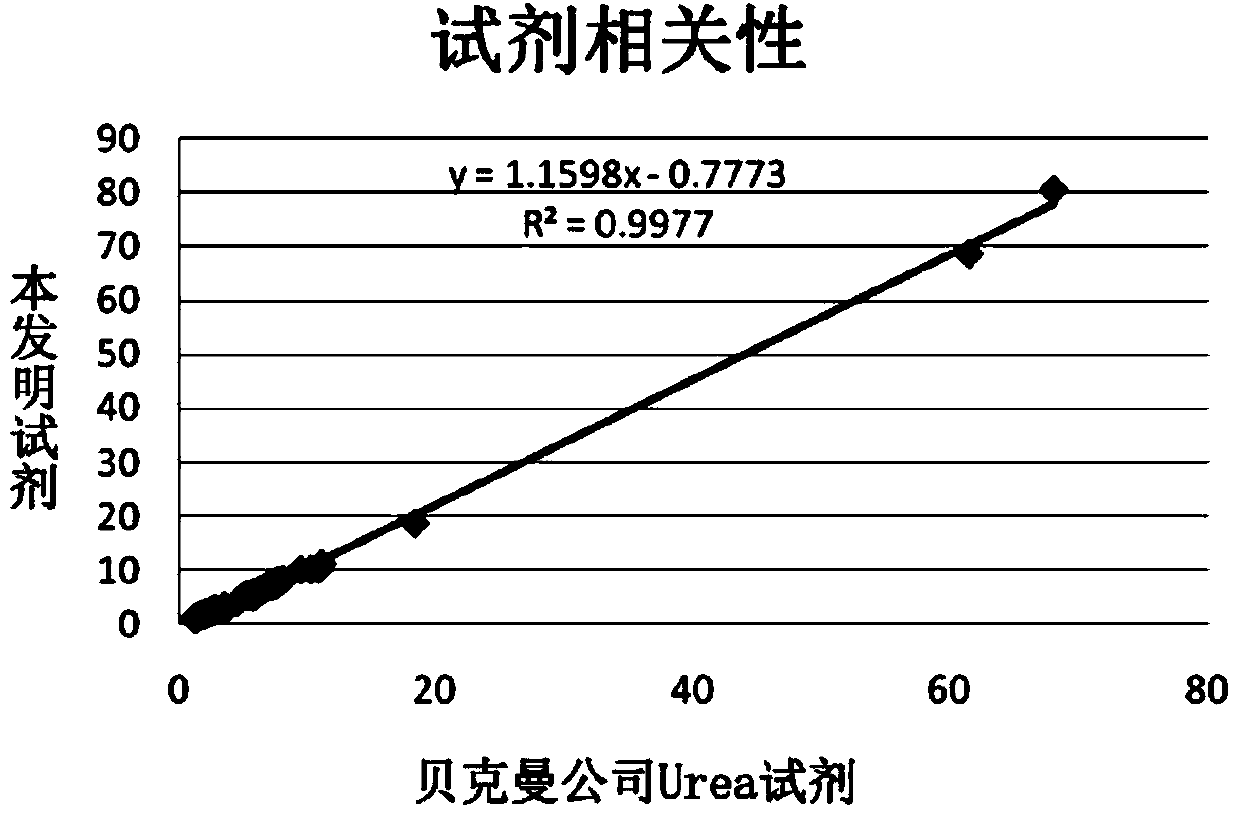
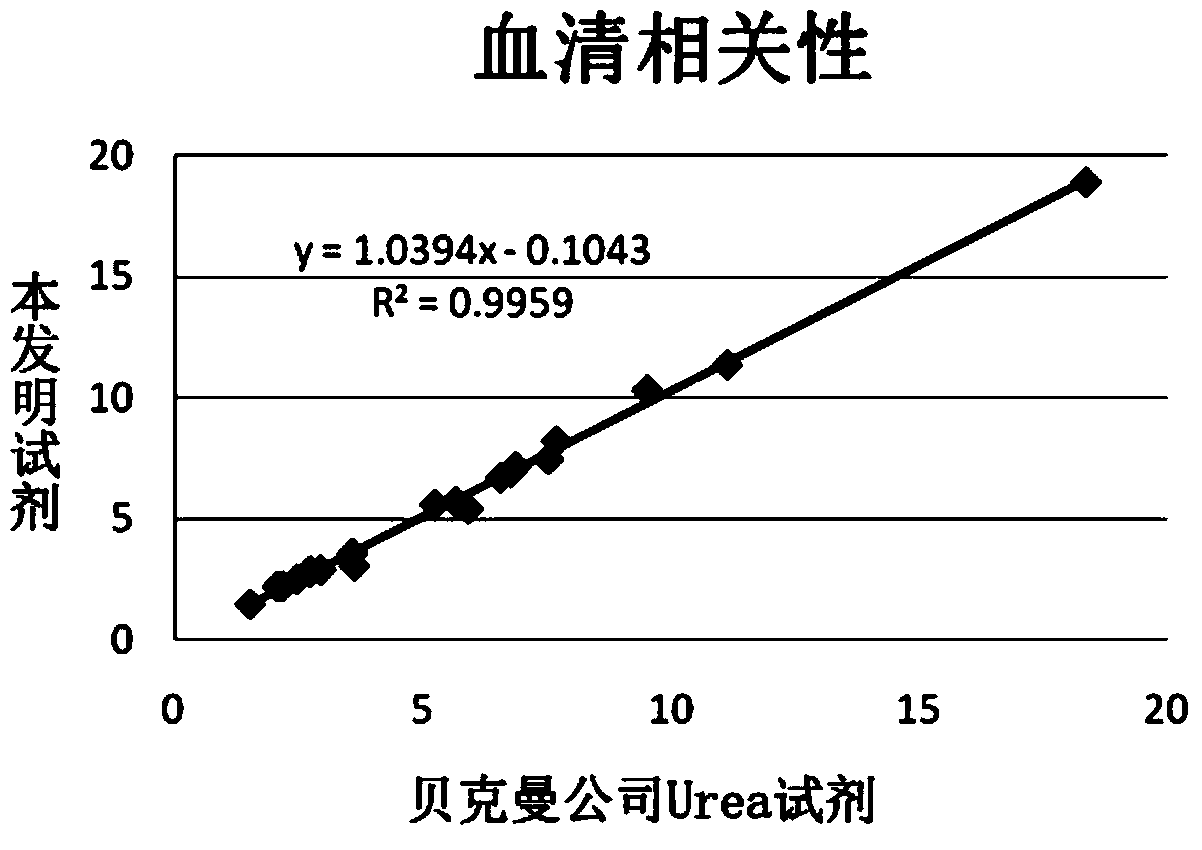
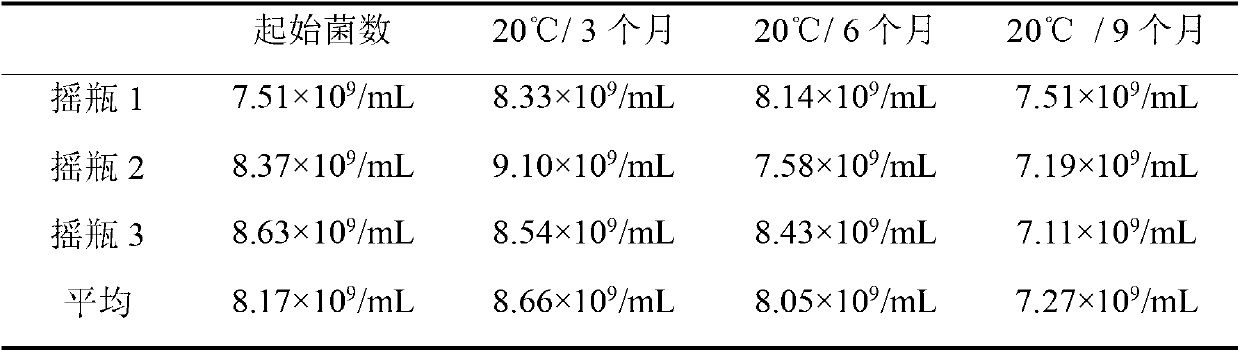
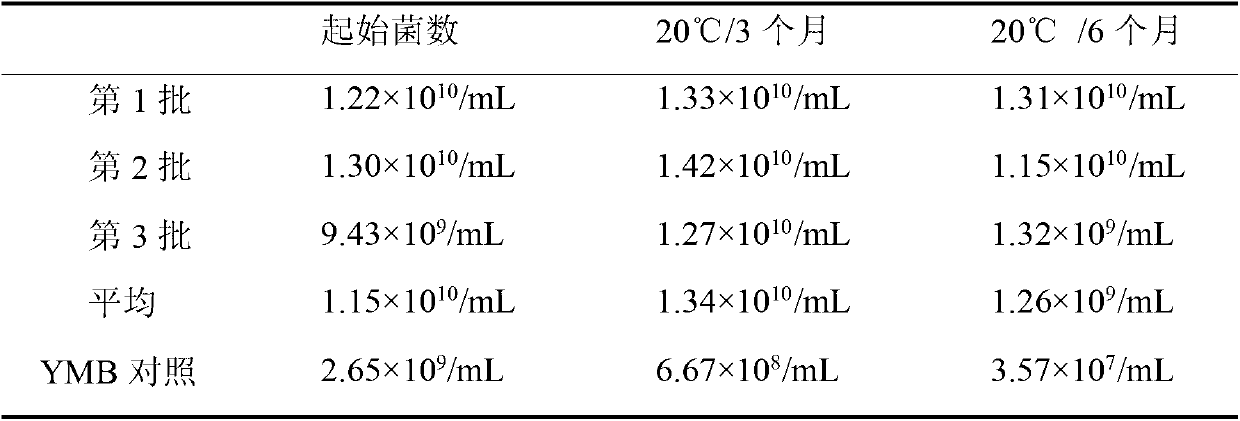
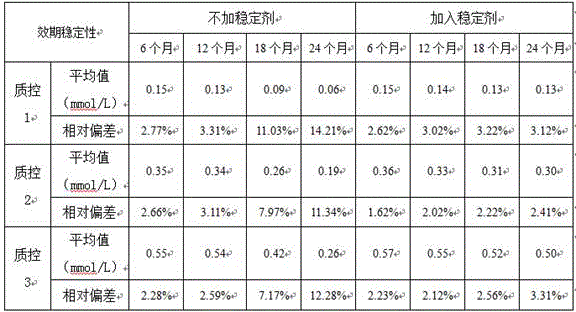
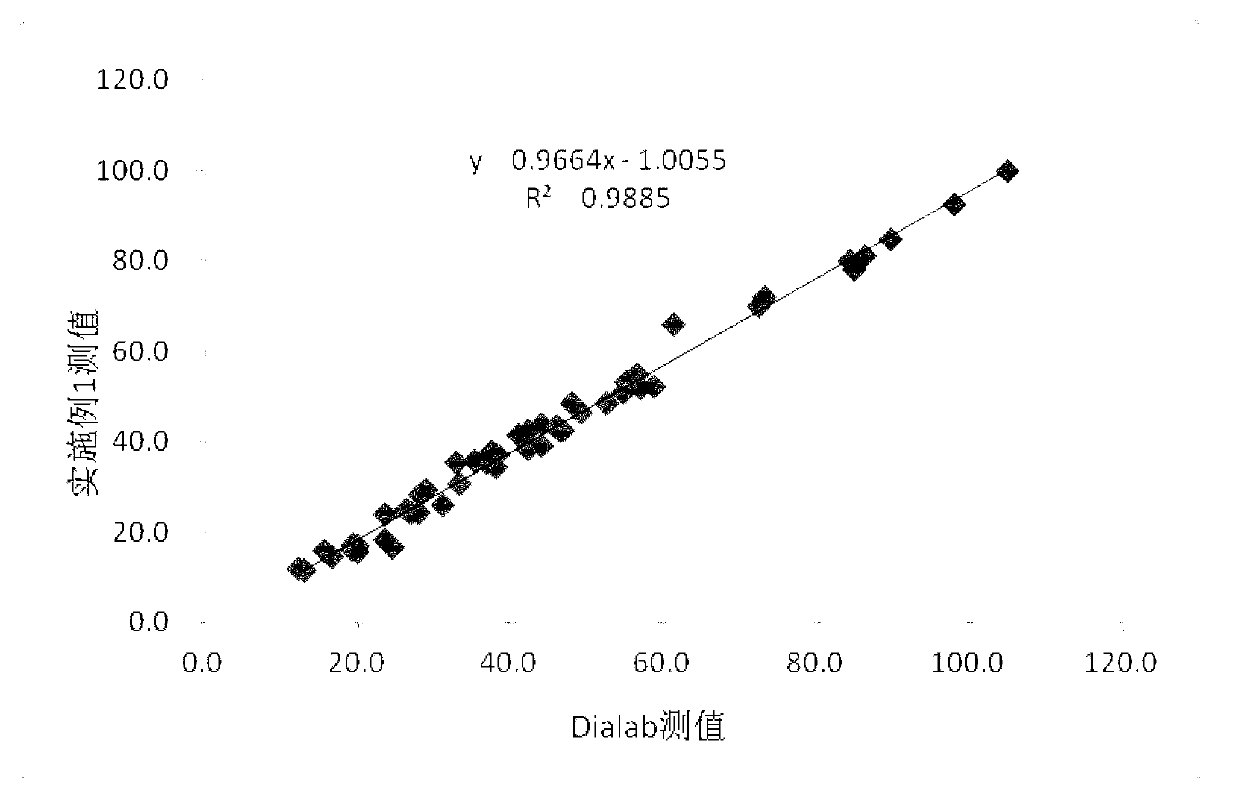
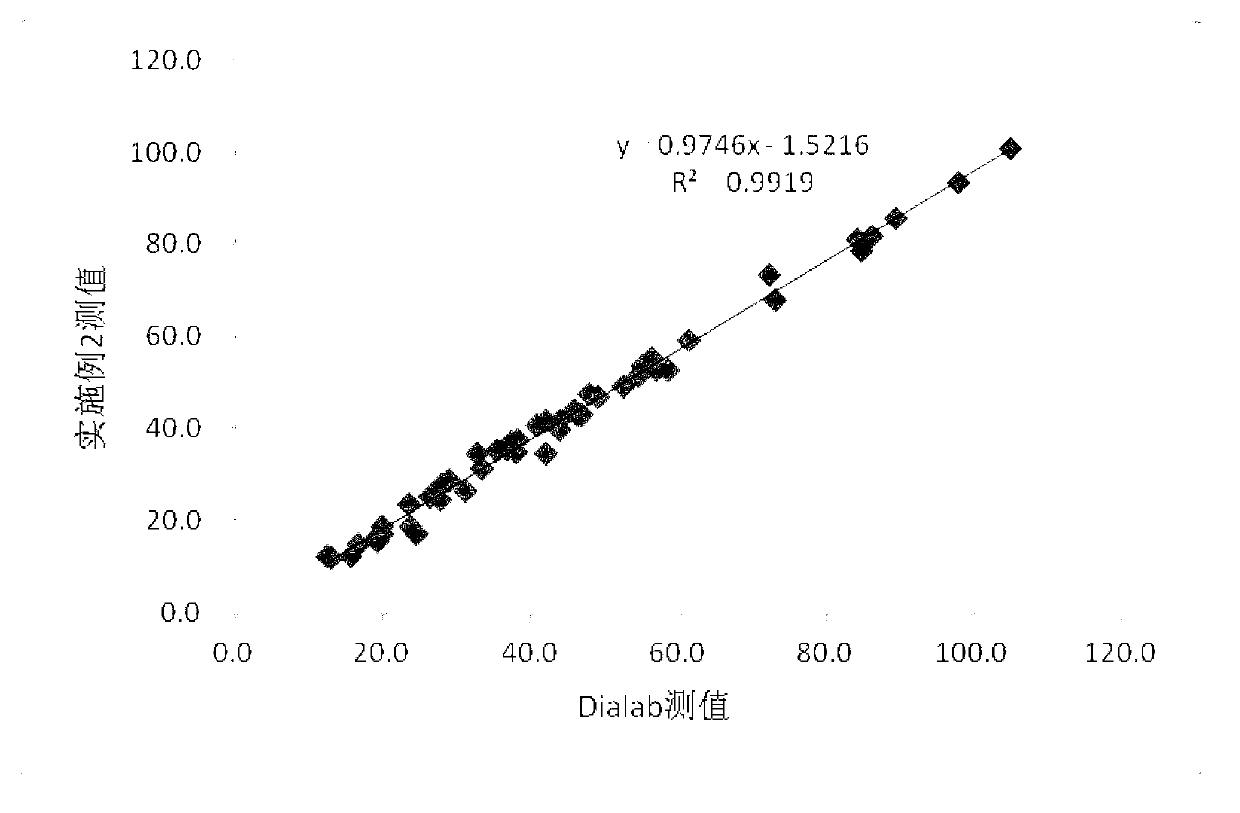
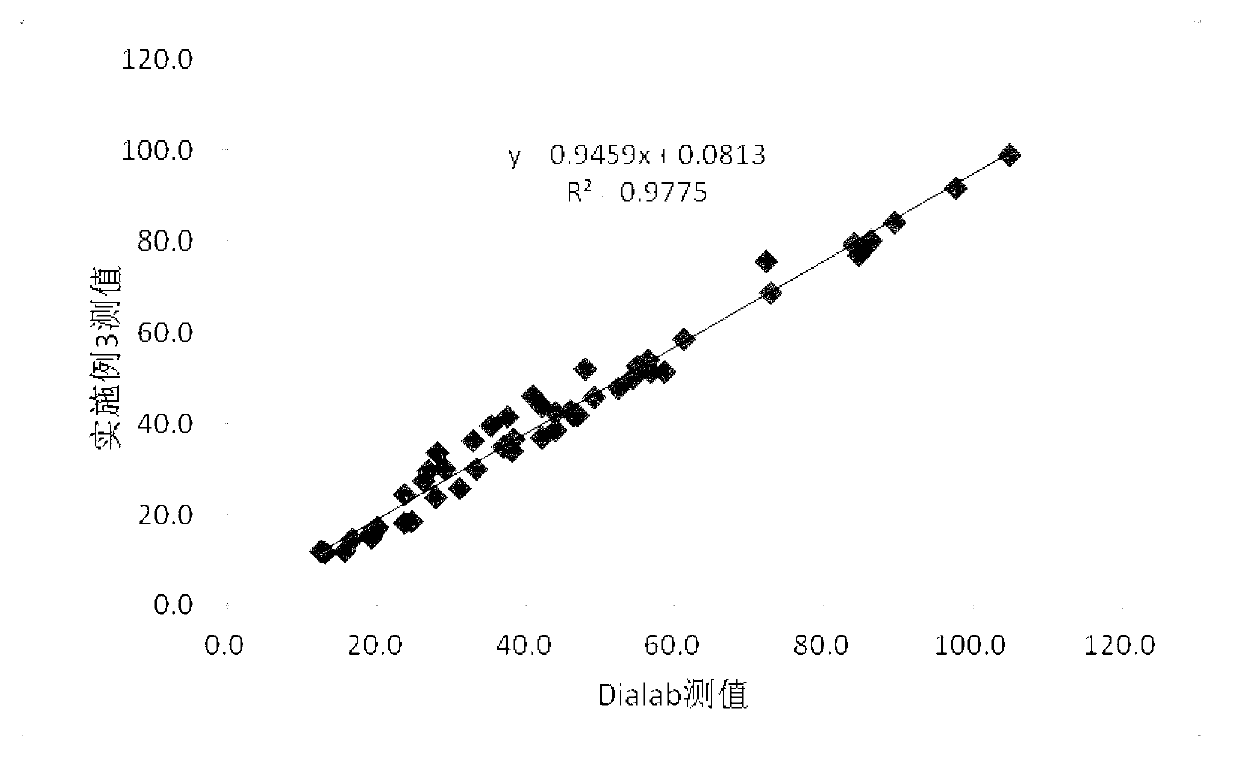
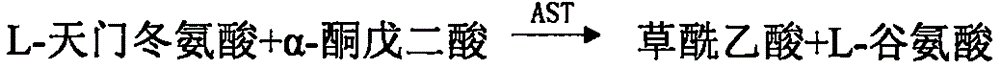Patents
Literature
56 results about "Alpha-oxoglutarate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
L-d-glutamic oxidase with substrate specificity and alpha-oxoglutarate produced by catalysis of same
InactiveCN102994467ANo pollution in the processSimple production processMicroorganism based processesEnzymesSodium GlutamateIsopropyl alcohol
The invention discloses L-d-glutamic oxidase with substrate specificity and alpha-oxoglutarate produced by catalysis of the same, and belongs to the field of enzyme-method catalytic production of fine chemicals. The invention has the advantages that the L-d-glutamic oxidase which only has the substrate specificity to L-glutamic acid, L-sodium glutamate and glutamine is utilized, 20g / L L-sodium glutamate solution is added in fermented liquid which is fermented for 60 hours and contains the L-d-glutamic oxidase, carrying out conversion for 12 hours under the ventilating condition and the conditions that the temperature is 30 DEG C, the pH is 8.5 and the 5% (v / v) isopropyl alcohol, and measured by a high-performance liquid chromatography, the content of alpha-oxoglutarate reaches 14.5g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for efficiently producing alpha-oxoglutarate by adopting whole-cell transformation
ActiveCN103911400AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationBacillus subtilisBiology
The invention discloses a method for efficiently producing alpha-oxoglutarate by adopting whole-cell transformation. L-amino acid deaminase genes transformed by easily wrong PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) or site-saturation mutagenesis are expressed through bacillus subtilis, the transformation rate of the alpha-oxoglutarate produced by whole-cell transformation of L-glutamic acid is increased, and the gene sequence of the L-amino acid deaminase genes is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 or SEQ ID NO.2. A whole-cell transformation system in which the transformation rate is increased is constructed, the problem that a chemical method for synthesizing alpha-oxoglutarate is tedious in steps, low in yield and causes environmental pollution and the problem that the transformation rate during production of the alpha-oxoglutarate is low through enzymatic transformation are solved, the alpha-oxoglutarate is produced in a pollution-free mode at high yield through a one-step method, and a certain theoretical basis is laid for subsequent industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Identification method of aliphatic chain isomer alpha-oxoglutarate and 1, 3-acetone dicarboxylic acid
