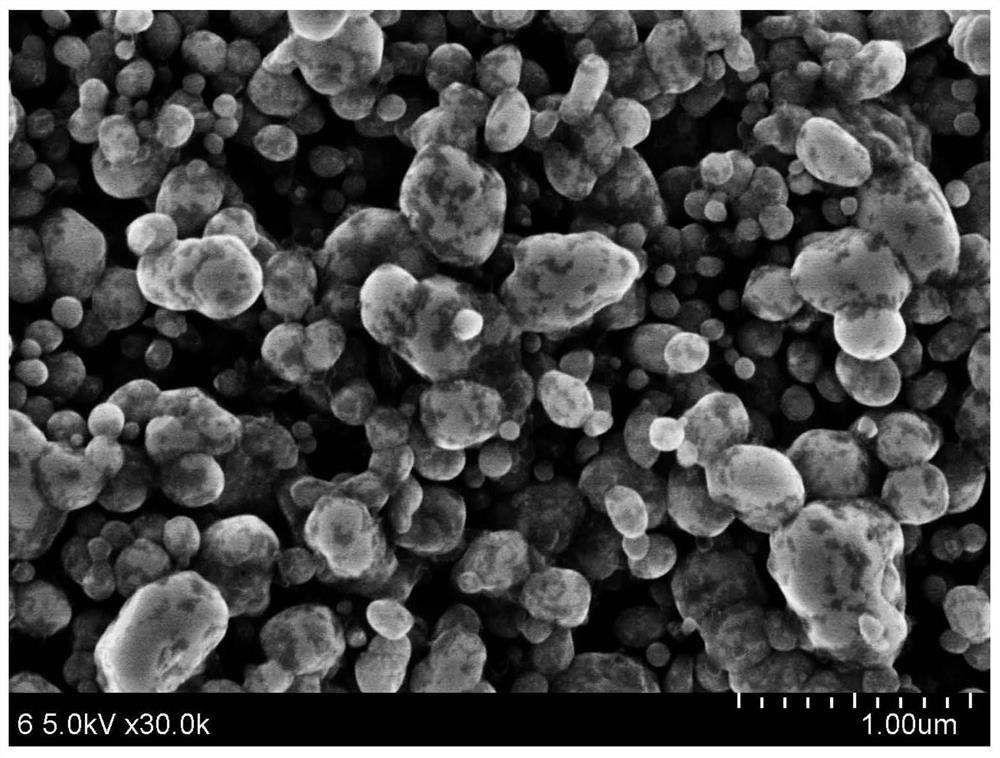
Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Reduce process energy consumption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
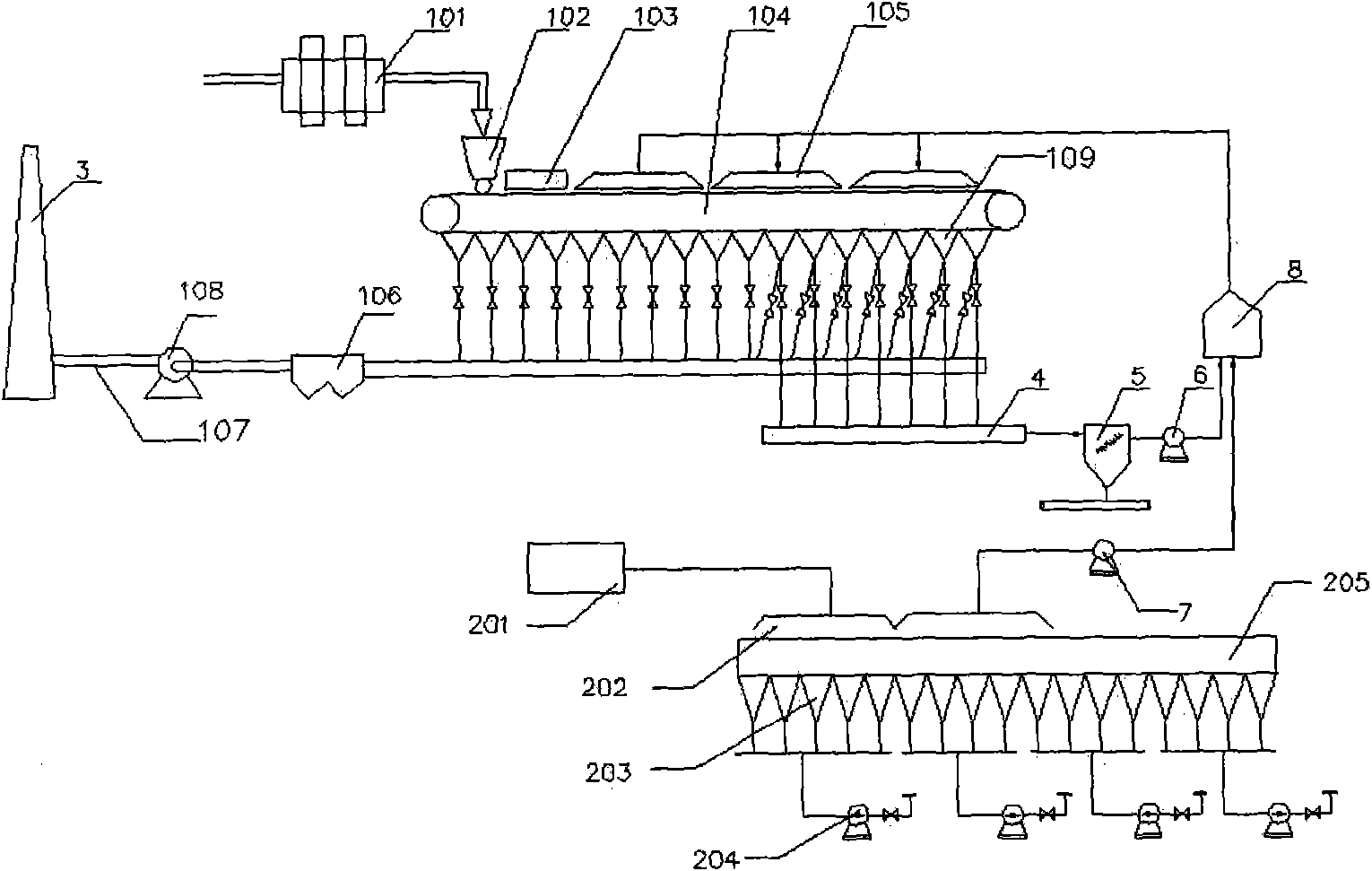
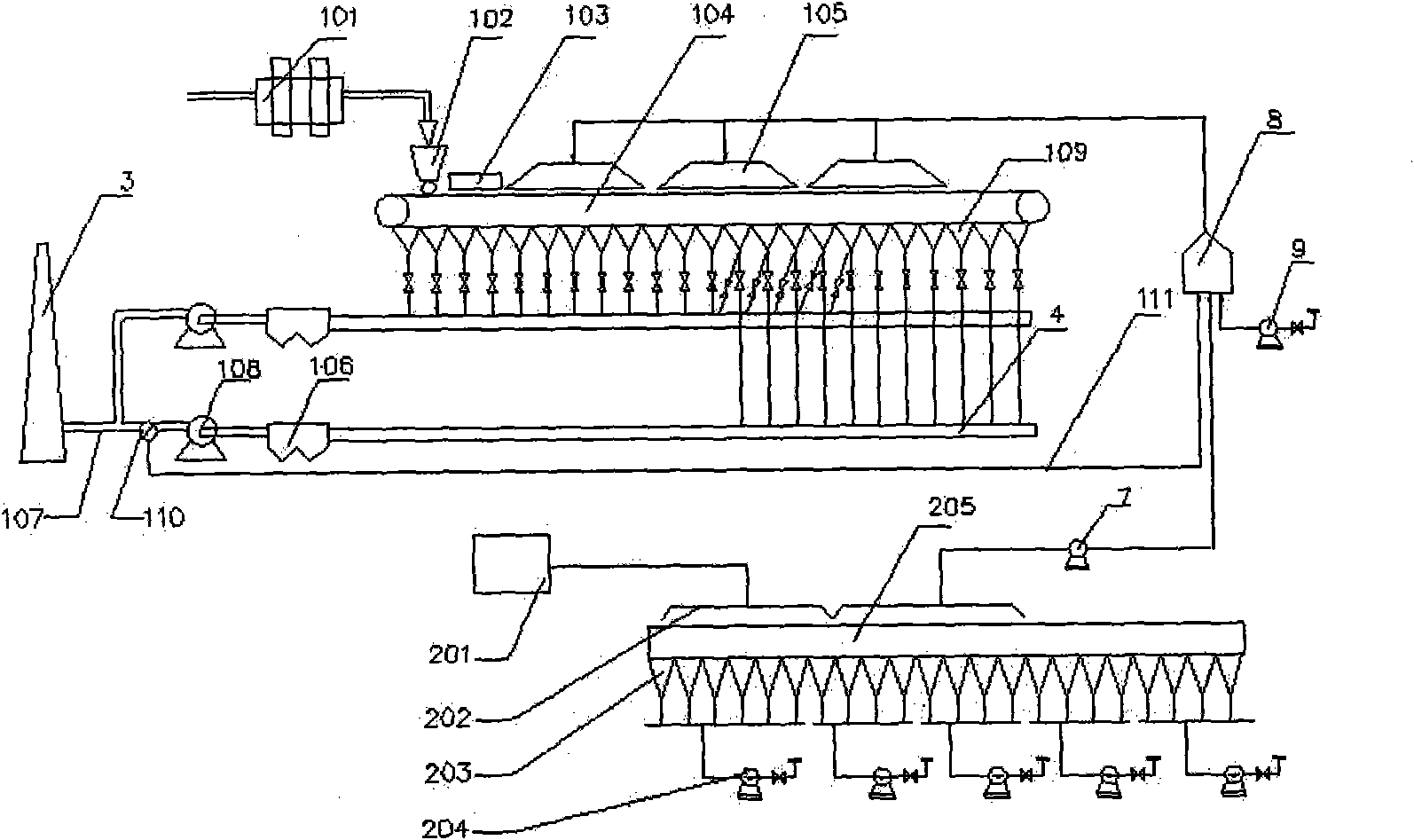
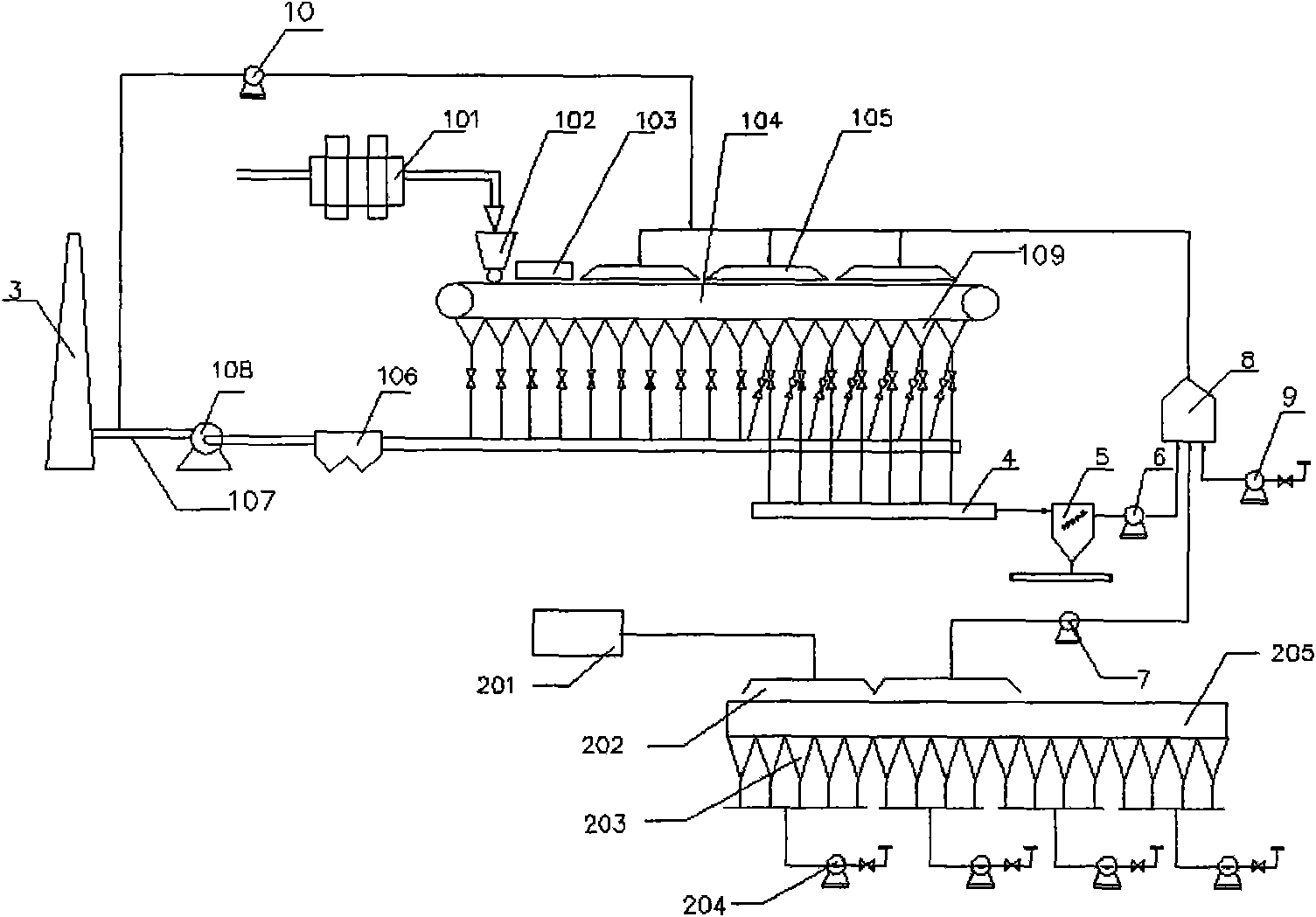
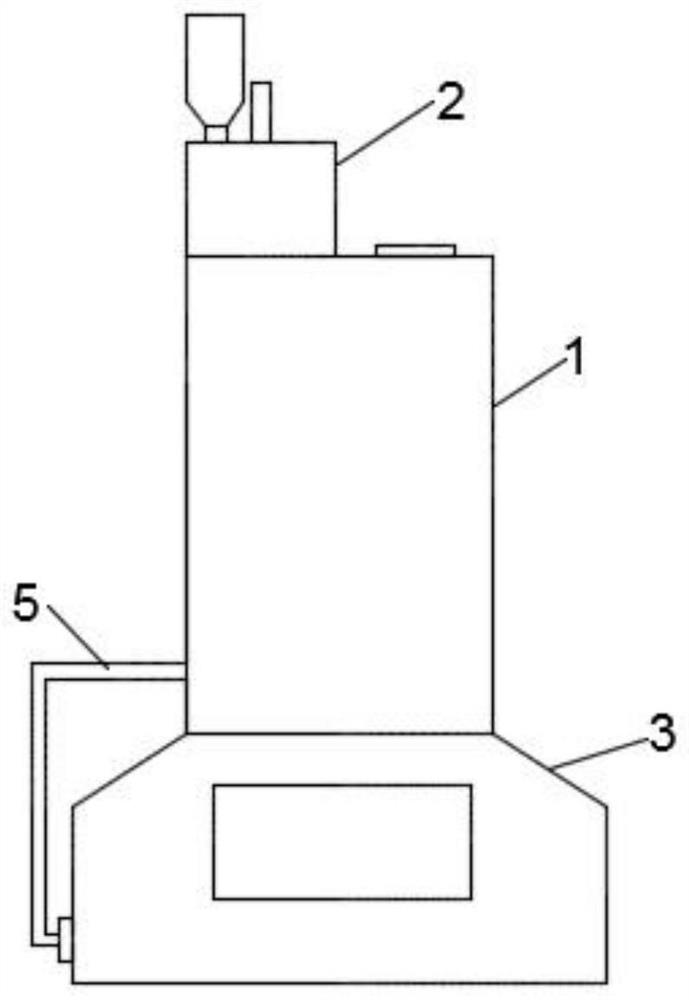
Method of sintering low temperature waste heat circulation and discharged waste gas reduction and device thereof
InactiveCN101893384AReduce process energy consumptionConducive to environmental protectionWaste heat treatmentFluePollutant
The invention discloses a method of sintering low temperature waste heat circulation and discharged waste gas reduction and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: drawing out flue gas having a high temperature in an air bellow on the rear part of the main-flue of a sintering machine; dedusting; mixing the flue gas with hot waste gas extracted from a sintering cool machine into a mixer to form the mixed hot waste gas; and transmitting the mixed hot waste gas on the surface of the material layer of the sintering machine for circular sintering. The device comprises a high temperature flue gas circulation pipeline of the sintering machine connected with a high temperature flue of the sintering machine, a hot waste gas circulation pipeline of a sintering cool machine connected with the sintering cool machine and a total circulation pipeline connected with a sintering machine fan cover. By using the invention, the waste gas discharging total amount and the pollutants discharging amount produced in a sintering process can be greatly reduced, the low temperature waste heat in the flue gas can be recycled and energy consumption of the sintering process can be saved, thus, the method of the invention has significant energy saving and emission reduction value.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Comprehensive treatment process of desulfuration waste water
InactiveCN102531229AReduce process energy consumptionReduce maintenance workloadSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningMultistage water/sewage treatmentHeavy metalsIntegrated processing
The invention discloses a comprehensive treatment process of desulfuration waste water. The process steps include: (1) collecting and buffering of waste water; (2) lime treatment by means of a chemical method; (3) heavy metal removing; (4) coagulation treatment of suspended matter; (5) sediment treating of the suspended matter; and (6) dehydrating treatment of sludge. The comprehensive treatment process can not only treat various pollution factors in the waste water but also reduce energy consumption.
