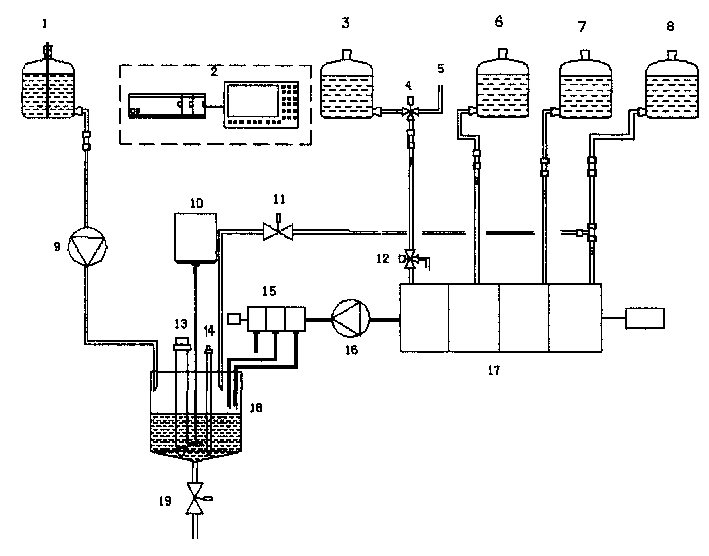
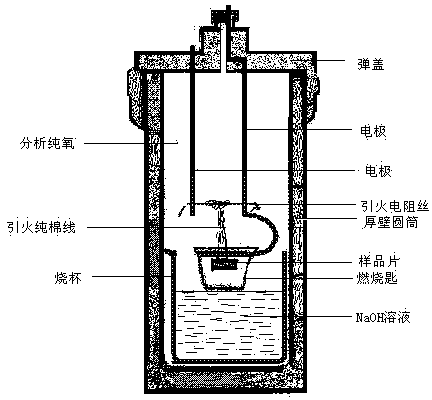
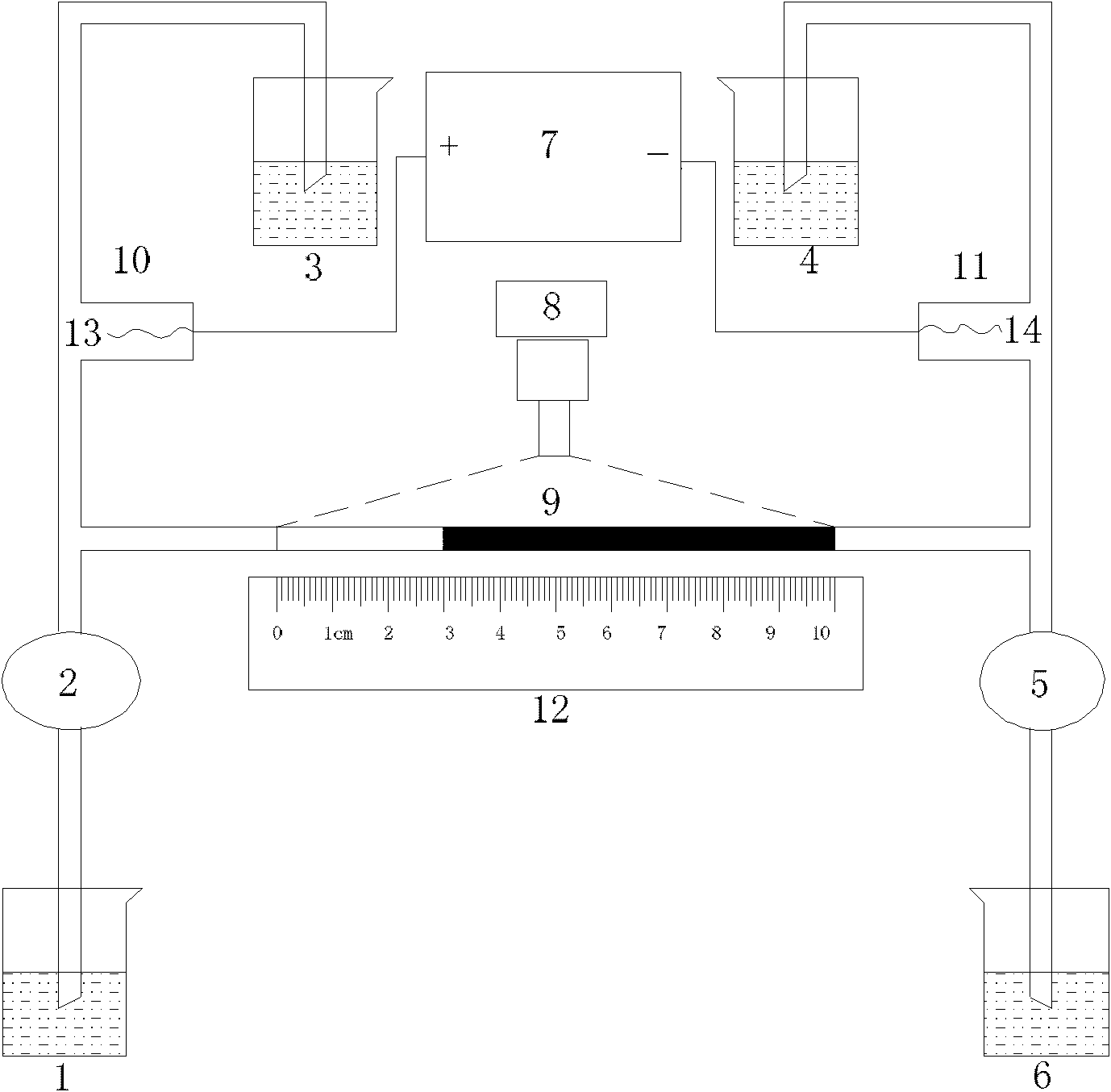
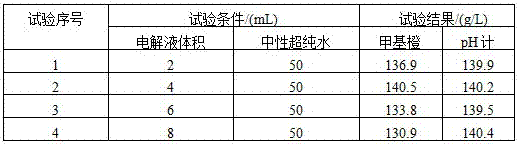
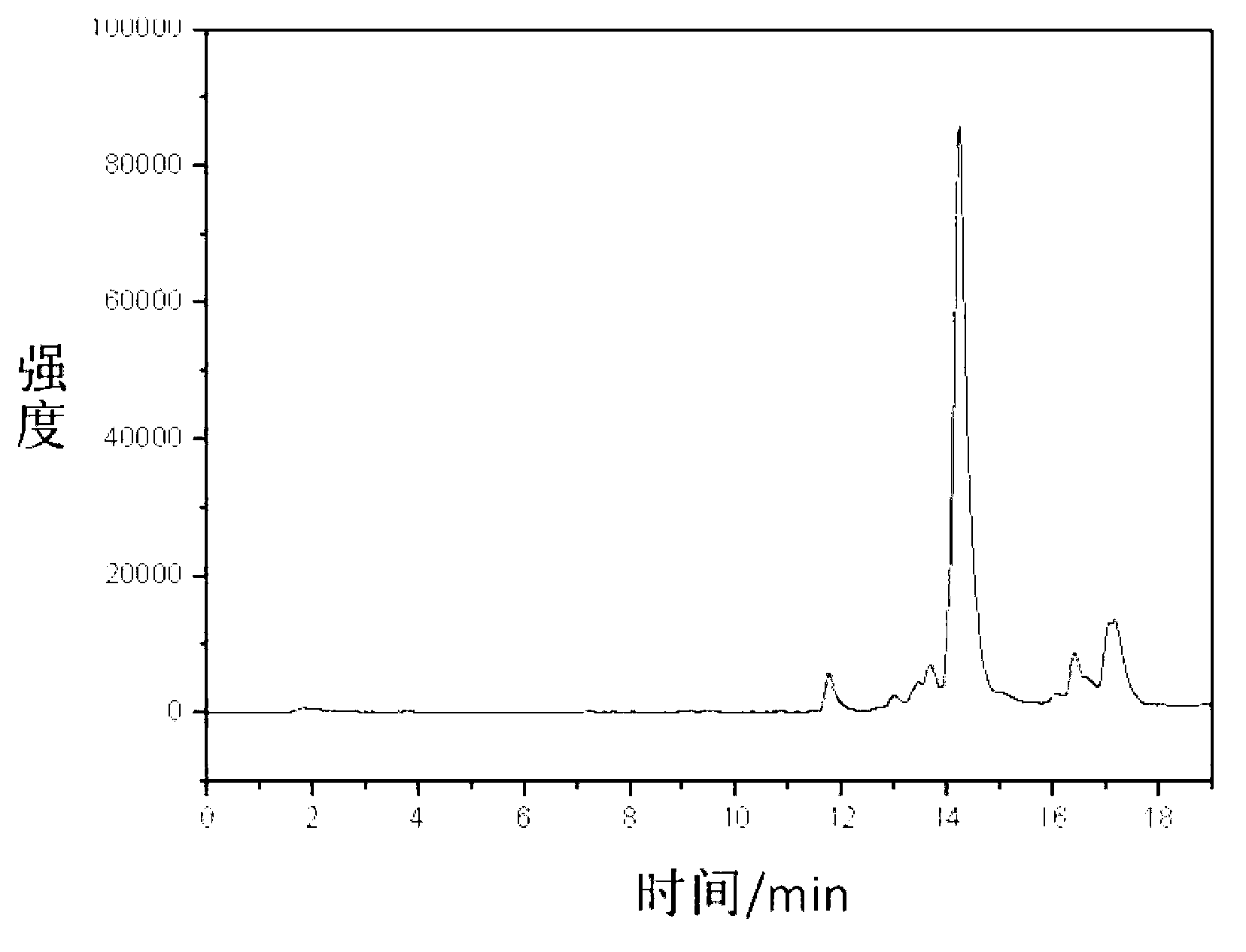
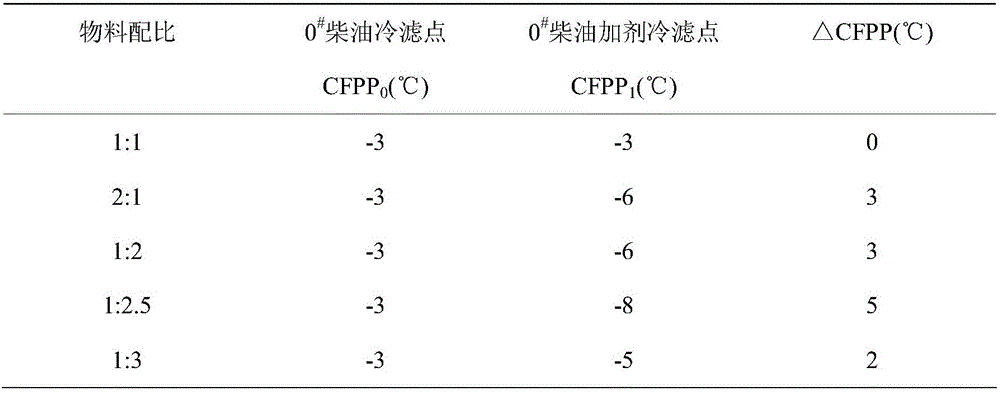
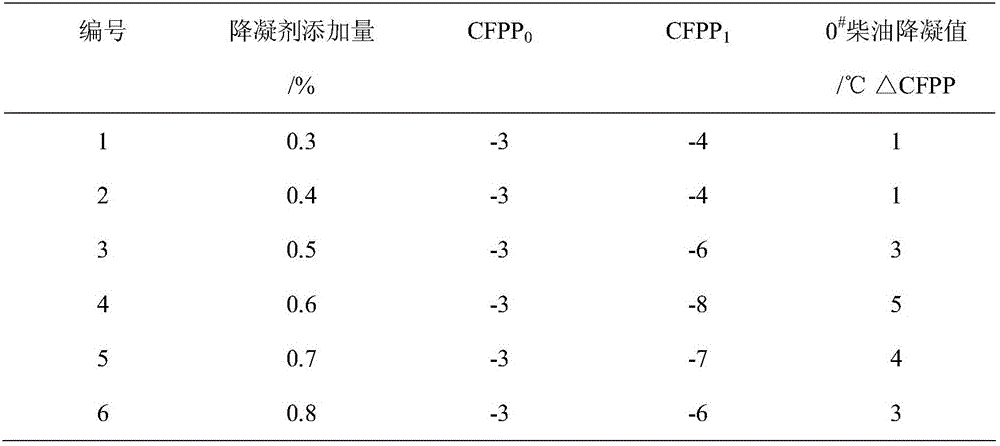
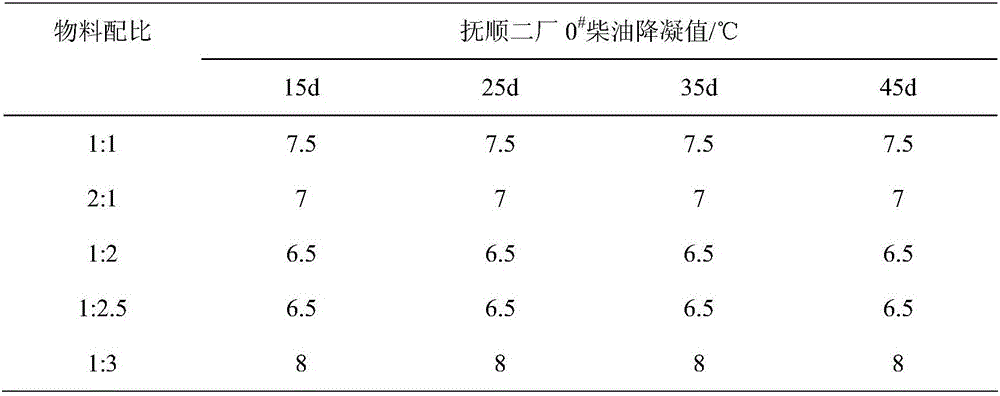
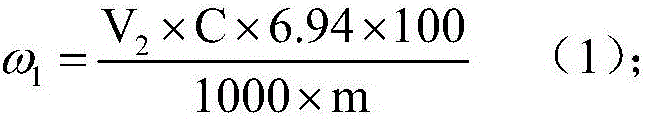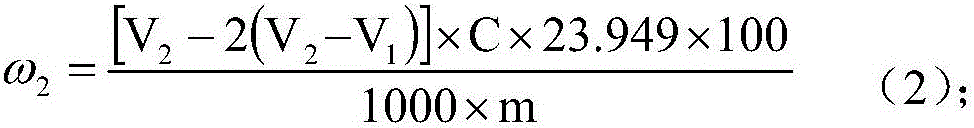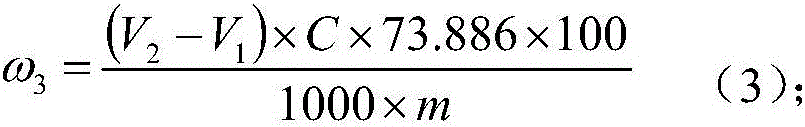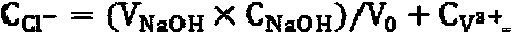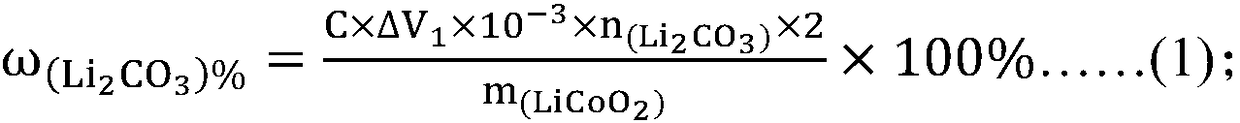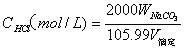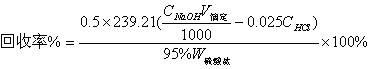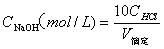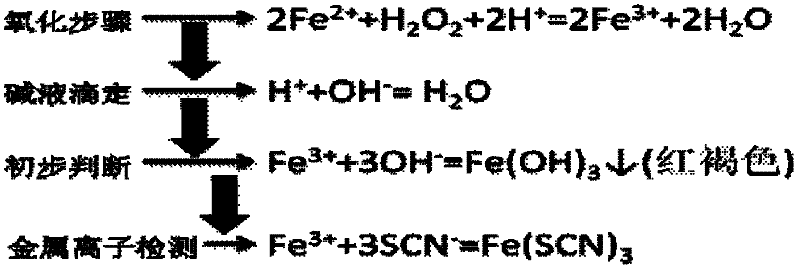Patents
Literature
107 results about "Acid–base titration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An acid–base titration is a method of quantitative analysis for determining the concentration of an acid or base by exactly neutralizing it with a standard solution of base or acid having known concentration. A pH indicator is used to monitor the progress of the acid–base reaction. If the acid dissociation constant (pKa) of the acid or base dissociation constant (PKb) of base in the analyte solution is known, its solution concentration (molarity) can be determined. Alternately, the pKa can be determined if the analyte solution has a known solution concentration by constructing a titration curve.
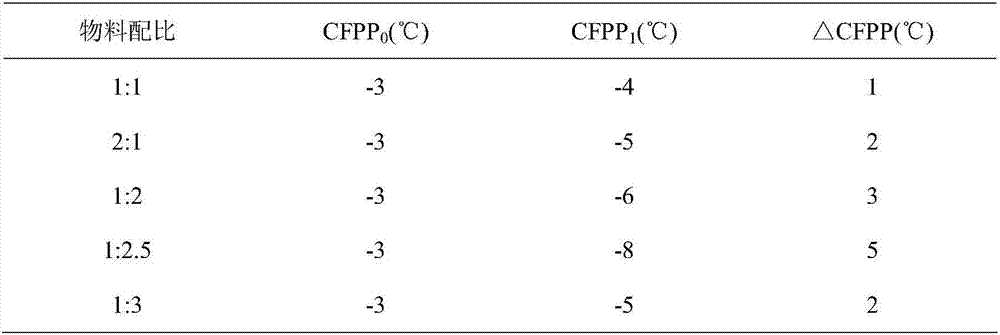
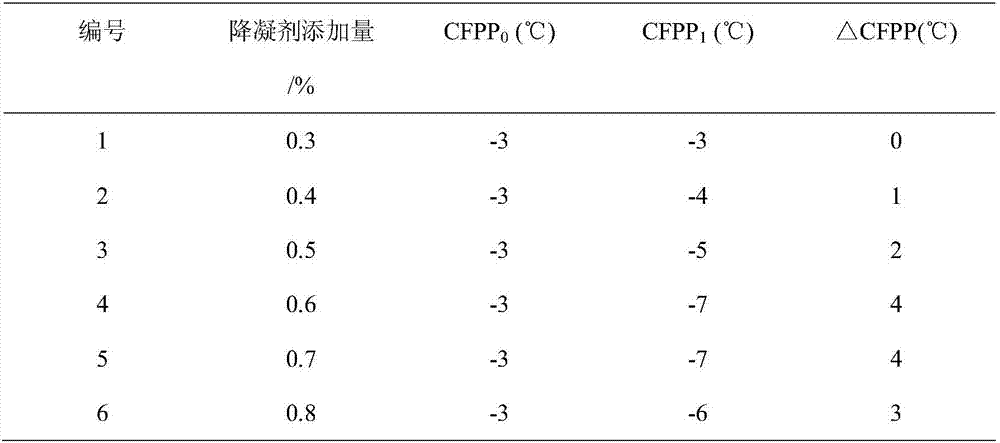
Clean diesel pour point depressant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106947556ARaise the ratioLow costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationRotary evaporatorDiesel combustion
The invention relates to a clean diesel pour point depressant and a preparation method thereof. The clean diesel pour point depressant is composed of long carbon chain fatty acid, low-carbon alcohol and low-carbon acid. The preparation method comprises the following concrete steps: weighing oleic acid by weight; adding glycerol, and carrying out heating under stirring until the oleic acid and the glycerol are dissolved; measuring the rate of esterification through an acid-base titration method; after a period of time, adding methacrylic acid, carrying out caustic washing and alcohol washing, then removing water through a rotary evaporator, and carrying out drying in an oven so as to obtain a target product namely methacrylic acid-glyceryl monooleate. According to the invention, by adopting an additive-free solvent and a catalyst, materials are economical, and cleanness and environment protection are realized. The pour point depressant provided by the invention has a formula applicable to good improvement of fluidity of diesel at a low temperature, and specifically meets the requirements of a diesel engine for clean and environment-friendly combustion tail gas emission in the process of diesel combustion.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
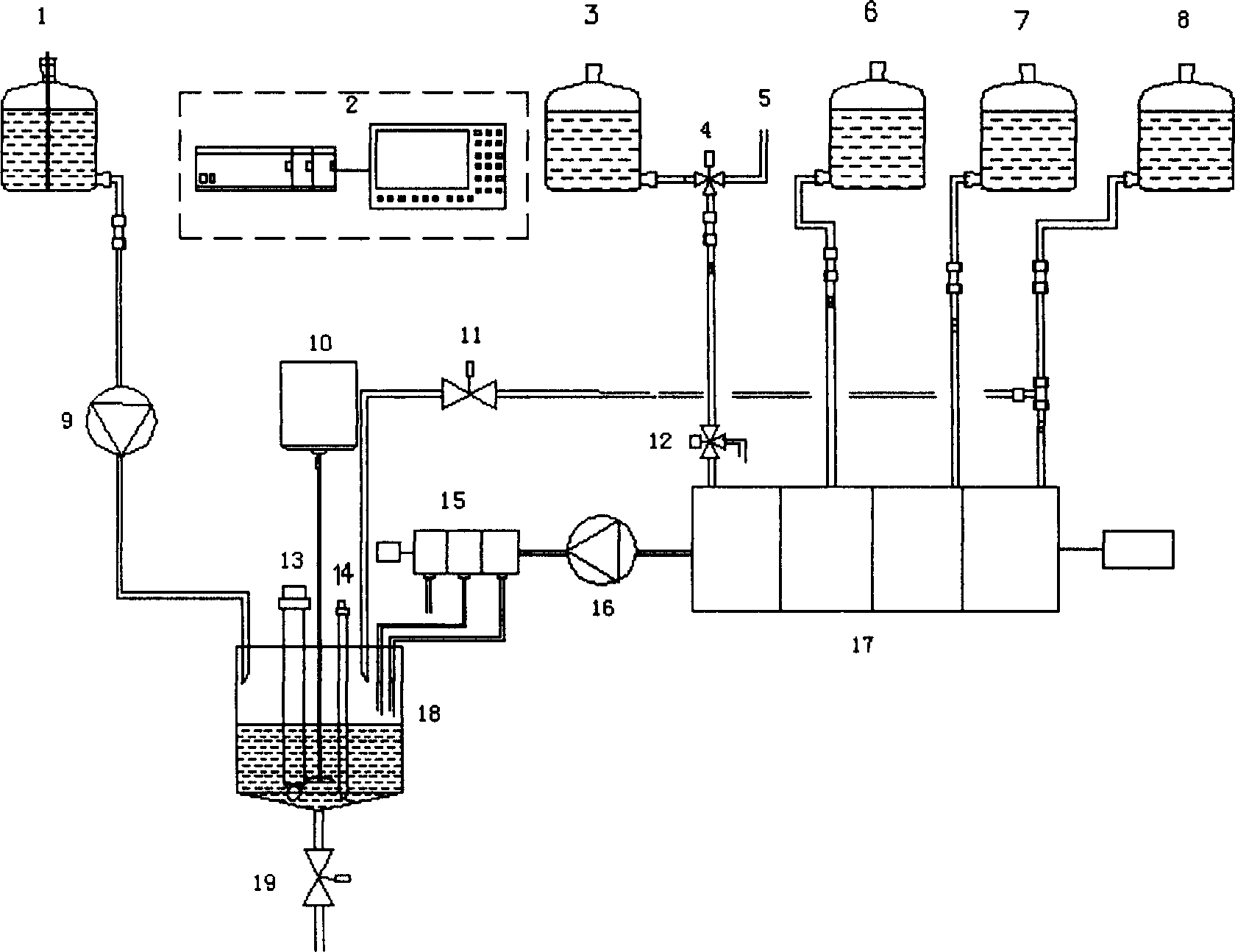
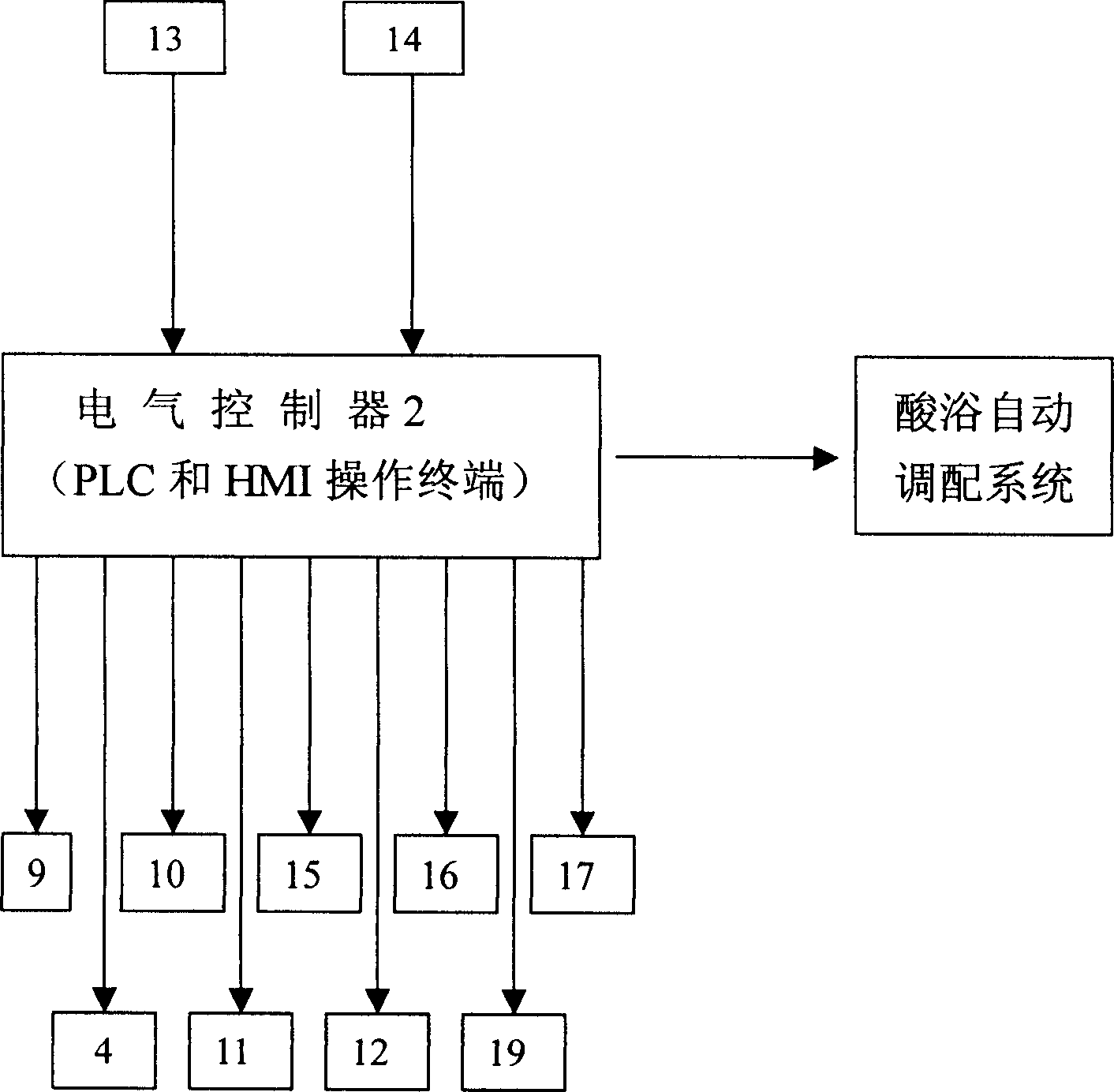
Method of on line detecting acid bath components and its detecting apparatus
InactiveCN1414393AImplement isolated additionReflect changes in a timely mannerControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsChemical analysis using titrationFiberMicrometer
The electric controller and the neutral titration devices and used to simulate the manual method of the volumetric chemical analysis. The technique used in the invention includes the technique for adding liquid drop in micrometer level, the cleaning technique against mixing multiple flow paths and the technique of PH value and the variable speed control of flow rate addition. The measuring deviceincludes the electric control set, the creepage-metering pump, the stirrer, the pH probe and the temperature compensation probe as well as various control valves and pipes, etc., the invented device can detect the constitutents and concentrations of the acid bath on-line automatically. The detected signals can be transferred to the autoamtic allotment system so as to control the procedure of the acid bath and guarantee the quality of the fibers.
Owner:米文达
Determination method for total organic carbon (TOC) of solid combustible matters
InactiveCN103529162ADetermination is clearThe principle is clearChemical analysis using combustionChemical analysis using titrationEnvironmental resistanceCombustor
