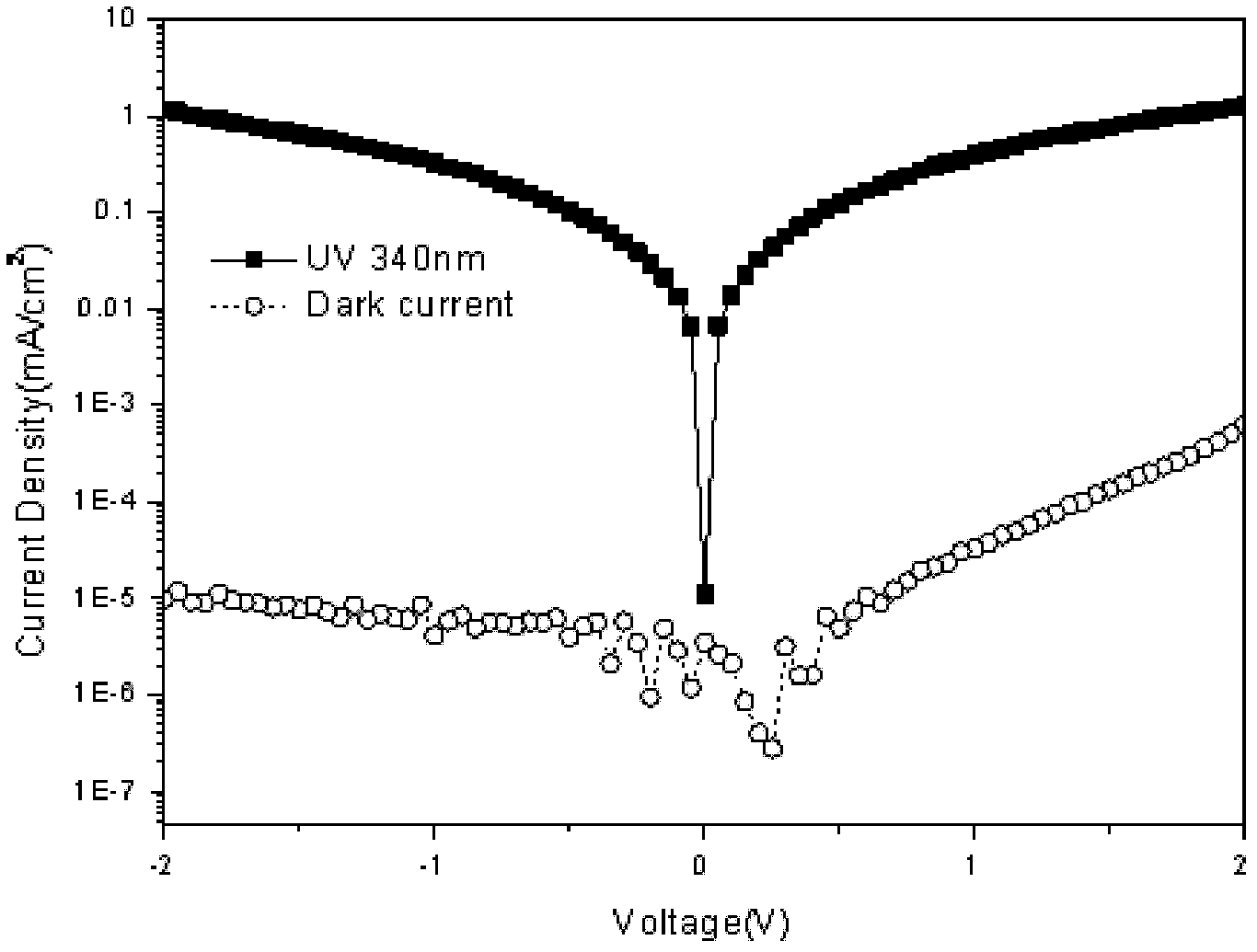
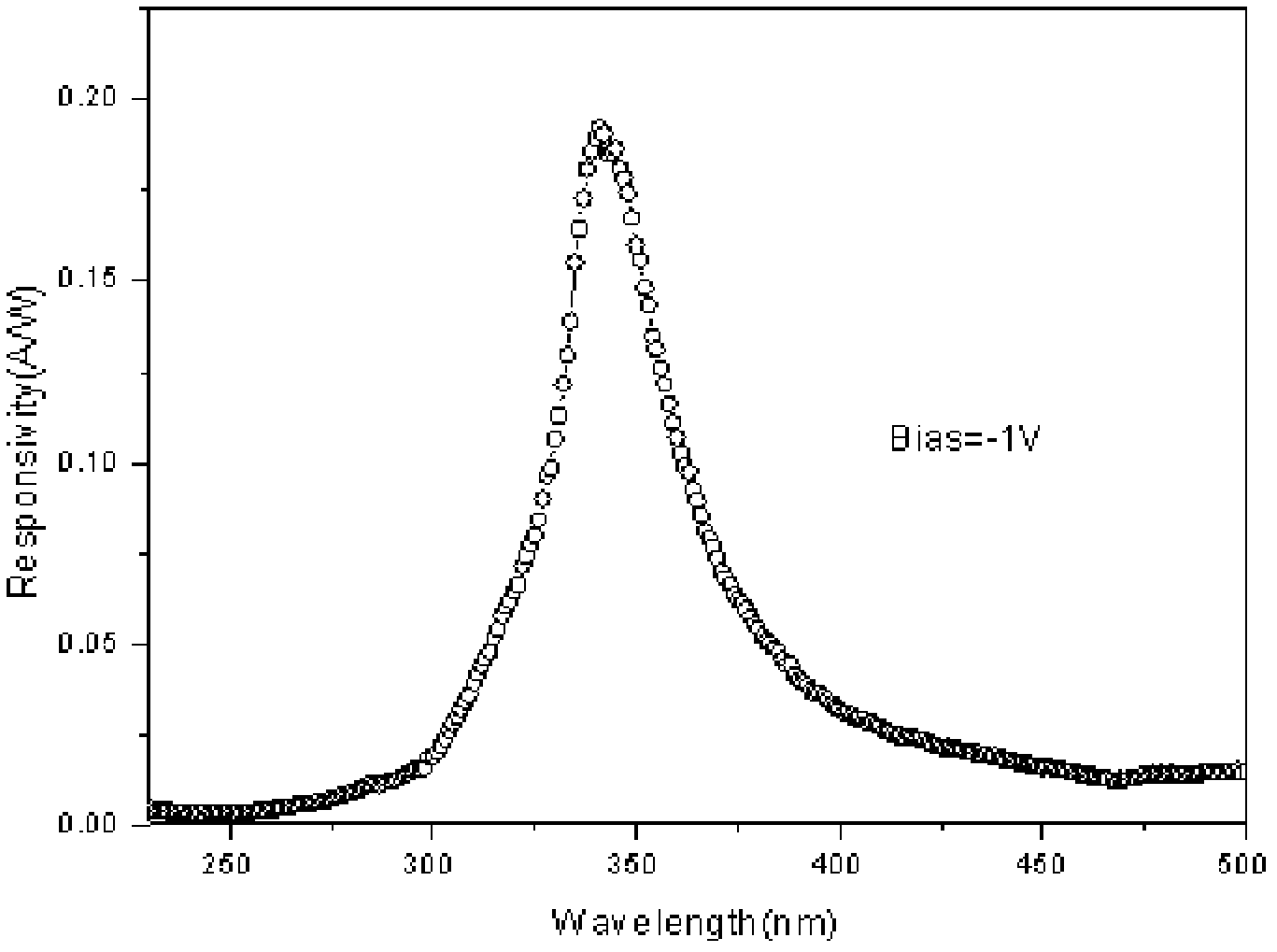
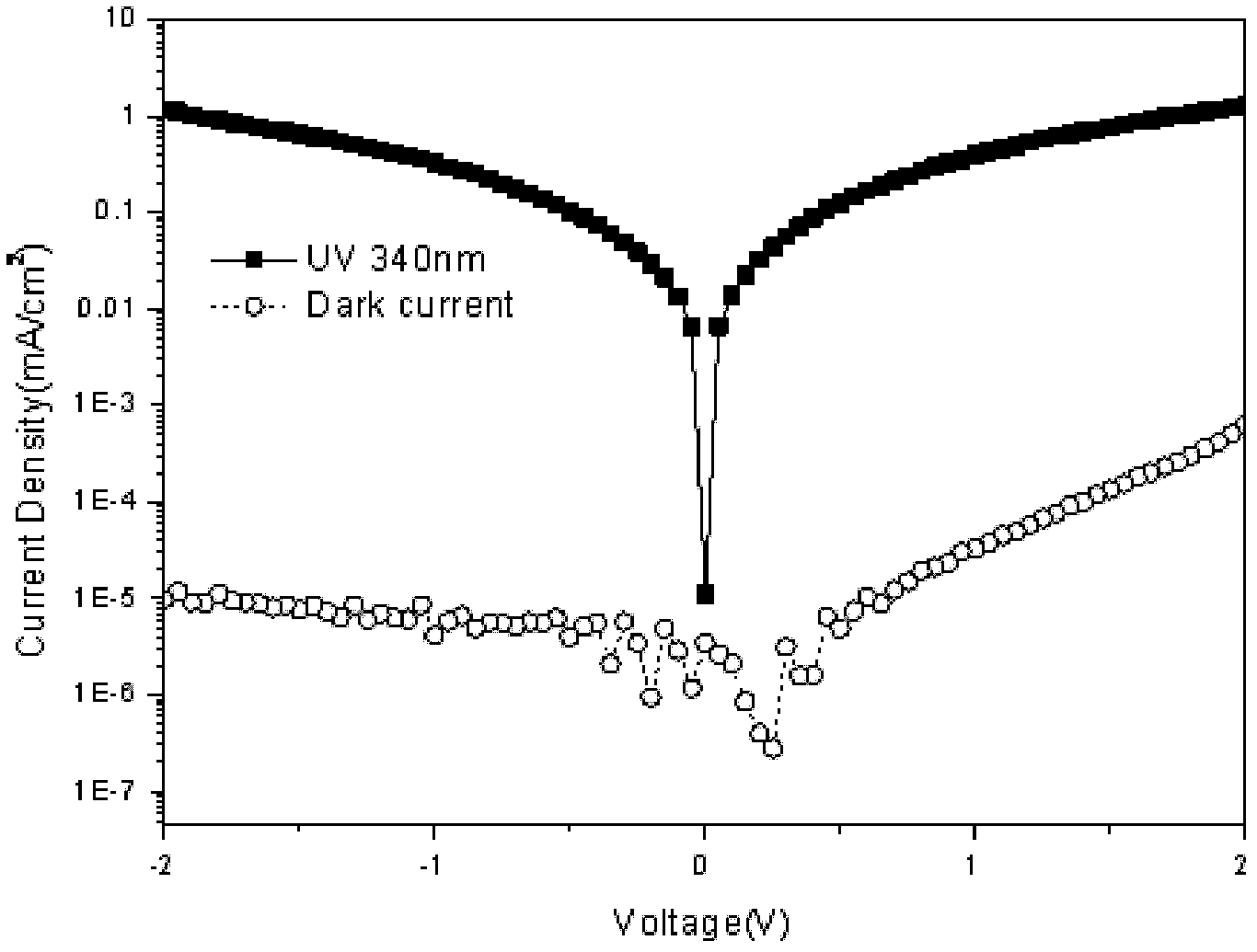
Patents
Literature
66results about How to "Improve photoresponse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
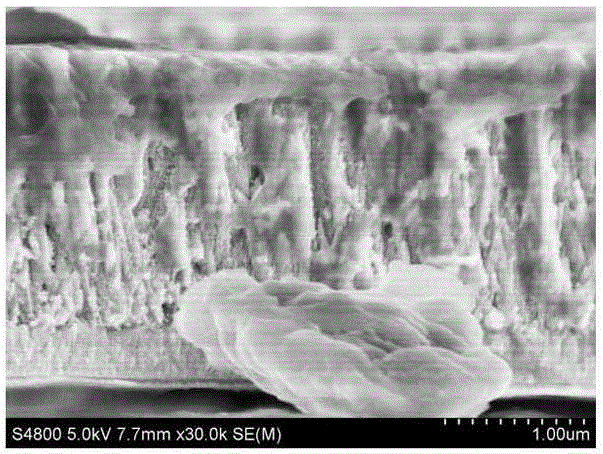
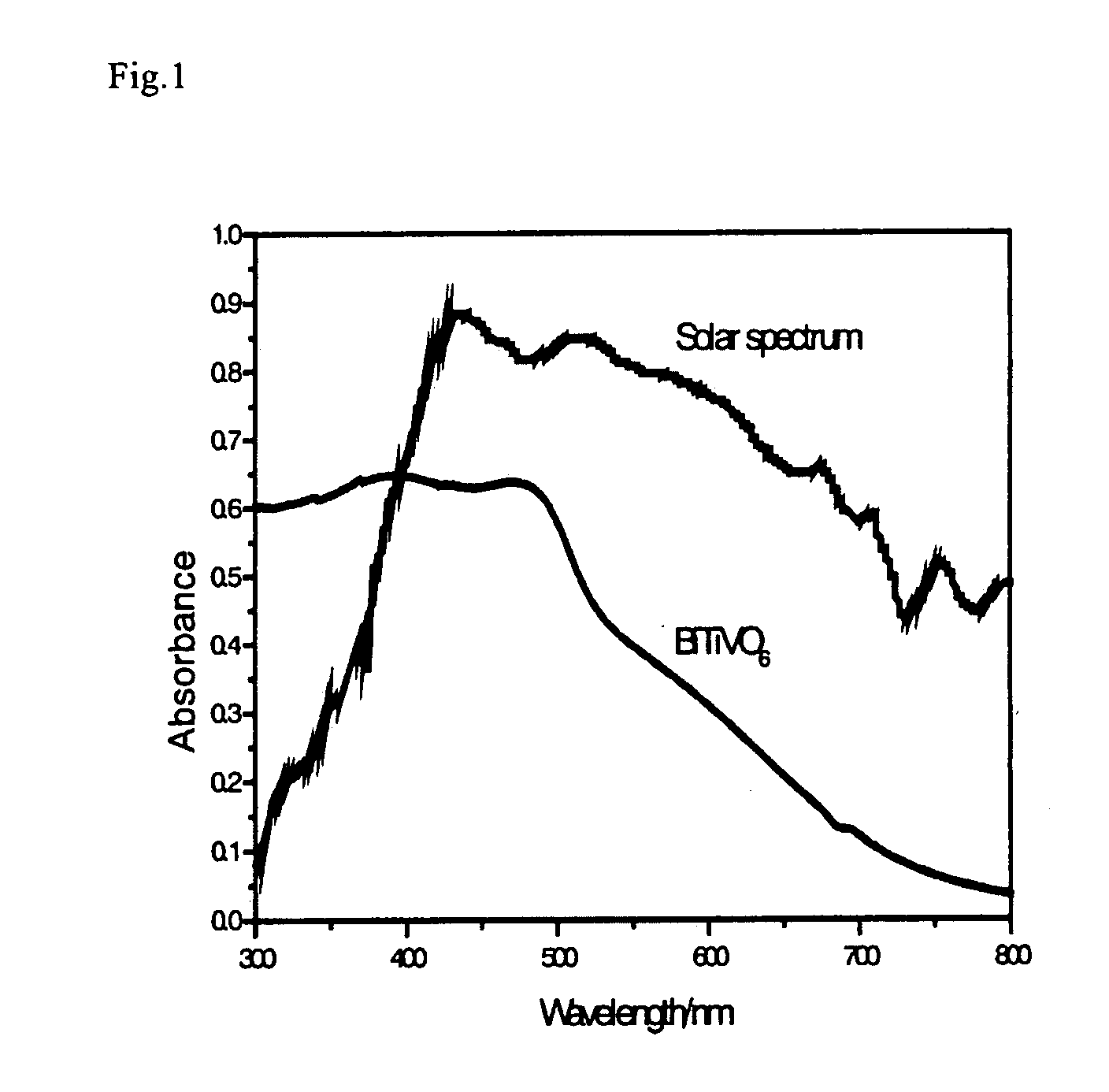
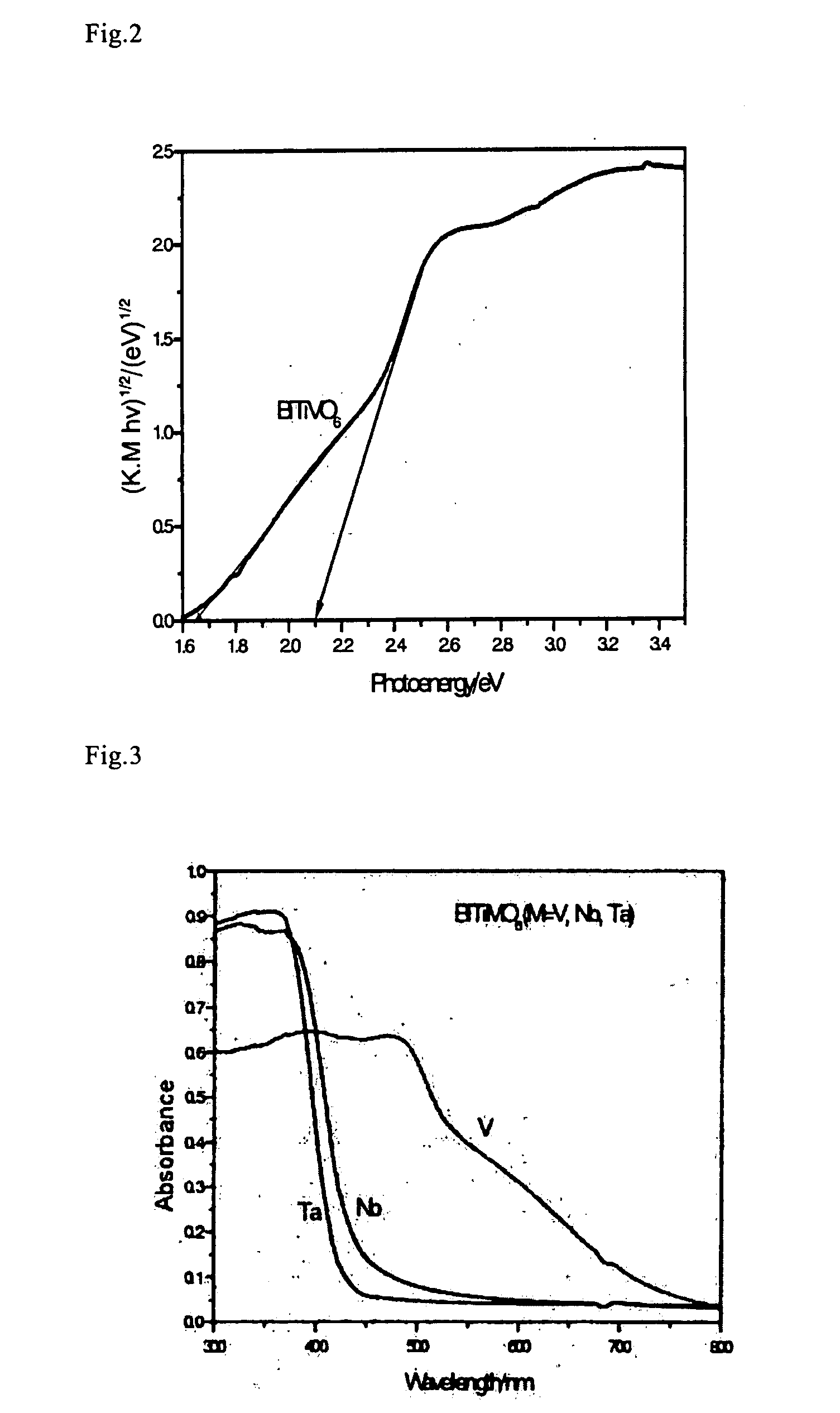
Composite Metal Oxide Photocatalyst Exhibiting Responsibility to Visible Light
A new photocatalyst, which is high in visible light response, is great in quantum efficiency, and is more excellent in photocatalytic activity, is provided. A composite metal oxide, prepared combining two photocatalytic systems of TiO2 and BiVO4, including elements of Bi, Ti, and Vi as composition elements, can be a photocatalyst having a high activity under visible light. Particularly, BiTiVO6, which is obtained at a compounding ratio of 1:1, can be a photocatalyst having a remarkably high activity under visible light. Moreover, a composite metal oxide expressed by a general formula BiTiMO6 (in the formula, M represents at least one element selected from a group consisting of V, Nb, and Ta) can be a photocatalyst having a high activity under visible light.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV +1
Asymmetrical electrode two-dimensional material/graphene heterojunction cascaded photodetector and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105789367APromote formationImprove photoresponseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionNon symmetric
The invention discloses an asymmetrical electrode two-dimensional material / graphene heterojunction cascaded photodetector and a manufacturing method thereof. The detector comprises a Si / SiO2 substrate, a first electrode is arranged on the Si / SiO2 substrate, a two-dimensional material layer is arranged on the first electrode, a second electrode is arranged on the two-dimensional material layer, and the two-dimensional material layer is an n-layer heterojunction formed by graphene and two-dimensional material which are overlapped. The asymmetrical electrodes with different work functions are adopted, formation of a Fermi energy level difference from the first electrode to the second electrode is promoted, photocarriers are generated and then quickly diffused to an external circuit, quick combination of an electron hole can be avoided due to existence of the energy level difference, and the photo response of the device can be enhanced; and as the graphene and the two-dimensional material are combined, the high carrier mobility and the super quick response time of the graphene, and the high absorption rate towards light by the two-dimensional material are used respectively, and a super quick and super high-response photodetector can be realized.
