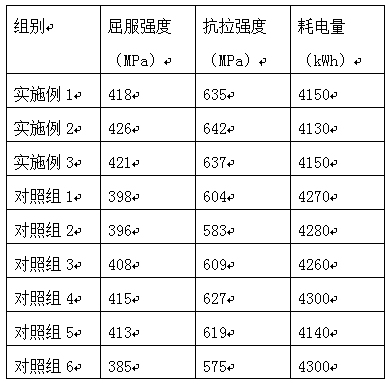
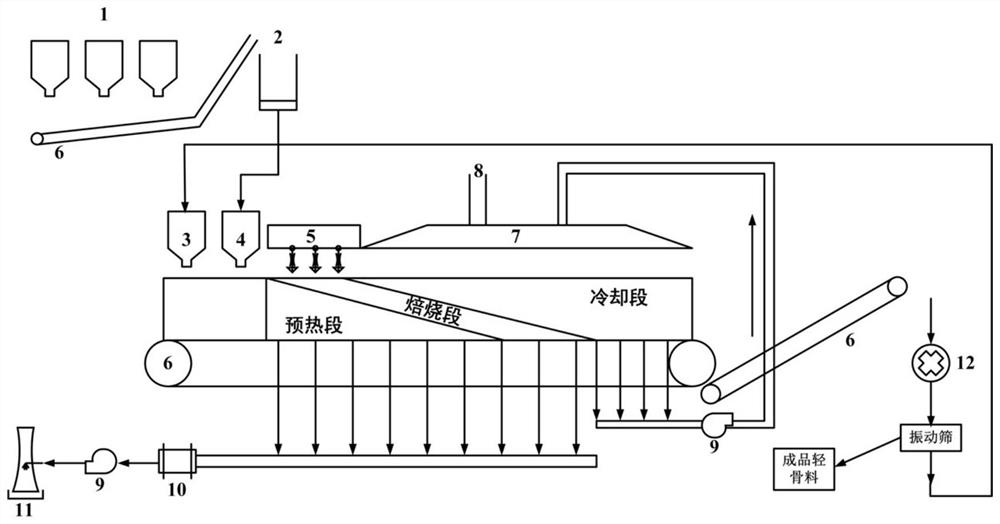
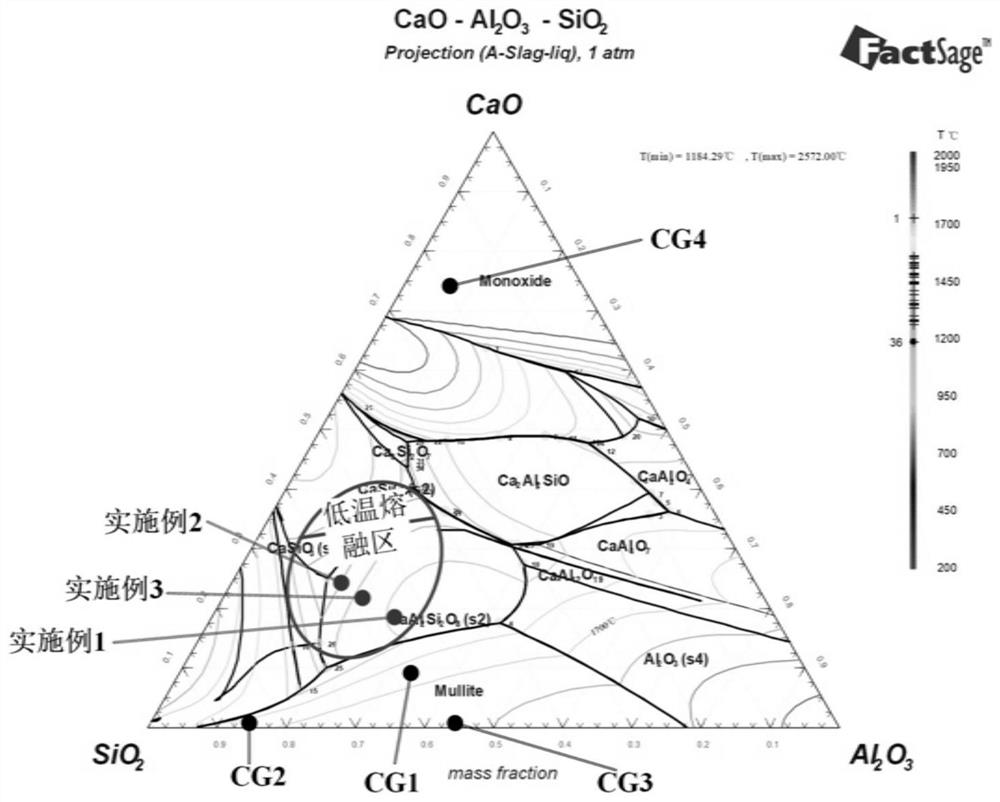
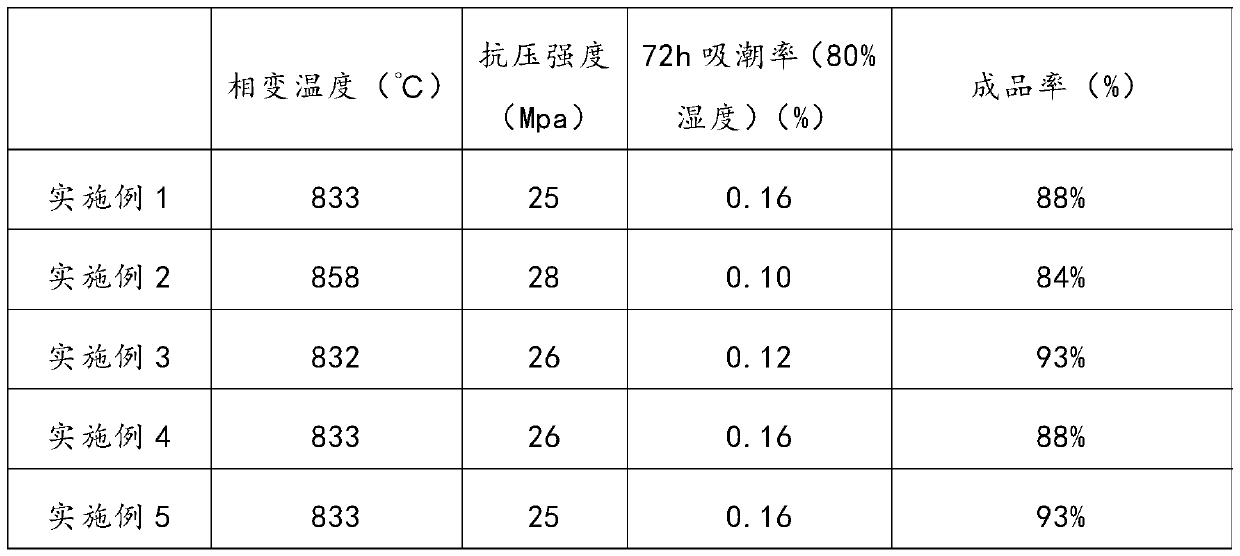
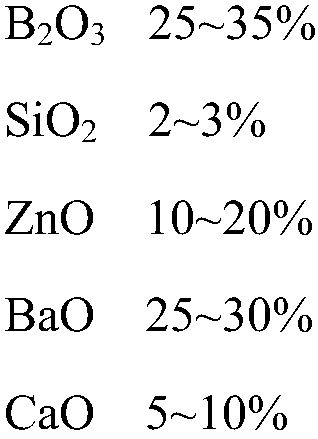Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Play a role in fluxing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Production process of honey peach CZ diamond
InactiveCN102838277ANo pollution damagePlay a role in fluxingGlass furnace apparatusGlass productionMachine toolKiln
The invention relates to a production process of a honey peach CZ diamond. The honey peach CZ diamond comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 60-70 parts of SiO2, 0.5-1.5 parts of Al2O3, 0.5-2.5 parts of BaO, 1.5-5 parts of ZnO, 1.0-2.5 parts of B2O3, 3-8 parts of K2O3, 8-15 parts of Na2O, 0.5-1.5 parts of CaO, 0.3-1.5 parts of Se and 0.03-0.3 parts of S. The production process comprises the following steps of: smelting by a hot smelting kiln and classifying; discharging to obtain a CZ diamond bead blank; sequentially carrying out fire polishing by a fire polishing furnace, and grinding by a grinding machine; and grinding a plurality of cutting surfaces of the CZ diamond by a multi-faced grinding machine tool and chemically plating to obtain a CZ diamond finished product.
Owner:JIANGSU JINCHENG GRP TECH
Method for production of high-activity soil conditioner and co-production of sulfuric acid employing phosphorus gypsum and potassium feldspar
ActiveCN104498050AHigh practicality and economic valueReduce energy consumptionSulfur compoundsOrganic fertilisersPotassium feldsparChemistry
The invention relates to a method for production of a high-activity soil conditioner and co-production of a sulfuric acid employing phosphorus gypsum and potassium feldspar. The method comprises the following steps: (1) naturally airing, drying, crushing and sieving phosphorus gypsum, crushing, grinding and sieving potassium feldspar, and grinding and sieving sodium sulfate; (2) mixing the sieved phosphorus gypsum, potassium feldspar and sodium sulfate, adding coal and mixing evenly, so as to obtain a mixture; (3) adding water to the mixture, so as to prepare a spherical material or a block material; (4) sintering the spherical material or the block material at 900-1100 DEG C for 1-3 hours, so as to prepare a sintered clinker; and (5) crushing, grinding and sieving the sintered clinker, adding biochemical fulvic acid potassium powder, mixing evenly, and packaging to obtain a soil conditioner product, and introducing a tail gas in the step (4) into a sulfuric acid preparation system after cooling and removing dust, so as to prepare the sulfuric acid. The residue phosphorus gypsum from acid preparation of phosphate ore is reasonably utilized, and waste is changed into treasures, so that the maximal economic benefits are generated.