The invention belongs to the field of analysis and testing technology and specifically discloses a determination method for TOC of solid combustible matters. The method comprises the following steps: placing a solid combustible matter sample with certain mass into a combustor (an oxygen bomb) filled with an excess NaOH solution for complete combustion so as to thoroughly oxidize organic carbon into CO2; allowing the NaOH solution to completely absorb CO2 and converting CO2 into Na2CO3; adjusting a pH value to 8.32 by using a hydrochloric acid solution to convert Na2CO3 to NaHCO3; and measuring carbon content in NaHCO3 by using acid-base titration and calculating the TOC value of the solid combustible matter. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of clear chemical principles, direct carbon measurement, reliable analysis, accurate analysis results, easy and convenient operation, low analysis cost and environmental protection and is applied to determination of TOC of solid combustible matters with complex composition and to related fields.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV +1
Temperature-sensitive hydrogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108047377AHigh viscosityImprove adsorption capacityFire extinguisherMethyl celluloseNitrogen
The invention discloses temperature-sensitive hydrogel and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of hydrogel. The preparation method of the hydrogel comprises the followingsteps: (1) preparing reaction solution by using methyl cellulose and deionized water; (2) by using the reaction solution as a solvent, respectively preparing NaHCO3 solution and NaOH solution, and then mixing the NaHCO3 solution and the NaOH solution to carry out acid-base titration on a certain amount of acrylic acid, thus obtaining sodium-acrylate monomeric correction liquid with a PH value being 7.0; (3) adding N-isopropylacrylamide into a four-port bottle according to a certain proportion, and slowly dripping a certain amount of the sodium-acrylate monomeric correction liquid into the four-port bottle under the condition of nitrogen protection, thus obtaining dissolving liquid; (4) adding a crosslinking agnet, an initiator and a catalyst into the dissolving liquid to prepare the temperature-sensitive hydrogel. The temperature-sensitive hydrogel disclosed by the invention has good fire-extinguishing performance.
Owner:SICHUAN POLICE COLLEGE
Electromigration acid-base titration device for measuring acid and alkali concentration
InactiveCN102121918AChanges have no noticeable effectEliminate troubleMaterial electrochemical variablesPeristaltic pumpStrong acids
The invention discloses an electromigration acid-base titration device for measuring acid and alkali concentration in the technical field of analytical chemistry. The device comprises two electrolyte tanks, a gel tube, two peristaltic pumps, two waste liquor tanks, a voltage supply device and a data recording device, wherein the anode of the voltage supply device is respectively connected with one end of the gel tube, the anode peristaltic pump and the anode waste liquor tank; the cathode of the voltage supply device is respectively connected with the other end of the gel tube, the cathode peristaltic pump and the cathode waste liquor tank; the anode peristaltic pump and anode peristaltic pump are respectively connected with the anode electrolyte tank and the cathode electrolyte tank; and the data recording device is arranged on the gel tube. Through the device, the trouble of selecting an indicator is eliminated to a great extent; and the device can be applied to strong acid-strong base titration, weak acid-weak base titration and analysis on nitrogen content of a protein.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
A method of detecting surface lithium of a ternary cathode material
InactiveCN106556670AEasy to operateShort detection timeChemical analysis using titrationPhenolphthaleinRoom temperature
Owner:DO FLUORIDE NEW ENERGY TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Experimental method measuring soil respiration via laboratory simulating dry-wet alternate responses
ActiveCN105301178ALong-term determinationContinuous measurementChemical analysis using titrationAcid–base titrationEngineering
