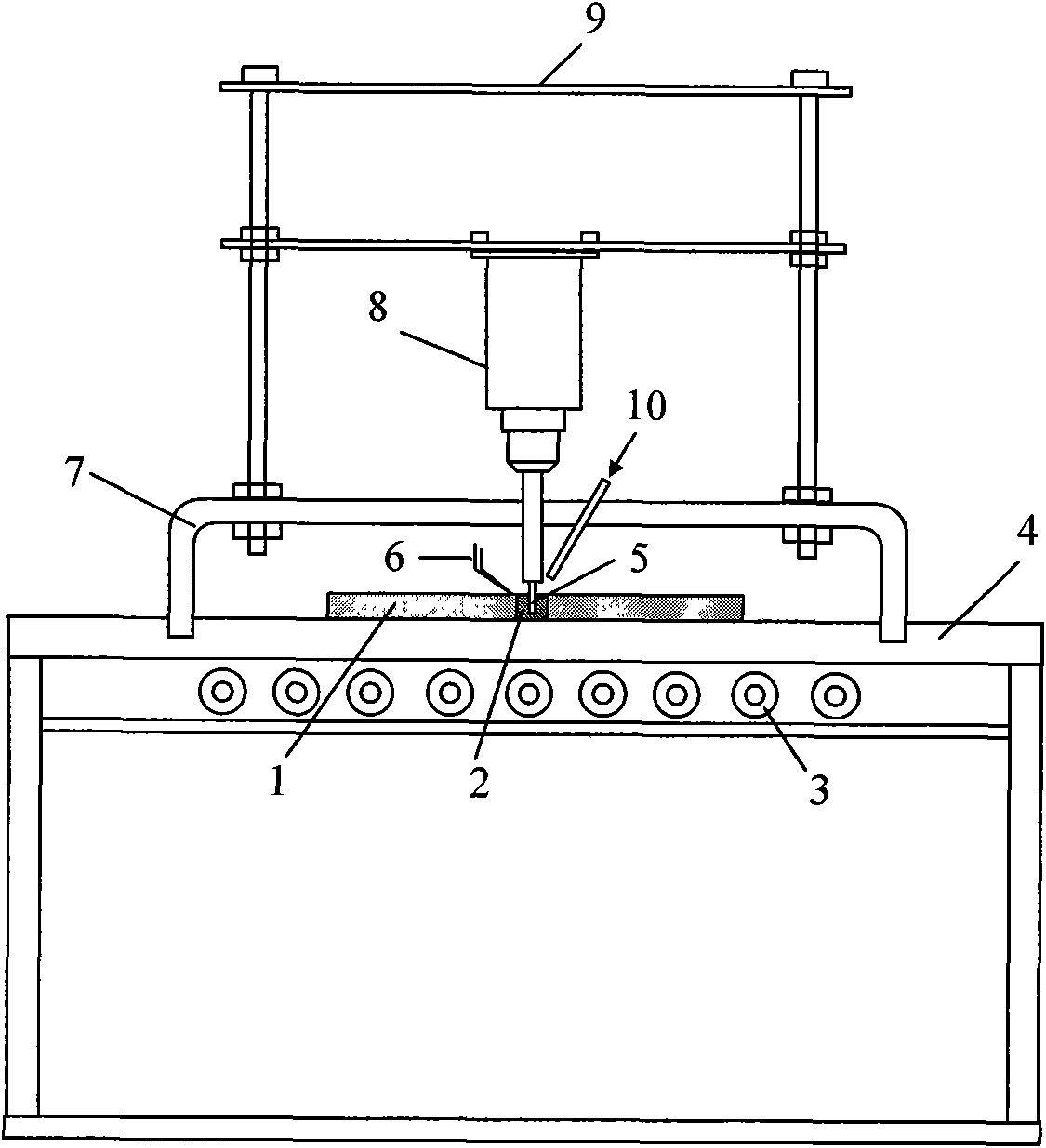
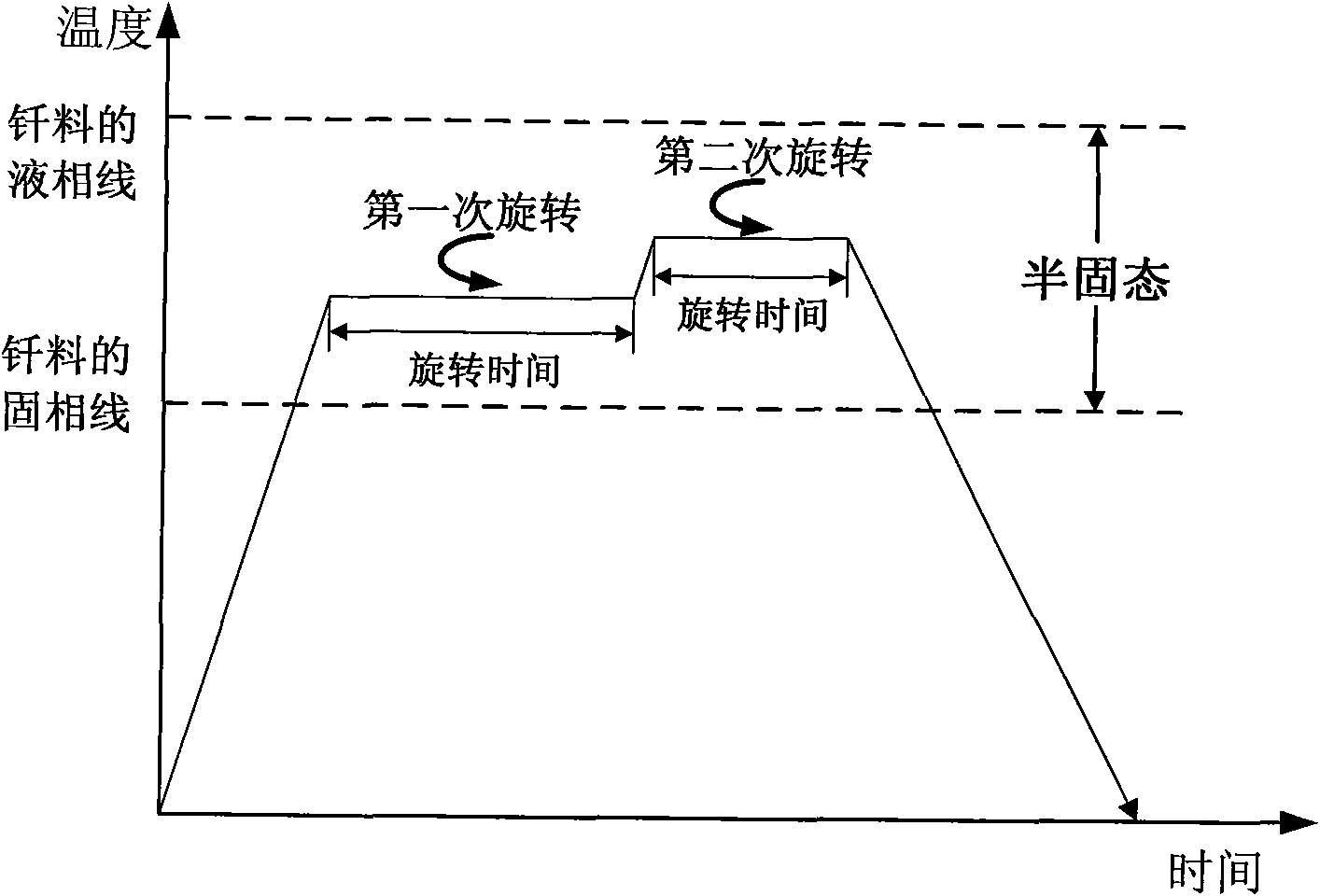
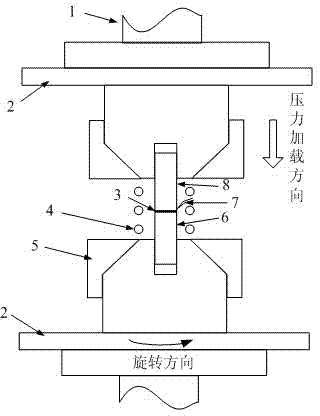
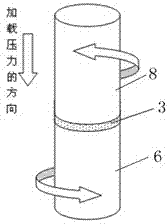
Patents
Literature
105results about How to "Small size deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
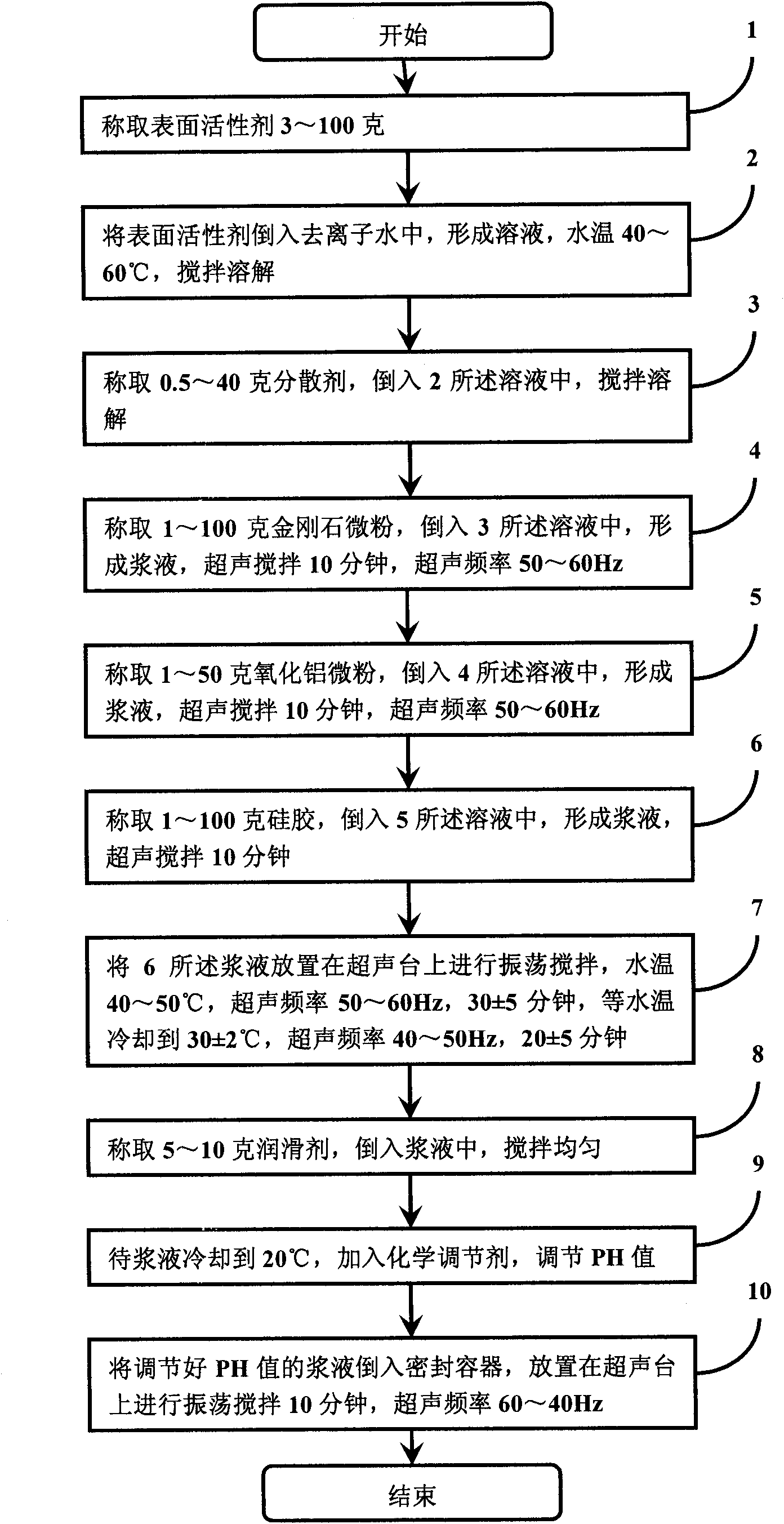
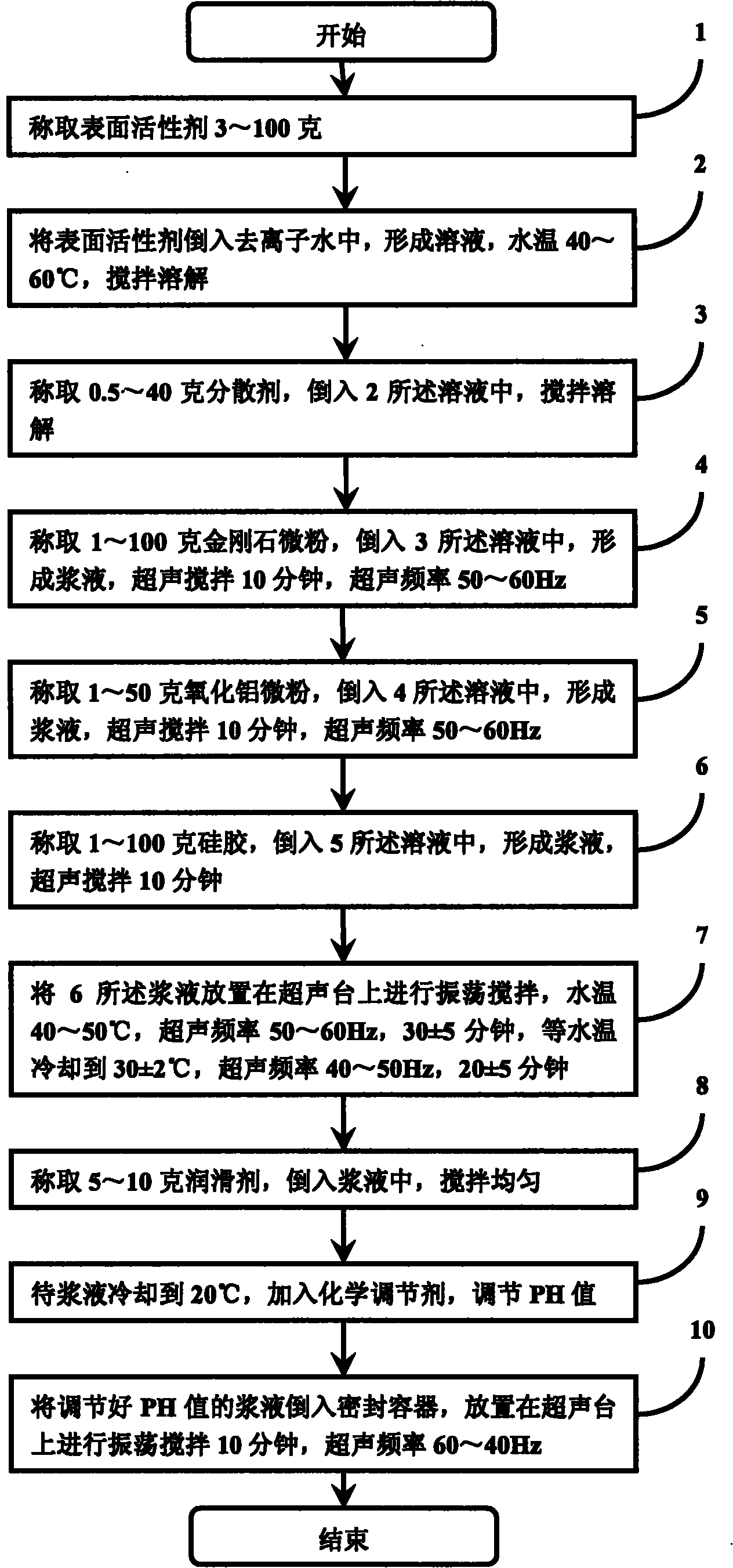
Nanometer level polishing solution and preparation method thereof
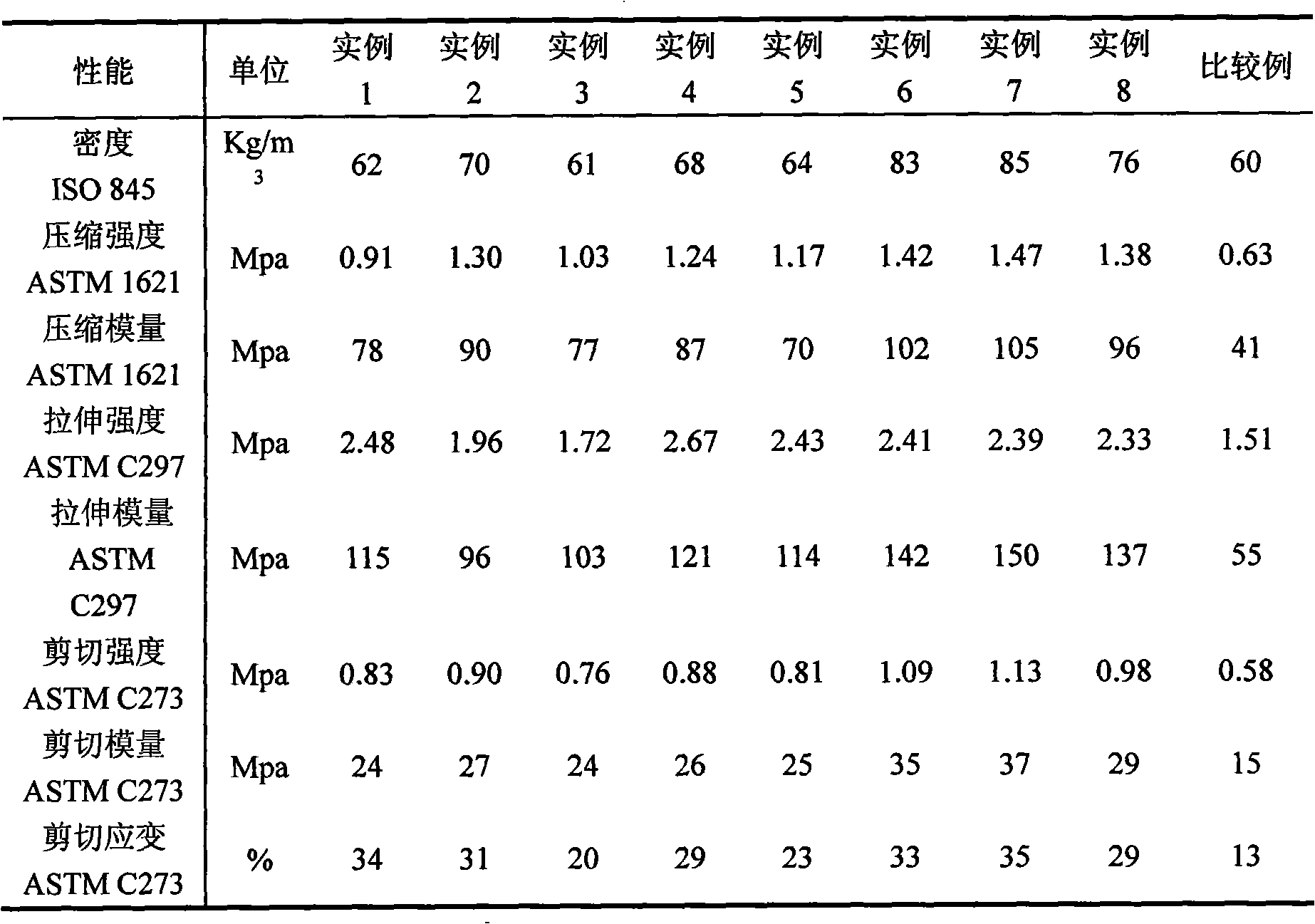
ActiveCN102311706AMeet the requirements of thinning grinding processEasy to polishPolishing compositions with abrasivesSilica gelSolvent
The invention discloses a nanometer level polishing solution and a preparation method thereof. The polishing solution is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 0.1 to 10 percent of monocrystal artificial diamond micro powder, 0.1 to 5 percent of aluminum oxide micro powder, 0.1 to 10 percent of silica gel, 0.3 to 10 percent of surfactant, 0.05 to 4 percent of dispersing agent, 0.5 to 1 percent of lubricant, 0.01 to 1 percent of chemical PH value regulator and 60 to 98.2 percent of solvent. The invention also discloses the preparation method for the nanometer level polishing solution. By the method, mixed serous fluid is prepared from the nanometer level diamond, the aluminum oxide and the silica gel, so an ideal polishing effect is achieved, the requirement of a process for thinning and grinding substrates (silicon carbide and sapphire) for GaN extension is met, and a technical means is provided for a polishing process for semiconductors.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Asphalt self-adhesive and high-polymer self-adhesion rubber waterproof coiled material prepared from asphalt self-adhesive
InactiveCN102559135AGood compatibilityHigh composite strengthMineral oil hydrocarbon copolymer adhesivesNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesUltimate tensile strengthButadiene-styrene rubber
The invention discloses asphalt self-adhesive. The asphalt self-adhesive comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 45 to 65 percent of asphalt, 16 to 25 percent of rubber oil, 5 to 15 percent of styrene butadiene styrene (SBS), 1 to 6 percent of styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), 1 to 6 percent of petroleum resin, 1 to 7 percent of ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), and 