Owner:常州江南电力环境工程有限公司
Method of preparing stannic oxide/graphene composite lithium ion battery anode material under the assistance of chitosan oligosaccharide self-assembly
ActiveCN103985847AReduce process energy consumptionEase of mass productionCell electrodesSecondary cellsCvd grapheneChemistry
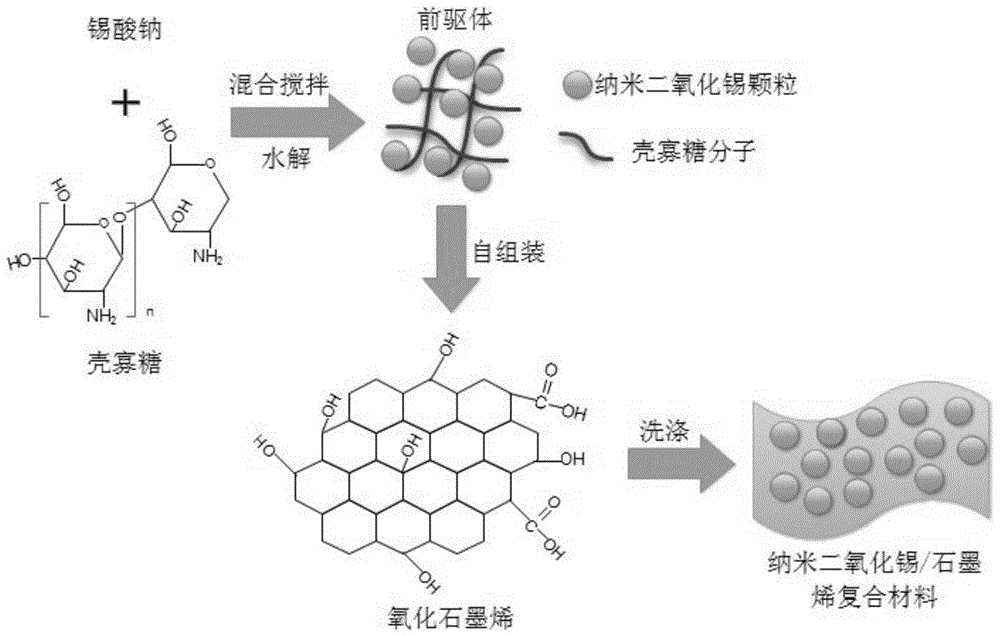
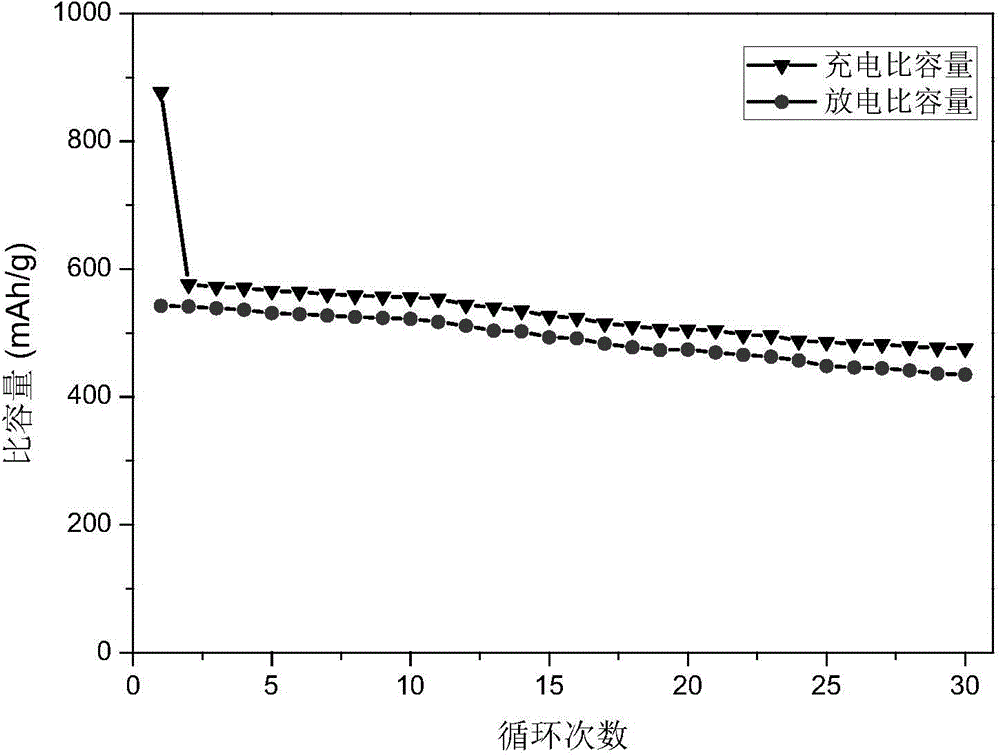
The invention discloses a method of preparing a stannic oxide / graphene composite lithium ion battery anode material under the assistance of chitosan oligosaccharide self-assembly. The method includes: 1) adding sodium stannate and chitosan oligosaccharide into water to form a nanometer stannic oxide self-assembly precursor modified by the chitosan oligosaccharide; 2) adding graphene oxide into the self-assembly precursor to obtain a solution mixture, and mixing and reacting at 20-60 DEG C for 6-20 h to obtain the nanometer stannic oxide / graphene oxide composite material modified by the chitosan oligosaccharide; and 3) washing to remove the chitosan oligosaccharide after solid-liquid separation, and drying to prepare the stannic oxide / graphene composite lithium ion battery anode material. The method can be performed at room temperature under normal pressure, and is free of use of organic solvent, convenient in operation, easily available in raw materials, free of pollution and prone to popularization and application. The stannic oxide / graphene composite lithium ion battery anode material prepared by the method has good electrochemical properties, can be used for preparing lithium ion battery anodes, and has wide market and application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
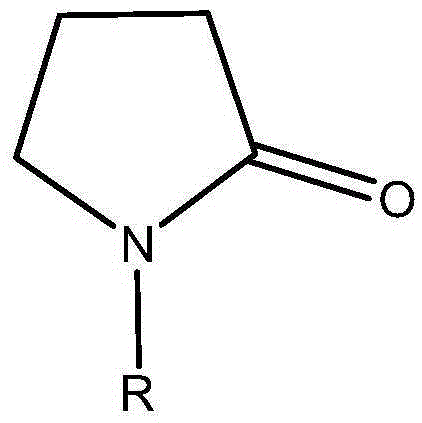
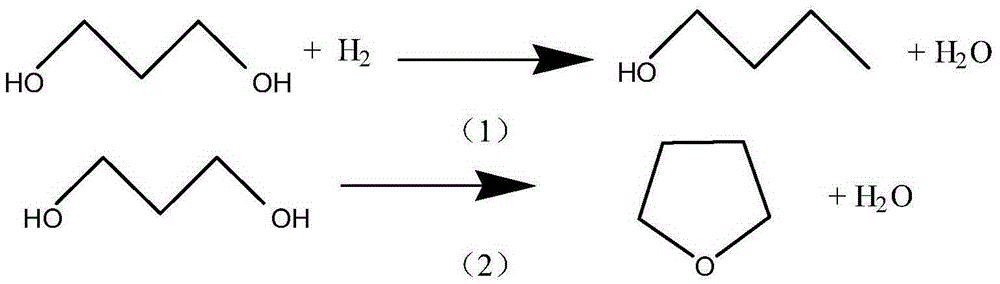
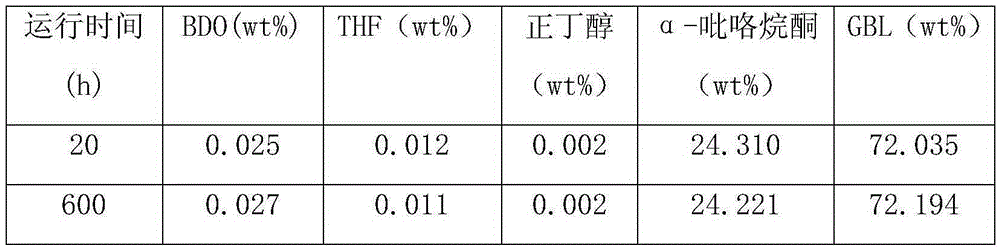
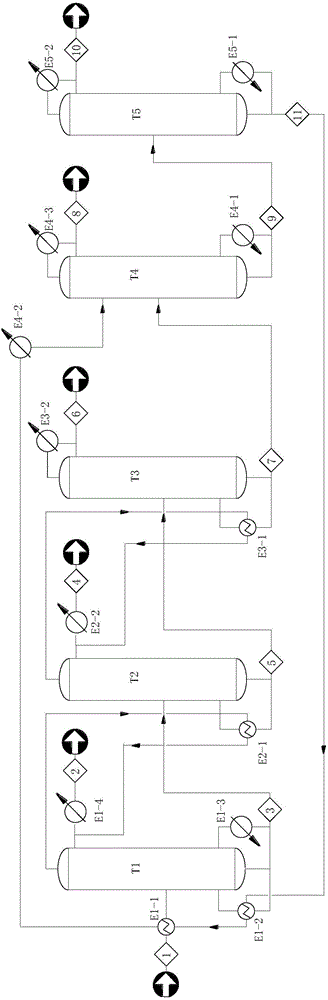
Production method of pyrrolidone products
ActiveCN105237456ASave refining energyReduce process energy consumptionOrganic chemistryETHYL PYRROLIDONEChemistry
The invention discloses a production method of pyrrolidone products. The method includes the steps that 1,4-butanediol serves as the raw material for conducting a one-step reaction, pyrrolidone is directly produced, 1,4-butanediol is converted into the pyrrolidone series products in a reaction unit through a dehydrogenation-amination reaction in the modes of a stagewise reactor and composite catalysts, such as, alpha-pyrrolidone or N-methyl pyrrolidone or N-ethyl pyrrolidone. According to the production method, the 1,4-butanediol is dehydrogenized into gamma-butyrolactone, gamma-butyrolactone is converted into pyrrolidone in an amination mode, the gamma-butyrolactone and the pyrrolidone are coupled into the same reactor, the separation and refining steps in a traditional process are omitted, energy consumption is saved, heat emitted by amination is fully utilized, the production method is easy to conduct, the yield is raised compared with a traditional process, and the production method is more environmentally friendly.
