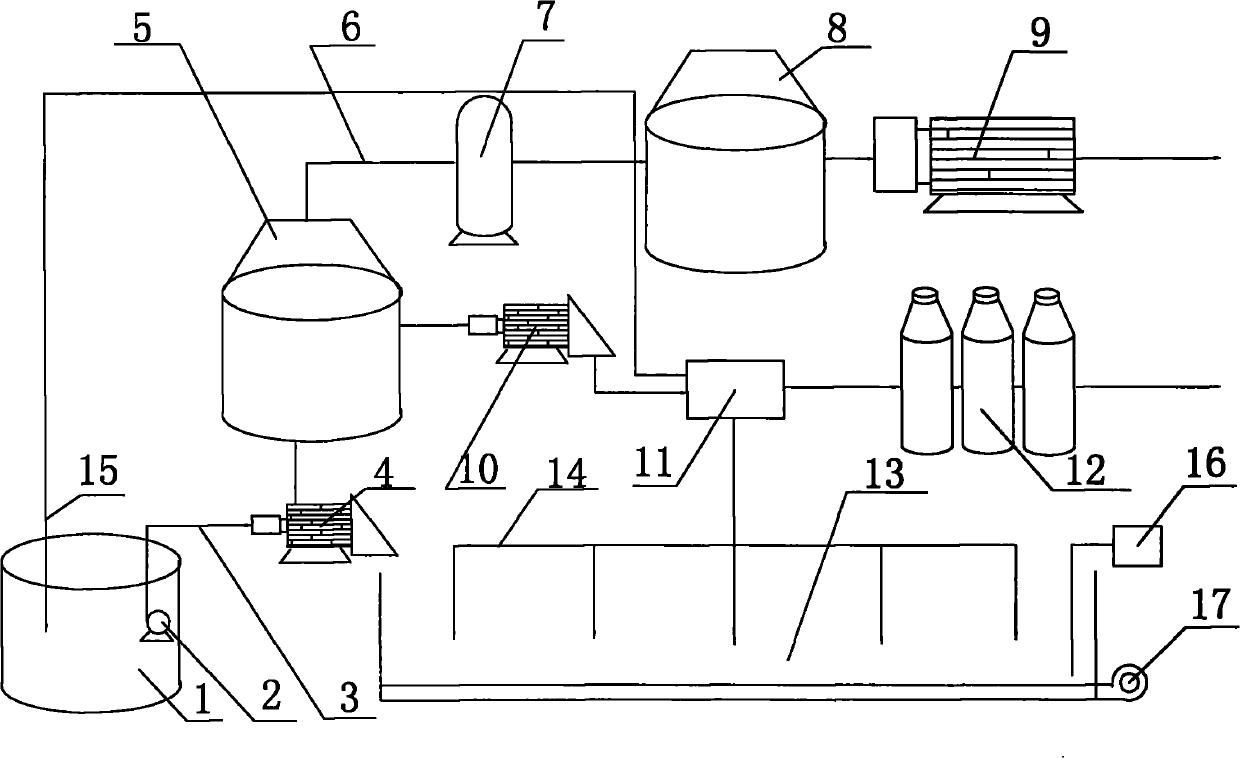
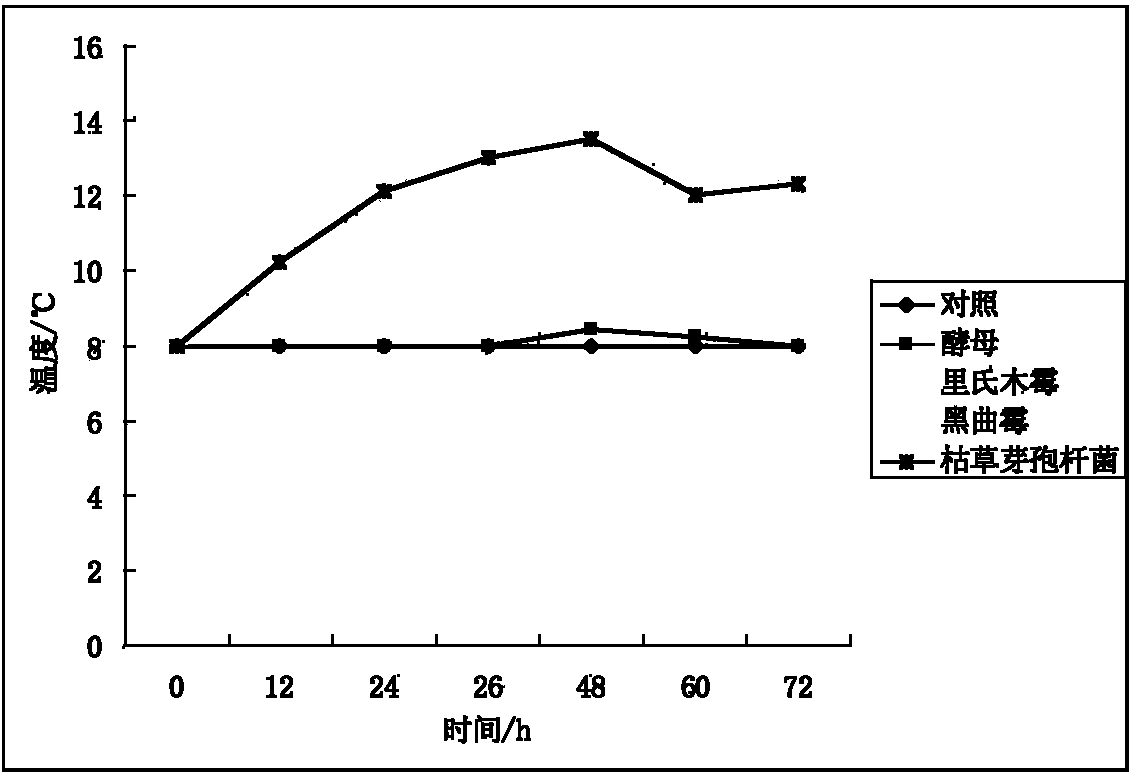
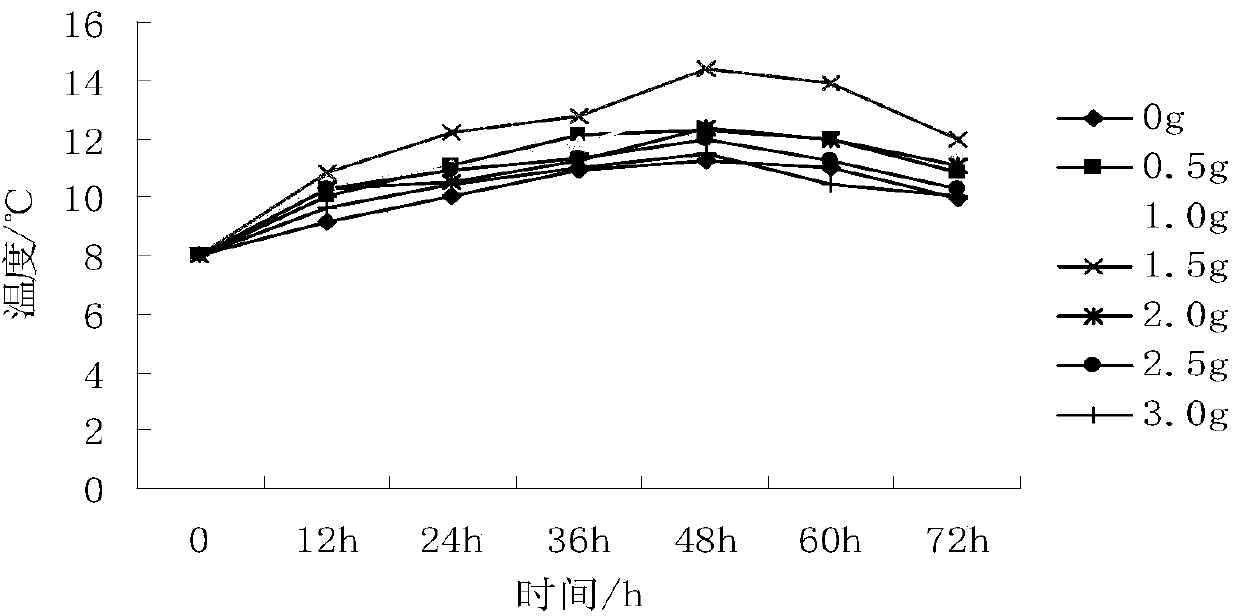
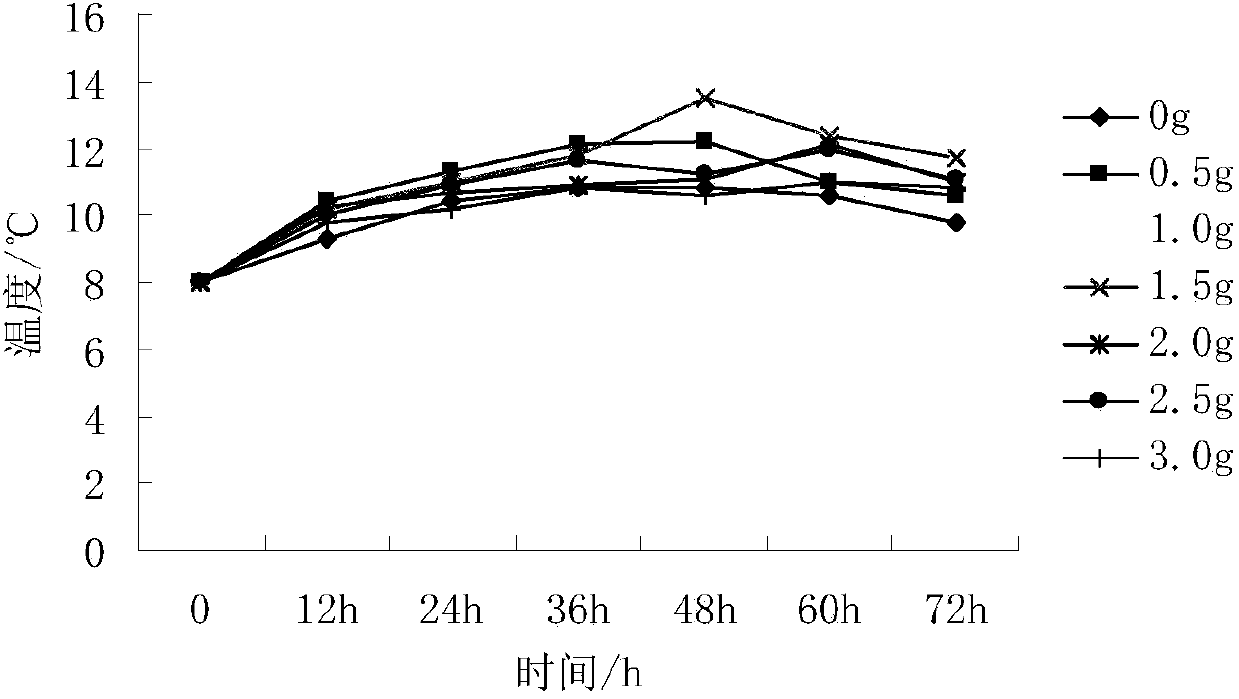
Patents
Literature
275results about How to "Improve the surrounding environment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
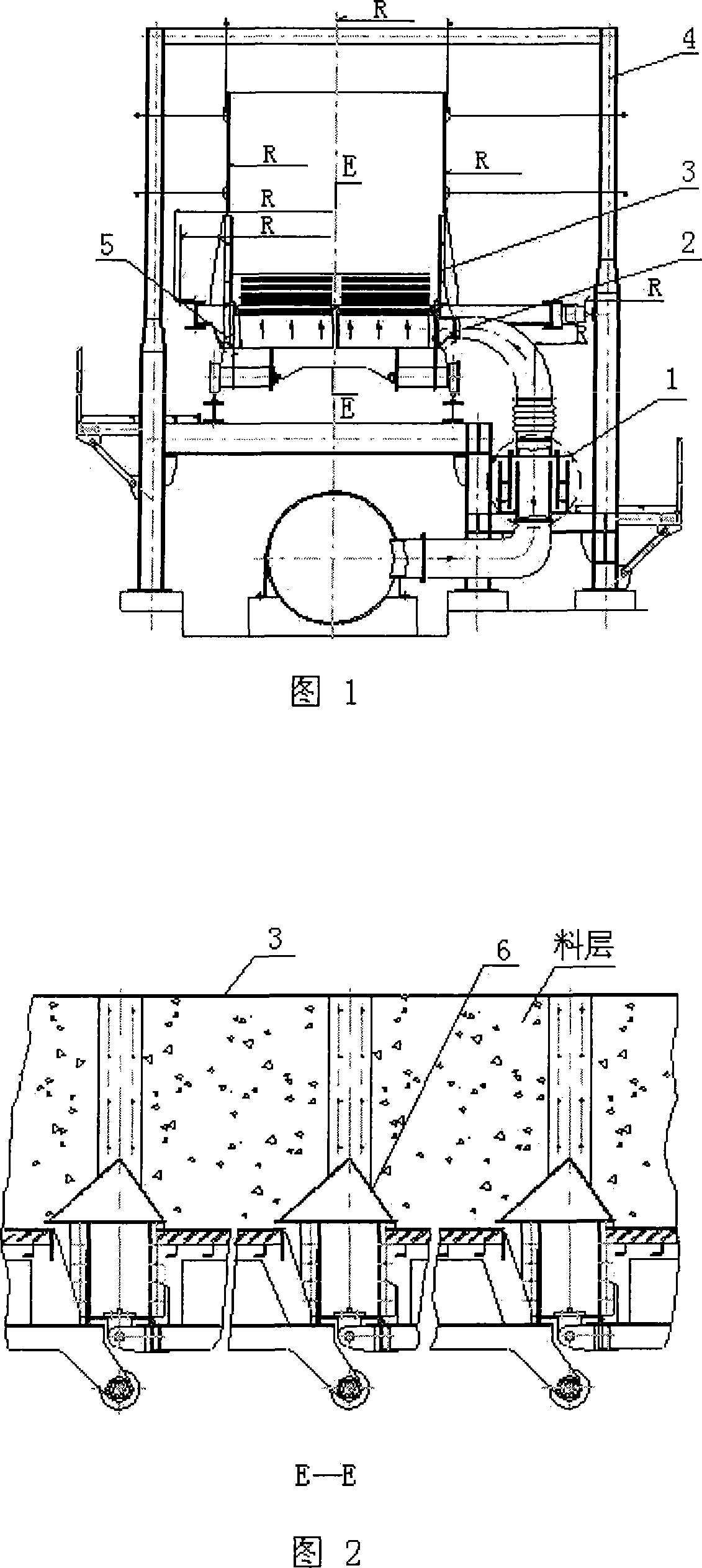
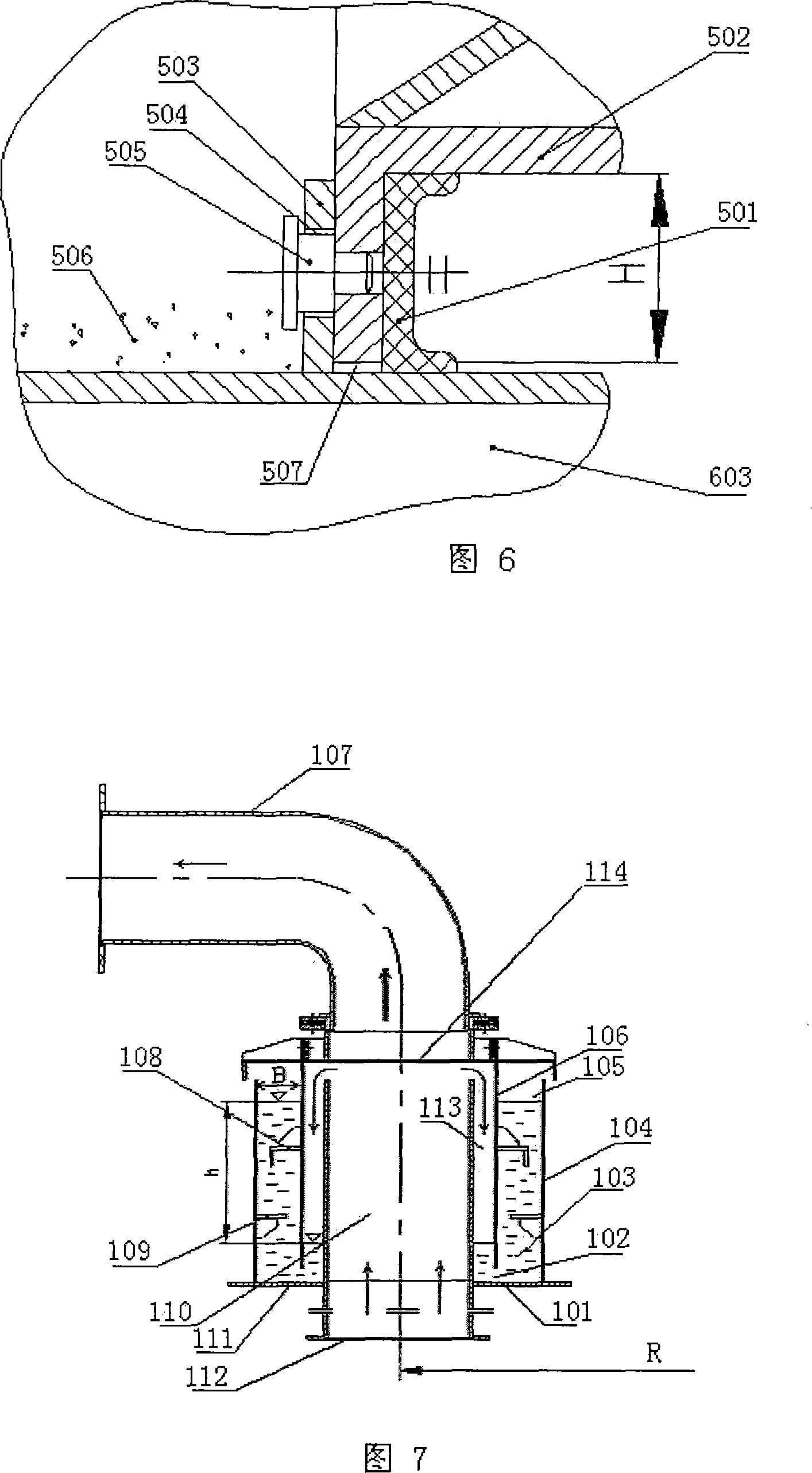
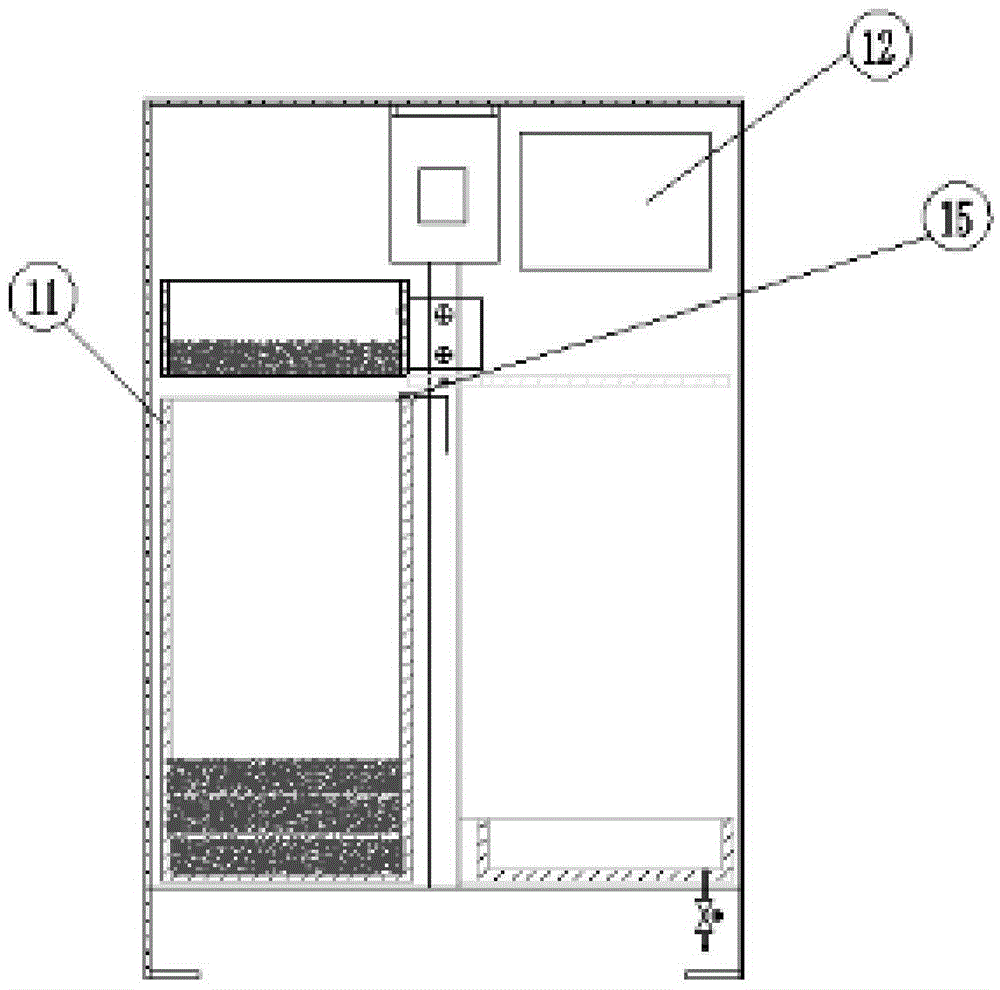
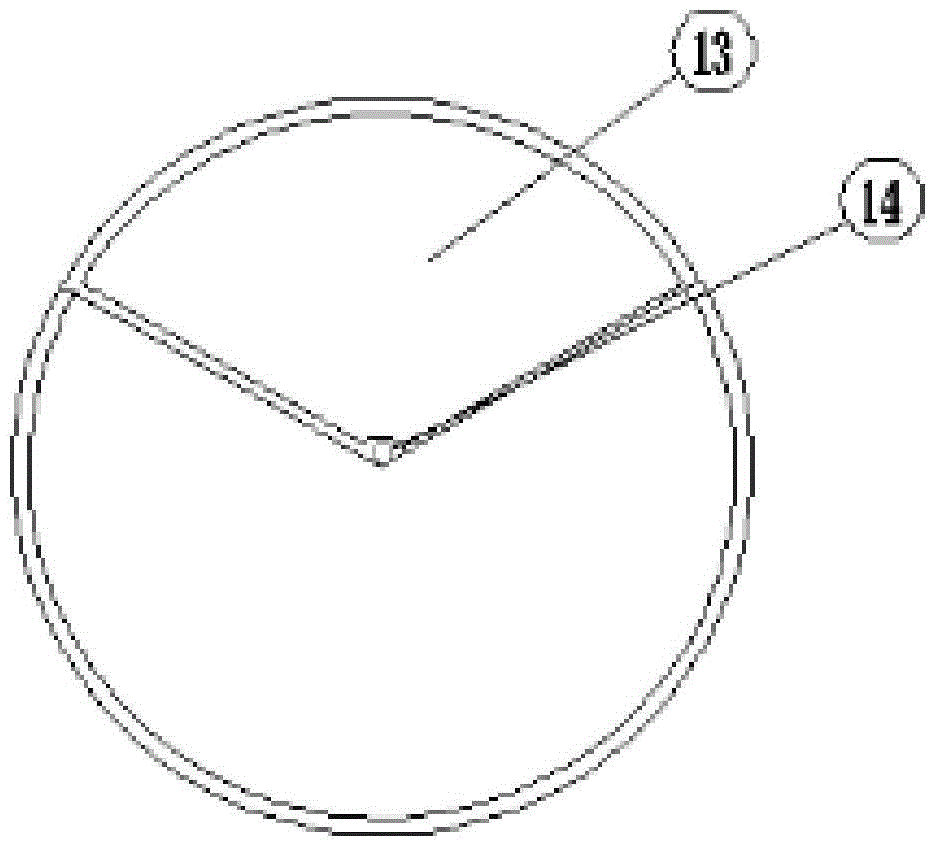
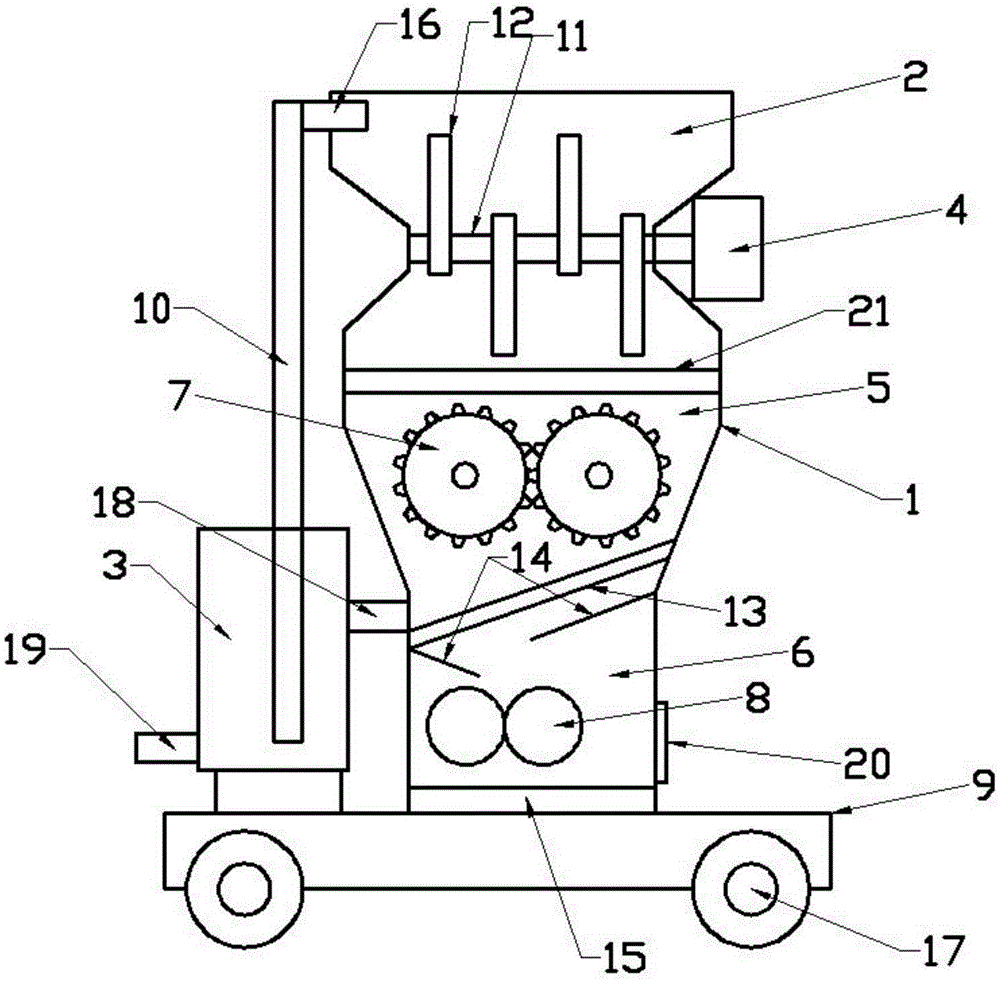
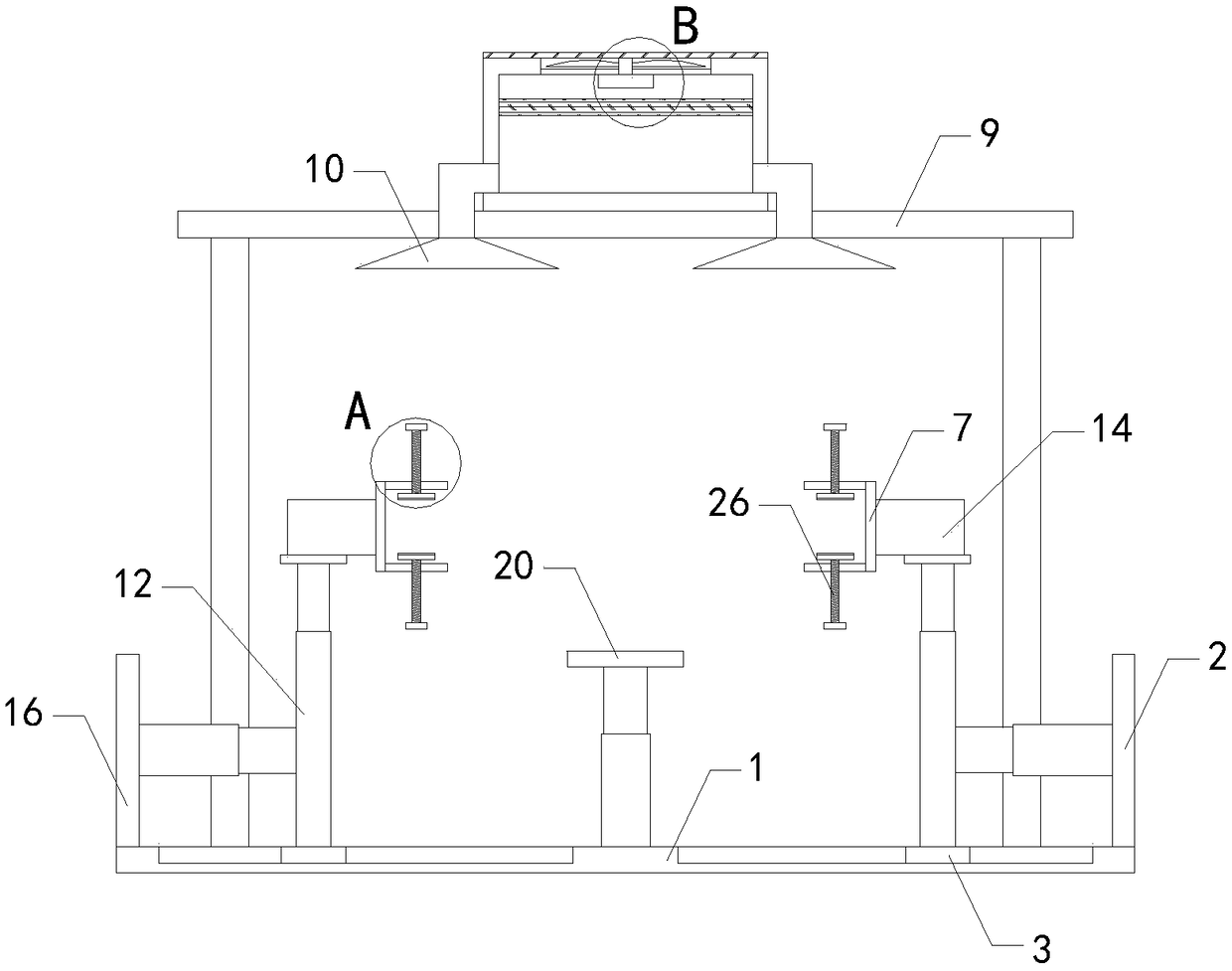
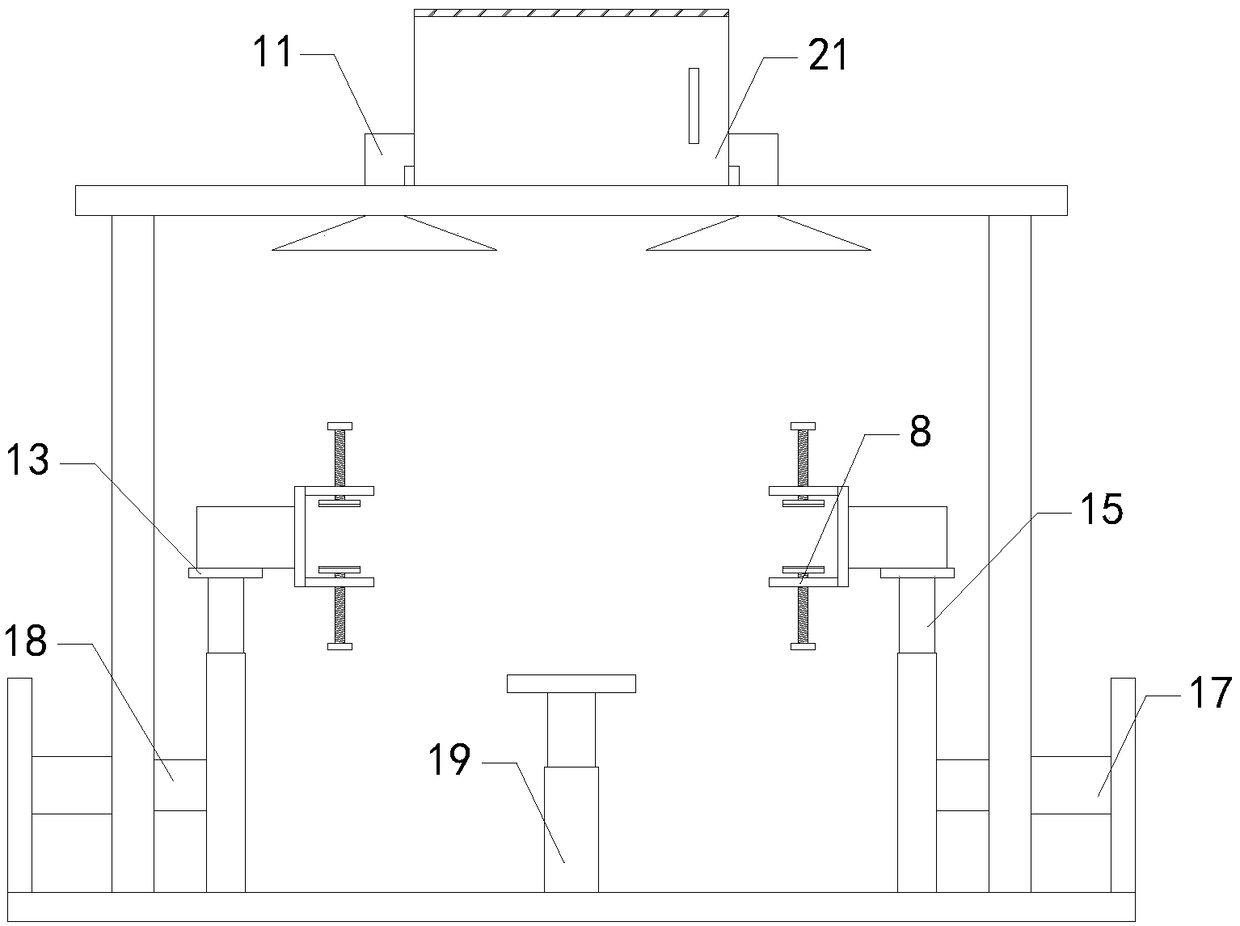
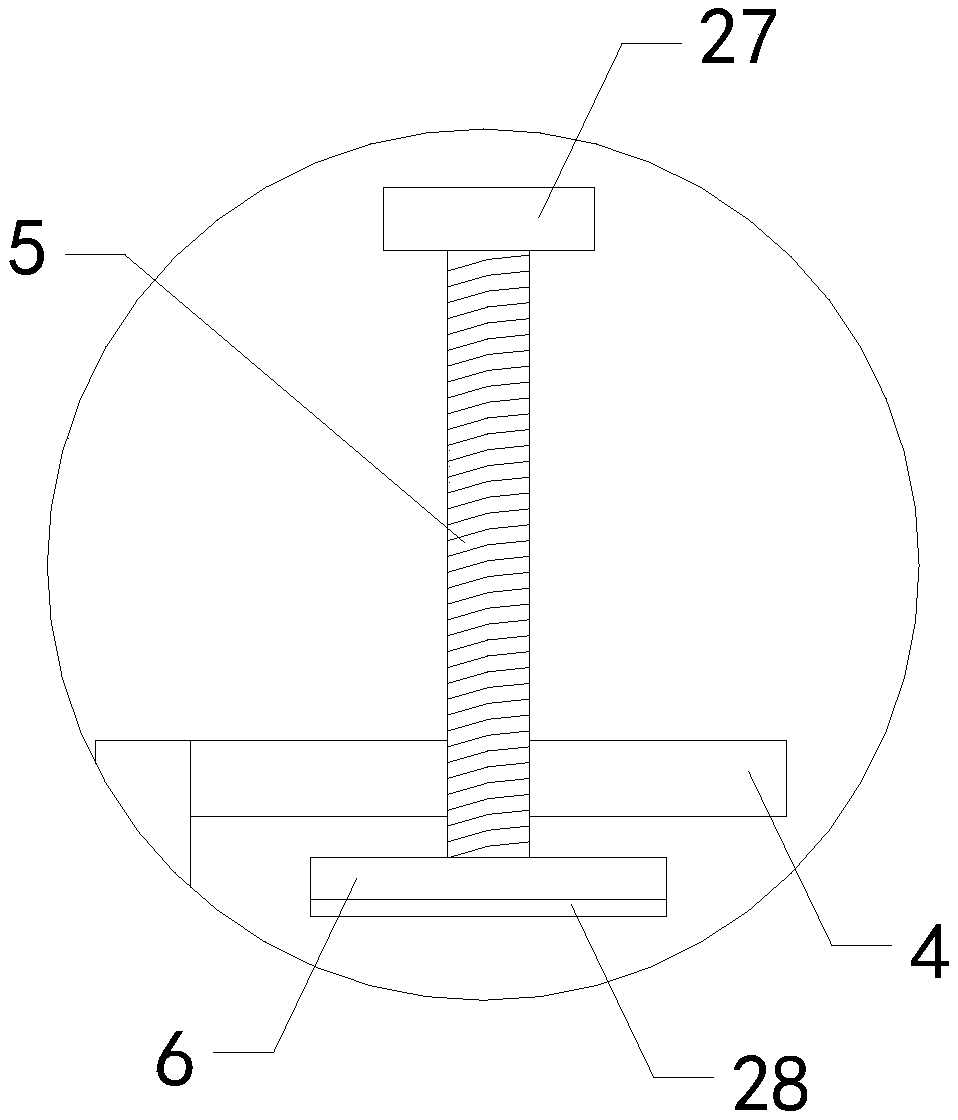
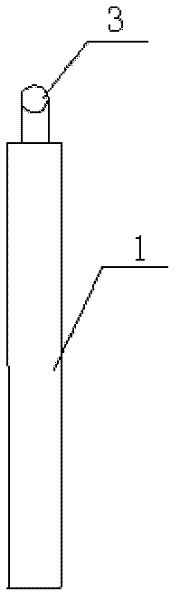
Improved blast circular cooling machine
ActiveCN101118118AImprove cooling effectImprove sealingCharge manipulationFurnace typesForced-airEngineering
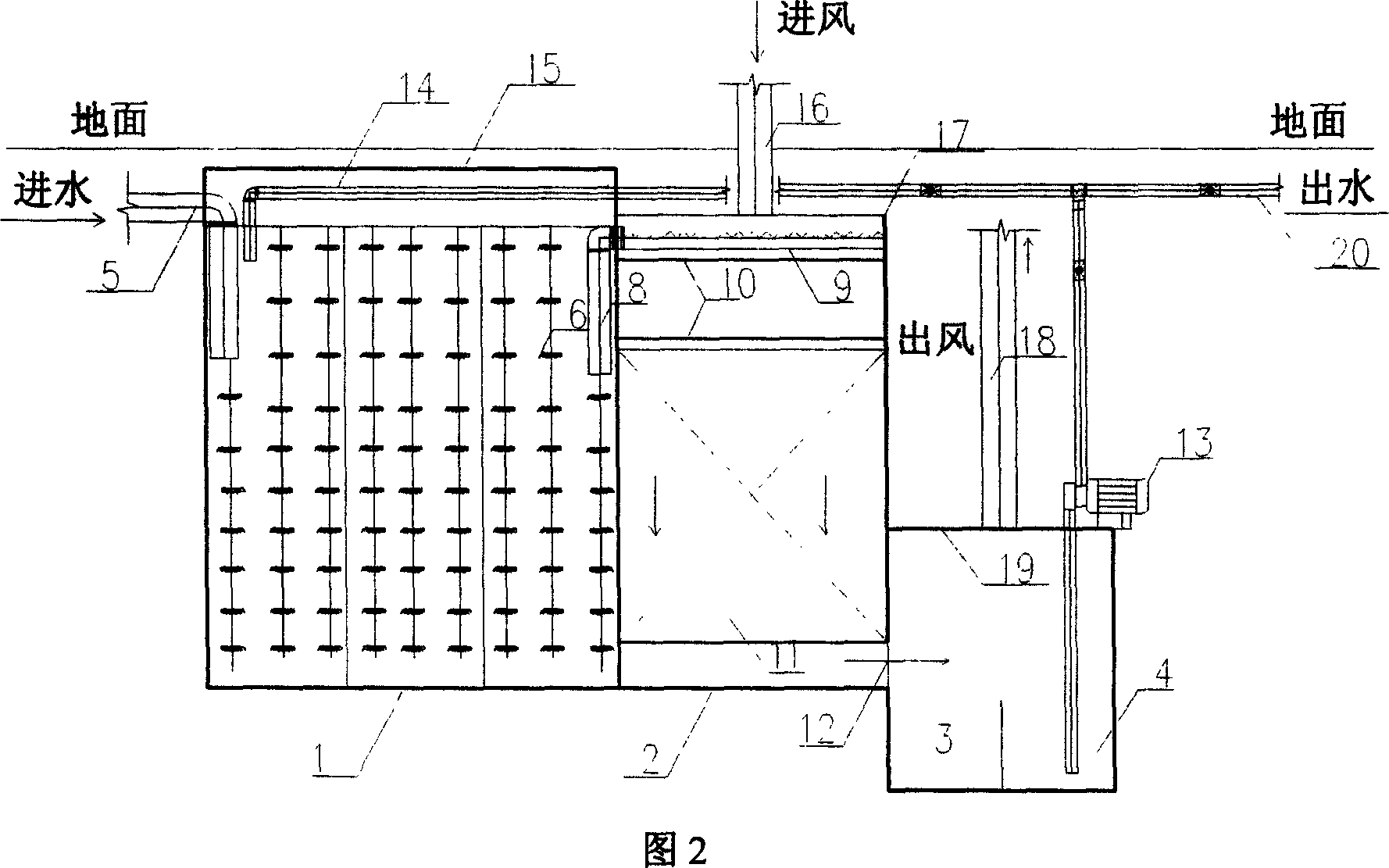
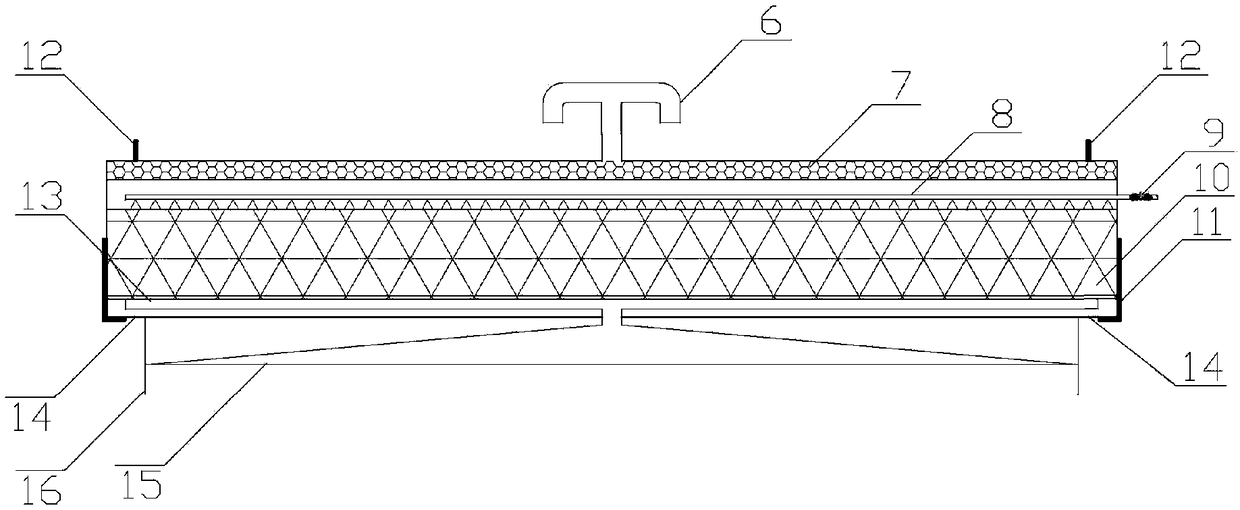
The present invention discloses an improved rotary forced-air cooler, which comprises a double layer trolley, a supporting beam structure, a material blocking proof air duct sealing plate arranged at the connecting part of the double layer trolley and an air supplying system, a double layer trolley unit static seal device and an air duct device. The supplying system structure is based on a rectangular beam, a triangle beam is arranged on the rectangular beam, and a plurality of ventilation channels are arranged on the bevel edge steel plates at the both waists; an air duct pipe is arranged on the air vent of the material blocking proof air duct sealing plate, an inclined plate inclining upwards from the air vent at the bottom part of the air duct pipe has a transition to a horizontal plate, a stopping ventilation fence is added to the air duct pipe at the side of the trolley; two rubber sealing parts with extended bottom edges are arranged at the outer sides of the lower parts of inner and outer sealing plates of the double layer trolley unit static seal device, an ash baffle plate which can move up and down is hung at the inner side; an air water sealing wave subduing device adopting a damping plate is arranged on the air duct device. The present invention further improves the sealing performance of the equipment, and reduces energy consumption and pollution.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
Pig manure centralized treatment and resource utilization method
InactiveCN101792340AImprove working environmentImprove the surrounding environmentBio-organic fraction processingWaste based fuelSpecial effectsZero emission
The invention discloses a pig manure centralized treatment and resource utilization method, which comprises processes of pretreatment, squeezing treatment, biogas production, biogas purification, biogas power generation, biogas slurry separation, guanite crystallization, residual liquid treatment and composting treatment, wherein a biological treatment process is set to be combined with a series of resource recovery strategies so as to realize the zero-emission treatment of the pig manure, and thereby the working environment and the peripheral environment of a hoggery are greatly improved, and the environmental protection and the comprehensive treatment of the hoggery are benefited; the