10 to 20 percent of talcpowder. The invention also provides a high-polymer self-adhesion rubber waterproof coiled material which comprises a non-woven fabric coating, a high-polymer sheet coating, and an asphalt self-adhesive coating which consists of the asphalt self-adhesive from bottom to top. Two ends of the waterproof coiled material are provided with joint sides. The asphalt self-adhesive contains EVA, so the compatibility of the self-adhesive and a high-polymer sheet is improved, and compounding intensity of the high-polymer sheet coating is improved. The problem that the high-polymer sheets cannot be jointed reliably in a self-adhesion joint process is solved, so the coiled materials are jointed by the adhesive; and the coiled materials can be adhered firmly and reliably, and adjusted freely and flexibly.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHUOBAO TECH
Improved crosslinked polyvinyl chloride structural foam and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101580573ASimple manufacturing process controlWide operating range of parametersFoaming agentPolyvinyl chloride
The invention relates to improved crosslinked polyvinyl chloride structural foam and a preparation method thereof. The foam is prepared from the following materials in portion by weight: 100 portions of polyvinyl chloride resin, 30 to 120 portions of isocyanate, 0.05 to 10 portions of epoxy components, 1 to 12 portions of foaming agent, 0.5 to 10 portions of triazine compound, and 1 to 30 portions of acid anhydride. The preparation method thereof comprises the following steps: (1) mixing the raw materials evenly to obtain a pasty mixture; (2) pouring the pasty mixture obtained in step (1) into a die, and fully decomposing the foaming agent to obtain a semi-foaming die pressing block; (3) cooling the semi-foaming die pressing block to room temperature; (4) placing the semi-foaming die pressing block obtained in step (3) into hot bath or steam to carry out swelling; and (5) cooling a swelled semi-finished product obtained in step (4) to room temperature, and then adopting hot water spray or curing post treatment in the steam to fully react the isocyanate so as to obtain cured block or plate crosslinked polyvinyl chloride structural foam. The foam has fine and even holes, and has good mechanical property and temperature resistance.
