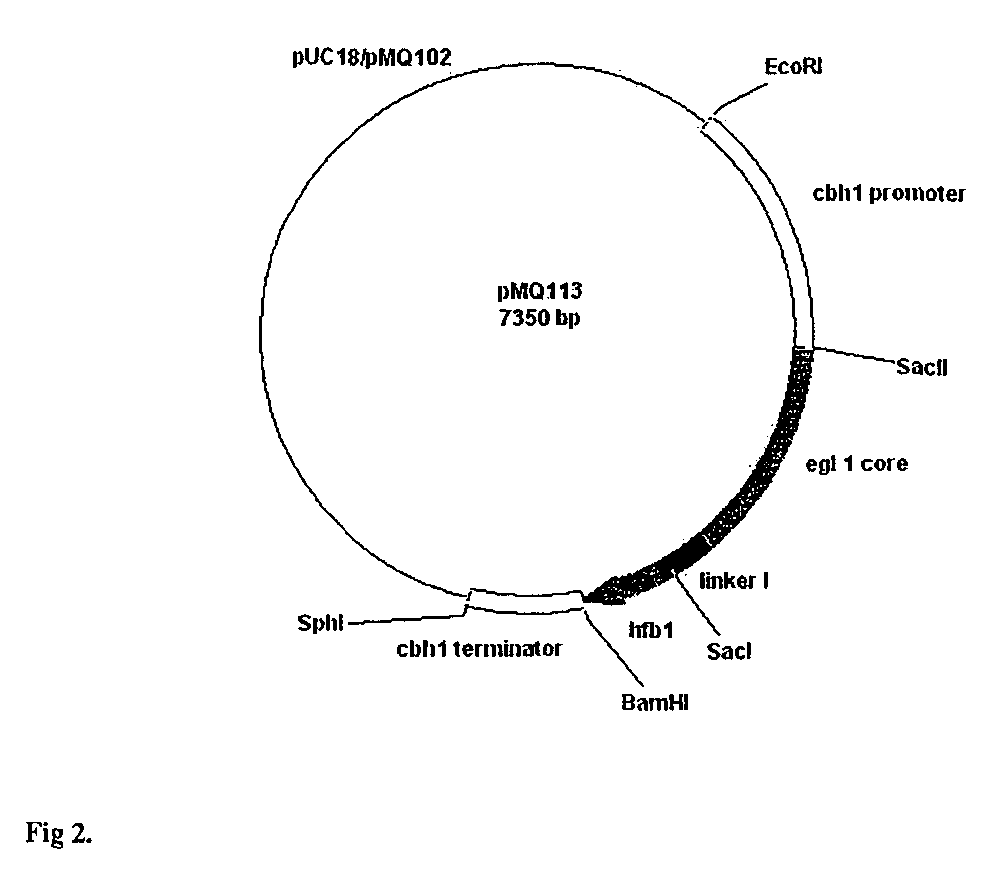
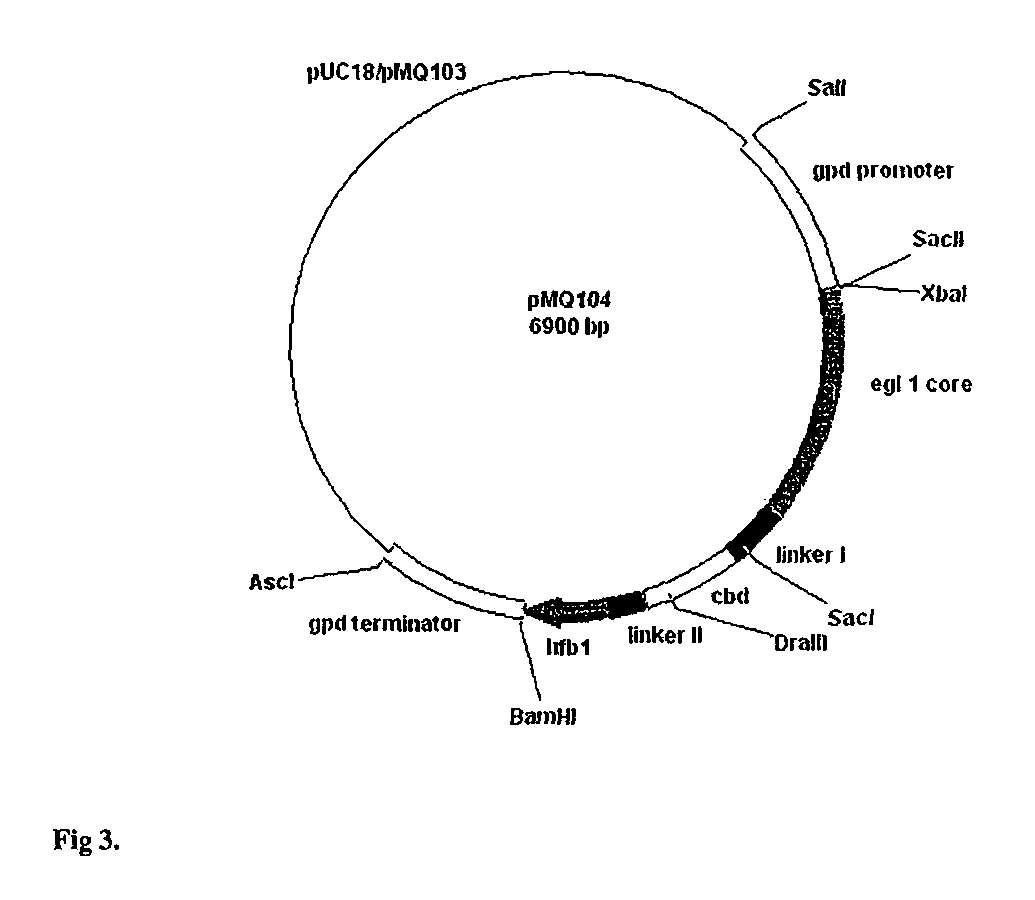
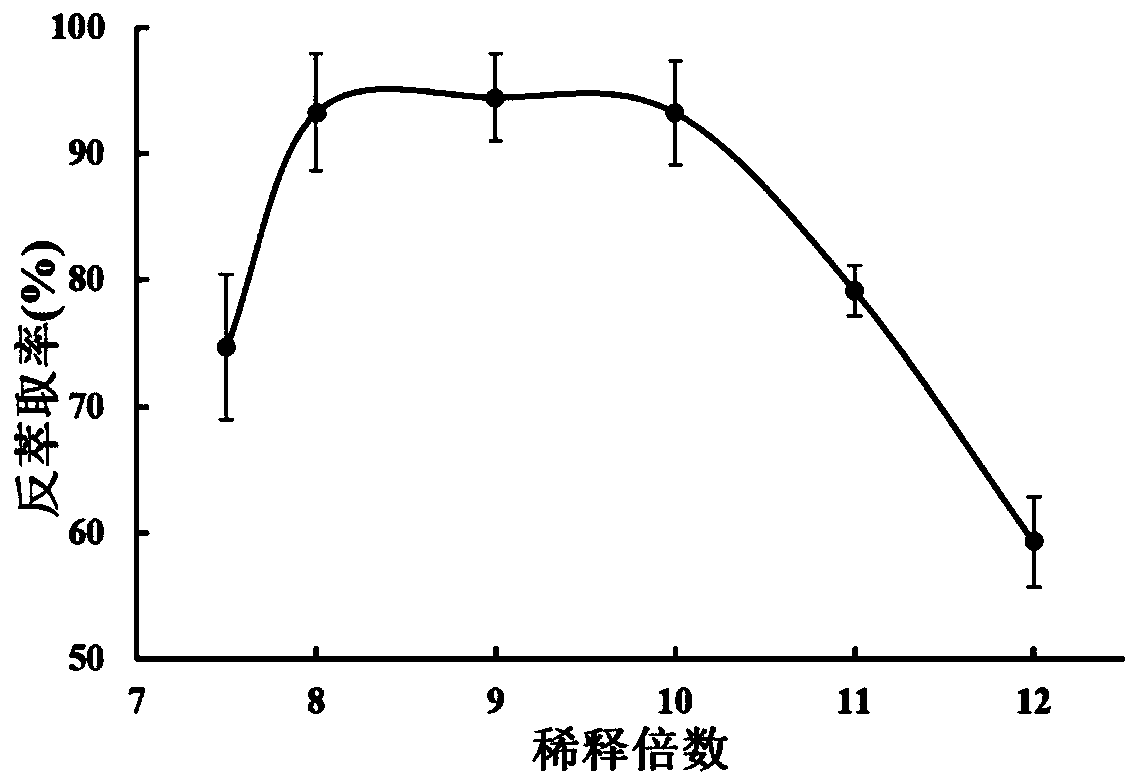
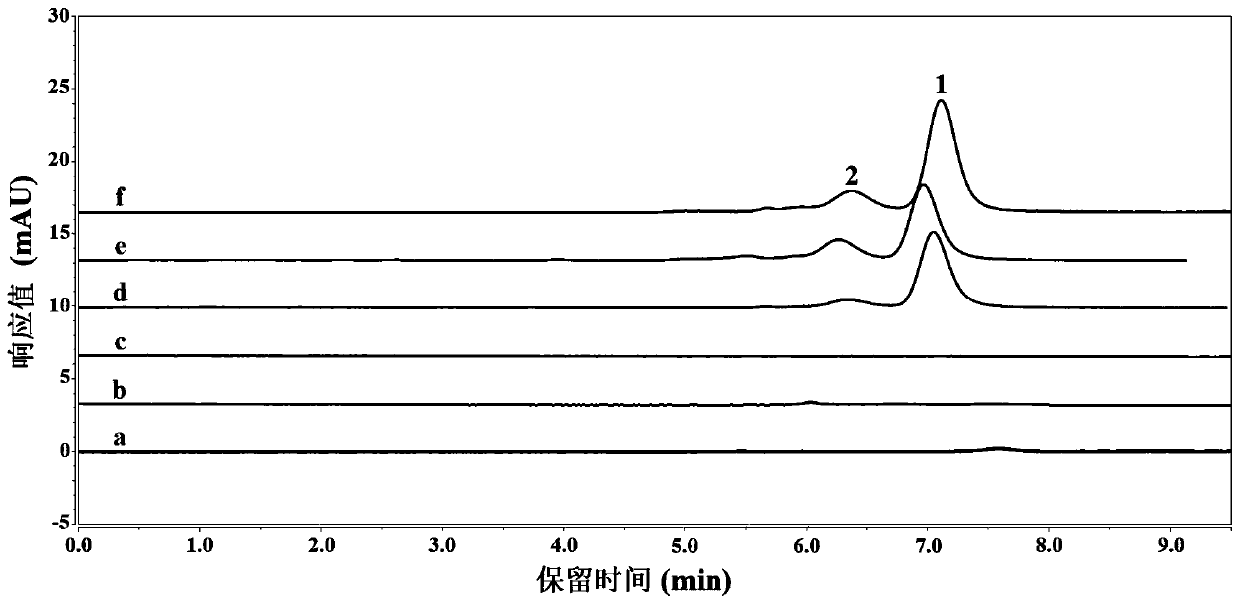
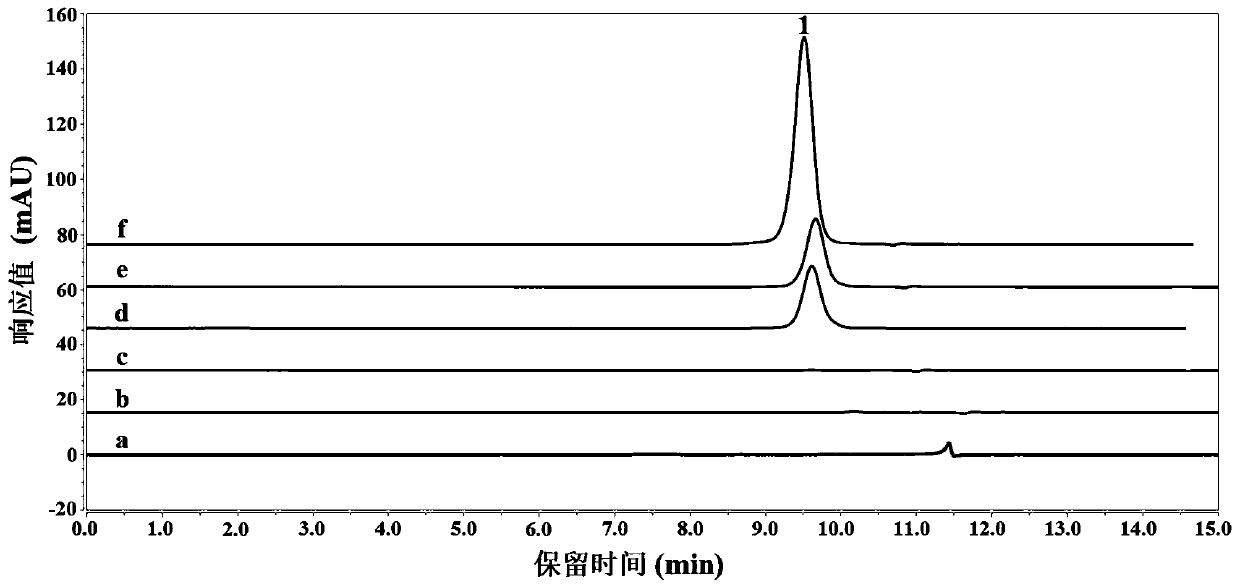
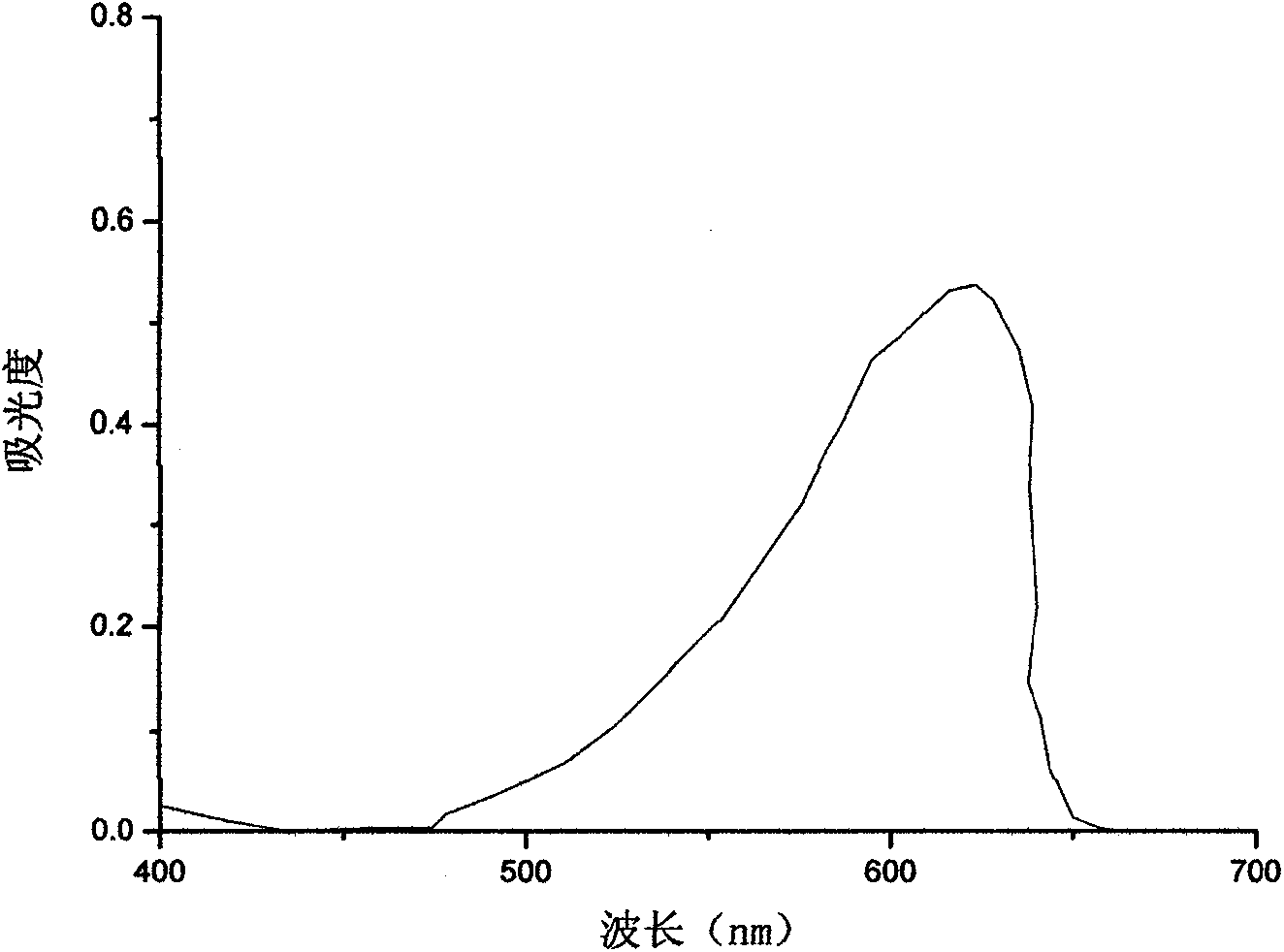
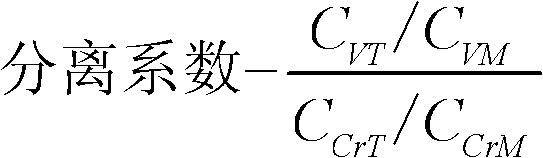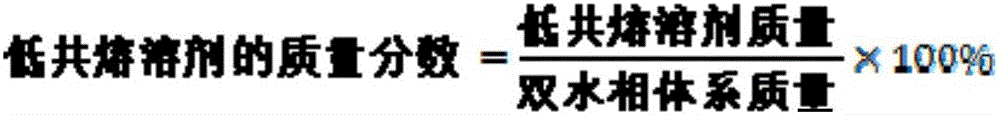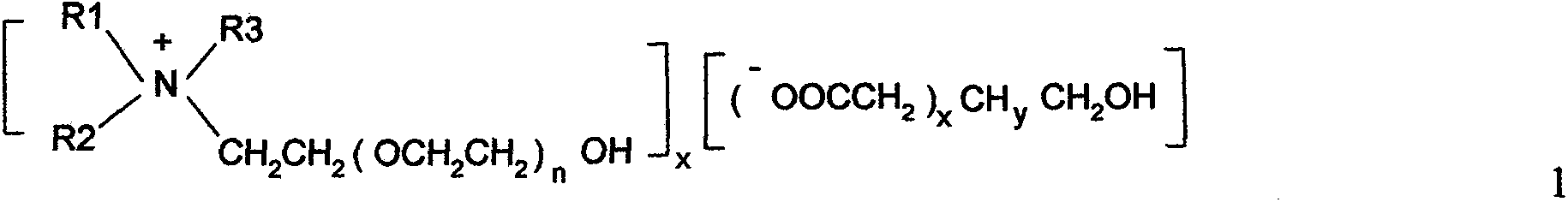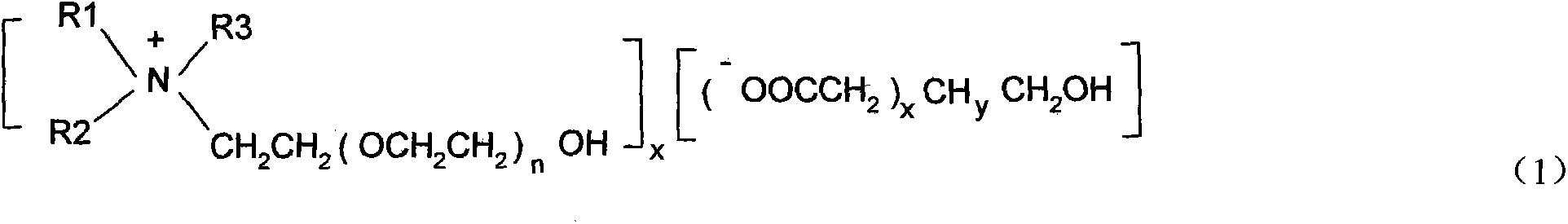Patents
Literature
236 results about "Aqueous two-phase system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
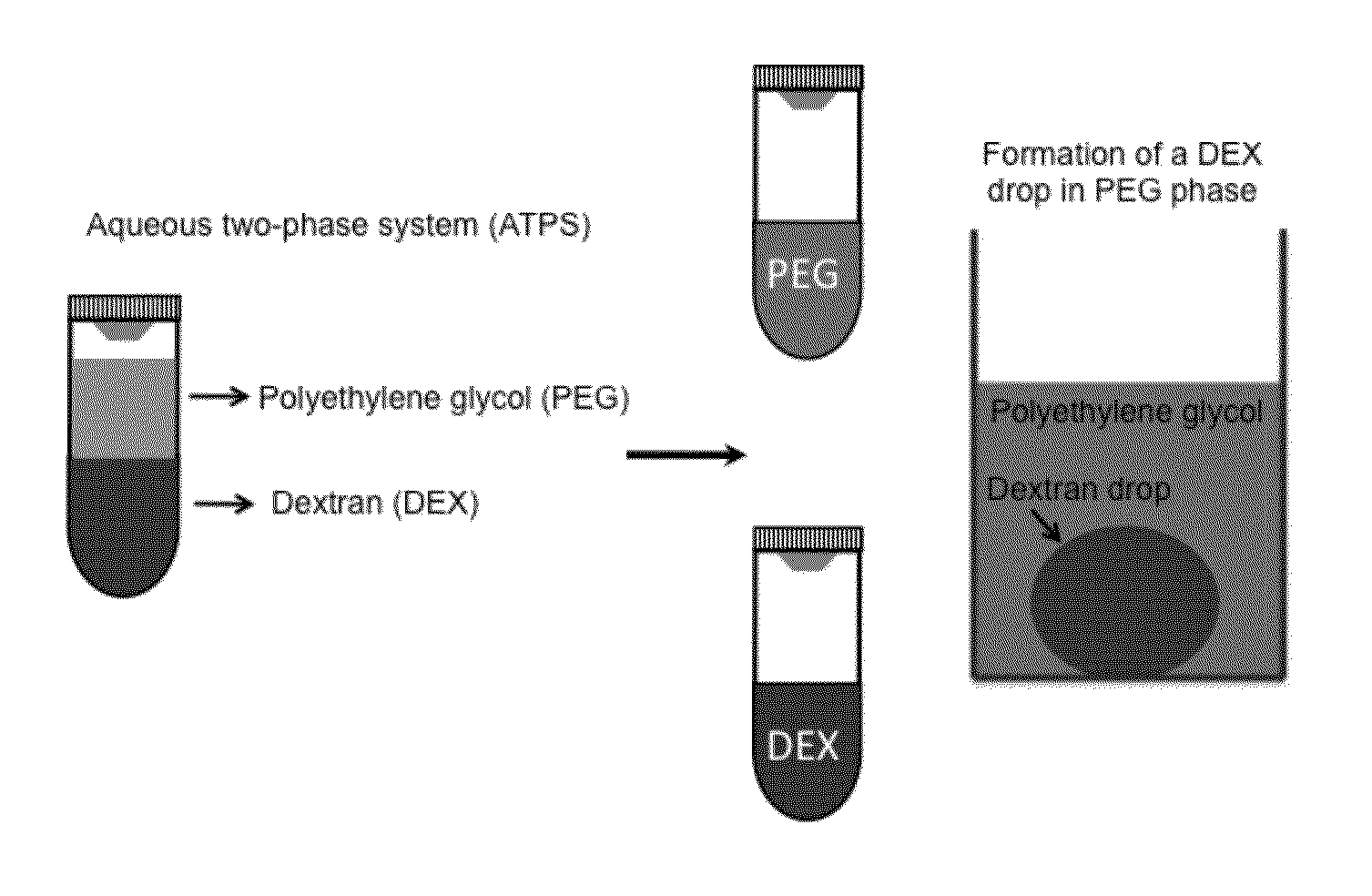
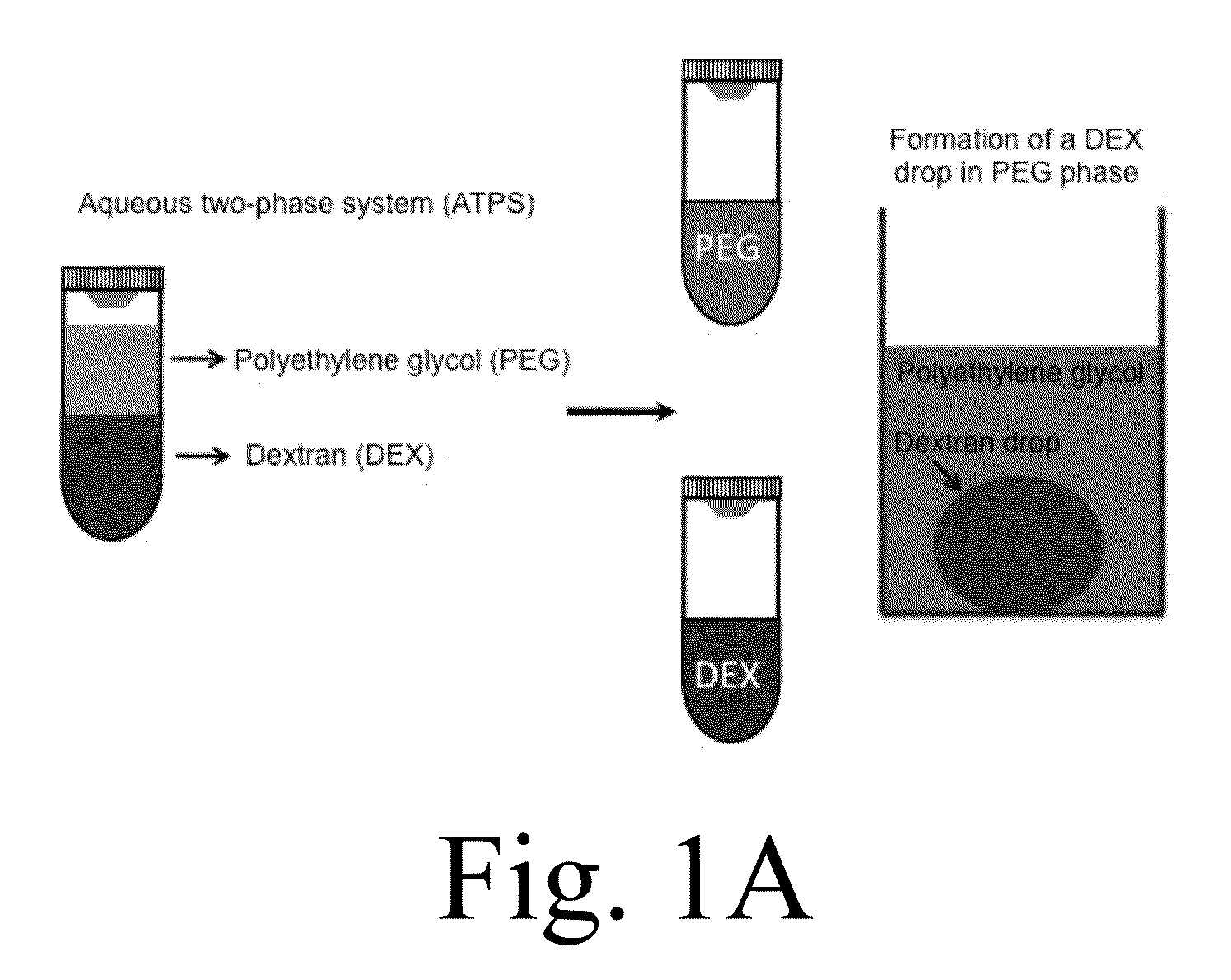
Aqueous biphasic systems (ABS) or aqueous two-phase systems (ATPS) are clean alternatives for traditional organic-water solvent extraction systems. ABS are formed when either two polymers, one polymer and one kosmotropic salt, or two salts (one chaotropic salt and the other a kosmotropic salt) are mixed at appropriate