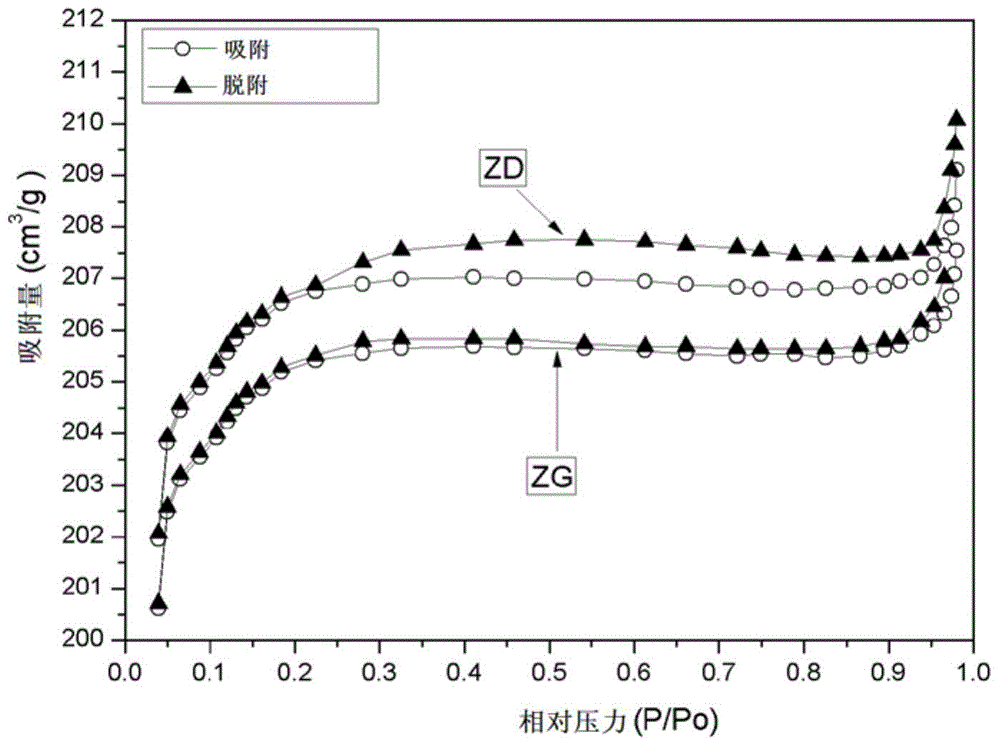
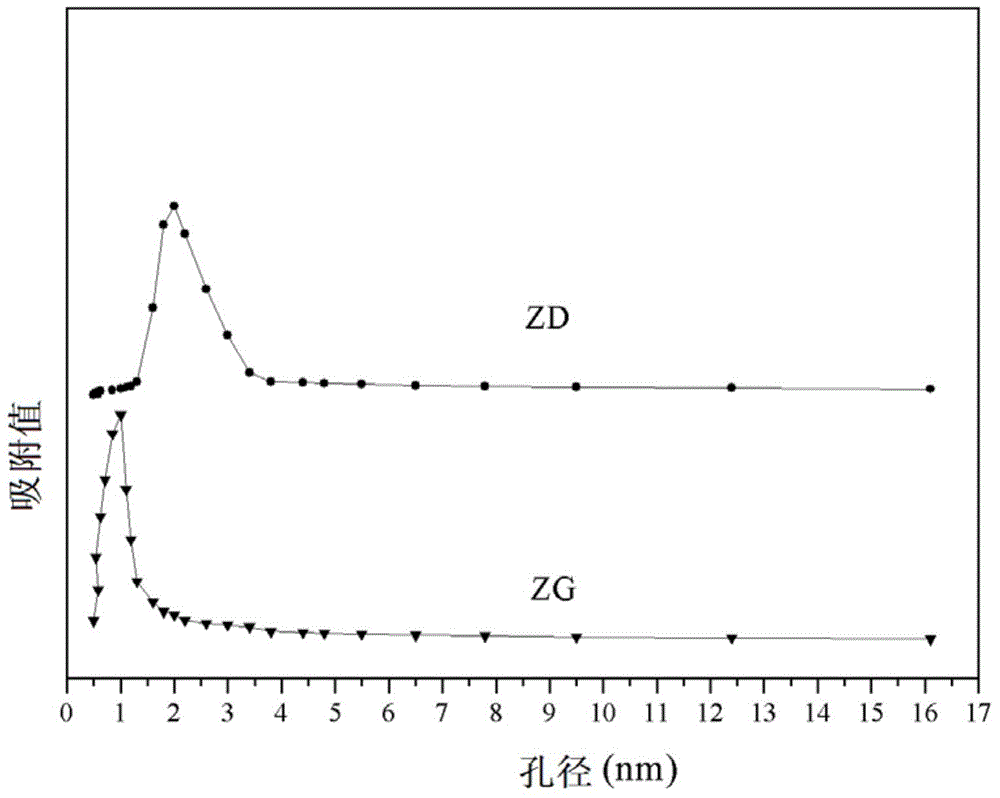
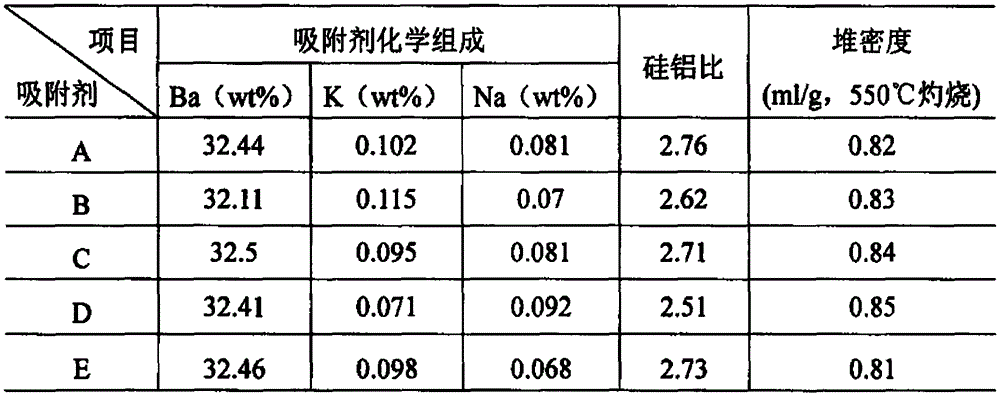
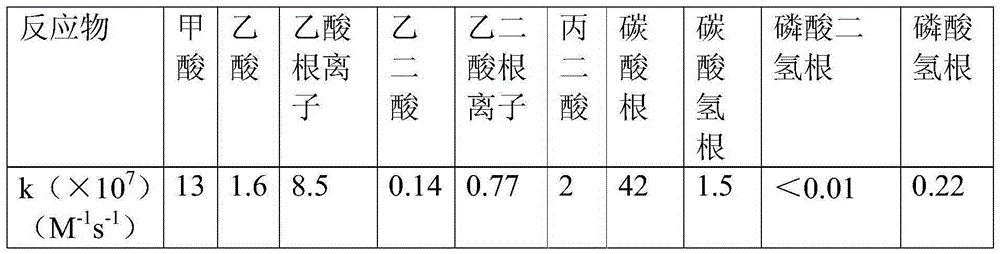
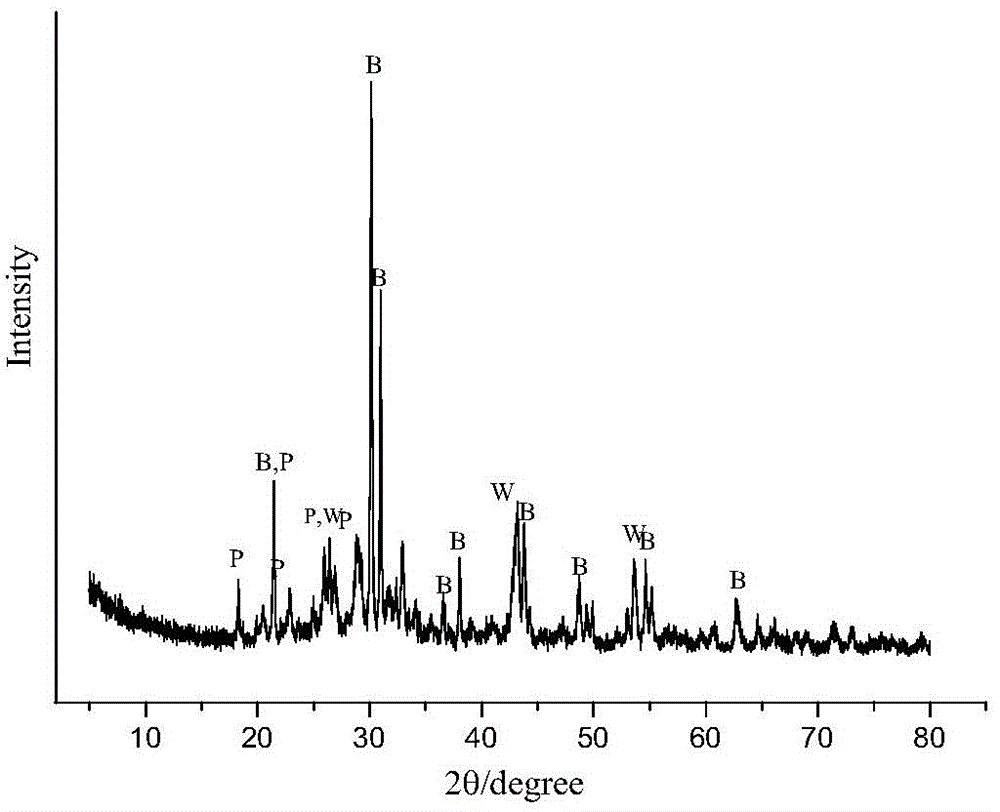
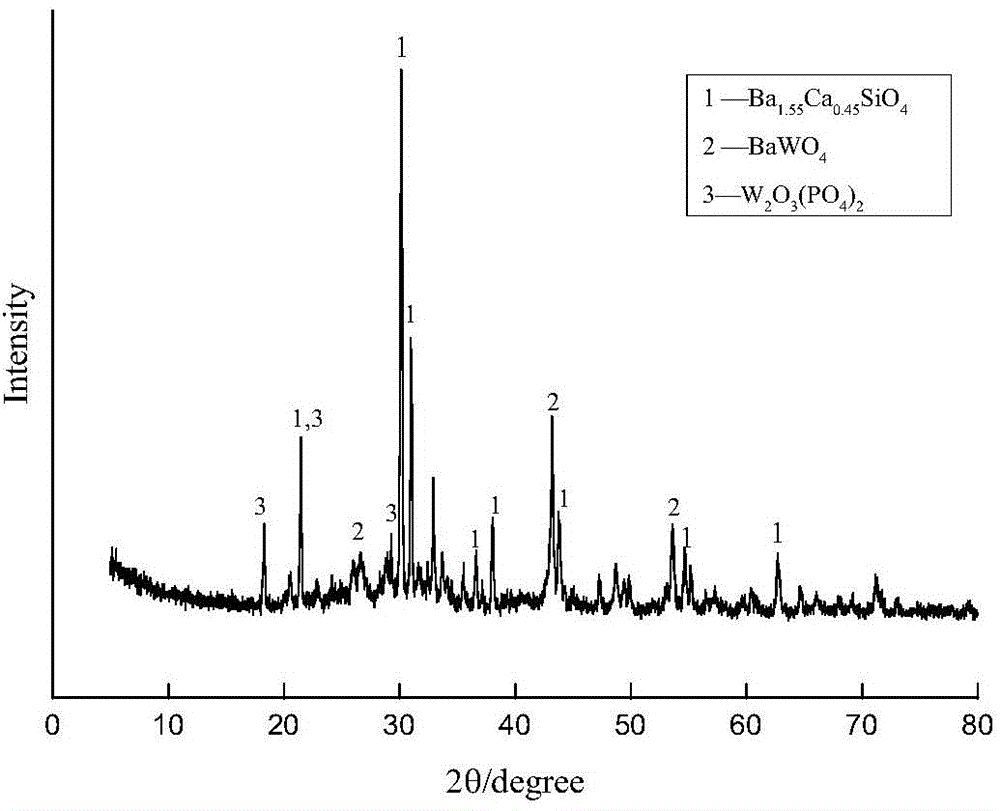
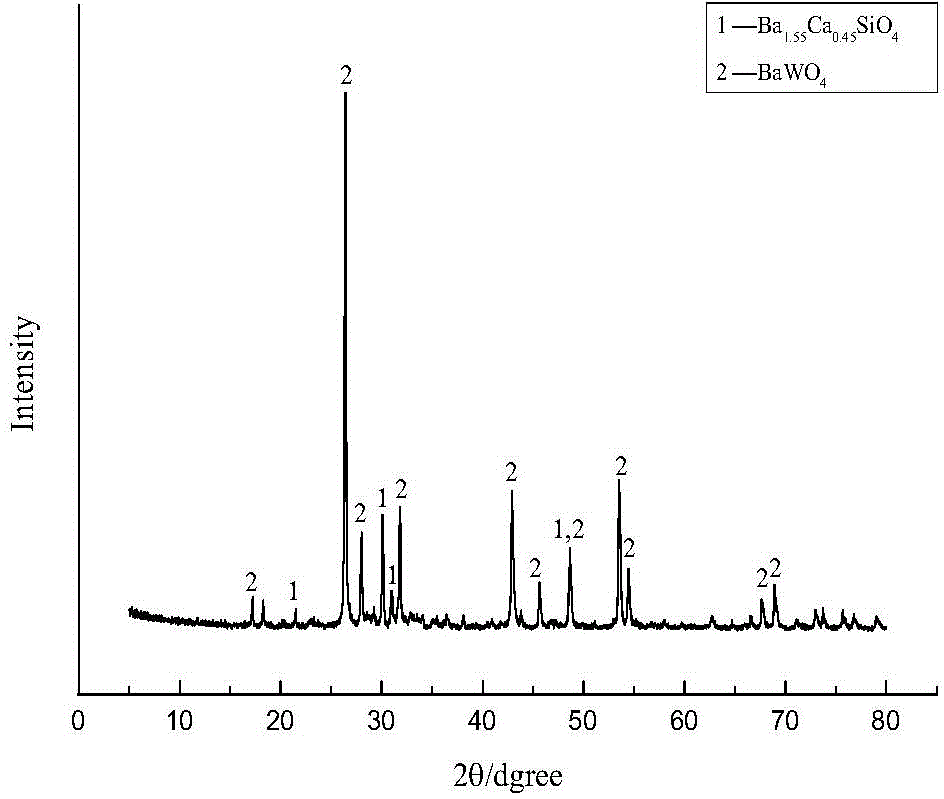
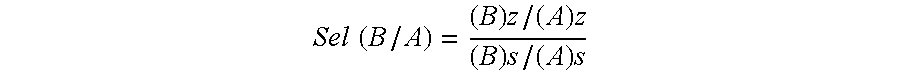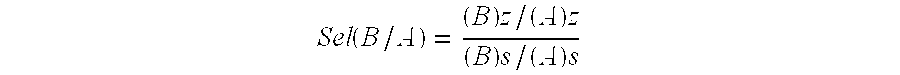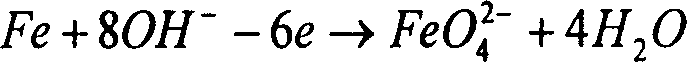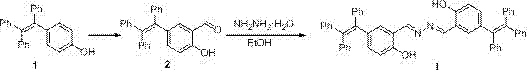Patents
Literature
276 results about "Barium Ion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Agglomerated zeolite adsorbents, process for their preparation, and their use for adsorbing paraxylene from aromatic C8 fractions
InactiveUS6410815B1Improve efficiencyImproved kineticsMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesSorbentPotassium
The present invention relates to agglomerated zeolite adsorbents based on faujasite with an Si / Al ratio such that 1<=Si / Al<=1.15, at least 70% exchanged with barium and optionally with potassium, and on a binder, preferably a zeolitizable binder.They are obtained by agglomerating zeolite powder with a binder, followed by exchange of the zeolite ions for barium ions and activation of the adsorbents thus exchanged.These adsorbents are particularly suitable for the adsorption of the para-xylene contained in aromatic C8 hydrocarbon fractions in the liquid phase, in processes of simulated fluid-bed type.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +1
Agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents, method for obtaining same uses thereof
InactiveUS6884918B1Amino compound purification/separationOrganic compound preparationSorbentSimulated moving bed
The present invention relates to agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents based on zeolite X with an Si / Al ratio such that 1.15<Si / Al≦1.5, at least 90% of the exchangeable cationic sites of the zeolite X of which are occupied either by barium ions alone or by barium ions and potassium ions whose Dubinin volume is greater than or equal to 0.240 cm3 / g.They are obtained by agglomerating zeolite powder with a binder, followed by the zeolitization of the binder, the exchange of the ions of the zeolite by barium ions (and potassium ions) and the activation of the adsorbents thus exchanged.These adsorbents are particularly suited to the adsorption of the para-xylene present in C8 aromatic hydrocarbon fractions in the liquid phase in processes of simulated moving bed type but also to the separation of sugars, polyhydric alcohols, cresols or substituted toluene isomers.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Mesoporous X-type molecular sieve, adsorbent based on molecular sieve, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN104477937AHigh adsorption selectivityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesFaujasite aluminosilicate zeolitePore distributionSorbent