The invention discloses an identification method of aliphatic chain isomer alpha-oxoglutarate and 1,3-acetone dicarboxylic acid. The identification method is characterized by comprising the following steps that with an H<2>SO<4>-KIO<3>-[NiL](ClO<4>)<2>-MA-H<2>O<2> nonlinear chemical oscillation system as an identification solution, differential identification of the aliphatic chain isomer is realized according to an oscillation response of the system generated by the aliphatic chain isomer; L in [NiL](ClO<4>)<2> is 5, 7, 7, 12, 14, 14-hexamethyl-1, 4, 8, 11-tetraaza tetradecyl-4, 11-diene. An oscillation map provided by the identification method is relatively high in intuition; moreover, the aliphatic chain isomer alpha-oxoglutarate and 1,3-acetone dicarboxylic acid can be conveniently and quickly identified, and the method can also be widely used in other isomers; in addition, identification equipment is simple, high in accuracy and easy to operate and observe.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
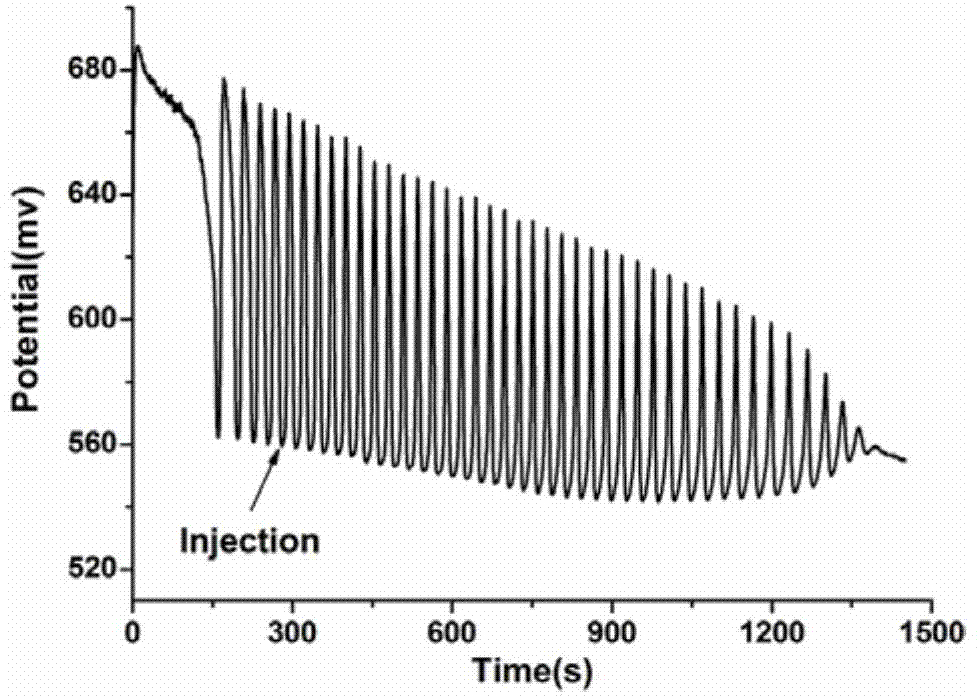
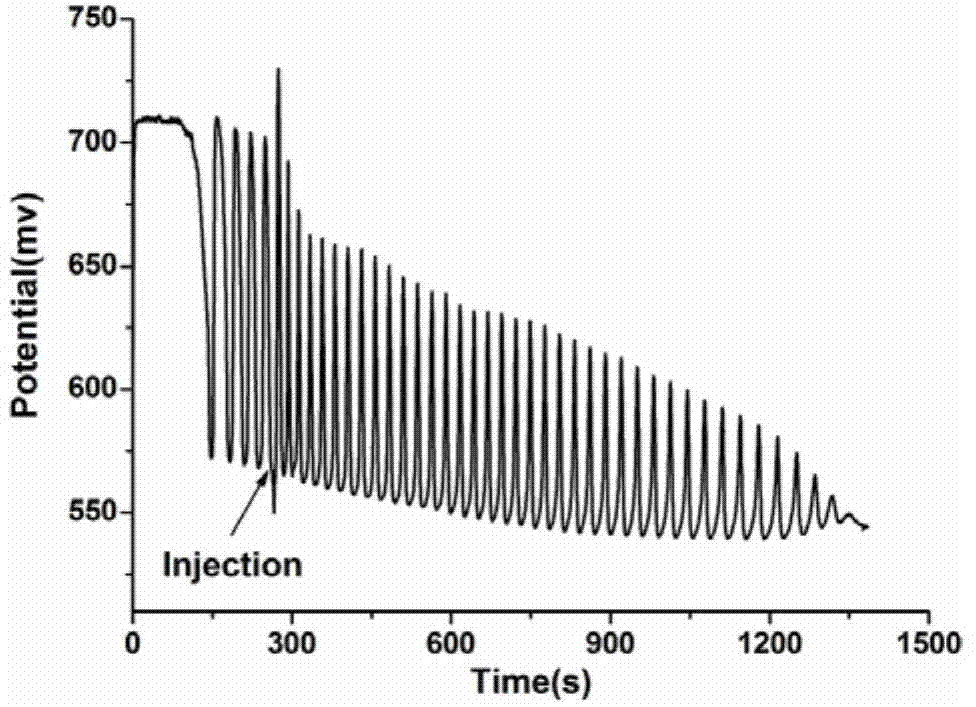
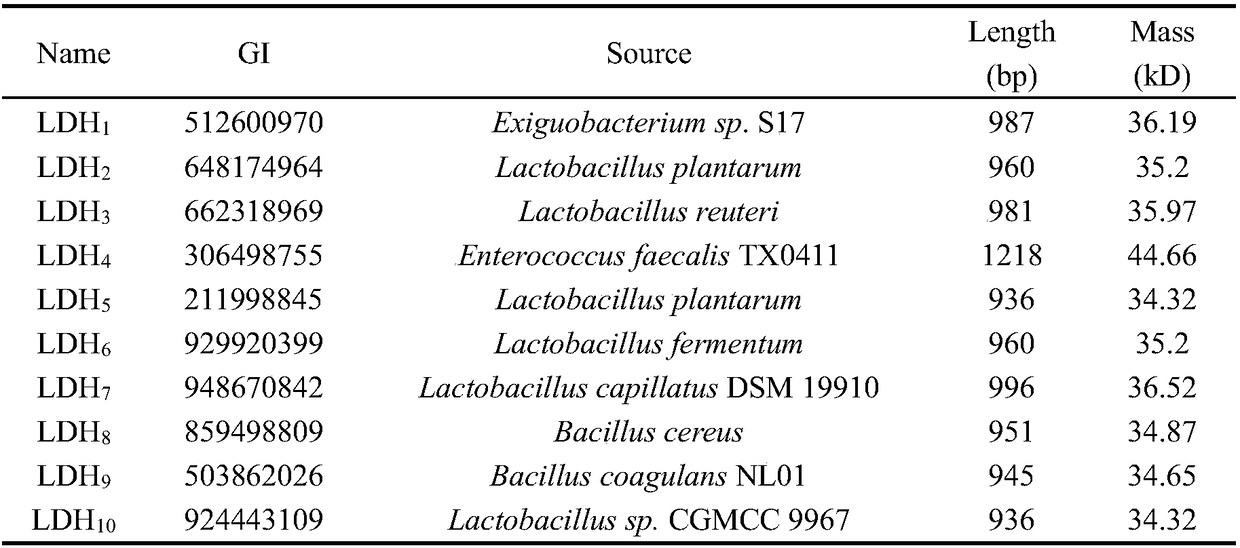
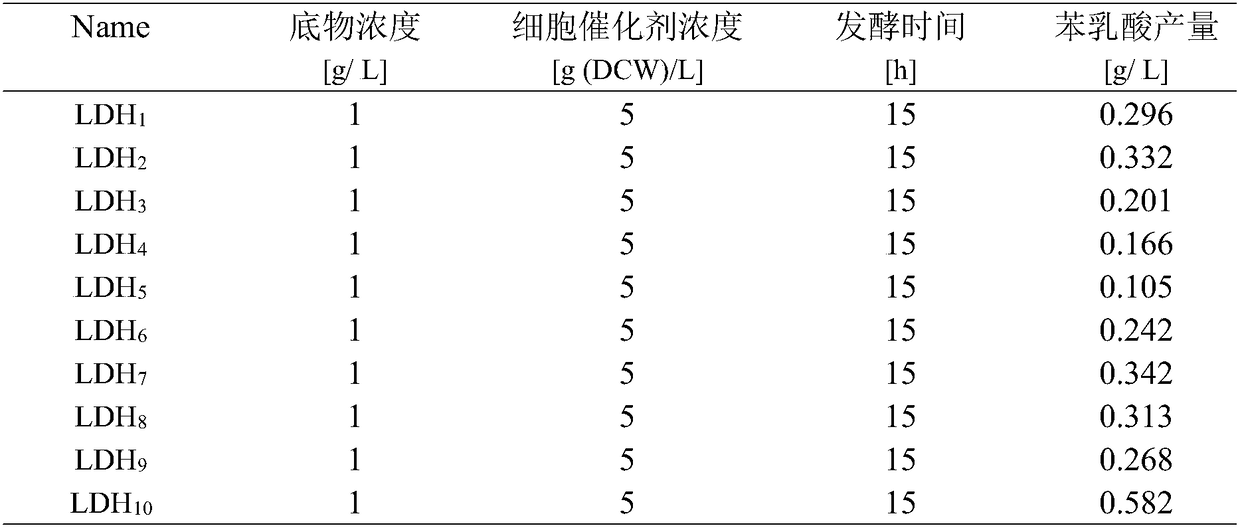
Method for producing phenyllactic acid through whole-cell transformation of phenylalanine
InactiveCN108277190AThe solution steps are cumbersomeLow resolutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisPhenylalanine
The invention discloses a method for producing a phenyllactic acid through whole-cell transformation of phenylalanine, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The method successfullyconstructs an L-amino acid deaminase, L-lactic dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase co-expressed strain. Phenyllactic acid of 30 g / L is produced through the whole-cell transformation of phenylalanine, and the transformation rate is 100%. The establishment of a whole-cell transformation system solves the problems of complicated steps, low yield and environment pollution in the chemical synthesis of the phenyllactic acid as well as the problem of low transformation rate in the production of the alpha-oxoglutarate through the enzymatic conversion, the phenyllactic acid is produced through a one-step method at high yield without pollution, and a certain theoretical foundation is laid for the subsequent industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
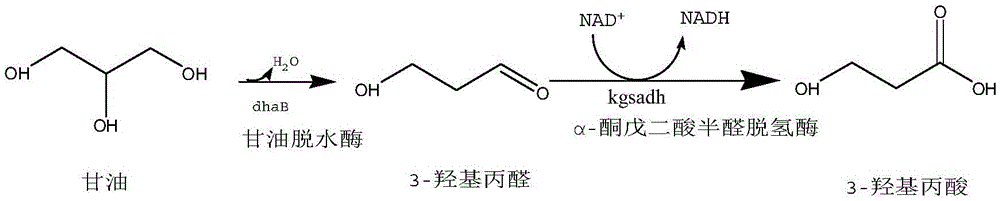
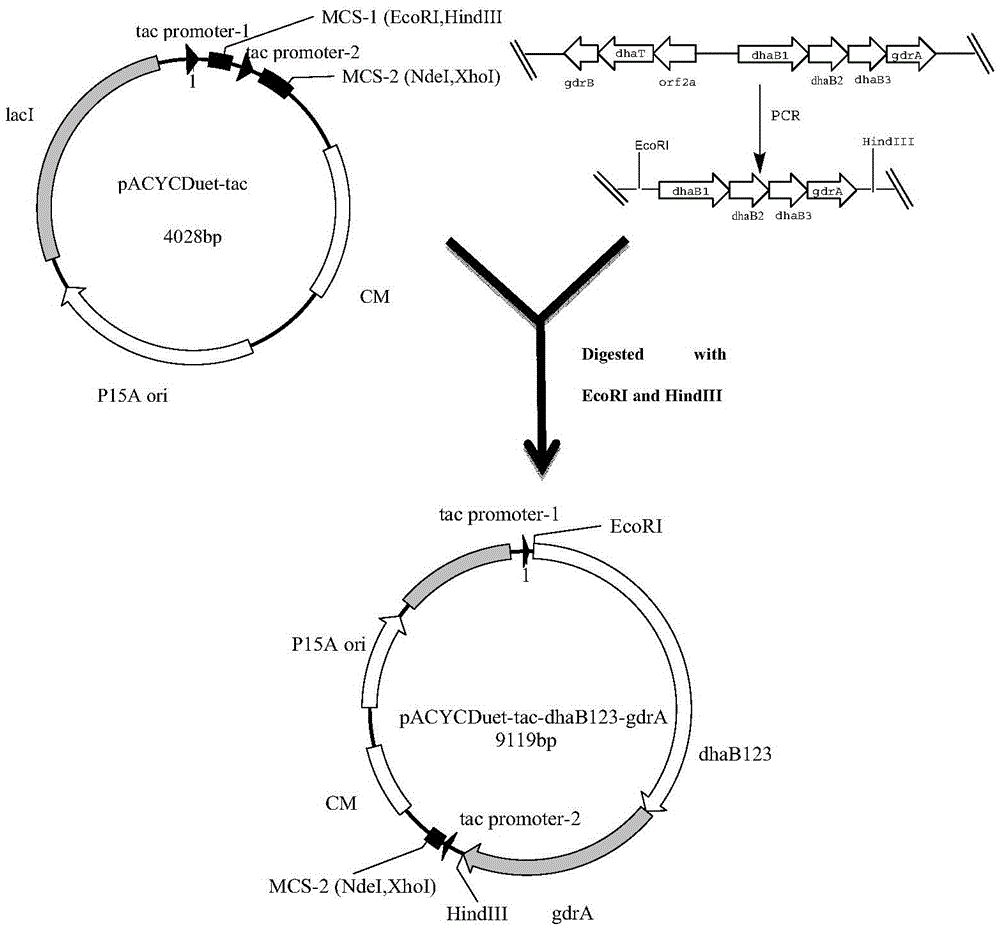
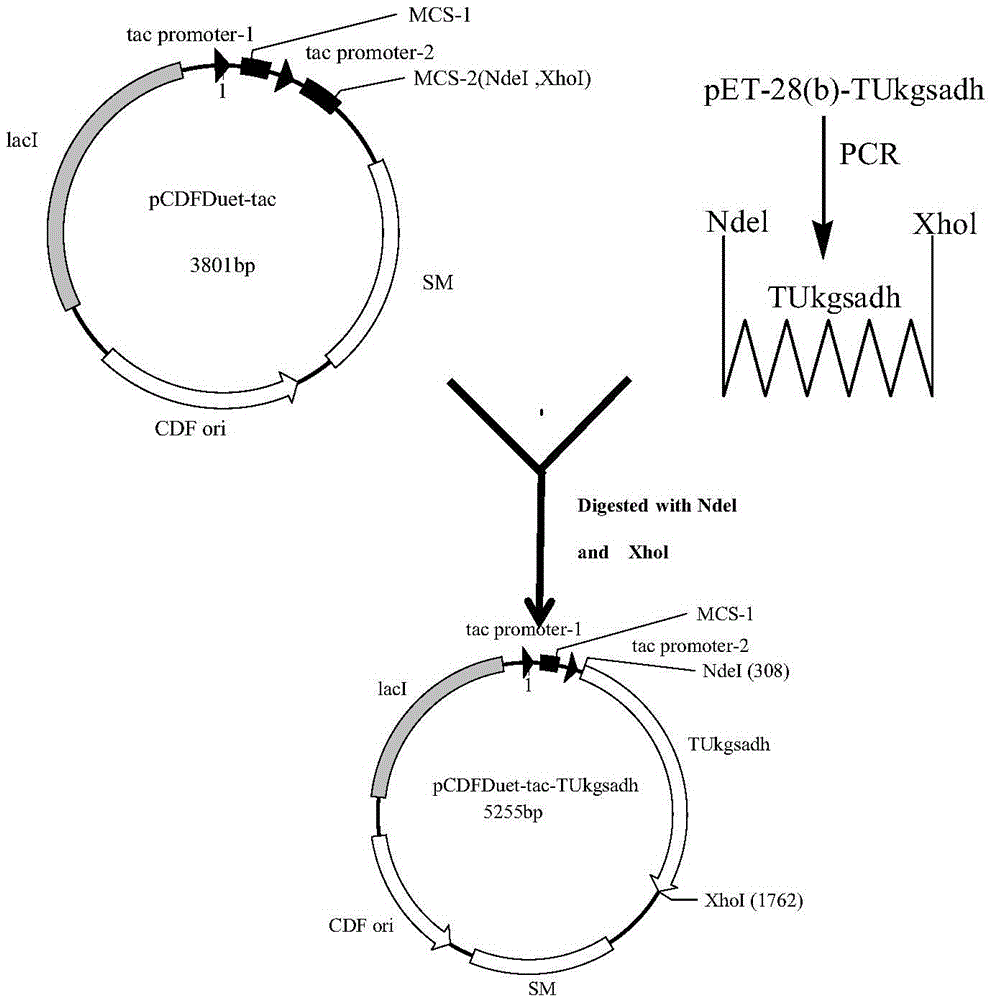
Recombinant Escherichia coli and application of recombinant Escherichia coli in synthesizing 3-hydroxypropionic acid
ActiveCN105567622AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coli3-Hydroxypropionic acid
The invention discloses recombinant Escherichia coli and application of the recombinant Escherichia coli in synthesizing 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The recombinant Escherichia coli is formed by glycerol dehydratase genes dhaB123, glycerol dehydratase reactivating factor genes gdrA, alpha-oxoglutarate semialdehyde dehydrogenase mutant coding genes TUkgsadh and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase coding genes gpdl which are guided into host bacteria. By means of the gene knockout technique, the yield of byproduct 1,3-propylene glycol is reduced, and meanwhile, cofactors NAD+ of aldehyde dehydrogenase are regenerated. Thus, the yield of the 3-hydroxypropionic acid is improved by 1.5 times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Pig feed additive for improving intestinal health and boosting immunity
