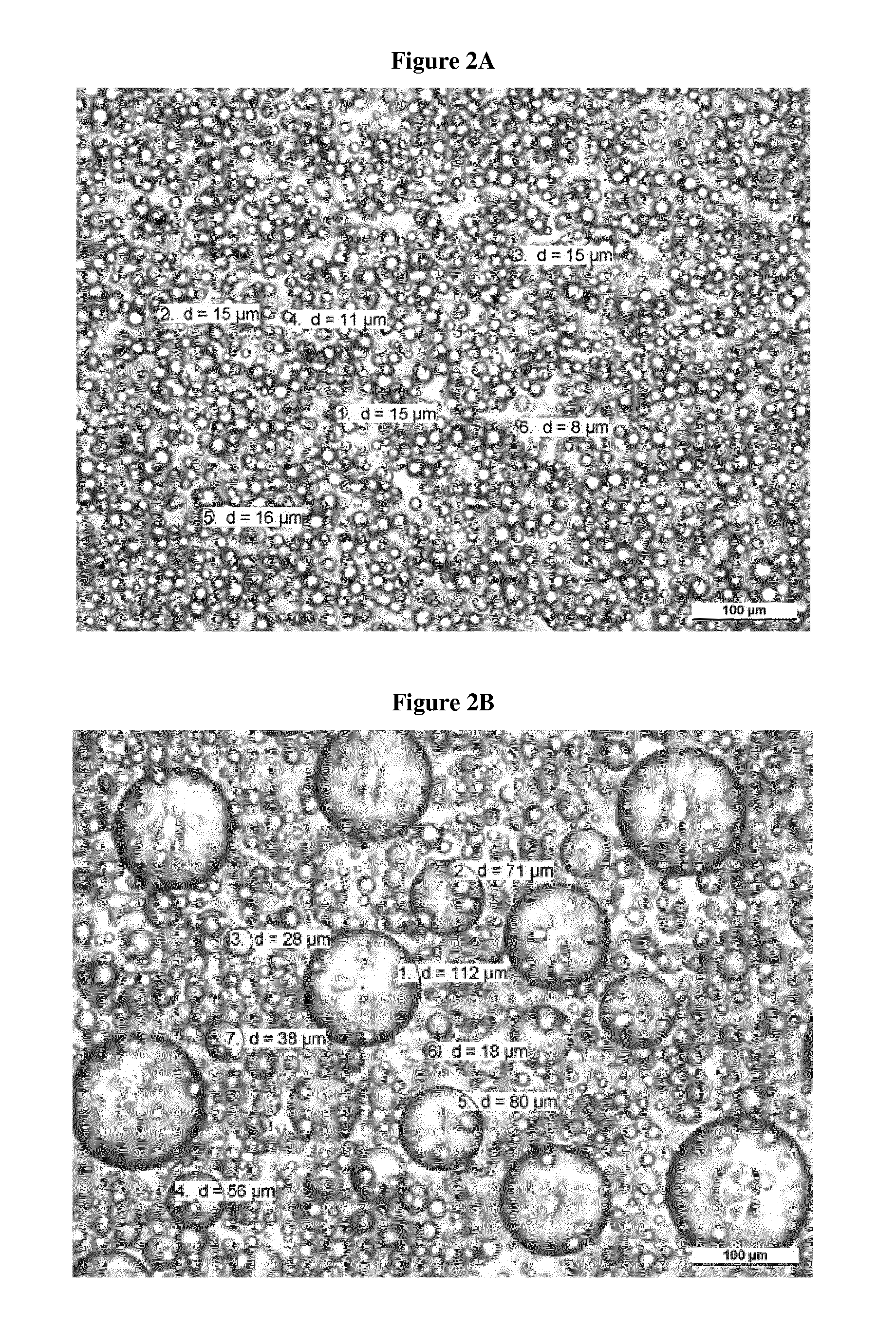
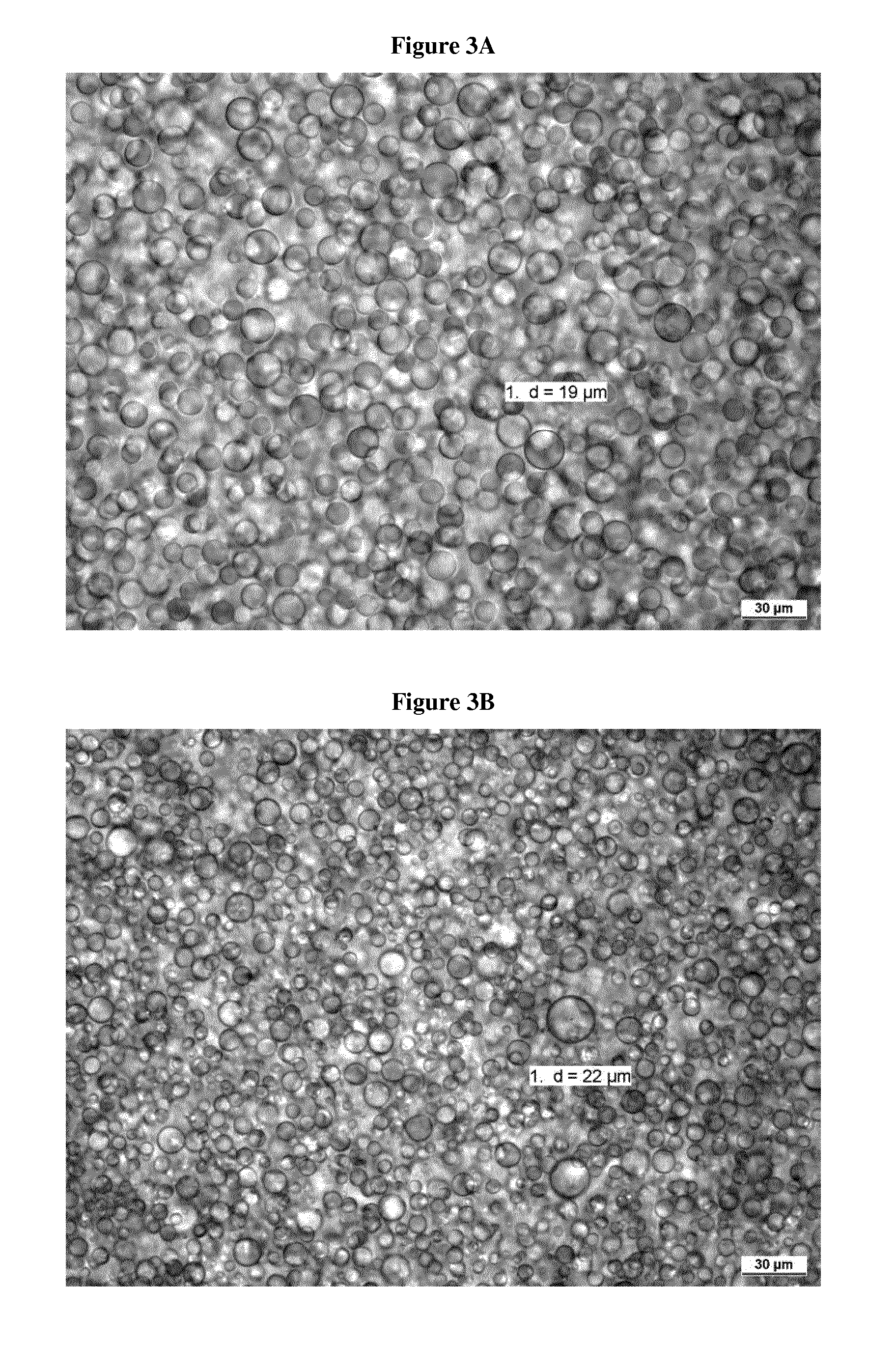
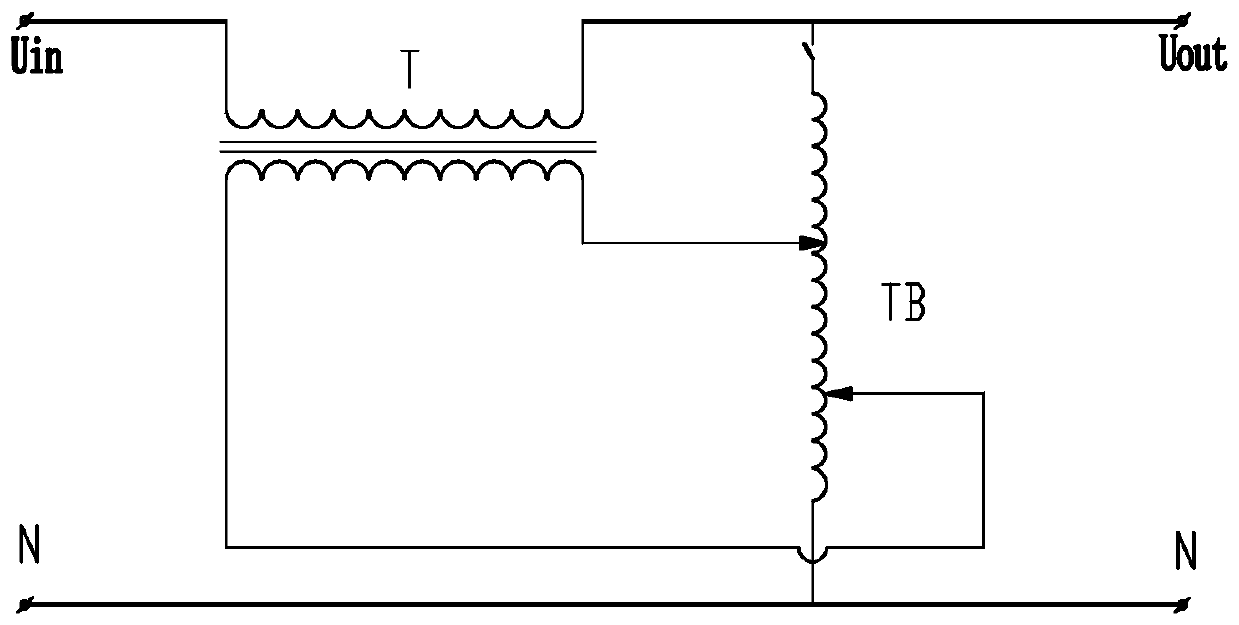
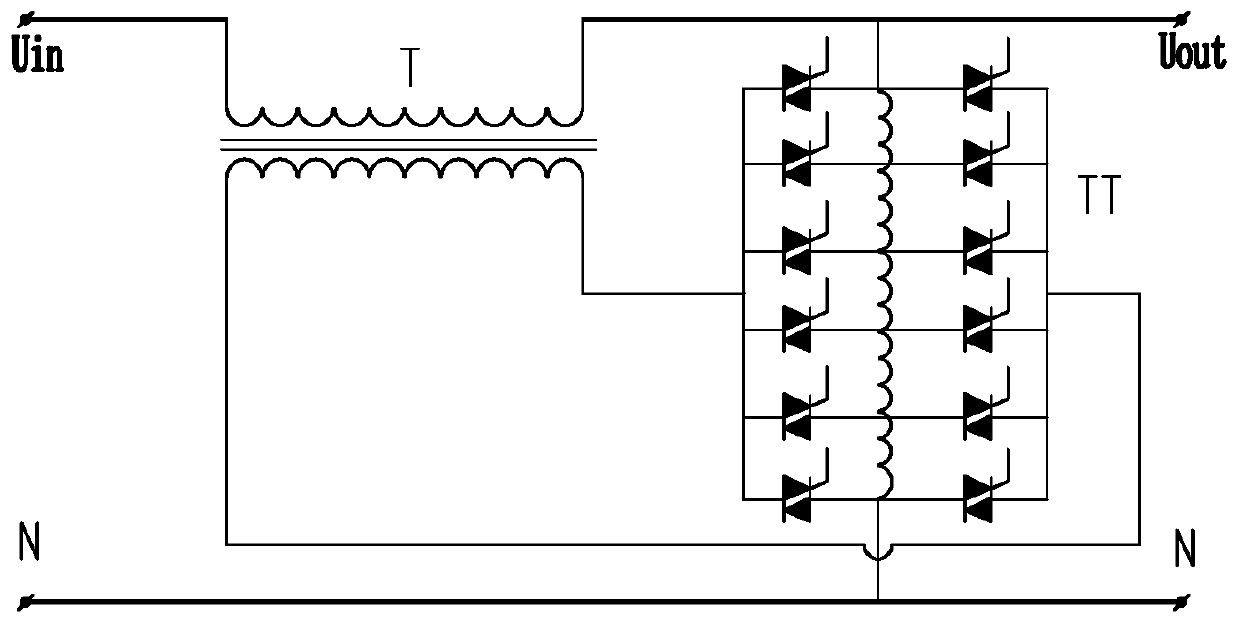
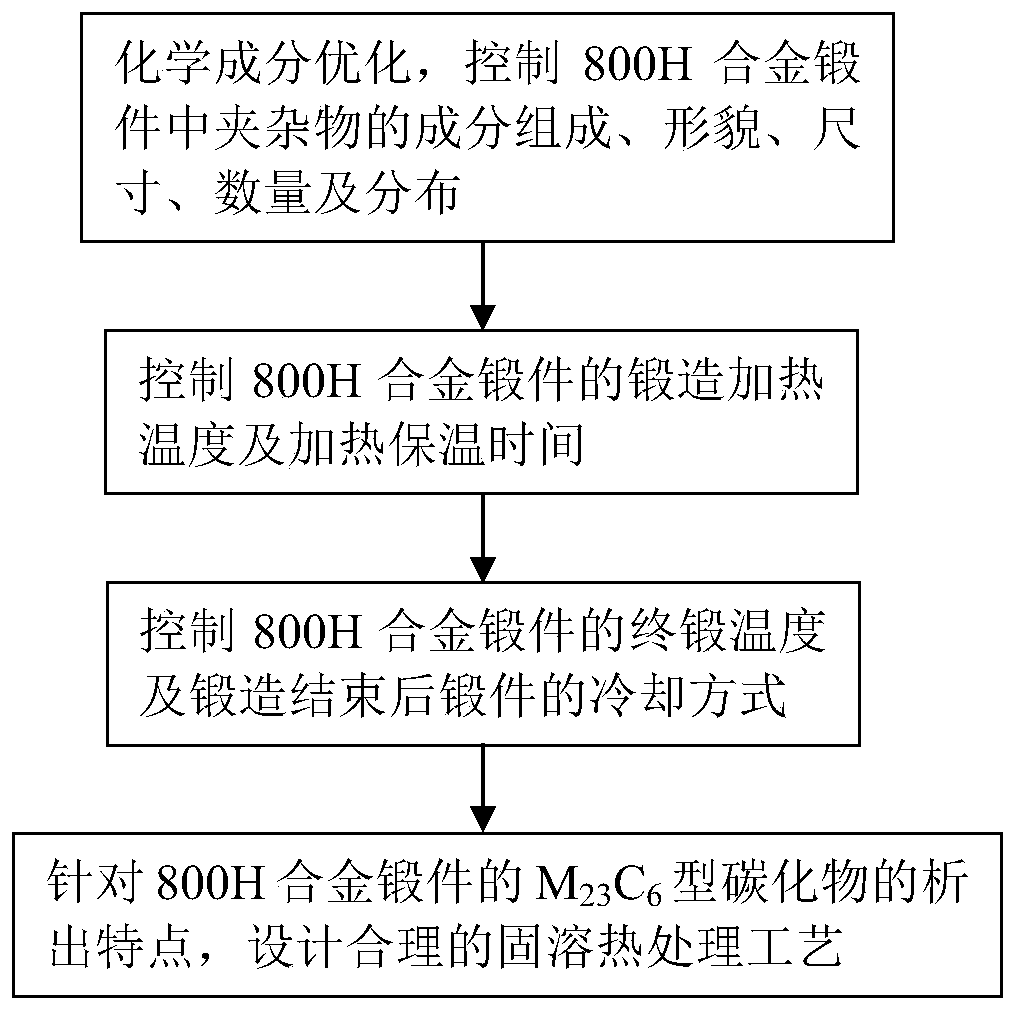
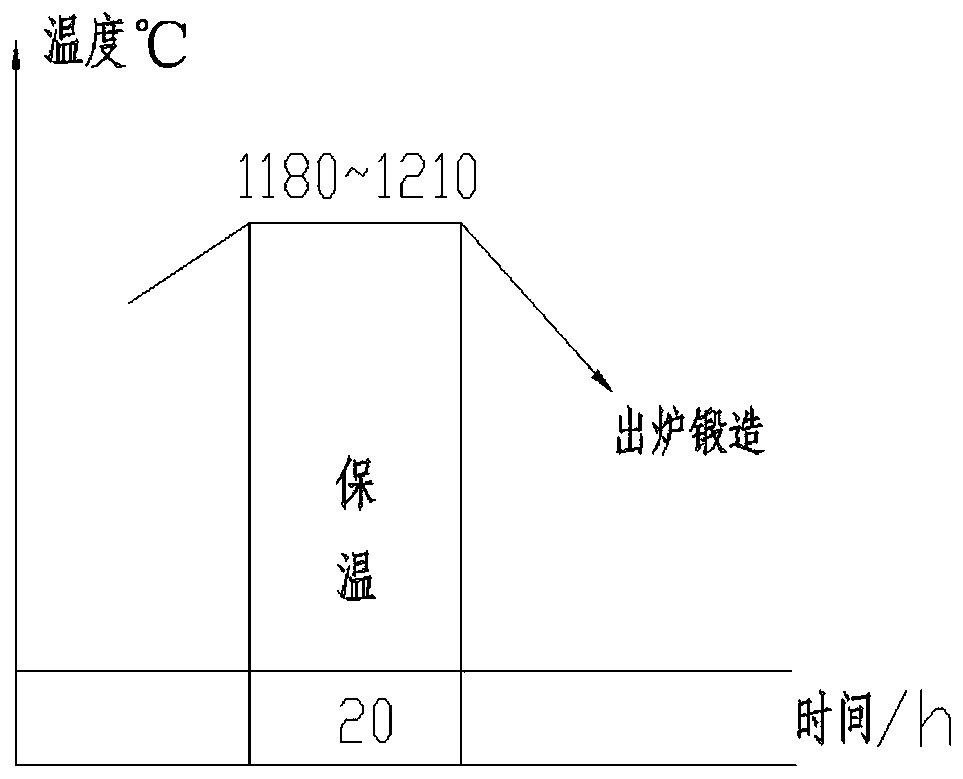
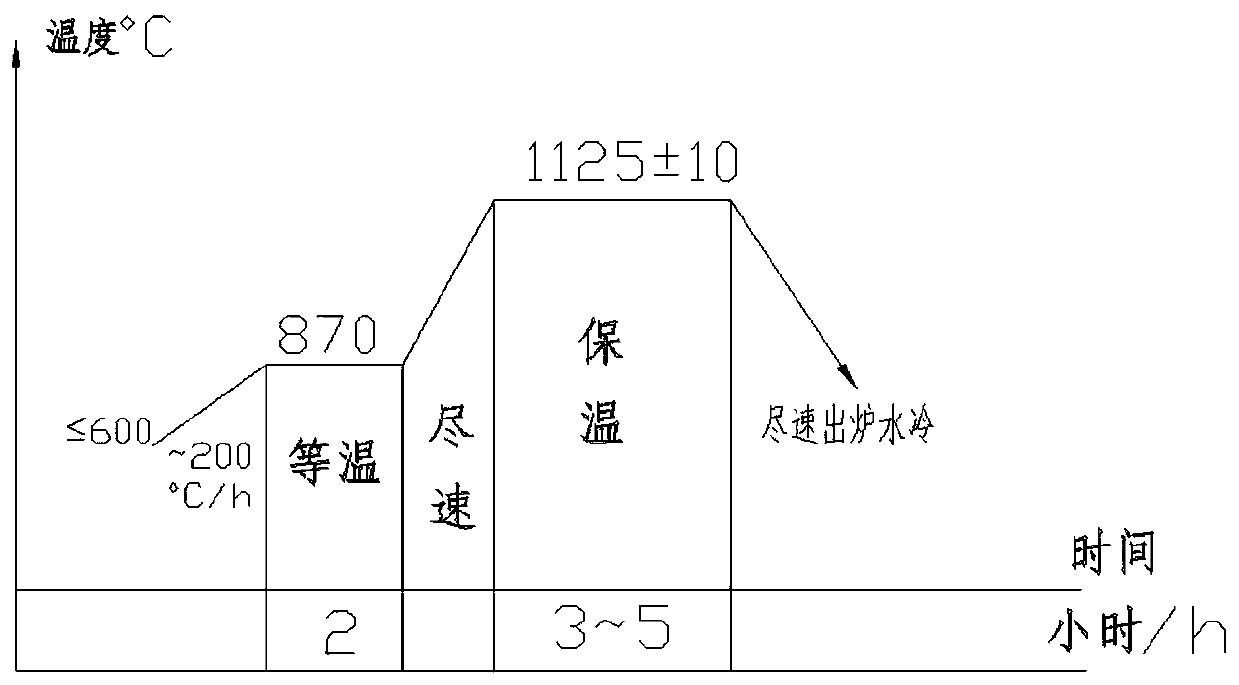
Patents
Literature
61results about How to "Reliable manufacturing process" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
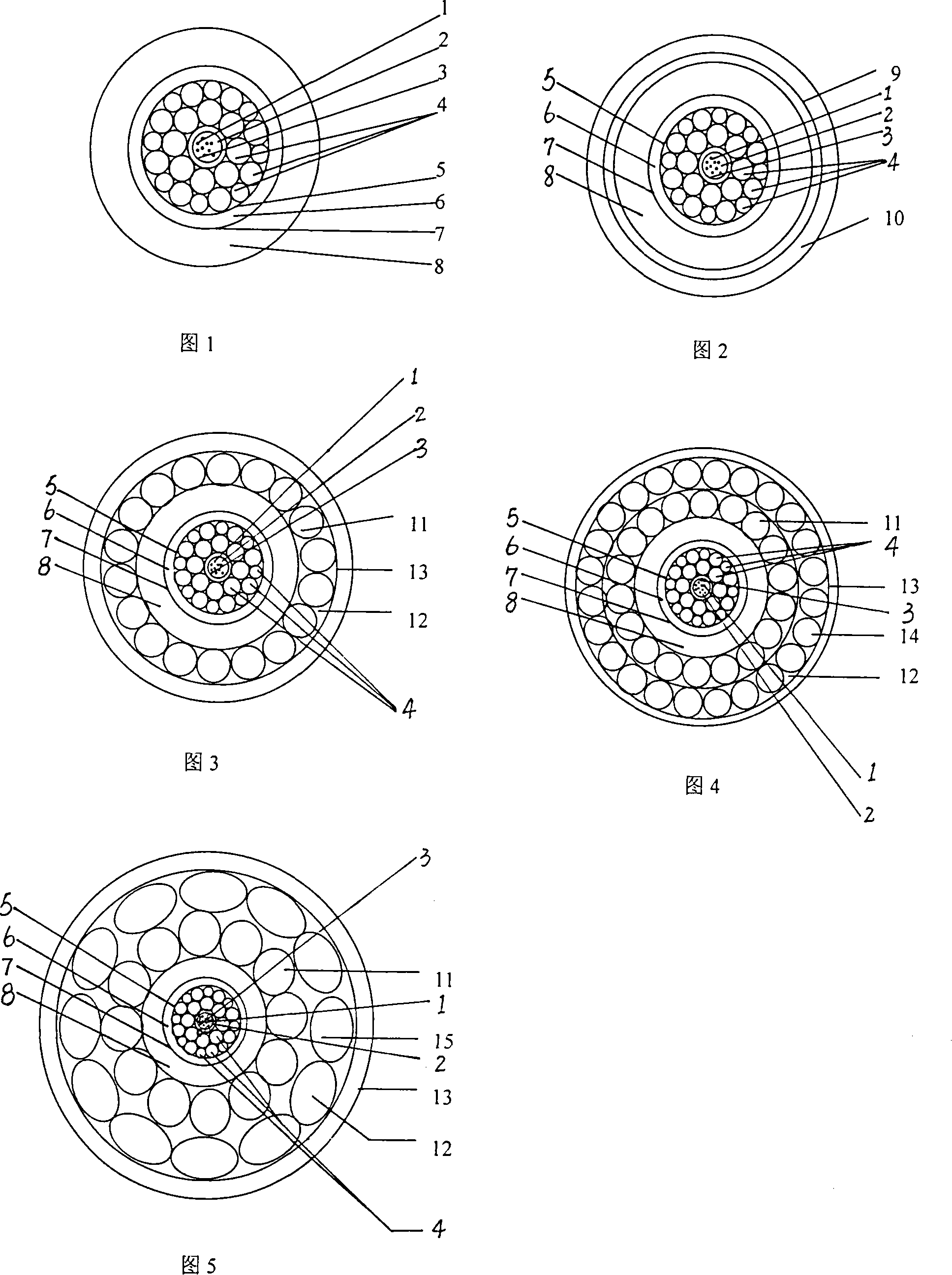
Deep sea optic cable and its manufacture method
InactiveCN101241213AGuaranteed lifeReasonable and reliable structureFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringHigh intensity
The invention provides a deep sea optical cable and producing method thereof, relating to a deep sea optical cable with a tension-resistant compact composite structure and producing method thereof. The structure of the deep sea optical cable comprises a plurality of full chromatogram high-strength optical fibres, high-strength anti-corrosion stainless steel tubes, ointment exclusive for sea cable optical fibre, special-high-strength armouring wires with three diversified diameters, a heavy viscous waterproof agent, metallic conductor brass pipes, organic plastic composite materials, and a polythene insulation material protective layer. High-strength anti-corrosion stainless steel tubes are sleeved on several full chromatogram high-strength optical fibres, ointment exclusive for sea cable optical fibre is filled into the high-strength anti-corrosion stainless steel tubes, special-high-strength armouring wires with three diversified diameters are inlaid on the outside of the high-strength anti-corrosion stainless steel tubes