Owner:KINGENTA NORSTERRA CHEM CO LTD +1
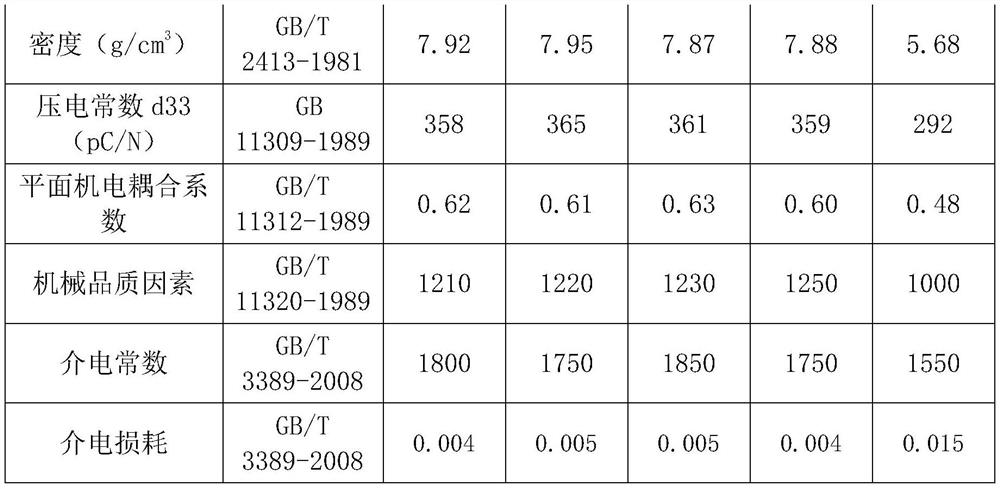
Doped and modified lead zirconate-titanate piezoelectric ceramic and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107986782ALower sintering temperatureHigh electromechanical coupling coefficientPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyLead zirconate titanateElectromechanical coupling coefficient
The invention discloses a doped and modified lead zirconate-titanate piezoelectric ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The doped and modified lead zirconate-titanate piezoelectric ceramic is shown in a following chemical formula I, namely xPb(Mg1 / 3Nb2 / 3)O3-yPb(Ni1 / 3Nb2 / 3)O3-(1-x-y)Pb(Ti1 / 2Zr1 / 2)O3+lSrCO3+mZnO+nQ, wherein Q is at least selected from Li2CO3 (lithium carbonate), CuO (copper oxide), SiO2 (silicon dioxide), MnO2 (manganese dioxide), Bi2O3 (bismuth oxide) and La2O3 (lanthanum oxide); l, m and n are respectively the mass percentages of SrCO3 (strontium carbonate), ZnO (zinc oxide) and Q in the compound Pb(Mg1 / 3Nb2 / 3)O3-Pb(Ni1 / 3Nb2 / 3)O3-Pb(Ti1 / 2Zr1 / 2)O3; x is greater than or equal to 0.10 and is smaller than or equal to 0.70, y is greater than or equal to 0.08 and is smallerthan or equal to 0.38, l is greater than 0 and is smaller than or equal to 0.5, m is greater than 0 and is smaller than or equal to 0.50, and n is greater than or equal to 0 and is smaller than or equal to 0.5. The doped and modified lead zirconate-titanate piezoelectric ceramic has the excellent properties of low sintering temperature, high electromechanical coupling coefficient, high piezoelectric strain coefficient, small dielectric loss and the like.
Owner:WEIFANG GOERTEK MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for preparing foamed ceramic with nickel slag and pulverized biomass
ActiveCN106187289APlay a role in fluxingEfficient use ofCeramic materials productionCeramicwareFoaming agentSlag
The invention discloses a method for preparing lightweight foamed ceramic with nickel slag and pulverized biomass. The method includes the following steps: mixing, by mass, 27-72 parts of nickel slag, 28-73 parts of aluminium silicon waste slag, 15-30 parts of pulverized biomass and 1-6 parts of foaming agent prior to uniform blending and forming to obtain green bodies; putting the green bodies into a high temperature furnace for sintering, and cooling to room temperature to obtain the lightweight foamed ceramic.
Owner:射阳县射阳港渔工贸开发有限公司
Method for producing nutrient-type soil heavy metal solidifying agent from low-grade phosphate ore
ActiveCN103360015AWide variety of sourcesIncrease profitSolid waste managementMining engineeringSoil heavy metals
The invention discloses a method for producing a nutrient-type soil heavy metal solidifying agent from low-grade phosphate ore, which comprises the following steps: proportionally mixing main raw materials low-grade phosphate ore, dolomite and phosphogypsum, wherein the mol ratio of the apatite (the molecular formula is Ca5(PO4)3(F,Cl,OH)) to the dolomite (the molecular formula is CaMg(CO3)2) is 1:(0.5-2.25), the addition amount of the phosphogypsum (the molecular formula is CaSO4.2H2O) is 5-25 wt% of the sum of dried low-grade phosphate ore and dolomite; and adding an additive, roasting at 1050-1200 DEG C for 0.5-2 hours, cooling the product, and pulverizing by grinding to obtain the nutrient-type soil heavy metal solidifying agent. The invention has the advantages of wide sources, cheap and accessible raw materials and low energy consumption, and can enhance the utilization ratio of the low-grade phosphate ore, thereby solving the problems of more rich phosphate ore and less lean phosphate ore in China.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Glaze material with fluxing agent
The invention relates to a glaze material used in the production process of ceramic products, in particular to a glaze material with fluxing agent. The glaze material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-32 parts of quartz, 25-29 parts of potash feldspar, 2-4 parts of aluminium oxide, 13-15 parts of calcite, 4-6 parts of dolomite, 1-2.5 parts of zinc oxide, 3-4.5 parts of kaoline, 1-2.5 parts of fluxing agent, 9-11 parts of zirconium silicate and 1-2.5 parts of fusion cake. A part of zinc oxide is replaced with finished products in the ceramic glaze material disclosed by the invention so that the aim of greatly reducing the production cost while ensuring thermal stability is ensured is achieved. The ceramic glaze in which the fluxing agent is added has the advantages that the added fluxing agent plays a fluxing role, the expansion coefficient of the glaze material is reduced, the thermal stability of ceramic products is improved, and the quality of the ceramic products can be ensured.
Owner:TANGSHAN HUALI CERAMICS CO LTD
Method for producing ammonium sulfur and potassium-calcium-silicon fertilizer by using phosphogypsum
InactiveCN101792154ALow melting pointReduce break down costAmmonium salt fertilisersAmmonia compoundsPhosphogypsumDiammonium carbonate
The invention discloses a method for producing ammonium sulfur and potassium-calcium-silicon fertilizer by using phosphogypsum. The method comprises the followings steps of: adding solution of ammonium carbonate and dried phosphogypsum into a reaction kettle, and performing solid-liquid separation of the obtained pulp by a filter press after reaction; adjusting a pH value of filtrate to 5.6 to 6.0, performing concentration and crystallization of the filtrate and drying the crystals to obtain the fertilizer-graded ammonium sulfate products; washing filter cakes by water, putting the filter cakes in drying equipment, introducing tail gas in a roller kiln furnace to dry the materials, performing heat-exchange drying of the materials in the drying equipment, and using the dried filter cakes a raw material for producing the potassium-calcium-silicon fertilizer; and drying and grinding potassium feldspar and the phosphogypsum, mixing the powder of the potassium feldspar and the phosphogypsum and the dried filter cakes, putting the mixture in a ball mill, putting the mixture in the drying equipment for drying, continuously putting the mixture in the roller kiln furnace for calcining, performing a solid-phase reaction, cooling the reaction products, and dry-grinding and granulating the cooled reaction products to obtain the potassium-calcium-silicon fertilizer, wherein the tail gas in the roller kiln furnace enters the drying equipment to perform the heat-exchange drying of the materials. The method has the advantages of simple process, low raw material cost and low energy consumption.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Ultrathin photovoltaic rolled glass
InactiveCN107162407AReduce glass expansion coefficientIncrease glass refractive indexExpansion factorOxide
The invention discloses ultrathin photovoltaic rolled glass. The ultrathin photovoltaic rolled glass comprises the following oxides by mass percentage: 71.0-73.18% of SiO2, 8.0-8.50% of CaO, 3.50-4.50% of MgO, 1.35-2.8% of Al2O3, 13.30-14.0% of Na2O, 0.6-1.0% of B2O3, 0.05-0.18% of Sb2O3, 0.05-0.1% of CeO2 and 0.01-0.012% of Fe2O3. According to the content of the oxides, the raw materials are compounded, and the photovoltaic rolled glass of which the thickness is less than 2.0 mm is prepared by founding, rolling forming and annealing processes; a glass component system is optimized, the B2O3 is introduced to reduce the glass expansion factor and increase the glass refractive index so as to play the fluxing action; the CeO2 and nitrate perform the combined action, so the clarification and decoloration effects are improved, the drawability of the glass is enhanced, and the plasticity of the photovoltaic rolled glass is improved; and the content of the Al2O3 and MgO is high, and the frit performance is improved. The final performance can satisfy the high-transparent and high-speed formability requirements of the industrial production of the photovoltaic glass of which the thickness is less than 2.0 mm, the production cost is saved, and the industrial production of the light and thin photovoltaic glass is realized.