concentrations or at a particular temperature. The two phases are mostly composed of water and non volatile components, thus eliminating volatile organic compounds. They have been used for many years in biotechnological applications as non-denaturing and benign separation media. Recently, it has been found that ATPS can be used for separations of metal ions like mercury and cobalt, carbon nanotubes, environmental remediation, metallurgical applications and as a reaction media.
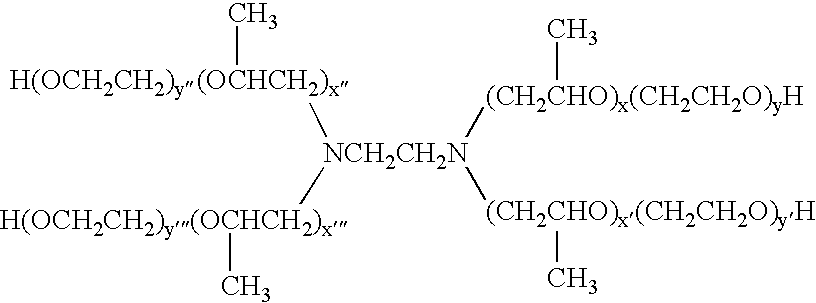
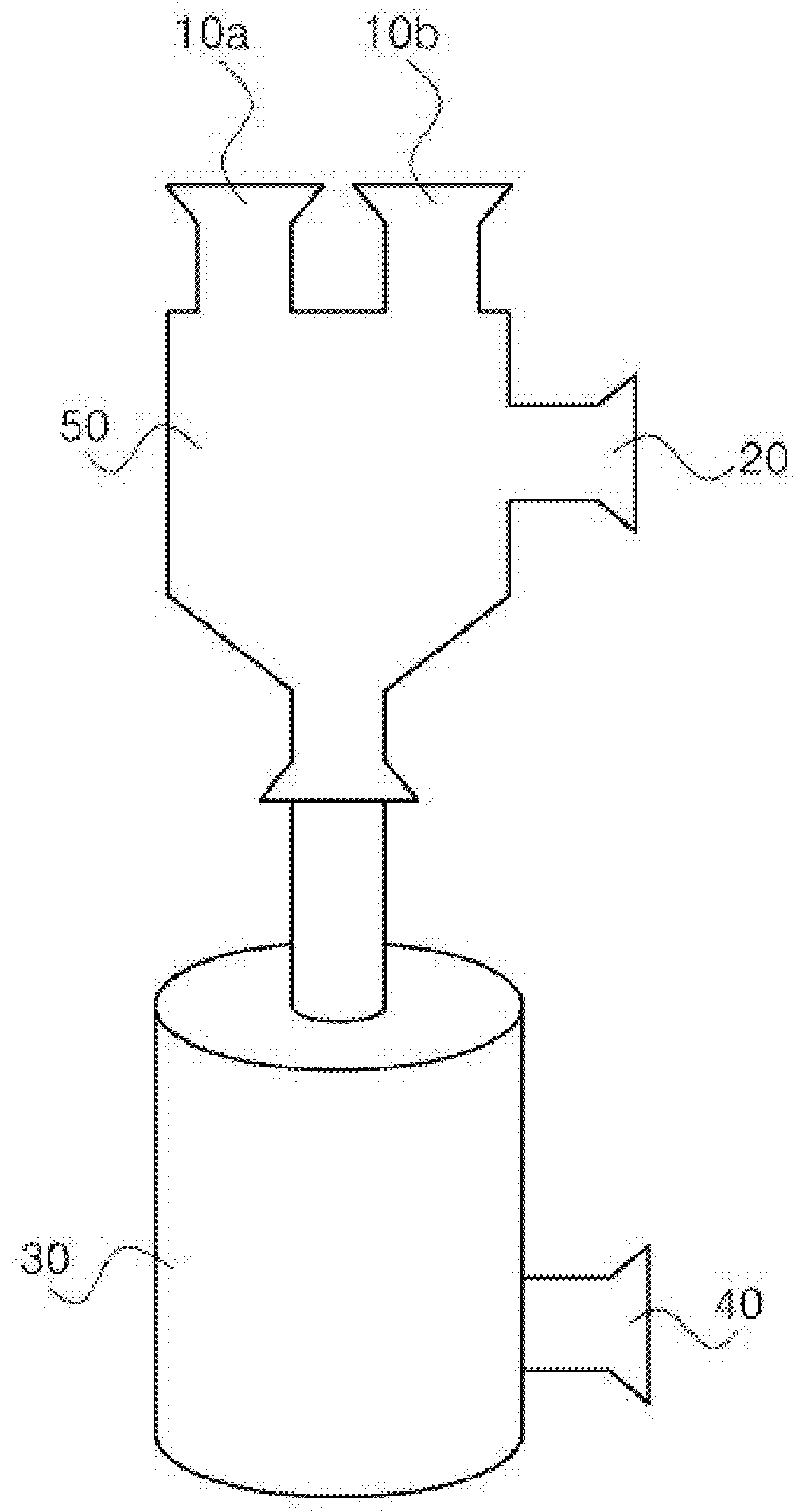
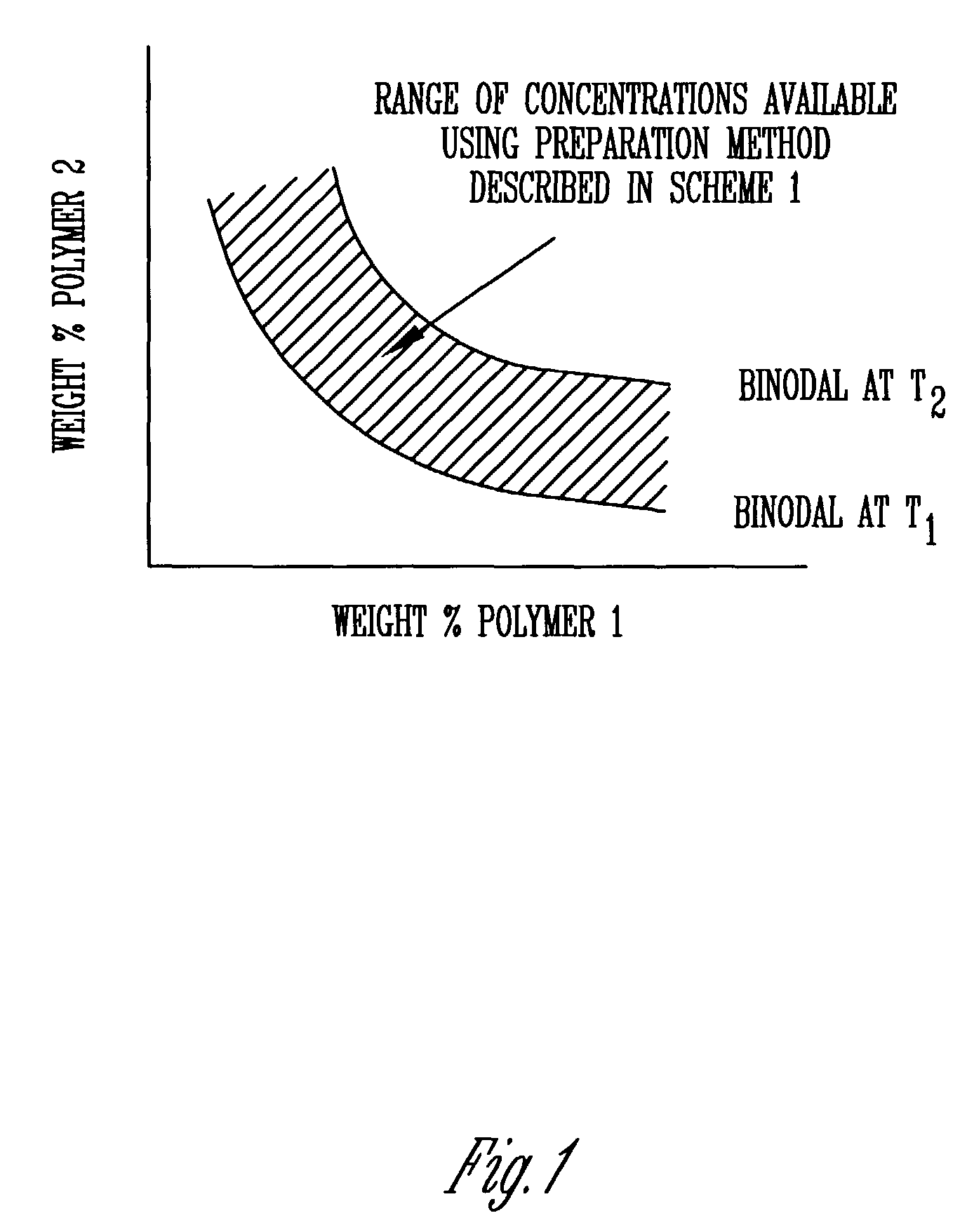
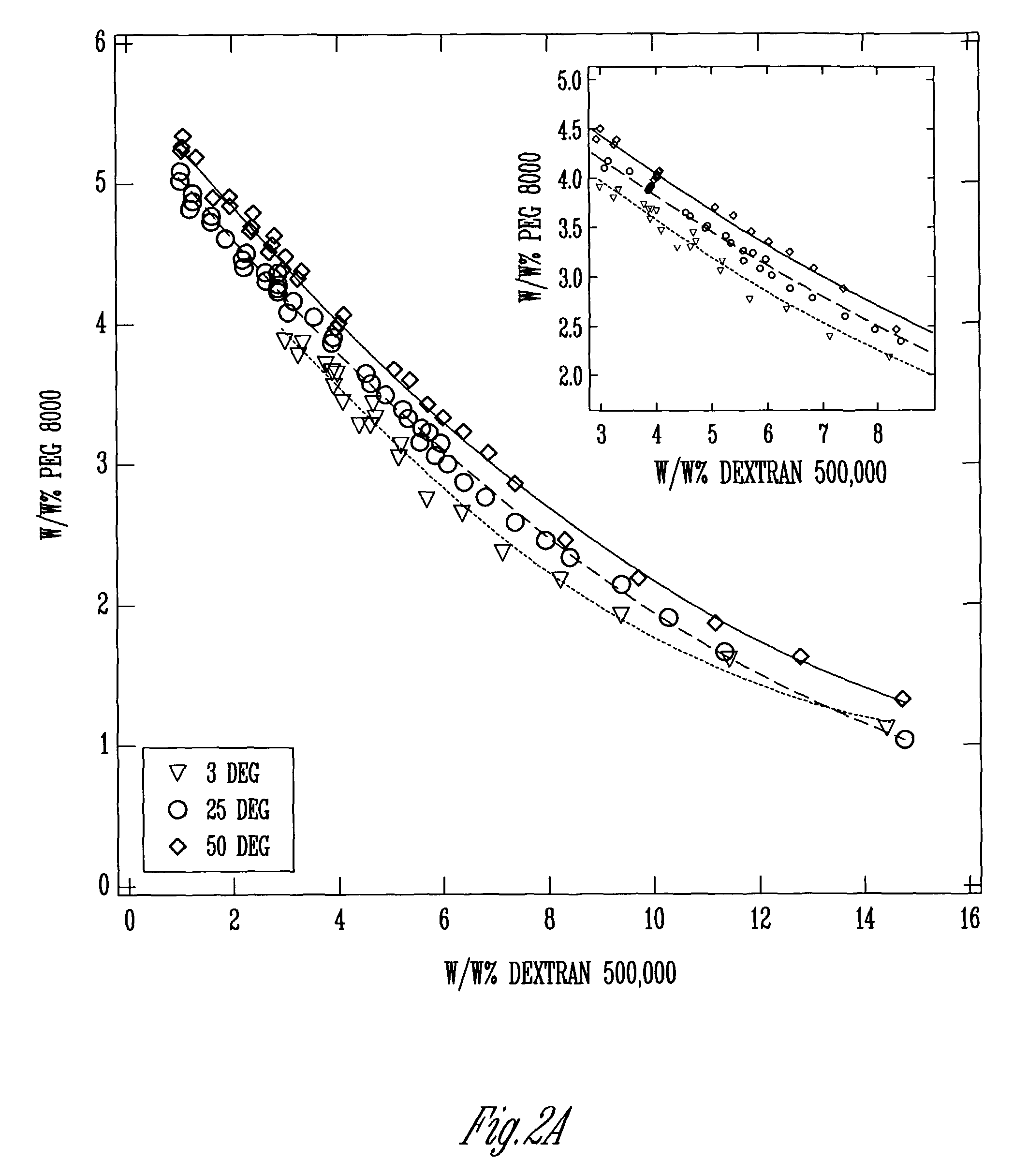
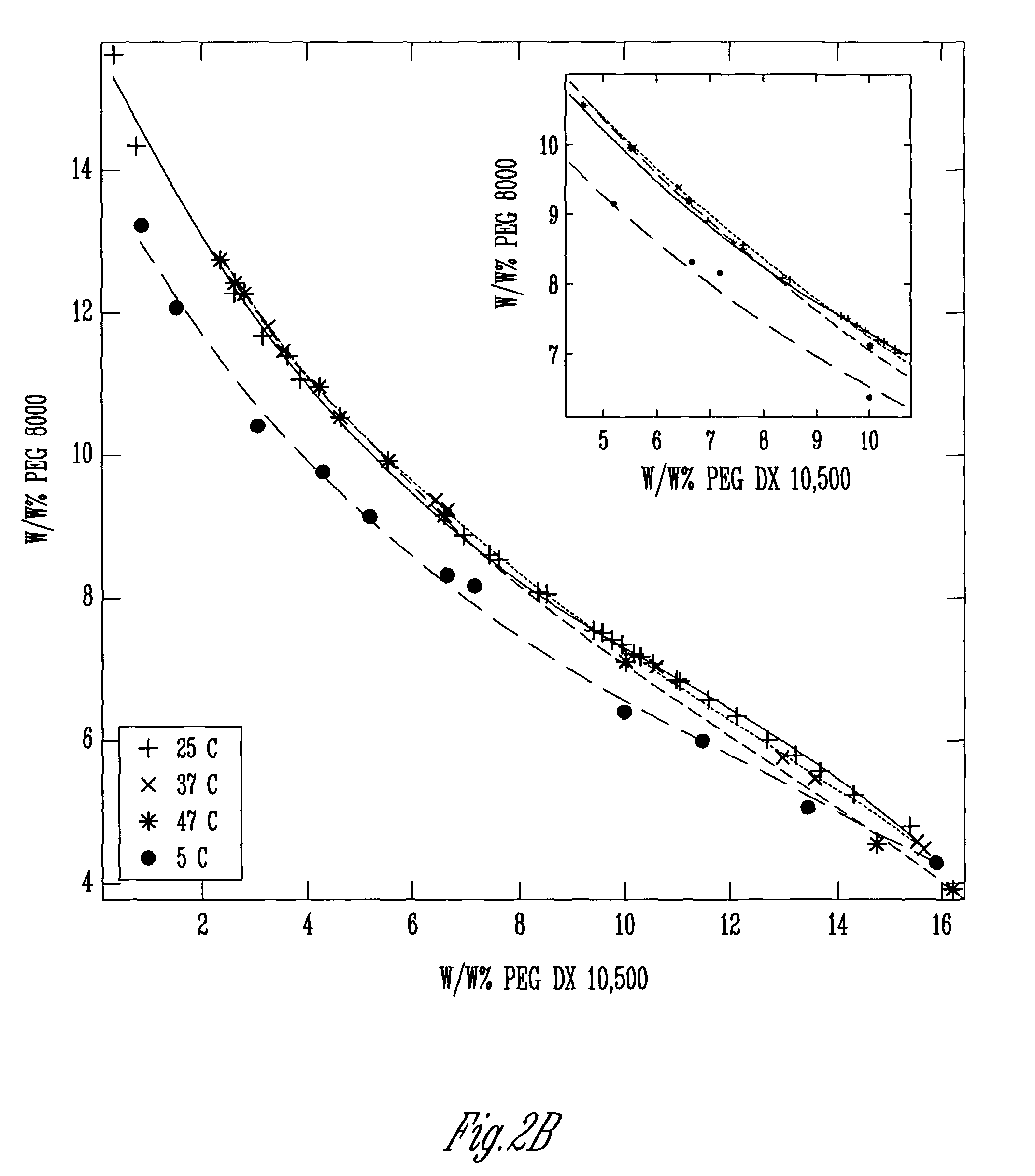
Process for the fractionation of polymers
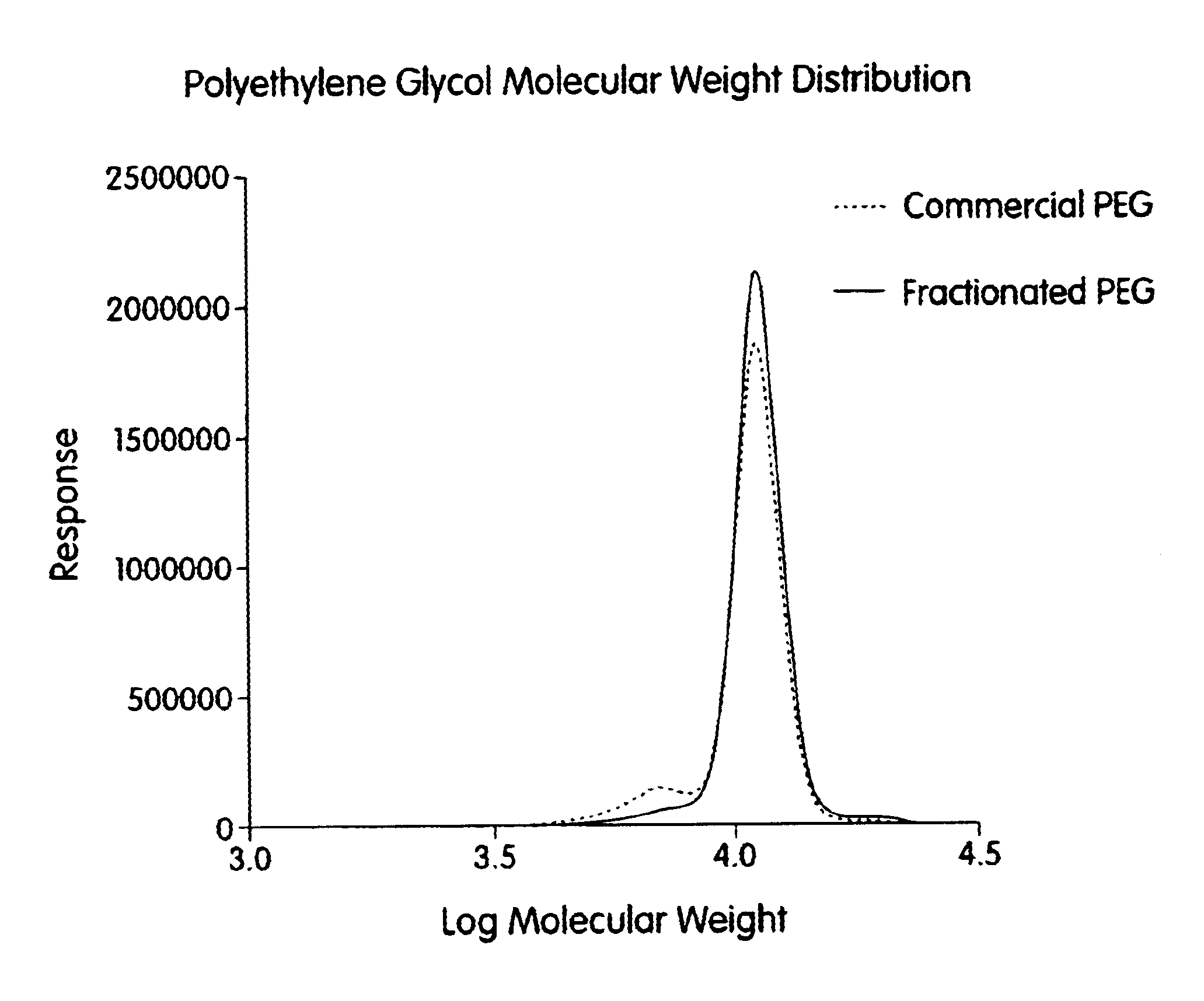
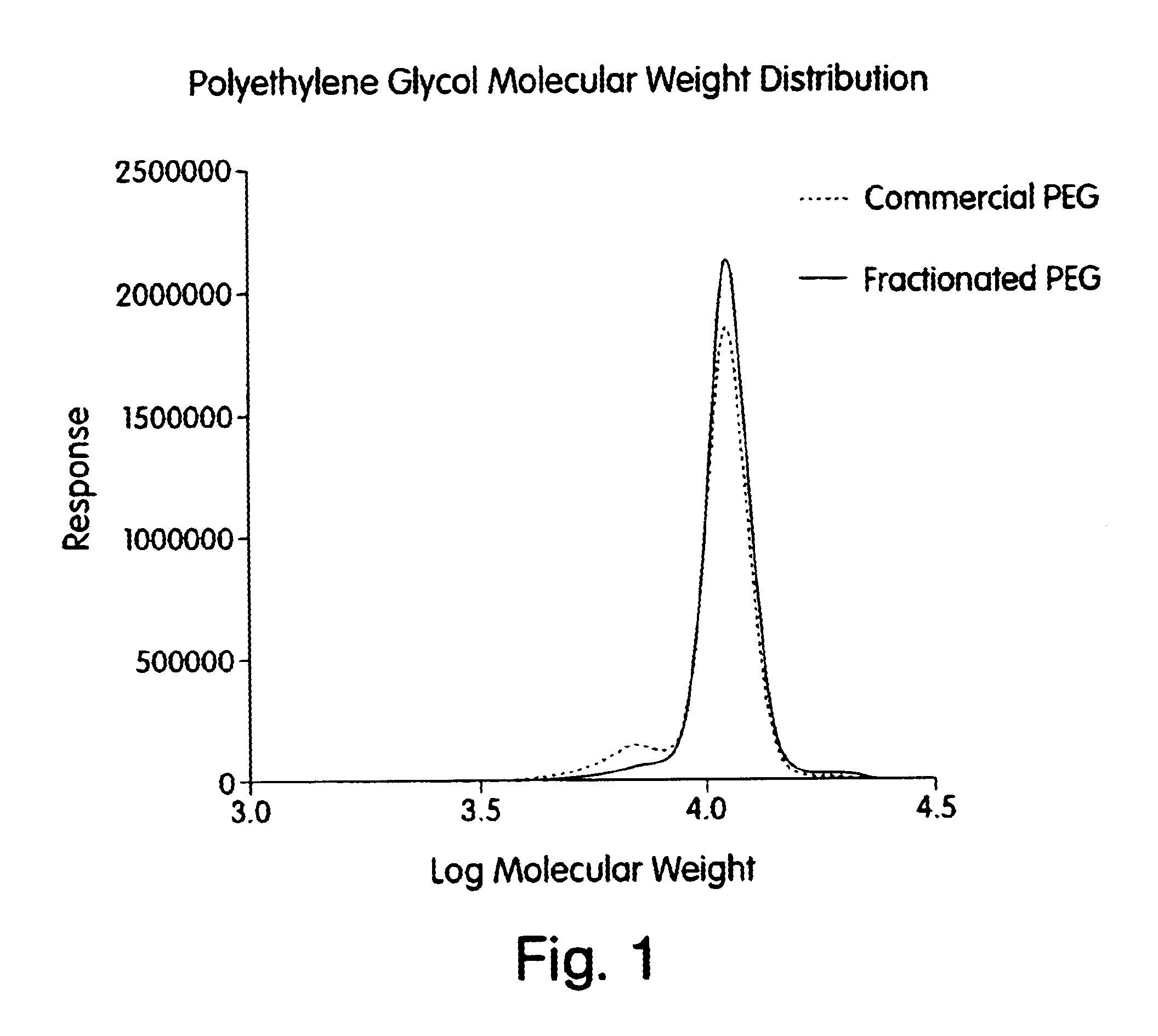
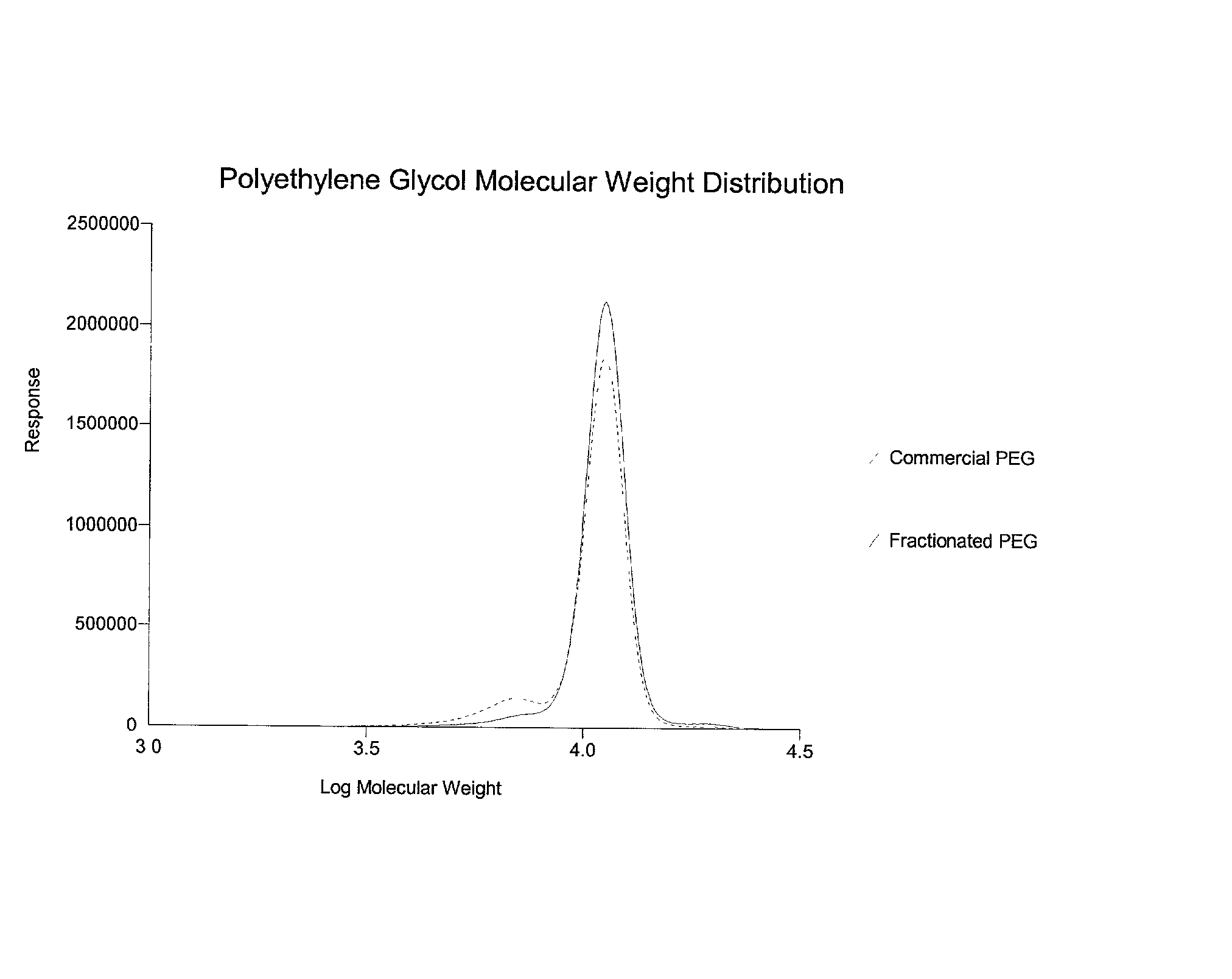
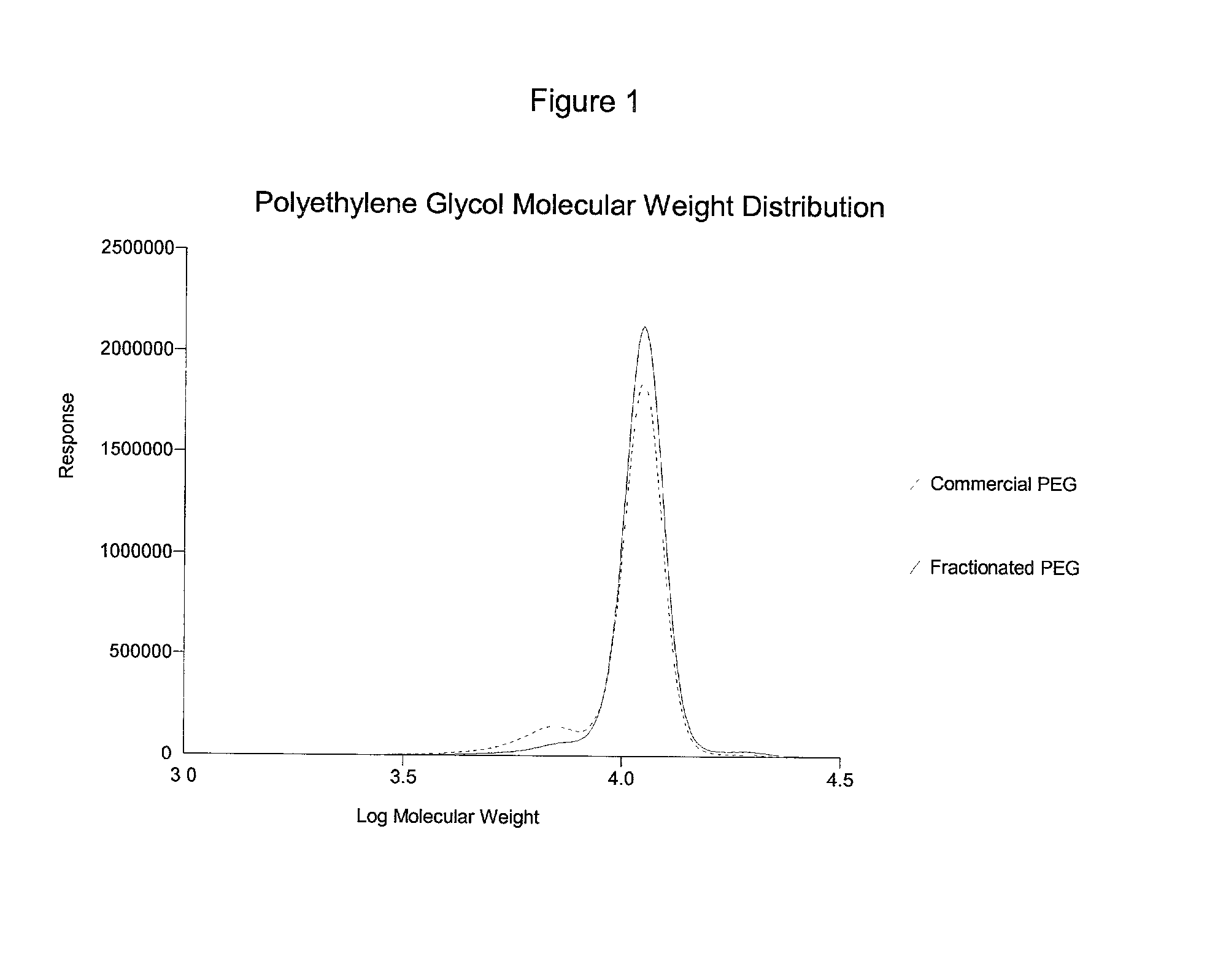
A process for the purification or fractionation of aqueous soluble polymers using an aqueous two-phase system is described. The concentrations of the polymer to be fractionated and of an aqueous soluble salt, and the temperature of the aqueous fractionation medium are adjusted so that two phases form, the lower molecular weight polymer molecules partition into the high salt concentration phase, and the higher molecular weight polymer molecules partition into the low salt concentration phase. The resulting high molecular weight polymers are characterized by a higher average molecular weight and a narrower molecular weight distribution and decreased unsaturation than the unfractionated polymers. After being subjected to the fractionation process, polyol polymers that form hydrogels in aqueous solution exhibited higher viscosities and a liquid to gel transition over a narrower temperature range than the unfractionated polyol polymers.