InactiveCN105146230AGood for healthImprove immunityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDipeptideAnimal science
The invention discloses a pig feed additive for improving intestinal health and boosting immunity and belongs to the field of feed additives. The additive is prepared from compound plant polysaccharide, complex enzyme preparation, lactobacillus plantarum powder, lactobacillus buchneri powder, stevia rebaudiana powder, fructus chebulae powder, orange peel powder, arginine, glutamine dipeptide, alpha-oxoglutarate, cystine, taurine and a carrier, wherein corncob powder and peanut shell powder serve as the carrier. By the adoption of the additive, pig intestinal health can be improved, intestine development of live pigs can be promoted, the feed digestibility and absorptivity of live pigs can be improved, pig growth can be promoted, marketing period can be shortened, economical benefits can be increased, and feeding effect can be improved. Meanwhile, the immunity of pigs can be improved, the morbidity of pigs can be reduced, and application prospects are quite broad.
Owner:YUNNAN TWINS FEED CO LTD
Aspartate amino transferase detection kit
InactiveCN106644976AEliminate distractionsImprove accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsAmidinotransferasesTransferase
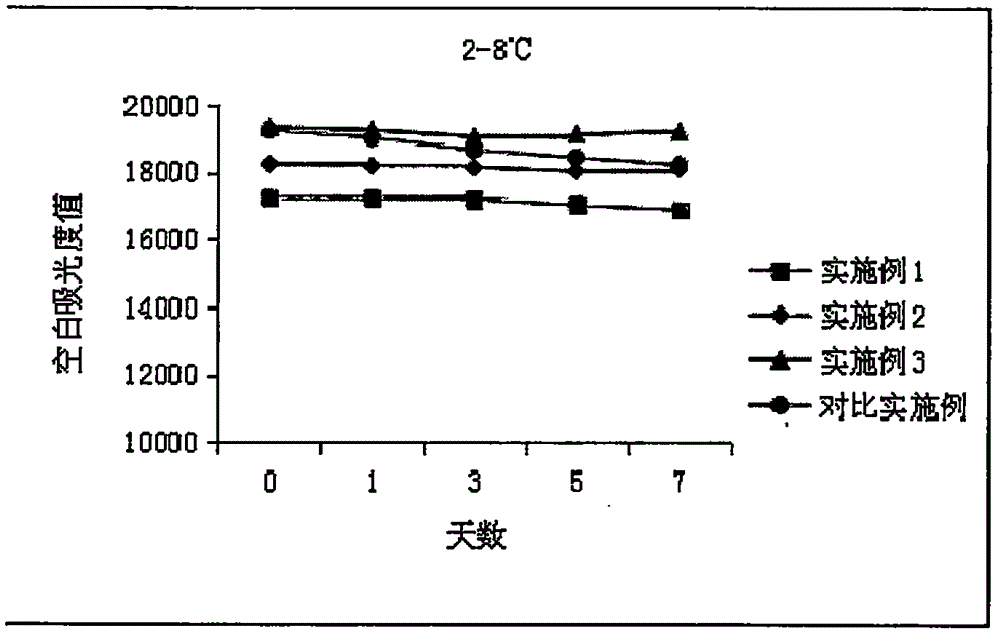
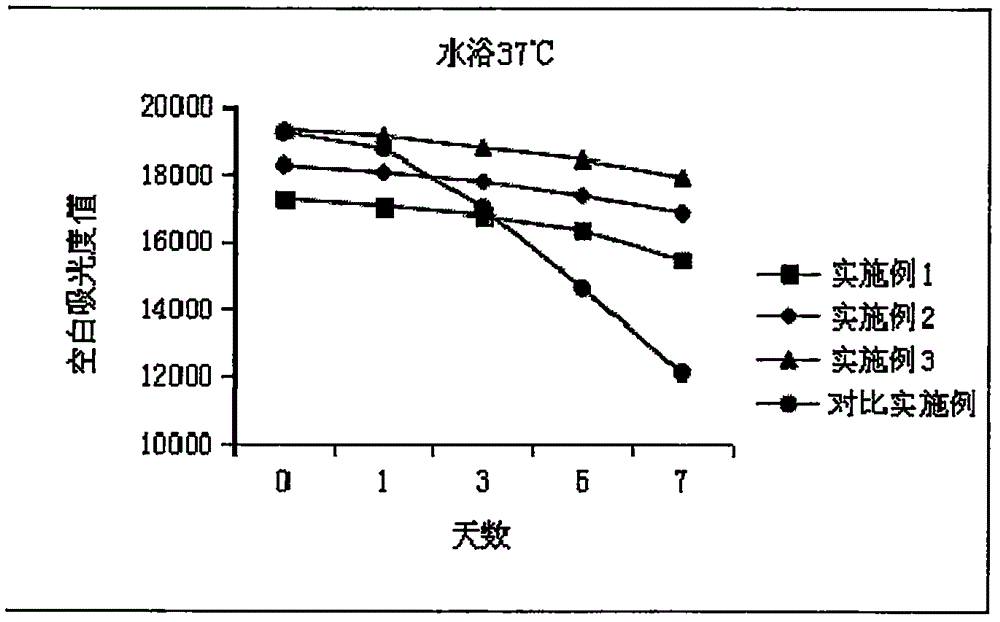
The invention relates to an aspartate amino transferase (AST) detection kit and belongs to the technical field of clinic in vitro diagnostic reagents. The invention aims to provide the aspartate amino transferase detection kit with capability of effectively eliminating endogenous alpha-oxoglutarate interference and high stability in order to achieve more accurate and reliable determination results of aspartate amino transferase. The kit provided by the invention comprises a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 comprises the following components: Tris-HCl buffer solution, L-asparaginic acid, reduction coenzyme (NADH), malic dehydrogenase (MDH), enzyme protective agent, stabilizer and preservative, and the reagent 2 comprises the following components: Tris-HCl buffer solution, alpha-oxoglutarate, a stabilizer and a preservative. The enzyme protective agent and the stabilizer are added into the AST detection kit provided by the invention so that the stability of the aspartate amino transferase detection kit is promoted; the aspartate amino transferase detection kit is suitable for various full-automatic biochemical analyzers; the operation is simple and safe; the aspartate amino transferase detection kit has convenience in clinical application and popularization.