whole process is better integrated, can be combined into an integral device, also can be modularly divided into a functional module of a biogas production generating system, a water purification functional module in high-concentration hoggery sewage and a special-effect organic fertilizer production functional module, and the whole facility occupies small area, has lower investment and operational cost, and is easy to realize equipping; and the invention organically combines the production of biogas, electricity generation, organic fertilizer and guanite, and has good social and economic benefits.
Owner:SHANGHAI RUIDAO ENERGY SAVING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Polyacetal resin composition and molded article thereof
InactiveCN1875066AImprove the surrounding environmentImprove impact resistanceAntioxidantAcetal copolymer
A polyacetal resin composition which comprises a polyacetal resin having a trioxane content of 100 ppm or lower (desirably 50 ppm or lower, preferably 10 ppm or lower) and at least one stabilizer selected among an antioxidant, formaldehyde depressant, processing stabilizer, and heat stabilizer. The polyacetal resin may be a polyacetal resin (especially a copolyacetal) whose trioxane content has been reduced by a solvent treatment and / or heat treatment. The polyacetl resin composition may further contain at least one additive selected among a weathering (light) stabilizer, impact modifier, gloss control agent, sliding modifier, colorant, and filler. This polyacetal resin composition can give a molded article significantly reduced in trioxane extraction and / or volatile-organic amount.
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
Polyacetal resin composition
ActiveUS20070054998A1Improve the surrounding environmentInhibit formaldehyde generationSpecial tyresChemical/physical processesAntioxidantColoring agents
A polyacetal resin composition comprises a polyacetal resin and a hetero atom-containing aliphatic carboxylic acid hydrazide. The proportion of the hetero atom-containing aliphatic carboxylic acid hydrazide may be about 0.001 to 20 parts by weight relative to 100 parts by weight of the polyacetal resin. The polyacetal resin composition may further comprise at least one member selected from the group consisting of an antioxidant, a heat stabilizer, a processing stabilizer, a weather (light)-resistant stabilizer, an impact resistance improver, a gloss control agent, an agent for improving sliding property, a coloring agent, and a filler. Such a resin composition improves stability of the polyacetal resin and inhibits formaldehyde emission.
Owner:POLYPLASTICS CO LTD
Environment-friendly fertilizer for strawberries and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104193516AAchieve recyclingHarm reductionFertilizer mixturesMinor elementEnvironmental resistance