Owner:HINSBERG MICHAEL G +1
Injectable hydrogel microspheres from aqueous two-phase system
InactiveUS7776240B2Big lossSustained releaseLiquid surface applicatorsPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityEmulsion
Injectable hydrogel microspheres are prepared by forming an emulsion where hydrogel precursors are in a disperse aqueous phase and polymerizing the hydrogel precursors. In a preferred case, the hydrogel precursors are poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate and N-isopropylacrylamide and the continuous phase of the emulsion is an aqueous solution of dextran and a dextran solubility reducer. The microspheres will load protein, e.g., cytokines, from aqueous solution.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Aqueous two-phase extraction and separation method for flavonoids, saponins and polysaccharides of astragalus
InactiveCN102697839AShort experiment cycleHigh recovery rateAntipyreticDigestive systemDipotassium hydrogen phosphateMedicinal herbs
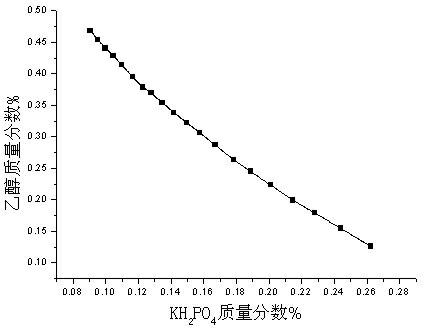
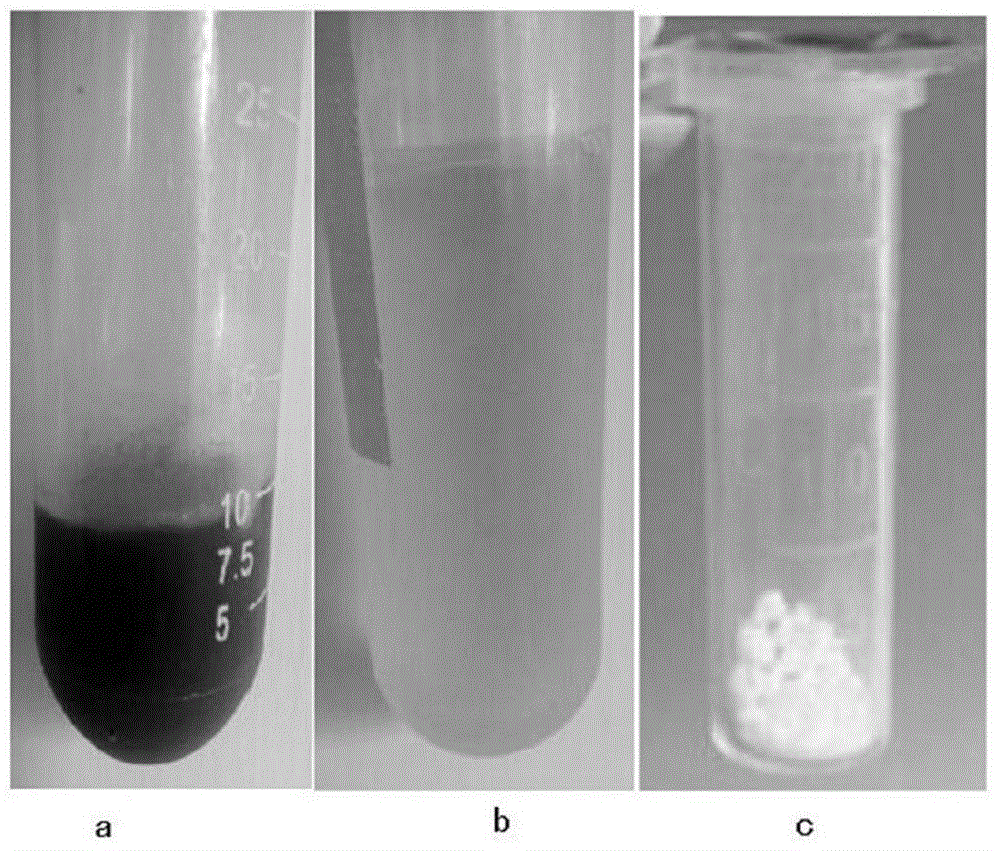
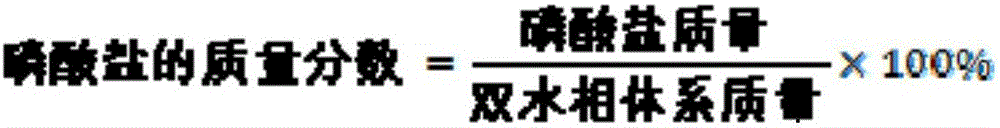
The invention relates to an aqueous two-phase separation method for total flavonoids, saponins and polysaccharides in astragalus. The method comprises the following steps of smashing an astragalus medicinal material; adding a solvent and performing solid-liquid extraction; filtering and removing impurities to obtain crude extract of the total flavonoids and the saponins of the astragalus; taking and concentrating the crude extract of the astragalus; adding an aqueous two-phase system formed by absolute ethyl alcohol / dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, adding water to make the total amount of the system be a constant value; mixing uniformly and standing, wherein the aqueous two-phase system is divided into an upper phase and a lower phase; taking an ethanol phase which contains a large amount of total flavonoids and saponins of the astragalus out; and concentrating the ethanol phase under a reduced pressure to obtain the extract of the total flavonoids of the astragalus. The method has the beneficial effects that the extraction rate of the total flavonoids and the total saponins of the astragalus; simultaneously the total flavonoids and the total saponins can be separated from the polysaccharides of the astragalus in the crude extract; the used solvent is low in toxicity, favorable to environment friendliness and low in cost; the inactivation or the denaturation of the flavonoids and the saponins of the astragalus cannot be caused; the phase separation time is short; the interfacial tension is low; and residual organic solvent does not exist.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Mixer settler for three-phase extraction
InactiveCN101991971AAchieve separationSolving Three-Phase Flow ProblemsLiquid solutions solvent extractionPhase mixingThree stage
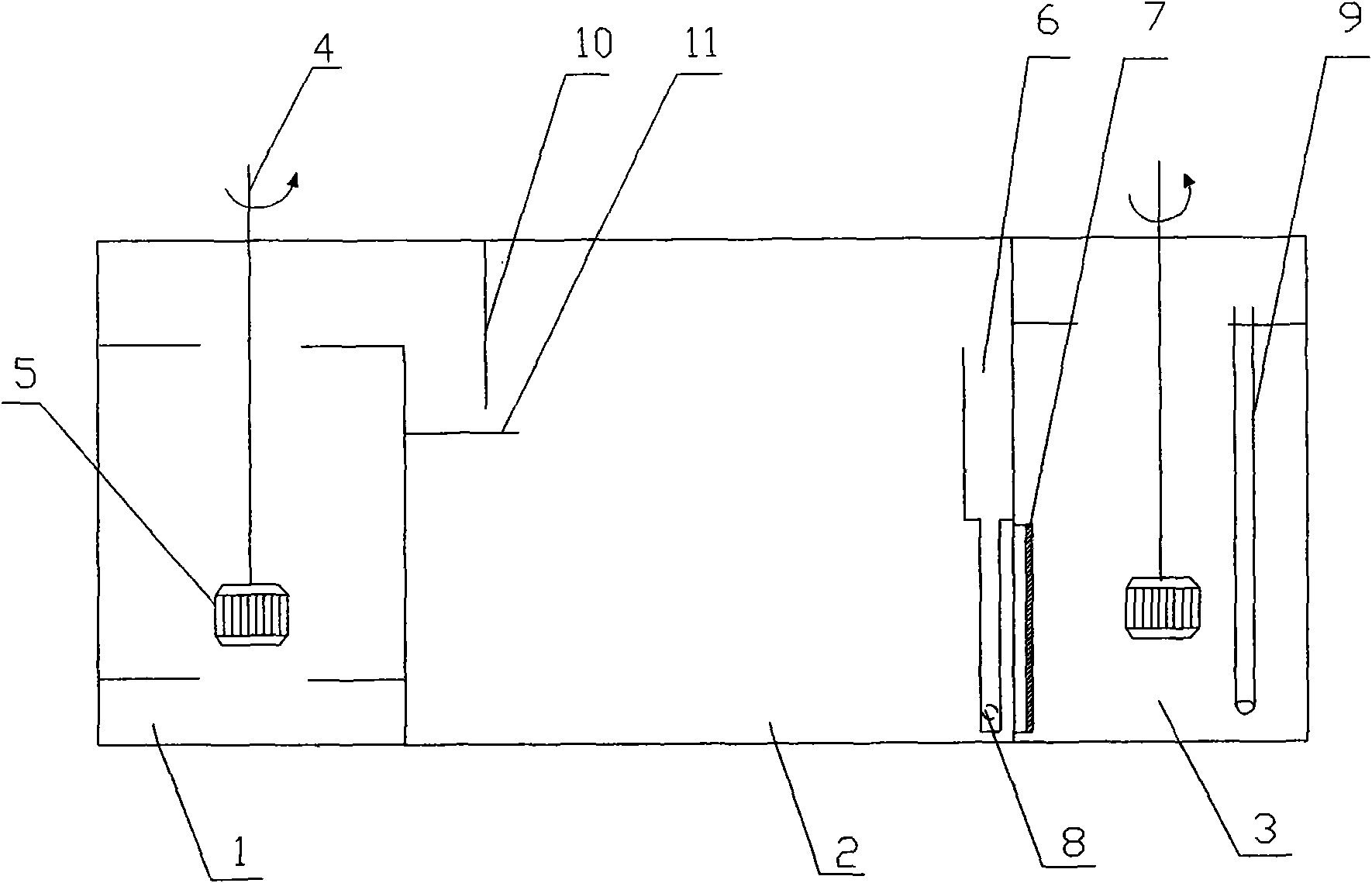
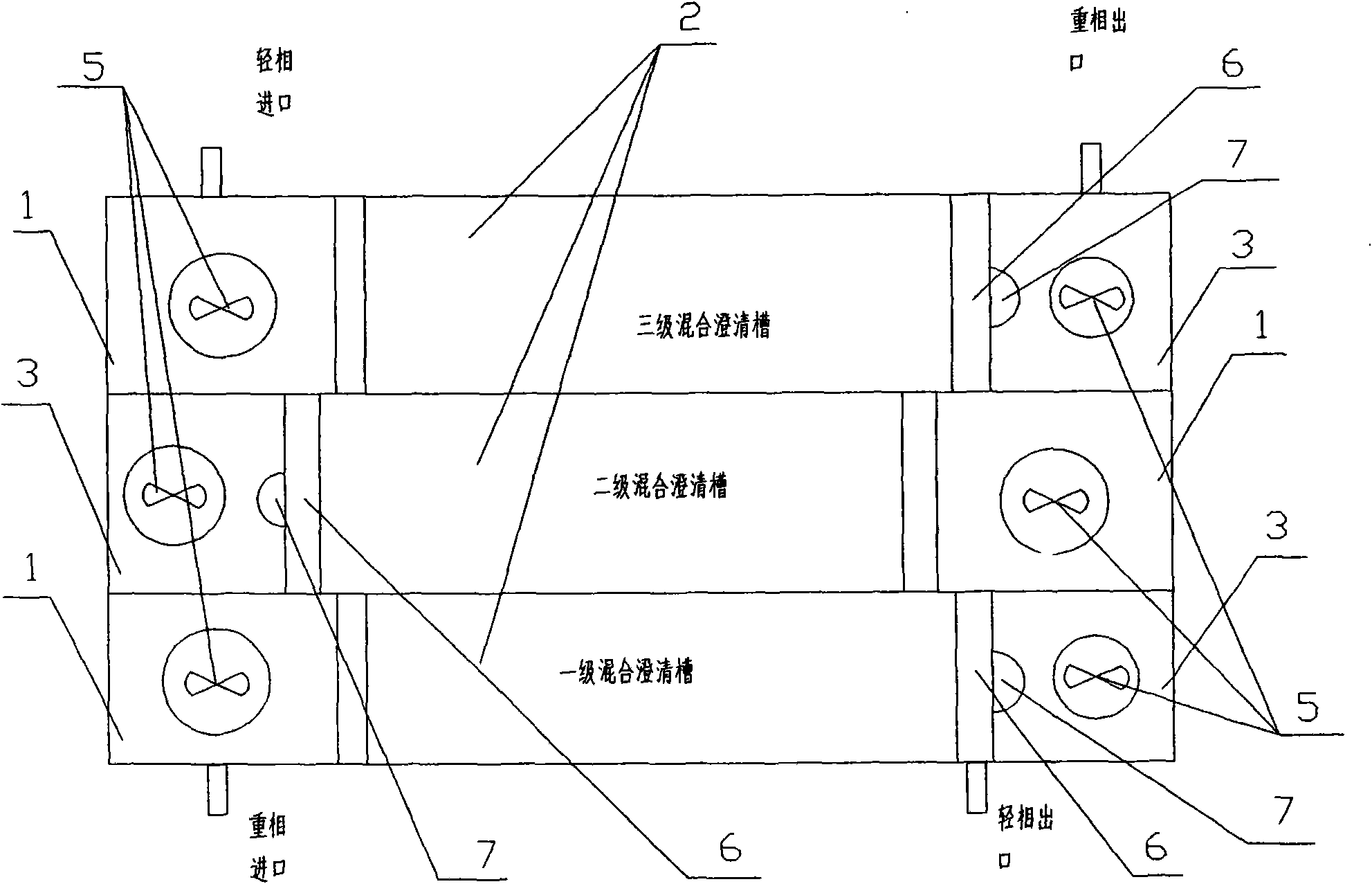
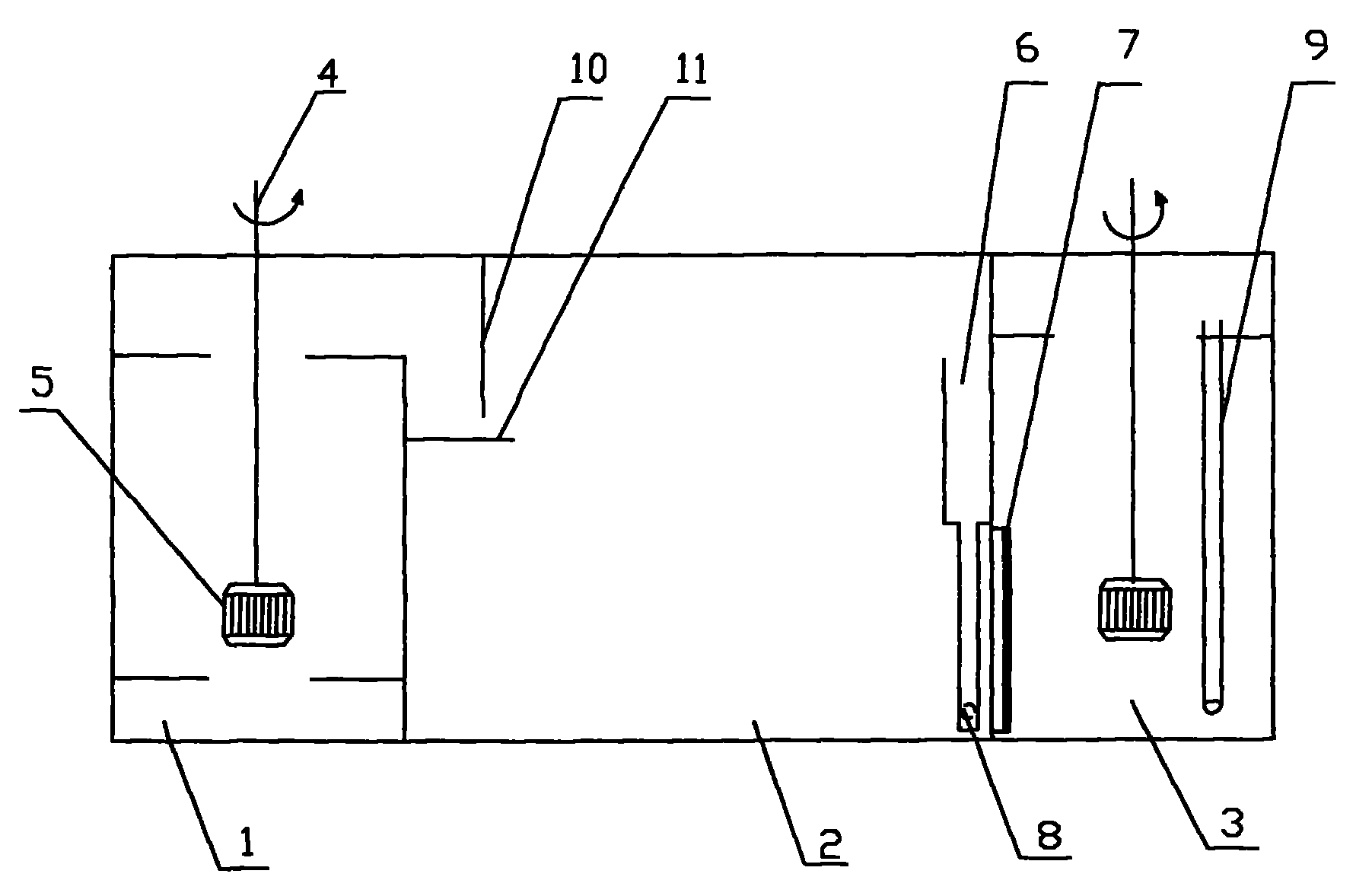
The invention belongs to a liquid-liquid-liquid three-phase multi-stage continuous extraction device, and particularly relates to a mixer settler for three-phase extraction, which can extract the target component in one step and realizes high-level separation in a multi-component complex system. The mixer settler for three-phase extraction comprises a first-level mixer settler, a second-level mixer settler and a third-level mixer settler which have the same structure; and every mixer settler comprises a three-phase mixing chamber, a clarifying chamber, an intermediate-low phase mixing chamber, and the like. As an aqueous two-phase system, an intermediate phase and a salt-rich low phase rich in polymer are used as one phase under the condition of stirring to transfer mass during counterflow with the organic phase so that the problem of three-phase flow in the three-phase extraction process is solved and the multi-stage continuous extraction can be carried out. Under the circumference that the one-stage extraction separating effect is unsatisfactory in the multi-component complex system, the mixer settler for three-phase extraction can realize three-stage reverse flow continuous extraction and high-level multi-component separation according to the components. The invention successfully solves the problem of three-phase flow in the three-phase extraction process.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for the fractionation of polymers
A process for the purification or fractionation of aqueous soluble polymers using an aqueous two-phase system is described. The concentrations of the polymer to be fractionated and of an aqueous soluble salt, and the temperature of the aqueous fractionation medium are adjusted so that two phases form, the lower molecular weight polymer molecules partition into the high salt concentration phase, and the higher molecular weight polymer molecules partition into the low salt concentration phase. The resulting high molecular weight polymers are characterized by a higher average molecular weight and a narrower molecular weight distribution and decreased unsaturation than the unfractionated polymers. After being subjected to the fractionation process, polyol polymers that form hydrogels in aqueous solution exhibited higher viscosities and a liquid to gel transition over a narrower temperature range than the unfractionated polyol polymers.
Owner:HINSBERG MICHAEL G +1
Method for extracting Olea europaea leaf polyphenol by aqueous two phase system
ActiveCN104922220AHigh extraction rateHigh purityAntinoxious agentsPlant ingredientsInorganic saltsUltrasonic assisted
The invention discloses a method for extracting Olea europaea leaf polyphenol by an aqueous two phase system. The method comprises the following steps of adding dried and crushed Olea europaea leaves into the aqueous two phase system containing hydrophilic low molecules organic solvent and inorganic salt solution, mixing, performing ultrasonic extraction, and extracting the Olea europaea leaf polyphenol to an upper phase; performing enrichment on the upper phase with macroporous resin, eluting the upper phase with the organic solvent, and concentrating and drying eluant to obtain the Olea europaea leaf polyphenol; the recovery rate of the Olea europaea leaf polyphenol is more than 90 percent, and the purity of the Olea europaea leaf polyphenol is more than 80 percent. The aqueous two phase extraction technique, which is a new isolation technique, is applied to isolation and extraction of the Olea europaea leaf polyphenol by combing with the traditional ultrasonic-assisted organic solvent extraction technique, therefore the method has the advantages that the product yield is high, the product purity is high, extraction is rapid, the condition is mild, equipment is simple, the Olea europaea leaf polyphenol is easy to amplify, and the like.
