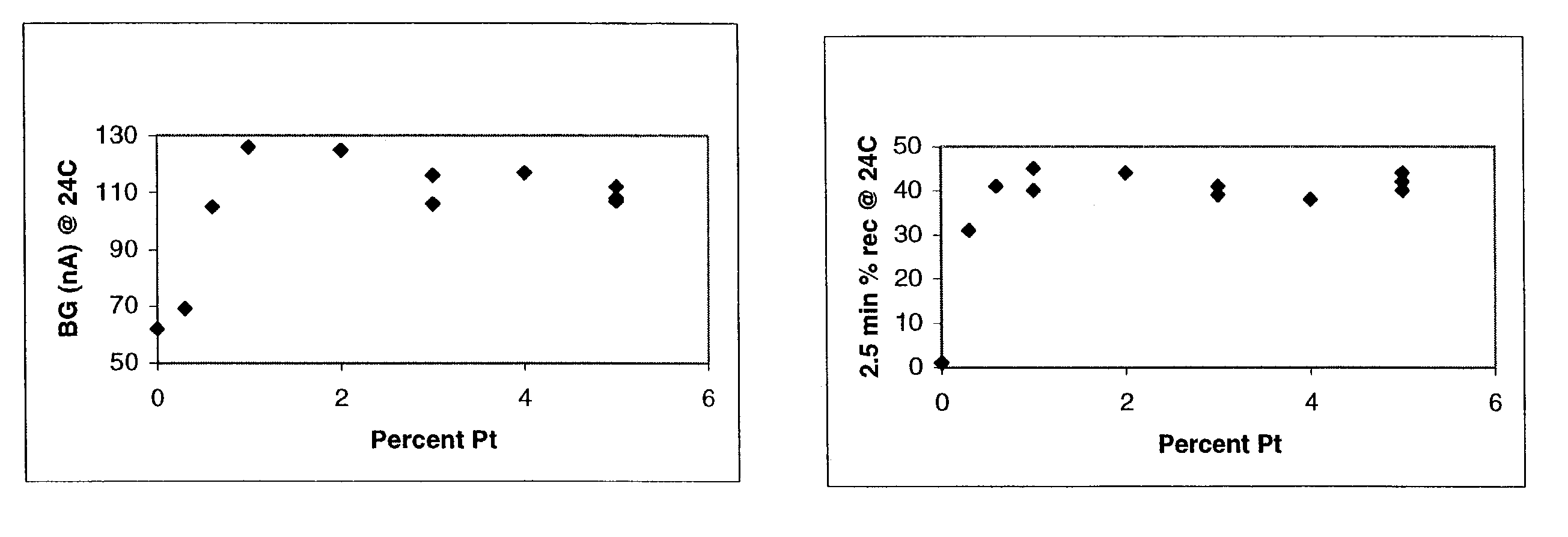
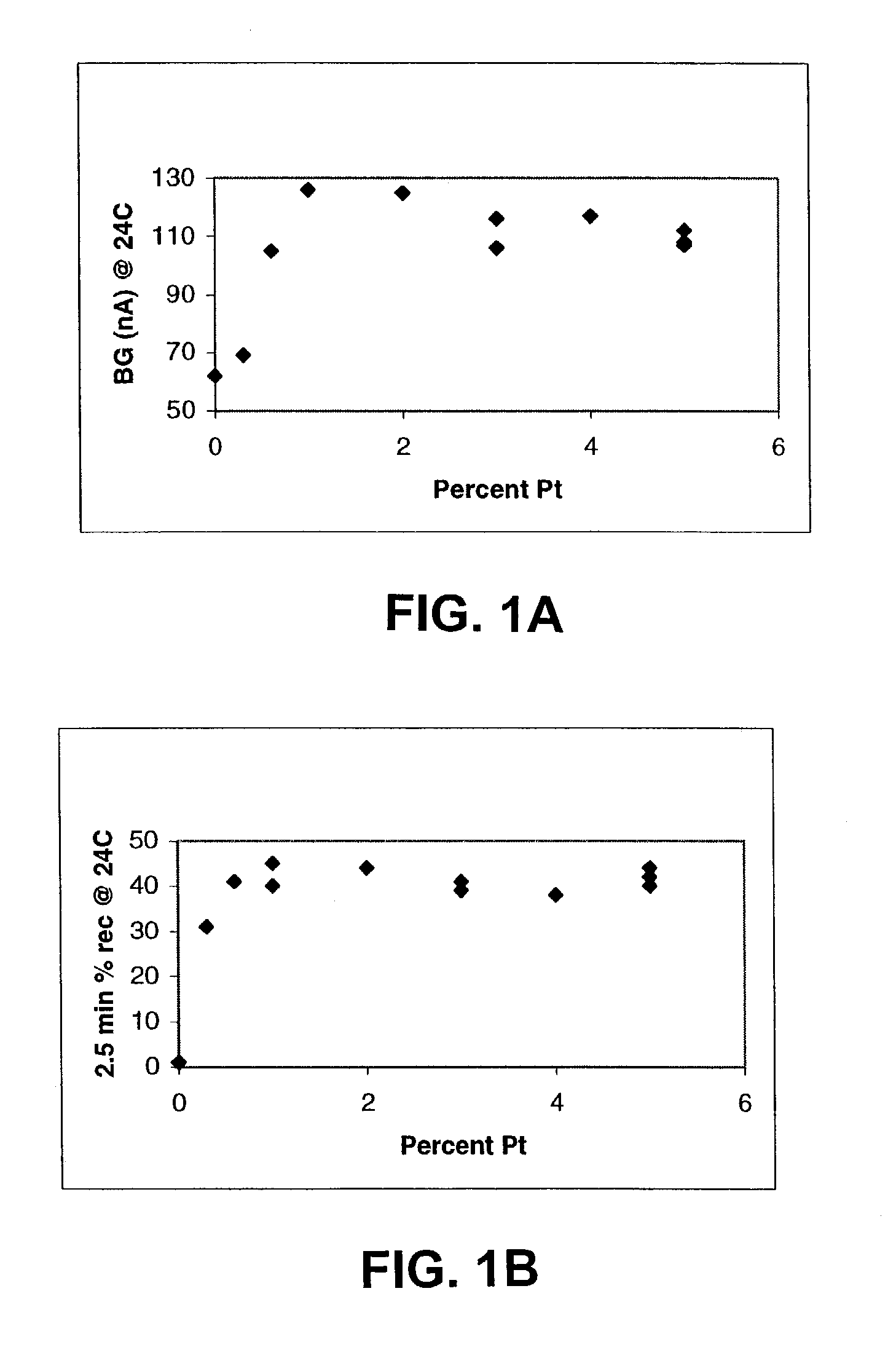
Patents
Literature
111 results about "Platinum black" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
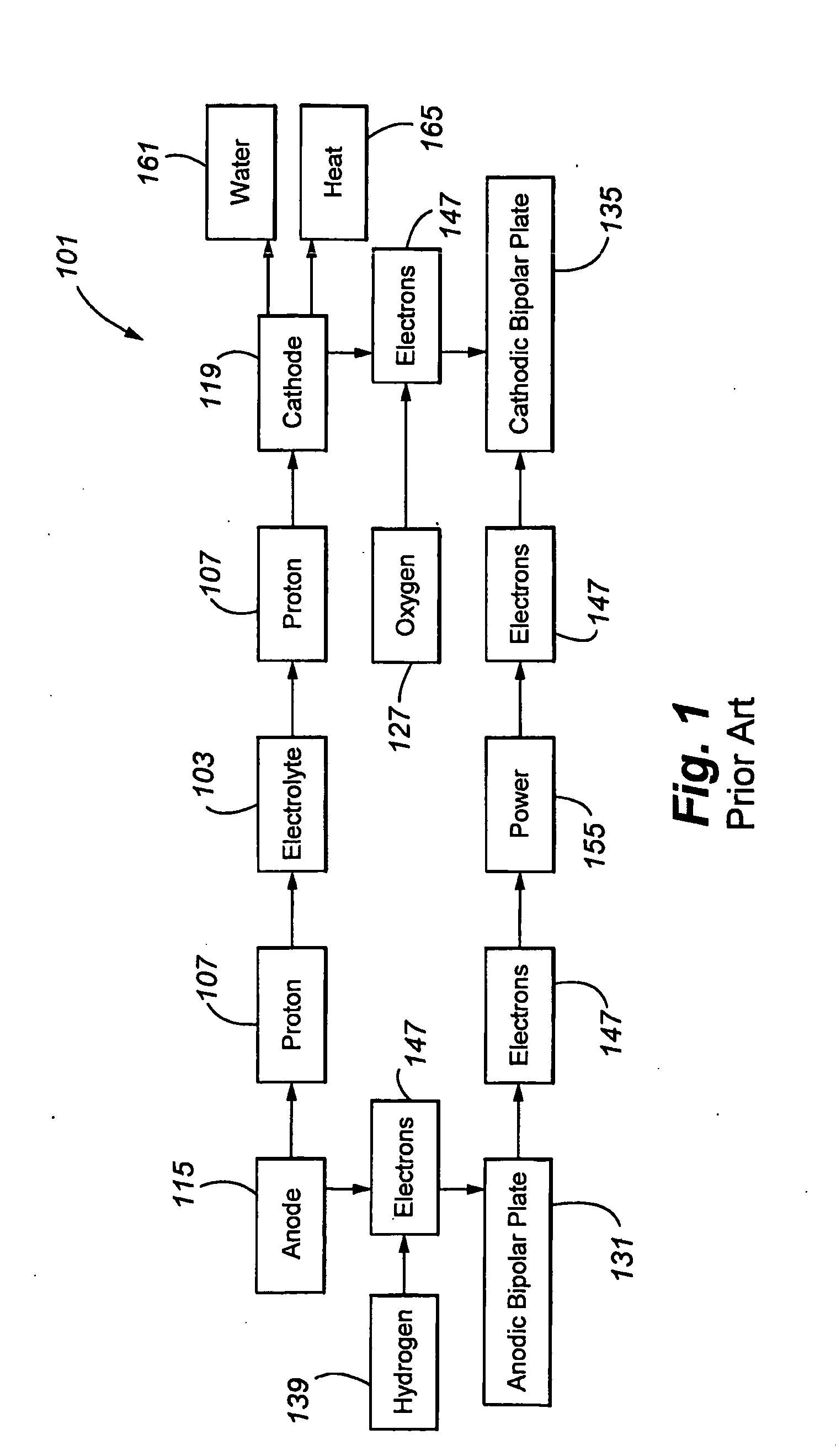
Platinum black (Pt black) is a fine powder of platinum with good catalytic properties. The name of platinum black is due to its black color.
Highly catalytic screen-printing ink
ActiveUS7018568B2Easy to produceConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive materialConductive polymerPrinting ink
The invention is directed to conductive polymer compositions, catalytic ink compositions (e.g., for use in screen-printing), electrodes produced by deposition of an ink composition, methods of making, and methods of using thereof. An exemplary ink material comprises platinum black and / or platinum-on-carbon as the catalyst, graphite as a conducting material, a polymer binding material, and an organic solvent. The polymer binding material is typically a copolymer of hydrophilic and hydrophobic monomers. The conductive polymer compositions of the present invention can be used, for example, to make electrochemical sensors. Such sensors can be used in a variety of analyte monitoring devices to monitor analyte amount or concentrations in subjects, for example, glucose monitoring devices to monitor glucose levels in subjects with diabetes.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
Platinum electrode and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6974533B2Increase surface areaSufficient physical and structural strengthCellsHead electrodesMetallurgyPt element
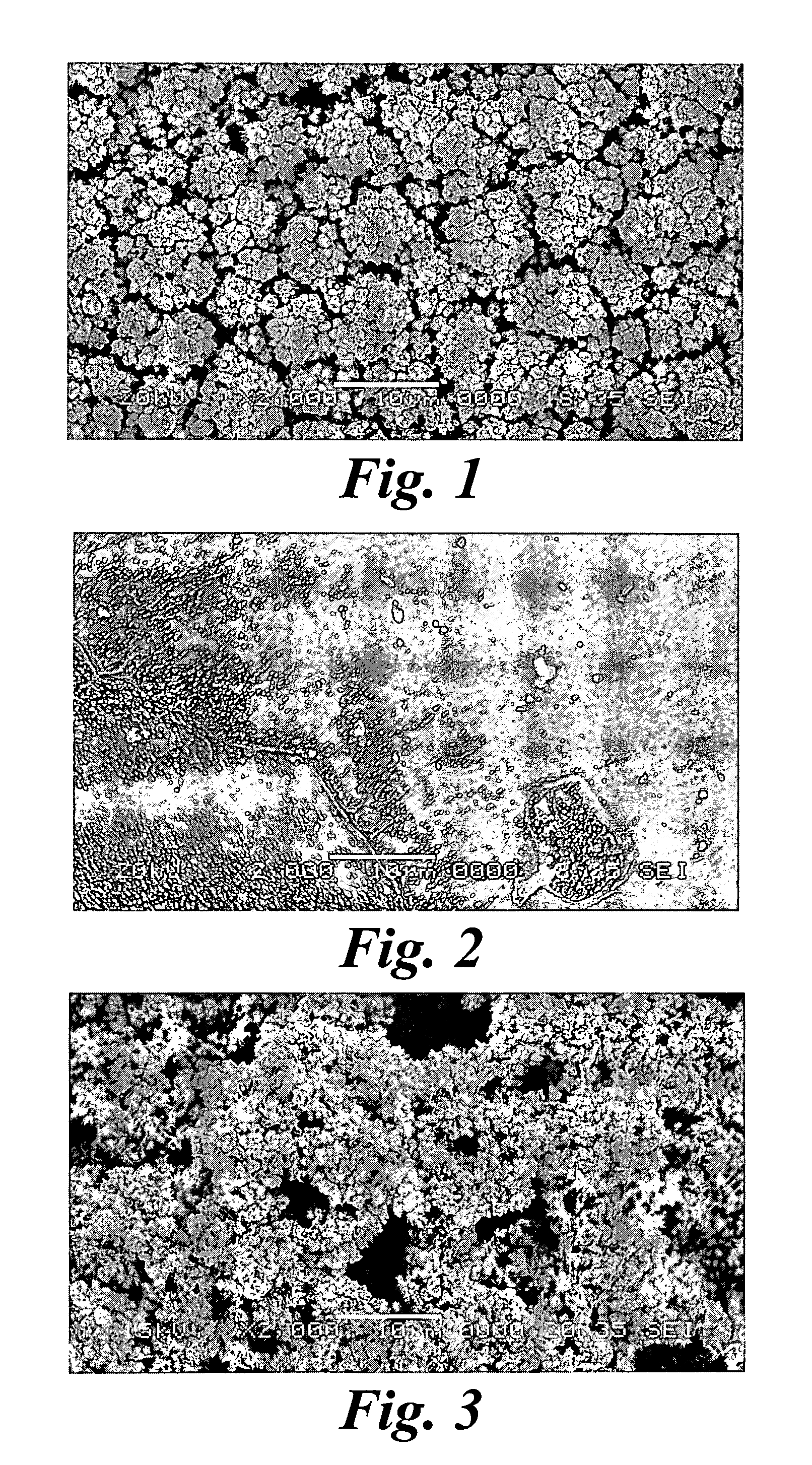
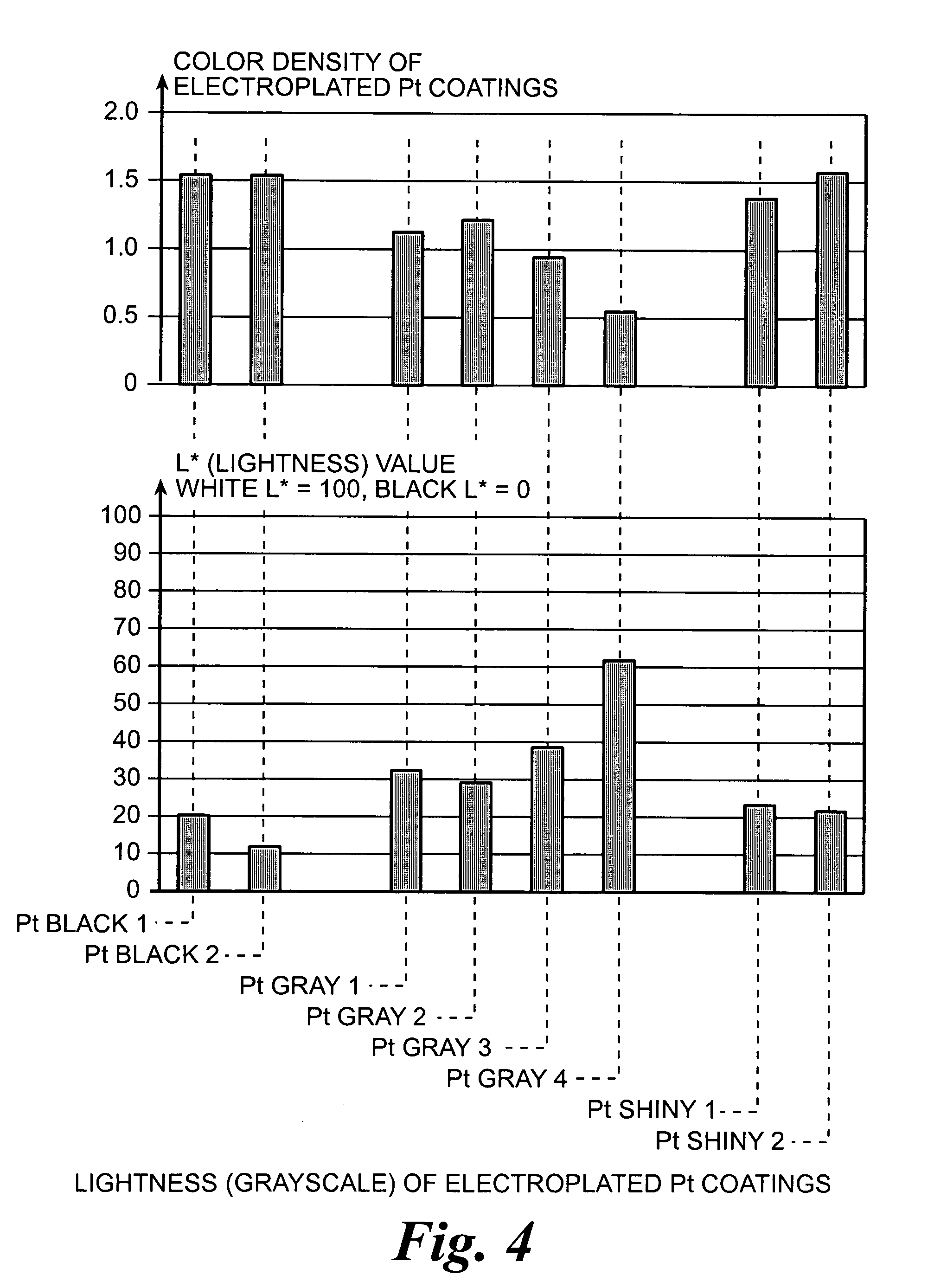
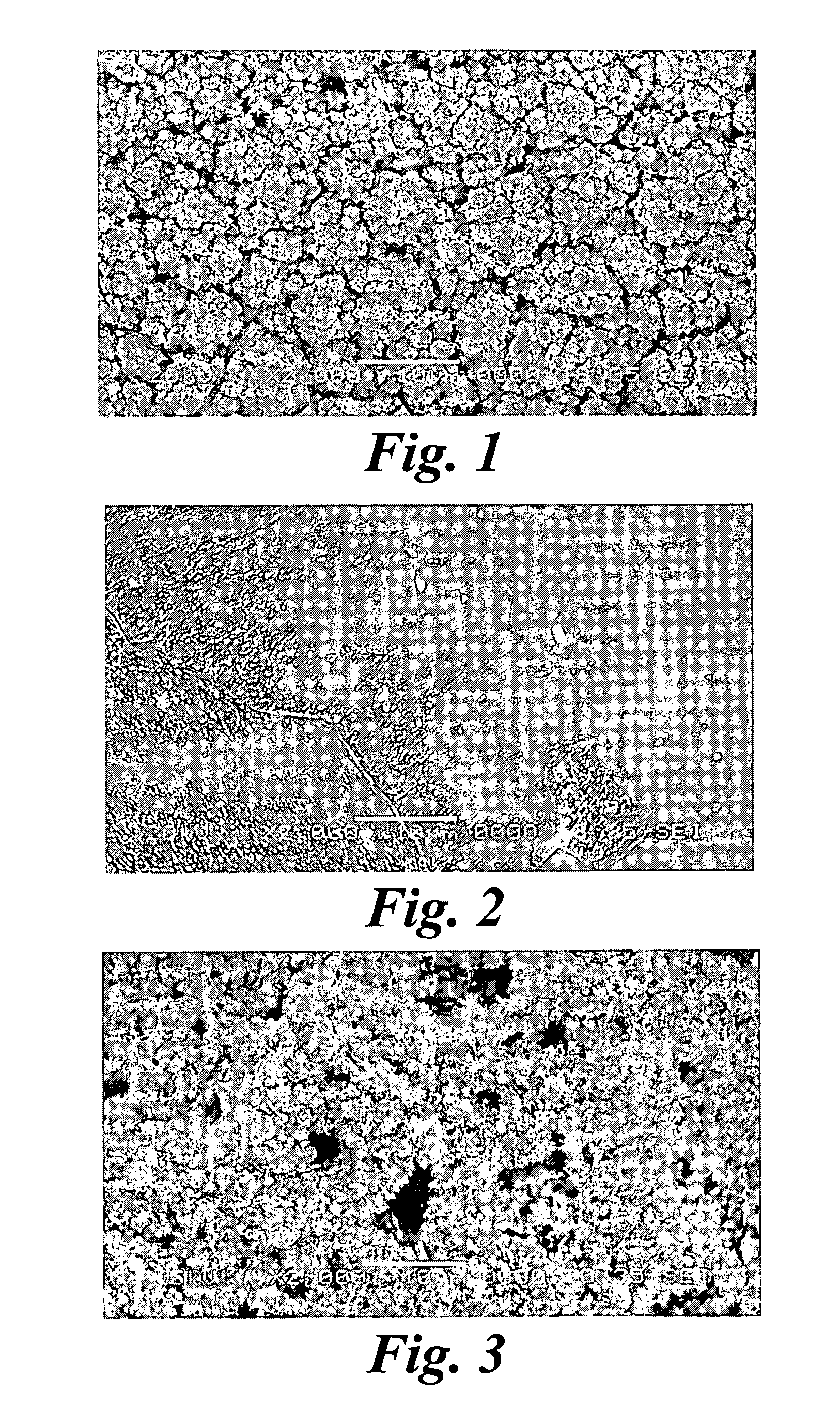
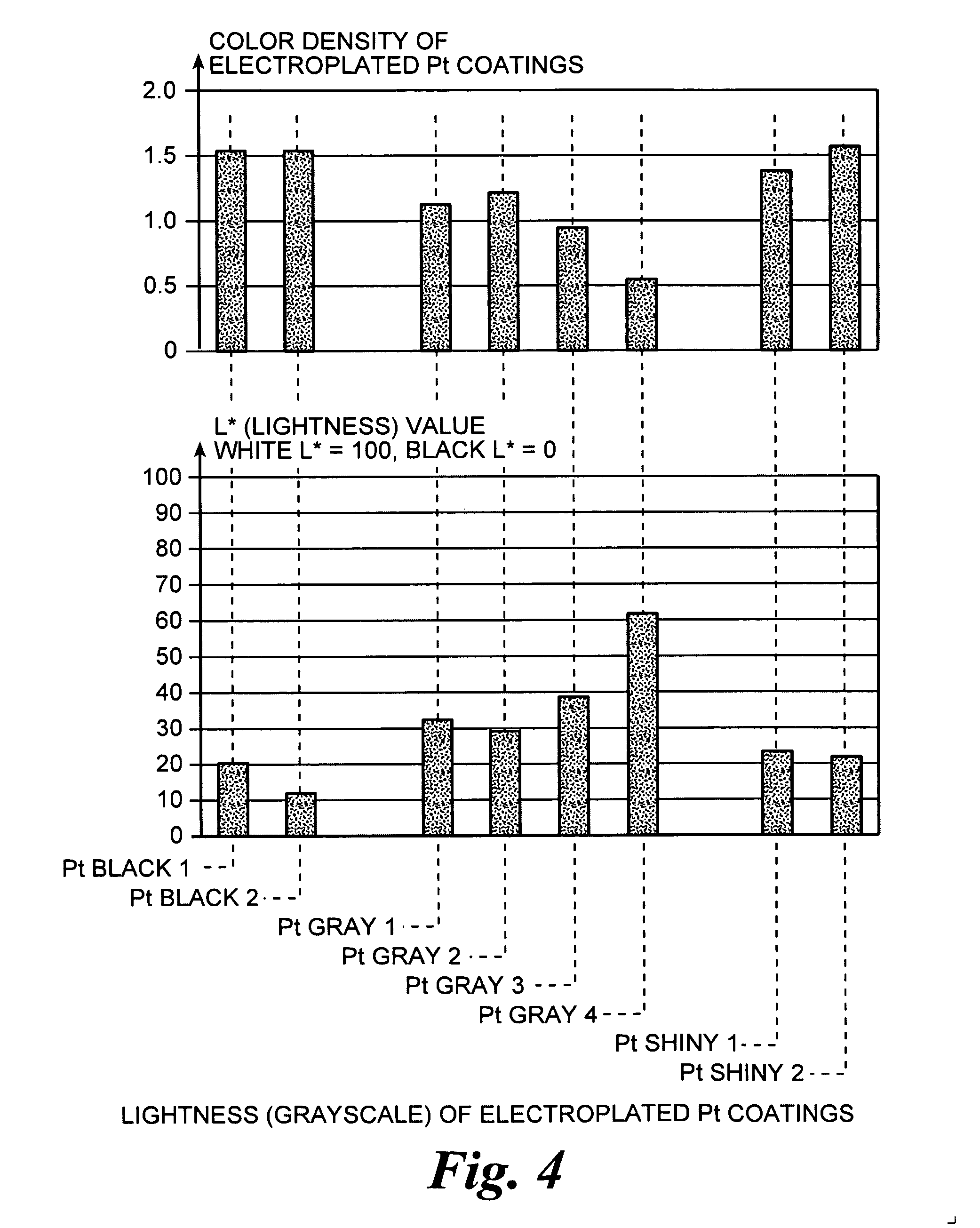
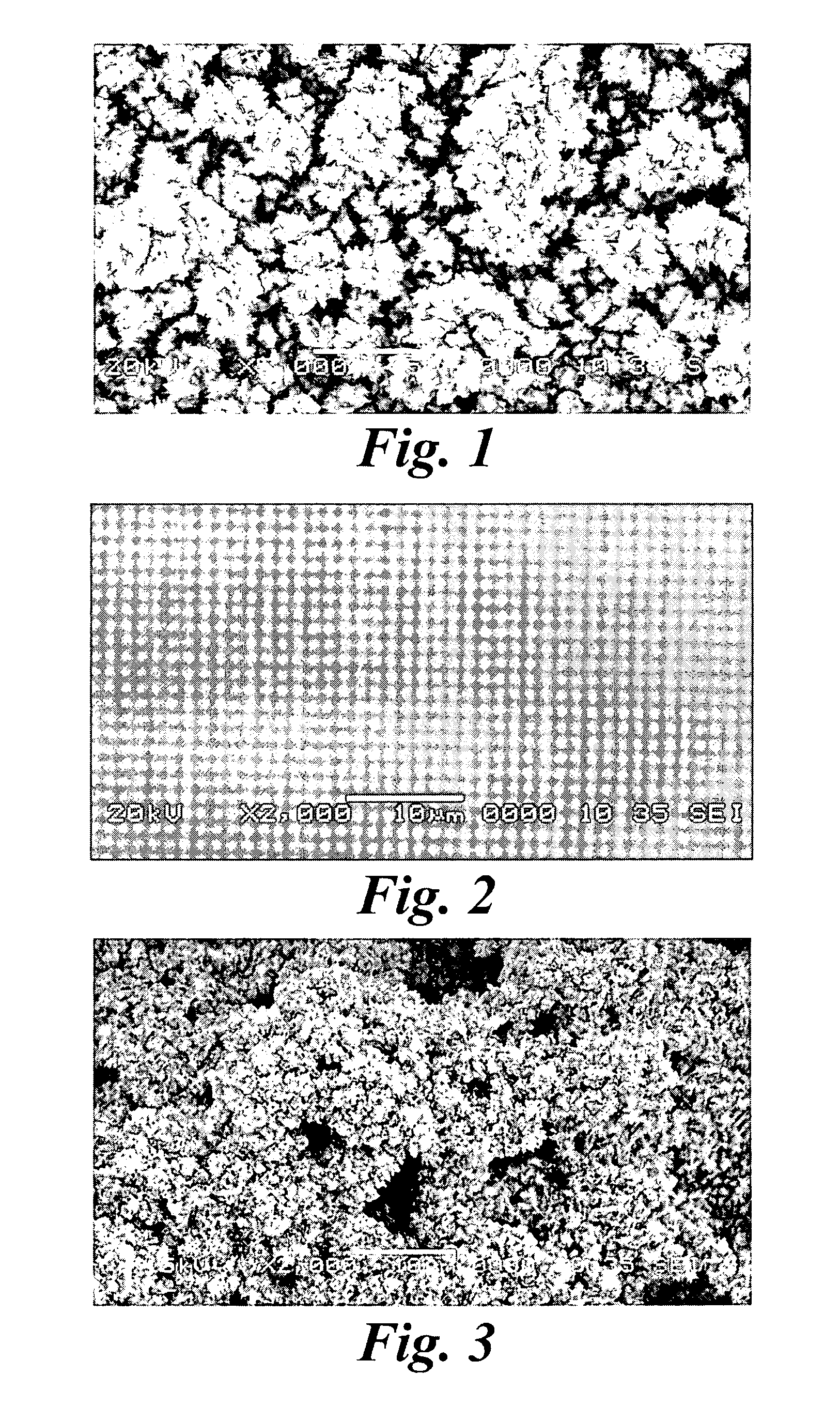
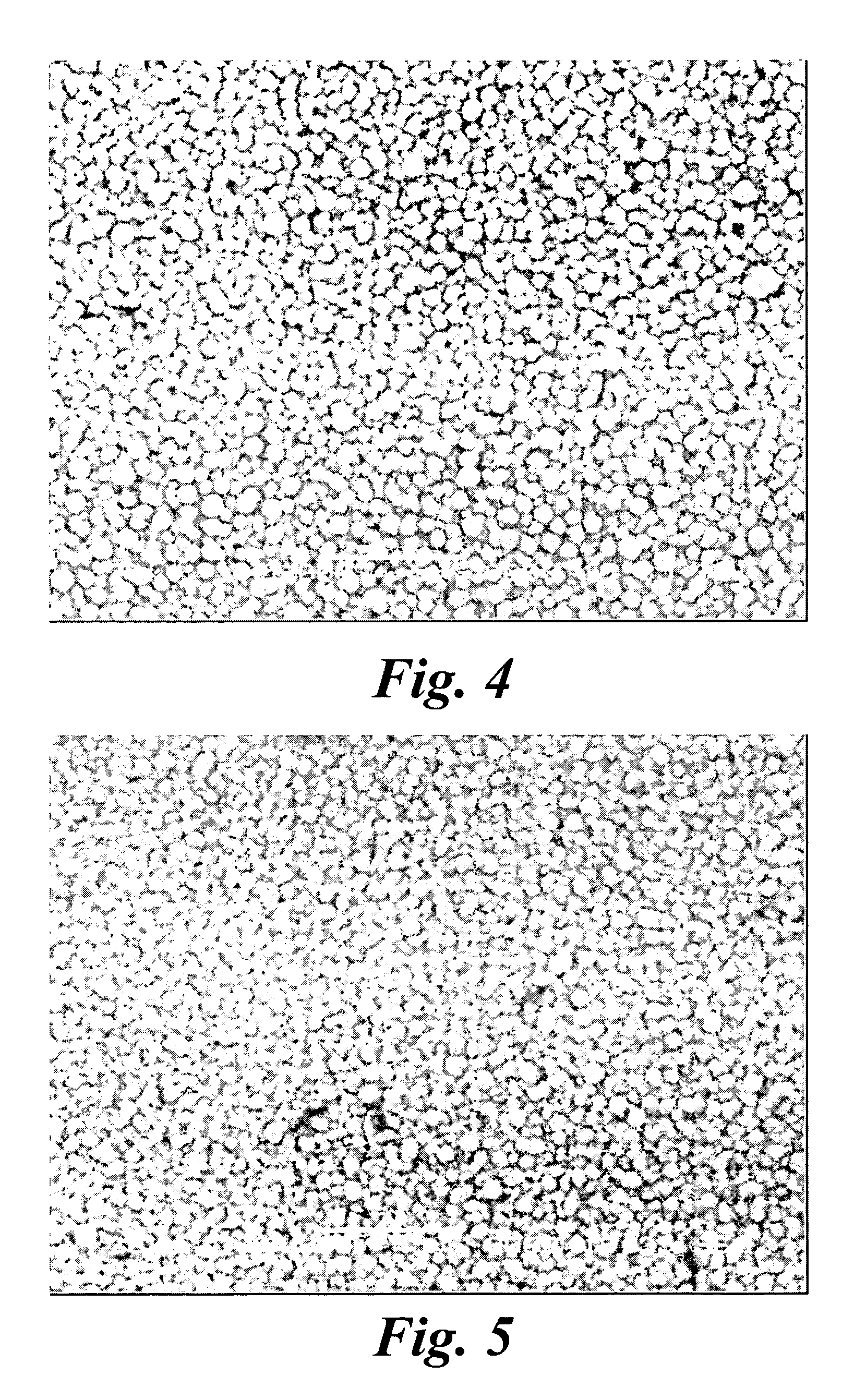
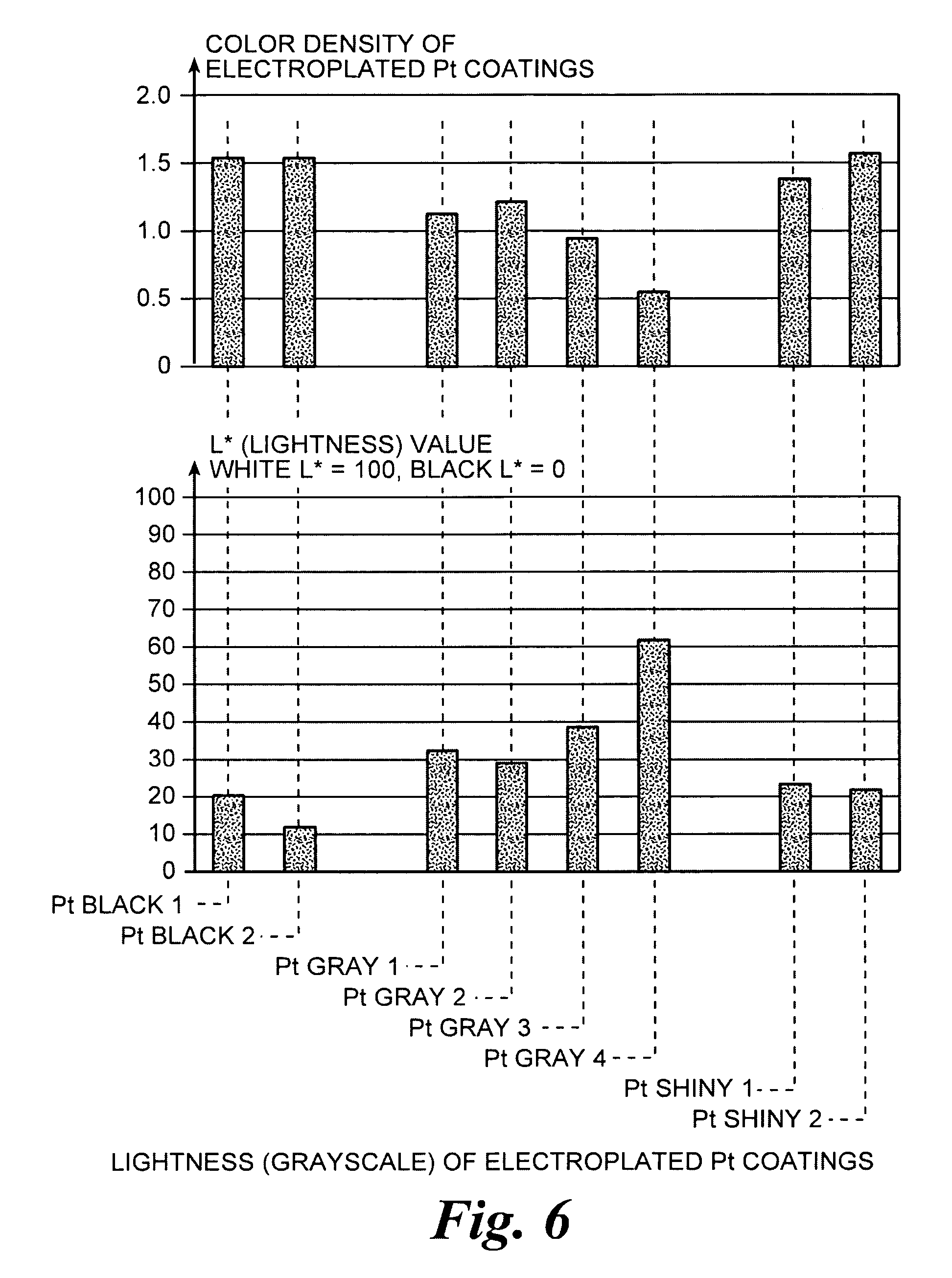
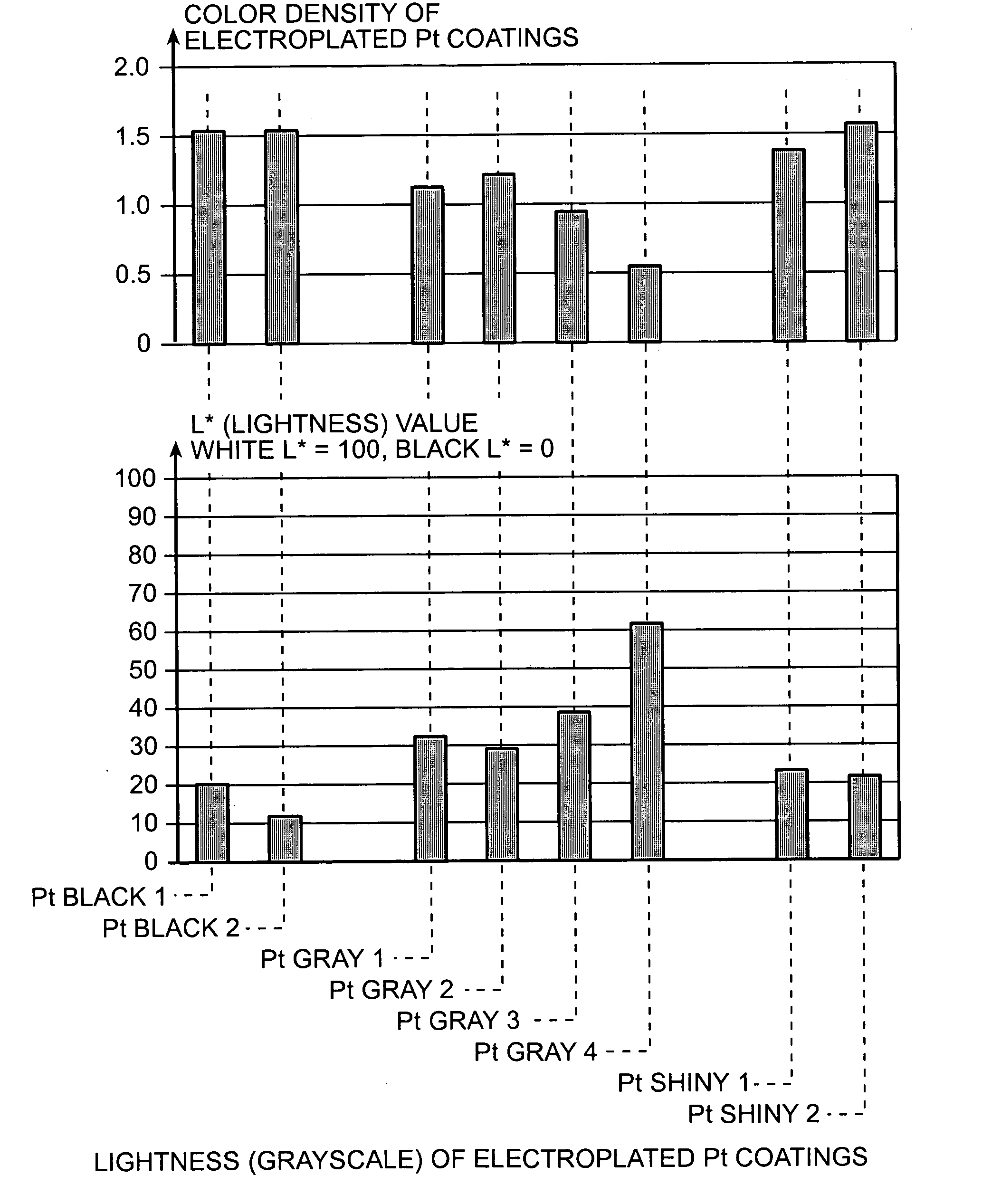
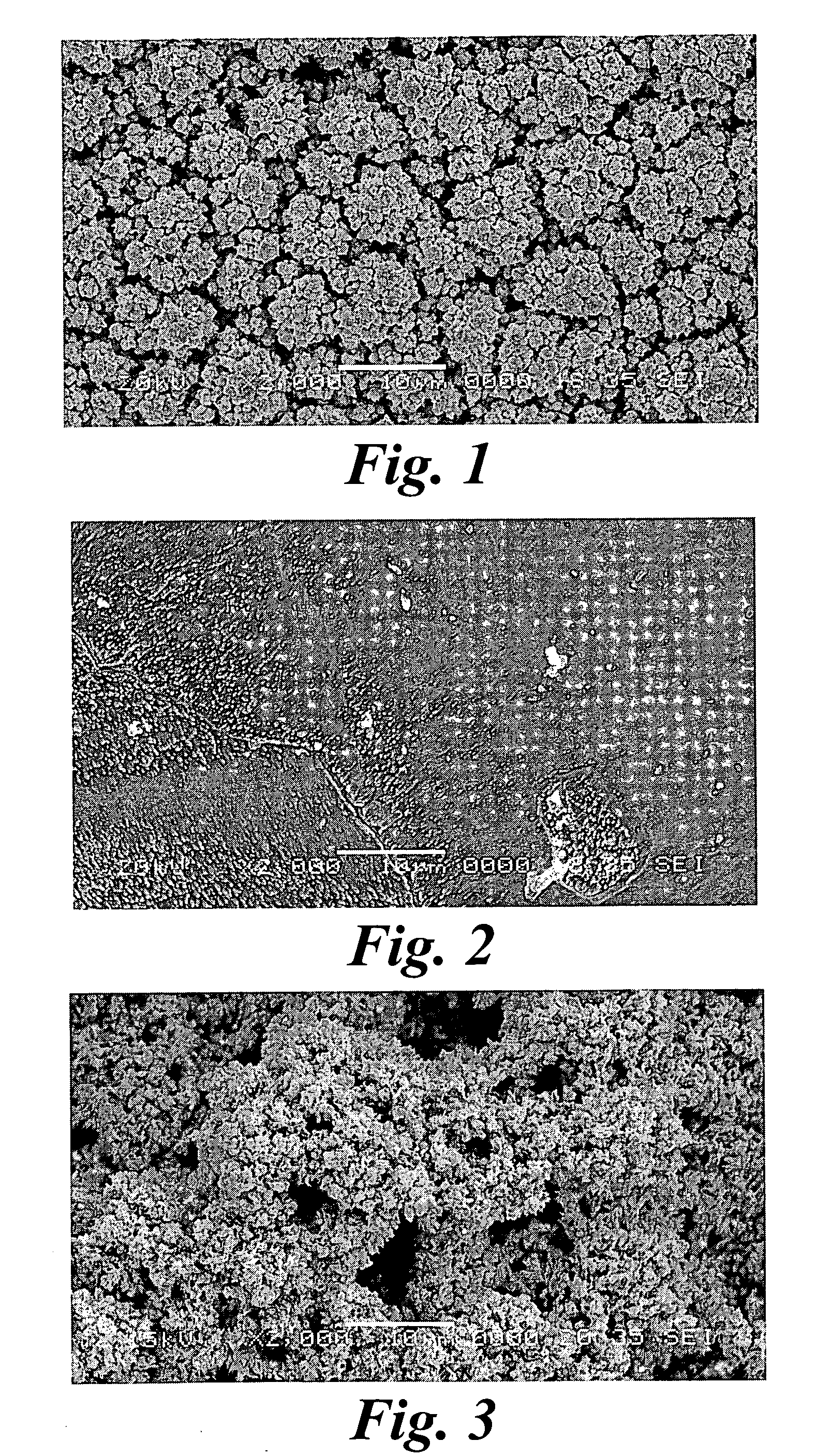
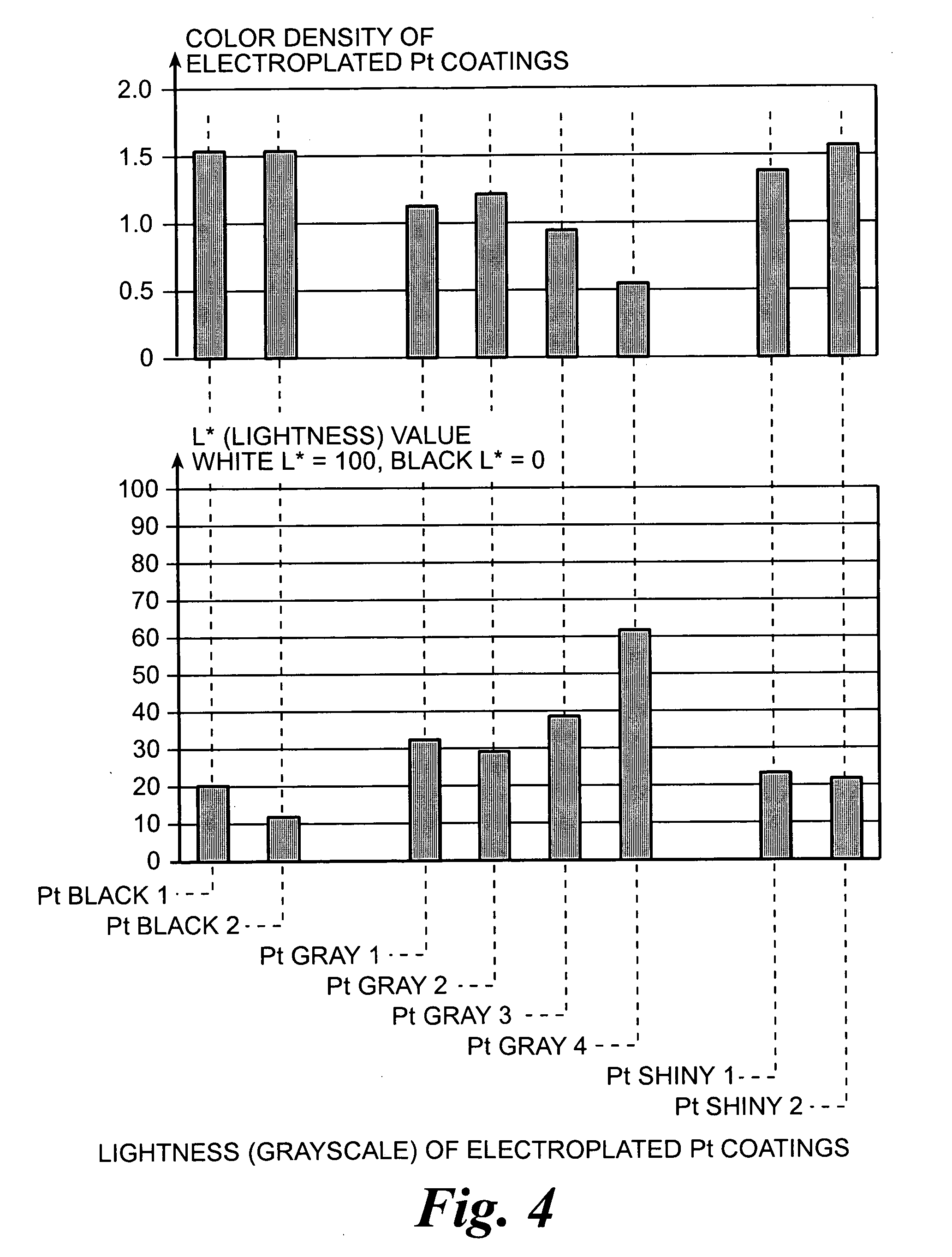
An improved electrode and method for manufacturing the improved electrode wherein the electrode having a fractal surface coating of platinum [which the present inventor refers to as “platinum gray”] with a increase in surface area of at least 5 times when compared to shiny platinum of the same geometry and also having improved resistance to physical stress when compared to platinum black having the same surface area. The process of electroplating the surface coating of platinum gray comprising plating at a moderate rate, i.e., at a rate that is faster than the rate necessary to produce shiny platinum and that is less than the rate necessary to produce platinum black.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Catalyst and a method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060063062A1Increase surface areaCellsInternal combustion piston enginesFuel cellsPhysical stress
An improved platinum and method for manufacturing the improved platinum wherein the platinum having a fractal surface coating of platinum, platinum gray, with a increase in surface area of at least 5 times when compared to shiny platinum of the same geometry and also having improved resistance to physical stress when compared to platinum black having the same surface area. The process of electroplating the surface coating of platinum gray comprising plating at a moderate rate, for example at a rate that is faster than the rate necessary to produce shiny platinum and that is less than the rate necessary to produce platinum black. Platinum gray is applied to manufacture a fuel cell and a catalyst.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS
Platinum electrode surface coating and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7887681B2Increase surface areaSufficient physical and structural strengthInternal electrodesActive material electrodesRough surfaceMetal particle
An electrode surface coating and method for manufacturing the electrode surface coating comprising a conductive substrate; a surface coating of platinum having a rough configuration and an increase in the surface area of 5 times to 500 times of the corresponding surface area resulting from the basic geometric shape of the electrode. A method for electroplating an electrode surface with platinum coating having a rough surface, comprising electroplating the surface of a conductive substrate at a rate such that the metal particles form on the conductive substrate faster than necessary to form shiny platinum and slower than necessary to form platinum black.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS
Refined platinum producing process
The present invention relates to wet noble metal smelting process. The process includes dissolution of coarse ammonium chloroplatinate with sodium hydroxide solution, reduction by adding hydrazine hydrate and filtering to obtain platinum black, hydrogen peroxide and hydrochloric acid dissolution to obtain platinum black, adidng ammonium chloride for fractional deposition of platinum in the form of ammonium chloroplainate, and conventional calcinatino to obtain spongy platinum. The present invention has short technological process, low productino cost, low power consumption, and good operationcondition, and it is possible to produce various products in different grade.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Platinum electrode surface coating and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070092786A1Increase surface areaSufficient physical and structural strengthInternal electrodesActive material electrodesRough surfaceMetal particle
An electrode surface coating and method for manufacturing the electrode surface coating comprising a conductive substrate; a surface coating of platinum having a rough configuration and an increase in the surface area of 5 times to 500 times of the corresponding surface area resulting from the basic geometric shape of the electrode. A method for electroplating an electrode surface with platinum coating having a rough surface, comprising electroplating the surface of a conductive substrate at a rate such that the metal particles form on the conductive substrate faster than necessary to form shiny platinum and slower than necessary to form platinum black.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS
Muting glucose sensor oxygen response and reducing electrode edge growth with pulsed current plating
ActiveUS20140243634A1Increased surface area ratioHigh ratio of surface areaImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGlucose sensorsAnalyte
The invention disclosed herein includes amperometric glucose sensors having electrodes formed from processes that electrodeposit platinum black in a manner that produces relatively smooth three dimensional metal architectures, ones that contribute to sensor reliability and stability. Embodiments of the invention provide analyte sensors having such uniform electrode architectures as well as methods for making and using these sensor electrodes. A number of working embodiments of the invention are shown to be useful in amperometric glucose sensors worn by diabetic individuals.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Catalyst using metal oxide as carrier for fuel cells and application thereof
ActiveCN101773826AImprove performanceIncrease profitCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystElectrolysis
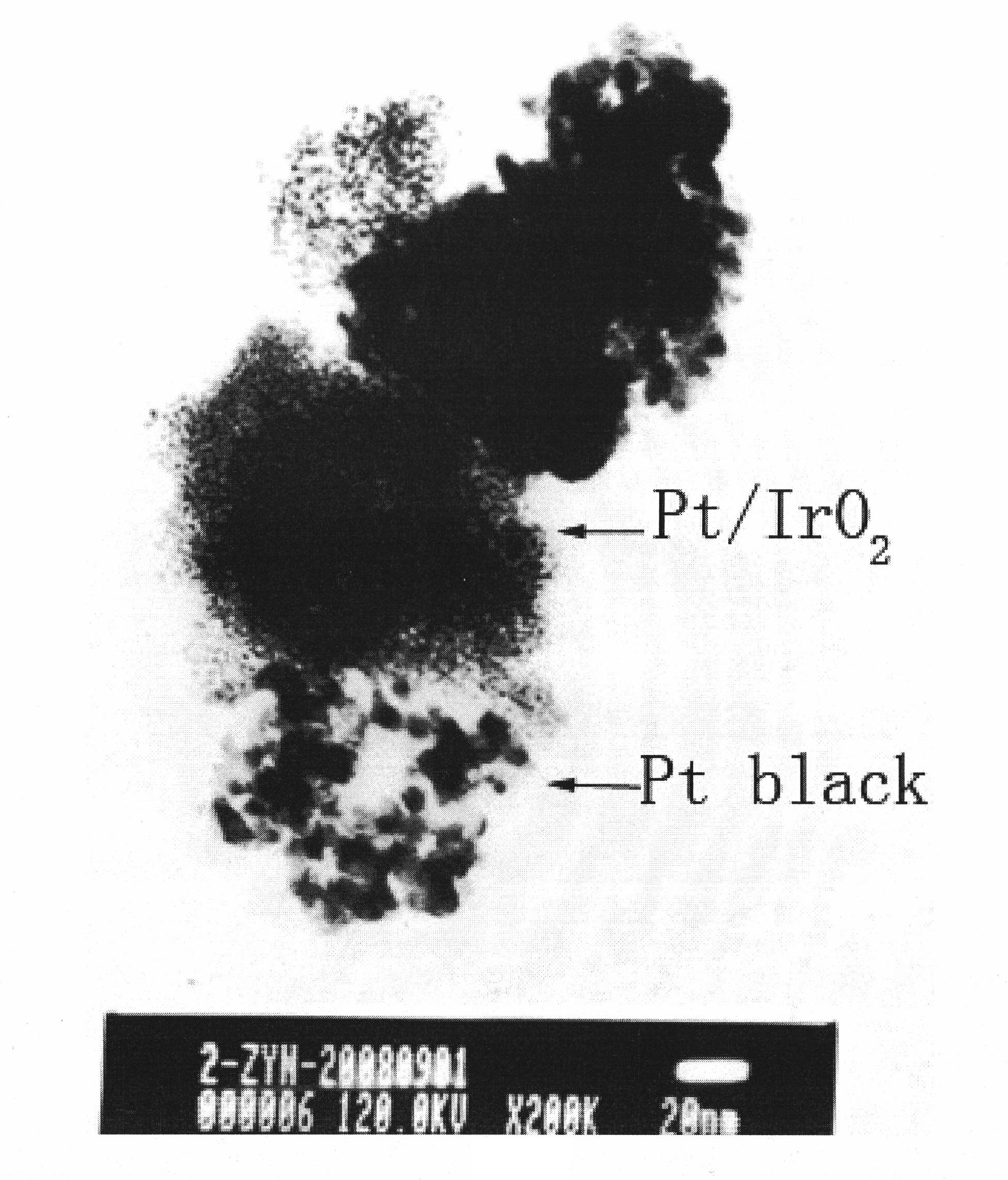
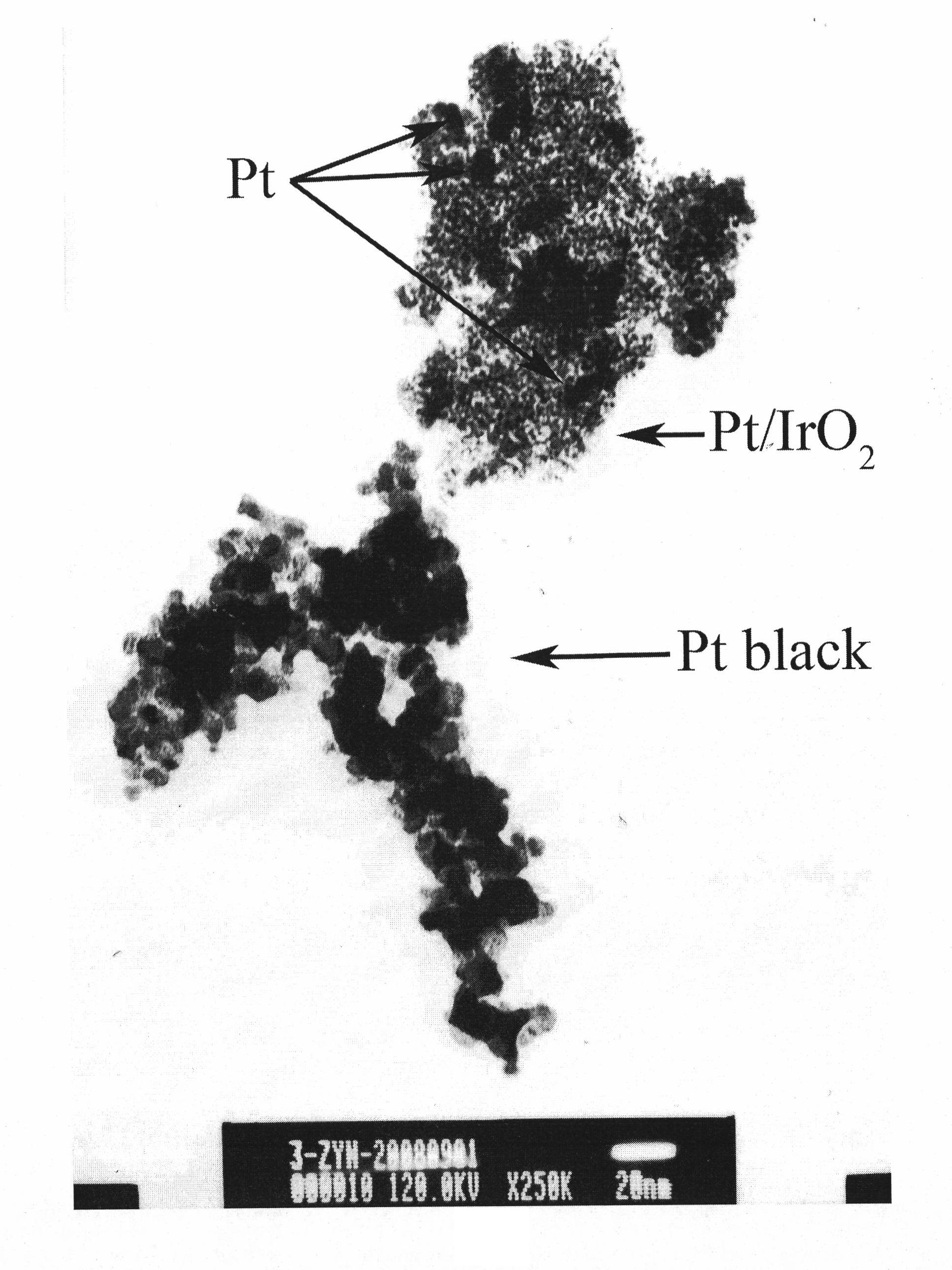
The invention discloses a catalyst using a metal oxide as a carrier for fuel cells and application thereof. The catalyst is characterized in that: the metal oxide as the carrier has catalytic oxygen evolution function simultaneously, and a noble metal with catalytic oxygen reduction function is supported on the metal oxide; the nanoparticles of the noble metal are highly dispersed on the surface of the metal oxide as the carrier, wherein the mass fraction of the noble metal is 2 to 70 percent in the catalyst. The catalyst alone or the catalyst mixed with platinum black in a certain proportionis applied to bifunctional oxygen electrodes for utilized regenerative fuel cells. Compared with the traditional mechanical mixture of platinum black and an oxide from catalytic oxygen evolution reaction, the fuel cell and water electrolysis performances of the cells are greatly improved, and the performance is close to that of a commercial Pt / C catalyst in fuel cells. The catalyst is applied to fuel cell oxygen electrodes to effectively solve the problems that the activity of the catalyst is deceased by the corrosion of the carrier.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electrolysis vessel and apparatus for generating electrolyzed water