Owner:CHANGZHOU TIANSHENG NEW MATERIALS
Microporous polymer isolating film for Li-ion battery and method for producing the same
ActiveCN101212036AIncrease surface areaHigh porositySolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
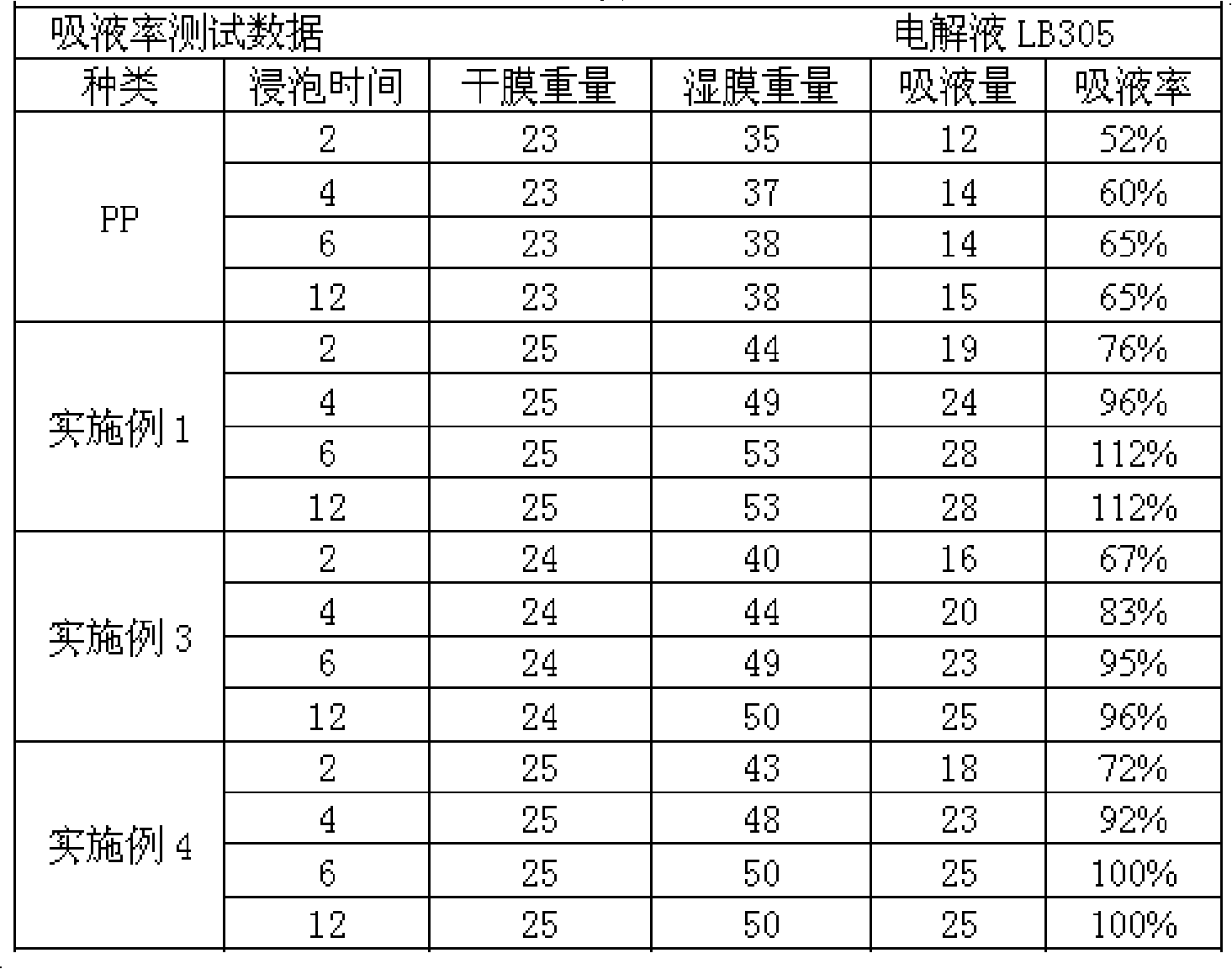
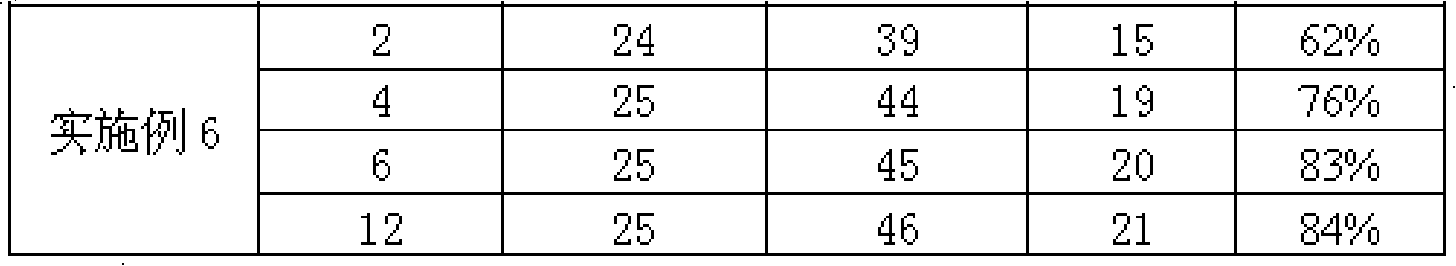
The invention relates to a diaphragm used for power maintaining device as a lithium ion secondary battery and a preparation method thereof, which belongs to a field of manufacturing battery and capacitor. The diaphragm of the invention takes water as reaction medium; polymers colloid and emulsion are obtained through polymerization reaction generated by polyvinyl alcohol, hydrophobic monomer and hydrophilic monomer with an initiator in water solution; by adopting tape-casting and coating process, the polymers colloid and emulsion are coated on a plastic baseband; the diaphragm is obtained through stripping after drying. The diaphragm has good liquid absorbability, high liquid absorption rate and retention, low resistivity, good mechanical strength and good thermal stability (little thermal shrinkage and little size distortion) as well as electrochemical stability; and the prepared lithium ion battery is characterized by good cycle stability and long service life.
Owner:CHENGDU ZHONGKE LAIFANG POWER SCI & TECH CO LTD
Lathe precise machining method for ultrathin-wall-thickness metal pipe part
The invention discloses a lathe precise machining method for an ultrathin-wall-thickness metal pipe part. The ratio of the pipe diameter to the wall thickness of the related part exceeds 100; and in the machining process, an appropriate clamping tool and a reasonable machining sequence are selected to reduce overall deformation of a workpiece in the machining process, and in the machining steps, the appropriate feed cutting quantity and a cutter matched with the feed cutting quantity are selected to reduce heat of the cutter in the cutting process, and stress exerted on the workpiece in the cutting process is reduced. According to the method, stress deformation caused by the fact that external force is exerted on the workpiece in the turning machining process can be effectively controlled, and therefore internal stress generated in the part cutting process can be fully released; the higher size and form and location tolerance requirement of the ultrathin-wall-thickness metal pipe part in the machining process is met, and the machined part is small in size deformation and has the long-term stability. The method has the common referential meaning in machining and manufacturing of the small-type ultrathin-wall-thickness metal pipe part which is urgently required in the special field.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aluminum alloy and its composite material non-vacuum semi-solid state vibration-rheological connection method
InactiveCN1876302AAchieve weldingShort welding cycleSoldering apparatusNon-electric welding apparatusForce constantSemi solid
The invention provides a method for anti-vacuum vibrating theological connecting aluminum alloy and its complex material. The invention is characterized in that: clamping aluminum alloy or complex material weldment on chucking appliance and placing medium temperature welding material on two pre-welding surface, heating weldment with temperature being 380-400 Deg. C, starting vibrating device after welding material fusion, the amplitude is 0.1-0.5 mm. The temperature during vibrating process is the same, and the vibrating time is 10-300 seconds. The temperature is increased to 450-520 Deg. C after vibration, and it is kept for 1-5 minutes. Then starting vibrating device again, the amplitude is 0.1-1 mm, stopping after 3-60 seconds, forcing constant pressure with pressure range being between 0.1-2 Mpa, keeping temperature for 5-30 minutes, and cooling. The invention is characterized by low cost, high efficiency and quality.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Aluminum alloy semi-ring for fairing of launch vehicle and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101760682AGuaranteed performanceLess metallurgical defectsExtrusion control devicesHardnessHigh intensity
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy semi-ring for a fairing of a launch vehicle and a preparation method thereof, relating to an alloy semi-ring and a preparation method thereof. The invention solves a problem that the traditional aluminum alloy semi-ring for the fairing of the launch vehicle has a low intensity and cannot satisfy the application requirements of large-scale launch vehicles. The aluminum alloy semi-ring for a fairing of a launch vehicle is made of Si, Fe, Cu, Mn, Mg, Ni, Zn, Ti and Al. The tensile strength of the semi-ring is 380-450MPa, the percentage elongation after fracture is 6.0-10% and the Brinell hardness is 110N / sq.m-150N / sq.m. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing the raw material, melting, casting, homogenizing annealing, forging, extruding, bending, quenching, coldly compressing to deform, flattening and ageing the raw materials to obtain the aluminum alloy semi-ring for the fairing of the launch vehicle. The aluminum alloy semi-ring for the fairing of the launch vehicle has a high intensity and can be applied to the large-scale launch vehicle.
Owner:NORTHEAST LIGHT ALLOY CO LTD
Lithium ion battery and combination electrode used for the same and production method thereof
ActiveCN101246958AGood compatibilityGood diaphragm wettingElectrode manufacturing processesSecondary cellsSolubilityHydrophilic monomer
The present invention relates to compound electrode slices applied in lithium ion battery and producing method thereof, which belongs to fields of battery production, in order to provide a new septum and cathode two-in-one electrode slices. The provided compound electrode slices is polymer colloid latex initiated, grafted and copolymerized by 1-5 portion initiator in aqueous solution containing 100 portion water-solubility polymer by 30-500 portion hydrophobic monomer and 0-200 portion hydrophilic monomer. Counted as that the solid content in the polymer colloid latex is 100%, the inorganic filler of 0-100% and the plasticizer of 20-100% are added, and the slurry is coated on the carbon cathode slice which is obtained by drying. The electrode slices has good heat stability and electrochemistry stability, super water absorptivity and rapid water absorption speed, and keeps higher water absorptivity in whole circle service life period. The battery has credible safety and circle service life, and the present invention provides a new thinking for lithium ion battery fields.
Owner:CHENGDU ZHONGKE LAIFANG POWER SCI & TECH CO LTD
Heterogeneous semi-solid brazing method of aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy assisted by external vibration energy
InactiveCN102266994AAvoid serializationEfficient weldingSoldering apparatusRoom temperatureSemi solid
The invention provides a heterogeneous semi-solid brazing method for an aluminum alloy and a magnesium alloy under assistance of external vibration energy. According to the invention, the method comprises the following steps of: clamping an aluminum alloy weld member and a magnesium alloy weld member on a fixture and placing medium-temperature brazing filler metals of a Zn-Al or Al-Si series on two surfaces to be welded, wherein the brazing filler metals can be of flaky shapes or foil shapes, can be plating layers or can be sprayed on the surfaces to be welded in advance; heating the weld members so that the middle layer of brazing filler metal is in a semi-solid state; adjusting the pressure to be matched with the amplitude of the applied vibration; starting a vibrating device with amplitude of 0.01-2mm, wherein the brazing filler metals vibrate along with the two weld members, and the vibration time is 0.5-3 minutes according to actual requirements; stopping the vibration; and cooling the weld members to room temperature by air, wherein a certain pressure of 0.1-5 Mpa is always applied in the brazing process. According to the invention, high-efficiency, high-quality and economic connection between the aluminum alloy and the magnesium alloy can be realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Machining process of large duplex stainless steel impeller
ActiveCN103418991APrevent thermal deformation during hoistingUniform outlet widthStructural engineeringSS - Stainless steel
The invention relates to a machining process of a large duplex stainless steel impeller. The machining process comprises the steps of casting, thermal treatment of a front deformation protector, solutionizing treatment, finishing and rough polishing, component re-inspection, mechanical property inspection, RT radiographic inspection, defect treatment, repair welding and rough polishing, rough machining, trimming, stress relief thermal treatment, semi-finish machining, fine polishing, finish machining, balance test duplicate removal and the like. The machining process is small in hardening effect, small in dimension deformation, good in impeller machining dimension accuracy and high in surface smoothness. The work completion size inspection is controlled at the temperature lower than 40 DEG C. In addition, the processing efficiency is high, the quality is good, the dimensional accuracy and the position dimension tolerance deformation of the impeller can be ensured to be small, and the graph dimension requirement and the technical requirements can be met.