The invention relates to a preparation method of a mesoporous X-type molecular sieve and a method for preparing an adsorbent by using the molecular sieve as an active component. The prepared adsorbent based on the mesoporous X-type molecular sieve is used as a paraxylene adsorptive separation adsorbent. The method for preparing the mesoporous X-type molecular sieve comprises the following steps: by using water glass as a silicon source and aluminum hydroxide as an aluminum source, adding a template, and carrying out hydrothermal synthesis to obtain the mesoporous X-type molecular sieve. The mesoporous molecular sieve and kaolin are proportionally molded to obtain 0.3-0.8mm granules, and the granules are subjected to barium ion or (and) potassium ion exchange until the exchange degree is greater than 99%, thereby obtaining the adsorbent which has excellent adsorptive separation capacity for paraxylene in C8 aromatic hydrocarbons. Compared with the prior art, the active component mesoporous X-type molecular sieve of the adsorbent, which is prepared by using the template, has the crystal form structure of the X-type molecular sieve and the pore distribution of the mesoporous and microporous dual models; the mesoporous pore size distribution is 2nm or so; and thus, the problem of overlow mass transfer rate in the adsorbent can be solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI LVQIANG NEW MATERIALS CO LTD +1
Agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents, their process of preparation and their uses
InactiveUS20050170947A1Amino compound purification/separationMolecular sieve catalystsSorbentSimulated moving bed
The present invention relates to agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents containing zeolite X and an inert binder, the inert binder containing at least 80% by weight of clay which has undergone zeolitization by the action of an alkaline solution, the zeolite X having with an Si / Al ratio such that 1.15<Si / Al≦1.5, at least 90% of the exchangeable cationic sites of the zeolite X of which are occupied either by barium ions alone or by barium ions and potassium ions whose Dubinin volume is greater than or equal to 0.240 cm3 / g. They are obtained by agglomerating zeolite powder with a binder, followed by the zeolitization of the binder, the exchange of the ions of the zeolite by barium ions (and potassium ions) and the activation of the adsorbents thus exchanged. These adsorbents are particularly suited to the adsorption of the para-xylene present in C8 aromatic hydrocarbon fractions in the liquid phase in processes of simulated moving bed type but also to the separation of sugars, polyhydric alcohols, cresols or substituted toluene isomers.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Methods for preserving fresh produce
Methods of preserving fresh produce with a produce preservative which extends the shelf life of fresh produce, particularly cut fresh produce, and preserves the texture, flavor, appearance, crispness, and color of the fresh produce, particularly the exposed surface of the fresh produce, are provided. The method comprises: providing a solution of produce preservative comprising: water; a preservative cation which is selected from the group consisting of a strontium ion, lithium ion, barium ion, aluminum ion, copper ion, ammonium ion, iron ion, manganese ion, potassium ion, or mixtures thereof; and ascorbate ions, or erythorbate ions; wherein the ascorbate ions or erythorbate ions and the preservative cation are present in an ion ratio of preferably from 0.2:1 to 8:1, more preferably 0.75:1 to 8:1, even more preferably from 1:1 to 4:1, yet more preferably 1.5:1 to 3:1; most preferably 1.1:1 to 2.5:1; and, applying said produce preservative to the produce. The invention also relates to fresh produce preserved with the produce preservatives.
