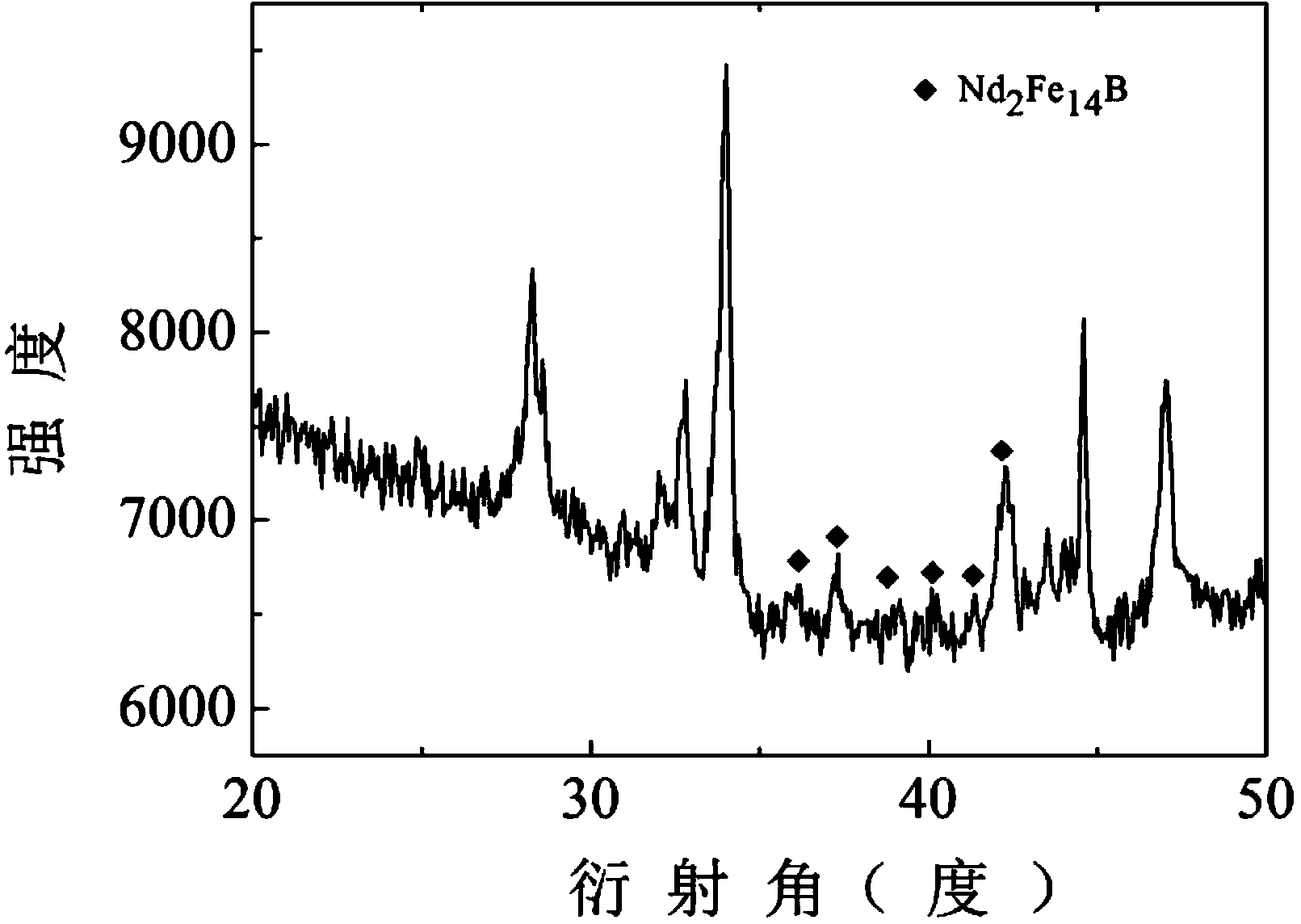
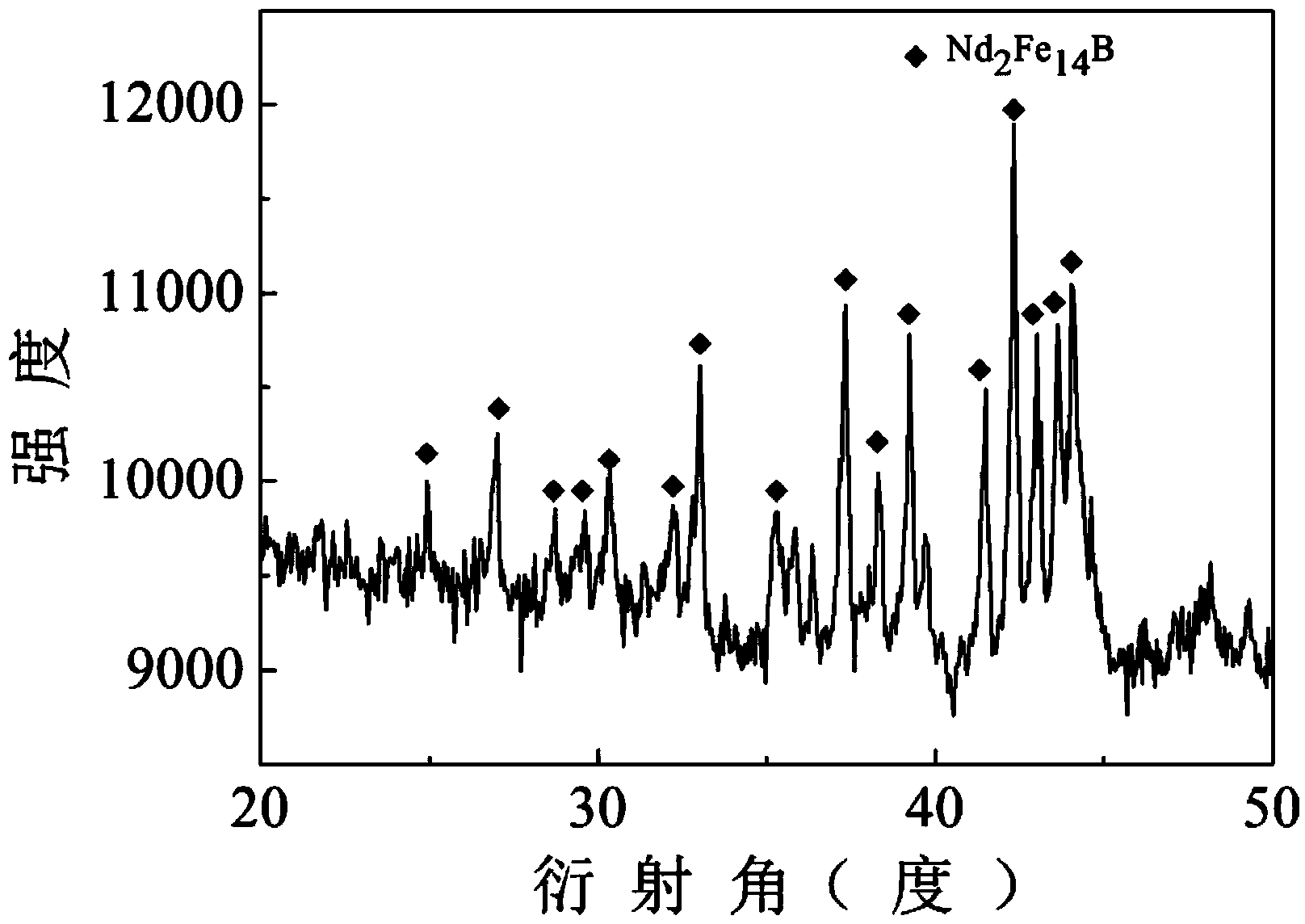
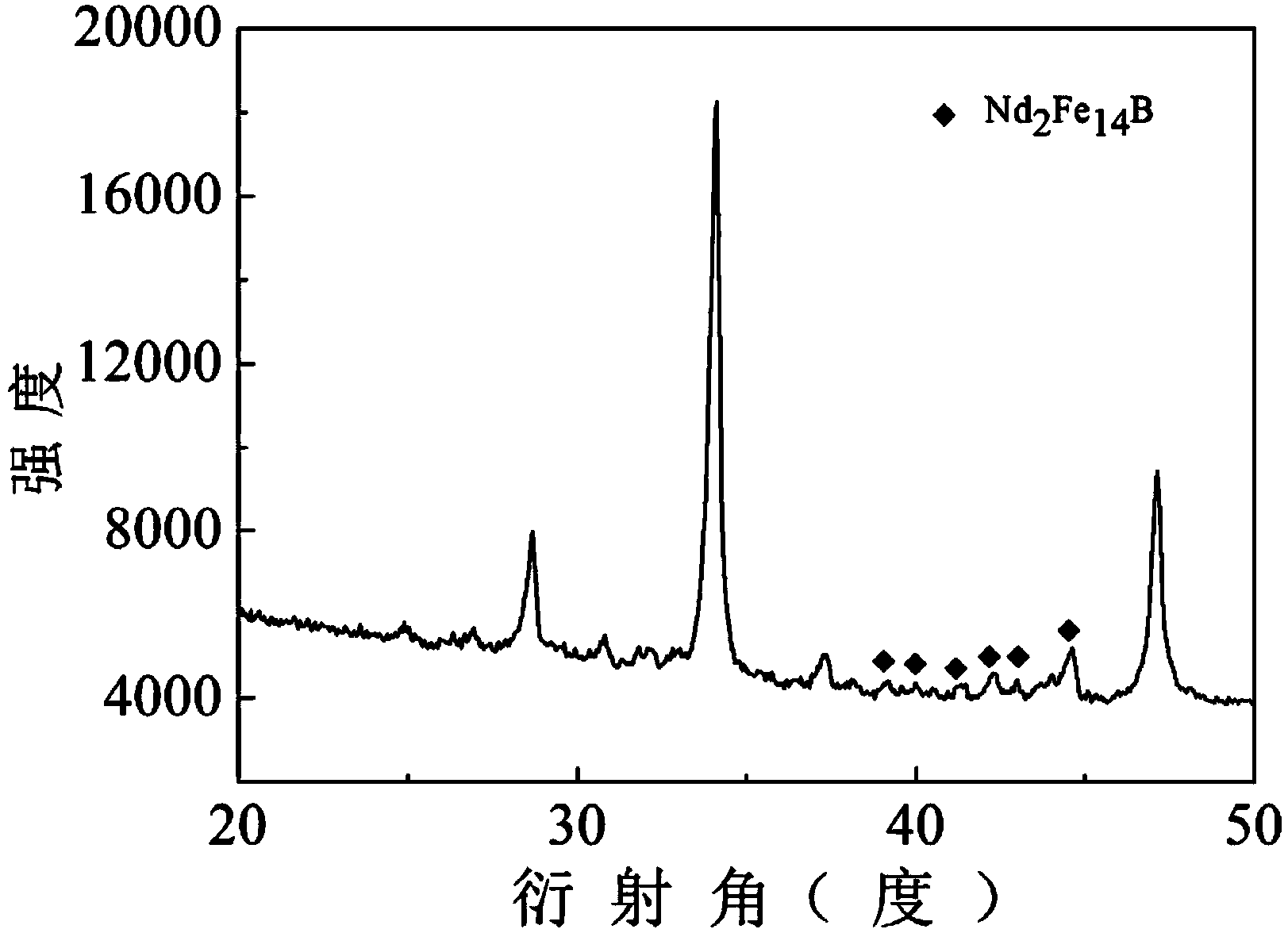
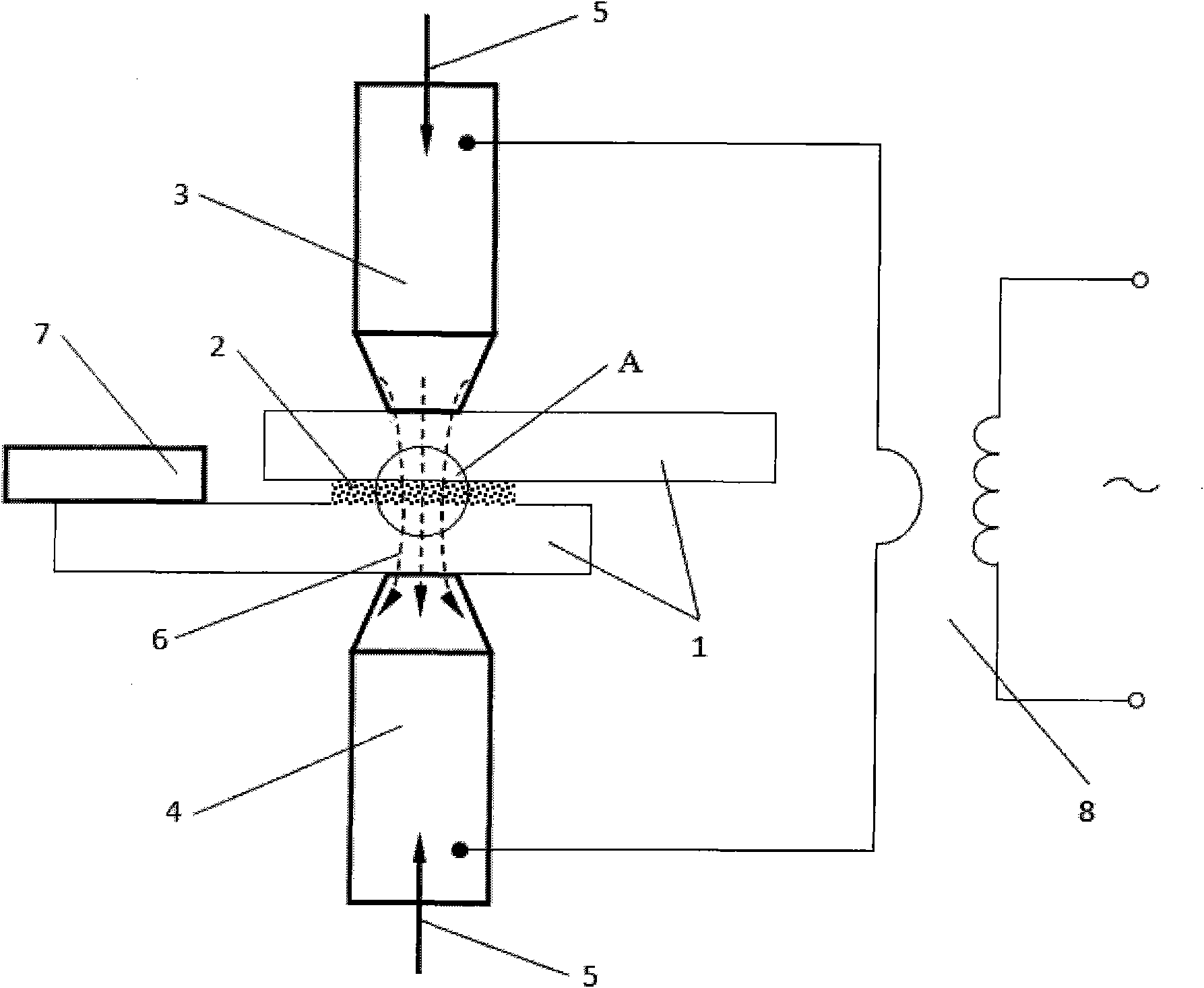
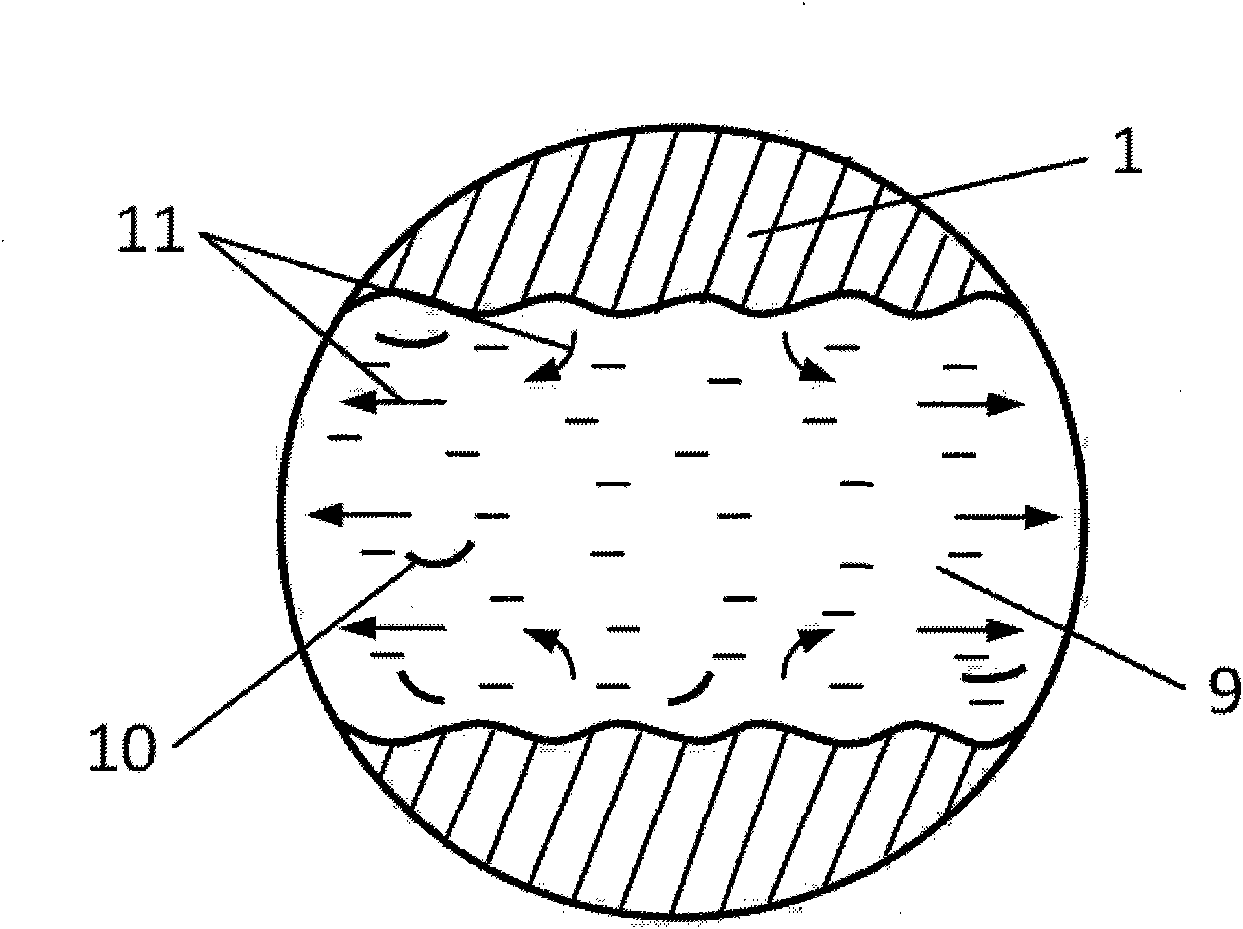
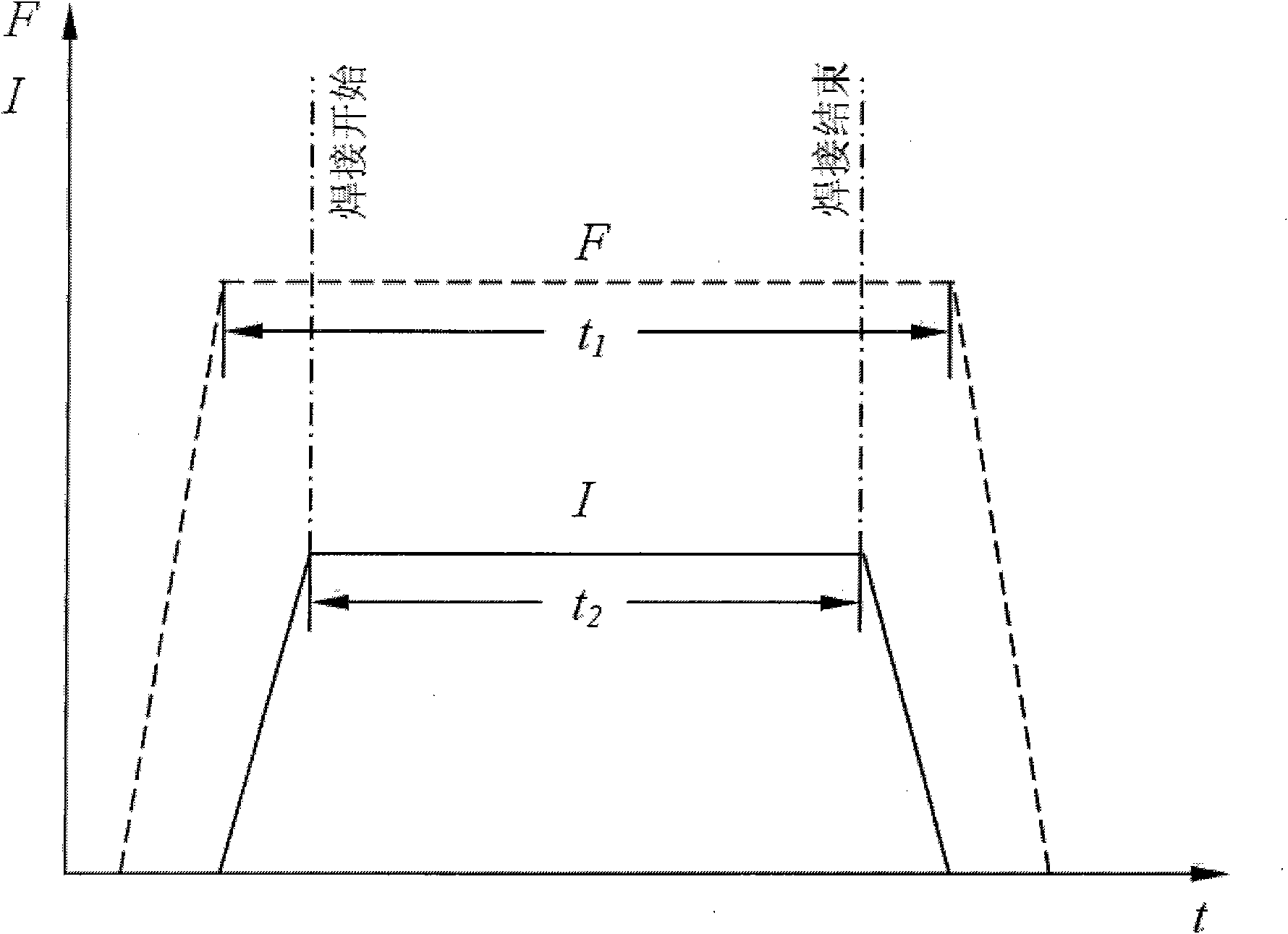
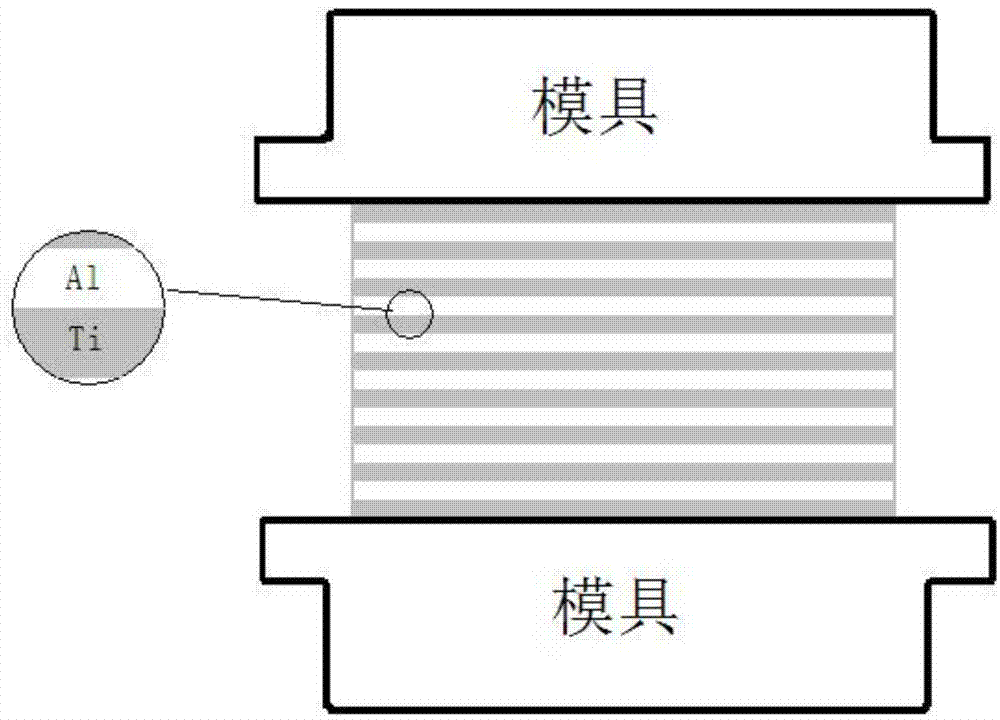
Patents
Literature
200 results about "Diffusion reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
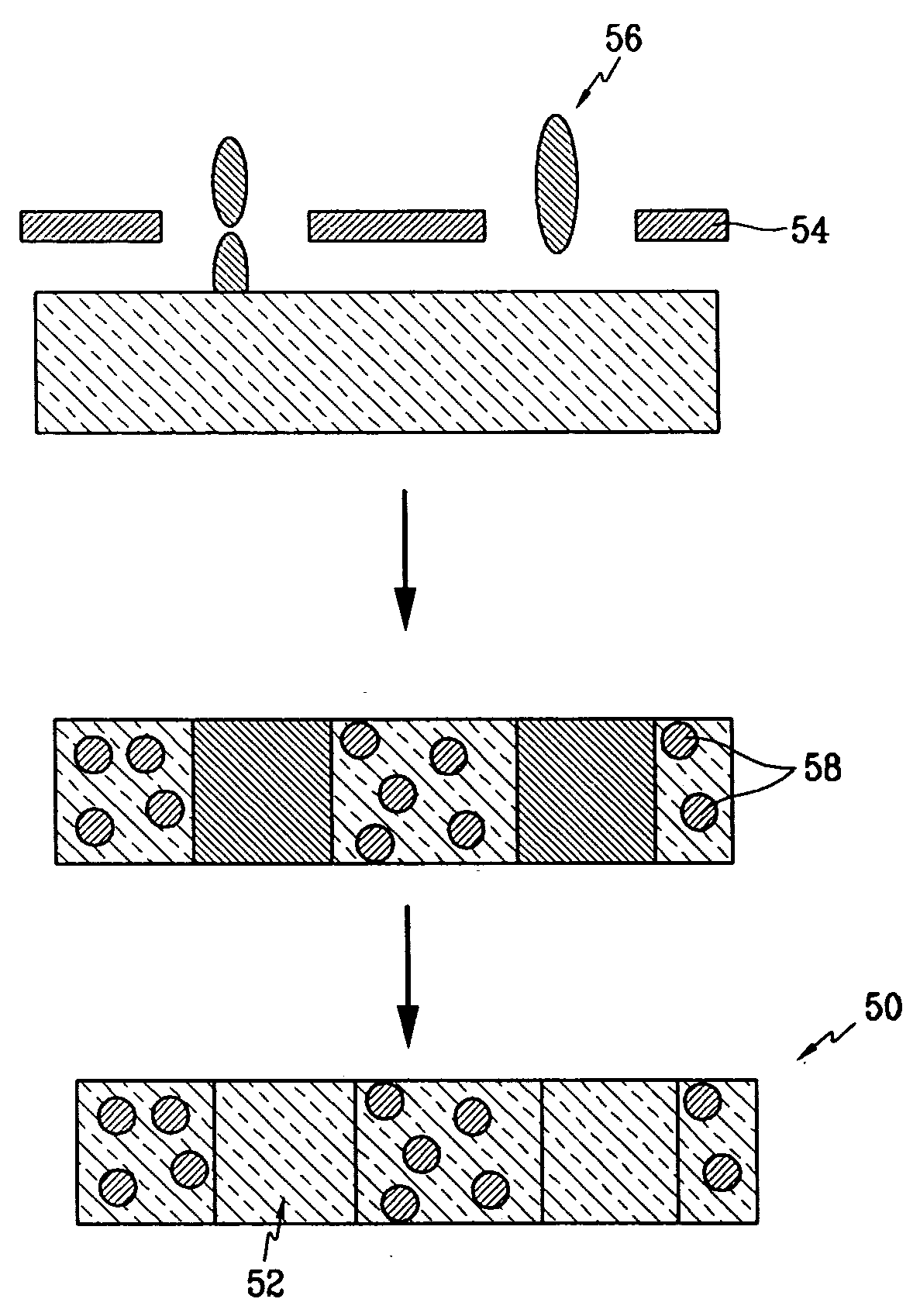
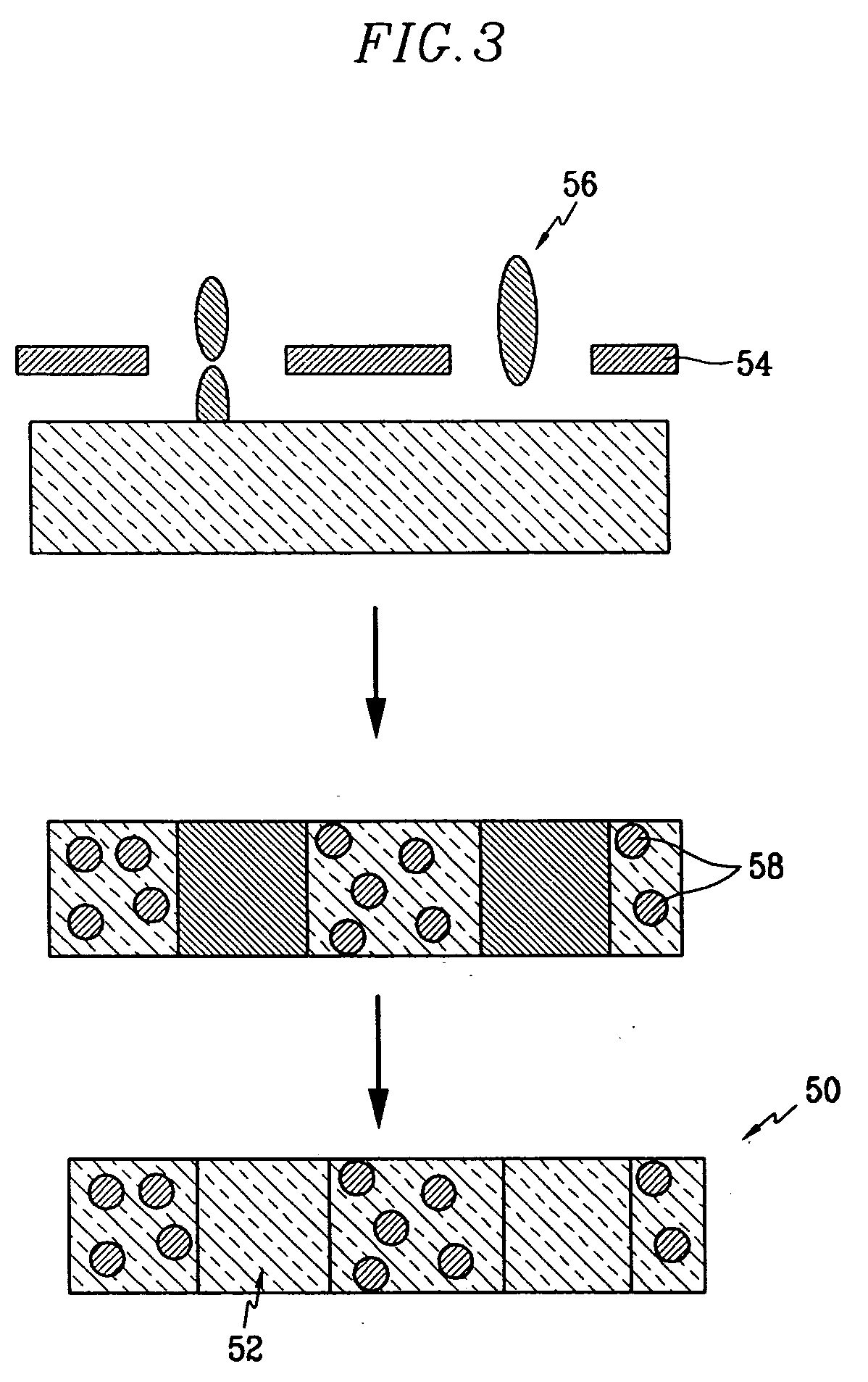
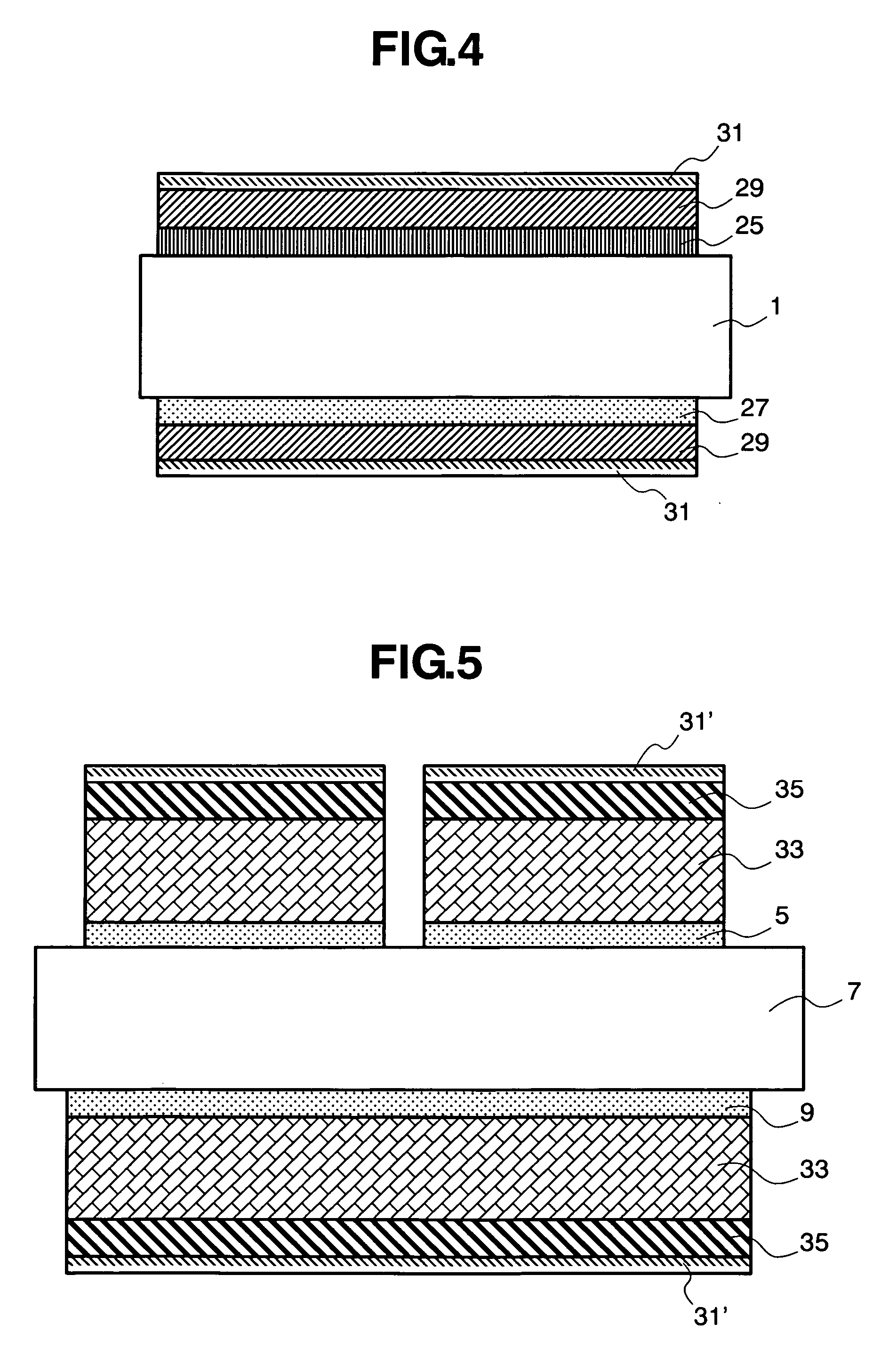
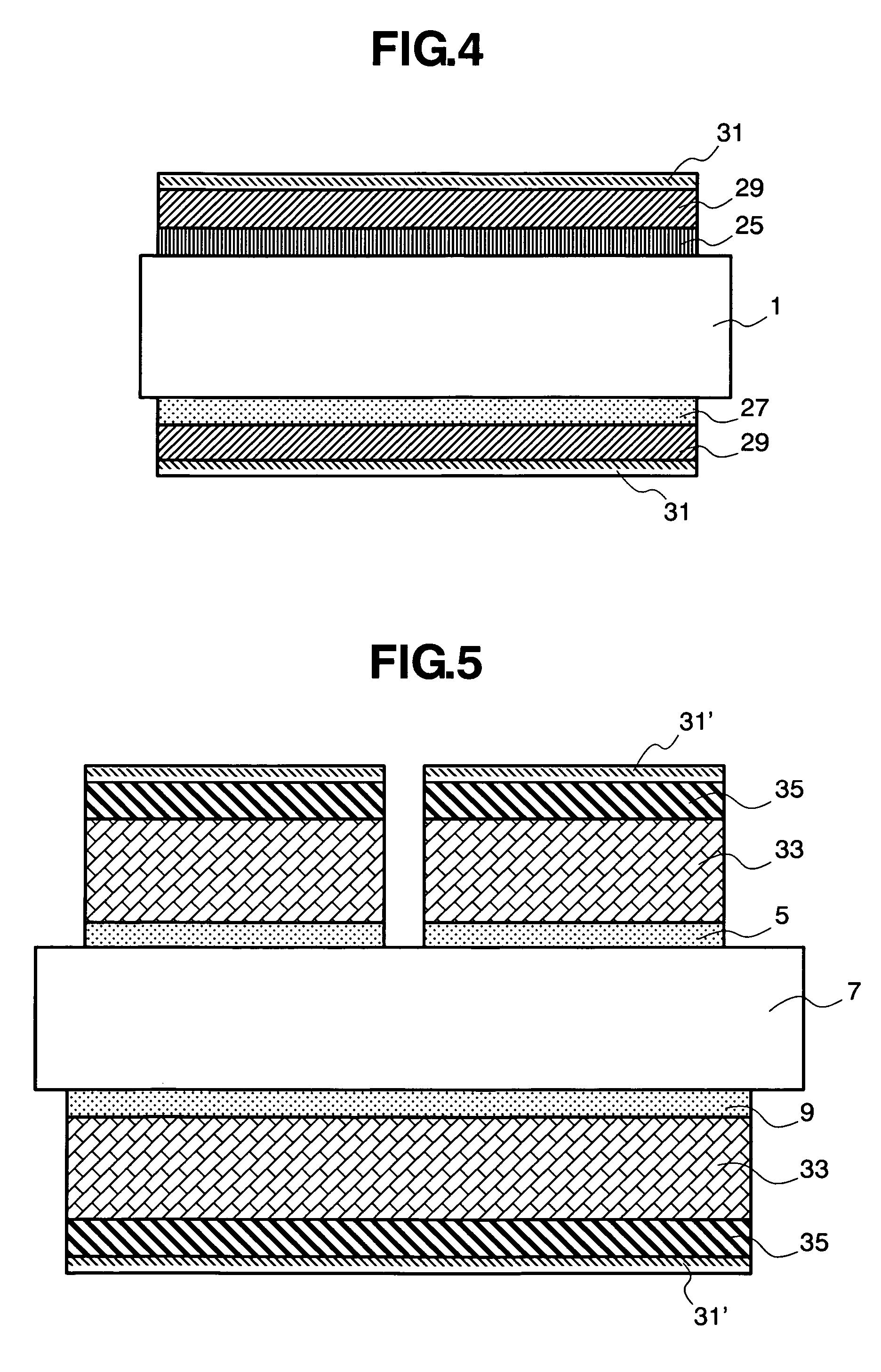
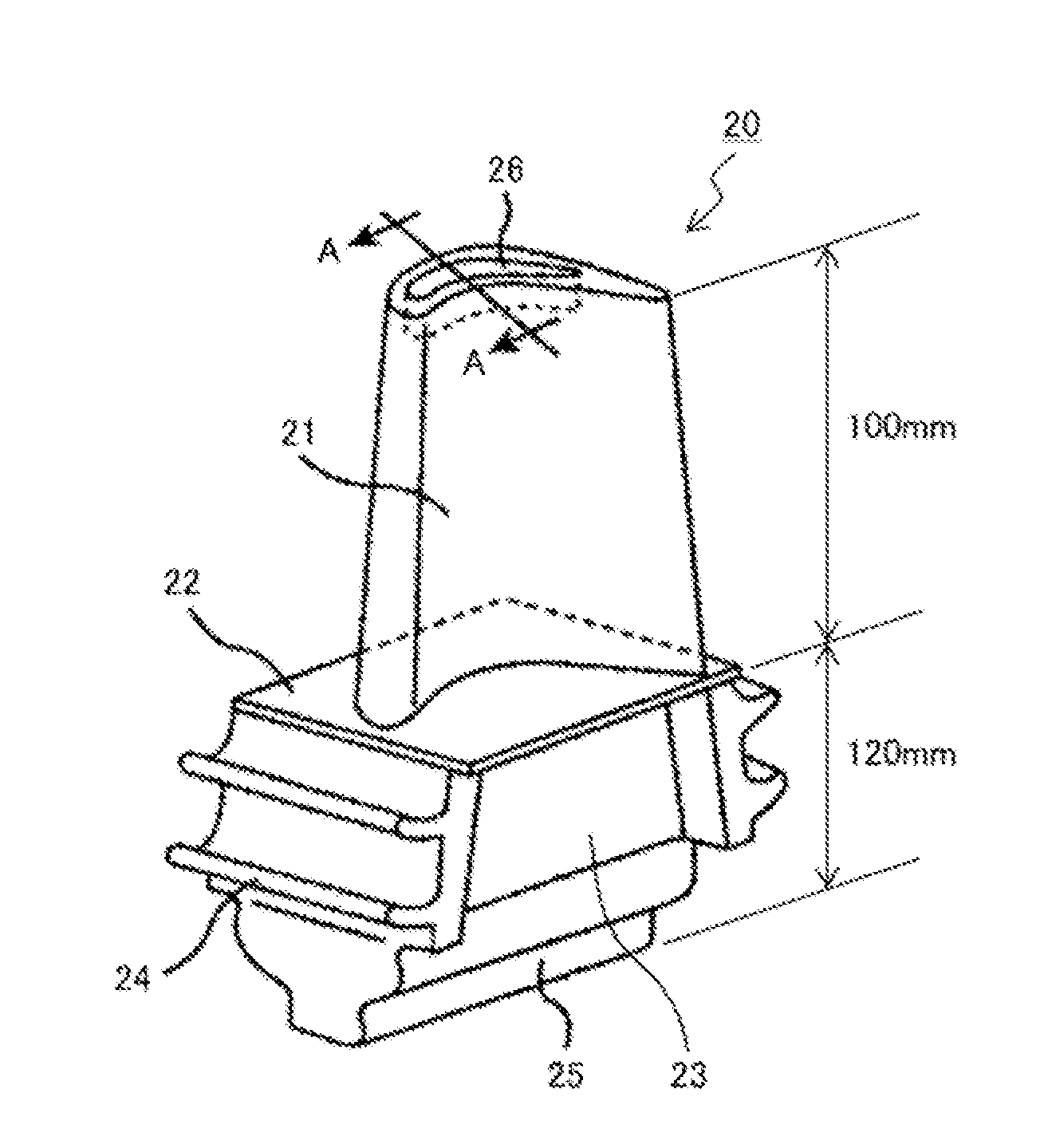
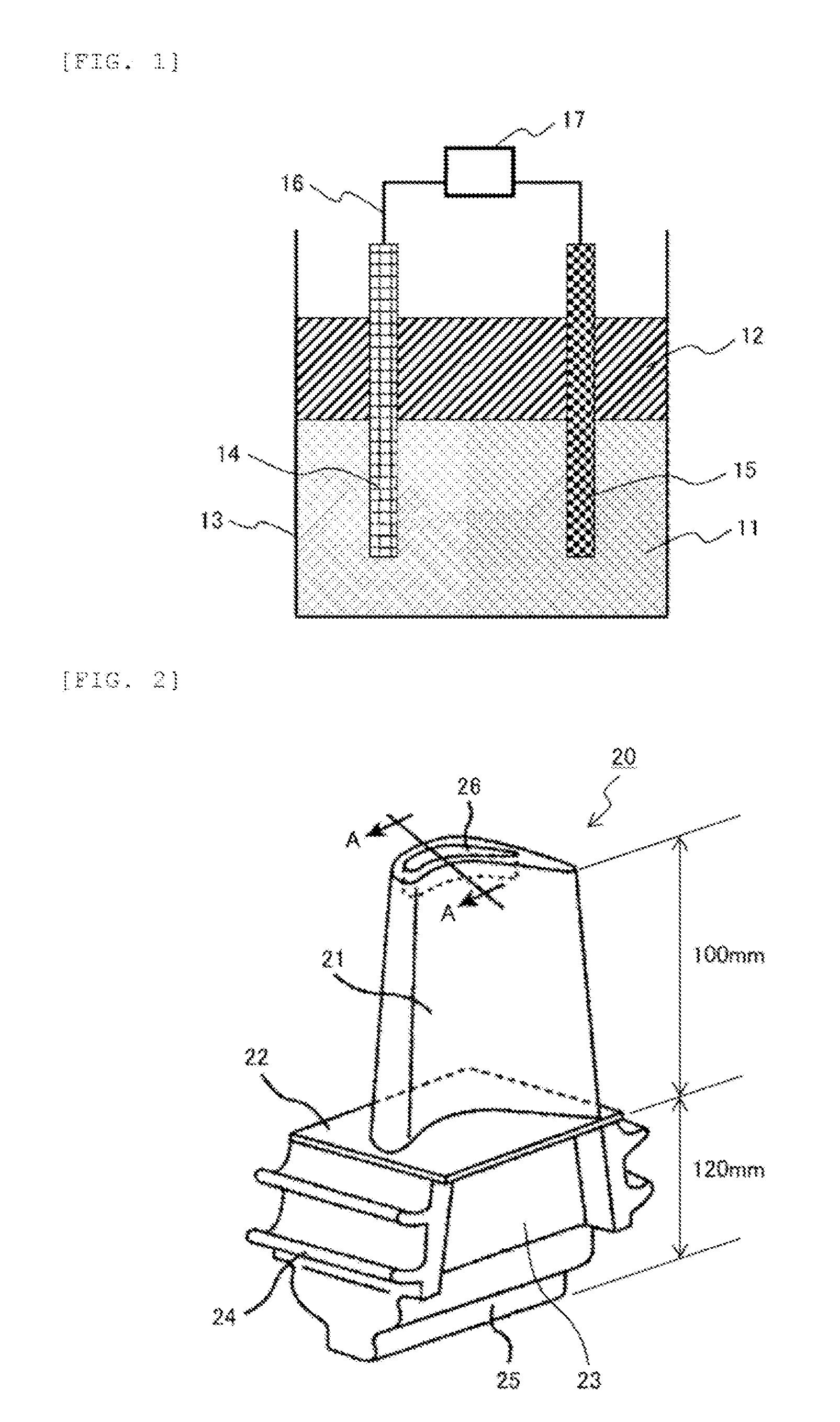
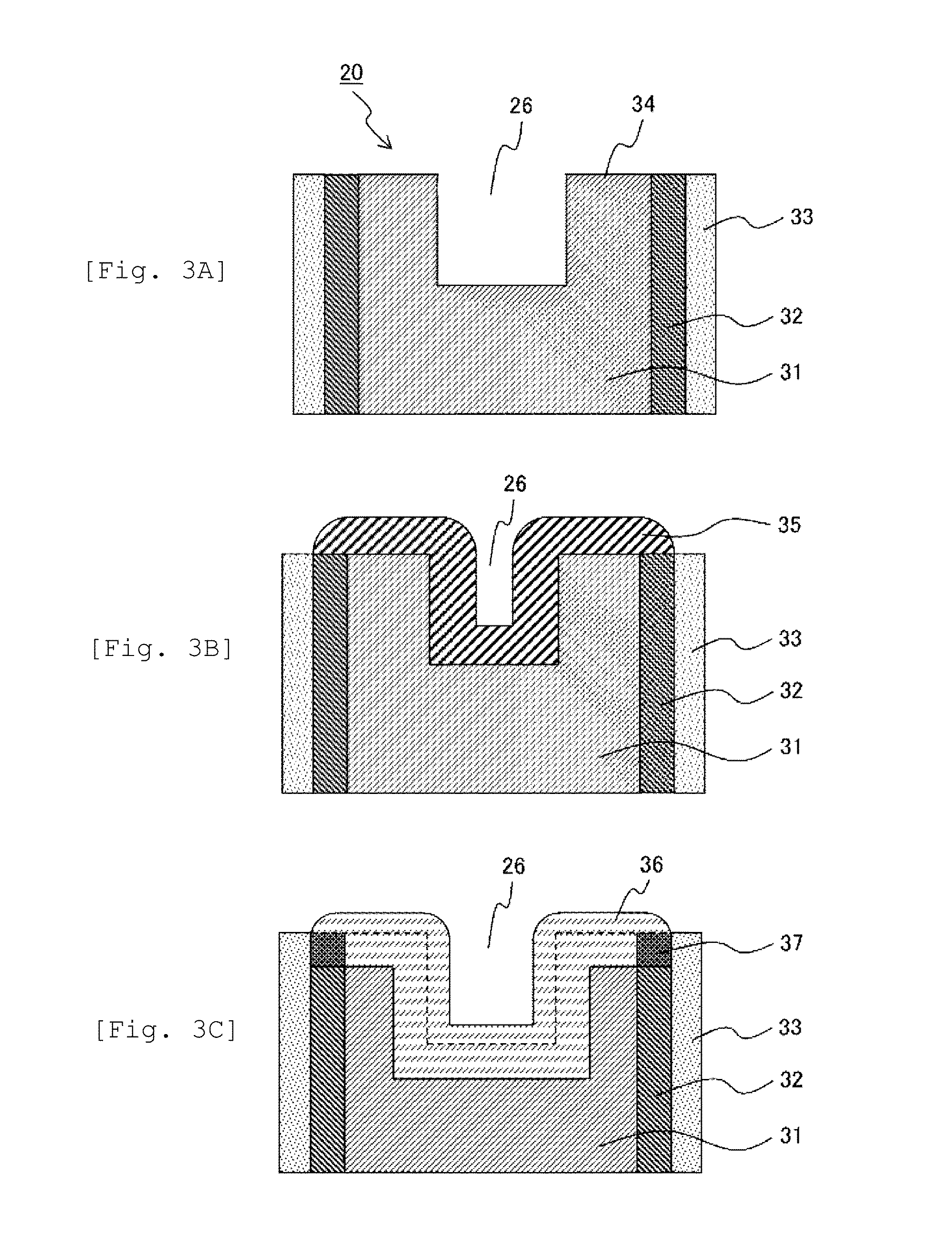
Electrode for fuel cell, and membrane-electrode assembly and fuel cell system comprising the same
InactiveUS20060105227A1Avoid cloggingHigh densityNon-metal conductorsFinal product manufactureHigh current densityFuel cells
The electrode for a fuel cell of the present invention includes a catalyst layer and an electrode substrate supporting the catalyst layer, where the electrode substrate includes a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region separated from each other. The hydrophilic region and the hydrophobic region that are separated from each other can easily release water produced at the cathode, and thereby prevent clogging of pores of the membrane by water, and smoothly diffuse the reactants resulting in obtaining a high current density.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
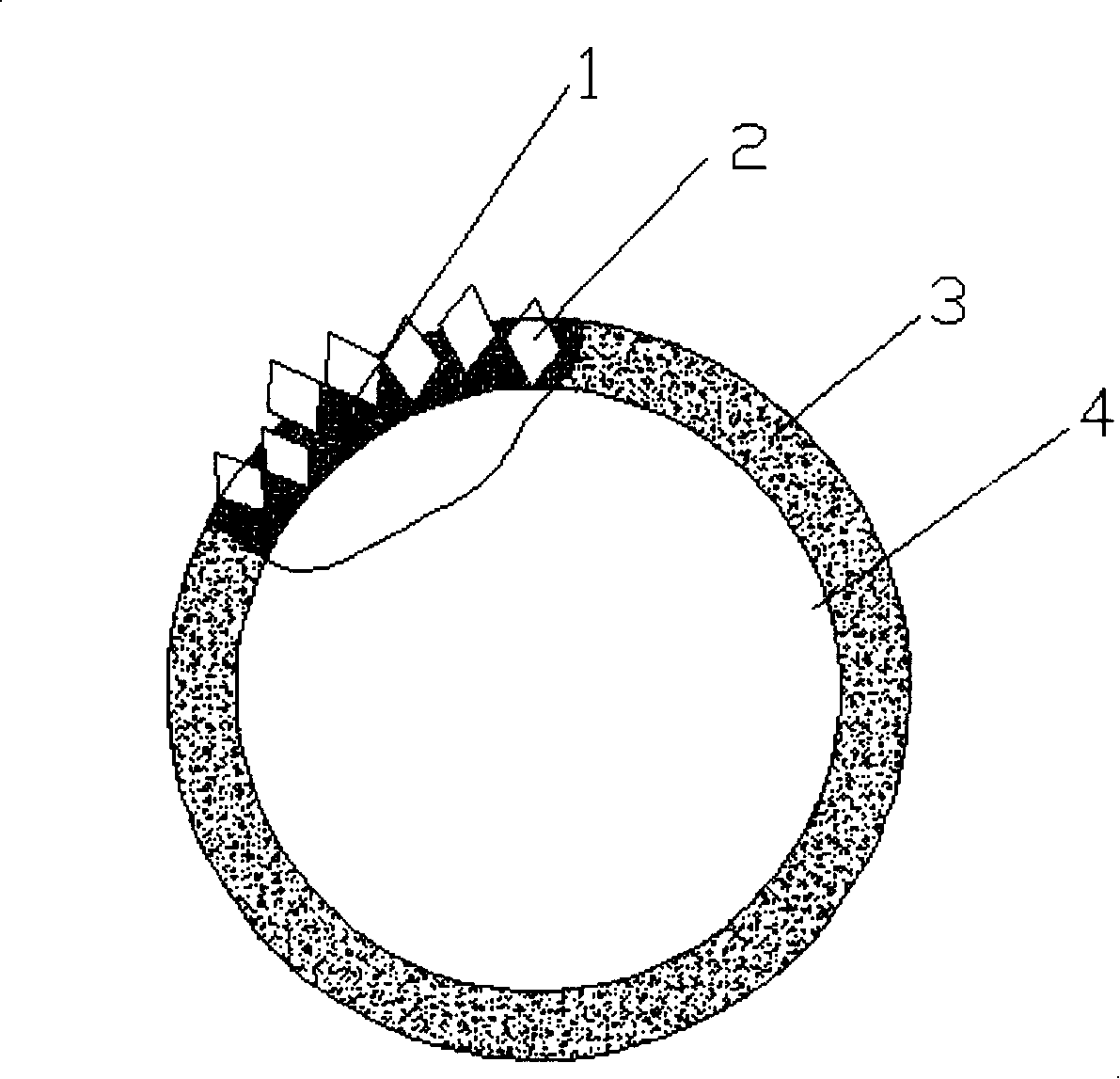
Method for preparing metal binding agent diamond scroll saw
InactiveCN101209505ATo achieve the purpose of cuttingImprove bindingMetal sawing tool makingMetal sawing toolsDiamond wire sawDiffusion reaction
The invention provides a preparation method and the product of a metal binder diamond wire saw, comprising the preparation steps of (1) steel wire surface, (2) plating auxiliary disposal of the steel wire, (3) burdening, (4) plating of steel wire and (5) post-processing. The thickness of the binder coating ranges from 1 / 2 to 2 / 3 of the grain diameter of the diamond. By a series of chemical and diffusion reaction, the surface of the steel wire is covered by a layer of uniform and firm coating 3; a diamond mill grain 2 is also uniformly held in a metal binding layer 1, thus achieving the cutting object.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
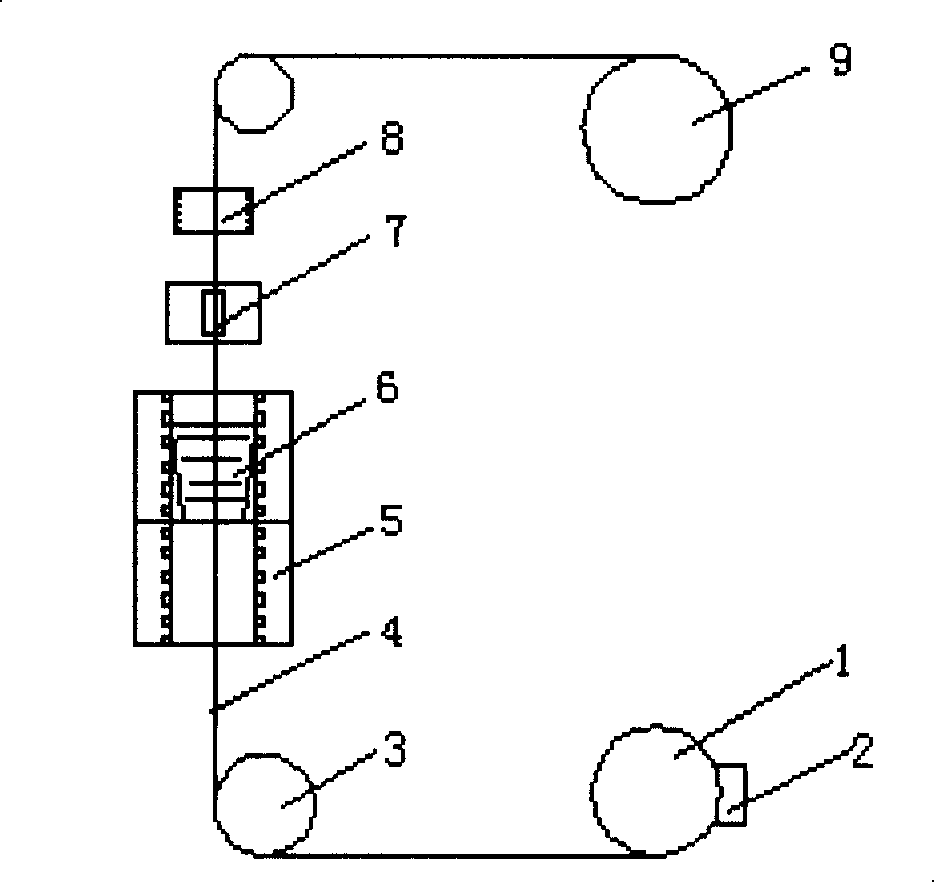
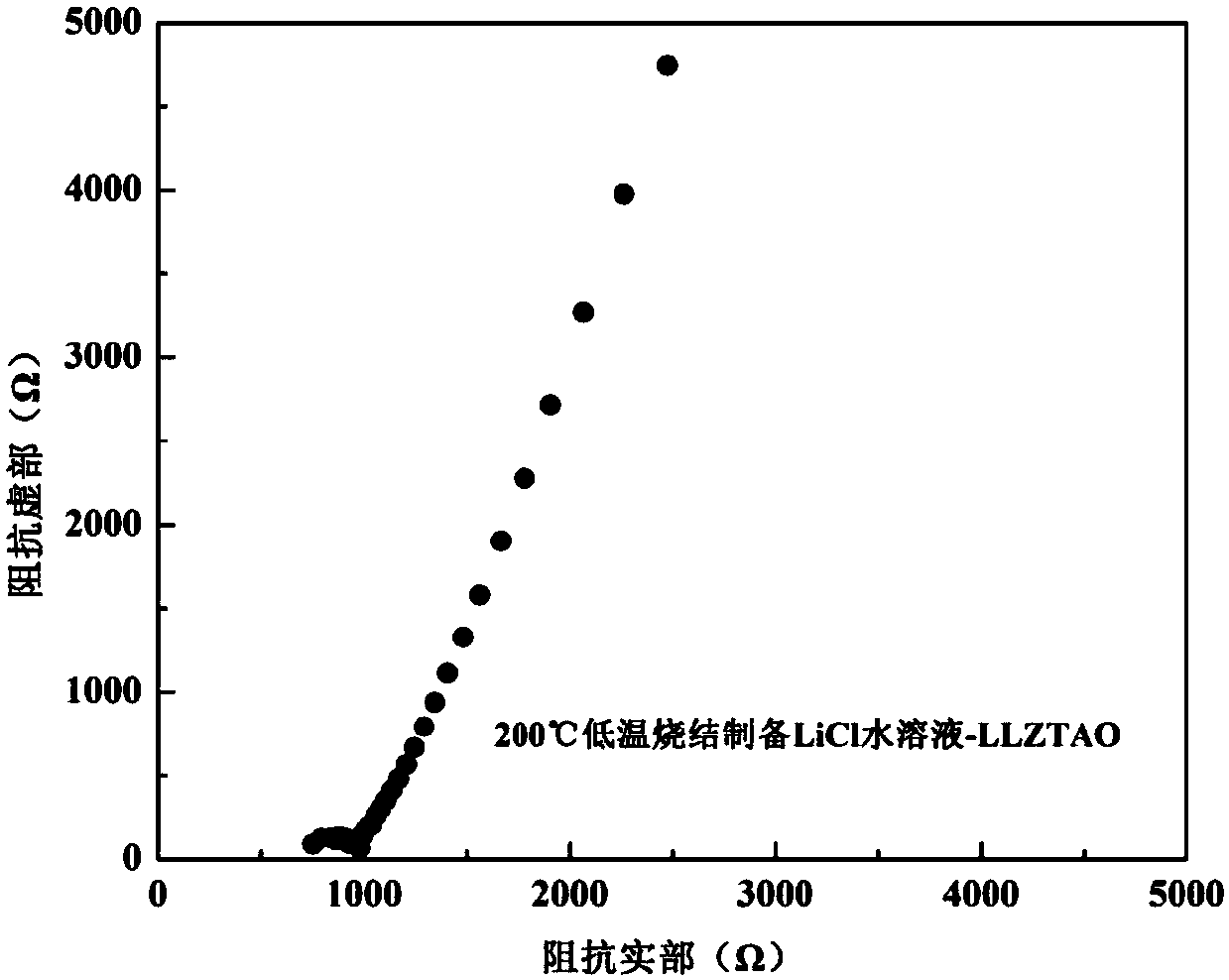
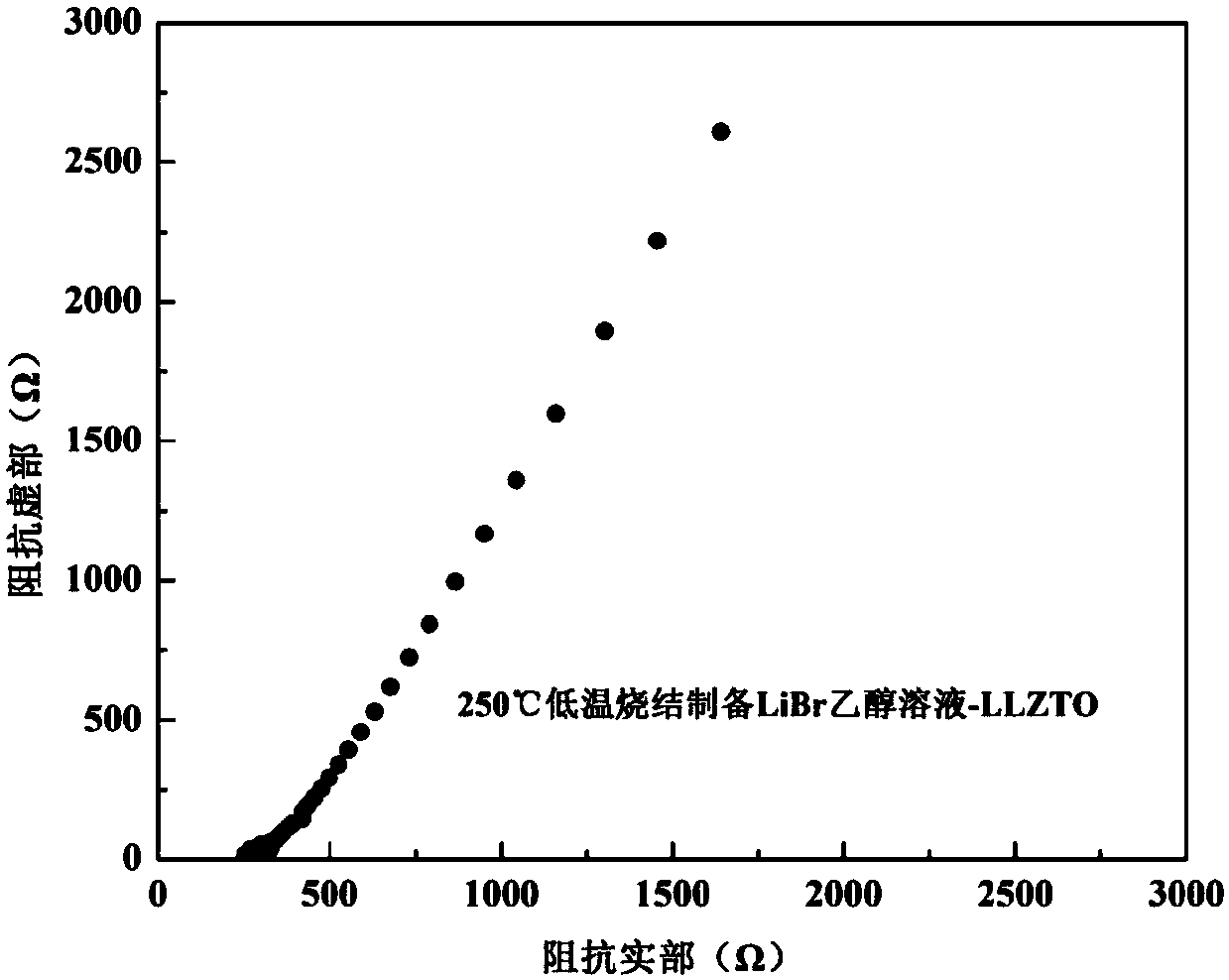
Oxide solid electrolytes based on lithium halide-doping and low-temperature sintering method thereof
InactiveCN107732295AImprove ionic conductivityImprove performanceSecondary cellsElectrolytesSolid state electrolyteLanthanum
Provided is an oxide solid electrolyte based on lithium halide-doping. The oxide solid electrolyte is a lithium solid electrolyte, wherein electrolytes in a perovskite type, an NASICON type and a garnet type are taken as substrates, and a lithium halide solution and the oxide solid electrolytes are compounded and sintered at a low temperature. A preparing method comprises the steps that LATP, LLTOand LLZO solid electrolytes are subjected to ball-milling, or self-produced cubic-phase lithium-lanthanum-zirconium-oxygen solid electrolyte powder is subjected to ball-milling and sintered to prepare cubic-phase LLZO solid electrolyte powder, an LIX solution is added to the solid electrolyte powder, and the mixture is pressed into