Owner:SHENYANG SANKE VALVES IND CO LTD
Gypsum base material system for 3-D spraying binding and preparing method therefor
The invention relates to a plaster base material system for 3D spray bonding fast forming technique, comprising composite base material and auxiliary bonder, where the composite base material is mixed uniformly of plaster powder, bonder, accelerator anhydrous calcium sulphate, dispersant, white carbon black, and intensifier; and the bonder is mixed of water base polyurethane glue, phenol resin, nonionic surface active agent, and alcohol cosolvent, dissolving in deionized water. And the composite base material and auxiliary bonder can completely meet use requirements.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
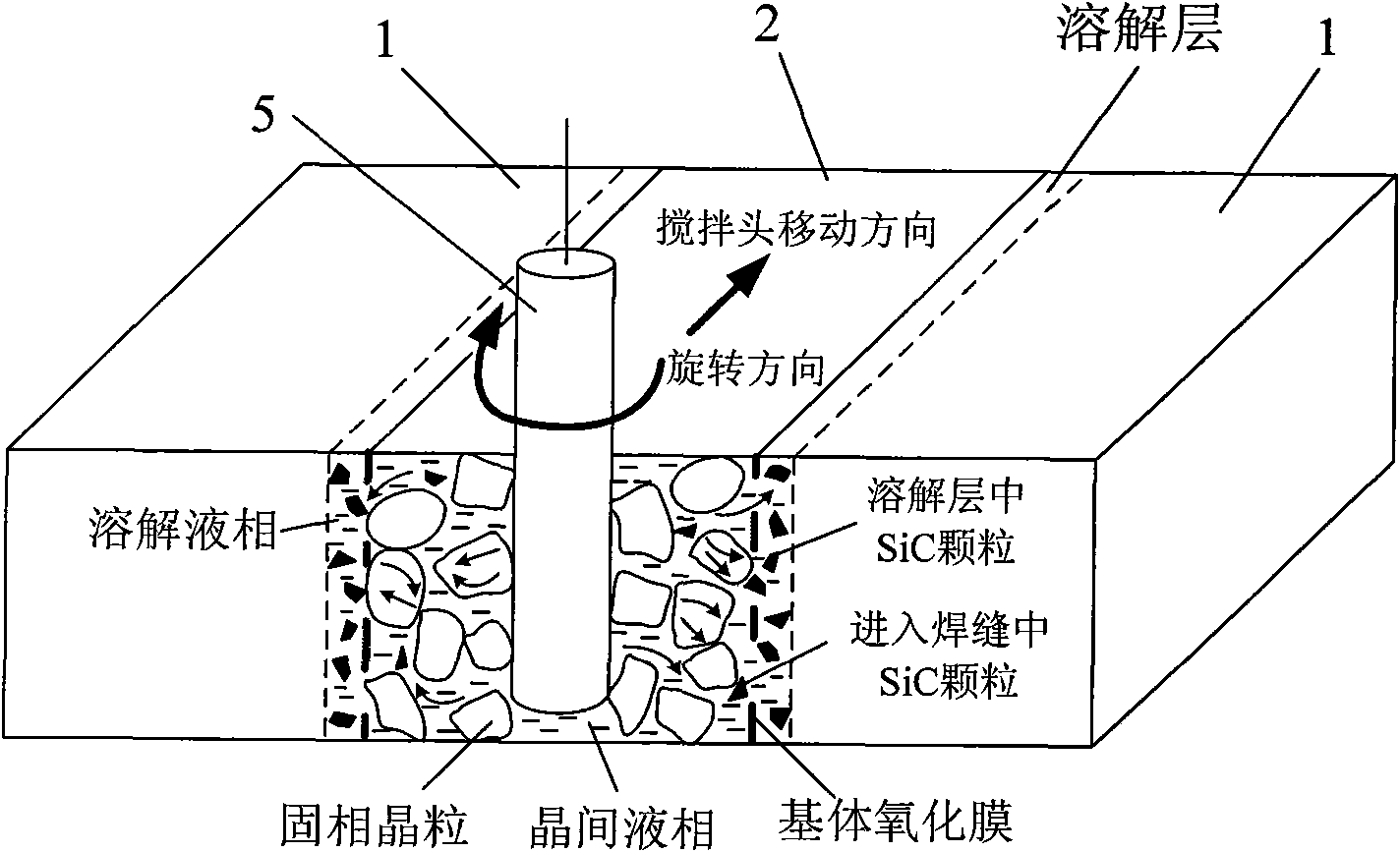
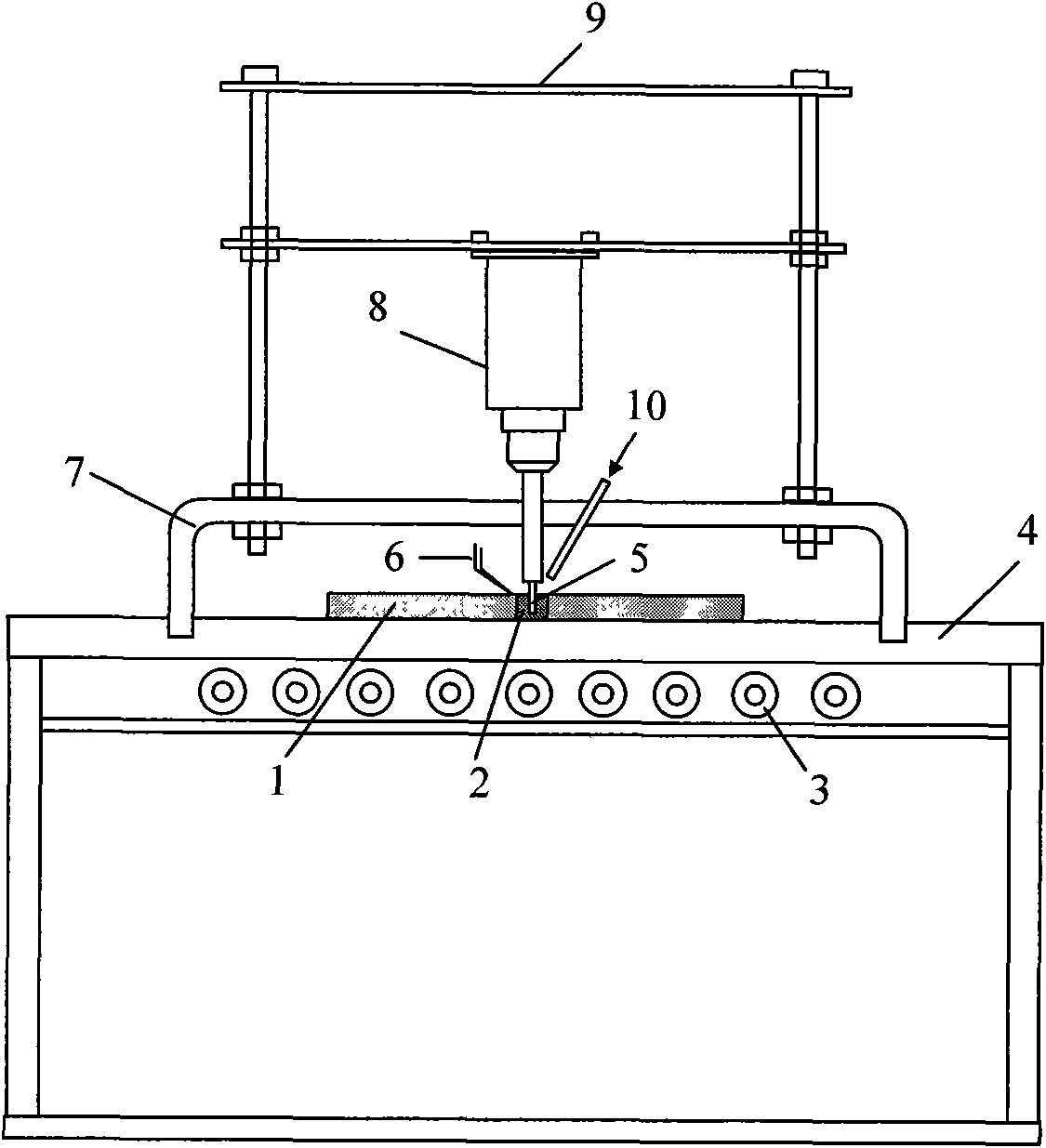
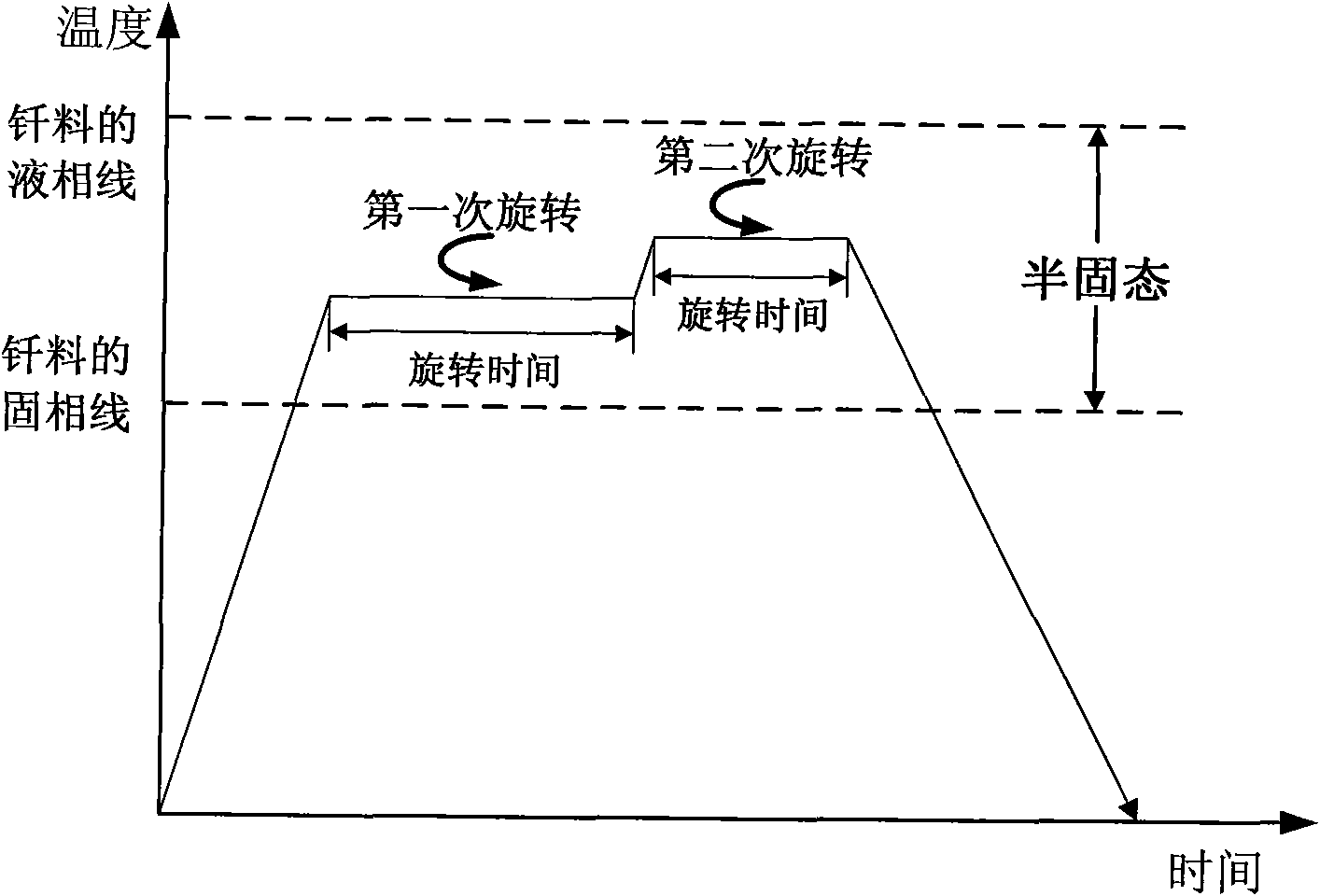
Non-vacuum semi-solid stirring brazing method for aluminum alloy and composite material thereof
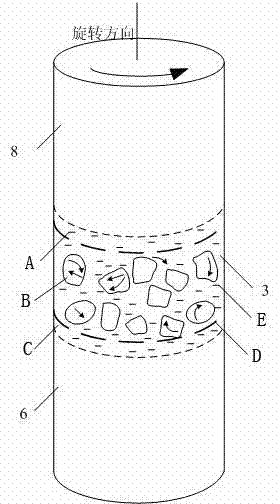
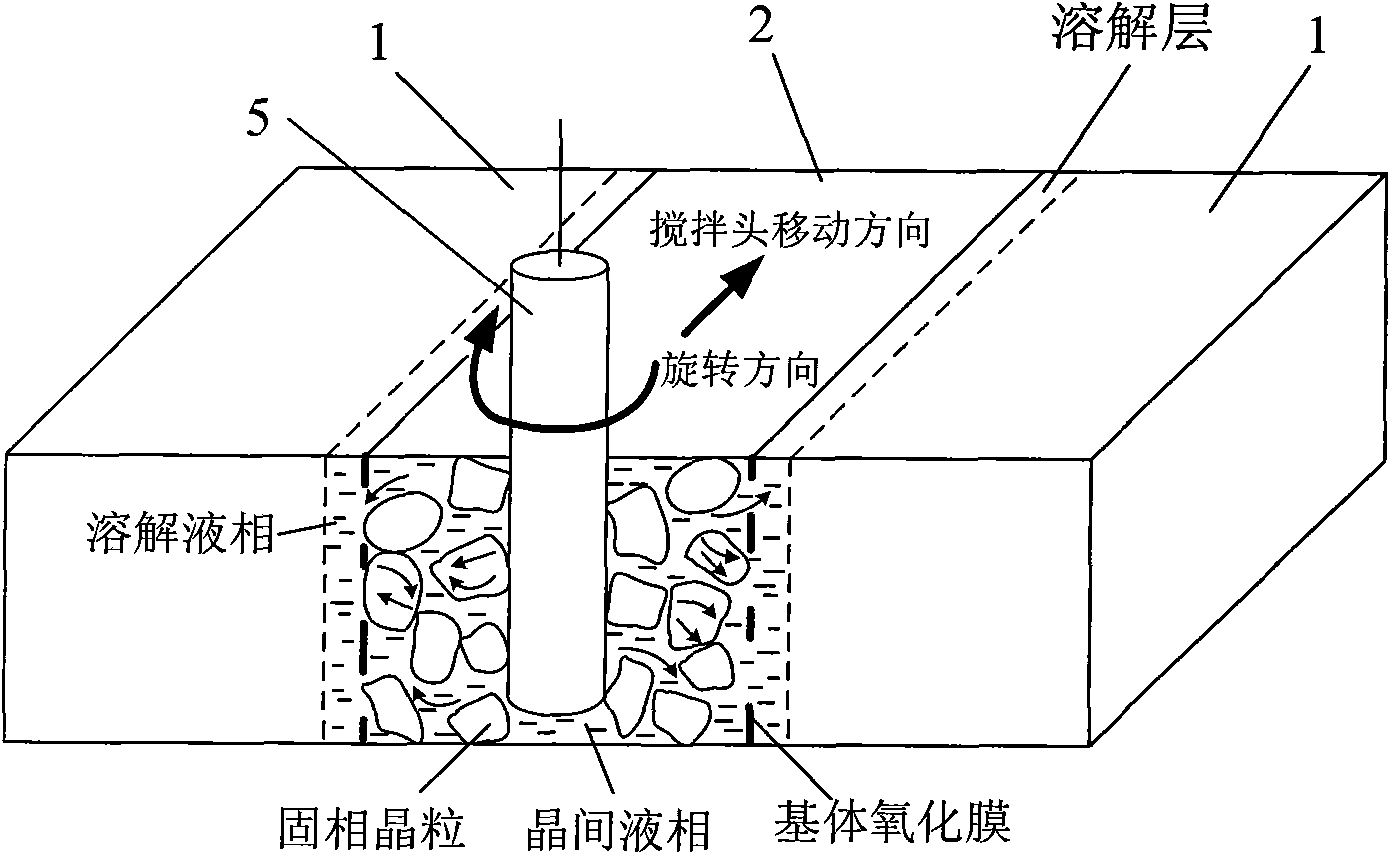
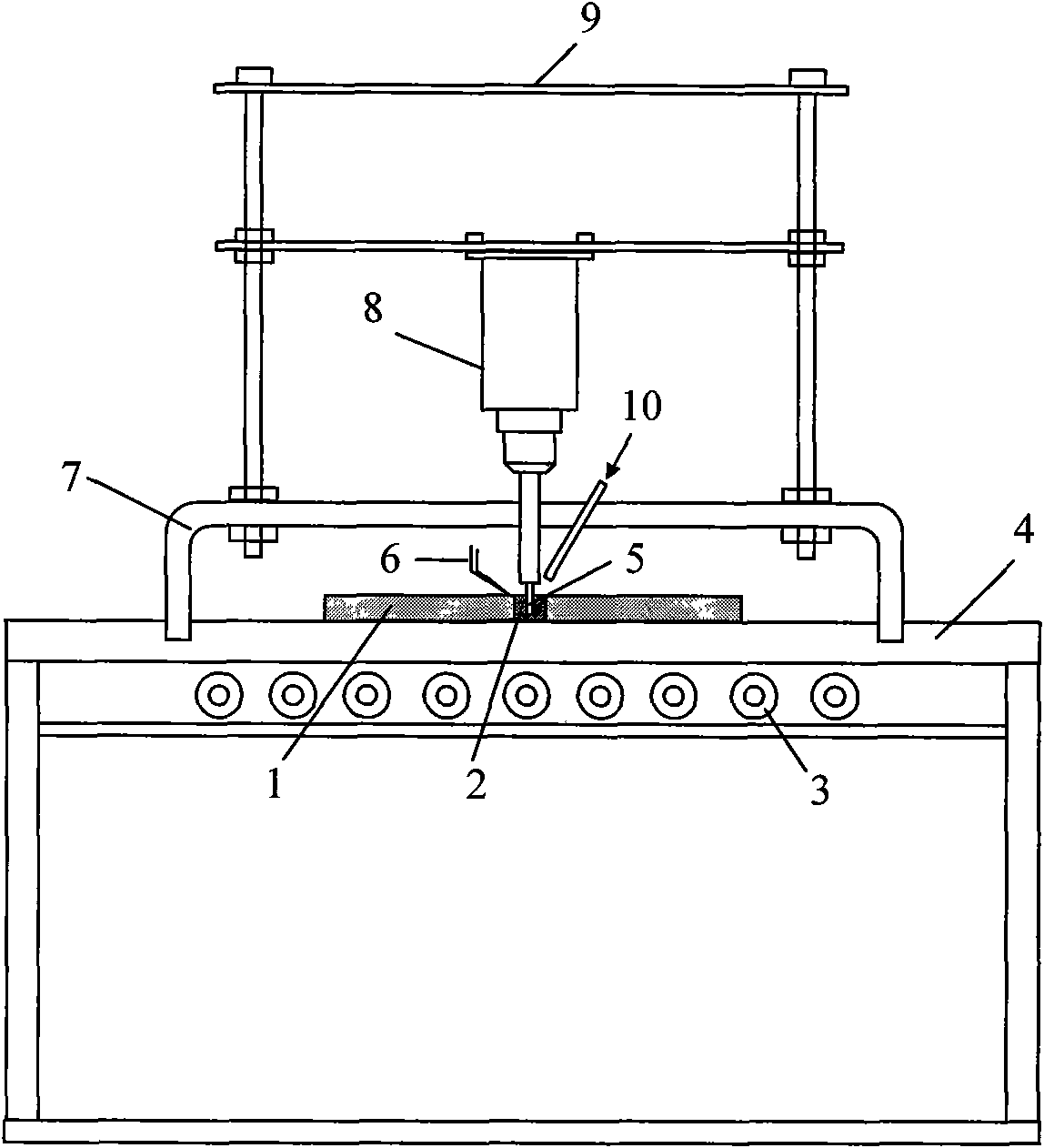
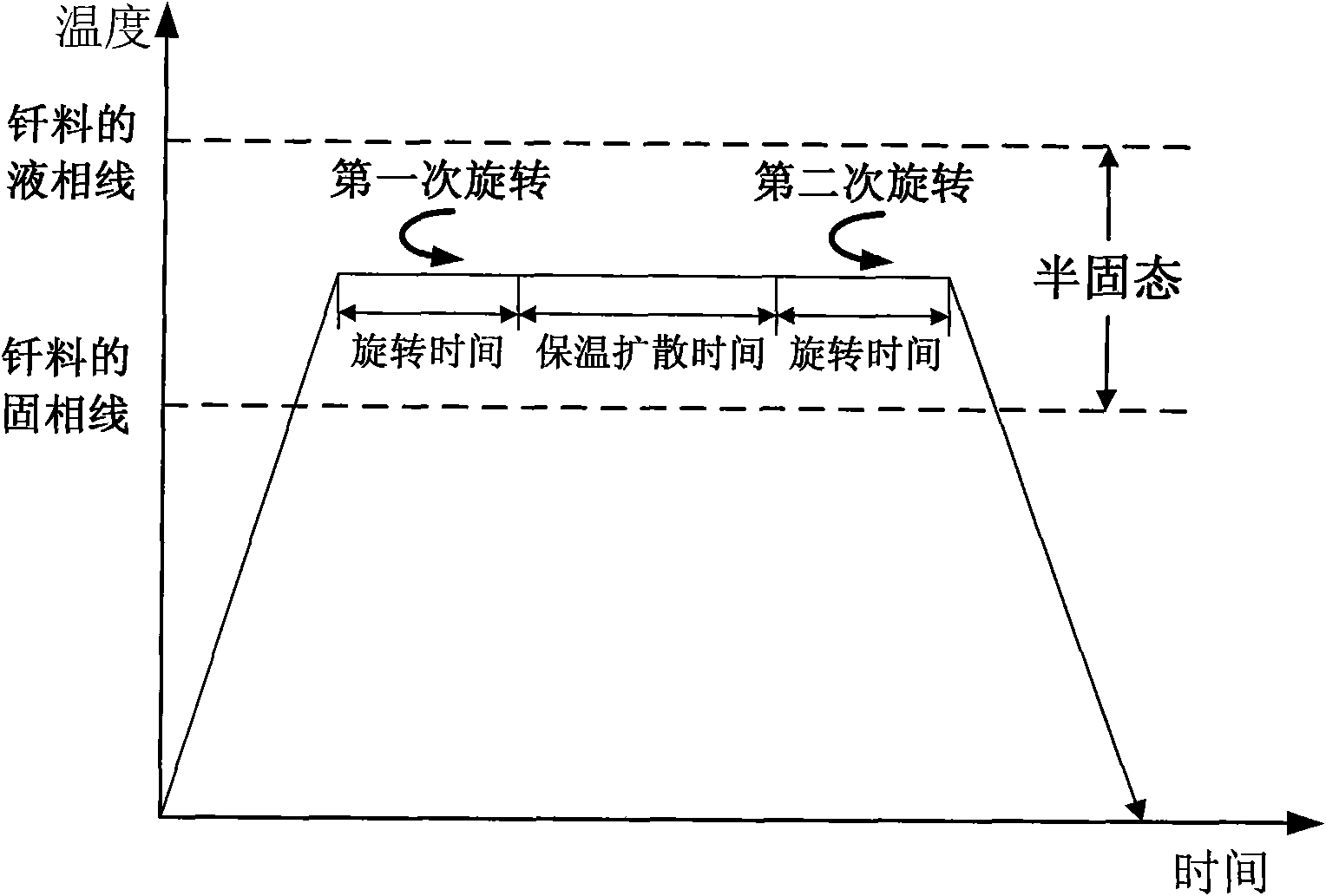
The invention provides a semi-solid brazing method for aluminum alloy and a composite material thereof under the assistance of non-vacuum mechanical stirring, which comprises the steps of: mounting a weldment taking the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof as a base material on a welding platform first; placing intermediate-temperature solder on two surfaces to be welded, heating the weldment to between 390 and 420 DEG C, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 50 and 80 percent; staring a rotary sliding device, wherein the rotating speed is between 150 and 300 r / m, the temperature is constant, and the longitudinal movement rate, which is parallel to a welding seam, of a stirring head is between 0.5 and 2 cm / min; stopping the rotary sliding when the stirring head moves to the terminal of the welding seam; increasing the temperature to between 430 and 450 DEG C, performing thermal insulation for 1 to 5 minutes, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 10 and 40 percent; restarting the rotary device again, wherein the rotating speed is between 20 and 150 r / m; sliding the stirring head in a reverse direction, wherein the movement speed is between 1 and 2 cm / m; stopping the rotation, when the stirring head moves to the initial end of the welding seam, and lifting the stirring head; and cooling the solder along with a furnace after thermal insulation for 5 to 30 minutes. The method can realize the low-cost, high-efficiency and high-quality welding of the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy heterogeneous non-vacuum mechanical forced rotation semi-solid brazing method
InactiveCN102284758ALow costHigh quality weldingSoldering apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSemi solidMagnesium alloy
The invention relates to a magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy heterogeneous non-vacuum machinery forced rotation semi-solid brazing method; a magnesium alloy weldment and an aluminum alloy weldment are clamped on a clamp, Zn-Sn or Zn-Al-Sn system other brazing materials are arranged on two surfaces to be brazed, the weldments are heated, the heating temperature is between 350DEG C to 450DEG C, simultaneously pressure is increased, the pressure range is 0.1MPa to 1MPa, so that the brazing materials on a middle layer are in a semi-solid state, a rotary device is started, the rotating speed is 65r / min to 1500r / min, the temperature is constant during a rotation process, and the rotation time is 10s to 300s. After the rotation, the temperature rises by a certain rate, the heat is insulated at preset temperature, so that the brazing materials dissolve parent materials with a certain thicknesses, the