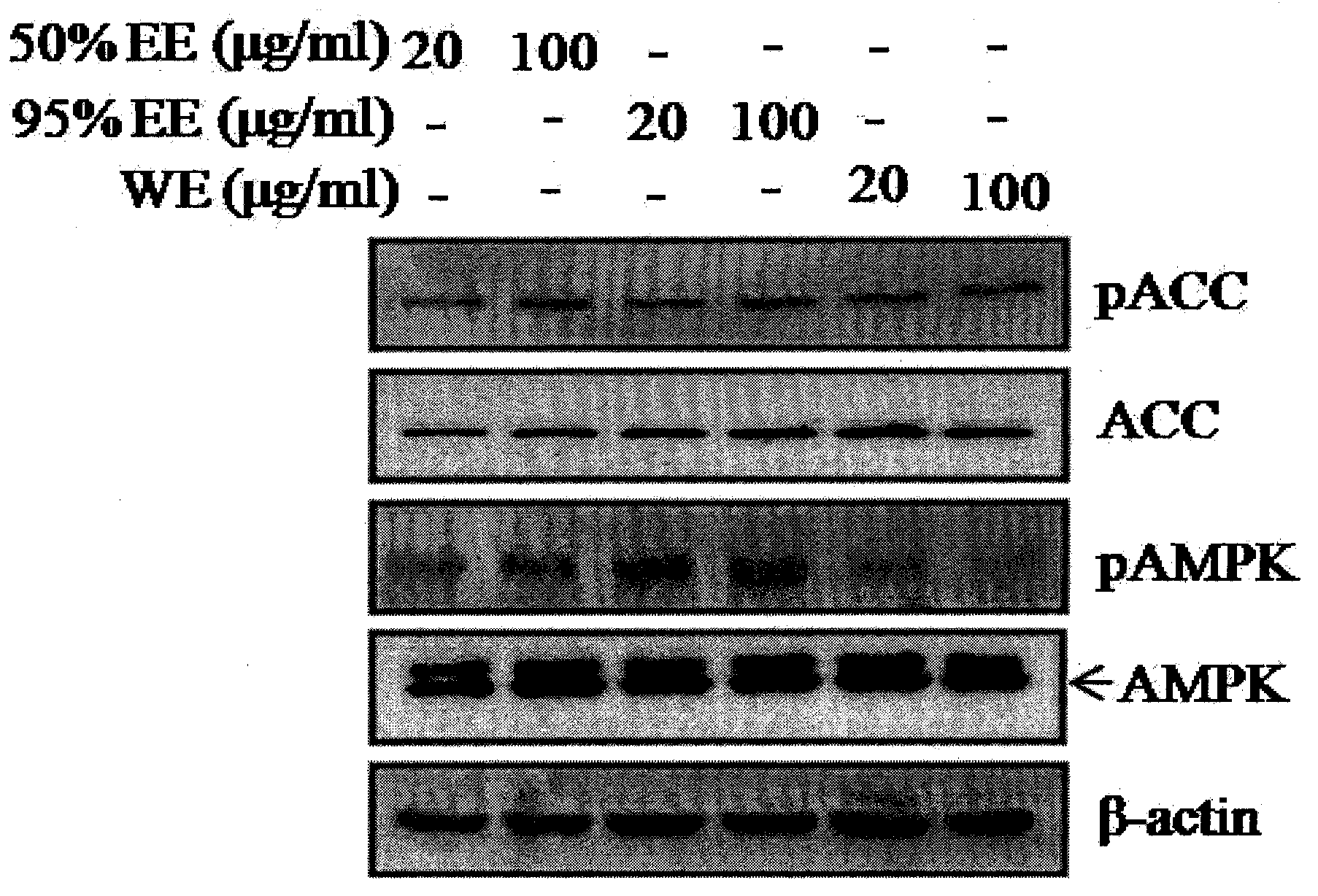
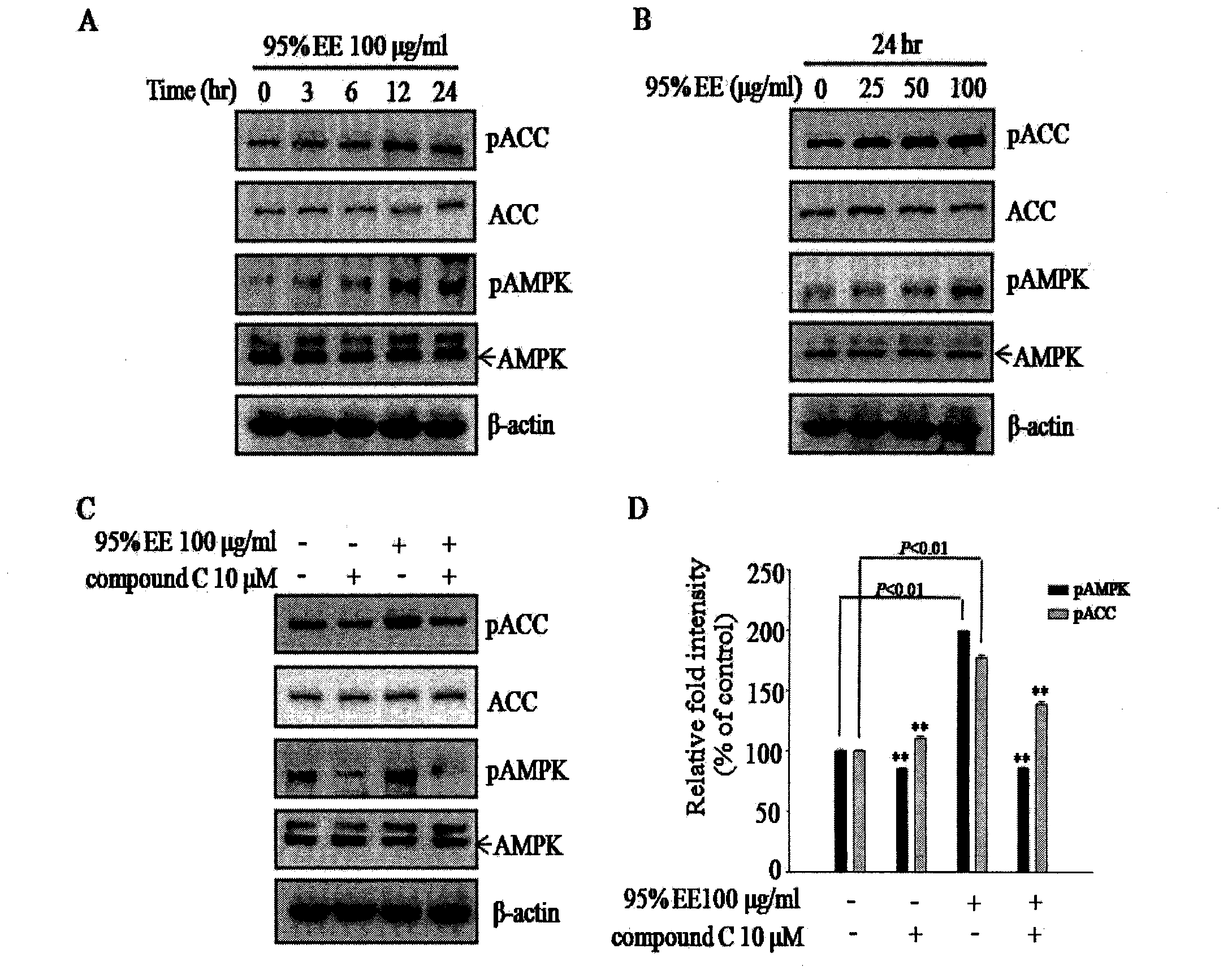
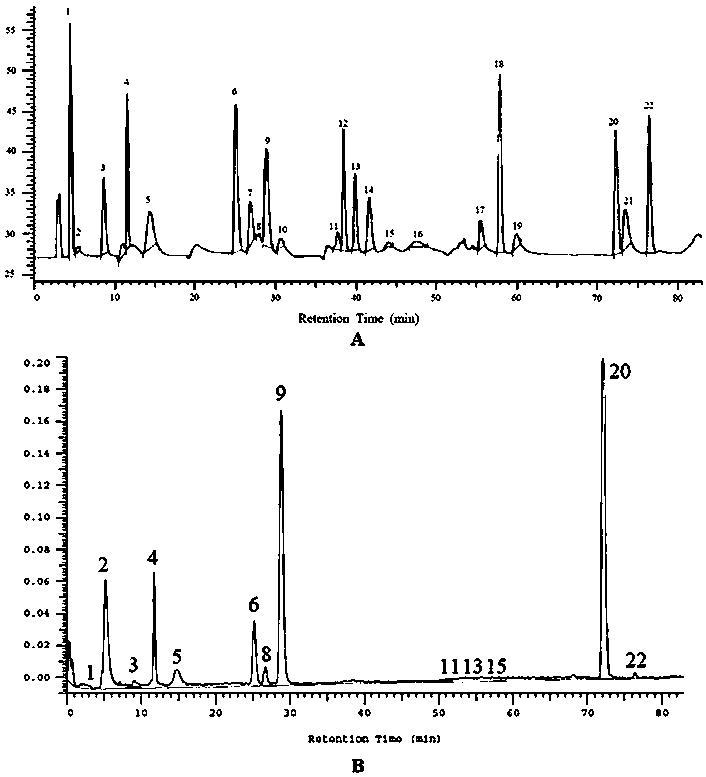
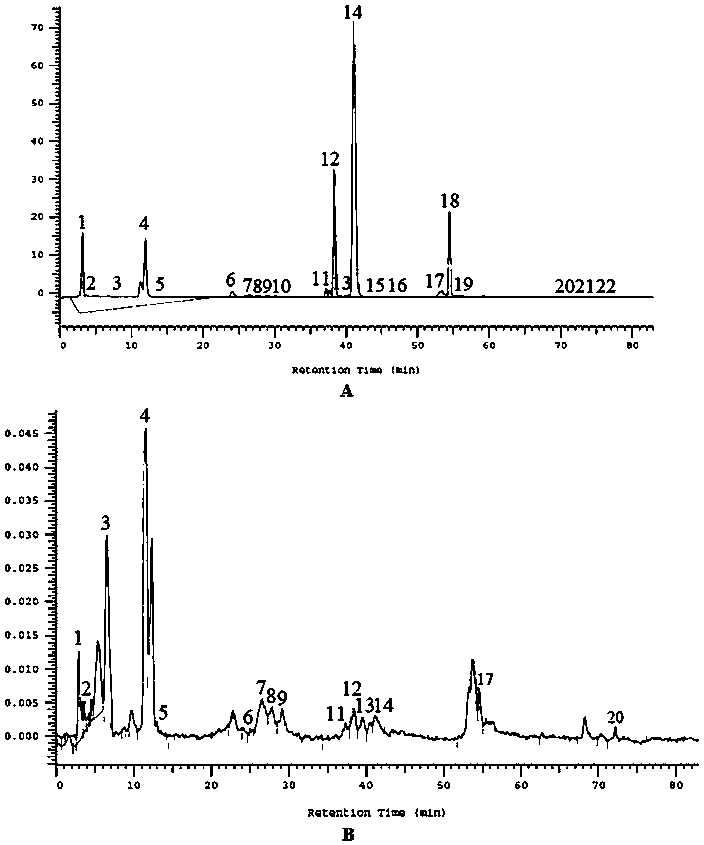
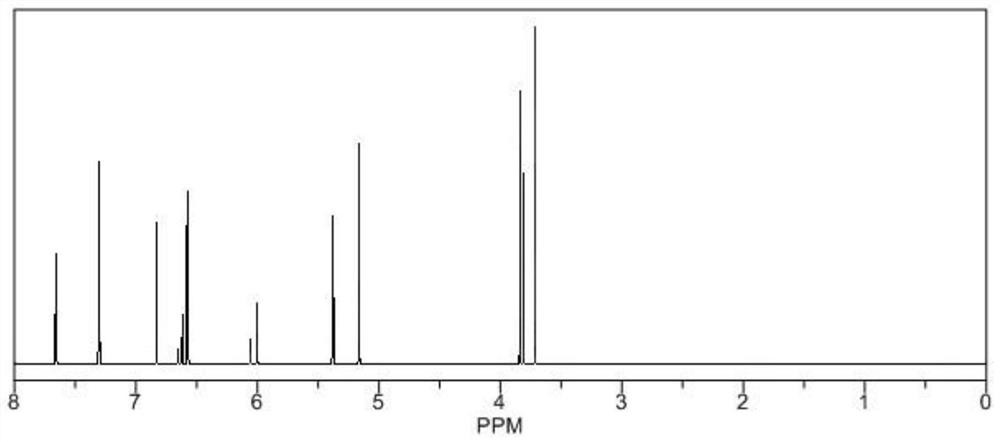
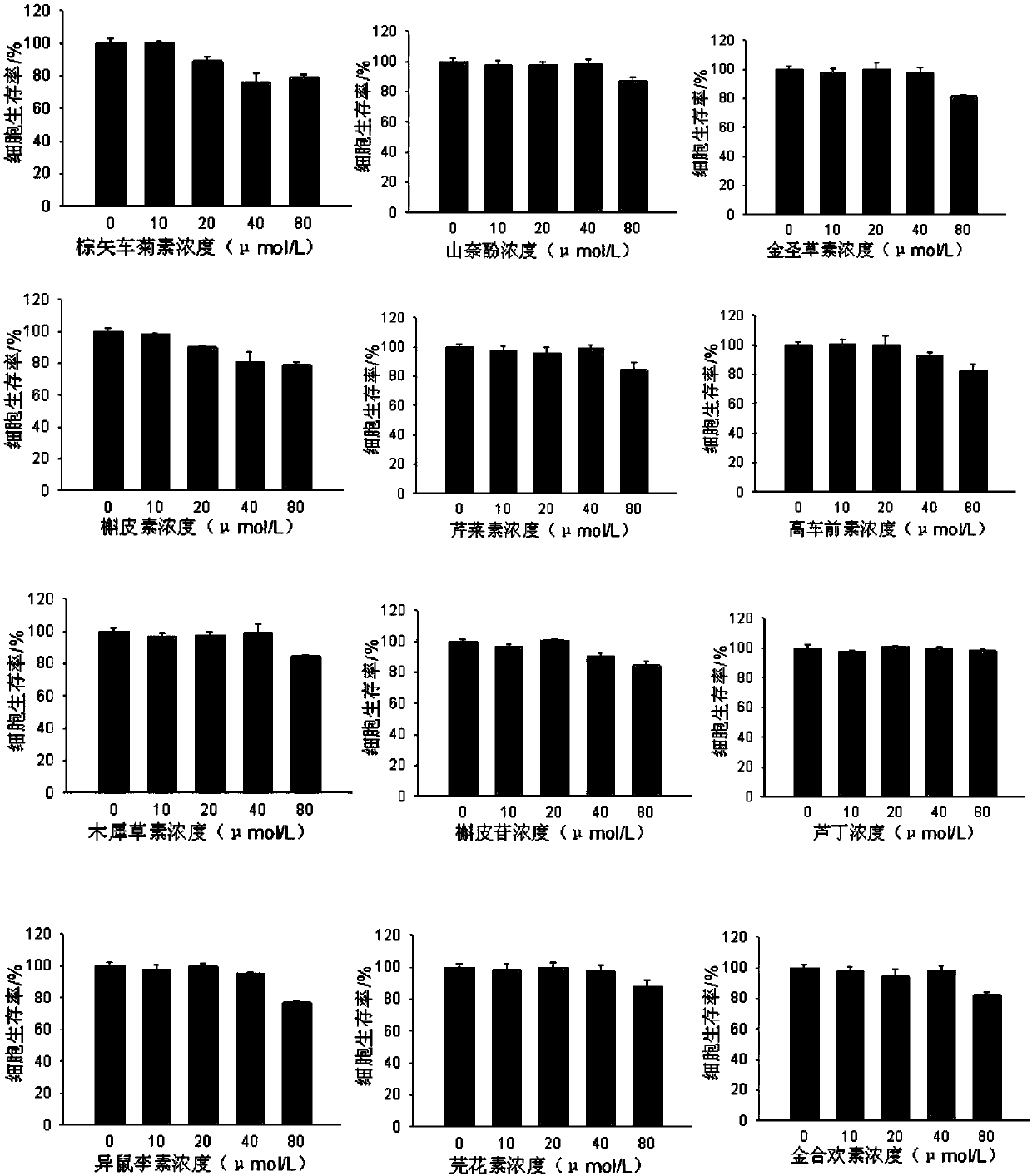
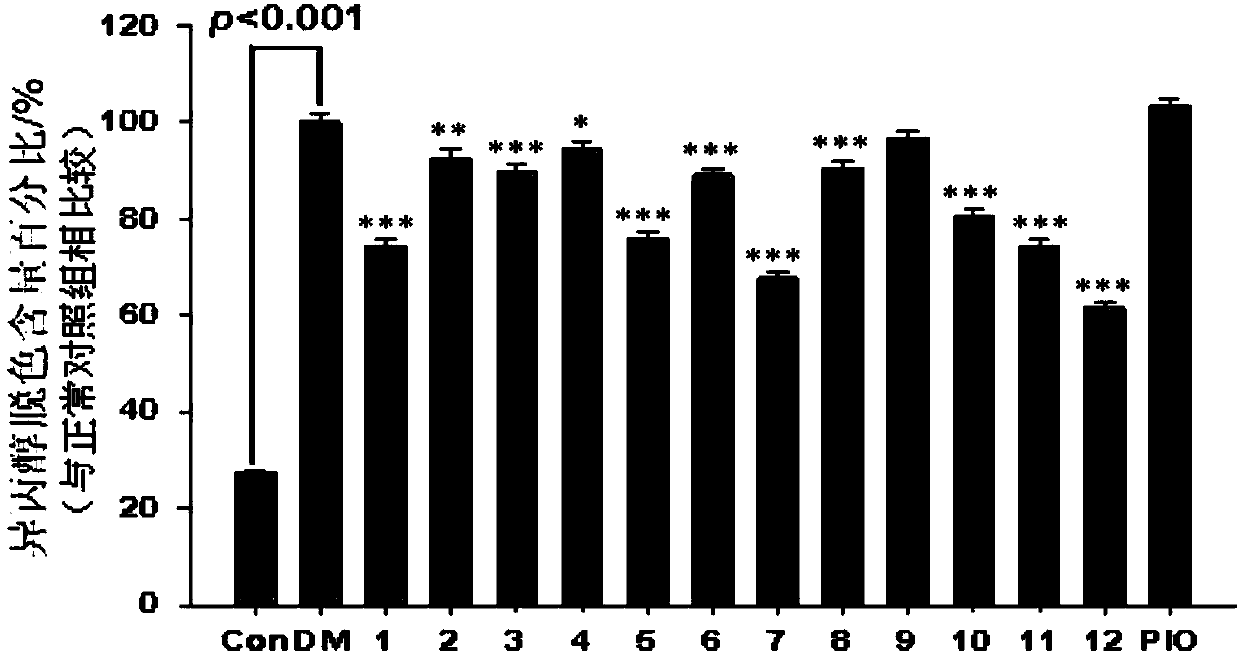
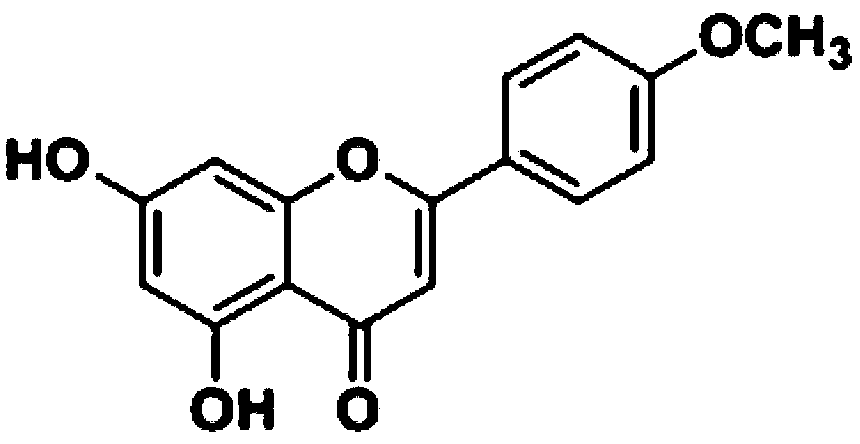
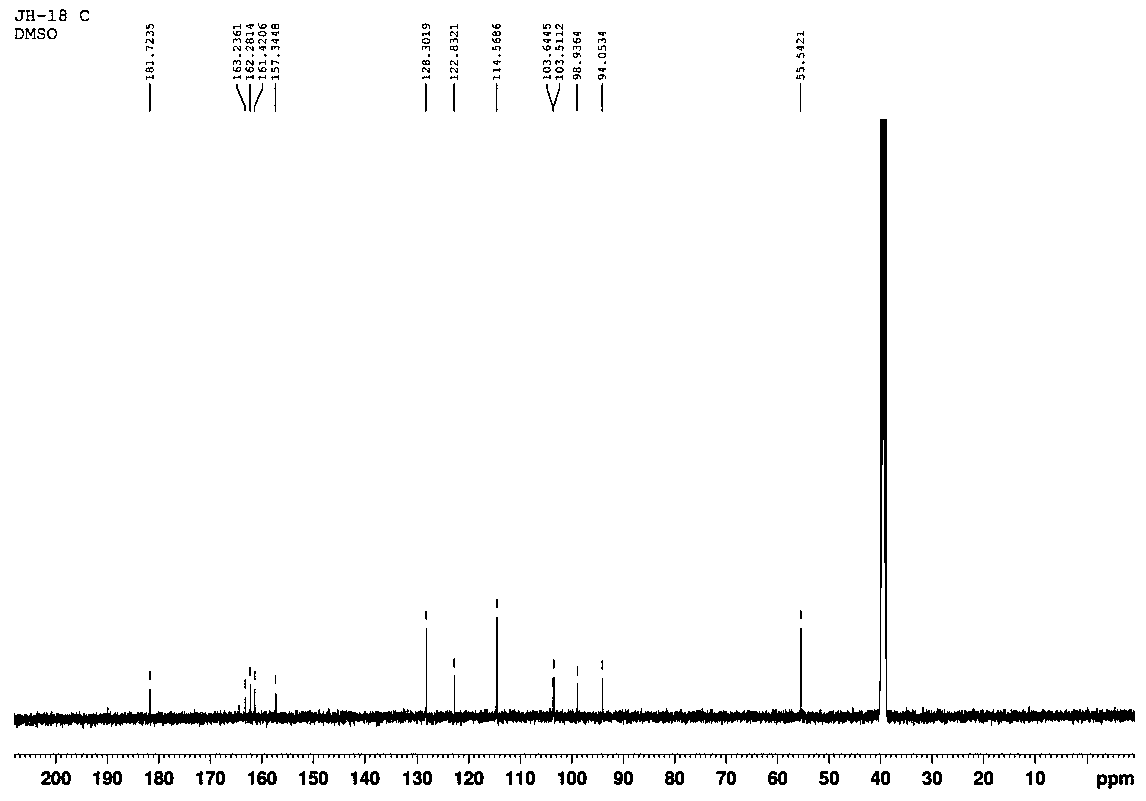
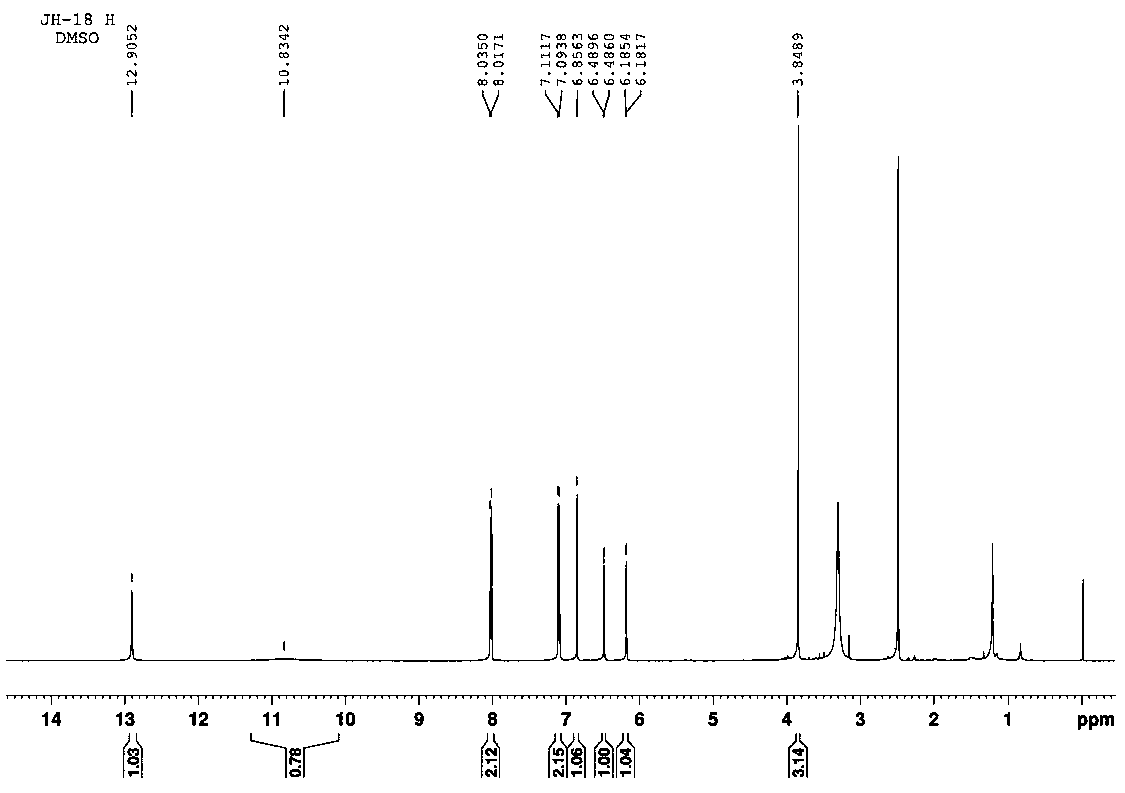
Patents
Literature
40 results about "Acacetin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
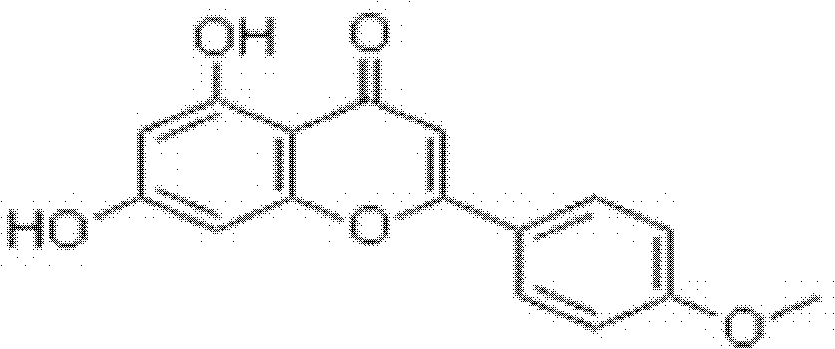
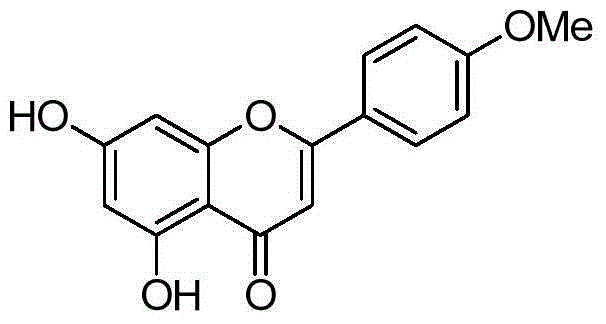
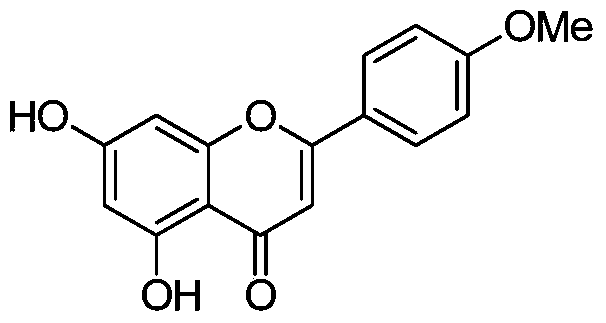
Acacetin is an O-methylated flavone found in Robinia pseudoacacia (black locust), Turnera diffusa (damiana), Betula pendula (silver birch), and in the fern Asplenium normale. The enzyme apigenin 4'-O-methyltransferase uses S-adenosyl methionine and 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone (apigenin) to produce S-adenosylhomocysteine and 4'-methoxy-5,7-dihydroxyflavone (acacetin).
Method for extracting and preparing flavonoids pigment from chrysanthemum
The invention relates to a method for ultrasonically extracting and preparing flavonoids pigment from chrysanthemum, belonging to the field of food processing and especially used for deep processing chrysanthemum. The process comprises the following steps of: blanching, drying and hermetically storing chrysanthemum at a low temperature, filtering by using a 100-mesh sieve, soaking in 60% ethanol as an extraction solvent in a liquid-material ratio of 40 / 1 (v / w) for 2 h, ultrasonically extracting a dry base in a water bath at 70 DEG C for 10 min to acquire the yield of 13.34 percent; and evaporating in the water bath at 70 DEG C by using the 60% of ethanol extraction liquid in a rotating way to release an ethanol taste; and freezing and drying in