a slice or painted into a membrane, then placed in a muffle furnace at a low temperature of 100-250 DEG C and sintered for 1-10 hours. The oxide solid electrolyte is simple in technology and low in cost, and the prepared lithium solid electrolyte has high ionic conductivity and high repeatability; the oxide solid electrolyte can be on a par with electrolytes prepared through a traditional high-temperature technology, and meanwhile low-temperature sintering canavoid high-temperature diffusion reaction with cathode materials.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Method for preparing regenerated neodymium iron boron magnetic powder by using neodymium iron boron oily sludge
ActiveCN103882234AAvoid dischargeImprove protectionMagnetic materialsProcess efficiency improvementSludgeDistillation
The invention discloses a method for preparing regenerated neodymium iron boron magnetic powder by using neodymium iron boron oily sludge, and belongs to the technical field of recovering and recycling of the neodymium iron boron oily sludge. The method comprises the following technological processes: distilling and separating neodymium iron boron oily sludge; coprecipitating and recovering all valuable elements; mixing oxides; adding the substances such as calcium metal and the like according to the ratio; mixing reactants; carrying out thermal reduction and diffusion at high temperature; removing a calcium oxide in the product; drying in vacuum; forming the regenerated neodymium iron boron magnetic powder, wherein the step of 'coprecipitating and recovering all valuable elements' can be accepted or rejected according to existence of metal elements harmful to the magnetic property in the neodymium iron boron oily sludge; a part of impurities are removed from the neodymium iron boron oily sludge by distillation and separation; the mixed oxides are obtained by coprecipitation of the valuable elements; calcium metal particles are added, and subjected to reduction diffusion reaction at 850-1150 DEG C; the regenerated neodymium iron boron magnetic powder can be directly obtained from the product after chemical separation and drying. The method has the advantages that environmental protection is facilitated, the technological process is shortened, the recovery cost is reduced, and a part of technical problems are solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of refractory high-entropy alloy powder
The invention discloses a preparation method of refractory high-entropy alloy powder, which is composed of four or more elements of titanium, vanadium, chromium, zirconium, niobium, molybdenum, tantalum and tungsten in equivalent ratio or near equivalent ratio. According to the invention, ball milling mixing and discharging plasma sintering technologies are used, a solid phase diffusion reaction is carried out at a lower temperature to achieve the alloying process between the refractory metals with high melting points, the process for heating and melting the alloy elements is avoided, the preparation of the refractory high-entropy alloy powder at lower temperature is achieved; meanwhile, the disadvantages of long time of mechanical alloying process and low efficiency are avoided. The preparation method of the refractory high-entropy alloy powder has the advantages of high efficiency and low cost.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Membrane electrode assembly, fuel cell using the same and manufacturing method of membrane electrode assembly