Owner:西安绿泉科技有限公司
Method for extracting and separating vanadium from chromium by using three-phase system
InactiveCN102534266AHigh separation factorEfficient separationProcess efficiency improvementPolymer dissolutionSeparation coefficient
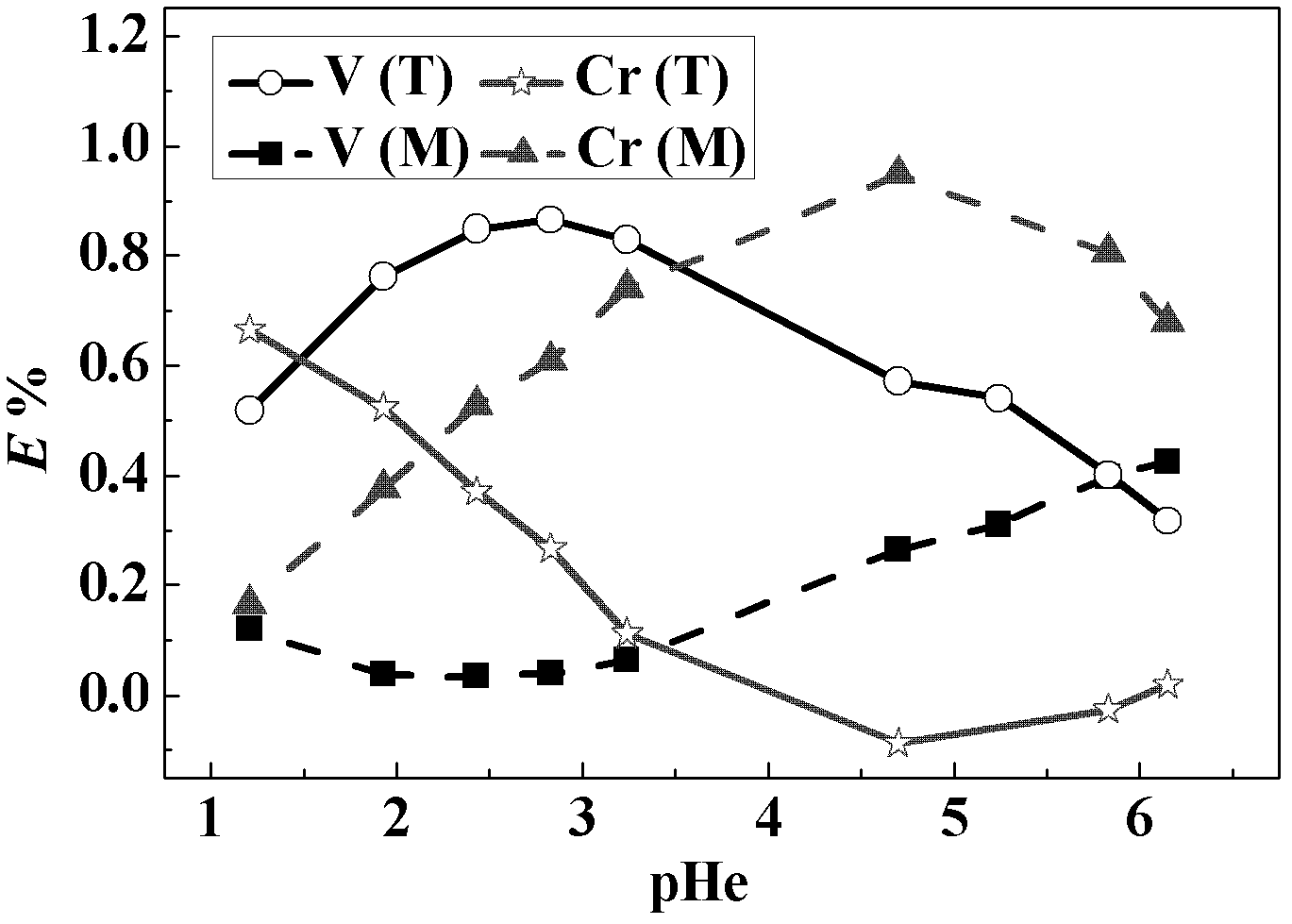
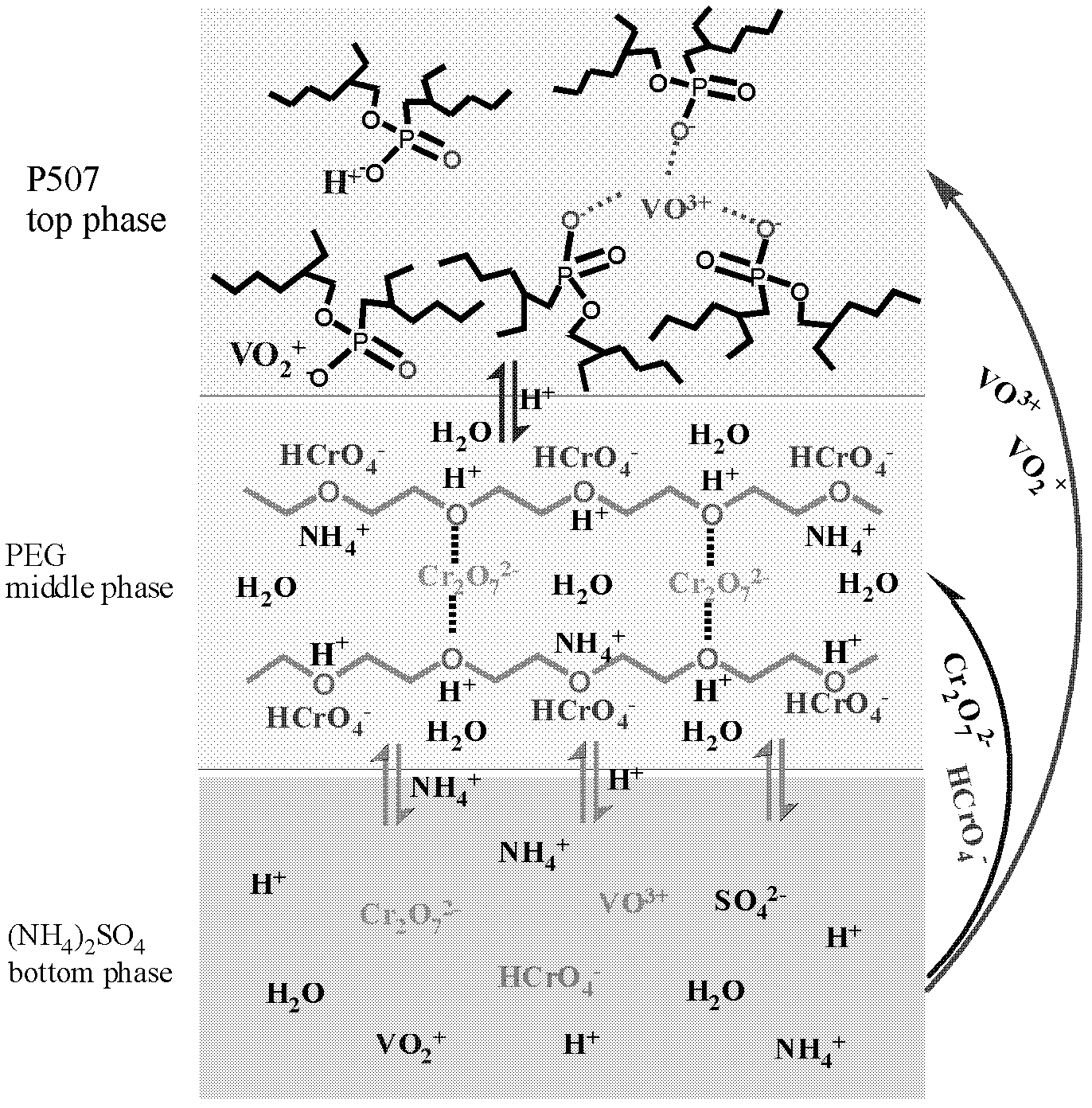
The invention relates to a method for extracting and separating vanadium from chromium by using liquid-liquid-liquid three-phase system, which comprises the following steps of: adding phase forming salt and a polymer in vanadium and chromium solution and forming an aqueous two-phase system after the phase forming salt and the polymer are dissolved; and then adding an organic phase in the formed aqueous two-phase system, vibrating and carrying out phase separation to obtain the three-phase system. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that: (1) the separation coefficient of vanadium from chromium is large, so that the effective separation of vanadium from chromium can be realized in one step; (2) the utilization rate of vanadium and chromium is high, so that the resource waste is effectively reduced; (3) the method is good in physical phenomenon, short in process flow, simple and convenient in operation, low in cost, less in energy consumption and good in control, and as long as the effective separation of vanadium from the chromium can be realized, the production process for further recovering vanadium and chromium is mature.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction and separation method of kudzu root total flavones
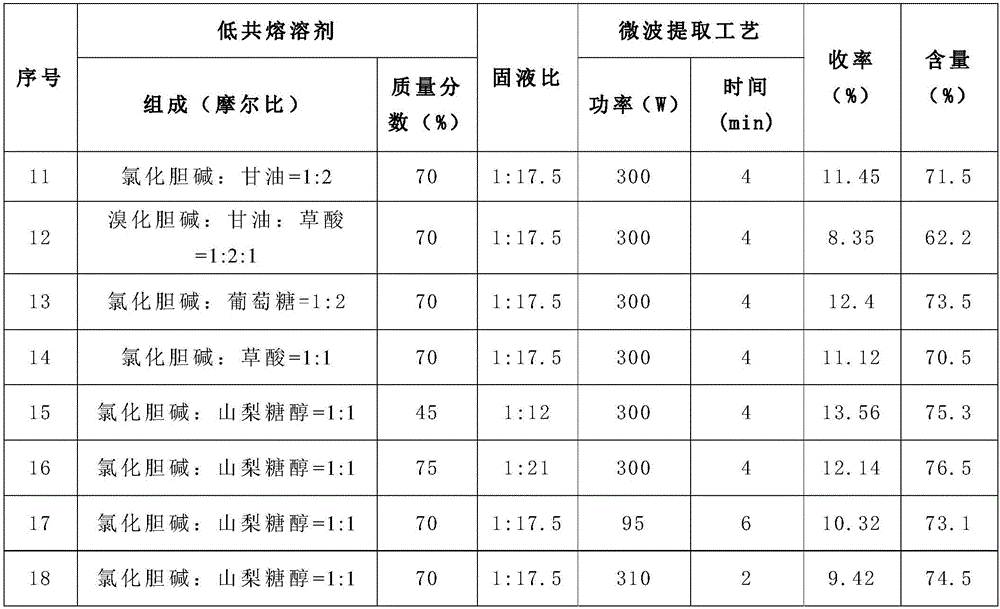
The invention relates to a microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction method for separating kudzu root total flavone, which comprises the following steps: 1) preparation of an aqueous two-phase system: taking an inorganic salt, adding water to dissolve the inorganic salt, and adding an organic solvent to obtain a aqueous two-phase extractant; and 2) microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction: adding kudzu root powder into the aqueous two-phase extractant obtained in the step 1), carrying out microwave-assisted extraction, and carrying out vacuum filtration to obtain an obvious phase-separated kudzu root flavone extracting solution. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the following advantages: (1) the method is simple to operate and does not need to wait for phase separation; 2) the process is integrated; 3) the extraction process is quick and efficient; 4) the extraction solvent is low in toxicity; 5) the interfacial tension is small, thereby being beneficial to mass transfer between the two phases; 6) abundant impurities can be removed along with solid matters, thereby being beneficial to purifying the sample; and 7) the extraction method does not have obvious scale-up effect, can easily implement technique amplification and continuous operation, and can be directly connected with the subsequent purification procedure without special treatment.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Recovery and purification of b-phycoerythrin produced by porphyridium cruentum using two-aqueous-phase systems and isoelectric precipitation
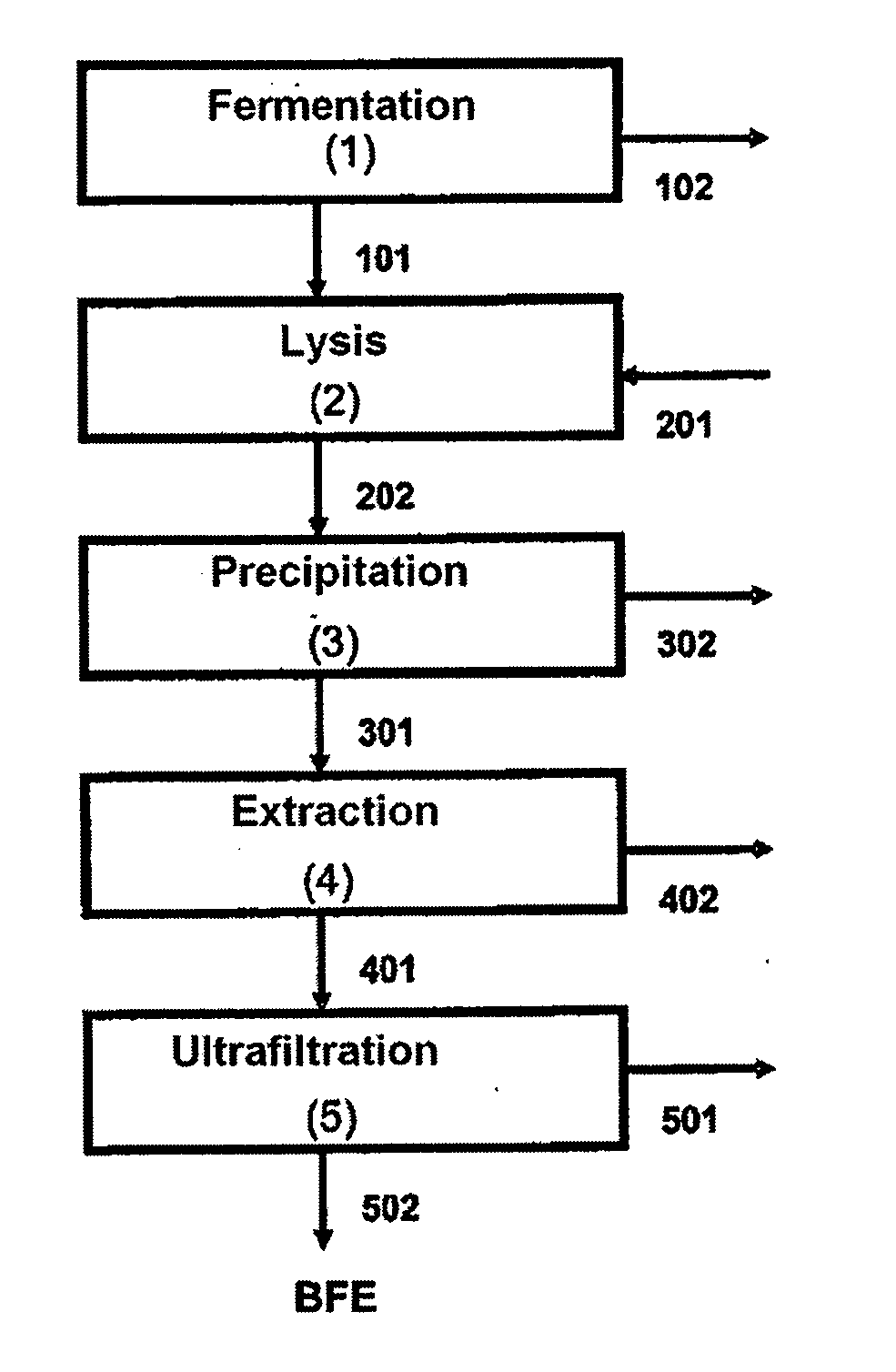
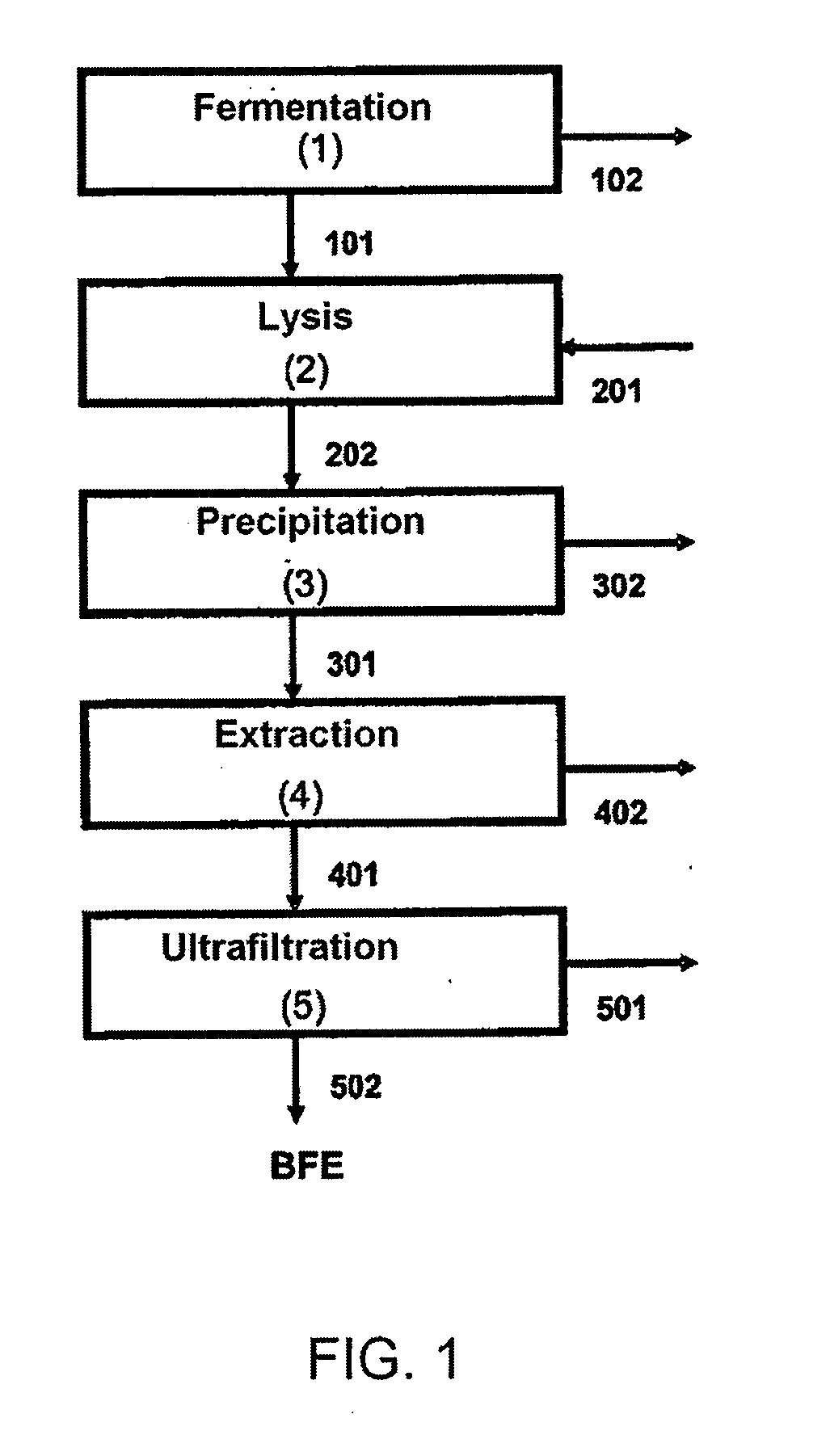
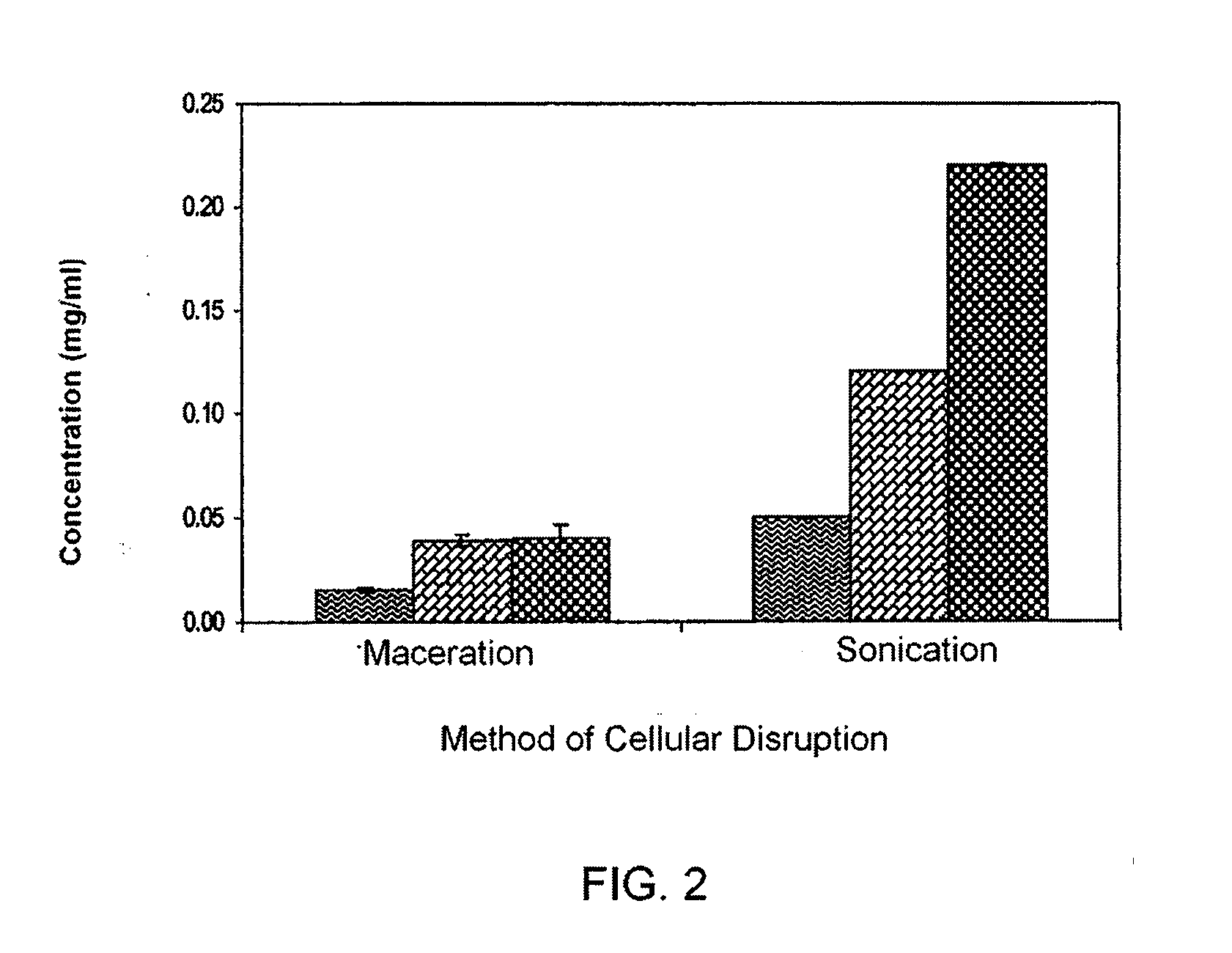
This invention focuses on a novel process in which Porphyridium cruentum biomass first undergoes a stage of cellular disruption and subsequently stages of recovery and purification in order to achieve the purified B-phycoerythin (BFE) protein dye, using isoelectric precipitation and two-aqueous-phase systems. The steps of recovery and purification include isoelectric precipitation followed by a step of liquid / liquid extraction by means of two-aqueous-phase systems that use polyethylene glycol (PEG) and phosphate salts. The BFE protein dye obtained in the two-aqueous-phase extraction step undergoes an ultrafiltration step in order to remove the polymer (PEG) and to obtain a dye with a purity greater than 4.0 defined as the relationship between the absorbencies at 545 and 280 nm (BFE purity=Abs 545 nm / Abs 280 nm).