vacuum, wherein analytical compositions reach 52.01% of the dry base and comprise flavonoids, linarin, flavonoids (luteolin, acacetin and apigenin), flavonols (quercetin), phenolic acid (chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid), metal elements, and the like. The invention provides a new method for deep processing the chrysanthemum and has strong maneuverability, good safety and good repetitiveness.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Artemisia sacrorum extract as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104257715APrevention and treatment of drug-induced liver injuryPreventing and Treating Alcoholic Liver DamageDigestive systemAntiviralsPentahydroxyflavoneTreatment effect
The invention discloses an artemisia sacrorum extract which contains total-flavone compounds, wherein the total-flavone compounds comprise one or more of 6-methoxy-quercetagetin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside, quercetin-3-O-beta-D-glucoside, isorhamnetin, queretagetin-3-O-beta-D-glucoside, acacetin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside, rutin, 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone, 3,3',4',5,7-pentahydroxyflavone, 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3'-methoxyflavone, kaempferol, 3,5,7,4'-tetrahydroxy-6-methoxyflavone, 3',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone, 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-6,3'-dimethoxyflavone, 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-6-methoxyflavone, quercitrin, 7,3',4'-trimethyl quercetin, 5-hydroxy-7,4'-dimethoxyflavone, 5,4'-dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavone genkwanin, 5,7-dihydroxy-4'-methoxyflavone, 5,7,3'-dihydroxy-4-methoxyflavone and derivatives. The artemisia sacrorum extract has remarkable prevention and treatment effects on liver injury.