The invention discloses an environment-friendly fertilizer for strawberries and a preparation method thereof. The environment-friendly fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 70-80 parts of organic fertilizer, 10-25 parts of inorganic fertilizer, 0.5-1 part of minor element, 0.1-0.3 part of fermentation composite bacteria, 1-2 parts of ferment bacteria, 3-7 parts of humic acid, 3-7 parts of amino acid and 0.2-0.7 part of antibiotics. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the fermentation composite bacteria with water to obtain a dilute bacterium solution; adding the dilute bacterium solution into the organic fertilizer, uniformly mixing, piling, and circularly overturning to obtain primary leavening; adding the ferment bacteria, fermenting until the materials are completely rotten, drying at low temperature, and pulverizing to obtain secondary leavening; and finally, adding the inorganic fertilizer, minor element, humic acid, amino acid and antibiotics, uniformly mixing, granulating, and sorting to obtain the environment-friendly fertilizer for strawberries. The environment-friendly fertilizer for strawberries is mainly prepared from agriculture and animal husbandry wastes, thereby solving the problem in crop nutrient supply and restricting the pathogenic microorganisms from reproduction.
Owner:WUHAN RUIZE SOURCE BIOLOGICAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Biological deodorant
InactiveCN102732452AImprove the farmImprove the surrounding environmentFungiBacteriaRhodobacter sp.Biotechnology
The present invention discloses a biological deodorant. The biological deodorant is characterized in that the biological deodorant comprises molasses, water and a composite strain, wherein the composite strain comprises Bacillus sp, Actinomyces sp, Saccharomyces sp, Lactobacillus sp and Rhodobacter sp, a weight ratio of the bacteria is 2:2:1:3:2, the bacteria are inoculated into a medium prepared by dissolving molasses in water, and the sugar degree of the molasses is more than or equal to 5%. Compared to the biological deodorant in the prior art, the biological deodorant of the present invention has the following advantages that: various foul gases generated by a large amount of livestock and poultry manures due to breeding can be completely removed so as to improve environmental conditions of farms and farmers, reduce surrounding environmental pollution, and ensure lives and productions of local residents; a good foundation is established for comprehensive recovery and utilization, and harmless treatment of livestock and poultry manures, and strong technical supports are provided for improvement of circulation of agricultural economy.
Owner:绍兴虞林生物科技有限公司
Novel product for improving hair-growing based on nitric oxide and the preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101062050AAvoid bacterial infectionImprove local immunityInorganic boron active ingredientsDermatological disorderOrganic acidNitric oxide
The invention discloses a hair tonic appliance and health products, which is characterized by the following: constituting with nitrogen agent and acid agent; choosing the nitrogen from sodium nitrite (sodium nitrite density at 0. 02%-2. 0%) or plant extract of concentrated enriched nitrite; choosing the acid agent from organic acid or inorganic acid; combining the nitrogen agent and the acid agent; discharging effective element nitric oxide; diastolizing capillary blood of brain with nitric oxide; accelerating blood circulation; increasing local blood providing quantity and oxygen delivery. This invention can reach ideal germinal effect.