Owner:MANTROSE HAEUSER
Method for preparing barium-activated lithium iron phosphate cathode material
ActiveCN102347486AShape is easy to controlGood for particle size controlCell electrodesLithium iron phosphateAlcohol
The invention relates to a method for preparing a barium-activated lithium iron phosphate cathode material. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of: mixing raw materials of a lithium source, a ferrum source, a phosphate source and a barium source according to the proportion of Li:Ba:Fe:P of 1mol:(0.0003mol):1mol:1mol, performing high-speed ball-milling (at the rotating speed of 200r / min) on the mixed raw materials in an absolute ethyl alcohol (AR) medium and drying at 105-120 DEG C to obtain a precursor; and placing the dried precursor in a high-temperature furnace and calcining for 24h at a high temperature of 500-750DEG C in an ordinary pure nitrogen atmosphere to obtain the barium-activated lithium iron phosphate cathode material. The chemical general formula of the material can be represented as Li Ba FePO4. As a bit of substituent barium is doped, the appearance and the particle size of the product are favorably controlled, and a stable lithium iron phosphate compound is obtained. Barium ions replace lithium ions in an occupation manner, the crystal lattice of the compound is activated, the diffusion coefficient of the lithium ions is increased, and the first discharge capacity of the cathode material reaches 145.52mAh / g. The potential of a charge-discharge platform of the cathode material is about 3.5V compared with that of a lithium electrode, the initial discharge capacity exceeds 162mAh / g, and the capacity is attenuated by about 3.2% after 100 times of charge-discharge circles. Compared with the undoped LiFePO4 contrast embodiment, the cathode material has greatly increased specific capacity and cyclical stability. As the price of barium is more than 100 times lower than the price of lithium, the production cost can be reduced by more than 10 times.
Owner:桐乡乐维新材料有限公司
Direct electrochemical process of preparing ferrate
InactiveCN1740398AImprove electrolysis efficiencyReduce manufacturing costElectrolysis componentsHigh concentrationElectrolysis
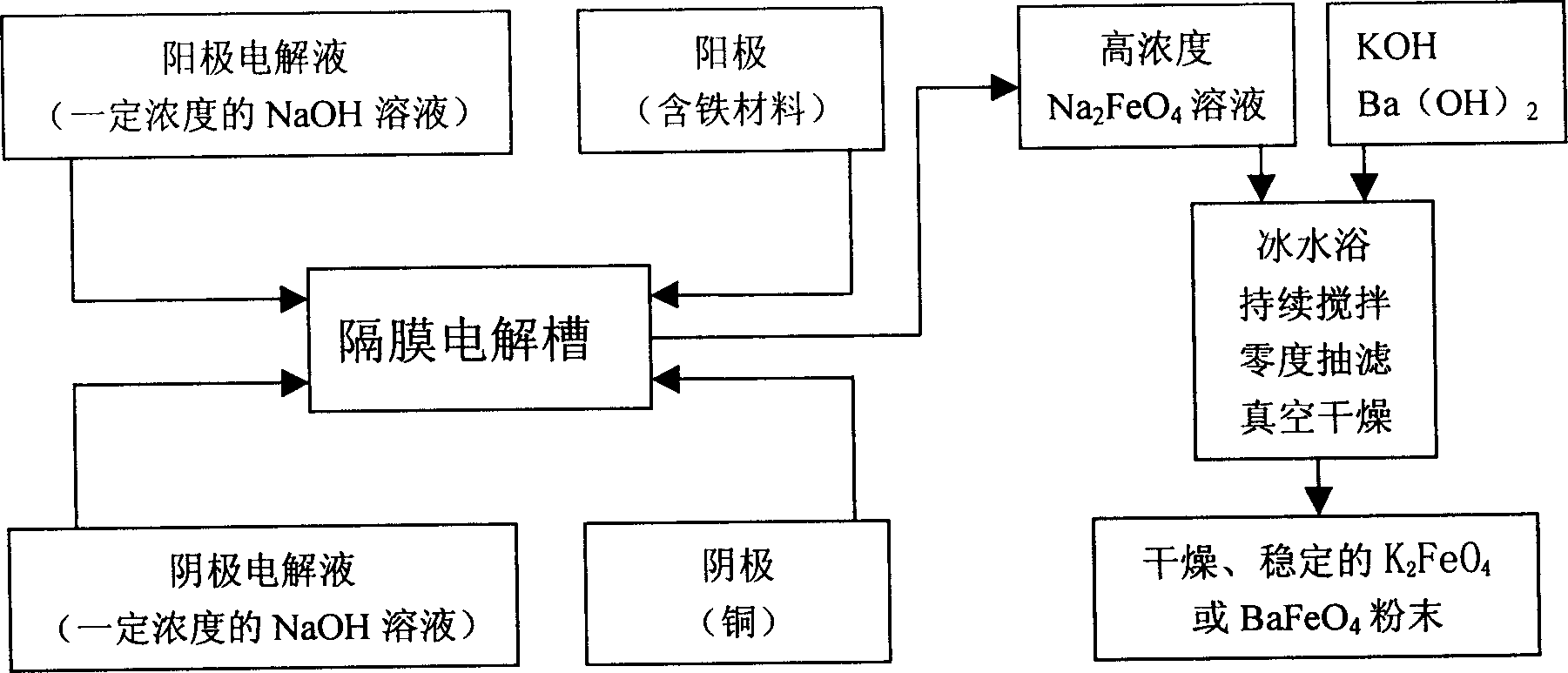
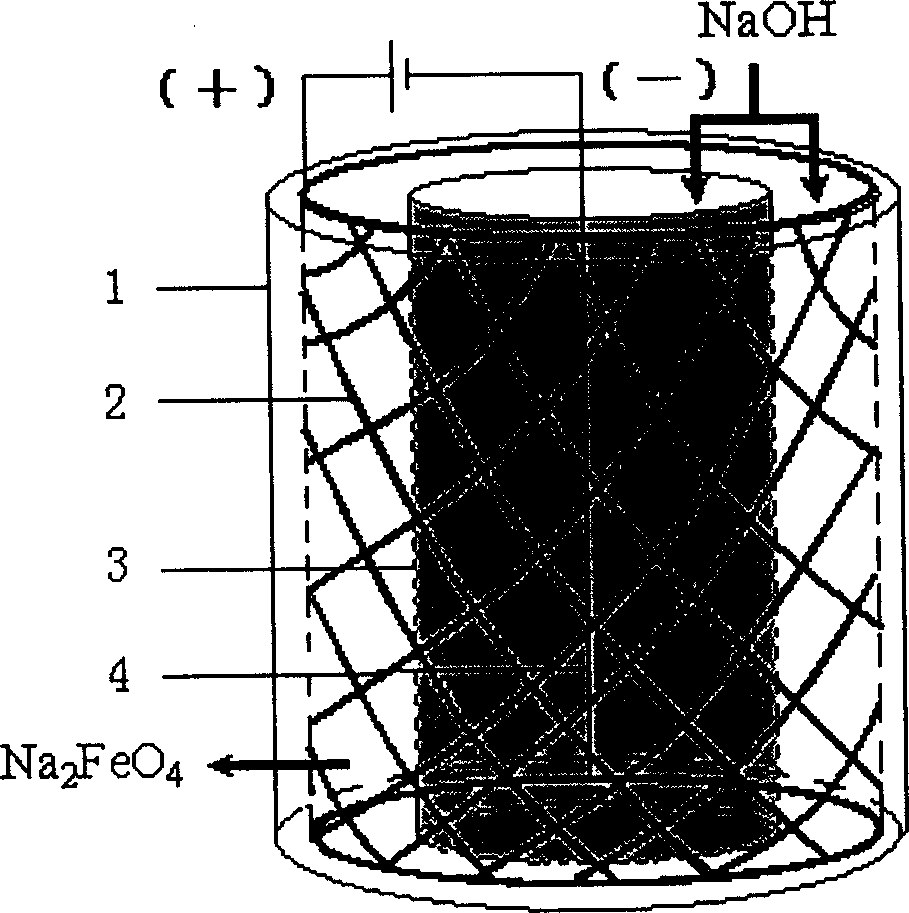
The present invention belongs to the field of chemical preparing technology, and is especially direct electrochemical process of preparing ferrate. The preparation process prepares ferrate inside one diaphragm type cylindrical electrolytic bath with pure sodium hydroxide as electrolyte. While controlling electrolyte concentration, reaction temperature and applied voltage, high concentration sodium ferrate solution is first prepared, and potassium ferrate or barium ferrate is then prepared via adding potassium ion or barium ion. The present invention has simple technological process and low cost, and is suitable for large scale preparation of ferrate.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for improving utilization efficiency of ozone and reducing COD of wastewater
InactiveCN105366785AReduce CODReduce total phosphorusWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsOrganic matter mineralizationReaction rate
The invention provides a method for increasing the utilization efficiency of ozone and reducing the COD of wastewater. According to the method, a chemical agent for removing a hydroxyl radical capture agent generated in base catalysis ozone advanced oxidation is added into the wastewater so as to achieve the purposes. Calcium ions, barium ions and the like are added into a base catalysis ozone oxidation system, so that the hydroxyl radical capture agent becomes precipitate to be separated from the water and loses the capacity for capturing hydroxyl radicals, and accordingly the utilization efficiency of ozone is improved. In addition, part of organic acid generated by the calcium ions, the barium ions and the like and the ozone oxidation wastewater precipitates to be separated from the water, so that the consumption of ozone is reduced, and the utilization efficiency of the ozone treatment wastewater is indirectly improved. By means of the method, the reaction rate of ozone can be obviously increased, the utilization efficiency of ozone can be obviously improved, reaction time can be shortened, cost can be reduced, organic matter in the wastewater can be thoroughly mineralized, and the COD and the total phosphorus content of the wastewater can be significantly reduced.