Owner:王贤俊
Textile chitosan coating additive with color gradual changeability along with time passing and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a textile chitosan coating additive with color gradual changeability along with time passing and a preparation method thereof. The composition comprises, by weight, 140-180 parts of high-molecular chitosan, 140-180 parts of chitosan fibers, 3-5 parts of sodium alginate, 4-5 parts of ethylene diamine tetra(methylene phosphonic acid), 4-5 parts of hyaluronic acid, 5-6 parts of a pigment 1, 5-6 parts of a pigment 2, 0.1-0.3 parts of nanometer TiO2, 3-5 parts of a TPP ion cross-linking agent, 2-3 parts of a hydrophobic essence material, 1-2 parts of alpha-oxoglutarate and a proper amount of water. Different chitosans coat different pigments and the coated product is used as a textile dye additive. Chitosan is degraded along with time passing and the textile color is gradually changed so that the dual purposes are realized and textile color diversity and durability are realized.
Owner:CHANGZHOU NANFEI MACHINERY
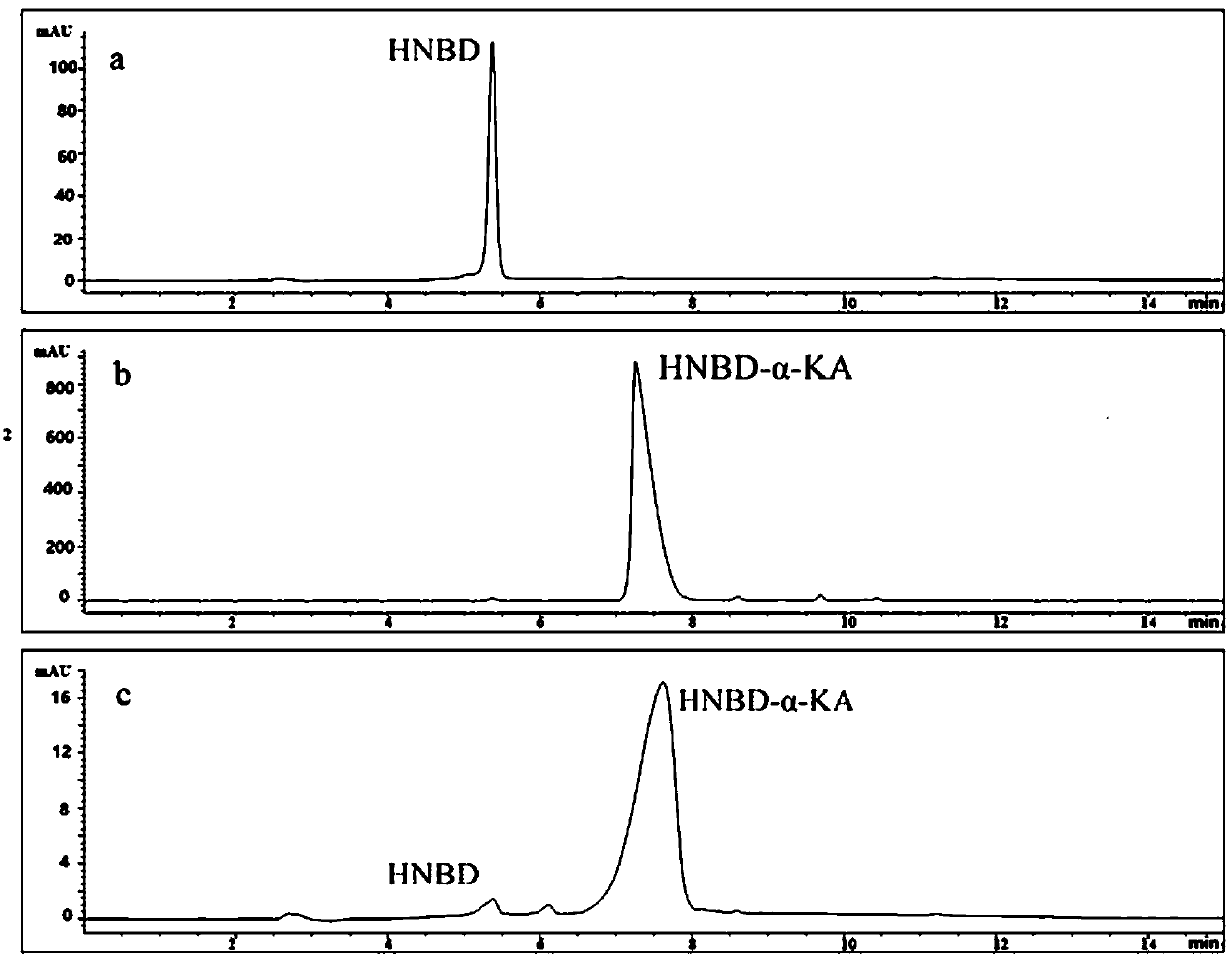
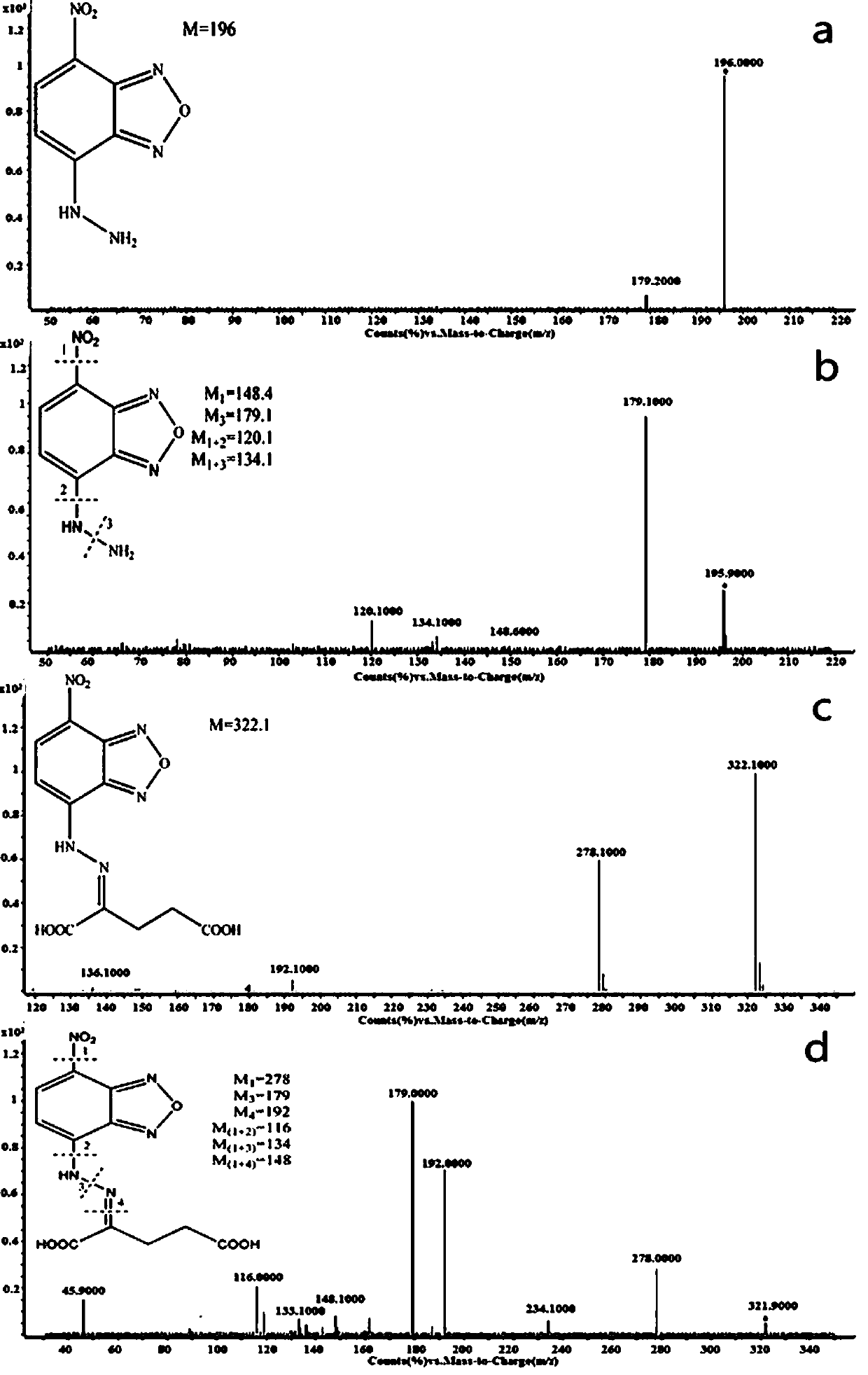
Preparation method of alpha-oxoglutarate fluorescent/ultraviolet molecular probe and application of alpha-oxoglutarate fluorescent/ultraviolet molecular probe to biological samples
InactiveCN105503768AHigh sensitivityEasy to solveOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsDiseaseFluorescence
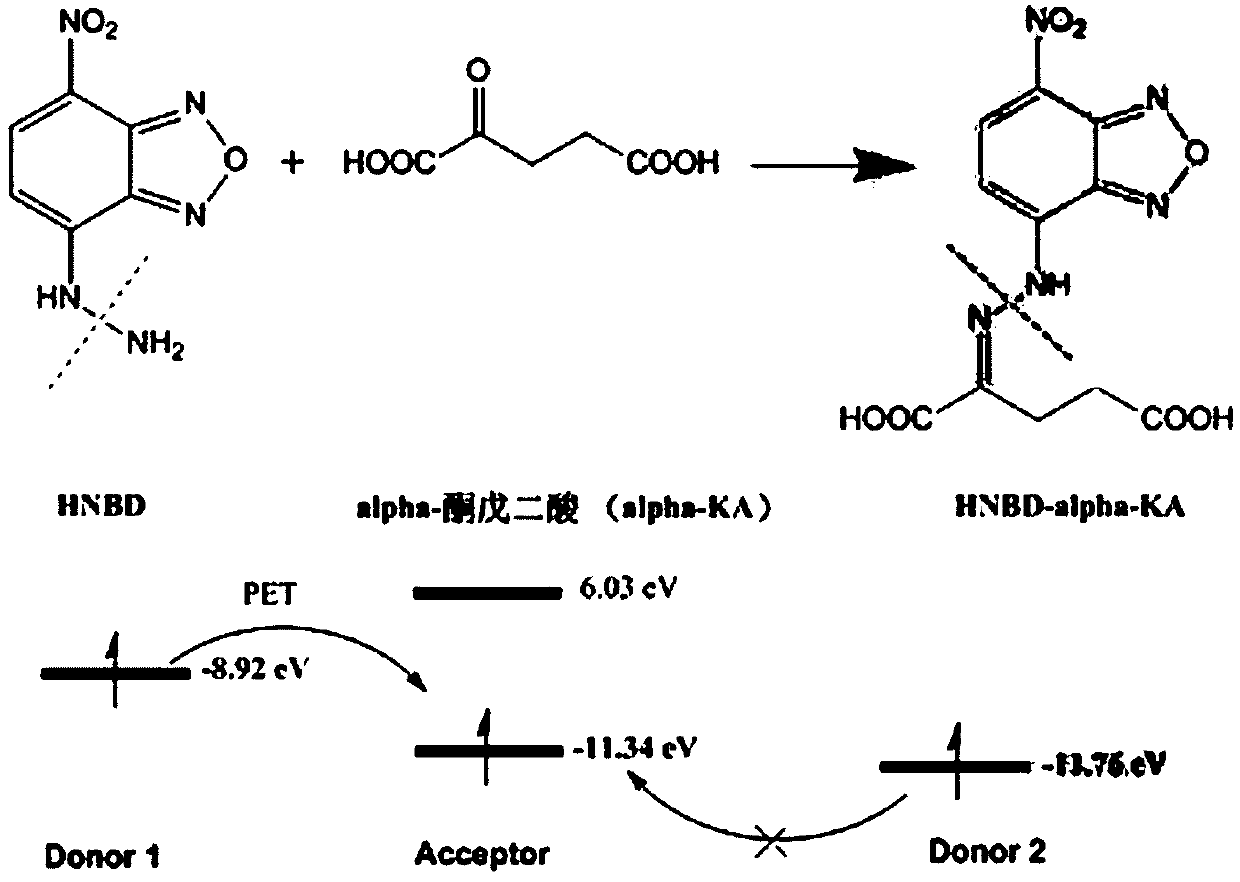
The invention relates to a preparation method of an alpha-oxoglutarate fluorescent / ultraviolet molecular probe and application of the alpha-oxoglutarate fluorescent / ultraviolet molecular probe to biological samples. The preparation method includes the steps that NBD-Cl is dissolved in chloroform, the dissolution concentration is 0002-0.012 g / ml, then a hydrazine hydrate-methanol solution with the volume concentration being 0.2-1.2% is added in and uniformly mixed, brown precipitate is obtained through stirring at room temperature and filtered, a filter cake is washed through ethyl acetate and dried, and the brown product alpha-oxoglutarate fluorescent / ultraviolet molecular probe is obtained. The alpha-oxoglutarate fluorescent / ultraviolet molecular probe is applicable to qualitatively and quantitatively analyzing alpha-oxoglutarate in the biological samples, and detection is sensitive, accurate and fast. The biological samples mainly comprise serum, living cells, muscle tissue and the like. The alpha-oxoglutarate fluorescent / ultraviolet molecular probe can be applied to analytical chemistry, life organic analysis, disease pre-diagnosis, medical clinical inspection and other related fields. The alpha-oxoglutarate fluorescent / ultraviolet molecular probe has the advantages of being good in response performance and high in data accuracy, repeatability and precision, equipment is convenient, fast and easy to operate, operability is high, and the alpha-oxoglutarate fluorescent / ultraviolet molecular probe is particularly suitable for large-batch sample combined screening and other large-data research.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
Method for increasing yield of alpha-oxoglutarate produced through whole-cell transformation
ActiveCN103937842AAvoid absorptionIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationIntracellularDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for increasing yield of alpha-oxoglutarate produced through whole-cell transformation, and belongs to the technical field of biotechnology. The method is characterized in that recombinant bacillus subtilis is used as a producing bacterial strain, and an sucA gene in a genome of the recombinant bacillus subtilis is knocked out. The sucA gene is knocked out so as to block the decomposition approach of intracellular L-glutamic acid, so that the bacterial strain is transformed so as to efficiently transform L-glutamic acid for producing alpha-oxoglutarate, thus the problems of high cost, low yield and serious pollution of industrialized alpha-oxoglutarate are solved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Feed additive for improving growth properties of weaned piggies and improving functions of intestinal tracts as well as preparation method and application of feed additive
InactiveCN107259155AImprove growth performanceImprove bowel functionAccessory food factorsFood additiveAtrophy
The invention discloses a feed additive for improving growth properties of weaned piggies and improving functions of intestinal tracts as well as a preparation method and application of the feed additive, and relates to the field of pig feeds. The feed additive provided by the invention comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5-10 parts of sodium glutamate, 5-8 parts of arginine, 5-10 parts of tributyrin, 5-8 parts of glutamine, 10-20 parts of glucose, 5-10 parts of alpha-oxoglutarate, 20-30 parts of calcium formate and 4-45 parts of zeolite powder. After the feed additive provided by the invention is fed to the weaned piggies, the height of villi of the weaned piggies can be increased, the depth of crypts is increased, the atrophy of intestinal villi is alleviated, the functions of the intestinal tracts are improved, reduction or avoidance of diarrhoea of the weaned piggies is facilitated, the growth and the development of the weaned piggies are promoted, and the growth properties of the weaned piggies are improved.