Owner:ZHOUKOU NORMAL UNIV
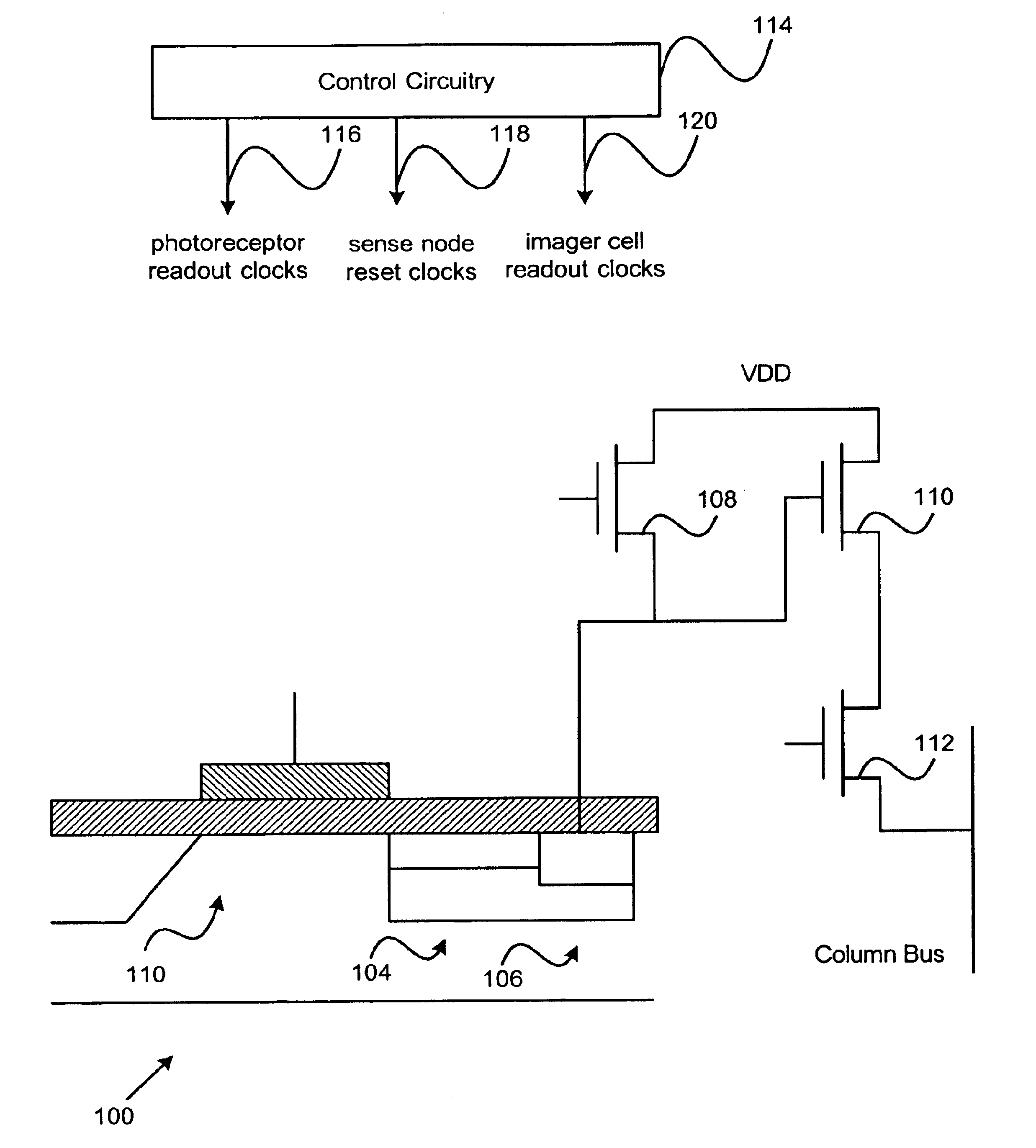
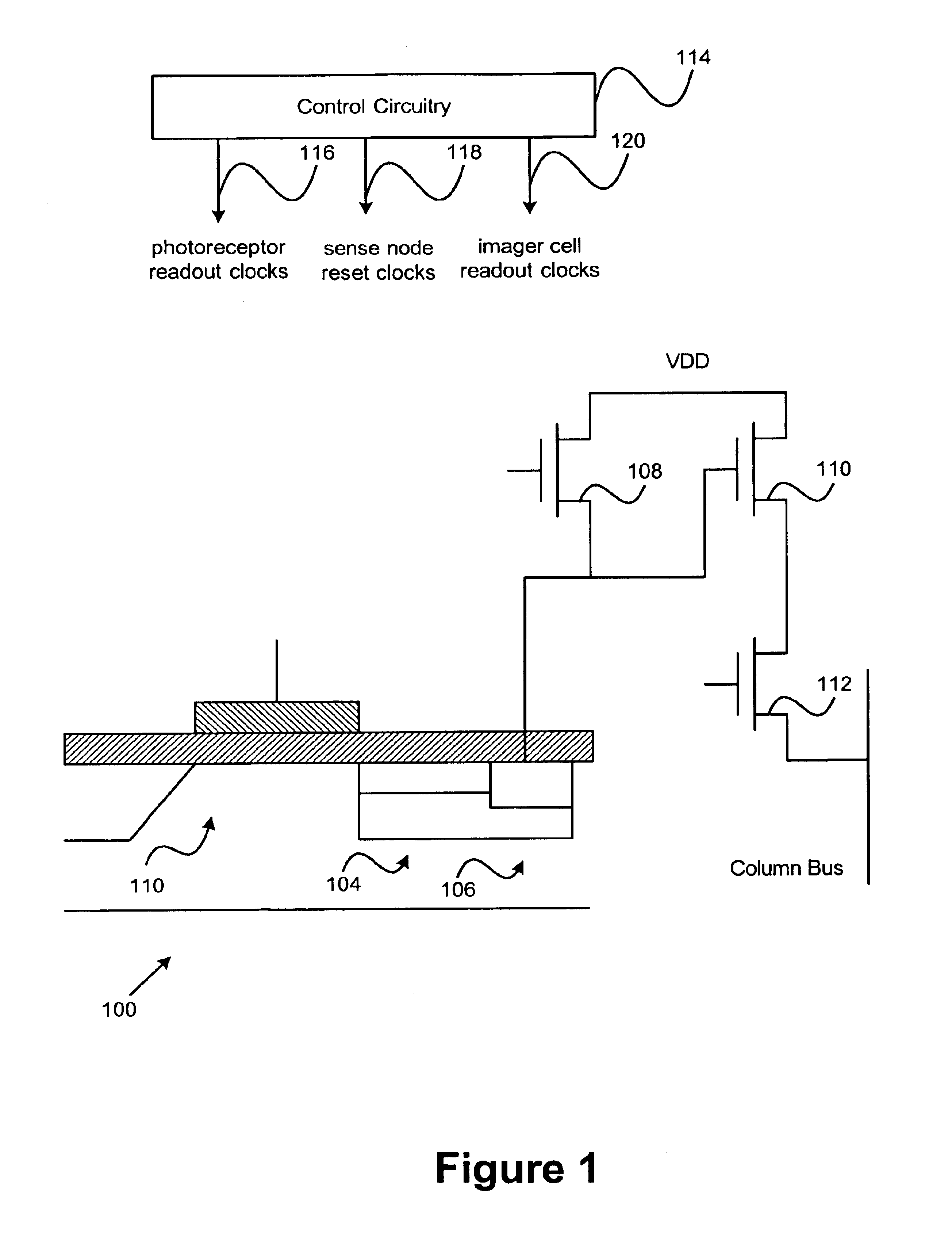
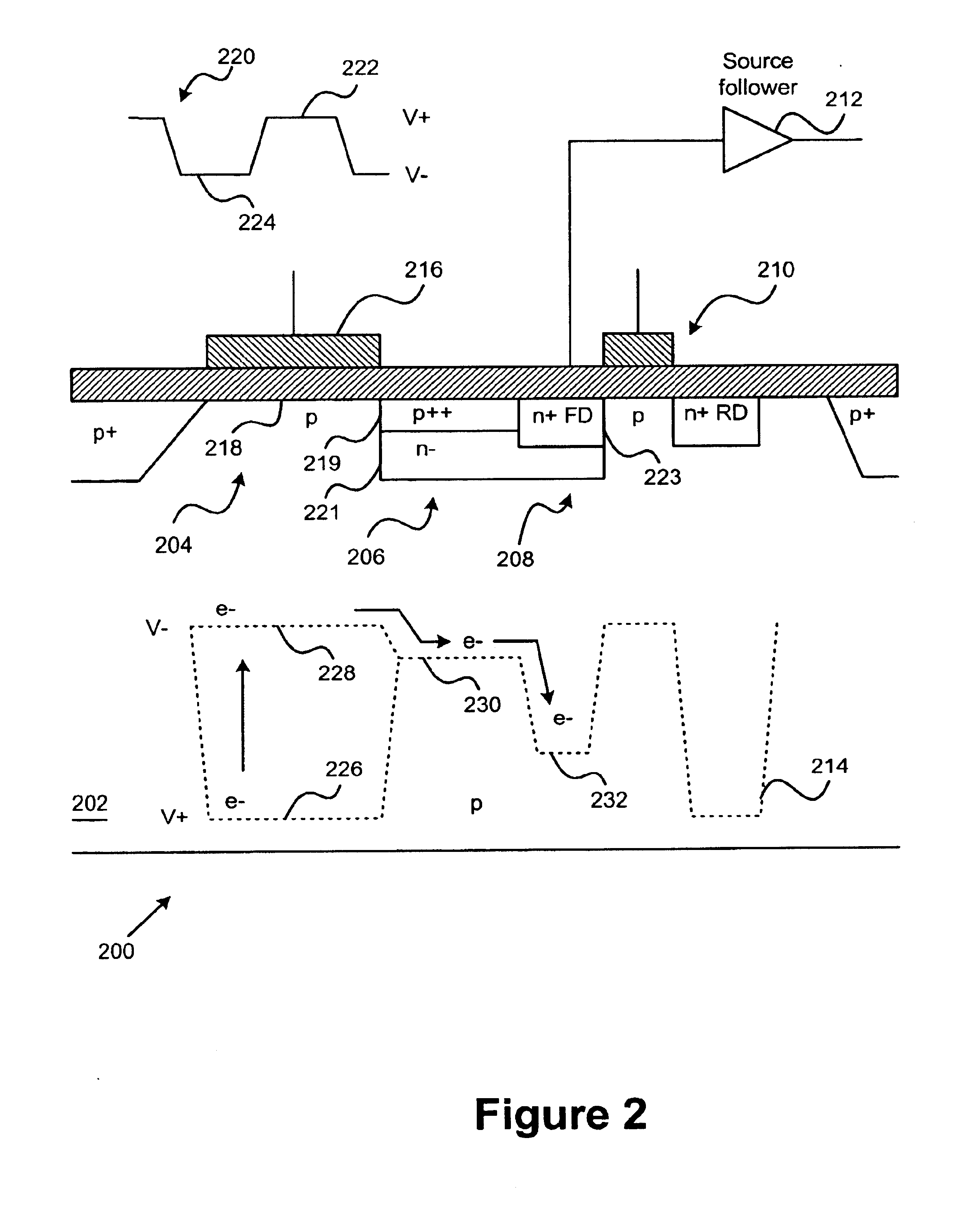
Imager cell with pinned transfer gate
InactiveUS6909126B1Reduce noiseEnhanced blue light responseSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesAudio power amplifierEngineering
An imager cell includes a photoreceptor, a sense node, and a pinned transfer gate. The pinned transfer gate is tied to the same potential of a substrate of the imager cell and is disposed between the photoreceptor and the sense node in order to transfer charge between the photoreceptor and the sense node. The imager further includes a reset transistor disposed to reset the sense node, and an output amplifier coupled to the sense node. Control circuitry supplies a photoreceptor readout clock to the photoreceptor. The readout clock includes an integration period and a transfer period. According to various embodiments of the invention, the imager cell provides improved noise performance, selective charge capacities, and improved blue light response beyond that of conventional imager cells.