Owner:CNBM YIXING NEW ENERGY CO LTD
Glass powder for PERC aluminum paste and preparation method thereof
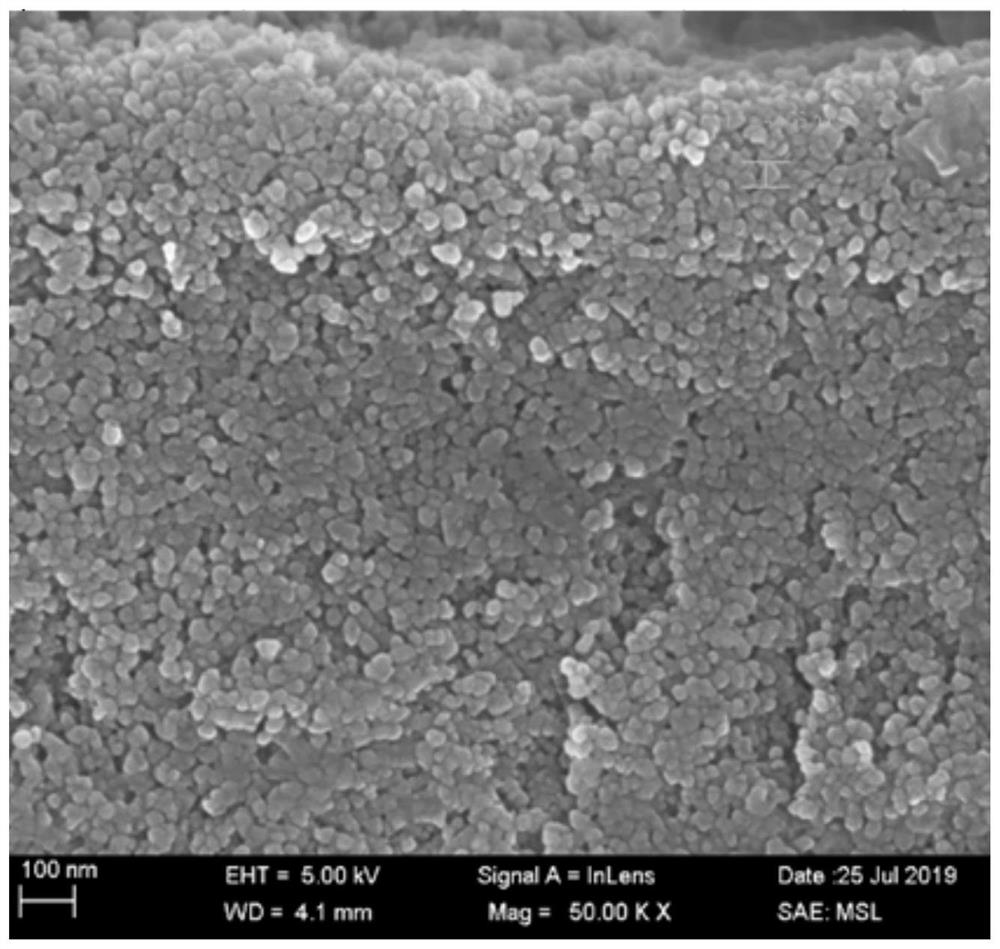
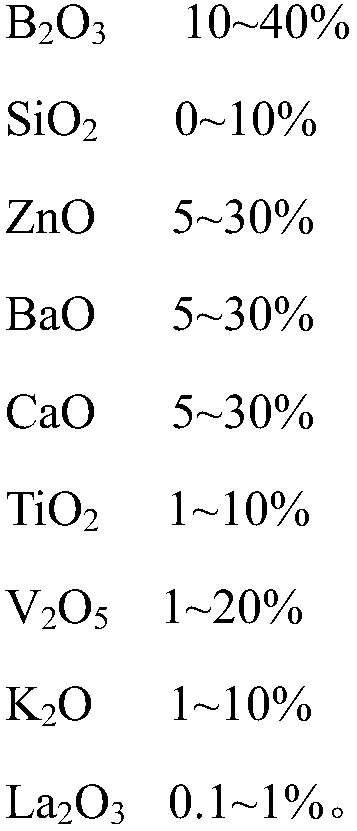
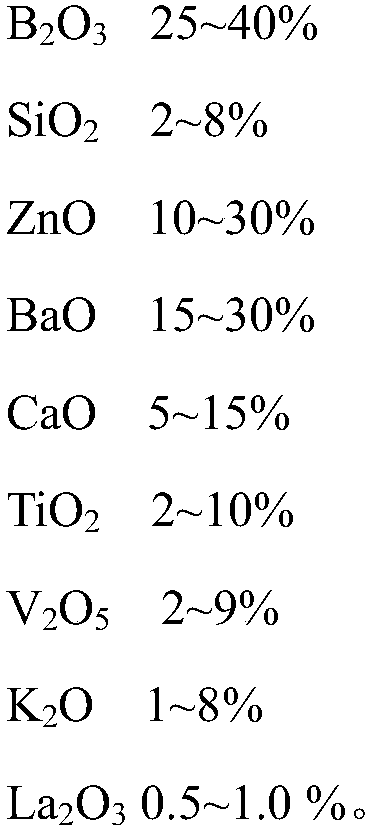
The invention discloses glass powder for PERC aluminum paste. The glass powder is mainly prepared from the following raw materials by mass: 10 to 40% of B2O3, 0 to 10% of SiO2, 5 to 30% of ZnO, 5 to 30% of BaO, 5 to 30% of CaO, 1 to 10% of TiO2, 1 to 20% of V2O5, 1 to 10% of K2O and 0.1 to 1% of La2O3. When applied to the PERC aluminum paste, the glass powder can reduce corrosion of the aluminum paste to a passive film layer at a high temperature and promote formation of alloy in local contact areas. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the glass powder applied to the PERC aluminum paste.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RUXING TECH DEV +1
Conductive glass powder and its preparation method, crystalline silicon solar battery aluminum conductive paste and preparation method
InactiveCN103204632AImprove performanceImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureMetallic lithiumElectrically conductive
The invention provides a conductive glass powder and its preparation method. The glass powder comprises a glass oxide and 10-40wt% of a halogen compound of metal lithium or silver. The invention also provides a crystalline silicon solar battery aluminum conductive paste containing the conductive glass powder and a preparation method thereof. The aluminum conductive paste prepared from the conductive glass powder provided by the invention can improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency of a crystalline silicon solar battery. The formed aluminum film has small square resistance and high fill factor, the battery piece has small bending, the silicon-aluminum layer is smooth and has good adhesion, and the average photoelectric conversion efficiency of an ordinary monocrystalline silicon battery is greater than 18.20%.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
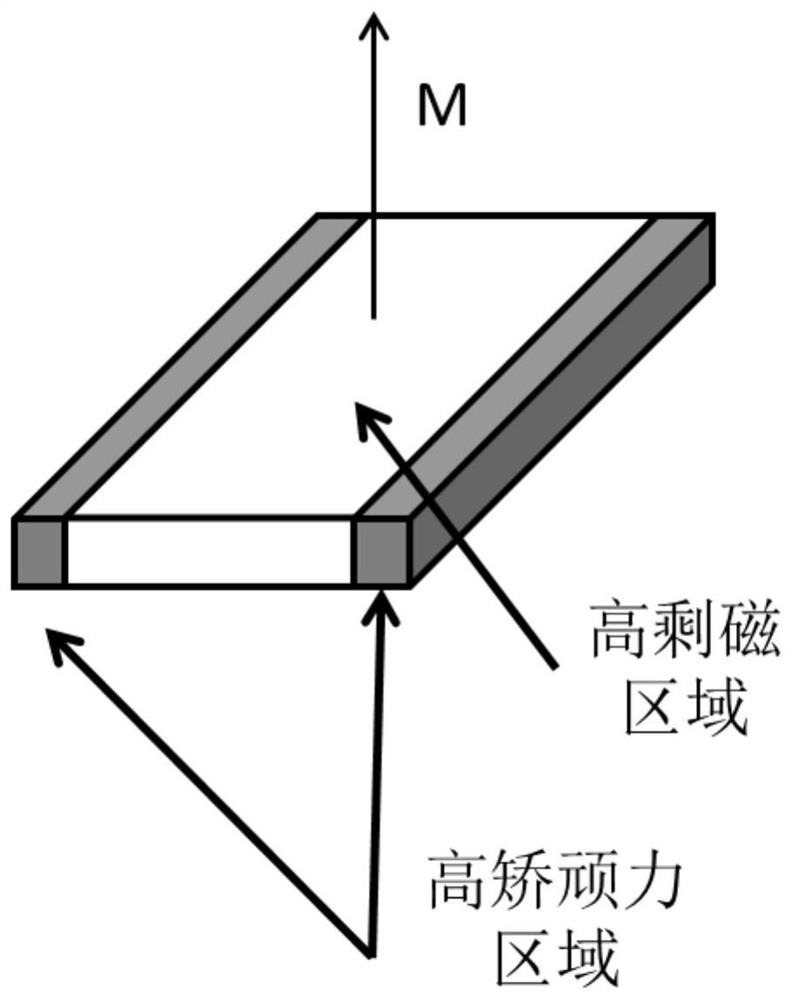
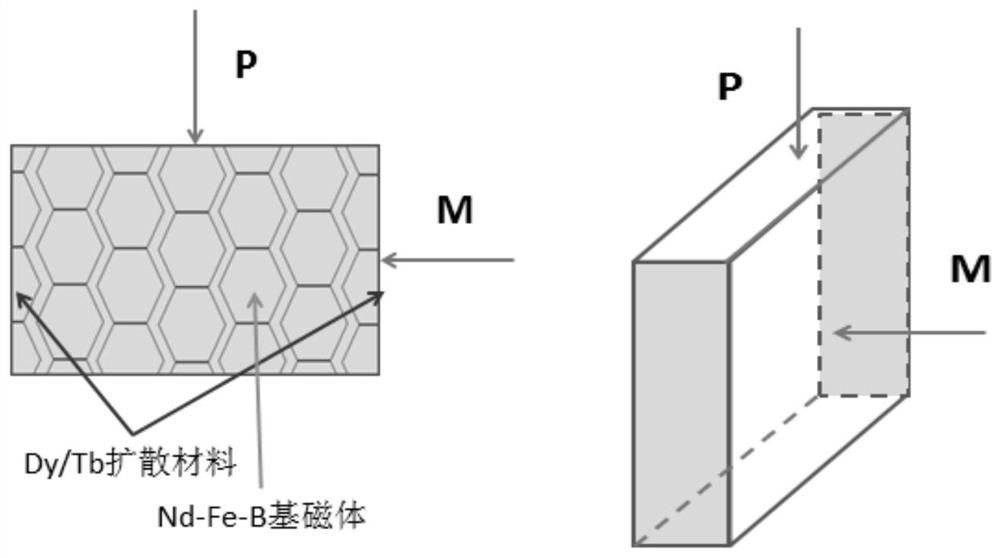
Neodymium-iron-boron magnet and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111653404AImprove high temperature demagnetization resistanceReduce fluxTransformersVacuum evaporation coatingRare-earth elementRemanence
The invention provides a neodymium-iron-boron magnet and a preparation method and application thereof. The neodymium-iron-boron magnet is represented by a chemical formula R1-R2-Fe-M-B, and the neodymium-iron-boron magnet has a composite structure of a high-coercivity region and a high-remanence region, wherein R1 is a rare earth element at least containing Nd, R2 is a heavy rare earth element atleast containing Dy and / or Tb, and M is a transition metal element at least containing Co. The magnet can adopt a small amount of Dy / Tb, the high-temperature demagnetization resistance of the magnet is greatly improved, the reduction of the magnetic flux of the magnet is inhibited, and the magnet is suitable for an embedded high-speed motor. The method for preparing the magnet can also greatly improve the utilization rate and the production efficiency of the material, and has mass production feasibility.
Owner:YANTAI ZHENGHAI MAGNETIC MATERIAL CO LTD
Glass ceramic with transmittance close to that of glass precursor and preparation method of glass ceramic
The invention provides a glass ceramic with transmittance close to that of a glass precursor. The glass ceramic comprises the following components in percentage by mole: 60 to 75 mol% of SiO2, 2 to 10mol% of Al2O3, 0 to 5 mol% of P2O5, 0.5 to 3 mol% of ZrO2, 0.5 to 6 mol% of Na2O, 15 to 28 mol% of Li2O, at least one of 0 to 5 mol% of B2O3, 0 to 5 mol% of MgO, and 0 to 5 mol% of ZnO, and at leastone of 0 to 2 mol% of HfO2, 0 to 2 mol% of Ta2O5, and 0 to 2 mol% of Y2O3, wherein the sum of the amounts of HfO2, Ta2O5 and Y2O3 is more than 0 and less than or equal to 2 mol%, and the difference between the visible light transmittance of the glass ceramic and the transmittance of the glass precursor for preparing the glass ceramic is 0.3-5%. According to the invention, the regulation and control difficulty of the visible light transmittance of the glass ceramic is reduced, so that the difference between the visible light transmittance of the glass ceramic and the visible light transmittanceof the glass precursor is only 0.3-5%.