ActiveUS20130177832A1Prevent degradationEfficiently provideFinal product manufactureSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cellsReactive gas
There is provided a technique of preventing degradation of an electrolyte membrane included in a fuel cell. A fuel cell includes a membrane electrode assembly. The membrane electrode assembly is provided as a power generation device where electrodes are arranged on both sides of an electrolyte membrane having proton conductivity. Each of the electrodes has a layered structure of stacking a catalyst layer arranged to support a catalyst and a gas diffusion layer arranged to spread a reactive gas over the entire electrode plane. The outer peripheral edge of the gas diffusion layer is located inward of the outer peripheral edge of the catalyst layer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Powder medium diffusion reaction resistance brazing method of magnesium alloy
InactiveCN101885095AWelding processing methods are enriched and supplementedReliable weldingSoldering apparatusShielding gasContact resistance
The invention discloses a powder medium diffusion reaction resistance brazing method of magnesium and a magnesium alloy material, applying in welding of the magnesium and the magnesium alloy material. In the method, a magnesium base powder medium is used as a filling layer, thus improving the problem that contact resistance of the magnesium alloy material is difficult to be welded at the initial stage of the welding; and resistance heat is used as a welding heat source, under the protection of a protective gas and the action of the resistance heat, the partial melting of the surface to be welded of the material and the rapid melting of the powder medium are synchronized to form an alloy solder. Under the impact action of an electrode voltage with a proper magnitude, an oxide film smashes, the powder medium generates an eutectic reaction on the interface of the material to be welded and an eutectic is formed on the interface by virtue of a diffusion action among dissimilar metals, thereby realizing the reliable connection of the materials. The method is mainly used for achieving the welding under the environment of inert gas protection and has strong flexibility and relative ideal project meaning.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of light-weight intermetallic compound based layered composite material
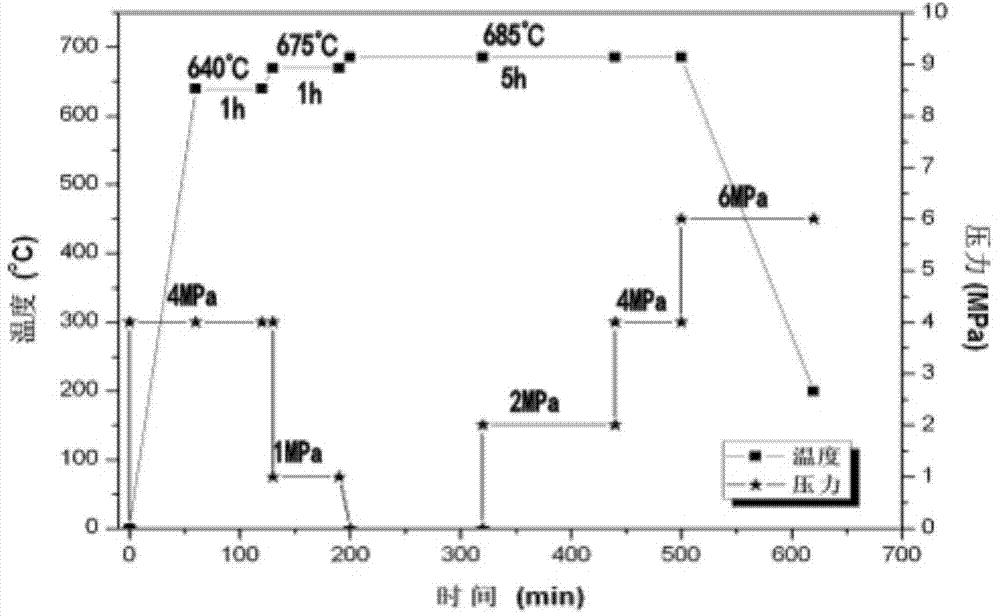
InactiveCN103572187AHigh strengthHigh hardnessLaminationLamination apparatusFragilityReaction temperature
The invention provides a preparation method of a light-weight intermetallic compound based layered composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with Ti foil and Al foil as raw materials, alternately stacking the pretreated Ti foil and Al foil, keeping the Ti foil at the outmost layer, and carrying out vacuum hot pressing treatment under the conditions that the base pressure is 6.67*10<-3>Pa, the reaction temperature is 640-685 DEG C, the heating rate is 1-10 DEG C / min, the applied pressure is 0-4MPa, and the temperature preservation time is 1-10h. According to the preparation method, the mutually stacked Ti foil and Al foil are subjected to diffusion reaction by using a vacuum hot pressing method to generate an intermetallic compound Al3Ti, and the intermetallic compound Al3Ti and the residual Ti layer are formed into a layered composite material with a Ti layer as a reinforcement body. The intermetallic compound Al3Ti has high strength and hardness, low density and higher fragility, while the Ti layer is the reinforcement body with better toughness, so that the obtained intermetallic compound based layered composite material has high toughness on the basis of high strength.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for performing insulating treatment on metal magnetic powder and preparing metal magnetic powder