heat insulating temperature is between 400DEG C to 480DEG C, and the heat insulating time is1min to 5min. Afterwards, pressure is increased, the pressure range is 0.1MPa to 1MPa, the rotary device is started again (secondary rotation), the rotating speed is 65r / min to 600r / min, rotation is stopped after 3s to 60s, and cooling is carried out with a furnace after the heat is insulated for 5 min to 30min. The magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy heterogeneous non-vacuum machinery forced rotation semi-solid brazing method can realize the high-efficiency, high-quality and economic connection of a magnesium alloy and an aluminum alloy.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Anti-vacuum semi-solid states stirring soldering method of magnesium alloy and composite material thereof
The invention provides an anti-vacuum semi-solid states stirring soldering method of magnesium alloy and composite material thereof, which comprises the following steps of: a weldment taking the magnesium alloy or the composite material thereof as a parent metal is arranged and blocked on a welding platform and medium temperature brazing filler metal is put on two surfaces to be welded; the weldment is heated in the temperature of 380 to 430 DEG C to cause that the solid phase ratio of the brazing filler metal is between 50 to 80%; hereupon, a rotational sliding device is started; the rotary speed is 150 to 300 r / m; the temperature is constant; a stirring head is parallel to the longitudinal movement speed of 0.5-2cm / min of a welding line; when the stirring head moves to the terminal of the welding line, the rotational sliding stops; the holding time is 1 to 5 minutes so that the weldment is further dissolved; the rotational device is started again; the rotary speed is 20 to 150 r / m; the stirring head slides in a negative direction; the movement speed is 1 to 2 cm / min. When the stirring head moves to the initial end of the welding line, the rotary stops; the stirring head is lifted; the holding temperature is 5-30 minutes, and a furnace cools. The method can realize the low cost, high efficient, high quality welding of the magnesium alloy and the composite material thereof.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Stainless steel water pump impeller investment casting process
The invention relates to the field of water pump impeller production, and discloses a stainless steel water pump impeller investment casting process. According to key points of the technical scheme, the stainless steel water pump impeller investment casting process comprises a wax mold forming process, a shell forming process and an impeller casting forming process. A formed wax mold has high quality, the hardness and air permeability of a formed shell are good, and the defect rate of a formed casting is low; rough machining can ensure that the dimensional accuracy of an impeller exit positionmeets the specified requirements, the exit width is uniform, and the error is small and ensured to be within a drawing tolerance range; after roughing machining and trimming, a large amount of stressis generated in the impeller casting; and after stress-relieving heat treatment, low-temperature stress relief is performed to stabilize the size and ensure the dimensional accuracy after machining.A stainless steel water pump impeller machined by the stainless steel water pump impeller investment casting process has a low defect rate, small dimensional deformation, good impeller machining dimensional accuracy, high surface smoothness and a long impeller service life.
Owner:宁波鑫象不锈钢制品有限公司
Mechanical rotary semi-solid welding method of aluminum alloy and its composite materials in atmospheric environment
InactiveCN102284759ALow costHigh quality weldingSoldering apparatusNon-electric welding apparatusSemi solidMetal
