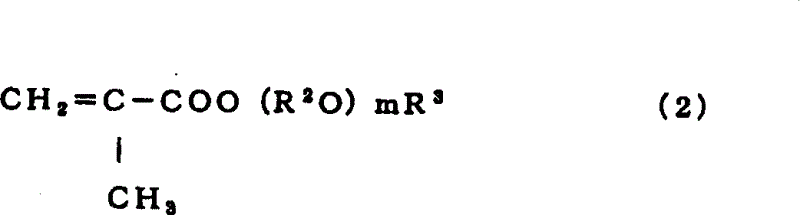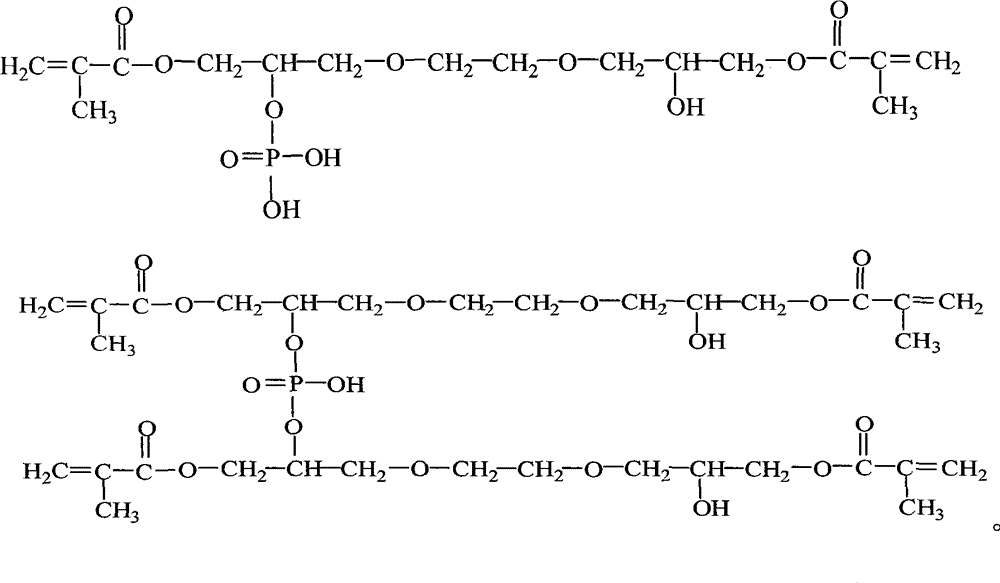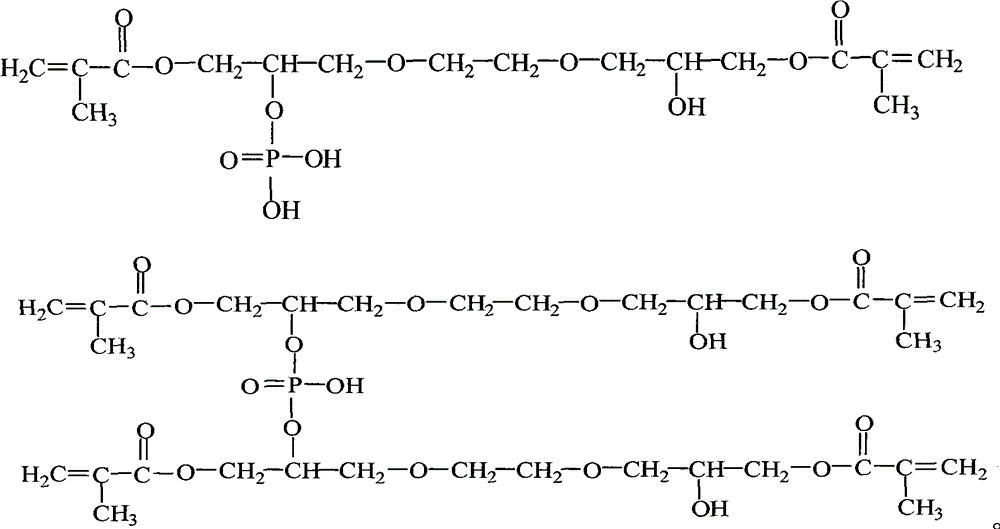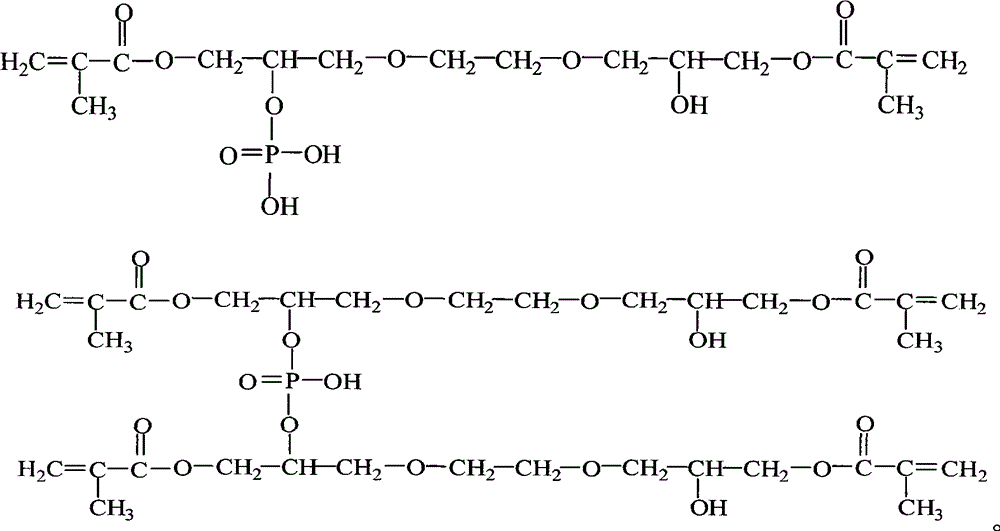Patents
Literature
49 results about "Poly(methacrylic acid)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Poly(methacrylic acid) (PMAA) is a polymer made from methacrylic acid (preferred IUPAC name, 2-methylprop-2-enoic acid), which is a carboxylic acid. It is often available as its sodium salt, poly(methacrylic acid) sodium salt. The monomer is a viscous liquid with a pungent odour. The first polymeric form of methacrylic acid was described in 1880 by Engelhorn and Fittig. The use of high purity monomers is required for proper polymerization conditions and therefore it is necessary to remove any inhibitors by extraction (phenolic inhibitors) or via distillation. To prevent inhibition by dissolved oxygen, monomers should be carefully degassed prior to the start of the polymerization.
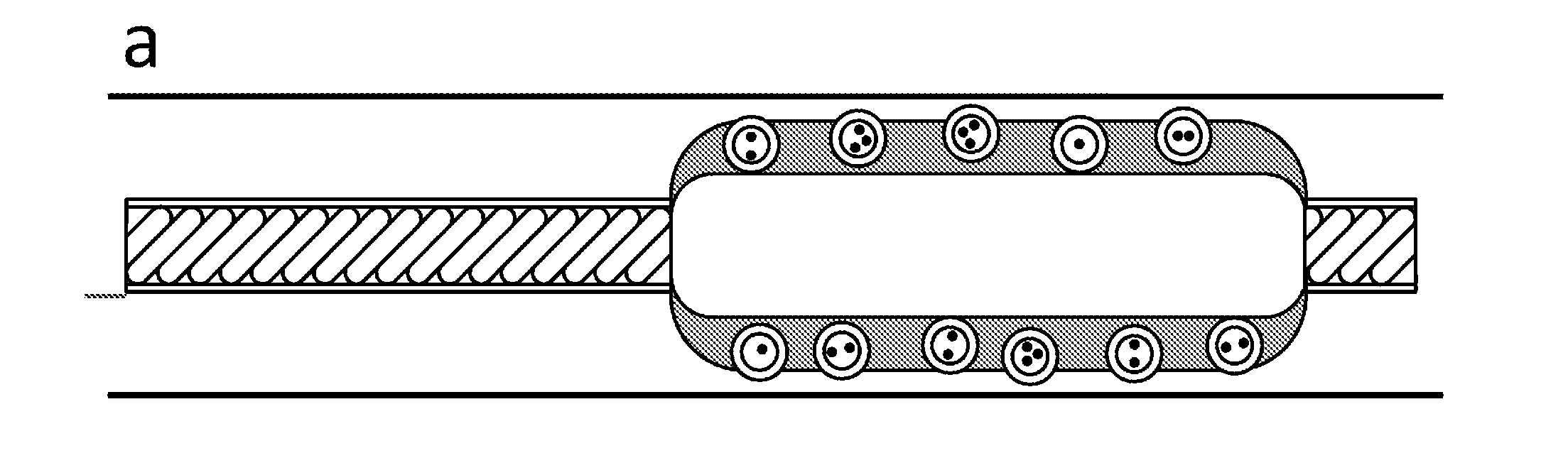
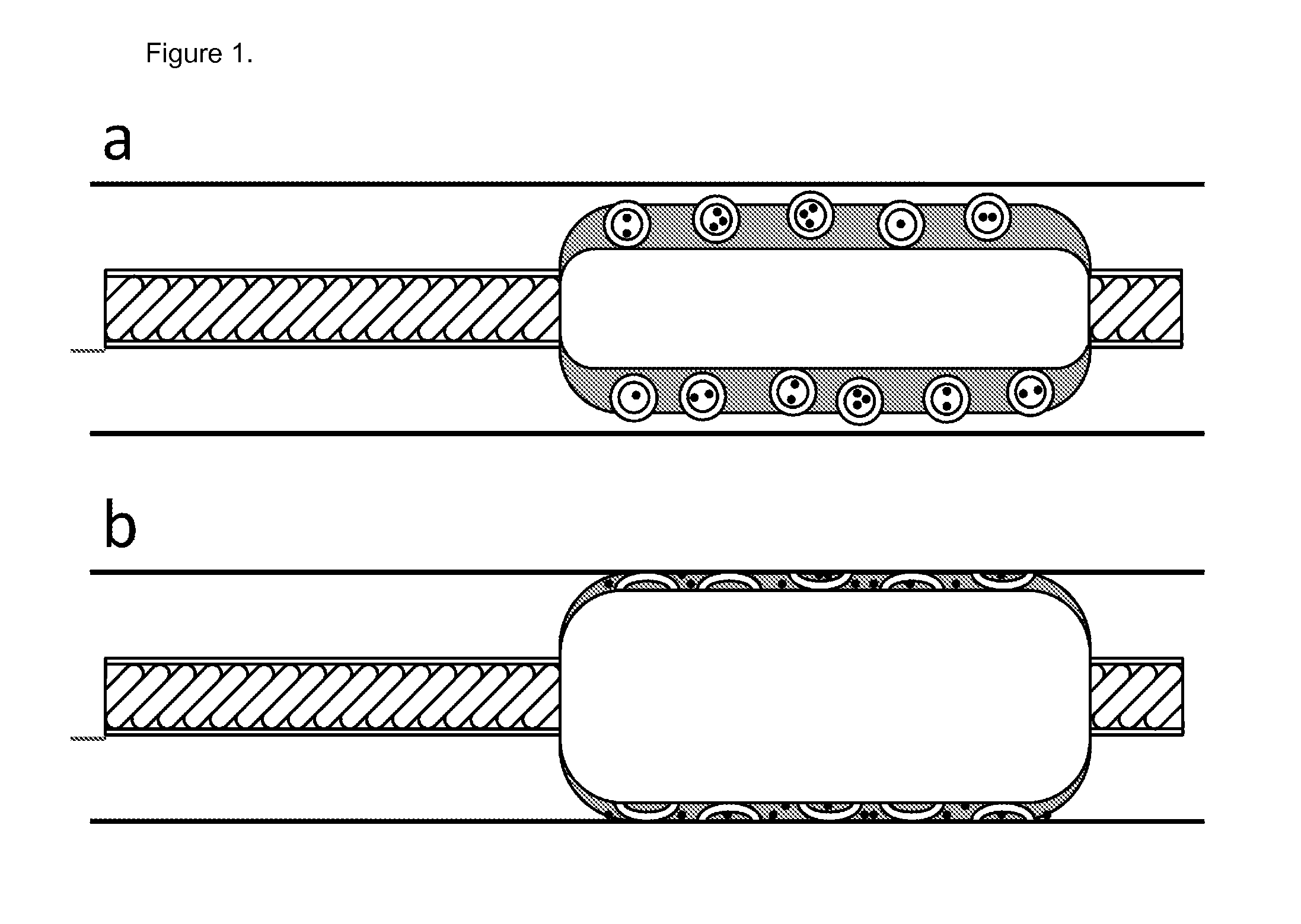
Balloon catheter comprising pressure sensitive microparticles
InactiveUS20120083734A1Improve brittlenessEffective treatmentSurgeryDilatorsPolyesterPoly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
The invention provides a solution to the above mentioned problem in that it provides a catheter balloon comprising a flexible coating on its outer surface wherein a plurality of microparticles are contained wherein said coating comprises a material selected from the group consisting of poly(N-vinyl-pirrolidone, poly(N-vinyl-pirrolidone-co-butylacrylate), poly(-vinyl pyridine), polyacrylamides, e.g. poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), poly(amido-amines), poly(ethylene imine), poly(ethylene oxide-block-propylene oxide), poly(ethylene oxide-block-propylene oxide-block-ethylene oxide), poly(styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene), poly(hydroxystyrene-block-isobutylene-block-hydroxystyrene), polydialkylsiloxanes, polysaccharides, polyacrylates and polyalkylmethacrylates, e.g. polymethylmethacrylate and poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) and wherein said microparticles comprise a material selected from the group consisting of polyesters, e.g. poly(lactic acid), poly(lactic-co-glycol acid), poly(glycolic acid), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), poly(3-hydroxyvalerate), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and polycaprolactone, polyamides, polysaccharides, polyurethanes, polyalkylmethacrylates and polyacrylates, e.g. polymethylmethacrylate and poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) and wherein the microparticles comprise a pharmaceutically active compound.