and are filled with heavy viscous waterproof agent of sufficient amount, the special-high-strength armouring wires are covered with the metallic conductor brass pipes, so that special tension-resistant compact composite structure is formed. Organic plastic composite materials are added on metallic conductor brass pipes, and then an insulation material protective layer is extruded thereon.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN TECH SUBMARINE CABLE CO LTD
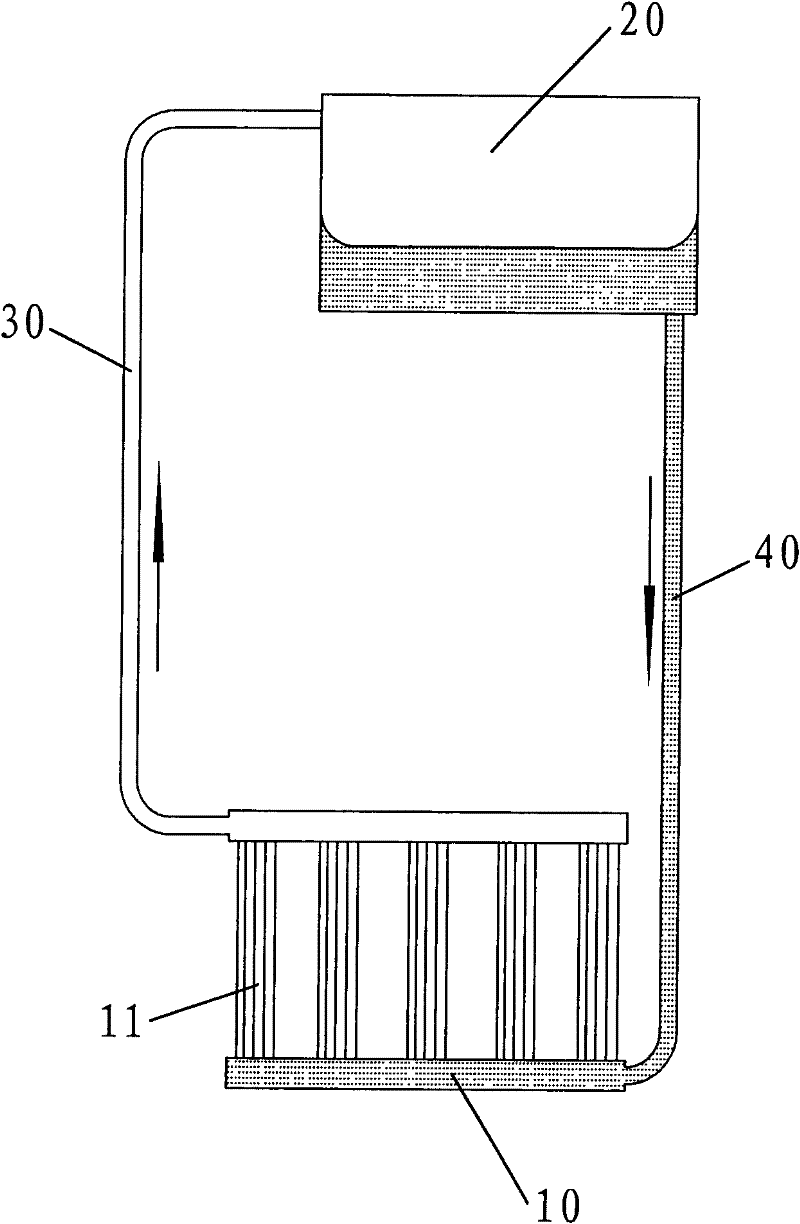
Loop gravity-assisted heat pipe heat transfer device
InactiveCN102538524AMeet the requirements for installation and useFully contactedIndirect heat exchangersGravity assistEngineering
The invention relates to a loop gravity-assisted heat pipe heat transfer device which mainly comprises an evaporator, a condenser, a steam pipe and a liquid pipe, wherein the evaporator is pipe-shaped, the evaporator is sealed and is filled with a working medium, an inlet of the steam pipe slightly extends into the top of the evaporator, and an outlet of the liquid pipe passes through the top of the evaporator and extends to the bottom of the evaporator; and an outlet of the steam pipe is communicated with the upper part of the condenser, and an inlet of the liquid pipe is communicated with the lower part of the condenser. The loop gravity-assisted heat pipe heat transfer device disclosed by the invention has excellent heat transfer performance and application expandability, can avoid installation difficulty, meets heat transfer requirements of vacuum tube heat collectors with any sizes and has the advantages of reliable structure and manufacturing process and lower cost.