Owner:ZHANGZHOU AONONG ANIMAL HUSBANDRY TECH +2
Natural and safe growth-type feed additive
InactiveCN102028102APromote growthImprove farming efficiencyAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsAnimal scienceAquatic animal
The invention relates to a natural and safe growth-type feed additive which contains L-arginine-alpha-oxoglutarate, wherein the L-arginine and alpha-oxoglutarate are salified in the mole ratio of 1:2-5:1 and the weight ratio of the L-arginine-alpha-oxoglutarate added to the feed and the daily ration for animals to the feed and the daily ration for animals is 1:50-200. The weight ratio of the additive to the feed is 1:50-100 for livestock animals, 1:100-200 for poultry animals and 1:50-100 for aquatic animals.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for promoting fermentation of microorganism to produce 1,3-propylene glycol
ActiveCN102864177APromote fermentation productionImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for promoting fermentation of microorganism to produce 1, 3-propylene glycol. The method comprises a seed liquid cultivation process and a fermentation process, wherein fermentation cultivation medium used in the fermentation process contains pyroracemic acid of which the concentration is 0.1-0.4g / L and / or alpha-oxoglutarate; the fermentation process orderly comprises micro-oxygen fermentation and anaerobic fermentation, and the micro-oxygen fermentation is converted into the anaerobic fermentation when an OD value is greater than 7. According to the method, conversion of glycerol can be effectively promoted, and the concentration of the 1, 3-propylene glycol in a final product is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Dastarcus longulus sharp larva artificial feed
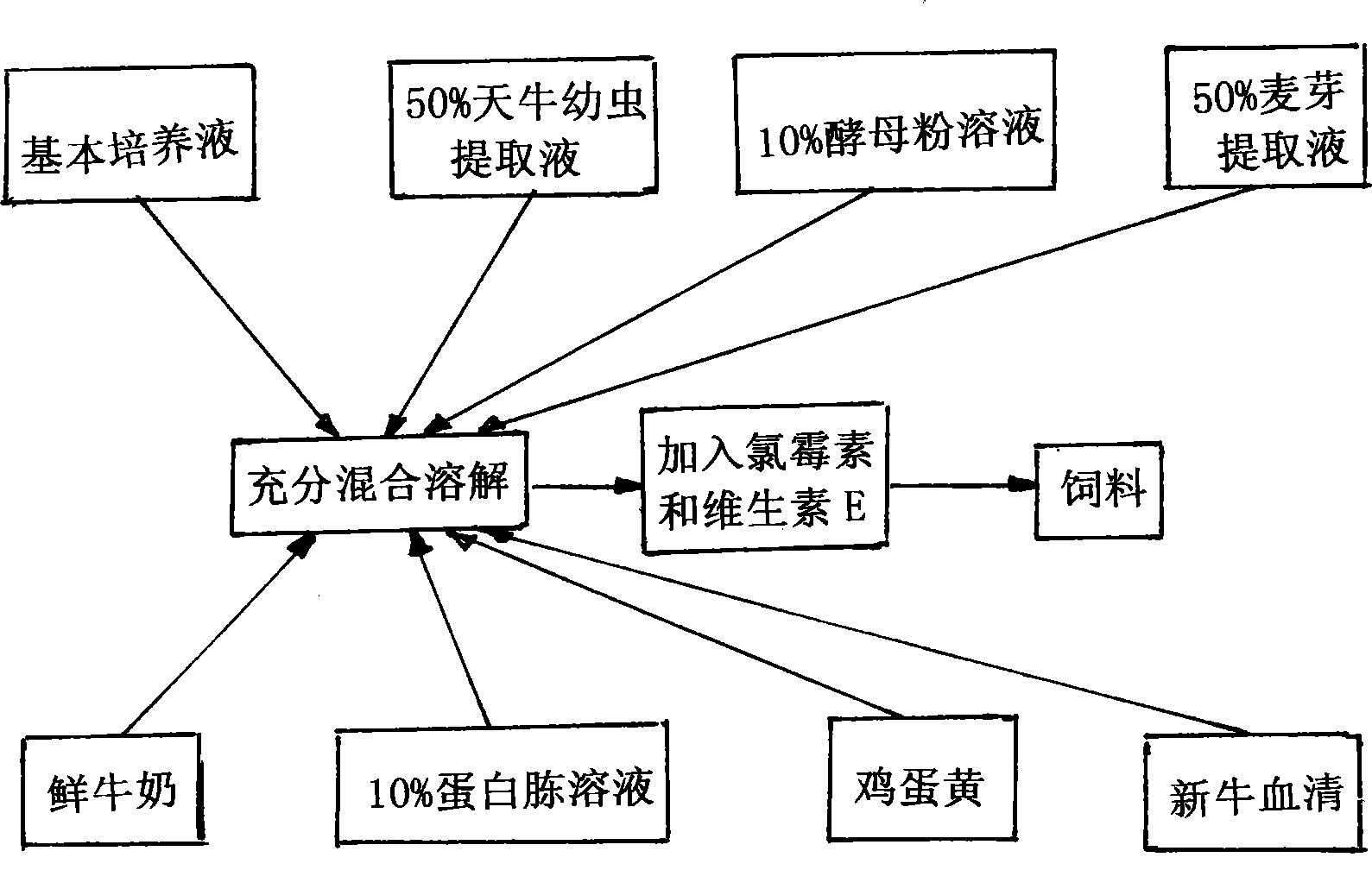
InactiveCN101543265AImprove the breeding effectReasonable formulaAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsSucroseArginine
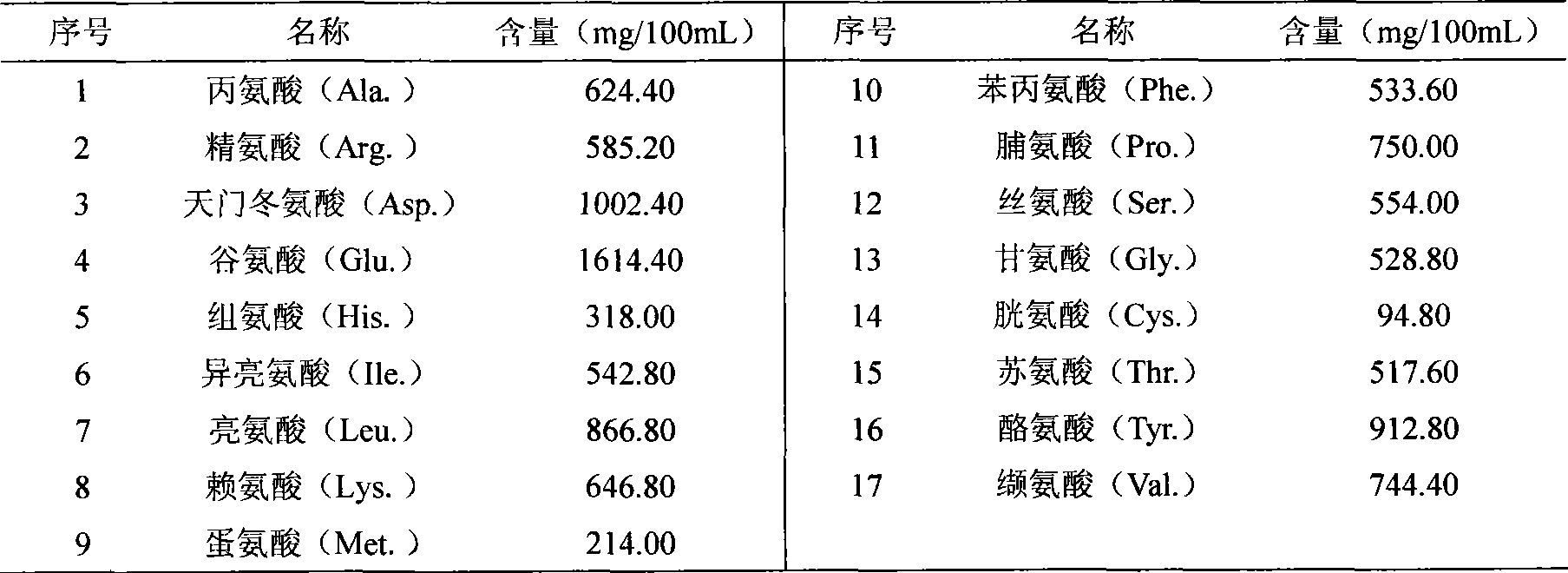
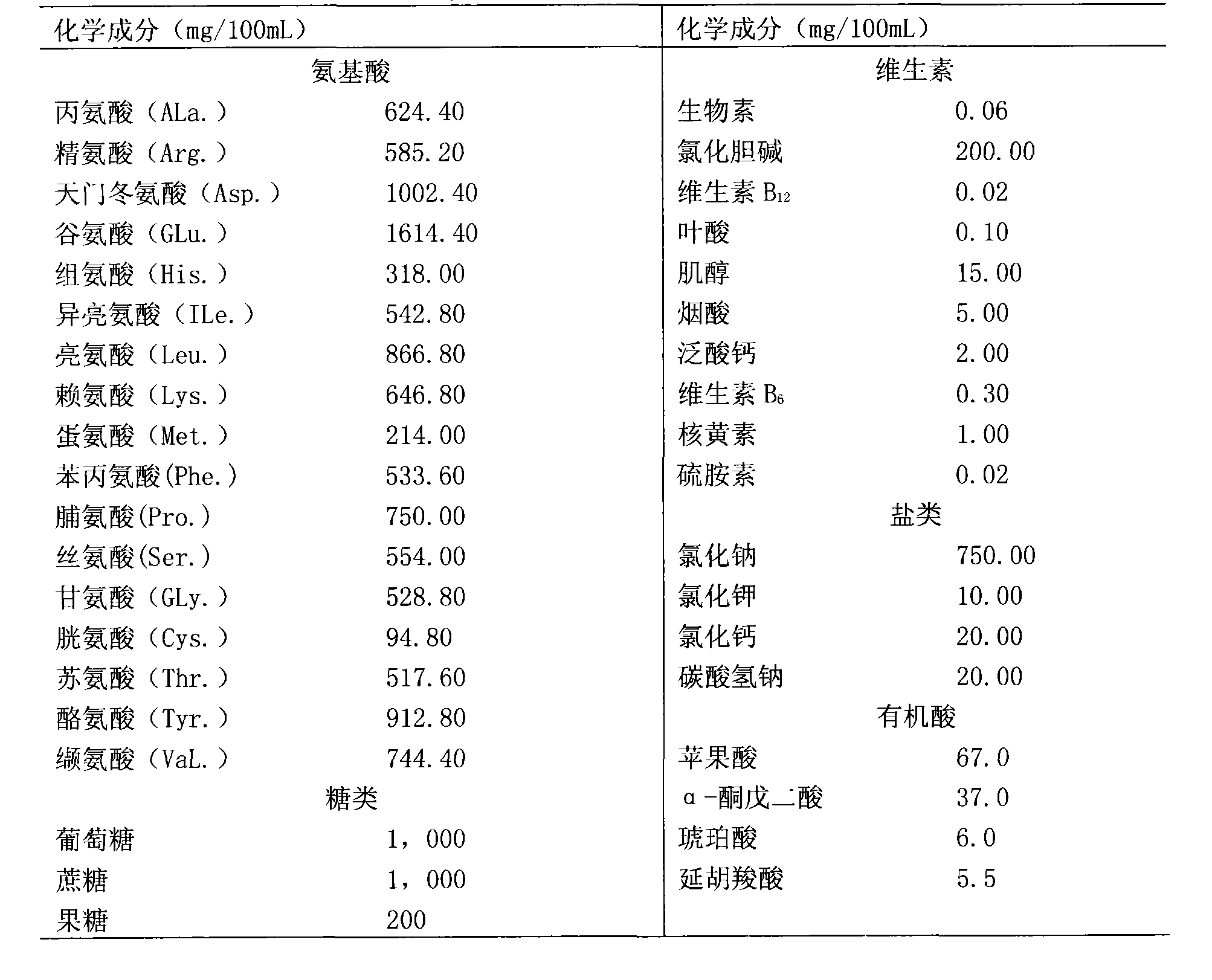
The invention relates to an artificial feed capable of meeting the requirement of growth and development of a natural enemy of longicorn beetle pest, namely dastarcus longulus sharp larva with the age of two years or more than two years, which is prepared from materials of amino acids of alanine, arginine, aspartic acid and the like, glucose, sucrose, biotin, choline chloride, vitamin, riboflavin, sodium chloride, malic acid, alpha-oxoglutarate, fumaric acid, a longicorn beetle larva extract, a yeast powder solution, a malt extract, fresh milk, peptone, egg yolk, new-born calf serum, chloromycetin and the like. Indoor feed experiments prove that dastarcus longulus sharp fed by the feed has an average growth period of 9.500+ / -0.548 days, and a mature larva has a body length of 9.642+ / -0.732 mm, and can normally spin cocoons and pupate with an eclosion rate of 95 to 100 percent.
Owner:李孟楼 +2
Detection kit for measuring content of urea without interference of endogenous ammonia in serum
InactiveCN104198421AEliminate distractionsImprove stabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsL-glutamate dehydrogenaseSerum ige
The invention discloses a detection kit for measuring the content of urea without the interference of endogenous ammonia in serum. The detection kit comprises a reagent R1 and a reagent R2, wherein the reagent R1 contains 1-500mmol / L buffer solution with the pH value of 3.0-8.0, 1-80KU / L glutamate dehydrogenase, 0.5-2KU / L NADH, 1-100mmol / L alpha-oxoglutarate, 0.1-0.5% of a surface active agent and 0.1-1g / L of preservative; the reagent R2 contains 1-500mmol / L buffer solution with the pH value of 3.0-8.0, 1-60KU / L urease, 0.5-2KU / L NADH, 1-100mmol / L alpha-oxoglutarate, 10-500mmol / L sodium chloride, 1-50mmol / L enzyme protective agent, and 0.1-1g / L preservative. The kit can eliminate the interference of the endogenous ammonia and has the characteristics of excellent stability and strong anti-interference ability.