Owner:北京尼奥克斯生物科技有限公司
Method for cultivating selenium-rich sweet potatoes
InactiveCN105993576ASufficient for absorptionReduce dosageAnimal corpse fertilisersExcrement fertilisersSite managementPlant Tubers
The invention belongs to the technical field of agriculture, and particular discloses a method for cultivating selenium-rich sweet potatoes. The method comprises the steps of land selection, seed selection, sowing, field management and pest control. According to field management, intertillage weeding and topdressing, reasonable irrigation and ridging are included; according to topdressing, selenium-rich organic fertilizer and selenium-rich leaf fertilizer are dressed, and 2 kg to 4 kg of the organic fertilizer and 1 kg to 2 kg of the leaf fertilizer are applied to each sweet potato. The organic fertilizer and the leaf fertilizer are applied together, growth of the sweet potatoes can be promoted, and the planting period can be shortened. During intertillage, the tubers of the sweet potatoes begin to grow, tuber growing is a guarantee of yield increasing, and therefore organic fertilizer application is critical during intertillage. According to the method, the organic fertilizer and the leaf fertilizer which can promote tuber growth and add selenium into the tubers are specially designed for the sweet potatoes, therefore, it is guaranteed that the sweet potatoes can absorb and utilize sufficient selenium in the whole growth process, the yield of the sweet potatoes is increased, and selenium in the sweet potatoes can be increased.
Owner:蒋丽红
Rack with automatic damping function
InactiveCN106979447AGuaranteed uptimeReduce vibrationNon-rotating vibration suppressionStands/trestlesMachining vibrationsDamping function
The invention discloses a frame with an automatic shock absorbing function, which includes a support plate, support frames are arranged on both sides of the top of the support plate, and fixed plates are fixedly connected to both sides of the bottom of the support plate. The bottom of the fixed plate is provided with a telescopic rod, the inner side of the telescopic rod is provided with an adjusting rod, the inner side of the regulating rod is provided with an operating handle, the bottom of the telescopic rod is provided with a shock absorber, and the bottom of the telescopic rod runs through to the inner cavity of the shock absorber. The present invention can effectively damp the textile frame by setting chute, connecting rod, pulley, damping spring, movable rod, movable shaft, slider, through hole and sliding rod, which can effectively reduce the vibration of the textile machine. The vibration generated during the working process of the textile frame solves the problem that the textile machine frequently breaks due to the large vibration of the textile frame during the working process.
Owner:浙江高派机器人科技有限公司
Novel environment-friendly crushing and compacting-type garbage can
The invention relates to a novel environment-friendly crushing and compacting-type garbage can. The novel environment-friendly crushing and compacting-type garbage can comprises a garbage can body, a door cover plate, a garbage pretreatment box body, a pressure-bearing baffle plate, a crusher, a compaction device, a water collection device, a garbage bearing barrel and a gear switch, wherein the door cover plate is movably connected onto the top part of the garbage can body; the garbage pretreatment box body is arranged in the garbage can body; the garbage pretreatment box body 3 is connected with a positioning rotary device 7; sewage draining holes are formed in the bottom of the garbage pretreatment box body; the pressure-bearing baffle plate is arranged at the bottom of the garbage pretreatment box body; the crusher and the compaction device are arranged at the top in the garbage can body; the water collection device and the garbage bearing barrel are arranged at the bottom of the garbage can body; and the bottom part of the water collection device is connected with a sewage draining pipe. The novel environment-friendly crushing and compacting-type garbage can has the advantages of being simple in structure and easy for manufacture, and being practical and high-efficient.
Owner:江苏泓润生物质能科技有限公司
Corn flour processing equipment
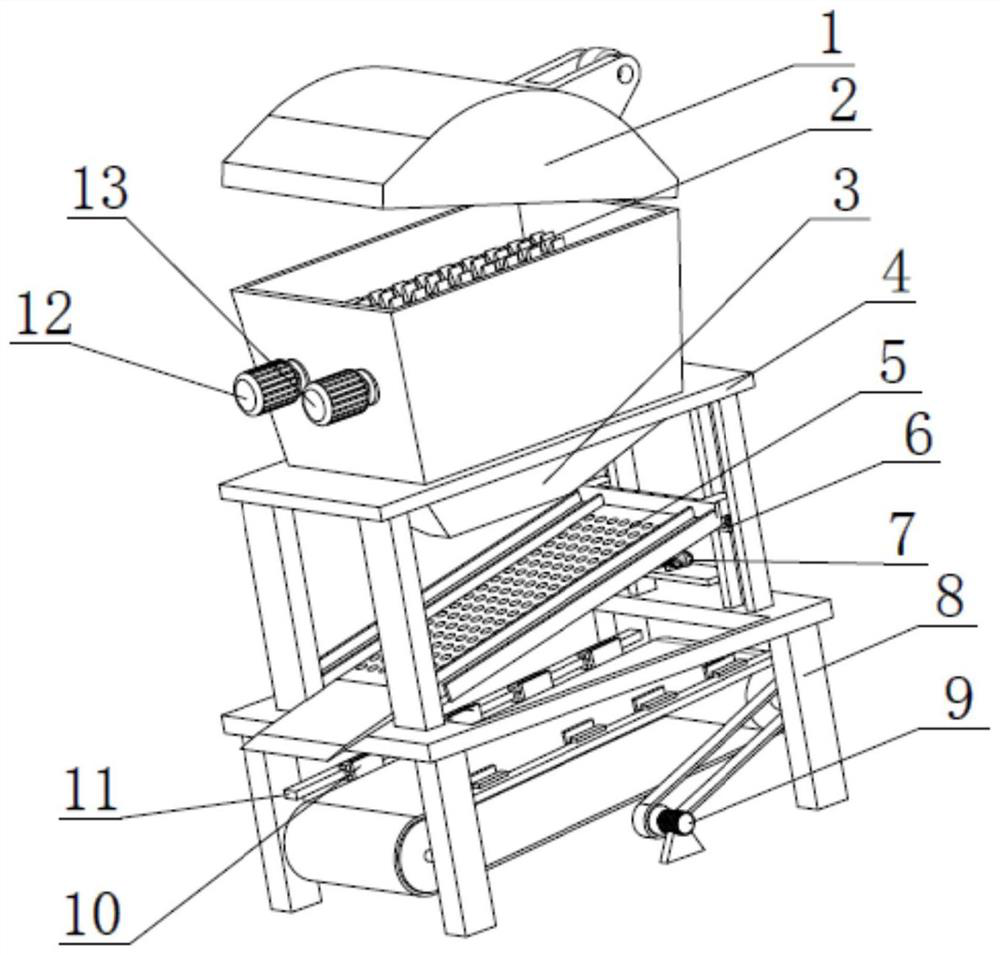
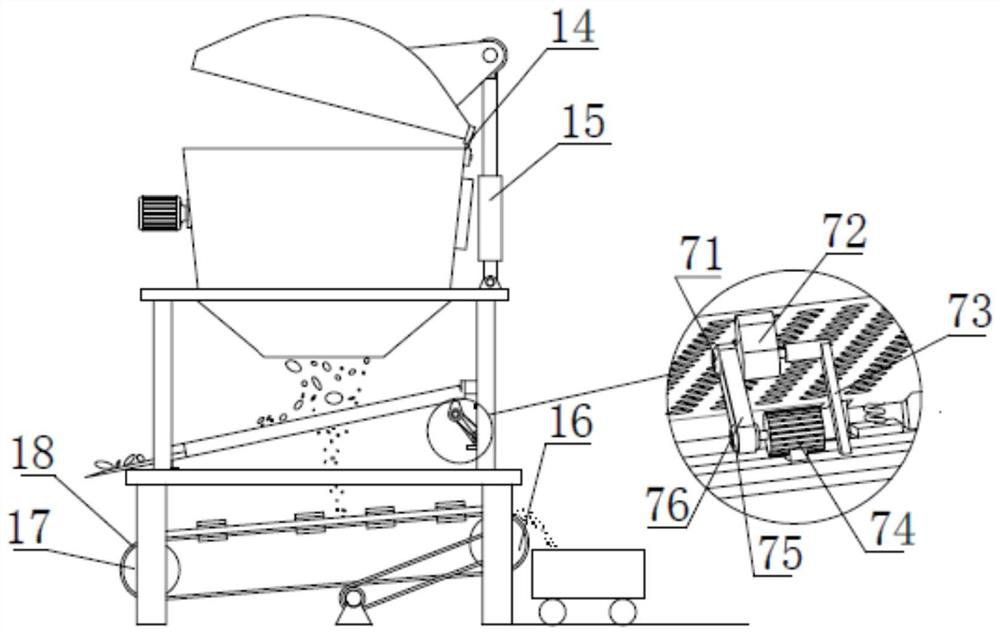
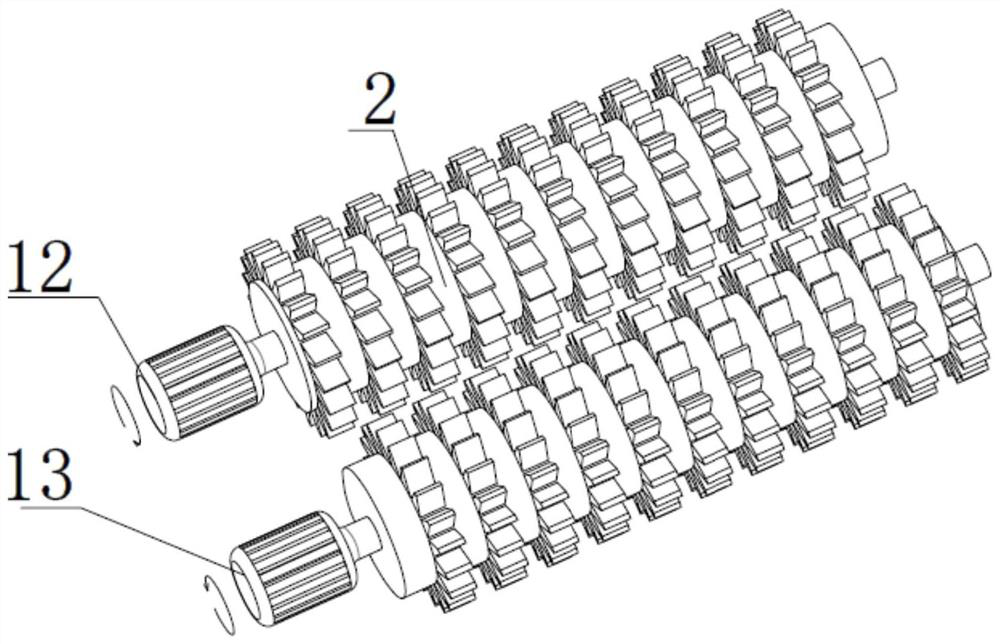
InactiveCN105233914AClear in timeProtection securityNon-rotating vibration suppressionMagnetic separationCorn flourEngineering
The invention discloses corn flour processing equipment. The corn flour processing equipment comprises an outer shell, a storage box, a motor and a base, wherein a shock absorption pad is arranged between the outer shell and the base; a feeding hopper, a first crushing chamber and a second crushing chamber are sequentially arranged in the outer shell from top to bottom; an eccentric wheel is fixedly installed on a stirring shaft; two crushing gears engaged with each other are arranged in the first crushing chamber; a circle of magnetic ring surrounds the inner wall of the first crushing chamber above the crushing gears; two crushing rollers attached to each other are arranged in the second crushing chamber; a material return pipe is communicated between the storage box and the first crushing chamber, and a lifting machine is introduced into the storage box; roller wheels are installed on the base. Through multiple times of crushing, crushing is thorough, large particles are automatically circulated and crushed again, the labor is reduced, and the crushing efficiency is improved. The magnetic ring can clean up iron matter mixed in corn kernels in time, so that safety of equipment and people is protected.
Owner:林桂清
Special culture medium for Lilium spp. and Lilium spp. culture method
ActiveCN102771363AImprove qualityReduce pollutionCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationCut flowersPeat
The invention provides a special culture medium for Lilium spp., which has great water and fertilizer conservation capacity and stable physical and chemical performance, is clean, also has a physical disinfection effect, can continuously provide nutrient elements required for growth of Lilium spp. and is suitable for the growth of the Lilium spp. The special culture medium for Lilium spp. is made of the following components: white peat, black peat, pine barks, maifan stone particles, perlite and trace element controlled-release fertilizers, wherein the white peat comes from moss peat; the black peat comes from moss peat; the pine barks are fermented pine bark particles with grain size being 3-6mm; the grain size of the maifan stone particles is 3-6mm; the perlite is expanded perlite with grain size being 2-4mm; and the trace element controlled-release fertilizers provide three secondary elements including calcium, magnesium and sulfur, and five trace elements including manganese, molybdenum, zinc, copper and iron. No matter whether the special culture medium is used for potted Lilium spp. or cut-flower Lilium spp., plants can grow more robustly, the quality of flowers is obviously improved, the planting of Lilium spp. is not restricted by nursery fields, the land utilization ratio is improved, the pollution and the harm to soil are reduced and the environment around Lilium spp. planting fields is improved.