Owner:ESS TECH INT INC +1
Cross-linked polyvinyl butyral binder for organic photoconductor
InactiveUS6136486AImprove mechanical durabilityImprove charge acceptanceElectrographic process apparatusCoatingsCross-linkPolyvinyl butyral
The invention is a self-cross-linked polyvinyl butyral (PVB) binder for organic photoconductors (OPC's) used in electrophotography. The no cross-linked form of the binder is available from Monsanto Co. in the U.S.A. a Butvar TM , and from Sekisui Chemical Co. in Japan as Slek TM . I discovered that the PVB may be self-cross-linked by subjecting it to a thermal cure at between about 150 DEG -300 DEG C. for about 2 hours. I think other ways of cross-linking, for example, e-beam, UV or X-ray radiation, will achieve results similar to those I obtained with heat. No cross-linker, nor cross-linkable copolymer nor catalyst is required to accomplish the cross-linking. After self-cross-linking, the PV has good mechanical durability and good anti-solvent characteristics. In addition, he self-cross-linked PVB's glass transition temperature (Tg) increases from about 65 DEG C. to about 170 DEG C. Also, when conventional photoconductor pigments are dispersed in the self-cross-linked PVB, they are well dispersed, and the resulting OPC's have good charge acceptance, low dark decay, and, in general, good photodischarge characteristics. Also, OPC's with the self-cross-linked PVB exhibited improved adhesion, so multi-layered OPC's made according to this invention will hav improved inter-layer bonding and longer economic lives.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
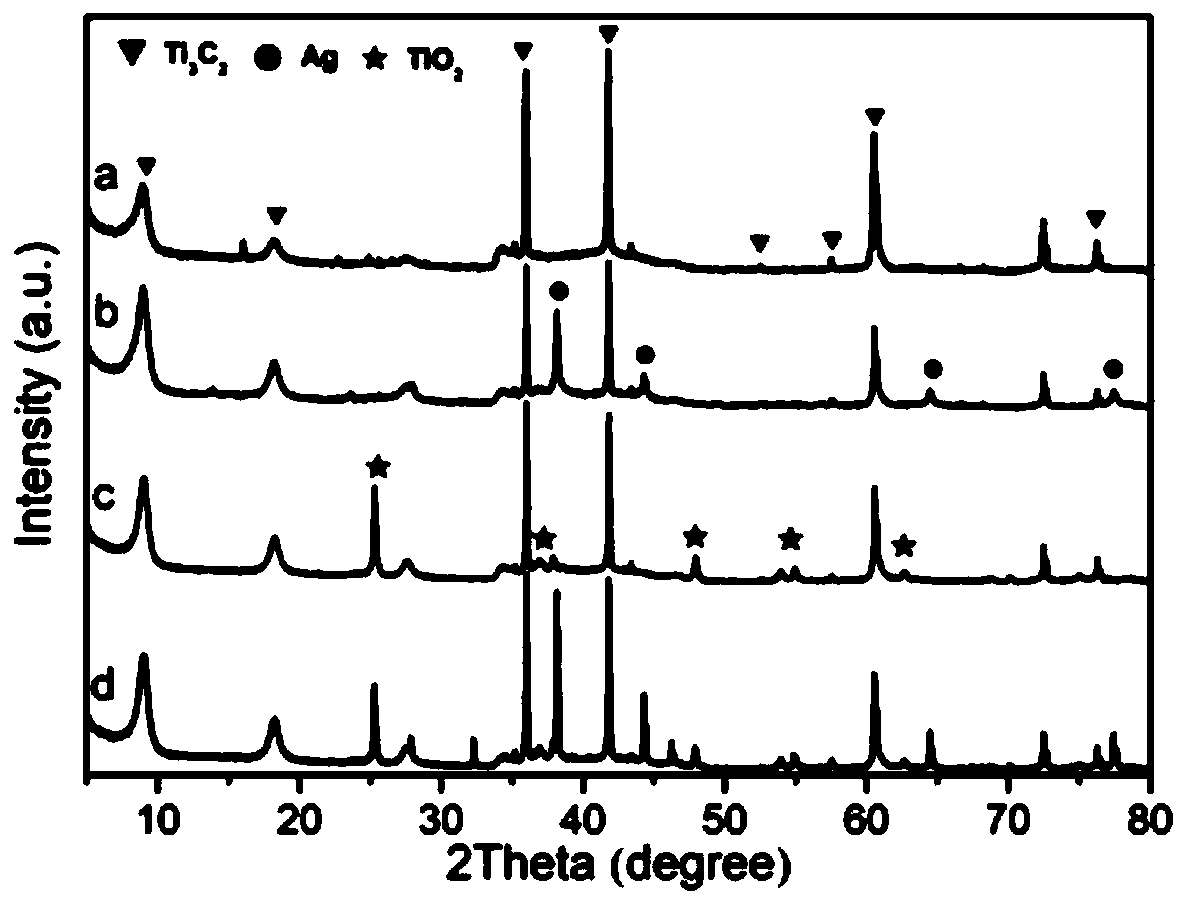
Nano noble metal modified Ag/MXene/TiO2 composite material and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111250122ALow costEasy to manufacturePhysical/chemical process catalystsPtru catalystTrifluoroacetic acid
The invention discloses a nano noble metal modified Ag / MXene / TiO2 composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a two-dimensional lamellar material MXene with a good lamellar structure; ultrasonically and uniformly dispersing MXene into an AgNO3 aqueous solution; then adding a formaldehyde aqueous solution containingstannous chloride (SnCl2) and trifluoroacetic acid (CF3COOH) to obtain an MXene composite material with uniformly distributed nano-Ag, and finally, separating out TiO2 sheets on the surface of the MXene by adopting a hydrothermal method to obtain the nano-Ag modified MXene / TiO2 composite material. The nano Ag and TiO2 sheets in the composite material are uniformly dispersed, the proportion of thenano Ag and TiO2 sheets is adjustable, and the photocatalytic performance of the composite material is greatly improved compared with that of commercial TiO2(P25). The addition of nano Ag enhances theabsorption of the composite material in a visible band, and the Ag / MXene / TiO2 ternary composite material has potential application in the field of photoelectrocatalysis as a catalyst material.
Owner:FUJIAN UNIV OF TECH
Graphene photodetector
ActiveUS8901689B1Distance minimizationIncrease heightSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationMeasurement deviceCharge carrier
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Two-dimensional superlattice indium selenide and preparation method and application thereof in fabrication of photoelectric detector
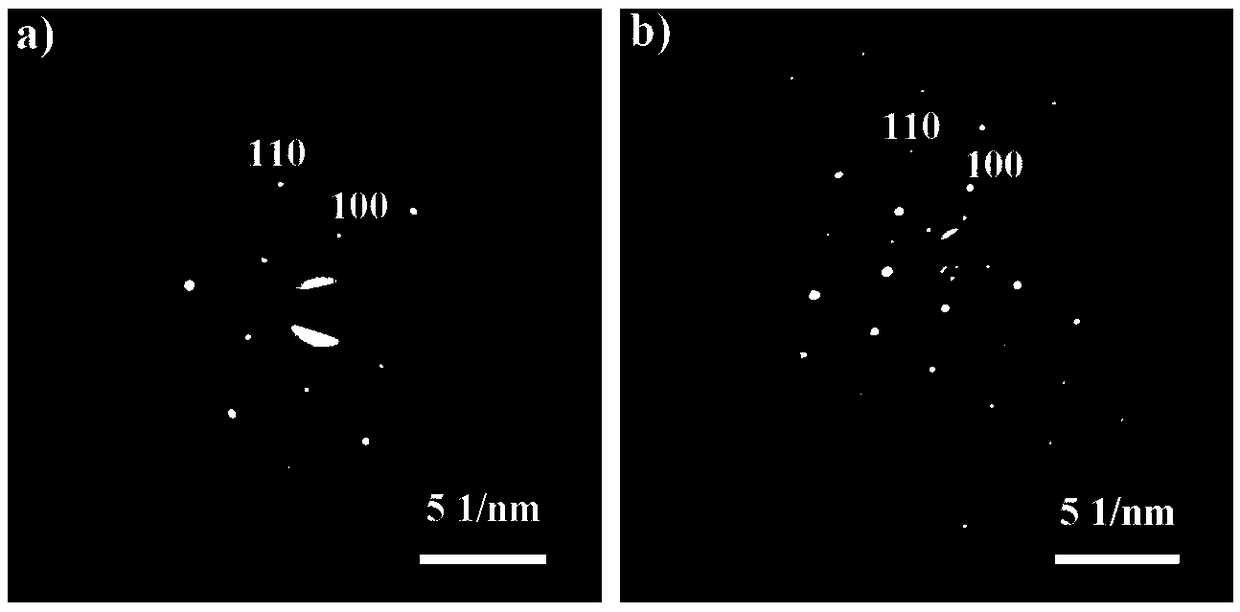
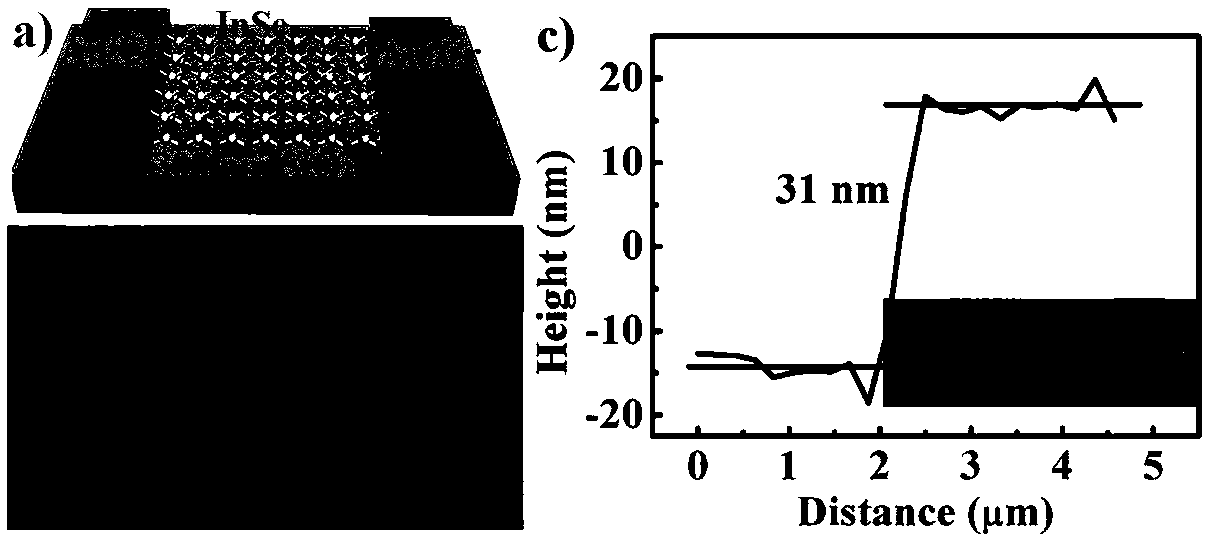
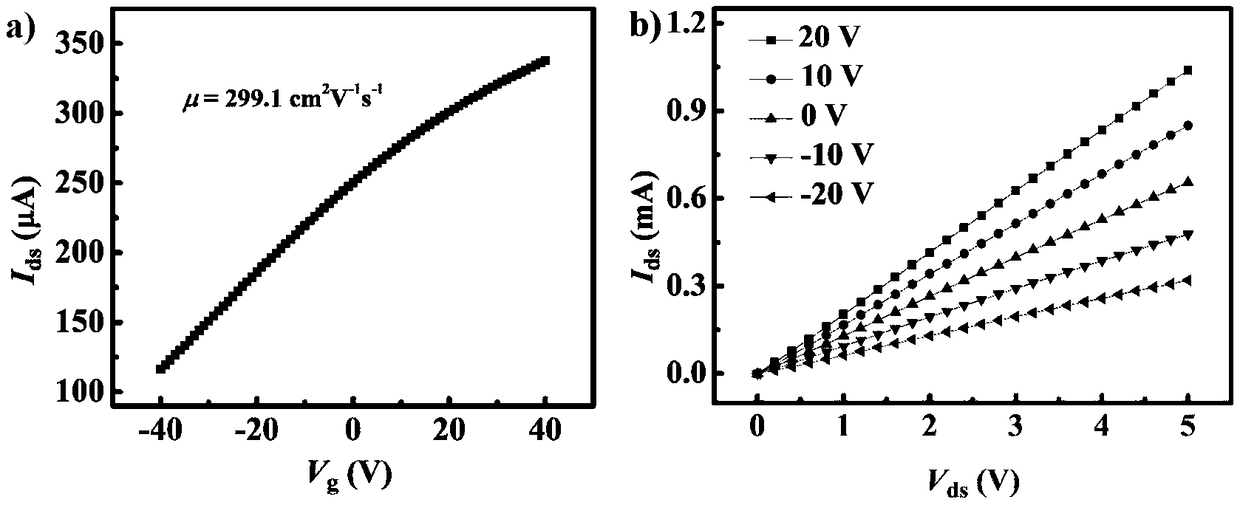
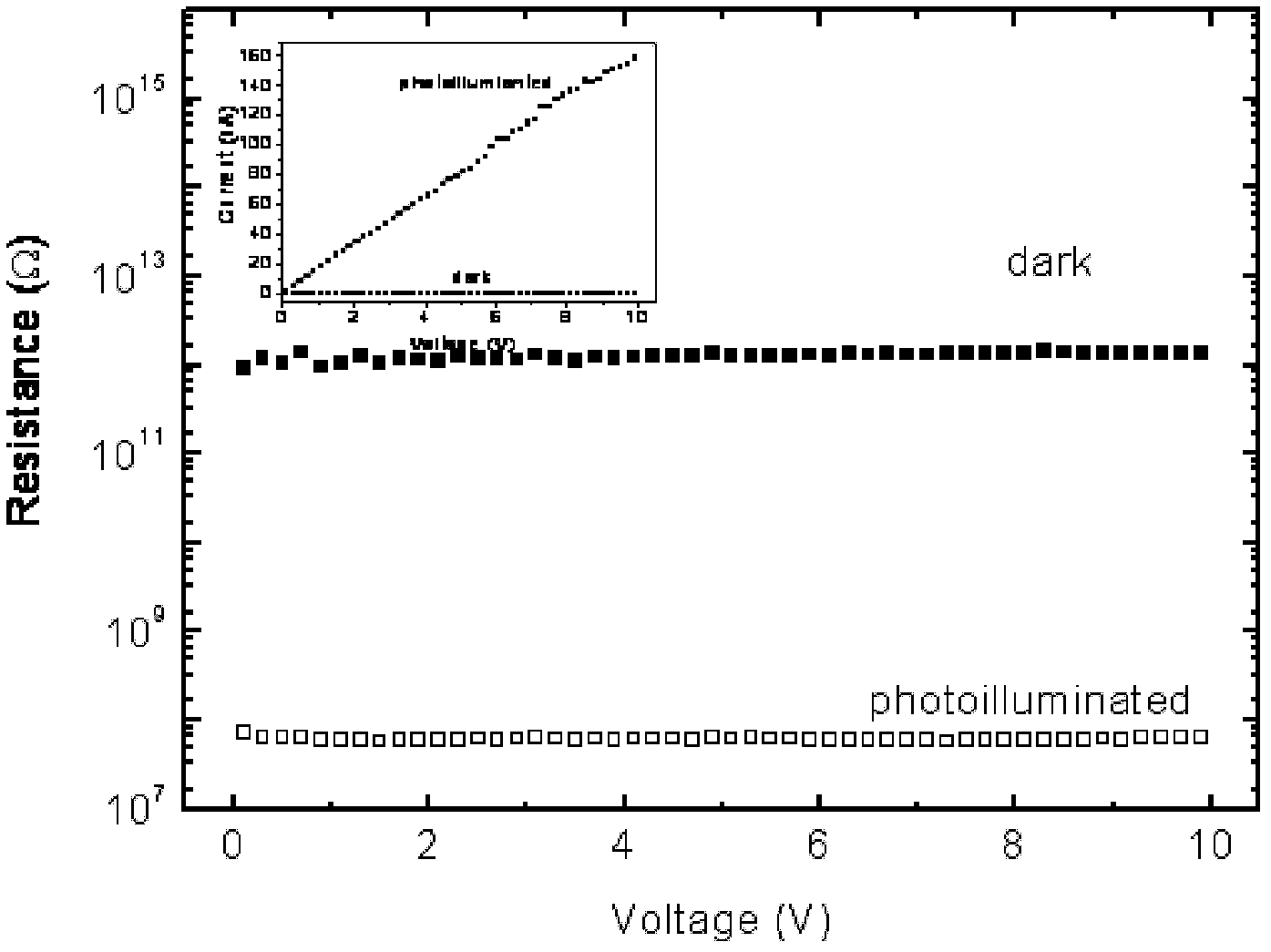
InactiveCN109411331AHigh electrical transport performanceImprove photoresponseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanotechnologyPhotovoltaic detectorsIndium
The invention discloses two-dimensional superlattice indium selenide and preparation method and application thereof in fabrication of a photoelectric detector, and belongs to the field of a high-performance photoelectric detector. The fabrication method of the two-dimensional superlattice indium selenide comprises the steps of pre-processing a SiO2 / Si substrate; transferring onto the SiO2 / Si substrate after an InSe material is pasted with transparent glue, and immersing in acetone; and performing high-temperature processing under a vacuum condition, thereby obtaining a two-dimensional superlattice InSe nanosheet on a surface of the SiO2 / Si substrate. The two-dimensional superlattice InSe prepared by the invention has the advantages of high electrical transmission performance, high light response, favorable stability and rapid light response speed and has a good application prospect in the field of the high-performance photoelectric detector.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
MgZnO solar-blind photoresistor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102569483ASimple preparation processLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesMetallic materialsMetal electrodes
The invention discloses a MgZnO solar-blind photoresistor and a preparation method thereof, belongs to the field of photoelectron information, and is mainly used in solar-blind photoresistors with low bias voltage and high response. The problem of separation during MgZnO preparation with a high component Mg is solved. According to the method for preparing the solar-blind photoresistor by a MgZnO thin film, a first MgxZn1-xO transition layer, a second MgyZn1-yO transition layer, a MgZZn1-ZO thin film with the high component Mg and an electrode grow on an R-surface sapphire substrate; and the method comprises the following steps of: 1, conveying the cleaned R-surface sapphire substrate into a molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) pregrowing chamber; 2, treating the R-surface sapphire substrate at the temperature of between 750 and 850 DEG C for 15 to 30 minutes in the pregrowing chamber; 3, conveying the R-surface sapphire substrate into a growing chamber; growing the first MgxZn1-xO transition layer which is 2 to 10nm thick at the growing temperature of between 400 and 500 DEG C, wherein x is in a range of 0.16 to 0.20; and then growing the second MgyZn1-yO transition layer which is 2 to 10nm thick at the same growing temperature, wherein y is in a range of 0.26 to 0.40; 4, growing the MgZZn1-ZO thin film at the growing temperature of between 400 and 500 DEG C, wherein z is in a range of 0.43 to 0.55; and 5, preparing the metal electrode which is 100 to 150 nm thick on the MgZZn1-ZO thin film, wherein metal materials are Al, Au and Pt. The preparation process is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Micro-bolometer based on graphene quantum points
ActiveCN106197687AHigh temperature coefficient of resistanceImplement detectionPyrometry using electric radation detectorsSemiconductor devicesMicro nanoPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention provides a micro-bolometer based on graphene quantum points. The micro-bolometer comprises a substrate whose middle part is provided with a groove. The graphene quantum points are hanged above the groove and are connected through a graphene strip. Two ends of the graphene strip extend out of a graphene film to cover the substrate at two sides of the groove to form graphene electrodes. The micro-bolometer is characterized in that a hanged island-shaped graphene quantum point array is formed through the micro nano processing technology, the device temperature change in a same incident light power is increased by using the heat insulation effect by groove suspension, the device resistance temperature coefficient is raised by using quantization graphene, and the photoelectric detection is realized based on a micro-bolometer principle. Due to the absorption characteristic of a graphene material in an infrared wave band, the micro-bolometer provided by the invention can be used for the photoelectric detection of middle and far-infrared and terahertz wave bands, and a novel solution is provided for a present infrared photoelectric detector.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Graphene photodetector
ActiveUS20140332757A1Improve efficiencyMinimize travel distanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationMeasurement devicePhotodetector
A set of buried electrodes are embedded in a dielectric material layer, and a graphene layer having a doping of a first conductivity type are formed thereupon. A first upper electrode is formed over a center portion of each buried electrode. Second upper electrodes are formed in regions that do not overlie the buried electrodes. A bias voltage is applied to the set of buried electrodes to form a charged region including minority charge carriers over each of the buried electrodes, and to form a p-n junction around each portion of the graphene layer overlying a buried electrode. Charge carriers generated at the p-n junctions are collected by the first upper electrodes and the second upper electrodes, and are subsequently measured by a current measurement device or a voltage measurement device.