InactiveCN1878729ALower overall flow resistanceLower resistanceCellsWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsConductive pasteElectrolysed water
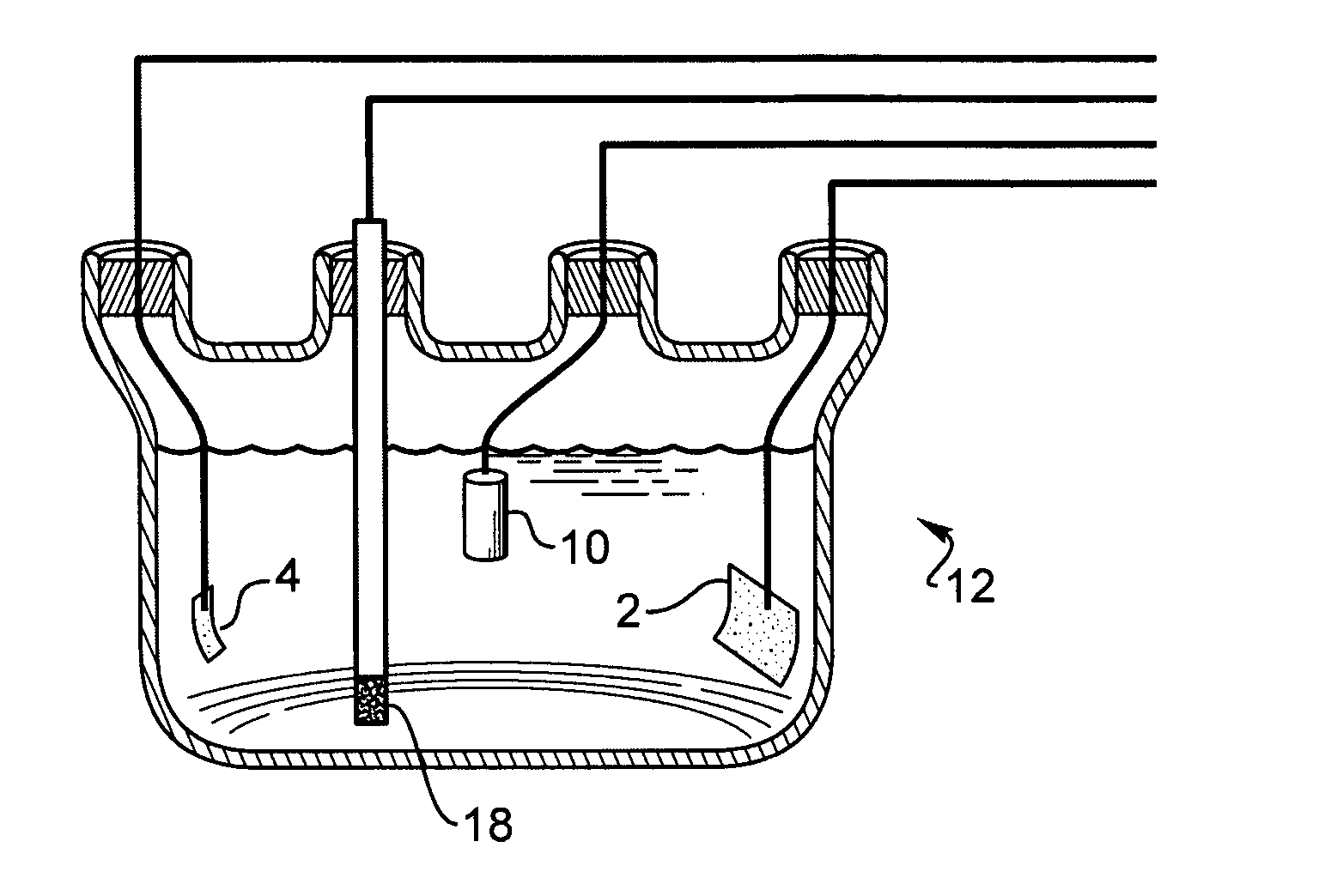
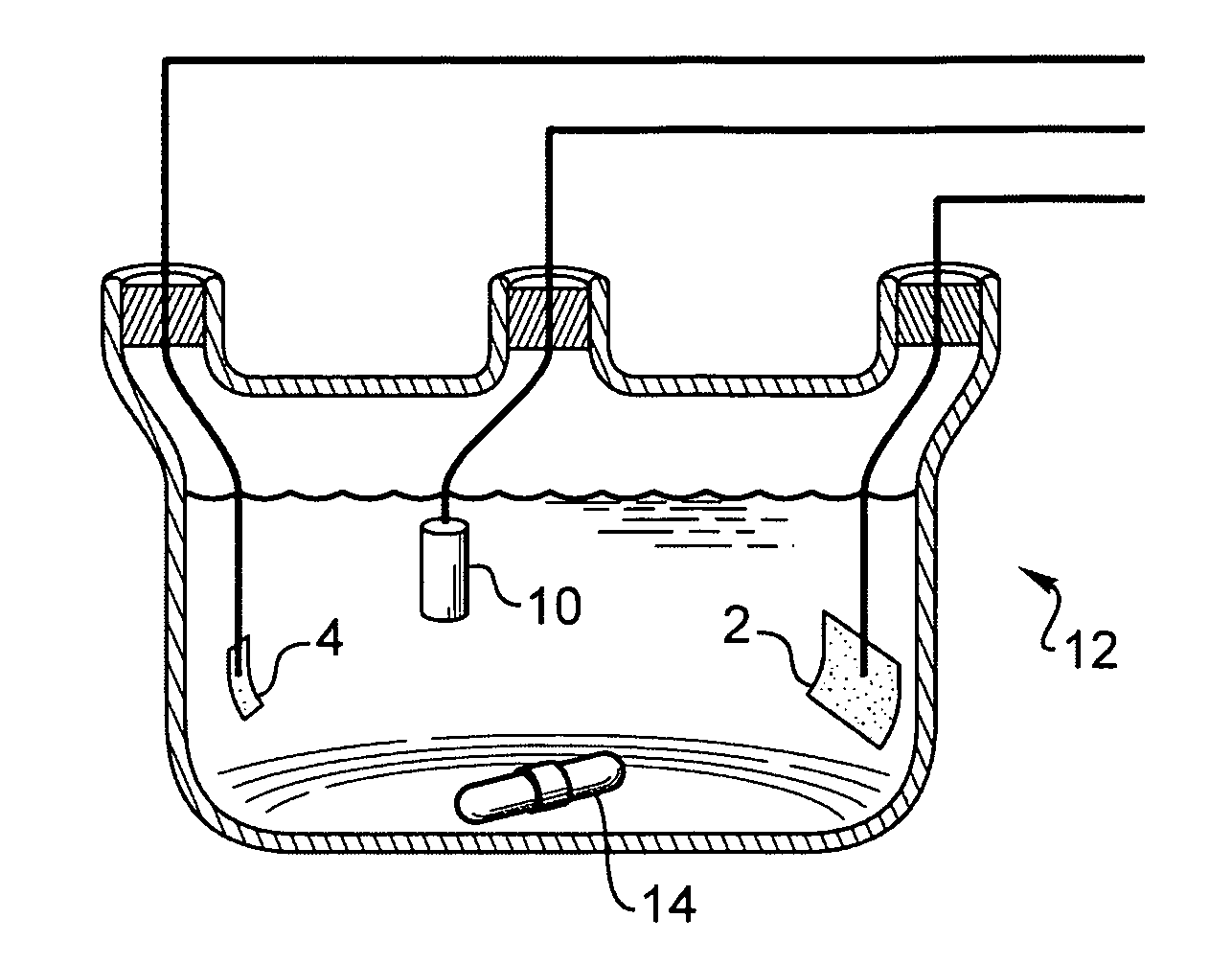
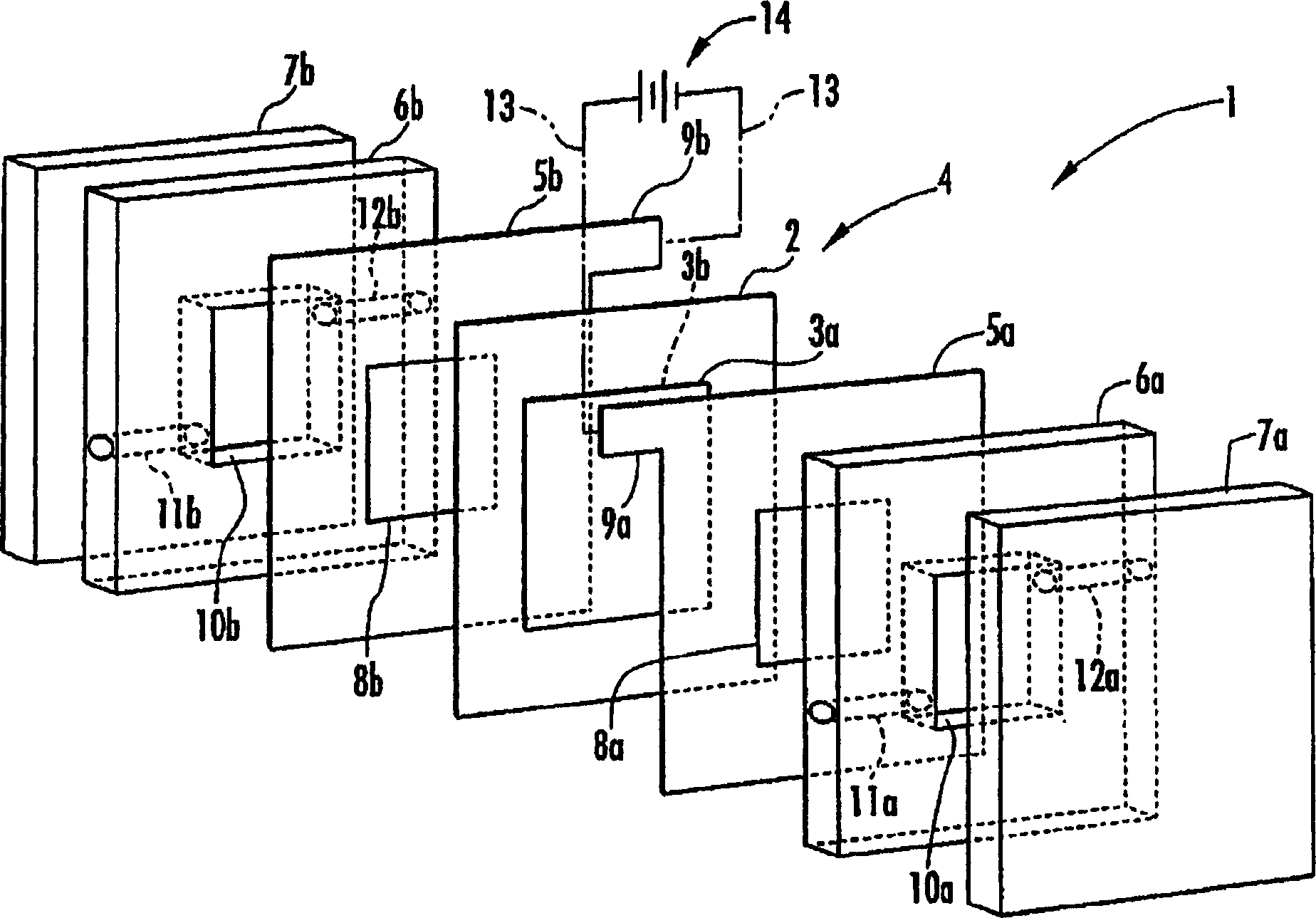
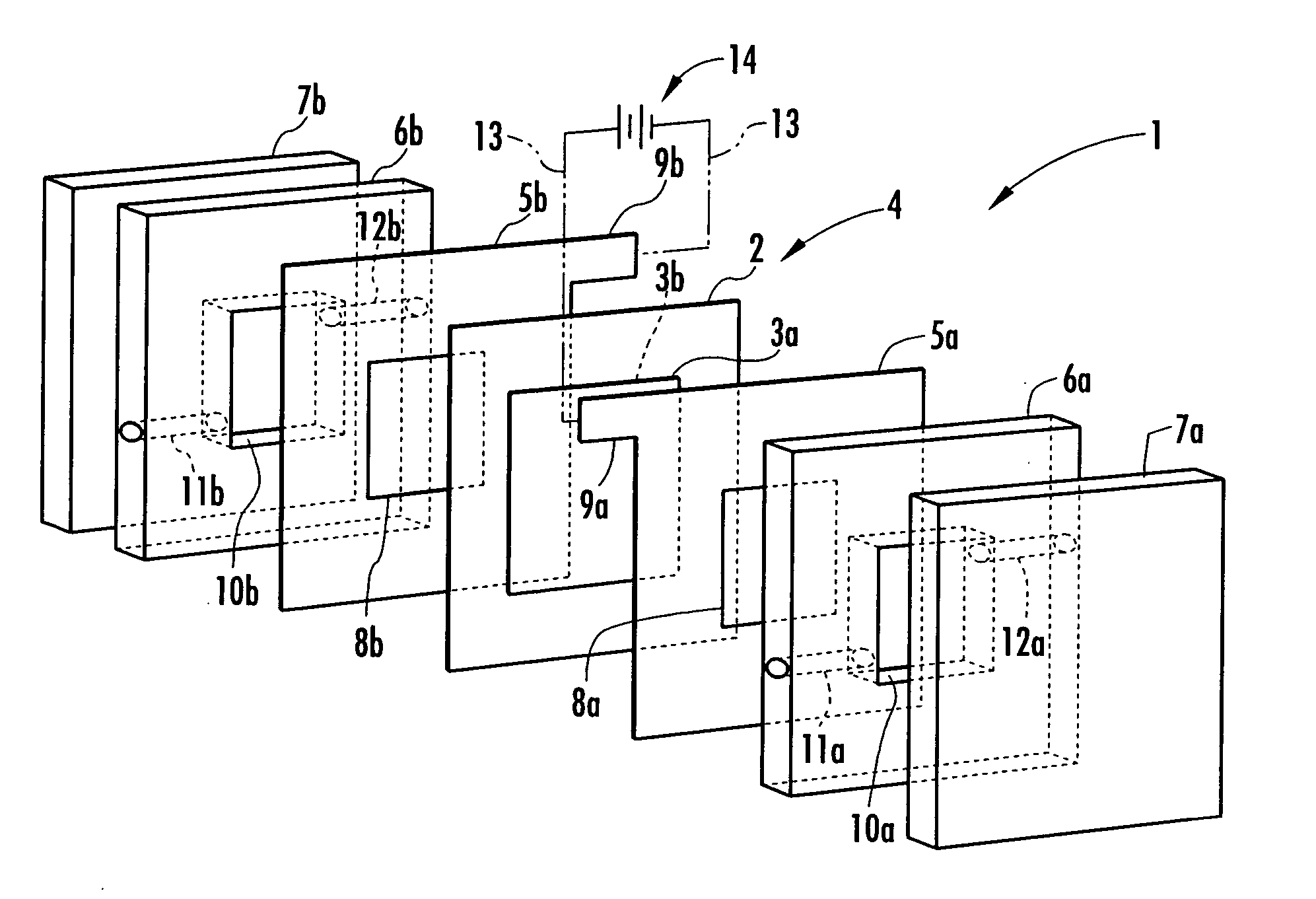
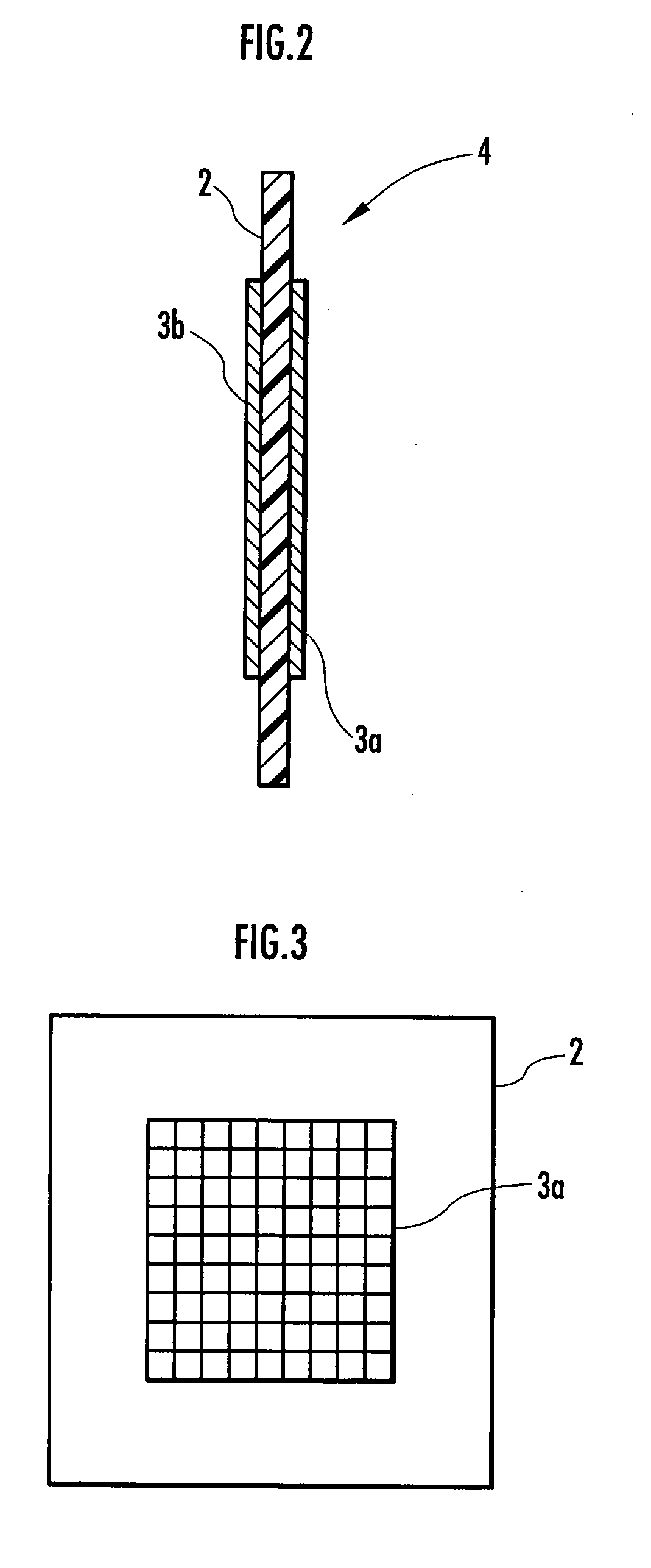
Disclosed are an electrolysis vessel and an apparatus for generating electrolyzed water which are small in size, excellent in electrolysis efficiency, and enable to reduce the anion concentration in the acidic electrolyzed water. The electrolysis vessel comprises electrolysis chambers (10a, 10b) arranged opposite to each other with an ion-permeable separating membrane (2) interposed between, raw material water supply means (11a, 11b), electrodes (3a, 3b) so arranged as to have the separating membrane (2) between them, and electrolyzed water taking-out means (12a, 12b). The separating membrane (2) is an anion permeable membrane, and the electrodes (3a, 3b) are formed on respective sides of the anion permeable membrane (2) in an appressed manner, while leaving a portion of the anion permeable membrane (2) exposed. Only raw material water supplied to the cathode side electrolysis chamber (10b) contains an electrolyte. The electrodes (3a, 3b) are porous bodies and contain an electrode base composed of a powder titanium compound such as TiC or TiN, a catalyst such as platinum black or iridium black, and a binder such as PVA. The electrodes (3a, 3b) may have a mesh-like shape or a comb-like shape, and are formed by applying a conductive paste containing a conductive powder on respective sides of the anion permeable membrane (2) and heating or pressurizing the thus-applied paste.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Platinum surface coating and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050271895A1Increase surface areaSufficient physicalHead electrodesDomestic articlesPt elementElectroplating
An improved platinum surface coating and method for manufacturing the improved platinum surface coating wherein the platinum surface coating having a fractal surface coating of platinum [“platinum gray”] with a increase in surface area of at least 5 times when compared to shiny platinum of the same geometry and also having improved resistance to physical stress when compared to platinum black having the same surface area. The process of electroplating the surface coating of platinum gray comprising plating at a moderate rate, i.e., at a rate that is faster than the rate necessary to produce shiny platinum and that is less than the rate necessary to produce platinum black.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS
Electrolysis vessel and apparatus for generating electrolyzed water
InactiveUS20070131541A1Reduce weightSimplifies circulation structureCellsWater/sewage treatment apparatusConductive pasteWater discharge
Provided is an electrolysis cell and an electrolyzed water producing equipment which are each small in size, has excellent electrolysis efficiency and can reduce an anion concentration in acidic electrolyzed water. The electrolysis cell is equipped with electrolysis rooms 10a and 10b located opposite to each other via an ion permeable membrane 2, raw water supply units 11a and 11b, electrodes 3a and 3bdisposed with the membrane interposed therebetween, and electrolyzed water discharge units 12a and 12b. The membrane 2 is an anion permeable film. The electrodes 3a and 3b are formed so as to firmly adhere to both surfaces of the anion permeable membrane 2 and expose a portion of the anion permeable membrane 2. Only raw water fed to the electrolysis room 10b on the cathode side contains an electrolyte. The electrodes 3a and 3b are porous and they each has an electrode base material made of a powdery titanium compound such as TiC or TiN, a catalyst such as platinum black or iridium black and a binder such as PVA. The electrodes 3a and 3b may be mesh-shaped or comb-shaped. The electrodes 3a and 3b are formed by applying a conductive paste containing conductive powders onto the surfaces of the anion permeable membrane 2, followed by heating or pressurization.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Platinum and Platinum Based Alloy Nanotubes as Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells
ActiveUS20090220835A1Easy to chargeEnhances mass transportationMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsDegradation pathwayAlloy
Electrocatalyst durability has been recently recognized as one of the most important issues that have to be addressed before the commercialization of the proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). The present invention is directed to a new class of cathode catalysts based on supportless platinum nanotubes (PtNTs) and platinum alloy nanotubes, for example, platinum-palladium nanotubes (PtPdNTs), that have remarkable durability and high catalytic activity. Due to their unique combination of dimensions at multiple length scales, the platinum nanotubes of the present invention can provide high platinum surface area due to their nanometer-sized wall thickness, and have the potential to eliminate or alleviate most of the degradation pathways of the commercial carbon supported platinum catalyst (Pt / C) and unsupported platinum-black (PtB) as a result of their micrometer-sized length. The platinum nanotube catalysts of the present invention asymptotically approach a maximum of about twenty percent platinum surface area loss in durability test, while the commercial PtB and Pt / C catalysts lose about fifty-one percent and ninety percent of their initial surface area, respectively. Moreover, the PtNT and PtPdNT catalysts of the present invention show higher mass activity and much higher specific activity than commercial Pt / C and PtB catalysts.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Platinum electrode surface coating and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070089994A1Increase surface areaSufficient physicalInternal electrodesRough surfaceMetal particle
An electrode surface coating and method for manufacturing the electrode surface coating comprising a conductive substrate; a surface coating of platinum having a rough configuration and an increase in the surface area of 5 times to 500 times of the corresponding surface area resulting from the basic geometric shape of the electrode. A method for electroplating an electrode surface with platinum coating having a rough surface, comprising electroplating the surface of a conductive substrate at a rate such that the metal particles form on the conductive substrate faster than necessary to form shiny platinum and slower than necessary to form platinum black.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC +1
Immobilized heteropoly acids and the use of the same for electrode stabilization and enhancement
InactiveUS20080299433A1Hybrid capacitor electrodesActive material electrodesHeteropoly acidConductive materials
The use of fuel cells to produce electricity are known as an environmentally clean and reliable source of energy, and show promise as an automotive power source if the polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell can be made less expensive, more durable, reduce or eliminate humidification of the reactive gases, and operate at temperatures encountered during automotive operating conditions. The use of an electro-catalyst formed from heteropoly acids immobilized by a conductive material, such as carbon or platinum black, and stabilizing a metallic black with the immobilized conductive material addressed these automotive fuel cell needs. Coating the fuel cell electrode, polymer electrolyte assembly with a nano-particle catalyst derived from a heteropoly acid provided anodic carbon monoxide tolerance at anodic overpotentials and an active cathodic oxygen reduction. The heteropoly acids can also function as supercapacitor electrode films.
Owner:COLORADO SCHOOL OF MINES
Anode catalyst suitable for use in an electrolyzer
An anode catalyst suitable for use in an electrolyzer. The anode catalyst includes a support and a plurality of catalyst particles disposed on the support. The support may include a plurality of metal oxide or doped metal oxide particles. The catalyst particles, which may be iridium, iridium oxide, ruthenium, ruthenium oxide, platinum, and / or platinum black particles, may be arranged to form one or more aggregations of catalyst particles on the support. Each of the aggregations of catalyst particles may include at least 10 particles, wherein each of the at least 10 particles is in physical contact with at least one other particle. The support particles and their associated catalyst particles may be dispersed in a binder.