Owner:BEIJING WEICHUANGLI TECH CO LTD
Agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents, their method of preparation and their uses
ActiveUS20100113854A1High mechanical strengthImproved kineticsAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsMean diameterSorbent
The present invention relates to agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents based on zeolite X with an Si / Al ratio such that 1.15<Si / AL<1.5, consisting of crystals with a mean diameter of 1.7 mm or less and of an inert binder, at least 90% of the exchangeable cationic sites of the zeolite X being occupied by barium ions. They may be obtained by agglomerating a zeolite X powder having a mean diameter of 1.7 mm or less with a binder, followed by zeolitization of the binder, exchange of the zeolite ions with barium (and potassium) ions and activation of the adsorbents thus exchanged. These adsorbents exhibit, simultaneously, excellent selectivity, reduced mass transfer resistance and excellent mechanical strength and are particularly suitable for the adsorption of the paraxylene contained in C8 aromatic hydrocarbon fractions in liquid phase in processes of the simulated moving bed type and especially for the separation of paraxylene of C8 aromatic hydrocarbon fractions by adsorption, but also for the separation of sugars, polyhydric alcohols, cresols, and substituted toluene isomers.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Method for oxidation degradation of wastewater organic pollutant by activating hydrogen peroxide
InactiveCN101503241ACompletely decolorizes and deodorizesMild reaction conditionsPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationDicarbonateAlkaline earth metal
The invention relates to a method which uses activated oxyful for oxidizing and degrading organic pollutants of waste water. Aiming at overcoming the defect of the complex catalyst preparation of the prior art, the invention provides a method, which is as follows: oxyful with a certain concentration and a catalyst or auxiliary catalyst acting as the activated oxyful are blended with organic wastewater to be treated, and then stirring is carried out for reaction. The catalyst acting as the activated oxyful is a supercarbonate which takes alkali metal lithium, sodium, potassium ion, alkaline-earth metal magnesium, calcium, cesium, barium ion or NH4 as an activated cation; and the auxiliary catalyst takes transition metal iron, manganese or copper as an activated cation and takes chloride ions, nitrate ion, or sulfate ion as an anionic salt. The method moderates reaction condition and has full decolorization and deodorizing effect on the treated sludge; and the COD removal rate can reach 25%-60%.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents, their method of preparation and their uses
ActiveUS8530367B2Loss of mechanical strengthMaintain good propertiesAluminium compoundsMolecular sieve catalystsAlcoholCresol
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Method of extracting tungsten from high-barium tungsten ore
InactiveCN104372169ASolve the low leaching ratePrevent precipitationProcess efficiency improvementHigh concentrationSlag
The invention discloses a method of extracting tungsten from high-barium tungsten ore. The method includes: mixing the high-barium tungsten ore and a certain amount of SiO2 and Na2CO3 to obtain mixture, roasting the mixture at the high temperature, and leaching roasting slag with Na2CO3 to obtain tungsten. By roasting the Na2CO3 and SiO2, the structure of the high-barium tungsten ore is fully broken to obtain stable (Ba or Ca)2SiO4 slag which is leached with high-concentration Na2CO3, water-soluble calcium and barium ions in roasting material are deposited, deposition of tungsten ions is prevented, leaching rate of the tungsten is greatly increased, reaching greater than 95%, and the problem that the high-tension alkaline leaching methods of the prior art fail to break the barite structure, leading to low leaching rate, is solved. The method according to the technical scheme is simple to operate, raw materials are cheap, processing can be performed with traditional equipment, and the method fully satisfies industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Aggregation-induced emission-based copper ion detection probe and preparation method and application thereof
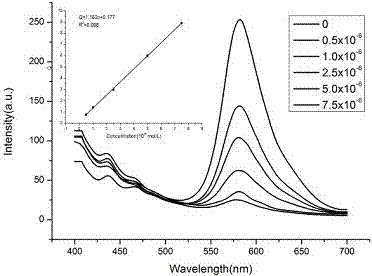
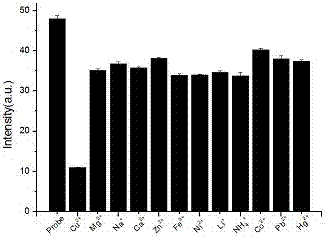
InactiveCN106957243ASensitive recognitionStrong specificityHydrazone preparationFluorescence/phosphorescenceSilver ion2-hydroxybenzaldehyde
The invention discloses an aggregation-induced emission-based copper ion detection probe and a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the fluorescent probe is as shown in a formula I, and the fluorescent probe is prepared through formylating hydroxytetrstyrene as a raw material and forming triphenylethylene-based salicylaldehyde azine together with hydrazine hydrate. The probe is stable in optical property, high in copper ion detection sensitivity and low in lower detection limit, the detection limit is 30.9nM and the response range is 0.5-7.5muM; the probe is good in selectivity and free of response to cations such as a silver ion, a barium ion, a calcium ion, a lithium ion, a magnesium ion, an ammonium ion, a nickel ion, a zinc ion, a mercury ion, a cobalt ion and a lead ion; and the probe is simple in synthesis, mild in condition and high in yield. The fluorescent molecular probe has practical application value in the field of copper ion detection in biochemistry and environmental chemistry.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Composite heat stabilizer for polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and preparation method for composite heat stabilizer
ActiveCN102432961AImprove thermal stabilityGet rid of dependenceSulfide preparationChemical industryCarboxylic salt
The invention belongs to the field of chemical industry and particularly relates to a composite stabilizer for polyvinyl chloride (PVC) processing. The composite stabilizer consists of the following components in part by weight: 55 to 105 parts of main stabilizer, 0.255 to 11 parts of auxiliary stabilizer, and 10 to 35 parts of inorganic filler. The main stabilizer is a 3-dodecylthiopropionic acid metal soap stabilizer, and the chemical formula of the metal soap stabilizer is [CH3(CH2)11S(CH2)2COO]mXn, wherein X is one or more of calcium ion, zinc ion, barium ion or magnesium ion; and the metal soap stabilizer consists of 5 to 20 weight parts of metal ion and 50 to 85 parts of sulfur-containing carboxylate group. The composite stabilizer has the advantages of high thermal stability, safety and no toxicity, certain processability and lubricity and low cost.