Owner:CHONGQING XINJING SPECIAL GLASS CO LTD
Light ceramsite prepared from oil shale semi-coke and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105731998AImprove use valueLower firing temperatureCeramic materials productionClaywaresCapacity valueOil shale gas
The invention relates to light ceramsite prepared from oil shale semi-coke and a preparation method thereof. The light ceramsite consists of the raw materials such as oil shale semi-coke, oil shale ash, clay and water glass. The preparation method comprises the process steps such as pulverization, pelletizing, sintering and cooling. The light ceramsite provided by the invention has the advantages of widely available raw materials, easiness in preparation, low production cost, environmental friendliness and the like; by implementing the technical scheme, much land occupation caused by stacking oil shale semi-coke and ash can be reduced, consequent severe threat to the ecology, environment and human health is relieved, the problems such as low capacity value, low water absorption and low cylinder compressive strength of the commercially available ceramsite products are solved, and the use value of the oil shale semi-coke is increased so that the oil shale semi-coke is turned into wealth; and the light ceramsite is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:陕西省能源化工研究院
Foam glass prepared from fused brown corundum dust-removing powder as raw material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to foam glass prepared from fused brown corundum dust-removing powder serving as a raw material and a preparation method thereof. The technical scheme comprises the following steps of: mixing 20 to 50 weight percent of fused brown corundum dust-removing powder and 50 to 80 weight percent of waste flat glass powder, adding 2 to 8 weight percent of foaming agent based on the weight of the mixed powder, and mixing uniformly; filling the mixture into a mould, heating to the temperature of between 850 and 1,100 DEG C in a sintering furnace, and preserving heat for 10 to 30 minutes; and naturally cooling, demoulding and cutting to obtain the foam glass. The fused brown corundum dust-removing powder mainly comprises the following chemical components: 20 to 56 weight percent of Al2O3, 10 to 50 weight percent of SiO2, 0.3 to 20 weight percent of K2O, 2 to 15 weight percent of igloss and 0 to 10 weight percent of Fe2O3+MgO+Na2O+TiO2. The preparation method has the characteristics of a few additives, short process period and easy operation. The volume weight of the product is 250 to 1,200kg / m<3>, the compressive strength is 4 to 20MPa and the heat conductivity is 0.070 to 1.200W / (m*K); and the foam glass is widely applicable and can meet the application requirements in different environments.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
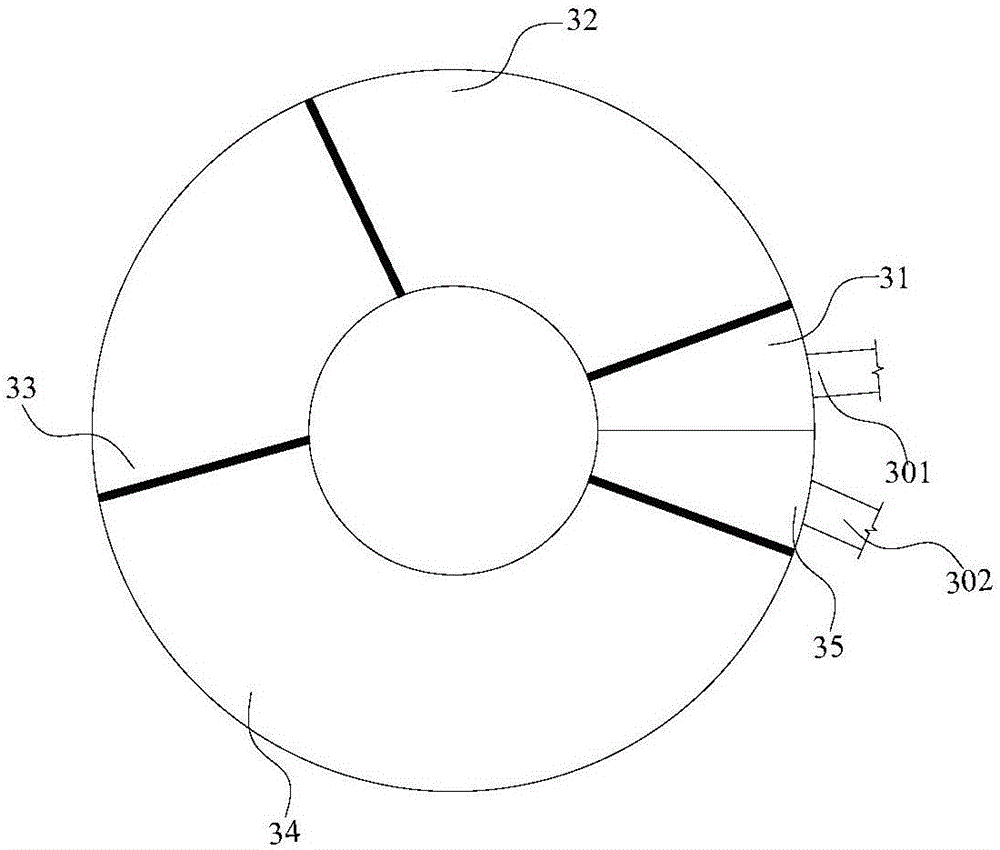
Ferrite material for communicating isolator and circulator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110451948APlay a contact areaIncrease contact areaCeramic shaping apparatusElectricityMicrowave
The invention relates to the technical field of ferrite materials, and discloses a ferrite material for communicating an isolator and a circulator and a preparation method thereof. The ferrite material is prepared from, by weight, 40-43.5 parts of Y203, 44-48 parts of Fe2O3, 3.5-4.5 parts of Gd2O3, 3-4 parts of CaCO3, 2.5-3.5 parts of MnCO3, 1-1.5 parts of Bi2O3, 0.4-0.6 part of ZrO2 and 0.4-0.6 part of Al2O3. The ferrite material has the good characteristics that the ferromagnetic resonance line width is small, and the microwave dielectric loss is small, on the whole, the ferrite material hasthe good electromagnetic performance and stability, and the technical requirements of high-performance microwave devices, in particular to small-line-width ferrite microwave device can be met.
Owner:三桥惠(佛山)新材料有限公司
Method and system for processing red mud
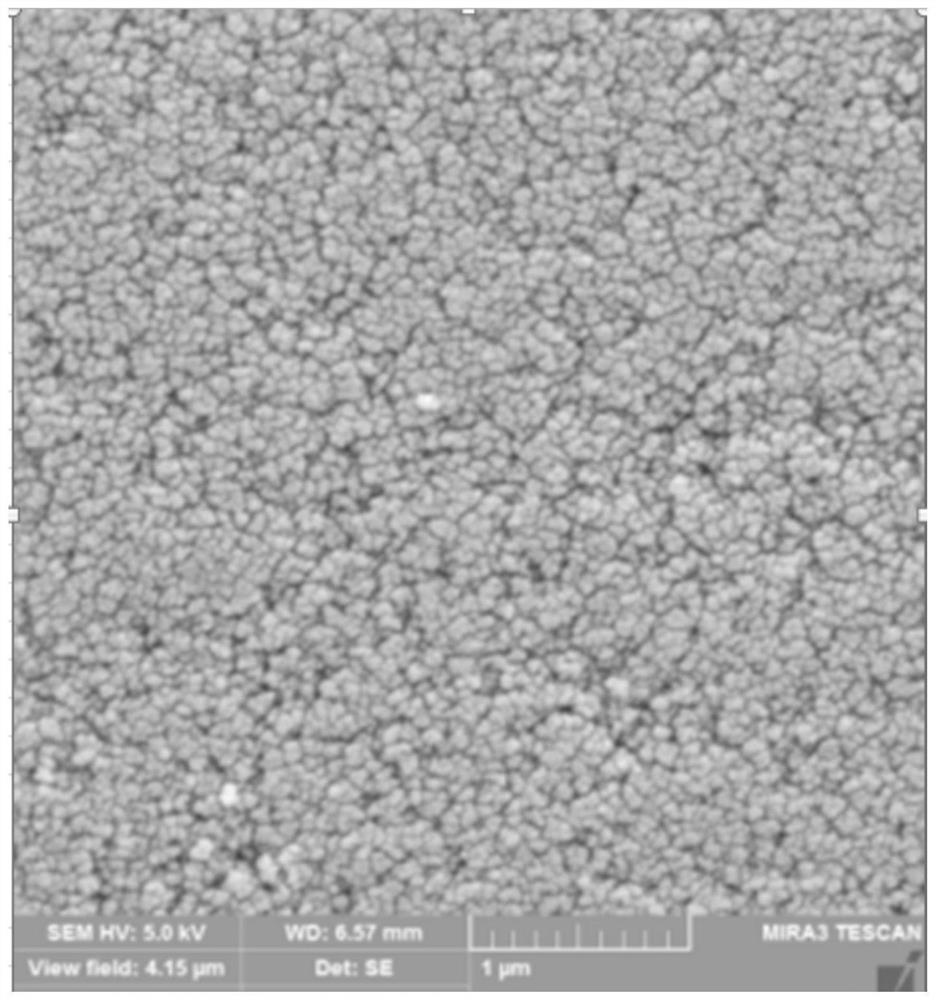
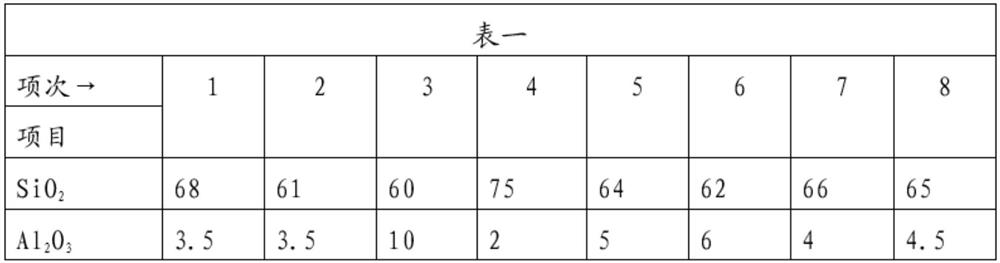
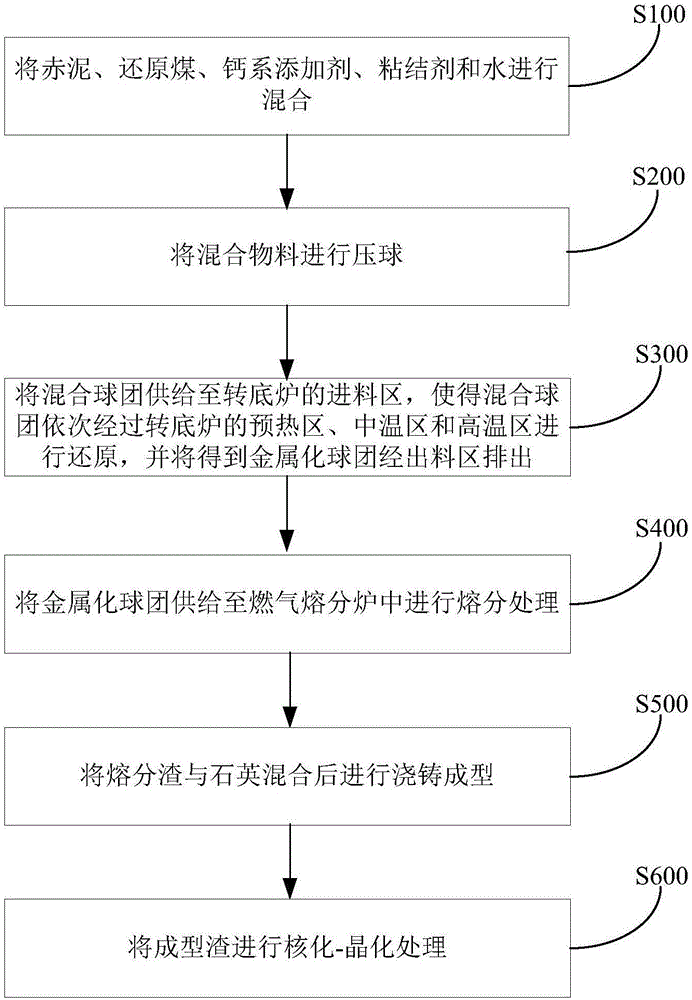
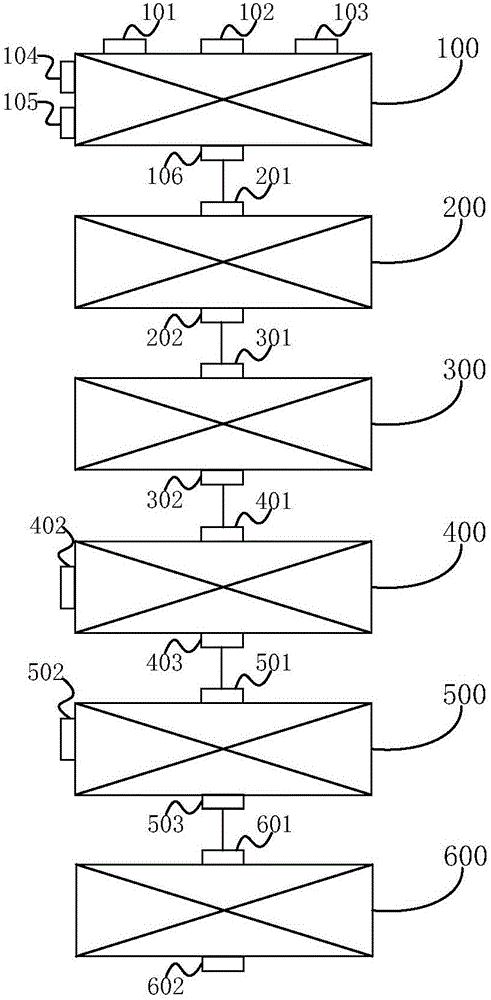
PendingCN106399676ARealize comprehensive utilizationRealize long-term stockpilingHearth type furnacesRed mudSlag