ActiveCN104759619AImprove insulation performanceHigh resistivityInorganic material magnetismPhosphatePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for performing insulating treatment on metal magnetic powder and preparing metal magnetic powder. The method comprises the following steps: reacting phosphoric acid and boric acid on the surface of metal magnetic powder, generating and absorbing a layer of phosphate and borate on the surface of the metal magnetic powder to obtain required B and P diffusion sources; under a vacuum atmosphere, performing diffusion reaction, diffusing B and P elements on the surface of the metal magnetic powder to inner part of the metal, and forming a metal gap compound containing B or P below a metal magnetic powder phosphate and borate coating layer after penetrating B and P on the surface of the metal magnetic powder. The metal gap compound and the boric acid left outside the magnetic powder have low melting point, are changed to be liquid at a high temperature to achieve the effects of an inorganic binder. The method has the beneficial effects of improving the insulation of the metal magnetic powder surface, and improving the resistance of the metal magnetic powder particles and the contact resistance of the magnetic powder; inorganic binding coater is adopted to directly form, so that the cost is reduced, the magnetic core strength is improved, and the atmospheric pollution is avoided.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
Environmental barrier coating used for poly-carbon and ceramic base compound material and preparation method thereof
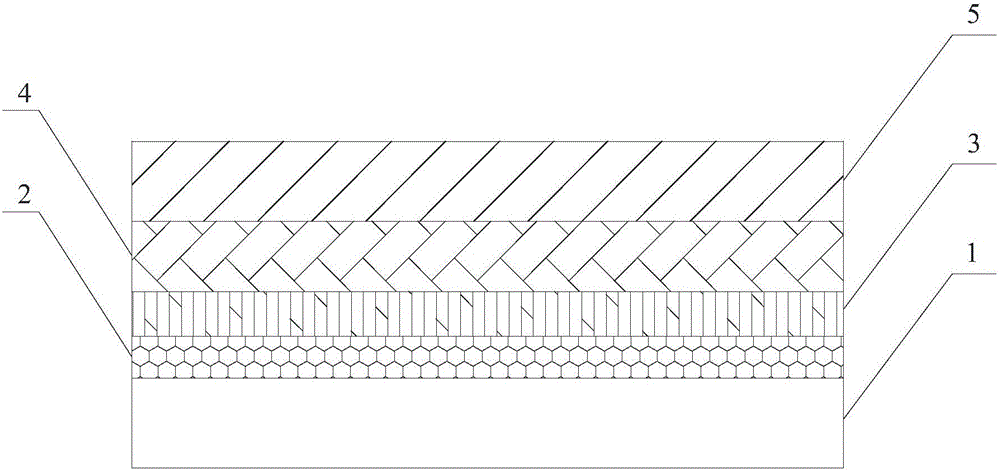
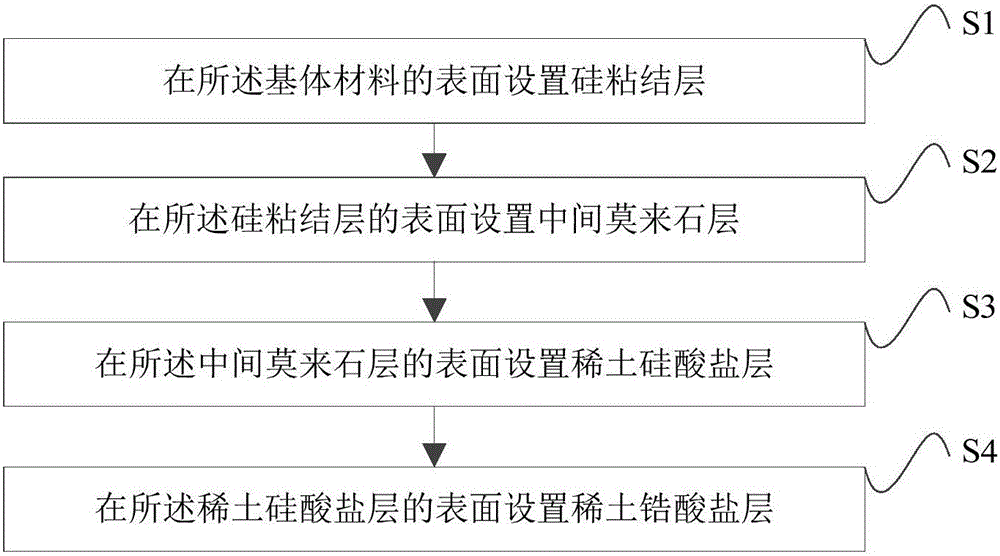
The invention relates to an environmental barrier coating used for a poly-carbon and ceramic base compound material and a preparation method thereof. The environmental barrier coating includes, successively from a substrate material to exterior, a silicon adhesion layer being 60-70 [mu]m in thickness, a mullite layer being 60-80 [mu]m in thickness, a rare earth silicate layer being 100-120 [mu]m in thickness, and a rare earth zirconate layer being 100-150 [mu]m in thickness. In the environmental barrier coating, the rare earth silicate layer can effectively inhibit an element diffusion reaction between the mullite layer and the rare earth zirconate layer, and the rare earth zirconate layer can significantly reduce volatilization of SiO2, so that a defect of poor high-temperature stability of the rare earth silicate layer is solved. During use, the components of the whole coating is not liable to change, so that service life of the coating under environment of an aero-engine can be greatly prolonged, and protective effect is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for preparing anti-oxidation multiple phase coating of carbon/carbon composite material surface
InactiveCN1821183AHigh temperature anti-oxidation temperature increaseImprove thermal shock resistanceCarbon compositesAlcohol