Owner:IBM CORP
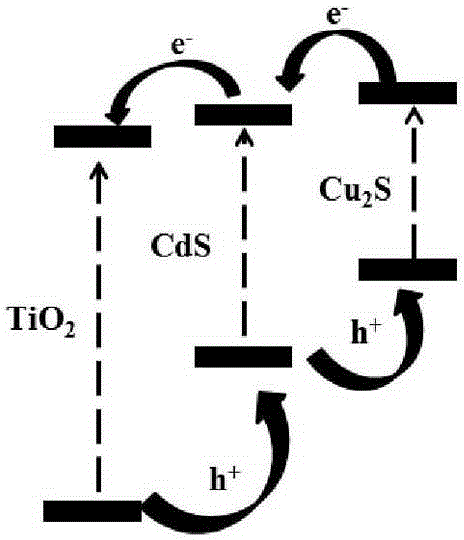
Titanium dioxide composite material and preparation method thereof, photo-anode and application of photo-anode
ActiveCN106548871AEasy to separateImprove transfer efficiencyElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufacturePower flowCuprous sulfide
The invention discloses a titanium dioxide composite material and a preparation method thereof, a photo-anode and an application of the photo-anode. The titanium dioxide composite material comprises a titanium dioxide carrier, cuprous sulfide and cadmium sulfide, wherein the cuprous sulfide and the cadmium sulfide are loaded on the surface of the titanium dioxide carrier. The preparation method comprises loading of the cadmium sulfide and loading of the cuprous sulfide. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the operation process is simple and the loading amount is easy to control; and the prepared titanium dioxide composite material has the advantages of being simple in preparation process, high in photoelectric conversion efficiency, fast in photoresponse, wide in photoresponse degree range, high in corrosion resistance and good in stability, and relatively high photo-generated current can be generated. The photo-anode disclosed by the invention comprises the titanium dioxide composite material, can be used for photoelectric catalysis cracking of water for hydrogen production, and has the advantages of being high in stability, long in service life, high in photoresponse degree, high in photo-generated current, high in photoelectric catalysis cracking capability on water and high in photoelectric conversion efficiency.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Colloid quantum dot infrared focal plane array based on interference enhancement structure and preparation method
ActiveCN110943138AHigh sensitivityLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesLight responsiveLight response
The invention discloses a colloid quantum dot infrared focal plane array based on an interference enhancement structure. The colloid quantum dot infrared focal plane array comprises a quantum dot pixel layer and the interference enhancement structure, the quantum dot pixel layer comprises a common electrode layer, an infrared quantum dot film layer and a semi-transparent counter electrode layer; the interference enhancement structure comprises an optical isolation layer and a reflection electrode layer. The novel colloidal quantum dot is used as a photosensitive