Owner:ENCAPSON
Process for preparing a catalyst for use in production of methacrylic acid and process of preparing methacrylic acid
InactiveUS6498270B1Lower performance requirementsHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsGas phaseDehydrogenation
The present invention provides a process for preparing a catalyst and the same for use in production of methacrylic acid, which is characterized by molding a raw material including a powder containing phosphorus and molybdenum at the specific pressure. The invention also provides a process for preparing methacrylic acid by gas phase oxidation and / or oxidative dehydrogenation of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of methacrolein, isobutyraldehyde and isobutyric acid in the presence of the catalyst.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
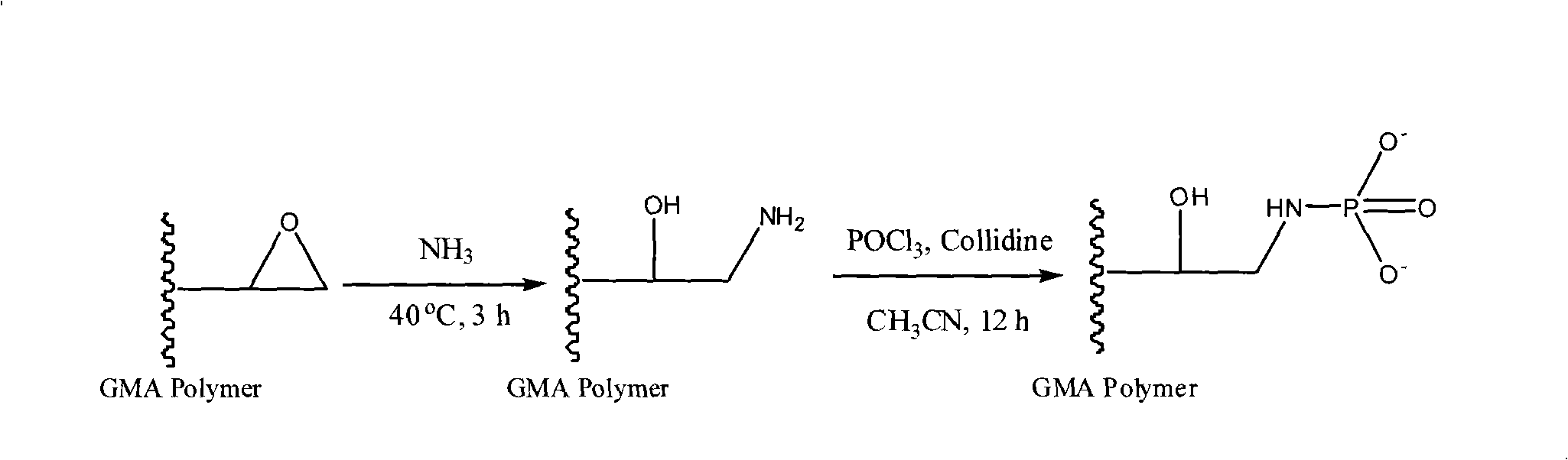
Affinity chromatography fixed phase of immobilization metal and its preparation method
InactiveCN101288844AImprove selective enrichment effectReduce non-specific adsorptionOther chemical processesSynthesis methodsMicrosphere
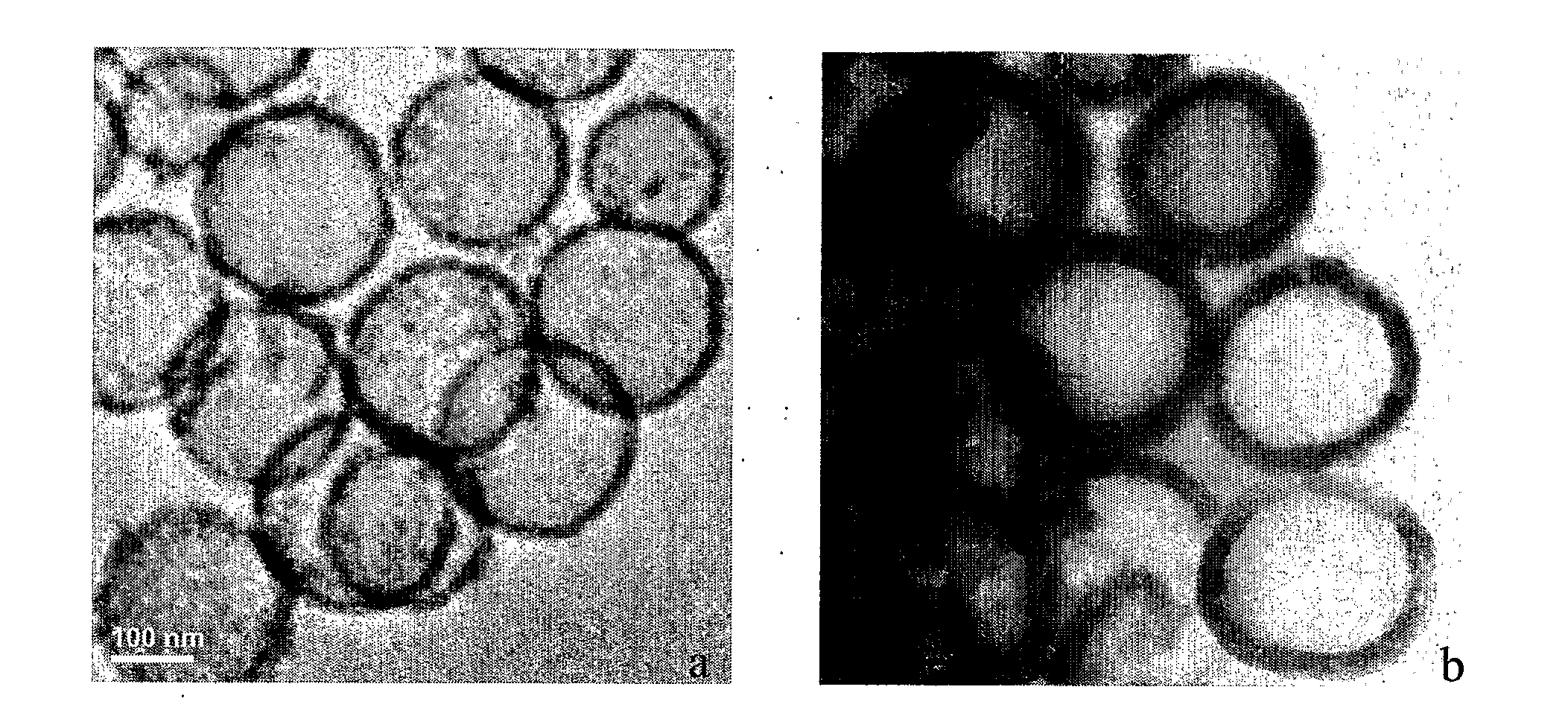
The invention relates to a separation and purification technique, in particular to an affinity chromatography stationary phase of immobilized metal and a preparation method thereof. The structure of the stationary phase is shown in the drawing; wherein, the particle size of GMAPolymer micro-sphere is 10nm-50um; the GMAPolymer micro-sphere is poly-methacrylic acid glycidyl esters micro-sphere. By carrying out amination and phosphoric esterification, a synthesis method of the high-performance poly-methacrylic acid glycidyl ester-group novel affinity chromatography stationary phase is gained and used for the research in phosphorylation proteomics and highly-selective separation, enrichment and purification of phosphopeptide by the chelation with zirconium ions and iron ions; meanwhile, compared with the traditional stationary phase, the affinity chromatography stationary phase reduces the nonspecific adsorption on the non-phosphopeptide.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Neural transfection reagents
The invention is directed to transfection reagents for the delivery of nucleic acids into neural cells, compositions including the reagents, methods of preparation of such reagents, methods of transfecting cells with such reagents, and uses thereof. In preferred embodiments the reagents comprise horseradish peroxidase and / or a polycarboxylic acid such as poly(acrylic acid) or poly(methacrylic acid).