The invention relates to an experimental method measuring soil respiration via laboratory simulating dry-wet alternate responses. The experimental method at least comprises the following steps: step 1, selecting a wide-mouthed bottle, recording the weight of the wide-mouthed bottle, filling the wide-mouthed bottle with air-dried soil, recording the total weight of the wide-mouthed bottle and the air-dried soil, hanging a desiccant bag in the wide-mouthed bottle, and placing the wide-mouthed bottle in a temperature control system, wherein the wide-mouthed bottle comprises a perforated rubber plug and a glass tube, the perforated rubber plug is arranged at the opening of the wide-mouthed bottle, the glass tube is arranged in the hole of the perforated rubber plug, the top end of the glass tube is sleeved by a latex tube, and the top end of the latex tube is blocked by a flatjaw pinchcock; step 2, measuring gas which is exhausted from soil respiration according an alkali absorption method and an acid-base titration method. The experimental method has the excellent effects that the values of soil respiration within the specified time in the design of different experiments can be achieved, and samples of different numbers can be measured; the operation is simple, convenient and rapid, and the production cost is low; the experimental method can be operated in a common laboratory.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Preparation of neodymium-doped aluminum yttrium borate nano powder by acid-base titration
The invention relates to a process for preparing neodymium-doped aluminum yttrium borate nano powder by acid-base titration. Chemical analysis and X-ray powder diffraction show that the powder is neodymium-doped aluminum yttrium borate polycrystalline powder, the spectrographic analysis under room temperature indicates that its spectrum property is similar to neodymium-doped aluminum yttrium borate crystal, electron microscopy analysis shows that the particle size of the powder is between 20-50 nanometer. The powder can be used as the raw material in preparing nano crystalline ceramic laser material or nano glass ceramic laser material.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Acid radical detection method for all-vanadium electrolyte
ActiveCN103454330ASimple methodFast measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesEthylene diamineHydrogen
The invention relates to an acid radical detection method for all-vanadium electrolyte. Vanadium is complexed by using EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid)-2Na, then the total number of hydrogen ions in a solution is determined by using a sodium hydroxide acid-base titration method, and by calculating, the acid radical content of an original solution can be obtained. The method is used for rapidly and accurately detecting the concentration of acid radicals. The method comprises the following main steps: 1, taking 0.5 ml of an original solution, and determining the concentration of vanadium in the solution and the concentration of vanadium of each valence state by using a redox potential titration method; 2, taking 0.5 ml of the original solution, adding EDTA-2Na into the original solution, wherein the amount of the EDTA-2Na is 1.1-2 times as much as the amount of a vanadium material; 3, by using an acid-base potentiometric titration electrode, titrating the solution by using a sodium hydroxide solution with a known concentration until a first potential is over completely, so that a total concentration of hydrogen ions is obtained; 4, calculating the concentration of original hydrogen ions according to the valence state and concentration of vanadium; and 5, according to the concentration of vanadium ions and the concentration of original hydrogen ions, calculating a total concentration of acid radicals. According to the method provided by the invention, the concentration of acid radicals in a solution can be determined quickly and accurately so as to provide guidance for the production of electrolyte.
Owner:DALIAN RONGKE ENERGY STORAGE GRP CO LTD
Catalytic material for degrading indoor formaldehyde in room temperature and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107362823AEasy to makeEasy to operateMolecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationManganeseElectric power
The invention provides a catalytic material for degrading indoor formaldehyde in a room temperature and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic material can be an active component of a pure active component MnO2, or comprises a molecular sieve carrier material. The active component MnO2 is generated by divalent manganese salt solution and alkali solution through an acid base titration reaction. The active component MnO2 is in-situ loaded on the molecular sieve carrier material. The preparation process of the catalytic material is simple, the operation is convenient, and the price of the catalytic material is cheap. A specific light source and additional electric power and heating power do not need to be provided in the preparation process, and the energy is saved. The catalytic material can be effectively used for degrading the indoor formaldehyde in the room temperature condition, and converting the formaldehyde into harmless carbon dioxide and water, wherein the formaldehyde conversion percent within 100 h is more than 90%.