Owner:朴光春
Method for simultaneously determining twenty-two flavones and phenolic acids in citrus fruits
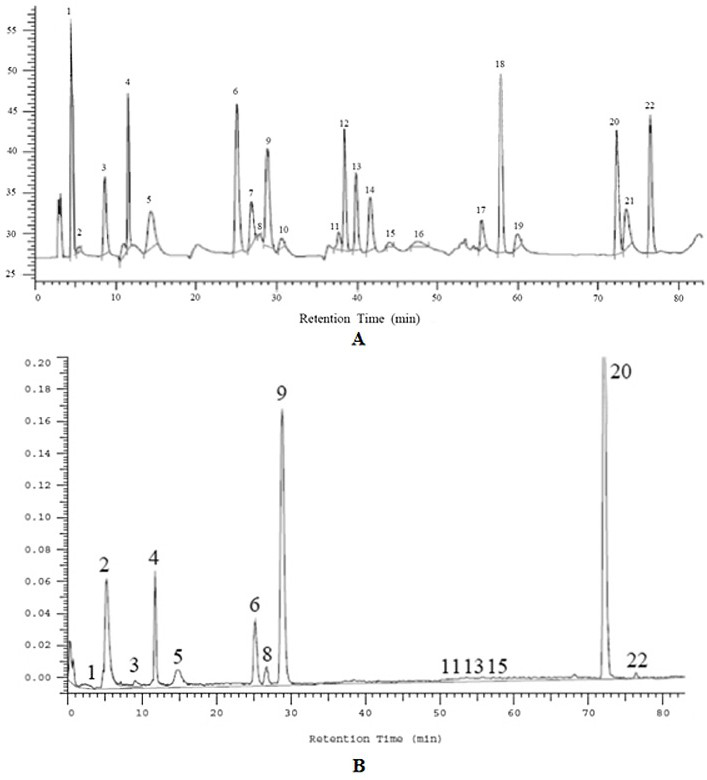
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously determining twenty-two flavones and phenolic acids in citrus fruits by adopting high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-fluorescence detector (HPLC-DAD-FLD). The method is capable of simultaneously determining twenty-two phenolic compounds in citrus fruits such as gallic acid, synephrine, chlorogenic acid, protocatechuic acid,caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, rhamnosylvitexin, eriocitrin, ferulic acid, rutin, benzoic acid, narirutin, naringin, hesperidin, diosmin, neohesperidin, quercetin, naringenin, kaempferol, nobiletin,hesperetin, acacetin and the like, derivatization is not needed, and the method is high in accuracy, high in sensitivity and excellent in repeatability.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENG TECH FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Preparation of chitosan-covering zein nanoparticles and application thereof in load acacetin sodium salt
InactiveCN109350609AImprove stabilityHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticZeta potentialAcacetin
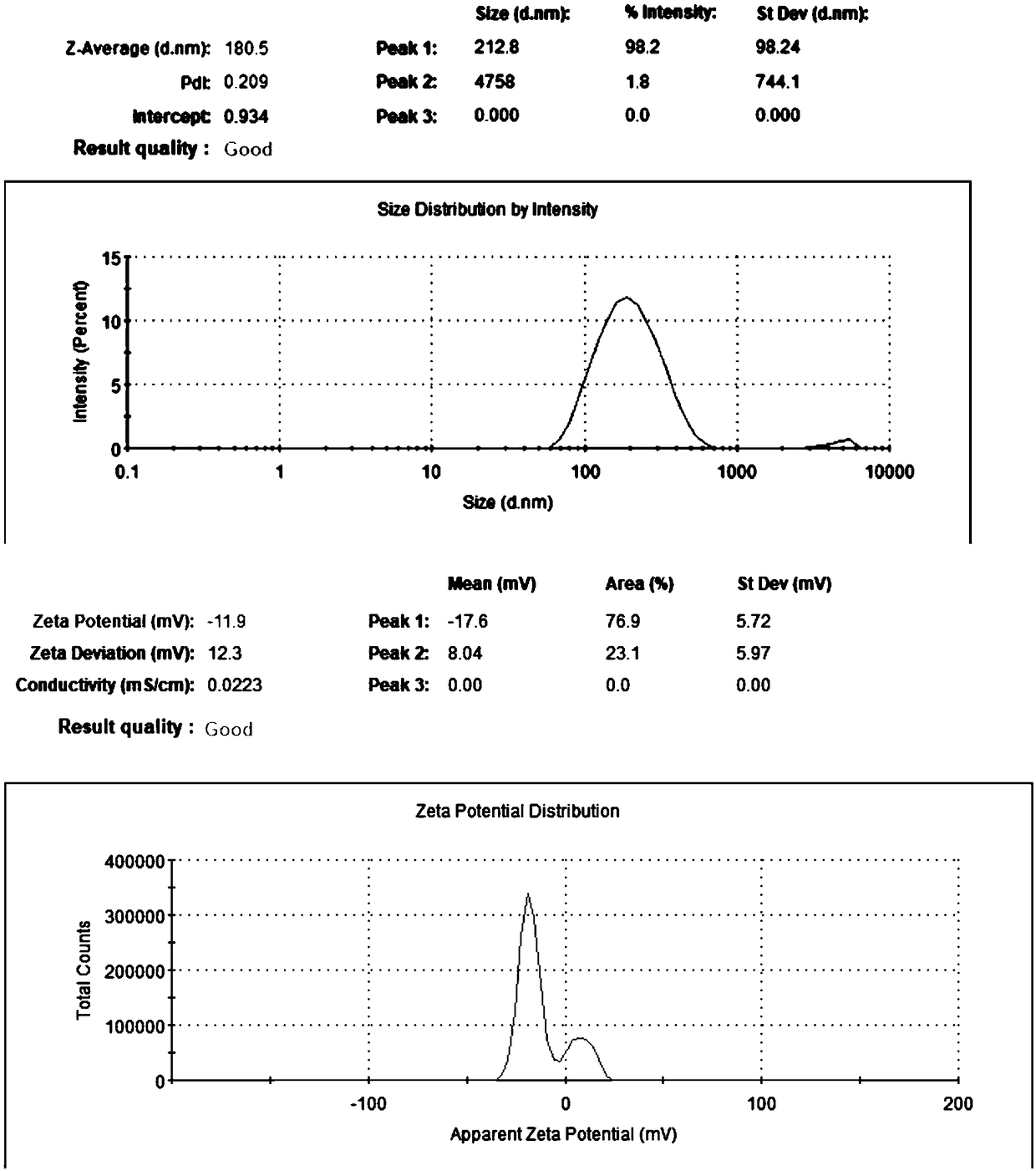
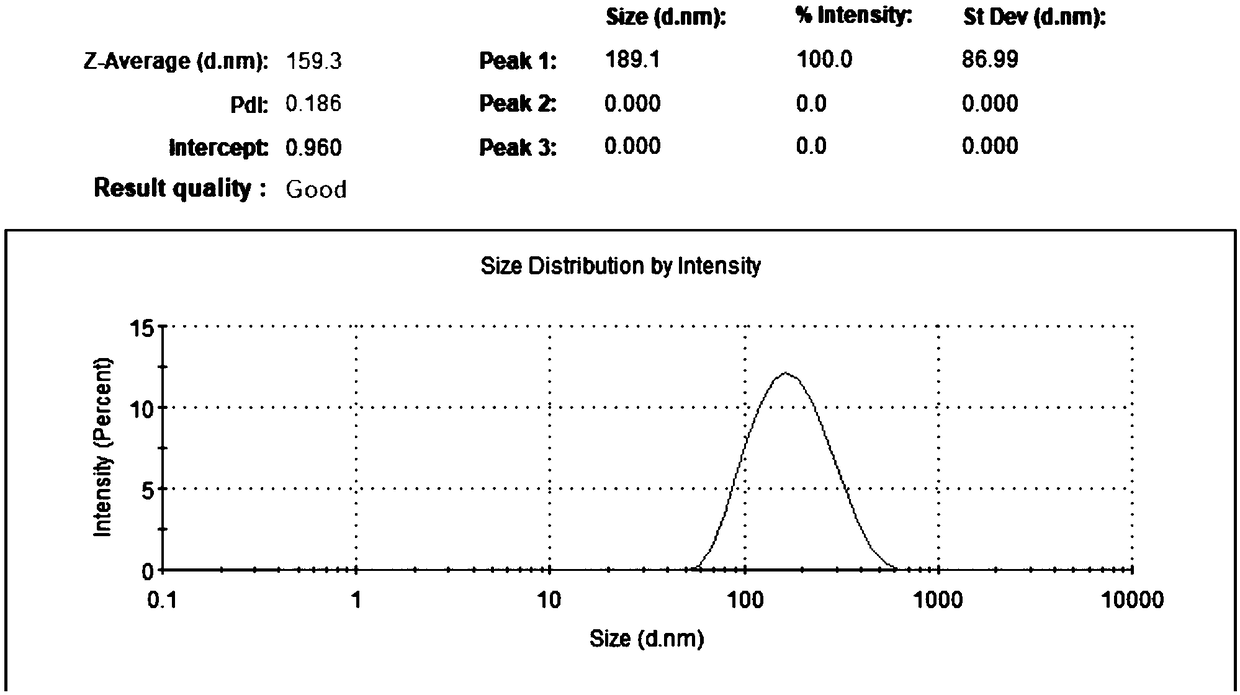
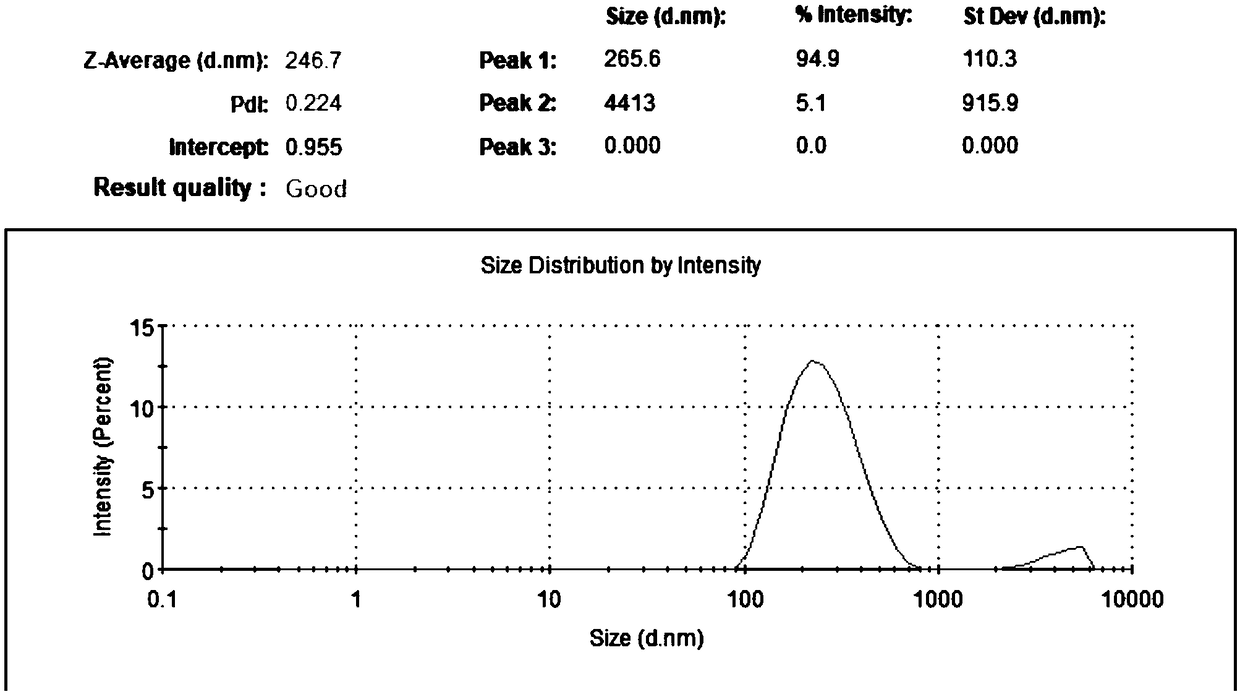
The invention discloses a preparing method and application of chitosan-covering zein nanoparticles. The preparing method of the nanoparticles comprises the steps that an ethanol solution of zein is added into a spraying bottle with the droplet particle size of about 10-50 microns, a water phase is added into another spraying bottle with the droplet particle size of about 10-50 microns, and the twospraying bottles conduct opposite spraying in a closed device to obtain a solution containing the zein nanoparticles, wherein for the zein nanoparticles, the particle size is about 160-200 nm, and the zeta potential is minus 8 to 12 mv. A proper amount of a zein nanoparticle solution is added into a chitosan solution, through incubation, the chitosan-covering zein nanoparticles can then be obtained, and for the chitosan-covering zein nanoparticles, the particle size is 160-180 nm, and the zeta potential is about 50 mv. According to the preparing method and application of the chitosan-coveringzein nanoparticles, the chitosan-covering zein nanoparticles can be continuously produced, and the preparing method is simple, free of pollution, mild, safe and high in yield. When the chitosan-covering zein nanoparticles are used for loading acacetin sodium salt, the drug loading capacity is about 20-30%, the particle size is 190-260 nm, the zeta potential is 35-45 mv, and the stability of the acacetin sodium salt can be improved after the acacetin sodium salt is covered with the nanoparticles.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Dendranthema morifolium nanotechnology skin care product and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111481481AUltimate skin care effectOptimal Screening of Nanotechnology Process ParametersCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticAcacetinPolyethylene glycol
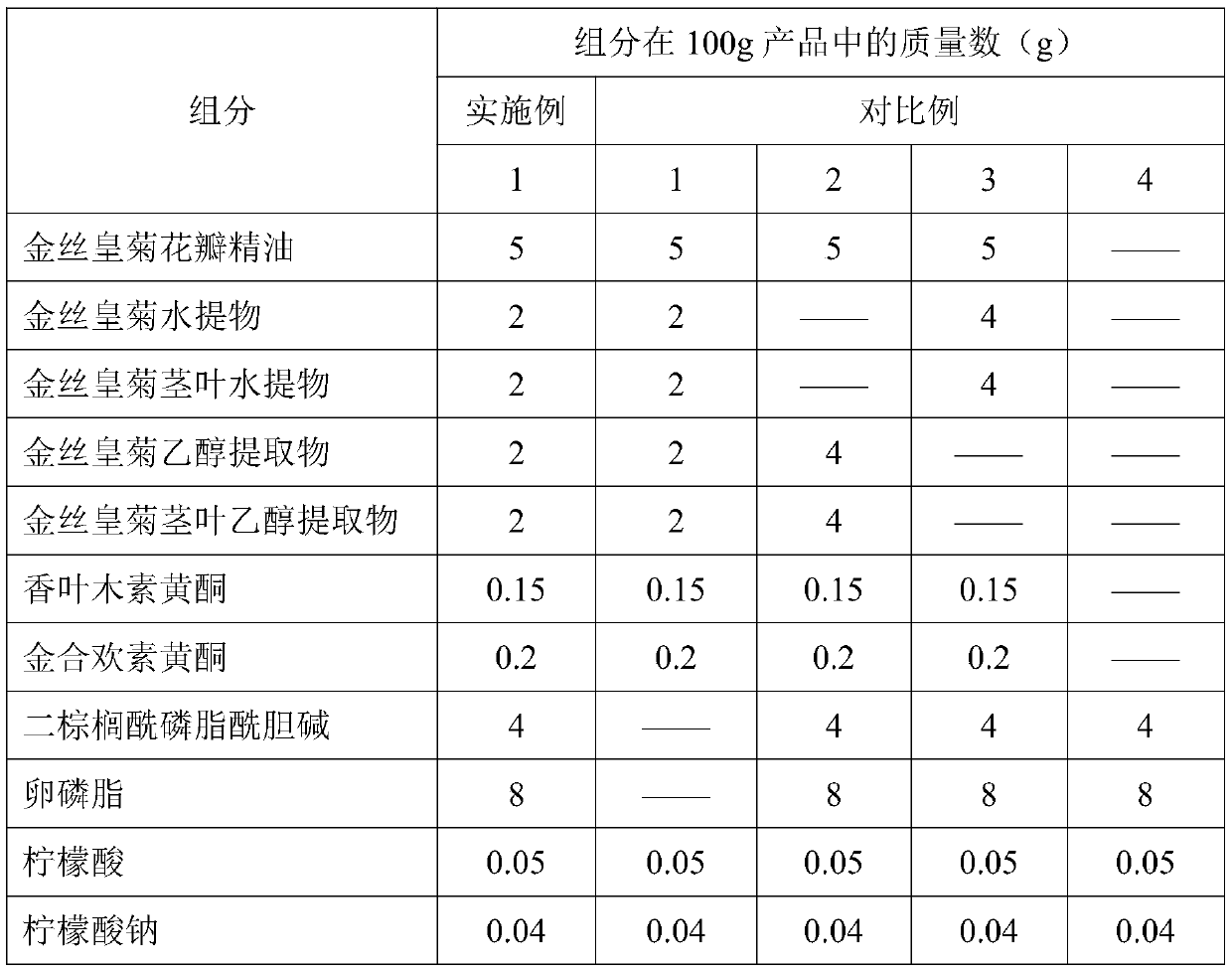
The invention relates to a Dendranthema morifolium nanotechnology skin care product which is composed of the following raw materials: Dendranthema morifolium petal essential oil, a Dendranthema morifolium aqueous extract, a Dendranthema morifolium alcohol extract, a Dendranthema morifolium stem and leaf aqueous extract, a Dendranthema morifolium stem and leaf alcohol extract, and diosmetin and acacetin flavones separated from Dendranthema morifolium; dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine, lecithin, polyethylene glycol 400, hyaluronic acid, trehalose, glyceryl stearate, sodium methyl hydroxybenzoate,polysorbate-20, citric acid, sodium citrate, sodium carbonate and distilled water supplemented to 100 parts. According to the nanotechnology skin care product added with multiple active ingredients of Dendranthema morifolium, multiple components and proportions are reasonably and scientifically designed, nanotechnology process parameters are optimized and screened, and the skin care effect of Dendranthema morifolium is brought into play to the maximum extent.