The present invention discloses the preparation process of antioxidant multiple phase coating on the surface of carbon / carbon composite material. On the surface of carbon / carbon composite material, one porous SiC whisker toughened SiC coating is first prepared with Si powder, C powder, Al2O3 powder and beta-SiC whiskcer as material and alcohol as dispersant, and through a slurry process. The carbon / carbon composite material with SiC whisker toughened SiC coating is coated in mixed powder of high purity Si powder, C powder and MoSi2 powder in certain weight proportion, and sintered in protecting atmosphere; and through serial diffusion reactions, the required coating is obtained. The present invention has the advantages of certain amount of free Si in the coating to result in high compactness, effective inhibition of crack expansion in the multiple phase MoSi2-SiC-Si coating, and raised antioxidant, heat shock resisting and eroslion resisting property.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Fe-Cr-Ni-Ti micropowder coated honeycomb ZTA ceramic preform as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN109053215AImproved interfacial bonding propertiesImprove wettabilityTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusSilicic acidLiquid metal
The invention belongs to the field of material processing, and discloses a Fe-Cr-Ni-Ti micropowder coated honeycomb ZTA ceramic preform as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Fe, Crand Ni are main elements in chromium-based cast iron and high-manganese steel; after the Fe, the Cr and the Ni are subjected to alloying treatment together with Ti powder, the reduction of the meltingtemperature of pure Ti powder is facilitated, and molten Ti is more easily formed in a liquid casting process at the high temperature of 1500+ / -20 DEG C; by means of a diffusion reaction of Ti and the oxygen in ZTA ceramic, a metal ceramic bonding interface with a higher bonding strength is realized. In addition, water glass reacts with CO2 so as to form silicic acid with certain connection strength, so that the bonding between ZTA ceramic particles and the shaping of the preform are promoted, and the resistance to scouring of poured liquid metal of the preform is improved. In addition, paraffin is used as a pore-forming agent, so that the uniform distribution and communication of holes in the preform can be facilitated. Therefore, the Fe-Cr-Ni-Ti micropowder coated honeycomb ZTA ceramicpreform can be well applied to preparation of metal-based composite materials.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Electronic device
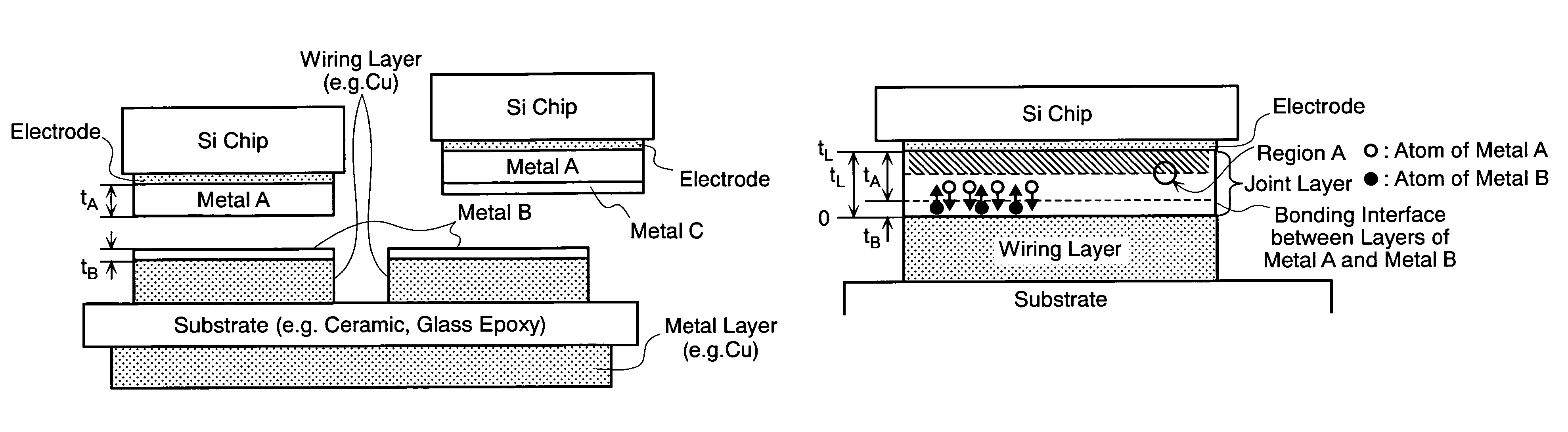
InactiveUS20060192291A1Reduce manufacturing costSolve the lack of reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal expansionDiffusion reaction
An electronic device according to an embodiment of the invention includes a pair of members which are connected to each other by a connecting portion layer interposed between connecting portions respectively formed thereon and have thermal expansion coefficients different from each other, wherein the connection layer is formed by diffusion reaction between the metal layers by which the metal layers are melted only in the vicinity of a contact interface between the layers, the metal layers being formed on the connecting portions with materials different from each other. At least one of the metal layers is formed by plating, thereby the connection layer is formed in a thickness sufficient to absorb difference in thermal expansion coefficient between the pair of members. Since melting temperature of the connection layer after the pair of members have been connected to each other is increased compared with melting temperature of each of the members in the diffusion reaction, the connection layer is prevented from being damaged due to heating treatment performed after the connection has been made, consequently excellent reliability of the electronic device is secured.