Owner:MAIQI CHEM CO LTD
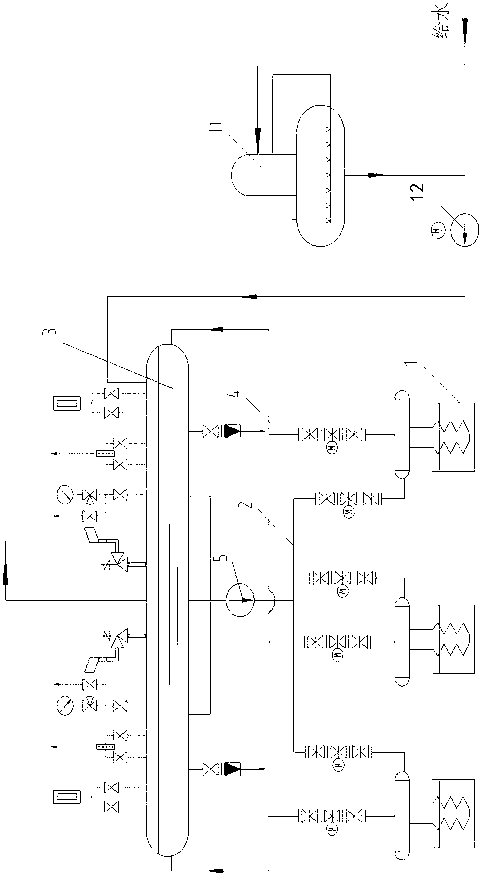
Device and method for deeply removing organic sulphides in methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE)
ActiveCN104829436AMTBE recovery increasedReduce process energy consumptionEther separation/purificationChemical industryReboilerMulti effect
The invention provides a device and a method for deeply removing organic sulphides in methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE). The device comprises a high-pressure multi-effect rectifying tower, a medium-pressure multi-effect rectifying tower, a normal-pressure multi-effect rectifying tower, an extraction rectifying tower and an extraction agent recycling tower connected in series; a condenser is arranged on the top of each tower; a reboiler is arranged at the bottom of each tower; a material outlet at the bottom of each tower is connected to a material inlet in the middle of a next tower through a pipeline; 90%-95% of qualified MTBE products can be distilled out through the tops of the multi-effect rectifying towers; the organic sulphides are enriched at the bottom of the extraction rectifying tower under the action of an extraction agent; remained MTBE distilled by the tops of the towers returns into a raw material tank; and the cycle repeats. By means of reasonable heat exchange network design, vapor from the tops of the towers and heat of the extraction agent are sufficiently utilized, so that energy consumption in a desulfurizing process is reduced; the total sulphur content of MTBE produced through a multi-effect rectifying and extraction rectifying coupling method is less than 10 ppm; deep sulphur removing requirements are satisfied; the total recovery rate of MTBE is up to 99.8%; and furthermore, the theoretical energy-saving efficiency is up to 53%.
Owner:CHINA CONSTR IND & ENERGY ENG GRP CO LTD +1
Device and method for preparing high-purity nitrogen monoxide from adipic acid production tail gases
ActiveCN105110304AReduce back flowReduce process energy consumptionChemical industryNitrous oxidesChemistryIntercooler
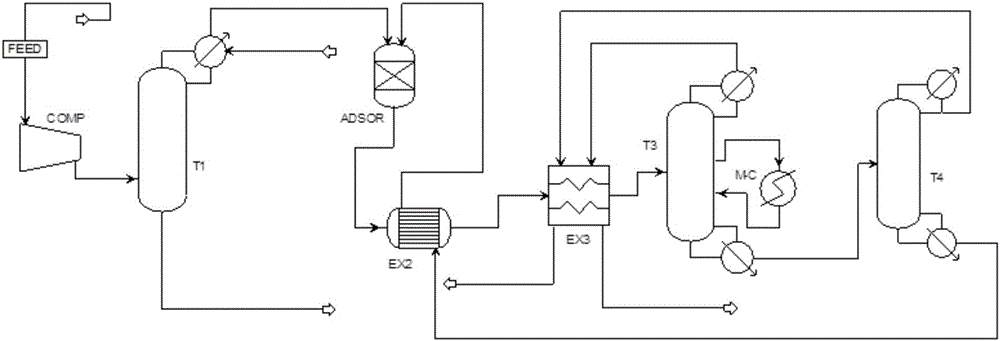
The invention relates to a device and method for preparing high-purity nitrogen monoxide from adipic acid production tail gases. The device comprises a compressor, an absorption tower, an adsorption device, a low-temperature rectifying tower and a low-temperature refining tower which are connected in sequence, wherein the low-temperature rectifying tower is provided with an intercondenser; airflow discharged from the adsorption device enters the low-temperature rectifying tower after being cooled through a heat exchanger; purge gases located at the top of the tower and treated by the intercondenser is delivered to a tail gas treatment system after the cold energy is recovered; a liquid flow at the bottom of the tower enters the low-temperature refining tower; high-purity N2O is obtained from the top of the low-temperature refining tower and is filled after cold energy is recovered; a pressurized absorption, pressurized adsorption and low-temperature rectification coupling method is adopted; and the low-temperature rectifying tower is internally provided with an intercooler, so that the process energy consumption is greatly reduced on the premise that the high purity of the product is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Technology of treating high-concentration organic wastewater with wet type catalytic oxidation
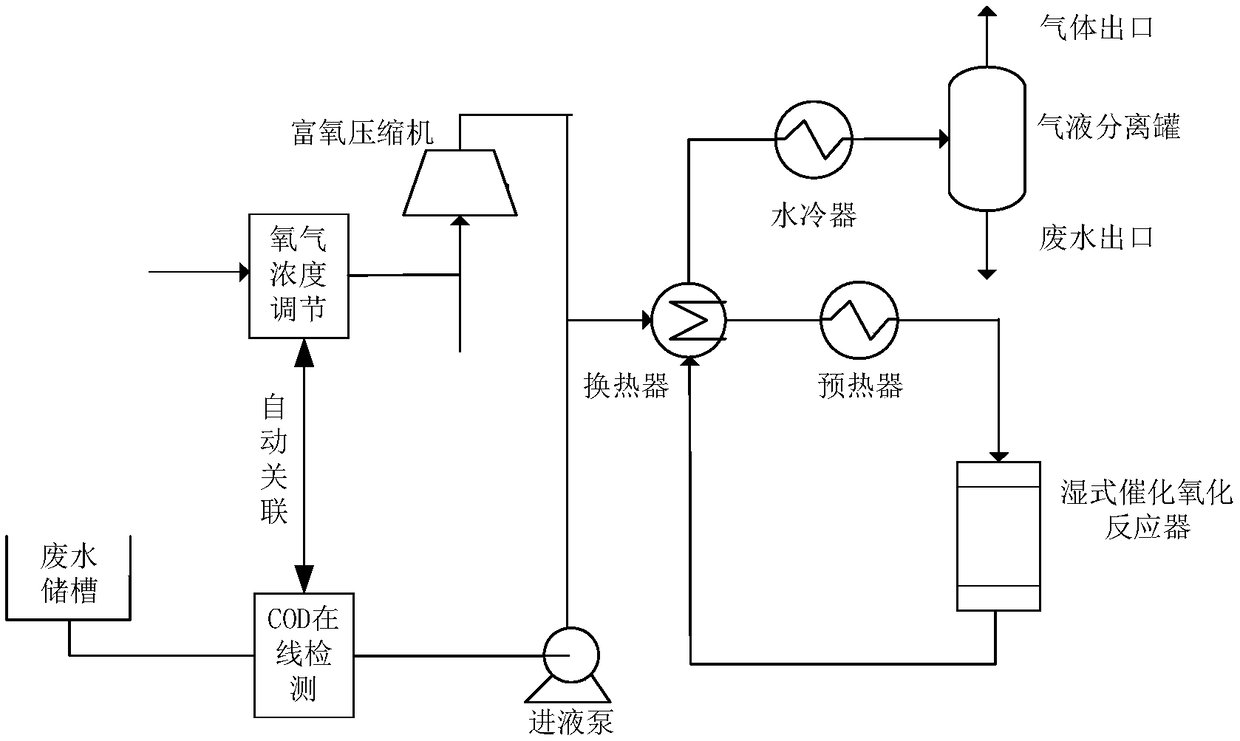
InactiveCN109455808AImprove wastewater treatment efficiencyReduce process energy consumptionWater/sewage treatment by oxidationChemistryCarbon dioxide
The invention discloses a technology of treating high-concentration organic wastewater with wet type catalytic oxidation. The technology comprises the following steps that the technology adopts COD concentration online detection and is automatically correlated to an oxygen concentration regulation device, organic wastewater with the COD content being 10000-50000 mg / L and the liquid space velocityof the wastewater being 0.5-2.5 h<-1> is mixed with enriched oxygen, the device automatically regulates the oxygen volume concentration to be 25-99 percent, water which is sent into a wastewater reactor charged with a catalyst for treatment is directly discharged or sent to a next treatment work section, and tail gas containing nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapor is directly exhaustedto atmosphere, wherein the space velocity of the enriched oxygen is 34-39 times the liquid space velocity of the wastewater, and the oxygen supply quantity is 1.1-1.2 times the theoretical oxygen demand. The technology disclosed by the invention has the advantages that high-concentration COD in acid or alkaline organic wastewater can be effectively removed.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
6063-T5 aluminum profile two-stage energy-saving aging process
InactiveCN105331910AReduce process energy consumptionReduced labor timeThermal insulationEnergy consumption
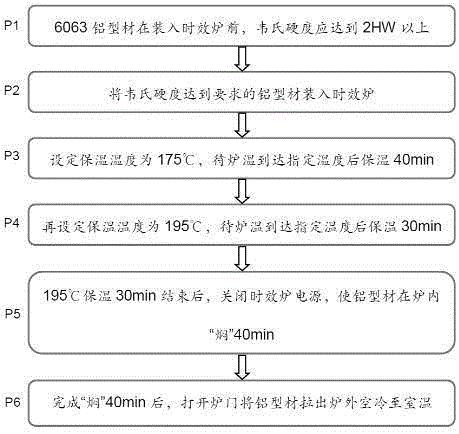
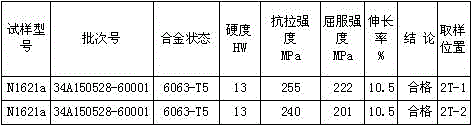
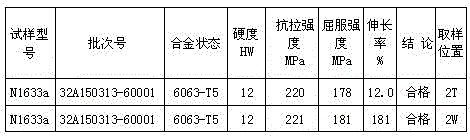
The invention discloses a 6063-T5 aluminum profile two-stage energy-saving aging process. The process includes the following steps that P1, the Vickers hardness is supposed to reach above 2HW before a 6063 aluminum profile is put in an aging furnace; P2, the aluminum profile of which the Vickers hardness meets the requirement is put in the aging furnace; P3, the thermal insulation temperature is set to 175 DEG C, and after the furnace temperature reaches the set temperature, heat preservation is conducted for 40 min; P4, the thermal insulation temperature is reset to 195 DEG C, and after the furnace temperature reaches the reset temperature, heat preservation is conducted for 30 min; P5, after 30-min 195-DEG C heat preservation is finished, a power source of the aging furnace is switched off, and the aluminum profile is braised in the furnace for 40 min; and P6, after 40-min braising is finished, a furnace door is opened and the aluminum profile is pulled out of the furnace for air cooling to the room temperature. Compared with a traditional single-stage aging process, the 6063-T5 aluminum profile two-stage energy-saving aging process can reduce the energy consumption by over 30%, shorten the manual aging time by over 20% and improve the tensile strength by over 10% and the yield strength by nearly 20% of the profile at the room temperature.