Owner:北京芯铠电子散热技术有限责任公司
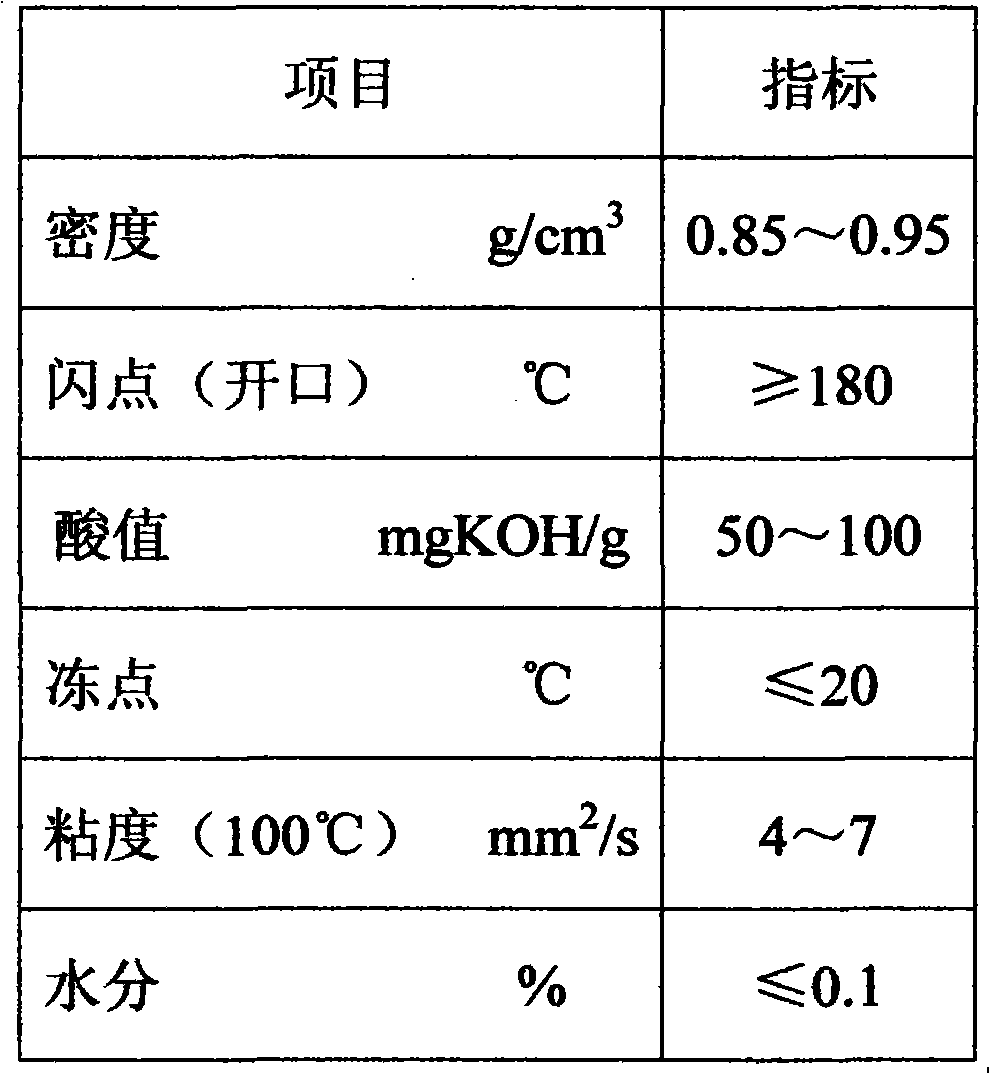
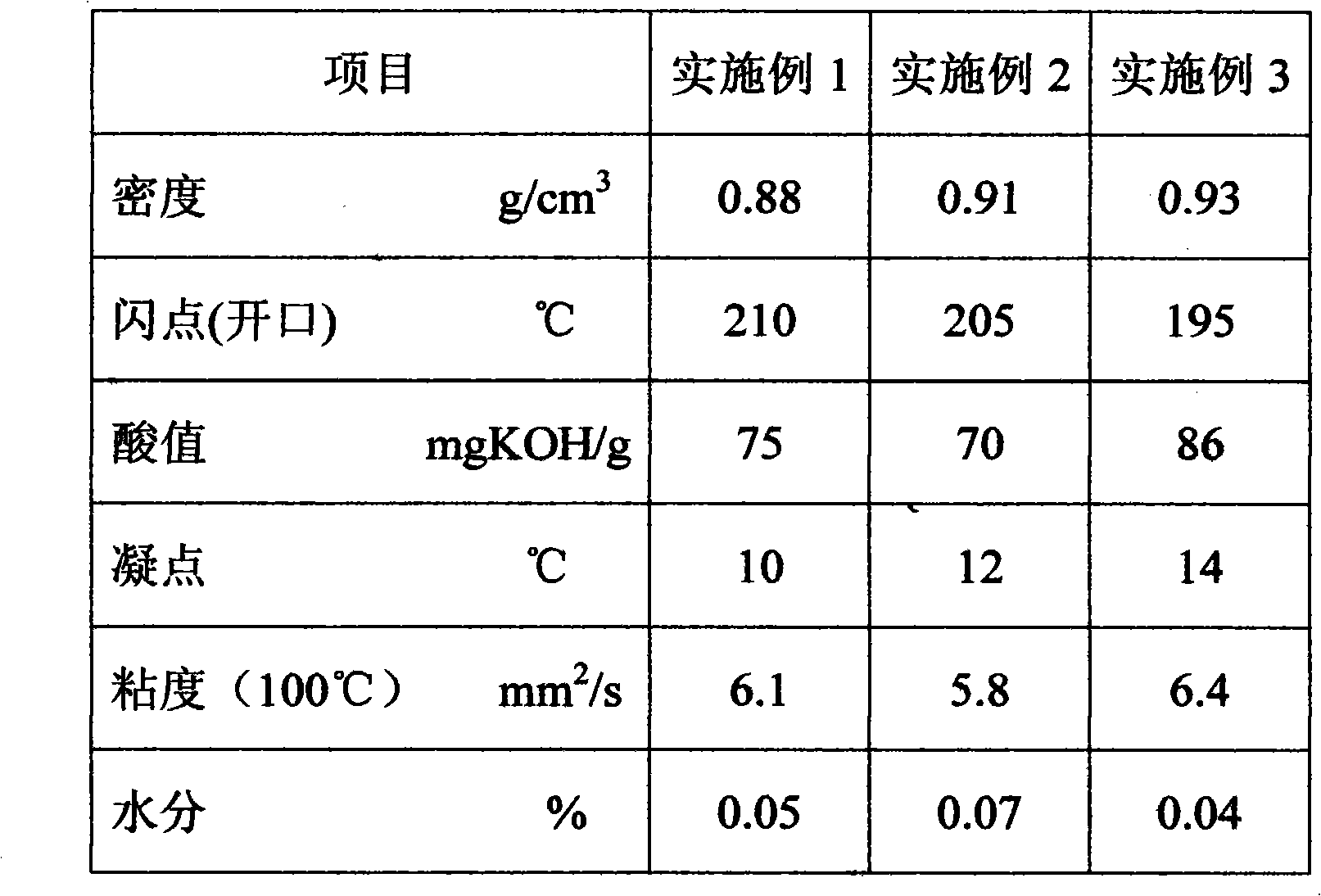
Water resistance vegetable composite oil phase
The invention relates to a water resistance vegetable composite oil phase which comprises the following components in percent by mass: 5-30 percent of hydrogenated vegetable fatty acid, 5-20 percent of vegetable wax, 20-50 percent of vegetable oil foot, 5-20 percent of vegetable oil and fat, 20-50 percent of decompressed cerate and 0.5-3 percent of surfactant. The water resistance vegetable composite oil phase is prepared by adopting the following steps of: firstly, heating various components in a single melting tank to the temperature of 75-85 DEG C and melting; and sequentially pumping the components into a reaction kettle through an oil pump according to the proportion requirement after weighted through an electronic scale, stirring, raising the temperature to 105-110 DEG C, starting a vacuum pump for dewatering, filtering, forming and packaging. The invention overcomes the defect of water resistance of the modified ammonium nitrate fuel oil explosive and extruded explosives, and provides a high-quality and low-cost water resistance vegetable composite oil phase used for the modified ammonium nitrate fuel oil explosive and extruded explosives; and the explosives produced by using the composite oil phase have excellent water resistance, and especially the extruded explosives really have excellent water resistance.