The invention relates to a mechanical rotation semi-solid welding method for an aluminum alloy and a composite material thereof in an atmospheric environment, which comprises the following steps of: clamping the aluminum alloy and a composite material weldment thereof on a fixture, putting intermediate temperature solders such as Zn-Al and the like on two surfaces to be welded, heating the weldment at the temperature of between 400 and 480 DEG C, and applying pressure of 0.1 to 2MPa to make the solder in an intermediate layer positioned in a semi-solid state; starting a rotating device, rotating at a speed of 65 to 1,500r / min for 10 to 300 seconds, and keeping the temperature constant in the rotating process; raising the temperature at a certain heating rate after rotation is stopped, andpreserving heat at the predetermined temperature of between 480 and 520 DEG C for 1 to 5 minutes to make the solder dissolve parent metal with certain thickness; and applying pressure of 0.1 to 1MPa,starting the rotating device again, rotating for the second time at a speed of 65 to 600r / min for 3 to 60 seconds, stopping rotation, preserving heat for 1 to 30 minutes, and cooling with a furnace. By the method, the aluminum alloy and the composite material thereof can be efficiently and economically connected at high quality.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Non-vacuum semi-solid mechanically assisted rotary brazing method for magnesium alloy and its composite materials
InactiveCN102284760ALow costHigh quality weldingSoldering apparatusNon-electric welding apparatusVacuum assistedSemi solid
The invention relates to a non-vacuum semi-solid machine-assisted rotary soldering method for a magnesium alloy and a composite material thereof, which comprises the following steps of: clamping the magnesium alloy and a composite material weldment thereof on a fixture, putting Zn-Sn or Zn-Al-Sn solders and the like on two surfaces to be welded, heating the weldment at the temperature of between 350 and 450 DEG C, and applying pressure of 0.1 to 1MPa to make the solder in an intermediate layer positioned in a semi-solid state; starting a rotating device, rotating at a speed of 65 to 1,500r / min for 10 to 300 seconds, and keeping the temperature constant in the rotating process; raising the temperature at a certain heating rate after rotation is stopped, and preserving heat at the predetermined temperature of between 400 and 480 DEG C for 1 to 5 minutes to make the solder dissolve parent metal with certain thickness; and applying pressure of 0.1 to 1MPa, starting the rotating device again, rotating for the second time at a speed of 65 to 600r / min for 3 to 60 seconds, stopping rotation, preserving heat for 5 to 30 minutes, and cooling with a furnace. By the method, the magnesium alloy and the composite material thereof can be efficiently and economically connected at high quality.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
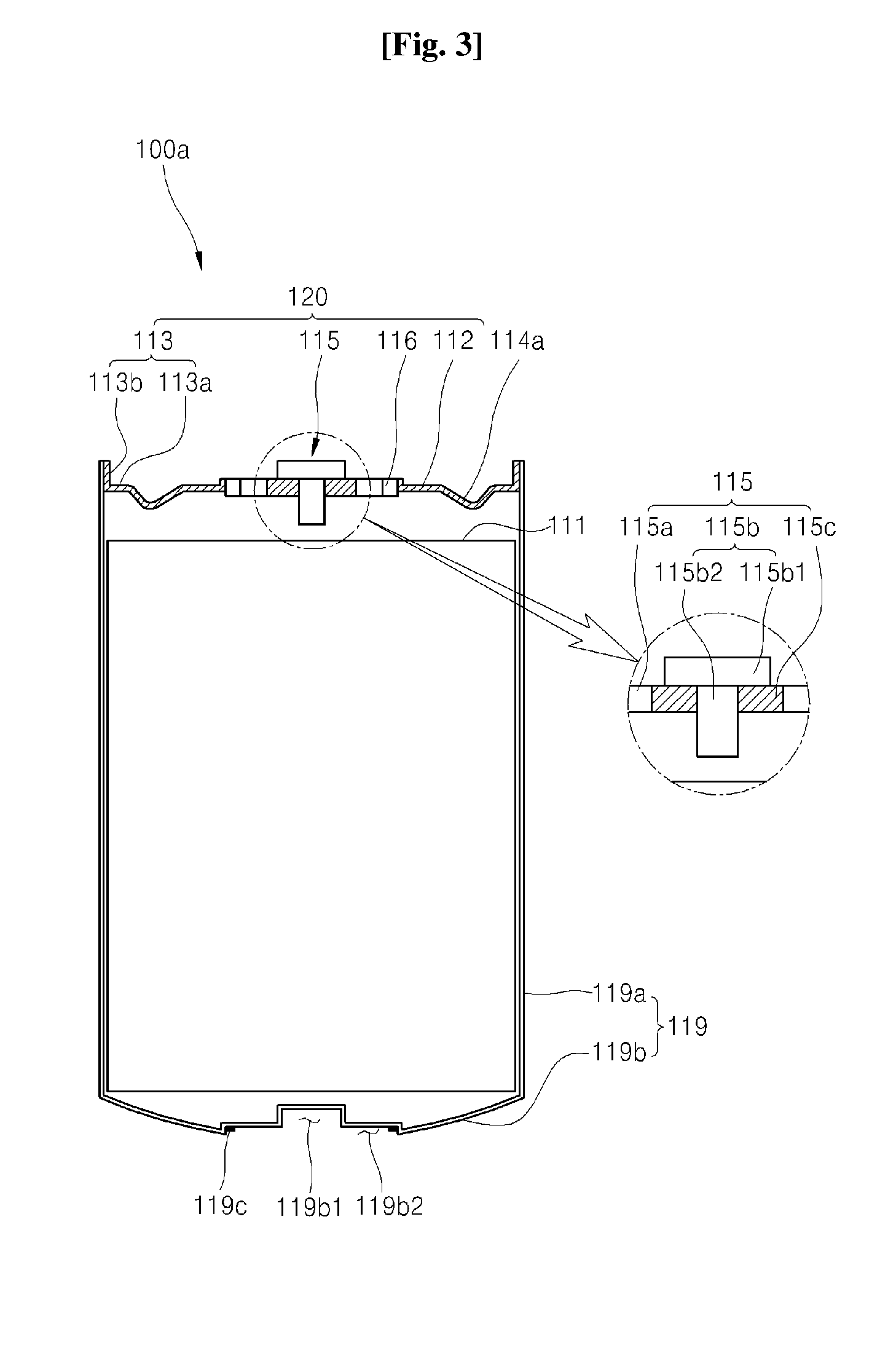
Lithium battery with excellent safety
InactiveUS20140134467A1Small size deformationEasy dischargeSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsLi-accumulatorsInternal pressureBarrel Shaped
Disclosed herein is a lithium battery which exhibits minimal dimensional deformation of a case thereof and easily discharges gas therefrom. The lithium battery includes an electrode assembly in which cathode and anode plates face each other with a separator therebetween; a case body receiving the electrode assembly and an electrolyte, the case body including a barrel-shaped sidewall open at a top thereof and a bottom bulging in a direction away from the electrode assembly; and a top cap disposed on the top of the case body and provided with a safety exhaust outlet through which gas is discharged upon increase in internal pressure.