The invention discloses a method and system for processing red mud. The method comprises the steps that (1) the red mud, reduction coal, a calcium system additive, a binding agent and water are mixed, and a mixed material is obtained; (2) the mixed material is subjected to pellet pressing, and a mixed pellet is obtained; (3) the mixed pellet is supplied to a feeding area of a rotary hearth furnace and made to sequentially pass a preheating area, a medium-temperature area and a high-temperature area of the rotary hearth furnace to be subjected to reduction, and an obtained metallized pellet is discharged through a discharging area; (4) the metallized pellet is supplied to a gas melt separation furnace to be subjected to melt separation processing, and metallic iron and melt separation slag are obtained; (5) the melt separation slag and quartz are mixed and then subjected to casting molding, and molded slag is obtained; and (6) the molded slag is subjected to nucleating-crystallization processing, so that microcrystal glass is obtained. According to the method for processing the red mud, the iron in the red mud is effectively extracted, in addition, the melt separation slag obtained in the melt separation process and the quart are mixed, molded and then subjected to nucleating-crystallization processing, and the microcrystal glass higher in economic value can be obtained.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
High-performance piezoelectric ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-performance piezoelectric ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The chemical general formula is Pb<n>Sr<m>(Mg<1 / 3>Nb<2 / 3>) Zr<y>Ti<x>O<3>+g%CeO<2>+h%PbO+b%CuO+d%Nb<2>O<5>, in the formula, 0.927 < = n < = 0.976, 0.024 < = m < = 0.073, 0.25 < = z < = 0.25, 0.35 < = y < = 0.35, 0.50 < = x < = 0.60, 0.4<=g<=0.7, 0.1<=h<=0.3, 0.1<=b<=0.3, 0.1<=d<=0.3. According to thepreparation method, Pb(Mg<1 / 3>Nb<2 / 3>)O<3> is synthesized, and adding into a PZT system is adopted to realize high intensity. The prepared product is high in density, high in power, high in efficiency, and high in quality. The piezoelectric ceramic is a modified hard PZT system piezoelectric ceramic, has high power bearing capacity and high comprehensive performance, can meet the requirements ofpeople, is extremely suitable for power type transducers with extremely high power and high driving requirements, and can be widely applied to sensors with extremely high power requirements such as high-power sound wave welding and fishery group detection.
Owner:李茂洪
Method for preparing bagasse biomass charcoal
InactiveCN107930582APrevent shrinkagePlay a role in fluxingOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesNitrogenPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing bagasse biomass charcoal and belongs to the technical field of adsorption materials. The method comprises carrying out steam explosion on bagasse to obtain bagasse subjected by steam explosion, mixing the bagasse subjected by steam explosion and a mixed enzyme liquid so that the bagasse is subjected to enzymolysis, drying the bagasse subjected to enzymolysis until constant weight, mixing the pretreated bagasse and tetraethoxysilane so that the pretreated bagasse is immersed, filtering the pretreated bagasse to obtain filter cake, mixing the filtercake and a saturated borax solution so that the filter cake is immersed, carrying out filtration and drying to obtain modified bagasse, mixing the modified bagasse and a phosphoric acid solution, adding a water-retaining agent into the mixed solution, carrying out immersion and filtration to obtain a blank, pre-carbonizing the blank in a nitrogen protective atmosphere at 300-350 DEG C for 2-3h, carbonizing the blank at 550-700 DEG C for 3-4h, discharging the blank, crushing the blank, and carrying out screening to obtain the bagasse biomass charcoal. The bagasse biomass charcoal has a high specific surface area and good adsorption performances.
Owner:常州琨瑶纺织品有限公司
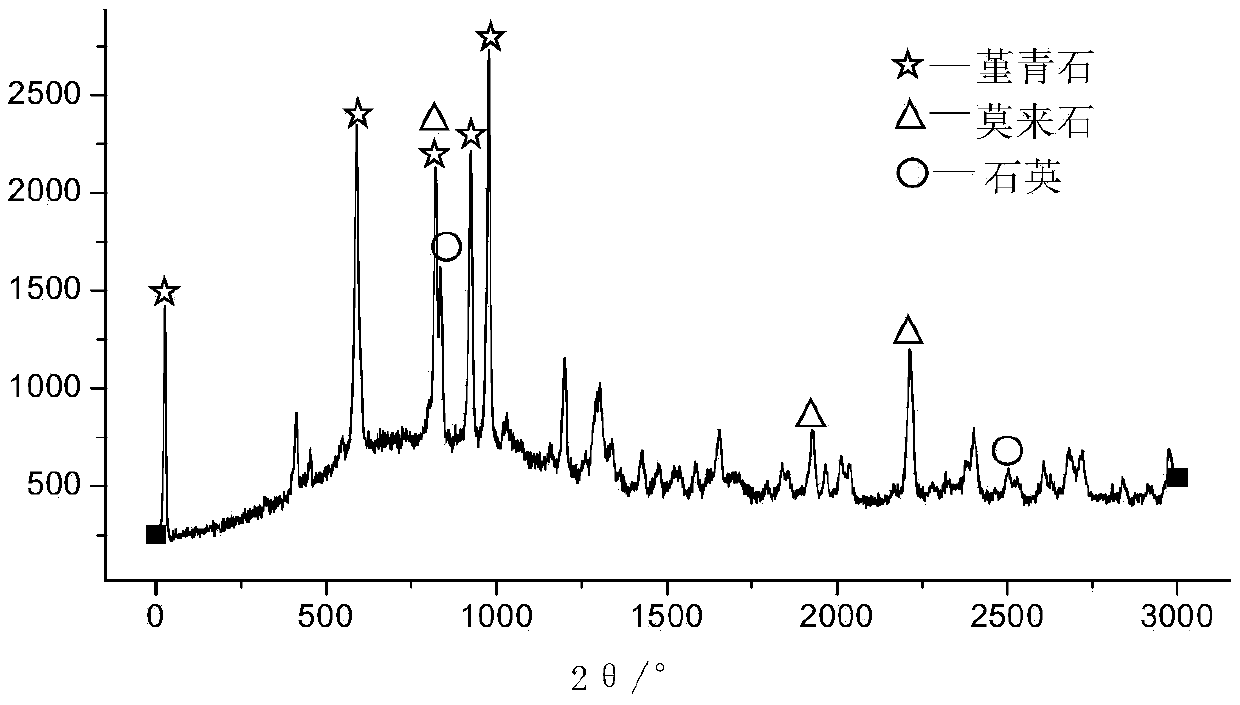
Preparation method of sintering body with principal crystalline phase of cordierite by using coal gangue and nickel slag