Owner:谢斌
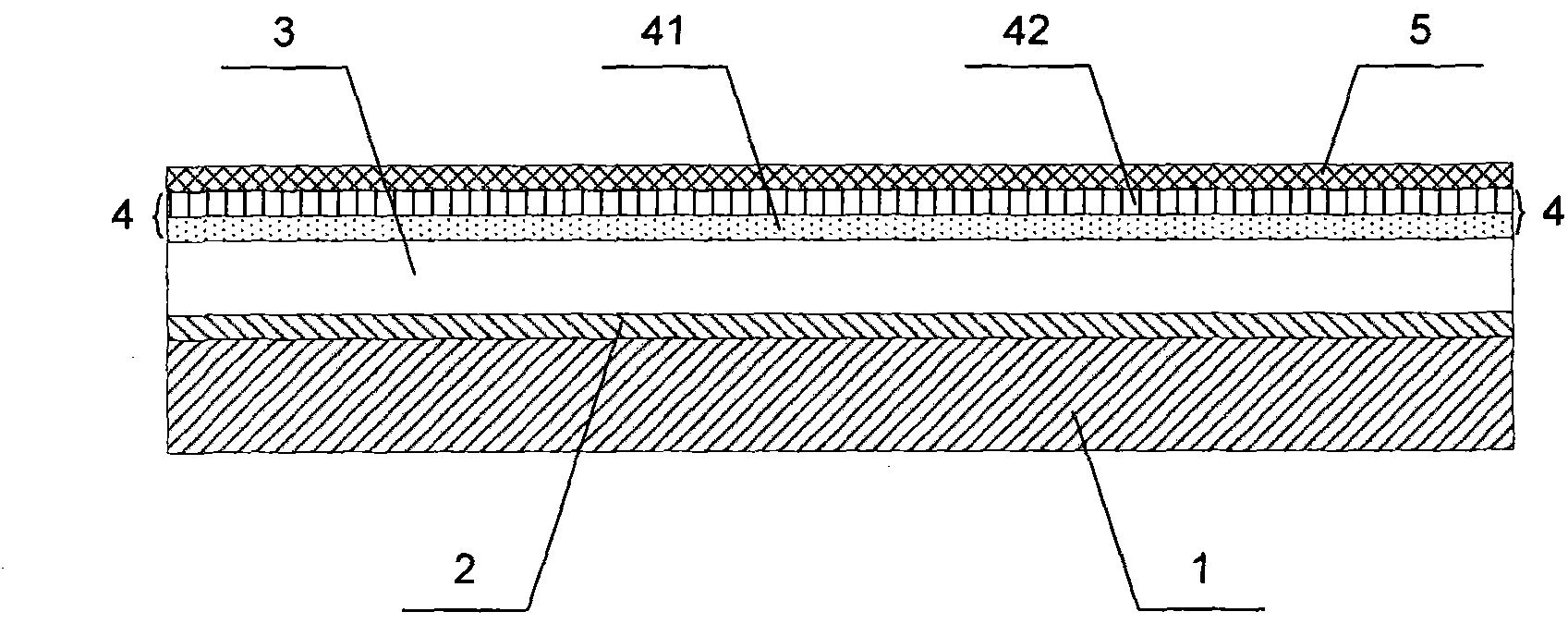
Organic electroluminescence component and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101783395ASolve defects such as low aperture ratioIncrease opening ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistanceDisplay device
The invention relates to an organic electroluminescence component and a manufacturing method thereof. The organic electroluminescence component comprises a basal plate, wherein a first electrode, an organic material layer, a second electrode and a sealing layer are sequentially formed on the basal plate, the first electrode is used as an anode, and the second electrode is used as a cathode and is a composite transparent structure layer for realizing the light emitting at the top. By forming the composite transparent cathode emitting light at the top, the invention enables the organic electroluminescence component to emit the light from the top and enhances the light-emitting utilization rate and the light transmission rate effectively, which not only enhances the aperture opening ratio of a display screen but also can obtain better display effect. Meanwhile, by adding a netty confluence layer on a semitransparent metal layer with high resistance, the invention ensures high transmissivity, also enhances the conducting power of current, meets the requirement of a top transmission type organic electroluminescence component effectively and can be applied to a display device with double-face display. The invention has simple and reliable structure and preparation process and extensive application prospect.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Manufacturing method of hard-base soft-structure internal combustion engine connecting rod
ActiveCN103921097AThe principle is simpleSimple and reliable manufacturing processMetal working apparatusBatch productionEngineering
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a hard-base soft-structure internal combustion engine connecting rod. The method includes the following steps of forging of a blank, coarse grinding of end faces, boring, rough boring of a large-head hole and a small-head hole, chamfering of the large-head hole, threaded hole machining, fracture splitting of a large-head end and assembling, accurate grinding of the end faces, semi-fine boring of the large-head hole and the small-head hole, tegular groove milling and oil groove boring, fine boring of the large-head hole and the small-head hole, flat grinding of the large-head end, parkerizing of the small-head hole, and cover removing, cleaning and assembling. The connecting rod comprises the large-head end, a rod body and a small-head end, the large-head end and the small-head end are arranged at two ends of the rod body respectively, the connecting rod is of an integral structure, and a connecting rod cover is arranged at the large-head end of the connecting rod. The manufacturing method is simple in principle, a manufacturing technique of a traditional internal combustion engine connecting rod is improved to provide a feasible and reliable manufacturing technique for the hard-base soft-structure internal combustion engine connecting rod, and particularly precision and performance of a soft structure of the small-head end of the connecting rod are guaranteed. Meanwhile, the method has the advantages of simple technique and low manufacturing cost, and is convenient for batch production.
Owner:广东四会实力连杆有限公司
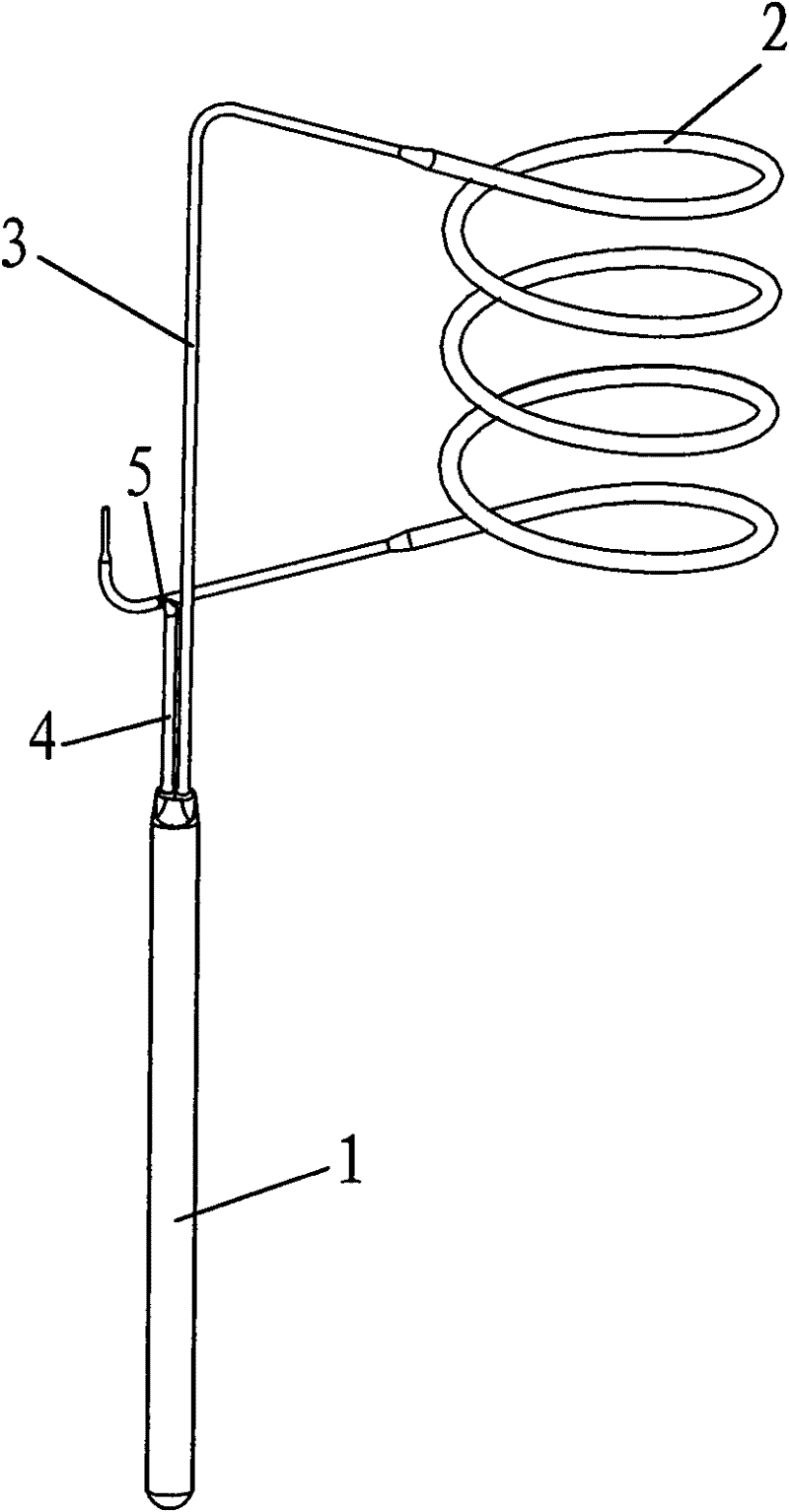
Electro-optic compound cable for towing and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101714425AReasonable designCompact structureCommunication cablesFibre mechanical structuresPolyesterSilver plate
The invention relates to an electro-optic compound cable for towing, which is an electro-optic compound cable capable of retracting and releasing repeatedly in special occasions, and used for transmitting optical signals and electrical signals. The cable core is formed by twisting high temperature silver-plated leads and optical fiber, and is protected by spiral metal hose at outside, and polyurethane material is extruded outside the steel tube. The cable is composed of a plurality of silver-plated leads, tight tube optical fiber, polyester belting, a spiral stainless steel hose, an aramid fiber twisted layer and a polyurethane jacket; the tight tube optical fiber and the silver-plated leads are twisted into the cable core in an S twisting form, the cable core is wrapped and fixed by the polyester belting, the spiral stainless steel hose is arranged outside the polyester belting, the aramid fiber twisted layer is arranged outside the spiral stainless steel hose, and the polyurethane jacket is extruded outside the aramid fiber twisted layer.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN BROADBAND TECH +1
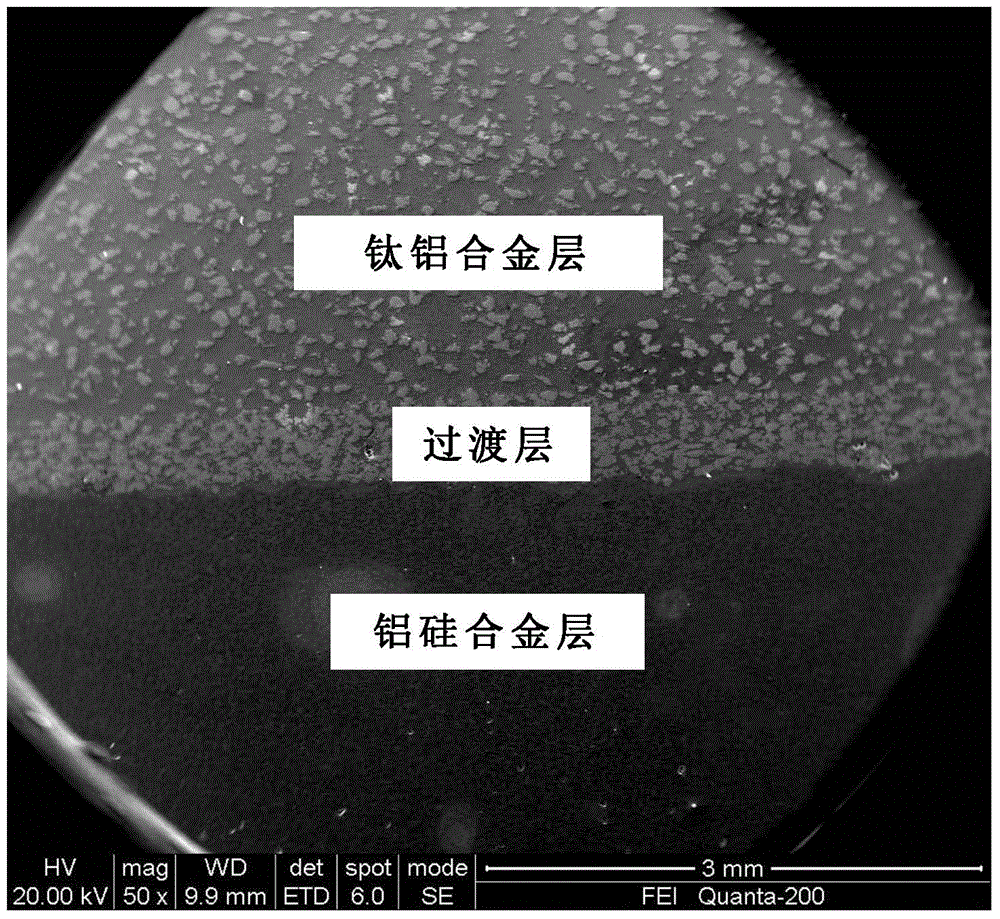
Double-layer titanium aluminum/aluminum silicon composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104651663ARealize the combinationInterface integration is goodSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicon alloyAlloy substrate
The invention relates to a double-layer titanium aluminum / aluminum silicon composite material as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of electronic packaging materials. The titanium aluminum / aluminum silicon composite material comprises a titanium aluminum alloy layer, an aluminum silicon alloy layer and a transition layer positioned between the titanium aluminum alloy layer and the aluminum silicon alloy layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: sintering aluminum powder and titanium powder under high temperature and high pressure to form a titanium aluminum alloy substrate, and then sintering premixed aluminum powder and silicon powder with the sintered and molded titanium aluminum substrate for the second time in a mold under a lower temperature and higher pressure, so as to obtain a titanium aluminum / aluminum silicon electronic packaging material blank with double-layer composite structure; and then annealing by vacuum diffusion, so as to obtain the titanium aluminum / aluminum silicon composite material. The preparation method has the advantages of short process, easiness in control over process parameters and the like; each performance of the prepared titanium aluminum / aluminum silicon composite material is excellent, especially the interface bonding property is attractive, so the material can be used as an electronic packaging material.
