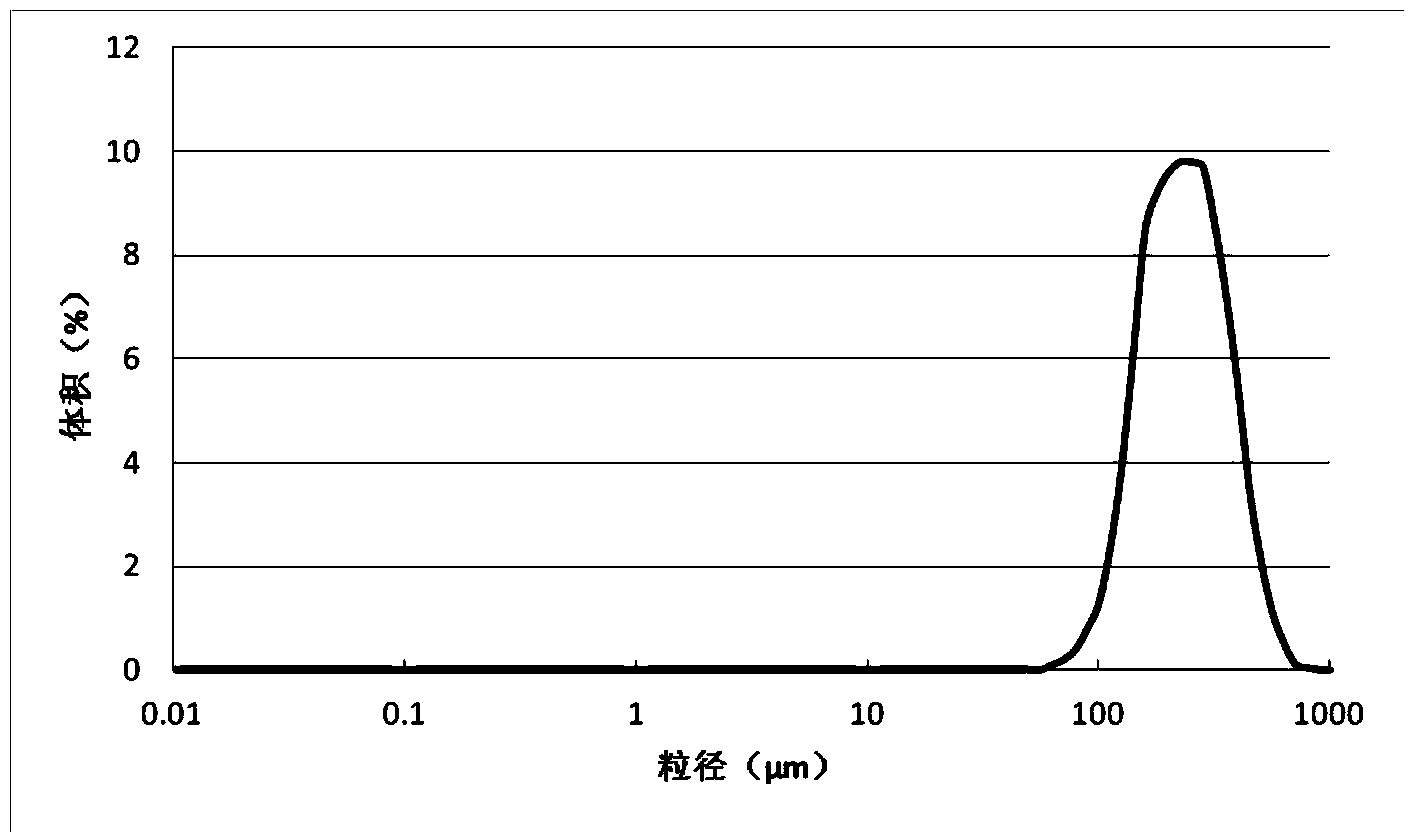
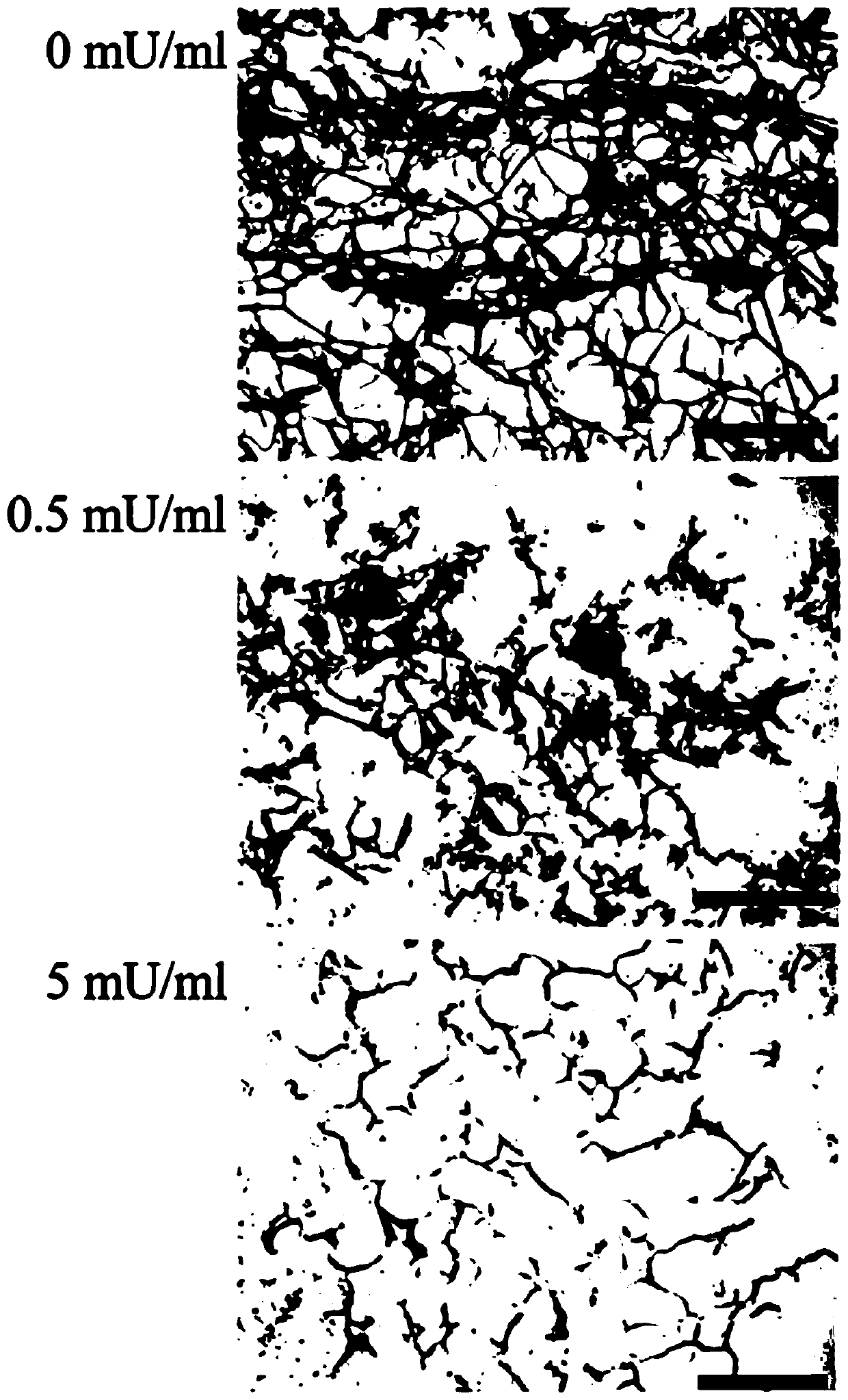
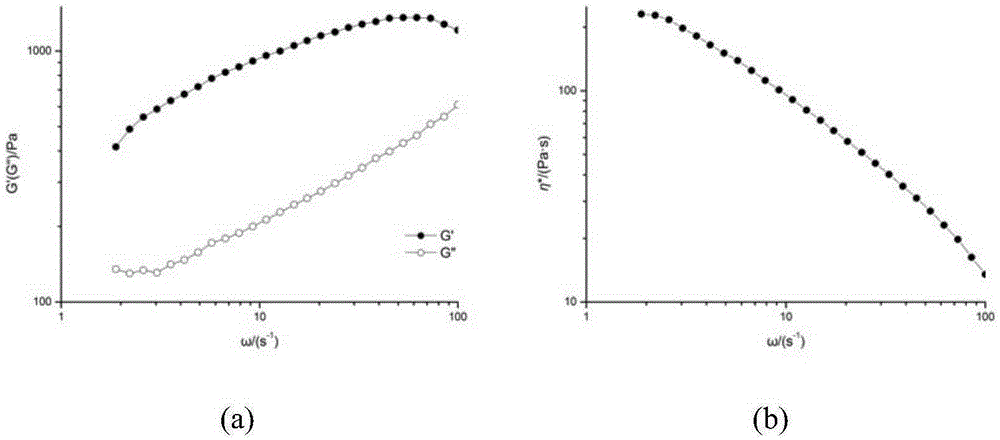
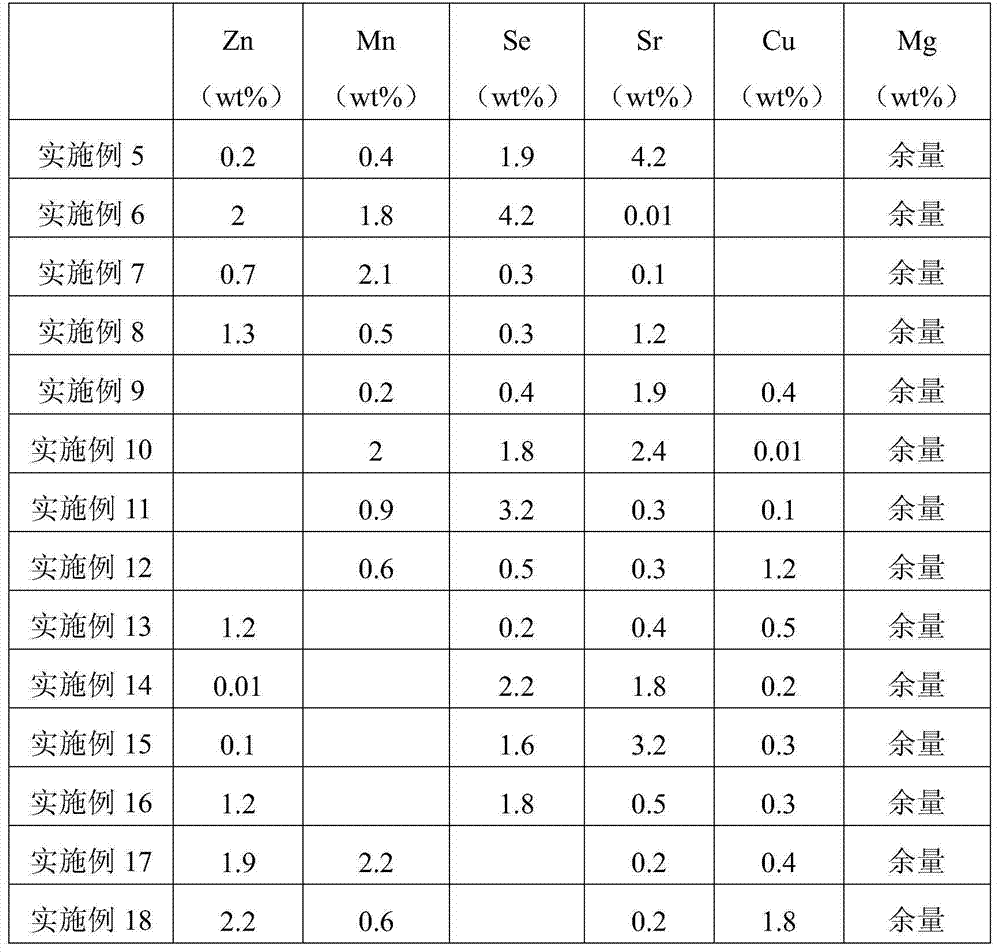
Patents
Literature
97 results about "In vivo degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
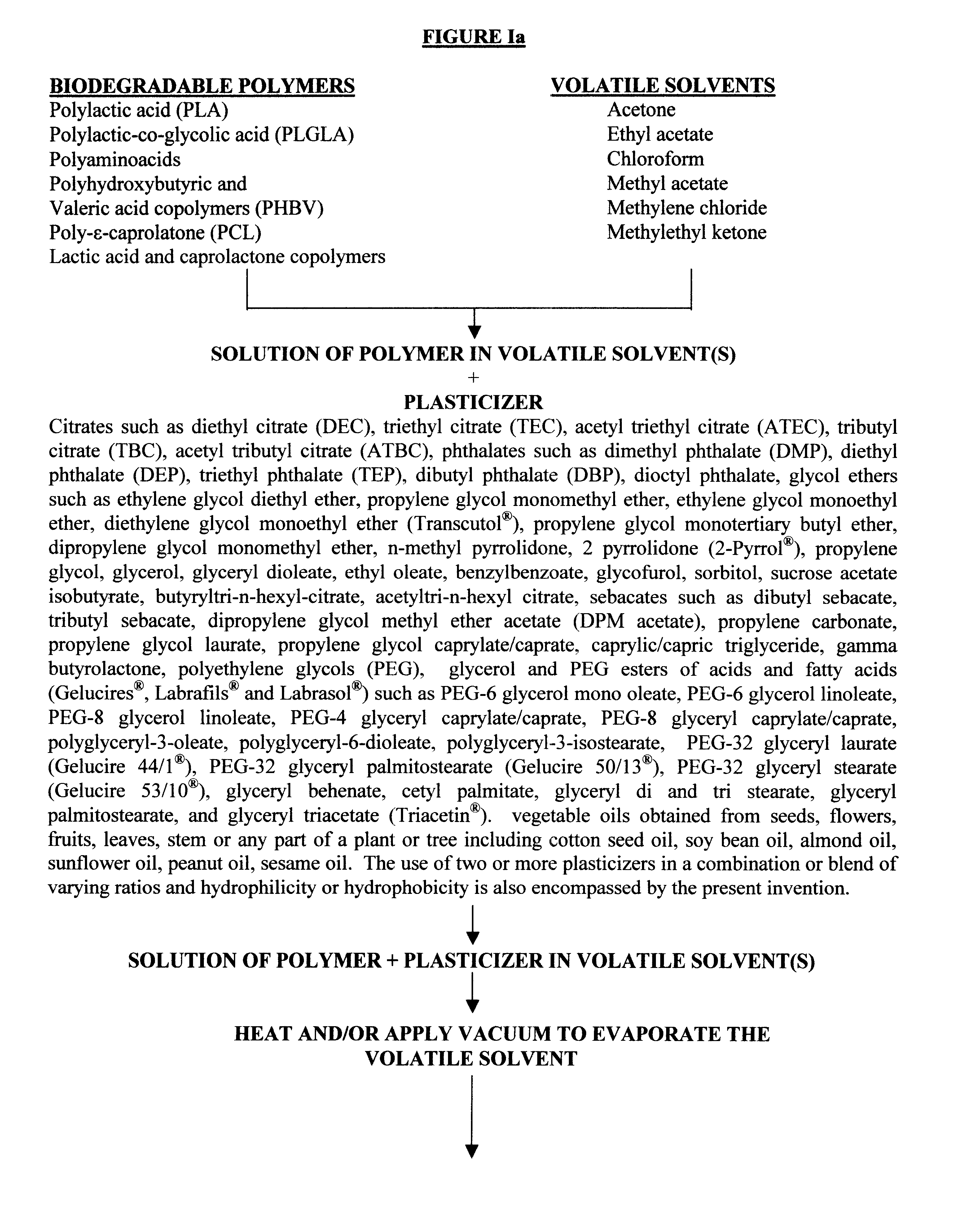
Biodegradable vehicle and filler
InactiveUS6432438B1Improve stabilityWell mixedOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolymer sciencePlasticizer
A biodegradable vehicle and filler (referred to in this invention as biodegradable vehicle), which can be mixed with one or more biologically active substances (BAS), or can be used as a biodegradable filler to fill in cavities or body tissues in animals, birds and humans. The consistency and rheology, hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity, and in vivo degradation rates of the biodegradable vehicle is controlled by modulating the molecular weight of polymers and copolymers, concentration of plasticizers, ratios of two or more plasticizer in the blends, types of polymers and copolymers, copolymer ratios, and ratios of blends of polymers with different molecular weights or different copolymers. The biodegradable vehicle is mixed with one or more BAS (which is separately stored away from the biodegradable vehicle in an appropriate container) just prior to use. Mixing of the BAS with the biodegradable vehicle can be accomplished by simply stirring the mixture with a stirring device, or by triturating the mixture or employing an ointment mill or a suitable device or apparatus or equipment that can be used for blending / mixing. Alternatively, a device, which resembles two syringes, attached together with a removable partition or a valve assembly can also be used to uniformly mix the BAS with the biodegradable vehicle. The mixing is performed in order to dissolve or uniformly suspend the BAS particles in the biodegradable vehicle. Modulating the polymer to plasticizer ratio, polymer molecular weight, copolymer ratio, and hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of the plasticizer controls the release of the BAS from the biodegradable vehicle.