material, and has the advantages of high sensitivity and low cost; an interference enhancement structure is added to gather infrared rays with specific wavelengths, so that light response is improved; quick light response is realized, and the response time is less than 20 nanoseconds; colloid quantum dots can be synthesized in a large-scale liquid phase, and the cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:唐鑫
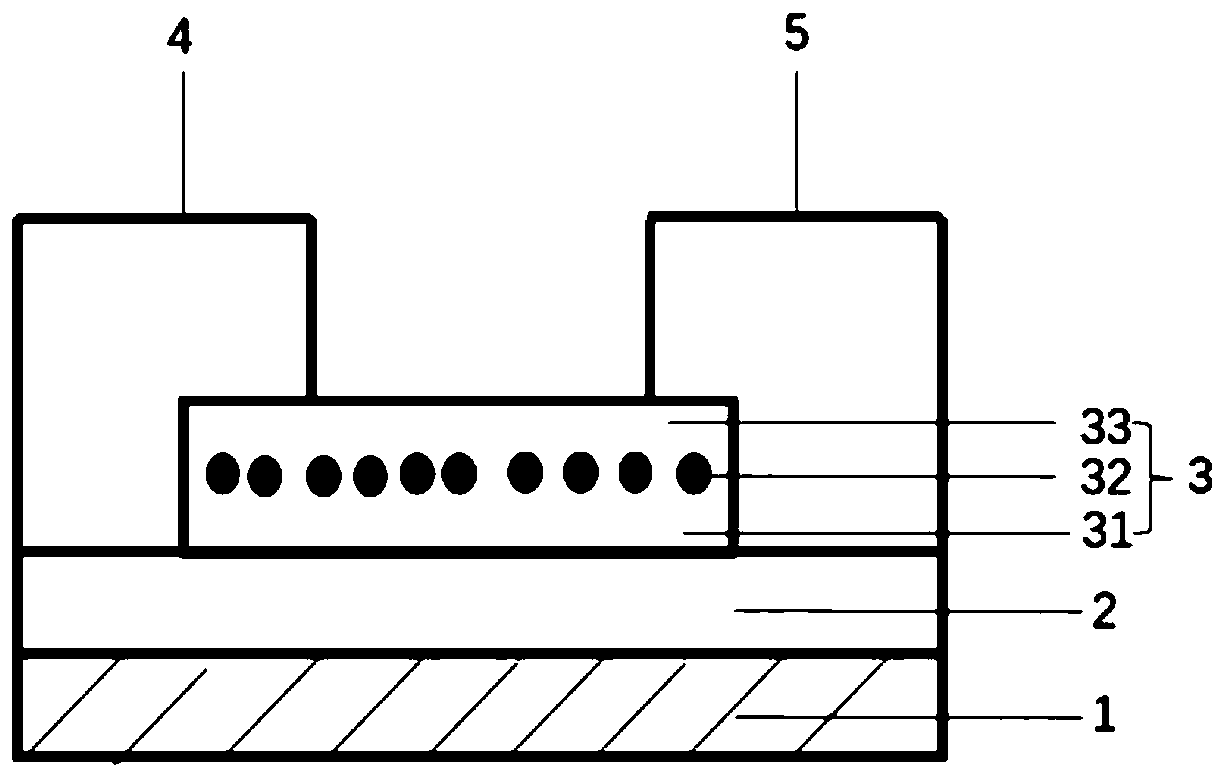
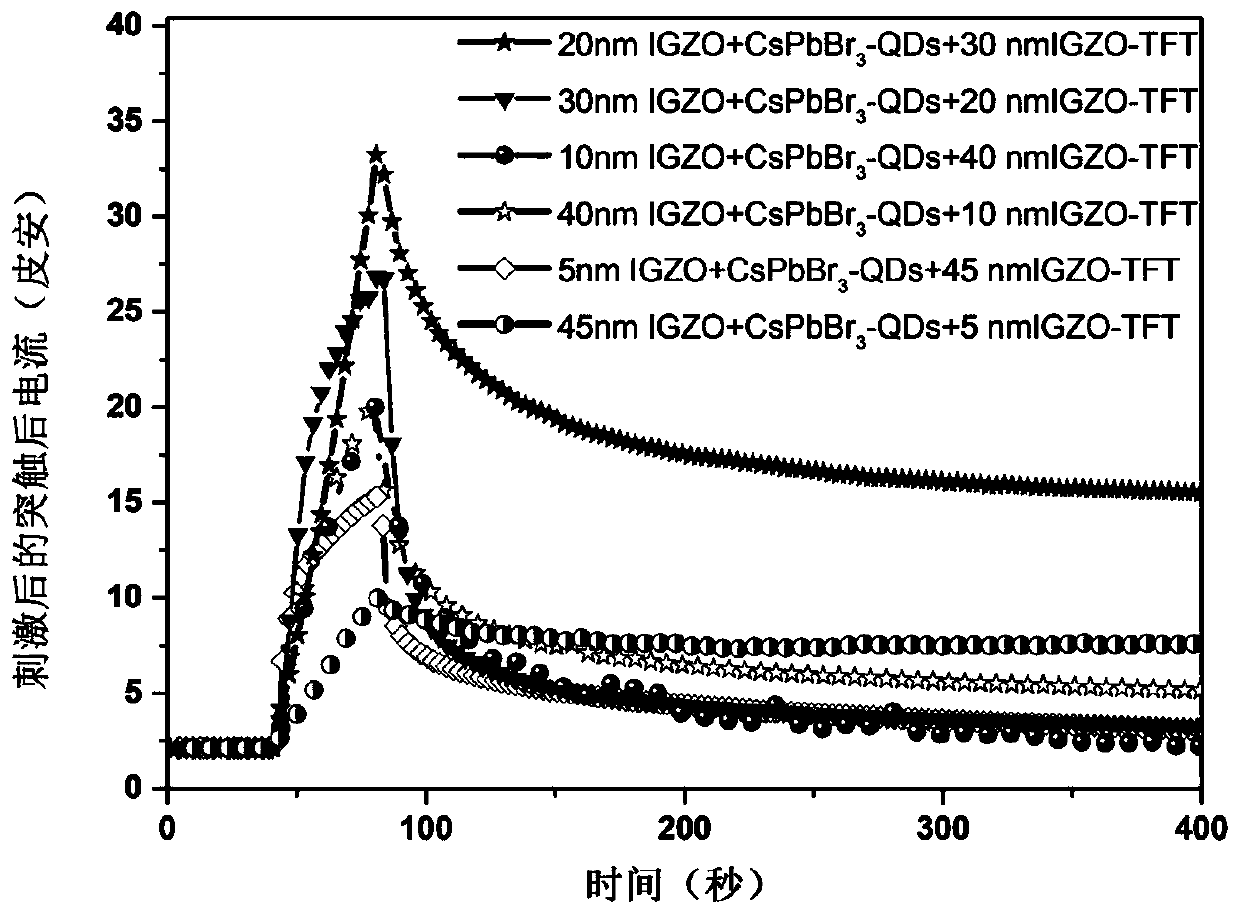
Three-terminal type thin film transistor, preparation method thereof and photosensitive nerve synapse device
InactiveCN111554770AReduce power consumptionEasy to makeFinal product manufacturePhysical realisationOxide thin-film transistorQuantum dot
The invention discloses a three-terminal type thin film transistor, a preparation method thereof and a photosensitive nerve synapse device. The three-terminal type thin film transistor comprises a substrate, a channel, a gate electrode, a source electrode and a drain electrode, wherein the channel is formed by compounding a metal oxide and a quantum dot material, and the quantum dot material is mixed in the metal oxide. The thin film transistor has the characteristics of high visible light response intensity and strong continuous photoconductive effect, so that the response spectrum of the photosensitive nerve synapse is broadened, the use requirements of the photosensitive nerve synapse in the visible light band can be met, and the thin film transistor is more suitable for being used as aphotosensitive nerve synapse device compared with the traditional oxide thin film transistor.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
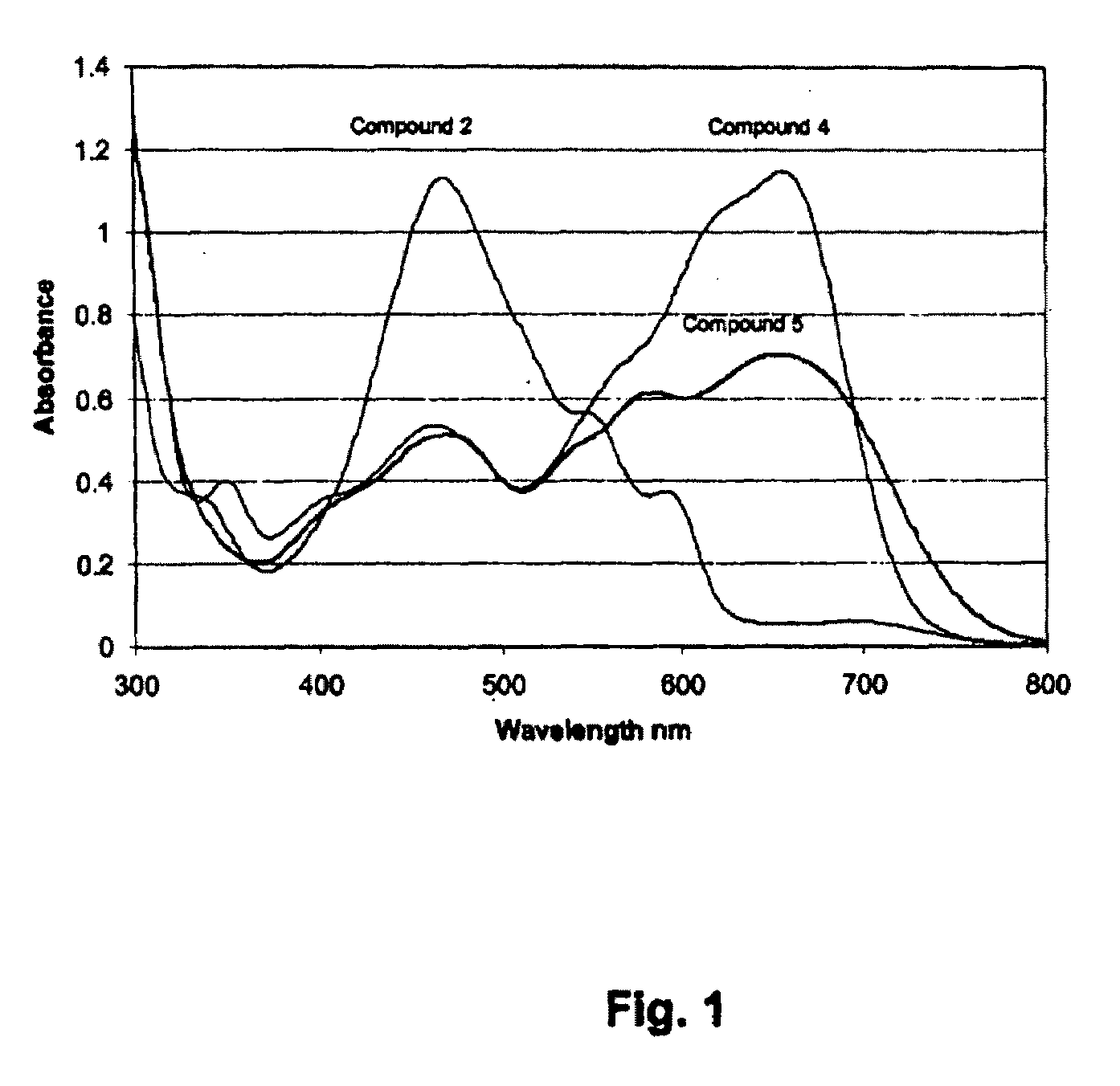
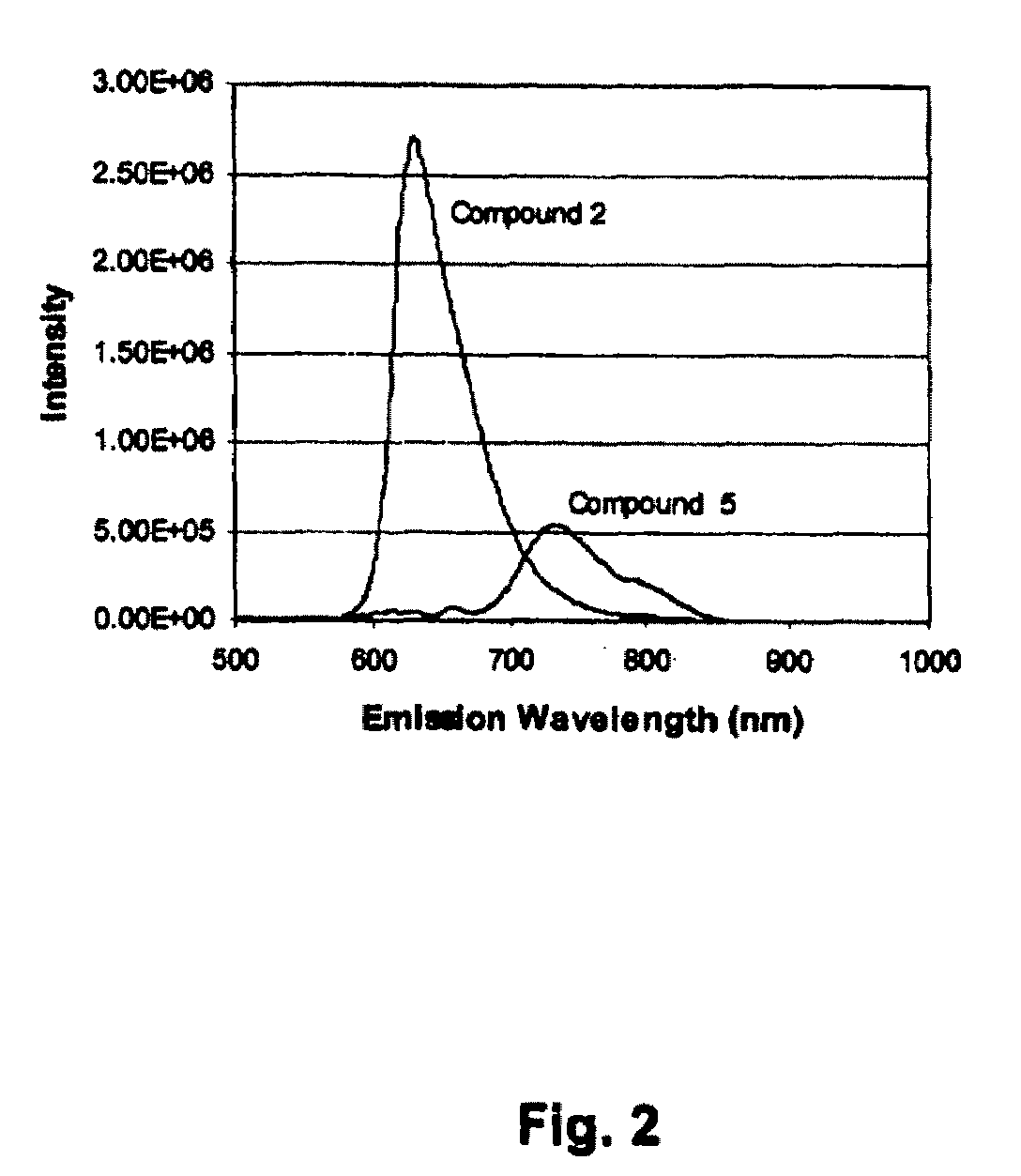
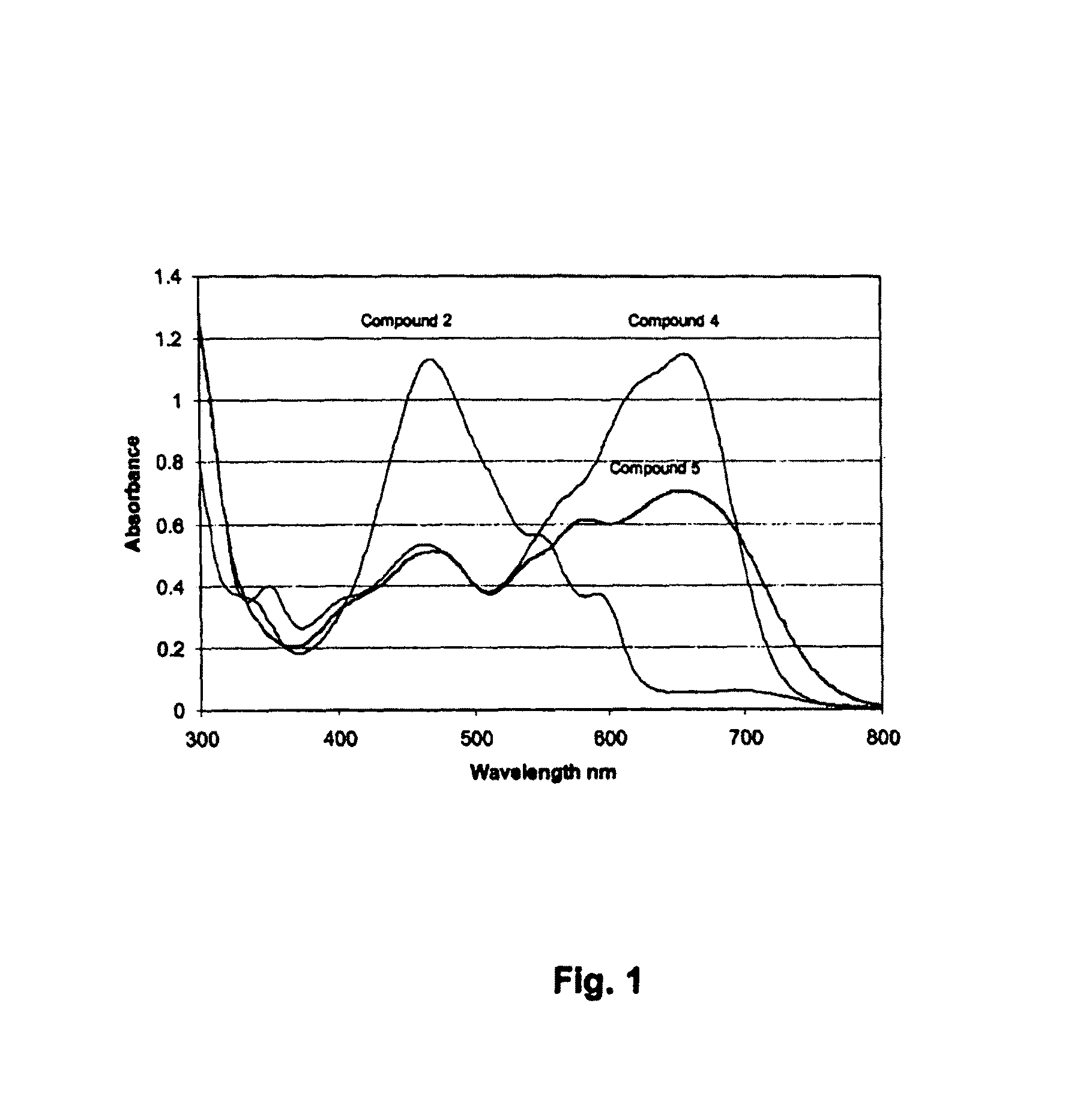
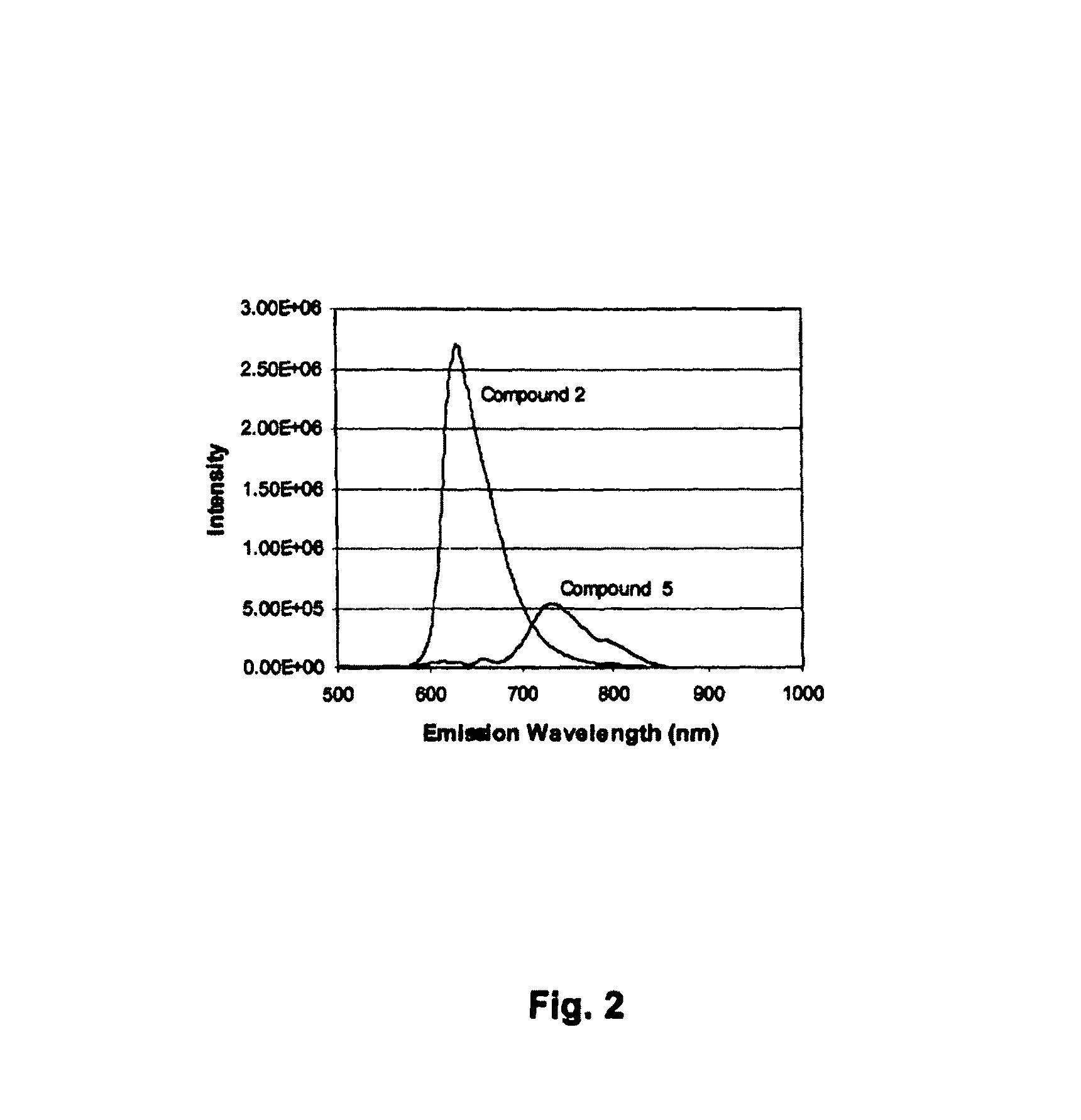
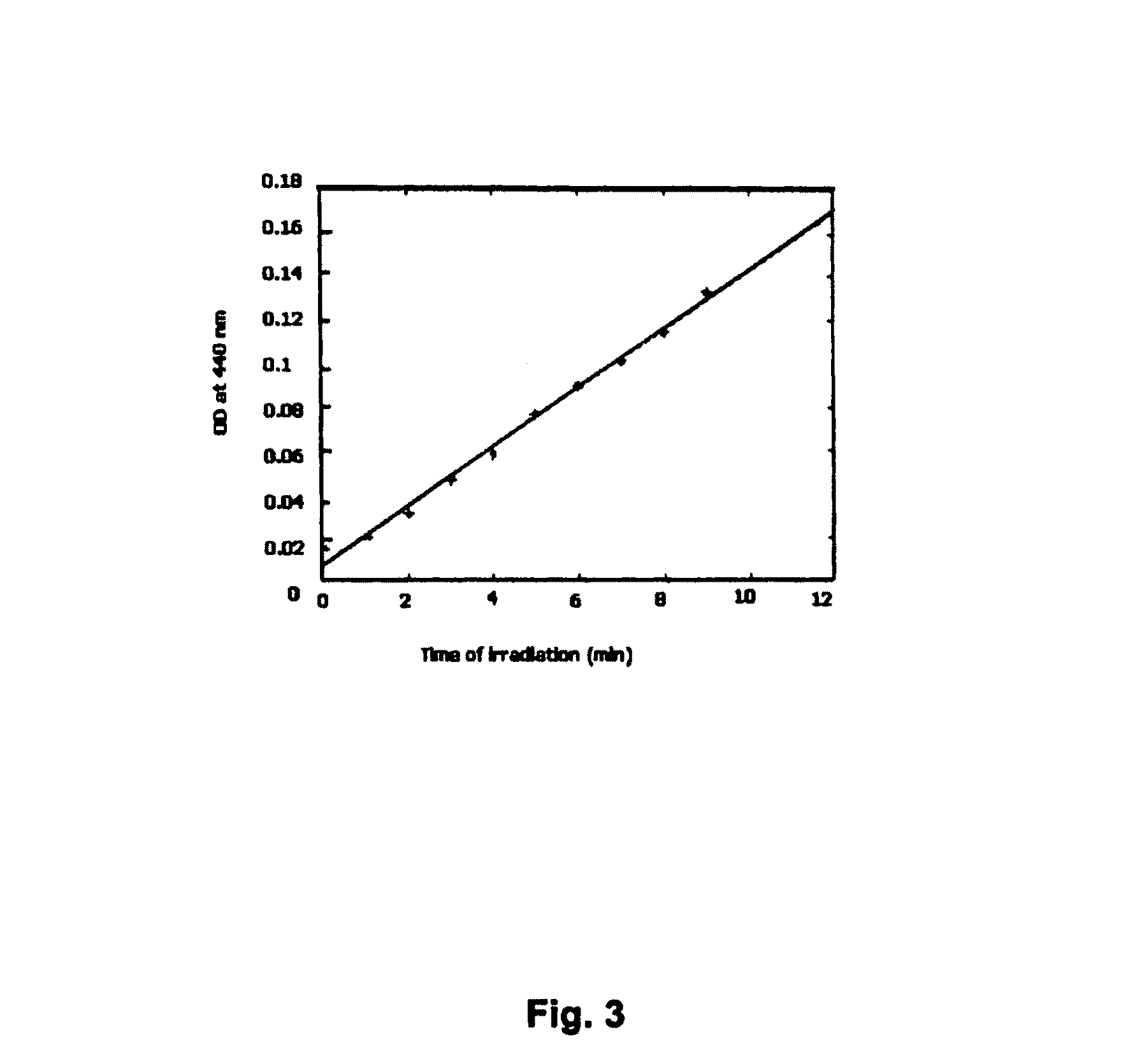
Perylenequinone derivatives and uses thereof
ActiveUS20100047178A1Improve photoresponseHigh activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseasePhotosensitizer
The present invention relates to compounds which are perylenequinone derivatives, their stereoisomers and atropisomers. These compounds can be particularly useful as photosensitizers or sononsensitizers in photodynamic or sonodynamic therapy. The invention also relates to various methods for using these compounds in photodynamic and / or sonodynamic therapy. The compounds also are useful as therapeutic agents for treating various hyperproliferative disorders.