Owner:临沂恺峰生物科技有限公司
Automatic acid-base titration instrument
InactiveCN104730202AGuaranteed accuracyEasy to operateChemical analysis using titrationBuretteEngineering
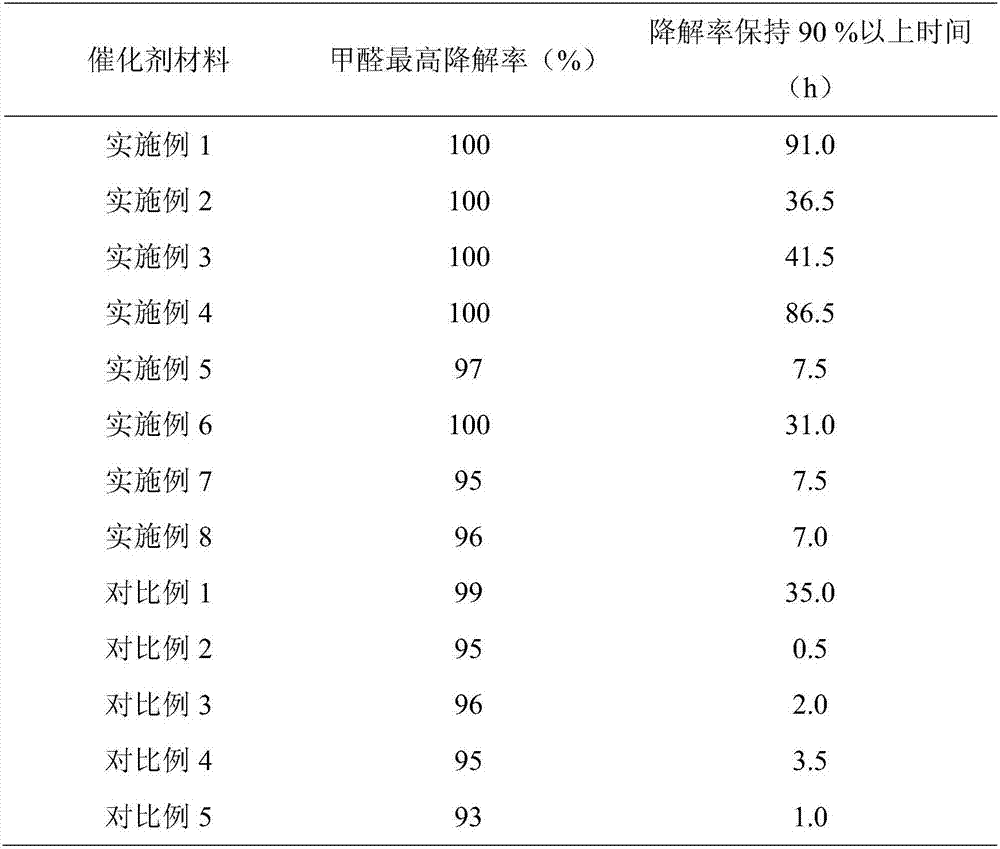
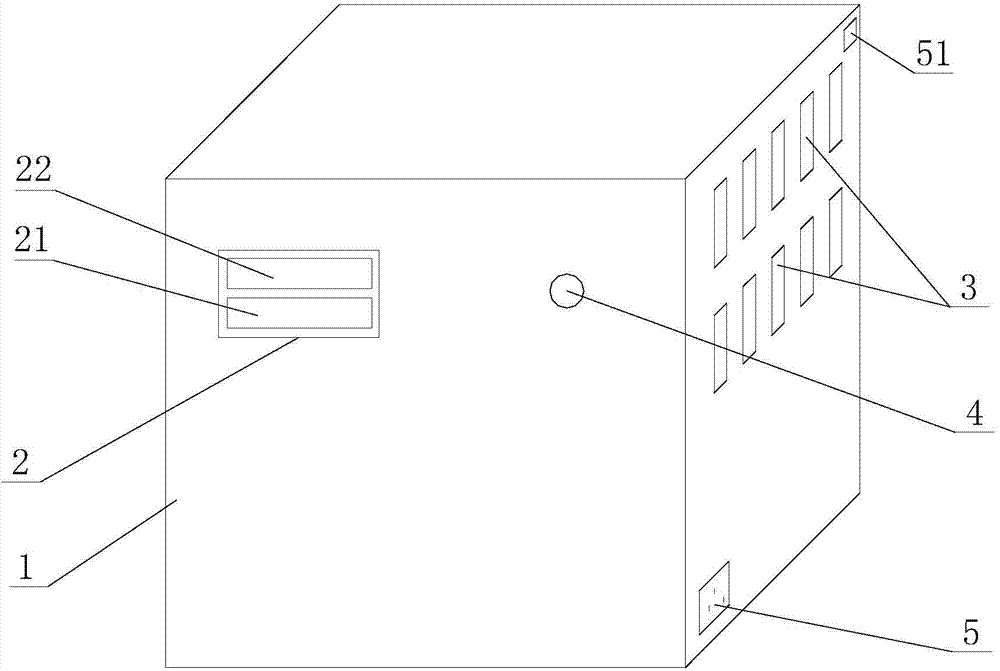
The invention relates to the technical field of experimental instruments, in particular to an automatic acid-base titration instrument, comprising a storage bottle, a titration tube, a vessel, a shell and an intelligent controller. The storage bottle is used for storing acid / alkali liquid; the vessel is used for storing liquid to be titrated; the shell is in a box structure. The storage bottle is fixed the top of an inner chamber of the shell through a fixing base. A vibrator is disposed within the inner chamber of the shell. The vessel is locked and fixed to the vibrator through a fixing clamp. The top end of the titration tube is connected to a liquid outlet of the storage bottle. The bottom end of the titration tube extends into the vessel. An orifice of the bottom end of the titration tube is connected with a sharp-tip titration tube. A micro-metering pump and an automatic valve are mounted on the titration tube in order from top to bottom. A pH sensor is disposed at the bottom of the inner chamber of the vessel. The automatic acid-base titration instrument is convenient to operate, safe and reliable, and time saving and labor saving, and accuracy of experimental results can be ensured.
Owner:HEZE UNIV
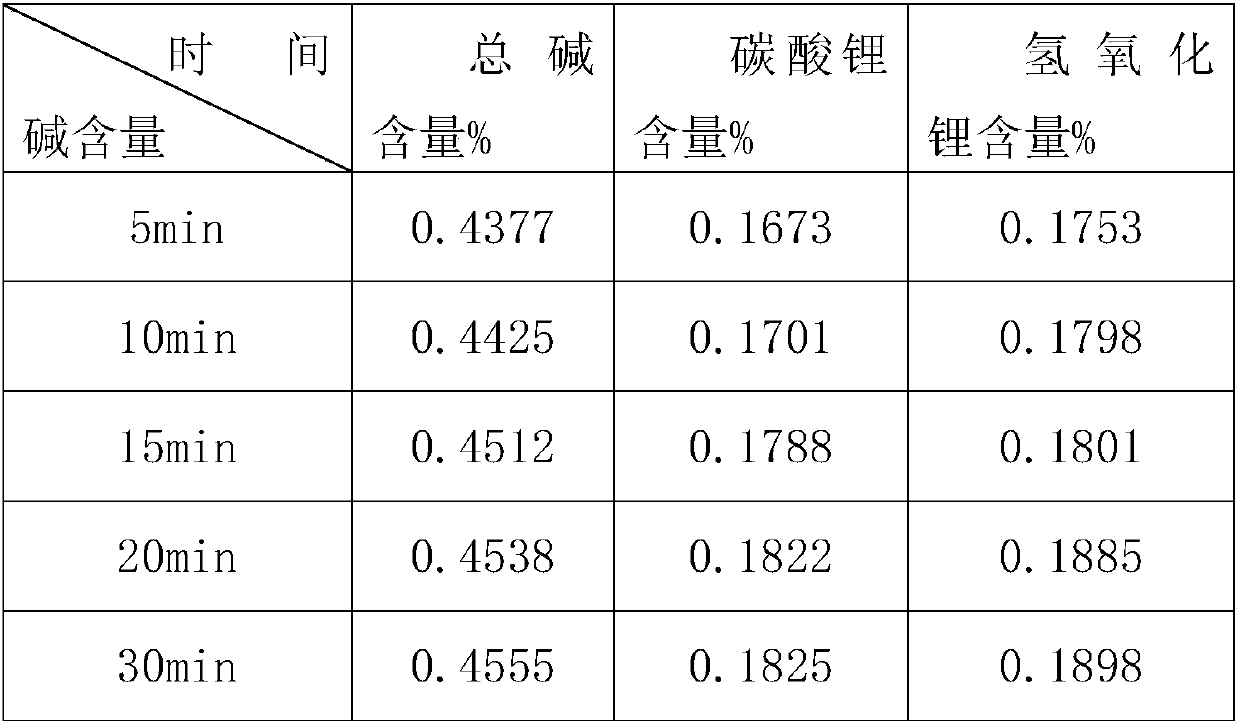
Method for detecting content of residual alkalis on surface of lithium battery ternary positive electrode material
InactiveCN107907625AReliable resultsImprove detection efficiencyChemical analysis using titrationPhysical chemistryAcid–base titration
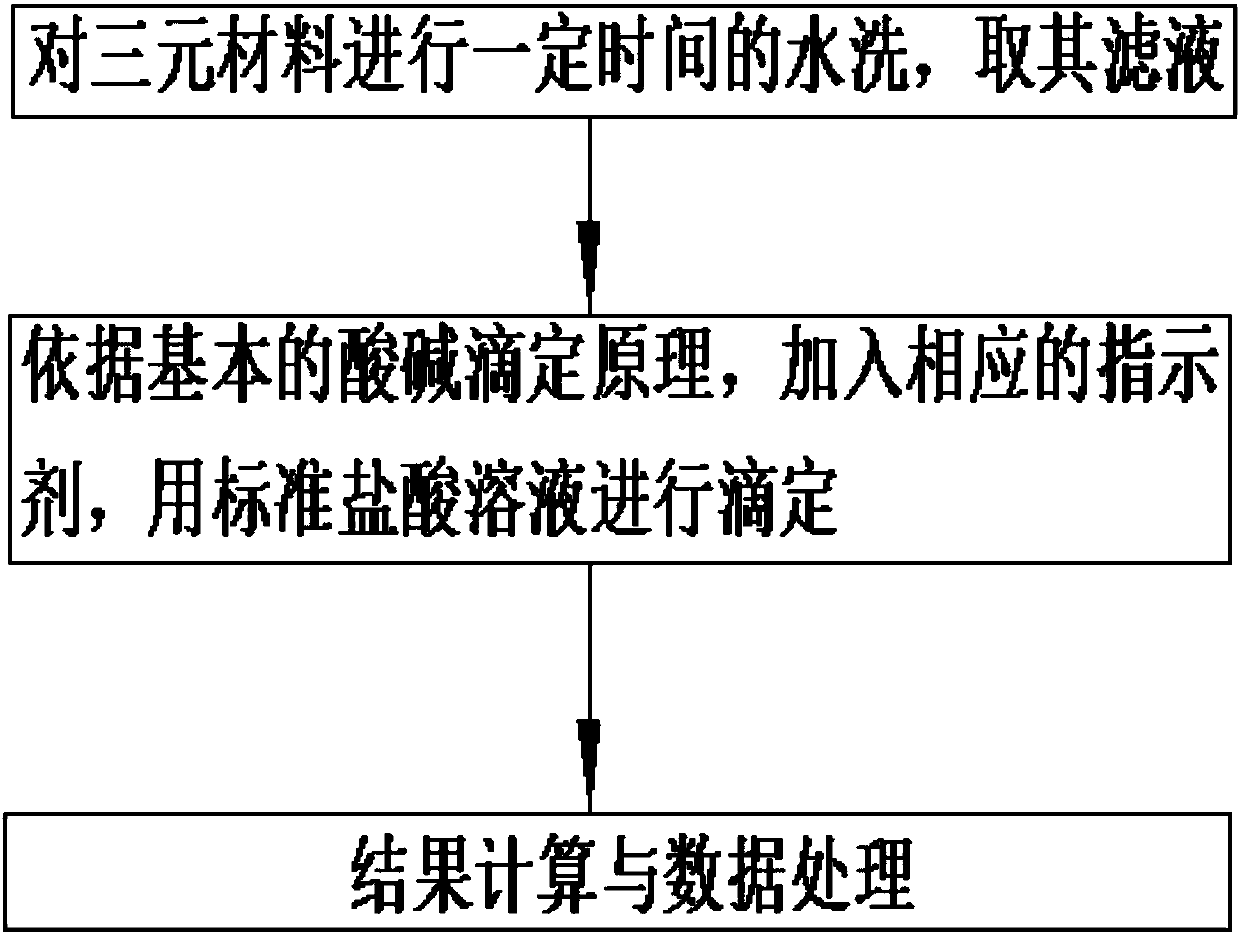
The invention discloses a detection method for the content of residual alkali on the surface of a lithium battery ternary positive electrode material. Firstly, the ternary material is washed with water for a certain period of time, and the filtrate is taken; secondly, according to the basic principle of acid-base titration, a corresponding indicator is added, and the Standard hydrochloric acid solution is used for titration; finally, result calculation and data processing are carried out. The beneficial effect of the present invention: by using the detection method of the present invention, the result is real and reliable, and the detection efficiency can be greatly improved, and the operation is simple and convenient to use.