Owner:CHANGSHA XUNYANG NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
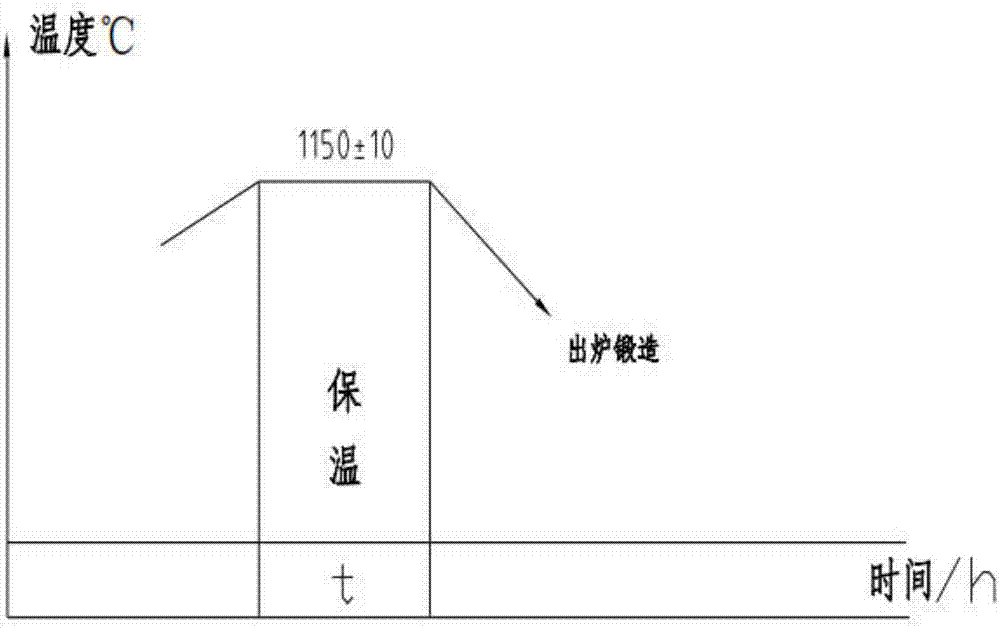
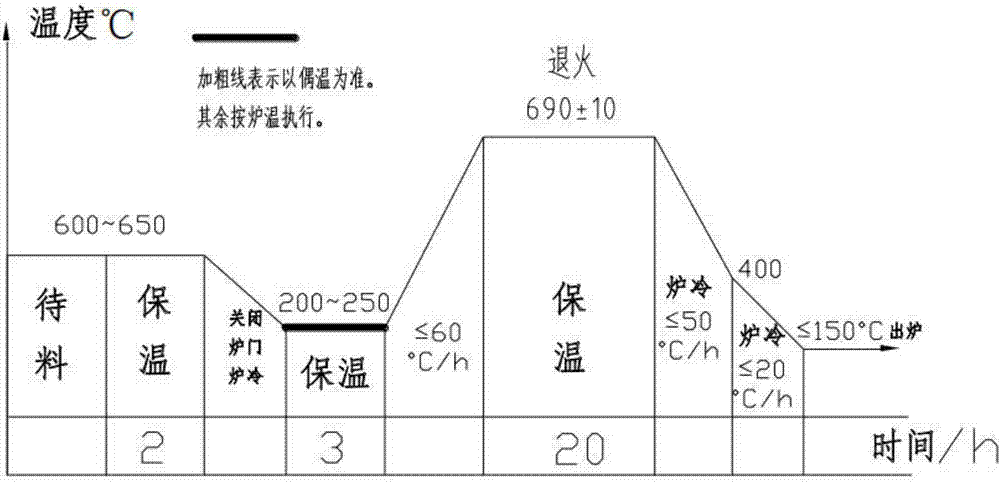
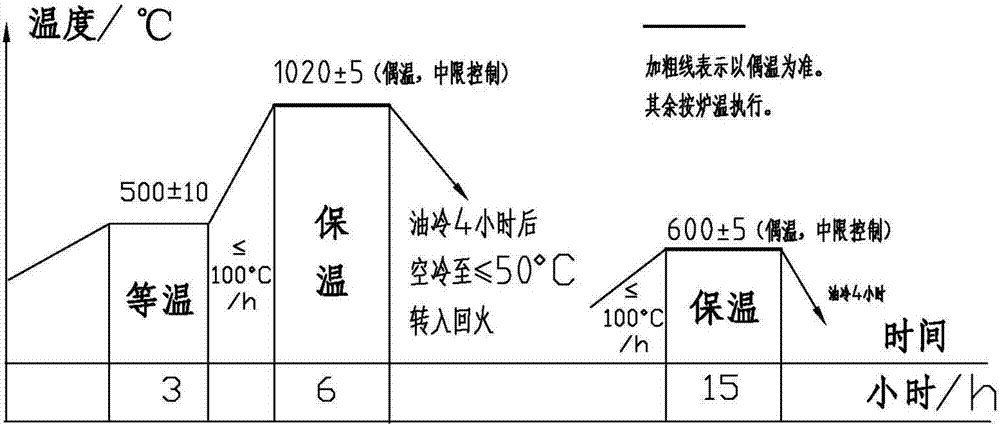
Manufacturing process of large 14Cr17Ni2 stainless steel forgings
ActiveCN106854733AImprove mechanical propertiesMeet the use requirementsChemical compositionThermal insulation
The invention discloses a manufacturing process of large 14Cr17Ni2 stainless steel forgings. The process comprises steps as follows: (1) optimization of chemical components: N elements with the content wt being 0.055%-0.065% are added, the content wt of Ti elements are controlled to be smaller than or equal to 0.010%; (2) forging: the large 14Cr17Ni2 stainless steel forgings are forged and heated at 1,100-1,180 DEG C, and the finish forging temperature is controlled to be larger than or equal to 950 DEG C; (3) thermal treatment: the large forgings are subjected to annealing, quenching and tempering, wherein annealing comprises steps as follows: after forging ends, the forgings are subjected to thermal insulation in a waiting furnace; a gate is closed, the furnace is cooled, and thermal insulation is performed; the temperature is increased to 690 DEG C plus or minus 10 DEG C for thermal insulation; the forgings are cooled and discharged from the furnace, and annealing is completed; quenching and tempering comprises steps as follows: the forgings are heated to 1,020 DEG C plus or minus 10 DEG C for thermal insulation, oil cooling is performed after the forgings are discharged from the furnace, and tempering is performed; the forgings are heated to 600 DEG C plus or minus 10 DEG C for thermal insulation and immediately subjected to oil cooling after being discharged out of the furnace. With the adoption of the manufacturing process, the problem that cracks are easily caused during forging of the large 14Cr17Ni2 forgings can be solved, mechanical properties of the large forgings are remarkably improved, and the use requirements of internal components of nuclear power reactors are completely met.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC SHMP CASTING & FORGING CO LTD
Plant type liquid composite oil phase
InactiveCN101973826AGet rid of dependenceGood explosive performanceExplosivesSocial benefitsPetroleum product
The invention discloses a plant type liquid composite oil phase. The oil phase comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 5 to 30 percent of stearic acid, 20 to 60 percent of plant oil extract, 20 to 60 percent of plant oil and 0 to 3 percent of surfactant; and a preparation process comprises the following steps of: heating each component in an independent heating groove to 70 to 80 DEG C; pumping the components into a reaction kettle by an oil pump in turn after metering the components by an electronic scale according to the matching requirement of the mass fraction; and stirring, filtering and filling. The dependency of the composite oil phase on petroleum products is completely got rid of, low carbon and environmental protection are ensured, and good explosion performance of explosive is kept; and the composite oil phase has a simple and reliable manufacturing process, and good economic benefit and social benefit and is suitable for industrial production and application.
Owner:谢斌
Compounded oil phase for powder nitramon
InactiveCN101172915AImprove detonation sensitivityImprove combustion effectExplosivesDetonationLiquid fuel
The invention discloses a composite oil phase with nitromethane, in particular to the composite oil phase for powder type ammon explosives. The invention comprises the raw materials by weight proportions: 72 to 92 proportions of solid fuel oil, 5.0 to 20 proportions of liquid fuel oil, 2.0 to 5.0 proportions of nitromethane, and 1.0 to 3.0 proportions of condensation compounds of aromatic sulphonate and aldimine. The invention also discloses a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps as follow: the solid fuel oil is firstly melted, and liquid fuel oil, condensation compound of organic acid salt aldehydes and nitromethane are added in turn for being mixed fully, and then the mixture is cooled and packed. The invention is characterized in that the burning thermal value is high; the viscosity is small; and the dispersion on the surface of powder type ammonium nitrate grain to form a moisture proof anti-blocking water resistance oil membrane is easy, thus the detonation Sensitivity and the detonation energy of the powder type ammon explosives are improved. The utility model used for the powder type ammon explosives has the advantages that the oil phase with the nitromethane is simple and reliable, has low cost and facilitates the industrialization production and utilization.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
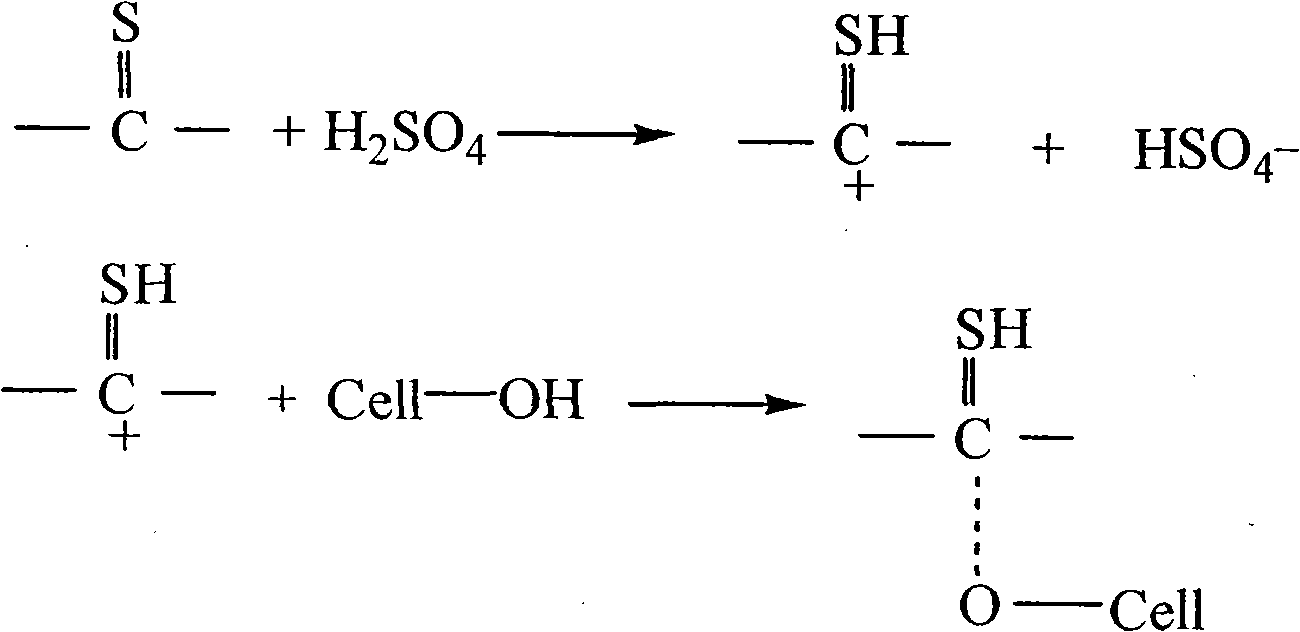
Protic ionic liquid, preparation method and application of protic ionic liquid in cellulose dissolution and regeneration
InactiveCN102146165ALow priceEasy to prepareArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsWet spinning methodsCelluloseFiber
The invention discloses protic ionic liquid used for dissolving cellulose. The components of the protic ionic liquid are shown in a formula of HB+A-, wherein B is sulfur-containing organic or inorganic compound, and A is 98 mass percent concentrated sulfuric acid. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: slowly dripping sulfuric acid into a sulfur-containing compound, and stirring to obtain the protic ionic liquid. The system is used for cellulose dissolution and regeneration and has high capacity of dissolving the cellulose, and after the system is fully stirred at room temperature, the cellulose dissolubility is 10 to 30 percent. The dissolved cellulose is subjected to a wet spinning technology, ethanol is used as setting liquid, drawing molding is carried out, and a solvent is recovered. The cellulose is directly dissolved in the prepared protic ionic liquid, and the cellulose dissolubility is obviously improved. Flows such as alkalization and sulfonation in the production process are simplified, and the problem of environmental pollution due to fiber processing is solved; moreover, the fiber production cost can be reduced and the quality stability of the fiber is improved.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG UNIVERSITY
A high-concentration saline organic waste liquid incineration boiler
ActiveCN105240861BReduce incineration costsSimple preparation processChemical industryIncinerator apparatusHigh concentrationCombustion chamber
The invention discloses an incineration boiler for high-concentration salty organic waste liquid. The environment-friendly and energy-saving requirements for harmlessness, reduction and resourcezation of high-concentration salty organic waste liquid are met through high-temperature incineration and waste heat recovery. The incineration boiler structurally and mainly comprises auxiliary combustors, waste liquid spray guns, a thermal insulation hearth combustion chamber, a steering chamber, a radiation cooling chamber, a radiation water-cooling pipe panel, convection current evaporation pipe panels, a steam pocket, a high-temperature economizer, a low-temperature economizer, an ash falling bucket, a flue connection expansion joint and a furnace wall. The thermal insulation hearth combustion chamber is formed by a hearth wall-covering film type water-cooling wall in a defined manner, salty waste liquid is combusted, and recycling is conducted in a salt dissolving tank. High-temperature smoke generated in combustion sequentially enters the thermal insulation combustion steering chamber, a quenching chamber, the multiple stages of convection current evaporation cooling chambers and the economizers to be subjected to heat energy recovery. The incineration boiler has the beneficial effects of being simple in manufacturing process, convenient to maintain, safe and stable in running, and suitable for being used and popularized in high-concentration salty organic waste liquid processing in the industries of chemical engineering, oil refining, papermaking and the like.