Owner:VITZROCELL
Decorative sheet structure and manufacturing method
ActiveCN105666597AReduce deformation defectsSmall machining allowanceWood veneer joiningFinger jointStress relief
The invention discloses a decorative sheet structure and a manufacturing method. The decorative sheet structure is formed by a finger joint sheet, veneers and facing paper in a composite mode; the finger joint sheet is formed by splicing a plurality of wood sheets with finger type teeth and stress relief grooves, wherein the finger type teeth and the stress relief grooves are located at the ends of the wood sheets; the finger joint sheet is connected through the finger type teeth for being longitudinally spliced and is fixed through glue for being transversely spliced. The manufacturing method mainly comprises the steps of cutting, rounding, stress groove forming and manufacturing, drying, board cutting, comb tooth treating, length jointing and width splicing, repairing, sanding, veneer gluing, paper gluing and sheet cutting. The decorative sheet structure has the advantages of being high in strength and good in stability. The manufacturing method of the decorative sheet structure has the advantages that the outturn percentage is high, the production technology is simple, the production efficiency is high, the labor intensity is low and the production cost is low, and the technical problems that the utilization rate of wood is low, the strength of decorative sheets is low and the stability is poor in the existingmanufacturing technology of the decorative sheets are well solved.
Owner:广州市欧亚床垫家具有限公司
Preparation method for Al2O3 dispersion strengthened copper-based oil bearing
A preparation method for an Al2O3 dispersion strengthened copper-based oil bearing comprises the steps that Al2O3 dispersion copper alloy powder and tin powder are mixed proportionally and evenly; mixed powder is subjected to diffusion alloying treatment, and Al2O3 dispersion strengthened copper-tin diffusion alloying powder is obtained after crushing, screening and blending; the obtained diffusion alloying powder is subjected to die forming, and a bearing green body is prepared; and the obtained bearing green body is sintered and then subjected to oil immersion and finishing, and the Al2O3 dispersion strengthened copper-based oil bearing is obtained. The dispersion strengthened copper-based oil bearing prepared through the method has the good strength, hardness and precision, the defects that existing bronze oil bearings are low in strength, poor in abrasion resistance, low in precision and the like commonly are overcome, and the method is suitable for scale production.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MATERIALS & PROCESSING +1
Axial fan blade with reinforced sweepforward blade and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a fan blade and a preparation method thereof. The axial fan blade with a reinforced sweepforward blade is prepared from, by mass, 76-89% of PP, 15-25% of glass fiber, 1.0-5.0% of carbon fiber, 3.0-10% of mica, 0.1-1.5% of silane coupling agent DB792, 0.1-1.5% of silane coupling agent KBM-403, 0.2-2.0% of cyclic anhydride compatibilizer, 0.5-1.0% of ethoxylated lauryl amide, 0.2-1.0% of silver-loaded inorganic antibacterial agent, 0.5-2.0% of ethylene bis-stearamide, 0.5-3.0% of methyl methacrylate-butadiene-styrene copolymer, 0.5-2.0% of halogen free flame retardant, 0.5-2.0% of anti-oxidant, 0.1-1.0 part of light stabilizer and 0.1-1.0% of heat stabilizer. The axial fan blade with the reinforced sweepforward blade has a high heat resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, anti-aging, anti-moulding, anti-ultraviolet properties and the like, the density and hardness are high, the size change is small, and the tensile strength of the plastic material is increased. At the same time, the axial fan blade with the reinforced sweepforward blade has the anti-static, antimicrobial, fire-retardant properties, and increased anti-aging property and a thermal decomposition performance.
Owner:NINGBO LANGDI IMPELLER MACHINERY
Inorganic mineral enhancer
The invention provides an inorganic mineral enhancer which is composed of anhydrous calcium sulphoaluminate, calcium sulfate, an activator and an initiator, and the anhydrous calcium sulphoaluminate is generated by reacting calcium oxide, aluminum oxide and calcium sulfate at the temperature of 1000 DEG C-1250 DEG C; calcium sulfate is formed by combining one or a combination of more of anhydrite,hemihydrate gypsum, dihydrate gypsum, desulfurized gypsum, phosphogypsum and fluorgypsum; the activating agent is formed by combining one or more of triethanolamine, diethanol amine, polyethylene glycol and fatty acid methyl ester; and the initiator is formed by combining one or more of potassium sulfate, sodium persulfate, ammonium persulfate, sodium nitrite and sodium hydroxide. 5 Kg-8 Kg / m<3>of the enhancer is added into per cubic meter of concrete and can replace 100 Kg-218 Kg of ordinary cement, so that the cement consumption is greatly reduced, the concrete cost is greatly reduced, theearly strength is improved, the later strength is increased, the size deformation is reduced, the hydration heat release is reduced, and the problem of shrinkage cracks of the concrete is solved.
Owner:TIANJIN JUSHI TECH DEV
Machining process of large super duplex stainless steel guide vane body
InactiveCN108608176APrevent thermal deformation during hoistingUniform relative positionSurface finishEngineering
The invention relates to a machining process of a large super duplex stainless steel guide vane body. The machining process comprises the steps of casting, deformation protection before heat treatment, solid solution treatment, casting cleaning rough grinding, component rechecking, mechanical performance checking, PT dye penetrant inspection, defect cleaning-away repair welding rough grinding, rough machining, finishing, stress relief heat treatment, semi-finish machining, finish grinding finish machining and the like. According to the machining process, the machining hardening effect is small, size deformation is small, the machining size precision of the guide vane body is good, and surface smoothness is high. Finishing size checking is controlled to be below 40 DEG C; and the machiningefficiency is high, quality is good, the size precision and small form and position and dimensional tolerance deformation of the guide vane body can be guaranteed, and the drawing size requirement andthe technical requirement are met.
Owner:SHENYANG SANKE VALVES IND CO LTD
Preparation method of aluminum oxide dispersion-strengthened copper-based diffusion alloy powder
InactiveCN109530705AHigh hardnessExcellent resistance to high temperature softening propertiesTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusApparent densityHydrogen atmosphere
The invention provides a preparation method of aluminum oxide dispersion-strengthened copper-based diffusion alloy powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) weighing luminumoxide dispersion-strengthened copper powder of which the particle size is smaller than 75 microns and metal powder of which the particle size is smaller than 45 microns according to a mass ratio, andmixing for 4 h to 8 h; (2) processing the mixed powder for 0.5 h to 4 h at the temperature of 600 DEG C to 900 DEG C in hydrogen atmosphere; (3) crushing the obtained material until the particle sizeof the material is smaller than or equal to 180 microns, and screening the material to form powder which is within four different particle size ranges including 180-150 microns, 15-75 microns, 75-45microns and smaller than 45 microns; and (4) processing the powder for 1 h to 3 h at the temperature of 450 DEG C to 650 DEG C in the hydrogen atmosphere, cooling to room temperature to obtain the aluminum oxide dispersion-strengthened copper-based diffusion alloy powder, and finally carrying out vacuum packaging. The invention provides a preparation method of the aluminum oxide dispersion-strengthened copper-based diffusion alloy powder which is uniform in components and controllable in particle size, apparent density and fluidity, and the aluminum oxide dispersion-strengthened copper-based diffusion alloy powder can meet various application requirements of oil bearings, diamond tools, friction materials and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MATERIALS & PROCESSING
Non-vacuum semi-solid stirring brazing method for aluminum alloy and composite material thereof
InactiveCN101596630BAchieve weldingShort welding cycleSoldering apparatusThermal insulationSemi solid
The invention provides a semi-solid brazing method for aluminum alloy and a composite material thereof under the assistance of non-vacuum mechanical stirring, which comprises the steps of: mounting a weldment taking the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof as a base material on a welding platform first; placing intermediate-temperature solder on two surfaces to be welded, heating the weldment to between 390 and 420 DEG C, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 50 and 80 percent; staring a rotary sliding device, wherein the rotating speed is between 150 and 300 r / m, the temperature is constant, and the longitudinal movement rate, which is parallel to a welding seam, of a stirring head is between 0.5 and 2 cm / min; stopping the rotary sliding when the stirring head moves to the terminal of the welding seam; increasing the temperature to between 430 and 450 DEG C, performing thermal insulation for 1 to 5 minutes, and ensuring that the solid fraction of the solder is between 10 and 40 percent; restarting the rotary device again, wherein the rotating speed is between 20 and 150 r / m; sliding the stirring head in a reverse direction, wherein the movementspeed is between 1 and 2 cm / m; stopping the rotation, when the stirring head moves to the initial end of the welding seam, and lifting the stirring head; and cooling the solder along with a furnace after thermal insulation for 5 to 30 minutes. The method can realize the low-cost, high-efficiency and high-quality welding of the aluminum alloy or the composite material thereof.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Manufacture method of quartz crucible for casting polycrystalline silicon ingot
InactiveCN102115305AReasonable particle size distributionImprove performanceGlass shaping apparatusCross-linkPorosity
The invention discloses a manufacture method of a quartz crucible for casting a polycrystalline silicon ingot. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing slurry and forming a blank; carrying out ball milling on partial quartz powder, partial additives containing a polymer monomer and a cross-linked body and all deionized water until required granularity is obtained; then, adding residential quartz powder and residential additives for secondary ball milling to obtain slurry and stirring a proper amount of qualified slurry; injecting an initiator and a catalyst at the same time of stirring, dynamically pressurizing and adding the stirred slurry into a die for heating and curing; and crosslinking and polymerizing an organic polymer monomer in the heating and curing process into three-dimensional grid-shaped polymer gel, and bonding and curing the quartz powder to form the blank. The manufacture method provided by the invention has a short production period, high efficiency and a low cost and meets the need of mass industrial production, and the quartz crucible for casting the polycrystalline silicon ingot, which is manufactured according to the invention, has small size distortion, low apparent porosity and high compressive strength and rupture strength.
Owner:江苏沂宝石英有限公司
Machining process of precipitation hardening stainless steel pump shaft
The invention relates to a machining process of a precipitation hardening stainless steel pump shaft. The machining process comprises the steps of: forging, rough turning I, UT inspection, heat treatment, rough turning II, high-temperature aging, semi-finish turning I, semi-finish turning II, low-temperature aging, grinding, finish turning I, polishing I, lineation, milling, polishing II, flaw detection, chromium plating, hydrogen removing treatment, chromium plating protection removal, polishing III, polishing IV, finishing, and obtaining of a finished product. The pump shaft machining process is low in hardening effect and size deformation, excellent in pump shaft machining size precision and high in surface smoothness, controls the size inspection below 40 DEG C after machining, is high in machining efficiency and quality, can guarantee the pump shaft size precision and low shape and position size tolerance deformation, and satisfies the drawing size requirements and the technical requirements.