Owner:SHANDONG NANSHAN ALUMINUM
Purifying apparatus for epoxypropane
ActiveCN106397364AReduce process energy consumptionGood technical effectOrganic chemistryChemistryMethanol
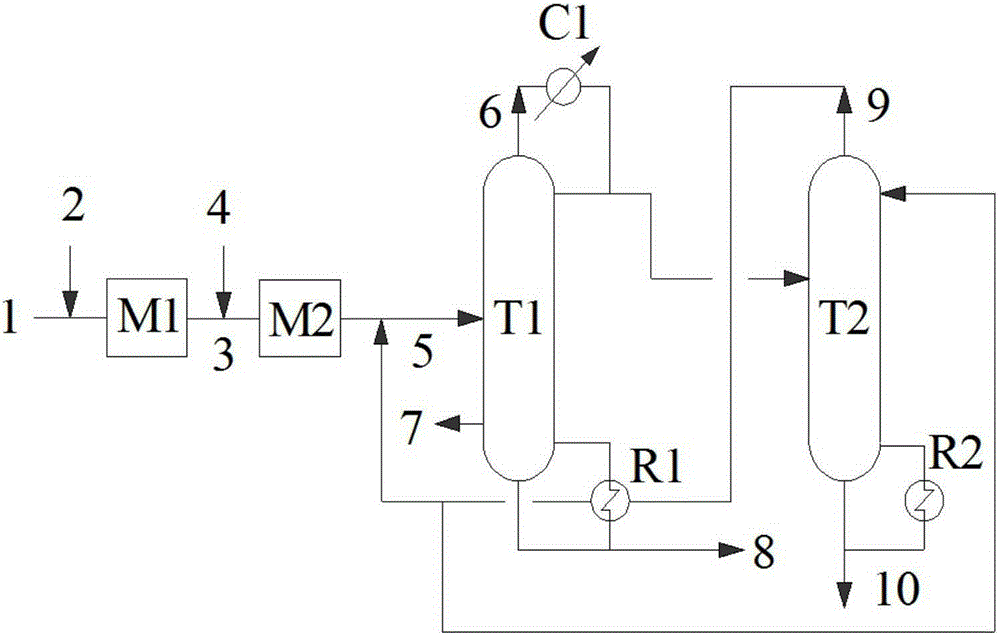
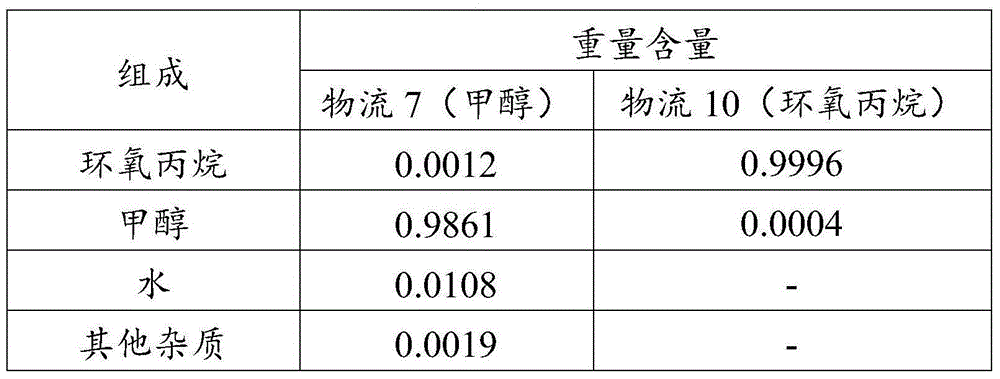
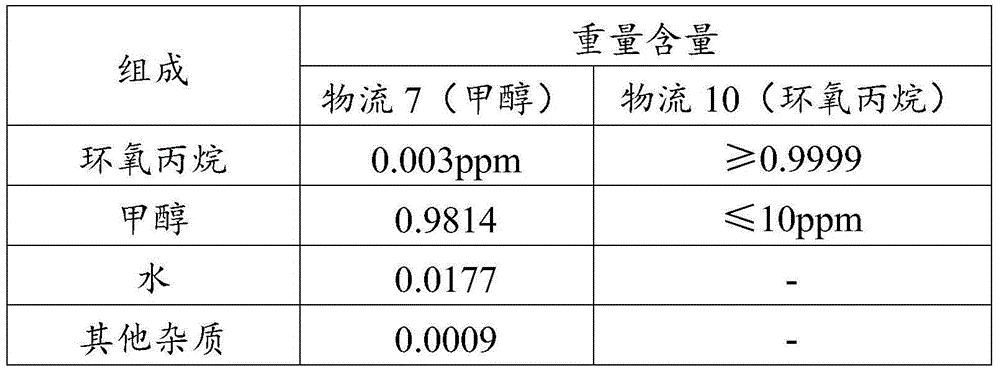
The invention relates to a purifying apparatus for epoxypropane. The purifying apparatus mainly overcomes the problems of high cost of an extractant due to introduction of a medium out of a system and incapability of recovery of methanol or material waste resulting from incapable recycling of recovered methanol due to low concentration of recovered methanol in the prior art. The purifying apparatus comprises a) a first mixer used for allowing crude epoxypropane containing impurities to contact with aqueous alkali so as to obtain first material flow; b) a second mixer used for allowing the first material flow to contact with hydrazine hydrate so as to obtain second material flow; c) a low-pressure rectifying tower used for separating the second material flow, wherein third material flow is obtained at the top of the rectifying tower, recovered methanol material flow is obtained at the side line of the tower, and a heavy-component material flow is obtained at the bottom of the tower; and d) a high-pressure rectifying tower used for separating the third material flow, wherein fourth material flow is obtained at the top of the rectifying tower and cyclically returns to the low-pressure rectifying tower, and an epoxypropane product is obtained at the bottom of the tower. Thus, the purifying apparatus overcomes the above problems and can be used for industrial purification of epoxypropane.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
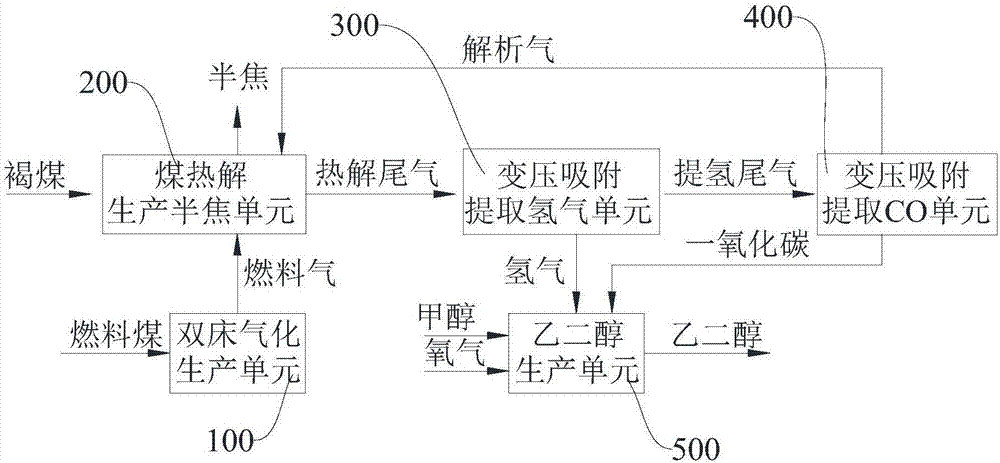
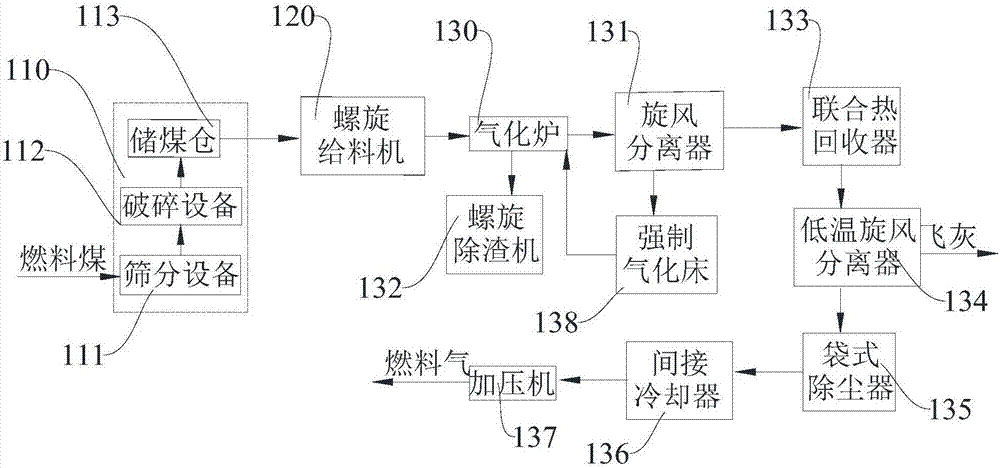
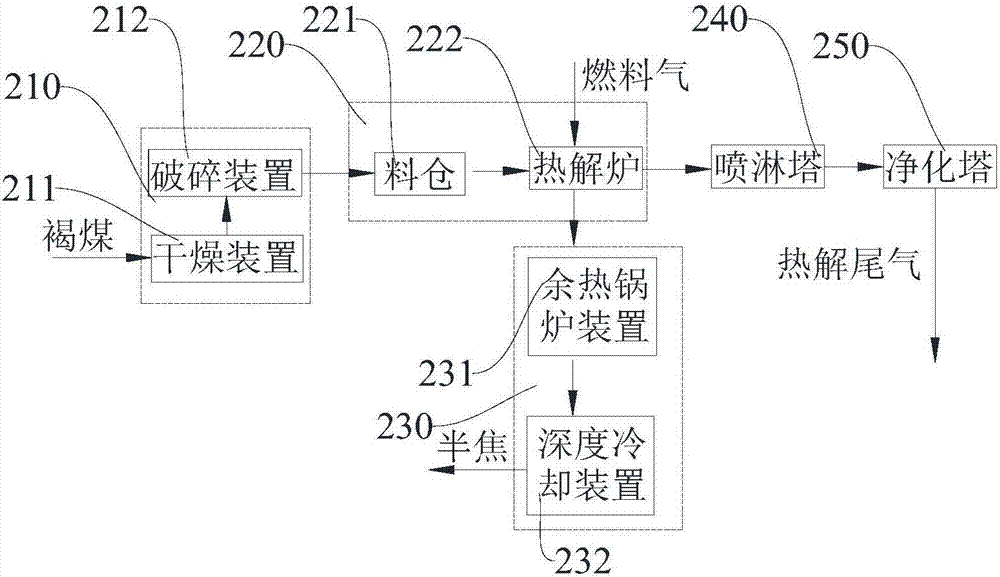
Device and method for cogeneration of ethylene glycol by coal pyrolysis production semicoke technique
PendingCN107964410AReduce manufacturing costReduce process energy consumptionOrganic compound preparationEnergy inputSide productChemical industry
The invention provides a device for cogeneration of ethylene glycol by coal pyrolysis production semicoke technique and a method for cogeneration of ethylene glycol by coal pyrolysis production semicoke technique, and belongs to the technical field of chemical industry. A dual-bed gasification production unit of the device comprises a gasifier; a raw material treatment device is connected with a coal pyrolysis device, and the coal pyrolysis device is connected with a shaping device and a purifying tower; the gasifier is connected with the coal pyrolysis device; the purifying tower is connectedwith a transforming absorbing extraction hydrogen unit and a transforming absorbing extracting carbon monoxide unit orderly; a dehydrating reactor is connected with the transforming absorbing extracting carbon monoxide unit, and a carbonylation reactor is connected with the reaction preheater; the heater is connected with the carbonylation reactor; the heater is connected with the hydrogenation reactor and the transforming absorbing extraction hydrogen unit. The method is completed through the devices; the method is simple and can produce semicoke and ethylene glycol at the same time, and utilizes the side product in the coal pyrolysis; thus the economic benefit is improved.
Owner:BEIJING HUAFU ENG
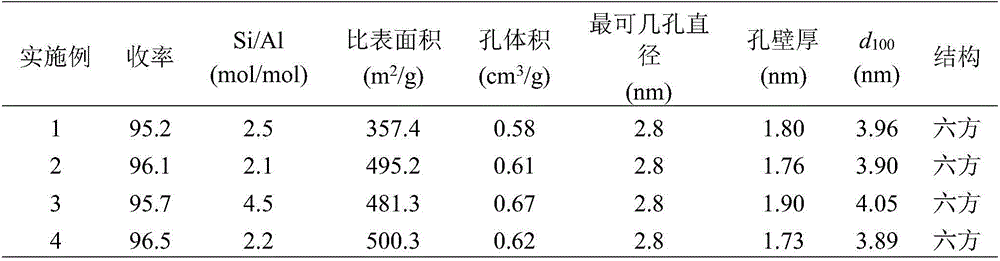
Method for directly synthesizing Al-MCM-41 mesoporous molecular sieve from kaolin or Hangjin 2# soil
ActiveCN106745032AShort synthesis timeReduce process energy consumptionNanotechnologyCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesAcid activationChemistry
The invention relates to a method for directly synthesizing Al-MCM-41 mesoporous molecular sieve from kaolin or Hangjin 2# soil. The method comprises (1) carrying out acid activation on layered clay raw ore through a sulfuric acid aqueous solution having a concentration of 4 mol / L to obtain acidified clay, (2) mixing the acidified clay and a hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide alkaline solution having a certain concentration in a water bath at a temperature of 70 DEG C for 1h, adjusting pH to 10 and carrying out stirring for 1h, (3) putting the mixture into a hydrothermal reactor and carrying out standing crystallization at a temperature of 110 DEG C for 12h, and (4) washing the product through water and carrying out drying and calcination to obtain an Al-MCM-41 mesoporous molecular sieve. The method is free of high energy consumption pretreatment processes such as high temperature calcination, high speed ball milling or high temperature alkali melting, greatly reduces the use amount of a template agent, produces the by-product of aluminum sulfate octadecahydrate, is simple and reduces a cost.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Desulfurization wastewater zero-discharge treatment system and method
PendingCN111635053ASmall scaleReduce process energy consumptionWater contaminantsWater softeningPre treatmentNanofiltration
The invention discloses a desulfurization wastewater zero-discharge treatment system and method. The desulfurization wastewater zero-discharge treatment system comprises an adjusting tank, an integrated pretreatment device, a microfiltration device, a nanofiltration device, a high-pressure reverse osmosis device, an ultrahigh-pressure reverse osmosis device, a horizontal pipe falling film concentration device and an evaporative crystallization device; wherein the adjusting tank, the integrated pretreatment device, the microfiltration device, the nanofiltration device, the high-pressure reverseosmosis device, the ultrahigh-pressure reverse osmosis device, the horizontal pipe falling film concentration device and the evaporative crystallization device are sequentially connected in the treatment direction of desulfurization wastewater. Zero discharge of wastewater is achieved, the scale of an evaporation system is reduced, the energy consumption of an evaporation crystallization processis reduced, the purity of crystalline salt is improved, the pretreatment process flow is simplified, and the floor area and equipment investment are reduced.
Owner:深圳能源资源综合开发有限公司
Building plate with gold tailing granules and making method of building plate
InactiveCN109133866AGood fire performanceReduce process energy consumptionCeramic materials productionCeramicwareScrapNational standard
The invention belongs to the technical field of gold tailing recycling and reuse, in particular relates to a building plate with gold tailing granules, and further discloses a making method of the building plate. The building plate is made of gold tailing granules together with red mud and kaolin as raw materials, and the gold tailing granules are made of conventional gold tailing wastes as a rawmaterial by using a special treatment process. The building plate has the advantages of being light in weight and rich in pore, the pressure resistance strength of the building plate meets national standards, meanwhile, the obtained plate is excellent in fireproof property, and a novel way is provided for utilization of gold tailings and red mud residues.