Owner:SHANDONG RUIFENG CHEM
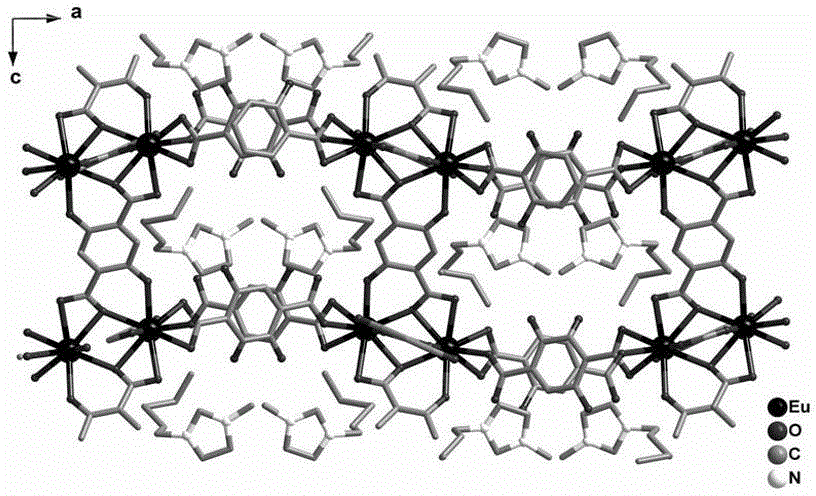
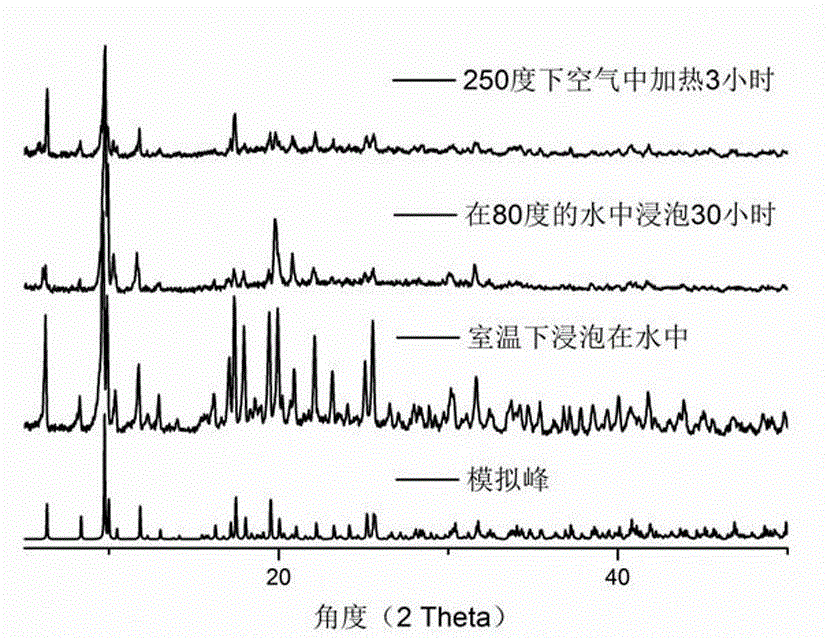
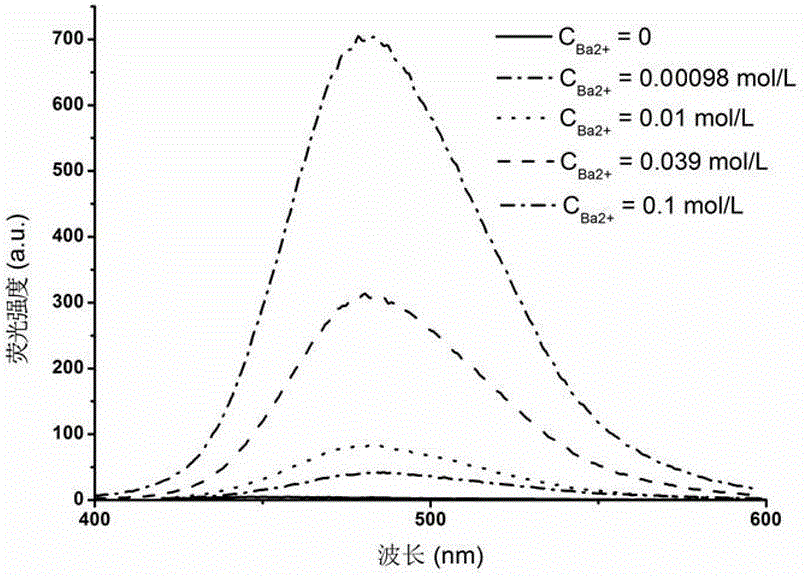
Fluorescent probe material prepared from Ln-MOFs (rare earth metal-organic frameworks) and application of fluorescent probe material
InactiveCN104672260AImprove stabilityEasy to manufactureGroup 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a fluorescent probe material prepared from Ln-MOFs (rare earth metal-organic frameworks) and an application of the fluorescent probe material. The fluorescent probe material can be used for testing barium ions in an aqueous solution qualitatively and quantitatively through changes of fluorescence intensity. The fluorescent probe material can be obtained quickly through 10-minute microwave heating. The preparation process is simple, the purity of an obtained product is high, the stability is good, fluorescence changes can be observed by naked eyes, the selectivity is very good, resistance to interference of other metal ions is high, and the fluorescent probe material is ideal and can be applied to testing of the barium ions.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
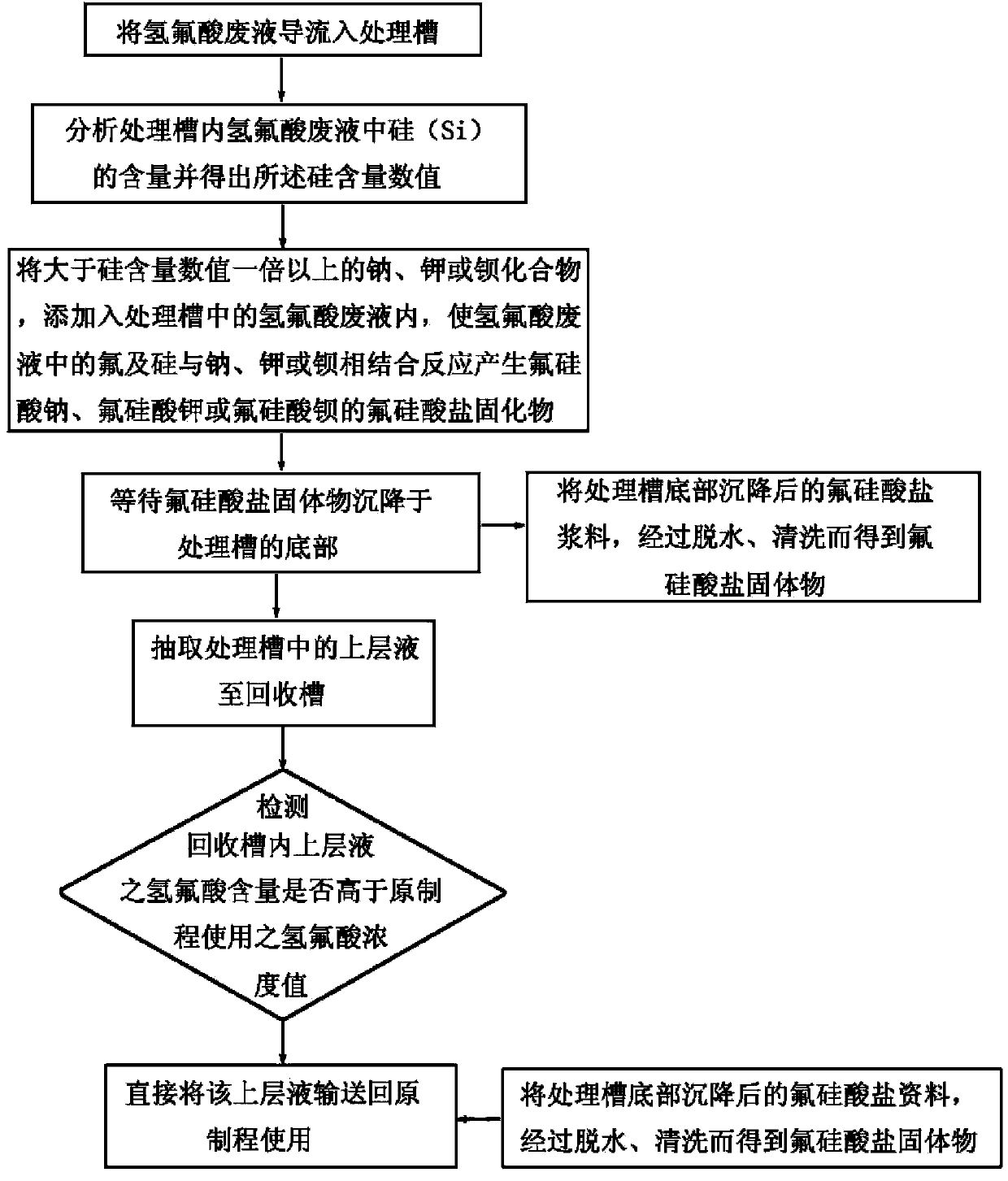
Treatment method for recycling hydrofluoric acid waste liquor
InactiveCN103373708AReduce spendingEmission reductionFluorine/hydrogen-fluorideHigh concentrationPotassium
The invention discloses a treatment method for recycling hydrofluoric acid waste liquor. The treatment method comprises the following steps of: analyzing the content of silicon in hydrofluoric acid waste liquor; adding a compound of sodium, potassium or barium, which is more than the content of silicon by once, into the hydrofluoric acid waste liquor in a treatment slot, so that the fluorine and silicon is combined with sodium, potassium or barium in the hydrofluoric acid waste liquor for a reaction to generate fluosilicate solids of sodium fluosilicate, potassium fluosilicate or barium fluosilicate; extracting the upper layer of liquor after settling the fluosilicate solids, and conveying back to the original process for use after adding high-concentration hydrofluoric acid to achieve a hydrofluoric acid concentration value satisfying the use of the original use. The hydrofluoric acid waste liquor is only added with a little sodium, potassium or barium ions to prepare the hydrofluoric acid which can be recycled, so that less chemical drug is consumed, the wastewater emission is greatly lowered, the hydrofluoric acid usage amount of the original process is saved and the extra purchase cost is saved, and therefore, the treatment steps are simplified, the treatment cost is lowered and environment-friendly benefits are achieved.