Owner:INNOVATIVE SURFACE TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Preparation f beta-poly malic acid and salt thereof
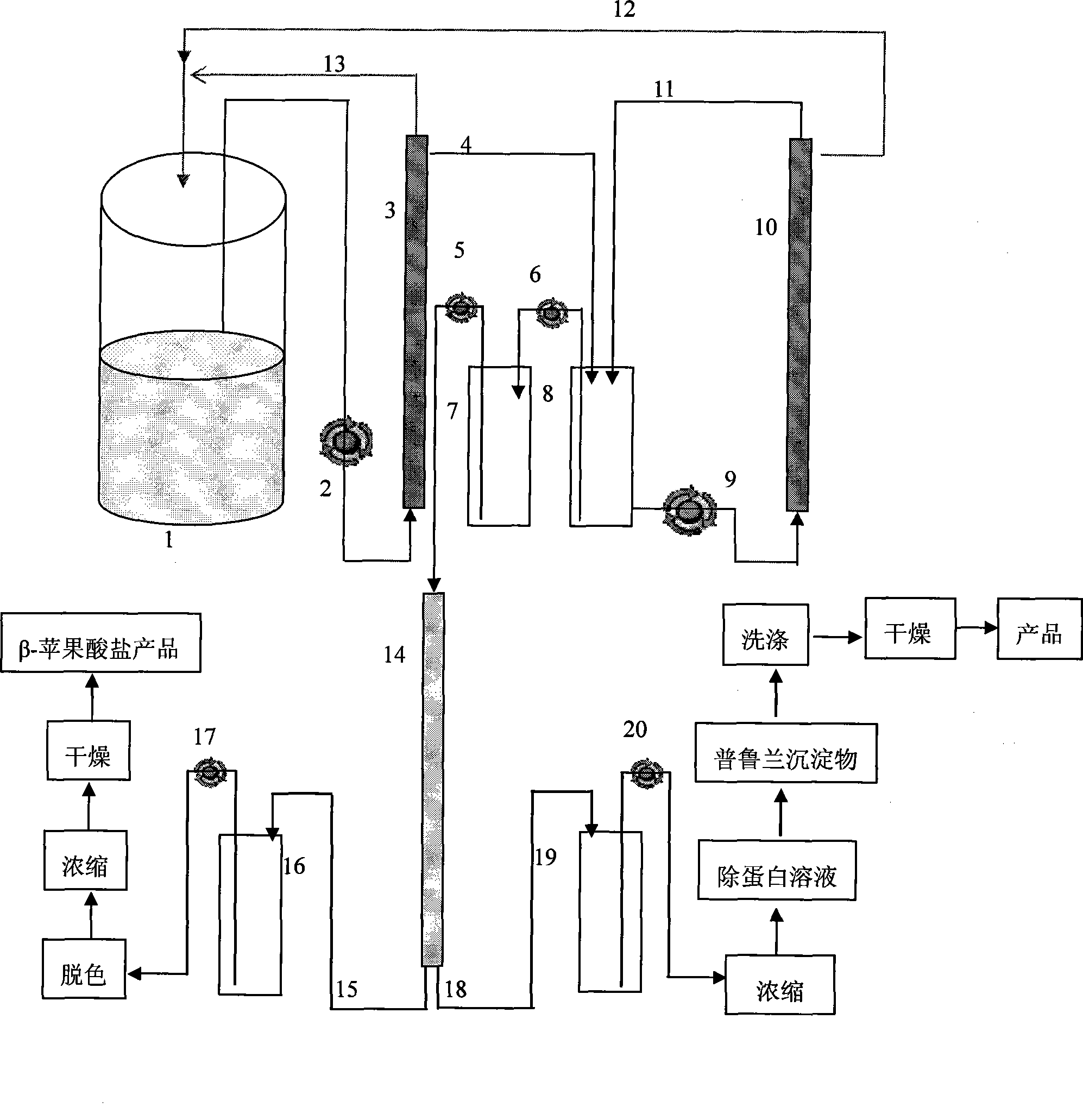
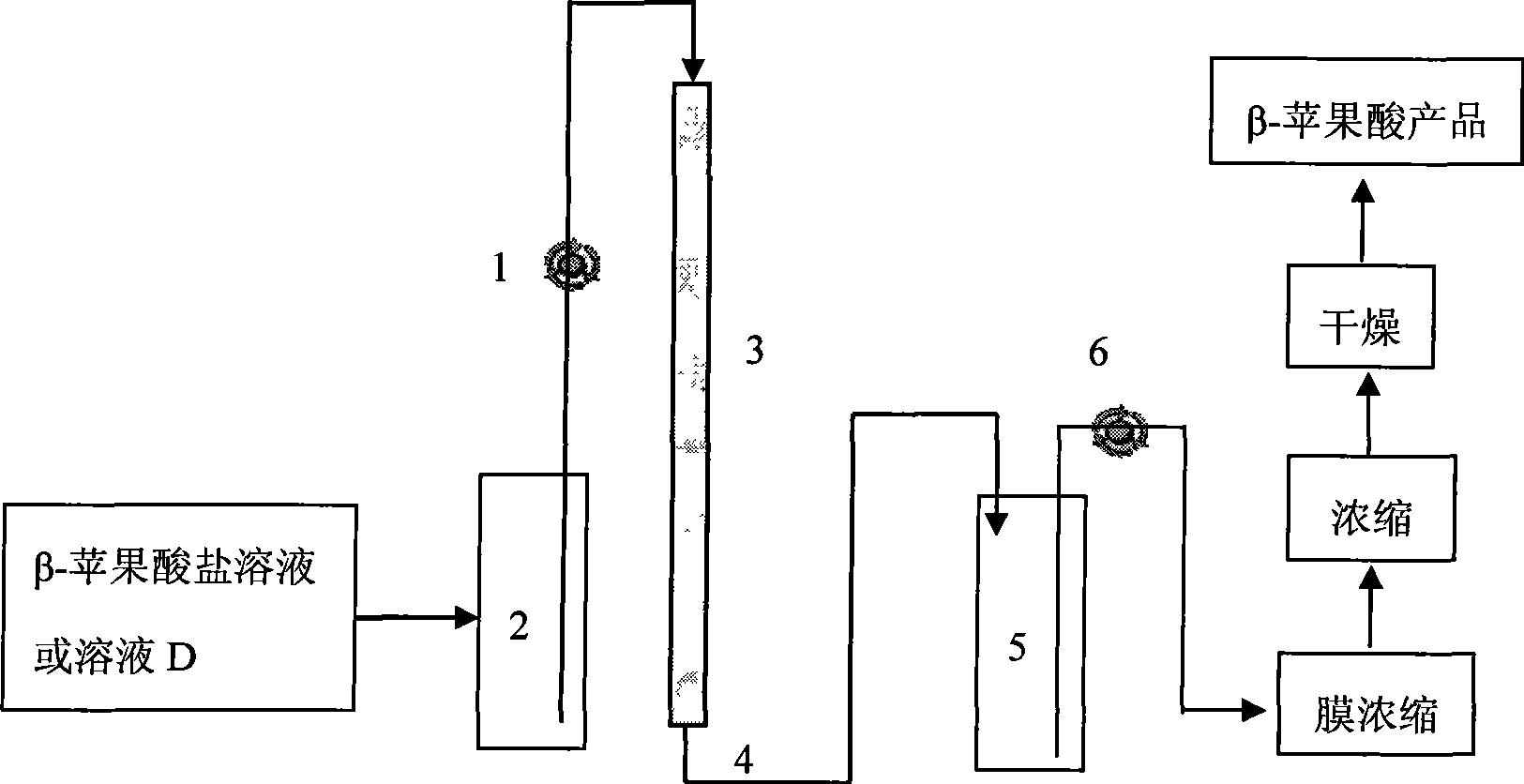
ActiveCN101487034AHigh yieldReduce feedback inhibitionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPullulanStrong acids
The invention discloses a method for preparing Beta-poly malic acid and a salt thereof and simultaneously obtaining a byproduct pullulan. The method is realized by adopting the following technical proposal: return thalli and interception are implemented by a membrane technique in a fermentation process, high molecular weight Beta-poly malic acid is concentrated, and low molecular weight Beta-polymalic acid, pullulan and other components are recycled in a fermentation system; a weakly basic anion exchange resin is adopted to absorb the Beta-poly malic acid and lead pullulan solution to penetrate, alkaline solution is adopted to elute the Beta-poly malic acid that is adsorbed on the resin, and eluting solution is purified and dried, thus obtaining the salt product of the Beta-poly malic acid; a penetrating fluid is concentrated, chloroform and butanone mixture solution is adopted to remove protein, and the pullulan is precipitated by ethanol alcohol precipitation, orderly washed by acetone and ethyl ether, and dried by P2O5, thus obtaining a powder pullulan product; a strong acid cation exchange resin is adopted to absorb salt ions in salt solution of the Beta-poly malic acid, a membrane is used for removing extra acid in the desalted solution, and the obtained solution is concentrated and dried, thus obtaining the Beta-poly malic acid product.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
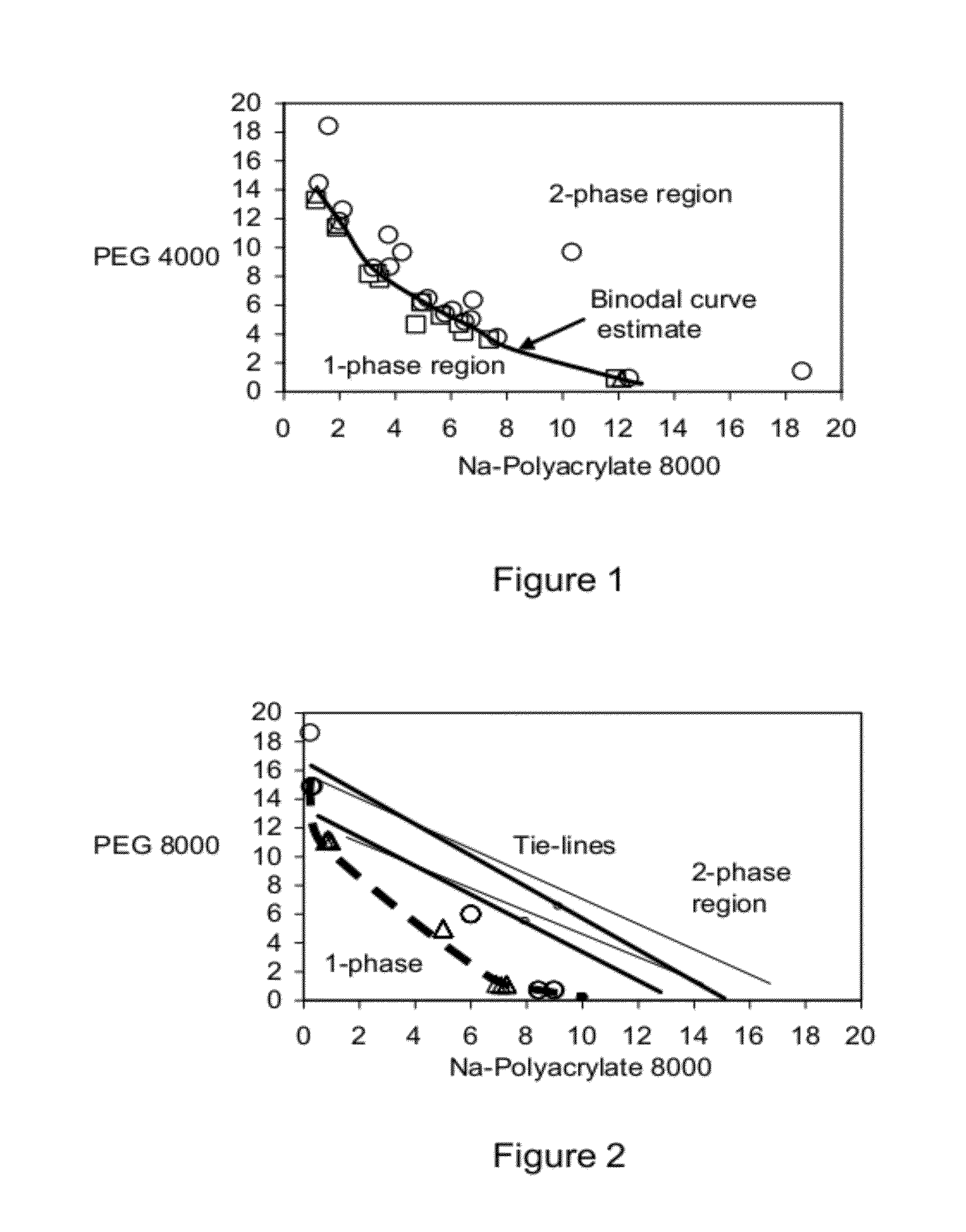
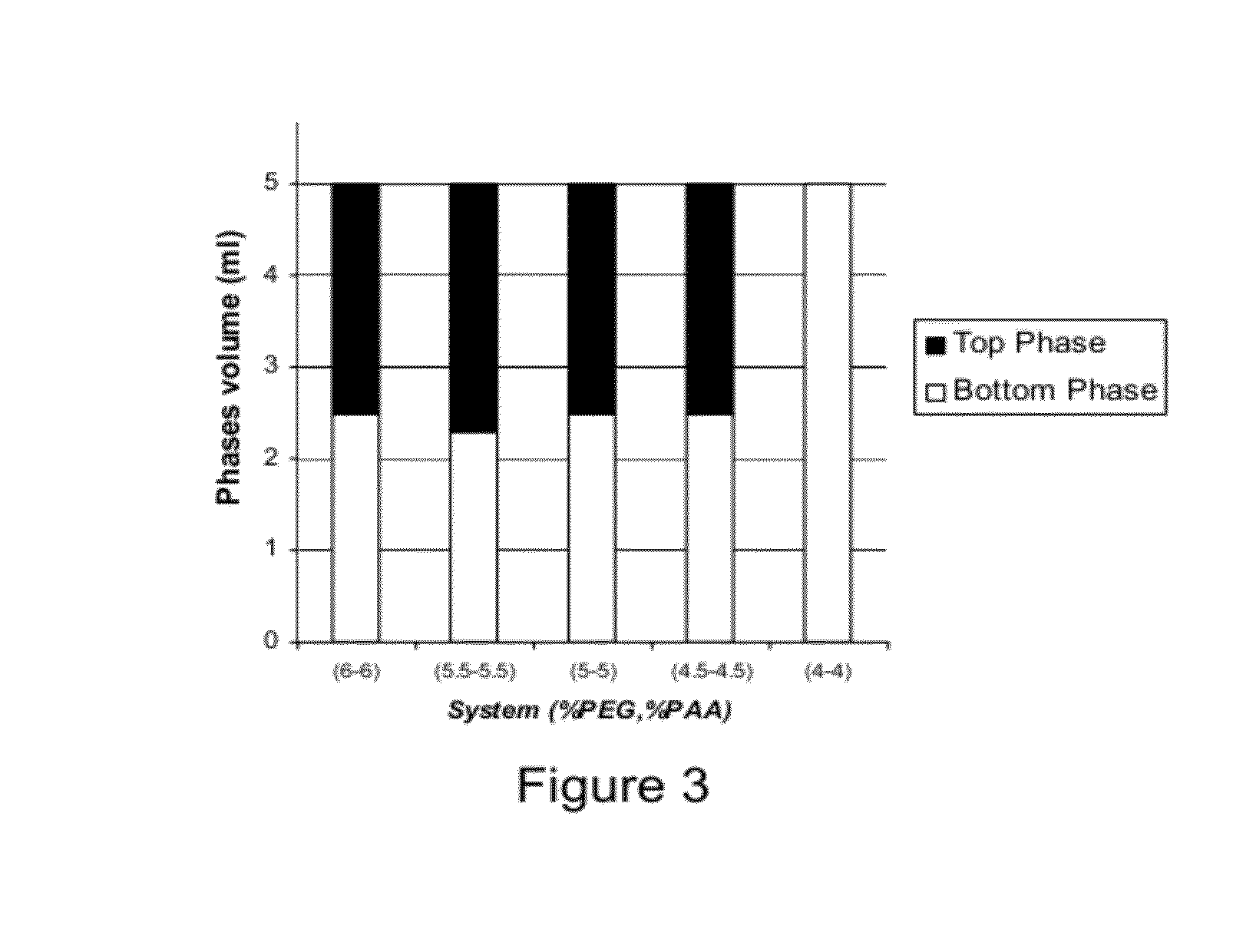
Polymer two phase system and use thereof
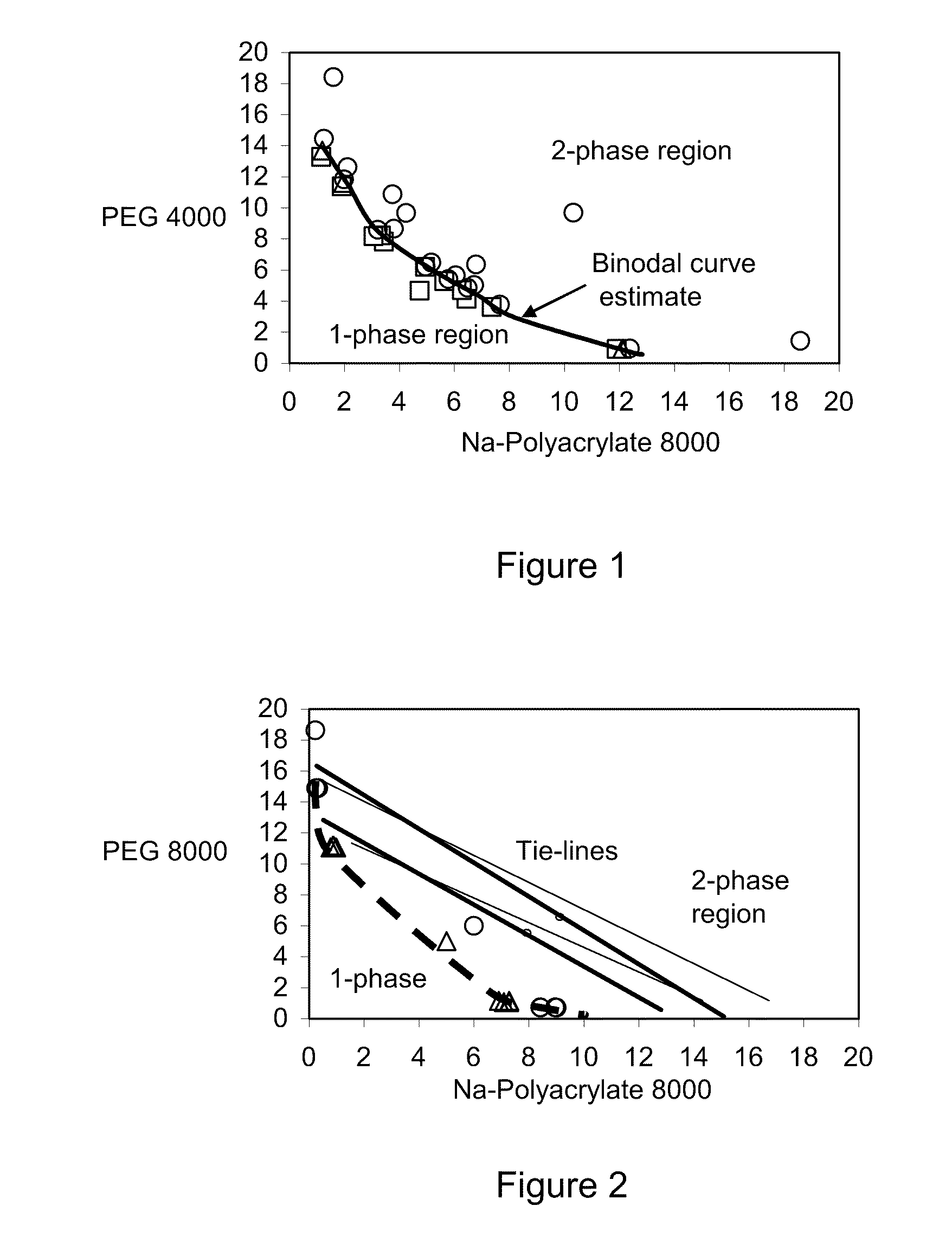
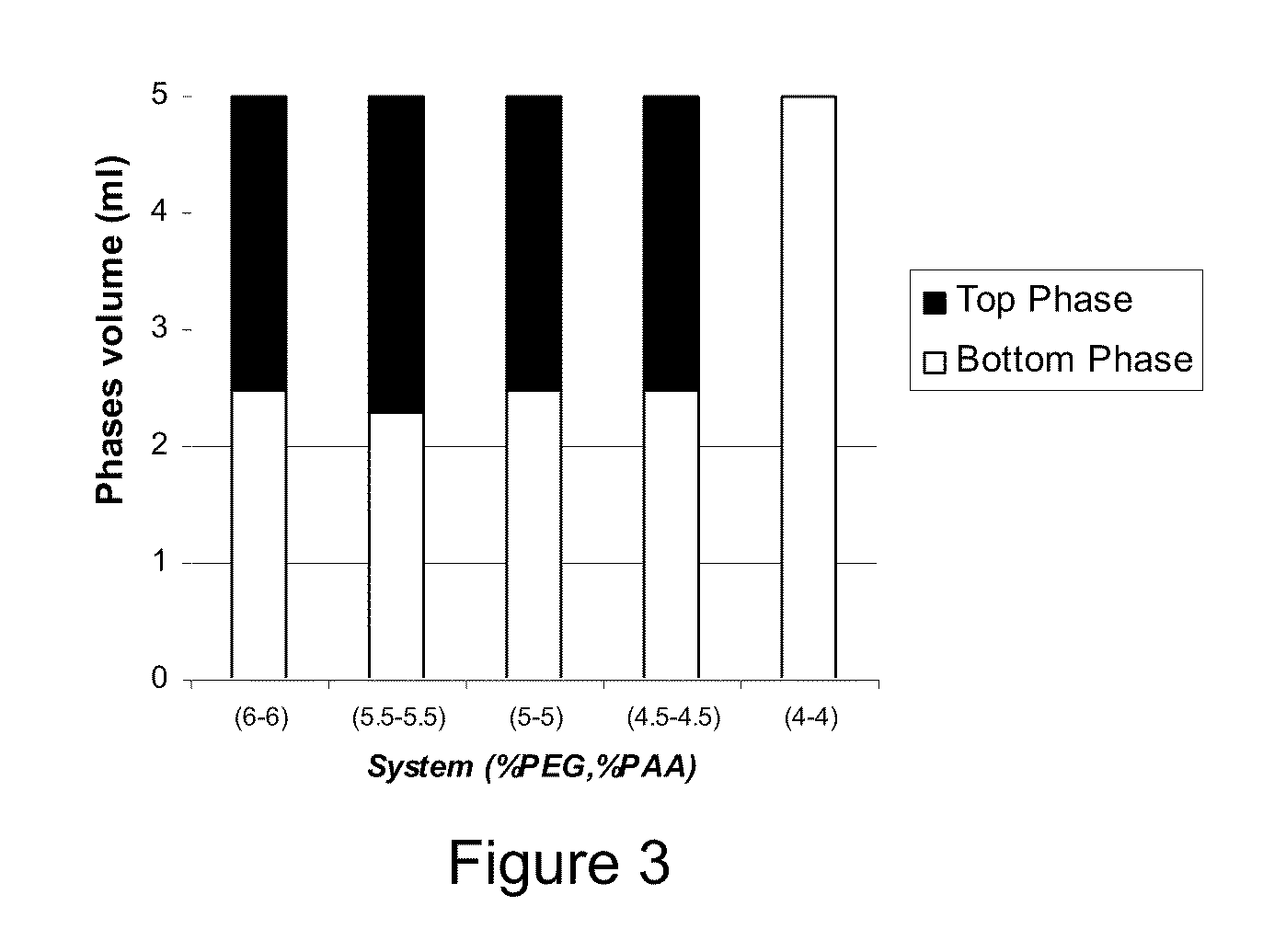
ActiveUS20100179252A1High dynamic capacityFast mass transferCosmetic preparationsSugar derivativesEthylene oxideEther
The present invention relates to a liquid mixture comprising a first polymer, which is a poly(acid), a second polymer, which is a poly(ether), and at least one salt, wherein the molecular weight of the poly(acid) is in the range of 1000-100,000 Da. The second polymer is selected to be capable of forming immiscible aqueous phases in the presence of the poly(acid) and salt. The poly(acid) may be selected from the group consisting of poly(acrylic acid) and poly(methacrylic acid), and the second synthetic polymer may comprise ethylene oxide. The invention may be used for separation of biomolecules, cells or particles.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Seed coatings, coating compositions and methods for use
ActiveUS20180251654A1Promote seedling establishmentEasy to grow plantsBiocideCellulose coatingsPolyethylene oxidePotato starch
A seed or seedling is coated with underivatized guar, cationic hydroxypropyl guar, polyacrylamide, poly(methacrylic acid), poly(acrylic acid), polyacrylate, polyethylene glycol), polyethyleneoxide, poly(vinyl alcohol), polyglycerol, polytetrahydrofuran, polyamide, hydroxypropyl guar, carboxymethyl guar, carboxymethylhydroxypropyl guar, underivatized starch, cationic starch, corn starch, wheat starch, rice starch, potato starch, tapioca, waxy maize, sorghum, waxy sorghum, sago, dextrin, chitin, chitosan, xanthan gum, carageenan gum, gum karaya, gum arabic, pectin, cellulose, hydroxycellulose, hydroxyalkyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose, carboxymethylhydroxyethyl cellulose, or hydroxypropyl cellulose, the coated seed or seedling having a shelf-life at room temperature in ambient conditions in an unsealed container to at least two months.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Smart polymers functionalized hollow silica vesicles
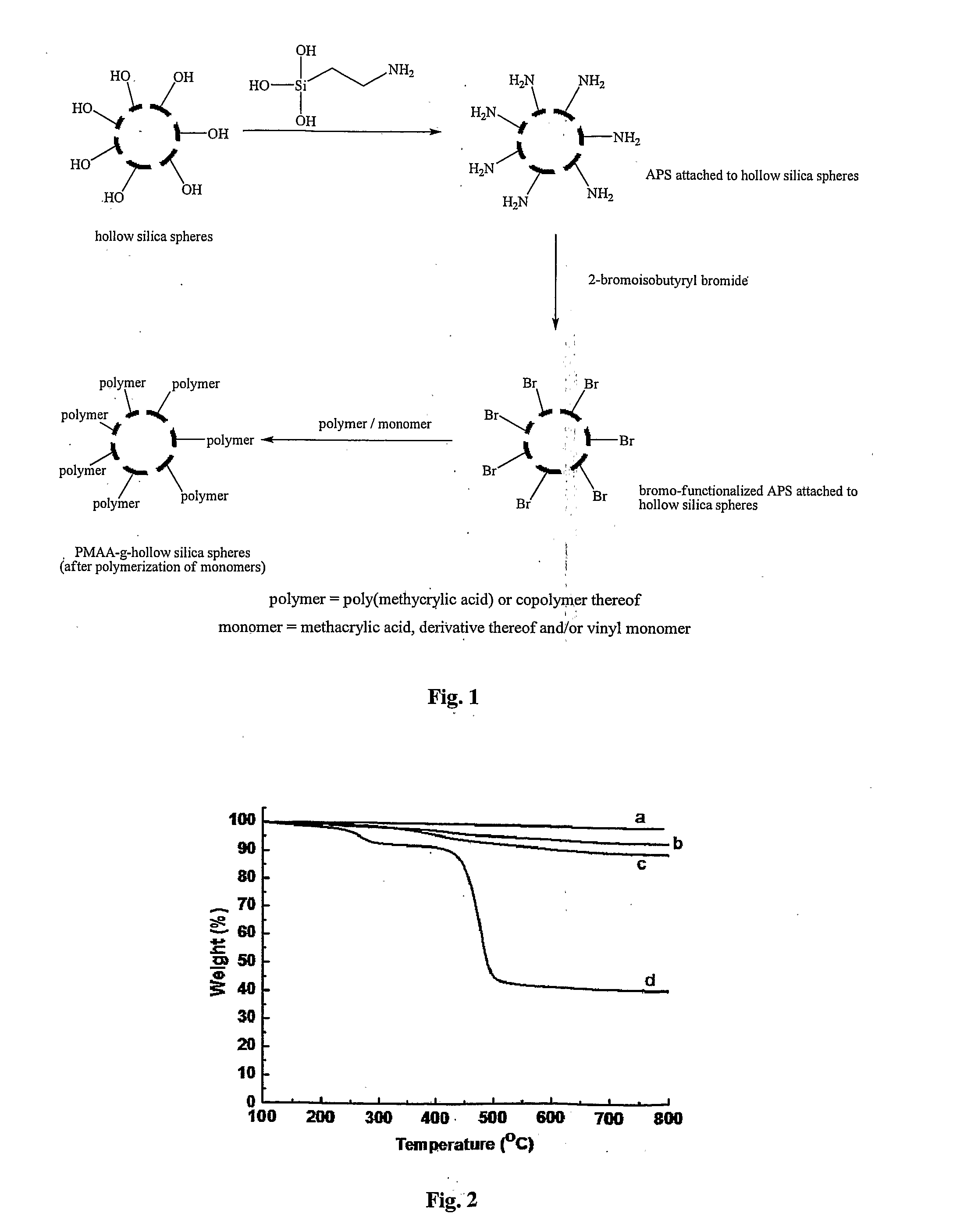
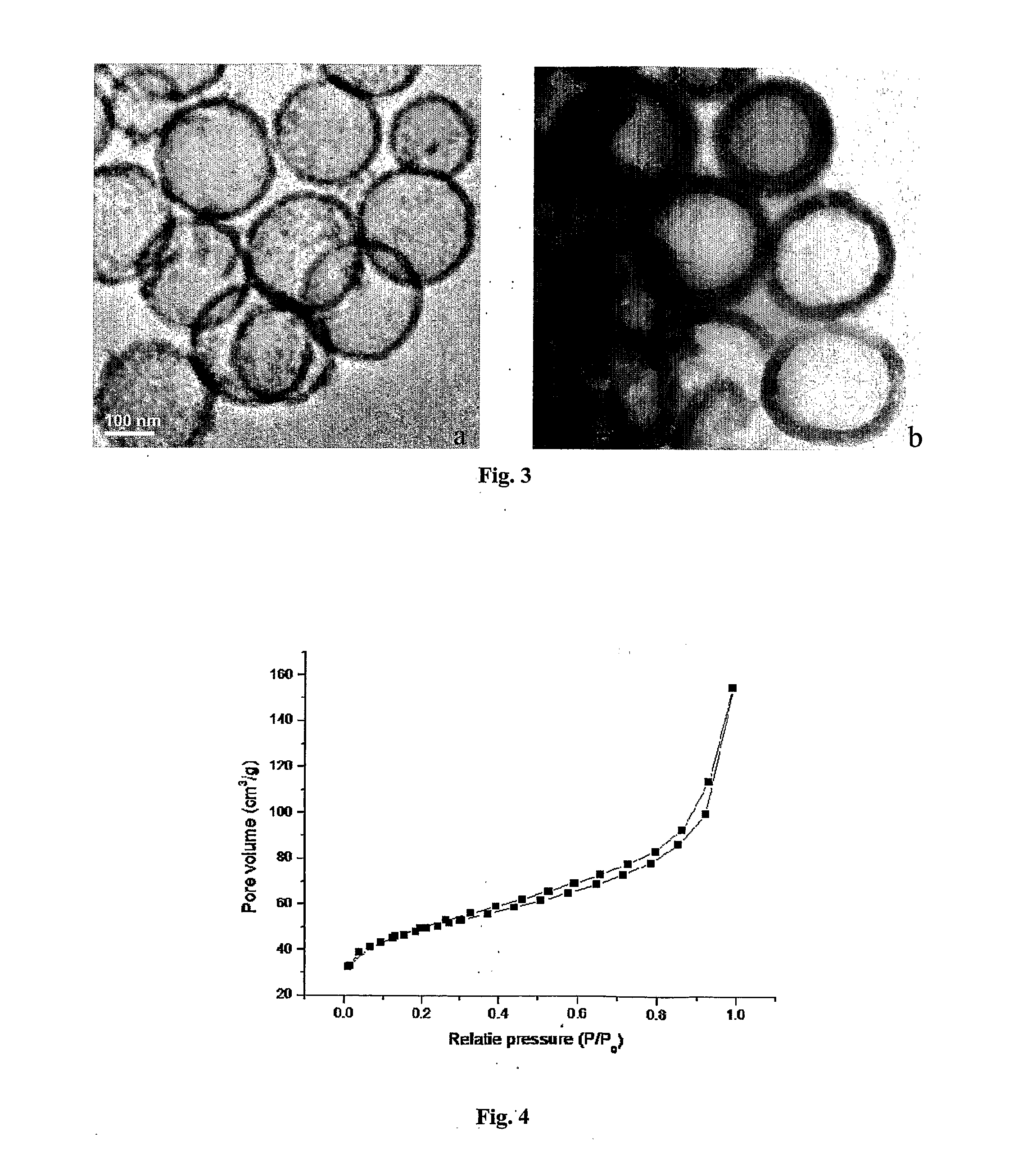
The present invention provides a porous hollow silica micro- or nanoparticle with a polymer grafted thereon, wherein the polymer is selected from poly(methacrylic acid) and copolymers thereof. The polymer may be covalently linked to the silica particle via a bridging group. Provided is also a method of covalently coupling a poly(methacrylic acid) to a silica surface of a hollow silica particle. The method comprises contacting a silica surface of a hollow silica particle that carries amino functional or halogen functional groups with a poly(methacrylic acid) or a copolymer or a respective monomer thereof. The method further comprises allowing the carboxyl group of the monomer or the poly(methacrylic acid) and an amino functional group or a halogen functional group on the silica surface to undergo a coupling reaction, thereby covalently coupling the polymer to the silica surface.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Cement dispersing agent and concrete composition comprising same
ActiveCN1777565AReduce viscosityLow initial adsorptionAmide/imide polymer adhesivesPolyamideMethyl group
A cement dispersant which comprises a water-soluble amphoteric copolymer produced from ingredients including an unsaturated polyamide-polyamine / alkylene oxide adduct and two or more polyalkylene glycol esters. After the dispersant is kneaded together with a concrete composition, the dispersing ability thereof increases with time. It is highly effective in reducing concrete viscosity. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] The cement dispersant composition comprises as an essential ingredient either a water-soluble amphoteric copolymer obtained through copolymerization from (A) an unsaturated polyamide-polyamine / alkylene oxide adduct, (B) (meth) acrylic acid or an alkali metal salt or ammonium or alkanolamine salt thereof, (C) a polyalkylene glycol ester of methacrylic acid, and (C) a polyalkylene glycol ester of acrylic acid or a neutral salt of the copolymer.