Owner:江苏灵源沂岸科技股份有限公司
Lowering blood and blood pressure plants extract, preparation and applications thereof
InactiveCN101248870AIdeal blood pressure effectRestore normal blood lipidsMetabolism disorderFood preparationAcacetinChlorogenic acid
The invention provides plant extract with blood lipid reducing and blood pressure lowering effects, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of mixing the flower and / or the flower bud of Chrysanthemum morifolium, extracting with 50-80% (v / v) aqueous ethanol at 60-100 DEG C for 1-3 hours to obtain extractive solution, adsorbing with macroporous adsorption resin, eluting with 60-90% (v / v) aqueous ethanol, collecting eluate, and drying until water content is lower than 12% to obtain the plant extract. The inventive extract contains more than 50% of effective ingredients such as galuteolin, celereoside, luteolin, apigenin, acacetin-7-rhamnosidgluoside, acacipetalin, flavonoid glycoside, and chlorogenic acid; and has blood lipid reducing and blood pressure lowering effects. Compared with the existing domestic and overseas products, the inventive extract has more complete efficacy, and more ideal effects in restoring normal blood lipid level and blood pressure level for demanded people.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Reversed-phase thin-layer chromatographic method for identifying florists chrysanthemum and bo chrysanthemum
The invention relates to a reversed-phase thin-layer chromatographic method for identifying florists chrysanthemum and bo chrysanthemum. The method particularly includes following steps: 1) employing luteolin, kaempferol and acacetin as reference substances and ethanol solutions of the florists chrysanthemum and the bo chrysanthemum as sample solutions, spotting the reference substances and the sample solutions on one reversed-phase thin-layer plate; 2) with methanol and water as developing solvents, developing the reference substances and sample solutions, air-drying the plate, performing development with an aluminum trichloride ethanol solution as a color developing agent; 3) after color development, performing inspection and identification under ultraviolet lights being 365 nm and 254 nm in wavelength, wherein in the position that the florists chrysanthemum is same as the luteolin reference substance, a weak fluorescent spot or dark spot is developed; and in the positions that the florists chrysanthemum is same as the kaempferol and acacetin reference substances, no fluorescent spot or dark spot is developed; in the position that the bo chrysanthemum is same as the luteolin reference substance, a strong fluorescent spot or a dark spot is developed; and in the position that the bo chrysanthemum is same as the kaempferol and acacetin reference substances, same fluorescent spot or dark spot is developed. In the invention, for the first time, the reversed-phase thin-layer chromatographic method is used for identifying the florists chrysanthemum and the bo chrysanthemum. The method is strong in specificity and can accurately identify the identifying florists chrysanthemum and the bo chrysanthemum.
Owner:BEIJING INST FOR DRUG CONTROL
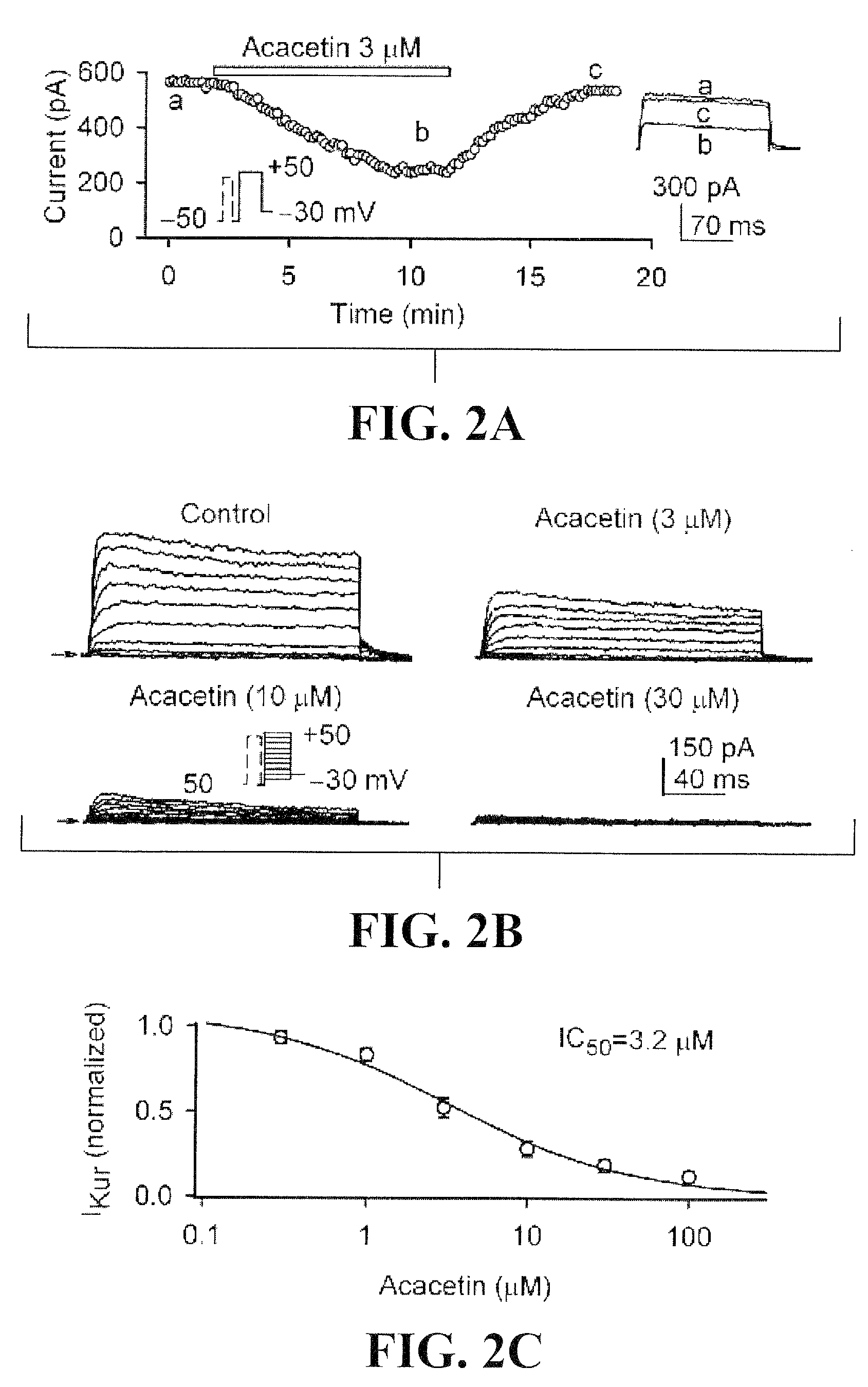
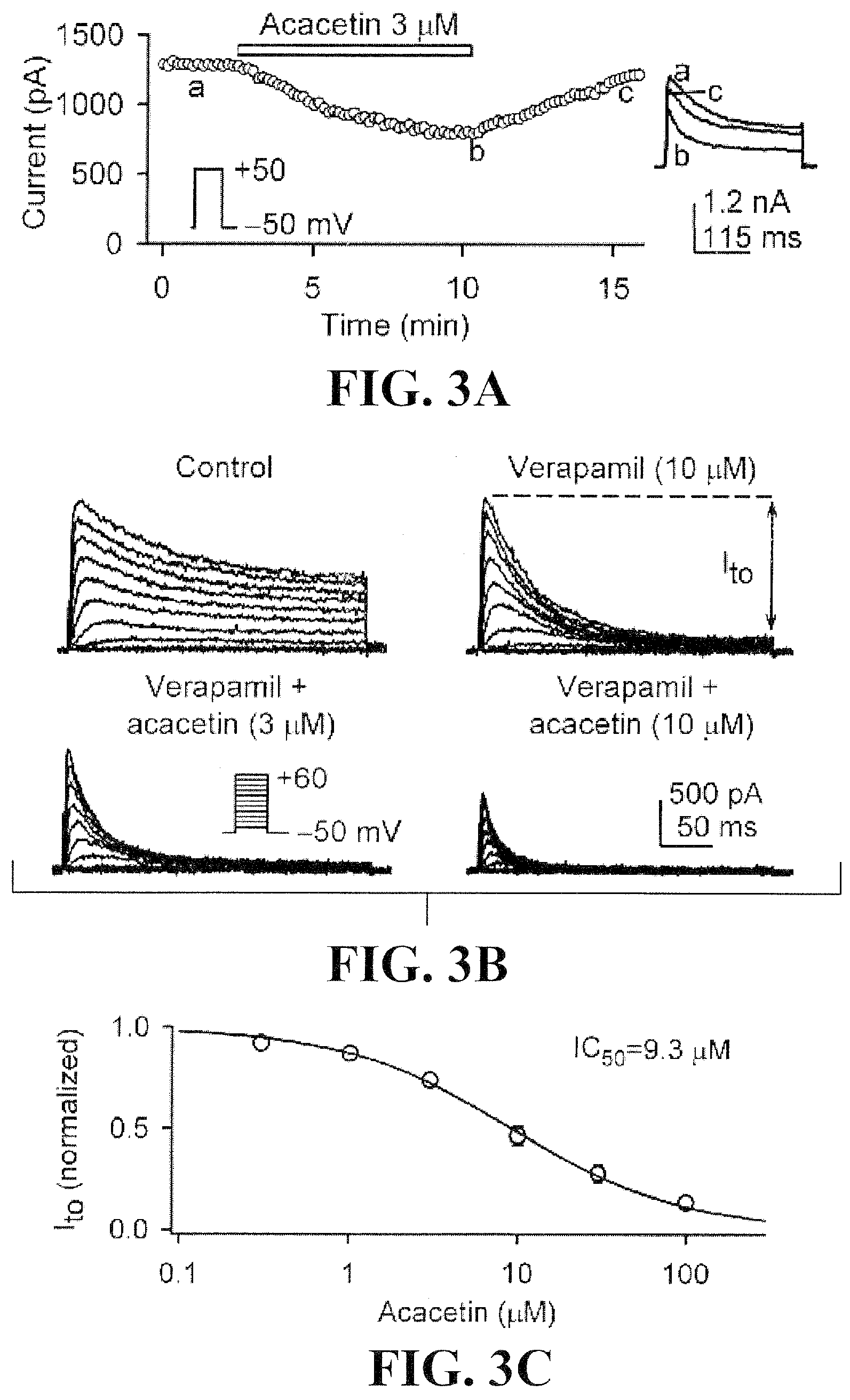
Use of Flavone Compounds as Potassium Channel Inhibitors
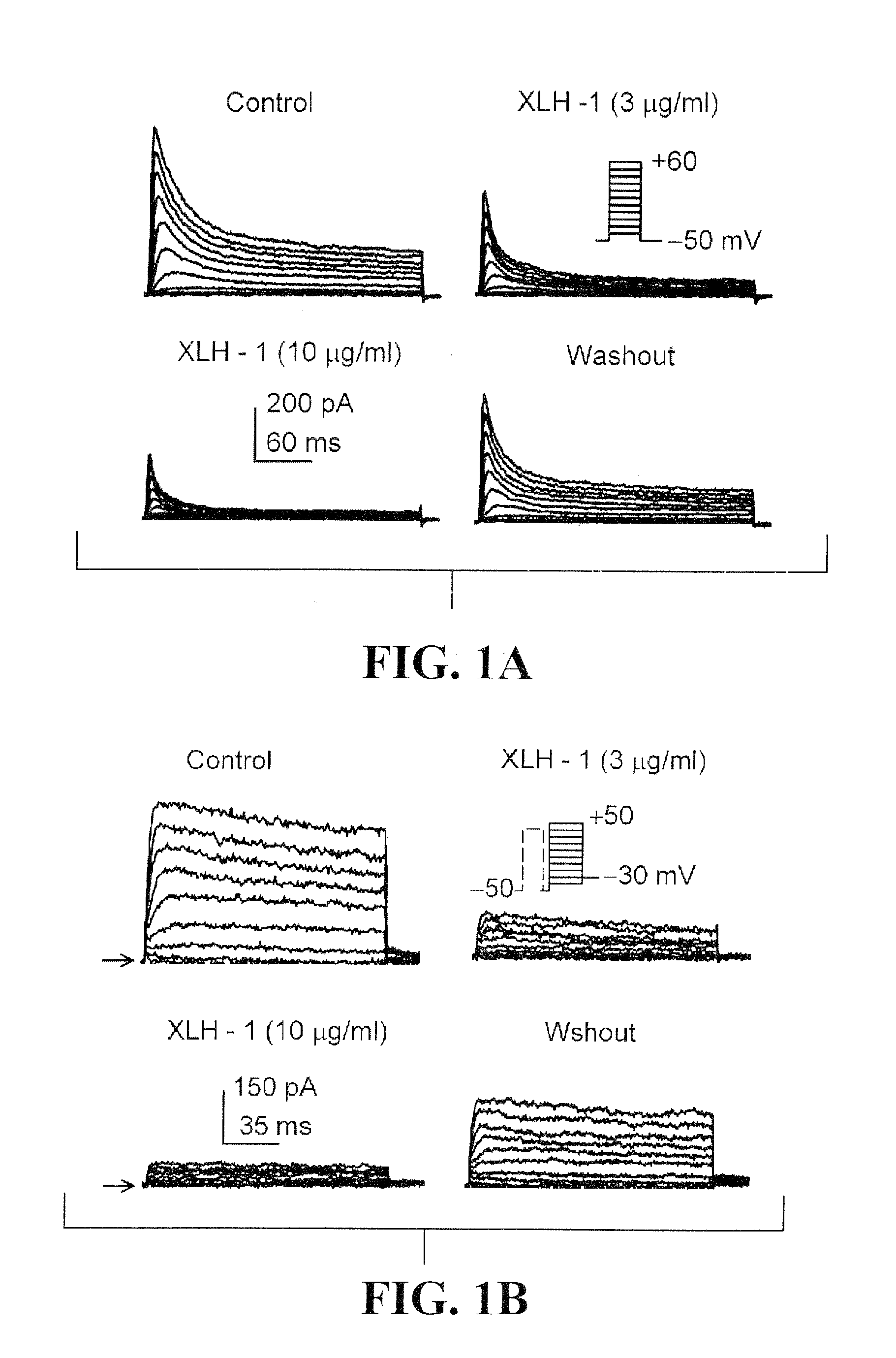
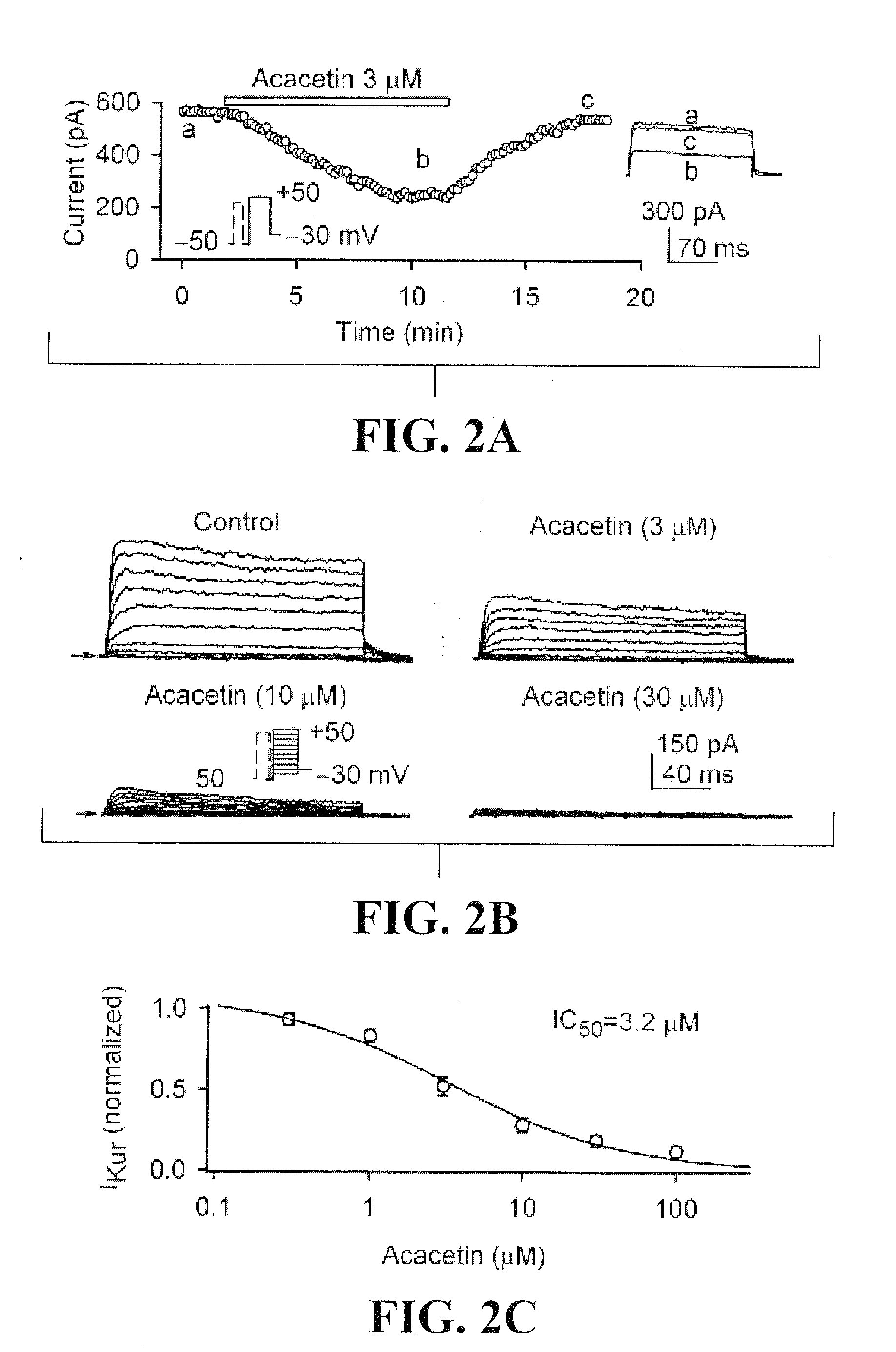
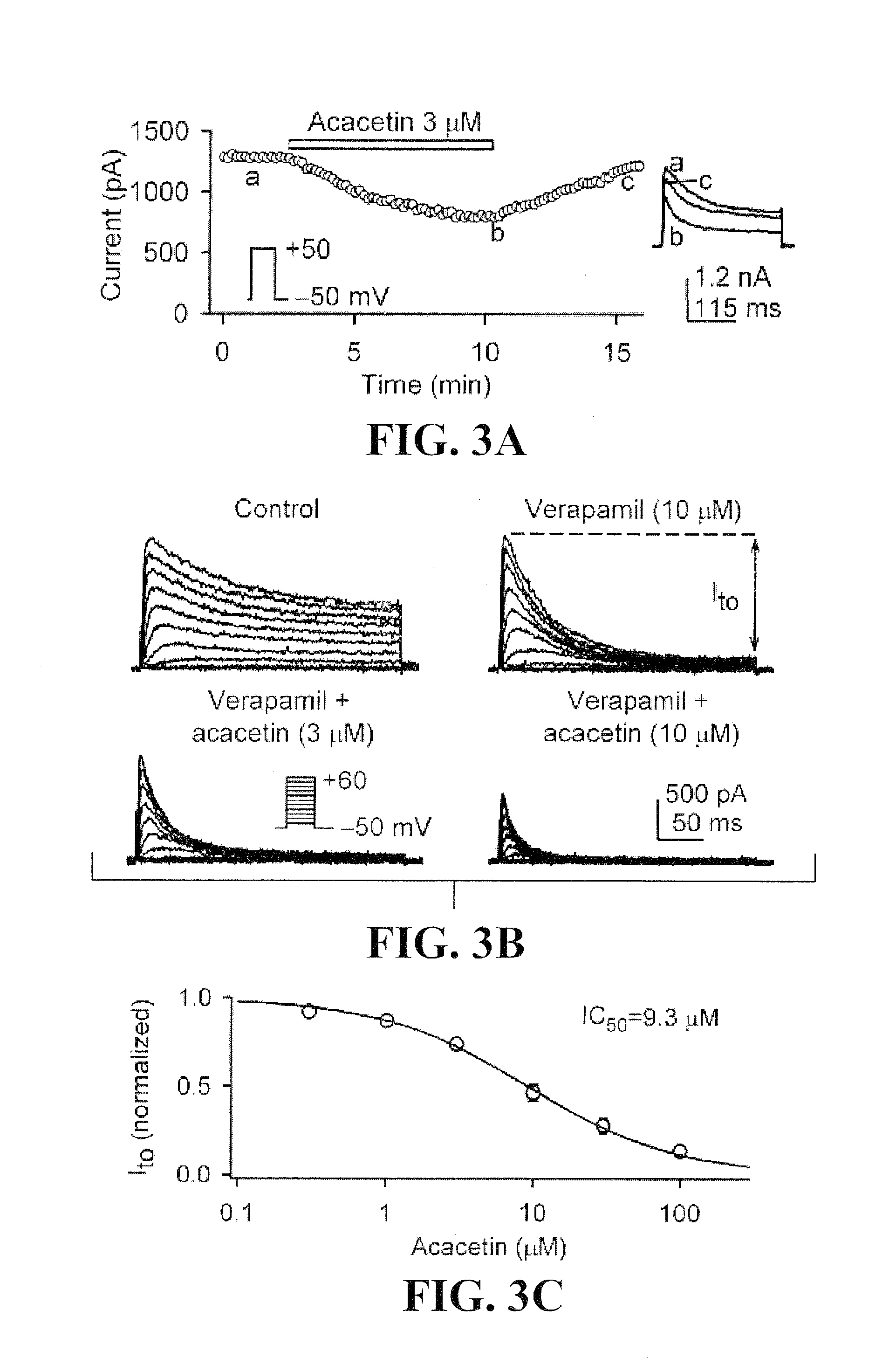
This invention provides a method for treating or preventing human atrial arrhythmia (fibrillation) using the leading flavone compound acacetin, and its derivatives and analogues that inhibit the ultra-rapidly-activating delayed rectifier potassium current (IKur or IKsus), transient outward potassium (Ito), and acetylcholine-activated potassium current (IK.ACh).
Owner:VERSITECH LTD +1
Quality control method of bone rehabilitation medicine
The invention discloses a quality control method of a bone rehabilitation medicine. The method is characterized in that a method for detecting the content of acacetin-6-C-beta-D-glucoside in oxalis corniculata and a fingerprint spectrum detection method are additionally provided. The method has the advantages that the high performance liquid chromatography is performed for detecting; the operation is simple and convenient; the reproducibility is high; the product quality can be controlled effectively.
Owner:贵州维康子帆药业股份有限公司
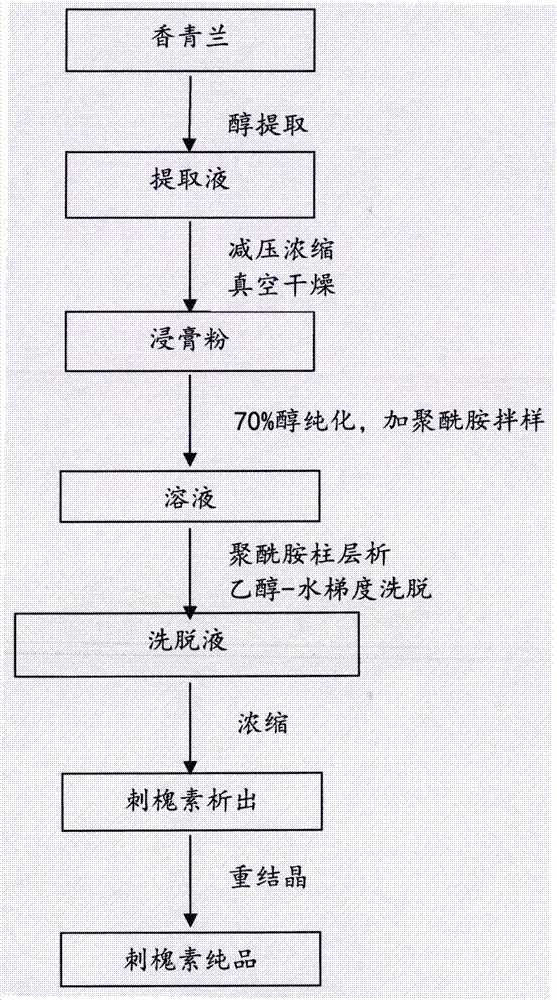
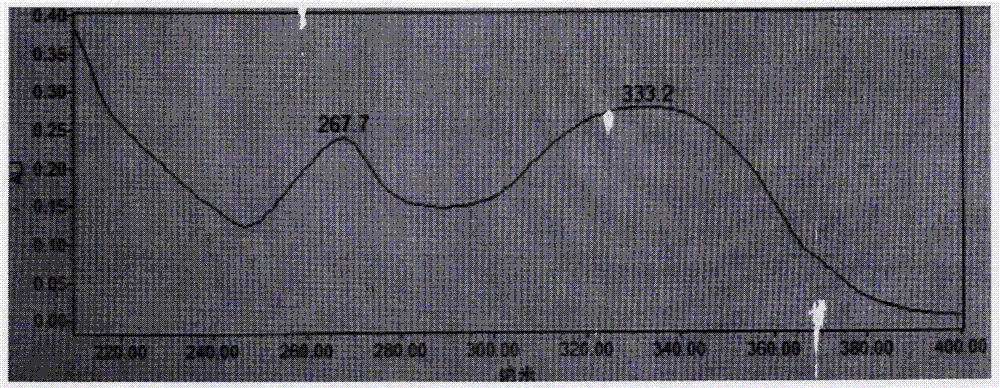
Method for extracting acacetin from chrysanthemum
The invention relates to a method for extracting acacetin from chrysanthemum, which includes: using microwave extraction to obtain extract, adding the extract on a macroporous adsorption resin column to be absorbed, eluting, decompressing, recovering and concentrating ethanol, adding the ethanol to a polyamide chromatographic column, eluting, using a homogeneous polyamide film which is unfolded by eluent to serve as matching detection, collecting, decompressing and recovering solvent, adding acetone in the solvent to obtain crystallization, separating the crystallization, washing, drying and obtaining the acacetin. The method is simple to operate, small in solvent consumption, low in production cost, stable in process, low in energy consumption, less in pollution, high in purity (99%) of obtained products and capable of being applied to laboratories and industrial semi-preparation and preparation production.
Owner:HUBEI NUOKETE PHARMA
Anti-osteoporosis acacetin derivative and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112876446AImprove solubilityEasy to manufactureOrganic chemistrySkeletal disorderChemical synthesisAcacetin