Owner:巫协森 +1
Methods for preserving fresh produce
InactiveUS20050084602A1Extended shelf lifePreserve textureMilk preservationDough treatmentAluminum IonFood flavor
Methods of preserving fresh produce with a produce preservative which extends the shelf life of fresh produce, particularly cut fresh produce, and preserves the texture, flavor, appearance, crispness, and color of the fresh produce, particularly the exposed surface of the fresh produce, are provided. The method comprises: providing a solution of produce preservative comprising: water; a preservative cation which is selected from the group consisting of a strontium ion, lithium ion, barium ion, aluminum ion, copper ion, ammonium ion, iron ion, manganese ion, potassium ion, or mixtures thereof; and ascorbate ions, or erythorbate ions; wherein the ascorbate ions or erythorbate ions and the preservative cation are present in an ion ratio of preferably from 0.2:1 to 8:1, more preferably 0.75:1 to 8:1, even more preferably from 1:1 to 4:1, yet more preferably 1.5:1 to 3:1; most preferably 1.1:1 to 2.5:1; and, applying said produce preservative to the produce. The invention also relates to fresh produce preserved with the produce preservatives.
Owner:MANTROSE HAEUSER
Anode material suitable for aqueous metal ion battery and preparation method for same
ActiveCN106229498AApplicable preparation processStable output voltageMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureAluminum IonSodium-ion battery
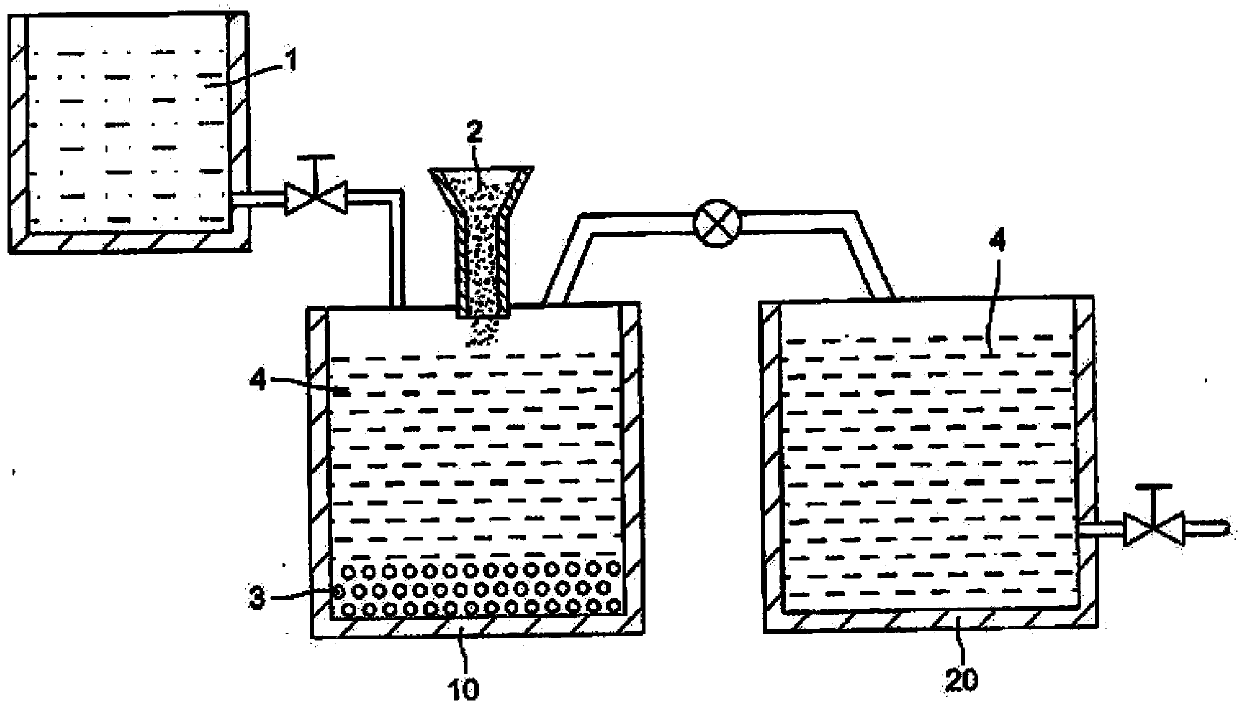
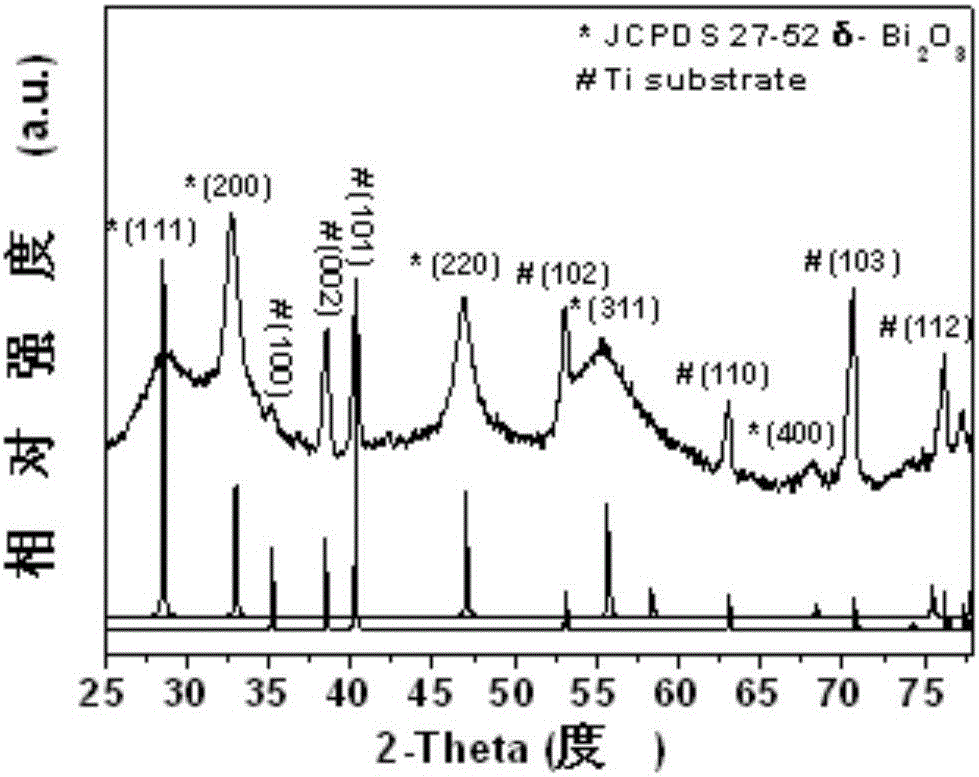
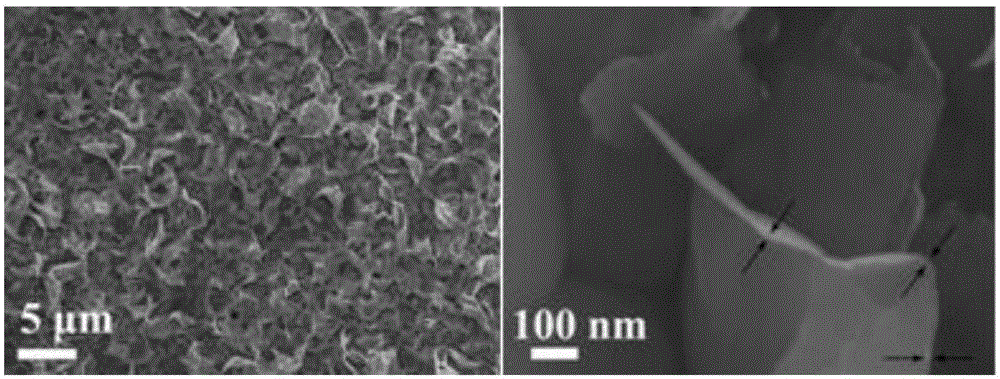
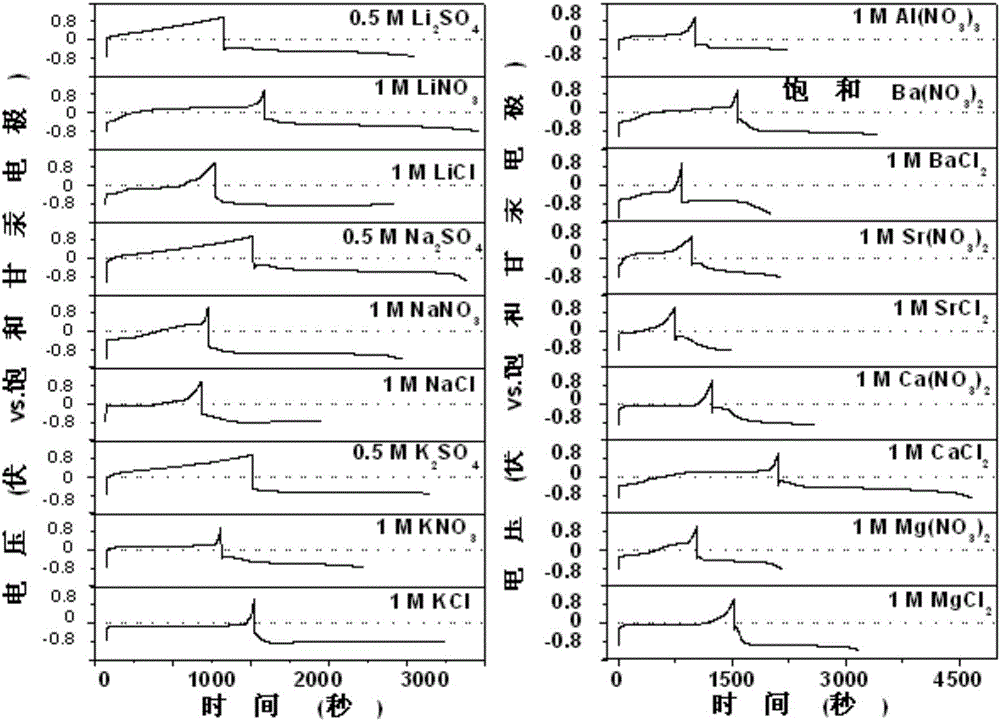
The invention relates to an anode material being suitable for an aqueous metal ion battery and a preparation method for the same. The anode material contains bismuth oxide and is a nano bismuth oxide array thin film, which is formed by oriented growth of bismuth oxide nano sheets on a metal substrate. The bismuth oxide nano sheets are vertically, uniformly and densely distributed on the metal substrate in an array structure, or that bismuth oxide powder is uniformly mixed with a conductive additive and a binder to form a film on the metal substrate. The anode material is suitable for many types of aqueous batteries, including aqueous lithium ion batteries, aqueous sodium ion batteries, aqueous potassium ion batteries, aqueous magnesium ion batteries, aqueous calcium ion batteries, aqueous strontium ion batteries, aqueous barium ion batteries, aqueous aluminum ion batteries, etc. The aqueous metal ion battery based on the anode material has high capacity, good charging / discharging platform, and high electrochemical reversibility.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents, their process of preparation and their uses
InactiveUS7452840B2Amino compound purification/separationMolecular sieve catalystsSorbentSimulated moving bed
The present invention relates to agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents containing zeolite X and an inert binder, the inert binder containing at least 80% by weight of clay which has undergone zeolitization by the action of an alkaline solution, the zeolite X having with an Si / Al ratio such that 1.15<Si / Al<=1.5, at least 90% of the exchangeable cationic sites of the zeolite X of which are occupied either by barium ions alone or by barium ions and potassium ions whose Dubinin volume is greater than or equal to 0.240 cm3 / g. They are obtained by agglomerating zeolite powder with a binder, followed by the zeolitization of the binder, the exchange of the ions of the zeolite by barium ions (and potassium ions) and the activation of the adsorbents thus exchanged. These adsorbents are particularly suited to the adsorption of the para-xylene present in C8 aromatic hydrocarbon fractions in the liquid phase in processes of simulated moving bed type but also to the separation of sugars, polyhydric alcohols, cresols or substituted toluene isomers.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Preparation method of high-purity strontium carbonate
InactiveCN101987736AHigh purityLow costCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesStrontium carbonateDistilled water
The invention belongs to a preparation method of high-purity strontium carbonate, comprising the following steps: (1) ammonium carbonate solution preparation; (2) strontium nitrate purification: placing the strontium nitrate into distilled water; heating the mixture to 60-70 DEG C; dissolving, filtering, and concentrating; controlling the relative density to be 18-20 Be; drying after cooling and crystallizing to obtain the purified strontium nitrate for later use; (3) impurity barium ions removing: placing the purified strontium nitrate into the distilled water; heating mixture to 40-50 DEG C; dissolving, adding sulfuric acid, stirring, precipitating for 2-3h, and filtering to obtain filter liquor; and (4) high-purity strontium carbonate synthesis: heating the filter liquor obtained in the step (3) to 60-70 DEG C; adding the ammonium carbonate solution obtained in the step (1); controlling the pH value at 8.5-9; and standing for 4-5h to obtain strontium nitrate precipitation; drying after pumping to dry to obtain the high-purity strontium carbonate finish product. The prepared strontium carbonate finish product has high purity and low impurity content, and the preparation process has simple process steps and higher production efficiency.
Owner:TIANJIN CHEM REAGENT RES INST
Method for quickly measuring sulfate radical content in magnesium method desulfurization process
InactiveCN102183518ARealize determinationRapid determinationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSulfate radicalsFiltration