Owner:虹越花卉股份有限公司
Slowly-recoverable polyurethane foam material
InactiveCN102115522AFeel goodWith decompression and anti-seismic functionHazardous substanceSynthetic materials
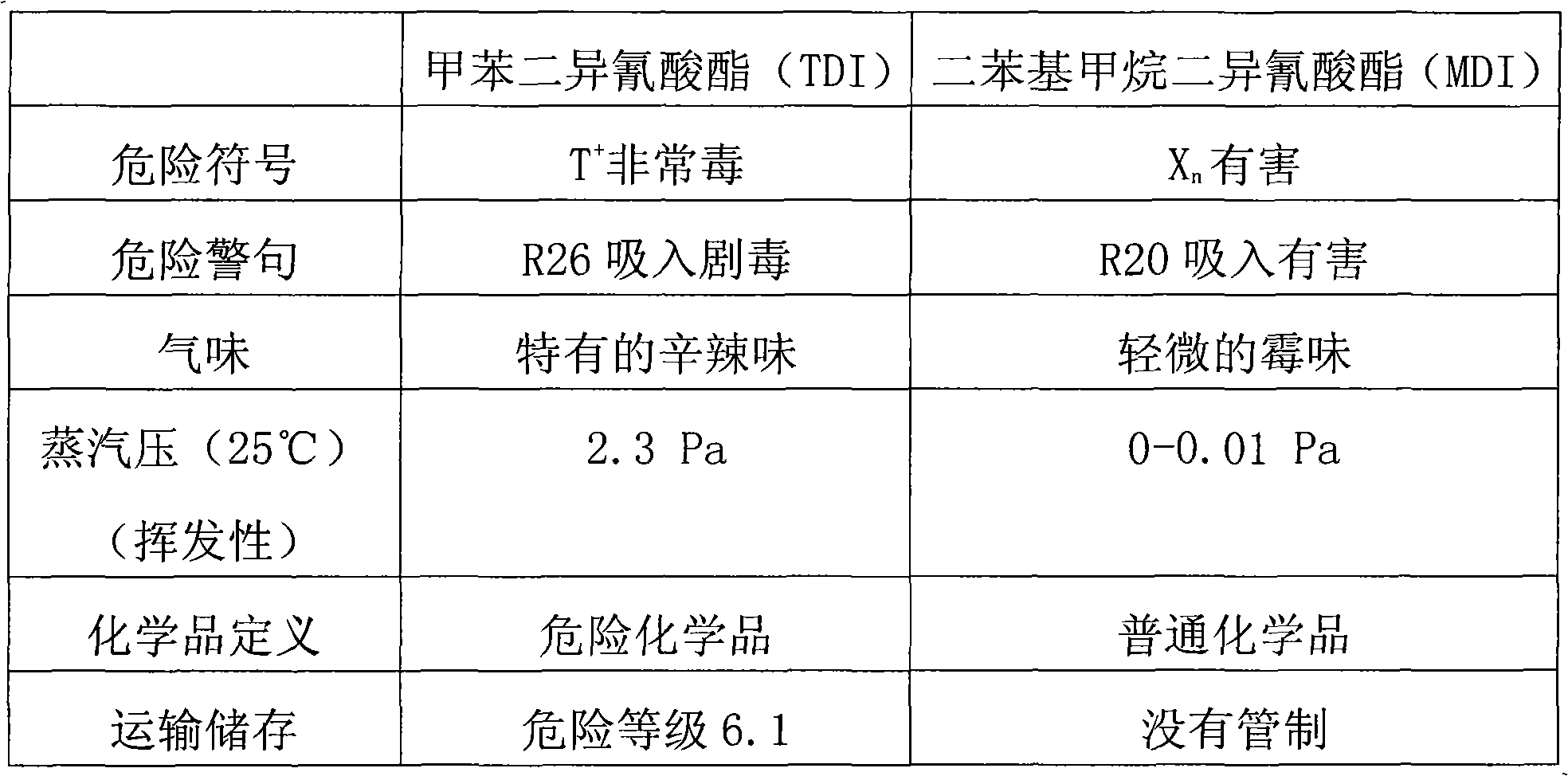
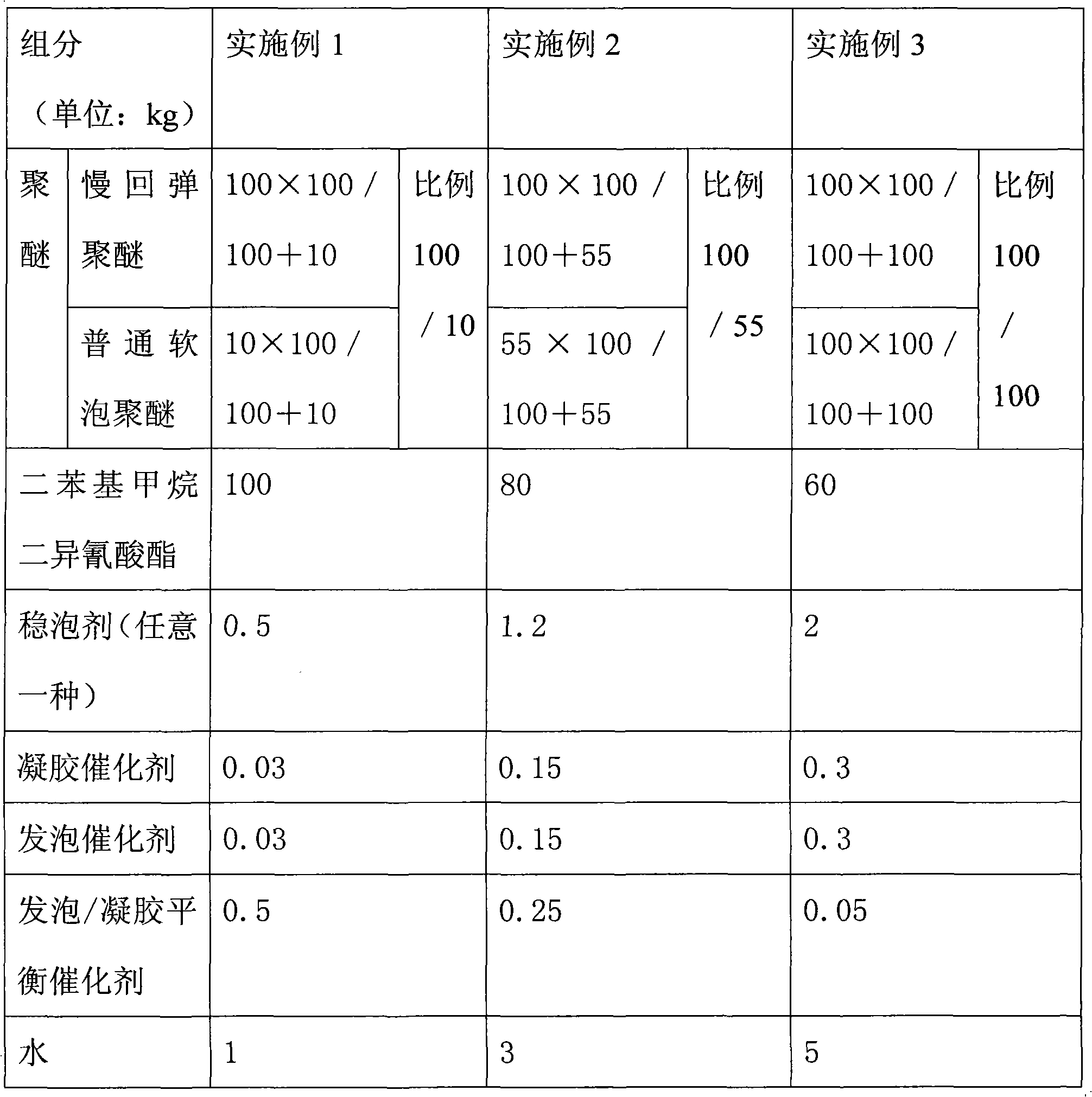
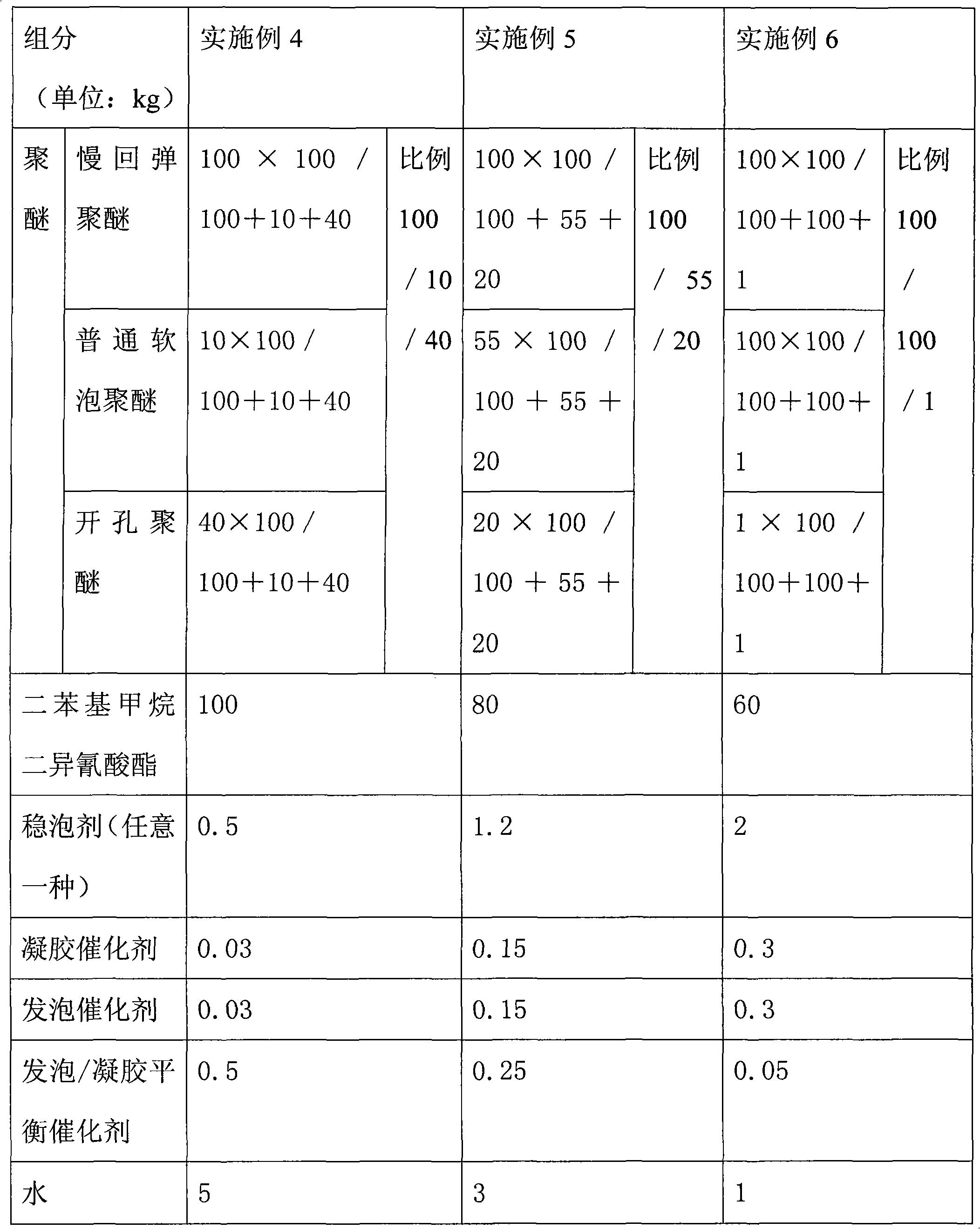
The invention relates to a high molecular synthetic material, in particular to a slowly-recoverable polyurethane foam material which is widely used as a filler. The slowly-recoverable polyurethane foam material comprises the following components in part by weight: 100 parts of polyether, 60 to 100 parts of diphenyl-methane-diisocyanate, 0.5 to 2 parts of foam stabilizer, 0.03 to 0.3 part of gel catalyst, 0.03 to 0.3 part of foam catalyst, 0.05 to 0.5 part of foam / gel equilibrium catalyst and 1 to 5 parts of water. The reaction activity of the diphenyl-methane-diisocyanate (MDI) is higher than that of toluene diisocynate (TDI), and the MDI can be fully reacted in the preparation process, so the final polyurethane product prepared from the MDI has a few residual harmful substances and nearly no toxicity, and also has properties of better handfeel, longer duration of slow recovery, better physical property, and higher flame retardancy.
Owner:上海人脊橡塑科技制品有限公司
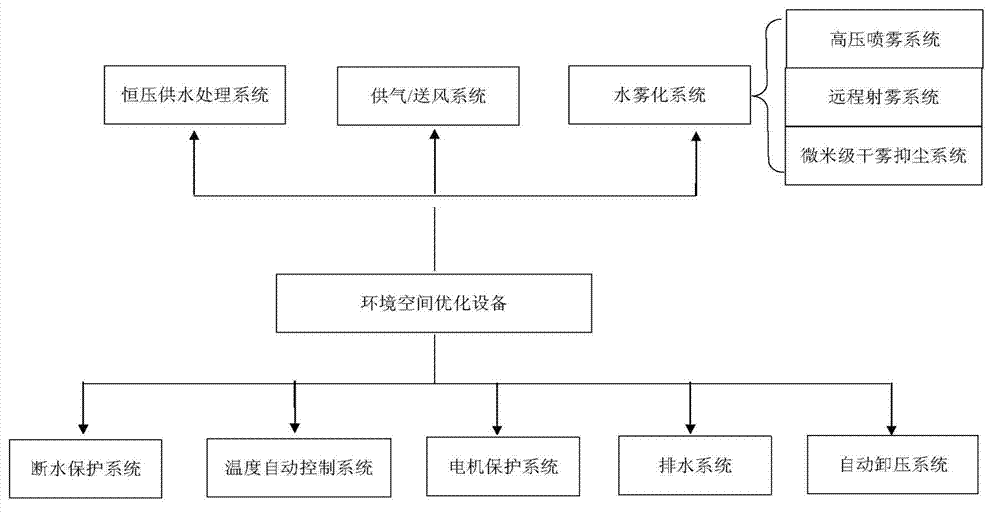
Cloud computing environmental space optimizing management system of smart city and implementation method
InactiveCN103246268AAchieve integrationEasy to integrateProgramme total factory controlThe InternetTreatment system
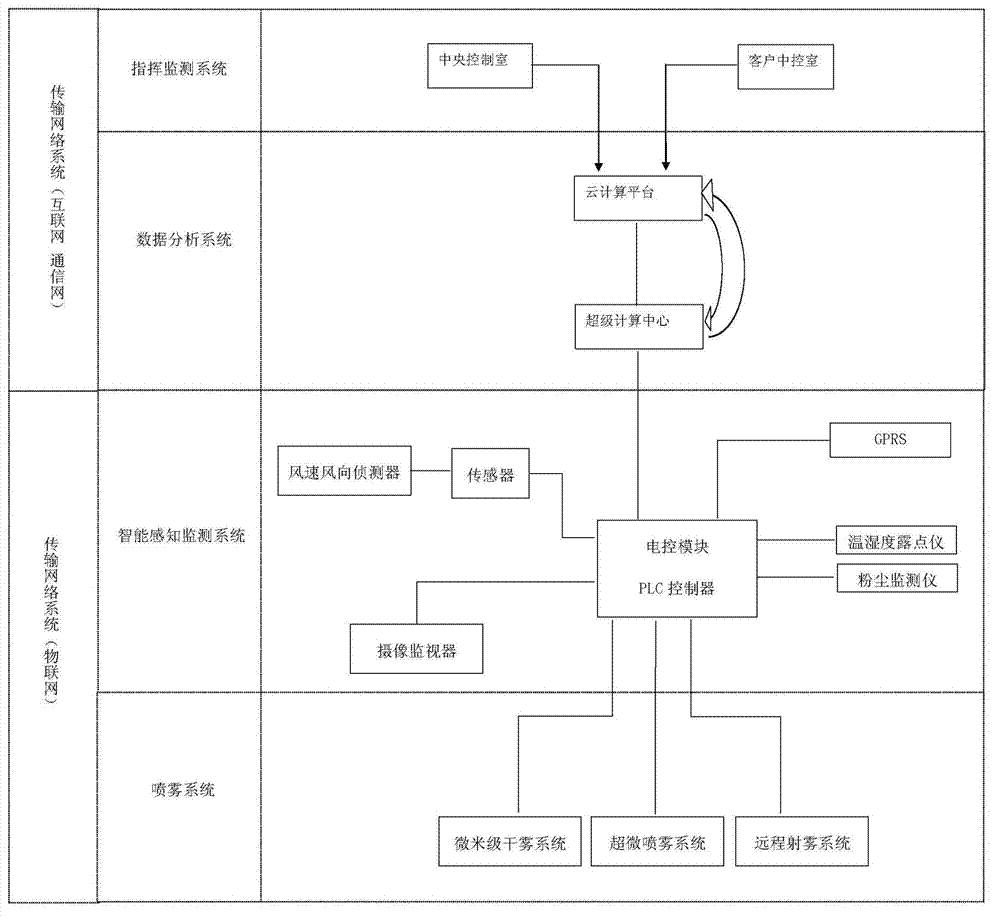
The invention discloses a cloud computing environmental space optimizing management system of a smart city and an implementation method. An on-site acquisition system module is an Internet of Things terminal device implemented by means of a sensing technology; an environmental space optimizing device module is an Internet of Things terminal device implemented by means of a control technology; an on-site controller module adopts a PLC (programmable logic controller) and is used for performing unified management on the terminal devices and transmitting parameters to a cloud computing control management module through a transmission network; a transmission network module is a data transmission system comprising the Internet, a wireless network, a communication network, a television network and the like; the cloud computing control management module is used for processing data of a system platform, adjusting an on-site control mode of the on-site controller to each environment space optimizing device and realizing interaction between an operation terminal user and an access device according to parameters which are collected on site and related to the environment space optimizing devices and parameters set by the user. According to the system and the method, smart environmental protection is realized finally, and the sustainable development of the city is maintained.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO CLOUD CUBE ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
Preparation method of healthy type low temperature hot melt adhesive
ActiveCN105400479AActivate moistureImprove the surrounding environmentNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesMetallurgyMaterials science
The invention relates to a preparation method of a healthy type low temperature hot melt adhesive, which comprises the following components by weight: 45-60 parts of TPU hot melt adhesive resin, 10-20 parts of PETG, 25-30 parts of a negative ion / bamboo-based activated carbon composite material, and 3-5 parts of a compatilizer. The method includes: (1) putting the raw materials into a material storage mechanism respectively to remove metals by high strong magnetism; (2) conveying the raw materials into a material cylinder to conduct complete stirring for 30-45min to an even state; and (3) subjecting the well mixed raw materials to secondary metal removal by strong magnetism, then conveying the treated raw materials to the feed hopper of a tape casting extruder, conducting constant speed feeding to a screw machine by a metering feed mechanism according to a preset quantity, carrying out 130-150DEG C high temperature melt mixing evenly by the screw machine to perform tape casting into a sheet, and then conducting cold pressing shaping. The healthy type low temperature hot melt adhesive provided by the invention contains organic bentonite, can significantly improve the quality homogeneity and breathability homogeneity of low temperature hot melt adhesive, and has greatly improved breathability and high quality.