Owner:PLUG POWER
Method for preparing high-efficiency membrane electrode of direct methanol fuel cell
InactiveCN103000912AGuaranteed continuitySimple manufacturing processCell electrodesPtru catalystNanowire
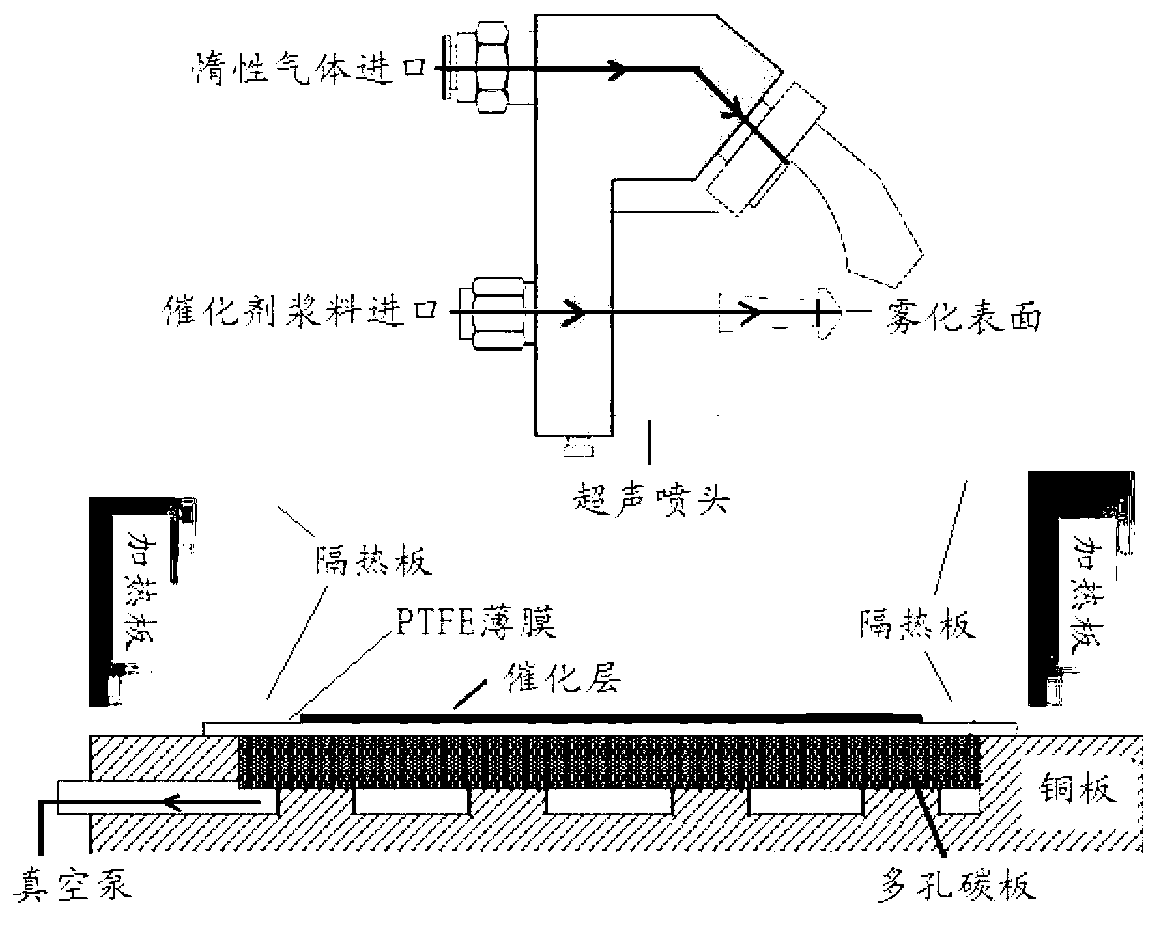
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-efficiency membrane electrode of a direct methanol fuel cell and belongs to the structure of a high-efficiency membrane electrode component of the direct methanol fuel cell and the technical field of manufacturing of structures of high-efficiency membrane electrode components. A proton exchange membrane is adopted as an electrolyte membrane by the membrane electrode, a platinum-ruthenium black catalyst and a platinum black catalyst are respectively adopted as a cathode catalyst and an anode catalyst, isopropyl alcohol and redistilled water are adopted as dispersing agents. During preparation, an ultrasound spray-coating technology is applied in a temperature field, the agglomeration morphology of catalyst particles is adjusted by the adjustment on factors such as ingredient proportioning and preparation environments of catalyst slurry, a proton channel with a nano wire structure is prepared in a catalytic layer, so that a continuous proton channel is established effectively in the microstructure of the prepared membrane electrode, the internal resistance of the cell is reduced, the electrochemical surface area of the electrode is increased, and therefore, the efficiency of the catalytic layer of the membrane electrode is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Dye sensitization nanocrystalline thin-film solar cell high pore space flexible carbon to electric pole and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101140956AReduce manufacturing costReduce thicknessLight-sensitive devicesElectrode manufacturing processesComposite filmNanocrystalline thin films
A highly porous flexible carbon counter electrode used for solar battery of the dye sensitize amino-quinoline thin film is provided, which comprises an composite film composed by a carboform membrane layer with a microstructure of three dimensional porous diffusion and polyafluortetraethylene thin membrane layer; a titanium dioxide semiconductor expanded film equipped on the said composite film as the working electrode of the semiconductor. The preparation method of the electrode is: greying the arboform membrane and platinum black to the nanometer-carried; sensitizing the counter electrode used of the solar battery with the dye of the composite film, which forms dye sensitize solar battery with the working electrode of the semiconductor oxide based on the rigid stratum; greying the arboform membrane and platinum black to the nanometer-carried, which is composed with the polyafluortetraethylene thin membrane to form a composite film, which forms dye sensitize solar battery with the working electrode of the semiconductor oxide based on the rigid stratum.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
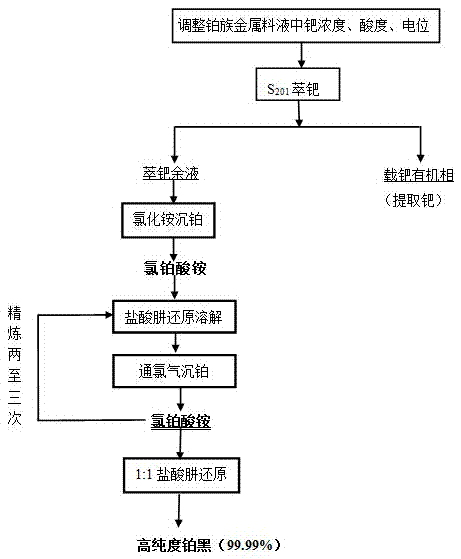
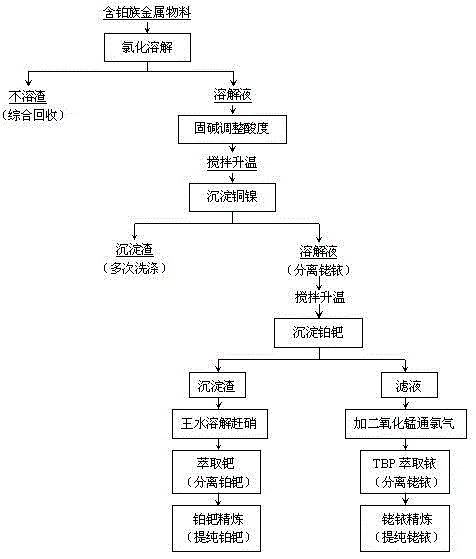
Method for separating and extracting platinum group metals
The invention provides a method for separating and extracting platinum group metals. The method comprises the steps that the palladium concentration of feed liquid containing the platinum group metals is controlled to be 1.5-5.5g / L, the electric potential of the feed liquid is controlled to be 850-950mv, palladium is extracted by means of S201 organic phases, and palladium is extracted from the palladium-loaded organic phases through the following process. Ammonium chloride is added into palladium extraction raffinate to deposit platinum, obtained ammonium chloroplatinate is subjected to reduction and dissolution by being added with hydrazine dihydrochloride solution and is heated to 90-95 DEG C, and chlorine gas is introduced; after the obtained ammonium chloroplatinate is repeatedly subjected to the hydrazine dihydrochloride reduction process for 2-3 times, and high-purity platinum black can be obtained by reducing the ammonium chloroplatinate through the hydrazine dihydrochloride according to the mass ratio of 1:1. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that the process is simple, the precious metal separation efficiency is high, generation of a larger amount of ammonia-contained waste gas is avoided in the process of reducing ammonium chloroplatinate through hydrazine hydrate, and no nitrogen oxide pollution is produced.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Quick electrochemical electrode activating method
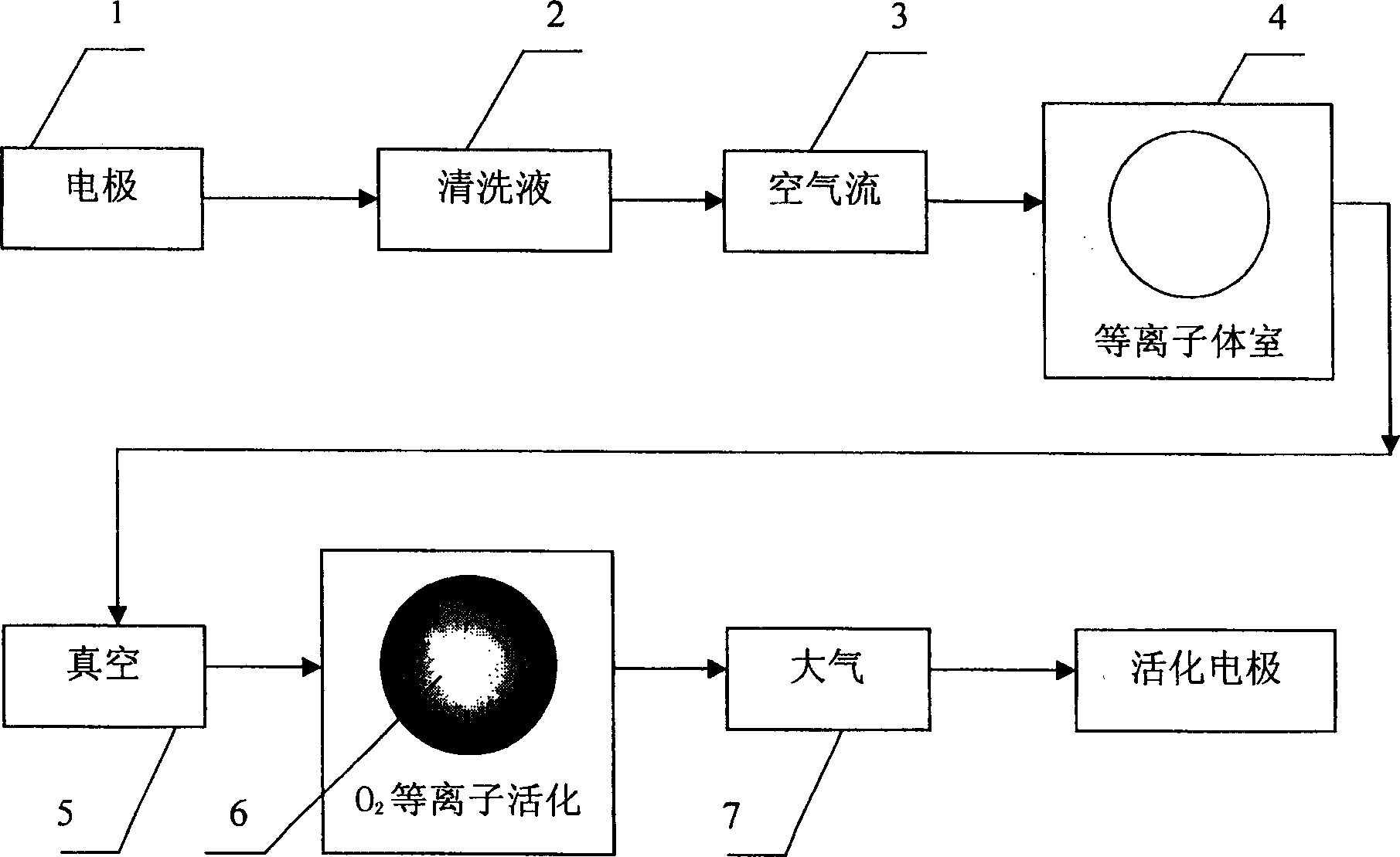
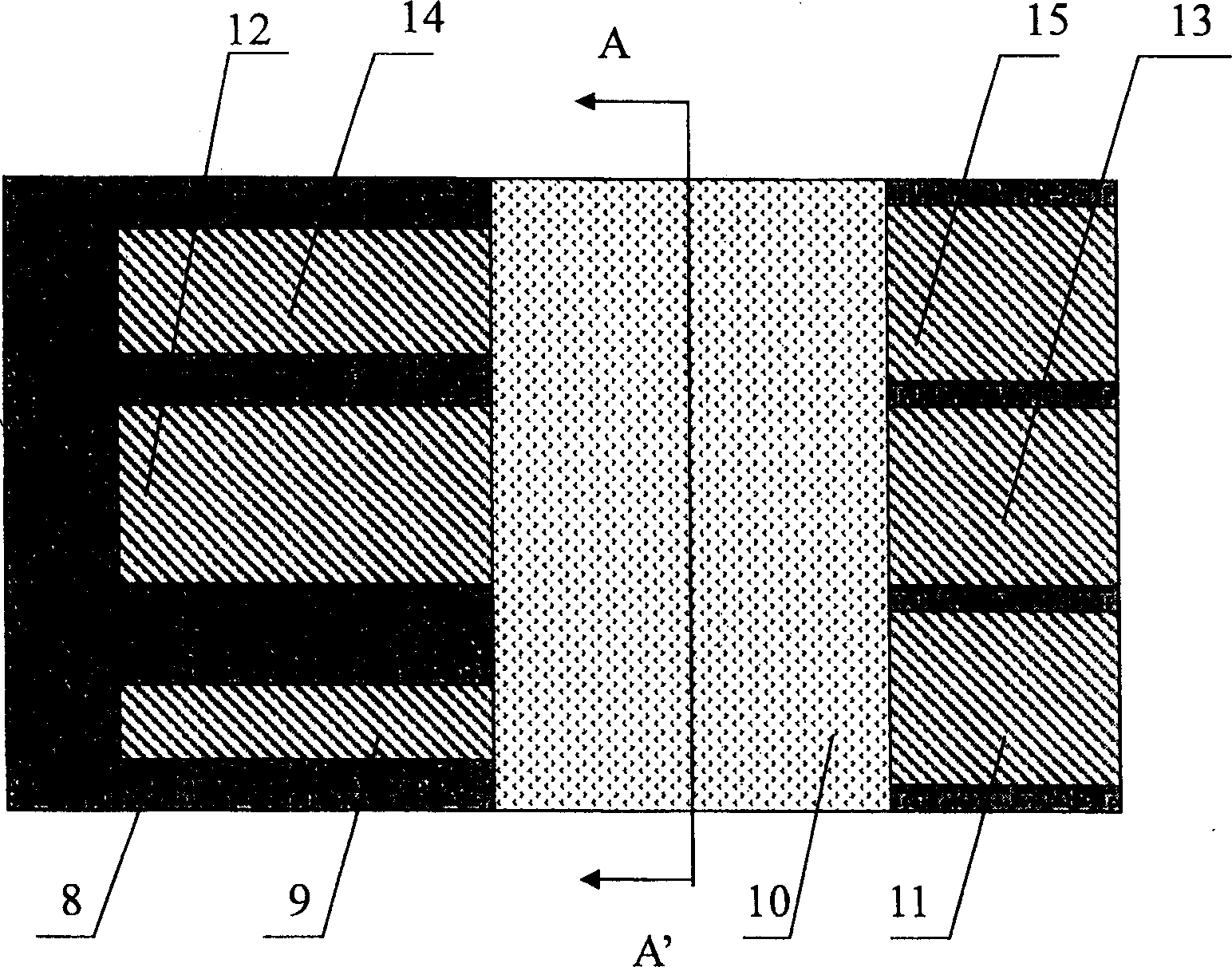
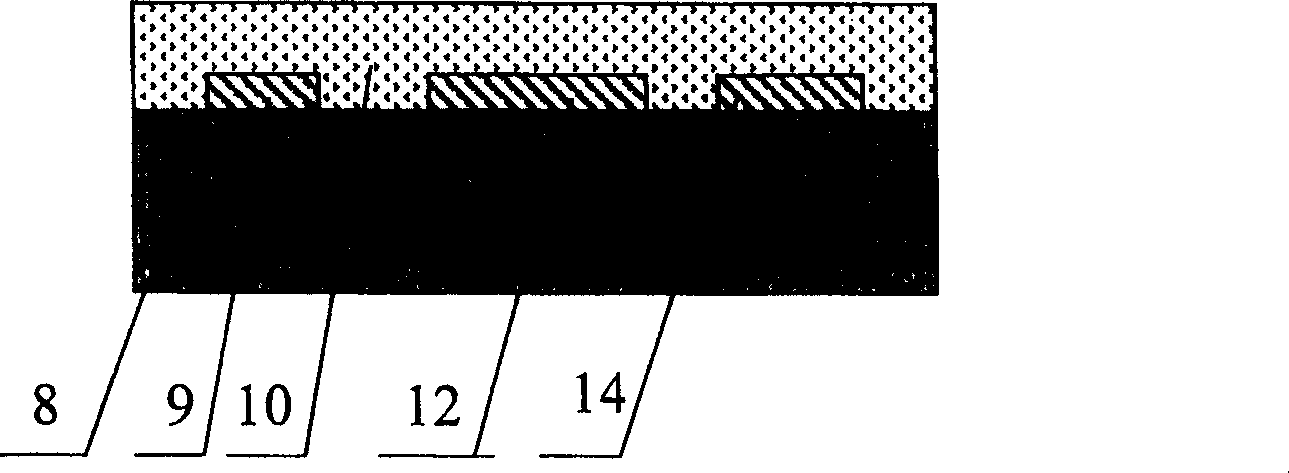
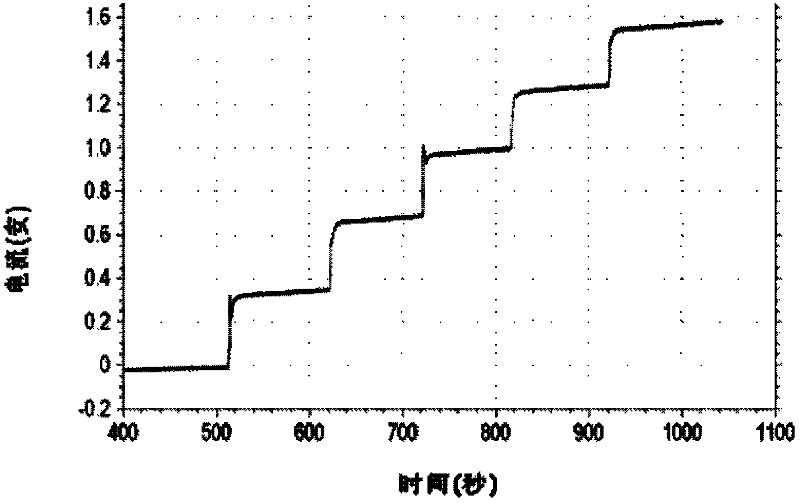
The present invention relates to quick electrochemical electrode activating method. The device or chip with the electrode to be activated is first cleaned, then fed to a plasma chamber and vacuum pumped, and finally exposure activated in oxygen and nitrogen discharging atmosphere. The present invention describes the activating process of deactivated micro electrodes, including planar micro electrode, platinum black decoration electrode and micro electrode probe. The present invention has the advantages of simple operation, fast process and high repeatability, and is suitable for activation of electrochemical electrode in device and array chip, so that the present invention may find its wide application in the research and development of biological sensor, biochip and micro system integral chip.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biological enzyme sensor capable of being implanted into human body and production method thereof
ActiveCN102499696AReduced activityActivity will not decreaseDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPolyesterBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a novel biological enzyme sensor capable of being implanted into a human body and a production method thereof. The surface of a substrate is cleaned via polishing, degreasing, activation and other physical and chemical processes, and the metal substrate is then coated with a layer of platinum black, platinum or gold via electroplating or sputtering. The surface of an electrode is modified with a layer of enzyme, the biological enzyme is cured through polymer embedding or cross-linking, one or more biocompatible polymer material(s) is / are used as a carrier, and the polymer material(s) as the carrier at least comprise(s) a polyamino, polyhydroxy or polythiol group. Reaction of polyisocyanate with polydimethylsiloxane and polyether polyol or polyester polyol, a small number of chain extenders are added, polyurethane prepolymer is produced, cross-linking curing of polyurethane prepolymer and polymer material(s) in the biological enzyme layer is carried out, the adhesion of the film can be improved, and the bio-sensing layer cannot fall off in long-time testing of an animal body or a human body. The method is simple, and the produced biological enzyme sensor has excellent mechanical flexibility, biocompatibility, adhesion and resistance to protein adsorption.