Owner:SHUKLA ATUL J
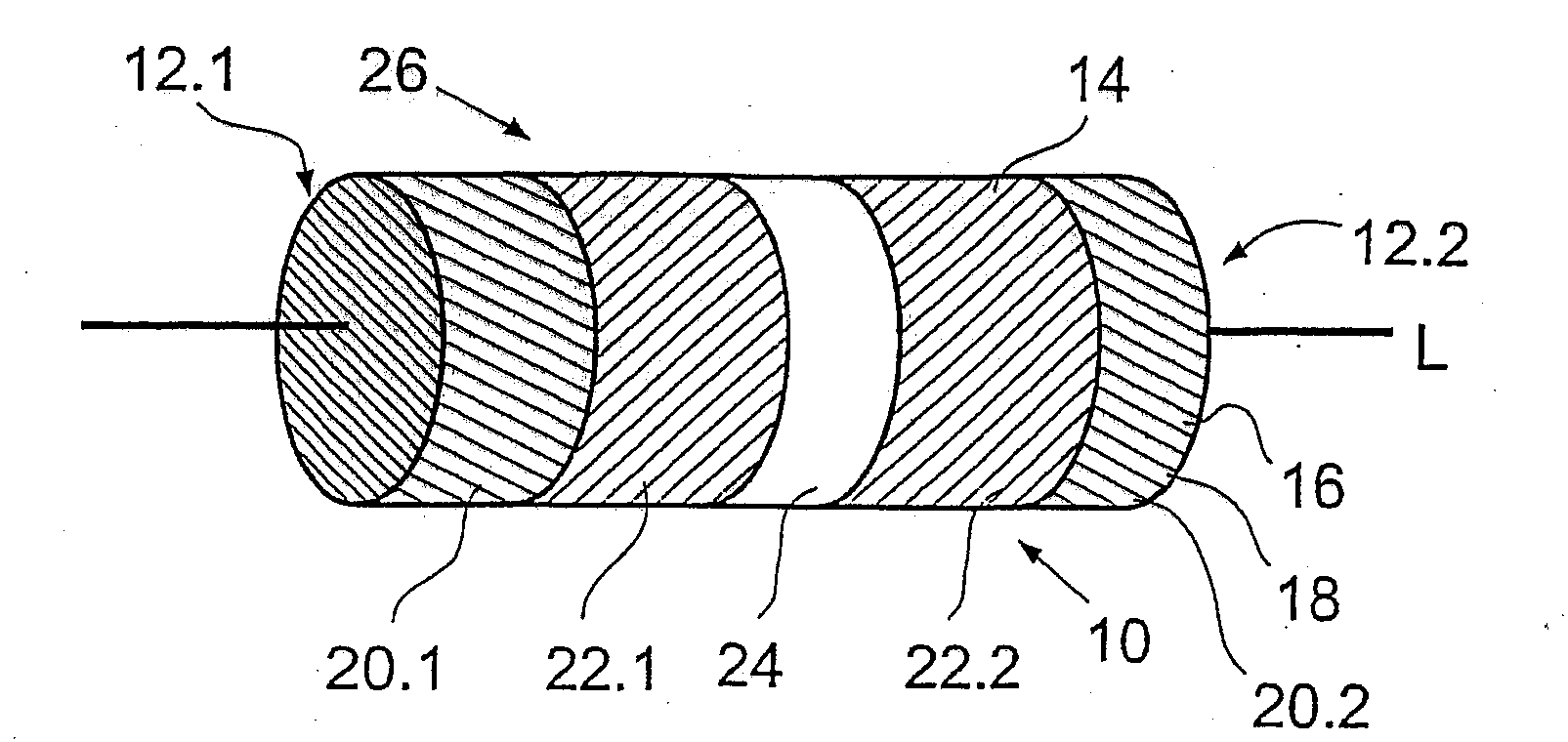
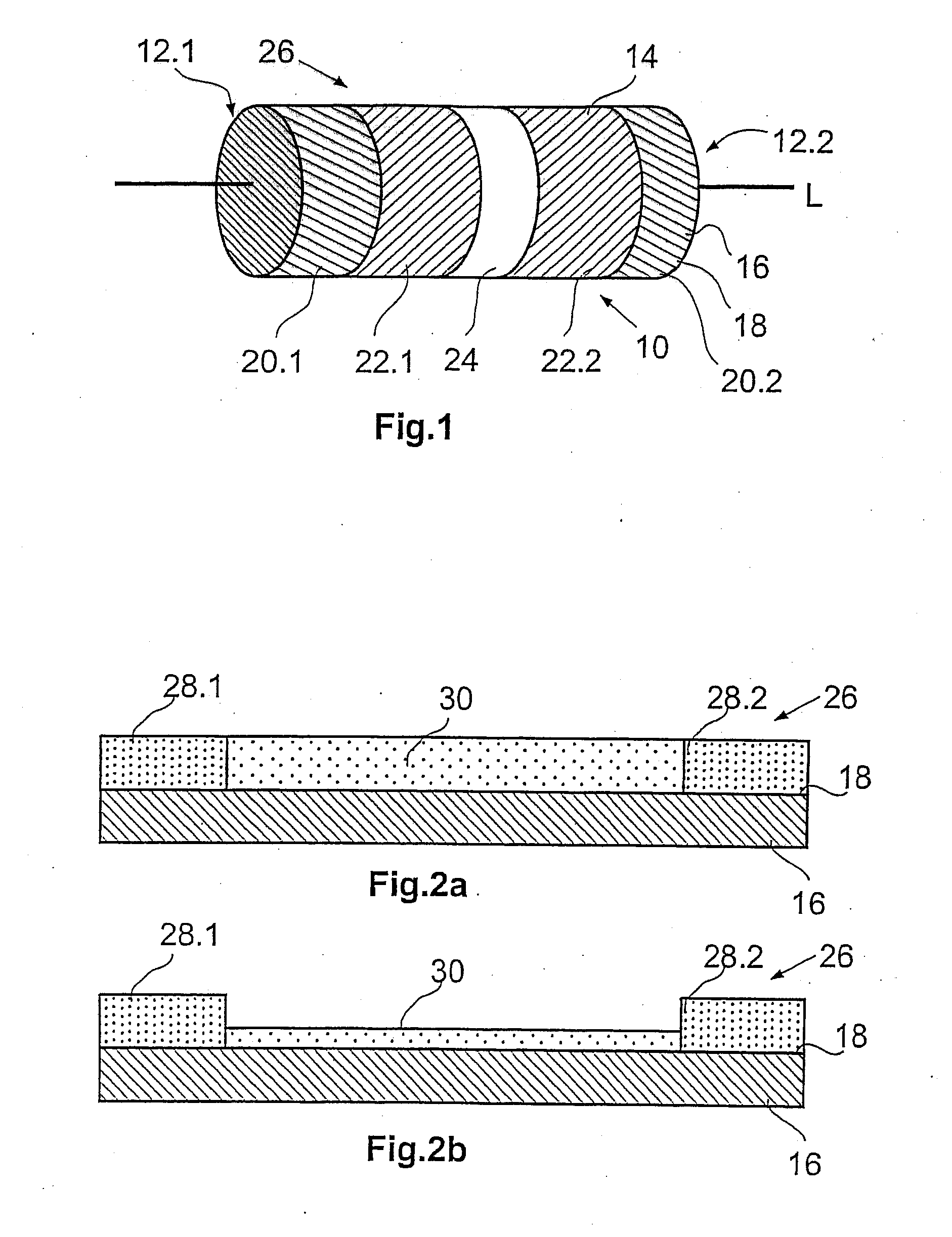
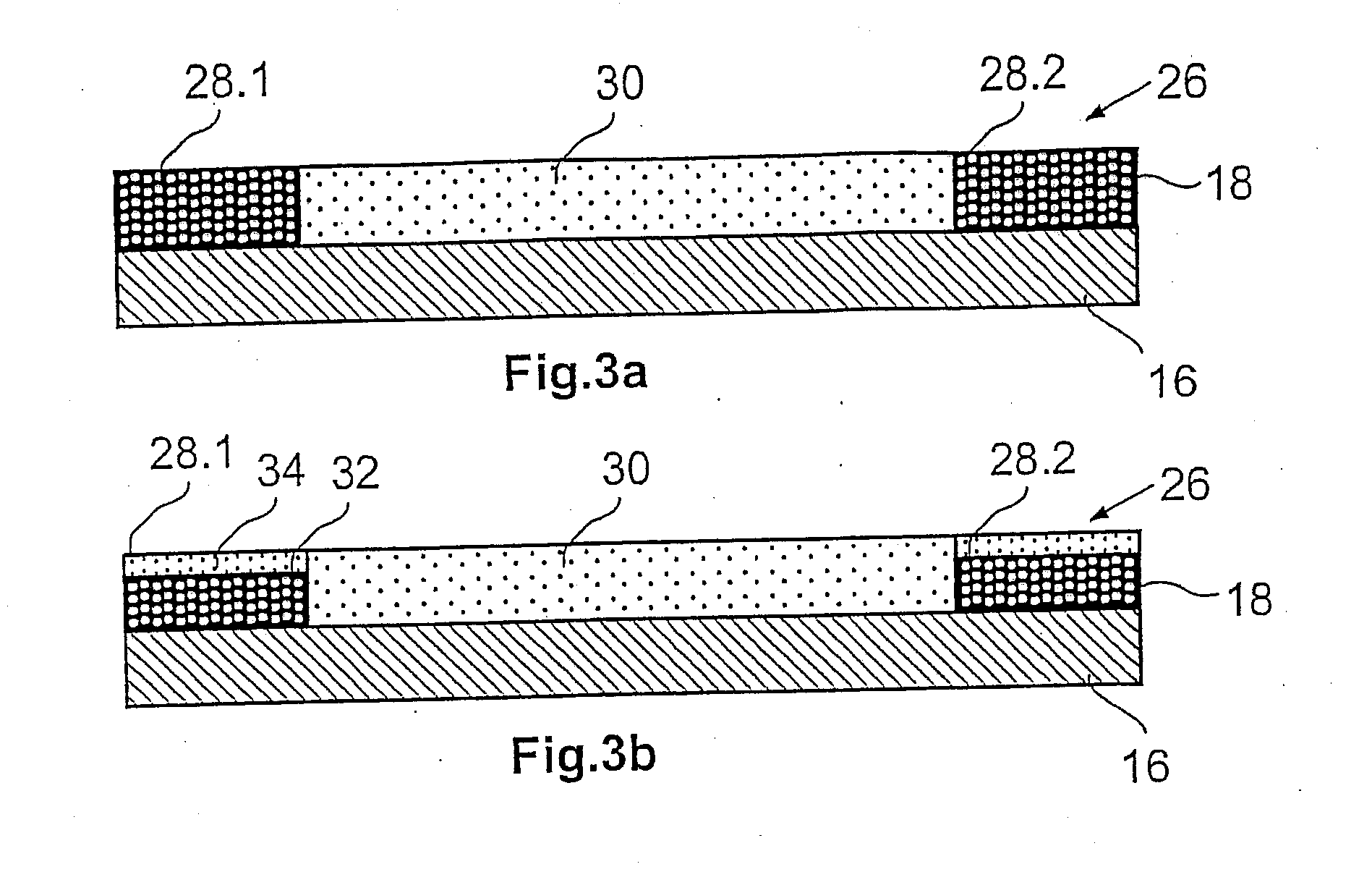
Control of the degradation of biodegradable implants using a coating
The invention relates to an endovascular implant, which is at least largely biodegradable and whose in vivo degradation can be controlled. To achieve this, the implant comprises a tubular base body, open on its end faces and consisting of at least one biodegradable material, said base body having an in vivo, location-dependent first degradation characteristic D1(x), in addition to a coating that covers the base body completely or in sections and consists of a biodegradable material, said coating having an in vivo, location-dependent second degradation characteristic D2(x). According to the invention, a location-dependent cumulative degradation characteristic D(x) in one location (x) is made up of the sum of the respective degradation characteristics D1(x) and D2(x) in said location (x) and the location-dependent cumulative degradation characteristic D(x) is predetermined by a variation of the second degradation characteristic D2(x) in such a way that the degradation in the given location (x) of the implant takes place over a predeterminable time period at a predeterminable degradation rate.
Owner:BIOTRONIK VI PATENT
Injectable crosslinked hyaluronic acid gel and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an injectable crosslinked hyaluronic acid gel and a preparation method thereof. The injectable crosslinked hyaluronic acid gel is prepared by blending hyaluronic acid gel granules and chlorinated sodium phosphate physiological buffer solution; the hyaluronic acid gel granules are prepared by comprising the steps of crosslinking treatment, emulsion crosslinking granulation, purification