The invention discloses a preparation method of a sintering body with a principal crystalline phase of cordierite by using coal gangue and nickel slag. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: evenly mixing coal gangue and nickel slag subjected to ball milling and sieving, adding water to form a Bingham slurry, molding, drying, and calcining the mixture in a high temperature furnace. SiO2 and Al2O3 produced from decomposition of the main mineral composition kaolinite in coal gangue and MgO produced from decomposition of the main mineral composition forsterite in nickel slag at certain temperature are subjected to physical-chemical reaction at more than 1200 DEG C to generate a cordierite phase, so as to prepare the sintering body with principal crystalline phase of cordierite. At the same time, the other impurity mineral components in coal gangue can play a role of fluxing action in the sintering process to reduce the sintering temperature.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE
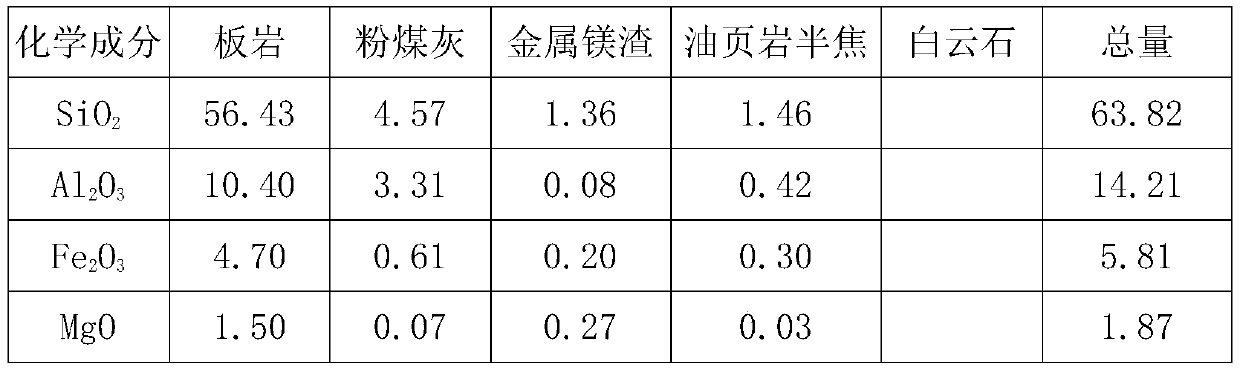
Lightweight and high-strength ceramsite prepared by taking slate as raw material, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110627521AHigh strengthLower firing temperatureCeramic materials productionCeramicwareSlagExpanded clay aggregate
The invention discloses a lightweight and high-strength ceramsite prepared by taking slate as a raw material, and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of preparation of building materials. The lightweight and high-strength ceramsite is prepared from the raw materials by mass percent: 50% -90% of slate, 5% -30% of fly ash, 2% -6% of metal magnesium slag, 1% -10% of oil shale semicoke and 1% -4% of dolomite. The fly ash added into the lightweight and high-strength ceramsite taking slate as the raw material can reduce SiOs as well as increase the Al2O3 content; the occupation on a large amount of land by the slate tailings piling can be reduced, thereby relieving the serious threat on the ecology, the environment and the human health, and further solving the problem that the ceramsite product on the former market is high in piling density, high in water absorption and low in cylinder pressure strength; a value in use of the slate taiings, the metal magnesium slag, the oil shale semicoke and flyash are improved, the solid wastes are changed into valuables, and the lightweight and high-strength ceramsite is suitable for the industrial production.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Prepraiton method of high-carbon metallized pellets for electric furnace
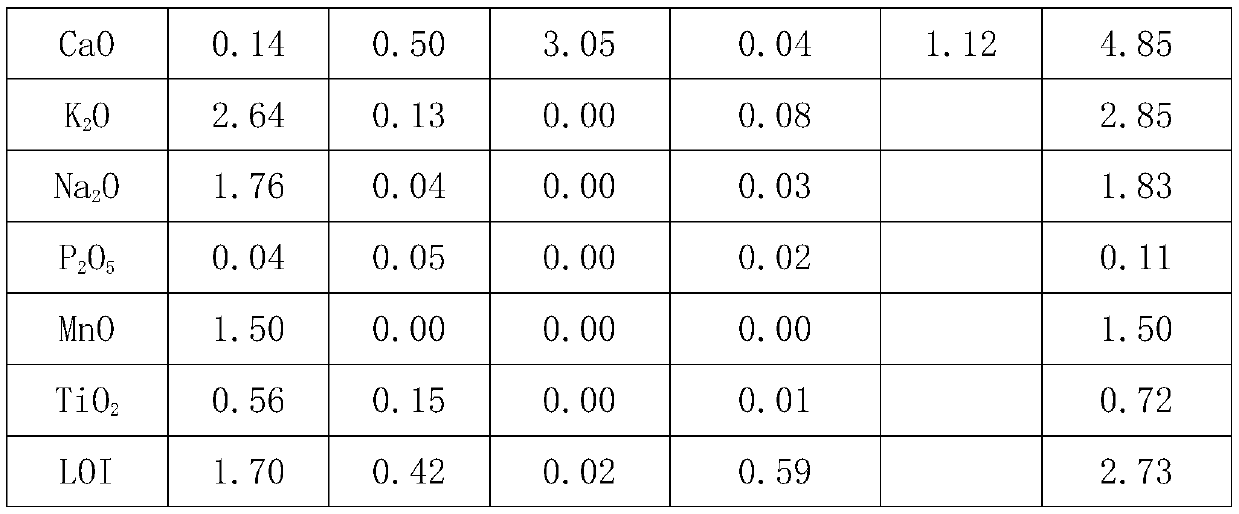
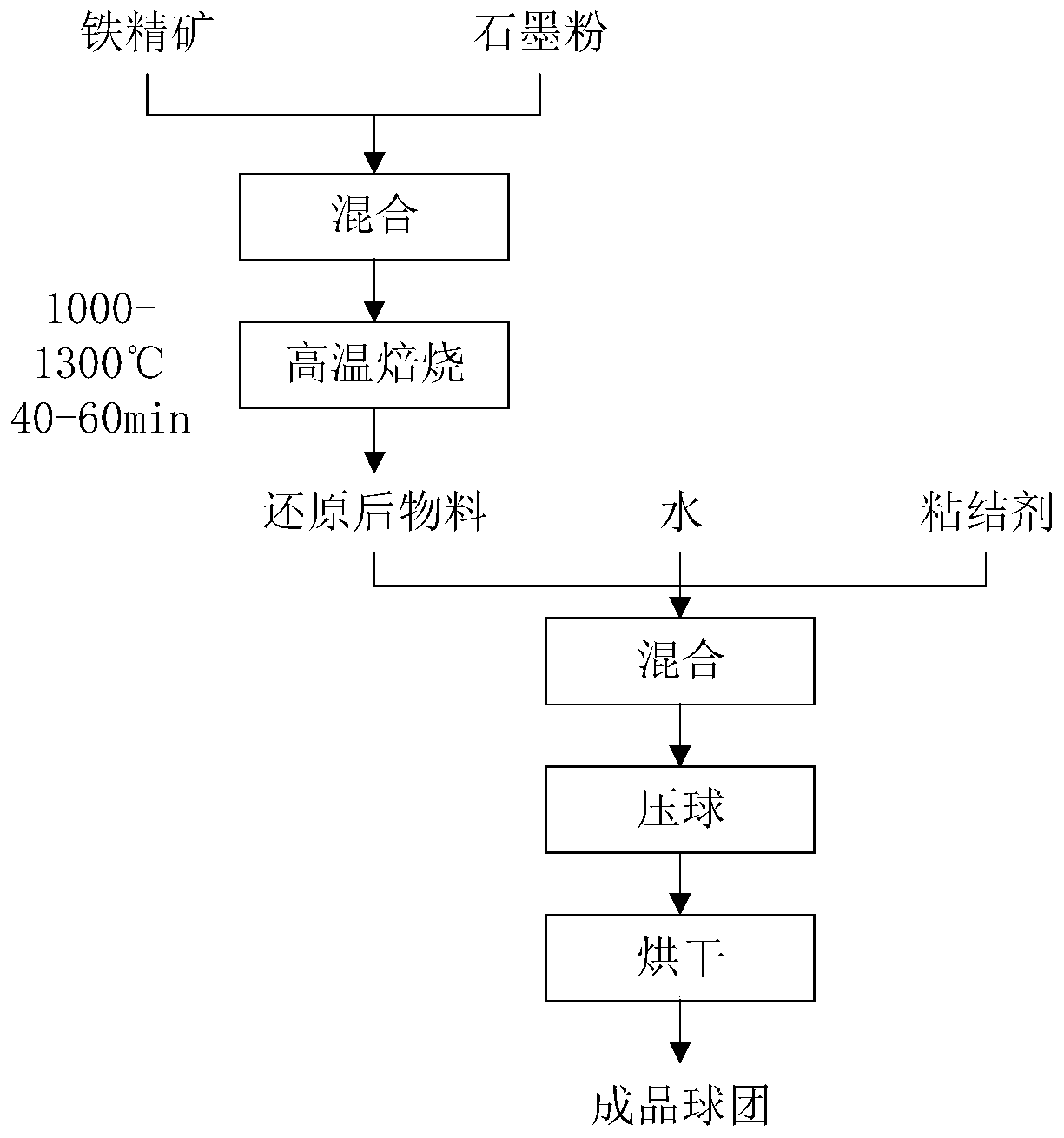
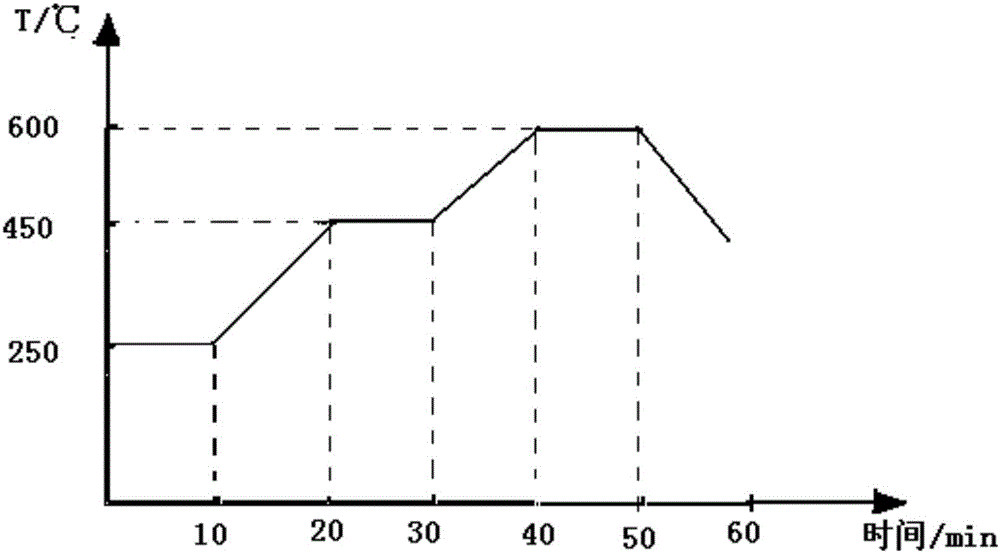
The invention discloses a preparation method of high-carbon metallized pellets for electric arc furnace smelting. The preparation method comprises the steps that carbon-containing powder is added intoiron concentrate for material preparation according to the mass ratio of carbon to iron of 1.5-2:1, prereduction is carried out at a reduction temperature of 1000-1300 DEG C for 40-60min, the reduction product is ground to 0.4-0.5 mm granularity, 4-6% of a binding agent and 9-12% of water are added, the mixture is mixed evenly, pressed into pellets and dried at the temperature of 120-140 DEG C for 60-90min, the high-carbon metallized pellets are obtained, and the pellets can reach the falling strength of 3-4 and reach the density of 2.6-3.3g / cm<3>. Molten steel can be stably and efficiently recarburized by the pellets below the slag-steel interface, the problems that the density of conventional carburant is insufficient, the carburant rapidly floats on the surface of furnace slag after being added, and the carburizing effect is poor are solved, meanwhile, the pellets can perform a good carbon-oxygen reaction below the slag-steel interface to remove inclusions and gas, formation of a large amount of foam slag is promoted, electric arc is stabilized, smelting time is shortened, iron loss is effectively reduced, steel material consumption is remarkably reduced, the metal yield is improved, and the smelting cost is reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Low-melting-point glass sizing agent and preparation method thereof
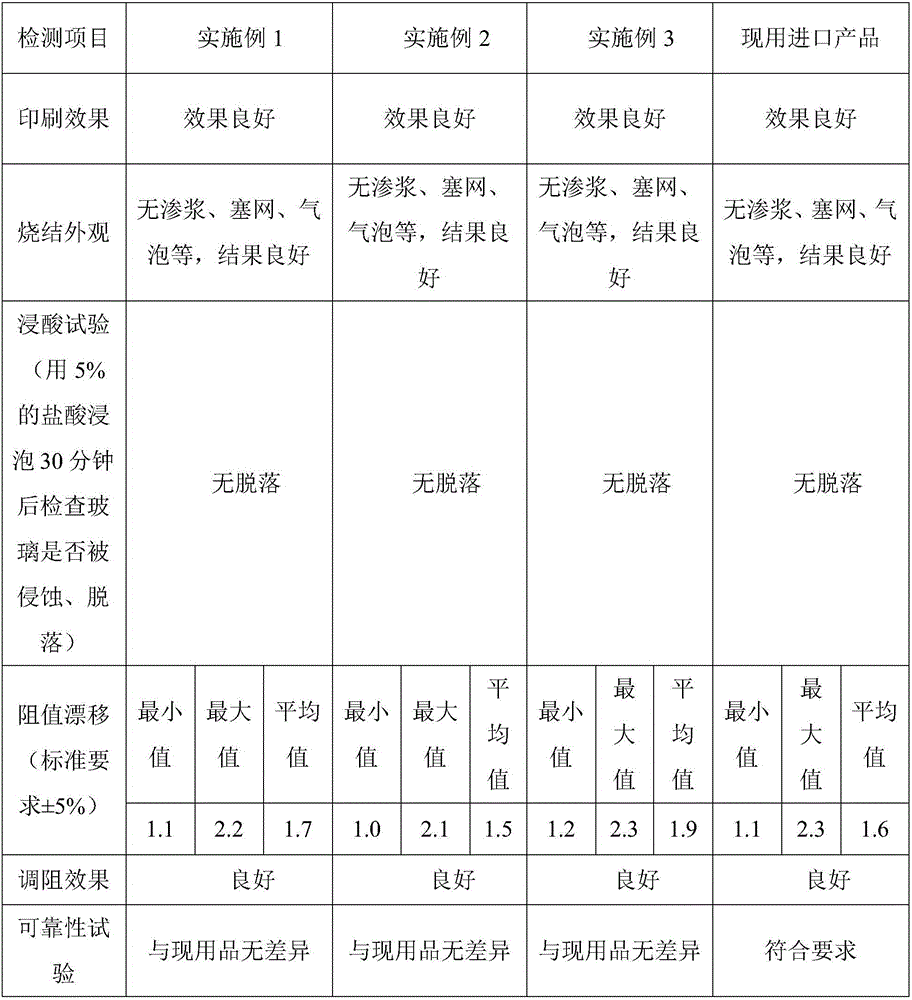