The invention discloses a method for quickly measuring sulfate radical content in a magnesium method desulfurization process. The method consists of the processes of filtration, constant volume determination, acidification, precipitation and back titration and comprises the following steps of: filtering a fetched sample by using filter paper; filling quantitative filtered clear solution with constant volume into a volumetric flask; filling proper constant volume clear solution in a beaker, and adding diluted hydrochloric acid of 1:1 concentration for acidifying; adding excessive barium chloride into the acidified clear solution to perform precipitation; filtering and fully washing the sediment, and titrating the total weight of barium, calcium and magnesium ions by using ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) coordination agent under the condition that chrome black T is used as an indicator; and meanwhile, calculating the content of the barium ions by measuring the total weight of the calcium and the magnesium so as to calculate the content of the sulfate radicals. The method has the advantages that: the control of solution concentration and measuring process conditions is accurate, the measurement of the content of the calcium and the magnesium is completed at the same time, and the preparation of barium and magnesium mixed solution is not needed; the accuracy of the sulfate radical detection is improved, and the detection time is shortened; and the method is suitable for quickly measuring the sulfate radical content in the debugging and operating process of a magnesium oxide method desulfurization system.
Owner:CECEP L&T ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Wafer planarization composition and method of use
InactiveUS6997785B1Improve performanceFast cutting speedPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesPhysical chemistrySemiconductor
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Titanium barium phosphate salt, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102517009AEasy to controlLuminous intensityX-ray/infra-red processesLuminescent compositionsPhosphateCrystallinity
The invention discloses a titanium barium phosphate salt, and a preparation method and application thereof. A chemical formula of the titanium barium phosphate salt is Ba2-2xM2xTiP2-2yN2yO9, in the formula, M is divalent metal ions or trivalent rare earth elements; x is a mol percentage of M-substituted barium ion Ba2<+>, and x is more than or equal to 0.00001 but less than or equal to 0.5; N is one or more of vanadium ion V<5+>, zirconium ion Zr<4+>, tungsten ion W<5+> and molybdenum ion Mo<5+>; and y is the mol percentage of N-substituted phosphorus ion P<5+>, and y is more than or equal to 0.00001 but less than or equal to 0.5. The titanium barium phosphate salt is high in crystallinity, good in lighting quality, low in cost, simple in preparation process and free of pollution. Under exciting of X-ray, light output of Ba2TiP2O9 is equal to that of a commercial scintillator bismuth germinate Bi4Ge3O12; a lighting peak position is excellently matched with a photomultiplier tube; and the titanium barium phosphate salt can be used for detecting energetic particles, X-ray computer tomography, positron emission tomography technology, security checking, industrial detection and nuclear medical imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Detection method of sulfate ion in electrolyte used for lithium ion battery
ActiveCN105987900ARealize determinationEasy to compare and observeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLyonium ionLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to a detection method of sulfate ion in an electrolyte used for a lithium ion battery. The method includes the steps of: preparing an organic solvent water solution; preparing a sulfate water solution; preparing a plurality of sulfate ion standard substances; preparing a sample; and calculating the content range of the sulfate ions in the electrolyte. According to the rule of similarity and dissolving, the organic solvent water solution is prepared from an organic solvent and water according to certain ratio, so that the polarity of the organic solvent water solution is similar to that of the electrolyte, and the electrolyte is soluble in the organic solvent water solution. In addition, through addition of an acidic barium chloride water solution, the barium ions form barium sulfate precipitate only with the sulfate ions, so that the method allows convenient observation and comparison, thereby achieving the detection of content of the sulfate ion in the electrolyte.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG GUOTAI HUARONG NEW CHEM MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for preparing ornithine aspartate powder injection for injection
InactiveCN101843587AReduce manufacturing costSimple production equipmentOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDepyrogenationBarium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing ornithine aspartate powder injection for injection. The method comprises the following steps of: taking arginine, adding the solution of barium hydroxide, stirring to dissolve the arginine, and heating to hydrolyze so as to completely transform the arginine into ornithine; adding aspartate, uniformly stirring, adding a precipitator, filtering to remove barium ion precipitate, and regulating the pH value of the solution to neutrality; adding an inert organic solvent for crystallization, filtering and pumping, adding water for injection to dissolve the crystals, adding active carbon for needle for decoloration and depyrogenation, coarsely filtering to remove carbon, and filtering to make the solution sterile and clarified by using a 0.22 mu m millipore filter; and adding ethanol for crystallization, obtaining ornithine aspartate sterile powder, packaging the powder into a sterilized vial, capping, and rolling an aluminum cover to obtain the ornithine aspartate sterile powder injection for injection. The method has the advantages of increasing the yield, preparing the ornithine aspartate by the one-pot method, along with easy operation, simple and convenient operation, low cost, short production period, and suitability for mass production.