and drying and swelling, filling and sterilization technologies. The hyaluronic acid gel granules are uniform in granule size, the residual of the crosslinking agent is less than 0.2ppm, the injection pushing is proper, and the in-vivo degradation time can last more than 8-12 months. The implant has an excellent esthetical restoration effect, is applicable to being injected to and subcutaneous dermis deep layer to subcutaneous superficial layer, restoration of moderate to severe wrinkles or folds, and can satisfy the restoration demand of wrinkles or folds caused due to skin aging.
Owner:SHAANXI BIO REGENERATIVE MEDICINE CO LTD
Medical blood-stopping healing agent for wound-surface and using thereof
ActiveCN101209354AGood biocompatibilityDoes not elicit an immune responseOrganic active ingredientsSurgerySide effectBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a medical wound surface hemostatic and wound healing agent, which is characterized in that the invention consists of two parts of water solution, one part is the oxidative polysaccharide water solution containing dialdehyde, and the other part is the water-soluable chitosan water solution. The medical wound surface hemostatic and wound healing agent can be applied in the preparation of drugs or medical devices for wound surface sealing and wound surface hemostasis, and the invention can also be applied in the preparation of drugs or medical devices for the promotion of wound surface healing and the prevention of postoperative tissue adhesion. The medical wound surface hemostatic and wound healing agent of the invention has significant effects on wound surface sealing, hemostasis, promotion of wound surface healing, prevention of postoperative tissue adhesion and other aspects, at the same time, the biocompatibility is good, which can not cause the tissue immune response, and the polysaccharides can not generate side effects on organisms after the in vivo degradation, so the safety is good.