Owner:SINOCARE
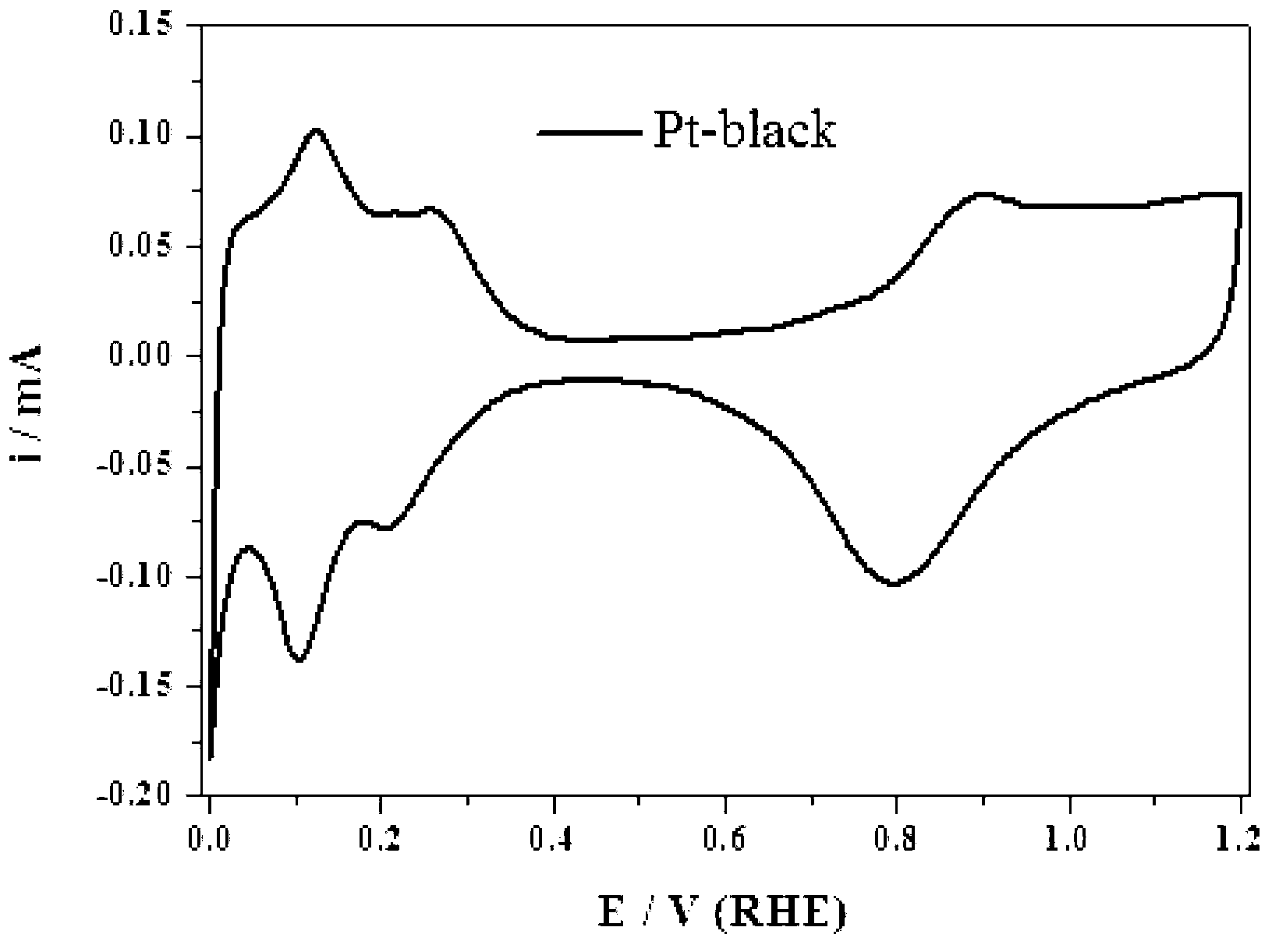
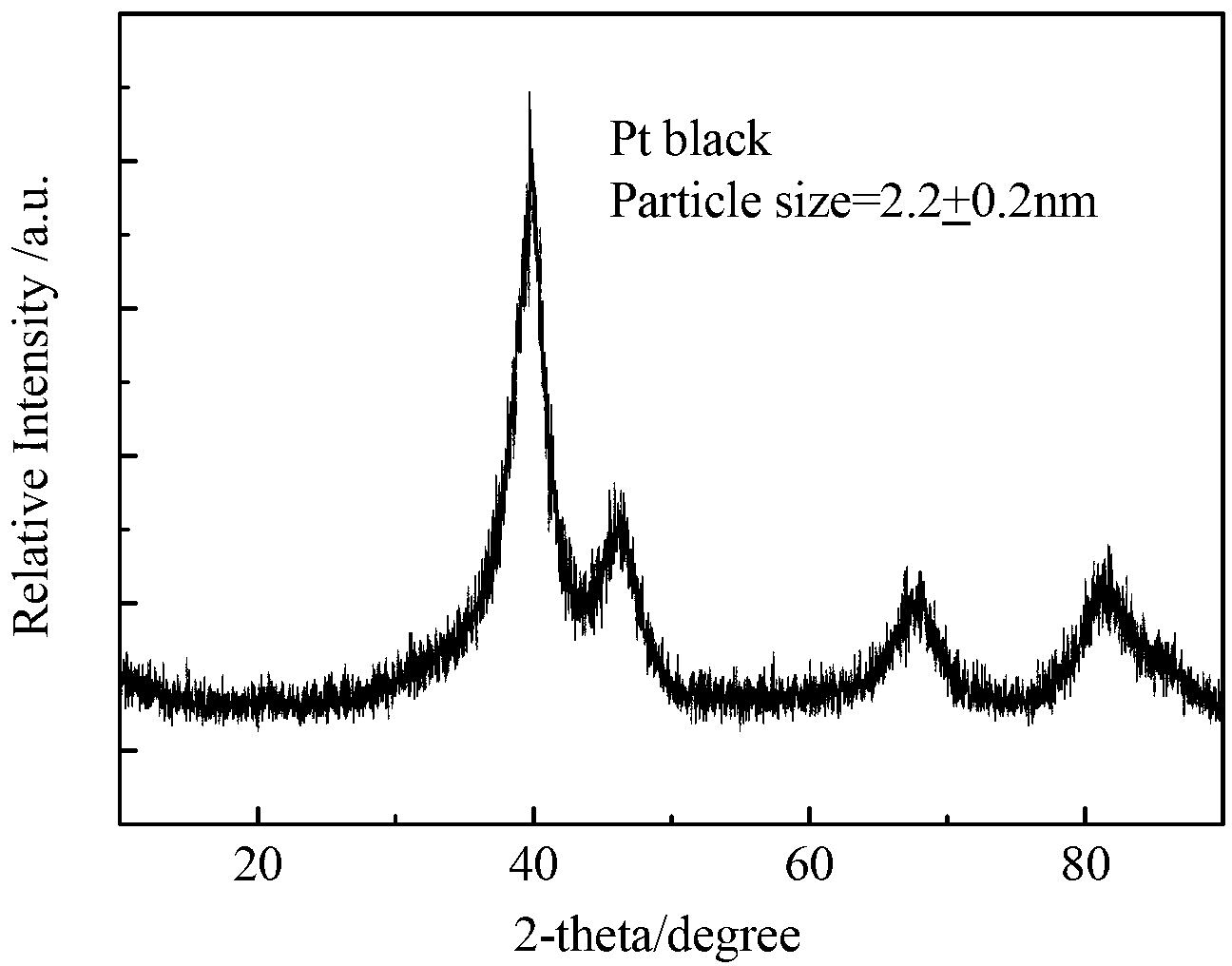
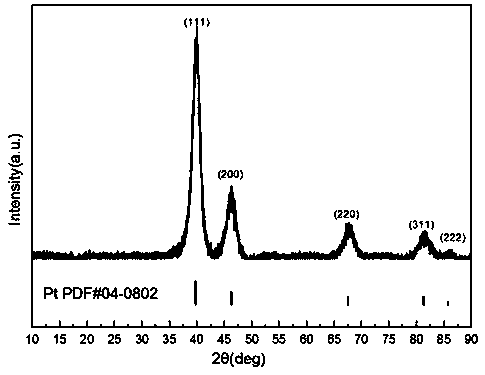
High-purity large-specific-surface platinum black and preparation method thereof
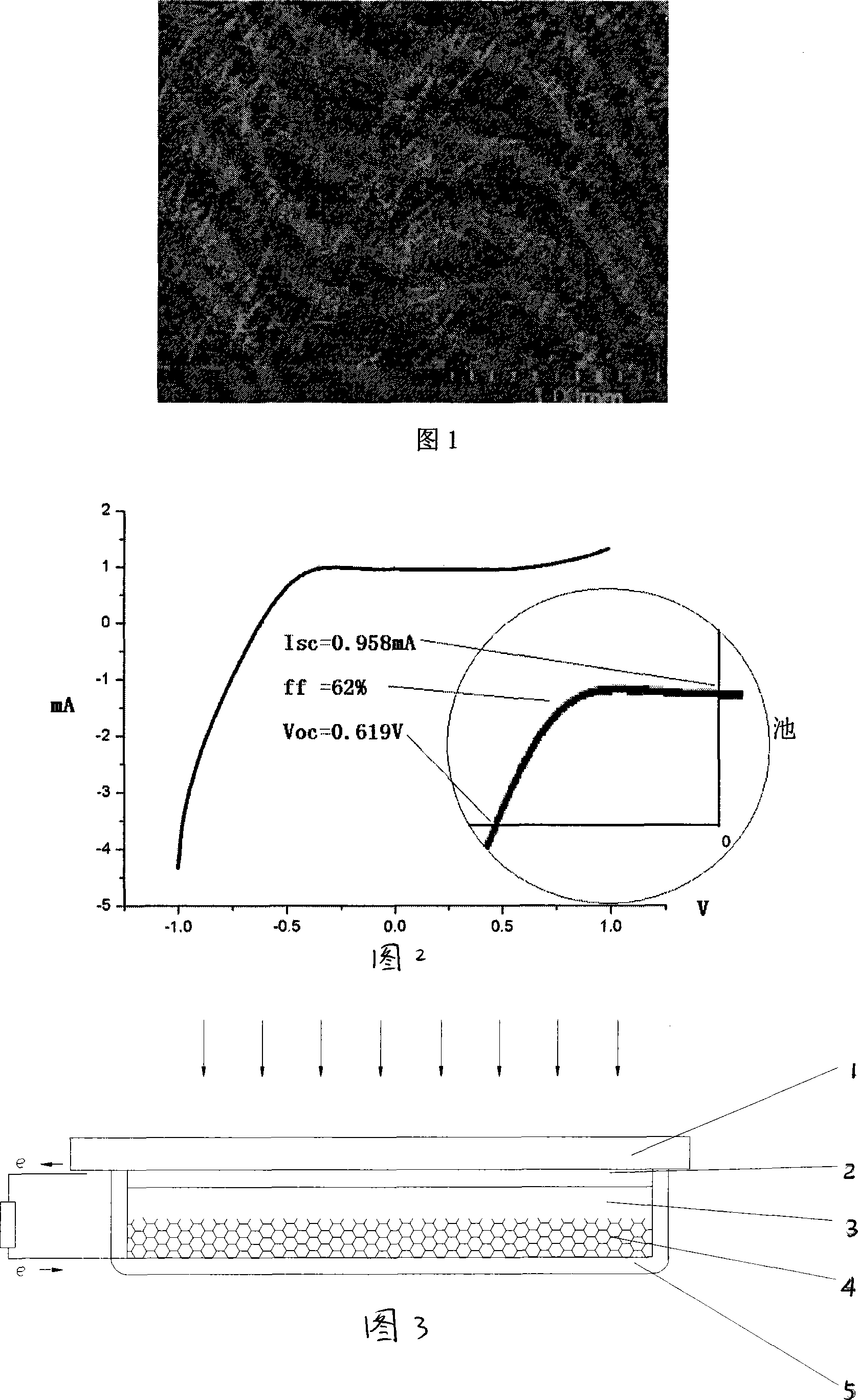
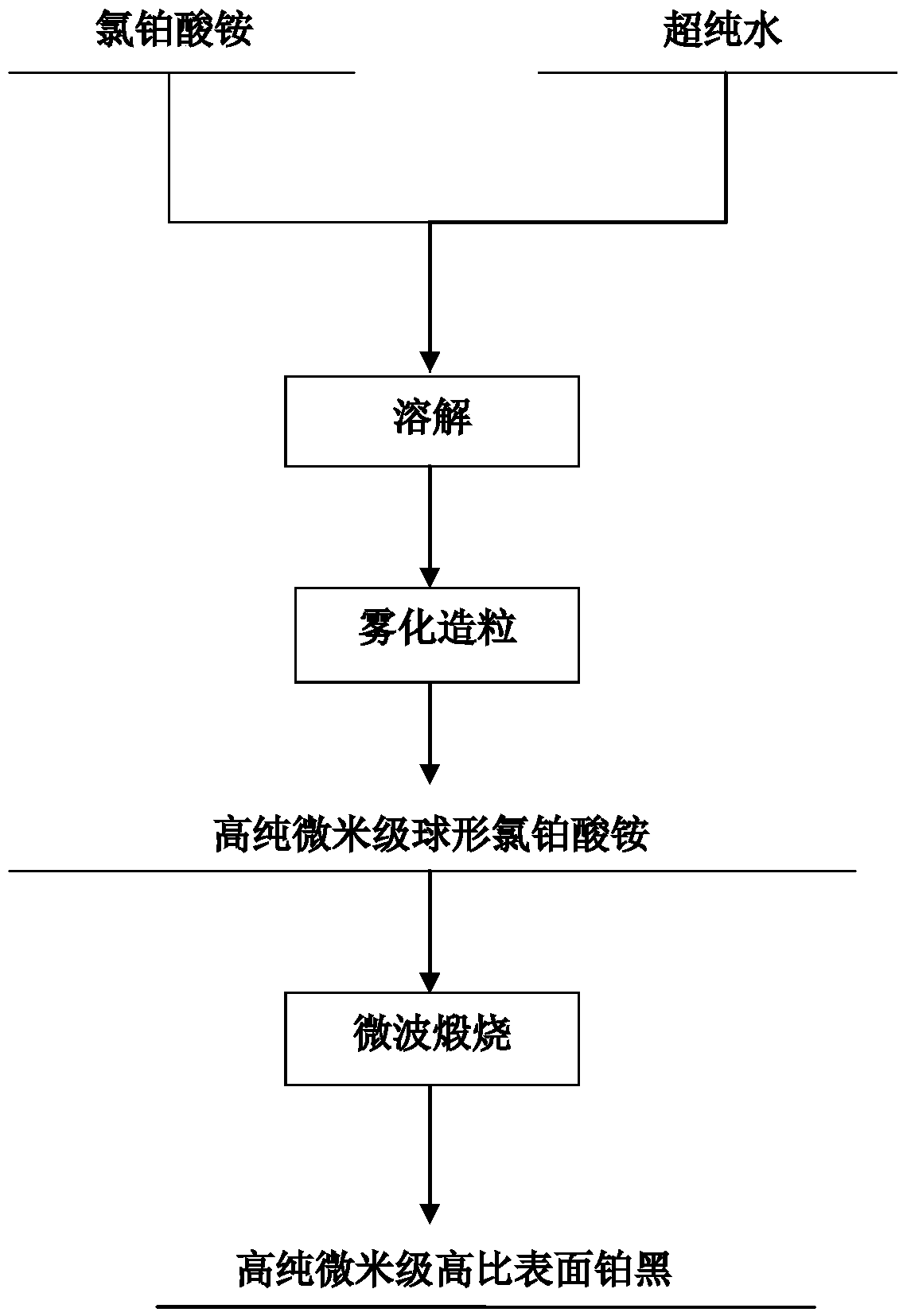
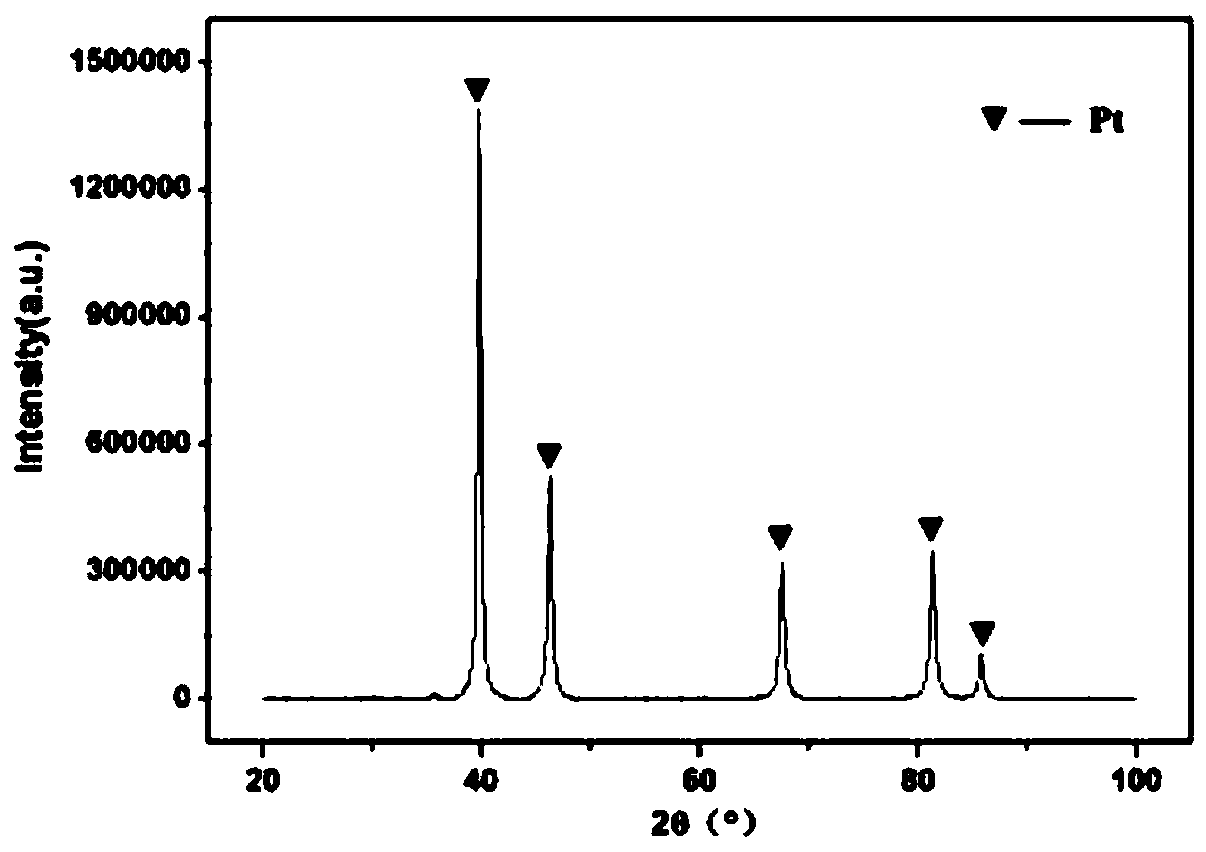
ActiveCN108620600ALarge specific surface areaGuaranteed purityTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusFuel cellsMicrowave
The invention discloses a kind of high-purity large-specific-surface platinum black and a preparation method thereof. The prepared platinum black has the average grain size being 2 microns, is spheroid and has the purity greater than 99.99 wt% and the specific surface greater than 27 m<2> / g. The platinum black for fuel cells is subject to reducing preparation through atomizing pelletizing and microwave calcinations. The platinum black has the purity greater than 99.99%, the average grain size being 2 microns and the specific surface greater than 27 m<2> / g and is spheroid. Platinum powder can be used for producing fuel cell electrode materials and has great market demands and wide application prospects. Meanwhile, the platinum powder can also be used for other catalyst fields.
Owner:SINO PLATINUM METALS CO LTD
Apparatus with nano-sized platinum black and oxygen-rich ceramic powder for filtering the incoming air into an internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060059876A1Large filter areaImprove filtering effectCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationChemical reactionMetallurgy
An air filter for an internal combustion engine having a rigid type ceramic filter element made by foaming oxygen-rich ceramic powder for creating a plurality of pass-through holes. In this way, the incoming air obtains a thorough contact with the oxygen-rich powder. Meanwhile, the material of the oxygen-rich ceramic releases negative ions to activate the air entering into the internal combustion engine. Moreover, nano-sized platinum black is coated to the surface of the pass-through holes of the ceramic filter element. So, the incoming air passing through the pass-through holes of the ceramic filter element is catalyzed in chemical reactions to divide the water molecule cluster into smaller particles. Meanwhile, the freedom of water molecule is increased to permit an instant decomposition of oxygen and nitrogen molecules, a complete combination with the fuel injected into the internal combustion engine, and a thorough mixing and a better combustion efficiency.