Owner:大连科林能源工程技术开发有限公司
Transdermal delivery system
InactiveUS20160008294A1Reduce areaImprove adhesionBiocideNervous disorderCarboxylic acidOleic Acid Triglyceride
The invention relates to transdermal therapeutic system for the transdermal administration of buprenorphine, comprising a buprenorphine-containing self-adhesive layer structure comprising A) a buprenorphine-impermeable backing layer, and B) a buprenorphine-containing pressure-sensitive adhesive layer on said buprenorphine-impermeable backing layer, the adhesive layer comprising a) at least one polymer-based pressure-sensitive adhesive, b) an analgesically effective amount of buprenorphine base or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, c) a viscosity-increasing substance in an amount of about 0.1% to about 8% of said buprenorphine-containing pressure-sensitive adhesive layer, and d) a carboxylic acid selected from the group consisting of oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, levulinic acid and mixtures thereof, in an amount sufficient so that said analgesically effective amount of buprenorphine is solubilized therein to form a mixture including said viscosity-increasing substance, and wherein the carboxylic acid-, buprenorphine- and viscosity-increasing substance-containing mixture forms dispersed deposits in the said pressure-sensitive adhesive, and wherein said buprenorphine-containing pressure-sensitive adhesive layer is the skin contact layer.
Owner:LTS LOHMANN THERAPIE-SYST AG
Epitaxial structure for vertical cavity emitting semiconductor laser diode
InactiveCN1848565AGood repeatabilityImprove stabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersQuantum wellReflective layer
An epitaxial structure using vertical cavity surface to emit semiconductor laser diode consists of GaAs substrate, grown single- layer GaAs transition layer, grown multilayer external N type of Bragg reflection layer and internal N type of Bragg reflection layer, grown multilayer quantum well structure, grown single-layer internal P type of Bragg reflection layer, grown multilayer P type of oxidation layer, grown multilayer internal P type of reflection layer and external P type of Bragg reflection layer, grown single- layer high doped P type of current expansion layer and ground single-layer super high doped P type of surface covering layer.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTRONIC DEVICES CHINA
Contactless voltage stabilizer main circuit with high voltage stabilization precision and contactless voltage stabilizer
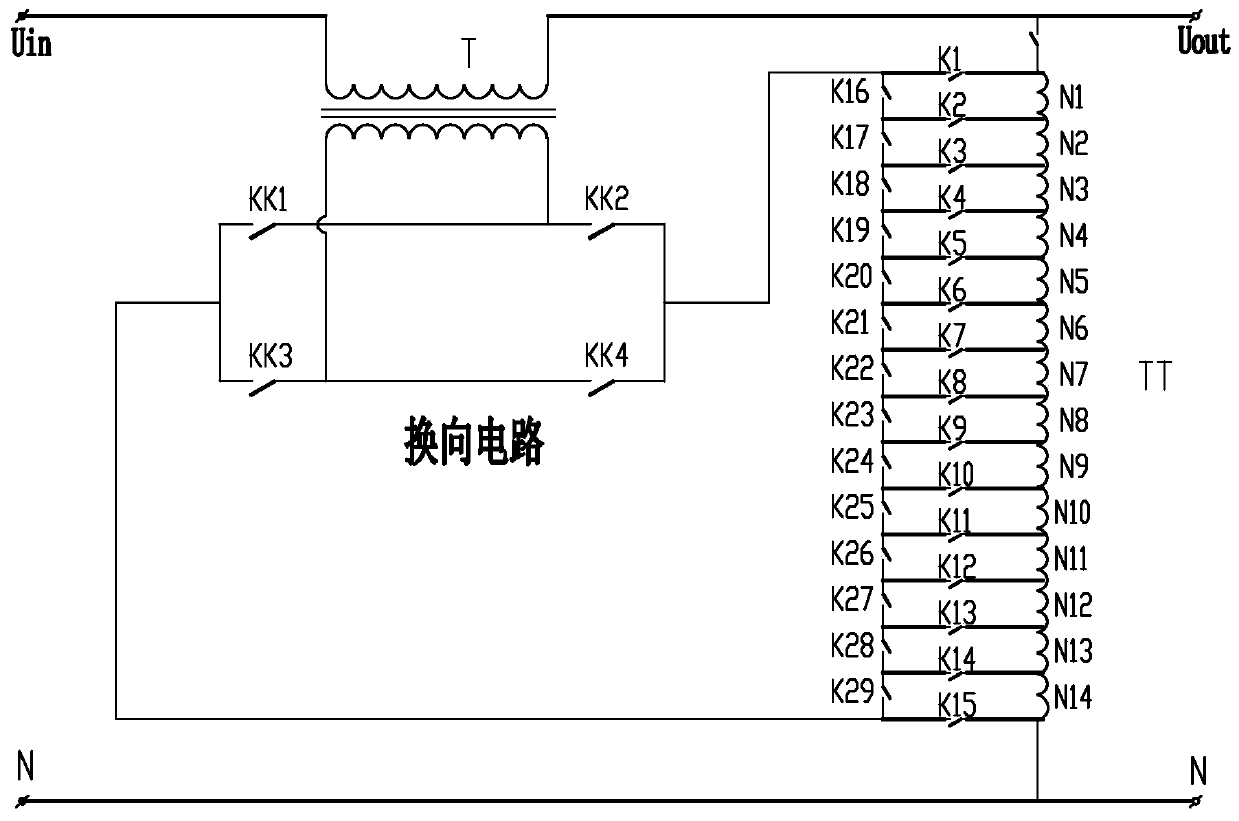
PendingCN110247556AFast adjustmentImprove reliabilityConversion without intermediate conversion to dcVariable inductancesAutotransformerTransformer
The invention discloses a contactless voltage stabilizer main circuit with high voltage stabilization precision. The contactless voltage stabilizer main circuit comprises a compensation transformer, an autotransformer and a reversing circuit. The two lead-out terminals and the n taps of the autotransformer are connected in parallel to be connected with a parallel wire through first contactor switches. Second contactor switches are arranged between every two adjacent connection points on the parallel wire. Both ends of the parallel wire are connected to the primary winding of the compensation transformer through the reversing circuit. The contactless voltage stabilizer main circuit has high voltage stabilization precision and a wide voltage stabilization range. The invention also discloses a contactless voltage stabilizer, which comprises a contactless voltage stabilizer main circuit, an output sampling circuit, a comparator and a control circuit, wherein the output sampling circuit acquires the voltage at the output end of a circuit to be subjected to voltage stabilization; the comparator is connected to the output sampling circuit; the control circuit is connected to the comparator, the reversing circuit, the first contactor switches and the second contactor switches. The contactless voltage stabilizer achieves high precision and voltage stabilization in a wide range.
Owner:PEARL ELECTRIC +1
Five-side packaged CSP (chip scale package) structure and manufacturing process
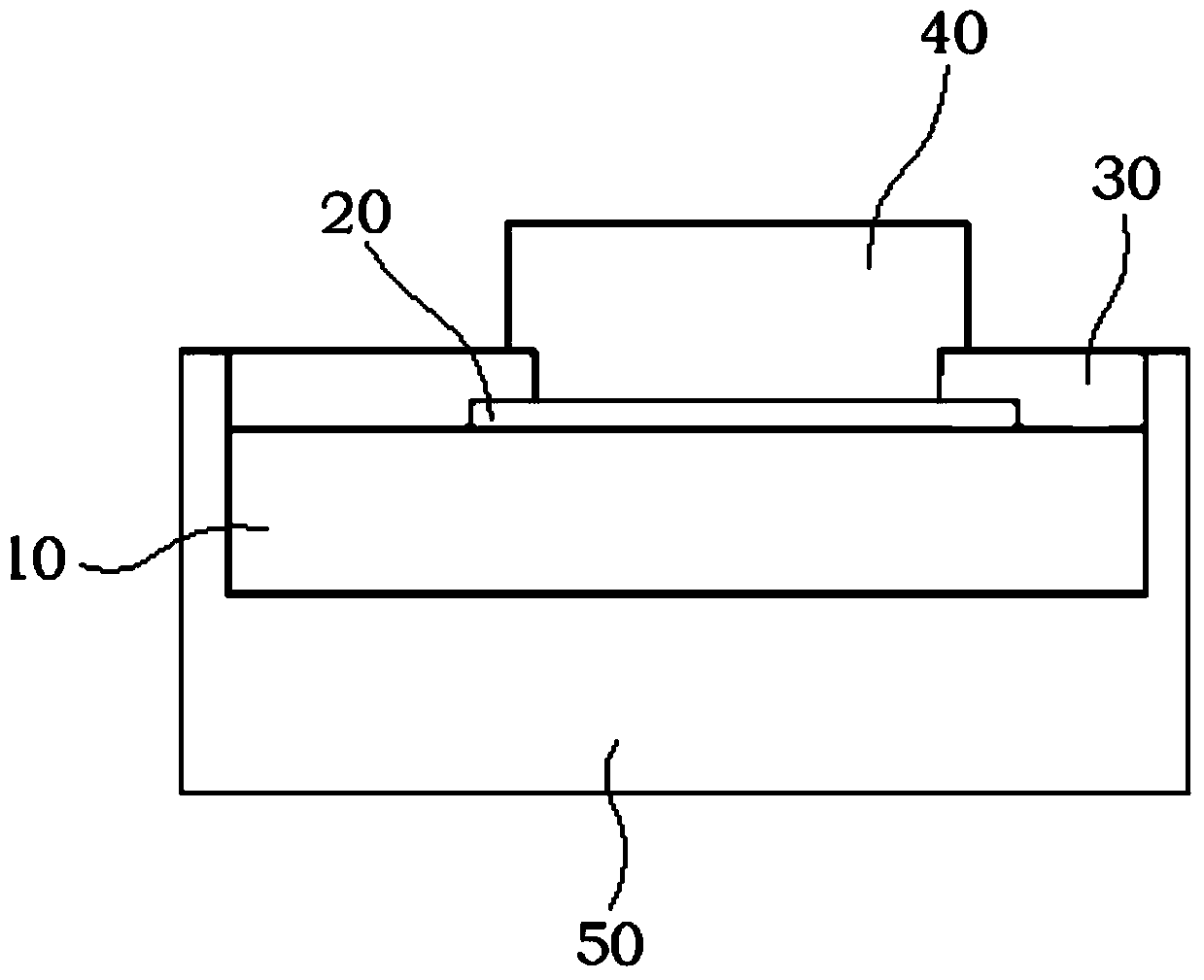
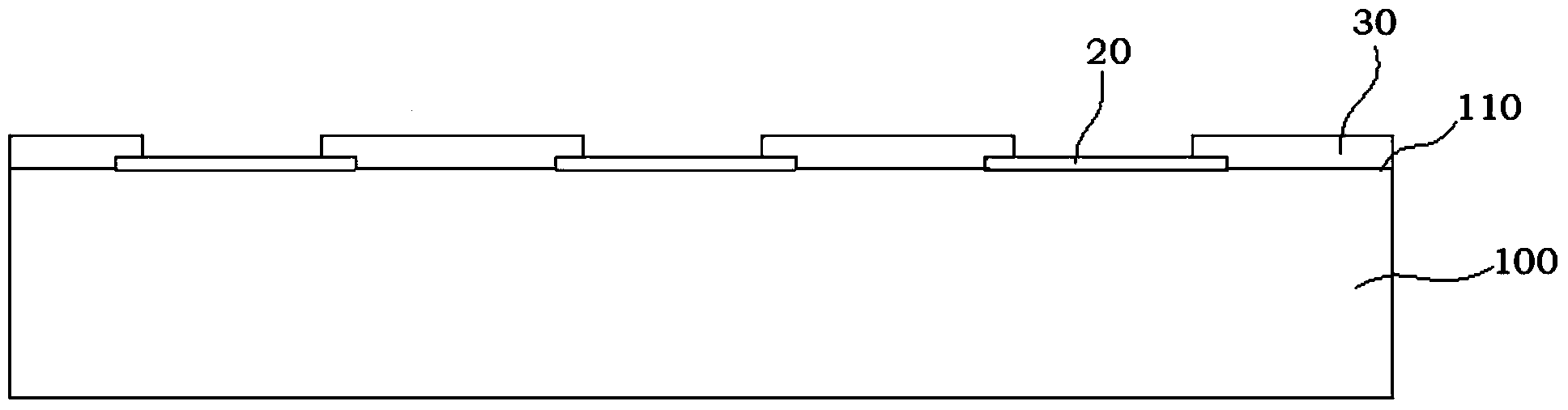
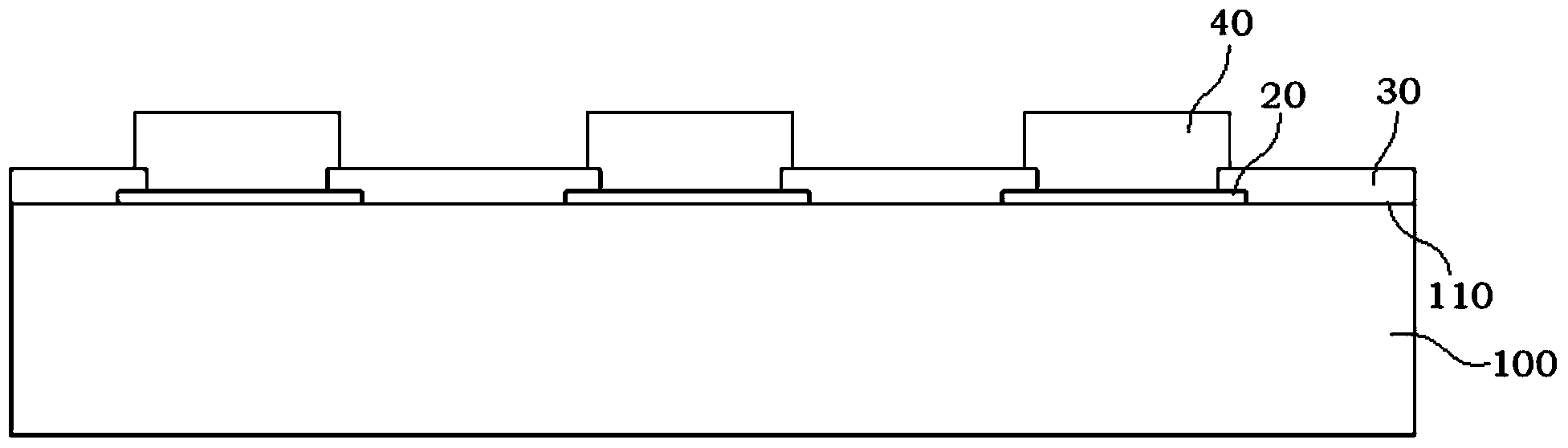
InactiveCN104347542AMiniaturizationImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEpoxyMiniaturization
The invention discloses a five-side packaged CSP (chip scale package) structure, which comprises a crystal particle, a press welding point, a passivation layer and a conducting body, wherein the press welding point is attached on the surface of the crystal particle, the conductor is attached on the press welding point, the passivation layer covers a region, not covered by the press welding point, on the upper surface of the crystal particle, and in addition, the passivation layer also covers a region, not covered by the conductor, of the press welding point. The five-side packaged CSP structure is characterized in that the bottom surface and the peripheral side surface of the crystal particle and the peripheral side surface of the passivation layer are packaged by epoxy resin. The invention also discloses a manufacturing process of the five-side packaged CSP structure. The five-side packaged CSP structure has the advantages that five sides (except the front side of a wafer) of a pipe core is packaged by the epoxy resin, the reliability of an electronic device and an integrated circuit can be favorably improved, in addition, WLCSP (wafer level chip scale package) packaging is adopted, and the miniaturization of an electronic product can be favorably realized. Meanwhile, the manufacturing process is simple and reliable.