Owner:青岛博益特生物材料股份有限公司
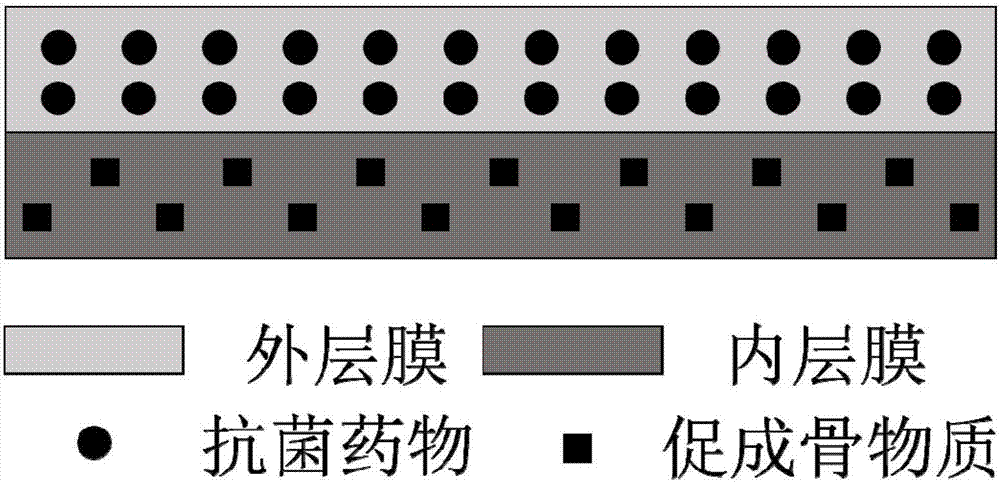
Double-layered bone repairing membrane material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106975106ACause targeted releasePromote repairConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsElectro-spinningPolyesterBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a double-layered bone repairing membrane material and a preparation method thereof and in particular provides a bone repairing membrane material with antibacterial and inflammation-diminishing and bone promotion functions and belongs to the field of biological materials. The material takes biodegradable aliphatic polyester with biocompatibility and natural polymers as main raw materials and is prepared by adopting an electrostatic spinning method. The material has a double-layered membrane structure and comprises an outer layer added with an antibacterial drug and an inner layer added with a bone promotion substance. The material provided by the invention has excellent biocompatibility and a controllable and long-period medicine releasing performance; meanwhile, an outer-layer membrane of the double-layered membrane structure can be used for inhibiting bacterial infection and inflammation, which are easily caused after bone defects occur, and preventing bacteria from entering defected parts; an inner-layer membrane can be used for promoting the repairing of the bone defects. The material can be used for realizing controllable in-vivo degradation according to requirements and the material does not need to be taken out by a second surgery.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Degradable magnesium alloy angiocarpy bracket with medicine and preparation method thereof
The present invention relates to technical field of biological material, and is especially suitable for surface modification field of biological medical material. Particularly the invention provides a medicine-taking degradable magnesium alloy cardiovascular bracket and a preparing method thereof. The aim of the invention is to reduce the initial degrading speed of magnesium alloy in biosome and carry therapeutic medicine on the surface of magnesium bracket thereby guaranteeing the mechanical performance of magnesium alloy bracket in vivo and better restraining the hyperplasia of newborn tunica interna. A fluoro-containing transition film is prepared on the surface of magnesium alloy bracket, and a medicine-carrying layer is prepared on the outer layer of magnesium alloy bracket. A protecting layer is the fluoro-containing transition film. The fluoro-containing transition film has self-concrescence capability in the degradation process of magnesium alloy and can effectively reduce the in-vivo degradation velocity of magnesium alloy bracket. The surface of degradable magnesium alloy cardiovascular bracket is smooth and is not easily generated with surface cracking and breaking-off. The medicine-taking layer is composed of medicine carrier polymer or protein and therapeutic medicine. The medicine-taking layer can release therapeutic medicine, reduce the generation rate of stenosis after the implantation of bracket and has a control function to the degradation velocity of magnesium alloy bracket.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
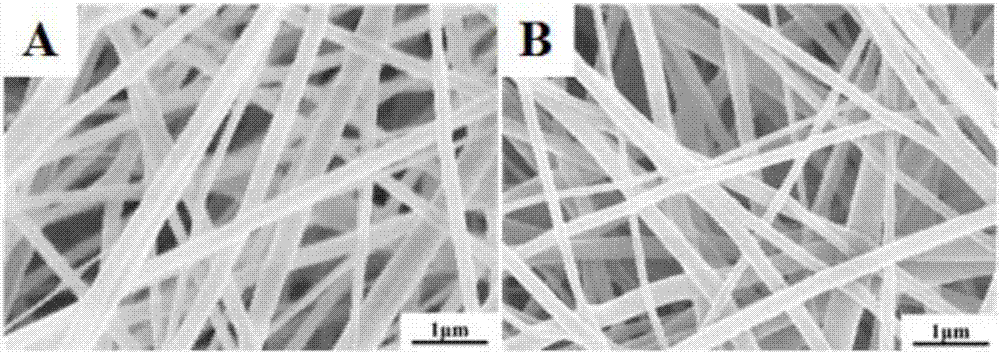
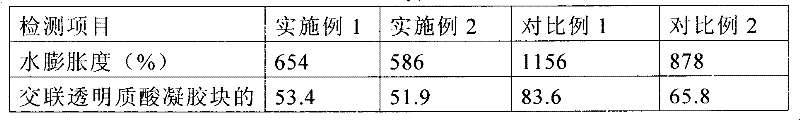
Cross-linked hyaluronan sponge and preparation method for same
The invention provides a method for preparing a cross-linked hyaluronan sponge, and the sponge obtained by the method. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) swelling a hyaluronan raw material in water to obtain a hyaluronan gel fluid; (2) adjusting the hyaluronan gel fluid to be alkaline, adding a cross-linking agent, and performing cross-linking reaction to obtain a cross-linked hyaluronan gel; and (3) cleaning the cross-linked hyaluronan gel, and freeze-drying at a low temperature to obtain the cross-linked hyaluronan sponge. The cross-linked hyaluronan sponge prepared by the method provided by the invention is low in the content of the cross-linking agent, good in biocompatibility, consistent in in-vivo degradation cycle and tissue healing cycle, and good in blood-stopping and anti-adhesion functions.
Owner:上海白衣缘生物工程有限公司
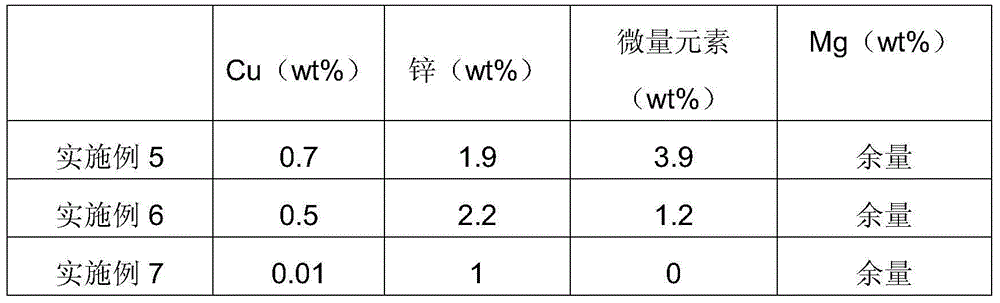
Biodegradable and absorbable magnesium-zinc-copper alloy with antibiotic function, and application thereof
InactiveCN104593650AGood biocompatibilitySatisfactory degradabilitySurgeryCoatingsExtremely goodBiocompatibility Testing
The invention provides a magnesium-zinc-copper alloy. The magnesium-zinc-copper alloy comprises 1-8wt% of zinc, 3wt% or less of copper, and the balance of magnesium. The magnesium-zinc-copper alloy has good biocompatibility, satisfactory degradability, high biological safety and extremely good biomechanical performances, can continuously slowly release metal ions having an antibiotic effect to surrounding tissues through in vivo degradation in order to effectively prevent and treat implant surrounding infection, has certain hematopoietic activity, and has good application values in implanting into bones and other medical fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Antibacterial medical metal material capable of being degraded in body fluid, and applications thereof
InactiveCN104513922AGood biocompatibilitySatisfactory degradabilityProsthesisBiomechanicsMetallic materials
The present invention provides a magnesium-copper alloy, which contains magnesium and copper, wherein the copper content is less than or equal to 3 wt%, and the balance is the magnesium. According to the present invention, the magnesium-copper alloy has characteristics of good biodegradability, satisfactory degradability, high biological safety, and excellent biomechanical property, has application values in medical fields of endosseous implants and the like, especially continuously and slowly releases metal ions with the bacterial inhibiting effect to the surrounding tissue through in vivo degradation, has effects of effective prevention and treatment of infections surrounding implants, and has a certain angiogenesis activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
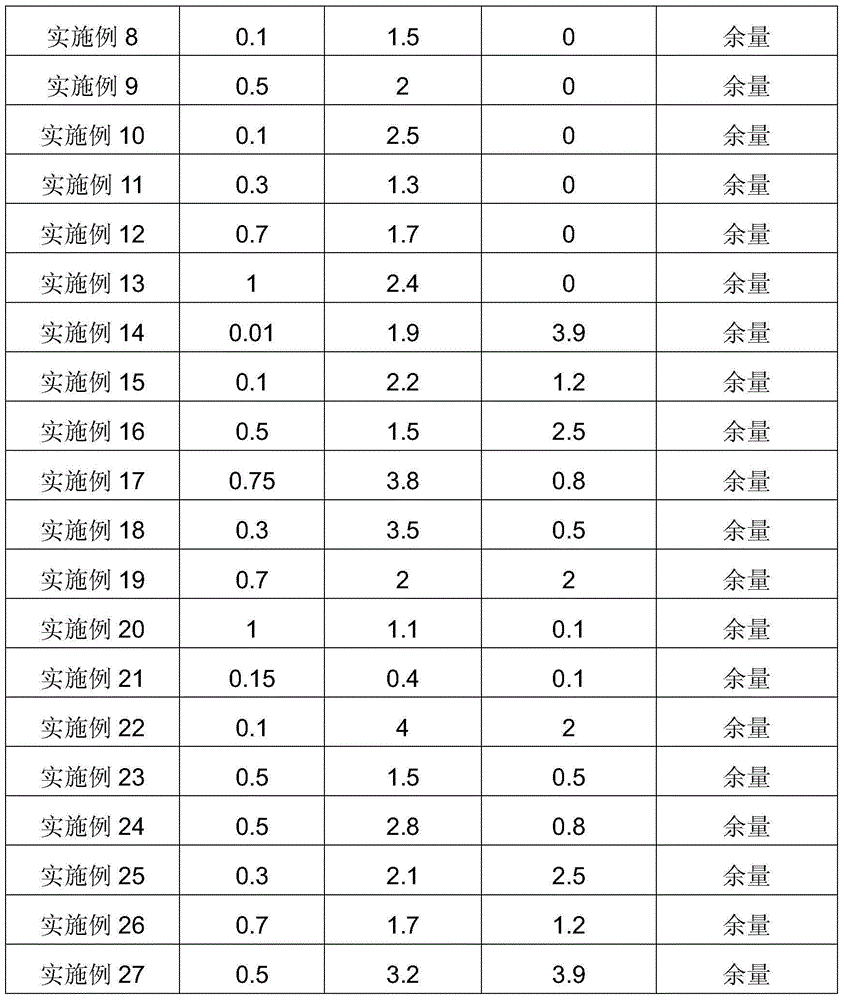
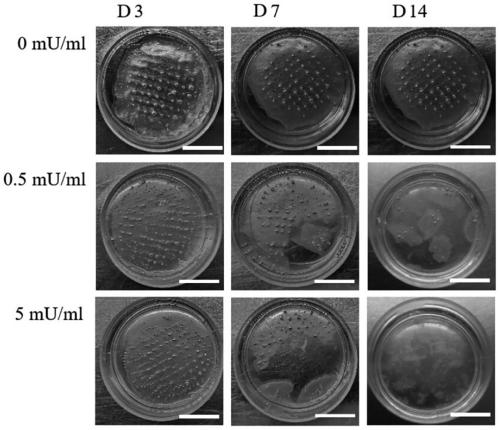
Method for promoting in-vitro and in-vivo degradation and cell extension adherence of alginate-based 3D printed bioink
InactiveCN110170071APromote internal and external degradationAdjust the degradation timeVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Production method of biodegradable nanometer fiber diaphragm applied to neurosurgery indirect vascular bypass
ActiveCN106390193AWon't happenHigh activityTissue regenerationAnimal fibresFiberBiocompatibility Testing
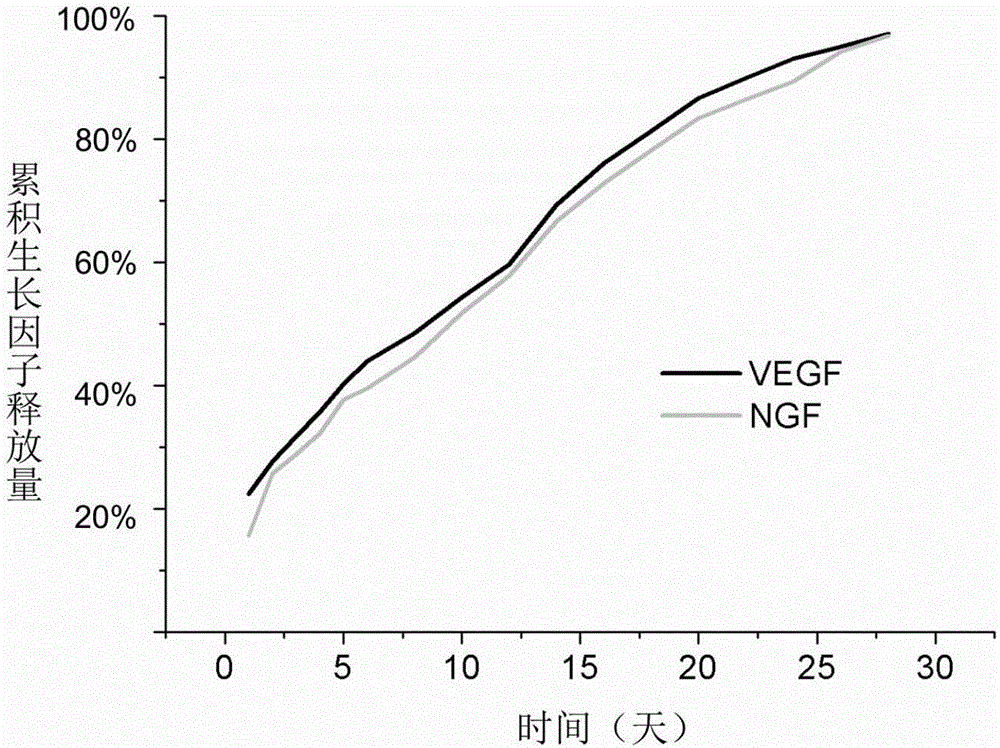