Owner:牛汶生
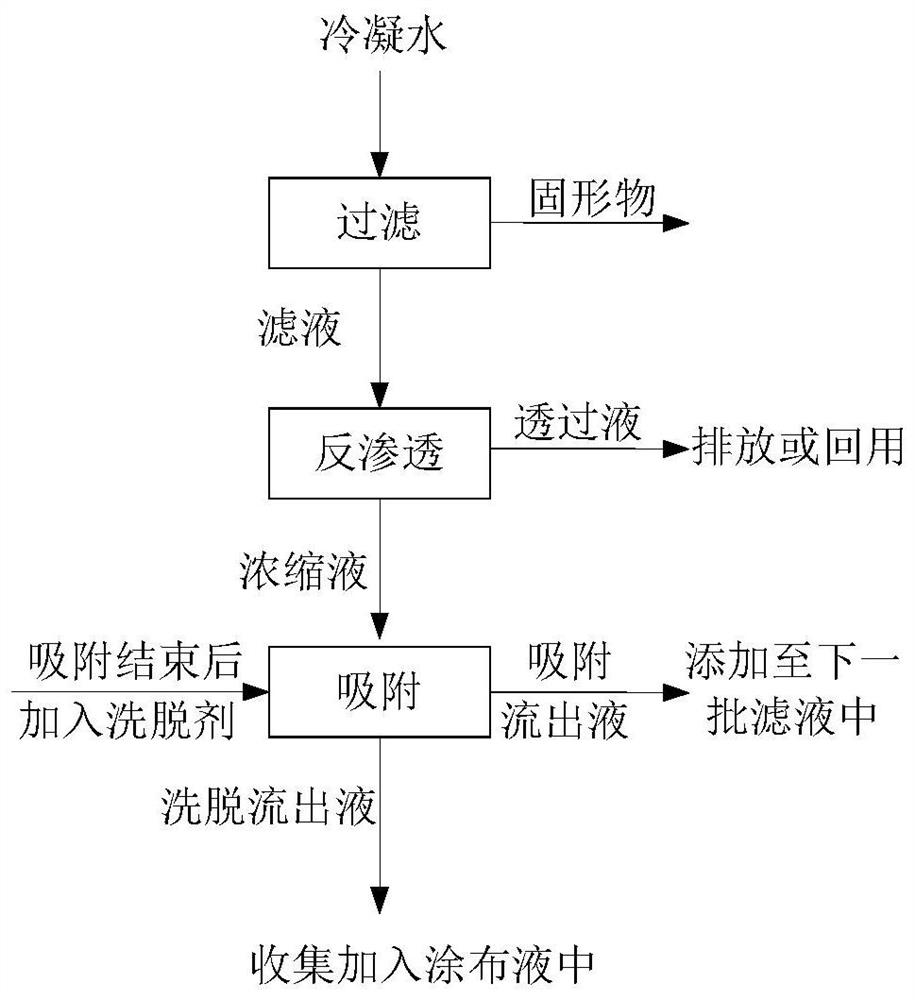
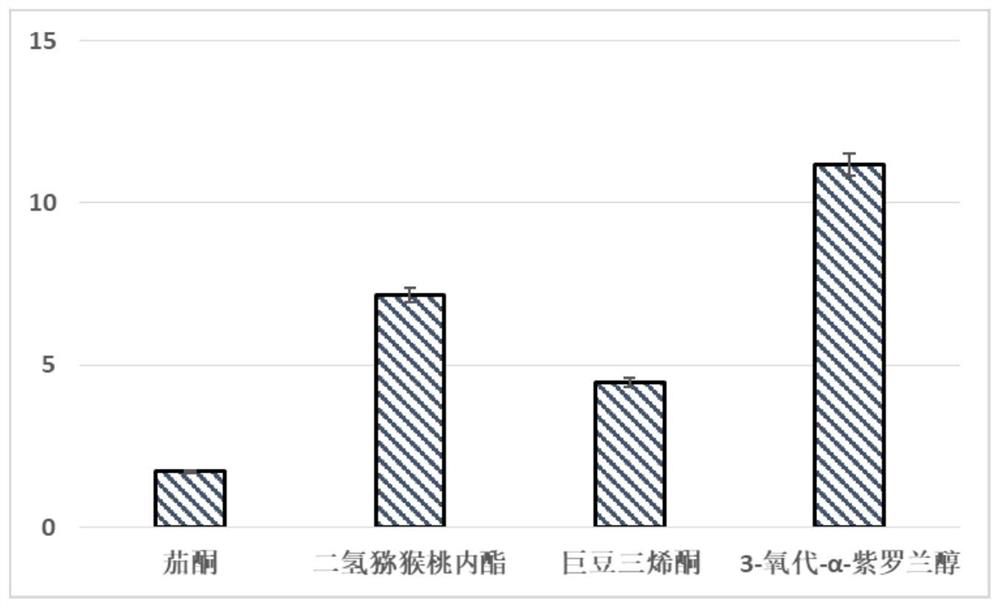
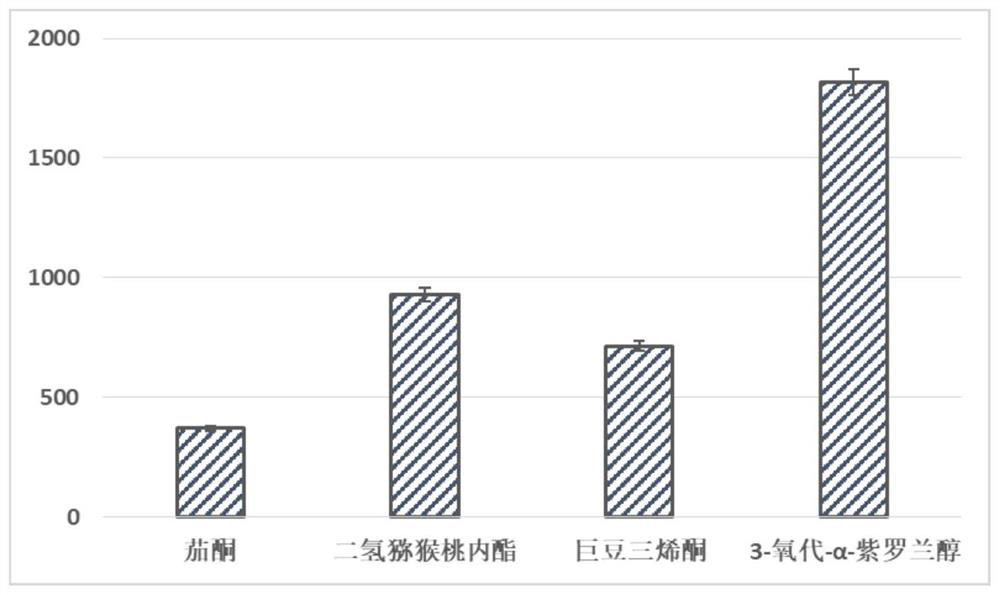
Recovery method of aroma components in reconstituted tobacco condensed water, eluent formed by method, and application of eluent
PendingCN112457917AReduce process energy consumptionReduce consumable costsEssential-oils/perfumesChemistryTobacco leaf
The invention provides a recovery method of aroma components in reconstituted tobacco condensed water, eluent formed by the method and application of the eluent. The recovery method comprises the following steps: 1) filtering condensed water generated in a production process of reconstituted tobacco to obtain filtrate; 2) carrying out reverse osmosis concentration on the filtrate to obtain an intercepted concentrated solution containing aroma components; 3) adsorbing the intercepted concentrated solution by an adsorbent; and 4) eluting the adsorbent with an eluent to obtain an eluent rich in aroma components. The recovery method is high in treatment efficiency, low in consumable cost, easy to operate and convenient to use on a large scale.
Owner:SHANGHAI TOBACCO GRP CO LTD
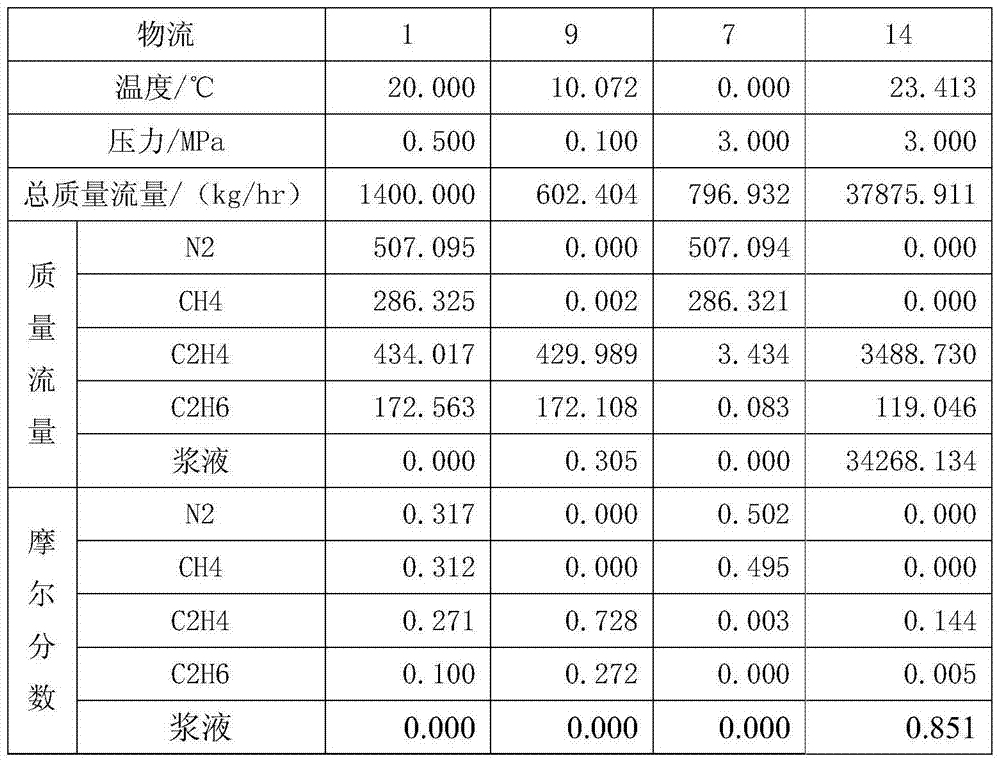
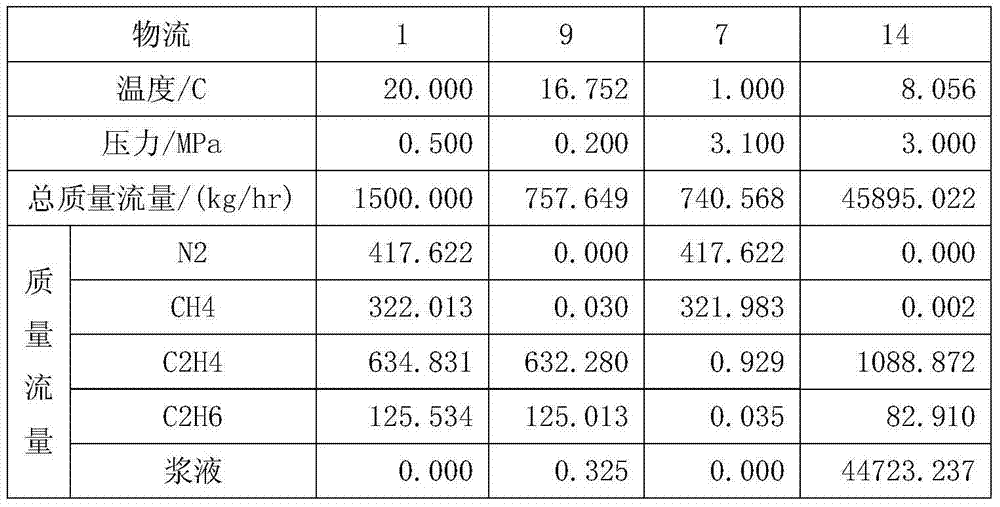
Hydration absorption gas stripping device and method for recycling ethylene and ethane from catalytic cracking dry gas or ethylene cracking gas
InactiveCN103772106ALow investment costReduce process energy consumptionHydrocarbonsEthylene productionConcentration effectAbsorption effect
The invention provides a hydration absorption gas stripping device and method of for recycling ethylene and ethane from catalytic cracking dry gas or ethylene cracking gas. The catalytic dry gas or ethylene cracking gas firstly enters a hydration absorption tower and is concentrated with slurry in the slurry, most of C2 components enter a tower bottom through the absorption effect, and the lean gas is discharged from a tower top and enters a hydration reactor. All C2 components in the hydration reactor enter the slurry in a form of hydrate, and the waste is directly discharged. The absorption slurry at the tower bottom of the hydration absorption tower is dissolved in a hydrate dissolving device, and the slurry is recycled after cooling and pressurization. By combining the absorption effect with a hydration separation process and using the concentration effect of the absorption process, the hydration separation process has the advantage of high separation efficiency for low-concentration gases, and the obtained C2 product with concentration of 99.6% can directly enter an ethylene tower. The method provided by the invention is expected to replace the common cryogenic separation process.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
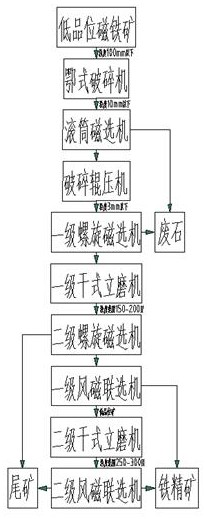
Process for producing iron ore concentrate by graded dry grinding and dry separation of low-grade magnetite
InactiveCN112264172AHigh metal recovery rateReduce process energy consumptionGrain treatmentsMagnetic separatorOre concentrate
The invention discloses a process for producing iron ore concentrate by graded dry grinding and dry separation of low-grade magnetite, and aims to solve the problems of long process flow, low concentrate grade and low recovery rate of a traditional iron ore dry fine separation process. The process comprises the steps that after low-grade iron ore is crushed by using a jaw crusher and subjected tomagnetic separation by using a roller magnetic separator, a part of large-particle waste rock is removed at first, then, the low-grade iron ore is subjected to fine crushing by adopting a crushing roller press and subjected to dry separation by adopting a spiral magnetic separator, and a part of small-particle waste rock is thrown off; and the obtained preseparated ore is subjected to coarse grinding by adopting a dry vertical grinding machine, dry separation by adopting the spiral magnetic separator, and dry separation by adopting a wind-magnetic combined separator, then a part of fine-graintailings is removed, a part of iron ore concentrate is recycled, residual materials is subjected to fine grinding by adopting the dry vertical grinding machine and magnetic separation by adopting thewind-magnetic combined separator so as to carry out iron mineral recovery. According to the process, excessive crushing and less grinding, multi-stage ore grinding and multi-stage dry separation are adopted, and the procedure energy consumption in the grinding and separation processes is reduced while the iron ore concentrate grade and the beneficiation metal recovery rate are increased.