Owner:YUAN ANDY +1
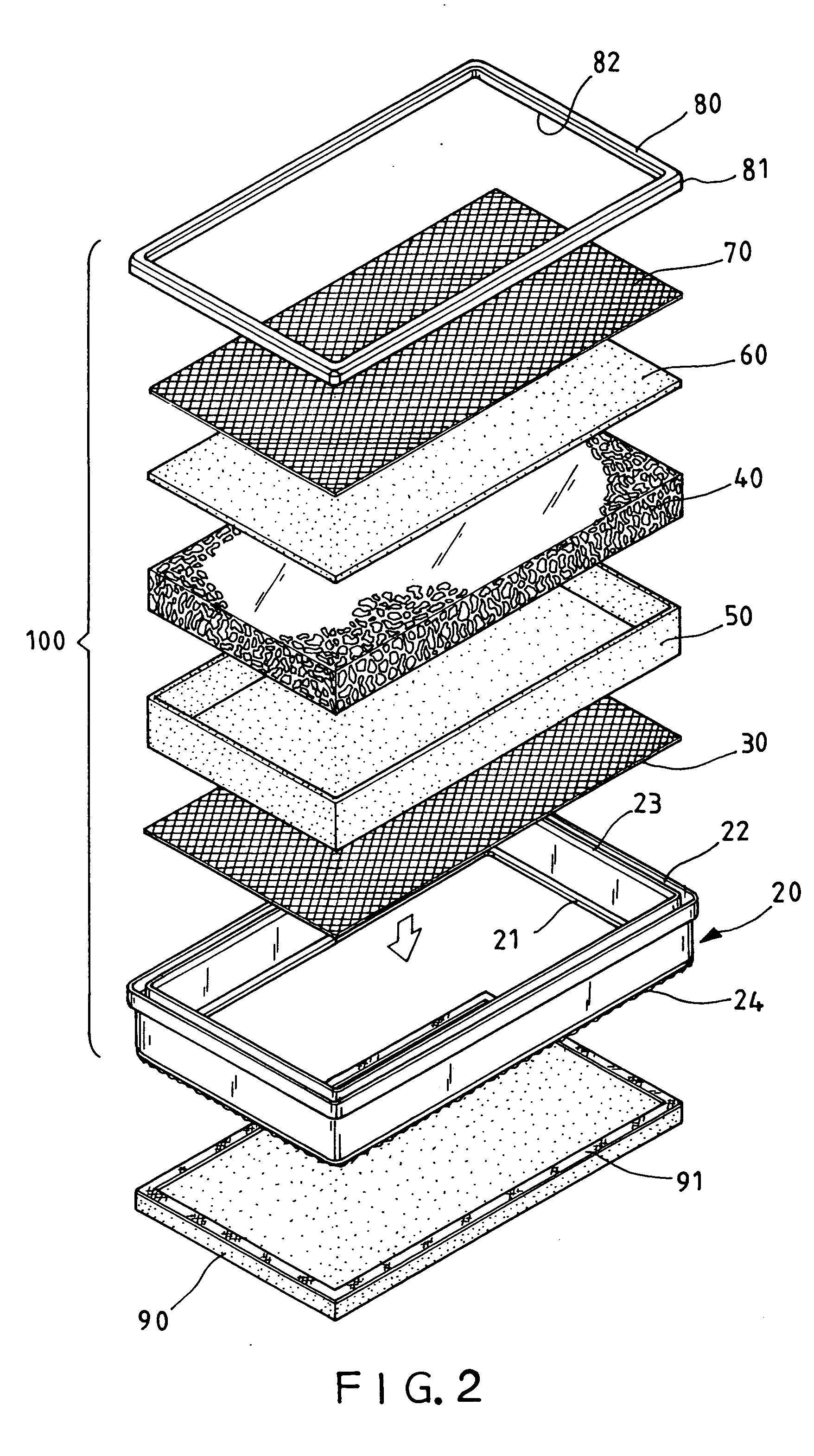
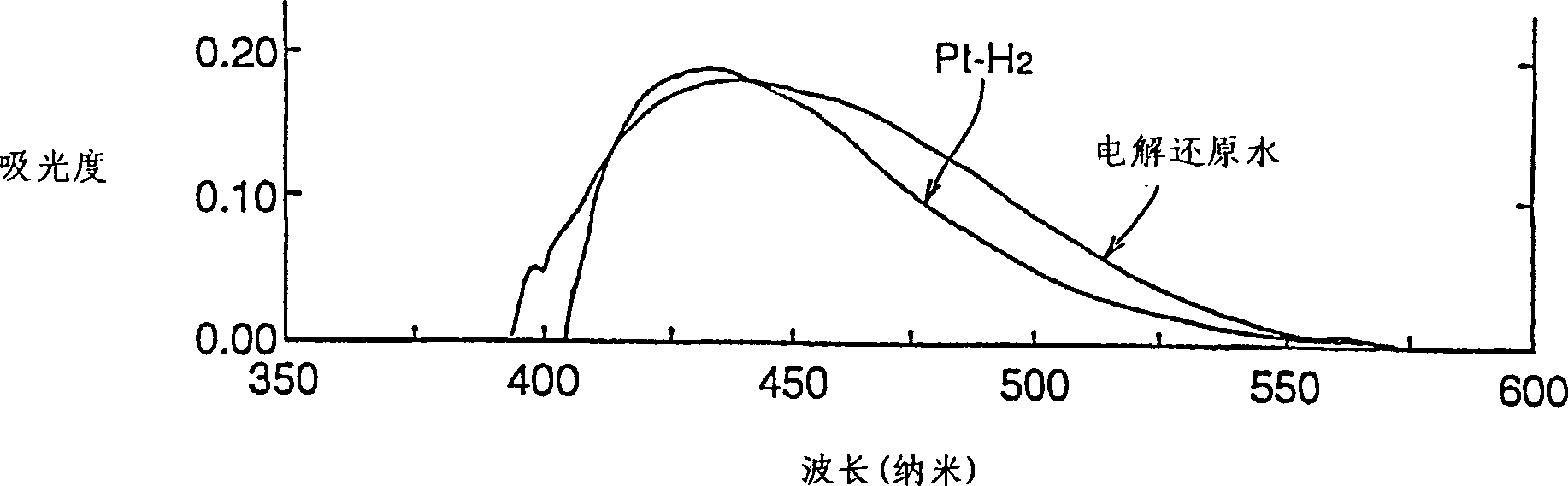
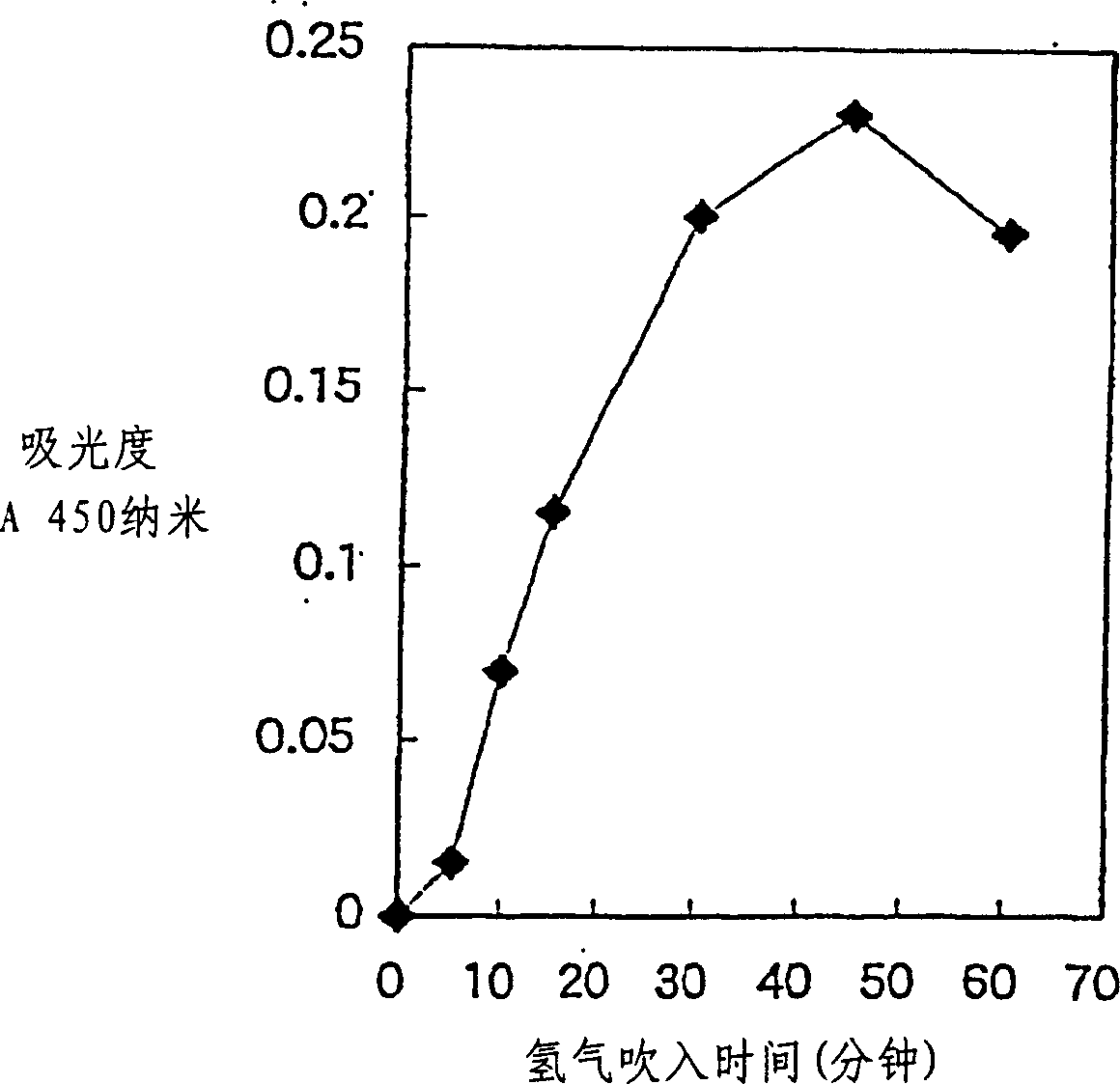
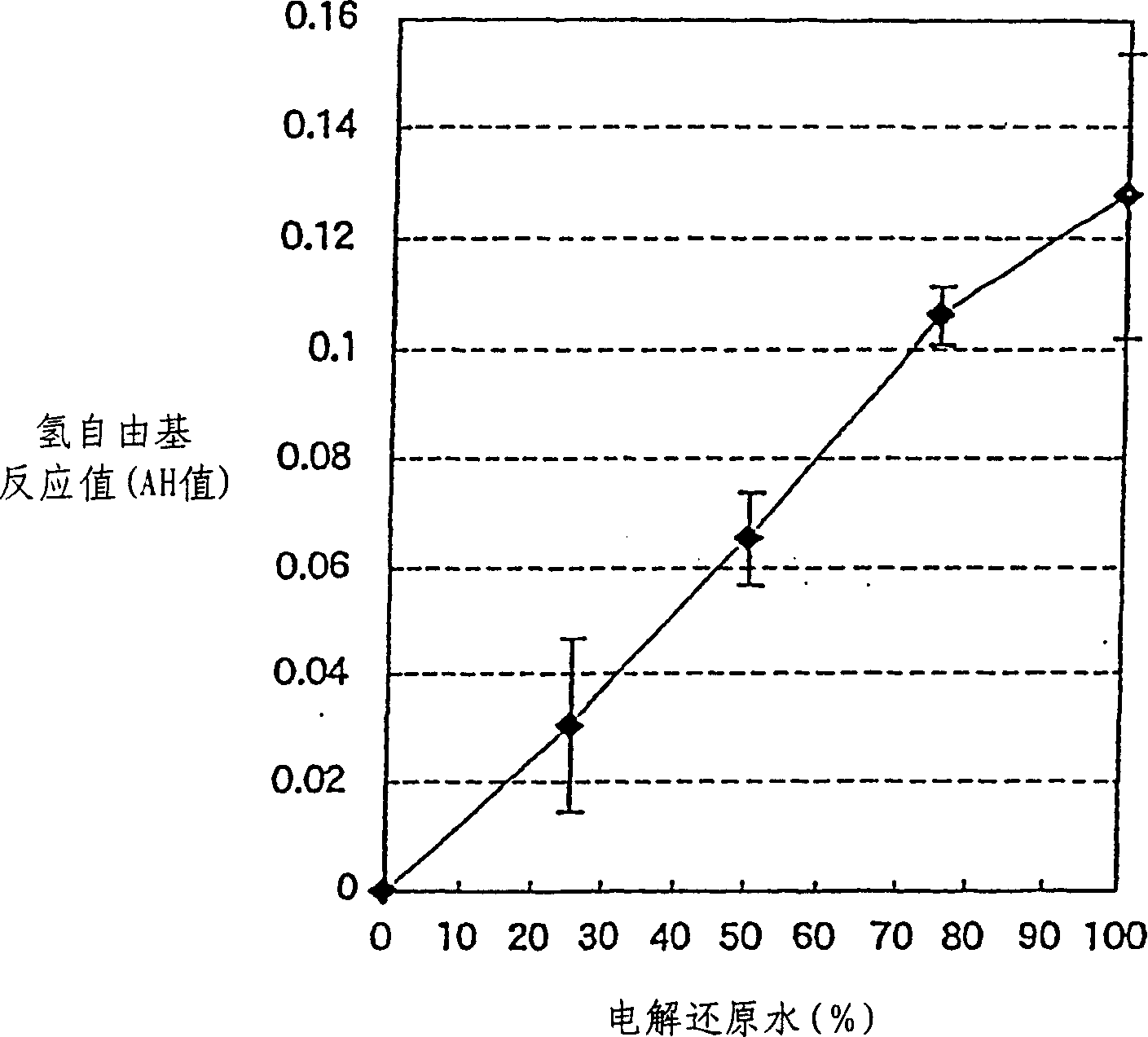
Detection method and quantitative analysis method for hydrogen radical
InactiveCN1463363AAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDPPHBromine
Owner:NIKHON TRIM KO LTD +1
Method for separating and purifying platinum metals through solvent extraction
The invention provides a method for separating and purifying platinum metals through solvent extraction, relates to a metal separating and purifying method, and particularly relates to a method for separating platinum, palladium, rhodium and iridium from a solution, slag or secondary resource containing platinum metals. The method is characterized in that the purifying process comprises the following steps: (1) chloridizing and dissolving materials containing platinum metals; (2) adding ammonium oxalate to perform copper-nickel precipitation separation; (3) adding organic reducing agent vitamin C to perform platinum-palladium precipitation reaction; (4) performing aqua regia dissolution and denitration on the platinum-palladium-containing precipitation slag, and feeding into a diisoamyl thioether platinum-palladium extraction separation procedure; and (5) adding manganese dioxide and introducing chlorine gas into the rhodium-iridium-containing filtrate, reacting, and feeding into a tributyl phosphate rhodium-iridium extraction separation procedure. According to the method provided by the invention, the platinum-palladium and rhodium-iridium separation rates are high, and further platinum-palladium separation and rhodium-iridium separation can be realized easily through subsequent extraction; after conventional refining, platinum black and palladium black of which the purities are above 99.99% can be produced, and spongy platinum and spongy palladium products meeting the national standard have been produced after treatment of subsequent procedures; and the purities of the produced rhodium powder and iridium powder can be up to 99.95%.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
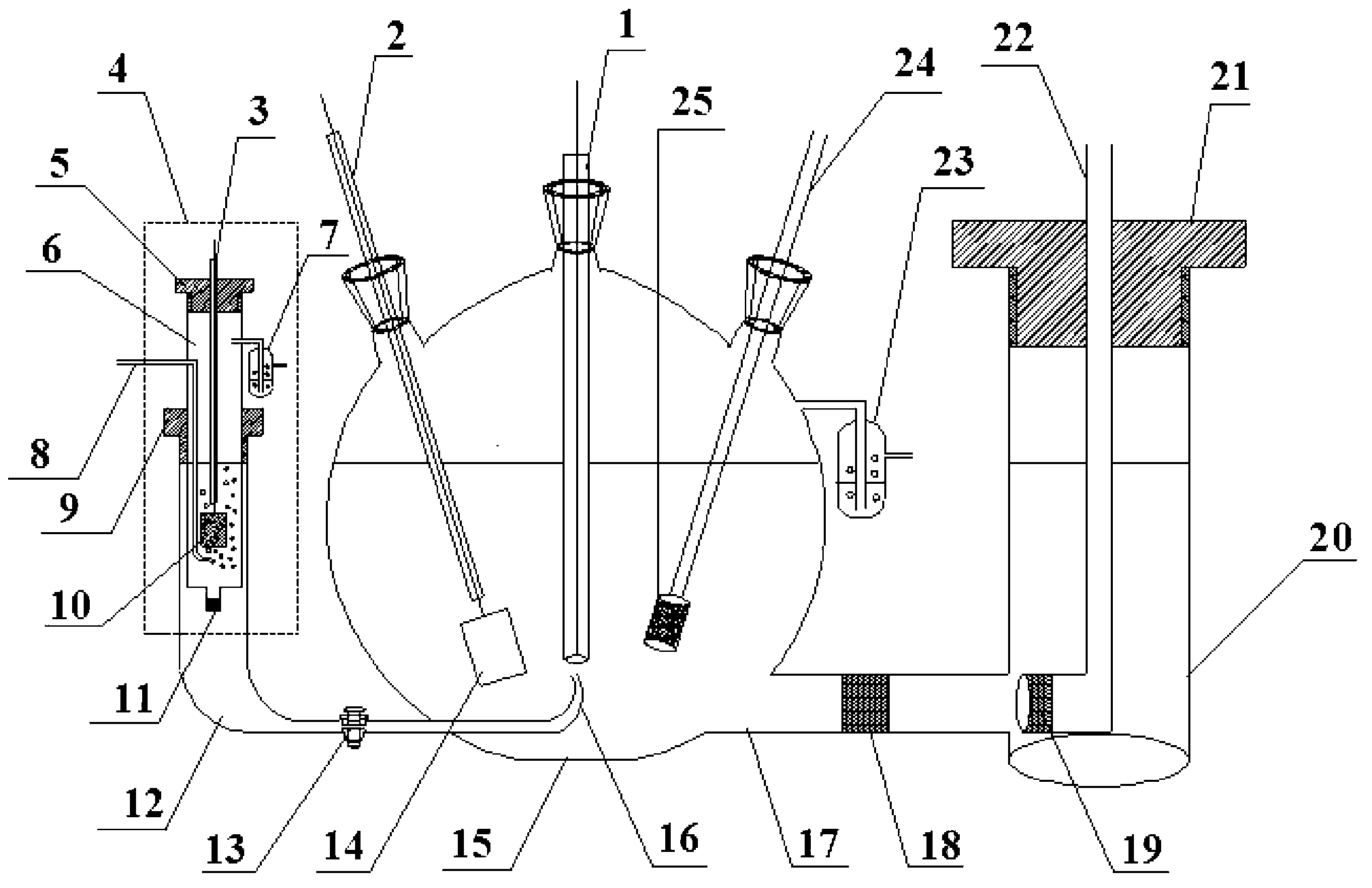
Test conjoined electrolytic bath provided with assisted ventilation chamber
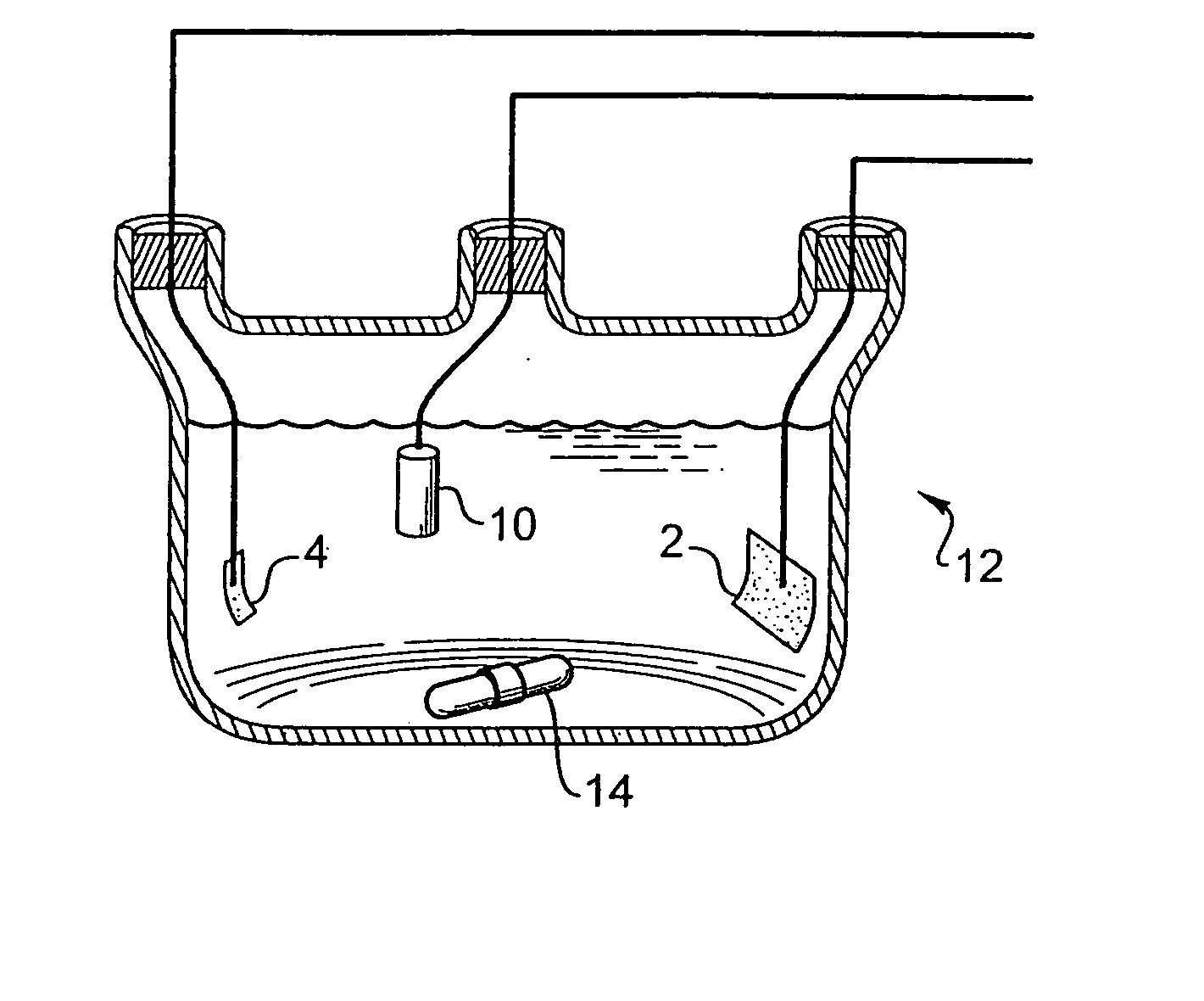
InactiveCN103323508AReduce disturbanceReduce signal to noise ratioMaterial electrochemical variablesAssisted ventilationElectricity
A test conjoined electrolytic bath provided with an assisted ventilation chamber is suitable for the electric performance test field of a fuel-cell catalyst. The test conjoined electrolytic bath mainly comprises three parts, namely a test pool, an assisted ventilation chamber and a reference hydrogen reference electrode chamber. The test pool is provided with a working electrode, a counter electrode with a platinum sheet and a glass core mounted at an inlet air pipe end. The reference hydrogen reference electrode chamber contains a reference hydrogen reference electrode liquid storage tube, a connecting pipe arranged between the reference hydrogen reference electrode chamber and the test pool, and a reference hydrogen reference electrode provided with an inlet air pipe and a platinum black plated platinum sheet. The reference hydrogen reference electrode chamber is connected with the test pool through the connecting pipe. The assisted ventilation chamber is provided with the inlet air pipe. The connecting pipe is fixed between the assisted ventilation chamber and a test cabinet. And the inlet air pipe faces a port of the connecting pipe. A porous glass plug is also arranged inside the connecting pipe.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
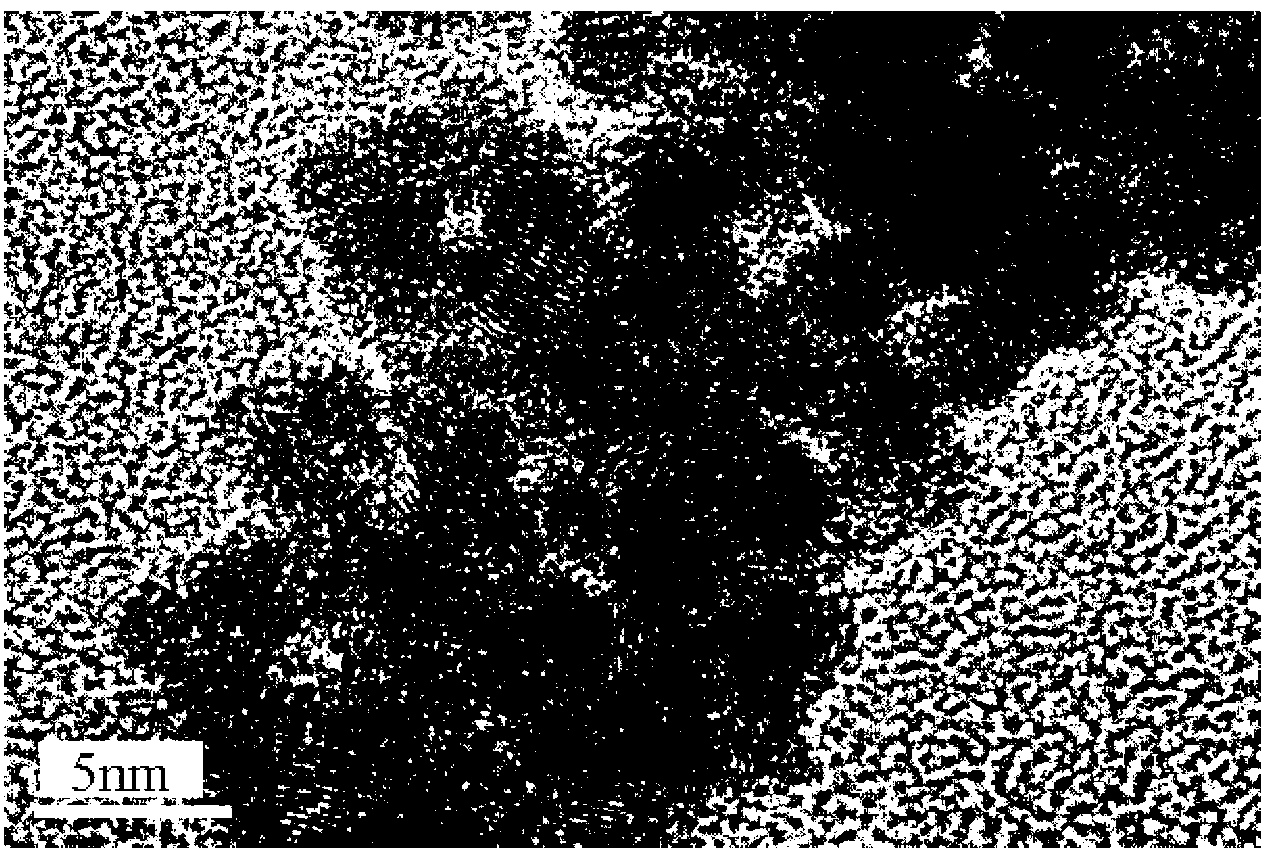
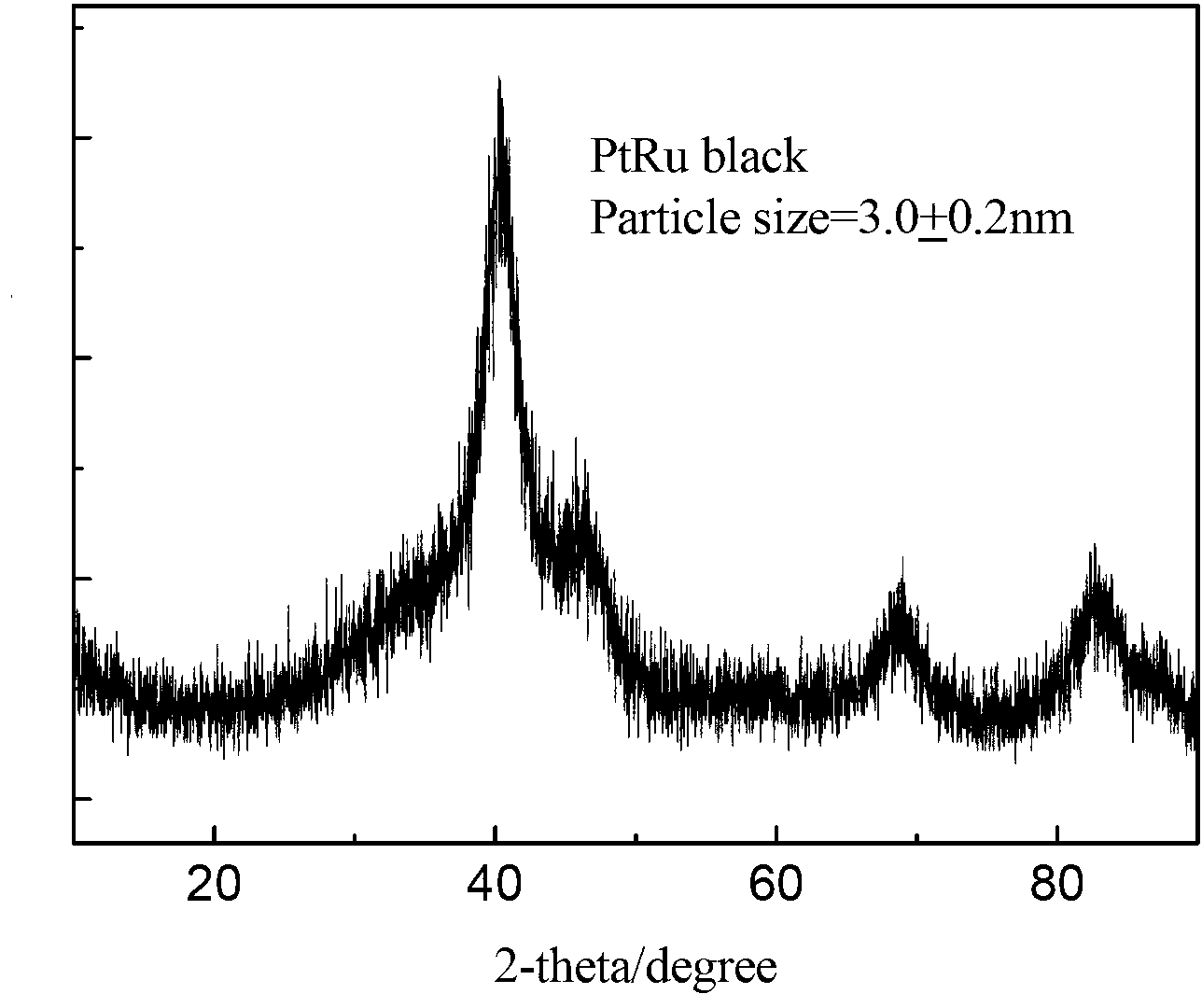
Method for preparing platinum black/ platinum ruthenium black nano electro-catalyst by using sacrificial magnesia carrier
The invention provides a method for preparing a platinum black / platinum ruthenium black nano electro-catalyst by using a sacrificial magnesia carrier. The method is used for preparing the platinum black / platinum ruthenium black nano electro-catalyst based on a metallic carbonyl cluster path, and comprises the steps of synthesis of a catalyst precursor, namely a metallic carbonyl cluster, injection of magnesia, heat treatment of an intermediate of the catalyst, dissolution of the magnesia and post treatment of the catalyst. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: introducing CO under an alkali condition to react with the precursor of the electro-catalyst to obtain the metallic carbonyl cluster, adding the magnesia in a protective atmosphere, stirring, and transferring the solvent at the temperature of between 30 and 120 DEG C in the protective atmosphere; performing heat treatment; and adding an acid solution to dissolve the magnesia, heating, performing post treatment, and thus obtaining the platinum black / platinum ruthenium black nano electro-catalyst with the particle diameter of 2 to 20 nanometers and narrow particle size distribution. The electro-catalyst is suitable for a cathode and an anode of a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
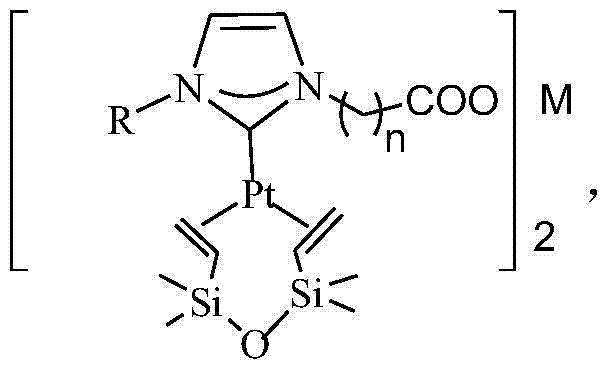
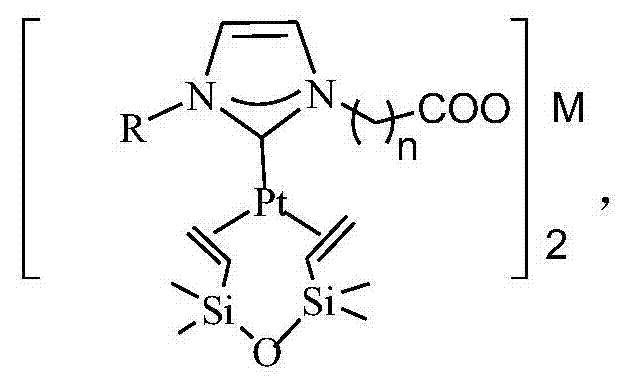
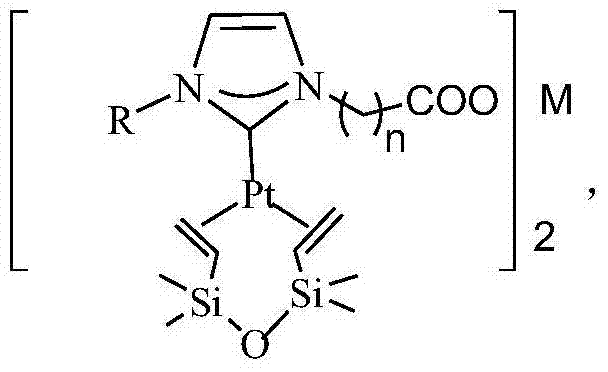
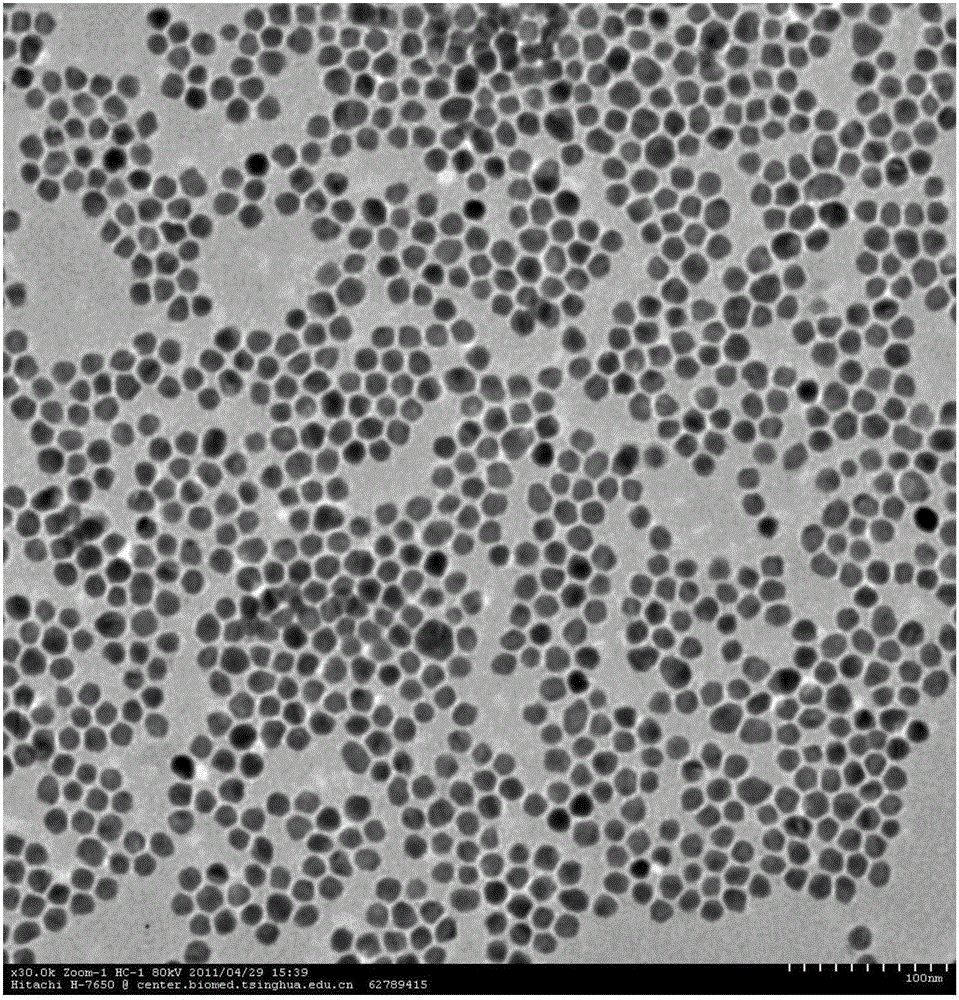
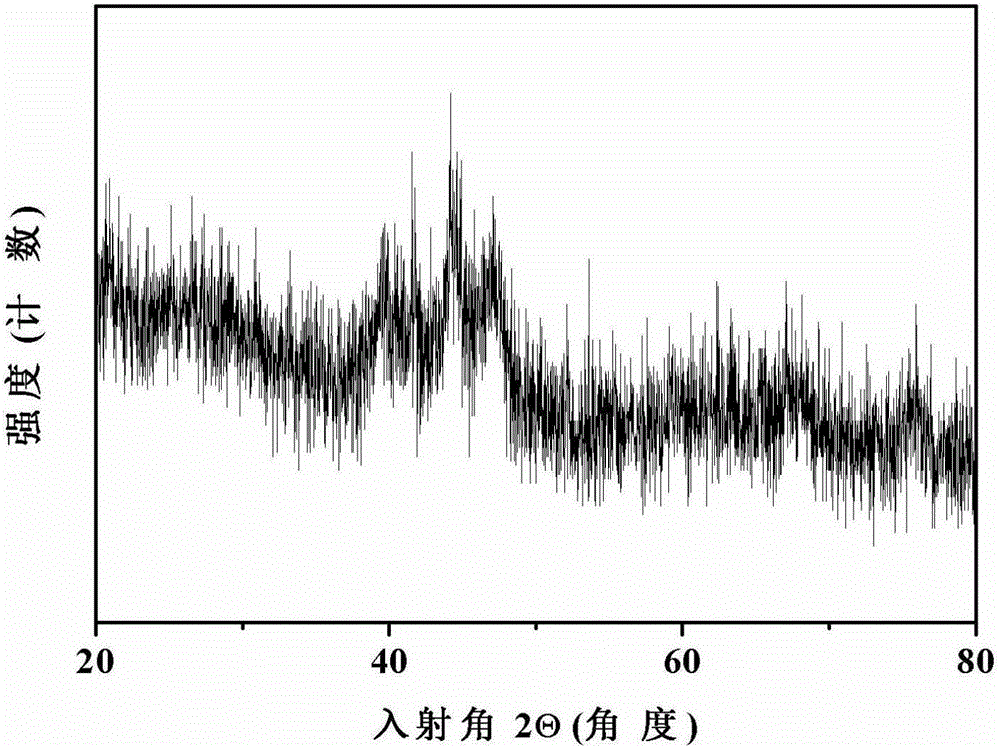
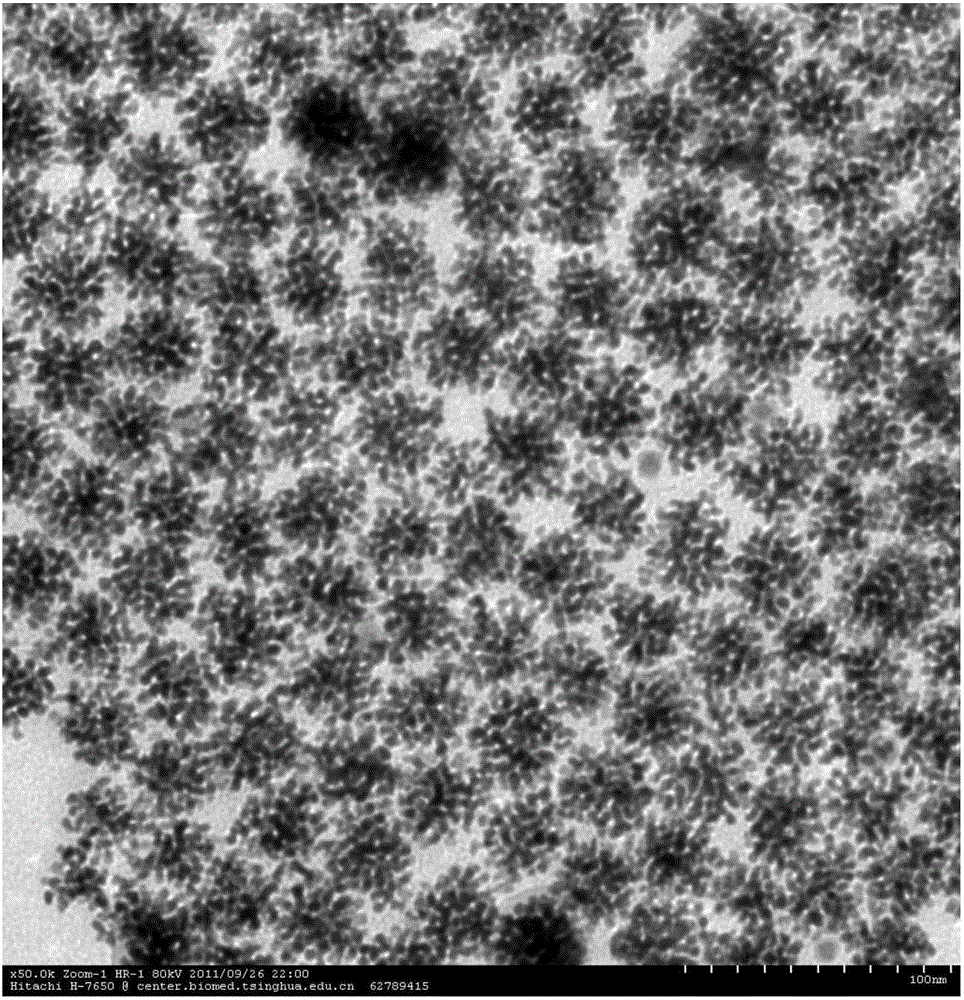