The invention relates to a biodegradable nanometer fiber diaphragm applied to neurosurgery indirect vascular bypass. The biodegradable nanometer fiber diaphragm can be produced through the following steps: dissolving a biodegradable polymer material in a polar and volatile organic solvent, carrying out electrostatic spinning to produce a diaphragm composed of ultrafine fibers with the nano-scale diameters; and loading growth factors for promoting brain tissue blood vessel regeneration and / or promoting nerve regeneration to the diaphragm through a layer and layer self-assembling technology, and drying the factor growth supported diaphragm. The biodegradable nanometer fiber diaphragm has the advantages of no toxicity, no generation of harmful substances after in vivo degradation, and good biocompatibility. The biodegradable nanometer fiber diaphragm can avoid growth factor inactivation caused by organic solvents, strong acids, strong alkalis and high temperature, and an assembled polyelectrode can guarantee the good activity of the growth factor supported on the diaphragm. The biodegradable nanometer fiber diaphragm can realize long-term controlled release of VEGF, NGF and other growth factors in the brain blood vessel obstruction position in order to induce blood vessel regeneration and nerve regeneration of the brain tissue blood vessel obstruction position.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
In vivo absorbable metal intervertebral fusion cage
InactiveCN102085387APromote repairAchieve bony healingInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsRare earthStress shielding
The invention discloses an in vivo absorbable metal intervertebral fusion cage, the fusion cage is made of high-purity magnesium or magnesium alloy, the purity of the high-purity magnesium is not less than 99.9%, the content of the magnesium in the magnesium alloy by weight is 10%-100%, the total content of an alloy element is 0-90%, and the content of other impurity ingredients is not more than 5%; and the alloy element comprises one or more of Zn, Ca, Mn, Fe, Al and rare earth. The in vivo absorbable metal intervertebral fusion cage can be gradually degraded and absorbed in vivo, and the elastic modulus is similar to that of bones, thereby making up for disadvantages that the fusion cage is sunk due to stress shielding effect of titanium alloy material and the like, and the loss of intervertebral support height is caused. Compared with a permanently implanted PEEK (polyetheretherketone) fusion cage, the in vivo absorbable metal intervertebral fusion cage can promote bone repair and enable bone absorption and formation of new bones to be in good matching during the in vivo degradation process; simultaneously, the support height is maintained, the intervertebral bone union can be realized without leaving foreign bodies, the second taking-out can be avoided, and the suffering of a patient can be greatly reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIGIN MEDICAL TECH
Guided tissue regeneration membrane and preparation method thereof
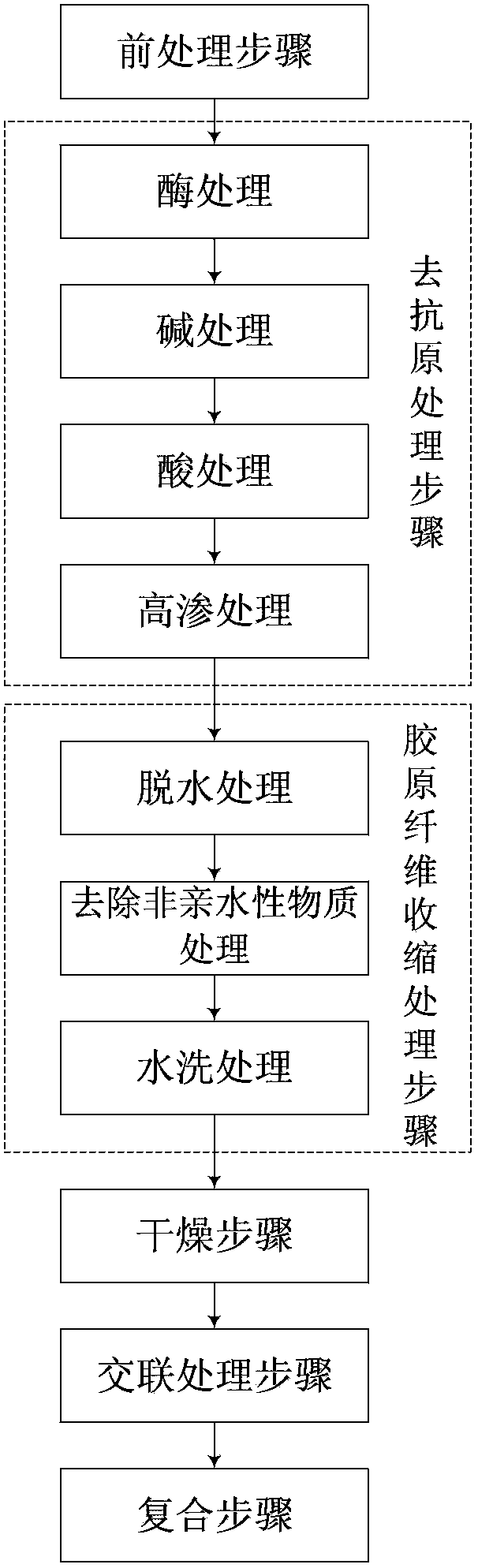
The invention relates to a guided tissue regeneration membrane and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises: a pretreatment step, i.e. collecting a mammalian peritoneum, conducting flowing water washing, hair removal and preliminary degreasing for standby use; an antigen removal treatment step, i.e. carrying out further degreasing on the standby peritoneum by means of an enzyme treatment process, an alkali treatment process, an acid treatment process and a hypertonic treatment process, and removing immunogenicity; a collagen fiber contraction treatment step, i.e. carrying out dehydration, non-hydrophilic substance removal and washing treatment on the peritoneum subjected to the antigen removal treatment so as to contract the collagen fibers of the peritoneum; and a drying step, spreading the contracted peritoneum on a culture dish surface to make the compact layer of the peritoneum contact the culture dish, rapidly transferring the peritoneum into a refrigerator at a temperature ranging from -60 to -80DEG C to undergo pre-freezing for 1-8h, then freeze-drying the peritoneums in a freeze dryer for 24-36h, thus obtaining a collagen membrane able to guide tissue regeneration. The guided membrane provided by the invention has a compact layer and a loose layer, also has good biocompatibility, hydrophilicity and bone induction ability, and has a long in-vivo degradation time.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDO BIOMATERIALS
Hyaluronic acid-methyl cellulose composite hydrogel as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN105330902AProlong the retention time in the bodyPromotes regenerative repairProsthesisRetention timeMass ratio
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical materials and tissue engineering technologies, and particularly relates to hyaluronic acid-methyl cellulose composite hydrogel as well as preparation and an application thereof. The hyaluronic acid-methyl cellulose composite hydrogel comprises methyl cellulose and hyaluronic acid in the mass ratio of (5-11):1 and adopts a crosslinking network structure, and the pore diameter ranges from 30 mu m to 100 mu m. The methyl cellulose with temperature-sensitive characteristic, good biocompatibility and small in-vivo degradation speed and hyaluronic acid molecules have a physical crosslinking reaction through polyethylene glycol, and the hyaluronic acid-methyl cellulose composite hydrogel is obtained. The composite hydrogel can be formed at the body temperature by controlling the concentration of the methyl cellulose and salt additives, the mechanical performance is improved, bioactive molecules can be controlled to be released, the in-vivo retention time is prolonged, regeneration and repair of soft tissue similar to nervous tissue are facilitated, and the hyaluronic acid-methyl cellulose composite hydrogel has wide application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Carrageenan and gelatin microsphere embolization agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103990185AAvoid the problem of staying foreverControl timeSurgeryGelatin microspheresEmulsion
The invention discloses a carrageenan and gelatin microsphere embolization agent and a preparation method thereof. The carrageenan and gelatin microsphere embolization agent comprises mixed glue formed by carrageenan and gelatin, a biodegradable polymer, an emulsifier and a crosslinking agent. The carrageenan and gelatin microsphere embolization agent is a novel microsphere integrated with embolism and medicine administration functions, and can be applied to treatment of diseases such as tumors and the like. By adopting the preparation method of the microsphere, the novel microsphere, which has the advantages of wide grain diameter distribution range, large drug loading capacity, long embolization time, controllable in-vivo degradation time and the like can be prepared. The function of the existing microsphere is perfected, the carrageenan and gelatin microsphere embolization agent is prepared by using an emulsion crosslinking method, the carrageenan and gelatin microsphere embolization agent is simple in process, and convenient to operate, and good news is brought about for a patient.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Biomedical degradable metal capable of treating rheumatoid arthritis, and applications thereof