Owner:SIKA LTD +1
Peptides having affinity for poly (benzyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) potassium salt copolymers and methods of use
Peptides are provided that have binding affinity for poly(benzyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) potassium salt copolymers (“BzMA-binding peptides”). The BzMA-binding peptides may be used to prepare peptide-based reagents suitable for use in a variety of applications. The peptide-base reagents may be used to couple benefit agents to a poly(benzyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) potassium salt copolymer surface or may be used to couple a benefit agent comprising a poly(benzyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) potassium salt copolymer surface to a target surface, such as a body surface.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Biopolymer-based seed coatings compositions and methods for use
ActiveUS20190150354A1Promote seedling establishmentEasy to keepAmylose/amylopectin coatingsDextran coatingsCross-linkCellulose
A seed or seedling is coated with a cross-linked biopolymer and, optionally, a second binder selected from underivatized guar, cationic hydroxypropyl guar, polyacrylamide, poly(methacrylic acid), poly(acrylic acid), polyacrylate, poly(ethylene glycol), polyethyleneoxide, polyamide, hydroxypropyl guar, carboxymethyl guar, carboxymethylhydroxypropyl guar, underivatized starch, cationic starch, corn starch, wheat starch, rice starch, potato starch, tapioca, waxy maize, sorghum, waxy sarghum, sago, dextrin, chitin, chitosan, xanthan gum, carageenan gum, gum karaya, gum arabic, pectin, cellulose, hydroxycellulose, hydroxyalkyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose, carboxymethylhydroxyethyl cellulose, or hydroxypropyl cellulose. The seed coating composition is characterized by a dust value, as measured using a Heubach dustmeter device, which is lower by at least 30% as compared to an analogous composition that does not contain the crosslinked biopolymer.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Catalyst for use in production of methacrylic acid, method for producing said catalyst, and method for producing methacrylic acid using said catalyst
InactiveCN104302391AHigh activityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsHeteropoly acidActive component
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for producing a catalyst for use in the production of methacrylic acid through the vapor-phase catalytic oxidation of methacrolein, isobutylaldehyde or isobutyric acid with high yield and high selectivity. A catalyst produced by adding an alkali metal element, particularly cesium among alkali metal elements, to a partially neutralized salt of a heteropoly acid by a specific method, wherein the partially neutralized salt contains Mo, V, P, an alkali metal element and NH4 as essential active components. The catalyst is characterized by having extremely high catalytic performance.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Solid superacid catalyzed esterification synthesis of methoxy polyethylene glycol methacrylic acid ester
InactiveCN102344563ASmall copolymerization effectNo side effectsOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationMethacrylateDistillation
The invention discloses a solid superacid catalyzed esterification synthesis method of methoxy polyethylene glycol methacrylic acid ester. Methoxy polyethylene glycol and methacrylic acid are treated with a esterification reaction under conditions of solid superacid catalyst SO4<2-> / ZrO2, polymerization inhibitor and water carrying agent. After the reaction, the solid superacid is removed by filtering separation; a filtrate is treated with reduced pressure distillation to recover the water carrying agent. Obtained high purity methoxy polyethylene glycol mono methacrylic acid ester is a macromonomer methoxy polyethylene glycol mono methacrylic acid ester for synthesizing polycarboxylic water carrying agent. The recovered water carrying agent and solid superacid SO4<2-> / ZrO2 can be reused. A conversion based on methoxy polyethylene glycol reaches higher than 98.2%, and an ester yield is higher than 98%.
Owner:湖北鑫汇生物科技有限公司
Dimethyl acrylic acid glyceride phosphate and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN103183703AReduce viscosityHigh content of C=C double bond functional groupsPhosphorus organic compoundsSolubilityGlycidyl methacrylate
The invention discloses a dimethyl acrylic acid glyceride phosphate being taken as UV photocureable coating adhesion promoter and a synthetic method thereof. A synthetic process is that glycidyl methacrylate is added in a mechanical stirring reaction kettle equipped with a cooling and heating device, and conducts ring-opening addition reaction with methacrylic acid under the quick stirring and a condition that catalyst and polymerization inhibitor exist to generate dimethyl acrylic acid glyceride; the dimethyl acrylic acid glyceride and phosphorus pentoxide conduct esterification reaction to generate dimethyl acrylic acid glyceride phosphate. The generated target product has light color, low acid value, good adhesion and four functional groups, can be taken as additive to be used for UV photocureable coating, has good solubleness in universal (methyl) crylic acid activated monomer and (methyl) crylic acid resin, and can improve adhesion of resin to metal, glass and other base materials and the UVcuring speed of resin.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether dimethacrylate organic phosphate and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN103145755AReduce viscosityLow acid valuePhosphorus organic compoundsSolubilityMethacrylate