Owner:HANGZHOU KAIYUE NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
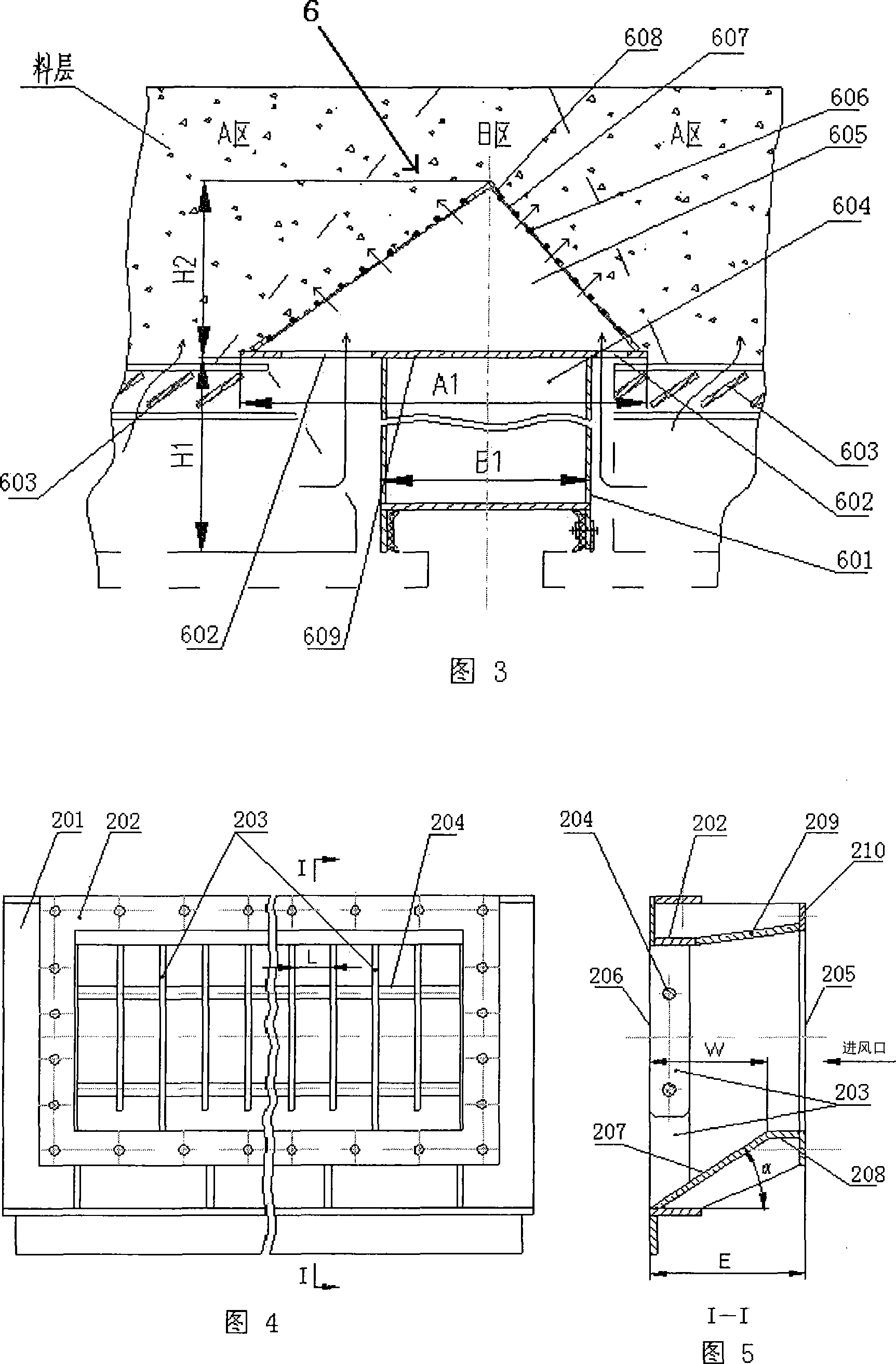
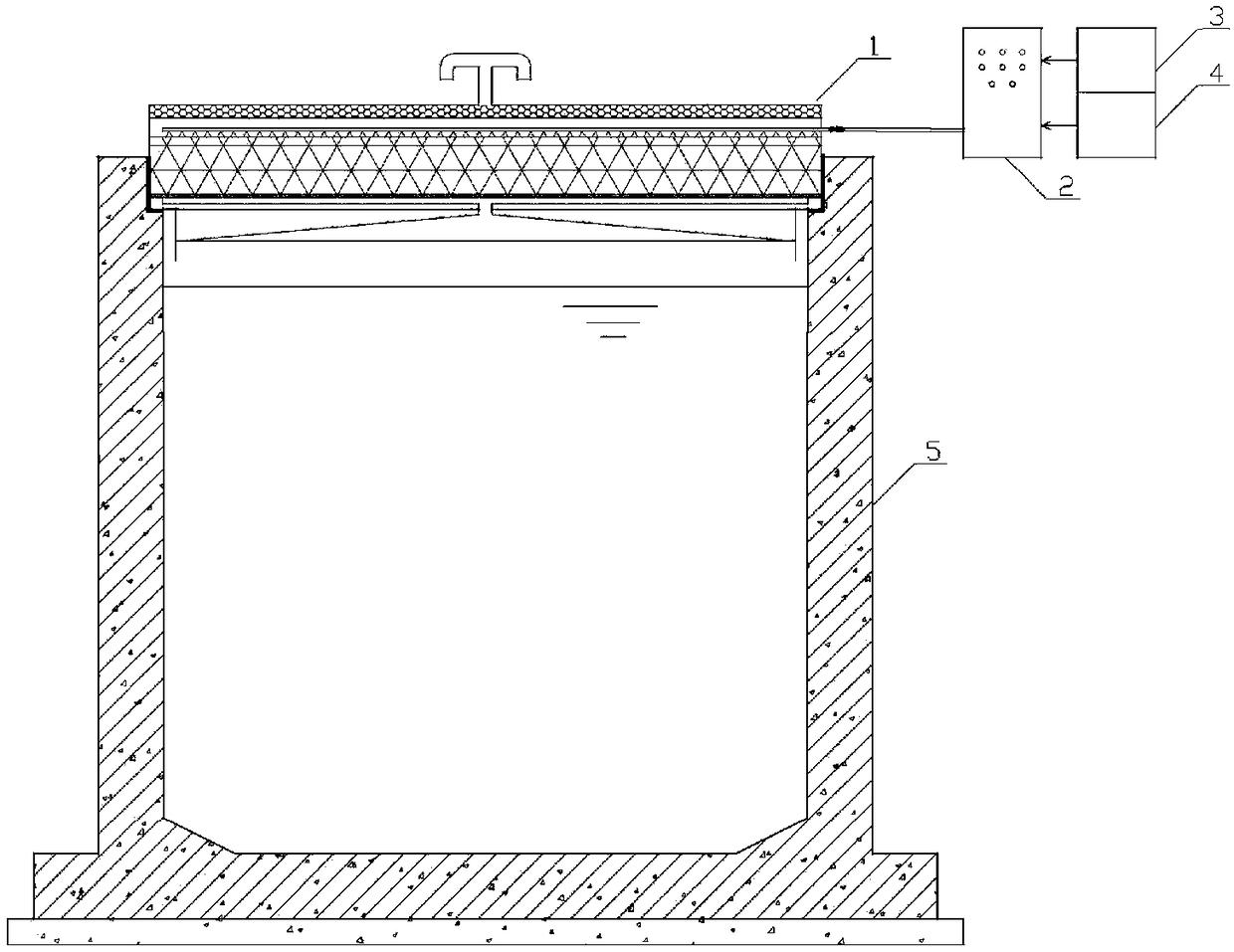
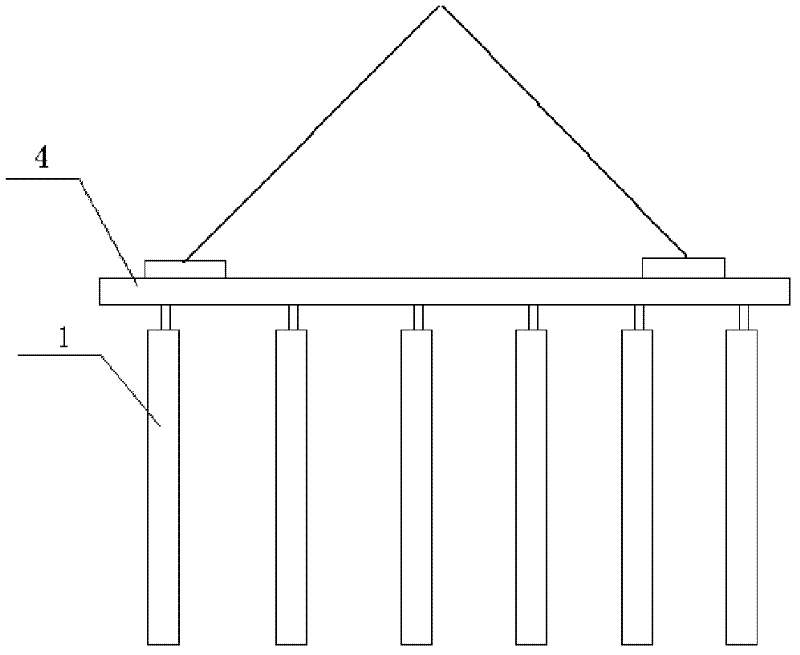
Supporting beam structure used for ring cold machine trolley
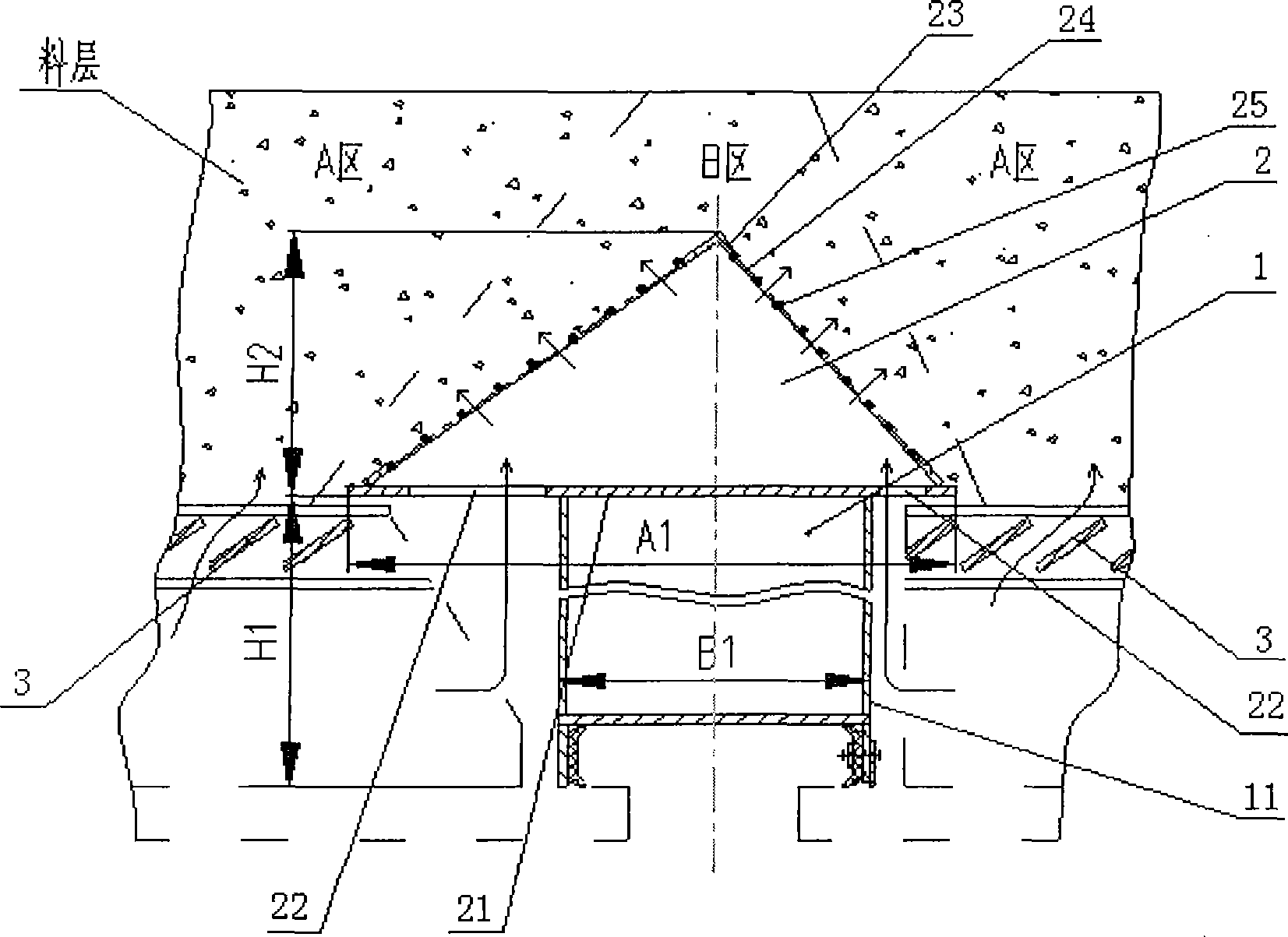
ActiveCN101118121AImprove sealingEliminate Cooling Dead ZonesCharge manipulationFurnace typesCold airEngineering
The present invention discloses a bearing beam structure for a circular cooling trolley. The present invention is based on a rectangular beam, and a triangle beam is designed at the upper part of the rectangular beam, the upper plate of the rectangular beam is extended and broadened to the both sides to form an upper cross section which is a bottom edge of the triangle beam, a plurality of ventilation channels are arranged on the bevel edge steel plates at the both waists, an air ventilating channel is arranged on the bottom edge of the triangle beam, and the side plate of the rectangular beam is a component element of the trolley static seal. The present invention is used on a water seal circular cooling machine, has the main structure character that the trolley loading is supported by the rectangular beam, the triangle beam is used to discharge and guide, through ventilating with the air ventilating channel of three edges of the triangle beam, cold air under the grid plate of the trolley can be led to the both sides and upper material layers of the triangle beam, not only the cooling dead zone is eliminated, but also the total ventilating area of the trolley can be increased about 16 percent. As a component element of the trolley static seal, the side plate of the rectangular beam can prefect the sealing of the bearing beam structure bottom part and the trolley.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
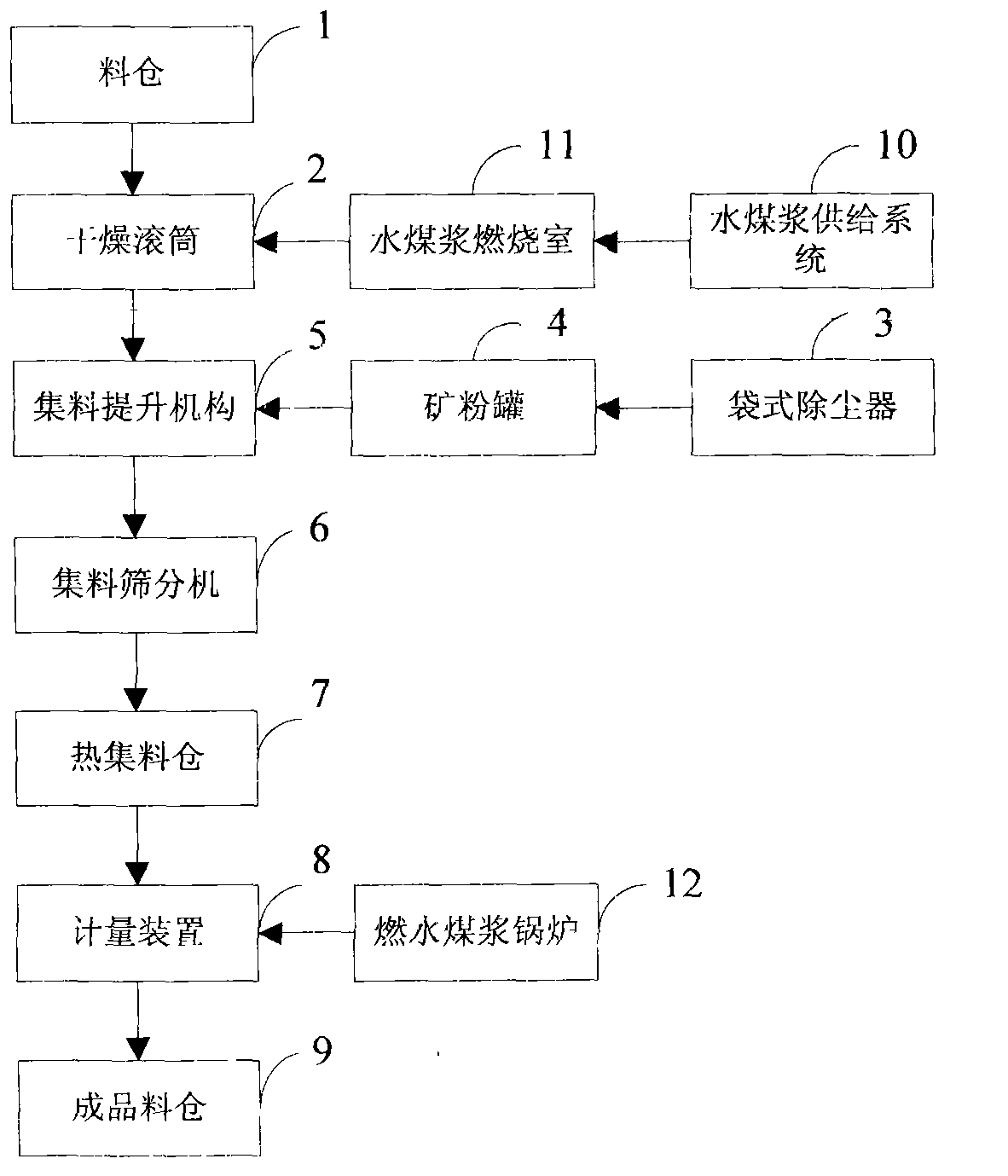
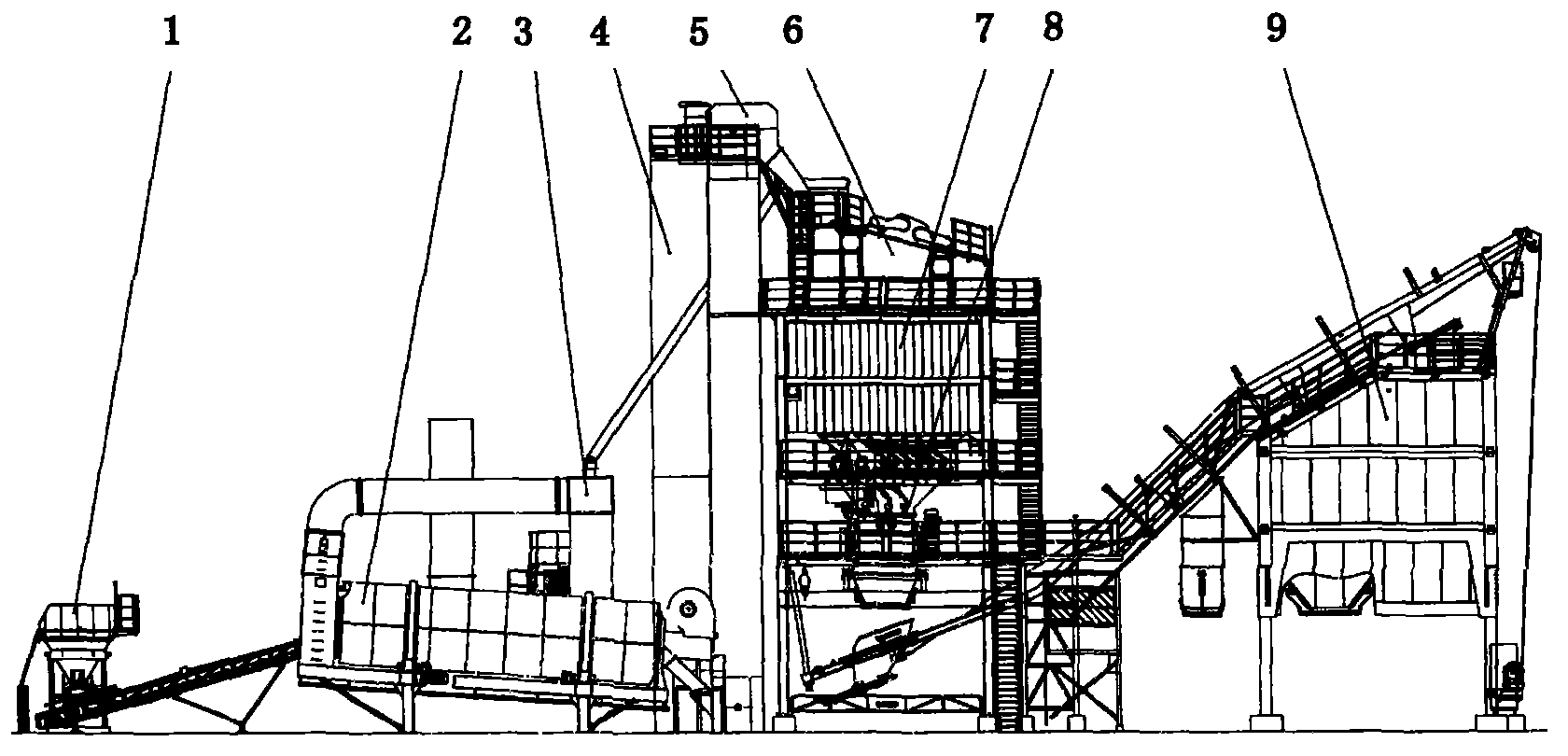
Efficient and energy-saving asphalt concrete stirring system
InactiveCN102797210ALow burnout rateReduce carbon contentRoads maintainenceCoal waterCombustion chamber
The invention provides an efficient and energy-saving asphalt concrete stirring system, which belongs to the technical field of mechanical manufacturing. In the asphalt concrete stirring system, the traditional fuel is replaced with a clean fuel of coal water slurry to provide hot air so as to dry and heat aggregates; the coal water slurry is fed to a coal water slurry combustion chamber by a coal water slurry feeding system; the coal water slurry combustion chamber is used for combusting the coal water slurry to heat the air so as to heat the aggregates; a coal water slurry combustion boiler is used for heating a heat conducting oil; and then the heated heat conducting oil is used for heating asphalt in an asphalt storage tank by a coiled tube; the coal water slurry is obtained physically machining 65% of coal, 34% of water and 1% of additive; lower burnout rate of the coal water slurry and lower carbon content in furnace slag are achieved, total space usage of a boiler room is reduced, the surrounding environment is improved, energy conservation and environment friendliness are achieved; the storage tank can be used for transporting and storing, so as to reduce pollution in the coal transporting process and storage space usage; lower hazards in storage and operation are achieved; and stronger promotion and application values are obtained.