ActiveCN104511049AGood biocompatibilitySatisfactory corrosion resistanceCoatingsProsthesisOsteoblastBone formation
The present invention provides a biomedical degradable metal capable of treating rheumatoid arthritis. The biomedical degradable metal is a magnesium alloy and contains magnesium and a second component, wherein the second component is one or a plurality of materials selected from zinc, manganese, selenium, strontium and calcium, the content of the second component is less than or equal to 10 wt%, and the balance is magnesium. According to the present invention, the magnesium alloy has characteristics of good biocompatibility, satisfactory corrosion resistance and no significant cytotoxicity, can be degraded and absorbed in biological body fluids or bloods, has application values in medical fields of endovascular interventional therapy, endosseous implant and the like, and especially releases beneficial elements through in vivo degradation so as to inhibit activation of macrophages and other inflammatory cells, promote osteoblast bone formation, and inhibit osteoclast bone resorption, such that the biomedical degradable metal has the potential effects of rheumatoid arthritis treating and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Injectable hydrogel, and preparation method
InactiveCN106866841AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryCross-linkArginine
The invention provides an injectable hydrogel, and a preparation method thereof. The injectable hydrogel is obtained via self-crosslinking reaction of arginine-modified chitosan with a structure represented by formula (I) with a cross-linking agent; the polymerization degree n of the arginine-modified chitosan is equal to or higher than 10, and is equal to or lower than 3200; the arginine substitution degree ranges from 0.1 to 80%; the cross-linking agent is oxidized dextran. Compared with the prior art, the injectable hydrogel possesses following advantages: the biocompatibility is high; in vivo in-suit formation, and in vivo degradation can be realized; it is beneficial for direct acting of drugs at diseased regions, and long lasting of drug effect; oxidized dextran is safe and notoxic as the cross-linking agent; environment pollution is reduced; the degradation products are amino acids and polysaccharides, and can be discharged out of human body via kidneys, so that the injectable hydrogel is harmless for human body.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Degradable gasket with anti-bacterial anti-adhesion performance
InactiveCN104606722AAntibacterial and anti-adhesion functionGood biocompatibilitySurgeryCoatingsBiocompatibility TestingKnee Joint
The invention provides a degradable gasket with anti-bacterial anti-adhesion performance. The degradable gasket is prepared via weaving or knitting of a plurality of bundles of magnesium-based metal wire, or via punching of magnesium-based metal sheets. The magnesium-based metal wire can be made of pure magnesium or a magnesium-based alloy of different elements based on disease characteristics and treatment requirements. The degradable gasket possesses excellent biocompatibility; in vivo degradation and absorption can be realized; degradation speed can be controlled; the degradable gasket is capable of preventing postoperative adhesion and infection, and promoting wound healing, can be used for preventing epidural adhesion after orthopedic surgery laminectomy, adhesion after tendon rupture repairing operation, adhesion after knee surgery, dura adhesion after transcranial surgery, eye socket soft tissue adhesion, intestinal adhesion after abdominal surgery, and intrauterine adhesion, is capable of reducing infection risk of the above surgeries, and possesses significant clinical application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Tissue sealing agent powder and preparation process thereof, and tissue sealing agent
ActiveCN111265711AFast postoperative recoveryPromote healingSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismChemical compoundFluidized bed
The invention relates to a tissue sealing agent powder and a preparation process thereof, and a tissue sealing agent. The sealing agent powder comprises a first component and a second component, the first component is an electrophilic raw material and contains an electrophilic functional group or a physically loaded electrophilic functional group compound; the second component is a botanical biological material; and a mass ratio of the first component to the second component is 1: 1-10. The preparation method adopts a physical melting method and a fluidized bed method. According to the preparation method, high-water-absorptivity substances of the first component and the second component contain active functional groups without any other catalysts and reagents or under a condition of changing self chemical properties, and the obtained tissue sealing agent has advantages of rapid liquid absorption, a high liquid absorption capacity, a high adhesion capacity, in-vivo degradation and a light inflammatory reaction, and can be directly applied to wounds.
Owner:北京爱特康医疗科技有限公司
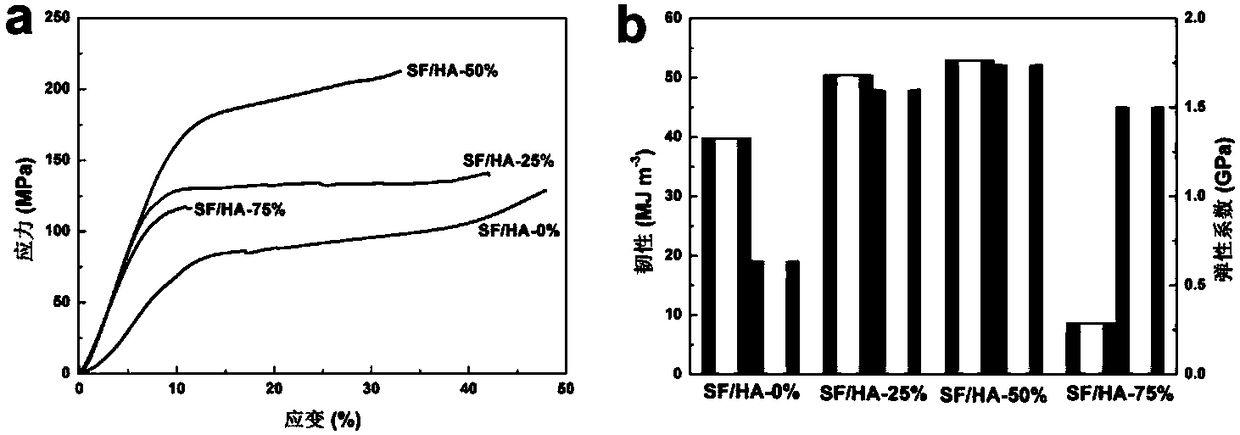
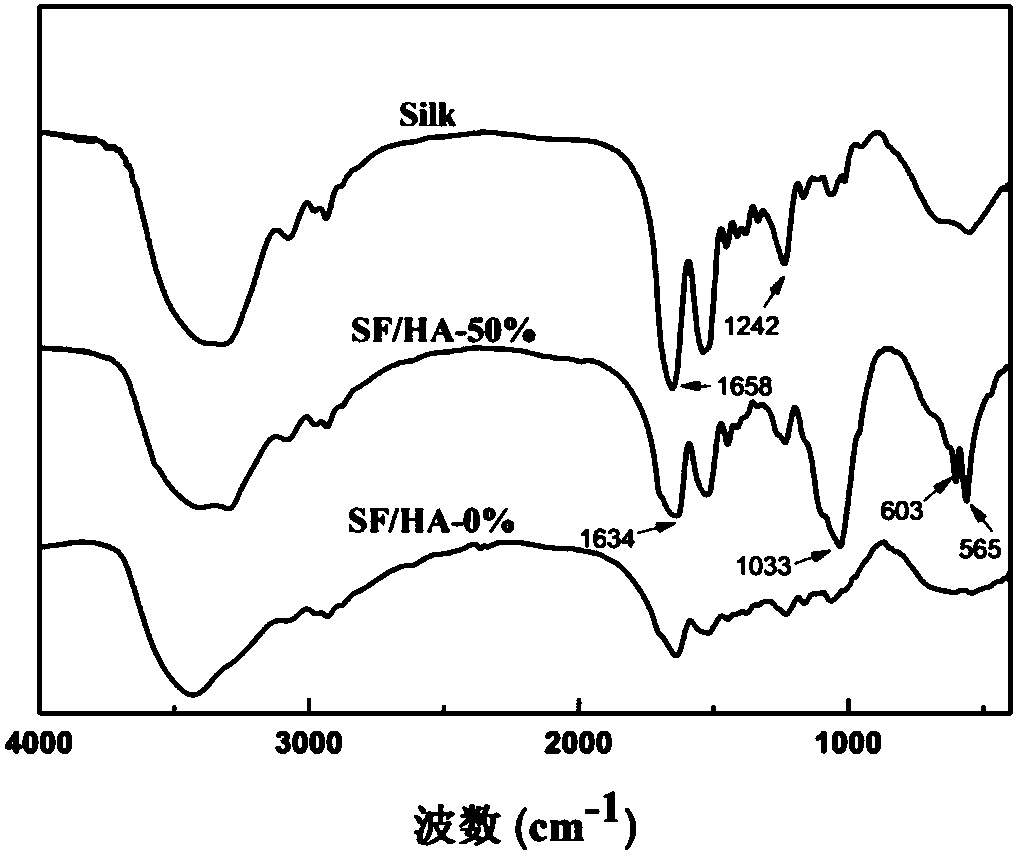
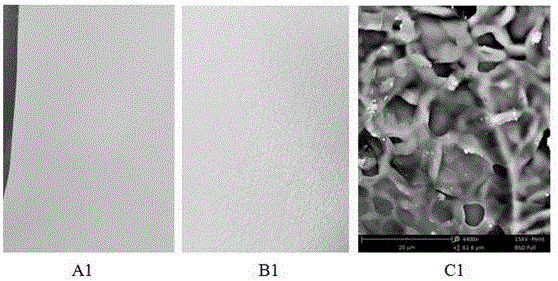
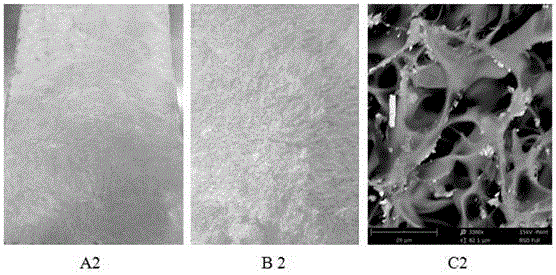
Preparation method of silk fibroin material of composite nano-grade hydroxyapatite and application of silk fibroin material in repairing bone fracture parts
PendingCN108159501AGood biocompatibilityGood mechanical propertiesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationApatiteInternal fixation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a silk fibroin material of composite nano-grade hydroxyapatite and application of the silk fibroin material in repairing bone fracture parts. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly dispersing nano-grade hydroxyapatite into silk fibroin in a certain ratio, dissolving the nano-grade hydroxyapatite with hexafluoroisopropanol, pouring a mixed solution into a columnar mold, soaking with methanol, performing self-assembling regeneration on a silk fibroin molecular chain so as to obtain a composite material which is excellent inmechanical strength, and finally manufacturing medicinal bone nails from the composite material by using a mechanical processing method. According to the characteristics that the material is good inbiocompatibility, excellent in mechanical property and good in in-vivo degradation controllability, the silk fibroin material can be applied to bone fracture fixation. A silk fibroin / nano-grade hydroxyapatite composite bone fracture internal fixation material with in-vivo degradation controllability can be prepared by using a method which is simple and feasible, high in finished product rate and free of toxicity, osteoporosis symptoms caused in the bone fracture repairing process can be effectively avoided, and because of the characteristic that the material does not need to be taken out through a second time of operation, bone fracture patients can be relieved from pain.