The invention discloses an anti-osteoporosis acacetin derivative and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical chemistry synthesis. The method comprises the following steps: under the protection of nitrogen, adding acacetin and 2,4-dimethoxy benzyl chloride into an organic solvent, reacting for 6-8 hours under the action of alkali, and carrying out silica gel column chromatography separation and recrystallization to finally obtain the acacetin derivative. According to the invention, pathological experiments find that the acacetin derivative can inhibit bone resorption increase and bone tissue destruction caused by lack of female hormone, can also improve the blood calcium concentration and is beneficial to bone deposition, which indicates that the new compound has a certain prevention and treatment effect on osteoporosis caused by lack of female hormone.
Owner:张洪胜
Drug composition for treating diseases caused by fat deposition and application of drug composition
ActiveCN107854692AReduce dosageLow costOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderAcacetinChrysoeriol
The invention discloses a drug composition for preventing and / or treating diseases caused by fat deposition. The drug composition comprises acacetin and synergistic compounds of the acacetin, whereinthe synergistic compounds include one or more of jaceosidin, kaempferol, chrysoeriol, quercetin, apigenin, hispidulin, luteolin, quercitrin, rutin, isorhamnetin and genkwanin. The acacetin can obviously inhibit 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation, when the acacetin is combined with the synergistic compounds in use, the inhibition effect of the acacetin can be obviously enhanced, the use amount ofthe acacetin and the synergistic compounds can be obviously reduced, and the cost of the preparation is reduced. The drug composition can be used for treating and preventing the diseases caused by fatdeposition.
Owner:YANBIAN UNIV
Application of acacetin extracted from Huai flos chrysanthemums in preparation of estrogenic medicines
InactiveCN110721178AOpen up new usesOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAcacetinWater methanol
The invention relates to application of acacetin extracted from Huai flos chrysanthemums in preparation of estrogenic medicines, which aims at extracting acacetin form Huai flos chrysanthemums and preparing the estrogenic medicines by using the extracted acacetin. The acacetin of the flos chrysanthemums is obtained by the steps of performing tissue breaking on Huai flos chrysanthemums with acetonetwice, performing extraction twice, combining filtrates, and performing lower-temperature decompressed concentration to obtain a total extract; dispersing and dissolving the total extract by water, performing extraction with petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and n-butyl alcohol, taking dried ethyl acetate portions, performing dissolving with ethyl acetate, uniformly blending silica gel, then performing evaporation to dryness, performing silica gel column chromatography, performing spin drying on an eluent, performing dissolving in water, adding Toyopearl HW-40, performing gradient eluting with water and aqueous methanol in different proportions sequentially, sequentially treating the eluted part with sephadexLH-20, ODS, Silica gel and MCL Gel CHP-20 columns, and performing separation and purification in combination with methods for preparing high-efficient liquid phases and recrystallization. For the first time, the invention finds that the acacetin of the Huai flos chrysanthemum has anestrogen effect in bodies and plays a role in an estrogen receptor way, and a new purpose of the acacetin is opened up.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Compositions that protect cells from oxidative and mitochondrial stress
There are described compositions comprising an effective amount of a combination of two or more components, said components selected from acacetin, ACT1 peptide, alpha-lipolic acid, alprostadil, anisomycin, apigenin, ascorbic acid, astragalus, berberine, beta-lapachone, beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl-butyrate, bacopa monnieri, catechin, catechol, chamomile, chrysin, coumestrol, curcumin, dinitrophenol,dinoprost, ellagic acid, (-)-epigallocatechin gallate, green tea extract, fisetin, genistein, ginsenoside RE, glabridin, 18-alfa-glycyrrhetinic acid, 18-beta-glycyrrhetinic acid, glycyrrhizin, hydroquinone, isoquercitrin (EMIQ), kaempferol, kuromanin, leucine, lithium, luteolin, luteolin, luteolinidin, melatonin, menadione, 1-methylnicotinamide (MNA), methyl salicylate, myricetin, nadide, niacin (vitamin B3), nicotinamide (NAM), nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), nicotinamide riboside (NR), nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (Na AD), nicotinic acid mononucleotide (Na MN), parsley (petroselinium crispum), phenylephrine, pokeweed mitogen, 15-Delta prostaglandin J2, puromycin, quercetin, quinolinic acid, retinoic acid, trichostatin A, troxrutin, rutin, tryptophan, vitamin D3, withaferin A, wortmannin and zinc (including salts thereof).
Owner:努其杜有限公司
Use of acacetin and related compounds as potassium channel inhibitors
This invention provides a method for treating or preventing human atrial arrhythmia (fibrillation) using the leading flavone compound acacetin, and its derivatives and analogues that inhibit the ultra-rapidly-activating delayed rectifier potassium current (IKur or IKsus), transient outward potassium (Ito), and acetylcholine-activated potassium current (IK.ACh).