Owner:SHANXI CHANGZHENG POWER TECH CO LTD
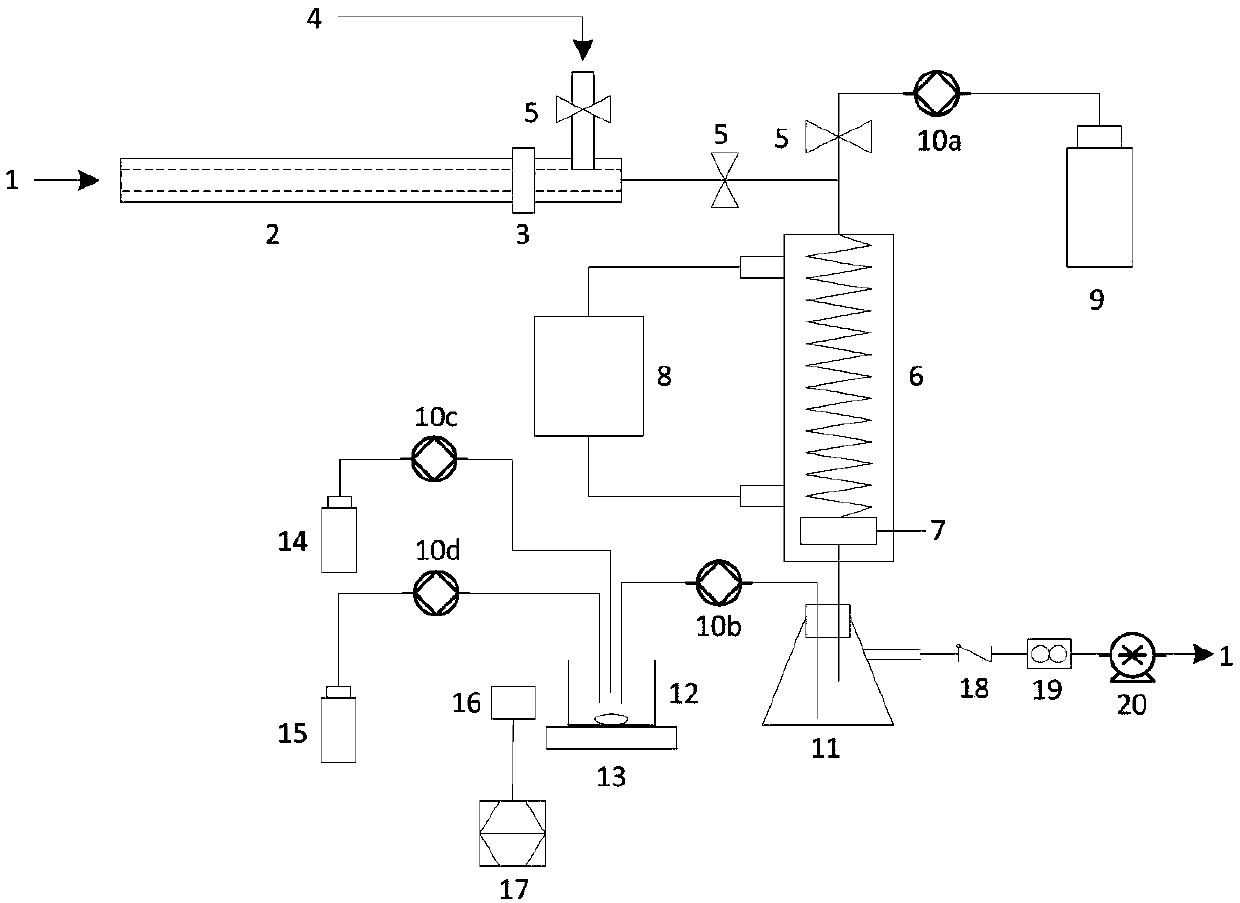
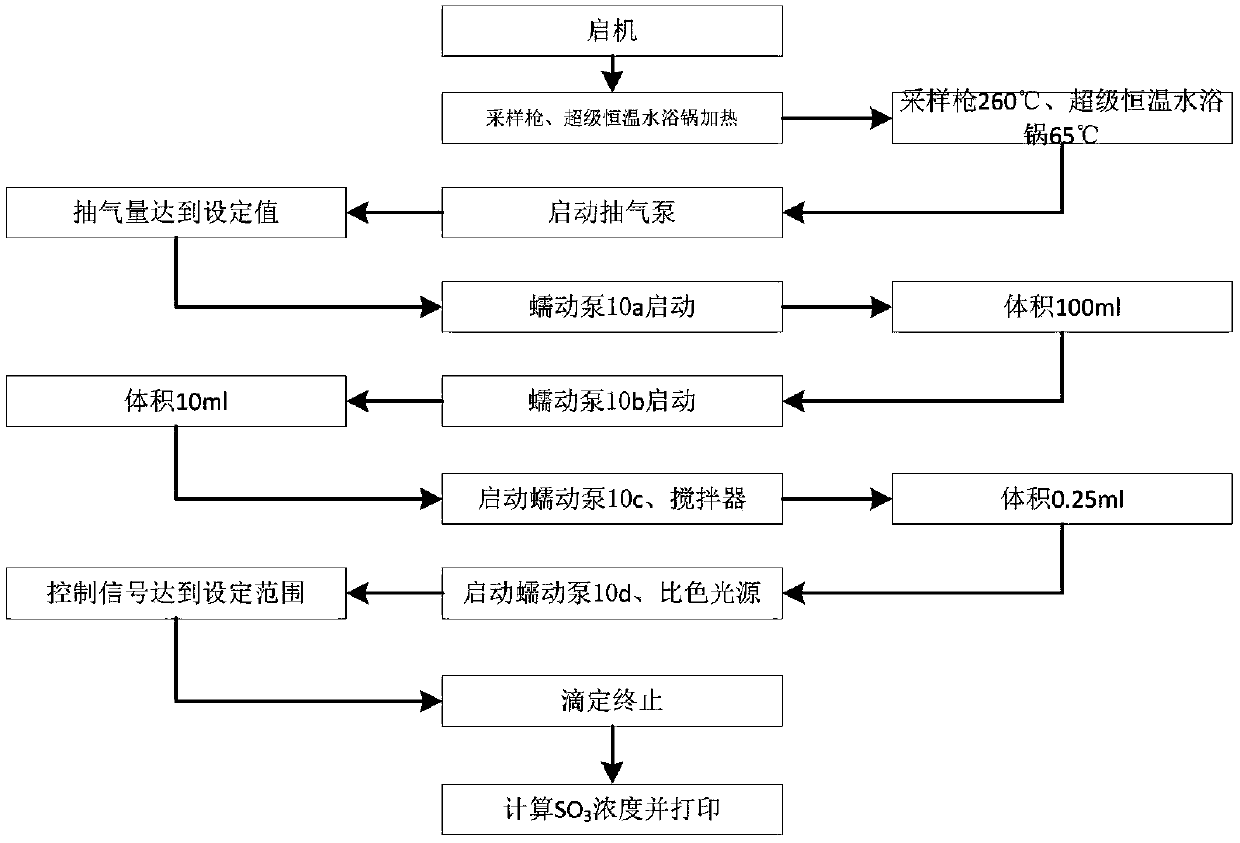
Automatic measuring device and method for SO3 in flue gas
PendingCN109632408AHigh measurement accuracyImprove reliabilityChemical analysis using titrationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorControl systemProcess engineering
The invention relates to the field of pollutant testing, and in particular relates to an automatic measuring device and method for SO3 in flue gas. The device provided by the invention comprises a sampling system, a collecting system, an analysis system and a control system. Flue gas enters the sampling system. The sampling system, the collecting system and the analysis system are sequentially connected through a pipeline. The sampling system, the collecting system and the analysis system are in signal connection with the control system. The sampling system comprises a sampling gun, a filter and a compressed air system. The filter is arranged on one end of the sampling gun. The compressed air system is connected with the upper part of the end of the sampling gun through a pipeline. According to the invention, SO3 in flue gas is collected based on a controlled condensation method; acid radical ion measurement is carried out based on acid-base titration; the SO3 concentration in flue gasis calculated in combination with the flue gas sampling volume, which can reduce the influence of flue gas dust on SO3 measurement and improve the measurement accuracy and reliability; and the deviceand method have the advantages of high automation and convenient operation, and are suitable for automatic measurement of SO3 in flue gas.
Owner:CHINA HUADIAN ENG
Method for measuring organic carbon content in sodium aluminate serosity
The invention provides a method for measuring the organic carbon content in the sodium aluminate serosity, relating to the method for measuring the organic carbon content in the sodium aluminate serosity in the process flow of manufacturing aluminium oxide by an ore dressing-Bayer process. The method is characterized in that the test procedures comprises the following steps in sequence: (1) adding sodium aluminate serosity samples to a porcelain boat, adopting a combustion method, taking an acid-washed asbestos as a slipcover, firstly, drying for 30 to 50 minutes at the low temperature, gradually heating up to 900 DEG C, firing for two minutes in the presence of oxygen, absorbing the generated CO2 with potassium hydroxide, and measuring the full carbon contents in the materials with a gas volumetric method; (2) adopting acid base titration to measure the inorganic carbon contents in the measuring sample; and (3) adopting a subtraction method to measure the organic carbon content in the sample. In the method of the invention, appropriate reaction conditions are selected for the materials in the process; the full carbon and inorganic carbon content in the materials are measured in sequence by the gas volumetric method and the acid base titration; the organic carbon content is measured by the subtraction method. The method is simple and effective.
Owner:中铝中州铝业有限公司
Measurement method for content of hydrofluoric acid in titanium alloy pickling solution
InactiveCN104730201AHigh spike recoveryAnalytical method is accurateChemical analysis using titrationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHydrofluoric acidTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a measurement method for content of hydrofluoric acid in a titanium alloy pickling solution. The titanium alloy pickling solution comprises the main components including nitric acid, the hydrofluoric acid and fluorotitanic acid. The measurement method adopts an acid-base titration method for measuring the content of the fluorotitanic acid, and adopts a calcium fluoride precipitation method for measuring the content of total fluorine in a bath solution; and the content of the fluorine in the fluorotitanic acid is subtracted by the content of the total fluorine to obtain the content of the hydrofluoric acid in the solution. The measurement method has the advantages that the interferences caused by the fluorotitanic acid can be effectively avoided; the adding standard recovery rate of the content of the hydrofluoric acid, measured by adopting the method, is more than 95%; and the determination requirements on the concentration of the hydrofluoric acid are met and the production can be smoothly carried out.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) quantitative method for cephaeline hydrochloride and ipecine hydrochloride in ipecacuanha medicinal material and preparation of ipecacuanha medicinal material
The invention relates to a HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) quantitative method for cephaeline hydrochloride and ipecine hydrochloride in an ipecacuanha medicinal material and a preparation of ipecacuanha medicinal material. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, performing common isocratic elution according to PHLC method, and taking acetonitrile-carbinol-0.1% of phosphoric acid at a volume ratio of (8-9.5):(3-5):(86-88) as a flowing phase, wherein a detecting wavelength is 205nm; and simultaneously measuring the contents of the cephaeline hydrochloride and ipecine hydrochloride in the ipecacuanha medicinal material and a fluid extract, extract and tincture thereof so as to end the history of the measurement of total alkaloids of the ipecacuanha alkaloids in an acid base titration form according to the standard in multiple countries: after performing column chromatography separation for 4 times, respectively measuring the cephaeline hydrochloride and ipecine hydrochloride through delta A at 283nm and 350nm by adopting differential spectrophotometry. According to the method, only acidic aqueous carbinol or aqueous carbinol is used; after fine powder of the medicinal material is ultrasonically extracted or each preparation is diluted, a certain amount of subsequent filtrate is absorbed; and an alumina column is used for removing impurities so as to measure. The method is quick, convenient, accurate and capable of reappearing.