Owner:HUBEI HOPE PHARMA
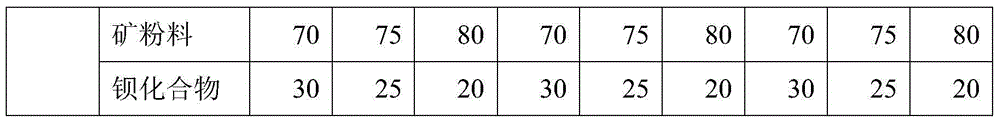
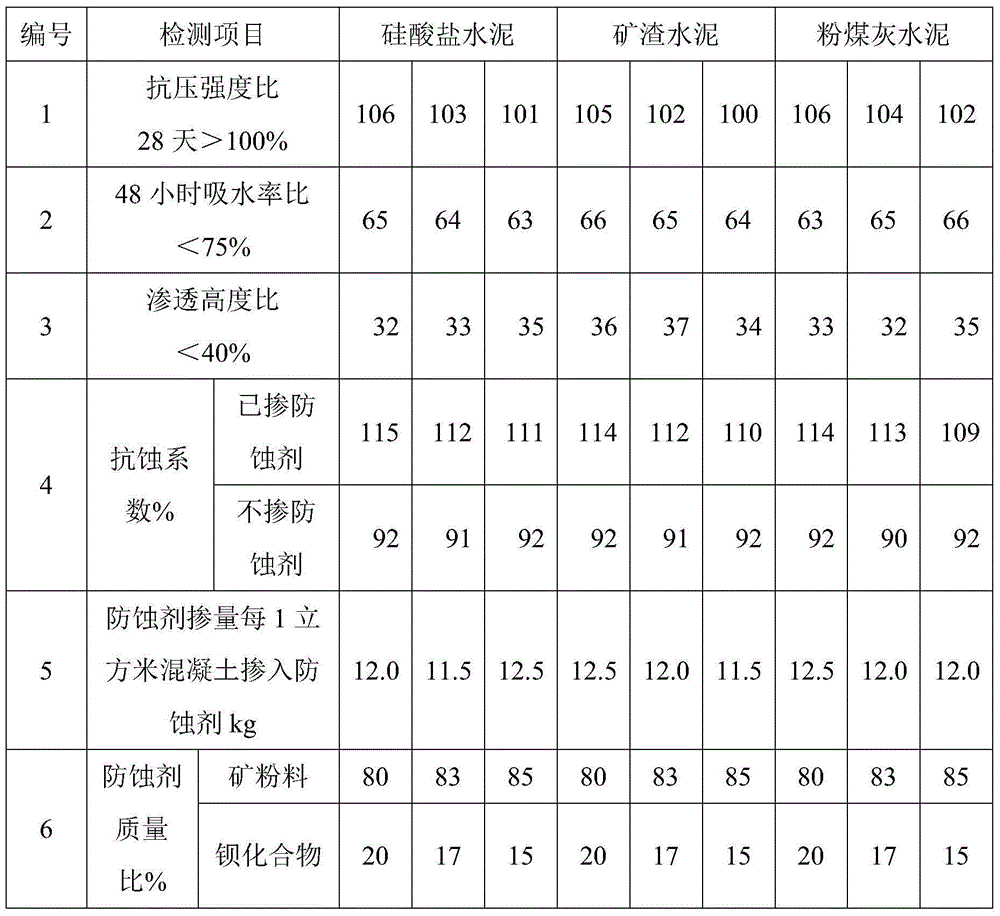
Anticorrosive agent for concrete and anticorrosive concrete
The invention provides an anticorrosive agent for concrete. The anticorrosive agent is a mixture of powder selected from the group consisting of fly ash, blast-furnace water-quenched slag powder, silica fume, light-burnt metakaolin powder, phosphorus slag powder, alum slag powder, natural zeolite powder and the like and a barium compound selected from the group consisting of barium chloride, barium nitrate, barium acetate, barium hydroxide, barium sulfide and the like. The anticorrosive agent for concrete provided by the invention enables Ca(OH)2 by-produced in hydration of cement to bond with SiO2 included in cement so as to produce secondary hydrated calcium silicate, so the strength and impermeability of concrete are improved; barium ions doped into concrete reacts with SO4<2-> from the outside in time to produce inertial and stable secondary barite, so deionization of SO4<2-> is realized and corrosivity of SO4<2-> is eradicated; the secondary barite forms a stable mineral inorganic protection film on the surface layer of concrete, so further invasion of external harmful ions is prevented, the strength, impermeability and corrosion resistance of concrete are further improved, the service life of concrete is substantially prolonged, and economic benefits are increased.
Owner:李亚铃
High-gravity reactive precipitation process for the preparation of barium titanate powders
InactiveUS20050019248A1High yieldShort timeMaterial nanotechnologyAlkaline earth titanatesBarium titanateOrganic base
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of fine barium titanate (BaTiO3) powders. The process comprises introducing an aqueous solution (I) containing salts of barium and titanium, and an aqueous basic solution (II) containing an inorganic or organic base separately and simultaneously into a high-gravity reactor with the high-gravity level of 1.25G to 12,500G and performing the reaction of the solution (I) with the solution (II) at a temperature of from 60 to 100° C. The solution (I) is preheated to a temperature ranging from 60° C. to 65° C. and the solution (II) is preheated to a temperature ranging from 60° C. to 100° C. respectively prior to the reaction, in which the Ba / Ti molar ratio in the solution (I) is more than 1 and the concentration of the base in the solution (II) is such that the reaction mixture is maintained at a constant OH− concentration, preferably a pH value of about 14. The reaction product is separated by filtering and washed with deionized water to remove the impurity ions and excessive barium ions, and then dried to obtain BaTiO3 powders. Said powders consist essentially of crystalline, primary particles having a uniform particle size ranging from 5 to 200 nm, an approximately spherical morphology and a high sintering activity.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Green silicate long afterglow luminescent material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107189776AGood chemical stabilityImprove thermal stabilityLuminescent compositionsChemical stabilityCalcination
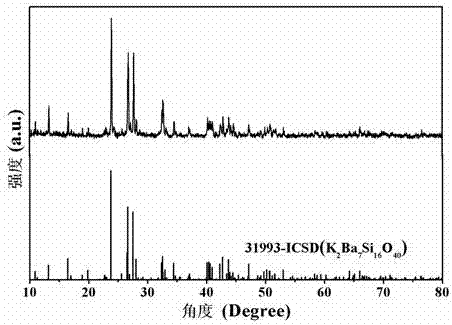
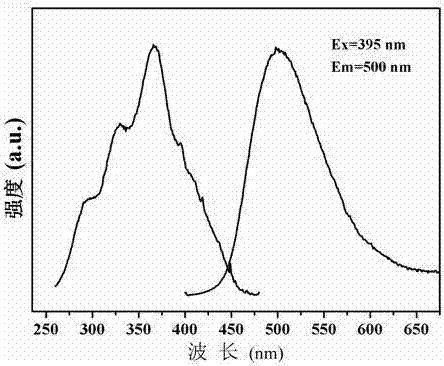
The invention relates to a green silicate long afterglow luminescent material and a preparation method thereof. The luminescent material has a chemical formula of K2Ba7-x-ySi16O40:xEu<2+>, yR<III>; wherein x is greater than or equal to 0.001 and smaller than or equal to 0.5, y is greater than or equal to 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.5. The preparation method includes: taking compounds containing potassium ion K<+>, barium ion Ba<2+>, silicon ion Si<4+>, rare earth ion Eu<2+> and R<III> as the raw materials, weighing the raw materials according to a stoichiometric ratio of elements in the chemical formula K2Ba7-x-ySi16O40:xEu<2+>, yR<III>, performing grinding and mixing the substances evenly to obtain raw material powder; conducting calcination in reducing atmosphere; performing furnace cooling to room temperature to obtain a calcined product; and conducting grinding to obtain the green silicate long afterglow luminescent material. The luminescent material has good chemical stability and thermal stability, and is stable after encountering water. The preparation method is simple, has no emission of waste water and waste gas, and the prepared long afterglow luminescent material can emit green afterglow continuously.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Rare earth doped barium titanate particles and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses rare earth doped barium titanate particles and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding barium carbouate powder, amide reagent solution for decomposing a rare earth oxide, titanium oxide powder and absolute ethanol into a ball mill sequentially; performing ball milling on the mixture for 90+ / -30min, wherein the mol ratioof the barium carbonate to the titanium dioxide is 1.000+ / -0.020 and the mol ratio of rare-earth ions to barium ions is between 0.001 and 0.005; performing vacuum drying on materials which are subjected to the ball milling and then initially sintering the dried materials; crushing the sintered materials, washing the crushed materials by using deionized water and sintering the washed materials forthe second time; decentralizing the obtained product to obtain liquid-phase doped rare earth-barium titanate power; and then placing the rare earth-barium titanate power into an osmosis furnace to perform osmosis in nitrogen (N2) at the temperature of between 800 and 1,000 DEG C for 4h to obtain the target particles. The resistivity of the prepared doped barium titanate particles is obviously changed.
Owner:HUNAN SEEDER ELECTRONICS CERAMIC TECH IND PARK DEV CO LTD
Bionic nano superstructure material preparation method using white envelope as model
InactiveCN1522794ALow priceReduce manufacturing costChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesLiquid-liquid reaction processesMaterials preparationBionics
The present invention relates to a method for preparing bionic nano superstructure material by using egg membrane as template. Said method includes the following steps: firstly, removing surface mineral from egg shell to obtain egg membrane, washing it with deionized water for stand-by; then using the calcium and barium ions contained cationic compound solution whose concentration is 0.05-0.20 mol / L and ionic mole number ratio is correspondent to product chemical formula and anionic compound solution containing chromic radical, sulfuric radical, molybdic radical and tungstic radical, placing them respectively at two sides of egg membrane, regulating pH, reacting for 10-15 hr. at room temp., finally taking out reaction products from two sides of egg membrane, centrifugal separating at room temp., removing clear liquor, successively using acetone and deionized water to wash precipitate and wash egg membrane, combining all the products so as to obtain bionic nano superstructure material with various forms.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com