Owner:JIUQUAN IRON & STEEL GRP
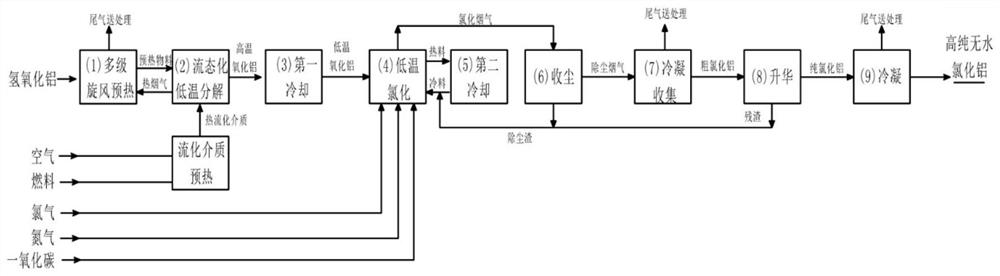
Method for producing high-purity anhydrous aluminum chloride from aluminum hydroxide
ActiveCN111661861AReduce process energy consumptionSpeed up the decomposition processEnergy inputAluminium chloridesAluminum chloride anhydrousFlue gas
The invention discloses a method for producing high-purity anhydrous aluminum chloride from aluminum hydroxide. The method comprises the following procedures: (1) a multistage cyclone preheating procedure; a fluidization decomposition step (2); a first cooling step (3); a low-temperature chlorination step (4); a second cooling step (5); a chlorinated flue gas dust collection process (6); a condensation collection step (7); a sublimation step (8); and a condensation step (9). Through the procedures, a high-purity anhydrous aluminum chloride solid product can be obtained. The method has the advantages of being high in production efficiency, low in cost, high in waste heat utilization rate, suitable for large-scale production and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
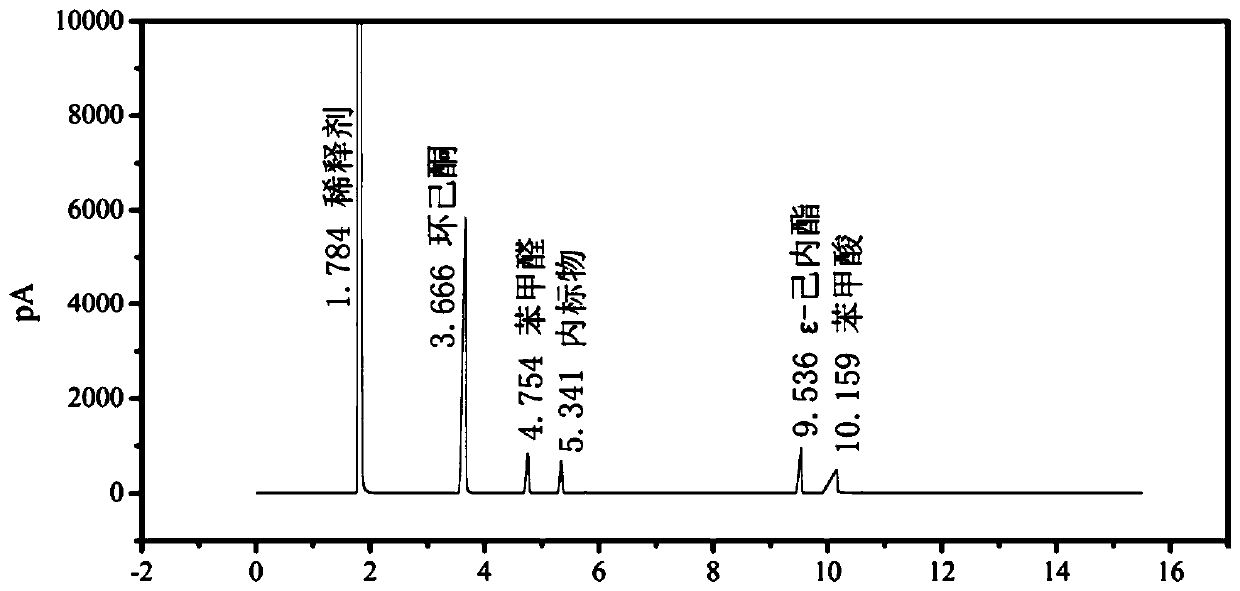
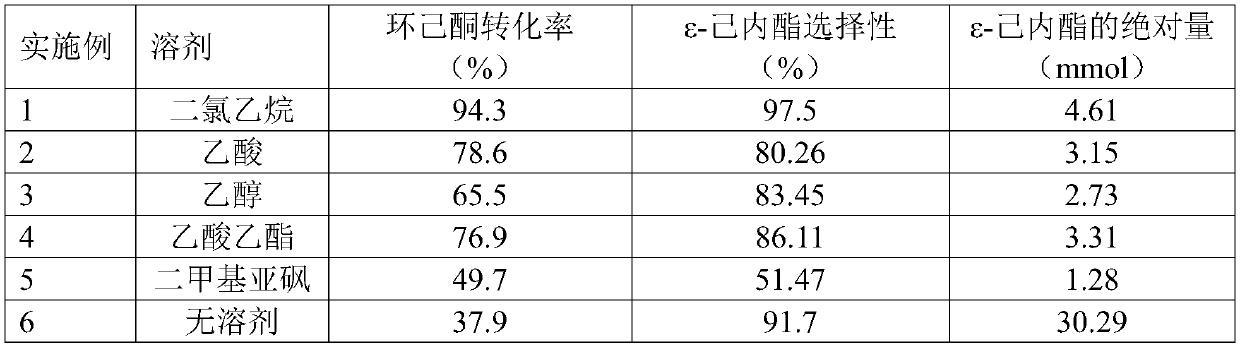
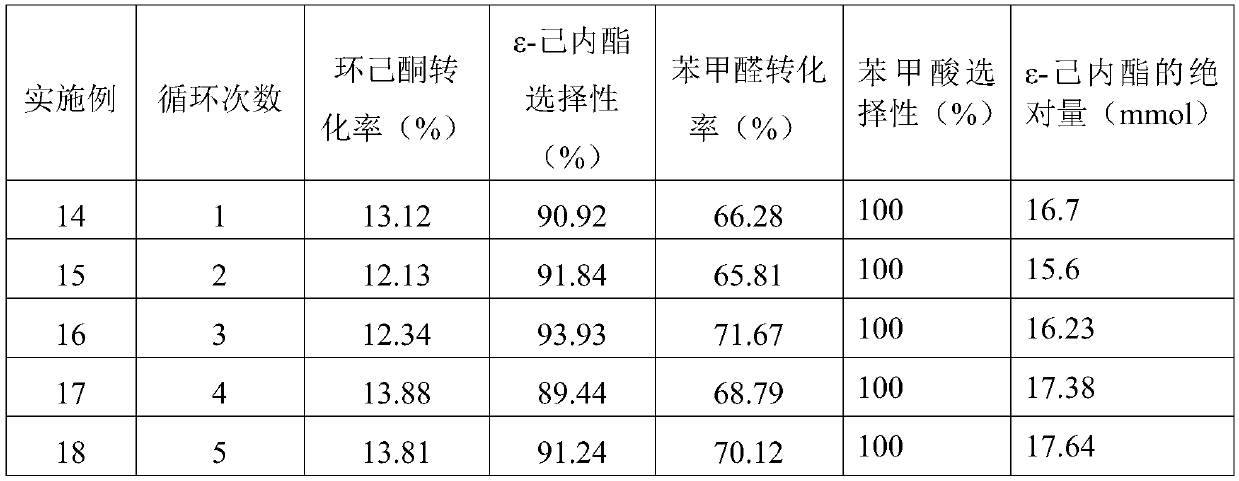
Method for preparing epsilon-caprolactone through solvent-free cyclohexanone-benzaldehyde oxidation
PendingCN110922385AReduce process energy consumptionReduce energy consumptionOrganic chemistryBenzaldehydeDoped carbon
The invention belongs to the technical field of epsilon-caprolactone preparation, and discloses a method for preparing epsilon-caprolactone through solvent-free cyclohexanone-benzaldehyde oxidation. The method comprises the steps: adding a catalyst into a mixture of cyclohexanone and a co-oxidant, taking oxygen as an oxidant, and carrying out stirring reaction under the conditions that the pressure is 0.1-10 MPa and the temperature is 25-150 DEG C, so as to obtain epsilon-caprolactone, wherein the co-oxidant is benzaldehyde, and the catalyst is a nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, and the process flow of solvent separation in the industry is removed by taking cheap and readily available oxygen as an oxidant under a solvent-free condition, so that the process energy consumption is reduced; and the epsilon-caprolactone is high in selectivity and high in yield.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
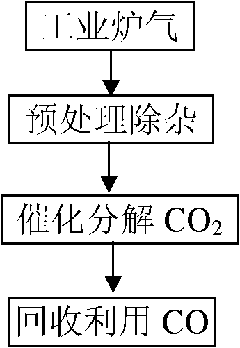
Comprehensive utilization method of industrial furnace gas
InactiveCN101799244AReduce process energy consumptionEnergy savingGas emission reductionWaste heat treatmentPre treatmentCarbon source
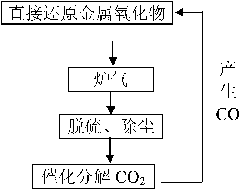
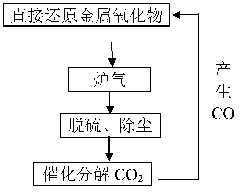
The invention relates to a comprehensive utilization method of industrial furnace gas, which belongs to the field of metallurgy, in particularly to utilization of industrial furnace gas which mainly comprises CO2. The invention achieves the purposes of providing the comprehensive utilization method of the industrial furnace gas and enhancing utilization value of components and heat in the furnace gas. The method comprises the steps of: A, preheating and removing impurities of the industrial furnace gas; B, decomposing CO2 in the industrial furnace gas treated in step A into CO by using a catalyst at the temperature of not more than 1450 DEG C; and C, usually only using waste heat resources in the reutilization of the industrial furnace gas of CO obtained in step B. In the method, CO2 is effectively used without waste; a catalytic technology is adopted for converting CO2 into CO; the waste heat of the furnace gas is thoroughly used for providing a heat source for a catalytic reaction; when CO2 is catalyzed and converted into CO gas, heat loss is less; therefore, the waste heat resources and CO can be used for largely reducing the utilization of the heat source and a carbon source for realizing the comprehensive utilization of the furnace gas.