The invention discloses a low-melting-point glass sizing agent, which is prepared from, by weight percent, 50-80% of glass powder, 1-10% of inorganic pigment, and 19-40% of organic carrier; the glass powder is prepared from, by weight percent, 10-30% of B2O3, 10-25% of SiO2, 50-70% of Bi2O3, and 1-10% of Nb2O5; the inorganic pigment is inorganic composite oxide and consists of at least two transition metal oxides; the organic carrier is prepared from, by weight percent, 10-30% of high-molecular polymer, 40-85% of organic solvent, 5-30% of organic additive. The low-melting-point glass sizing agent is used for a thick film type resistor and excellent in both printing property and insulation property. The invention can effectively solve the problems of glass packing sizing agent in resisting acid, electroplating, heat impact and others; the materials can meet the EU RoHS environmental-friendly requirements.
Owner:广东羚光新材料股份有限公司
Novel metallurgical auxiliary material flux and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a metallurgical auxiliary material flux and a preparation method thereof, which is characterized in that: the metallurgical auxiliary material flux is composed of the following components in percentage by weight: ferric oxide Fe2O3 60% to 75%, calcium oxide CaO 20% to 35% %, the sum of impurity content ≤5.0%. The components of the above-mentioned metallurgical auxiliary flux flux are crushed into particles of ≤20mm, mixed evenly, and then smelted at a high temperature of 1350°C to 1400°C, and the melting reaction produces a block material with a mineral phase structure of 2CaO·Fe2O3 as the main phase. After it is cooled, it is processed into a powder with a fineness of -200 mesh. The method of using the metallurgical auxiliary material flux is as follows: the added amount of the flux is 4-6% of the weight percentage of sintered ore or converter reduction pellets (at this time, the flux effect is the best). Mix well after adding. Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effects of the present invention are as follows: one is useful slagging material (CaO) and iron material (TFe) that can be reduced to iron; The auxiliary materials can be used for melting, and the effect of melting is stable; the third is that it does not pollute the environment.
Owner:LIAONING TIANHE TECH
Graphene ceramic material and preparation method thereof
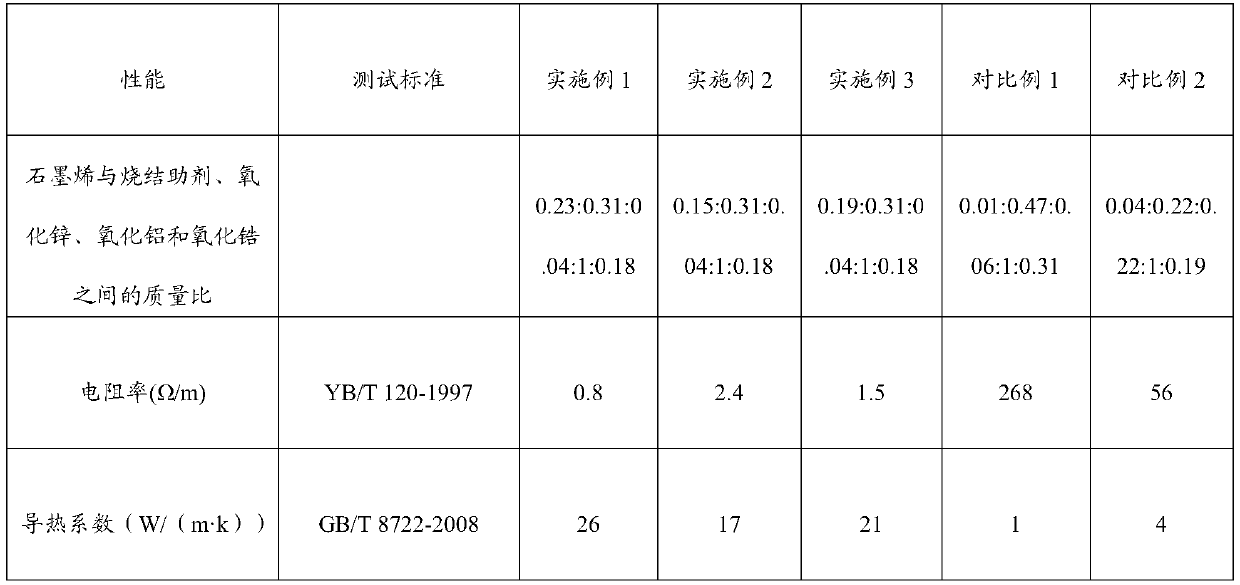
The invention provides a graphene ceramic material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of material preparation. The graphene ceramic material is prepared from the following rawmaterials: sintering auxiliaries, graphene, zinc oxide, aluminum oxide, zirconia and water; graphene accounts for 9%-13% of the total material mass; the total material comprises the sintering auxiliaries, graphene, zinc oxide, aluminum oxide and zirconia in a mass ratio of (0.25-0.35):(0.03-0.05):(0.5-1.5):(0.15-0.20). In the invention, by adjusting the mass ratio between graphene and the sintering auxiliaries, zinc oxide, aluminum oxide and zirconia, the thermal conductivity of the material is increased and the resistivity is reduced.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Additive for improving mechanical properties of a silicon-manganese alloy
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of silicon-manganese alloy, and specifically relates to an additive for improving mechanical properties of a silicon-manganese alloy, the additive includes the following raw materials: silicon powder, manganese powder, aluminum powder, a titanium dioxide composite, a surfactant, polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber, alpha-cyanoacryloyl isobutyl glycolate, a flux, heterocycle-containing aminophosphate, manganese hydroxide and guanidine nitrate. Compared with the prior art, the additive has the following advantages: the silicon-manganese alloy can be fluxed and refined by reasonable proportioning of raw materials, production of toxic substances can be avoided in the reaction process, by the synergistic effect of the polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber and the alpha-cyanoacryloyl isobutyl glycolate, the hard water resistance can be enhanced, and the abrasion performance of the heterocycle-containing aminophosphate can also be enhanced. The additive can effectively improve the mechanical properties of the silicon-manganese alloy, increases the melting-resistant temperature, reduces the power consumption during smelting, and is suitable for promotion and use.