Owner:田蒙奎
Manufacturing device for high strength bailing band
InactiveCN1631610AIncrease productivitySmall footprintOther manufacturing equipments/toolsProduction lineButt welding
The invention belongs to iron and steel field relates to packing steel belt production device. The invention high intensity steel packing belt producing device consists of unrolling machine, square joint machine, butt-welding machine, tractor, entrance loop machine, flat edge trimmer, quenching furnace, quenching water tank, tempering furnace, tempering water tank, leach drying stand, exit loop machine, tension machine, paraffin slot and rolling machine. The production device is adopted with an integral production line which has got on one line from unrolling machine, square joint machine, butt-linking machine, flat edge trimmer, to tempering insulation furnace, tempering water tank, quenching furnace, quenching water tank, paraffin slot and rolling machine all the devices all at the same level dragged by tractor and the production steel belt. The whole production line includes 1 to 10 production line unit namely installing 1 to 10 production line unit on the same line which means 1 to 10 high intensity steel packing belt can be producing at the same time on the same production line. The invention is of high efficiency, small area, low investment and non-polluting.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Silicon-containing sodium aluminate solution deep desiliconization method
InactiveCN101891227AReduce manufacturing costAchieve reuseAluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide purificationAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationSodium aluminateEconomic benefits
The invention belongs to a silicon-containing sodium aluminate solution desiliconization method and particularly relates to a silicon-containing sodium aluminate solution deep desiliconization method. In the invention, waste calcium chloride from industrial alkaline production is used to prepare a Friedel salt (FS:3CaO.Al2O3.CaC12.10H2O), and the FS is used as a desiliconizing agent to perform deep desiliconization of the silicon-containing sodium aluminate solution. The method of the invention can remove at least 60 percent of silicon dioxide from the silicon-containing sodium aluminate solution. The aim of the invention is to prepare FS by using the rich calcium chloride resource and apply the FS in the deep desiliconization of the silicon-containing sodium aluminate solution in an oxide aluminum industry. When the method is used, the recycling of waste resources can be realized, environmental pollution and the production cost of aluminum oxide can be reduced and the economic benefits of enterprises can be improved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
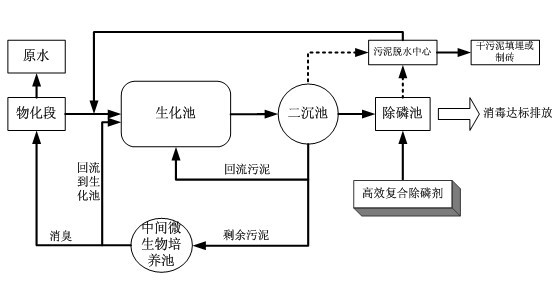
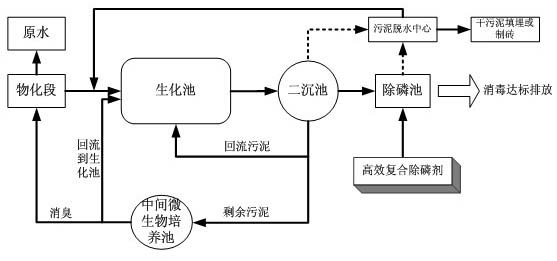
Sewage treatment method capable of sludge quantitative reduction
InactiveCN102358674AImprove the surrounding environmentReduce dosageMultistage water/sewage treatmentWastewaterSewage
The invention discloses a sewage treatment method capable of sludge quantitative reduction. According to the invention, raw water enters into a physicochemical section at first, treated raw water is discharged into a biochemical tank for biochemical treatment, treated waste water enters into a secondary sedimentation tank, is settled and then is discharged after the waste water reaches the standard, one part of sludge is extracted from the secondary sedimentation tank and is allowed to reflow into the biochemical tank, the other part of sludge is sent to an intermediate microbial cultivation tank for culture of indigenous microorganism, one part of the cultivated sludge is sent to the front of the biochemical tank, and the other part of the cultivated sludge is sent to the physicochemical section for spray deodorization of the raw water in the physicochemical section; effluent of the secondary sedimentation tank enters into a dephosphorization tank for post chemical dephosphorization, and effluent after dephosphorization is discharged after reaching the standard; all sludge in the secondary sedimentation tank is discharged into a sludge dehydration center after a certain period, supernatant obtained after dehydration reflows to the front of the biochemical tank, and dried sludge is delivered out for landfilling or brickmaking. The method enables sludge quantitative reduction of a system to be realized in the treating process of sewage, an average annual sludge output of the system being 15 to 20% of that of an original system. Deodorization is carried out in the phase of pretreatment, thereby improving surrounding environments.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGSHI ENVIRONMENT TECH
Combined technology for treatment and recycle of production sewage
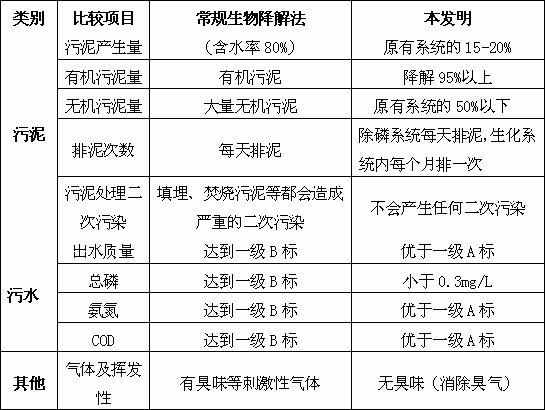
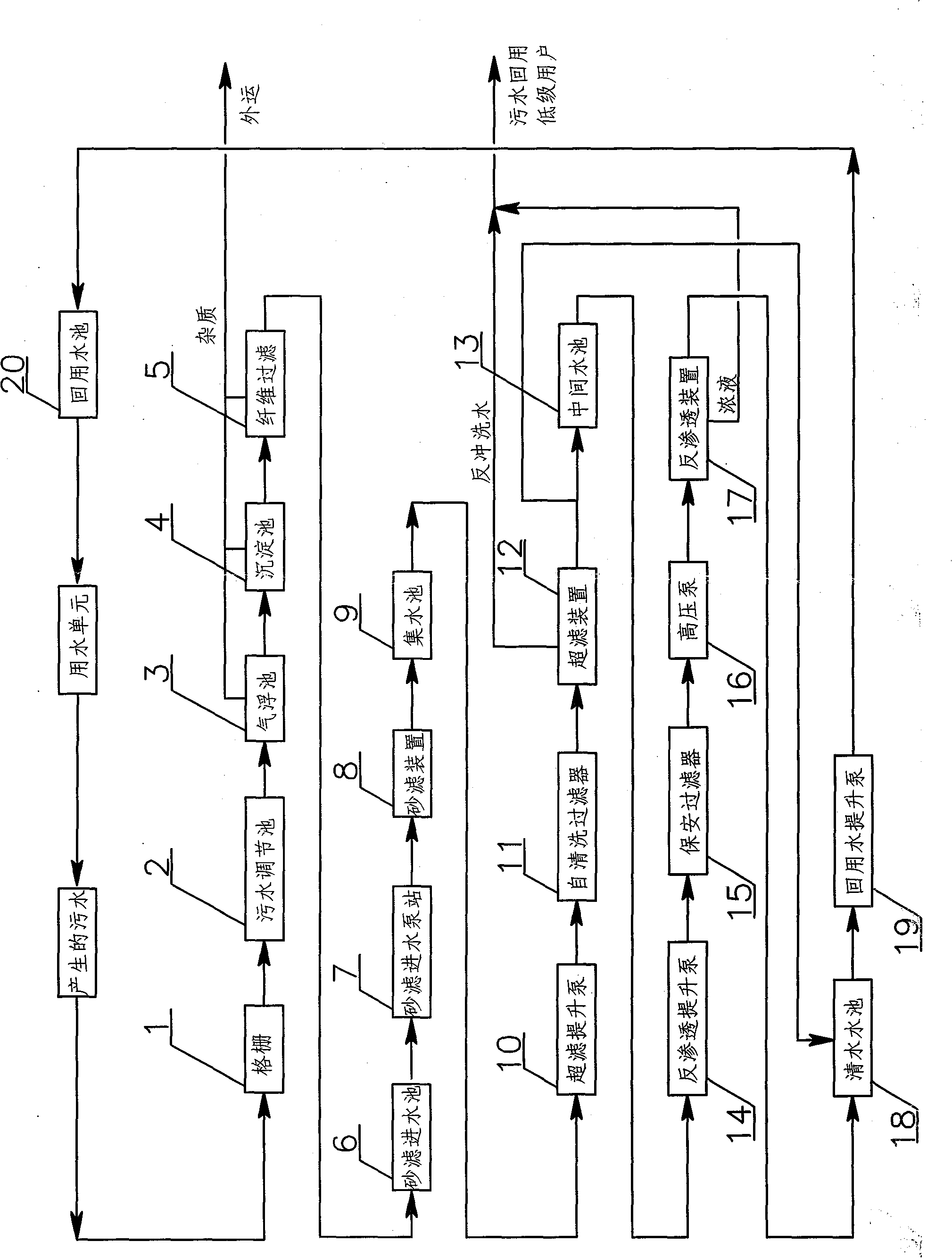
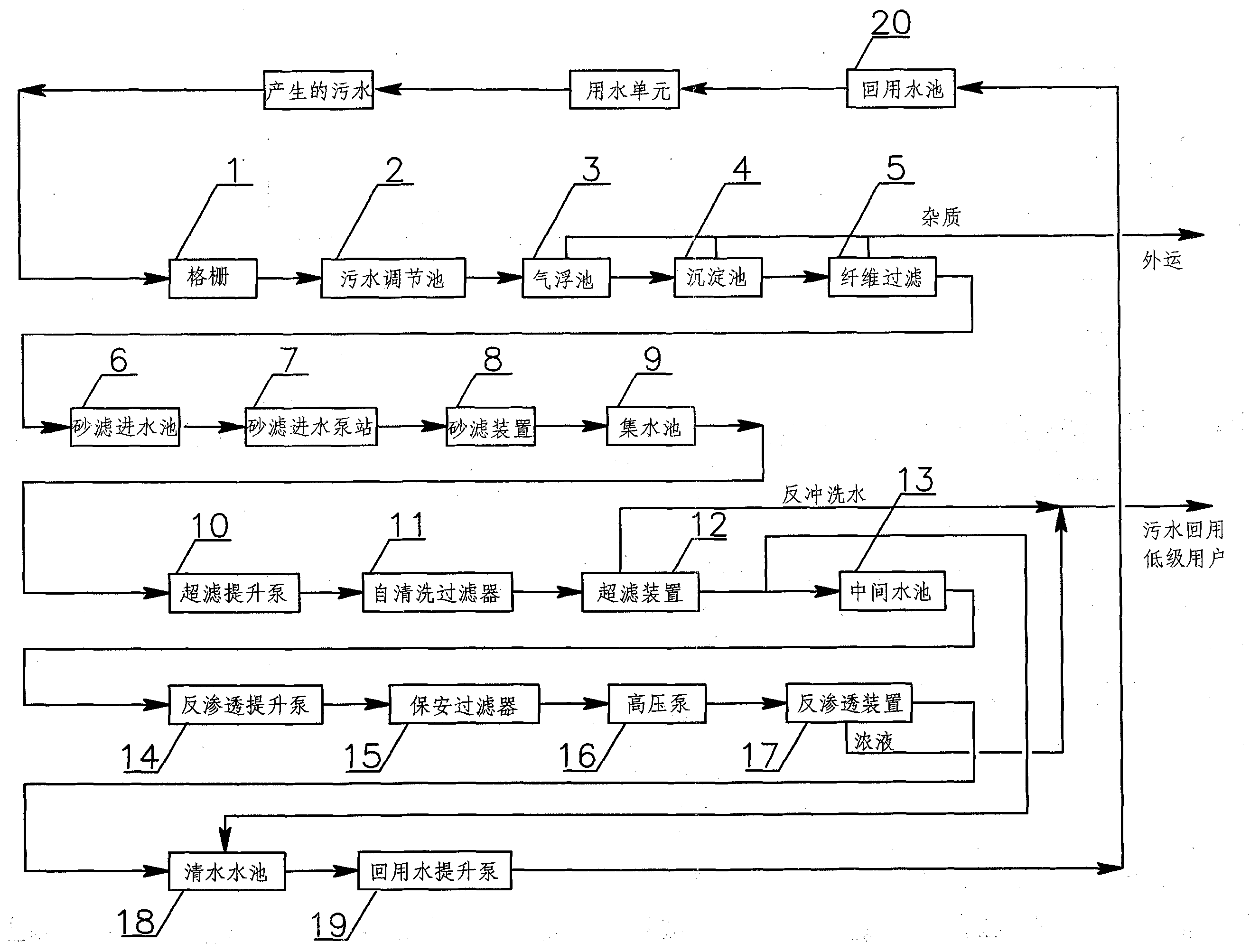
InactiveCN102399026AEfficient removalImprove water qualityGeneral water supply conservationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisFiberWater source
The invention discloses a combined technology for treatment and recycle of production sewage. The combined technology for treatment and recycle of production sewage comprises sewage pretreatment, sewage depth treatment and sewage desalination treatment. A process flow of the combined technology comprises that sewage is orderly treated by a grille, a sewage adjustment tank, an air floatation tank, a sedimentation tank, a fiber filtration unit, a sand filtration water inlet station, a sand filtration device, a water collecting tank, an ultrafiltration elevator pump, a self-cleaning filter, an ultrafiltration device, an intermediate water tank, a reverse osmosis elevator pump, a clear water tank, a reuse water elevator pump and a reuse water tank. The combined technology utilizes steel enterprise production sewage as a water source and mainly adopts an air floatation tank-sedimentation tank-fiber filtration unit-sand filtration device-ultrafiltration device combined way before a reverse osmosis desalination process. The combined technology can effectively remove oil pollutants, organic matter pollutants, colloid pollutants and suspension pollutants in sewage, improve reverse osmosis feed water quality, reduce chemical cleaning frequency of a reverse osmosis membrane, increase a service life of the reverse osmosis membrane, and reduce an operation cost.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Integral sputtering-oxygenating-biofiltering waste water purifying apparatus and process
InactiveCN1931743AGood removal effectImprove denitrification effectTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentBio filtrationSewage
The present invention is integral sputtering, oxygenating and biofiltering waste water purifying apparatus and process, and belongs to the field of sewage treating technology in environmental engineering. The advanced sewage treating technology is for use in subzone, school and countryside. The sewage purifying apparatus includes parallel anaerobic denitrogenating reactors, sputtering, oxygenating and biofiltering reactor and precipitating area. Sewage is treated in the anaerobic denitrogenating reactors, the sputtering, oxygenating and biofiltering reactor and the precipitating area successively, and part of the output water is returned to the anaerobic denitrogenating reactors. The present invention has high organic matter and nitrogen eliminating efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Catalyst screening method during preparation of sulphuric acid
InactiveCN101391755AReduce energy consumptionImprove efficiencySulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidWorking environmentEconomic benefits
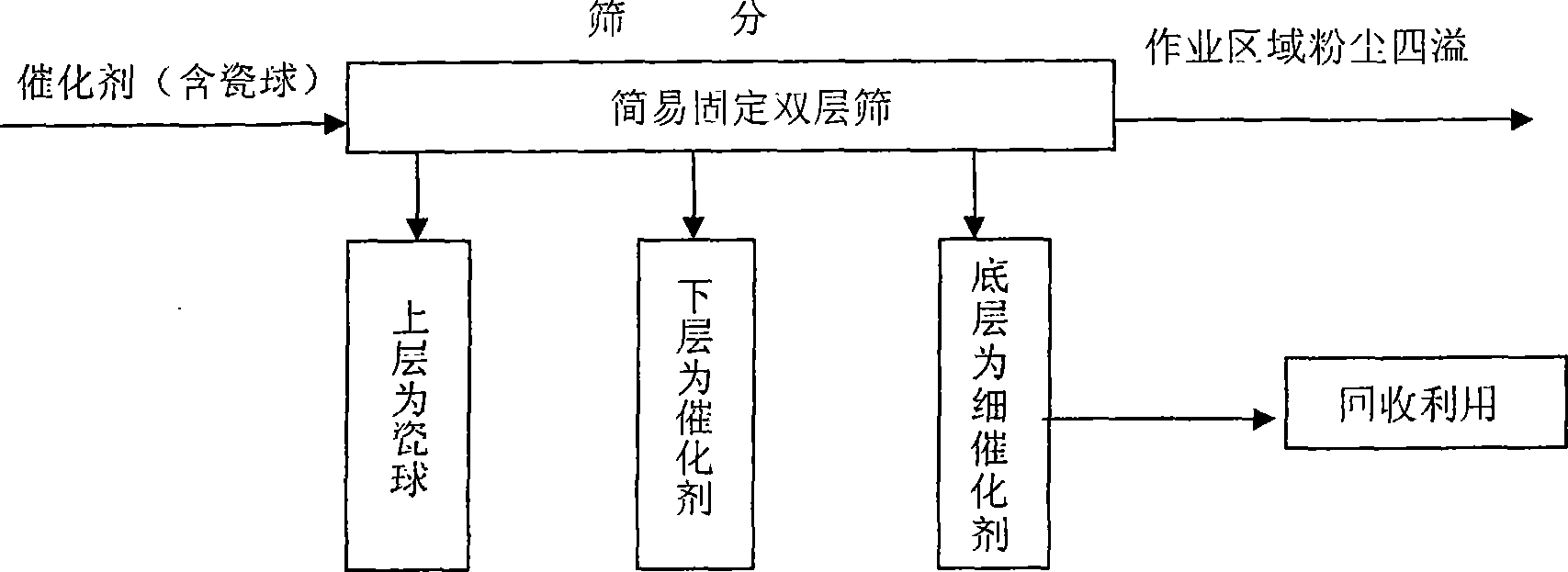
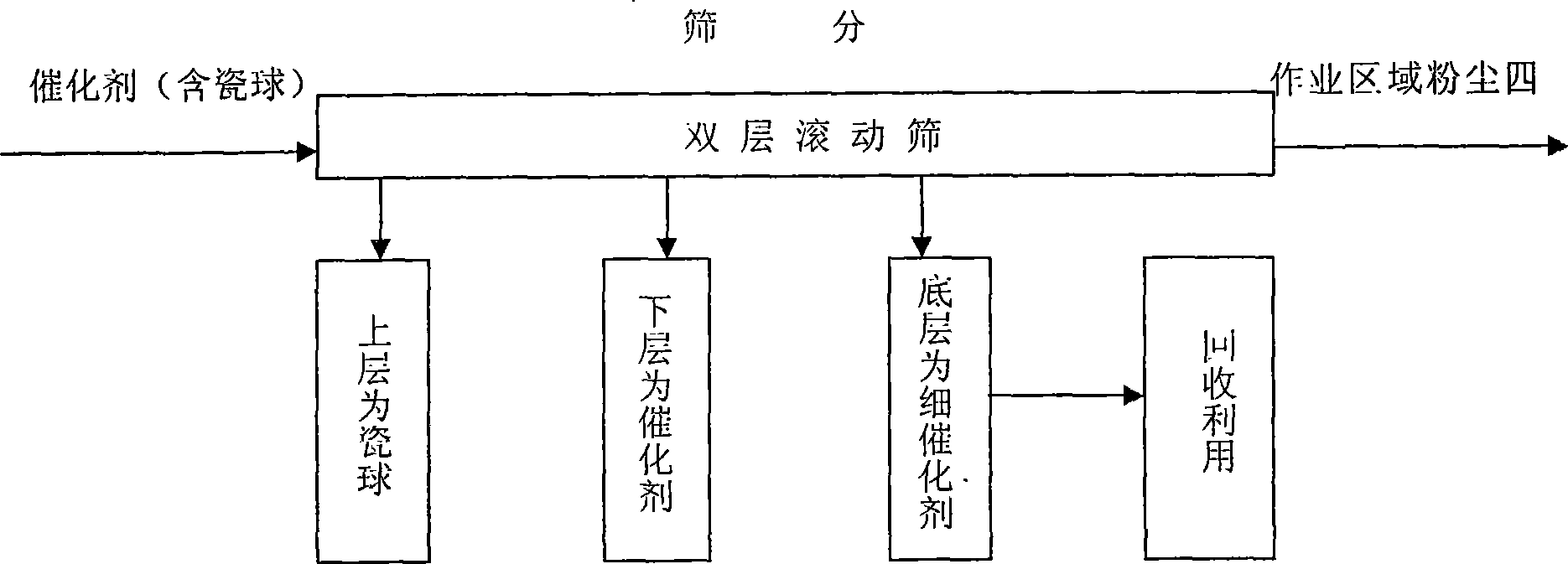
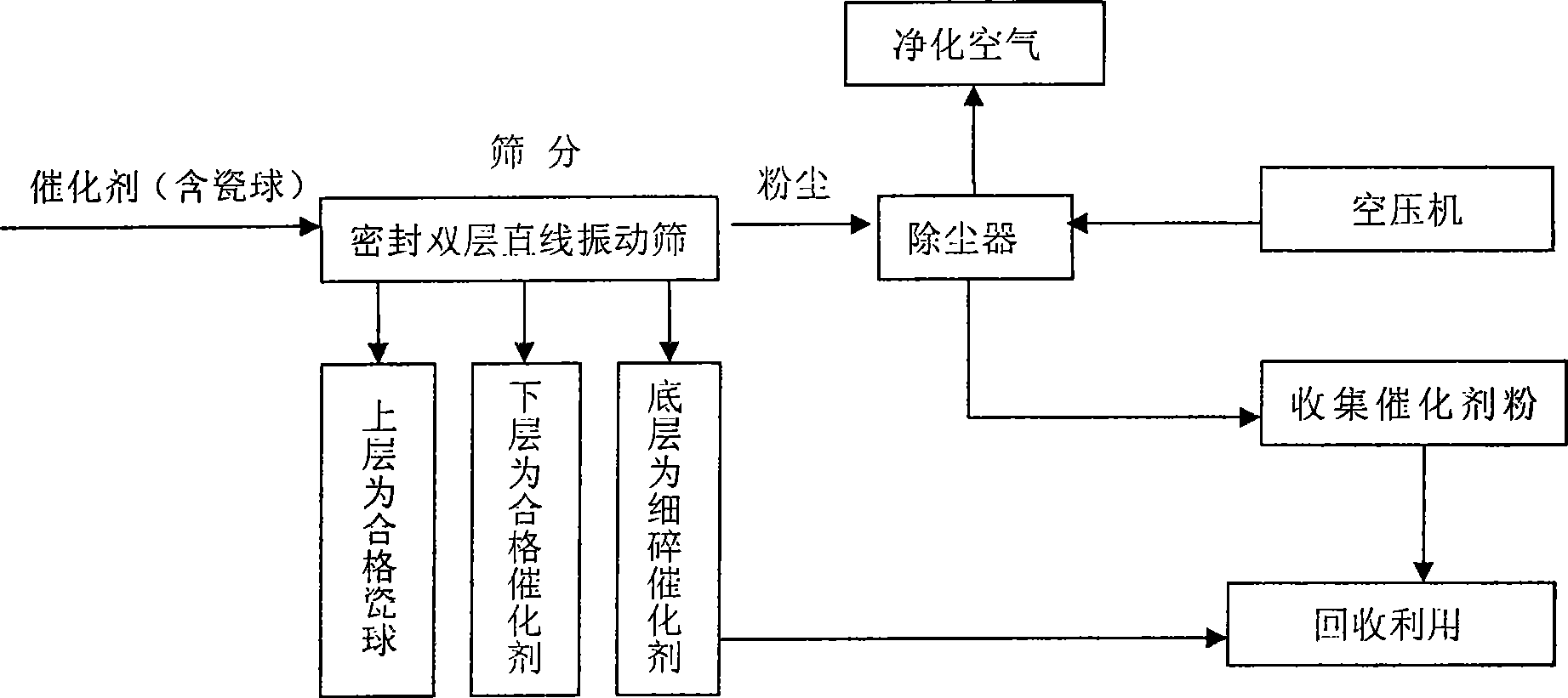
The invention discloses a sulfuric acid catalyst screening method, which comprises: the catalyst is placed in a sealed double-layer linear mechanical vibrating screen to be screened level by level and the dusts generated during screening are filtered by a dust catcher; the screened thin catalyst grains and the catalyst dusts collected by the dust catcher are bagged respectively for later recycling. The application of the method can dramatically enhance the work environment and the dust density of the screening work zone is less than 3mg / m<3>, thus effectively protecting the health of workers. The improvement of environment can reduce the investment cost and the total screening cost can be saved by 5 to 10 percent, thus enhancing the economic benefit. The screening time can be dramatically shortened so as to obtain more time for the starting of sulfuric acid apparatus and guarantee smooth completion of the manufacturing task, thus having positive practical meaning and high popularization and application value.
Owner:云南云天化股份有限公司三环分公司 +1
Air permeable and ion rich medium temperature hot melt leather