Owner:杨绍泉
Molten steel continuous pouring method for extremely-low phosphorus-sulfur high alloy steel through single LF furnace and multiple tanks
ActiveCN106702074AReduce process energy consumptionUnleash steelmaking capacityManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSlagDolomite
The invention provides a molten steel continuous pouring method for extremely-low phosphorus-sulfur high alloy steel through a single LF furnace and multiple tanks. Before production is conduced, to-be-used molten steel tanks and a to-be-used molten vacuum chamber which are used for low silicon-aluminum killed steel rinsing for a time are arranged, and after molten iron is desulfurized, sulfur is equal to or less than 0.0010%; after a converter starts blowing, active lime, light roasting dolomite and two-thirds ores are added, blowing is conducted for 4-5 min, deslagging is conducted in the molten iron, and then slagging is conducted again; blowing is conducted for 8.5-9.5min, when the temperature reaches 1400-1450 DEG C, steel tapping is conducted, steel tapping C is ensured to be 2.00-2.30%, and P is ensured to be less than 0.025%; before a decarburization furnace starts blowing, a carburant used for raising the temperature is added, when a terminal point C is 0.03-0.05%, steel tapping is conducted, and in the process of steel tapping, slag tapping is strictly prohibited; top slag Als of the LF furnace needs to be accurately controlled to be 0.015-0.020%; and the RH vacuum degree is equal to or less than 200 Pa, circulation is conducted for 30 min or more, and after vacuum is broken, argon bottom blowing is conducted for 15-20 min. Through the method, steel tapping P can be controlled to be 10-20 ppm, rephosphoration is within 15 ppm, and finished product P is within 35 ppm. The LF treatment period is shortened to 70 min, the number of continuous pouring tanks is increased to be four, and steel-iron materials are reduced 52 kg / t steel.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Device and method for separating n-butanol from n-butyl ether by using extraction and distillation process
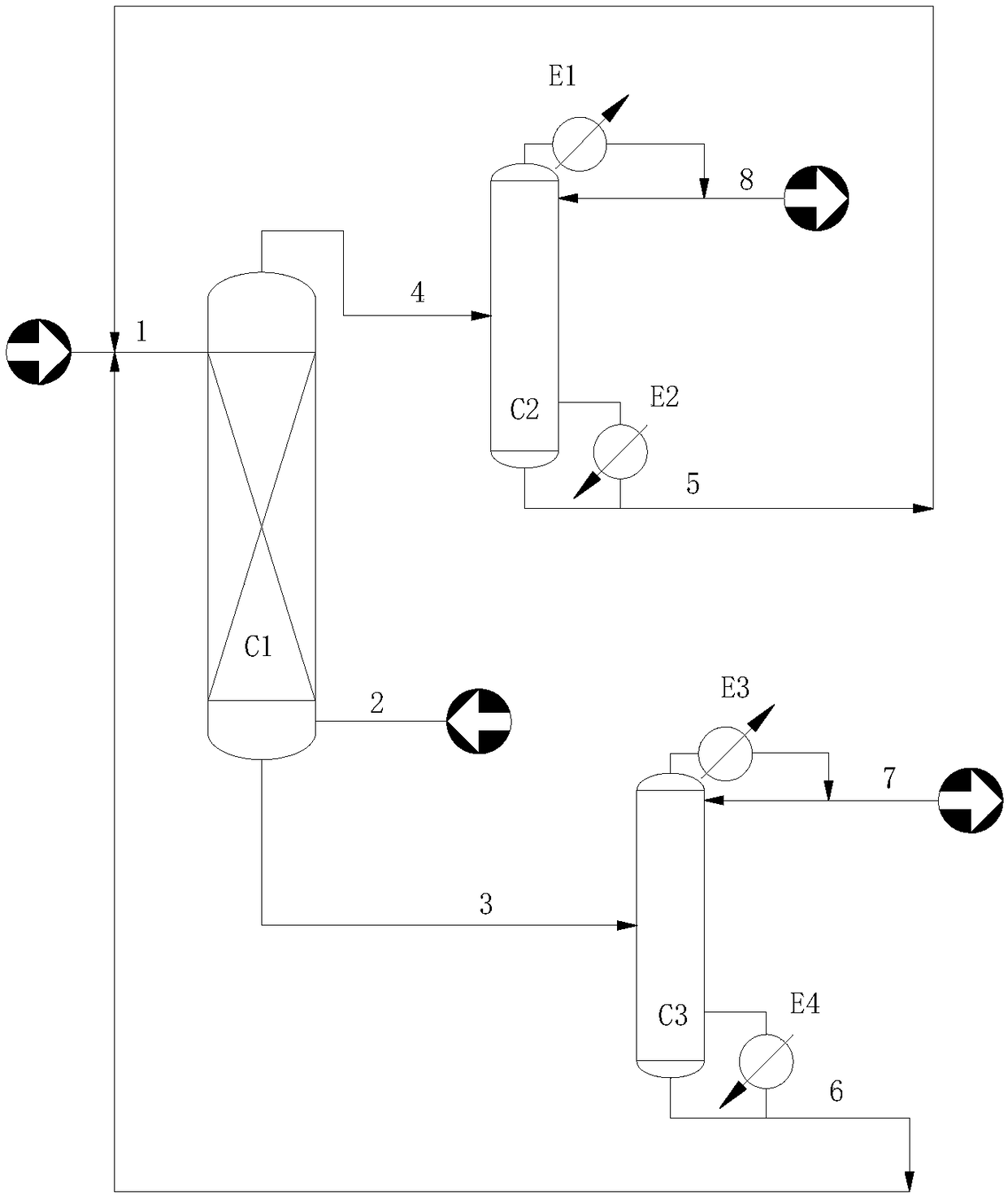
PendingCN109438178AThe process is simple and controllableReduce process energy consumptionEther separation/purificationOrganic compound preparationCounter currentScrap
The invention relates to a device and a method for separating n-butanol from n-butyl ether by using an extraction and distillation process. The device comprises an extraction column, a butyl ether recovering tower, an extractant regeneration tower, a butyl ether recovering tower overhead condenser, a butyl ether recovering tower bottom reboiler, an extractant regeneration tower overhead condenser,and an extractant regeneration tower bottom reboiler. The method is characterized in that an extractant and butanol and butyl ether feed solutions are subjected to continuous counter-current extraction in the extraction column; an extraction column overhead liquid phase enters the butyl ether recovering tower; the separated qualified butyl ether product is extracted from the tower top, and towerbottom regeneration extractant refluxes to enter the extraction column; an extraction column bottom liquid phase enters an extractant recovering tower; a separated qualified butanol product is extracted from the tower top; a tower bottom regeneration extractant refluxes to enter the extraction column, so that recycling of the extractant is realized. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the problem that the butanol is difficult to be separated from the butyl ether in an existing DBP production technology is solved. The technology disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, controllability, low energy consumption and no waste discharge.
Owner:BAILONG CHEM SHIJIAZHUANG +1
Production process of feed-grade copper glutamate
PendingCN113773213AReduce process energy consumptionReduce equipment costsOrganic compound preparationSolution crystallizationSide productProcess engineering
Owner:GUANGHAN LONGDA FEED
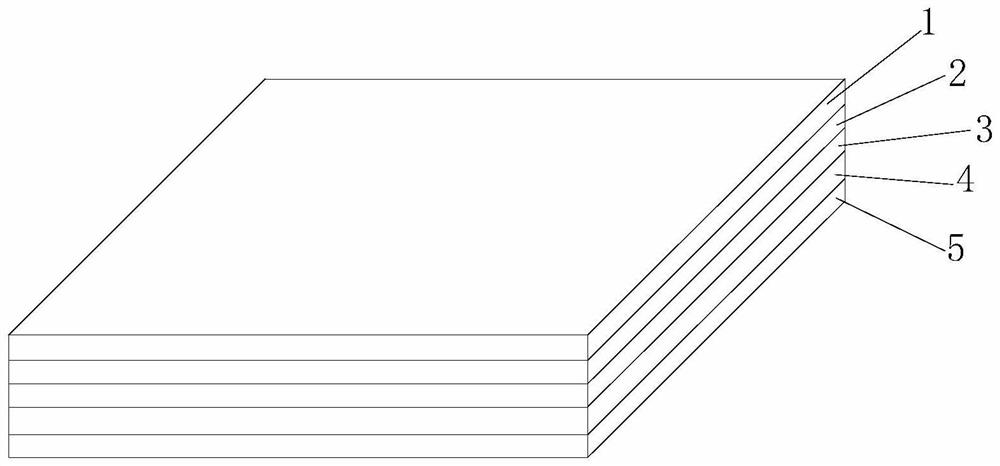
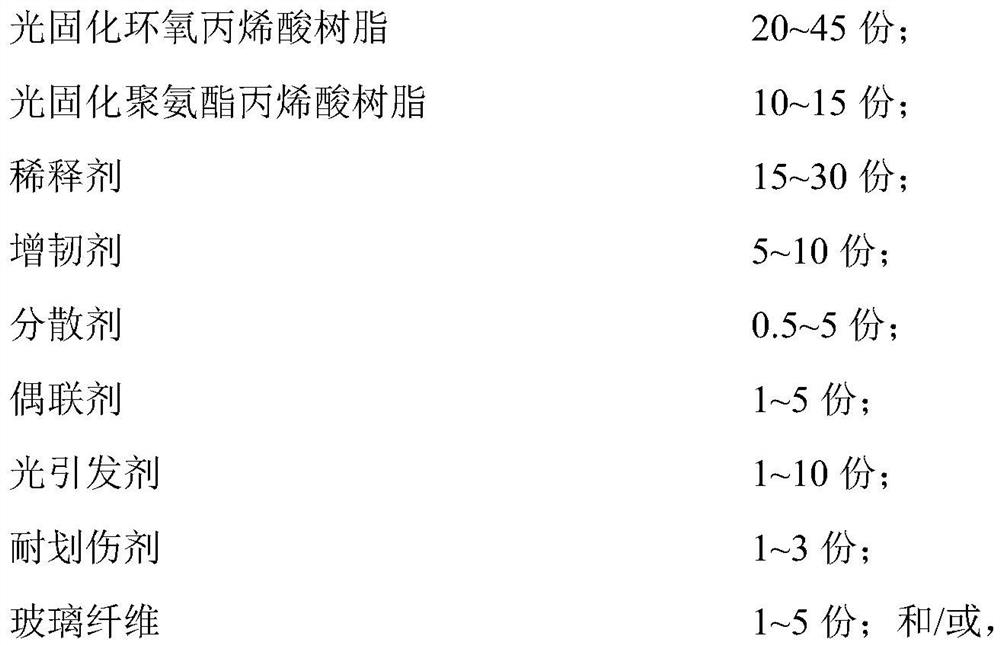
Anti-corrosion flexible epoxy composite coiled material as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114806092AGood flexibilityReduce process energy consumptionCovering/liningsLamination ancillary operationsWeather resistanceLong chain
The invention relates to an anti-corrosion flexible epoxy composite coiled material as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and the flexible epoxy composite coiled material comprises a first resin layer, a first reinforcing layer, a second resin layer, a second reinforcing layer and a third resin layer which are sequentially stacked, the first resin layer, the second resin layer and the third resin layer are respectively compounded by light-cured epoxy acrylic resin and light-cured polyurethane acrylic resin as main raw materials, and the light-cured epoxy acrylic resin is selected from aliphatic flexible long-chain modified epoxy acrylic resin; and the light-cured polyurethane acrylic resin is selected from aliphatic polyurethane acrylic resin with polyfunctionality. The three resin layers not only retain the inherent characteristics of epoxy resin, but also increase the advantages of acrylic resin and polyurethane resin, and meanwhile, the film layer is toughened from the molecular level to form a cross-linked network composite film layer structure reinforced in an elastomer; the composite resin system has weather resistance, flexibility and good mechanical strength at the same time.
Owner:JIANGSU CANLON BUILDING MATERIALS
ISP (imperial smelting process) cooling chute waste heat boiler system
InactiveCN103063041AImprove the level of energy savingReduce process energy consumptionEnergy industryIncreasing energy efficiencyCorrosion resistantSmelting process
The invention discloses an ISP (imperial smelting process) cooling chute waste heat boiler system comprising a steam manifold and a plurality of parallelly arranged chute heat exchangers. Each chute heat exchanger comprises a lead and zinc chute, a comb-shaped heat exchange box and a heat exchange tube, lead and zinc meltwater is filled in the lead and zinc chute, the lower portion of the comb-shaped heat exchange box is immerged into the lead and zinc meltwater, low-melting-point alloy meltwater is filled in the comb-shaped heat exchange box, and the heat exchange tube is immerged into the low-melting-point alloy meltwater. Further, the steam manifold is communicated with a water inlet of the heat exchange tube through a descending tube to supply water to the heat exchange tube, and a steam outlet of the heat exchange tube is communicated with the steam manifold through an ascending tube to discharge steam to the steam manifold. By the ISP cooling chute waste heat boiler system, waste heat of the lead and zinc meltwater from 550 DEG C to 450 DEG C during cooling is effectively recovered, corrosion to the heat exchangers from the lead and zinc meltwater can be avoided by corrosion-resistant insulation layers which are adopted in the chute waste heat exchangers, waste heat is recovered by saturated steam, modification of an original technical process body is omitted, and engineering application is easy to realize. Energy saving level of melting of a closed blast furnace can be improved and technical energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING CENTURY BENEFITS
Novel green lithium iron phosphate precursor as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113896182AHigh solid contentReduce process energy consumptionSecondary cellsPositive electrodesOrganic acidProcess engineering
The invention discloses a novel green lithium iron phosphate precursor as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the lithium iron phosphate precursor comprises the following steps: S1, reacting a mixture of an iron source and a phosphoric acid solution, and grinding after the reaction is completed to obtain a product A; reacting a mixture of an organic acid solution, a lithium source and a carbon source to obtain a product B after the reaction is completed; wherein the preparation sequence of the product A and the product B is not limited; and S2, grinding the mixture of the product A and the product B to obtain the lithium iron phosphate precursor. In the preparation process of the lithium iron phosphate precursor, the solid content can be greatly increased, the energy consumption of the subsequent process is small, and the preparation method is simple; the cost is low; and the prepared lithium iron phosphate precursor is extremely small in particle size and high in charge-discharge rate.
Owner:上海量孚新能源科技有限公司
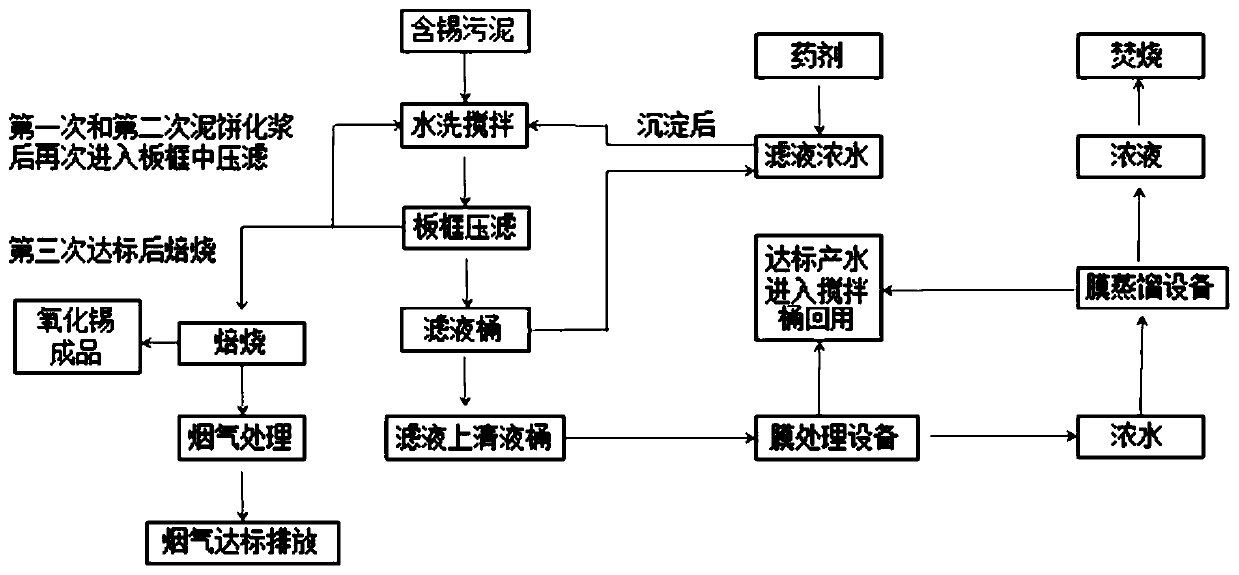
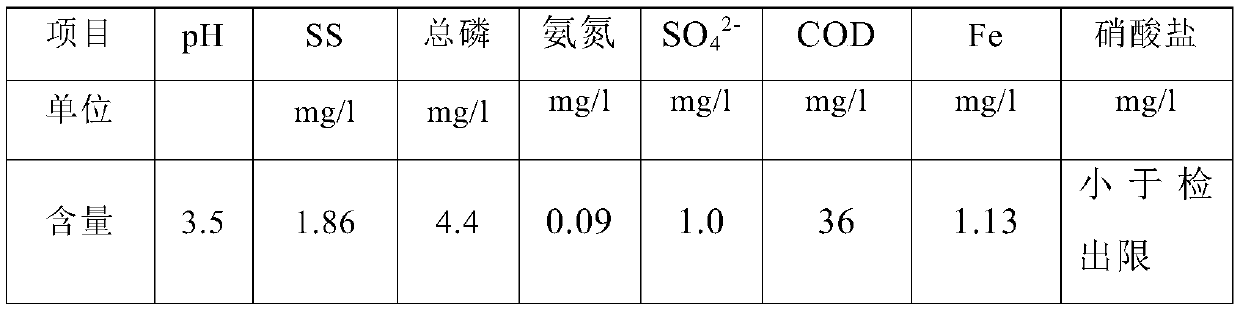
Tin-containing sludge treatment method
InactiveCN109896721AReduce process energy consumptionThe process is simpleSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater contaminantsSolid phasesChemistry
The invention relates to a tin-containing sludge treatment method which includes the steps: mixing tin-containing sludge and pure water to obtain slurry; performing solid-liquid separation on the slurry to obtain filter liquid and a solid-phase material; heating the solid-phase material to obtain a tin oxide product; filtering the filter liquid to obtain produced water and filter residues, takingstandard produced water in a the device as pure water to be reused, and selecting matched electroplating solution to return to production or enter an incinerator according to specific circumstances after concentrated solution reaches to a certain concentration. The method has the advantages that compared with the prior art, hazardous waste is quantitatively treated, a whole process is low in energy consumption, zero emission is achieved, a technological process is simple, and commercialization is facilitated.