Owner:INST TECHNOLOGICO & DE ESTUDIOS SUPERIORES DE MONTERREY
Aqueous two-phase extraction method for total flavones in kudzu root
InactiveCN102319282AReduce usageEasy to purifyCardiovascular disorderPlant ingredientsReflux extractionProcess integration
The invention relates to an aqueous two-phase extraction method for total flavones in kudzu root. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) solid-liquid leaching: smashing a kudzu root medicinal material, adding a leaching agent, heating, performing reflux extraction, and combining the filtrate to obtain a kudzu root crude extract; (2) aqueous two-phase extraction: concentrating the kudzu root crude extract obtained in the step (1), adding into an aqueous two-phase system formed by absolute ethanol / monopotassium phosphate, adding water, mixing uniformly, and standing to separate into an upper phase and a lower phase; and (3) distilling under reduced pressure, and drying in vacuum to obtain a kudzu root total flavone extract. The invention has the advantages: (1) phase separating israpid, and the recovery rate is high; (2) process integration is performed, the aim of purifying through aqueous two-phase extraction is fulfilled, and a material liquid is concentrated; (3) the use of n-butyl alcohol serving as a toxic solvent is avoided; (4) the boundary tension is small, and mass transfer between two phases is facilitated; (5) purification of a sample is facilitated; and (6) process amplification and continuous operation are easy, and a subsequent purification process can be directly connected without special treatment.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for separating and purifying beet red pigment by two aqueous phase extraction system
ActiveCN101735648AHigh separation selectivityLarge amount of processingNatural dyesUltrafiltrationPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a method for separating and purifying a beet red pigment, in particular to a method for purifying a crude extract of the beet red pigment by a two aqueous phase extraction method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: soaking the beet tuberous roots with acidic aqueous solution for extracting the beet red pigment and obtaining a pigment crude extract; then adjusting the pH; adding polyethylene glycol and ammonium sulfate to form a two aqueous phase system; fully mixing and extracting the mixture; forming two phases after standing, wherein the beet red pigment enters a top phase of the polyethylene glycol, and saccharide impurities enter a bottom phase of the ammonium sulfate; separating the beet red pigment from the polyethylene glycol in the top phase by using an ultrafiltration membrane method; concentrating the beet red pigment by using inverse penetration or nanofiltration membranes; then concentrating the beet red pigment in vacuum until the solid content of the beet red pigment is over 20 percent; and finally obtaining a beet red pigment product by using a spray drying method.
Owner:QINGDAO PENGYUAN KANGHUA NATURAL PROD
Oleoresin ginger microcapsule and preparation method
ActiveCN101473954AProtect natural componentsReduce concentrationFood shapingMicroballoon preparationFiberCyclodextrin
The invention relates to a ginger oil resin microcapsule and a preparation method thereof. Cyclodextrin is directly combined with functional components of ginger such as gingerol and the like in ginger juice (aqueous solution) to be stewed and refrigerated for split phase to realize separation. The method extracts ginger oil resin from ginger directly by an aqueous two-phase system and prepares the ginger oil resin microcapsule by a microcapsule technology at the same time, two steps of the technical process are integrated in one technology, so that the technology is simple; and at the same time, the extraction separation technical process is carried out in water phase under gentle condition, thereby being good for the comprehensive utilization of ginger starch and ginger dietary fiber. The ginger oil resin microcapsule has stable performance under dry state and has the advantages of good fluidity and crystallinity, good dispersibility, easy absorption, slow release of core material, good controlled release effect, etc.
Owner:CHONGQING FOOD IND RES INST
Process for partitioning of proteins
InactiveUS7060669B1Minimize impactEfficient purificationFungiBacteriaProtein targetAqueous two-phase system
The present invention relates to isolation and purification of proteins in aqueous two-phase systems (ATPS). Specifically the invention provides processes for partitioning of proteins of interest in ATPS by fusing said proteins to targeting proteins which have the ability of carrying said protein into one of the phases.
Owner:VALTION TEKNILLINEN TUTKIMUSKESKUS
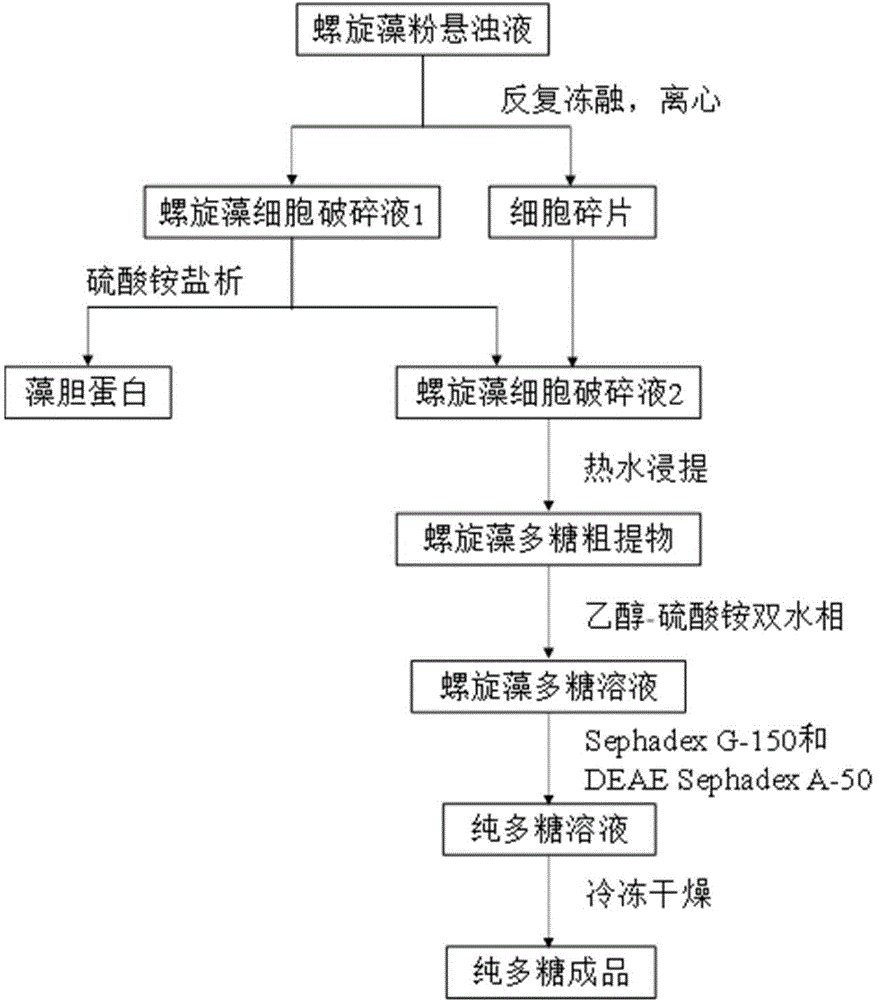
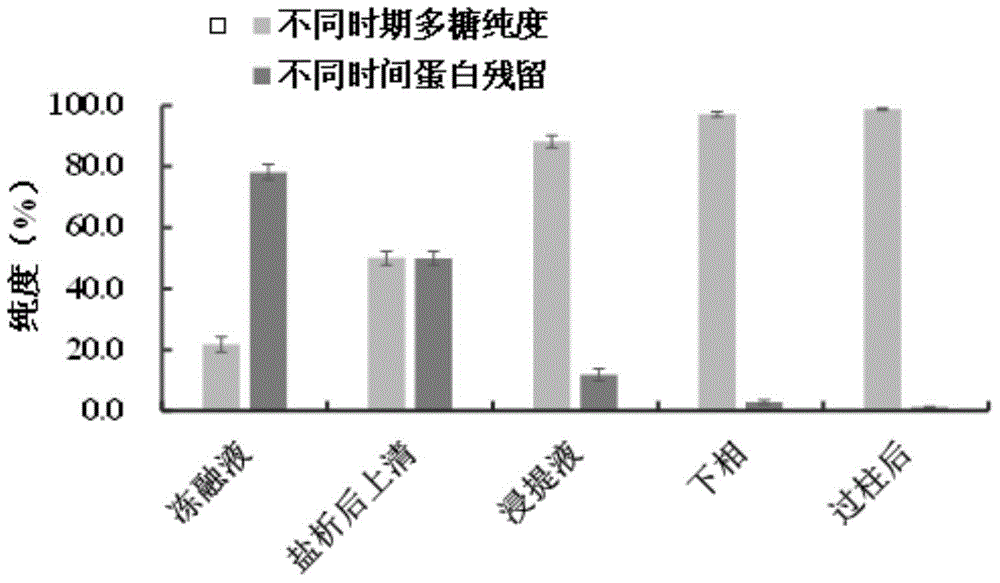
Spirulina phatensis polysaccharide and extraction method thereof
The invention relates to a spirulina phatensis polysaccharide and an extraction method thereof. The extraction method comprises the following steps: after multigelation and wall breaking of a spirulina phatensis powder suspension, centrifuging to obtain a cell lysate 1 and cell debris; adding ammonium sulfate in the cell lysate 1 until the saturation is 50%, after salting-out precipitation, centrifuging to remove phycobiliprotein to obtain a supernatant, and evenly mixing the supernatant and the cell debris to obtain a cell lysate 2; obtaining a spirulina phatensis polysaccharide crude extract by using a hot water extraction method; adding the crude extract to an ethanol / ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase system, and extracting to obtain a bottom-phase solution of spirulina phatensis polysaccharide with higher purity; after the bottom-phase solution is desalted by dialysis, eluting by using a Sephadex G-150 chromatographic column and a DEAE Sephadex A-50 anion exchange column to obtain a pure spirulina phatensis polysaccharide solution; and freeze-drying, thereby obtaining a pure spirulina phatensis polysaccharide finished product. The extraction method can be used for avoiding the traditional complicated protein removal operation steps, has low cost, high yield, and high purity and activity of polysaccharide, and is suitable for intermittent and large-scale production and processing.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Method for extracting phenylethanoid glycoside in herba cistanche by using salt-induced deep-eutectic solvent
ActiveCN106749442ALow separation and purification purposeLow costSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPhosphateAqueous two-phase system
The invention provides a method for extracting phenylethanoid glycoside in herba cistanche by using a salt-induced deep-eutectic solvent on the one hand. According to the method, the phenylethanoid glycoside in the herba cistanche is extracted by using a water solution of the deep-eutectic solvent to extract herba cistanche powder, and adding phosphate into extracting liquid to prepare an aqueous two-phase system. According to the method, conditions of the extraction environment are mild, and phase separation time is short; the yield of the phenylethanoid glycoside in the herba cistanche can reach up to 20%.
Owner:HEXI UNIV
Method for extracting tremella polysaccharide and tremella protein
InactiveCN102876750AAchieve serializationEase of industrial productionMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingTremella
The method relates to a method for extracting tremella polysaccharide and tremella protein. The method comprises the steps of (1) activated culture and fermentation culture of tremella fuciformis berk bacteria; (2) concentration with an ultrafiltration membrane and fragmentation tremella fuciformis berk spores; (3) preparation of a polyethylene glycol / inorganic salt aqueous two-phase system; (4) extraction of the polyethylene glycol / inorganic salt aqueous two-phase system; (5) preparation of the tremella polysaccharide via freeze drying; and (6) second extraction of the polyethylene glycol / inorganic salt aqueous two-phase system, filtration with the ultrafiltration membrane and preparation the tremella protein via freeze drying. The method can realize continuous and large-scale production of the tremella fuciformis berk spores and extraction of the tremella polysaccharide, and is convenient for industrialized production of the tremella polysaccharide. The obtained product has not only intercellular polysaccharide of the tremella fuciformis berk spores but also extracellular polysaccharide produced by the liquid fermentation of the tremella fuciformis berk spores, thereby increasing the yield of the tremella polysaccharide. Besides, the tremella polysaccharide and the tremella protein can be separated at the same time, so that the disadvantages of complex operations and pollutions of organic solvents in a conventional sevag method can be prevented; and the purity of the polysaccharide can be increased.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for separating and purifying protein through aqueous-two-phase system
ActiveCN110003323AHigh densityImprove solubilitySerum albuminPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingUltrafiltration
The invention relates to the technical field of separation and purification of natural products, in particular to a method for separating and purifying protein through an aqueous-two-phase system. Themethod comprises the following steps of A, protein extraction through the aqueous-two-phase system, wherein a low-eutectic solvent and an inorganic salt aqueous solution containing the protein are uniformly mixed, then centrifugation is conducted to obtain a liquid-liquid two-phase system, and then a hypophase extraction liquid is collected; B, protein reextraction, wherein the hypophase extraction liquid in step A is diluted with water and then centrifuged to obtain a liquid-solid two-phase system; C, preparation of a pure product of the protein, wherein a solid phase in step B is dissolvedwith water, and freeze drying is conducted after ultrafiltration centrifugation to obtain the pure product of the protein, wherein in step A, the low-eutectic solvent is prepared from quaternary ammonium salt and hexafluoroisopropanol. According to the method, a DES-salt aqueous-two-phase system based on HFIP is adopted, the DES phase is easy to collect, the extraction rate and reextraction rate on the protein are high, the protein purity is high, and the structure and activity of the protein are both maintained; the operation is simple.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method of extracting phycocyanin from ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system
InactiveCN103880950ASave operating timeEasy to operateDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsDipotassium phosphateCrusher
The invention discloses a method of extracting phycocyanin from an ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system and particularly relates to a method of extracting phycocyanin from spiral seaweeds. The method comprises the following steps of: mechanically crushing spiral seaweed materials, adding into proper amount of dipotassium phosphate aqueous liquor and soaking, placing into an ultrasonic crusher to carry out wall-breaking treatment on spiral seaweed cells; extracting crude extracting liquor of spiral seaweed phycocyanin by utilizing the ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system formed by ionic liquid, dipotassium phosphate and water; and adopting column chromatography for separating and purifying the ionic liquid containing the phycocyanin to obtain the phycocyanin fine powder.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Method for concentrating and separating flavonoids from toona sinensis leaves
InactiveCN101396432ARapid phase separationShort experiment cycleMetabolism disorderDigestive systemCedrela sinensisVacuum drying
The invention relates to a method for enriching and separating flavones in cedrela sinensis leaves by an aqueous two-phase system, the cedrela sinensis leaves are firstly dried and crushed, crude extract liquid of the cedrela sinensis leaves is obtained after reflux extraction and impurity removal, ammonium sulfate and ethanol are added according to the proportion after concentration, heating and the even mixing are carried out, thereby being split into upper and lower phases; the flavones are mainly distributed in the upper phase containing the ethanol and further concentrated and purified. The lower phase is cooled, crystallized and filtered after splitting the upper and the lower phases, ammonium sulfate crystals are recovered; anhydrous ethanol is added in the upper phase liquid for precipitating, removing the ammonium sulfate and other residual impurities and then recovering the ethanol, and a product is obtained by vacuum drying the concentrated liquid. The method has the advantages of rapid phase split, integrated process and improves the concentration and purity of the flavones in the upper phase; the material consumption is reduced, the toxicity is small, the ethanol and the ammonium sulfate are easy to be recovered and utilized; the recovery rate of the flavones in the cedrela sinensis leaves is high, the production method is simple, easy to master and not affected by the environment; the cost is low, and the method is applicable to industrial production.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
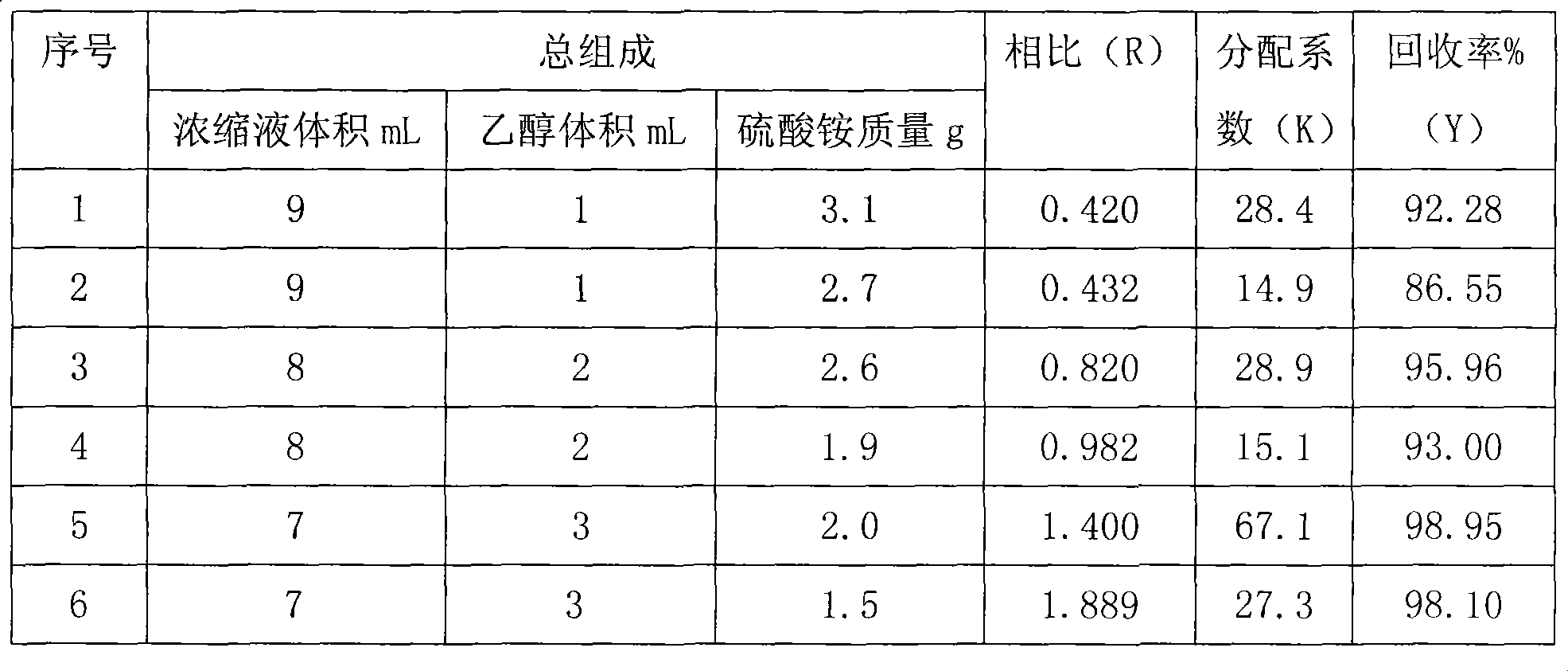
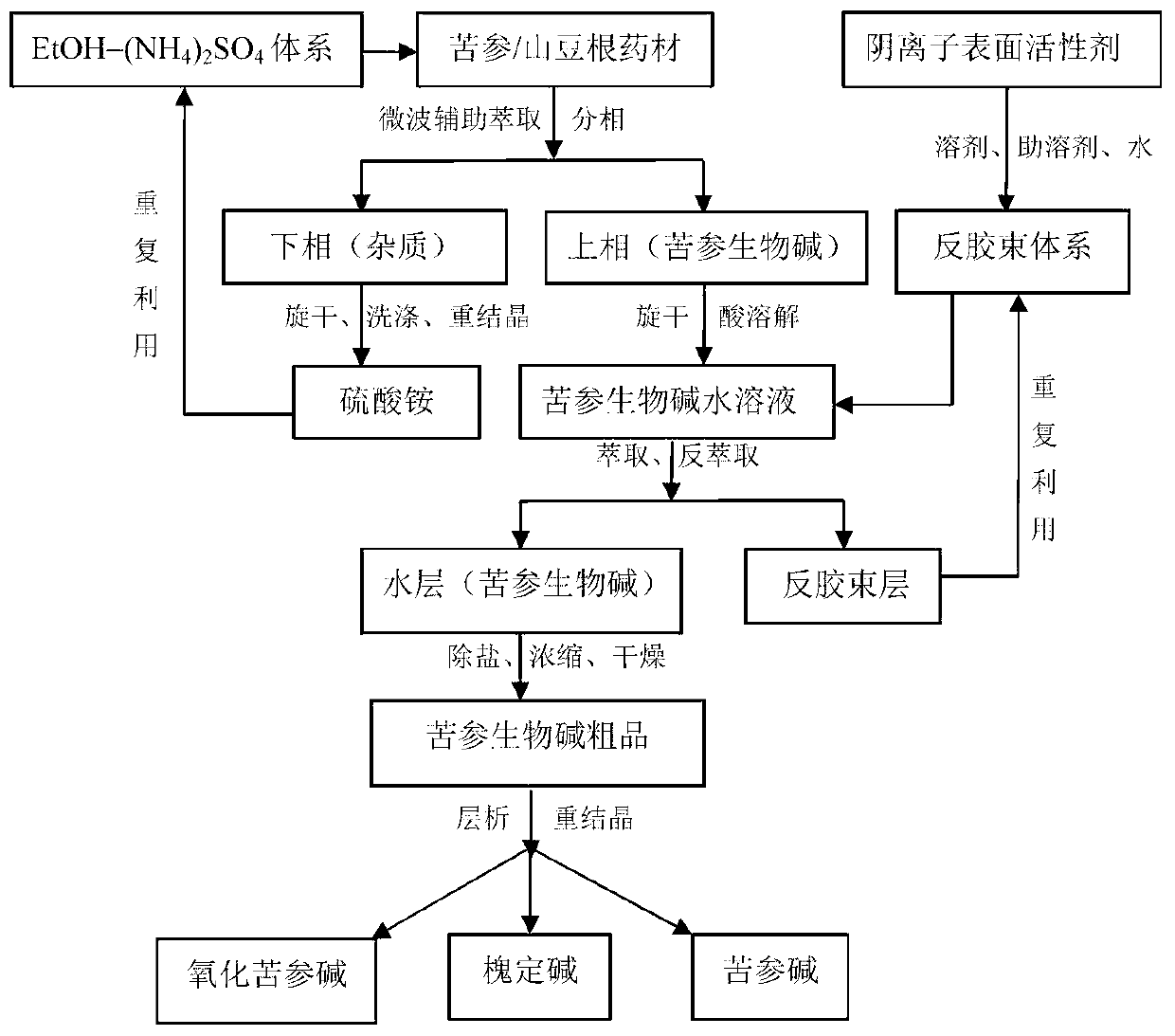
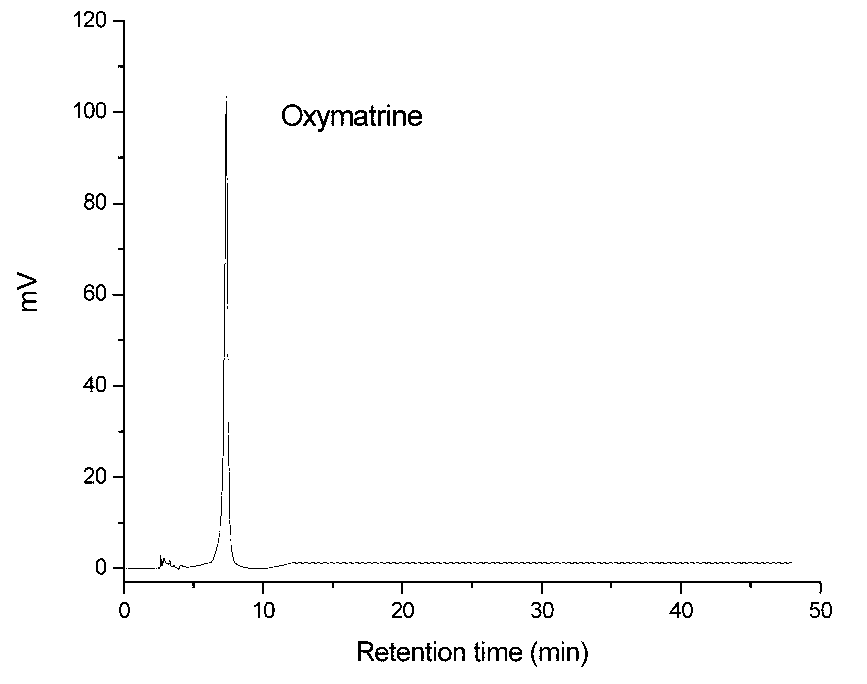
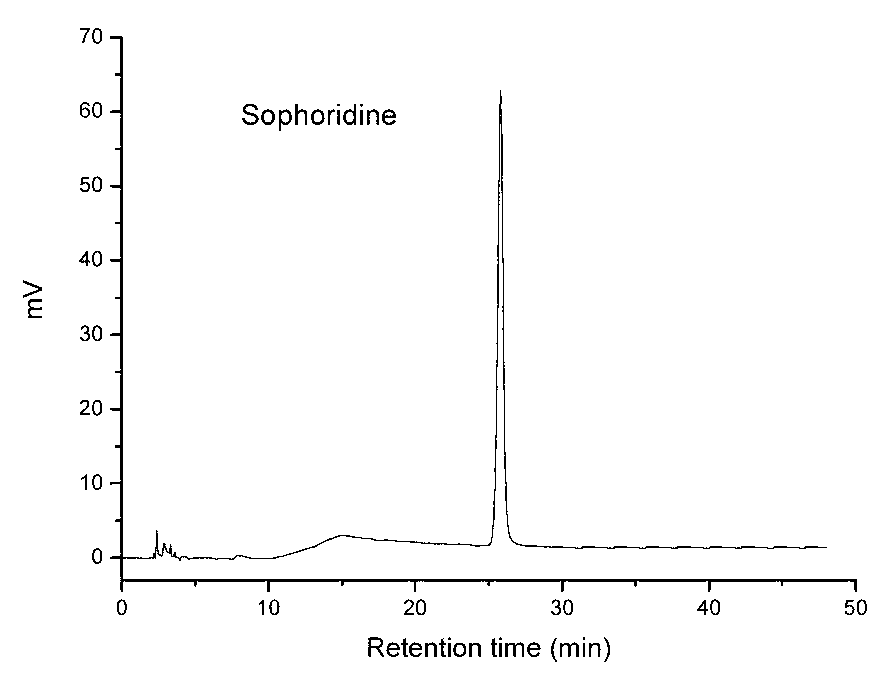
Microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase/reversed micelles extraction method of Sophora flavescens alkaloids
The invention discloses a microwave-assisted aqueous two-phase / reversed micelles extraction method of Sophora flavescens alkaloids. The method comprises the steps of extracting Radix Sophorae Flavescentis or Radix Sophorae Tonkinensis by use of microwave-assisted ethanol-ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase system, in which Sophora flavescens alkaloids are partitioned between the two aqueous phases and extracted into the upper phase to complete primary purification; selectively extracting Sophora flavescens alkaloids by use of SDBS (sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate) / isooctane / n-octanol reversed micelles system, to obtain Sophora flavescens alkaloids crude product with low impurity content; and performing separation and purification to obtain matrine, oxymatrine and sophoridine. The method combines reversed micelles extraction, microwave-assisted extraction and aqueous two-phase extraction technologies, to realize advantage complementation, simple method, high speed and efficiency, no pollution, low requirements for facilities, easy continuous production and scale-up. The extracted Sophora flavescens alkaloids have purity above 90.92% and yield up to 55.38 mg / g. The separated and purified matrine, oxymatrine and sophoridine have high purity above 94% and little organic solvent residue.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Multifunctional high performance counter current chromatograph
InactiveCN101229452AImprove retentionHigh retention rateComponent separationSolid sorbent liquid separationChromatographic separationCircular disc
The invention relates to a multifunctional highly efficient counter current chromatograph, which consists of a disc type counter current chromatographic separation column, a counterweight body, a planet carrier, a cylinder rotating axis, a planet wheel, a center wheel, a central revolution axis, an electrical motor, a transmission device, a speed control device and an insulated chassis. The disc type counter current chromatographic separation column comprises at least a or a plurality of discs provided with designing slots, clapboards at two sides of each disc, the cylinder rotating axis, an upper flange and a lower flange; the cylinder rotating axis is hollow and passes through the center of the upper flange, the lower flange, the discs and the clapboards; the inner edge and the outer edge of the upper flange, the lower flange, the discs and the clapboards are provided with a plurality of bolt pieces that fix the upper flange, the lower flange, the discs and the clapboards together. The advantages of the invention lie in that: the fixed phase retention value of a two-phase system comprising an organic phase is further promoted and highly efficient and fast separation of micromolecular substances is realized in high flowing speed. Meanwhile, the retention rate of an aqueous two-phase system is remarkably prompted, thus being applicable for the separation of biomacromolecule.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
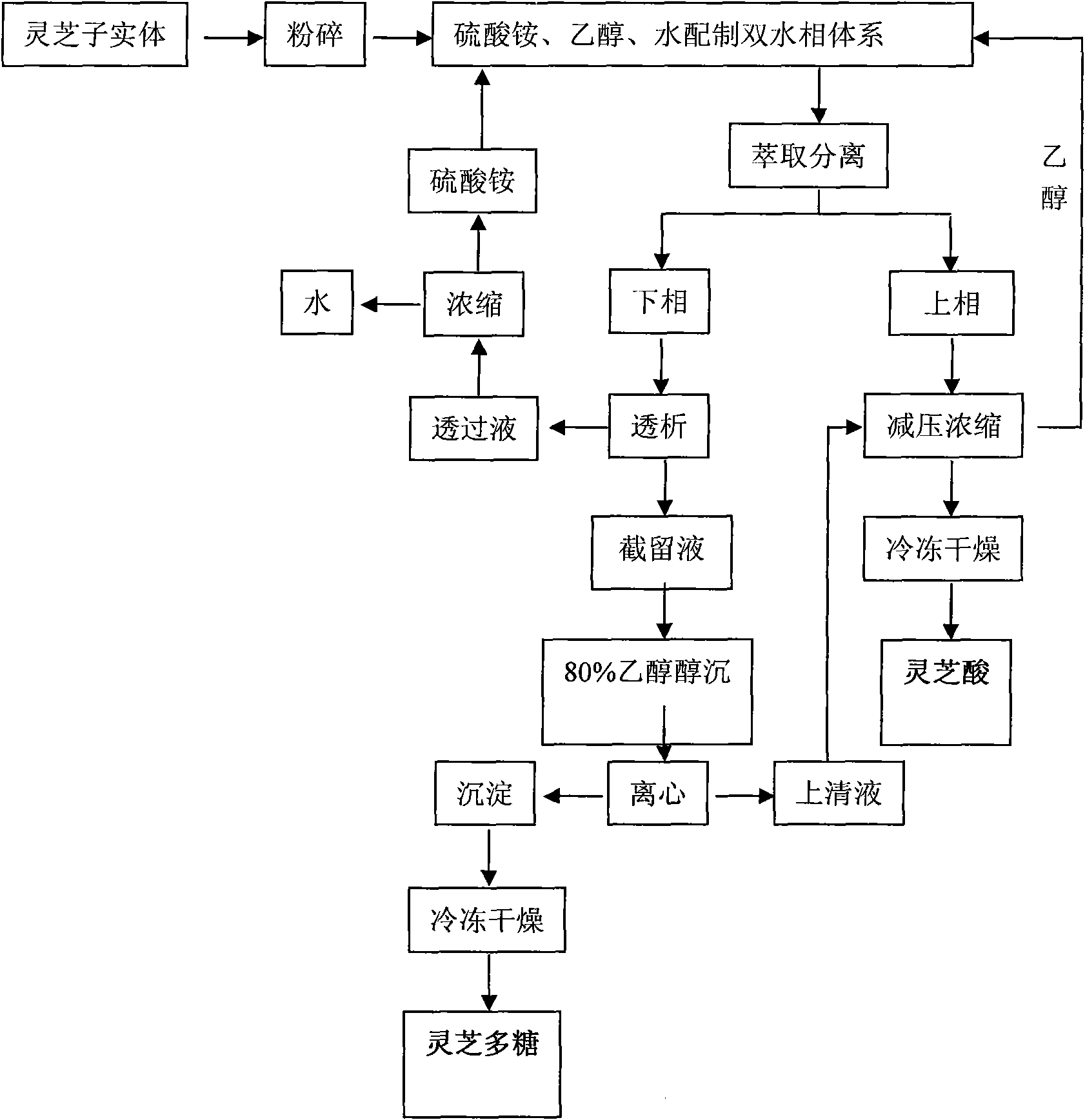
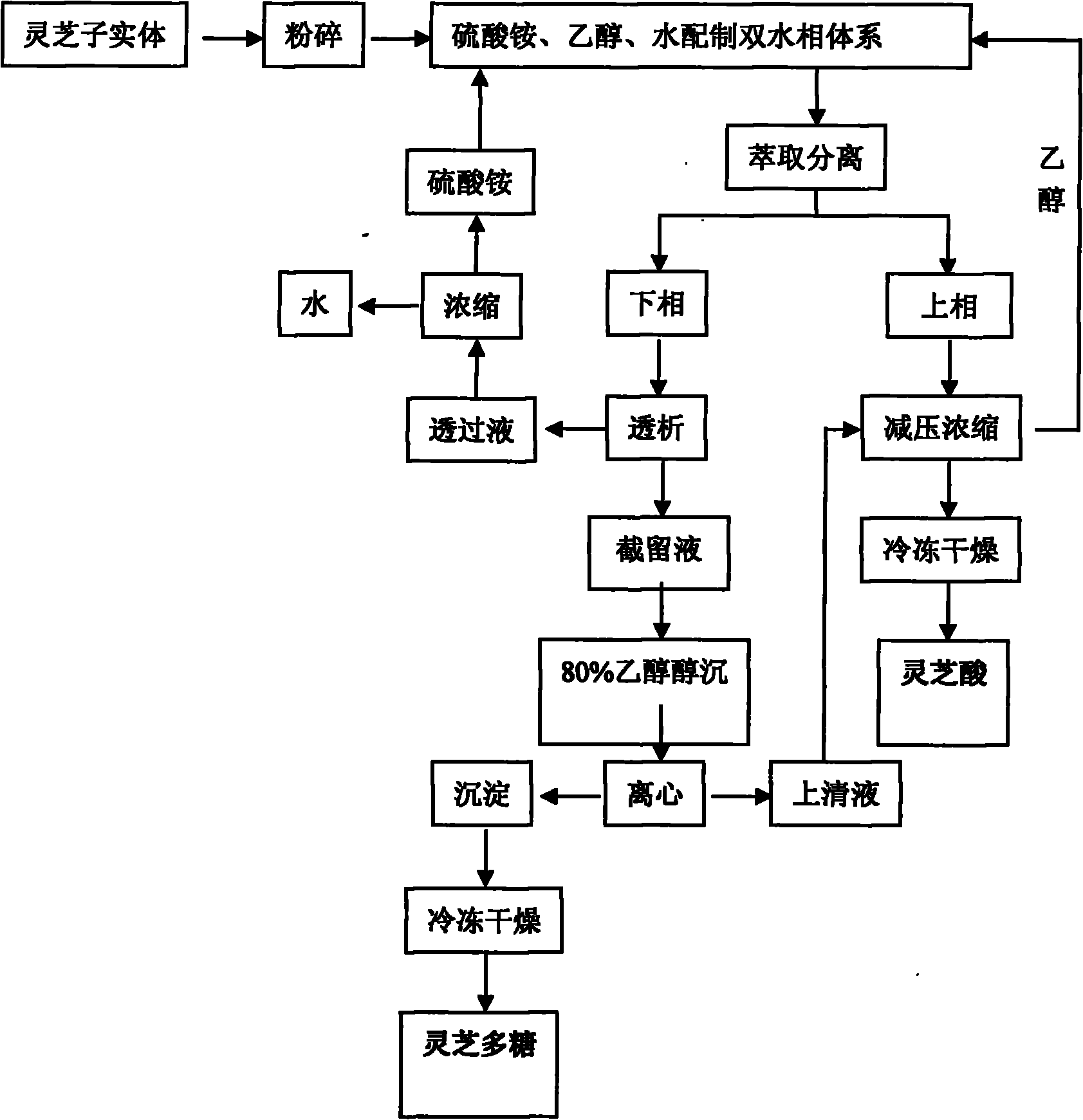
Aqueous two-phase system extraction method for ganodenic acid and ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide
InactiveCN101899122ASimple processAchieving simultaneous separation and extractionSteroidsChemical recyclingFreeze-dryingPollution
The invention relates to an aqueous two-phase system extraction method for ganodenic acid and ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: (1) pulverizing fresh or dry ganoderma lucidum fruiting bodies; (2) establishing an ethanol / ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase system; (3) performing extraction separation: adding ganoderma lucidum powder into the ethanol / ammonium sulfate aqueous two-phase system, shaking up the mixture by vibration or uniformly mixing the mixture by ultrasonic sound, and standing the mixture for phase splitting or centrifugally splitting the phase to obtain a top phase and a bottom phase; (4) concentrating the top phase under reduced pressure and freeze-drying the top phase to obtain the ganodenic acid; and (5) dialyzing the bottom phase to obtain permeate and intercept fluid, performing alcohol precipitation on the intercept fluid with 80 percent ethanol and centrifuging to obtain a precipitate and supernatant, and free-drying the precipitate to obtain the ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide. The method has the advantages of simple process, low equipment requirement, low cost, no pollution, suitability for batch production and capability of realizing synchronous extraction of the ganodenic acid and the ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
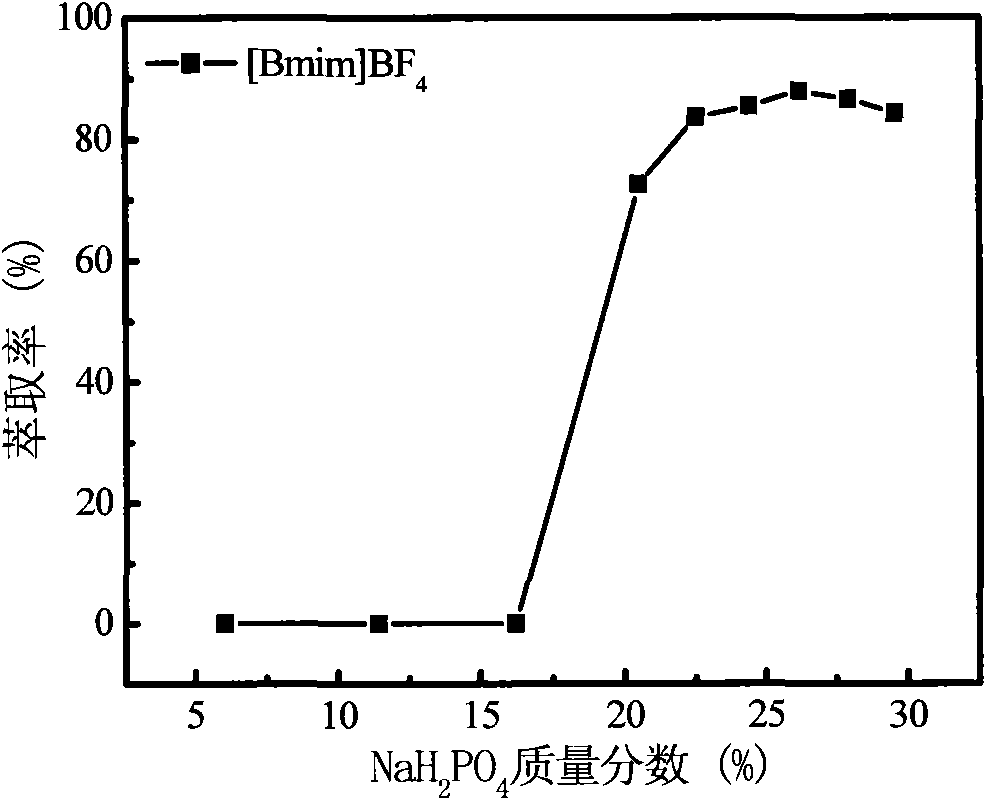
Method for measuring residual erythromycin in environment by using hydrophilic ionic-liquid aqueous two-phase system
InactiveCN101832992AHigh assay recoveryMeet the detection requirementsPreparing sample for investigationTesting foodRelative standard deviationGram
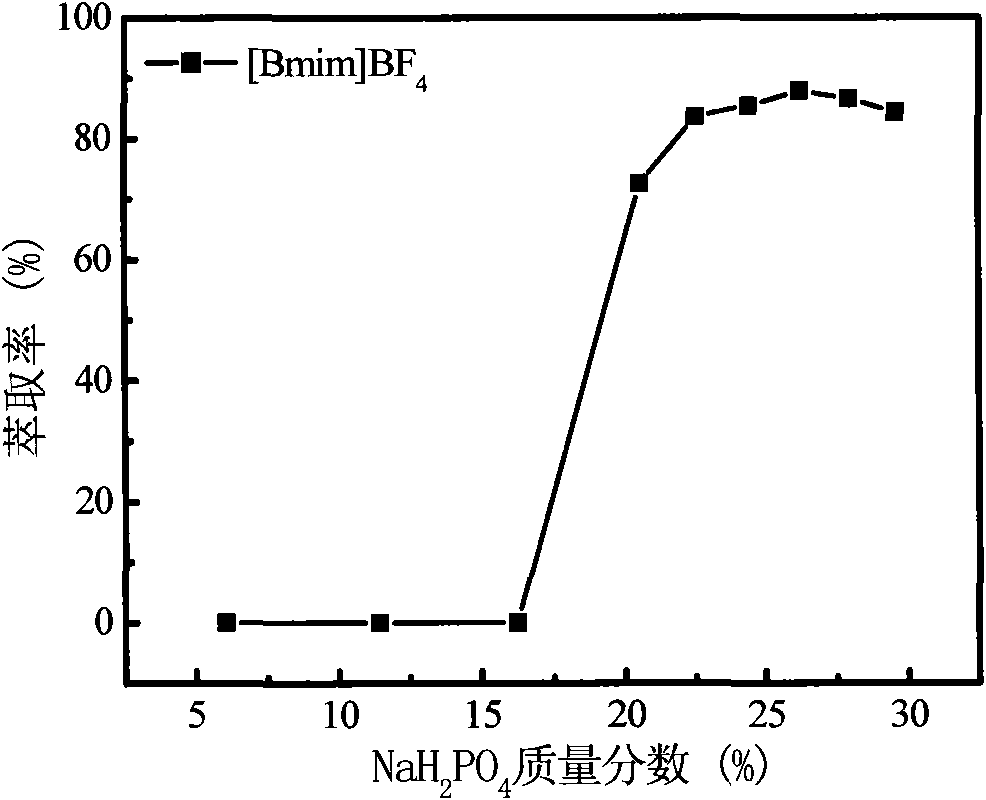
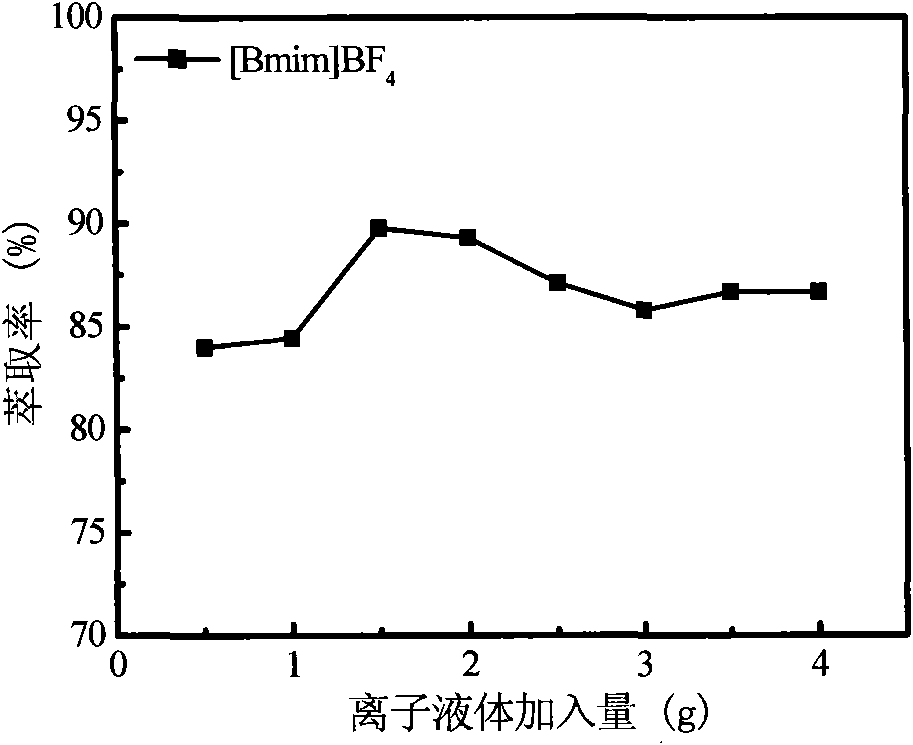