Owner:上海睿康生物科技有限公司
Rhizobium japonicum culture medium and method for preparing liquid rhizobium japonicum agent by adopting rhizobium japonicum culture medium
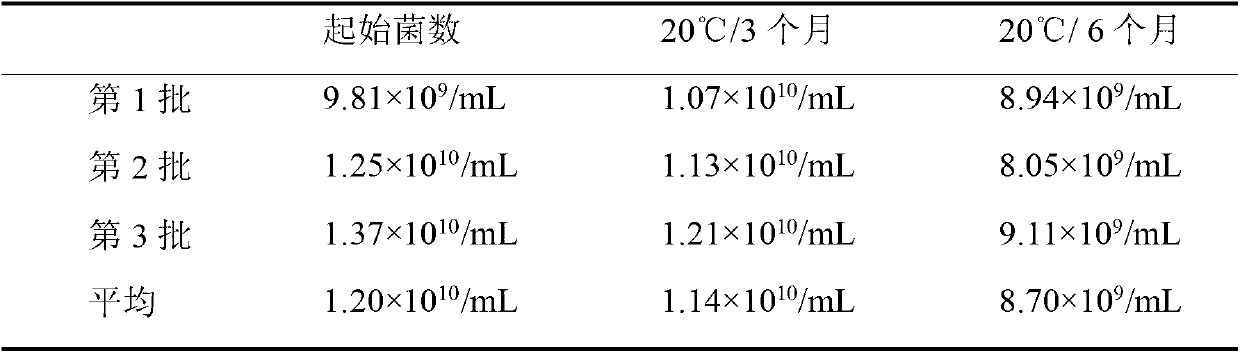
The invention relates a rhizobium japonicum culture medium and a method for preparing a liquid rhizobium japonicum agent by adopting the rhizobium japonicum culture medium and aims at solving the problem that an existing liquid rhizobium japonicum agent is unbalanced in nutrition and low in thallus activity and rhizobium japonicum prepared by means of a fermentation technology cannot stably survive at the room temperature. The rhizobium japonicum culture medium is an aqueous solution prepared by glycerin, mannitol, glucose, rhamnose, fructose, alpha-oxoglutarate, yeast powder, serine, arginine, NH4C1, K2HPO4, KH2PO4, MgSO4*7H2O, CaCl2*2H2O, FeSO4*7H2O, NaCl, Na2MoO4*2H2O and biotin, and can be obtained by controlling fermentation tank conditions. The viable count of microbial inoculum of the rhizobium japonicum culture medium preserved at 20 DEG C for 12 months can still reach to more than 100 hundred millions per milliliter.
Owner:黑龙江省华龙生物科技有限公司
Application of Chinese yarn glycoprotein in improvement of activities of oxidative metabolism enzymes of mitochondria of brain cell
ActiveCN102920998AHigh activitySimple extraction methodNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsYarnKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to an application of Chinese yarn glycoprotein in improvement of the activities of an oxidative metabolism enzymes of mitochondria of a brain cell. Selection and verification are carried out by an animal test so as to prove that the Chinese yarn glycoprotein can obviously improve the activities of key enzymes namely pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase used for oxidative metabolism in the mitochondria of the brain cell, so that brain cell deterioration and damage diseases, such as senile dementia, vascular dementia, cerebral infarction and cerebral palsy, accompanying with oxidative metabolism efficiency reduction caused by reduction of the activities of the enzymes can be effectively treated.
Owner:新乡博凯生物技术有限公司
Method for producing L-4-hydroxyisoleucine by microbial enzyme conversion method
ActiveCN105779522AIncrease production capacityImprove efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliUltrafiltration
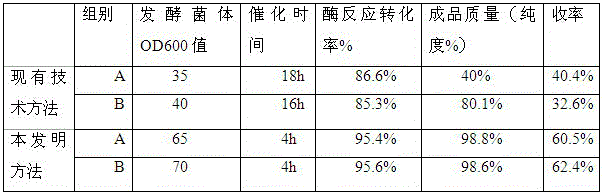
The invention relates to a method for producing L-4-hydroxyisoleucine by a microbial enzyme conversion method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, culturing a mature bacterial strain; 2, grafting mature escherichia coli recombinant bacteria which are capable of inducing production of L-4-hydroxyisoleucine into a fermentation tank, and carrying out fermentation culture, wherein the temperature of the fermentation process is controlled in two stages, i.e., 4 to 36 DEG C in the earlier stage and 30 to 32 DEG C in the later stage; 3, collecting thallus after fermentation, adding phosphate buffer and washing, then adding alpha-oxoglutarate, isoleucine, ferrous sulfate, magnesium sulfate and ascorbic acid, and carrying out forced ventilation for catalysis; 4, removing bacteria from the catalytic liquid with a ceramic membrane, filtering with an ultrafiltration membrane, decoloring with activated carbon, desalting with faintly acid cation exchange resin, adsorbing effluent with 732 cation exchange resin and eluting with ammonia water, carrying out evaporation concentration and recrystallization to obtain the L-4-hydroxyisoleucine. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and efficient in reaction system and simple and feasible in extraction process. The conversion rate is up to over 95.4 percent, and the purity of the product can reach over 98 percent.
Owner:HENAN JULONG BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD +1
Method for implementing excessive accumulation of alpha-oxoglutarate by regulation and control of carbon metabolism flow with assist factor
A method with adjuvant factor to regulate the carbon metabolism to accomplish the overdose accumulation of alpha-ketoglutarate (alpha-KG) is provided, which belongs to the technical field of fermentation process optimized by the strategy of adjuvant factor regulation. The invention adopts the method of adjuvant factors including vitamins and metal ions, etc. which are added into the fermentation process with the sub-proper amount, and then the pathway flux of PDH and PC are increased selectively to accomplish the overdose accumulation of alpha-KG. During the process of the production of alpha-KG through fermentation of T.glabrata, the concentration of vitamin B1 is raised to increase the accumulated alpha-KG to 10.3g / L; then the biotin concentration is raised to increase the accumulated alpha-KG to 43.7g / L, and the concentration of pyruvic acid is decreased to 21.8g / L. The strategy also has the significance to guide the production of the other fermented products.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
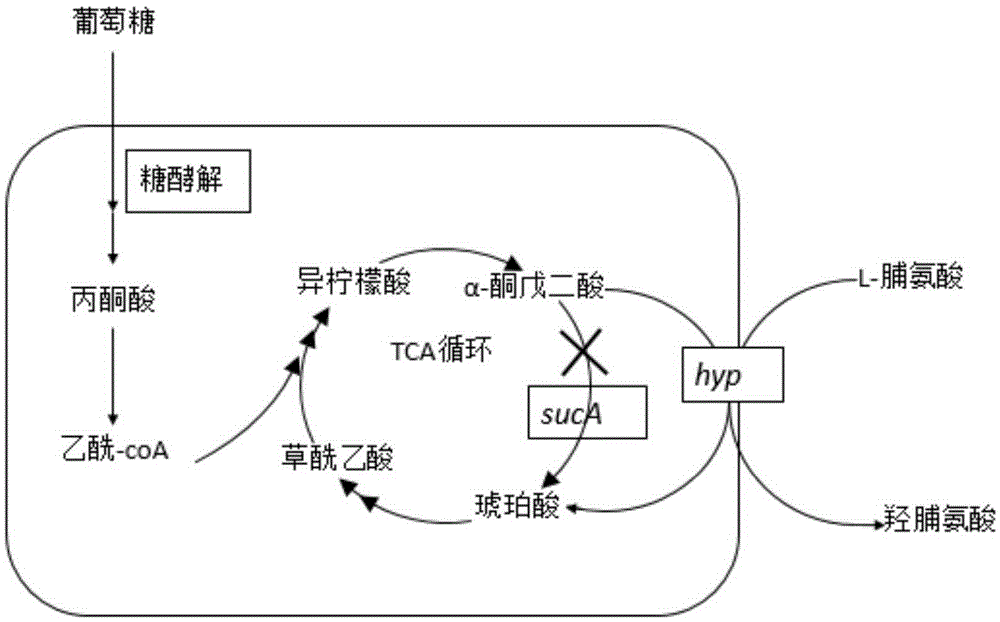
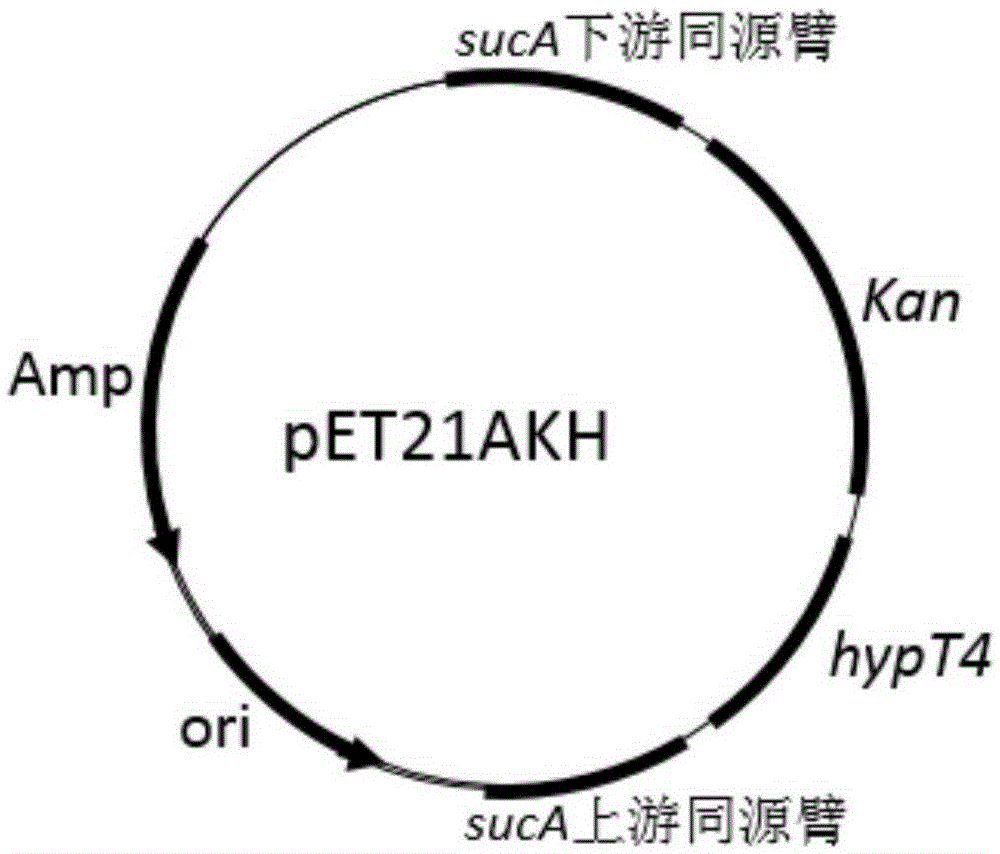
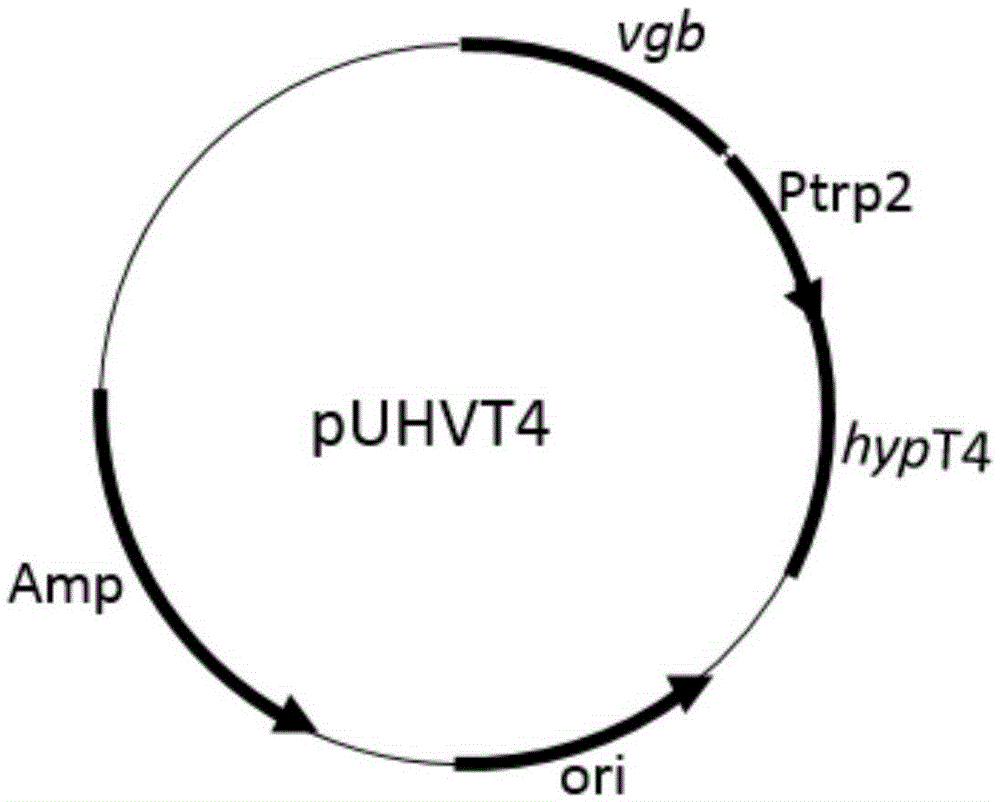
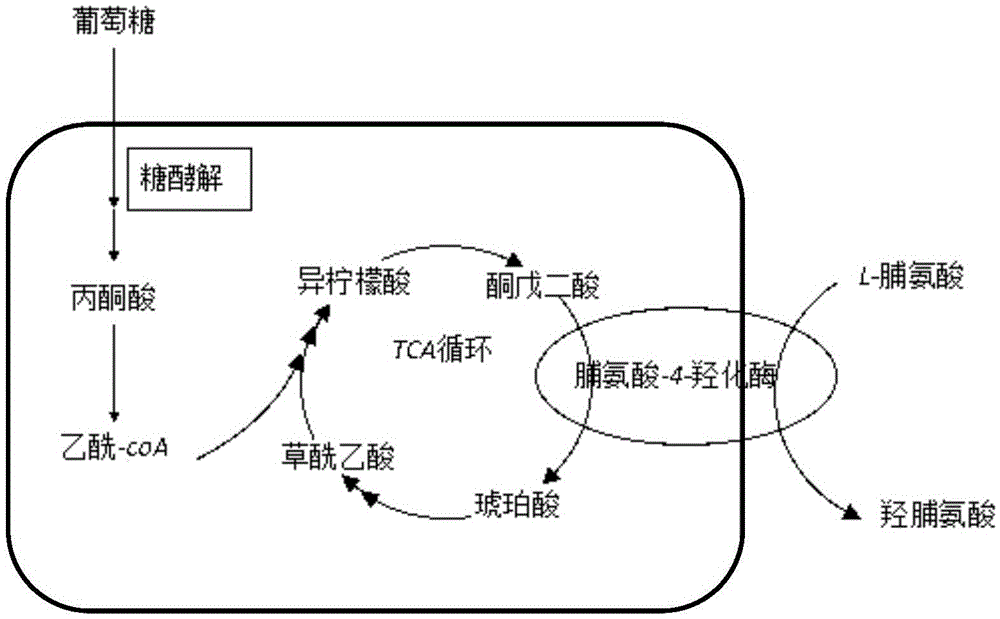
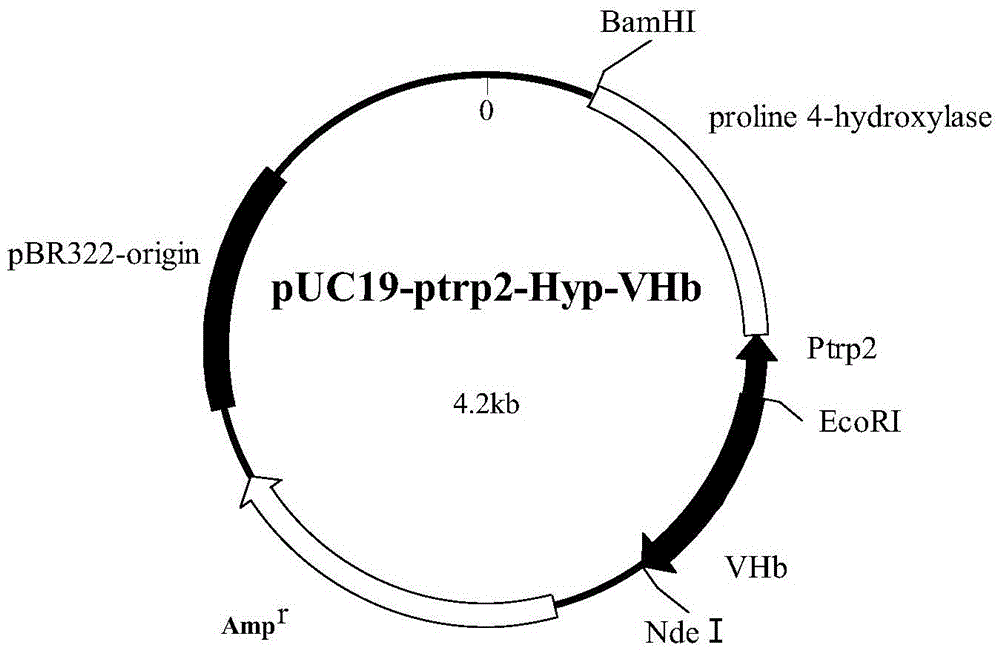
Construction of high-yield trans-4-hydroxyproline sucA gene knockout bacteria
The invention provides construction of high-yield trans-4-hydroxyproline sucA gene knockout bacteria and discloses a biosynthesis method of trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline through gene knockout. According to the method, the gene suc A is knocked out on the basis of escherichia coli BL21(DE3) delta put A, the process that alpha-oxoglutarate generates succinic acid or an alpha-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex is utilized for catalyzing in the TCA circulation process is disturbed, meanwhile, the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline hydroxylase gene (hyp) is inserted, and then plasmid pUC19-Ptrp2-hyp-vgb is converted; hydroxylase replaces functions of alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase, 'anaplerosis' is conducted on the TCA circulation process, and it is guaranteed that hydroxyproline is generated while the TCA circulation is conducted. The invention further discloses application of recombinant escherichia coli to production of trans-4- hydroxyproline, it is indicated by the flask shaking fermentation result that the yield of hydroxyproline obtained after mediumoptimization is 1344.1 mg / L and is about 5.53 times that before optimization; compared with original bacteria which are converted into the plasmid pUC19-Ptrp2-hyp-vgb in the same mode, advantages are achieved on the aspect of production of hydroxyproline.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