Owner:JING JING PHARMA
Method for rapidly determining content of free acid in lithium hexafluorophosphate product in non-aqueous system
InactiveCN110261464AMeet the densityMeet the accuracyChemical analysis using titrationMaterial electrochemical variablesChemical industrySupporting electrolyte
The invention relates to a method for rapidly determining the content of a free acid in a lithium hexafluorophosphate product in a non-aqueous system. According to the method, a water-free supporting electrolyte solution is used as an electrolytic solution; the free acid in the lithium hexafluorophosphate product is titrated with alkaline ions electrolyzed by the electrolytic solution; the content of the free acid in the sample is calculated according to the faraday's law; and the whole detection process can be finished within 5 minutes, and a result can be obtained. With the method of the invention adopted, three bottlenecks, namely, the poor thermal stability of the lithium hexafluorophosphate, interference caused by hydrofluoric acid generated by the reaction of the lithium hexafluorophosphate with water, and little possibility of accurately measuring trace free acids, can be broken; problems such as low precision, low accuracy and long detection time of acid-base titration methods, potentiometric titration methods and etching methods which are commonly used in current industrial production and scientific research can be overcome. The method can be applied to a wide range of samples, can practically promote the analysis and detection levels of fluorine chemical industries and lithium ion battery industries, and further improve the quality of related industrial products.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for detecting barium content in barium stearate via precipitation method
InactiveCN102980829AAccurate contentThe content is accurate and reliableWeighing by removing componentBarium titanateStearate
The invention relates to a method for detecting barium content in barium stearate via a precipitation method. The method comprises the steps of weighing the barium stearate accurately, titrating with a acid-base titration method, collecting precipitated barium sulfate, weighing the barium sulfate after being burned; and then calculating the barium content in the barium stearate. The method is simple and easy to operate. The detected barium content is accurate and reliable.
Owner:FAR EAST CABLE +2
Method of measuring content of trace-amount soluble impurities in lithium cobalt oxide
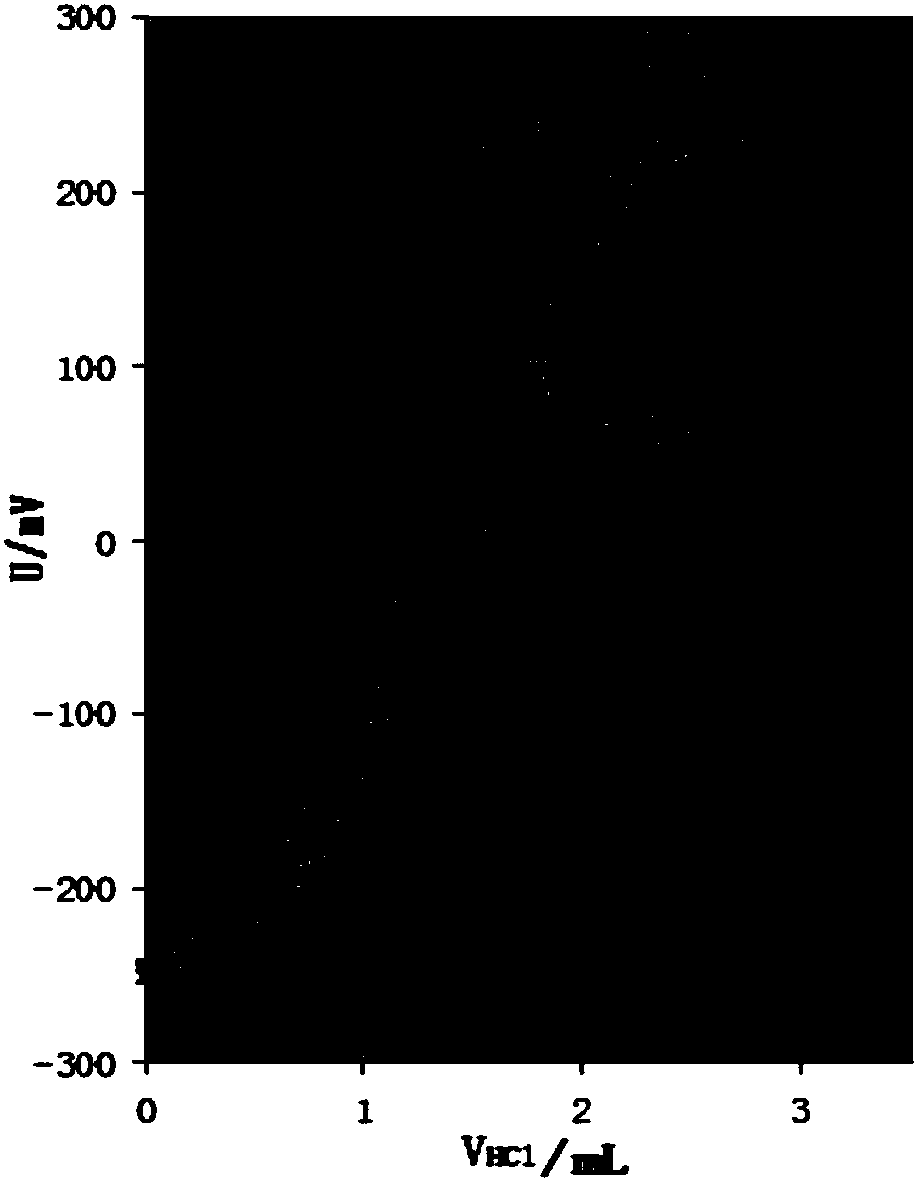
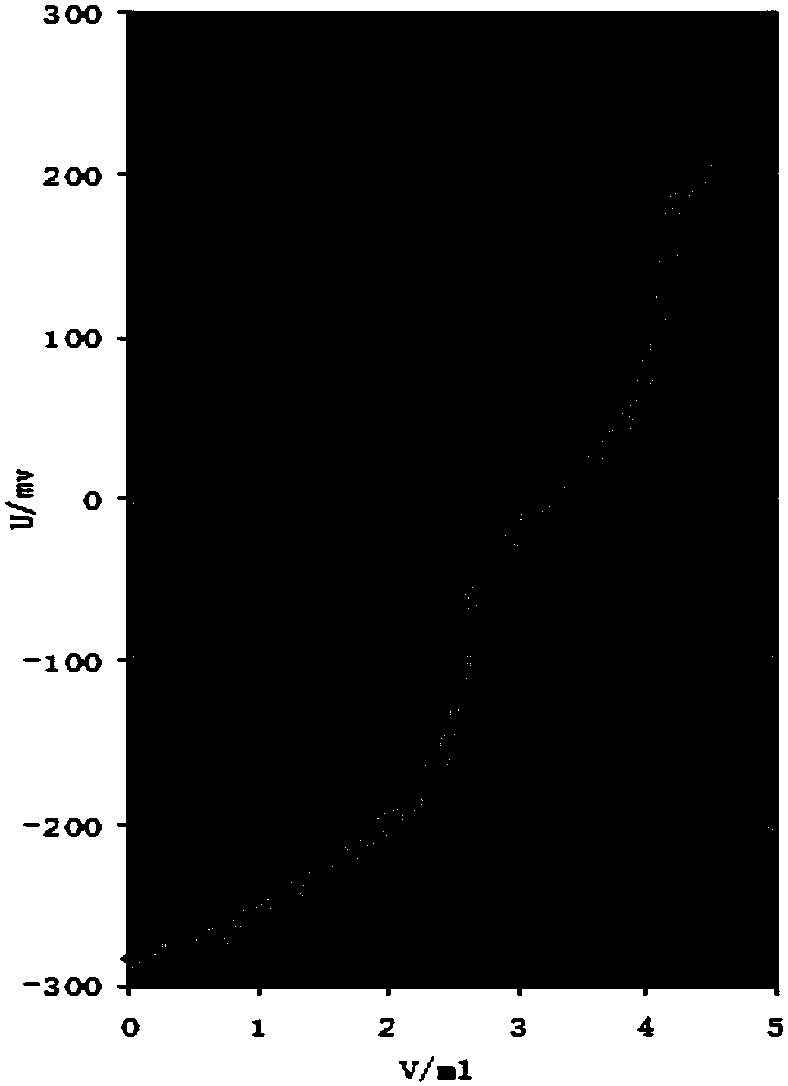
PendingCN108333294ANo pollution in the processHigh precisionChemical analysis using titrationAcid–base titrationHigh availability
The invention relates to the technical field of measurement of trace-amount impurities, and particularly discloses a method of measuring content of trace-amount soluble impurities in lithium cobalt oxide. The method at least includes steps of: S1) dissolving a lithium cobalt oxide sample (g) in distilled water and filtering the solution; S2) performing acid base titration to the filtrate in the step S1) by means of an automatic potentiometric titrator, and recording the usage amount of a titration agent and electrode potential change value; S3) according the consumption volume V1 and V2, whichare respectively corresponding to two jumps of the electrode potential change value, of the titration agent, calculating mass percentage of LiOH and Li2CO3 in the lithium cobalt oxide. The method issimple and quick, is free of pollution and is high in precision. The invention provides a scheme for detection of soluble salts in the lithium cobalt oxide at high availability and provides referencefor accurate measurement of contents of trace-amount impurities.