Owner:HUBEI SAILUO BIOLOGICAL MATERIAL CO LTD
Medical hemostatic sponge and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to medical hemostatic sponge and a preparation method thereof. The hemostatic sponge is formed by bonding freeze-dried chitosan sponge and carboxymethyl chitosan sponge, and tertiary butanol is added to freeze-dried chitosan sponge and carboxymethyl chitosan sponge in the preparation process. The hemostatic sponge prepared through the process is good in crystal type, short in in-vivo degradation cycle, capable of continuously and effectively adhering to wounds, strong in dissolution resistance, good in hemostatic effect, high in production efficiency, free of toxic and side effects and free of irritation.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG YISHENGTANG MEDICAL SUPPLIES
Polyester carbonic ester anhydride 3D printing bio-ink, and 3D printing method
ActiveCN107400412ALarge organizational structureThick tissue structureAdditive manufacturing apparatusInksBiological cellPolyester
The invention discloses a polyester carbonic ester anhydride 3D printing bio-ink, and a 3D printing method. The polyester carbonic ester anhydride 3D printing bio-ink is composed of a gel ink and a support ink; the gel ink is composed of a hydrogel and biological cells; the hydrogel contains a PLGA-PEG-PLGA triblock copolymer with temperature responsiveness; the support ink is a polyester carbonic ester anhydride copolymer (P(LLA-TMC-SA)copolymer) with surface degradation characteristics. The 3D printing bio-ink possesses thermosensitivity and surface degradable performance, and multicomponent gradient printing and coaxial printing are adopted based on requirements of 3D biologically printed scaffold in vivo degradation structure controllable maintenance so as to obtain models which contain biological cells and are supported by scaffolds with surface controllable degradability, nutrient and metabolism channels with porous structures are obtained, and it is beneficial for obtaining of larger and thicker tissue structures via 3D printing.
Owner:HANGZHOU MEDZONE BIO-TECH CO LTD
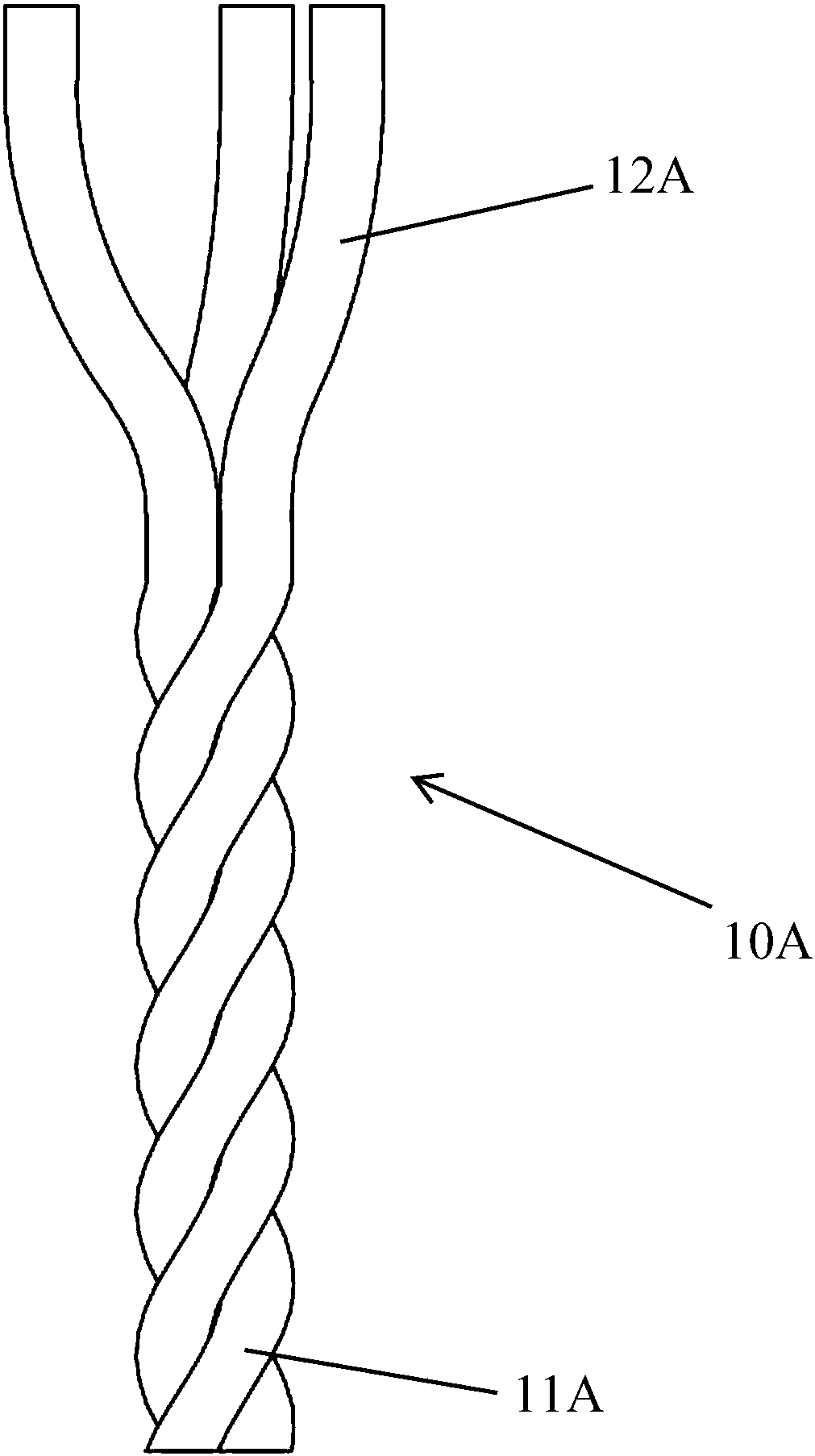
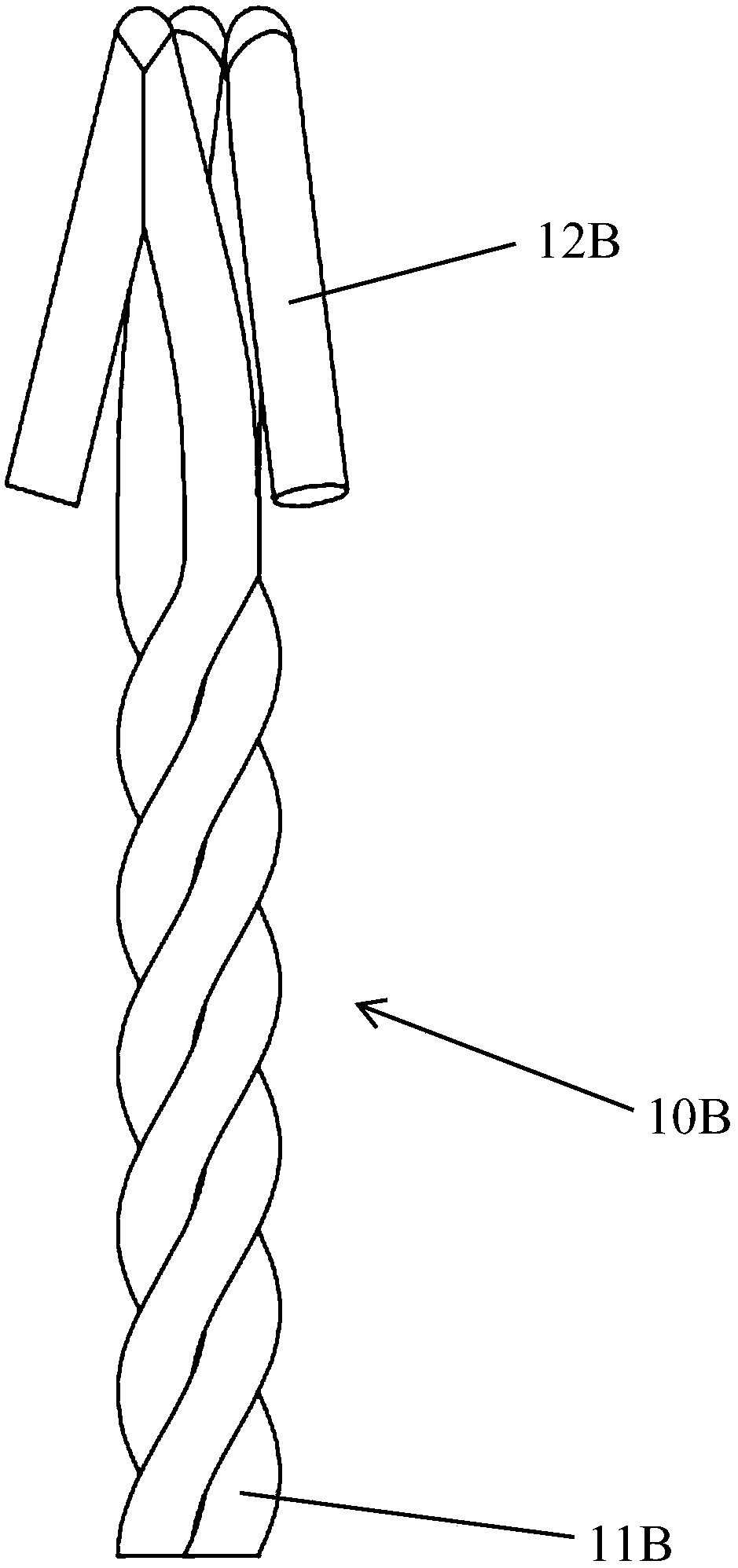
Positioning marker made of degradable metal and method for preparing positioning marker
PendingCN108378929AImprove efficacyGood biocompatibilitySurgeryEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsIn vivo degradationImpurity
The invention relates to a positioning marker made of degradable metal and a method for preparing the positioning marker. The positioning marker is made of pure magnesium or magnesium alloy. The totalcontent of impurities in the pure magnesium and the magnesium alloy is lower than 0.01% by mass fraction. At least three magnesium wires are woven to obtain the positioning marker. The positioning marker is provided with a wound end and a positioning end. The positioning end is connected to the wound end and is of a claw-shaped or anchor-shaped structure. The positioning marker and the method have the advantages that the tensile strength of the positioning marker is higher than 200 megapascal, the percentage elongation after fracture is higher than 10%, and the in-vivo degradation rate is lower than 0.5 mm / year; the positioning marker can be developed in ultrasonic and X rays, the locations of the positioning marker can be detected by the aid of ultrasonic or molybdenum target X rays in operative procedures and postoperative treatment procedures, and the positioning marker can be gradually degraded along with postoperative treatment, and can be absorbed by surrounding tissues or discharged from human bodies by means of metabolism without being taken out by means of second operation.