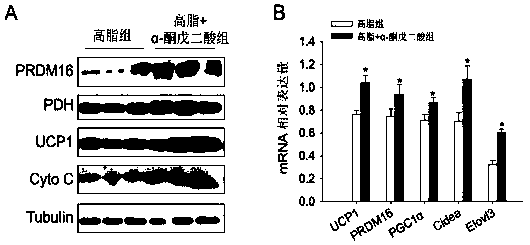
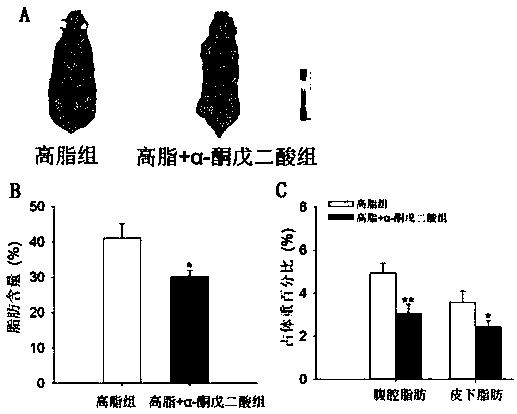
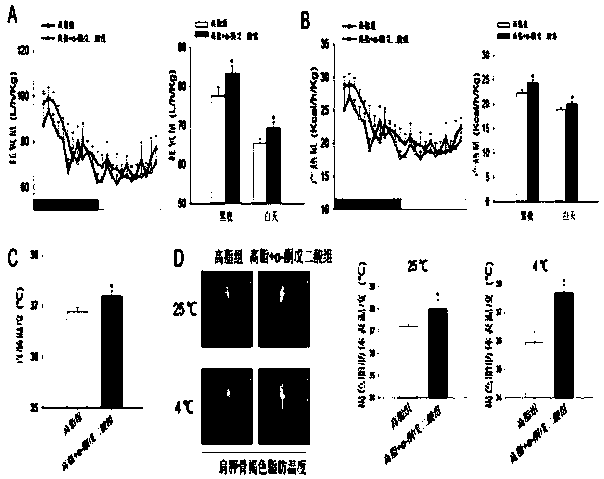
Application of alpha-oxoglutarate to improving heat production capability of fat animals and reducing body fat content
InactiveCN108542899AFast heat productionLow fat contentOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseaseAnimal science
The invention discloses application of alpha-oxoglutarate to improving the heat production capability of fat animals and reducing the body fat content. The invention provides new application of alpha-oxoglutarate, alpha-oxoglutarate can obviously improve whole heat production of high fat diet animal bodies and heat production of brown fat, can prominently improve expression of brown fat heat producing marker genes UCP1, PRDM16, PGC1alpha, Cidea and Elovl3, and meanwhile, can reduce the overall body fat content of the high fat diet animal bodies and the fat weight of different parts. In addition, alpha-oxoglutarate does not contain any substance harmful to animals or human body, the adding amount is less, and alpha-oxoglutarate can be directly added into animal drinking water, fodder, foodor drugs, has the advantages of safety, effectiveness and no toxic and side effects, has the wide application prospect at the aspect of improving heat production of the high fat diet animals and reducing the body fat content, and explores a new means for treating obesity and related diseases.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
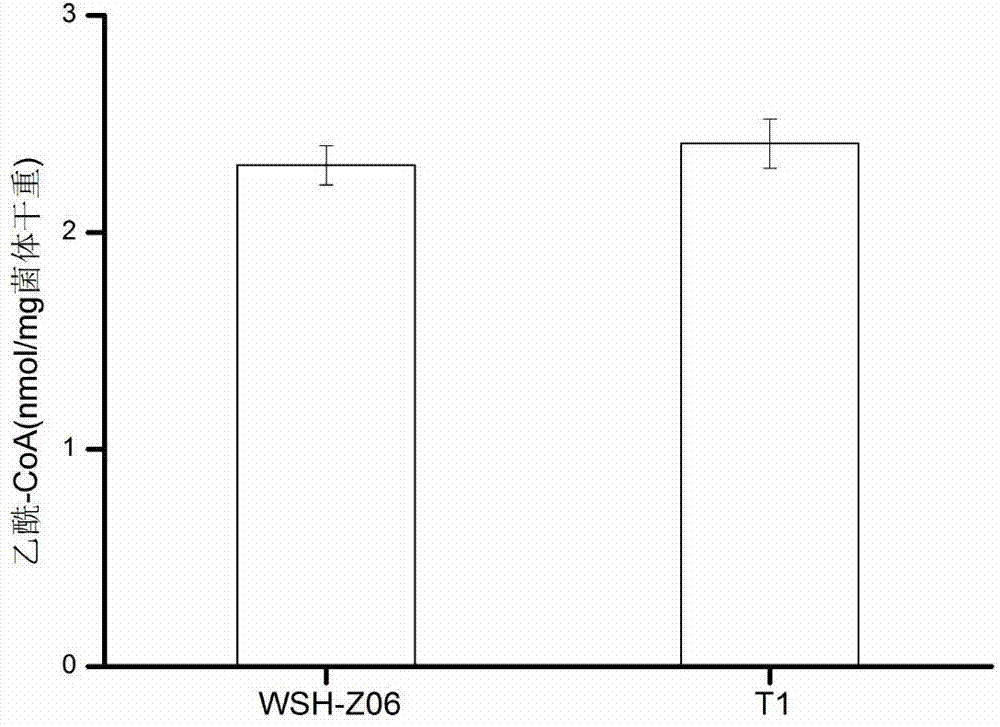
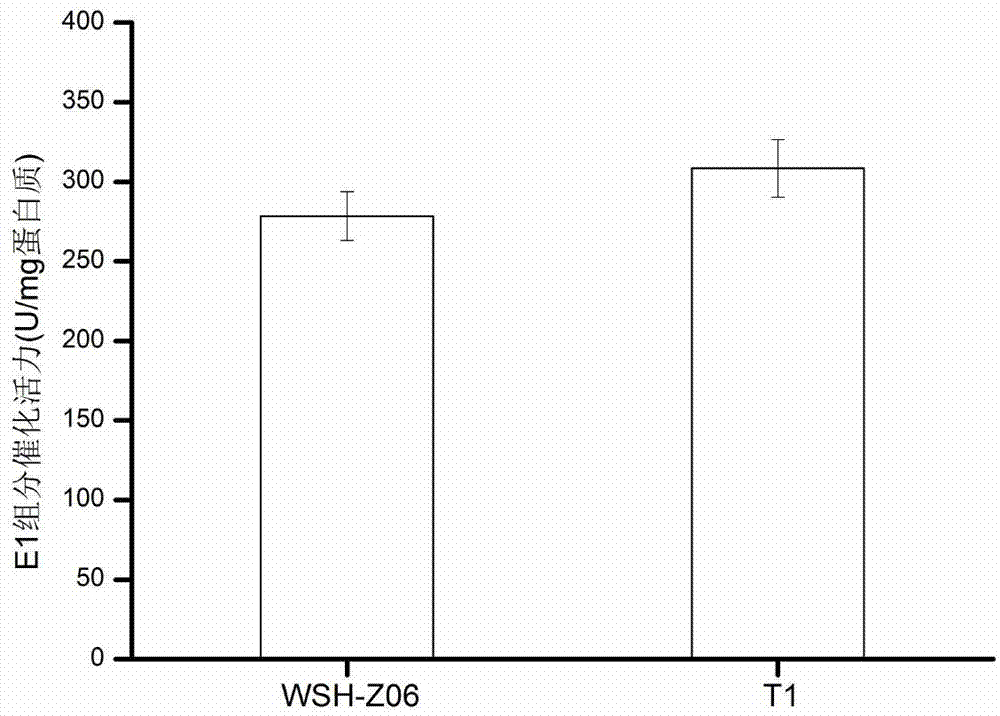
Yarrowia lipolytica capable of reinforcing precursor supply to enhance synthesis of alpha-oxoglutarate
InactiveCN103923847AReduce accumulationBoosts Acetyl-CoA SupplyFungiMicroorganism based processesOrganic acidMetabolite
The invention discloses Yarrowia lipolytica capable of reinforcing precursor supply to enhance synthesis of alpha-oxoglutarate, belonging to the technical field of metabolic engineering. According to the invention, catalytic activity of a pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component in a cell is improved through overexpression of PDA1, so the accumulation of an intermediate metabolite pyruvic acid is decreased, and supply of intracellular acetyl-CoA is reinforced; moreover, supply of intracellular acetyl-CoA is increased for accumulation of alpha-oxoglutarate for cells, which enables extracellular accumulation of alpha-oxoglutarate to be obviously increased. Thus, overexpression of PDA1 enables the content of the intermediate metabolite pyruvic acid to be decreased and accumulation of alpha-oxoglutarate to be reinforced and provides novel thinking for accumulation of organic acid in TCA cycle for cells.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Blocking agent for reducing content of heavy metal of edible part of crops and application method thereof
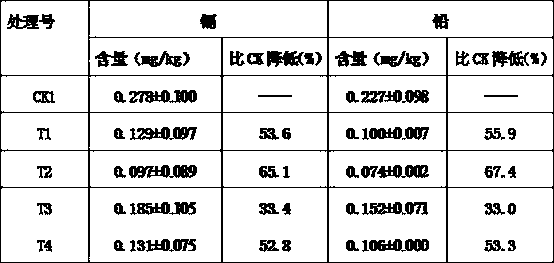
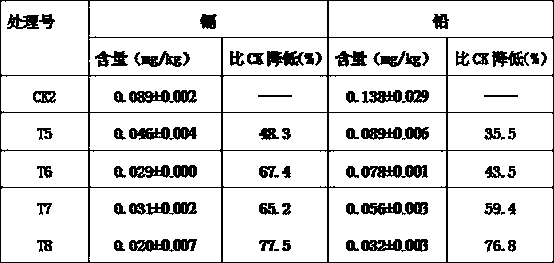
The invention discloses a blocking agent for reducing the content of heavy metal of edible parts of crops and an application method thereof. The blocking agent comprises glycerol or one or two of glycerol, oxaloacetic acid and alpha-oxoglutarate, and can realize the purposes of blocking absorption of heavy metal and transferring to edible parts through foliage spraying after vegetable farming andbefore harvesting. The blocking agent can obviously reduce the contents of heavy metal, such as plumbum and cadmium, at the edible parts of vegetables, so as to ensure that vegetables produced in mildor medium-heavy metal contaminated vegetable fields meet food safety standards. The blocking agent is low in effective spraying concentration, can be mixed with pesticide for controlling vegetable diseases and insect pests and then be sprayed, and is low in cost.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Stabilizing agent for uric-acid detection reagent
InactiveCN106244672AEasy to operateThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementPolyethylene glycolAdenosine diphosphate
The invention relates to the technical field of in-vitro diagnostic reagents, in particular to a stabilizing agent for a uric-acid detection reagent. The stabilizing agent is characterized by being prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 0.1-5g / L of MgSO4, 1-5ml / L of glycerinum, 0.1-20g / L of trehalose, 0.1-10ml / L of PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) 4000, 0.1-5g / L of adenosine diphosphate, 1-4g / L of alpha-oxoglutarate, 0.5-2g / L of polyvinylpyrrolidone and 0.5-2.0g / L of polyethyleneimine. The stabilizing agent for the uric-acid detection reagent has the advantages that the effective period of the uric-acid detection reagent can be obviously prolonged to 2 years, the stability after opening lasts for 3 months, a blank absorbency value is obviously reduced, single-reagent operation is simple, the result is accurate, and the stability is good.
Owner:威海威仕泰医疗科技有限公司
Liquid monomer reagent for determining content of ammonia in blood serum, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102994612AGuaranteed stabilityGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSemi automaticActivity ratios
The invention discloses a liquid monomer reagent for determining the content of ammonia in blood serum, a preparation method and an application thereof. The liquid monomer reagent comprises the following components: buffering solution, glutamate dehydrogenase, alpha-oxoglutarate, reduction type nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, glucose, glucose dehydrogenase and a stabilizing agent, wherein the enzyme activity ratio of the glutamate dehydrogenase and the glucose dehydrogenase is (3-3000):1. Shown by accelerating destruction test at the temperature of 37 DEG C and 42 DEG C, the blood-ammonia liquid monomer reagent is good in stability, solves the fussy problem that a lyophilized agent needs to be lyophilized and redissolved, can be prepared and used at any time, and can be stable for 18 mouths at the temperature of 2-8 DEG C; and shown by clinic correlation test, the liquid monomer reagent is stable in blood-ammonia determination, is high in determined-value accuracy, is applicable to manual, semi-automatic and automatic detection system and is easily promoted and used in all hospitals.