The invention discloses ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether dimethacrylate organic phosphate and a synthetic method thereof, wherein the ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether dimethacrylate organic phosphate is used for an ultraviolet (UV) photocureable coating adhesion promoter. Ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether is added into a reaction kettle provided with a cooling device, a heating device and a mechanical agitation device, a ring-opening addition reaction between the ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether and methacrylic acid is conducted on the conditions of methacrylic acid rapid agitation and the existence of catalyzers and polymerization inhibitors to generate ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether dimethacrylate, and an esterification reaction between the ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether dimethacrylate and phosphorus pentoxide is conducted to generate the ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether dimethacrylate organic phosphate. A generated target product is light in color, low in acid value and good in adhesive force, also has four functional groups, can be used as an addictive used for production of UV photocureable coatings, dissolves well in universal (methyl) crylic acid activated monomers and (methyl) acrylic resin, can increase adhesive force, on base materials such as metal, glass, plastics, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene(ABS), of resin and the UV photocureable speed of the resin.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for preparing narrow-dispersion high-magnetic chitosan sub-micron particles
The invention provides a method for preparing narrow-dispersion high-magnetic chitosan sub-micron particles. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing sub-micron spherical Fe3O4 colloidal nanocrystal clusters (MCNCs) with carboxylic groups on the surfaces according to a solvothermal method; dispersing the MCNCs in aqueous solution including chitosan and acrylic acid / methacrylic acid; adding initiator, so as to coat chitosan-polyacrylic acid / polymethacrylic acid compound shells on the surfaces of the MCNCs through radical polymerization reaction; adding cross linking agent, so that cross linking reaction is carried out between the MCNCs and part of amino groups in chitosan molecular chains; and finally, washing out polyacrylic acid or polymethacrylic acid with alkali aqueous solution. The method has the advantages that the quantity of organic solvent used during the preparation process is low, so that organic material residue is low; the sizes of magnetic polymer particles depend on those of the pre-prepared MCNCs, so that the regulation and the control are easy, and the particle size distribution is narrow; the magnetic content of the magnetic polymer particles is uniform and high; superparamagnetism is realized; and the method is particularly suitable for being applied to separation, analysis, enzyme immobilization, catalysis and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Polymer two phase system and use thereof
ActiveUS8268915B2Increase capacityFast mass transferCosmetic preparationsSugar derivativesEthylene oxideEther
The present invention relates to a liquid mixture comprising a first polymer, which is a poly(acid), a second polymer, which is a poly(ether), and at least one salt, wherein the molecular weight of the poly(acid) is in the range of 1000-100,000 Da. The second polymer is selected to be capable of forming immiscible aqueous phases in the presence of the poly(acid) and salt. The poly(acid) may be selected from the group consisting of poly(acrylic acid) and poly(methacrylic acid), and the second synthetic polymer may comprise ethylene oxide. The invention may be used for separation of biomolecules, cells or particles.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Dimethyl-siloxane-modified poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-methacrylic acid) amphiphilic copolymer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103012666AEasy to understand purposeEasy to understand technical contentPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChemical Linkage(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylate
The present invention relates to a soluble dimethyl-siloxane-modified poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-methacrylic acid) amphiphilic copolymer and a preparation method thereof. The soluble dimethyl-siloxane-modified poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-methacrylic acid) amphiphilic copolymer is synthesized based on the following components according to a chemical bonding mode: 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), methacrylic acid (MAA) and end3-propylamine polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The soluble dimethyl-siloxane-modified poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-methacrylic acid) amphiphilic copolymer can be better dissolved in alcohol dissolvent for facilitating subsequent machining requirement, and furthermore has adjustable hydrophibility and hydrophobility and excellent bio-compatibility. Therefore the soluble dimethyl-siloxane-modified poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-methacrylic acid) amphiphilic copolymer can be used for application in adhering prevention, medicine release, etc.