Owner:VERSITECH LTD +1
Artemisia ordosica root extract and preparation method and application thereof
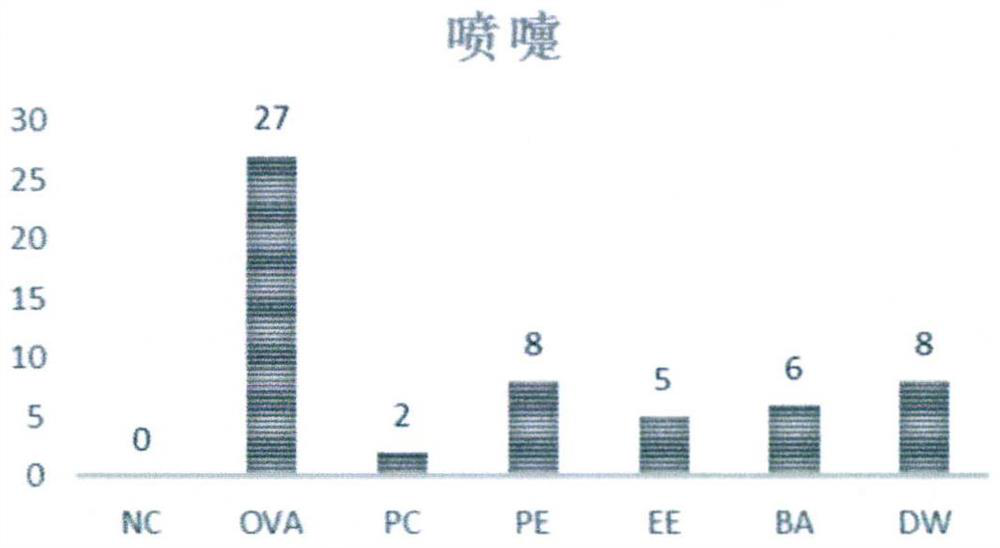
ActiveCN110960565AReduce allergic rhinitis symptomsReduce infiltrationRespiratory disorderImmunological disordersMorinAcacetin
The present invention discloses an artemisia ordosica root extract and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method of the artemisia ordosica root extract comprises the following steps: drying and crushing artemisia ordosica roots and adding an ethanol solution for ultrasonic extraction; then mixing each extract and conducting concentrating and drying to obtain an extract A; and (2) dissolving the extract A with distilled water, and sequentially conducting extraction with petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and n-butanol; and collecting an ethyl acetate layer extract, andconducting concentration under reduced pressure and drying to obtain a finished product. The artemisia ordosica root extract contains 50-90% of total flavonoids, and eriodictyol, isosakuranetin, naringenin, hydroxygenkwanin, genkwanin, acacetin, diosmetin, glycitein, isorhamnetin, morin and quercetin with the total content of more than 2%. The artemisia ordosica root extract can obviously reduceallergic rhinitis symptoms of guinea pigs, also reduces levels of inflammatory factors of histamine, ovalbumin specific IgE, IL-2 / 4 / 10, IFN-gamma, ICam-1, etc. in serum of the guinea pigs, and can also reduce infiltration of eosinophilic granulocyte of nasal mucosa of nasal cavities of the guinea pigs.
Owner:肖斌 +8
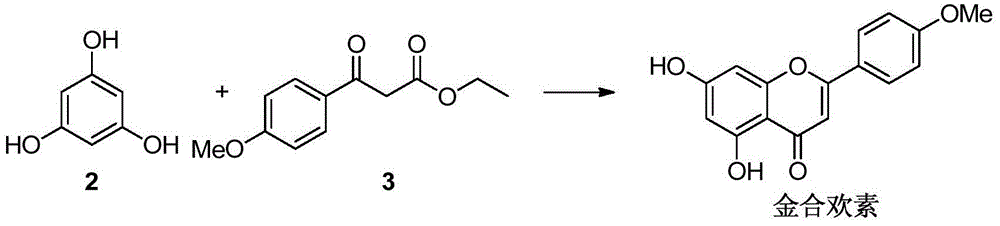
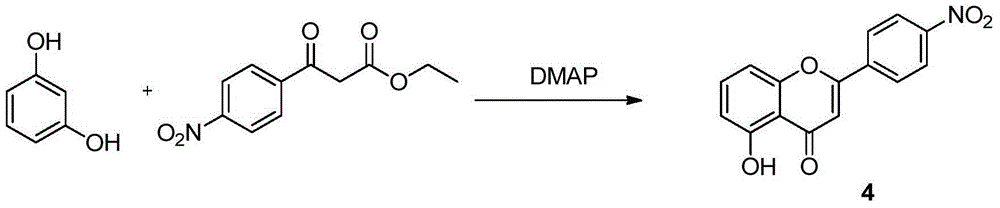
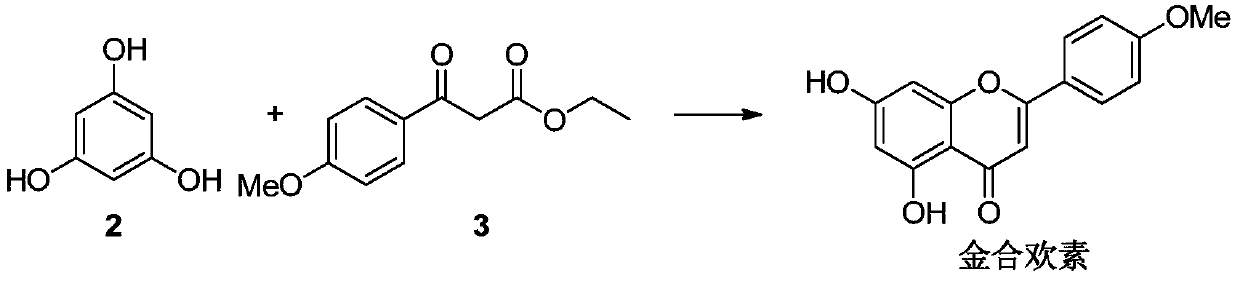
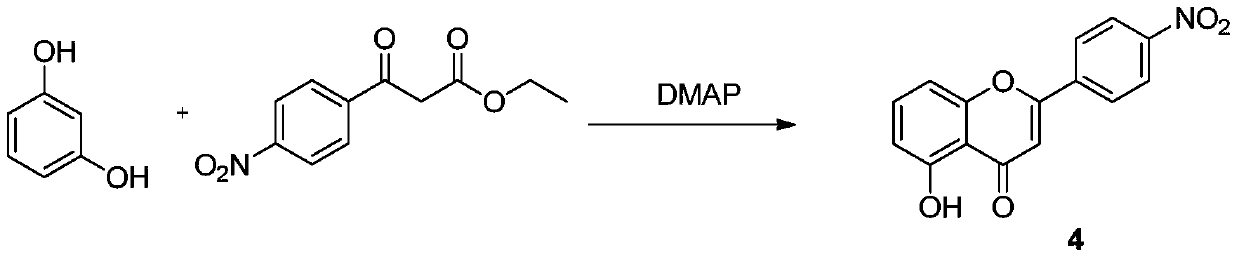
A preparing method of acacetin
A preparing method of acacetin is disclosed. The method includes subjecting a compound 2 and a compound 3 to a cyclization reaction under the existence of a catalyst, wherein the catalyst is one or more selected from 4-dimethylaminopyridine, 4-pyrrolidinopyridine and tri-n-butylphosphine, and the reaction is performed at 150-200 DEG C. The method is high in yield, low in cost, simple in operation and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Blueberry cultivating soil repairing agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108277009AUniform sizeSweet tasteAgriculture tools and machinesContaminated soil reclamationAcacetinBiology
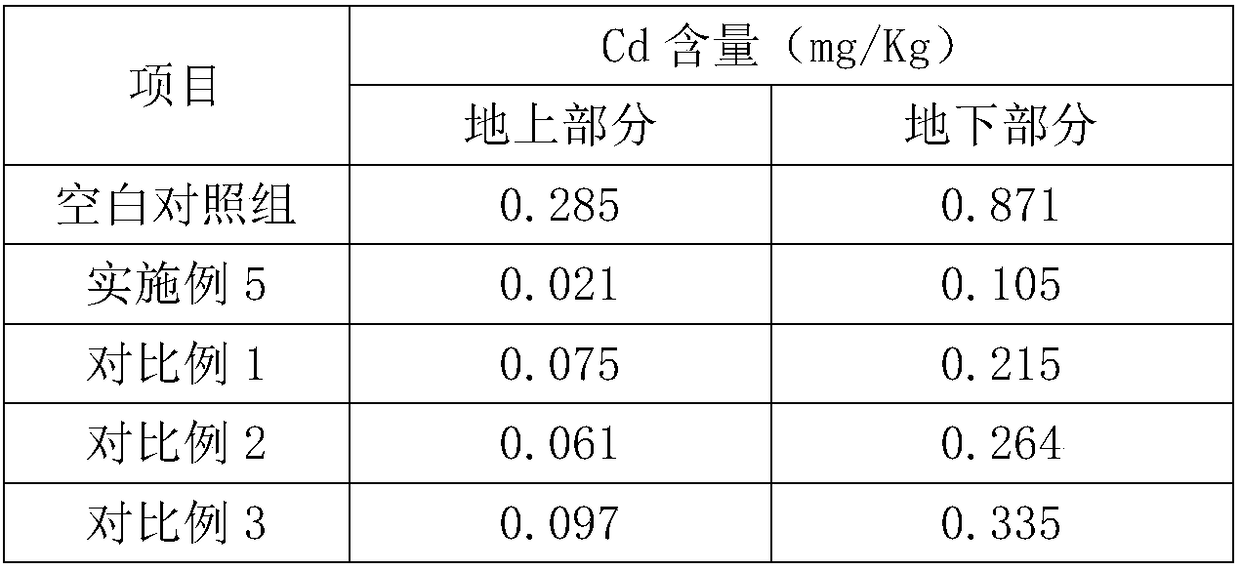
The invention discloses a blueberry cultivating soil repairing agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The soil repairing agent is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 26 to 35 parts of rhizome disporopsis asperae, 13 to 17 parts of acacetin, 12 to 17 parts of boschniakia rossica herb, 6 to 15 parts of herba rabdosiae, 5 to 11 parts of grubs and 10 to 20 parts of coconut cream powder. The blueberry cultivating soil repairing agent disclosed by the invention can be applied to the technical field of blueberry cultivation and is prepared by compounding the rhizome disporopsis asperae, the acacetin, the boschniakia rossica herb, the herba rabdosiae, the grubs and the coconut cream powder; the blueberry cultivating soil repairing agent has the effects that the content of heavy metal cadmium is reduced, sizes of the blueberry fruits are uniform and the taste is delicious and sweet; meanwhile, the preparation method is simple and production, processing and manufacturing are facilitated.
Owner:马骏
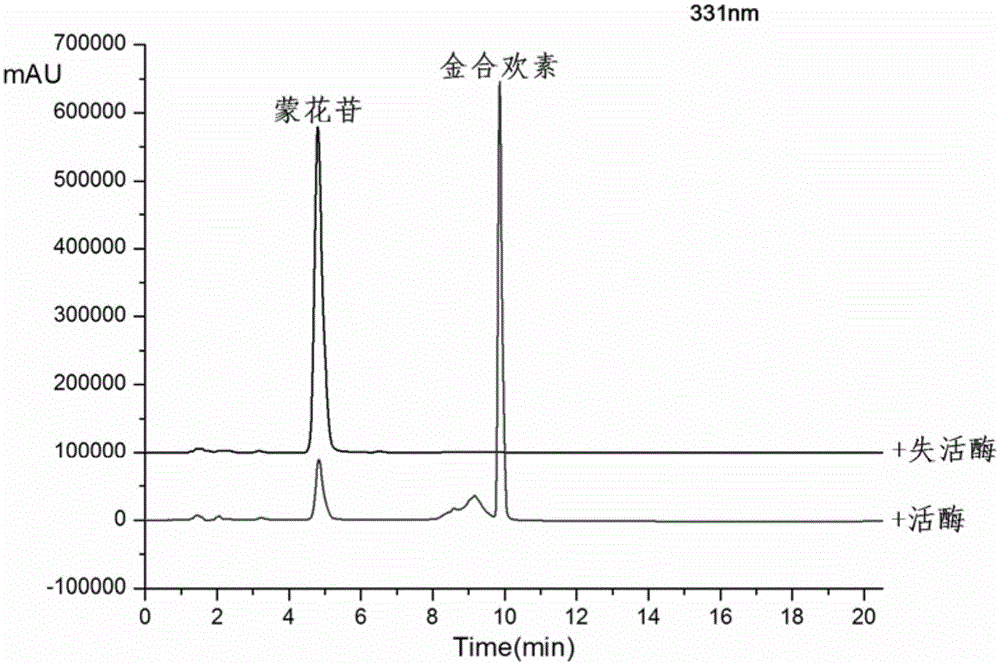
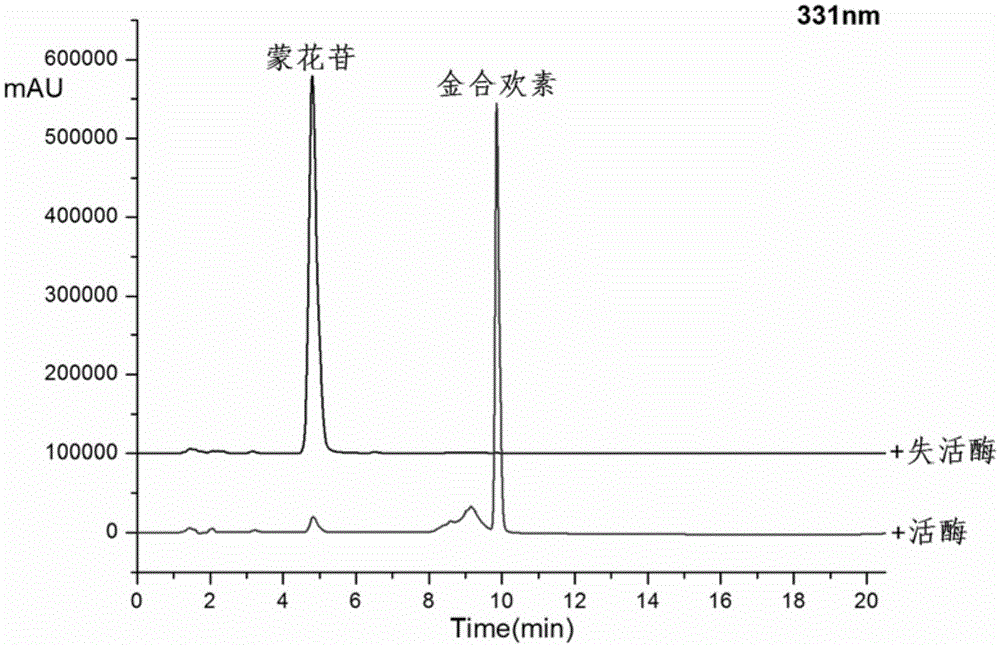
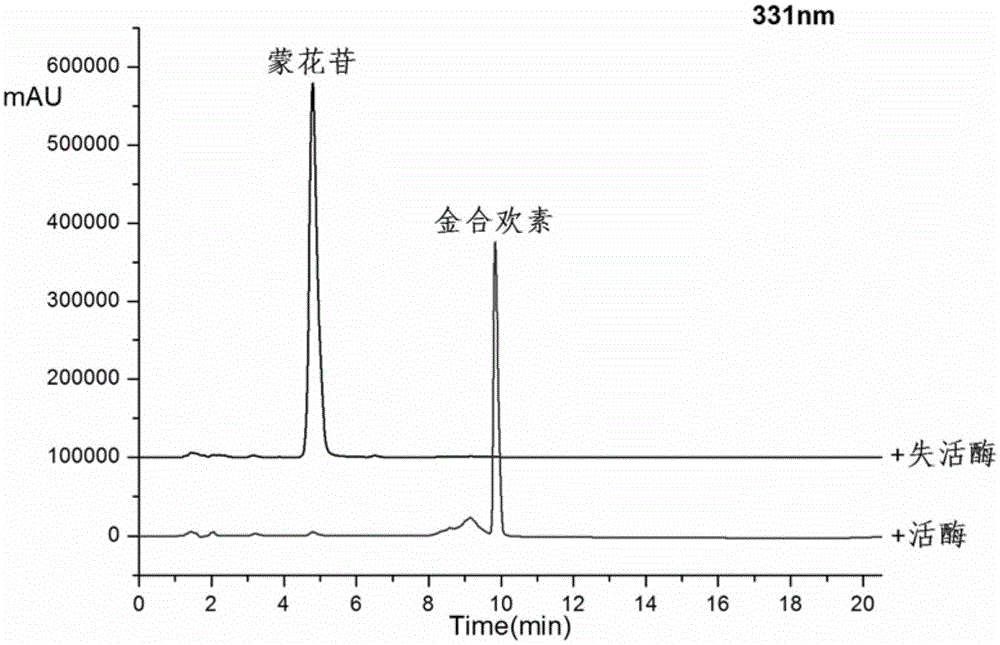
Method for preparing acacetin by enzymatic hydrolysis of buddleoside
The invention discloses a method for preparing corresponding aglycone acacetin by enzymatic hydrolysis of buddleoside, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises crude enzyme fluid preparation, enzymatic hydrolysis and purification steps, specifically comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of a crude enzyme fluid: inoculating cellulosimicrobium cellulans into a liquid culture medium, performing culturing for 40h at 30 DEG C, performing 9,000g centrifugation for 10min, extracting supernatant, precipitating ammonium sulfate, collecting 20 to 40 percent of components, and performing re-dissolving with a buffer solution; (2) enzymatic hydrolysis: converting the buddleoside serving as a raw material with the dissolved crude enzyme fluid to hydrolyze beta-D-glucoside bonds of 7 loci to obtain the acacetin; and (3) preparation of the acacetin: after a reaction is completed, mixing the conversion solution and methanol in a double volume, heating to 60 DEG C, repeatedly extracting for 3 to 5 times, and collecting, cooling and crystalizing an extracting solution to obtain the acacetin. The method has the advantages of mild reaction condition, high specificity, high efficiency, low cost and the like, and the purity of the obtained acacetin is over 98 percent.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Detection method of agastache rugosus and preparation thereof
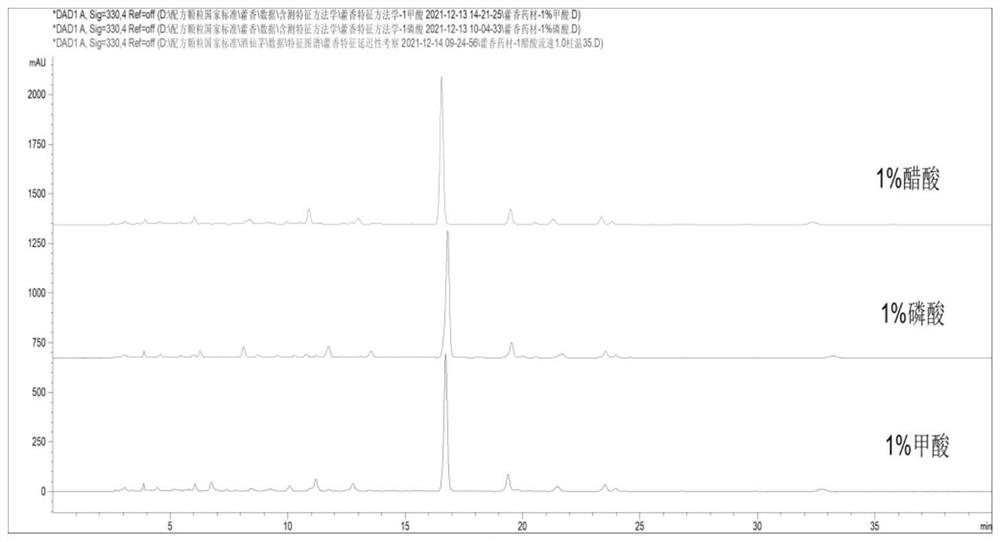
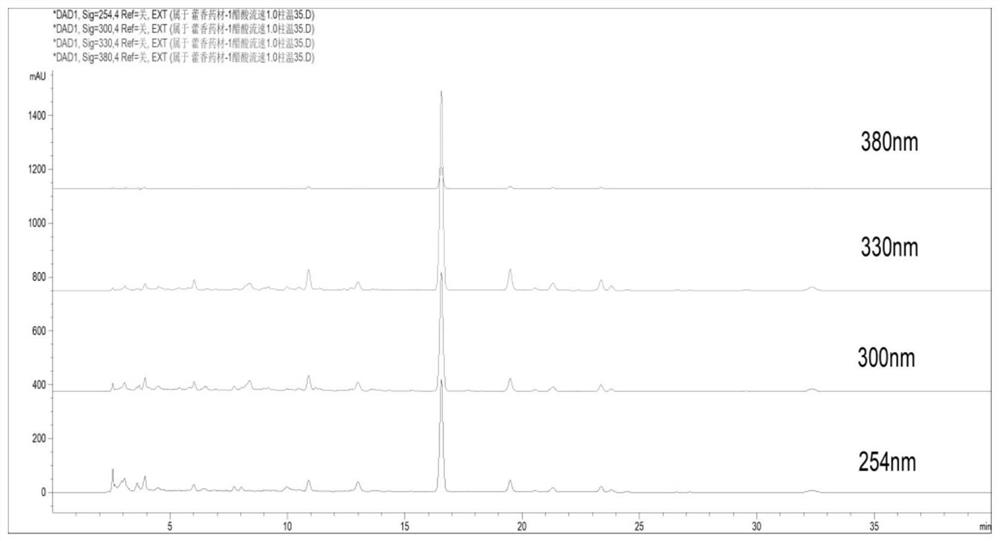
PendingCN114755338AAchieve quality controlImprove scienceComponent separationO-Phosphoric AcidAcacetin
The invention provides a method for detecting wrinkled gianthyssop herb and a preparation thereof, which is characterized by comprising the following step: detecting caffeic acid, tilianin and acacetin in the wrinkled gianthyssop herb and the preparation thereof by adopting a high performance liquid chromatography, the chromatographic conditions of the high performance liquid chromatography are as follows: methanol is taken as a mobile phase A, one of 1% acetic acid, 1% phosphoric acid and 1% formic acid solution is taken as a mobile phase B, and gradient elution is carried out. The method has better precision and repeatability, is strong in operability, and can realize quality control of the agastache rugosus and the preparation of the agastache rugosus. The scientificity and rationality of overall evaluation of the related technological process of agastache rugosus are improved, the inherent quality of agastache rugosus and preparations thereof can be controlled integrally, and the clinical curative effect of the preparations such as agastache rugosus formula granules is ensured.
Owner:SICHUAN NEO GREEN PHARMA TECH DEV