Owner:BEIJING LEADMAN BIOCHEM
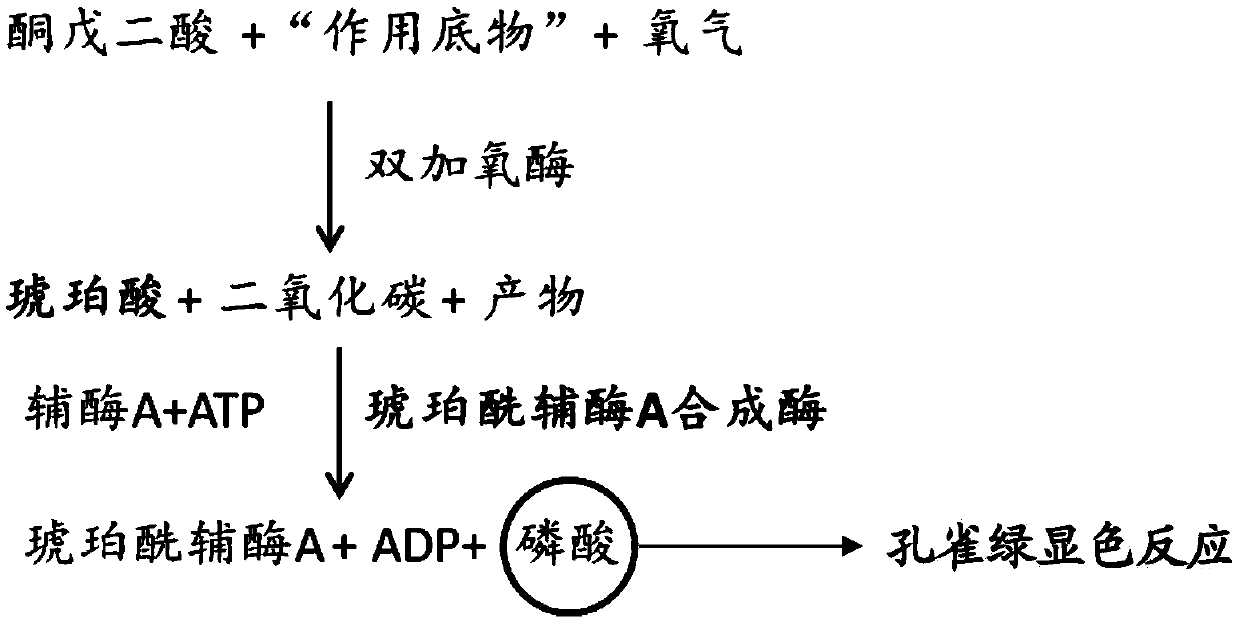
Enzyme activity detection system and method of Fe and alpha-oxoglutarate dependence dioxygenases
ActiveCN105506058AMeasurement saves time and effortMicrobiological testing/measurementMalachite greenMalachite green stain
The invention provides an enzyme activity detection method of Fe and alpha-oxoglutarate dependence dioxygenases, comprising a step of detecting the enzyme activity of the enzyme by a color reaction of inorganic phosphate generated by a coupled reaction of Fe and oxoglutarate dependence dioxygenases and succinyl-coenzyme A synthetase and ammonium molybdate malachite green dye. In addition, the invention also provides an enzyme activity detection system of dioxygenase, a kit and application of thereof.
Owner:SHENZHEN BEINUOBO BIOTECH CO LTD
Strain MQO-160 for generating L-glutamate oxidase and application of strain
InactiveCN106318888ASolve bottlenecksCheap and easy to getBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention relates to a strain MQO-160 for generating L-glutamate oxidase and application of the strain. The strain MQO-160 has the preservation number of CGMCC No.12892, the preservation organization of the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the preservation date of August 22nd, 2016 and the preservation address of the apartment No.3 of the yard No.1 in the Beichen West Road in Chaoyang District of Beijing. The invention further comprises the application of the strain MQO-160 to preparation of L-glutamate oxidase. The bottleneck defect of generating alpha-oxoglutarate through an L-glutamate oxidase conversion method is overcome, and the strain MQO-160 is low in price, easy to obtain, simple in process and high in product purity.
Owner:SHANDONG MINQIANG BIOTECH
Biosynthesis method for increasing yield of trans-4-hydroxyproline by knocking out other metabolic pathway
InactiveCN105543303AIncrease productionPromote accumulationFermentationBiological cellHydroxyproline
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method for increasing the yield of trans-4-hydroxyproline by knocking out other metabolic pathways. A system for producing hydroxyl-L-proline by using the biosynthesis method refers to a production method that free L-proline is converted into trans-4-hydroxyl-L-proline from a living body by virtue of proline hydroxylase in biological cells in the presence of alpha-oxoglutarate and ferrous ions. The method for increasing the yield of hydroxyproline comprises a step of cutting off other metabolic pathways of a precursor substrate glutamic acid which competes with L-proline in biological cells, wherein other metabolic pathways refer to an arginine metabolic pathway. By using the method, the yield of the trans-4-hydroxyl-L-proline can be up to 921 mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
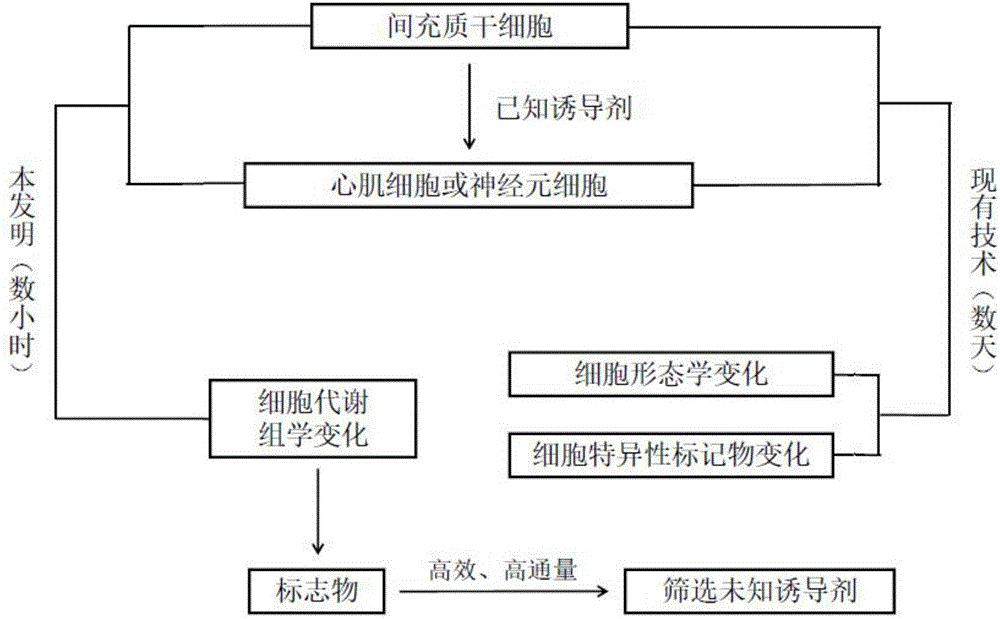
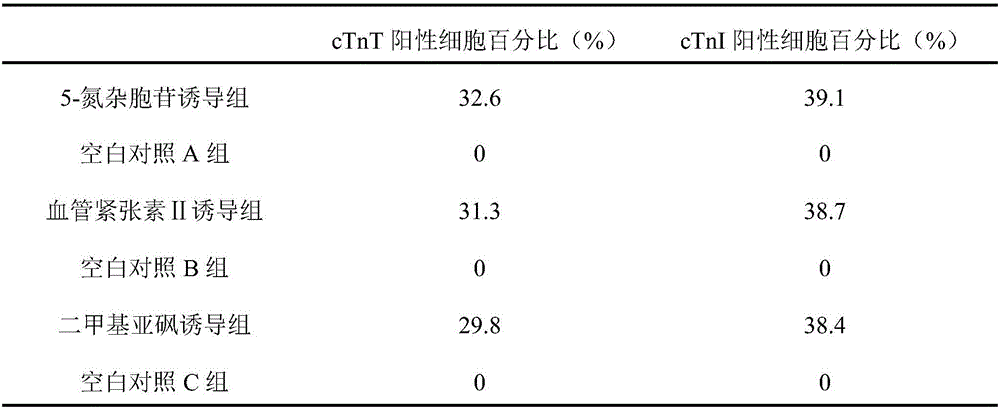
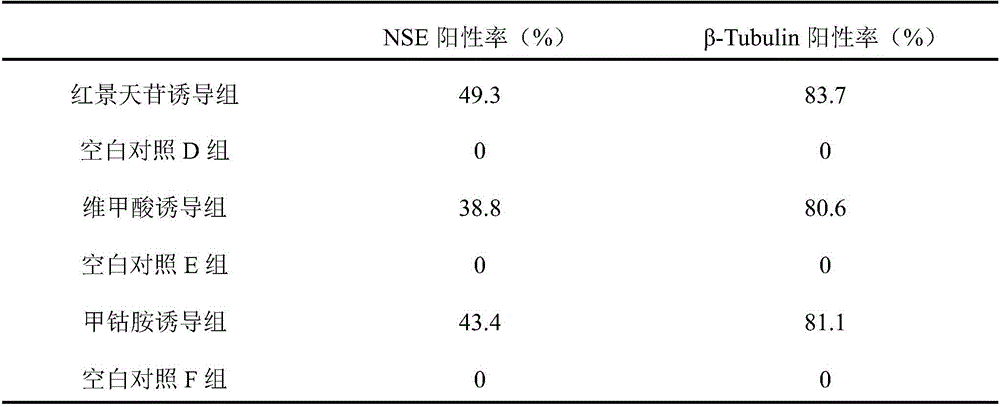
Markers, reagent and reagent box for indicating directional differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
InactiveCN106544394AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsCardiac muscle
The invention discloses markers, a reagent and a reagent box for indicating the directional differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), in particular to markers, a reagent and a reagent box for indicating the potential that bone mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) directionally differentiate into cardiomyocyte-like cells. The makers are composed of alpha-oxoglutarate, dihydroxyacetone phosphate, asparagines and arachidonic acid. Results prove that the alpha-oxoglutarate, the dihydroxyacetone phosphate, the asparagines and the arachidonic acid are quite high in united indicating value, can be used as the markers for indicating the potential that the BMSCs differentiate into cardiomyocytes, and are high in efficiency when used for high throughput screening of inducers capable of inducing the BMSCs to differentiate into the cardiomyocytes, and people do not need to wait for several weeks to know an induction result.
Owner:南京千年健干细胞基因工程有限公司
Clinic in vitro potassium determination reagent by enzyme method
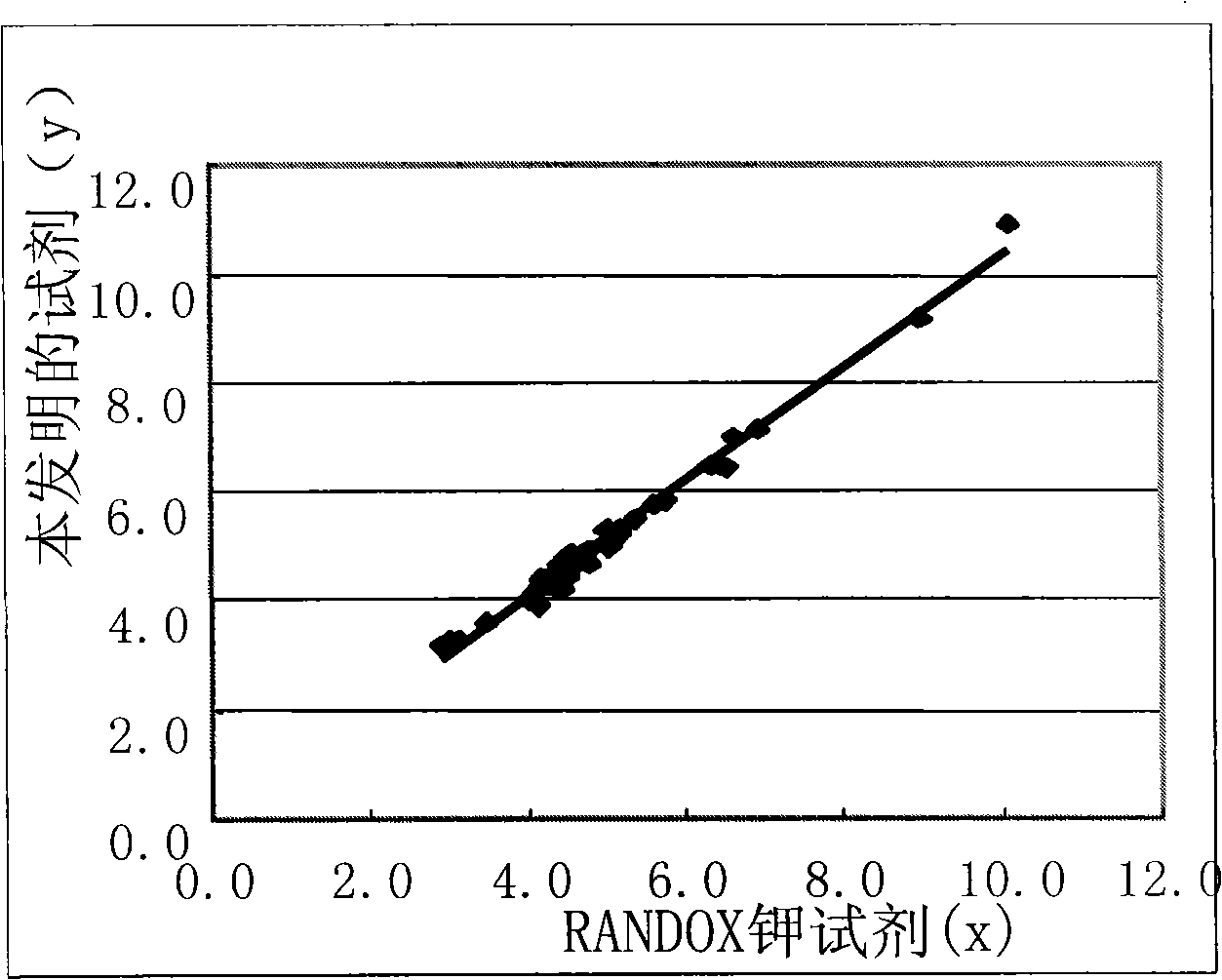
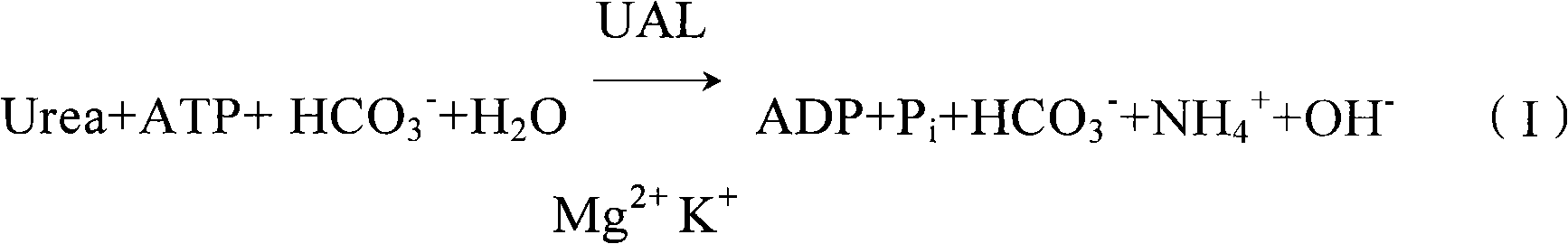
Under participation of ATP, HCO3 and Mg, urea is hydrolyzed by urea amidolyase (UAL; EC 3.5.1.45) to generate NH4, HCO3, ADP and Pi. K is activator of UAL enzyme, and activation speed of the UAL enzyme is proportional to concentration of the K. A auxiliary reaction is coupled, NH4 generated by the UAL enzyme reacts with alpha-oxoglutarate, NAD and Glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH) to generate glutamate and NAD, and under 340 nm wavelength, descent rate of the NADH is proportional to concentration of the K. Concentration of the K is calculate by the descent rate of the NADH. The invention applies the reaction to clinic in vitro determination potassium reagent, and provides optimum double-reagent composition to make stability, accuracy and precision of the agent to optimal state.
Owner:北京瑞正善达生物工程技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com