Owner:SHANGHAI FINE CHIP SEMICON
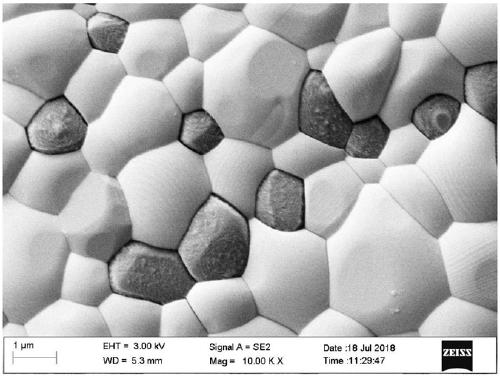
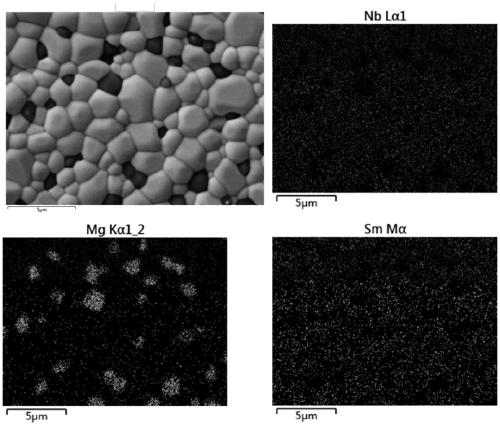
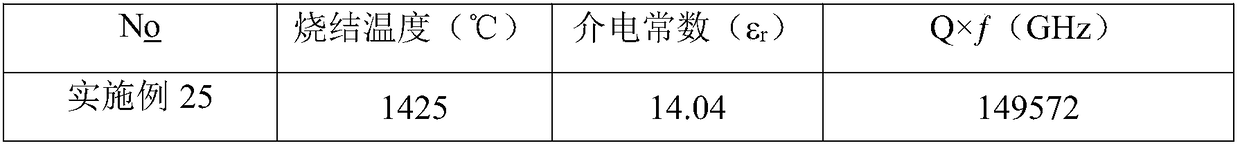
High performance microwave dielectric ceramic material with low dielectric constant as well as preparation method and application of ceramic material
The invention discloses a high performance microwave dielectric ceramic material with a low dielectric constant as well as a preparation method and application of the ceramic material. The chemical formula is SmNbO4-xMgO, wherein x is the molar addition amount of MgO, and the x is more than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 5. The multiphase microwave dielectric ceramic is obtained by adding the proper amount of MgO in to SmNbO4 ceramic and carrying out a solid phase reaction. Finally, a series of microwave dielectric ceramic materials with low dielectric constants and high quality factors are provided. The series of ceramic materials have a sintering temperature range of 1425-1550 DEG C, the dielectric constants of the ceramic materials are 13.27-17.87, and the quality factors ofthe ceramic materials are 87306-189978GHz. The preparation process provided by the invention is simple to operate, reliable in process, larger in optional parameter range during sintering, controllable, and higher in fault tolerance rate; the prepared microwave dielectric ceramic material has the dielectric constant epsilon r of 18 or less, and the quality factor is significantly improved; the microwave dielectric ceramic material can be applied to the manufacture of higher-end microwave components.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Large-diameter high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy pipe flanging method and large-diameter high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy pipe flanging device
In order to solve the problems of great work load, quality ensuring difficulty and the like of the large-diameter high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy pipe flanging method in the prior art, the invention provides a large-diameter high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy pipe flanging method and a large-diameter high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy pipe flanging device. The large-diameter high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy pipe flanging device comprises a support frame, a flanging cone, a pull rod, a cantilever, a left pipe blocking device, a right pipe blocking device and a cone moving rod. According to the method provided by the invention, an oval hole is formed in the radial direction of an aluminum alloy pipe through calculation, then, the large-diameter high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy pipe flanging device is adopted for flanging and deforming the oval hole formed in the aluminum alloy pipe into a cylindrical pipe opening, and the size and the shape meet the design requirements. The large-diameter high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy pipe flanging method and the large-diameter high-temperature-resistant aluminum alloy pipe flanging device have the beneficial technical effects that the cylindrical pipe opening formed by the flanging can be enabled to meet the design requirements, and in addition, the manufacturing process is simple and reliable. The flanging device has the advantages that the structure is simple, the manufacturing cost is low, and good economic technical benefits are realized.
Owner:CHENGDU AIRCRAFT INDUSTRY GROUP
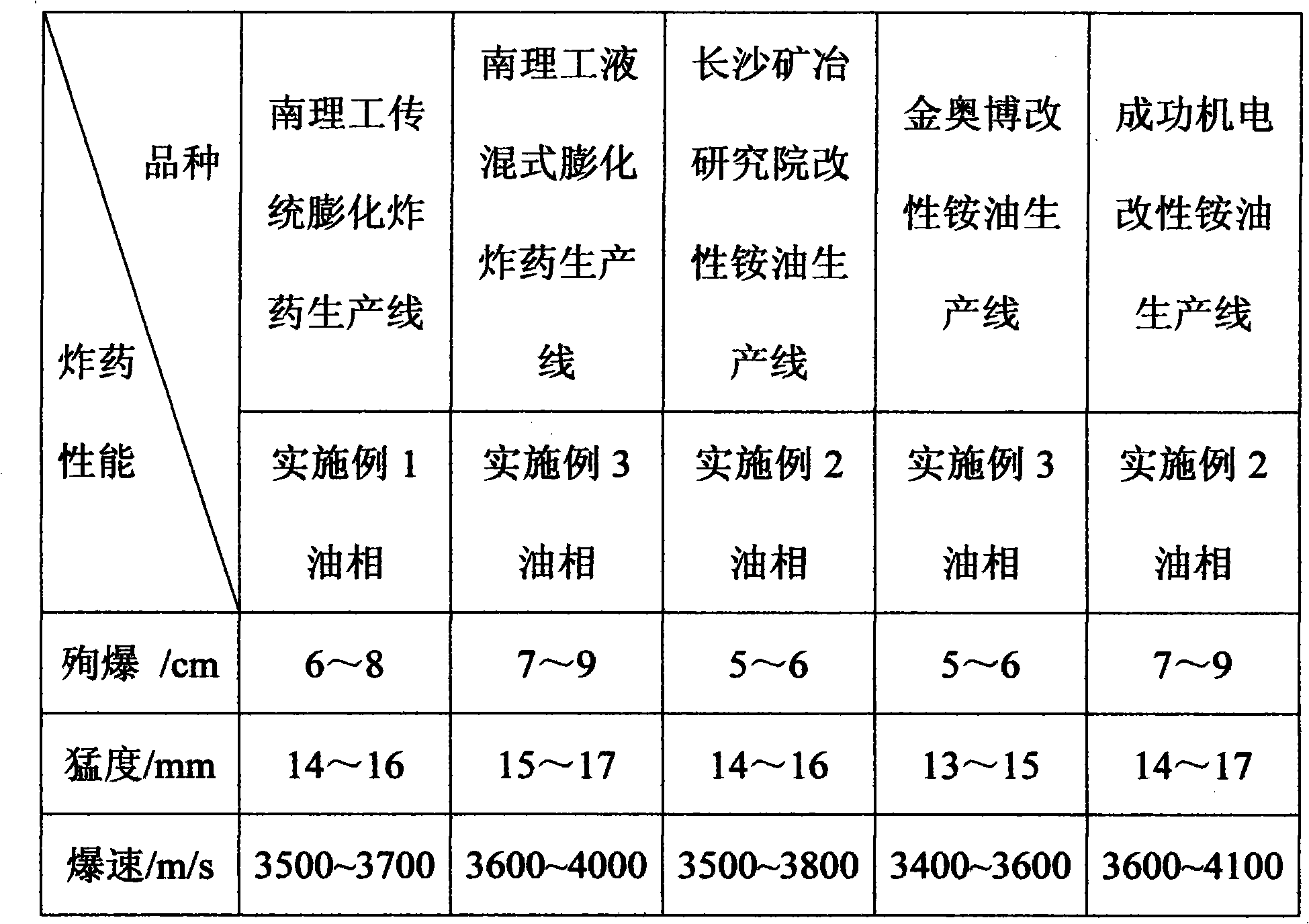
Emulsion explosive permissible in grade-three coal mine
InactiveCN105732240AGood effectGood emulsifying performanceNon-explosive/non-thermic compositionsWater in oilSensitization
The invention provides an emulsion explosive permissible in a grade-three coal mine. The emulsion explosive is prepared from the following components: ammonium nitrate, sodium nitrate, water, sodium chloride, microcrystalline wax, a continuous phase, an emulsifier and a sensitizing agent. With aqueous solutions of oxidizing agents like ammonium nitrate and a flame eliminating agent as dispersion phases and a special hydrocarbon (such as diesel fuel fraction, vacuum distillate oil, pressure-reduced cerate, residuum cerate, light deasphalted oil and heavy deasphalted oil) as a continuous phase, the emulsion explosive is prepared by carrying out emulsification under the action of a surfactant (an emulsifier) for formation of water-in-oil type emulsion colloid and then carrying out chemical sensitization. The emulsion explosive has good explosion performance, good security, small amount of fume, hard and non-sticky body, good water resistance, and small changing amplitude of indexes before an expriation data. The emulsion explosive is applicable to explosion of a high-gas mine, a high-gas area in a low-gas mine and a working face with the dangers of coal (rock) and gas outburst.
Owner:雅化集团旺苍化工有限公司
Roll bending forming method and device for straight edges of to-be-welded pipe
ActiveCN110788175AImprove forming qualityIncrease productivityElectric machineryStructural engineering
The invention discloses a roll bending forming method for straight edges of a to-be-welded pipe. The roll bending forming method comprises three steps of preforming, roll bending and reshaping; preforming is completed by a leading-in mould; roll bending is completed by a roll bending mould; reshaping is completed by a leading-out mould; and the leading-in mould, the roll bending mould and the leading-out mould are installed on the same equipment through a mould frame, and are driven by a motor, and thereby, integrated roll bending forming of the straight edges of the to-be-welded pipe is realized. The roll bending forming method is high in forming precision and high in consistency and stability and increases production efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Water sports boat and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN106080962ALow technical requirementsWeight optimizationNon-magnetic metal hullsDomestic articlesGlass fiberCounter pressure
The invention relates to a water sports boat and a manufacturing method thereof. Firstly, an upper template and a lower template of a shell are made through compression moulding forming, wherein the upper template and the lower template are made of ABS materials; then, glass fiber cloth fully covers the surface of an EPS foam structure, glue is evenly paved on the surface of the glass fiber cloth, the EPS foam structure is put into a cavity of the lower template, and then the upper template covers the lower template; finally, vacuumizing and counter pressure sealing processing are conducted; and air in the joints between the EPS foam structure and the upper and lower templates is pumped, to form the vacuum, pressure is maintained till solidification, and thus the boat is obtained. According to the water sports boat and the manufacturing method thereof, the boat manufactured through the brand new technology takes the ABS materials as basic raw materials and EPS foam as the filling core, a greater improvement is made on the weight, the technology process is simpler and more reliable, the technical requirements of workers are low, the defective rate is favorably decreased, and the yield is greatly increased.