Owner:SHENZHEN BAK POWER BATTERY CO LTD +1
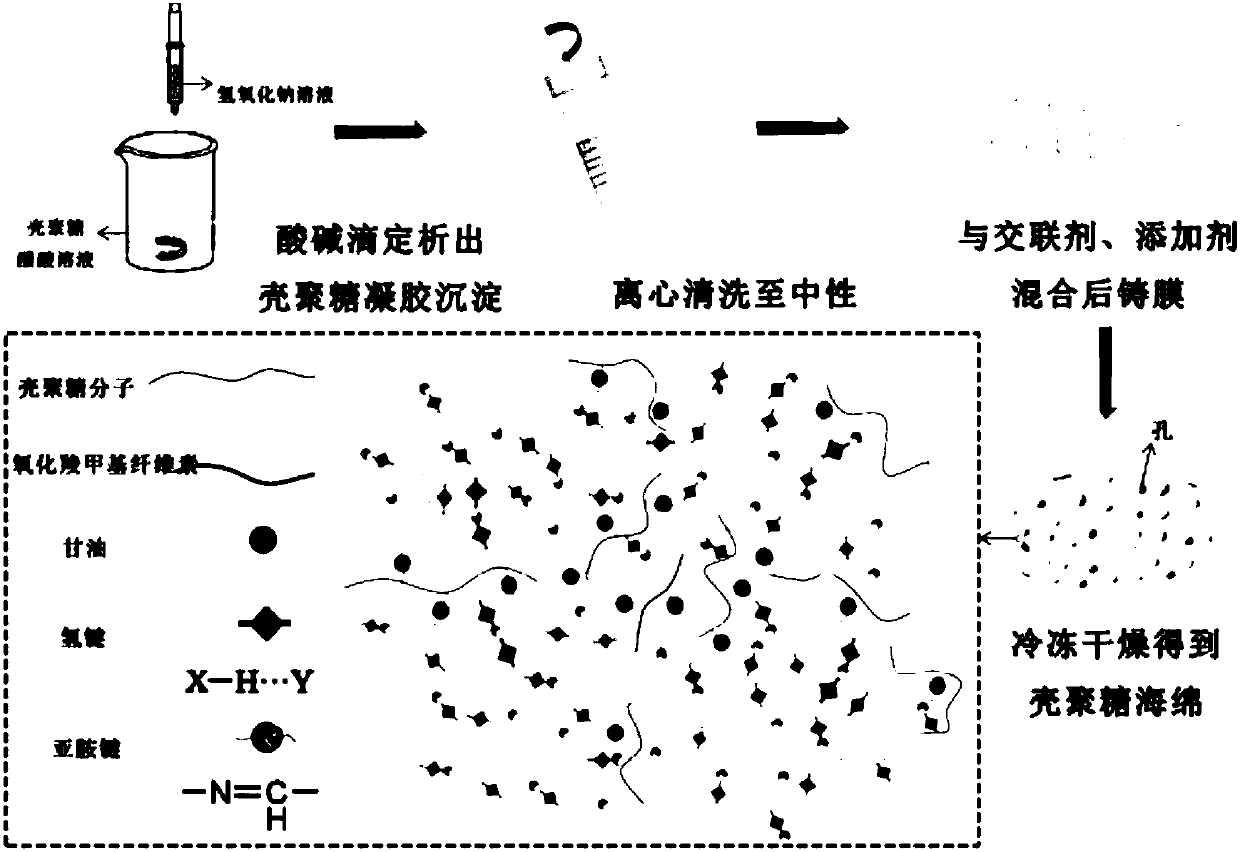
Preparation method of chitosan-based medicine-carrying flexible sponge
InactiveCN109745577AImprove stabilityPrevent structural collapseAbsorbent padsBandagesCross-linkFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of chitosan-based medicine-carrying flexible sponge. The method comprises the following steps: taking chitosan as raw material, dropwisely adding a precipitant sodium hydroxide to obtain chitosan gel precipitate in the process of continuously stirring an acetic acid solution of chitosan, centrifugally cleaning the chitosan gel precipitate, and then mixing the chitosan gel precipitate with a cross-linking agent of oxidizing carboxymethyl cellulose, a plasticizer glycerol and an antibacterial drug tetracycline hydrochloride, and freeze-drying the castfilm to obtain the medicine-carrying flexible sponge body. According to the invention, the chitosan gel precipitate prepared by acid-base titration is used for preparing the sponge body, and the stability of the sponge obtained by freeze-drying is good, and the structure is not damaged when swelling is caused, and one-step molding is carried out, and the structure collapse caused by alkali washing and secondary freeze-drying is avoided, and because of the one-step molding, the chitosan-based medicine-carrying flexible sponge is convenient to carry medicine. According to the invention, glycerol is added as a plasticizer, so that the sponge is soft and elastic. The method has the advantages of short process period, simple and convenient process, low cost and suitability for commercial production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for measuring formaldehyde content in tetrakis hydroxymethyl phosphonium sulfate
InactiveCN102507560AExtend the lifespanEasy to prepareMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSulfite saltDistilled water
The invention discloses a method for measuring formaldehyde content in tetrakis hydroxymethyl phosphonium sulfate, which comprises the steps of: weighing 2-5 g of sample and putting the sample in a 250 mL conical flask, adding 50 mL of distilled water therein, dripping 5 drops of thymolphthalein indicator, adjusting the test solution to microscopic blue by sodium hydroxide solution or hydrochloric acid solution; adding 50 mL of sodium sulfite solution and immediately titrating the solution to an end point by a standard hydrochloric acid titration solution; and performing a blank test in the same method. Compared with the method of measuring formaldehyde content by an instrument, the method of the invention has the advantages of utilizing acid-base titration and optimizing the conditions, thereby having few utilized reagents, simple preparation, long service life of reagents, simple and convenient operation and low detection cost.
Owner:HUBEI XINGFA CHEM GRP CO LTD
Device and method for measuring content of free carbon in boron carbide
InactiveCN106645559AImprove airtightnessEasy to observeChemical analysis using titrationBarium saltBoron carbide
The invention belongs to the field of analytical chemistry. A sodium dichromate-concentrated sulfuric acid-potassium iodate system serves as an oxidizing agent, the carbon dioxide produced in the reaction is collected by a standardized sodium hydroxide solution, a barium salt serves as a carbonate masking agent, and the content of free carbon in the sample is obtained by an acid base titration method. The device for measuring content of free carbon in boron carbide disclosed by the invention is composed of an oxidizing device, a gas absorption device and a titration device, and is characterized in that the gas absorption device is composed of a group of absorption bottles (1) connected in series and a precipitating bottle (2); the air inlet end of the absorption bottle group is connected with the oxidizing device (3), and the air outlet end of the absorption bottle group is connected with the precipitating bottle (2); the standardized sodium hydroxide solution (4) is filled in the absorption bottle; and a mixed solution (5) of barium chloride and sodium hydroxide is filled in the precipitating bottle. The device is simple in structure, convenient to use, high in gas circuit sealing property and high in reliability. According to the measurement method, the endpoint is easy to observe, the operability is high, the data repeatability is high, and the accuracy is high. The device and the method are suitable for detection of the free carbon in the boron carbide.
Owner:SHANDONG NON METALLIC MATERIAL RES INST
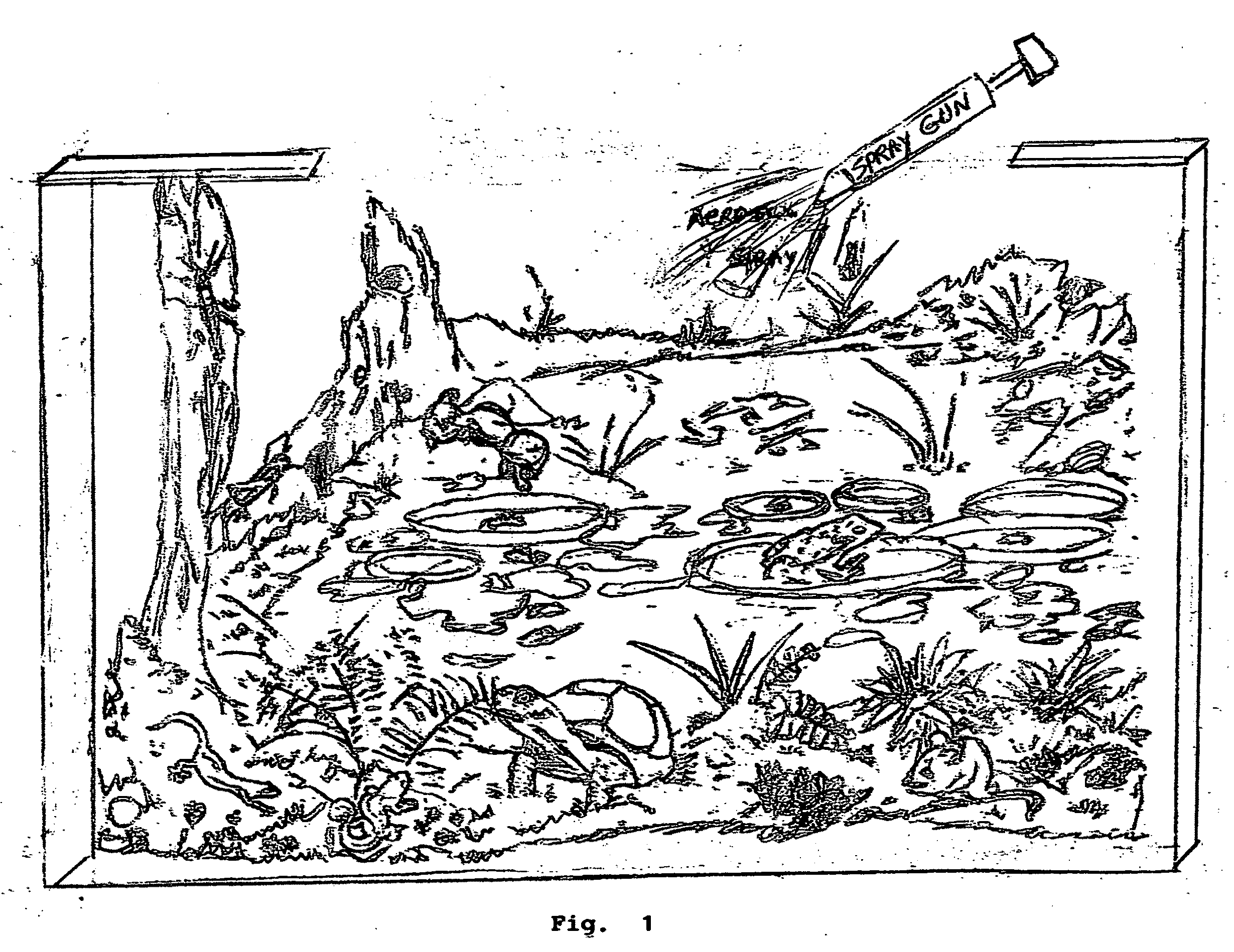
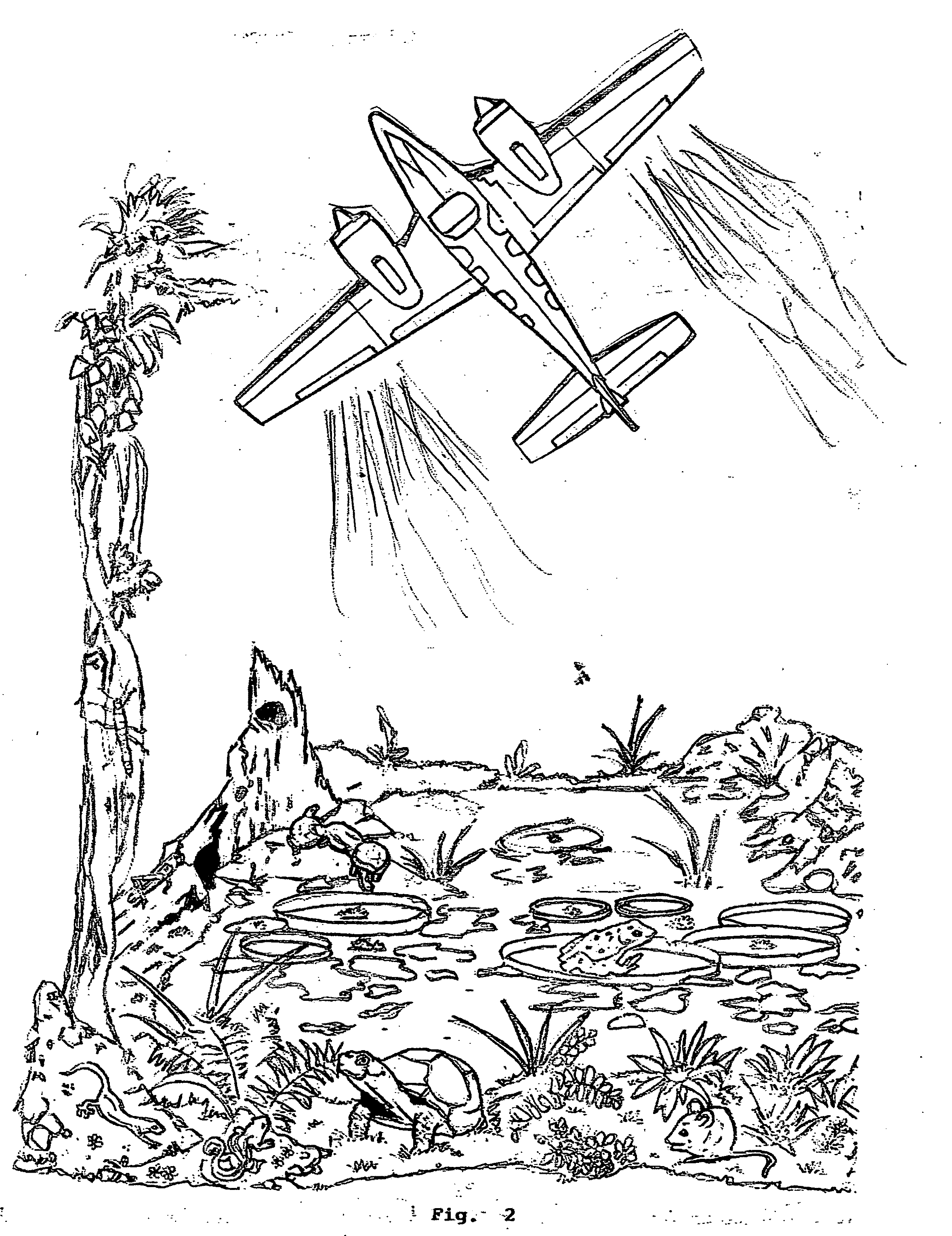
Method to scrub greenhouse gases from the atmosphere
InactiveUS20100005967A1Reduce buildEliminating fossil fuel useNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentFluorinated gasesAtmospheric air
Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and three groups of fluorinated gases have been referred to as greenhouse gases and the most offensive gases in contributing to Global Warming This invention comprises the use of Titration and other chemical oxidation—reduction reactions in novel ways to scrub these gases from the Earth's atmosphere. The invention comprises identifying, developing, and spraying base aerosols to neutralize carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, sulphur dioxide, and similar compounds whose oxides form acids when dissolved in water vapor. Acid-base titrations result in neutralization of the acid and the base. The formation of a salt and water typically are by-products. Salt precipitates such as CACO3—calcium carbonate or limestone settle into the oceans naturally forming limestone deposits which act as homes for microscopic sea life. Carbonic acid which results from CO2 being dissolved in water produces calcium carbonate when treated with a base. The invention proposes that by trials other natural salts may be identified which may safely be precipitated to the earth as it is important that the absorption into the Earth's environment occur with a minimum of deleterious effects. There exists a number of acids and The invention further comprises the novel use of vehicles such as space shuttles or a space station as delivery vehicles.