Owner:QUEST PHARMATECH INC
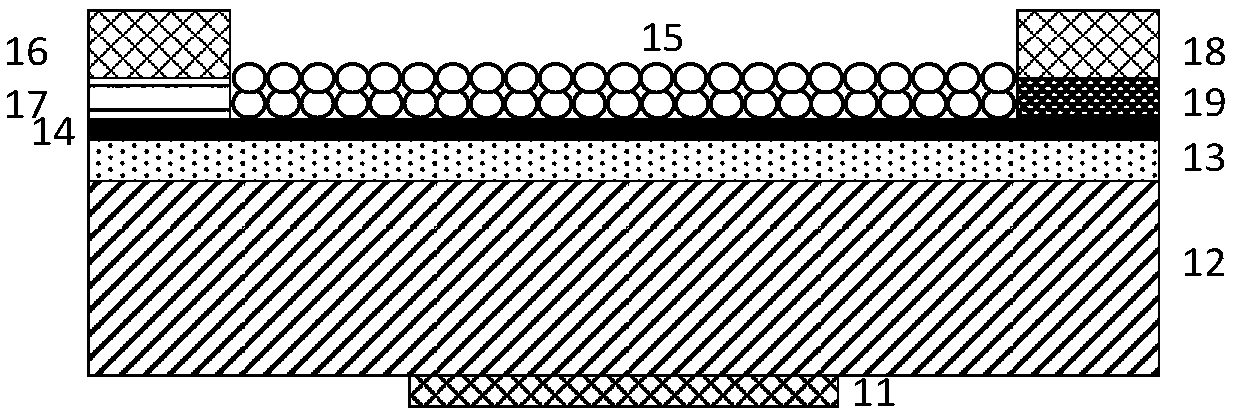
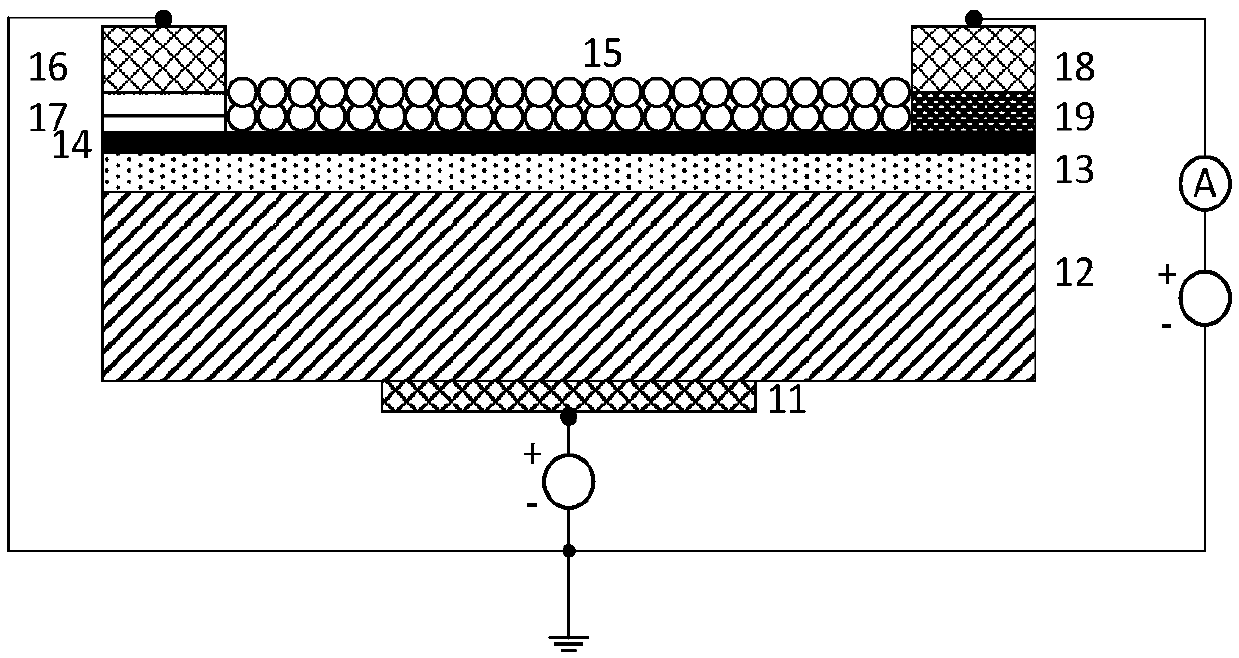
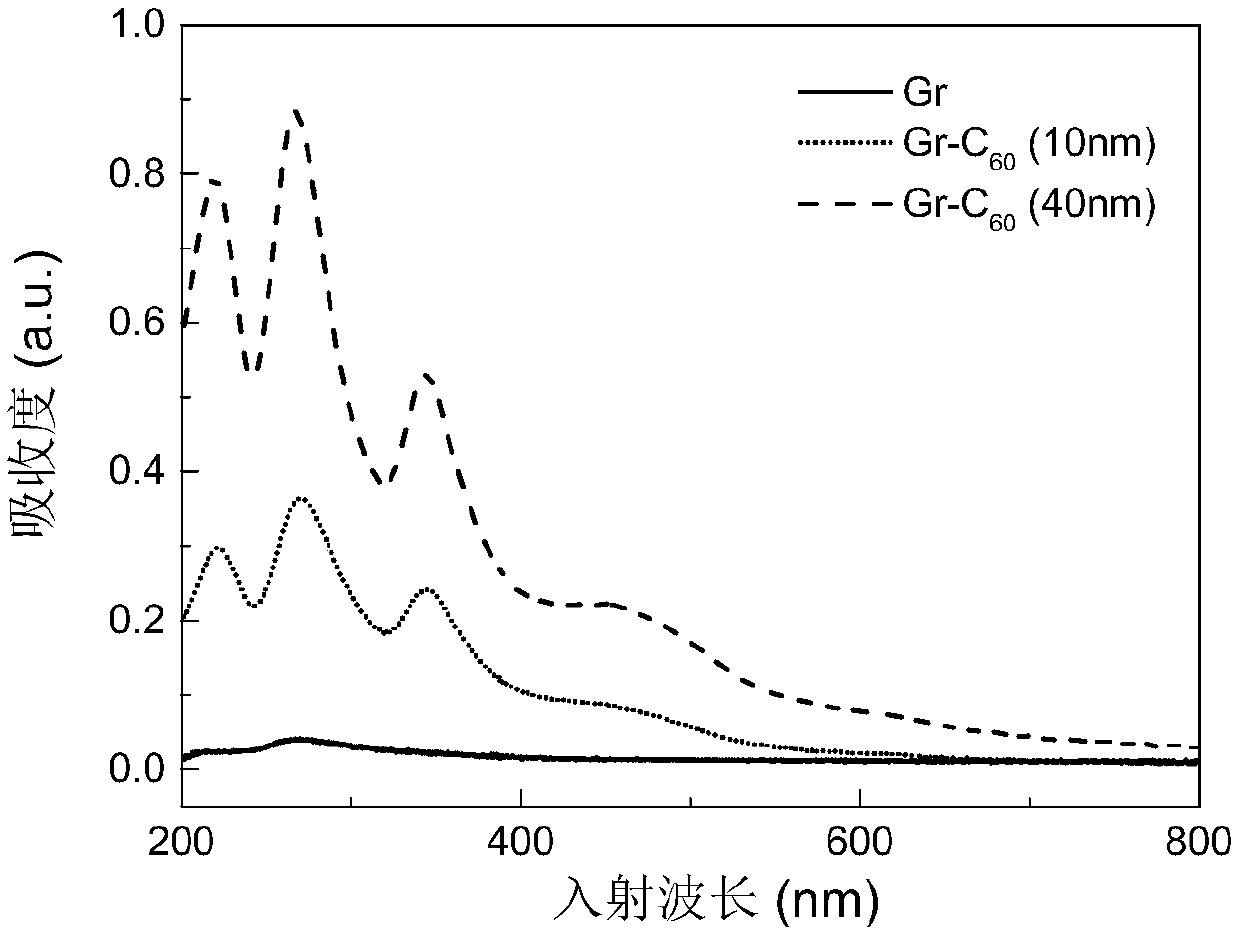
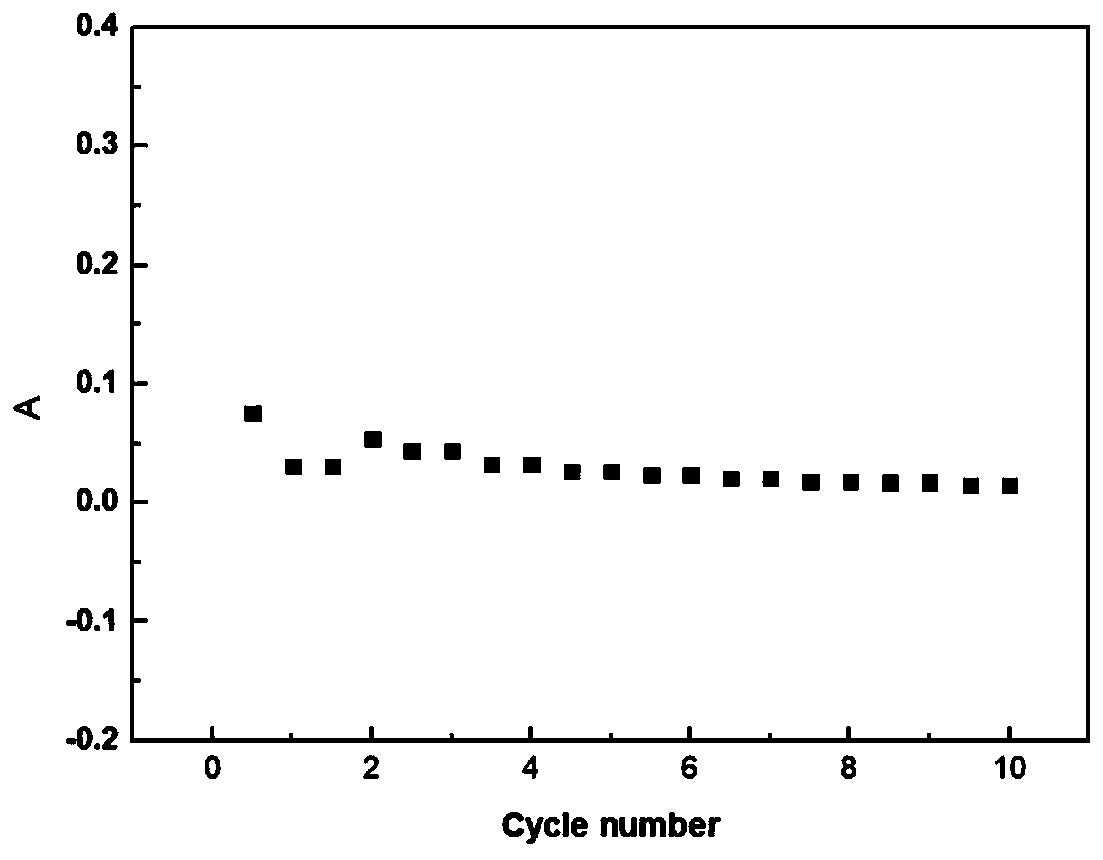
Graphene/C60 composite film ultraviolet detector and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108682697AStrong light absorptionAchieve large area and high uniformitySemiconductor devicesCvd grapheneImage identification
The invention provides an ultraviolet light detecting transistor based on a graphene / C60 composite absorbing layer. The transistor comprises a gate metal layer, a highly doped silicon gate, a gate dielectric layer, and a graphene / C60 composite absorbing layer, wherein the gate metal layer, the highly doped silicon gate, the gate dielectric layer, the graphene / C60 composite absorbing layer are successively arranged from bottom to top. The highly doped silicon gate and the gate dielectric layer simultaneously support the graphene / C60 composite absorbing layer film as the substrate of the whole transistor device. The graphene / C60 composite absorbing layer is composed of a single layer or multiple layers of graphene and the C60 with a certain thickness. The graphene is arranged at the lower end of C60 and is furthermore used as a C60 growth template, wherein the graphene contacts with the gate dielectric layer. Two ends of the graphene layer are respectively provided with a source electrode and a drain electrode. The graphene interacts with the C60 through a Van der Waals force, thereby forming a hetero junction transistor with an ultraviolet absorbing characteristic. Array integrationcan be performed on a plurality of ultraviolet light detecting transistors. The invention provides a specific plan of the array system for spectrum detection analysis and image identification.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Indeno-condensed naphtho-spirooxazine photochromic compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111440193AFade fastFast fadingOrganic chemistryTenebresent compositionsPolymer scienceHalogen
The invention belongs to the field of organic photochromic materials, and particularly discloses an indeno-condensed naphtho-spirooxazine photochromic compound, which has a structure shown as a formula I. In the formula I, R1 is hydrogen, straight-chain or branched-chain alkyl, straight-chain or branched-chain alkoxy, halogen or nitro; r2 and R3 are straight-chain or branched-chain alkyl with thecarbon atom number being 1-6. The invention further provides a synthesis method of the compound. The indeno-condensed naphtho-spirooxazine photochromic compound disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of fast photoresponse, fast fading, no ground color, good fatigue resistance and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
MgZnO/N-propyl bromide (NPB) ultraviolet light detector and producing method thereof
InactiveCN102623543ASimple preparation processLow costFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesUltraviolet lightsEvaporation
An MgZnO / NPB ultraviolet light detector and a producing method thereof belong to the field of optoelectronic information, are mainly used for ultraviolet light detectors which generate low bias voltage and high response and solve the problems of inorganic wide band-gap semiconductor p-type doping and low organic electronic mobility. The detector is composed of a single phase MgxZn1-xO film which is grown on a quartz indium tin oxide (ITO) substrate, a NPB film, an LiF film and an electrode. The producing method thereof comprises that the quartz ITO substrate is pretreated in a molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) growth chamber; the MgxZn1-xO film with the thickness of 200-300nm is grown at the growth temperature of 400-500 DEG C inside the MBE growth chamber, and x=0.1-0.4; then thermal evaporation is conducted, and the NPB film with the thickness of 50-120nm is grown on the MgxZn1-xO film; the LiF electrode modification layer with the thickness of 0.5-2nm is grown on the NPB film; and the electrode is produced on the LiF electrode modification layer, so that the MgZnO / NPB ultraviolet light detector having a quartz ITO / MgxZn1-xO / NPB / LiF / electrode structure is produced.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Small-pixel infrared focal plane detector based on metasurface lens
InactiveCN113013268ASmall sizeImprove photoresponseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPixel densityLight spot
The invention discloses a small-pixel infrared focal plane detector based on a metasurface lens. The small-pixel infrared focal plane detector based on the metasurface lens comprises an infrared focal plane detector body and the metasurface lens formed at a substrate. The metasurface lens is composed of a plurality of small cylinders with sub-wavelength scales, the positions and the diameters of the small cylinders are arranged according to a phase rule, and the metasurface can modulate wavefront of incident light so that the incident light can be focused on an absorption layer of a detector pixel. Compared with a traditional infrared focal plane detector, the infrared focal plane detector has the advantages that focusing light spots in the sub-wavelength magnitude can be achieved, the pixel size can be reduced to the wavelength magnitude, and development of a planar focal plane device towards smaller pixels and higher pixel density is facilitated. Meanwhile, under the condition that the light response of the device is not changed or improved, the dark current of the device is reduced, the signal-to-noise ratio is improved, and photoelectric crosstalk between pixels is inhibited.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical sensor, preparation method thereof and display panel
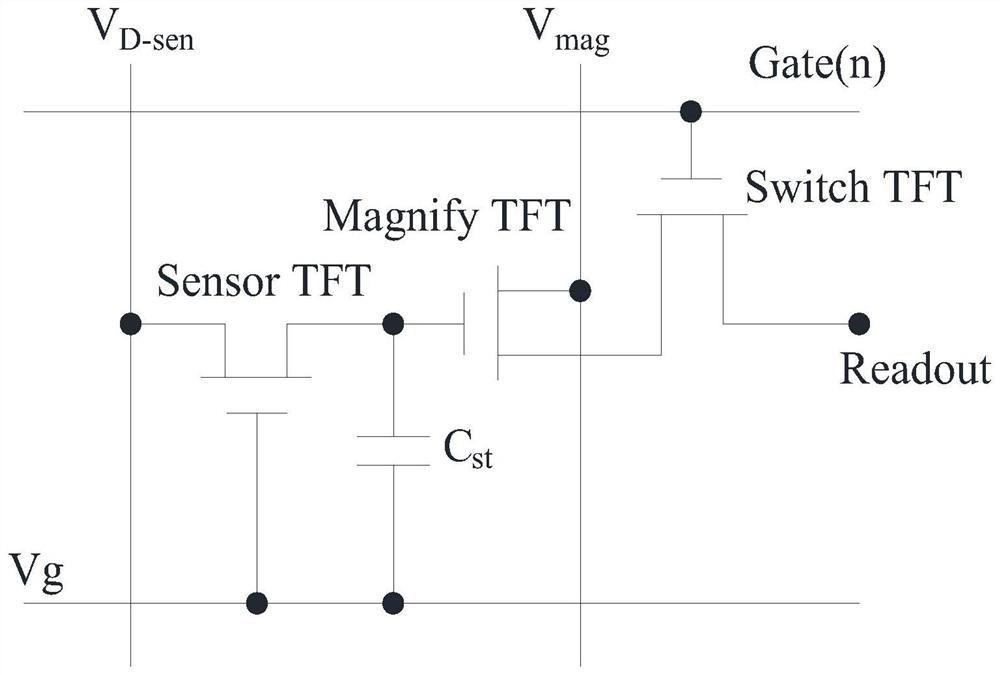
ActiveCN112670303ALimit detectionLimit SNRFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsAmorphous silicon
The invention provides an optical sensor, a manufacturing method thereof and a display panel. The optical sensor comprises a plurality of optical sensor matrix units, and each optical sensor matrix unit comprises an induction TFT, an amplification TFT, a switch TFT and a storage capacitor, wherein an active layer of the induction TFT is amorphous silicon, an active layer of the amplification TFT is an oxide semiconductor, the induction TFT is connected with the amplification TFT, the amplification TFT is connected with the switch TFT, the switch TFT controls reading of electric signals detected by the induction TFT and amplified by the amplifying TFT, and when the amplification TFT is in an on state, the electric signals are transmitted to the signal reading circuit. A 3T1C architecture is adopted as an optical sensor matrix unit to replace a traditional 2T1C architecture, detection of weak light by an optical sensor can be achieved, the optical response of the optical sensor is effectively improved, and the optical sensor has high optical response and a high signal-to-noise ratio; the preparation of the induction TFT and the amplification TFT shares a plurality of yellow light processes, so the cost is reduced, and the advantages of large area and high uniformity of aSi can be fully exerted.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Tunnel compensation multiple-active-region infrared detector
InactiveCN1953214AReduce power consumptionReduce noiseSemiconductor devicesLow noiseSemiconductor materials