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
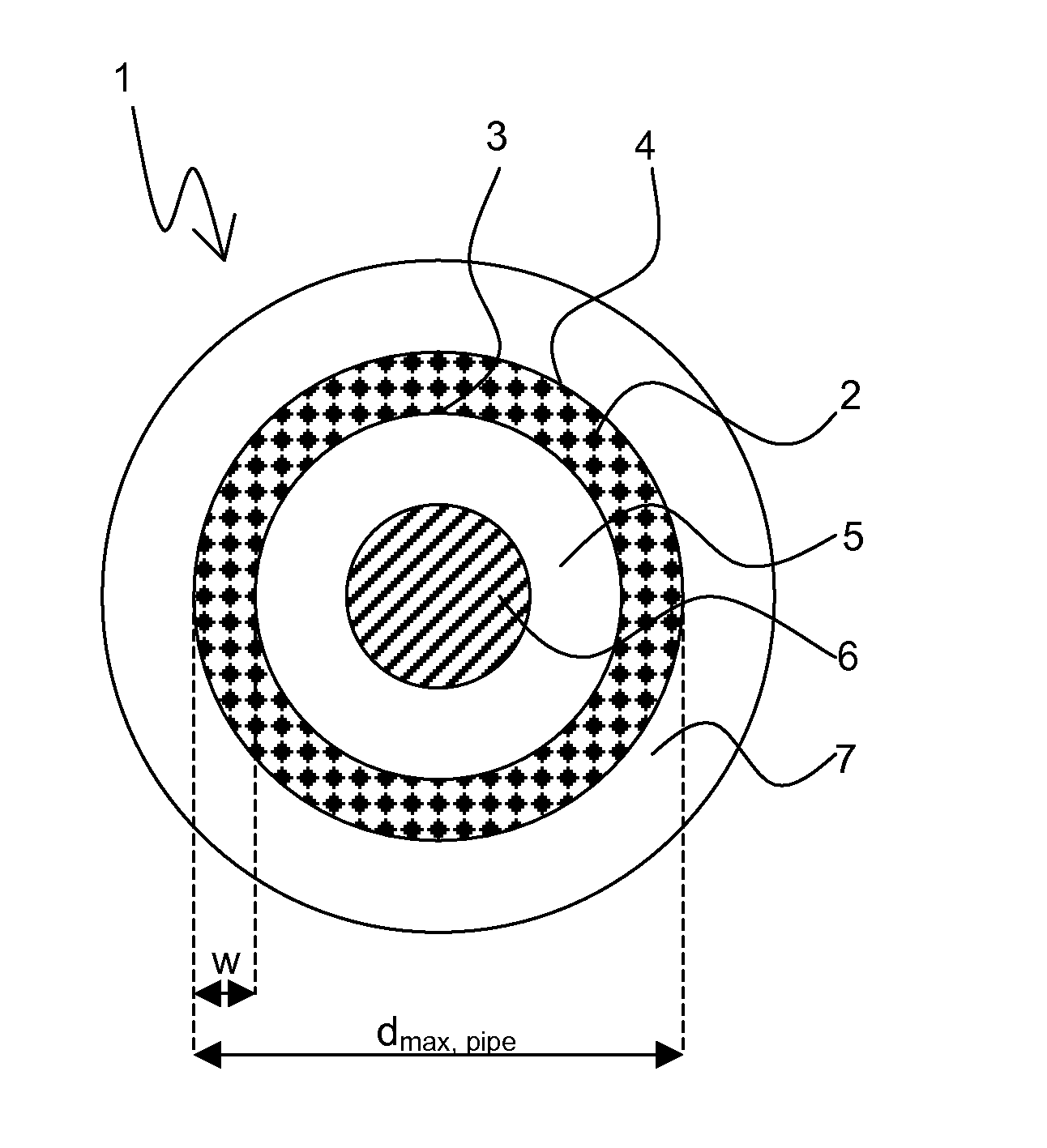
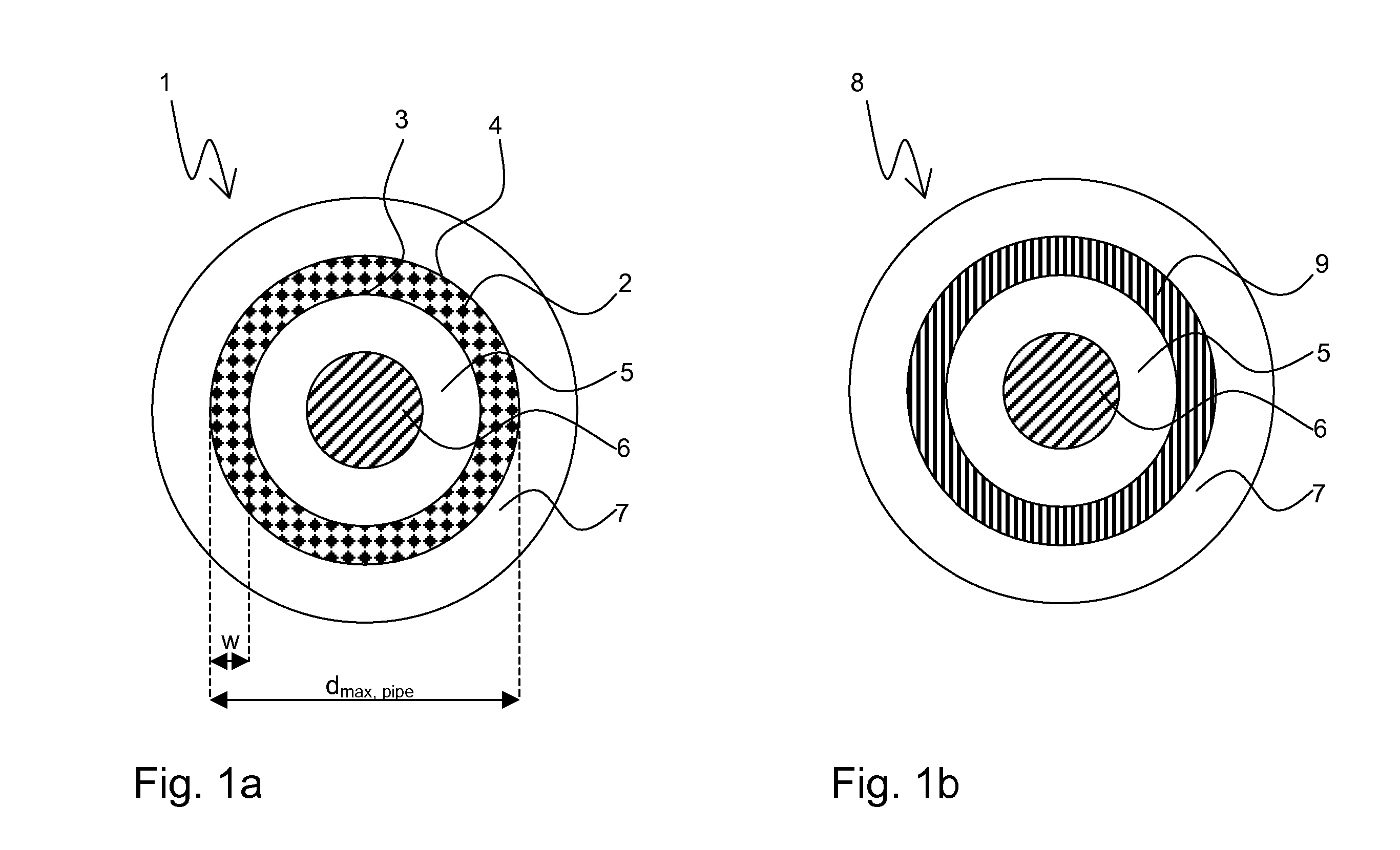
SUPERCONDUCTIVE ELEMENT CONTAINING Nb3Sn
InactiveUS20070238620A1Improve superconductivityHigh critical temperatureSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentHigh critical temperatureMetallic materials
A superconductive element containing Nb3Sn, in particular a multifilament wire, comprising at least one superconductive filament (8) which is obtained by a solid state diffusion reaction from a preliminary filament structure (1), said preliminary filament structure (1) containing an elongated hollow pipe (2) having an inner surface (3) and an outer surface (4), wherein said hollow pipe (2) consists of Nb or an Nb alloy, in particular NbTa, wherein the outer surface (4) is in close contact with a surrounding bronze matrix (5) containing Cu and Sn, and wherein the inner surface (3) is in close contact with an inner bronze matrix (5) also containing Cu and Sn, is characterized in that the inner bronze matrix (5) of the preliminary filament structure (1) encloses in its central region an elongated core (6) consisting of a metallic material, said metallic material having at room temperature (=RT) a thermal expansion coefficient αcore<17*10−6K−1, preferably αcore≦8*10−6 K−1, said metallic material having at RT a yield strength Rp0.2>300 MPa, said metallic material having at RT an elongation at rupture A>20%, and wherein the metallic material of the core (6) is chemically inert with respect to the material of the inner bronze matrix (5) up to a reaction temperature T of the solid state diffusion reaction. This element has improved superconductive properties in a large volume fraction of its superconductive filaments, in particular a high critical temperature Tc and a high critical magnetic filed strength Bc2, and is mechanically stable enough for commercial applications such as magnet coils.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
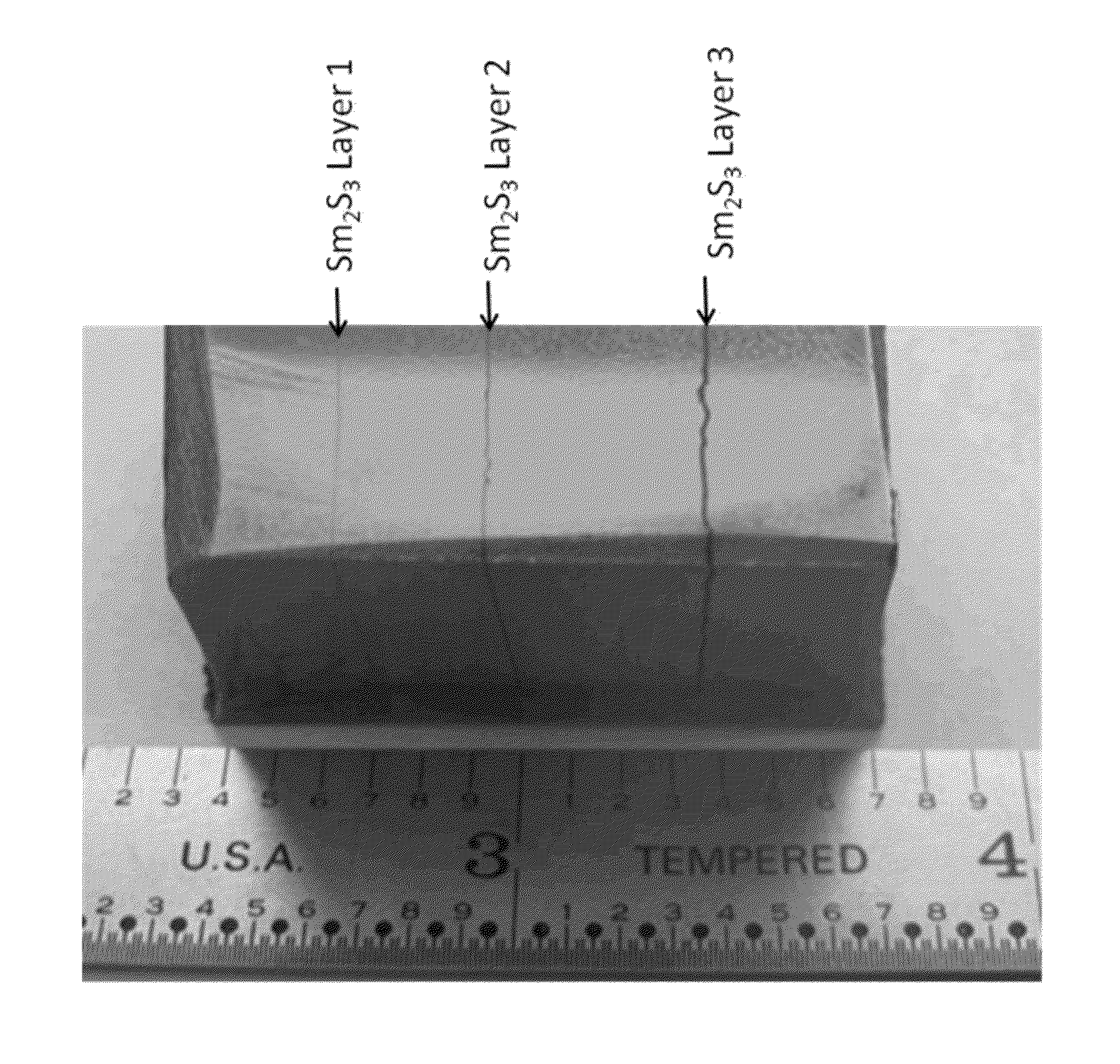
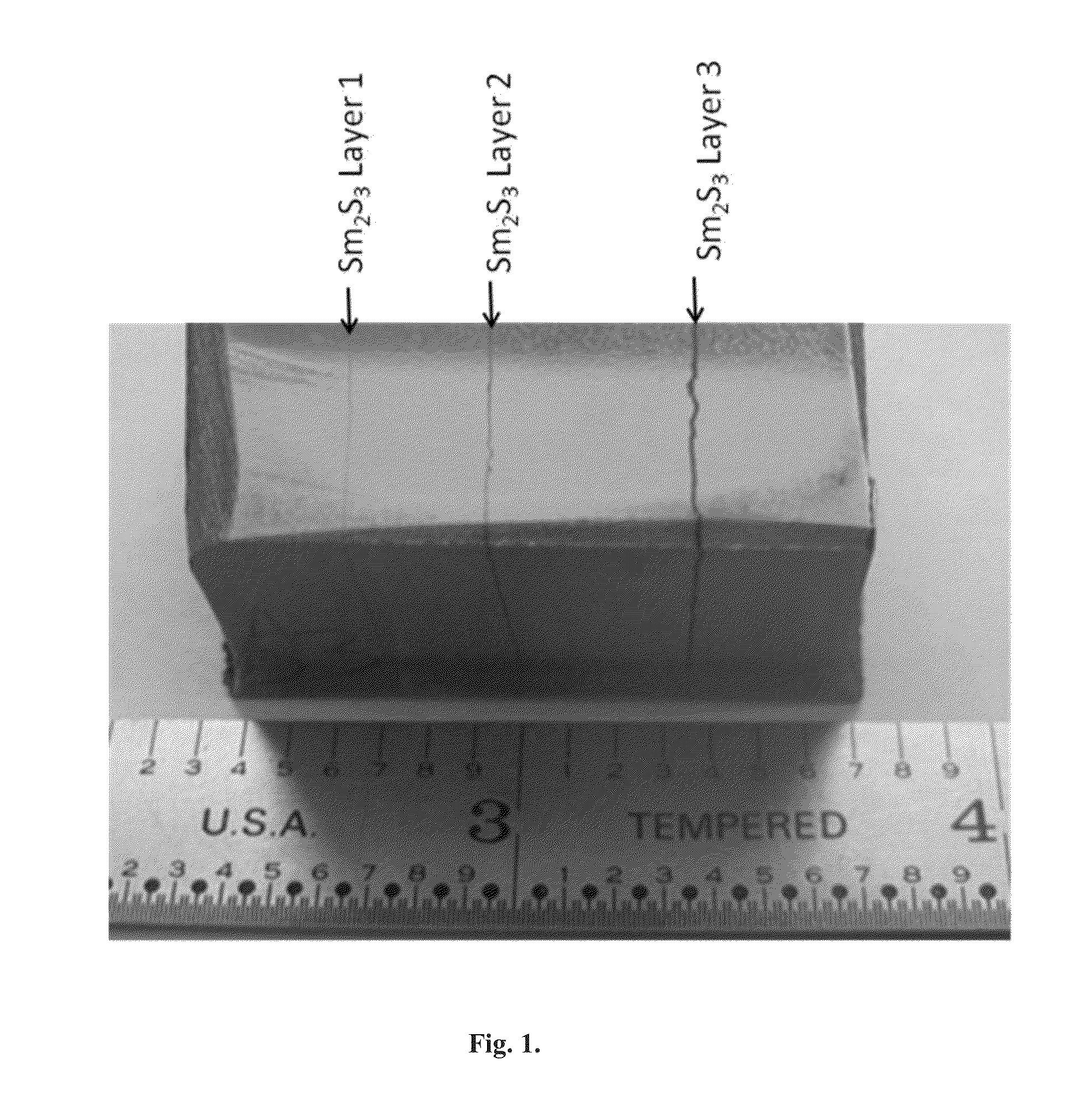
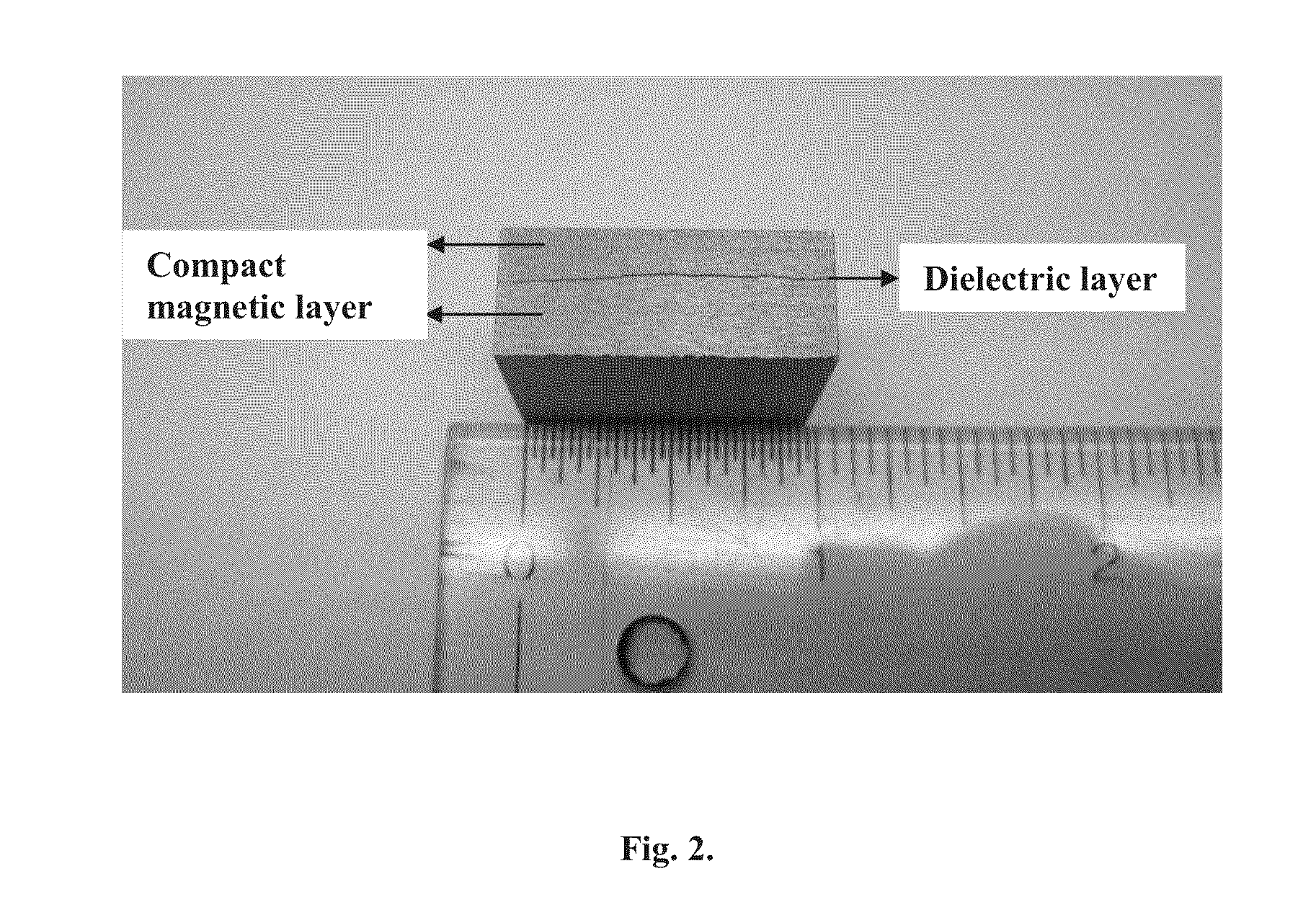
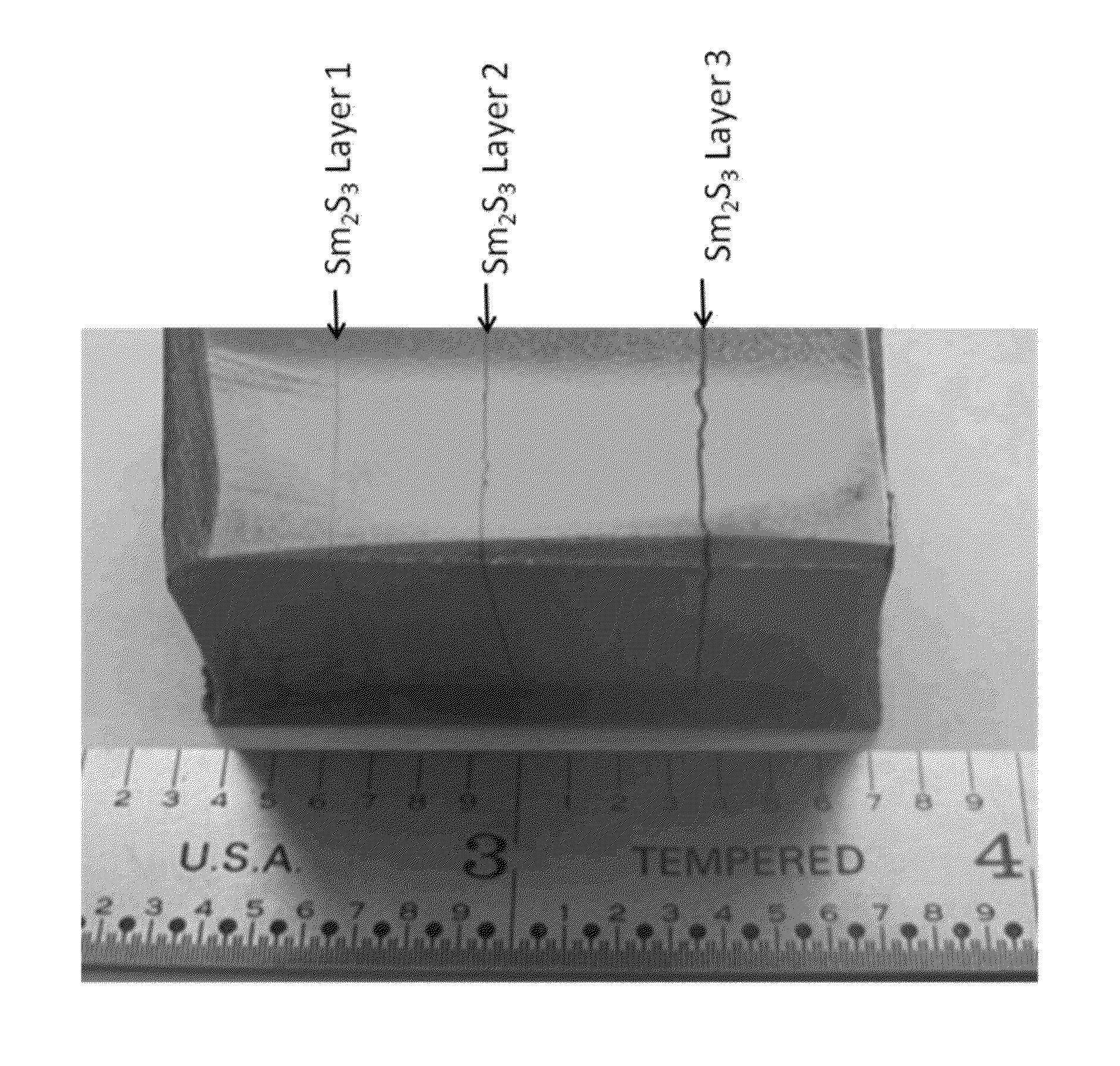
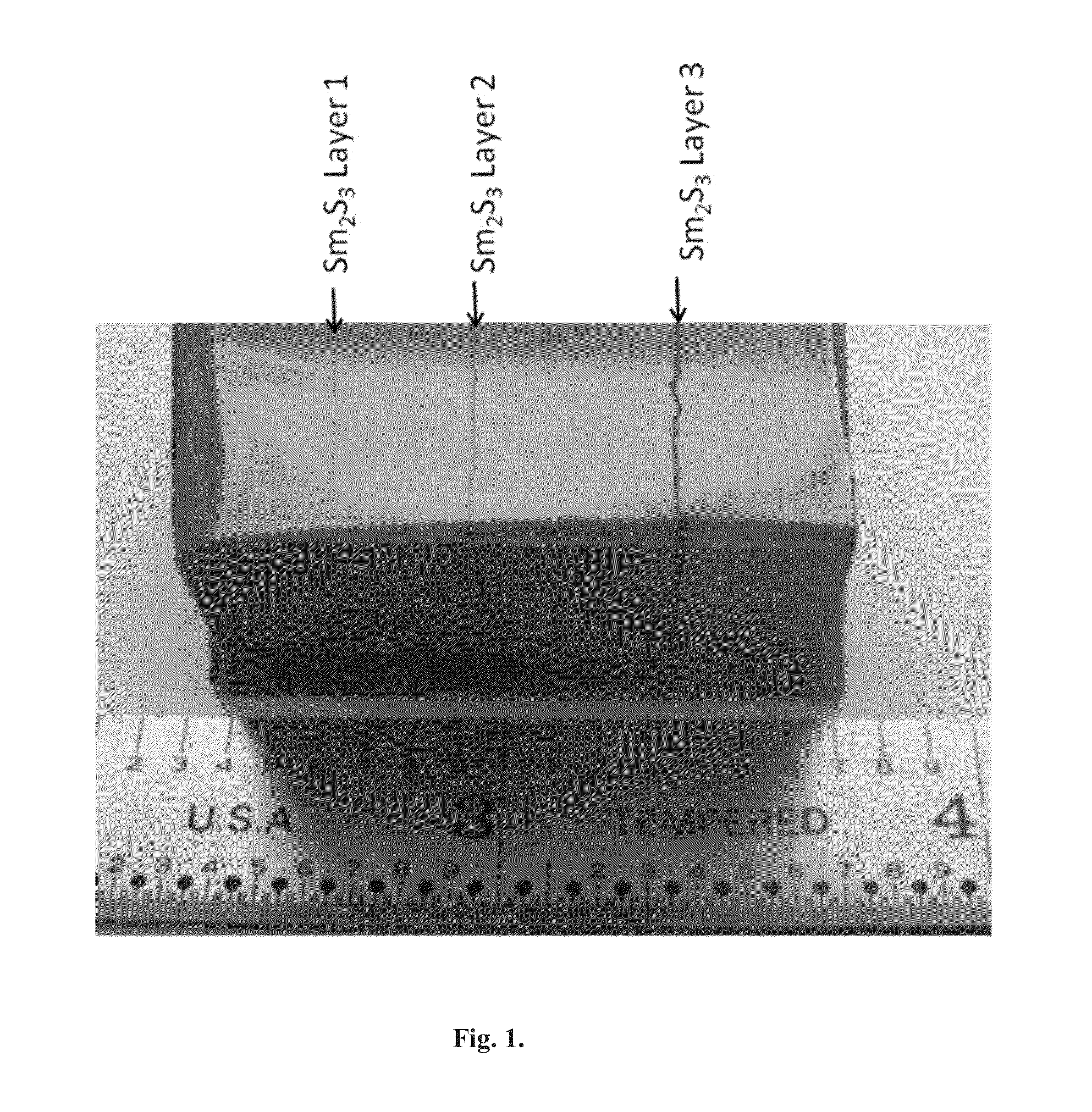
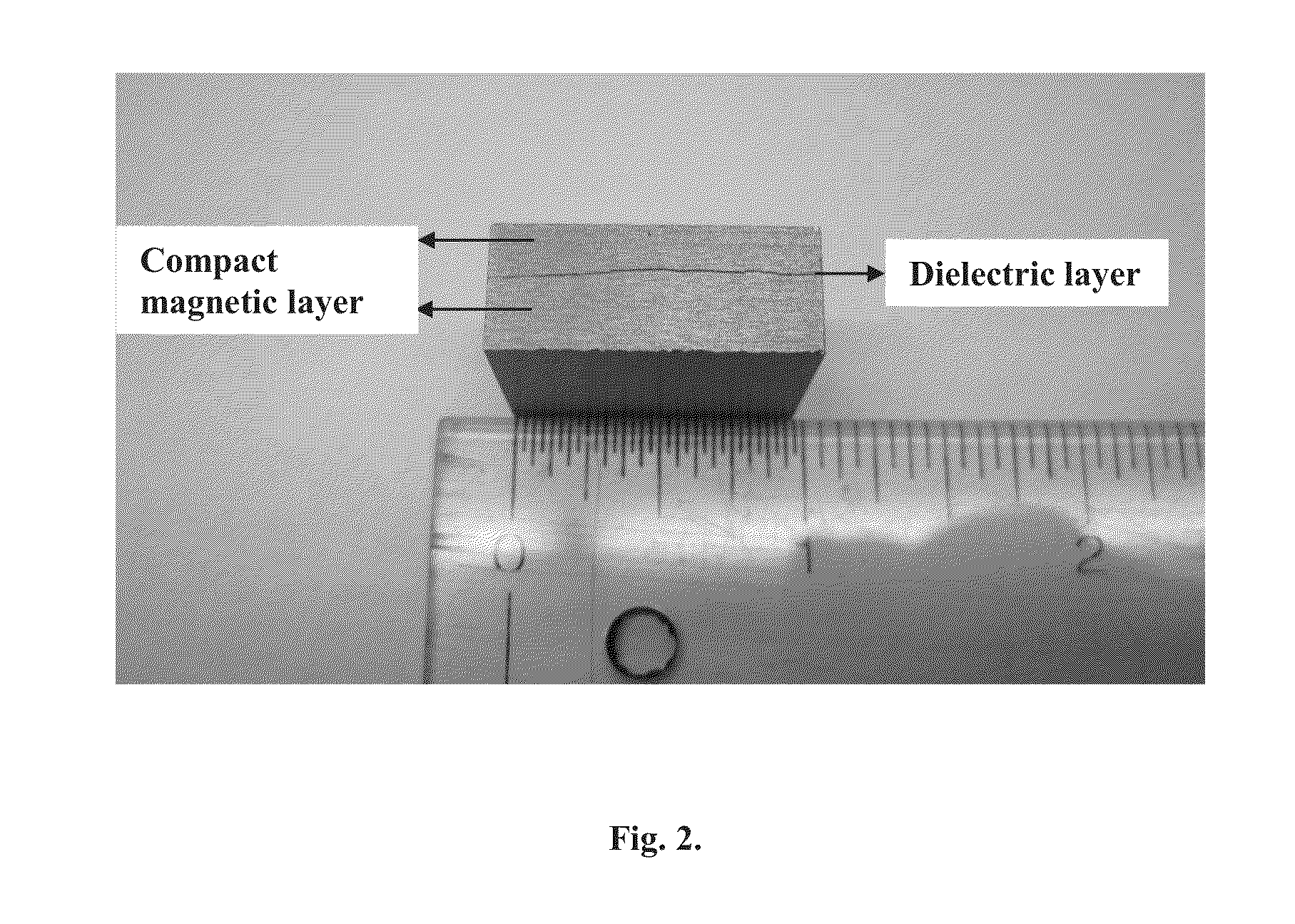
Methods for sequentially laminating rare earth permanent magnets with suflide-based dielectric layer
InactiveUS20130038159A1High resistivityTotal current dropFilm/foil adhesivesPermanent magnetsRare earthDiffusion reaction
Methods of manufacturing laminated, rare earth, permanent magnets with dielectric layers having increased electrical resistivity and improved mechanical strength suitable for use in high performance, rotating machines comprising sequentially laminating permanent magnet layers with transition and / or diffusion reaction layers; wherein the transition and / or diffusion reaction layers surround sulfide-based dielectric layers, thereby avoiding direct contact between the dielectric layers with permanent magnet layers.