Owner:宝武集团环境资源科技有限公司
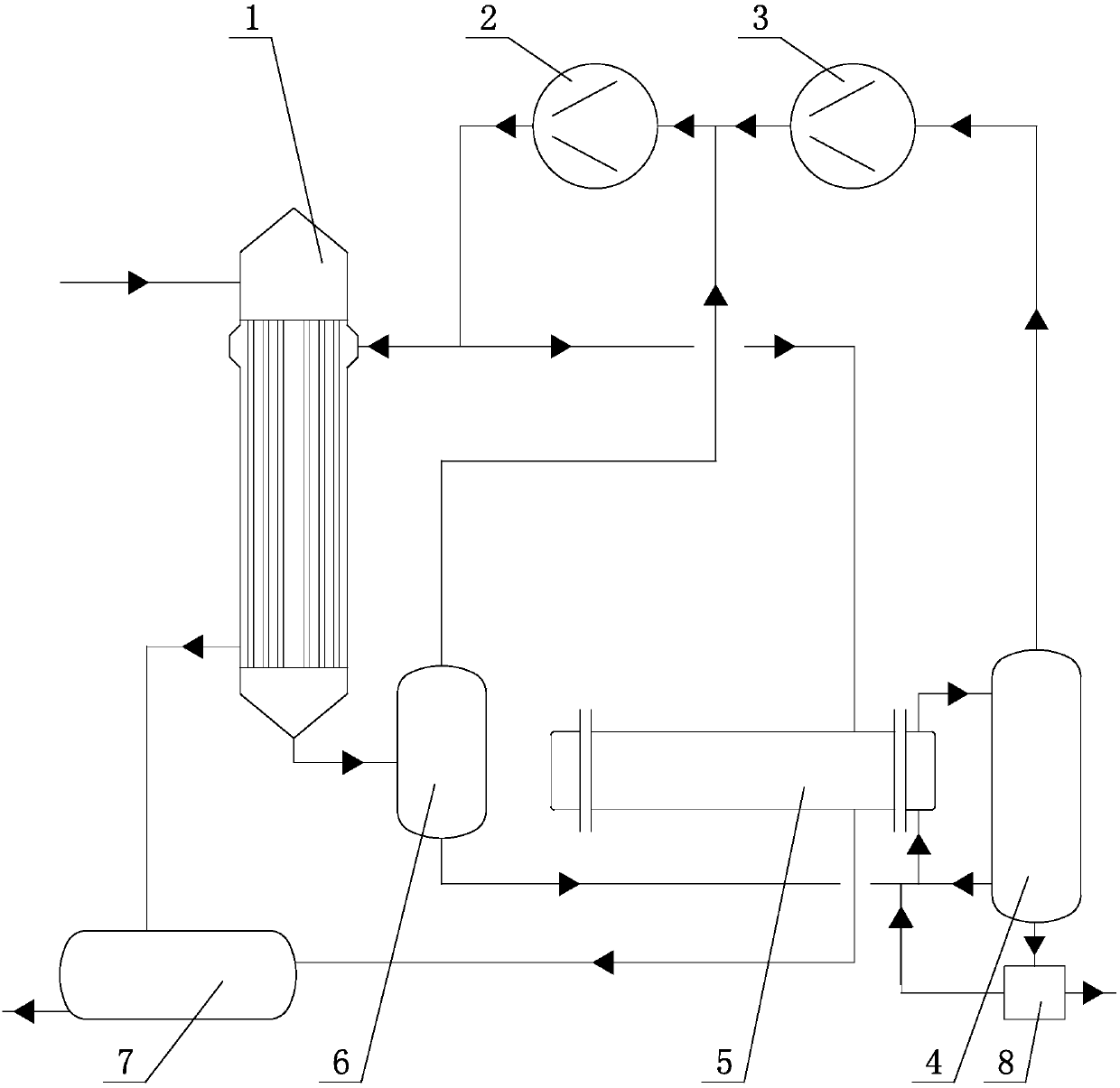
Double-stage MVR evaporation and crystallization process and equipment
InactiveCN107754357ALess investment in equipmentReduce process energy consumptionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationChemistryDouble stage
The invention is mainly applied to the fields of chemical engineering and process, and in particular relates to a double-stage MVR evaporation and crystallization process and double-stage MVR evaporation and crystallization equipment. The process comprises the following steps: inputting raw material liquid into a primary evaporator to perform heating, inputting the heated material liquid into a primary separation chamber to perform vapor and liquid separation, inputting the obtained liquid phase, cycling material liquid of a secondary separation chamber and a desalted liquid phase into a secondary evaporator to perform heating, inputting the heated material liquid into the secondary chamber to perform vapor and liquid separation, and inputting the obtained liquid phase into a desalting device to perform desalting; and after compressing the vapor phase obtained by the secondary separation chamber by a secondary compressor, inputting the compressed vapor phase and the vapor phase obtained by the primary separation chamber into a primary compressor, performing compression by the primary compressor, inputting the compressed vapor phases serving as heating sources into the primary evaporator and the secondary evaporator correspondingly to heat the material liquid, condensing into condensate after heating, inputting the condensate into a condensate storage tank, collecting and discharging. By implementation of the process method and the equipment, equipment investment can be obviously reduced, the process energy consumption can be reduced, and process operation and control are simplified.
Owner:SHANDONG BOZHONG VACUUM EQUIP LIMITED
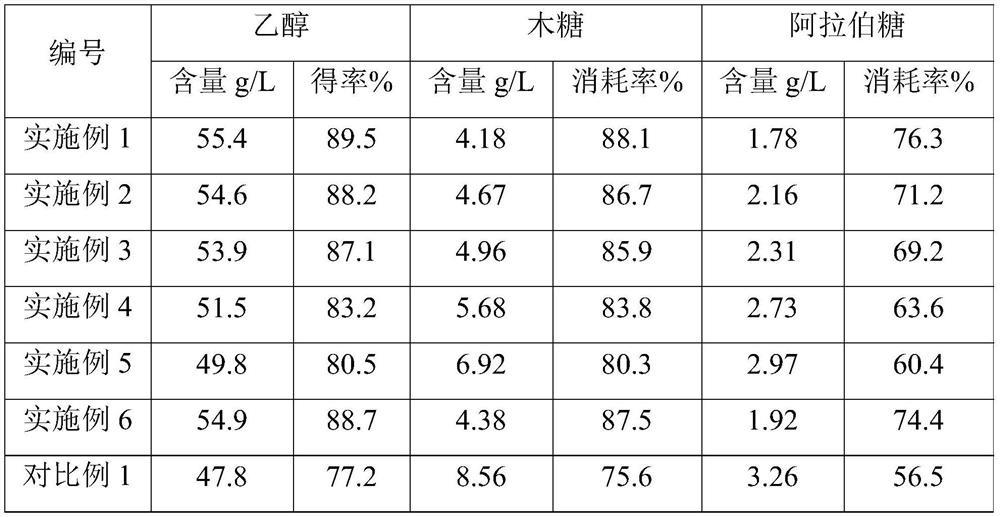
Method for producing ethanol through propagation fermentation of co-fermentation saccharomycetes
PendingCN113215203AReduce process energy consumptionImprove equipment utilizationBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesSaccharomycopsis fermentansArabinose
The invention relates to the field of ethanol production, in particular to a method for producing ethanol through propagation fermentation of co-fermentation saccharomycetes. The method comprises the following steps: performing propagation on activated saccharomycetes to obtain a seed solution, and then inoculating the seed solution into a fermentation culture medium for fermentation to obtain ethanol, wherein in the propagation process, the stirring rotating speed is controlled to be 40-100 rpm, the ventilation ratio is 0-0.4 vvm, and the liquid loading amount is 60-70% by volume; and the saccharomycetes is saccharomyces cerevisiae, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.16830. Compared with a traditional saccharomycetes propagation method, micro-anaerobic propagation is adopted in the propagation process, the process energy consumption can be reduced, the equipment utilization rate can be increased, and the strain fermentation performance can be improved; and then, the seed solution is fermented, so that the metabolism efficiency of the strain on arabinose and xylose can be remarkably improved, and the ethanol yield is improved.
Owner:COFCO BIOCHEM ENERGY ZHAODONG
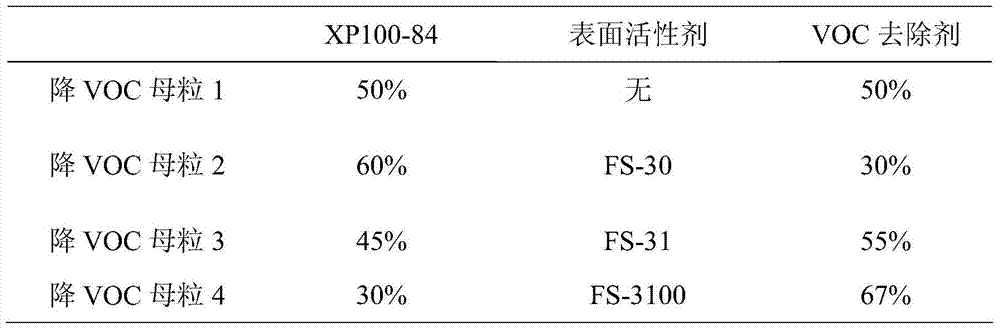
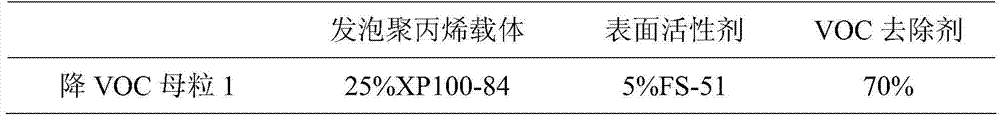
A kind of VOC-reducing masterbatch for polypropylene and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN105504507BImprove the devolatilization effectReduce process energy consumptionChemistryEnvironmentally friendly
The invention discloses a VOC-decreased master batch for polypropylene as well as a preparation method and application of the VOC-decreased master batch. The VOC-decreased master batch is prepared from a novel microcellular-foamed polypropylene carrier, an aqueous solution VOC remover adsorbed to the polypropylene carrier and a surfactant in parts by mass. According to the application, in a preparation process of a composite material, the VOC-decreased master batch and polypropylene resin are uniformly mixed and stirred by virtue of a VC efficient mixer, and the mixture is extruded and granulated by virtue of twin-screw extrusion to generate an environment-friendly modified polypropylene composite material; the addition amount of the VOC-decreased master batch is 1%-10%. The VOC-decreased master batch for polypropylene has good compatibility with the polypropylene resin and can be completely devolatilized in a vacuum manner without residues, so that the subsequent processing and performance of modified polypropylene are not influenced, VOC of a polypropylene product is effectively decreased, and the polypropylene product is relatively environmentally friendly and can meet requirements of automobile manufacturers on VOC.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Deep dehydration method based on sludge wall breaking
PendingCN113429103AEfficient wall breakingReduce process energy consumptionSludge treatmentBiomassPulverizer
The invention relates to the field of sludge treatment, in particular to a deep dehydration method based on sludge wall breaking, which is used for solving the sludge treatment current situation that the water content of sludge in a sewage treatment plant is difficult to further reduce. The method comprises the following steps: extracting biomass-rich sludge with the water content of 80-99wt% from a storage pool; inputting into a wet-process ultrafine grinder through a pipeline to carry out efficient reciprocating wall breaking; dewatering the sludge subjected to wall breaking through filter pressing, wherein the water content of the sludge subjected to filter pressing is smaller than or equal to 50 wt%, so that the purpose of deep dewatering of the sludge is achieved. Compared with the prior art, the wall breaking effect on sludge biological cells is outstanding; without any chemical reagents, the water content of the sludge can be obviously reduced, the subsequent utilization range of the dewatered sludge product is wide, and the treatment concept of solid waste recycling is met.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com