Owner:SPRING FOUND OF NCTU
Catalysts for methacrylic acid production and process for producing methacrylic acid
InactiveUS6476259B2High yieldGuaranteed uptimeOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsGas phaseCerium
Improved catalyst for use in production of methacrylic acid by vapor phase oxidation reaction and / or vapor phase oxidative dehydrogenation reaction of at least one compound selected from methacrolein, isobutylaldehyde and isobutyric acid is provided. This improved catalyst is a composition composed of (A) complex oxide containing as essential components molybdenum and phosphorus, which is per se known as a catalyst for the above reaction(s), and (B) complex oxide containing as essential components cerium and zirconium. When this improved catalyst is used, the operation for producing methacrylic acid can be stably continued over prolonged period.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Catalyst for selectively oxidizing methacrylaldehyde to prepare methacrylic acid and preparation and application methods thereof
ActiveCN109731592AHigh activityMeet the needs of actual industrial productionOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsRubidiumCerium
The invention discloses a catalyst for selectively oxidizing methacrylaldehyde to prepare methacrylic acid and preparation and application methods thereof. The catalyst for selectively oxidizing the methacrylaldehyde to prepare the methacrylic acid is composed of PaMobVcXxYyZz1HhOg1-Zz2Og2, wherein X is a combination of at least two from sodium, potassium, rubidium and cesium, Y is a mixture of one or at least two from calcium, magnesium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, copper, nickel, zinc, aluminum, silicon, germanium, antimony, bismuth, lanthanum or cerium, and Z comprises titanium and / or zirconium. Compared with traditional phosphovanadomolybdate catalysts. The catalyst for selectively oxidizing the methacrylaldehyde to prepare the methacrylic acid can be higher in activity when applied to selectively oxidizing the methacrylaldehyde to prepare the methacrylic acid, and during the catalytic process, when the methacrylaldehyde converting rate is 90%, and the selectivity to the methacrylic acid can reach up to 93%, so that the catalyst for selectively oxidizing the methacrylaldehyde to prepare the methacrylic acid can meet the demands of practical industrial production.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compostable reinforced paper, method of making same
A composite material includes at least one layer of fibrous material; and at least one biodegradable polymer layer composed of at least one biodegradable polymer, at least one biodegradable copolymer or both at least one biodegradable polymer and at least one biodegradable copolymer. The biodegradable polymer and biodegradable copolymer are each composed of a polymer block selected from the group consisting of poly(alkylene glycol), poly(alkylene oxide), poly(ethylene imine), polyalkylene, polyvinyl, polyvinylether, poly(vinylacetate), polyvinylpyrrolidine, polyester, polylactide, polyglycolide, polycaprolactone, poly(hydroxyalkanoate), poly(meth)acrylates, poly(acrylic acid) and salts thereof, polyether, polyurethane, poly(methacrylic acid) and salts thereof, polyacrylamide, polyepoxide, polyol, polysaccharide, and latex.
Owner:C J MULTI TECH ENTERPRISES
Continuous production method for isobornyl methacrylate
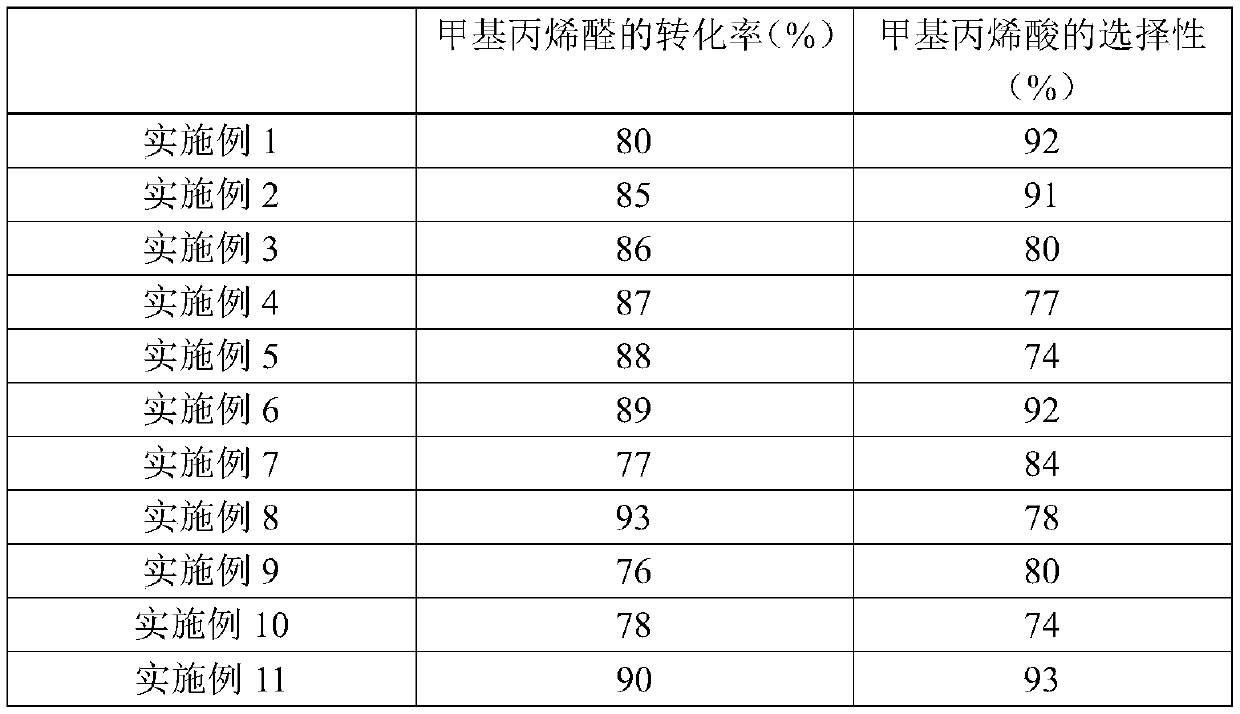
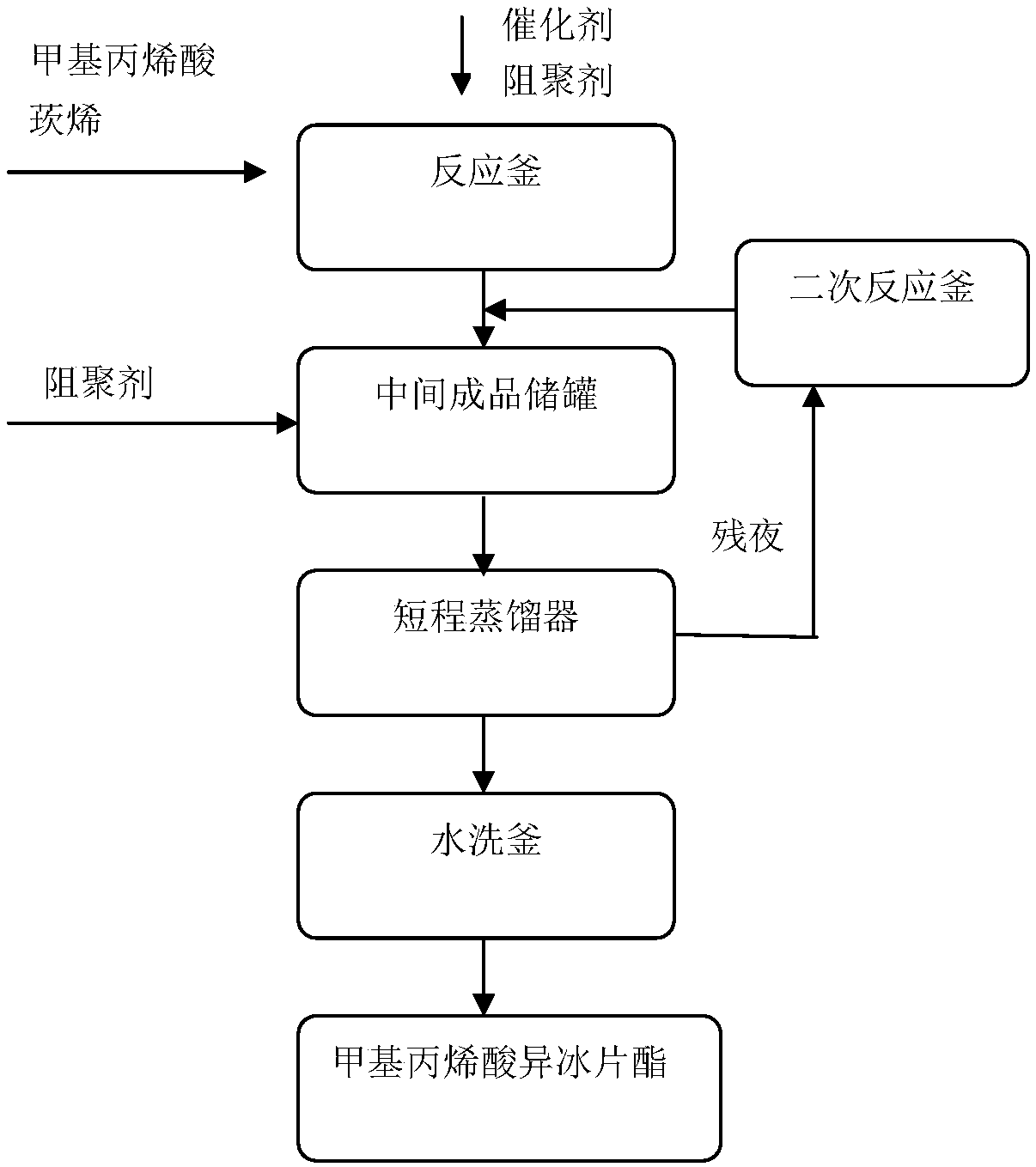
InactiveCN108409562AIncrease profitReduce lossOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationFiltrationDistillation
The invention discloses a continuous production method for isobornyl methacrylate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) putting methacrylic acid and camphene into a reaction kettle, after themethacrylic acid and the camphene are completely dissolved at room temperature, adding a polymerization inhibitor and a catalyst, performing a reaction, and performing filtration to obtain a reactionmixed liquid; (2) replenishing a polymerization inhibitor into the reaction mixed liquid, performing distillation to obtain unreacted methacrylic acid and camphene under negative pressure of 0.01-0.05 MPa, and collecting a fraction at the temperature of 113-120 DEG C and pressure of 0.6 kPa to obtain the isobornyl methacrylate; (3) putting the unreacted methacrylic acid and camphene into a secondary reaction kettle, performing a reaction, and performing filtration to obtain a secondary reaction mixed liquid; and (4) performing the step (2) and the step (3) on the secondary reaction mixed liquid repeatedly in sequence to realize continuous production of the isobornyl methacrylate. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of having a high utilization ratio of raw materials,reducing loss of the raw materials, improving a conversion rate of the raw materials, and improving product quality.