N-heterocyclic carbene platinum complex metal carboxylate integrated catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104324752ANo platinum black precipitationEasy to separateGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPotassiumCarbene
The invention relates to the field of organic high-molecular chemistry and discloses an N-heterocyclic carbene platinum complex metal carboxylate integrated catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes following steps: (1) carrying out a reaction between alkyl imidazole and halogenated carboxylic acid to obtain a carboxylic acid functionalized imidazolium salt; (2) carrying out a reaction with chlorides of ferrous, copper, zinc, calcium or magnesium to obtain a imidazole-based ionic liquid containing carboxylates containing the ferrous, the copper, the zinc, the calcium or the magnesium; (3) preparing an N-heterocyclic carbene ligand from the ionic liquid under effect of potassium tert-butyl alcohol; and (4) carrying out a reaction with a Karstedt catalyst to prepare the N-heterocyclic carbene platinum complex metal carboxylate integrated catalyst. The catalyst is high in selectivity, is free of generation of platinum black precipitation, is easy to separate and can be recycled.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparing method for Pt-Co flower-type nano-catalyst
ActiveCN105251509ASimple methodHigh catalytic activityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesNano catalystToluene
The invention discloses a preparing method for a Pt-Co flower-type nano-catalyst. The preparing method includes the following steps that 1, methylbenzene and oleylamine are added into a reaction kettle, and then cobalt acetylacetonate and a tributyl-borane-ammonia complex compound are added; after the mixture is stirred for 15 minutes to 30 minutes, the reaction kettle is put into a drying oven; Co nano-particles are obtained after the reaction is carried out for 6 hours to 12 hours at the temperature of 140 DEG C to 160 DEG C; 2, octadecylamine is added into a reactor and dissolved, and then the obtained Co nano-particles obtained in the step 1 and a tributyl-borane-ammonia complex compound are added; after stirring is carried out for 0.5 hour to 2 hours, a pentanedione platinum derivative is added; heating is stopped after the temperature rises to 150 DEG C to 170 DEG C and reacting is carried out for 0.5 hour to 2 hours, and the Pt-Co flower-type nano-catalyst is obtained after a product is washed. The Pt-Co flower-type nano-catalyst is prepared through a two-step reaction, and the catalytic performance is much higher than that of commercial platinum black.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing rod-shaped platinum nanoparticles
ActiveCN110640160ALower surface energyGrowth retardationTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusActive agentOrganosolv
The invention relates to a method for preparing rod-shaped platinum nanoparticles, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of noble metal nanomaterials. The method comprises the following steps: evaporating and crystallizing a platinum precursor solution to obtain a platinum precursor crystal; adding the platinum precursor crystal to a surfactant and ultrasonic processing to obtain a platinum precursor-surfactant mixed solution, wherein the surfactant is an oleic acid-oleylamine mixed solution; at the temperature of 70 to 90 EDG C, under stirring, dropwise adding the reducing agent oleic acid solution to the platinum precursor-surfactant mixed solution to react until the system became black to form platinum black, adding volatile organic solvents to destroy oil phase organics aggregated on the surfaces of the platinum particles, and continuing to react until the pH of the system is 6.5-7.5 to obtain a reaction product mixed liquid; and performing solid-liquid separation on the reaction product mixed liquid, washing the solid with anhydrous ethanol and deionized water sequentially, and drying under vacuum to obtain the rod-shaped platinum nanoparticles. The small-sized rod-shaped platinum nanoparticles with a length of several hundred micrometers are prepared in a liquid phase reaction system, and the yield reaches more than 90%.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Power generation system coupling photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide and photocatalytic fuel cells
The invention discloses a power generation system coupling photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide and photocatalytic fuel cells. A reaction block is internally provided with a vertically cut-through reaction chamber, and the left end and right end of the reaction block are respectively provided with a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet that are communicated with the reaction chamber. The upper end opening of the reaction chamber is sealed by upper conductive glass, the upper conductive glass surface facing the reaction chamber is coated with a photocatalyst. The lower end opening of the reaction chamber is sealed by a seal plate, which is formed by splicing of left lower conductive glass and a right carbon cloth, the carbon cloth surface facing the reaction chamber is coated with a platinum black catalyst, and the carbon paper is connected to the upper conductive glass through a lead. The system provided by the invention integrates photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide and power generation of photocatalytic fuel cells, couples the two reaction processes, reduces the raw material cost of fuel cells, and realizes zero discharge of carbon dioxide.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com