A method for the simultaneous determination of 22 flavonoids and phenolic acids in citrus fruits
ActiveCN108490094BSimple and fast operationImprove accuracyComponent separationBenzoic acidChlorogenic acid
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously determining twenty-two flavones and phenolic acids in citrus fruits by adopting high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detector-fluorescence detector (HPLC-DAD-FLD). The method is capable of simultaneously determining twenty-two phenolic compounds in citrus fruits such as gallic acid, synephrine, chlorogenic acid, protocatechuic acid,caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, rhamnosylvitexin, eriocitrin, ferulic acid, rutin, benzoic acid, narirutin, naringin, hesperidin, diosmin, neohesperidin, quercetin, naringenin, kaempferol, nobiletin,hesperetin, acacetin and the like, derivatization is not needed, and the method is high in accuracy, high in sensitivity and excellent in repeatability.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENG TECH FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for extracting acaciacin-6-c-β-d-glucoside from sorrel
ActiveCN107586311BHigh purityQuality is easy to controlSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationAcetic acidAcacetin
The invention provides a method for extracting acacetin-6-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside from Oxalis corniculata L.. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the Oxalis corniculata L. with waterto obtain Oxalis corniculata L. water extract, drying and crushing the Oxalis corniculata L. water extract to obtain powder, carrying out reduced pressure concentration through a rotary evaporator after the extraction to obtain ethyl acetate extract, and separating the ethyl acetate extract to obtain the acacetin-6-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside. When an effective component is separated from the Oxaliscorniculata L. extract through the method, the obtained effective component is highly pure, especially the purity of the acacetin-6-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside is 99% or more, the acacetin-6-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside can be used as an Oxalis corniculata L. monomer reference substance, and the development and the quality control of an Oxalis corniculata L. medicinal material and its preparation are facilitated.
Owner:贵州维康子帆药业股份有限公司
Application of a root extract of Artemisia syringae in preparation of medicine for treating allergic rhinitis
ActiveCN110960565BReduce allergic rhinitis symptomsReduce infiltrationRespiratory disorderImmunological disordersInflammatory factorsAcacetin
The invention discloses an extract of the root of Artemisia sativa and its preparation method and application. The preparation method of the root extract of Artemisia syringae comprises the following steps: after drying and crushing the roots of Artemisia syringae, adding ethanol solution for ultrasonic extraction; then combining the extracts of each time, and concentrating on drying to obtain extract A; (2) Dissolve the extract A with distilled water, and then extract with petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and n-butanol in sequence; collect the extract from the ethyl acetate layer, concentrate under reduced pressure, and dry to obtain the product. The root extract of Artemisia japonica root of the present invention contains 50-90% of total flavonoids, which at least contains eriodictyol, isosakurain, naringenin, hydroxygenkwain, genkwain, acacetin, diosmin, soybean The sum of the contents of flavin, isorhamnetin, morin and quercetin is greater than 2%. Can significantly reduce the symptoms of allergic rhinitis in guinea pigs, and can reduce the levels of inflammatory factors such as histamine, ovalbumin-specific IgE, IL‑2 / 4 / 10, IFN‑γ, ICam‑1 in guinea pig serum, and can reduce Eosinophilic infiltration of nasal mucosa in the nasal cavity of guinea pigs.
Owner:肖斌 +8
Preparation method of acacetin
The invention relates to a method for extracting and separating acacetin from Dracocephalum moldavica L.. The method comprises the following steps: crushing the dry overground part of Dracocephalum moldavica L., carrying out collection and extraction by using a percolation process to obtain a percolation liquid, and concentrating the percolation liquid through a reduced pressure distillation device to obtain thick extract; carrying out water bath drying on the thick extract to obtain extract powder; dissolving the extract powder in high-concentration alcohol, carrying out dry stirring, carrying out polyamide column chromatography, carrying out elution, and evaporating the obtained eluate by the reduced pressure distillation device until the eluate is dry in order to obtain extract powder; and re-crystallizing the extract powder, and evaporating obtained crystals through the reduced pressure distillation device until the crystals are dry in order to obtain pale yellow crystals which are the compound acacetin.
Owner:石河子大学医学院第一附属医院
External pharmaceutical composition for treating vasogenic vertigo and application thereof
ActiveCN114796196AGood effectSignificant modulator functionOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemAcacetinTherapeutic effect
The invention belongs to the field of medicine research and development, and particularly relates to an external medicine composition for treating vasogenic vertigo and application. The pharmaceutical composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5.8 to 57.6 parts of isorhamnetin; 2.5 to 24.7 parts of kaempferol; 3.4 to 33.6 parts of nobiletin; 3.0 to 29.7 parts of calycosin; 7.1 to 70.7 parts of acacetin; 3.1 to 31.3 parts of aloe emodin; 7.4 to 74.1 parts of luteolin; 4.6 to 45.6 parts of baicalein; 6.3 to 62.9 parts of hydroxy genkwanin; and 4.0 to 39.7 parts of hesperetin. The effective rate of the pharmaceutical composition can reach 92.08%. The artemisia argyl oil is used as a penetration enhancer, so that the transdermal absorption curative effect of the medicine is improved, the liver first-pass effect of the medicine can be avoided, the bioavailability of the medicine is improved, the interference on the medicine absorption is reduced, the treatment effect is enhanced, and the administration can be continuously controlled and interrupted at any time.