Owner:安徽联化新材料有限公司
Synthesis of methacrylic acid from methacrolein-based alkyl methacrylate
ActiveUS10479754B2Large volumeEconomically viableOrganic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesMethacroleinOrganic chemistry
The present invention relates to a process for preparing alkyl methacrylates, especially MMA, and methacrylic acid, based on methacrolein, which has been oxidatively esterified in a second process stage. Methacrolein is obtainable in principle from C2 and C4 units. The present process has the advantage that the alkyl methacrylate and methacrylic acid can be obtained in a simple manner, in high yields and high purities, either as a mixture or as isolated product streams. In particular, the process of the invention has the great advantage that especially the ratio of the desired methacrylic acid and alkyl methacrylate, especially MMA, products can be adjusted freely within a wide range and varied by chemical engineering measures and operating parameters.
Owner:ROHM GMBH
Binder, electrode and lithium battery including the same, and method of preparing the binder
ActiveUS20190067699A1Less curved surfaceGood physical propertiesNegative electrodesAcid polymer adhesivesCross-linkPolymer science
A binder includes a cross-linked product of at least a first polymer, a second polymer, and a third polymer, wherein the cross-linked product is cross-linked by at least two ester bonds; the first polymer includes polyimide, polyamic acid, a copolymer thereof, or a combination thereof, wherein the first polymer includes a structural unit including an alkali metal and a structural unit including at least one hydroxyl functional group; the second polymer includes poly(acrylic acid), poly(methacrylic acid), a copolymer thereof, or a combination thereof; and the third polymer includes polyvinyl alcohol, polyacrylamide, polymethacrylamide, a copolymer thereof, or a combination thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Preparation method for anode device of microbial fuel cell
InactiveCN105680056AStable in natureEasy to makeCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cells2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholineDistillation
The invention provides a preparation method for an anode device of a microbial fuel cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps of dissolving methacrylic acid in dichloromethane; adding dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and alkylamine osmium bipyridine chlorate for reaction; drying an organic phase to obtain a monomer Y after washing; dissolving 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine, 2-butyl methacrylate, 4-vinylbenzene boronic acid and the monomer Y in absolute ethyl alcohol; adding azodiisobutyronitrile for reaction; depositing a product in a chloroform / ethyl ether mixed solvent, dissolving the product in deionized water, and carrying out reduced pressure distillation to obtain a copolymer PMBVY; mixing the copolymer PMBVY and a culture solution loaded with Shewanella to obtain a constituent I; mixing polyvinyl alcohol and a sterile culture solution to obtain a constituent II; placing an electrode in a die; adding the constituents I and II in same volume; uniformly mixing the constituents I and II until a sol is cured; and combing the electrode, an electrode plate, a substrate and a filter net to obtain the anode device. By the method, materials are recycled, and the anode device is convenient to maintain.
Owner:南京斯博伏特新材料有限公司
A kind of alkali-soluble acrylate polymer composition and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104448107BSpeed up entryHigh viscosityCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsCross-linkEmulsion polymerization
Owner:GUANGZHOU TINCI MATERIALS TECH
Polymer capable of responding to acid and oxidation-reduction environment in cells as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN108003354AImprove distributionImprove tumor treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLysosomeTumor targeting
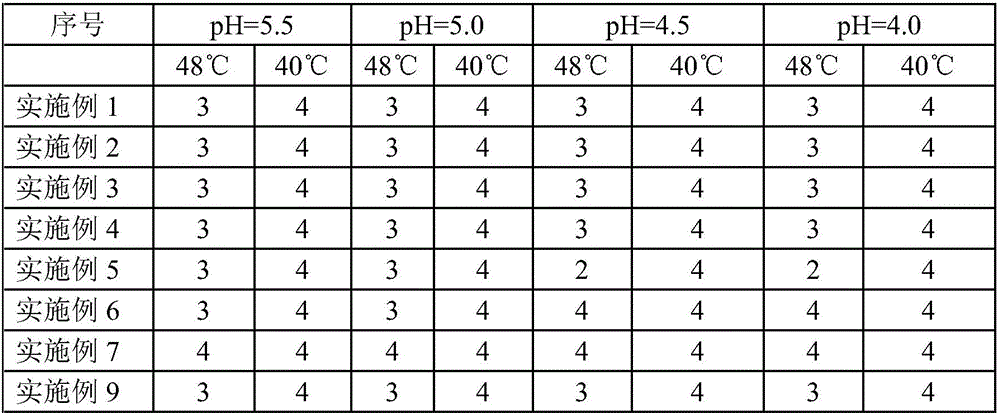
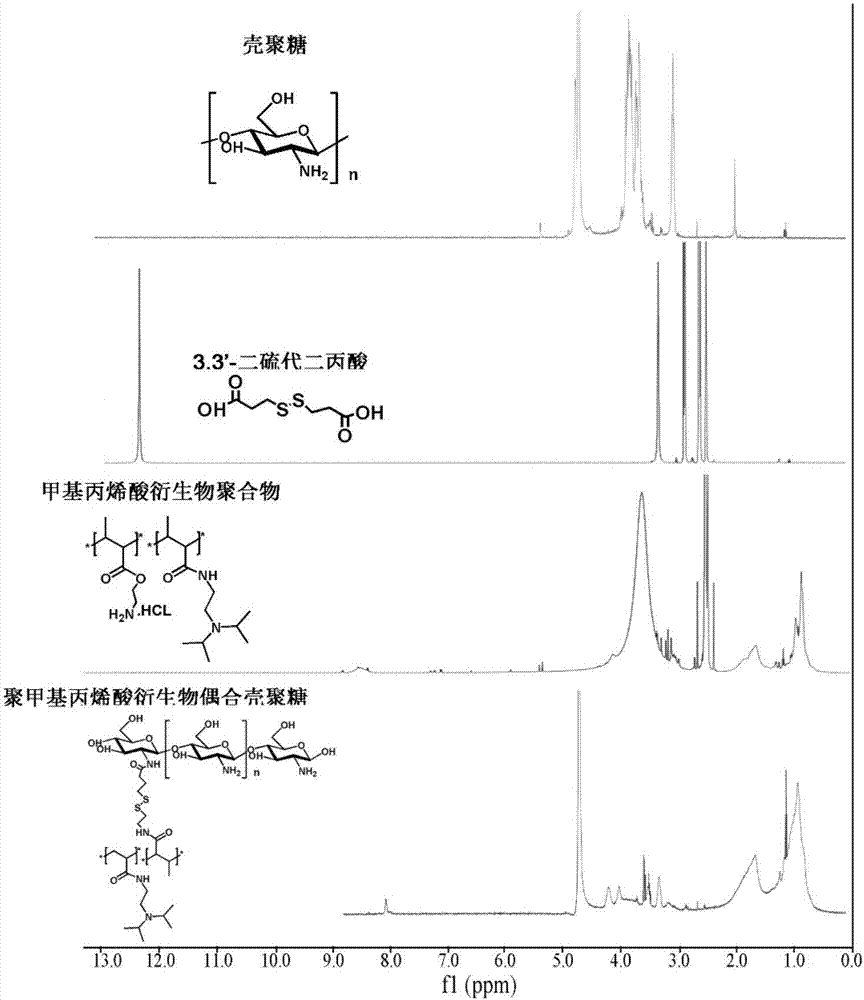
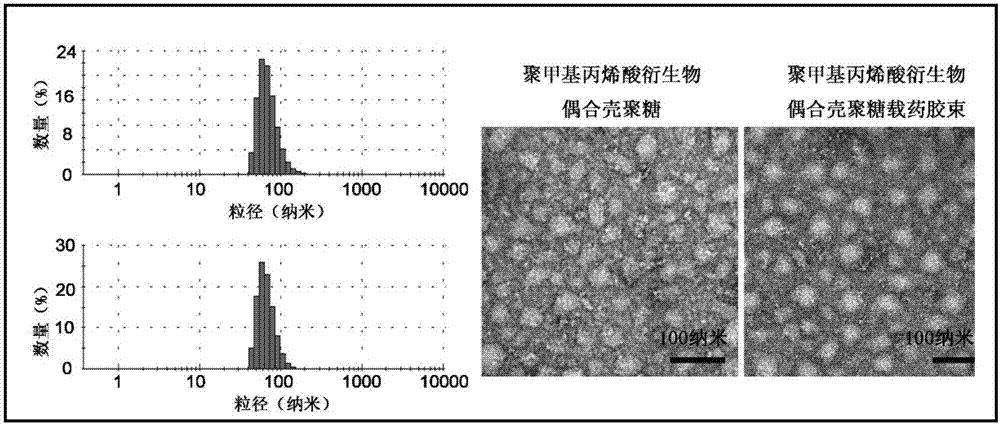
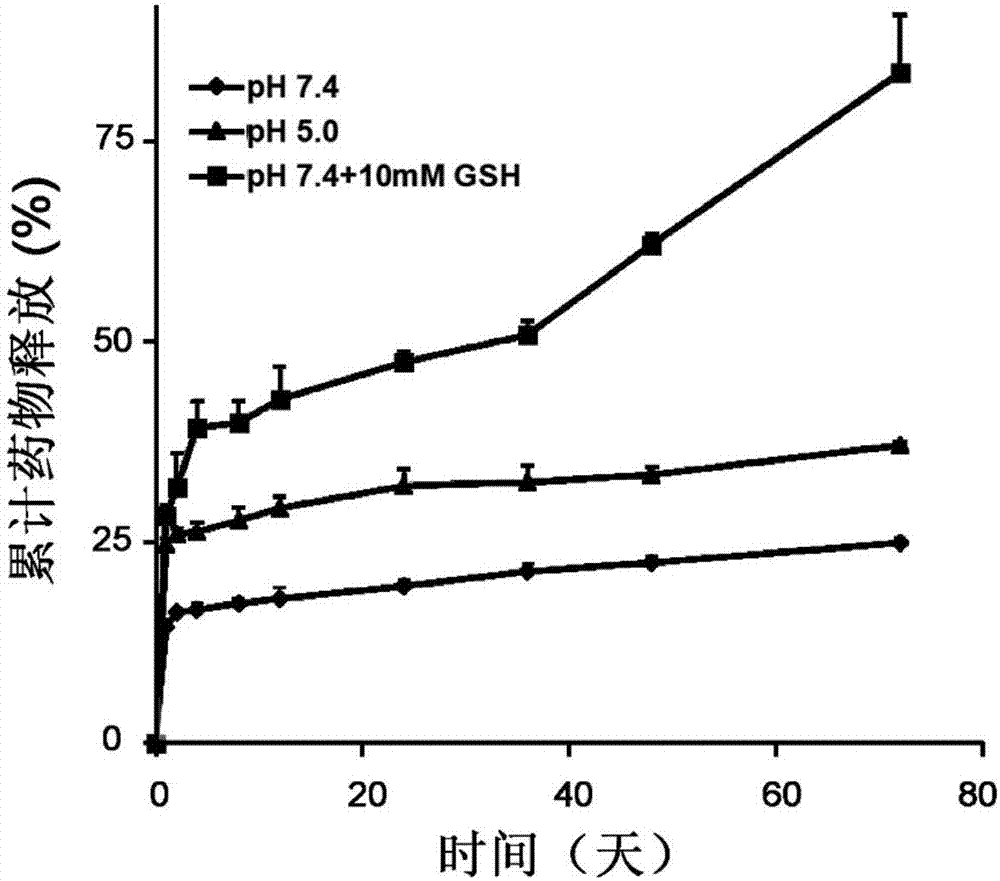