Owner:西安卓恰新材料科技有限公司
Preparation method of tubular silk fibroin/keratin composite nanofiber material
InactiveCN104018245AAdjustable inner diameterGood biocompatibilityConjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsFilament/thread formingFiberComposite nanofibers
The invention relates to a preparation method of a tubular silk fibroin / keratin composite nanofiber material. The preparation method comprises the steps of adding silk fibroin into a solvent and stirring until dissolving completely to obtain silk fibroin solution with the concentration of 5-20mg / ml; adding keratin into the solvent and stirring until dissolving completely to obtain keratin solution with the concentration of 10-20mg / ml; mixing the silk fibroin solution with the keratin solution in a mass ratio of 95:5-5:95, stirring to obtain a spinning solution, then performing electrostatic spinning and using a cylindrical collecting roller as a receiver. The tubular material has the advantages of adjustable inside dimension, good biocompatibility and in-vivo degradation, and is expected to be used in the field of biological medical materials such as artificial blood vessels and urethra substitutions.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing bioactivity gradient hard tissue alternate material
ActiveCN101185773AReduce temperature riseThe composition of the coating is uniform and stableVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAcid etchingRetention time
The invention relates to a preparation method of bioactive gradient hard tissue replacement material. Firstly, the pure FHA target material and the FHA plus YSZ compound target materials are prepared by vacuum hot-pressing sintering; the medical metal substrate test sample which is obtained by wire cutting is polished by a metallographical sand paper and then washed, and the substrate after washing is firstly processed by acid etching and then the alkali-heat treatment, so as to obtain the substrate which is processed by activation; the FHA target material, the self-made various groups of compound target materials with different components (FHA plus YSZ) and the medical metal substrate are respectively arranged in a main sputtering chamber and a sample introduction chamber to carry out magnetron sputtering, and post-treatment is carried out in a heat treatment furnace after the completion of magnetron sputtering, then the artificial bone implant which is based on the medical metal surface (FHA plus YSZ) gradient biological coating is obtained. The adhesive strength of the gradient biological coating of the gradient hard tissue replacement material (FHA plus YSZ) which is prepared by the invention and the substrate is high, the temperature increase of the medical metal substrate is low, the components of the coating are even and stable, and the cost is lower; the gradient coating is thinner, the in vivo degradation speed of the FHA gradient coating is lower, the retention time is longer, and the invention is more conductive to the repair and reconstruction of the bone tissues with defects.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Surface-degradable three-dimensional (3D) printing bio-ink and 3D printing method
The invention relates to surface-degradable three-dimensional (3D) printing bio-ink and a 3D printing method. The 3D printing bio-ink consists of gel ink and support ink, wherein the gel ink is prepared from hydrogel and biological cells, wherein the hydrogel contains a poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-polyethylene glycol-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA-PEG-PLGA) triblock copolymer with temperature response; the support ink is a poly(trimethylene carbonate)-poly(L-lactide) (PTMC-PLLA) copolymer having the surface degradation characteristic. By utilizing the temperature-sensitive and surface-degradable properties of the 3D printing bio-ink and aiming at the requirements of structural controllability and maintenance in an in vivo degradation process of a 3D bio-printing support, a double-layer printing structure similar to a coaxial tube is constructed by using a multi-component material gradient printing technology; after the 3D printing bio-ink and the 3D printing method are adopted, a model which contains biological cells and is supported by a controllably surface-degradable support can be obtained by printing and molding at a time, nutritional and metabolic channels of a porous structure can be also obtained, and a bigger and thicker structure can be promoted to be obtained by means of 3D printing.
Owner:HANGZHOU MEDZONE BIO-TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of absorbable haemostasis material
InactiveCN107029281AShorten the dissolution timeReduce the risk of contaminationSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismWound healingCross-link
The invention discloses a preparation method of an absorbable haemostasis material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out a cross-linking reaction on a raw material hyaluronic acid or hyaluronate under the action of low-temperature intermittent ultrasonic treatment, uniformly mixing the crosslinked hyaluronic acid or hyaluronate with low-temperature intermittent ultrasonic treatment unreacted hyaluronic acid or hyaluronate, and carrying out ultralow-temperature freeze drying to obtain the absorbable haemostasis material. The low-temperature ultrasonic dissolving technology greatly shortens the hyaluronic acid dissolving time and reduces the pollution probability of the product in the production process; high-molecular weight hyaluronic acid or hyaluronate which can prolong the in-vivo degradation time through improving the solution concentration to meet the wound healing time has large production cost, and is bad for the reduction of the production cost of enterprises; and medium-and-small-molecular weight hyaluronic acid or hyaluronate undergoes the chemical crosslinking reaction under the low-temperature intermittent ultrasonic conditions, and the crosslinked hyaluronic acid or hyaluronate is mixed with the low-temperature intermittent ultrasonic treatment unreacted hyaluronic acid or hyaluronate according to a certain ratio, so the obtained haemostasis material has the advantages of improvement of the anti-adhesion performance, low residual amount of a crosslinking agent, stabilization of the residual amount in a certain range, reduction of the biological risk brought by free crosslinking agents, and reduction of the production cost of the enterprises.
Owner:JIANGSU CHANGJIYONG BIOTECH CO LTD
Degradable porous iron-based bone fracture plate with pore-forming agent and additional material manufacturing method of bone fracture plate
PendingCN110152070ALow elastic modulusIncreased degradation rateAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyDiagonalIn vivo degradation
The invention relates to a degradable porous iron-based bone fracture plate with a pore-forming agent and an additional material manufacturing method of the bone fracture plate. The bone fracture plate comprises a main plate body part and side wing parts, and the main plate body part is a porous unit cell structure array composed of multiple micro fine cylinders and is used for fitting the skeleton of a fractured part; the whole porous unit cell structure is of a hexahedral structure, the centers of the adjacent faces of the hexahedral structure are connected through the first micro fine cylinders, the diagonals of all the faces in the hexahedral structure are connected through the second micro fine cylinders, and vertical lines of the hexahedral structure are connected through the third micro fine cylinders; the side wing parts are arranged at the two sides of the main plate body part and used for fixing the main plate body part and the skeleton of the fractured part; micro holes withthe diameter of 1-50 microns are distributed in the main plate body part and the side wing parts. The bone fracture plate has proper in-vivo degradation speed and mechanical properties.
Owner:南通罗伯特医疗科技有限公司
Radioisotope labeled meso-porous bioglass porous scaffold and making method thereof
InactiveCN104117090AMarked validDetection of in vivo degradationProsthesisIn vivo absorptionIn vivo degradation
The invention provides a radioisotope labeled meso-porous bioglass porous scaffold. A meso-porous bioglass porous scaffold is labeled with radioisotope, and the radioisotope can be one or more of <31>Si, <32>P and <45>Ca. The radioisotope labeled meso-porous bioglass porous scaffold can effectively label the meso-porous bioglass porous scaffold, can quantitatively and intuitively detect the in vivo degradation situation of the meso-porous bioglass porous scaffold, and can be used to research the in vivo absorption and the organism distribution of the bioglass scaffold.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for extracting water-insoluble collagen from thoracic aorta of pig
ActiveCN104805165ATo achieve the effect of removing impuritiesEasy to purifyConnective tissue peptidesPeptide preparation methodsWater insolubleHydrolysis
The invention relates to a method for preparing water-insoluble collagen by using thoracic aortas of pigs as raw materials through process steps such as degreasing, impurity removal, enzyme hydrolysis, salt induced precipitation and dialysis. The process steps of the method are simple, safe and easy to operate, the cost is low and the purity of the obtained product is high. Compared with water-soluble collagen, the in-vivo degradation speed of the water-insoluble collagen obtained by the invention is reduced, the blood coagulation speed is faster and the water-insoluble collagen can be used for stopping wound bleeding or preparing other medical biological materials.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com