Owner:7112751加拿大公司
Externally-connected adjustable limiting device
InactiveCN103291795AEasy maintenanceSave manpower and material resourcesShock absorbersLower limitEngineering
The invention relates to an externally-connected adjustable limiting device. The limiting device is characterized by comprising an upper limiting plate, an upper buffer block, a lower limiting plate and a lower buffer block which are arranged from top to bottom successively. The upper buffer block is connected with the lower buffer block through a steel sleeve and fixedly connected with the upper limiting plate, and a bolt is arranged in the steel sleeve and penetrates the steel sleeve and fastens the upper limiting plate, the upper buffer block and the lower buffer block through a nut and a spring washer. The diameter of a central hole of the lower limiting plate is larger than outer diameters of bosses of the buffer blocks. The upper buffer block is fixedly connected with the upper limiting plate through a pin. By means of the limiting device, the limiting problem during large spatial three-dimensional deformation produced by ordinary vibration isolation is solved, and the specific limiting requirements are met on the premise that the vibration isolation requirements are met.
Owner:WUXI HONGYUAN DEVFLEX
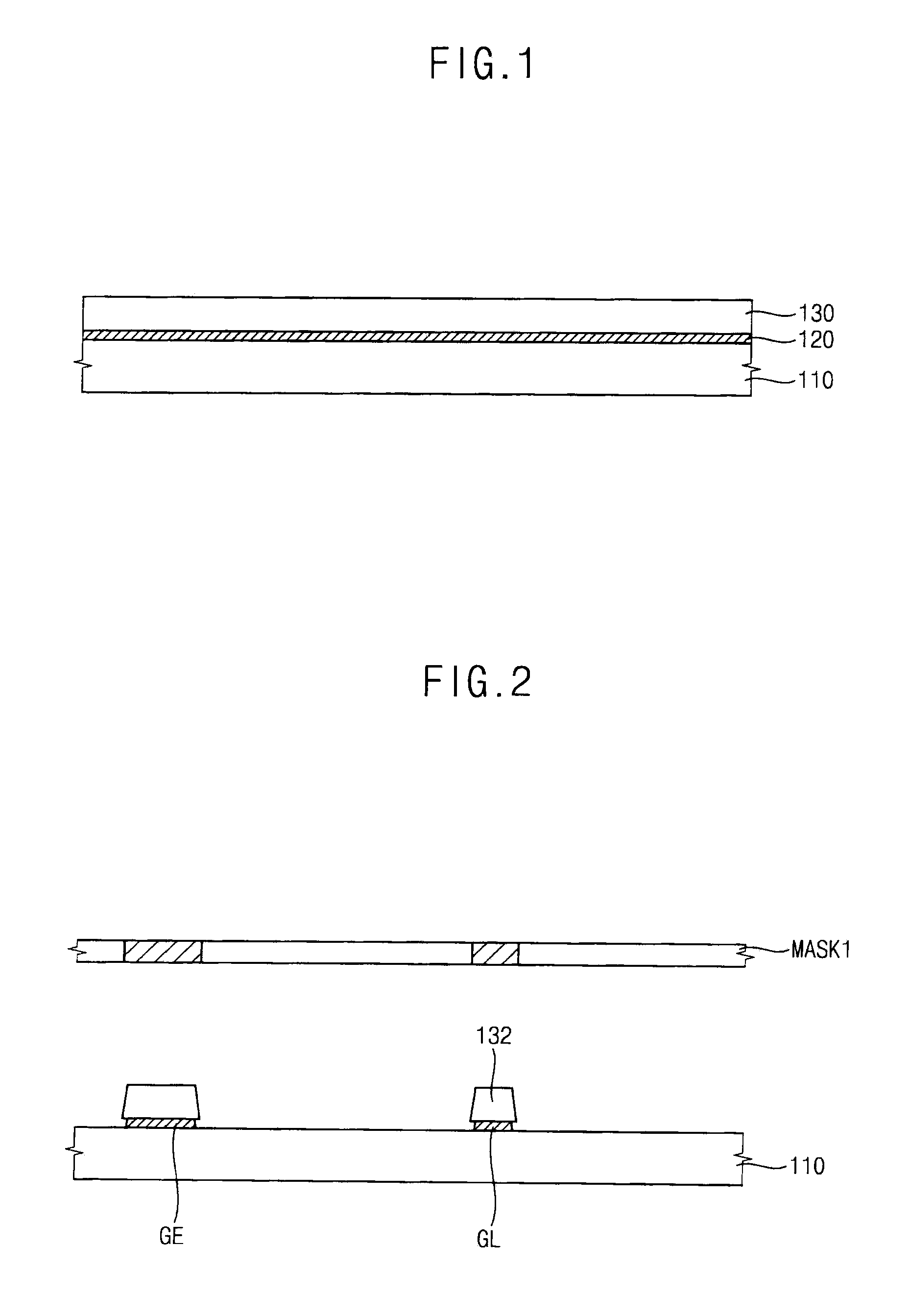
Composition for removing photoresist and method of manufacturing an array substrate using the same
ActiveUS8084184B2Preventing and reducing corrosionImprove abilitiesPhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlycol ethersSolvent
A composition for removing a photoresist includes a) an amine compound having a cyclic amine and / or a diamine, b) a glycol ether compound, c) a corrosion inhibitor and d) a polar solvent. The composition further includes a stripping promoter. Further disclosed is a method of manufacturing an array substrate using the composition for removing a photoresist.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) chip structure
InactiveCN106129014ASimple manufacturing processLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPrinted circuit boardHeat conducting
This application relates to the field of chip technology, in particular to a PCB chip structure, including a PCB and a chip mounted on one side of the PCB, and a heat dissipation layer is provided on the surface of the area corresponding to the chip on the other side of the PCB ; The PCB is located in the corresponding area between the chip and the heat dissipation layer, and a thermal hole is provided; this structure can quickly dissipate the heat accumulated in the PCB in the chip area, and the manufacturing process is simple, reliable, and low in cost. It is also very low, which can effectively reduce the chip junction temperature in high-density PCB design and improve product reliability.
Owner:SHENZHEN TINNO WIRELESS TECH
Manufacturing method of large-diameter steel tube socket and spigot joint
ActiveCN106583493ASmall spinning forceSmall investment in spinning forming equipmentShaping toolsPipe-jointsSteel tubeForming force
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a large-diameter steel tube socket and spigot joint. Acting force is applied to the two ends of a steel tube through a spinning roller correspondingly, so that the two ends of the steel tube are partially subjected to plastic deformation to form a socket and a spigot. The manufacturing method of the large-diameter steel tube socket and spigot joint is simple, reasonable and easy to implement. The manufacturing process is stable and reliable. The large-diameter steel tube socket and spigot joint is suitable for volume production. The ends of the steel tube are subjected to direct spinning forming without welding. A sealing ring mounting position can be arranged on the spigot to facilitate mounting and fixing of a sealing ring. Moreover, spinning forming force is small, spinning forming equipment investment is small, and the production and maintenance cost is low.
Owner:上海佳方钢管集团太仓有限公司
Anhydrous phosphoric acid/phosphate solvent and application thereof in dissolving cellulose
InactiveCN102731800ALow priceEasy to prepareArtificial filaments from cellulose solutionsSpinning solutions preparationSolventDidelphostrongylus
The invention discloses a solvent for dissolving cellulose. The composition of the solvent is an anhydrous phosphoric acid / phosphate system. The general formula of the phosphate is disclosed in the specification, wherein R1, R2 and R3 are respectively hydrogen or alkyl group, all of R1, R2 and R3 are not H; and the general formula of R is CnH2n+1, and n<=4. The phosphate can be trimethyl phosphate, dimethyl phosphate, monomethyl phosphate, triethyl phosphate, diethyl phosphate, momoethyl phosphate, tripropyl phosphate, dipropyl phosphate, monopropyl phosphate, tributyl phosphate, dibutyl phosphate, monobutyl phosphate or the like. The preparation method of the solvent for dissolving cellulose comprises the following steps: putting anhydrous phosphoric acid in a beaker, adding the phosphate into the anhydrous phosphoric acid, and slowly stirring to completely dissolve the phosphate, thereby obtaining the anhydrous phosphoric acid / phosphate system cellulose solvent. The system is used for dissolving and regenerating cellulose, and has high dissolving capacity for cellulose. The solvent is spun with a spinning machine by wet spinning technology to implement regeneration and solidification in the curing agent, and is washed several times to obtain the regenerated cellulose. The invention simplifies the alkalification, sulfonation and other processes in the production technique, solves the problem of fiber processing environment pollution, can lower the fiber production cost, and enhances the fiber quality stability.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG UNIVERSITY
Manufacturing method of high-temperature alloy forge piece for nuclear power steam generator
ActiveCN109967674AStable manufacturing processReliable manufacturing processMetal-working apparatusNuclear powerSuperalloy
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a high-temperature alloy forge piece for a nuclear power steam generator. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps 1, a 800H alloy forgepiece for a nuclear power high-temperature gas cooled reactor steam generator is provided; 2, by weight, the content of O is controlled to be less than or equal to 35 ppm, the content of N is controlled to be less than or equal to 130 ppm and the content of Nb is controlled to be less than or equal to 0.01%; and 3, by weight, the content of an Al element and the content of a Ti element are controlled to be 0.37-0.45% and 0.37-0.45% respectively. The finished forge piece prepared through the method meets the grain size and inclusion detection requirements of the 800H alloy forge piece for thenuclear power high-temperature gas cooled reactor steam generator, and the high-temperature mechanical property meets the standard detection requirements.
Owner:SHANGHAI ELECTRIC SHMP CASTING & FORGING CO LTD
Shadow mask for patterned vapor deposition of organic light emitting diode (OLED) material, shadow mask module comprising same and method for manufacturing shadow mask module
PendingCN113675357AReliable manufacturing processImprove yield rateLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingPhysical chemistryCeramic membrane
The invention relates to a shadow mask and a shadow mask module for organic light emitting diode (OLED) material patterning vapor deposition. The shadow mask includes a ceramic membrane under tensile stress, the ceramic membrane including a central membrane region having a plurality of through holes. The through holes form a hole array, so that the vaporized deposition material can pass through the hole array. A peripheral membrane region surrounds the central membrane region. A multi-layer peripheral support is attached to the rear surface of the peripheral membrane region and has a hollow portion below the central membrane region. The multi-layer peripheral support has a base layer and an intermediate layer under compressive stress over the base layer and attached to the lower surface of the peripheral membrane region. The compressive stress of the intermediate layer is selected to balance the tensile stress of the ceramic membrane such that the ceramic membrane remains in a planar state. A shadow mask module includes a rigid carrier having a plurality of support windows and a plurality of shadow masks attached to the support windows.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Extrusion-resistant colloidal explosive for underwater explosion and preparation process of extrusion-resistant colloidal explosive
InactiveCN108586168AImprove detonation sensitivityImprove explosive powerExplosive working-up apparatusCross-linkMicrocrystalline wax
The invention discloses an extrusion-resistant colloidal explosive for underwater explosion. The extrusion-resistant colloidal explosive comprises the following components: microcrystalline wax, a methylamine nitrate solution, methylamine nitrate, ammonium nitrate, sodium nitrate, perlite, a foaming agent, a foaming accelerant, sesbania powder, a stabilizer, a cross-linking agent, a surfactant, water, an oxidant, a sensitizer, an emulsification foaming adhesive and an emulsifier. The invention further designs a preparation process of the extrusion-resistant colloidal explosive for underwater explosion. The preparation process is simple and feasible, and the prepared explosive is high in extrusion resistance, high in bubble immobilization capability, long in preservation life and stable inquality, and bubbles are not liable to aggregate or overflow after being extruded.
Owner:宜兴市阳生化工有限公司
High-performance powdery emulsion explosive for three-level coal mine and preparation method of high-performance powdery emulsion explosive
InactiveCN107382639AGood foam fixing abilityReduce free air bubble accumulationExplosivesThree levelChemistry
The invention discloses a high-performance powdery emulsion explosive for a three-level coal mine. The powdery emulsion explosive is prepared from components in parts by mass as follows: 70.0-80.0 parts of ammonium nitrate, 7.0-11.0 parts of sodium nitrate, 7.5-11.0 parts of water, 6.0-10.0 parts of sodium chloride, 1.2-1.5 parts of microcrystalline wax, 3.5-4.8 parts of hydrocarbon, 0.3-0.6 parts of a sensitizing agent and 2.0-2.5 parts of an emulsifier. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the high-performance powdery emulsion explosive for the three-level coal mine. The preparation method is simple and easy, the preparation cost is low, the prepared emulsion explosive is good in explosion performance and good in safety and produces little blasting fume, the explosive body is harder in form, non-sticky and high in water resistance, besides, index variation amplitude within the validity period is smaller, quality and stability of the emulsion explosive are improved, the quality guarantee period is prolonged, and the storage is stable.
Owner:宜兴市阳生化工有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com