Owner:SHANDONG ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICINE
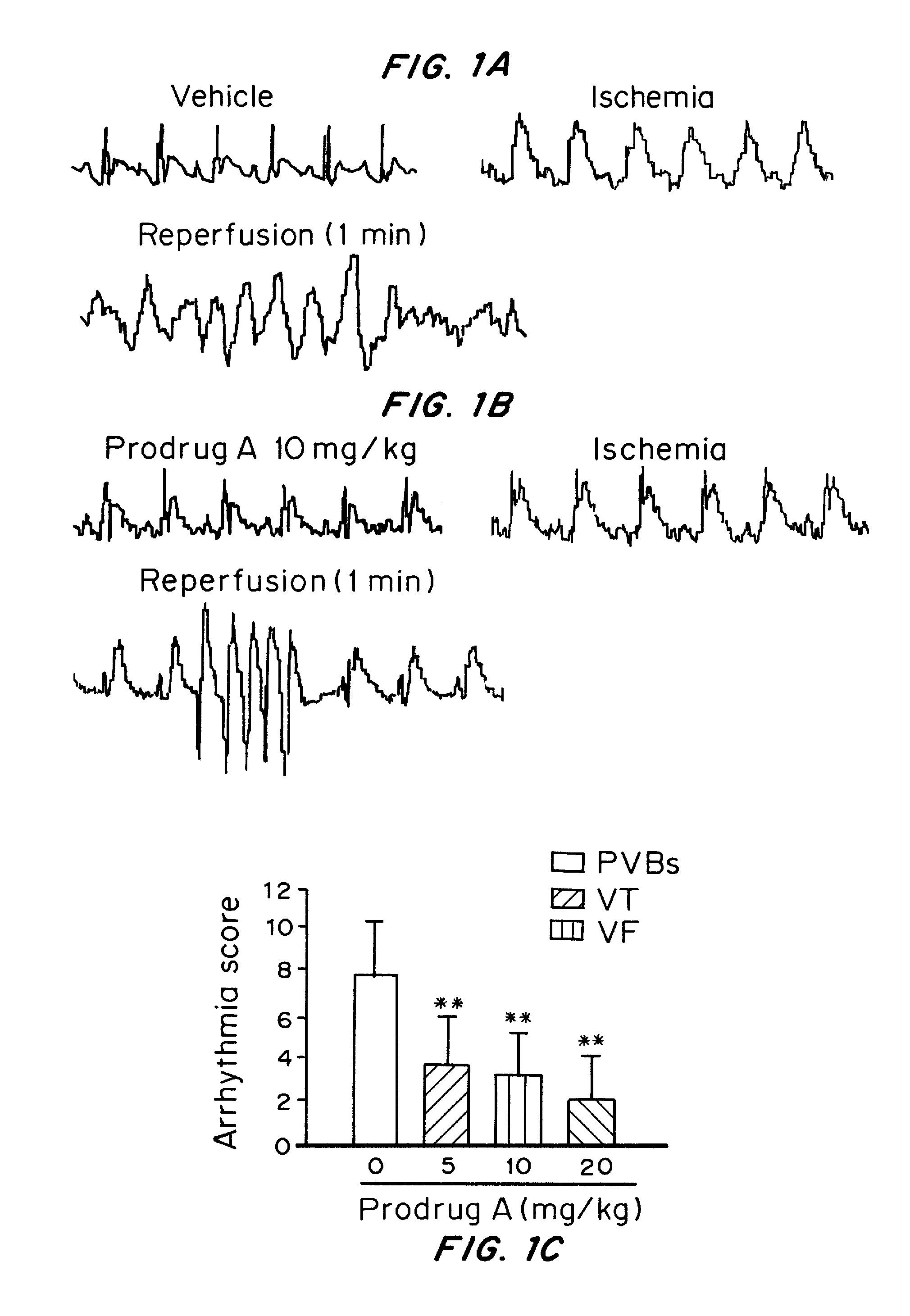
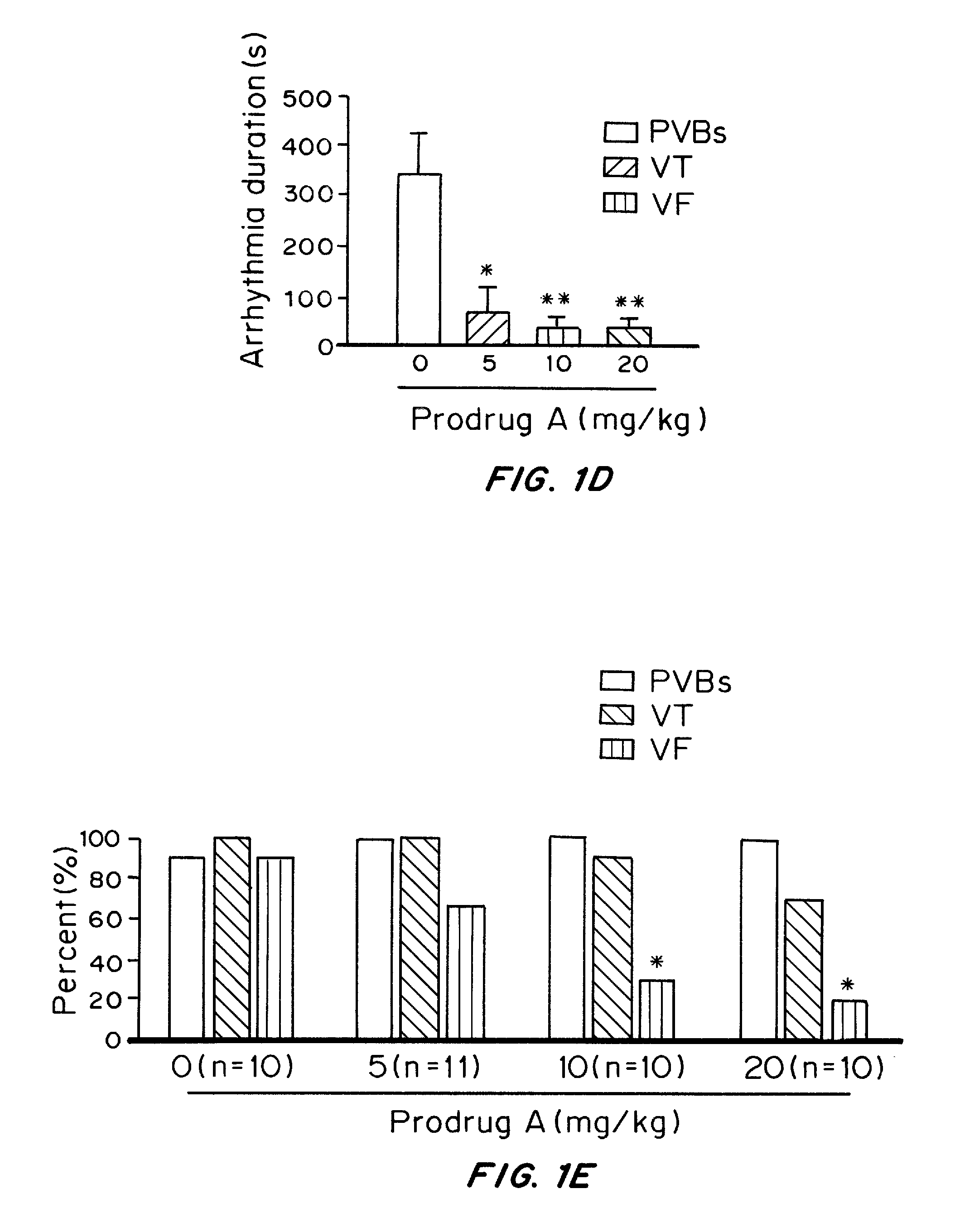
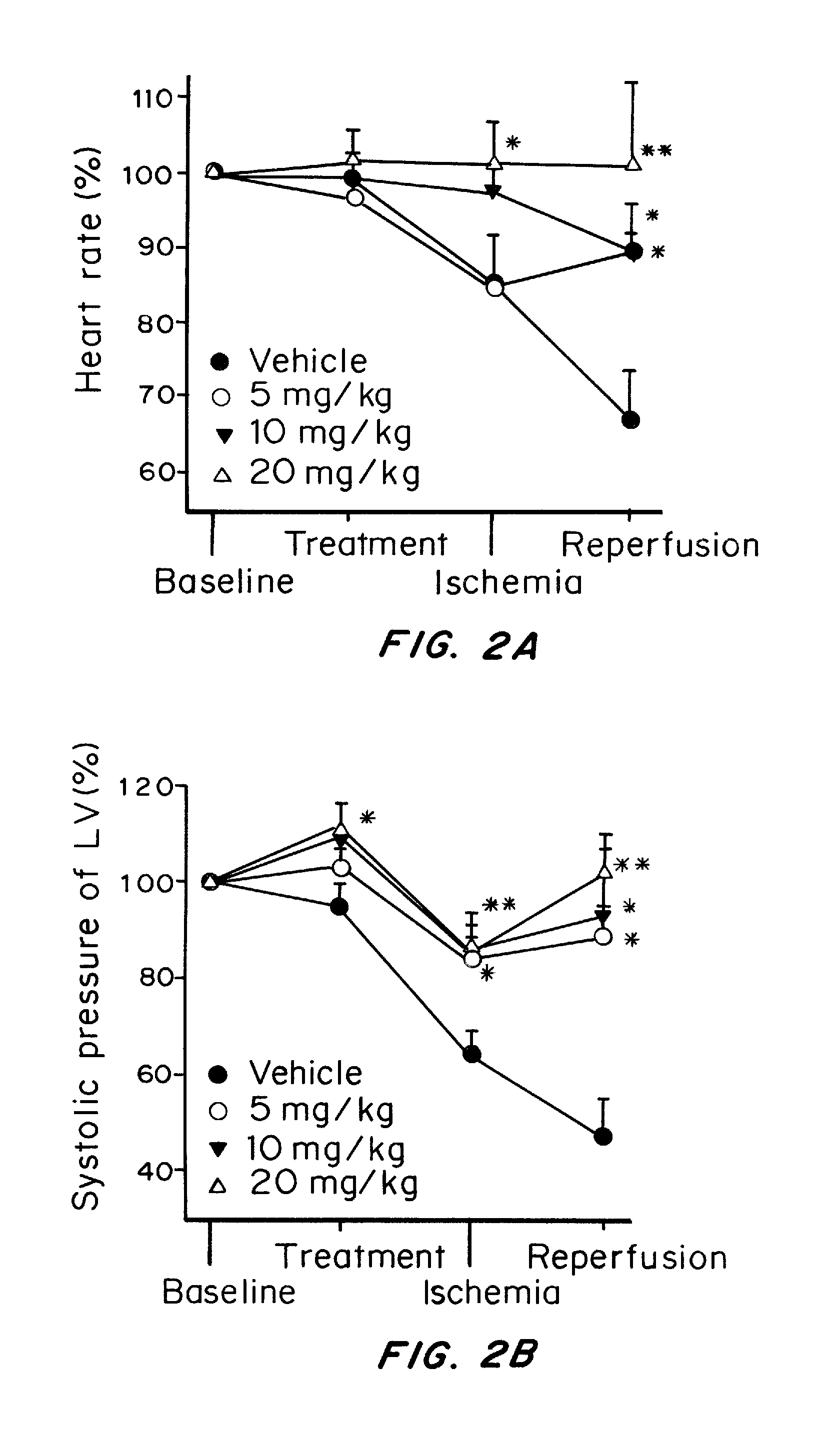
Water-soluble derivatives and prodrugs of acacetin and methods of making and using thereof
Water-soluble derivatives and / or prodrugs of acacetin are described herein. The compounds can be used as cardioprotection agents against myocardial infarction induced by ischemia-reperfusion. In one embodiment the compounds are used to treat ischemic cardiac diseases. In the preferred embodiment, the compounds are used to treat and / or prevent myocardial infarction in humans.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
A kind of preparation method of acacetin
A preparing method of acacetin is disclosed. The method includes subjecting a compound 2 and a compound 3 to a cyclization reaction under the existence of a catalyst, wherein the catalyst is one or more selected from 4-dimethylaminopyridine, 4-pyrrolidinopyridine and tri-n-butylphosphine, and the reaction is performed at 150-200 DEG C. The method is high in yield, low in cost, simple in operation and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
A kind of pharmaceutical composition for promoting gastrointestinal motility function and application thereof
ActiveCN104127428BPromote gastrointestinal motilityImprove biological activityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemAcacetinMedicine
The invention discloses a medicinal composition with a gastrointestinal peristalsis promoting function, and its application. The composition is prepared by using an active component and auxiliary materials, and the active component comprises acacetin-7-O-rhamnose glucoside. The medicinal composition has an obvious intestinal peristalsis acceleration effect, and can be developed to form digestion aiding or constipation treatment medicines to be clinically applied.
Owner:方海丽
Wild chrysanthemum flower active site capable of regulating epigenetic expression balance and resisting liver cancer as well as preparation method and application of wild chrysanthemum flower active site
ActiveCN114209728AConcept showing the cure for cancerReduces oxidative stress damageDigestive systemAntineoplastic agentsBiotechnologyAcacetin
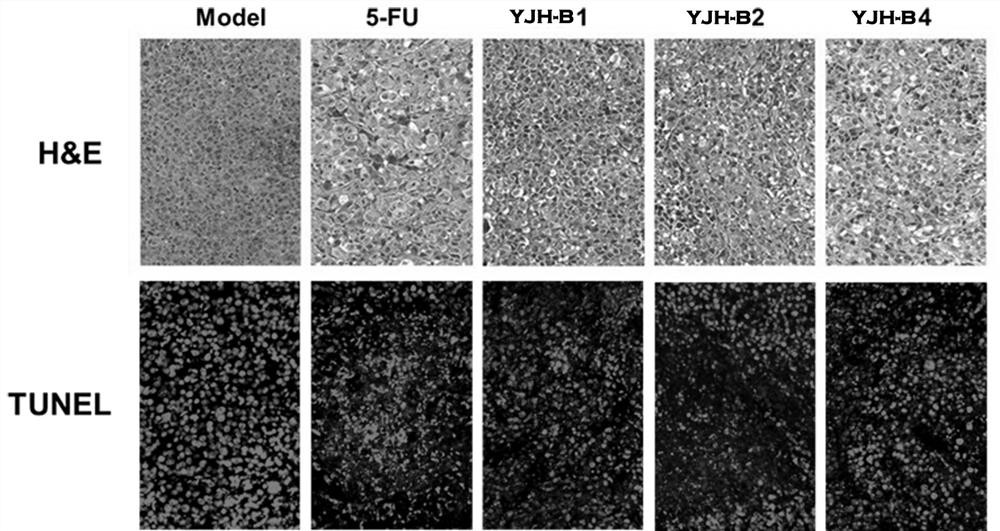
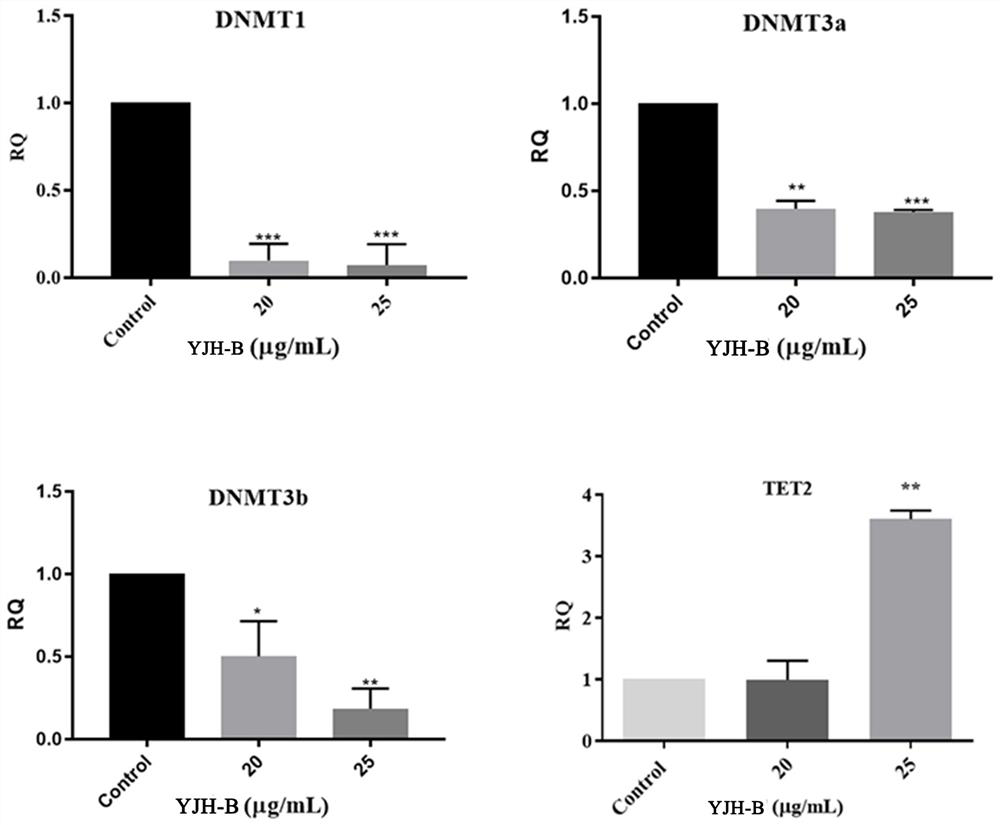
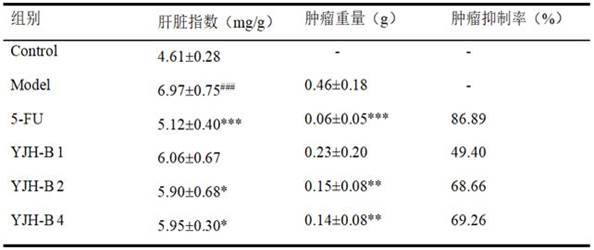
The invention belongs to the field of biological pharmacy, and relates to application of a traditional Chinese medicine wild chrysanthemum active component, in particular to a wild chrysanthemum active part with the effect of regulating epigenetic expression balance and resisting liver cancer as well as a preparation method and application of the wild chrysanthemum active part. The content of total sesquiterpenes in the wild chrysanthemum flower active part is more than or equal to 50%, and the content of total flavonoids is more than or equal to 30%; the index components comprise greater than or equal to 4.0% of ambrotin A, greater than or equal to 3.0% of wild chrysanthemum lactone, greater than or equal to 0.5% of apigenin and greater than or equal to 0.7% of acacetin. According to the invention, an active site (YJH-B) with anti-liver cancer and liver protection effects is extracted and separated from wild chrysanthemum flower for the first time, and it is found for the first time that the molecular mechanism of the action of the active site is realized by regulating the balance relationship of DNMTs / TET2, so that the idea of eliminating pathogens and strengthening body resistance of traditional Chinese medicines for treating cancers is shown; and a new thought and a new strategy are provided for research and development of innovative anticancer drugs based on epigenetic targets.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
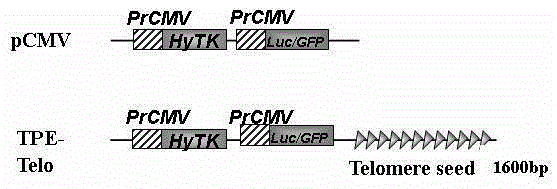
Use of 5,7-dihydroxyflavone and 5,7-dihydroxy-4'-methoxyflavone in inhibiting telomere function
The invention relates to an application of chrysin and acacetin in restraining telomere functions, and specifically provides an specific application of chrysin and acacetin in preparing drugs taking telomeres as the targets for cancer treatment or anti-aging, wherein the fact that the telomeres are taken as the targets for cancer treatment or anti-aging refers to causing of telomere injury, telomere function loss and genomic instability. According to the application, a TPE (telomere position effect) cell model is used for confirming that the two compounds can cause telomere injury, telomere function loss and genomic instability, and defining the value and the mechanism of chrysin and acacetin in cancer and anti-aging treatment because chrysin and acacetin affect the telomere functions; since the telomeres are the important targets for anti-aging and anti-cancer treatment, the invention broadens the application range of chrysin and acacetin in clinical treatment.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com