The invention provides a polymer capable of responding to acid and oxidation-reduction environment, namely, a poly-methacrylic acid derivative coupled chitosan polymer. The polymer is a high-molecularsubstance, wherein the molecular weight of a hydrophobic poly-methacrylic acid derivative is 4.1 to 18.8kDa; the molecular weight of chitosan oligosaccharide is 5 to 20kDa; the deacetylation degree is 70 to 100 percent. Chitosan and the poly-methacrylic acid derivative are subjected to an amide reaction with 3,3'-dithiodipropionic acid to obtain poly-methacrylic acid derivative coupled chitosan.Nanoparticles formed by the polymer are stable in structure, and have a good passive tumor targeting effect and high in-vivo stability. The structure contains a large quantity of tertiary amine groupsand disulfide bonds capable of responding to the oxidation-reduction environment, the nanoparticles have the capability of rapidly escaping from lysosome in tumor cells and rapidly releasing medicaments in plasma, and the curative effect of an antitumor medicament in tumor treatment is enhanced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methacrylic acid production method
ActiveUS10138306B1Increase processing costReduce the amount of solutionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation by ozone oxidationHydrotalciteOrganic chemistry
A method of producing methacrylic acid using a hydrotalcite catalyst and subcritical water is described.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Process for producing (meth) acrylic acid compound
InactiveUS7166741B2Promote swellingEfficient removalOrganic compound preparationHollow article cleaningCompound aAlkaline water
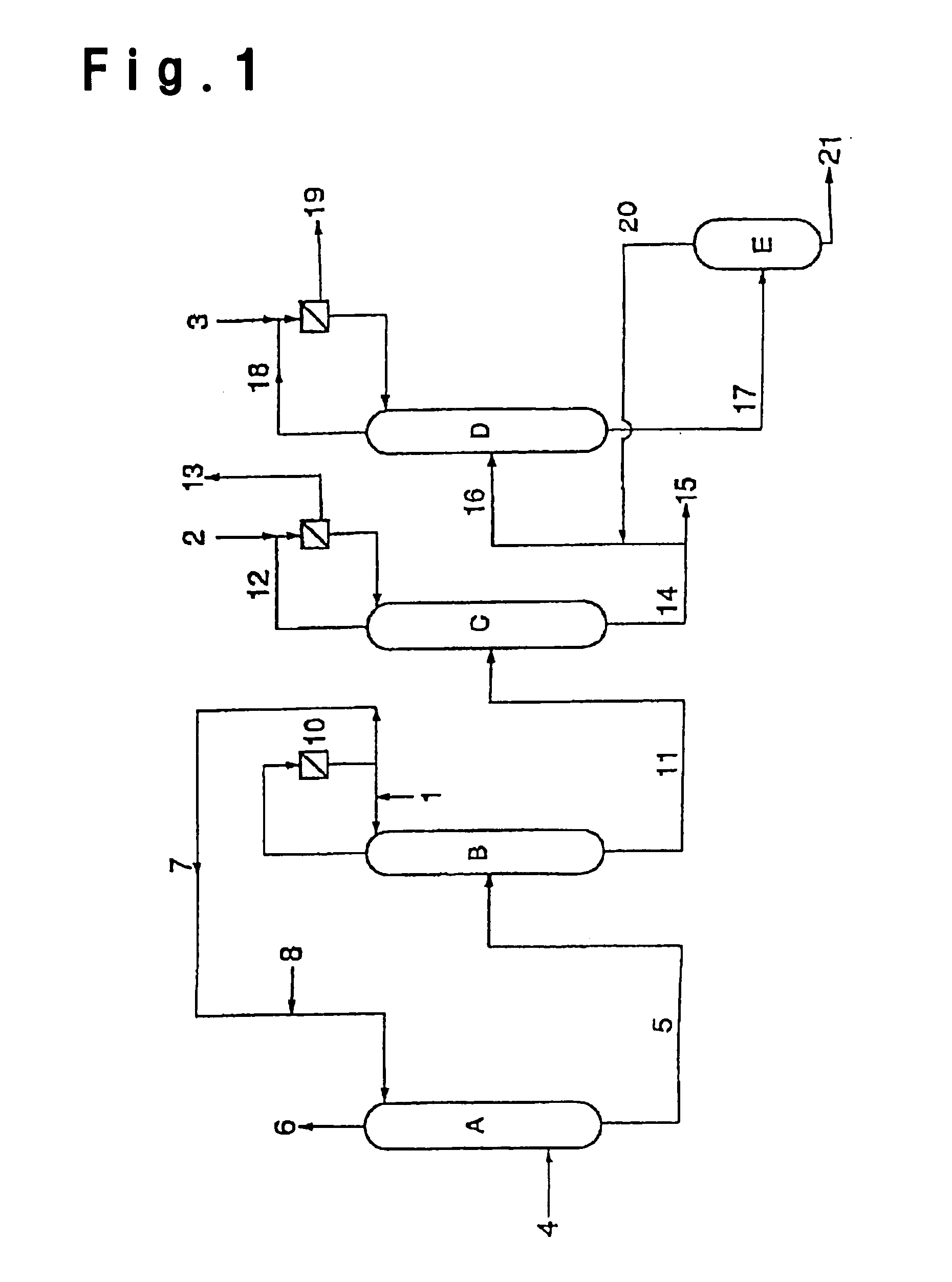
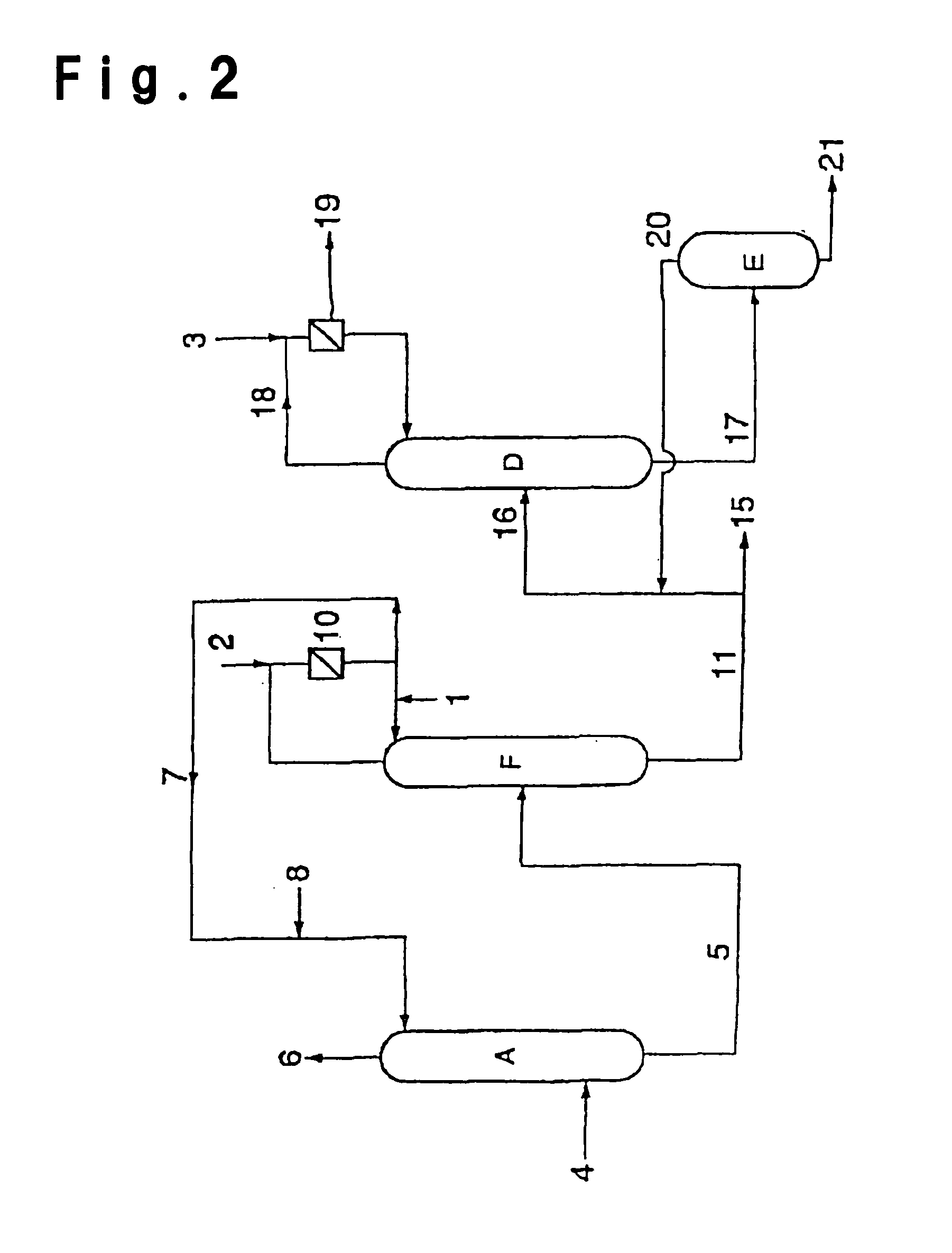
A process for producing a (meth)acrylic acid compound, which comprises distilling acrylic acid, methacrylic acid (these will hereinafter generally be referred to as “(meth)acrylic acid”) or an ester thereof (these will hereinafter generally be referred to as “a (meth)acrylic acid compound”) in a distillation column to obtain a purified (meth)acrylic acid compound, characterized in that in the course of operation of the distillation column including suspension and resumption of the operation, the distillation column is washed with water and, thereafter, inside washing with an organic solvent and / or azeotropic distillation in the presence of the organic solvent is conducted. In some cases, washing with alkaline water may be added prior to the washing with water. Washing of the distillation column for separating and purifying a crude (meth)acrylic acid compound, can be carried out easily. In particular, in a process for producing a (meth)acrylic acid compound, a substance used in a step before or after the distillation column can be utilized to recover a valuable substance, and the distillation column can be efficiently cleaned.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Preparation method of methacrylic acid bentonite
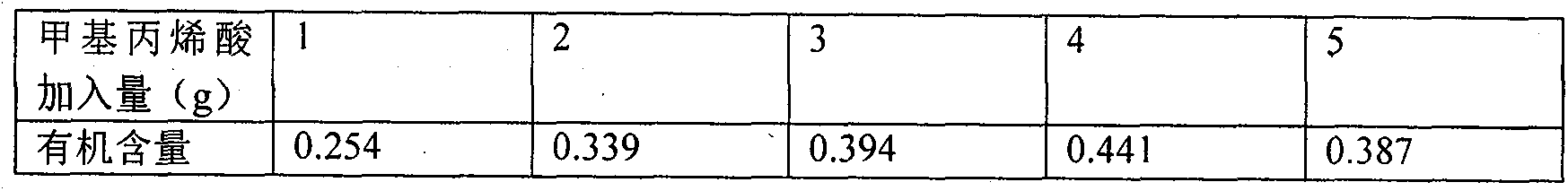
InactiveCN104069817AHigh organic contentPrevent self-aggregationOther chemical processesWater bathsCyclohexene
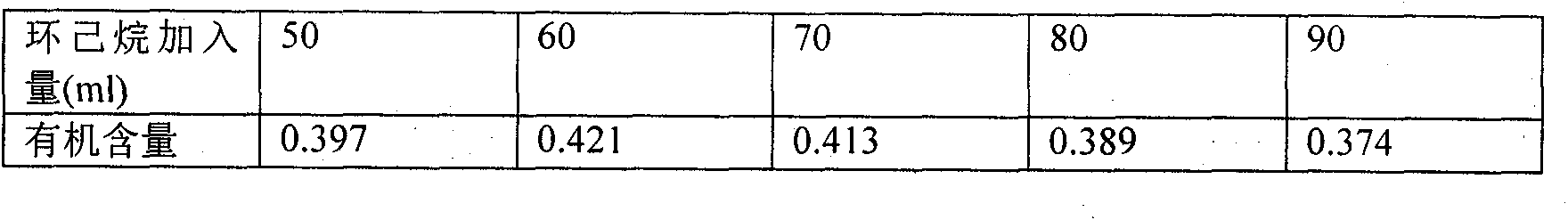
The invention relates to a preparation method of methacrylic acid bentonite with a structure of vertically and crossly distributed lamellas. The preparation method of methacrylic acid bentonite is characterized in that alkaline calcium base soil and methacrylic acid act as raw materials, and cyclohexene acts as a dispersing agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting alkaline calcium base bentonite into a three-opening flask, adding a proper amount of cyclohexene, and carrying out ultrasonic dispersion with the power of 50-900W for 1-150 minutes; then putting the three-opening flask into a water bath pot at 30-100 DEG C, and carrying out thermostatic waterbath mechanical stirring, adding a mixed solution of methacrylic acid, alcohol and residual cyclohexene dropwise, then condensing and backflowing, carrying out water diversion reaction for 0.5-12 hours, carrying out suction filtration, drying, and cooling naturally to room temperature, thereby obtaining the methacrylic acid bentonite. The organic content of methacrylic acid bentonite is as high as 30%-50%. The methacrylic acid bentonite is novel organic bentonite. Meanwhile, the preparation method enables the reaction to be more uniform and full, so that the favorable bentonite with vertically, crossly and uniformly distributed lamellas can be obtained, and moreover, the organic content is as high as 44.1%.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com