Owner:SHENYANG SANKE HYDRAULIC MACHINERY MANUFACTORY
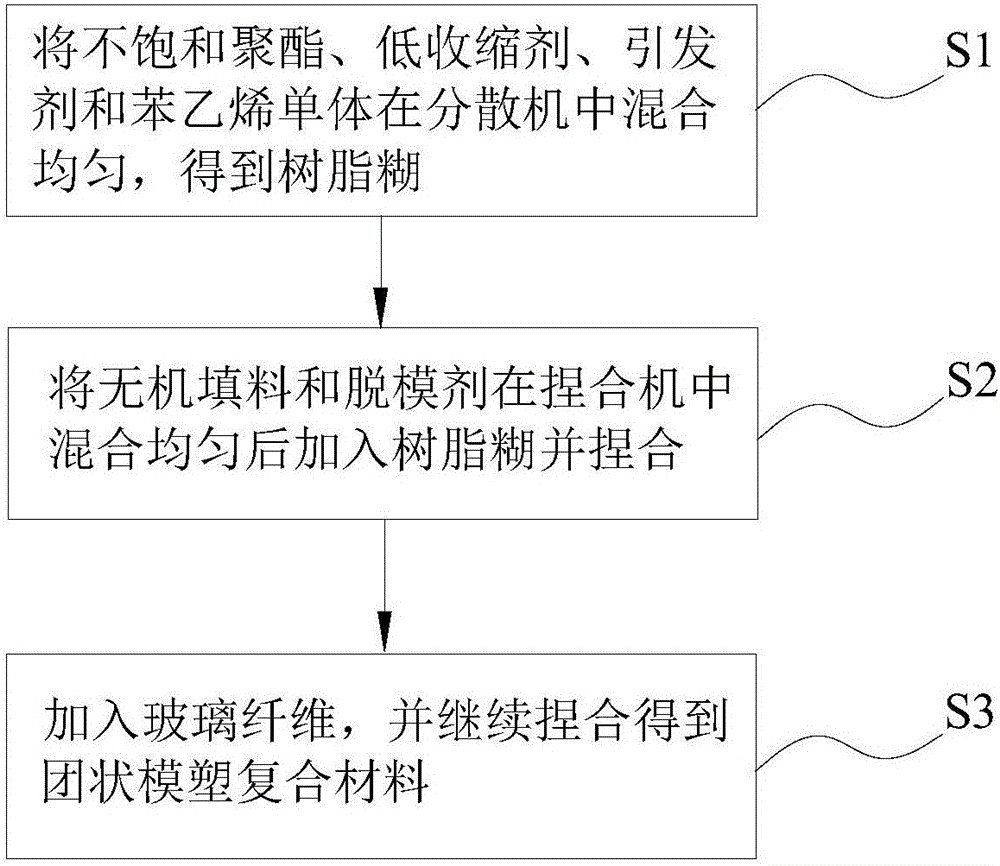
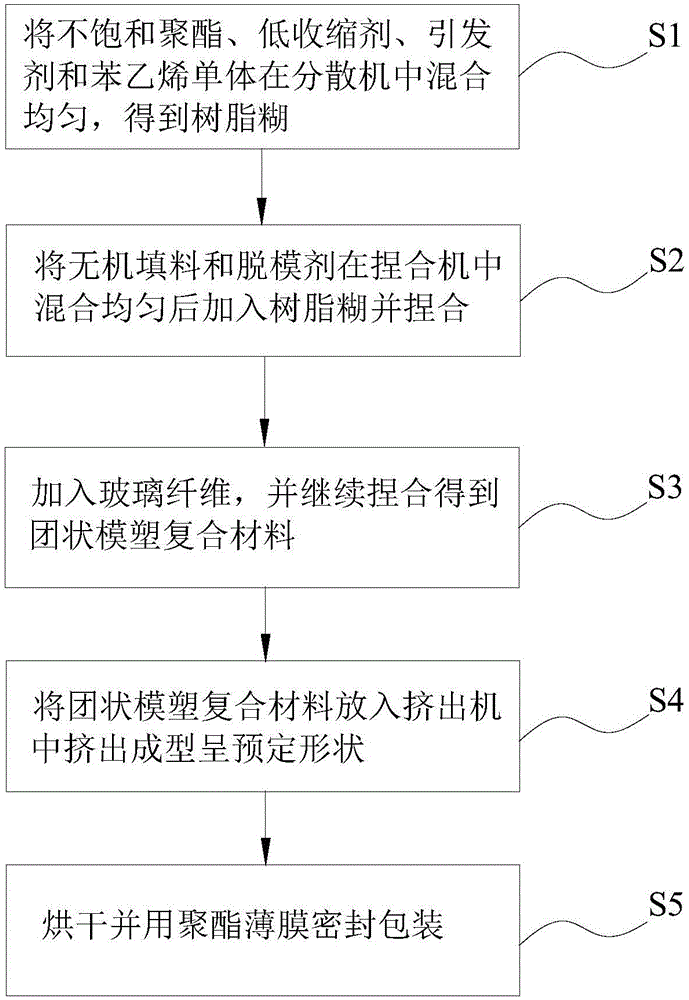
Air-conditioning air deflector, clustered molding composite material for manufacturing same and preparation method
The invention discloses an air-conditioning air deflector, a clustered molding composite material for manufacturing the same and a preparation method of the clustered molding composite material. The clustered molding composite material is prepared from 60-65 phr (parts per hundred resin) of unsaturated polyester resin, 35-40 phr of a low shrinkage agent, 100-110 phr of inorganic filler, 3.5-4.0 phr of a release agent, 1.0-1.2 phr of a thickening agent, 0.8-1.0 phr of an initiating agent, 3.3-3.5 phr of pigments and 35.0wt% -45.0wt% of glass fibers, wherein the low shrinkage agent is prepared from high-polymerization-degree polystyrene with molecular weight of 20,000-60,000 and low-polymerization-degree polystyrene with molecular weight of 5,000-15,000, and a weight ratio of high-polymerization-degree polystyrene to low-polymerization-degree polystyrene is (75-50):(25-50). With the adoption of the air-conditioning air deflector manufactured from the clustered molding composite material in the embodiment, requirements for working performance and appearance can be met simultaneously.
Owner:WUHU MATY AIR CONDITIONING EQUIP CO LTD +1
Outdoor non-structural heavy bamboo board and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105034124AImprove water resistanceSmall size deformationNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesWood working apparatusMaleic anhydridePolytetrafluoroethylene
The invention discloses an outdoor non-structural heavy bamboo board. The outdoor non-structural heavy bamboo board comprises the raw materials: in parts by weight, 100 parts to 120 parts of dry bamboo filament sheets, 400 parts to 450 parts of an oil-tea-fruit-shell liquidation resin adhesive (the solid content ranges from 20% to 22%), 0.4 part to 0.5 part of a penetrant, 5 parts to 6 parts of trifluoroethyl acrylate, 5 parts to 6 parts of nano-polytetrafluoroethylene, 6 parts to 7 parts of dodecafluoroheptyl methacrylate, 0.5 part to 0.8 part of titanate coupling agent, 0.4 part to 0.5 part of dicumyl peroxide, 2 parts to 3 parts of nano-zinc oxide, 1 part to 1.5 parts of amino resin, 2 parts to 2.5 parts of maleic anhydride and 2 parts to 3 parts of nanometer titania. According to the outdoor non-structural heavy bamboo board, glue liquor is modified through the trifluoroethyl acrylate, the nano-polytetrafluoroethylene and the dodecafluoroheptyl methacrylate, the water resistance, the oil resistance, the corrosion resistance and the antifouling performance of the heavy bamboo board can be improved, and the size deformation of the board can be reduced; and the stability, the high temperature resistance, the acid-base resistance and the light aging resistance of the board are improved through the nano-zinc oxide, the maleic anhydride, the titanate coupling agent and the nanometer titania.
Owner:王慧
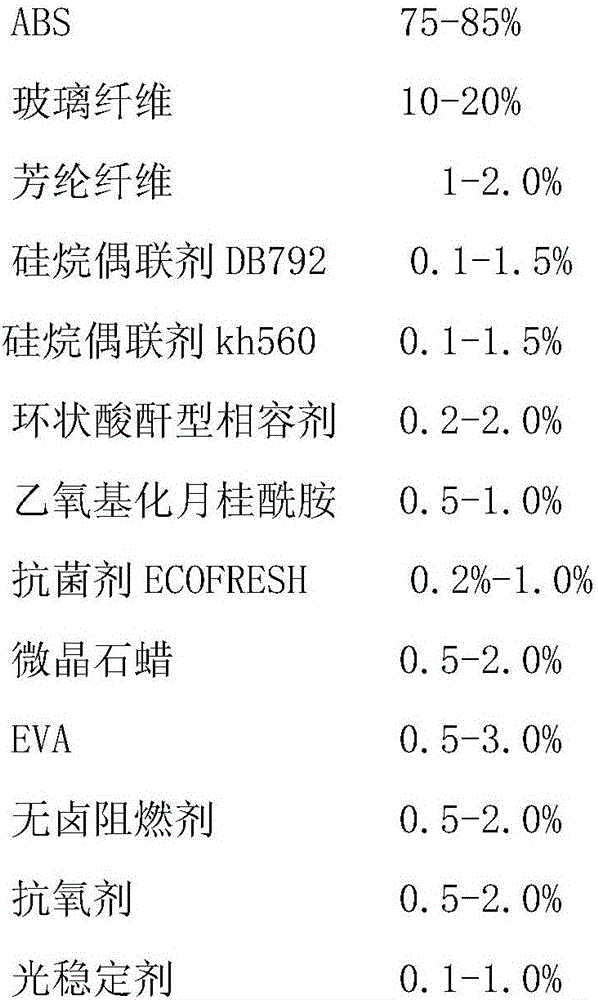
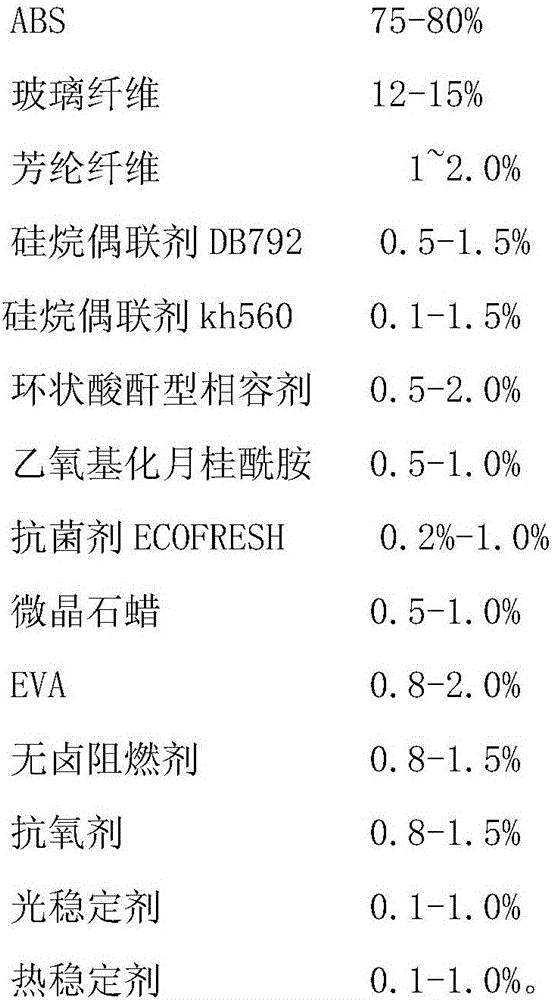
Centrifuging fan blade and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106700401AImprove heat resistanceGood chemical resistanceMicrocrystalline waxPlastic materials
The invention relates to a fan blade and a preparation method of the fan blade. The centrifuging fan blade is prepared through injection moulding from the following materials by mass percent: 75-85% of ABS, 10-20% of glass fiber, 1.0-2.0% of aramid fiber, 0.1-1.5% of a silane coupling agent DB792, 0.1-1.5% of a silane coupling agent kh560, 0.2-2.0% of a cyclic anhydride type compatilizer, 0.5-1.0% of ethyoxyl lauramide, 0.2%-1.0% of antibacterial agent ECOFRESH, 0.5-2.0% of microcrystalline wax, 0.5-3.0% of EVA, 0.5-2.0% of a halogen-free flame retardant, 0.5-2.0% of antioxygen, 0.1-1.0% of a light stabilizer, and 0.1-1.0% of a heat stabilizer. The centrifuging fan blade has the higher performances of heat resistance, resistance to chemical attack, ageing resistance, mildew prevention, protection from ultraviolet rays and the like, is high in density and hardness and small in size deformation, and improves the tensile strength of a plastic material.
Owner:安徽朗迪叶轮机械有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com