Owner:刘少标
Method for preparing lightweight aggregate through low-temperature self-heating sintering of multiple types of coal gangues
ActiveCN113387605AEasy to handleRealize multi-level utilizationCeramic materials productionCeramicwareUltimate tensile strengthParticle-size distribution
The invention discloses a method for preparing lightweight aggregate through low-temperature self-heating sintering of multiple types of coal gangues. The method comprises the following steps: crushing, proportioning, mixing, granulating, distributing, igniting, sintering, cooling, crushing and screening multiple different types of coal gangues in sequence to obtain the lightweight aggregate with the density grade of 500-700. According to the method, multiple types of coal gangues are matched and combined for use, the lightweight aggregate with small density and high mechanical strength is obtained through self component adjustment under the condition of not additionally using a sintering additive, and a large amount of multiple types of coal gangue solid waste can be consumed at the same time; in the preparation process of the lightweight aggregate, the aim of reducing the sintering temperature is achieved by adjusting the particle size distribution and proportion of the raw materials, so that the addition of a fluxing agent can be avoided; and the method realizes low energy consumption, high yield and low cost in the production process of the coal gangue lightweight aggregate, has the advantage of large quantity by utilizing a sintering machine for treatment, and is beneficial to large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-temperature phase-change heat storage material, heat storage brick and preparation method of heat storage brick
ActiveCN111004018AImprove surface activitySmall coefficient of thermal expansionHeat-exchange elementsThermal dilatationBrick
The invention provides a high-temperature phase-change heat storage material, a heat storage brick and a preparation method of the heat storage brick. The high-temperature phase-change heat storage material comprises a base material, a phase-change material, an adhesive and a sintering aid, and the base material comprises fused magnesium oxide. The high-temperature phase change heat storage material comprises the fused magnesium oxide. The fused magnesium oxide has relatively high surface activity and relatively low thermal expansion coefficient; the surface tension of particles in the sintering process can be reduced, so that the raw material particles can be fully contacted and fused in the sintering process, the cohesiveness among the particles is better, the sintering is facilitated, and the phenomena of serious cracking, deformation or insufficient strength cannot occur when the heat storage brick, especially a large-size heat storage brick, is prepared.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD +2
Foaming ceramic based on phosphate tailings and coal gangue and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114409431APromote generationLow viscosityCeramic materials productionCeramicwareHeat conservationCoal gangue
The invention relates to foamed ceramic based on phosphate tailings and coal gangue and a preparation method of the foamed ceramic. According to the technical scheme, 60-80 wt% of phosphate tailings and 20-40 wt% of coal gangue serve as raw materials and are mixed and stirred, 3-5 wt% of a binding agent and 5-9 wt% of water are added, stirring, mechanical pressing and drying are conducted, and a green body is prepared; and heating the green body to 600-650 DEG C at a rate of 5-10 DEG C / min, then heating to 900-950 DEG C at a rate of 3-4 DEG C / min, then heating to 1150-1200 DEG C at a rate of 1-2 DEG C / min, carrying out heat preservation for 30-90 minutes, and carrying out furnace cooling to room temperature, thereby obtaining the foamed ceramic based on the phosphate tailings and the coal gangue. The method is high in recycling rate, low in cost and simple in process, and the prepared product is low in volume density, high in compressive strength, small in heat conductivity coefficient and high in acid resistance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Alkali-free substrate glass and thinning method thereof
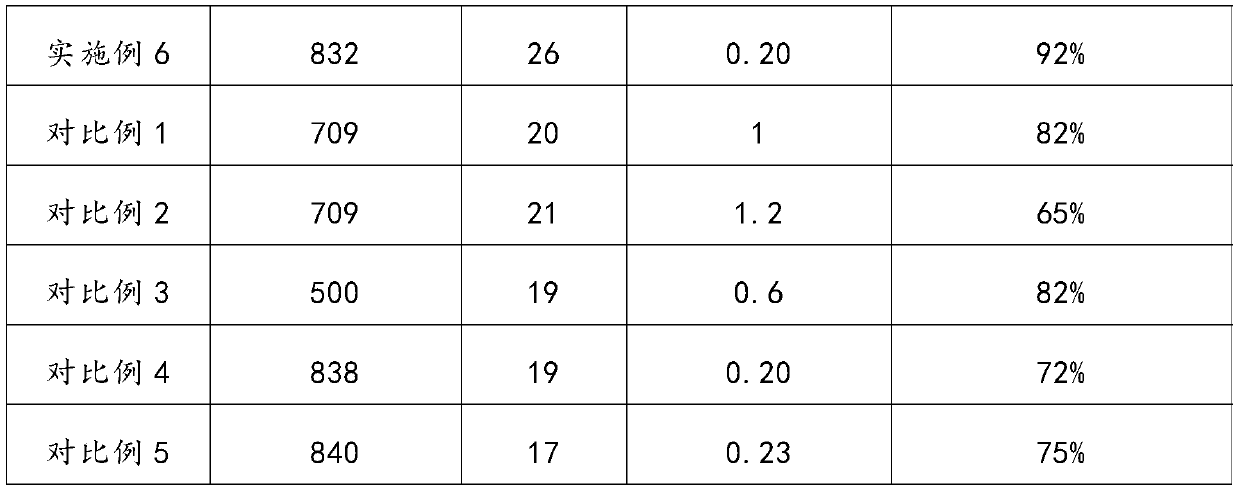
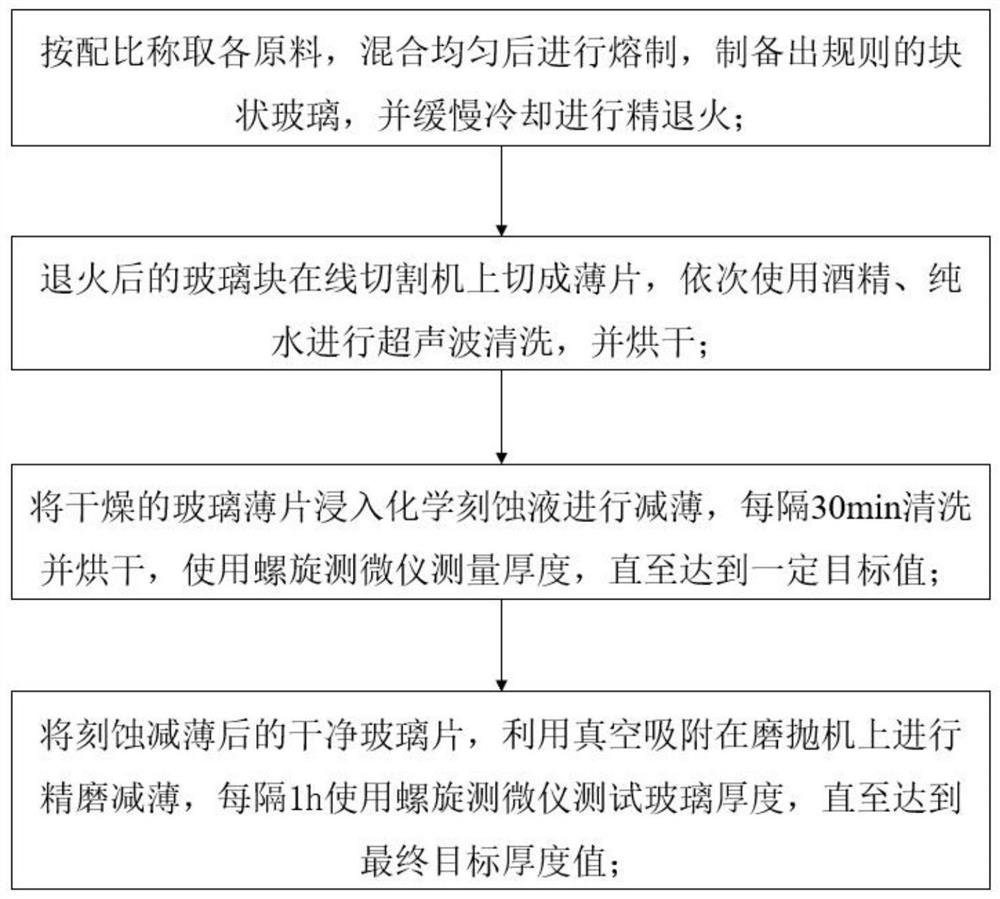
PendingCN113880429AReduce thicknessBendableLapping machinesWork carriersHydrofluoric acidAcetic acid
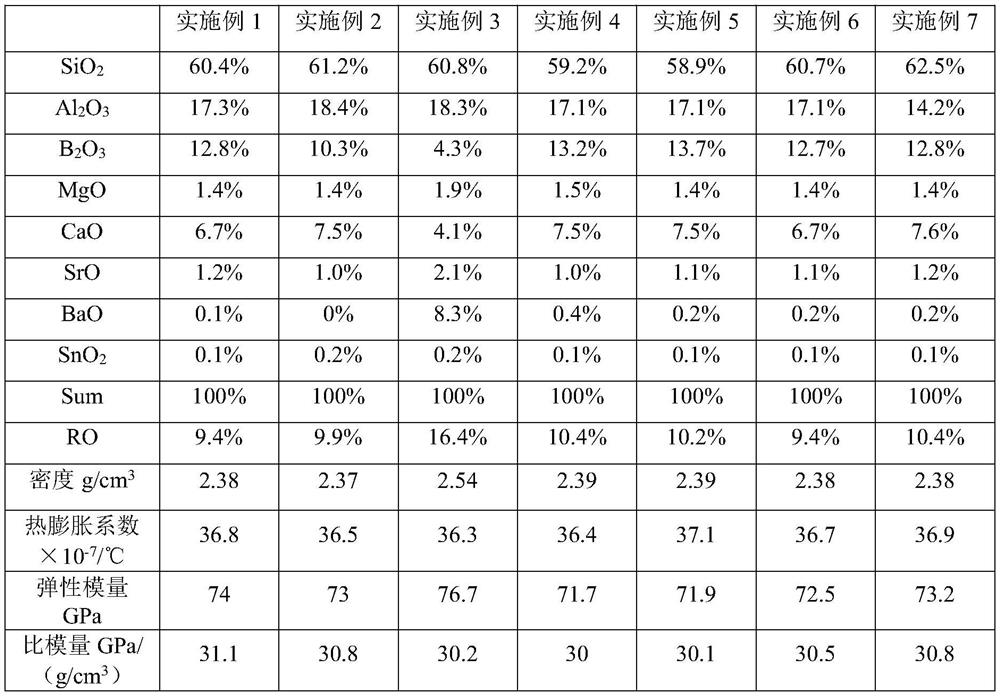
Alkali-free substrate glass comprises the components in percentage by mass: 58.9% to 62.5% of SiO2, 14.2% to 18.4% of Al2O3, 4.3% to 13.7% of B2O3, 1.4% to 1.9% of MgO, 4.1% to 7.6% of CaO, 1.0% to 2.1% of SrO, 0 to 8.3% of BaO and 0.1% to 0.2% of SnO2. The thinning method comprises the following steps: immersing the alkali-free substrate glass into a chemical etching solution composed of hydrofluoric acid, a glacial acetic acid surfactant and the balance being water, thinning the alkali-free substrate glass to 0.4 mm-0. 5mm, taking out the alkali-free substrate glass, and carrying out ultrasonic cleaning and drying; and placing the alkali-free substrate glass on a grinding disc of a grinding and polishing machine, and carrying out mechanical polishing, thinning the alkali-free substrate glass to 0.3 mm-0.35 mm, and thus obtaining the flexible substrate glass. The alkali-free substrate glass is reasonable in composition, the specific modulus value of the prepared alkali-free glass is moderate, the glass has good flexibility, the thinning method is convenient to operate, the alkali-free substrate glass with the thickness of 0.7 mm is thinned by combining two modes of chemical etching thinning and mechanical polishing thinning, and the flexible substrate glass with smooth surface and bendable performance is obtained.
Owner:IRICO DISPLAY DEVICES
Honey peach rhinestone
Owner:JIANGSU JINCHENG GRP TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com