The invention relates to a tunnel compensate active infrared detector. Wherein, it grows lower contact layer on substrate, grows multi-quantum well, upper contact layer, prepares table and electrode; the invention is characterized in that said multi-quantum well comprises at least one repeat structure formed by at least one basic unit; said basic unit comprises buffer barrier, N-type infrared adsorption area and P-type barrier layer, while they are doped to form tunnel connector; the thickness of buffer barrier is 30-50nm; its forbidden band is wider than the forbidden band of semi-conductor of N-type infrared adsorption area, while bottom of conductor band is higher than the bottom of N-type infrared adsorption area. The invention has high light response, while its light current will increase along the increase of infrared adsorption area, with low hidden current, low power and low noise.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Mid-far infrared avalanche photodetector
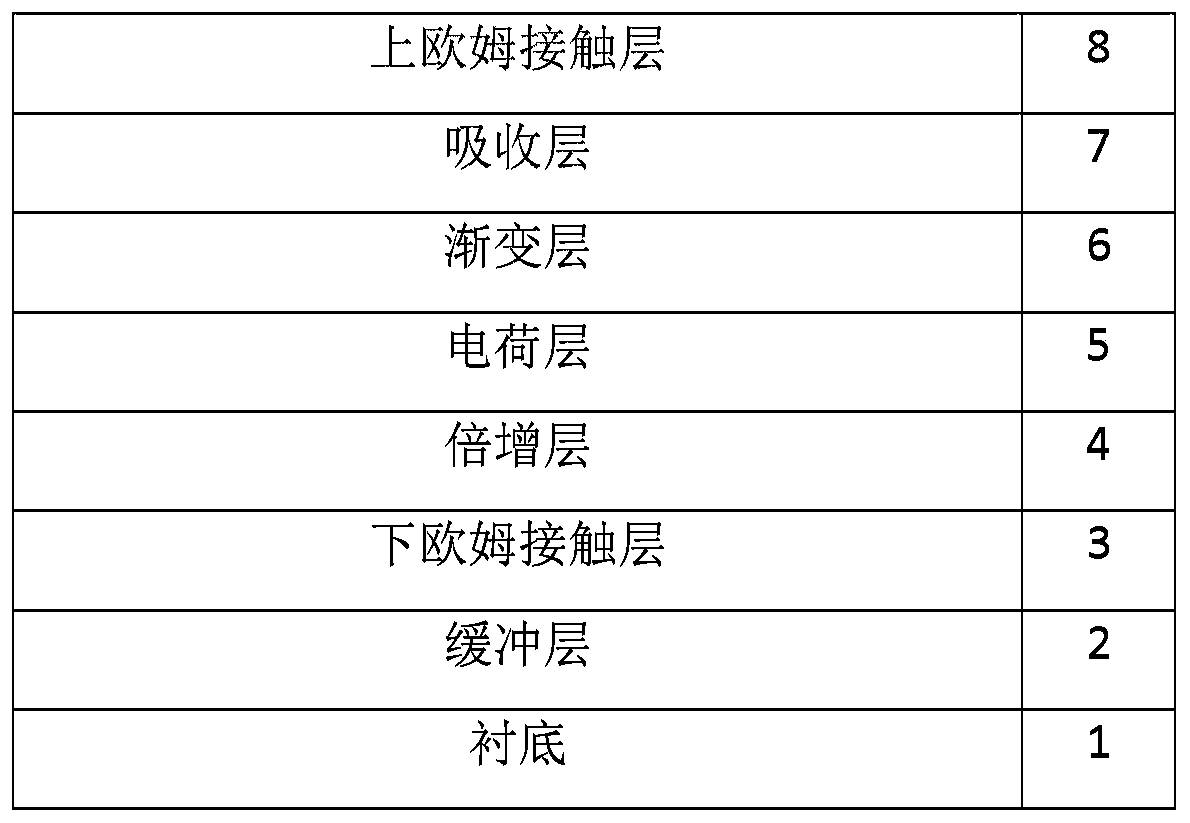
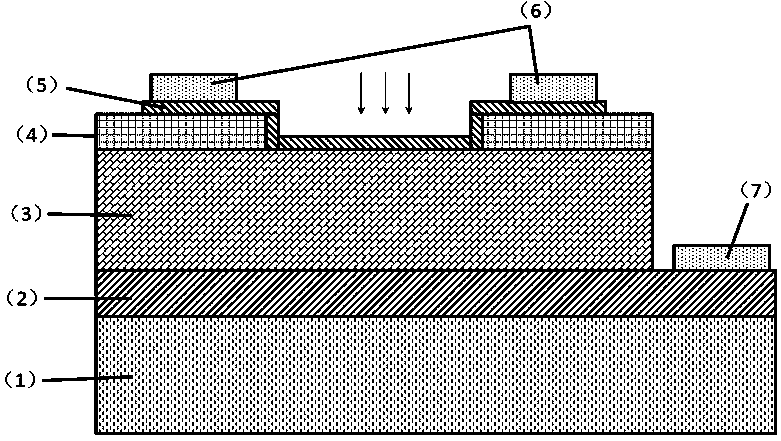
InactiveCN111540797AMature technologyImprove compatibilitySemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsFar-red
The invention discloses a mid-far infrared avalanche photodetector which comprises a substrate, a buffer layer, a lower ohmic contact layer, a multiplication layer, a charge layer, a gradient layer, an absorption layer and an upper ohmic contact layer which are sequentially connected from bottom to top, and the doping type of the substrate and the buffer layer is n type. Or the mid-far infrared avalanche photodetector comprises the substrate, the buffer layer, a second ohmic contact layer, the absorption layer, the gradient layer, the charge layer, the multiplication layer and a first ohmic contact layer which are sequentially connected from bottom to top, and the doping type of the substrate and the buffer layer is p type, wherein the multiplication layer is made of an AlAsxSb1-x material, x is greater than or equal to 0.12 and less than or equal to 0.18, the gradient layer is of a plurality of (InAs)m / (AlAs0.15Sb0.85)n quantum well structures or an InyAl1-yAszSb1-z material, and thedetection wavelength of the absorption layer is a middle and far infrared band. The mid-far infrared avalanche photodetector provided by the invention can block dark current and reduce noise, does notneed a cooling device, improves the working temperature of the device, reduces the cost, and is convenient to use.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molybdenum disulfide-based visible near-infrared InGaAs detector and fabrication method thereof
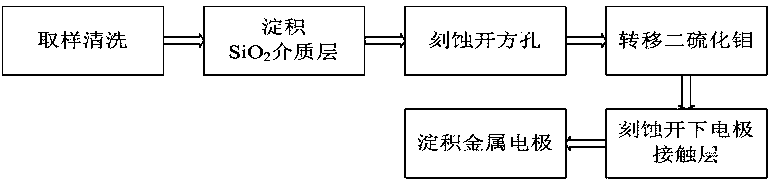
InactiveCN108831951ARealize the combinationRealize spectral detectionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesVisible near infraredContact layer
The invention belongs to the technical field of detectors, and particularly relates to a molybdenum disulfide-based visible near-infrared InGaAs detector and a fabrication method thereof. The detectorstructure comprises a substrate material, wherein indium phosphide is used as the substrate material, an InP contact layer, an InGaAs absorption layer and a silicon oxide dielectric layer are sequentially grown on the substrate, a square hole is formed in the center of the silicon oxide dielectric layer, a molybdenum disulfide layer is transferred onto the silicon oxide dielectric layer, the square hole of the silicon oxide dielectric layer is filled with the molybdenum disulfide layer, Schottky contact is formed between the molybdenum disulfide layer and the InGaAs absorption layer, an uppermetal electrode is grown on a contact region of the molybdenum disulfide layer and the silicon oxide dielectric layer, and a lower metal electrode is grown on one side of the InP contact layer. By the InGaAs detector, wide spectrum detection within a range from near infrared light to visible light can be achieved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Deep ultraviolet photodetector for solar blind area based on organic field effect transistor
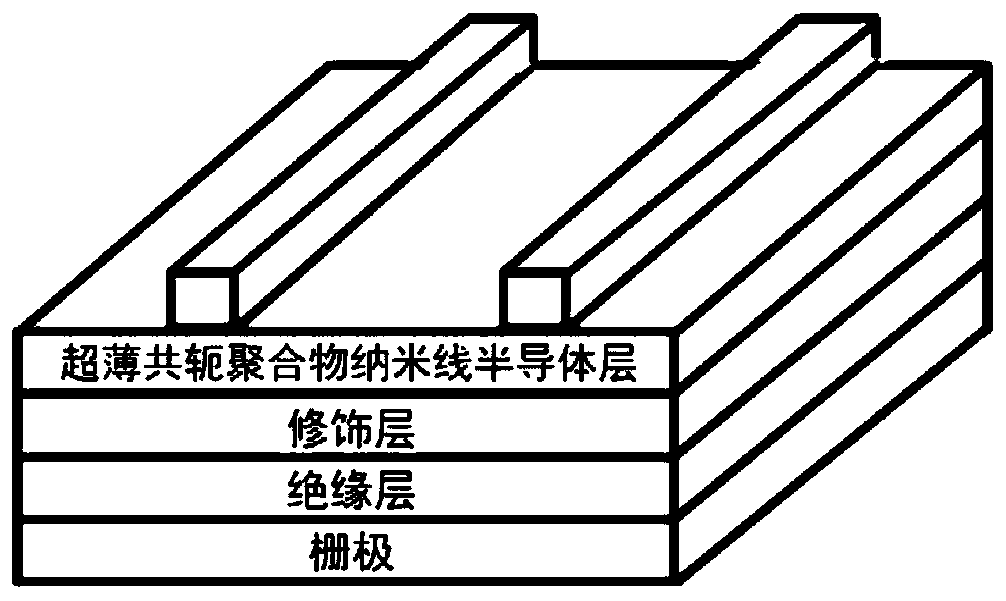
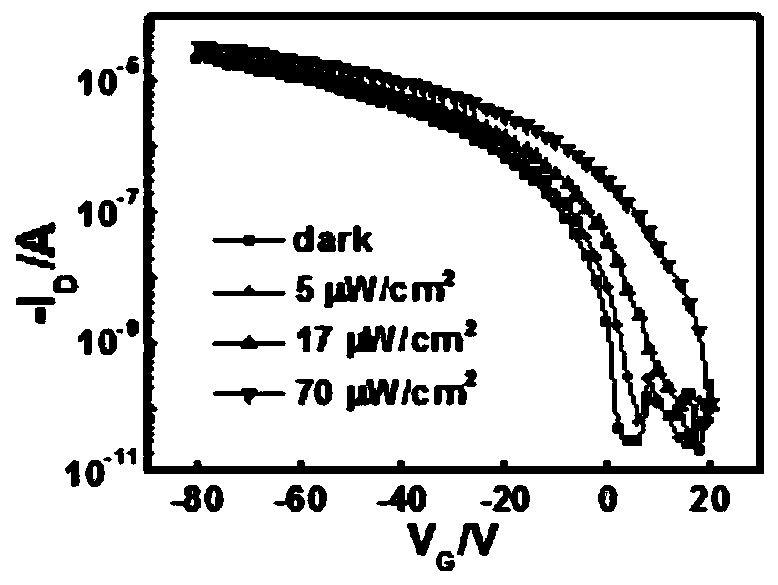
ActiveCN109888102AImprove photoresponseGood photoresponse performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum efficiencySemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a deep ultraviolet photodetector for a solar blind area based on an organic field effect transistor. An organic field effect transistor semiconductor layer of the deep ultraviolet photodetector is formed by block conjugated polymer nanowires; a block copolymer semiconductor material and a polymer insulating material are respectively dissolved in a solvent and then are mixedto form a blended solution; and block copolymer semiconductor nanowires with different densities are obtained by controlling a mass ratio of the block copolymer semiconductor material to the polymerinsulating material. The block copolymer semiconductor nanowires disclosed by the invention are used as the semiconductor layer of the photodetector based on the organic field effect transistor, so that the optical response to a deep ultraviolet region can be enhanced. According to the deep ultraviolet photodetector, a conjugated polymer is used for responding to deep ultraviolet light of the solar blind area for the first time, and the high-performance deep ultraviolet photodetector for the solar blind area based on the organic field effect transistor is prepared; good light selectivity and light responsiveness are achieved in the deep ultraviolet region, the light response reaches 120 A / W, and the external quantum efficiency is up to 50000%.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Nano-micelles activated by short-time near-infrared illumination for rapidly releasing medicines
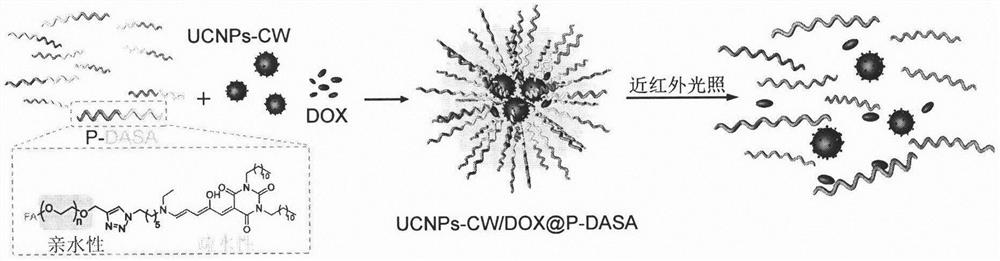
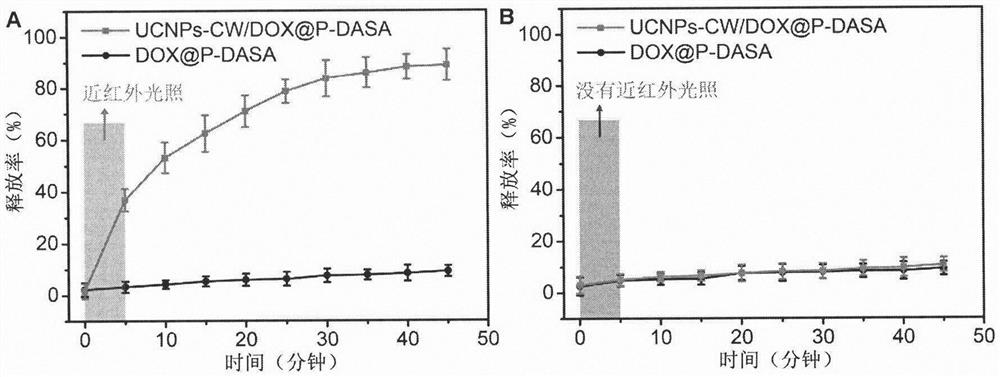
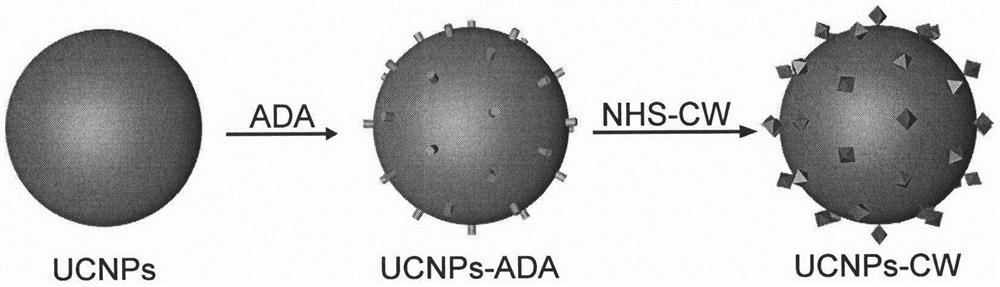
ActiveCN112451485AImprove stabilityImprove photoresponseOrganic active ingredientsDrug photocleavageCancers diagnosisReceptor
The invention relates to a preparation method of nano-micelles with a short-time near-infrared illumination response and use of the nano-micelles in rapid medicine release. The method uses an amphiphilic polymer chain P-DASA formed by utilizing hydrophilic polyethylene glycol and a hydrophobic donor receptor Stenhouse adduct (DASA), and the nano-micelles coated with Er <3+> doped up-conversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and an anti-cancer medicine adriamycin are prepared. Under a near-infrared irradiation, green light (541 nm) emitted by the UCNPs promotes the hydrophobic DASA to be converted intohydrophilicity, micelle disintegration is caused, adriamycin is released, and after a stimulation of the illumination (808 nm, 2 W / cm<2>) for only 5 min, a release rate of the medicine reaches 80% orabove within 30 min. The invention provides a near-infrared light-controlled medicine release system activated by short-time illumination and the near-infrared light-controlled medicine release systemhas important significance in clinical use and development of up-conversion nano materials in the fields of medicine carrying and accurate cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
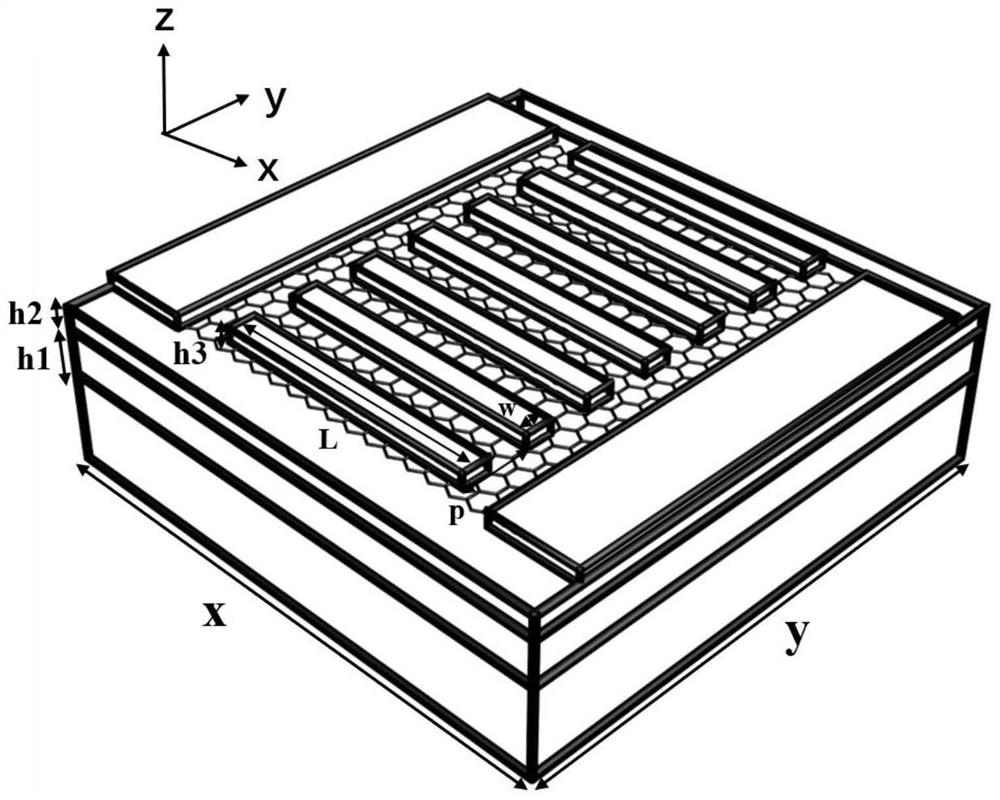
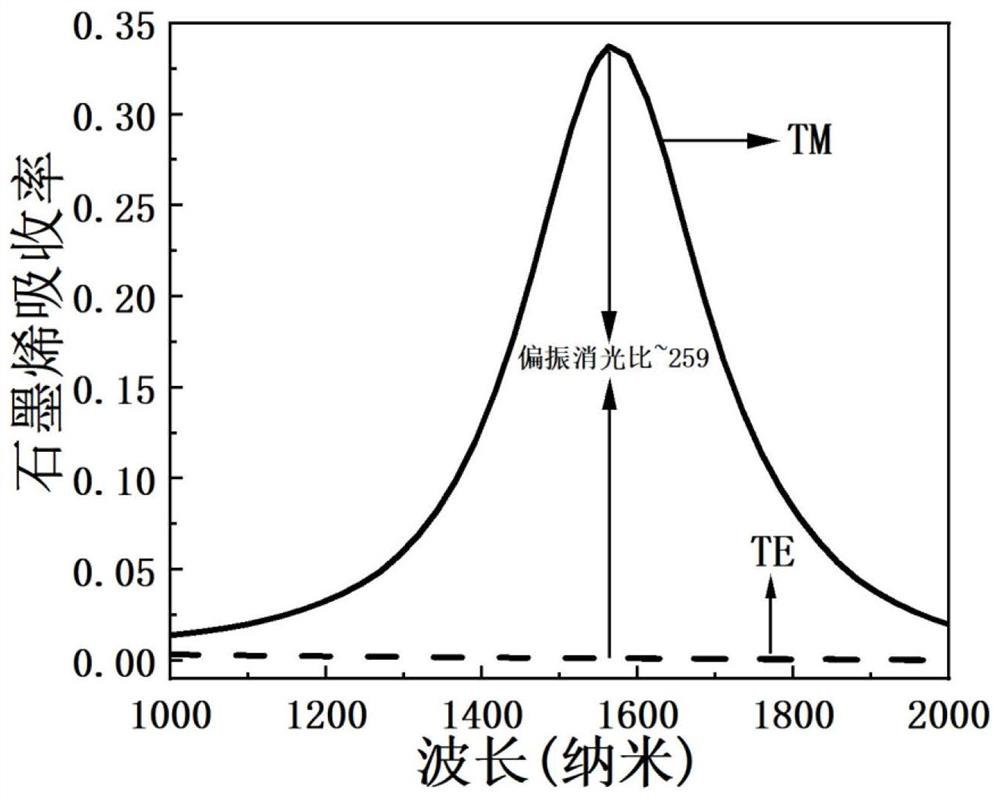
Anisotropic plasmon resonant cavity graphene polarization detector and design method
InactiveCN112504459APromote absorptionImprove photoresponseLight polarisation measurementWaveguide modeParticle physics