The invention relates to an air permeable and ion rich medium temperature hot melt leather. The preparation technology of the hot melt leather includes: fully stirring 25-35 parts by weight of a negative ion / diatom mud composite material and 15-25 parts by weight of deionized water evenly, then adding 45-55 parts by weight of emulsion resin, conducting mixing for 25-35min to make the prepared slurry fully mixed uniformly, then subjecting non-woven fabric to dip padding in a rubber dipping groove, carrying out 175-185DEG C drying tentering shaping, and then performing cooling shaping. The air permeable and ion rich medium temperature hot melt leather provided by the invention contains organobentonite, and the moisture absorption and air permeability of the air permeable and ion rich medium temperature hot melt leather can be significantly improved. Tests find that the ageing resistance and antistripping performance are also greatly improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU KAIYUE NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Polishing auxiliary device for vehicle production
InactiveCN108789038AEasy to fixWide thickness rangeGrinding machinesGrinding work supportsFixed frameUsability
The invention relates to the technical field of vehicle production auxiliary devices, in particular to a polishing auxiliary device for vehicle production; and the device can adjust the distance between a left fixed piece and a right fixed piece to conveniently fix parts with multiple sizes to reduce the use limitation, meanwhile, improves the fixing effect of the left fixed piece and the right fixed piece on uneven areas of the parts to widen the thickness range of the parts fixed by the left fixed piece and the right fixed piece to improve the use reliability, and meanwhile, can treat dust generated in the polishing process to improve surrounding environment, the protecting effect on the respiratory tract health of workers and the usability. The device comprises a base, a support frame,a left bracket, a right bracket, the left fixed piece and the right fixed piece, and further comprises a left adjusting piece and a right adjusting piece; and the left fixed piece comprises a left connecting plate, a first upper connecting plate, a first lower connecting plate, a first upper thread rod and a first upper fixed plate. The device further comprises a fixed frame, two sets of suckers,two sets of communicating pipes, an exhaust piece and a dust removing box.
Owner:太仓葛龙模具有限公司
Anaerobic tank sealing deodorization cover for rural domestic and breeding sewage treatment and treatment method of anaerobic tank sealing deodorization cover
InactiveCN108079763ANo manual operationReduce human inputDispersed particle separationTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBio filtrationSewage
The invention discloses an anaerobic tank sealing deodorization cover for rural domestic and breeding sewage treatment and a treatment method of the anaerobic tank sealing deodorization cover. A deodorization cover is arranged at the top of an anaerobic tank, a treatment device is arranged on the deodorization cover and comprises a gas collecting hood, an efficient biofiltration deodorization layer and an adsorptive deodorization layer from bottom to top; an automatic spray device for spraying a deodorization agent or a biological nutrient solution onto the deodorization cover is arranged at the top of the deodorization cover. By means of the anaerobic tank sealing deodorization cover, the operation difficulty of rural domestic sewage odor treatment can be reduced, labor investment can bereduced, the use enthusiasm of farmers can be raised, and the pollution to the environment and atmosphere can be effectively reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Preparation method of one-way water-permeable and breathable type fibrosis fiberboard
ActiveCN105437698AHigh utility valueTo promote metabolismSynthetic resin layered productsWoven fabricPolymer chemistry
The invention relates to a preparation method of a one-way water-permeable and breathable type fibrosis fiberboard. The method includes the steps of firstly, evenly stirring 25-35 weight parts of anion / diatom ooze composite material and 15-25 weight parts of deionized water, adding 45-55 weight parts of emulsion resin to be mixed and stirred for 25-35 min, conducting pad-rolling on non-woven fabric through a glue soaking tank, conducting drying, stentering and shaping at a temperature of 175-185 DEG C, and conducting cooling and shaping to obtain a water-permeable and breathable type semi-finished product material; secondly, conducting pad-rolling after waterproof emulsion resin treatment is conducted on spunlace non-woven fabric 0.6 mm thick, punching holes vertically by means of high pressure through a drying box, conducting drying, stentering and shaping at a high temperature of 175-185 DEG C, and obtaining a waterproof semi-finished product material after cooling and shaping, wherein the mass ratio of emulsion resin to spunlace non-woven fabric is 1:(3-5); thirdly, attaching and forming the water-permeable and breathable type semi-finished product material and the waterproof semi-finished product material through a polyurethane hot melt mesh film by means of high temperature and high pressure, and obtaining the one-way water-permeable and breathable type fibrosis fiberboard. The moisture absorption performance, breathability, ageing resistance and stripping resistance of the prepared product are greatly improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU KAIYUE NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Construction waste treatment device
The invention relates to a construction waste treatment device. The construction waste treatment device comprises a feeding box, a crushing mechanism, a bracket, a screening device, a vibrating deviceand a conveying device, wherein the feeding box is arranged at the top of the bracket; the crushing mechanism is arranged in the feeding box; the screening device is arranged on the bracket below thefeeding box; the vibrating device is arranged on the screening device; a conveying device is arranged on the bracket below the screening device; According to the multifunctional construction waste treatment device, the feeding box in the crushing device of the device is provided with a box cover controlled by a hydraulic mechanism to be opened and closed; a large amount of noise and dust can be closed by closing the box cover after feeding, so that the surrounding environment in a construction waste treatment process is greatly improved; when the box cover is closed for crushing, a spraying mechanism above the box cover works, so that cleanliness of the crushing device can be maintained; dust flying is reduced; crushing efficiency is greatly improved; an effect of cleaning broken stones can also be achieved; the workload of recycling construction wastes is reduced; and construction wastes cannot be stuck together.
Owner:CCCC HIGHWAY MAINTENANCE ENG TECH
Method for removing harmful anions from aqueous solution by adopting Friedel salt or Kuzel salt
InactiveCN103523860AExcept haveRemove reachWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeAnion exchangersIndustrial effluentWater source
The invention discloses a method for removing harmful anions from an aqueous solution by adopting a Friedel salt or Kuzel salt. The method comprises a step of removing the harmful anions from the aqueous solution by adopting the Friedel salt or Kuzel salt, wherein the harmful anions comprise one or more of F<->, CN<->, SCN<->, As (III, V) and Cr (VI), and the aqueous solution comprises one or more of drinking water, underground water sources, industrial wastewater and tailings water containing harmful anions. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the Friedel salt or Kuzel salt is applied to the aqueous solution containing the harmful anions, the removal efficiency of the harmful anions is very high, and the effect is obvious; the materials required for preparing the Friedel salt or Kuzel salt are wide in source, low in preparation energy consumption and less in investment; by adopting the method to remove the anions from the aqueous solution, the flow is short and the cost is low, so that the method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A continuous casting tundish casting residual steel processing device and its method
InactiveCN102266937AReduce the amount of cuttingReduce the loss of metallic ironCasting cleaning apparatusTundishSteelmaking continuous casting
The invention discloses a method for treating excess cast steel in a continuous casting tundish: after the steelmaking and continuous casting tundish is replaced, before the remaining molten steel in the tundish is solidified, several dividing plates are vertically inserted into the tundish at intervals In the molten steel in the tundish, after the molten steel in the tundish is cooled and solidified, the cut off steel block is taken out. This treatment method can reduce the cutting amount of residual steel in the tundish, reduce the loss of metallic iron, increase the recovery rate of metallic iron, reduce the labor intensity of workers, and at the same time avoid the smoke and dust pollution caused by cutting, improve the working area and surrounding environment, and reduce the investment in dust removal And operating costs, reduce production costs, do not need to use large vehicles for reverse transportation, and save cutting and processing sites.
Owner:邱艳生 +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com