The invention discloses a method for measuring residual erythromycin in an environment by using a hydrophilic ionic-liquid aqueous two-phase system. The method comprises the following steps of: forming the ionic-liquid aqueous two-phase system by using 1.5 grams of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ([Bmim]BF4) and 11 grams of NaH2PO4, at least extracting the solution for 2 hours once by using the extracting system, standing the solution after extraction, measuring the concentration of the residual erythromycin in the water phase after the split phases are clear, and calculating the extraction rate of the erythromycin by using the erythromycin content of the water phase before and after the extraction. According to the method, the extraction rate of the erythromycin can reach 99.31 percent. The method has the characteristics of wide linear range, low detection limit, small relative standard deviation and high measuring yield of a sample. The method can meet the national detection requirement for the residual erythromycin, is simpler to operate, and is suitable for quantitative analysis of residual trace erythromycin in food.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method for producing low polyxylose with dual-aqueous phase hydrolyzation system
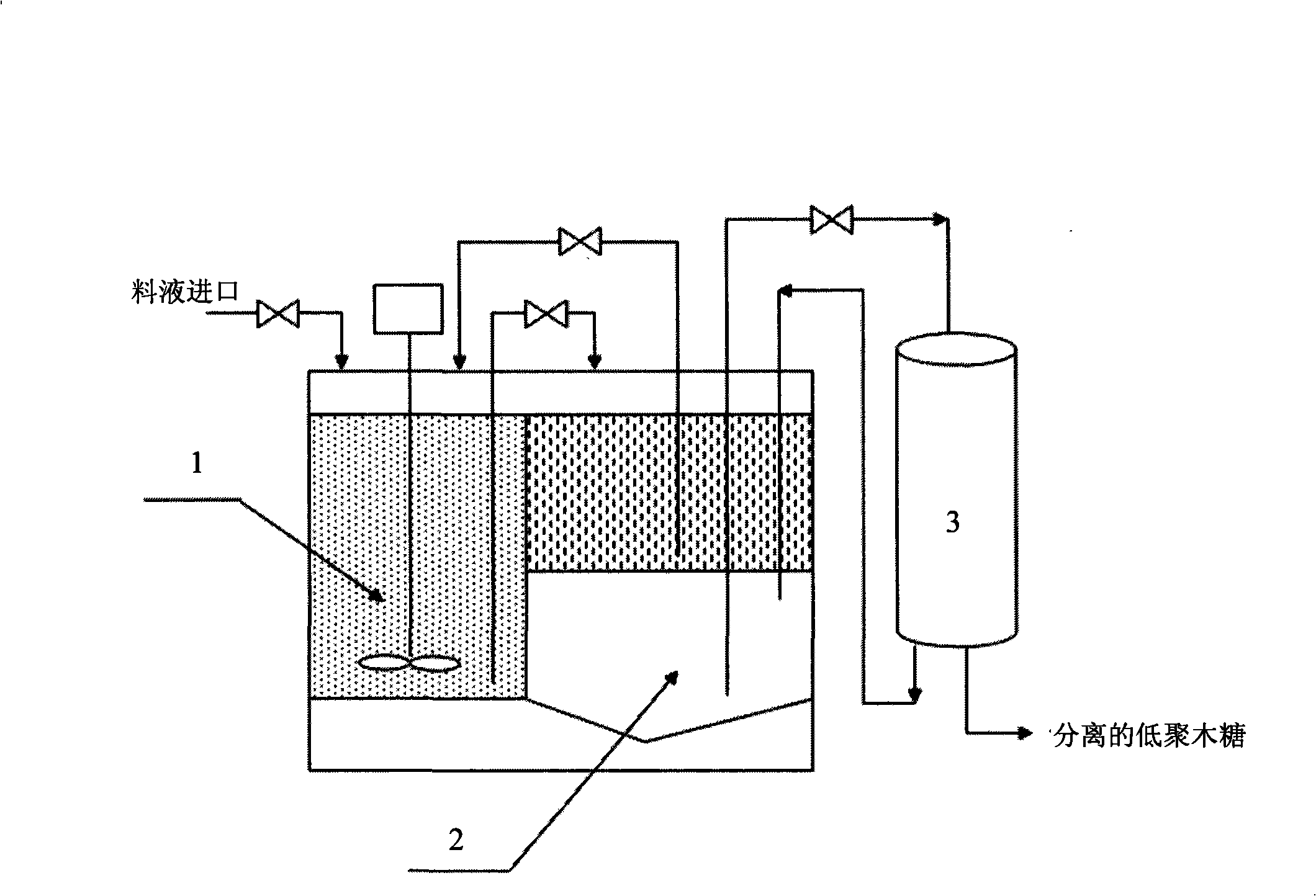
InactiveCN101294175AIncrease profitStabilize and improve enzyme activityFermentationXylanUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for preparing xylooligosaccharides by using a double water-phase hydrolysis system, which comprises the following steps: (1) configuring a double water-phase system containing polyethylene glycol and ammonium sulfate or polyethylene glycol and glucan in a hydrolyzing tank; (2) adding crude xylan solution and xylanase for hydrolyzing; (3) adding the reactive solution to a dispensing groove, standing for separating phases, separating the lower phase by an ultrafiltration membrane, separating with nanofiltration membrane to obtain xylooligosaccharides, recovering the residues obtained by ultrafiltration, mixing with the upper phase and adding into the hydrolyzing tank; and (4) adding ammonium sulfate in the hydrolyzing tank for the original double water-phase system containing polyethylene glycol and ammonium sulfate, returning to step (2), and returning to step (2) for the original double water-phase system containing polyethylene glycol and glucan. The method can recover xylanase by using the double water-phase system, and has the advantages of improved utilization rate of xylanase, simple operation, easy scale up, and low production cost.
Owner:QINGHAI WEIDE SPECIAL SUGAR
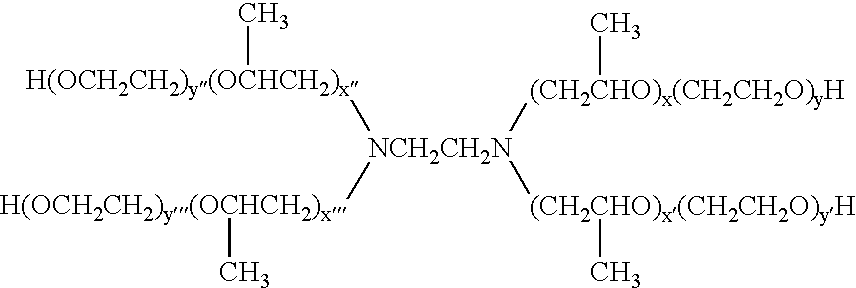
Polyethylene glycol/glucan aqueous two-phase system emulsion stabilizer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a polyethylene glycol / glucan aqueous two-phase system emulsion stabilizer and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps: adding mPEG-CHO (methoxy polyethylene glycol aldehyde) to a protein aqueous solution, and fully stirring until being dissolved, wherein the molar ratio of a protein to mPEG-CHO is 1:10-1:13; then adding a certain amount of dilute hydrochloric acid into the aqueous solution to adjust the pH value to be slightly higher than a protein isoelectric point, carrying out full reaction for 20 h at a constant temperature of 0-4 DEG C, then precipitating, and drying to obtain the target product. The method is simple and convenient, mild in preparation conditions and easy to control, and has fewer side reactions. Because the surface of the product has moderate wettability with two phases of both polyethylene glycol and glucan, the product is adsorbed on a two-phase interface, enables the stable aqueous two-phase emulsion effect to be achieved by changing the interfacial tension, can retain the biological activity of the protein to a larger extent, can achieve aqueous two-phase emulsion loading of bioactive substances, and has good application prospects in the fields of foods, cosmetics and drug controllable release.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
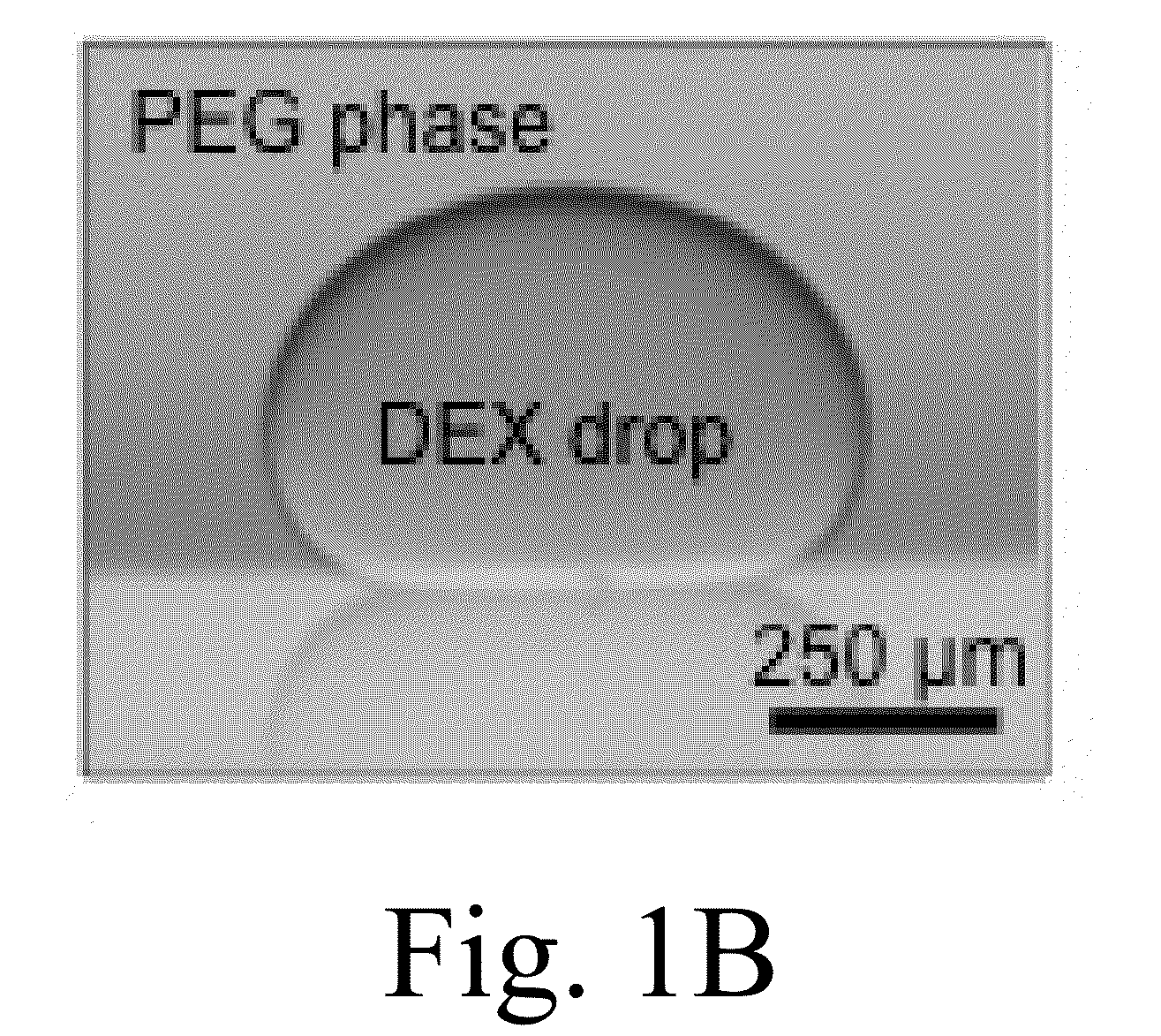
Engineering individually addressable cellular spheroids using aqueous two-phase systems
Provided is multi-phase systems that may be used to prepare a three-dimension aggregate of cells referred to as a cellular spheroid. The multi-phase system includes a droplet of an aqueous polymer phase within an immersion aqueous polymer phase. The droplet of the droplet aqueous polymer phase contains a three-dimensional aggregate of cells (cellular spheroid). Types of cells that may be used in the multi-phases system include stem cells and cancer cells. The cellular spheroids with the multi-phase system may be used to monitor cell growth in three-dimensional systems, or screen drugs in a three-dimension aggregate of cells.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Method for rapidly detecting contents of lemon yellow and sunset yellow in food
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting contents of lemon yellow and sunset yellow in a food. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a standard solution of the lemon yellow and the sunset yellow; measuring the peak area of the standard solution of the pigments by using high performance liquid chromatography, and drawing a standard curve to obtain an equation of linear regression; filtering a liquid food sample or solid food sample solution, extracting by using an ionic liquid aqueous two-phase system composed of 1-butyl-3-methylimidzaole bromine salt and K2HPO4, and directly carrying out high performance liquid chromatography analysis on an ionic liquid after phase splitting; and respectively calculating the contents of the lemon yellow and the sunset yellow in the food according to the equation of linear regression. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation, free of a great deal of volatile solvents, short in separation time, good in ionic liquid phase mobility and capable of inter-dissolving with water or methanol and directly injecting for chromatography analysis. By using the method, the rapid, simple, convenient, environment-friendly, economic, qualitative and quantitative measurement can be provided for quality control departments and production enterprises.
Owner:JIANGSU MARINE RESOURCES DEV RES INST LIAN YUNGANG +1
Method for isolating extracellular vesicles using aqueous two-phase system
ActiveUS20180164197A1Improve efficiencySimple processSolvent extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseExtracellular vesicle
Disclosed is a method of isolating extracellular vesicles using an aqueous two-phase system (ATPS), including (a) preparing an ATPS by mixing a first material and a second material, which are immiscible with each other, with a body fluid or an aqueous solution containing extracellular vesicles and (b) isolating extracellular vesicles concentrated in the second material of the ATPS. This method can exhibit very high isolation efficiency, a simple isolation manner, and a very short isolation time. The isolation of extracellular vesicles using the ATPS requires no ultracentrifuge and achieves almost 100% isolation efficiency within a short time of about 10˜20 min, and thus the method of the invention is practical, is economical due to low costs thereof, can increase the purity of extracellular vesicles contaminated with protein, enables the diagnosis of disease using the isolated extracellular vesicles, and can be applied to various fields using extracellular vesicles.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
Encapsulation of aqueous phase systems within microscopic volumes
InactiveUS7803405B2Increase ionic strengthReduce interfacial tensionIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicroencapsulation basedLipid filmChemical compound
A means and method for preparing vesicles and freestanding two-dimensional assemblies using aqueous two-phase systems (ATPS) is described. The surface tension of the ATPS is sufficient to support the assembly of various types of particles, and provide the advantage of being biocompatible with DNA and other types of biological molecules that may be used in the assembly. Vesicles are formed by mixing chemically dissimilar compounds in appropriate concentrations and at a temperature sufficient to form a monophasic mixture. This mixture is then heated above the temperature at which the polymer mixture is monophasic, added to a lipid film, and allowed to hydrate at this elevated temperature.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method for ionic liquid aqueous two-phase extraction of flavones and saponins in songaria cynomorium herb
ActiveCN103690577AIncrease profitReduce the cost of deep processingAntibacterial agentsAntinoxious agentsIonic liquidVacuum drying
The invention discloses a method for ionic liquid aqueous two-phase extraction of flavones and saponins in songaria cynomorium herb. The method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment of the songaria cynomorium herb; (2) ultrasonic crude extraction; (3) aqueous two-phase extraction, namely utilizing an ionic liquid / salt aqueous two-phase system to perform extraction; (4) back extraction; (5) vacuum distillation and vacuum drying; (6) recovery of ionic liquid. The method for ionic liquid aqueous two-phase extraction of the flavones and the saponins in the songaria cynomorium herb, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of simple method, easiness in operation, fast phase splitting, high extraction rate, no need of volatile organic solvents, low environmental pollution and effects of recycling an extraction solution of an extraction system, saving resources, realizing relatively high selectivity and specificity, simultaneously extracting the flavones and the saponins in the songaria cynomorium herb, effectively avoiding the waste of the resources caused by single component extraction, effectively improving the extraction rate of the flavones and the saponins in the songaria cynomorium herb and the comprehensive utilization rate of the songaria cynomorium herb and reducing the deep processing cost of the songaria cynomorium herb.
Owner:甘肃凯源生物技术开发中心有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com