The invention discloses an anisotropic plasmon resonant cavity graphene polarization detector and a design method. The anisotropic plasmon resonant cavity graphene polarization detector structurally comprises a substrate material layer, a metal reflecting layer, a dielectric spacer layer, a graphene layer and a metal bar grid layer. The polarization detector is based on a plasmon resonant cavity structure, a plasmon waveguide mode is formed between a top metal surface and a bottom metal surface, the cavity length of a resonant cavity is defined by a top metal boundary, and when the wavelengthand the cavity length meet the interference phase length condition, the mode reaches a resonance state, and a local strong light field of a deep sub-wavelength scale is realized. Due to anisotropy ofthe metal strip structure, the mode can only be excited by incident light with the polarization direction perpendicular to the metal strip grid, and light absorption and light response of graphene canbe improved; most of incident light with the polarization direction parallel to the metal bar grid is reflected, absorption and photoresponse of graphene cannot be effectively excited, and thereforethe high polarization extinction ratio and photoresponse enhancement of the selected polarization state are achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bismuth-tungstate-modified antimony-doped stannic oxide compound photoelectrocatalysis electrode, preparing method and application
ActiveCN109772295AImprove electrocatalytic performanceImprove photoresponseWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsTin dioxideTungstate
The invention relates to a bismuth-tungstate-modified antimony-doped stannic oxide compound photoelectrocatalysis electrode, a preparing method and application, and belongs to the field of photoelectrocatalysis. The compound photoelectrocatalysis electrode is an electrode composed of bismuth tungstate and antimony-doped stannic oxide, wherein the mole ratio of the stannic oxide to the bismuth tungstate is 9:(0.1-2). The preparing method of the bismuth-tungstate-modified antimony-doped stannic oxide compound photoelectrocatalysis electrode comprises the steps of adopting a hydrothermal synthesis method for synthesizing bismuth tungstate powder, after high-temperature treatment, adding bismuth tungstate when tin-antimony sol gel is prepared, and adopting a sol gel coating thermal decomposition method for preparing the compound photoelectrocatalysis electrode. It is shown through photoelectric property experiments that the compound photoelectrocatalysis electrode has a higher catalytic activity and photoelectric current relative to the antimony-doped stannic oxide electrode, and has a potential application prospect in the field of solar energy utilization and wastewater treatment.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-solubility photochromic compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113603667AImprove solubilityImprove photoresponseOrganic chemistryTenebresent compositionsMorpholineStructural formula
The invention relates to a high-solubility photochromic compound and a preparation method thereof. The high-solubility photochromic compound has a structure as shown in a formula I. In the formula, R1, R2, R3 and R4 are the same or different and independently represent hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, C1-C6 alkyl alcohol, halogen, trifluoromethyl, phenyl, morpholine, piperidine or indole, R5 represents an alkyl group of C1 to C6, an alkoxy group of C1 to C6 or an alkyl alcohol of C1 to C6. R < 6 >, R < 7 > and R < 8 > are the same or different, at least one of theR < 6 >, R < 7 > and R < 8 > is-O-(CH2CH2O) m-Z, and the rest of theR < 6 >, R < 7 > and R < 8 > is hydrogen, C1-C6 alkyl, C1-C6 alkoxy, halogen, trifluoromethyl, phenyl, morpholine, piperidine or indole; m represents an integer of 0-6; z represents hydrogen or-(CH2) p-CH3; and p represents an integer of 0-6. The invention also provides a preparation method of the compound, and the prepared compound shows excellent compatibility in an organic solvent system or a polymer system, has the characteristics of rapid photoresponse, fast fading rate, good fatigue resistance and the like, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UVOS TECH CO LTD
Two-dimensional material heterojunction photoelectric detector with surface plasmon and preparation method thereof
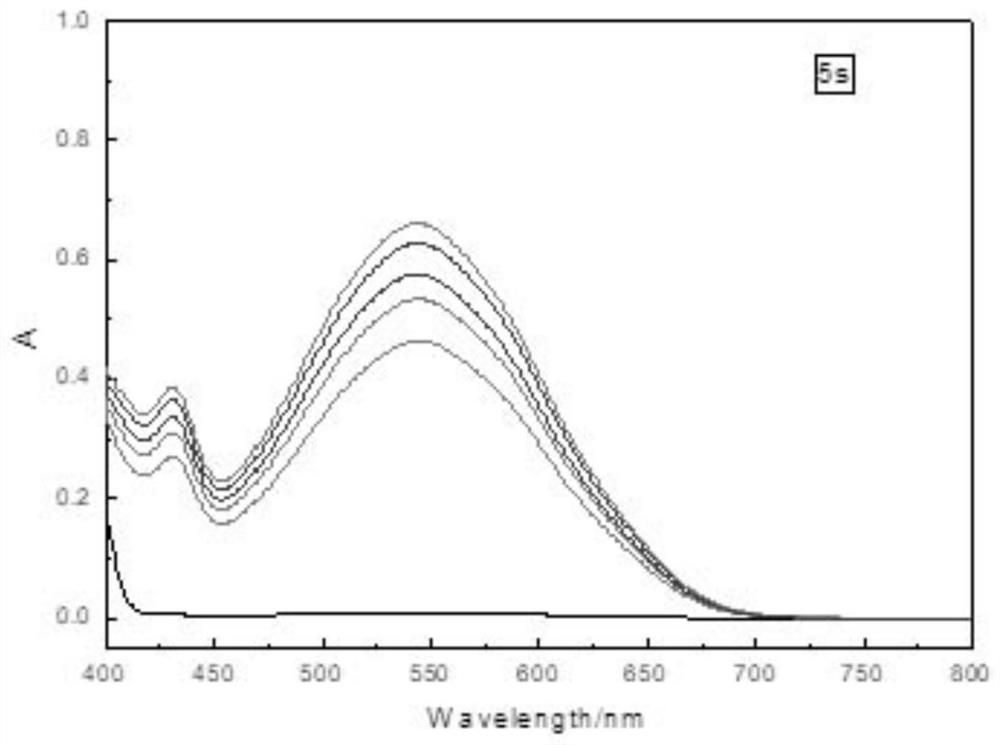
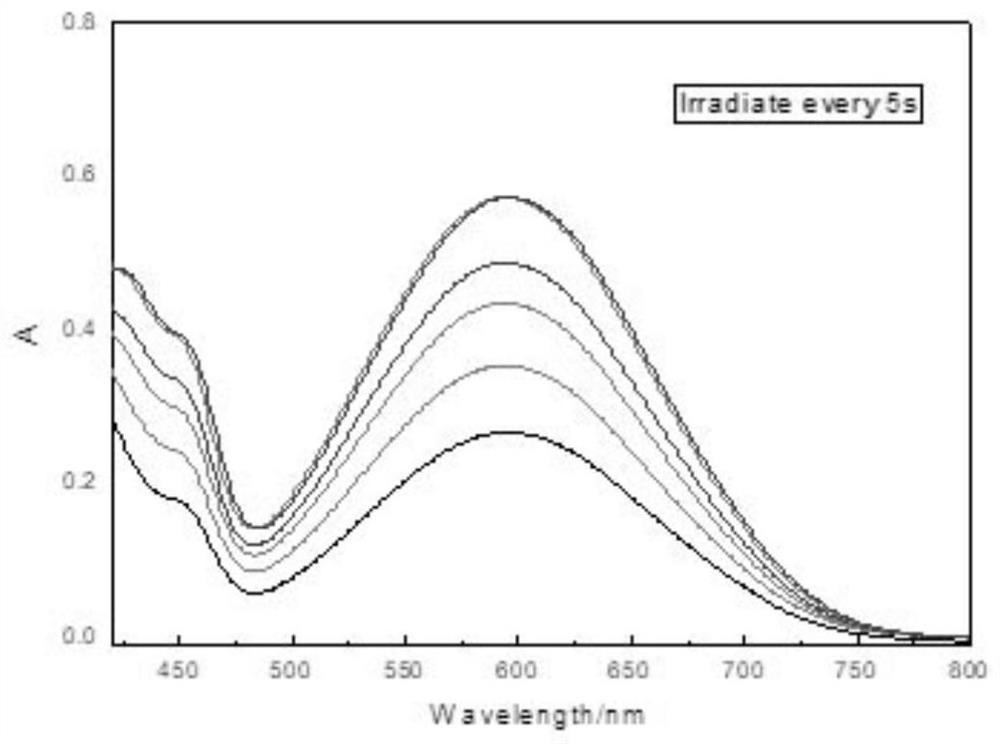
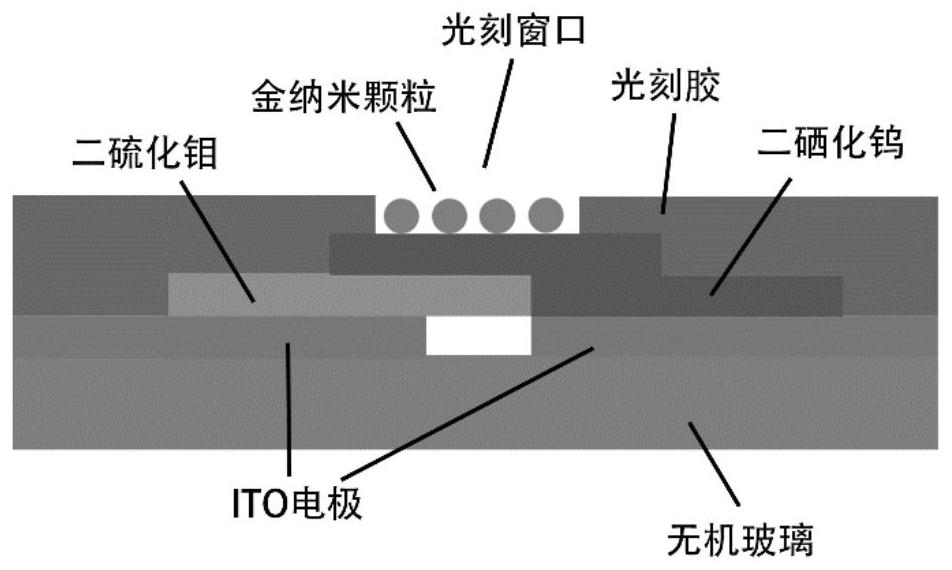
ActiveCN113410317APromote absorptionImprove photoresponseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionLight responsive
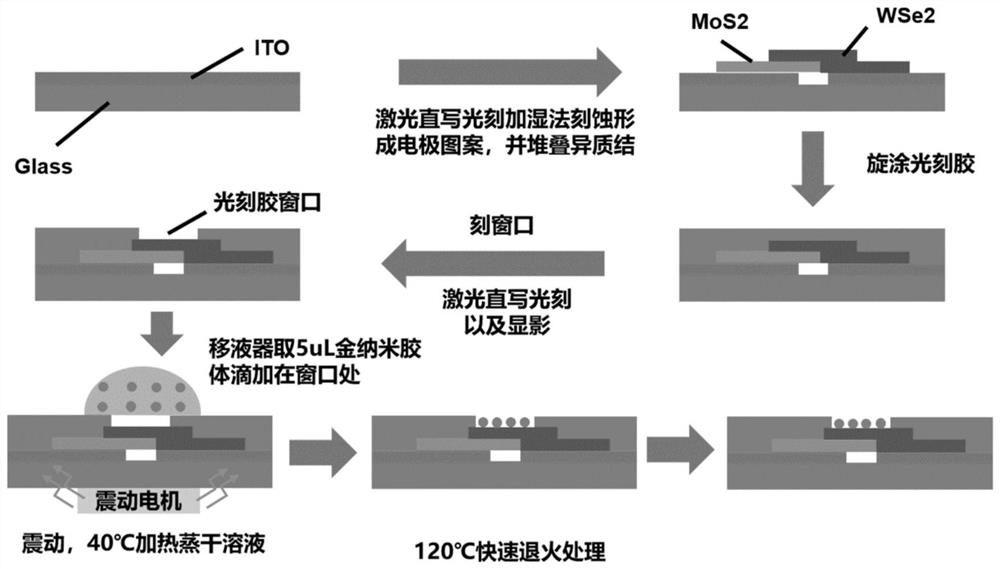
The invention relates to a tungsten diselenide / molybdenum disulfide heterojunction photoelectric detector with surface plasmon and a preparation method of the tungsten diselenide / molybdenum disulfide heterojunction photoelectric detector. The tungsten diselenide / molybdenum disulfide heterojunction photoelectric detector comprises an ITO electrode, a heterojunction and gold nanoparticles, wherein the heterojunction is formed by combining two-dimensional tungsten diselenide and molybdenum disulfide through Van der Waals force and by introducing the surface plasmon. According to the photoelectric detector provided by the invention, the light absorption and the light response of the two-dimensional tungsten diselenide / molybdenum disulfide heterojunction are enhanced by utilizing the absorption effect of surface plasmons on photon energy. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: accurately etching a window with a submicro-size specific pattern, such as a rectangle or a circle, on photoresist in a heterojunction region through a laser direct writing photoetching technology, and dropwise adding a nano-particle solution, such as a gold nano-particle solution or a silver nano-particle solution, in a window region by using a pipettor; introducing the surface plasmon on the heterojunction region in a manner of enriching the gold nanoparticles in a rectangular window in a vibration and heating environment. The structure of the two-dimensional material heterojunction photoelectric detector with the surface plasmon and the preparation method of the two-dimensional material heterojunction photoelectric detector have the advantages of being novel and simple.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
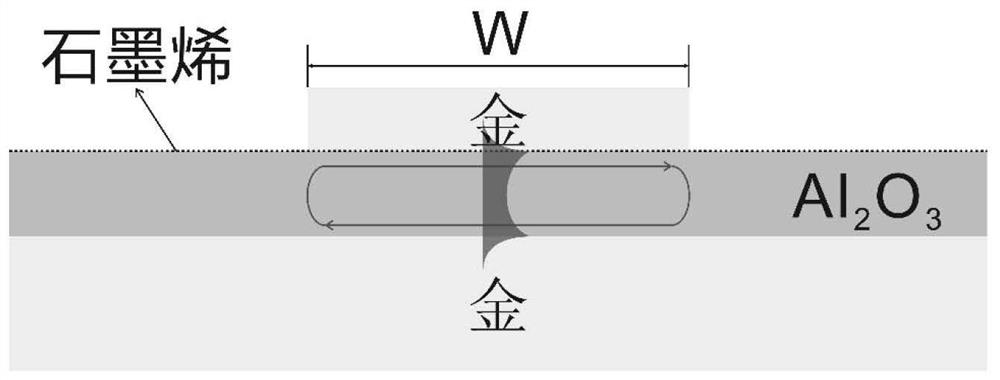
Terahertz detector
PendingCN113540260APromote absorptionImprove photoresponseFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesDielectricEngineering
The invention provides a terahertz detector. The terahertz detector comprises a substrate layer; a metal reflecting layer which is arranged on the substrate layer; a dielectric spacer layer which is arranged on the metal reflecting layer; a first Dirac semimetal layer and a second Dirac semimetal layer which are symmetrically arranged on the dielectric spacer layer; and a metal grating layer which is arranged on the dielectric spacer layer and is positioned between the first Dirac semimetal layer and the second Dirac semimetal layer. According to the terahertz detector, a composite structure of the anisotropic optical antenna and the Dirac semimetal layer is designed, and high polarization discrimination excitation and impedance matching coupling are based on the plasmon resonant cavity; incident light with the polarization direction perpendicular to the metal grating is efficiently converted into a sub-wavelength strong light field fully overlapped with the Dirac semimetal layer. According to the device, the light absorption and the light response of the Dirac semimetal layer are greatly improved, and the device has a higher polarization extinction ratio, a higher integration level, a higher response rate and lower power consumption.
Owner:深圳网联光仪科技有限公司
Perylenequinone derivatives and uses thereof
ActiveUS8506931B2Improve photoresponseHigh activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhotosensMedicine
Owner:QUEST PHARMATECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com