Owner:ELECTRON ENERGY CORP
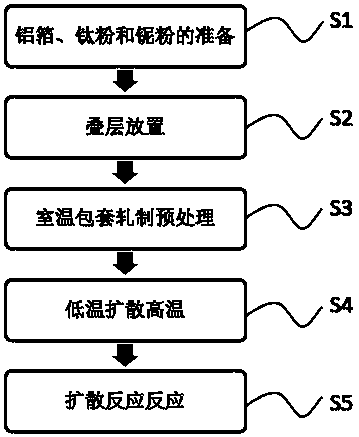
Layered high niobium-titanium-aluminum alloy composite plate and preparation method thereof
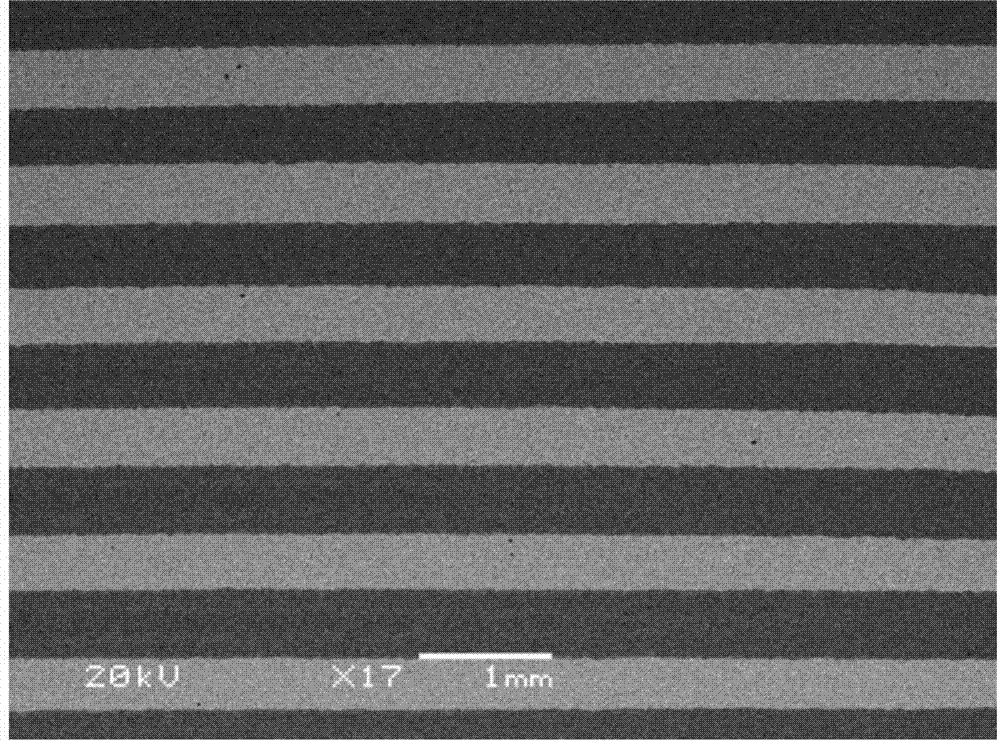
The invention provides a layered high niobium-titanium-aluminum alloy composite plate and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of materials and preparation thereof. A new thought is provided for preparation of a metal-base composite by adopting the laminating hot-pressing composite process of mixed powder of a pure aluminum foil material and titanium powder as well as niobium powder. Titanium-aluminum-based layered materials prepared by adding the niobium element have more excellent mechanical properties such as the high strength and the high toughness. The preparation method comprises the steps that S1, the aluminum foil, the titanium powder and the niobium powder are prepared; S2, laminated storing is conducted; S3, room-temperature pack rolling pretreatment is conducted; S4, a low-temperature diffusion reaction is conducted; and S5, a high-temperature diffusion reaction is conducted. The preparation method of the layered high niobium-titanium-aluminum alloy composite plate can be applied to preparation of the layered high niobium-titanium-aluminum alloy composite plate.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Sequentially laminated, rare earth, permanent magnets with dielectric layers reinforced by transition and/or diffusion reaction layers
InactiveUS20130038164A1High strengthHigh resistivityPermanent magnetsThin magnetic filmsRare earthHigh resistivity
Laminated, rare earth, permanent magnets with one or more dielectric layers, suitable for use in high performance, rotating machines comprising: sequential laminates of permanent magnet layers and dielectric layers separated by transition and / or diffusion reaction layers, where said sequentially laminated magnets indicate increased electrical resistivity with improved mechanical strength.
Owner:ELECTRON ENERGY CORP
Preparation method of TiAl-based laminar composite material plate
InactiveCN102729575AIncreased toughnessImprove plasticityLaminationLamination apparatusAviationDiffusion reaction
The invention discloses a preparation method of a TiAl-based laminar composite material plate, which is used for solving the problems of poor tissue compactness and poor tissue uniformity existing in the conventional TiAl-based material. The method comprises the following steps of: performing ball milling and powder mixing on reinforced bodied and Ti powder, and performing hot pressed sintering, linear cutting and surface pretreatment to obtain a TiB / Ti composite plate on which reinforced bodies are distributed continuously; performing surface treatment on the TiB / Ti composite plate and a pure Al plate, and performing laminating and hot pressing alternatively; and performing thermal treatment to perform a diffusion reaction on the Ti plate and the Al plate to obtain a TiAl-based laminar composite material plate. The TiAl-based laminar composite material plate disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing parts of aviation or space flight engines or wings or shell of ultrahigh-speed flying vehicles and preformed materials formed in a super plasticizing way.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Si power device mounted on a substrate including arrangements to prevent damage to connection layers due to heat treatment
InactiveUS7535092B2Improve reliabilityReduce strainSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal expansionDiffusion reaction
An electronic device includes a pair of members which are connected to each other by a connecting portion layer interposed between connecting portions respectively formed thereon and which have thermal expansion coefficients different from each other. The connection layer is formed by diffusion reaction between the metal layers by which the metal layers are melted only in the vicinity of a contact interface between the layers, the metal layers being formed on the connecting portions with materials different from each other. At least one of the metal layers is formed by plating, thereby the connection layer is formed in a thickness sufficient to absorb differences in thermal expansion coefficients between the pair of members. Since melting temperature of the connection layer after the pair of members have been connected to each other is increased compared with melting temperature of each of the members in the diffusion reaction, the connection layer is prevented from being damaged due to heating treatment performed after the connection has been made, consequently excellent reliability of the electronic device is secured.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Hot isostatic pressing forming method for homogeneous sheath with gradient gradual change structure at connection interface
ActiveCN105170978AReduce the number of processesShorten the overall cycleIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingDiffusion reaction
The invention discloses a hot isostatic pressing forming method for a homogeneous sheath. According to the method, a hot isostatic pressing (HIP) / selective laser melting (SLM) 3D printing compound technology is adopted. The problems that the production period is long, the manufacturing cost is high, the sheath removing process is complicated, the connection interface has diffusion reaction to pollute a manufactured piece and the like when a heterogeneous sheath with a complicated shape is formed by the traditional method is solved by the homogeneous sheath which is formed by the SLM adopted by the invention. Meanwhile, the inner side surface (the surface where the homogeneous sheath is in contact with powder in hot isostatic pressing) of the homogeneous sheath is designed into a gradient porous gradual change structure, so that the tissue at the connection interface has a gradient change structure after hot isostatic pressing, so that the defect that the tissue and performance of an interface between the homogeneous sheath formed by SLM and an HIP compact body are choppy is overcome, and the manufacture piece with excellent mechanical performance is finally formed.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for Forming Aluminide Coating Film on Base Material
There is provided a method for forming an aluminide coating on a surface of a heat resistant superalloy substrate, comprising the steps of: exposing a base metal of the substrate in a selective area; forming a aluminum or an aluminum alloy film on the exposed base metal, by a non-aqueous electroplating; and conducting a heat treatment to the substrate on which the film is formed, in order to make a diffusion reaction between an aluminum component in the film and the base metal, and form the aluminide coating, wherein: there is used, as a plating liquid, a non-aqueous plating liquid containing a halide of the metal to be plated and an organic compound which forms an ion pair with the metal halide; and the electroplating is conducted by immersing the selective area into the plating liquid through the use of predetermined means for shielding the plating liquid from the atmosphere.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Surface plasma cladding method of metal turbine runner
InactiveCN102230176ALow priceHigh hardnessMetallic material coating processesMolten stateCarbide coating
The invention relates to a surface plasma cladding method of a metal turbine runner. The problems of turbine runner blades such as surface hardness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, shock resistance and prolonged service life can be effectively solved. The surface plasma cladding method comprises the following steps: a worktable of plasma cladding wear-resistant equipment is started to run so that a plasma torch moves to the position above cladding positions of the turbine runner blades; protective argon and a power supply for the plasma torch are started for arc striking to enter a plasma beam cladding process; under a direct current (DC) plasma beam at high temperature of 10,000-16,000 DEG C, iron-nickel alloy powder is synchronously transferred into the plasma beam of the plasma torch, and then the powder is rapidly heated into a molten or semi-molten state so as to perform mixed diffusion reaction with metal in a molten pool; as the plasma beam moves, the alloy molten pool is rapidly frozen into hard alloy coatings with thickness of 1-10mm; and after completion of cladding operation, grinding or polishing the hard alloy coatings on the surfaces of the blades. The surface plasma cladding method is simple; and by utilizing the method, the blades have the advantages of high hardness, high compactness, wear resistance and long service life.
Owner:王建升
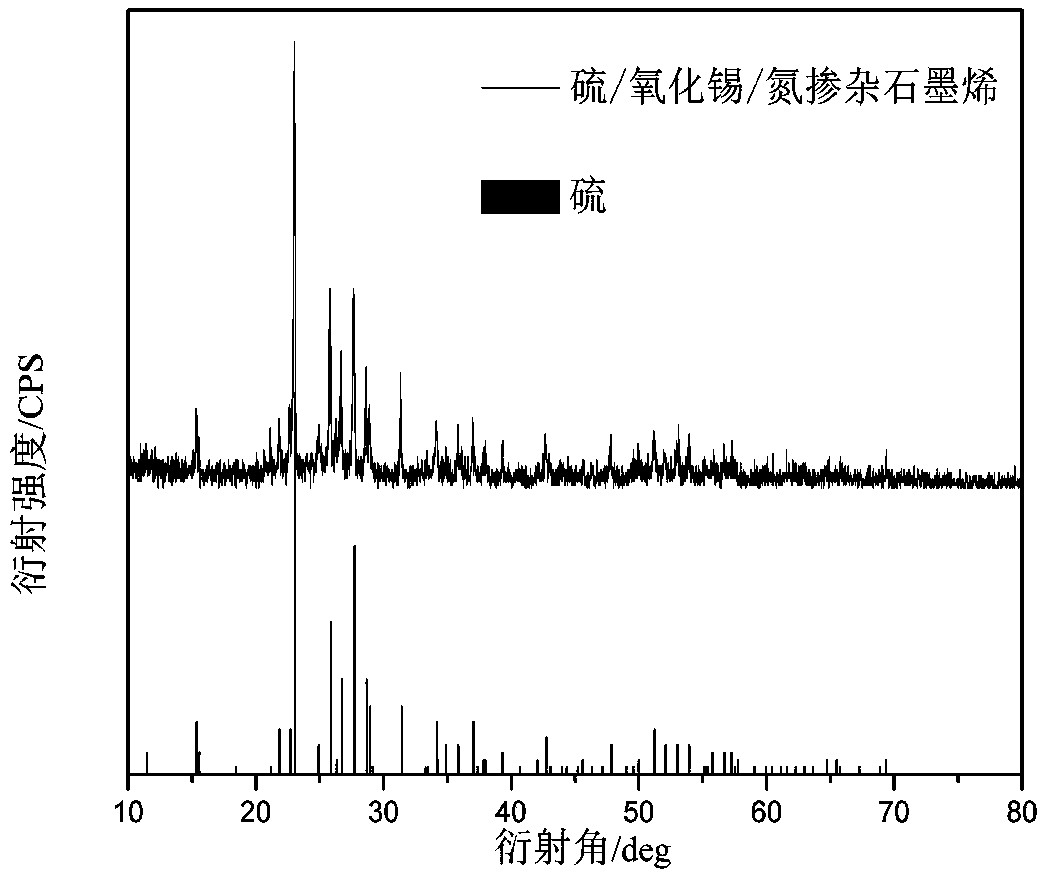
Sulfur/tin oxide/graphene battery cathode material, preparation method and lithium sulfur battery
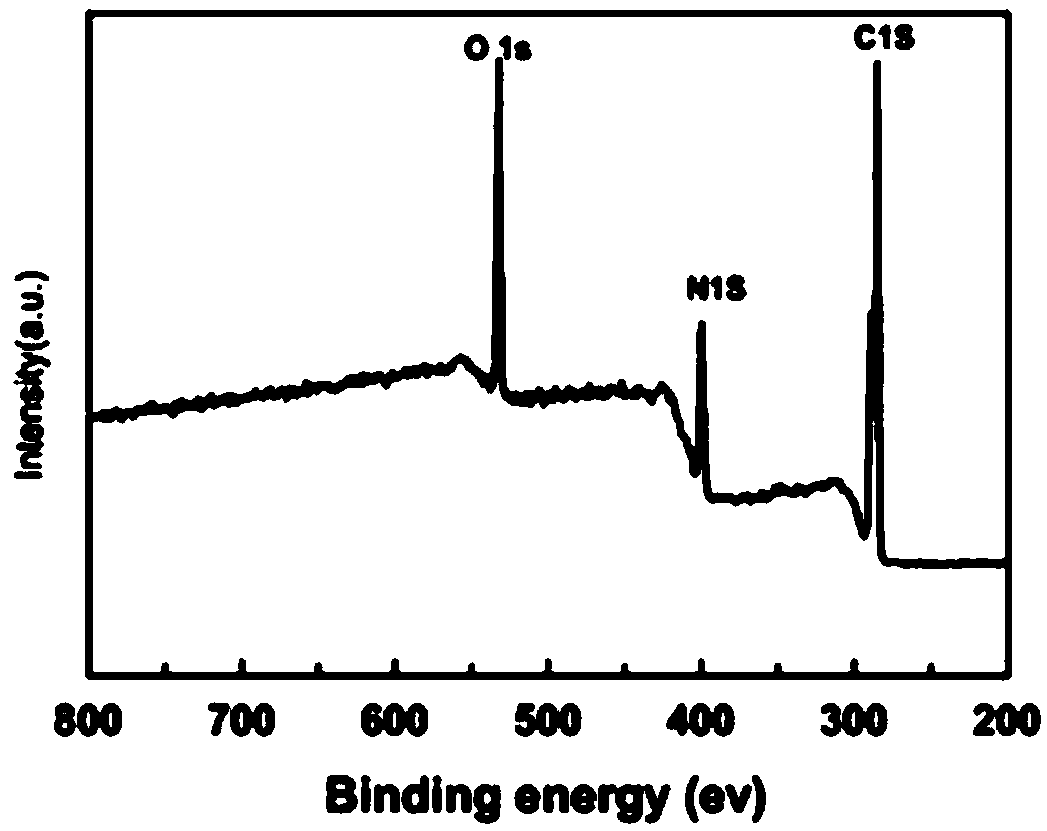
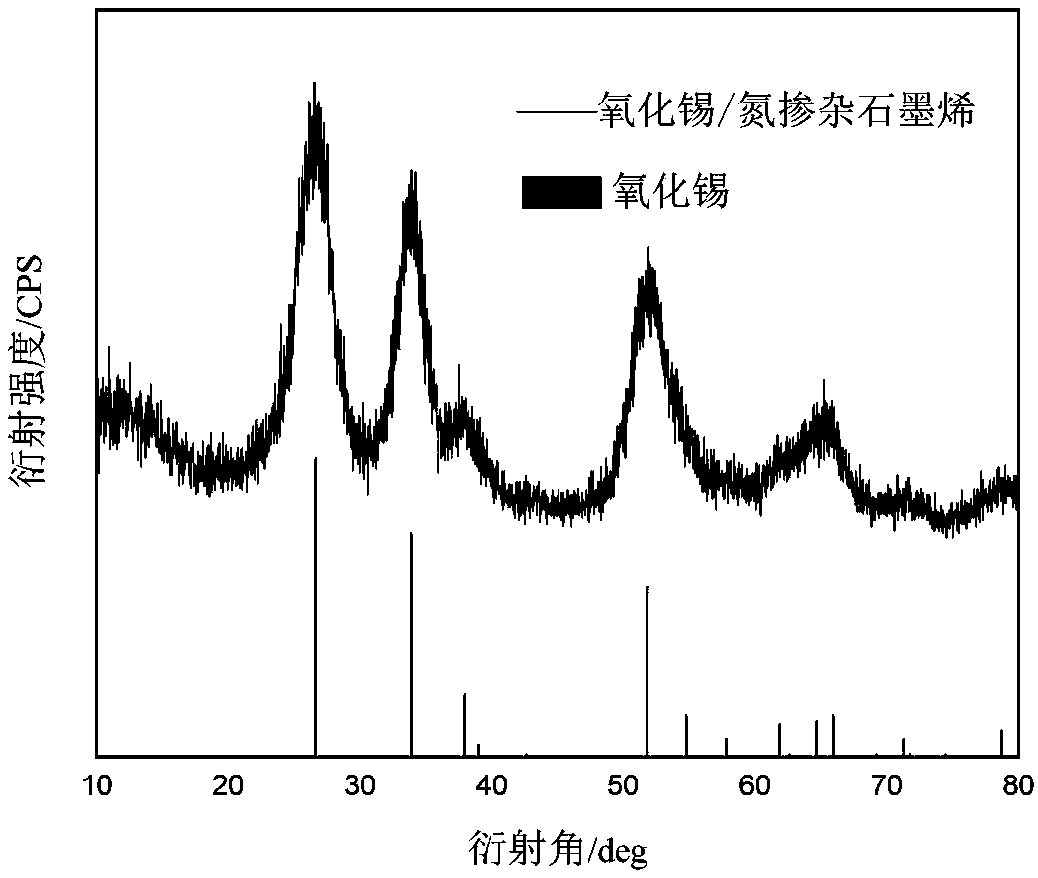
InactiveCN109119616ALarge specific surface areaIncrease loadMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesNitrogen doped grapheneTin