Owner:ABFY SELLERS GRP
Method for analyzing purity of 2,4,5-triamino-6-hydroxy pyrimidine sulfate sample by utilizing titration
The invention discloses a method for analyzing the purity of a 2,4,5-triamino-6-hydroxy pyrimidine sulfate sample by utilizing titration, and the method belongs to the field of medical intermediate analysis. The quantitative analysis of products is carried out by adopting a method of converting sulfate into hydrochloride which is easily dissolved into water and titrating the total acidity in a solution through strong base. The destination of a titration reaction is indicated through an acid-base indicator or an acidometer, and the recovery rate and precision tests of the method verify that the analysis result of the method is accurate and reliable. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of mature method, low cost and simplicity and convenience in operation because an acid base titration analysis method is adopted. The accuracy and precision of the method are high by adopting a macro analysis method.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Continuous determination method for contents of sulfuric acid, copper and nickel in copper electrolyte
InactiveCN107271603AThe result is stableSave labor timeChemical analysis using titrationMurexidePotassium iodine
The invention discloses a continuous determination method for the contents of sulfuric acid, copper and nickel in a copper electrolyte. The method comprises the following steps: adding neutral ultrapure water into a same copper electrolyte, and with a pH meter used for indication of terminal points, determining sulfuric acid by using an acid-base titration method; adding ammonia water into the sample where determination of sulfuric acid is finished so as to adjust a pH value to 3.0 to 4.0, adding ammonium bifluoride, potassium iodide and a starch indicator and determining copper in the copper electrolyte by using sodium hyposulfite titration; and adding a tartaric acid solution into the sample where determination of copper is finished, adjusting a pH value to 8.0 to 9.0 by using ammonia water, adding a sodium hyposulfite solution and a murexide indicator and carrying out titration with an EDTA standard solution so as to determine the content of nickel in the electrolyte. The continuous determination method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, short determination time, accurate results, low cost, etc. The continuous determination method is applicable to rapid continuous determination of the contents of sulfuric acid, copper and nickel in copper electrolytes from copper smelting plants and provides instant rapid analysis for quality control of the copper electrolytes.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS
Method for purifying ruthenium complex crude product through recrystallization method
The invention discloses a method for purifying a ruthenium complex crude product through a recrystallization method, which comprises the following steps: A) dissolving 1g of ruthenium complex crude product and 10-20mL of alkali liquor in organic solvent while stirring, and filtering to remove insoluble impurities; B) acidifying the filtrate with dilute acid until the pH value is 3-6, thus precipitating a large amount of solids; C) filtering; D) washing; E) drying; and F) repeating the steps A)-C), or the steps A)-D), or the steps A)-E) 2-5 times, thus obtaining the ruthenium complex product. Through simple acid-base titration and pH value regulation recrystallization, the purity of the ruthenium complex dye can be effectively increased; and the purity of the dye is increased from 52.1% to 70.25% and is increased by 34.8%.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
Clean type diesel oil pour point depressant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106479584ARaise the ratioLow costLiquid carbonaceous fuelsEnvironmental resistanceDepressant
The invention belongs to the field of novel additives for petrochemical engineering, and particularly relates to a clean type diesel oil pour point depressant and a preparation method thereof. The clean type diesel oil pour point depressant is prepared from acid anhydride, long-carbon-chain fatty acid and low-carbon alcohol. The concrete preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) taking 25.0 to 28.0 parts by mass of the acid anhydride; (2) adding 43.0 to 45.0 parts by mass of the low-carbon alcohol; heating and stirring until mutual dissolution is realized; (3) measuring an esterification rate by an acid-base titration method; (4) after a period of time, adding 27.0 to 29.0 parts by mass of the long-carbon-chain fatty acid, thus obtaining a target product. Solvents and catalysts are not used; the materials are economic; the effects of cleanness and environment protection are achieved. A pour point depressant formula is applicable to better flow performance improvement when diesel oil is at low temperature; the requirements of cleanness and environment protection of combusted tail gas exhaust in the diesel oil combustion process of a diesel engine can be particularly met.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Wet process metal ion detection method for solar cell
InactiveCN102507577AHigh sensitivityHas limitationsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorStrong acidsPotassium
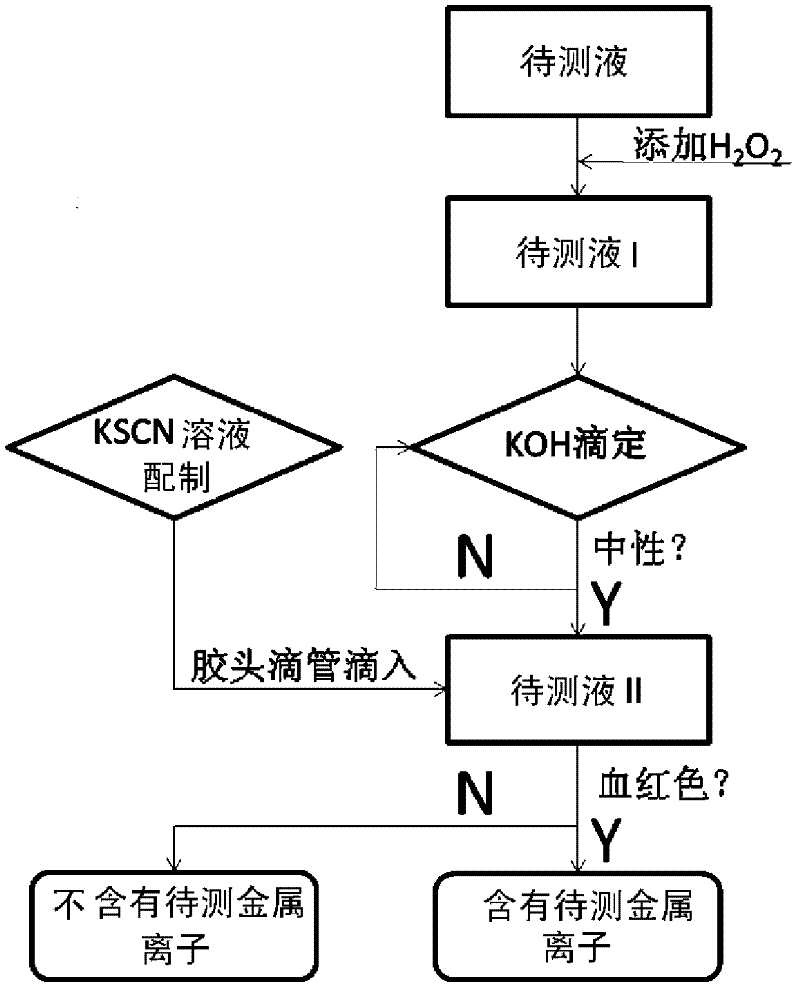
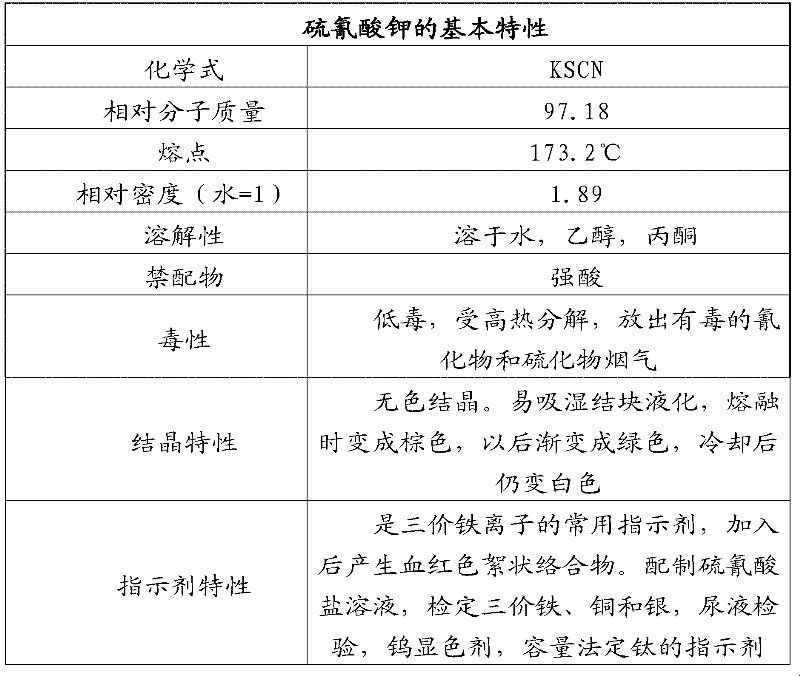
The invention discloses a wet process metal ion detection method for solar cell. The method comprises oxidation of to-be-detected solution; acid-base titration; preliminary judgment of metal ions; and KSCN metal ion detection, so as to eliminate the influence of a strong acid environment on the detection result while the oxidation of to-be-detected solution ensures that low-valence metal ions can be detected out by the KSCN reagent after oxidation of the low-valence metal ions to guarantee accuracy of the detection result. The invention integrates advantages and disadvantages of a potassium thiocyanide metal ion detection method, adopts two pretreatment steps of to-be-detected solution oxidation and acid-base titration to eliminate inaccuracy of detection result caused by acid environment and low-valence metal ions, guarantees reliability of the test result, makes full use of sensitivity of KSCN in metal ion detection under conventional conditions, and carries out metal ion detection in a wet process of solar cell production by preparing KSCN solution.
Owner:XINYU GIGA SOLAR NEW ENERGY
Pre-lithiation preparation method of lithium ion battery pasting agent and production and application
InactiveCN110212197AImprove the first effectImprove cycle lifeCell electrodesSecondary cellsLithium hydroxideALLYL SUCROSE
The invention proposes a pre-lithiation preparation method of a lithium ion battery pasting agent and production and application. The pre-lithiation preparation method of the lithium ion battery pasting agent comprises the following steps of introducing lithium ions into a polyacrylic acid binging agent in a lithium ion battery electrode material, wherein the molecule formula of the polyacrylic acid binding agent is [CH2CH]<n>COOH; performing acid base titration on the polyacrylic acid and lithium hydroxide so that pH is equal to 7, wherein the molecule formula of the binging agent is [CH2CH]<n>COOLi; and employing [CH2CH]<n>COOLi to prepare electrode mixed paste to achieve a pre-lithiation effect. The lithium ions are introduced into the polyacrylic acid binding agent in the electrode material, acid base titration is performed on the polyacrylic acid and the lithium hydroxide, the preparation method is simple and efficient and is easy to operate, the initial efficiency of the batteryis effectively improved, and the cycle lifetime of the battery is prolonged.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Method for assaying residual acid of nitroglycerin
ActiveCN103245543AAvoid interferenceGuaranteed freeChemical analysis using titrationPreparing sample for investigationOrganosolvMedicinal chemistry
The invention discloses a method for assaying residual acid of nitroglycerin, belonging to the field of inorganic chemical analysis. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting alkaline liquid from the nitroglycerin by using water; completely dissolving the extracted nitroglycerin by using a neutral organic solvent which is a mixture of nitroglycerin and water; and assaying the residual acid content of the dissolved nitroglycerin by an acid base titration method. The invention relates to a method for assaying the residual acid (nitric acid and sulfuric acid) of the nitroglycerin.
Owner:宜宾北方川安化工有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com