The invention relates to the technical field of nanometer materials, in particular to a sulfur / tin oxide / graphene battery cathode material, a preparation method and a lithium sulfur battery. The invention discloses a preparation method of a sulfur / tin oxide / graphene battery cathode material, comprising the following steps: Step 1, nitrogen doped graphene and a tin salt solution are hydrothermallyreacted to obtain a graphene-tin oxide nano-composite material; and Step 2: the graphene-tin oxide nano-composite material and elemental sulfur are mixed to obtain a mixture, and a vacuum melting diffusion reaction is carried out on the mixture to obtain a sulfur / tin oxide / graphene battery cathode material. The invention also discloses a sulfur / tin oxide / graphene battery cathode material preparedby the method and a lithium sulfur battery thereof. The invention solves the technical problems that the elemental sulfur in the prior art cannot be effectively utilized in the cathode material of thelithium sulfur battery, thereby leading to short service life, and poor conductivity, cycle stability and safety performance of the lithium sulfur battery.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Supersaturated brazing filler metal and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105345304AIncrease contentReduce contentWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaDiffusion reactionThermal treatment
The invention discloses supersaturated brazing filler metal. The supersaturated brazing filler metal comprises base brazing filler metal and a metal electroforming layer covering the base brazing filler metal, and a transition layer formed by diffusion reaction between solid solutions in the base brazing filler metal and the metal electroforming layer is arranged between the base brazing filler metal and the metal electroforming layer. A preparation method comprises the steps of placing raw metal material of the base brazing filler metal into a smelting furnace and prefabricating the raw metal material to form the base brazing filler metal through casting, annealing, extruding and rolling or drawing formation; electroforming the metal layer on the surface of the base brazing filler metal through the electroforming process, placing the base brazing filler metal into a vacuum drying oven of 25-250 DEG C for permeation for 0.5-10 minutes after the electroforming process is completed, placing the permeated base brazing filler metal into a thermal treatment furnace of 20-230 DEG C for diffusion for 2-30 hours and finally cooling the base brazing filler metal naturally in the furnace so as to obtain the supersaturated brazing filler metal. The supersaturated brazing filler metal is low in melting temperature and good in wettability and can be applied to the medium-temperature brazing field after being machined into strip shapes or thread shapes or rod shapes. The preparation method provides a new technological approach for manufacturing and producing of the brazing filler metal.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Preparation method of 2:17 type rare earth-iron-nitrogen composite magnetic material for high frequency use
ActiveCN110047637AImprove permeabilityReduce eddy current lossTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusRare earthDehydrogenation
The invention discloses a preparation method of 2:17 type rare earth-iron-nitrogen composite magnetic material for high frequency use. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) carryingout reduction-diffusion reaction by using rare earth oxide, carbonyl iron powder and / or iron oxide and reductant as raw materials; performing hydrogen absorption and dehydrogenation; and carrying outnitrogen absorption reaction to obtain 2:17 type rare earth-iron-nitrogen magnetic powder; 2) mixing the2:17 type rare earth-iron-nitrogen magnetic powder, a self-curing resin, an auxiliary agent anda solvent to prepare magnetic slurry; casting the magnetic slurry into a composite magnetic sheet; and pressing and curing the composite magnetic sheet by adopting a flat vulcanizer to obtain the product. The 2:17 type rare earth-iron-nitrogen composite magnetic material is suitable for high-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding materials such as electronic devices and electronic equipment with functions of 1 GHz and above, and has the characteristics of high permeability and low eddy current loss.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Reaction diffusion connection method of ceramic composite material and metal
The invention relates to a reaction diffusion connection method of ceramic composite material and metal, which belongs to the technical field of connection of ceramic material and metal material, and is characterized in that corresponding mixed powder is added between the ceramic composite material and the metal, combustion reaction heat is generated under the activation of an electric field, and the ceramic composite material and the metal material are locally smelted respectively and generate diffusion reaction to form connection. The combustion synthesis of the metal powder forms an intermetallic compound with the performance between ceramic and metal, thus alleviating the problem of mismatching between the metal and the ceramic; and the action of the electric field causes elements between interfaces to diffuse mutually, thus being beneficial to improving the strength of the connecting interfaces. By combustion heat release, the method realizes the synthesis of an intermediate layer and the connection of metal and ceramic simultaneously, and has the characteristics of being low in energy consumption and high in connection strength.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Reaction diffusion connecting method of superhard material aluminum magnesium boron-titanium diboride and metal
InactiveCN103342575AImprove mechanical propertiesIncreased shear strengthSuperhard materialMetallic materials
The invention discloses a reaction diffusion connecting method of superhard material aluminum magnesium boron-titanium diboride and metal, and belongs to the technical field of connection of the superhard material and a metal material. The reaction diffusion connecting method is characterized in that the surface of high-temperature metal Ta, Mo or Nb is pressed by mechanical pressure to form a corresponding metal powder layer; a lot of joule heat is generated under an electric field activation effect, so as to achieve connection of diffusion reaction with the metal material when an AlMgB14-TiB2 composite material is synthetized. The method has the advantages that mutual diffusion of elements between interfaces is facilitated by the effect of the electric field; improvement of the strength of connecting the interfaces is facilitated. More importantly, synthesis of the superhard material and connection with the metal material are achieved in one step; the method has the characteristics of high preparation efficiency and high energy utilization rate.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Process for producing rare-earth-iron-boron permanent magnet alloy powder by reduction diffusion
InactiveCN1424164ASolve the problem of damaging the magnetic properties of powder particlesEliminate the extraction processDiffusion methodsIron powder
A process for preparing permanent-magnet RE-Fe-B alloy powder by reduction-diffusion method includes such steps as choosing raw materials, pretreating, proportioning, mixing RE oxide, Fe powder, Ca, CaH2, NdCl3 and CaCl3, thermal reducing and diffusion alloying at 820-960 deg.C, chemical separating, dewatering, drying and preparing anisotropic RG-Fe-B magnet.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
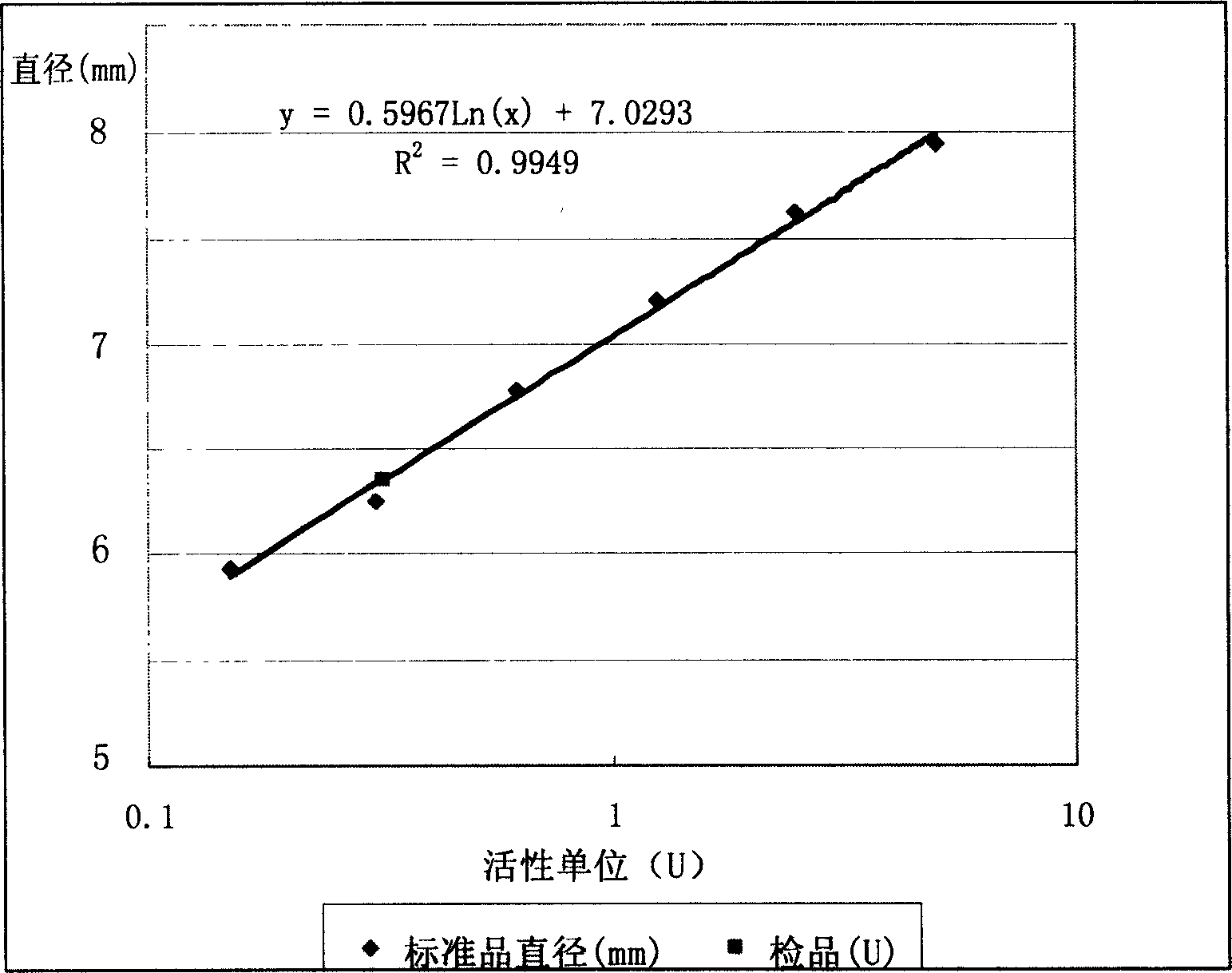
Fibrinogen plate assay for detection of thrombin, thrombin-like enzyme and thrombin inhibitor
InactiveCN1763219AOt affected by turbidityUndisturbedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingTurbidityBiology
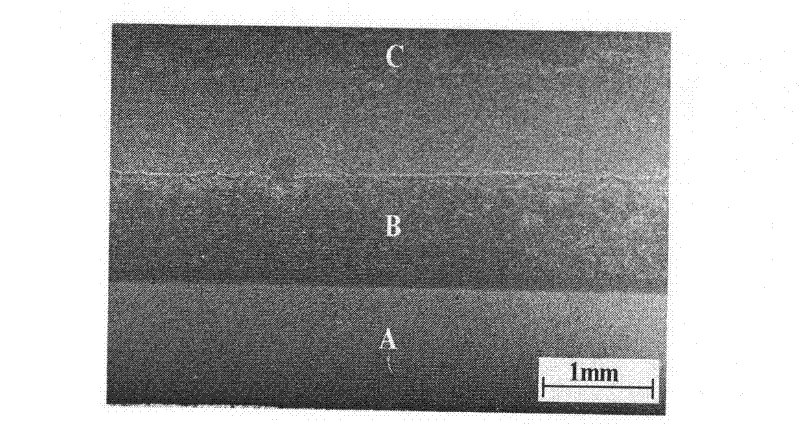
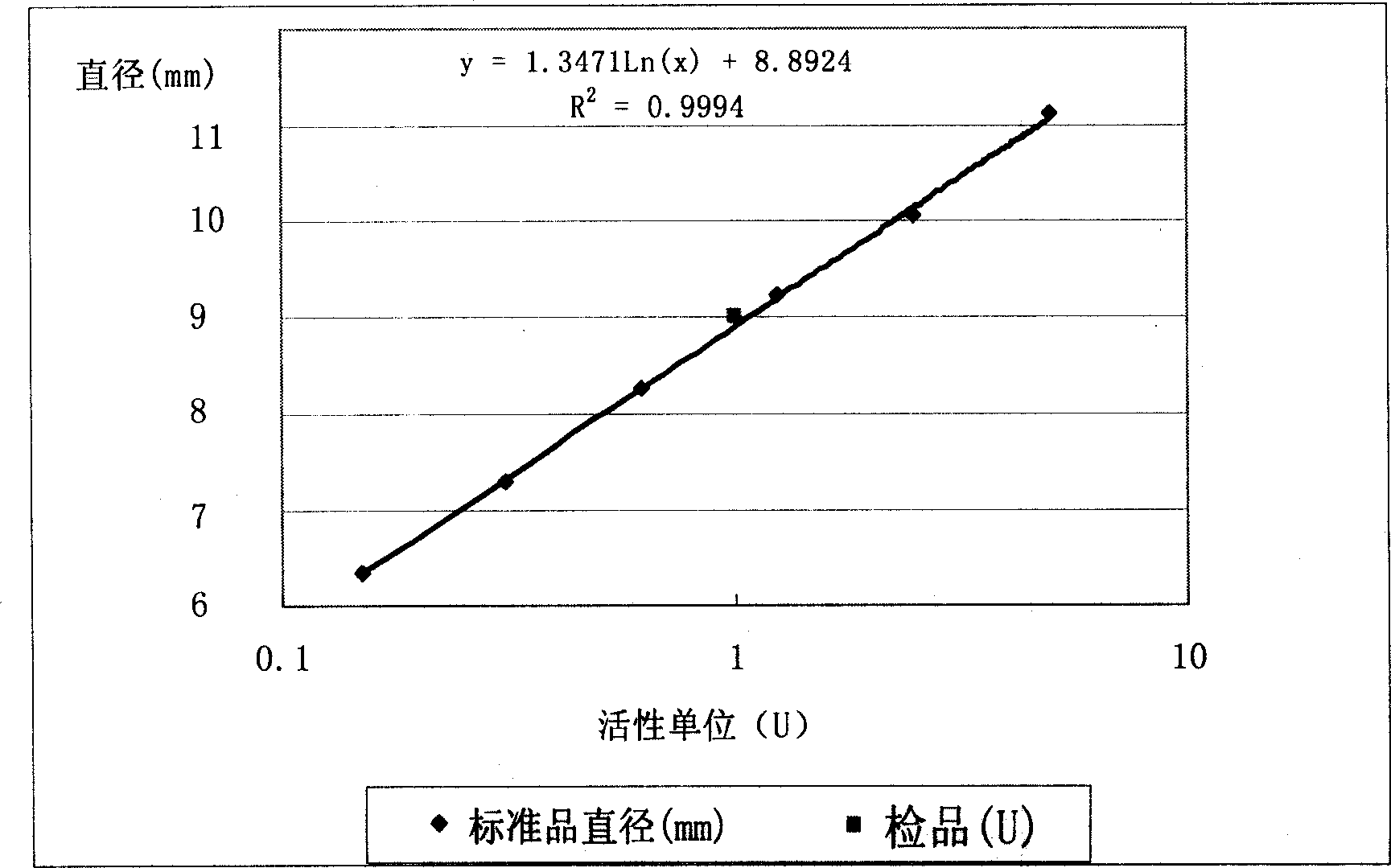
The fibrinogen plate method for detecting thrombase, batroxobin and thrombase inhibitor includes preparing fibrinogen plate with agarose and fibrinogen and quantitative detection via the diffusion reaction of standard sample and detected sample on the plate. The detection method of the present invention has simple operation, high sensitivity, being intuitive and stable, no interference of the turbidity and color of the detected sample and low cost. The detection method may be realized simply in lab with thermotank.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Laser preparation device and method for in-situ synthesis of TiC-reinforced titanium-based composite material
ActiveCN108465814AShort cycleImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyTitanium matrix compositesSelective laser melting
The invention relates to a laser preparation device and method for in-situ synthesis of a TiC-reinforced titanium-based composite material. The laser preparation device comprises a numerical control system, an atmosphere control system, a powder feeding and laying system, a laser system and a forming chamber. A scraper for laying titanium alloy spherical powder is arranged at the lower end of thepowder feeding and laying system; the device combines the selective laser melting and laser chemical vapor deposition technology for pyrolysis of carbon source gas by the high energy and high temperature characteristics of a laser beam, carbon of the pyrolysis product reacts with matrix titanium in situ to form a uniformly dispersed TiC-reinforced phase which is compounded with matrix titanium inthe melting-solidification process, and the TiC-reinforced titanium-based composite material is finally prepared by SLM layer-by-layer operation. The interface between the in-situ synthesized TiC-reinforced phase and the matrix titanium is clean, and the problems of poor interface bonding strength and reinforced-phase agglomeration of existing composite materials can be effectively solved. Throughgaseous carbon source diffusion-reaction, the in-situ synthesized TiC-reinforced titanium-based composite material is controllable in structure and the mechanical properties are significantly improved.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com