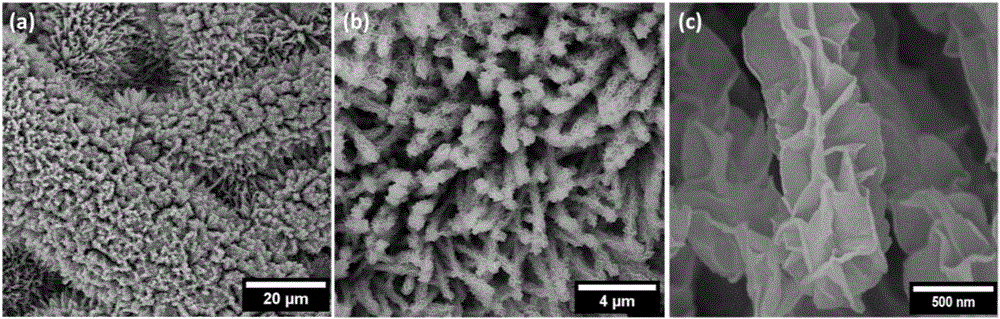
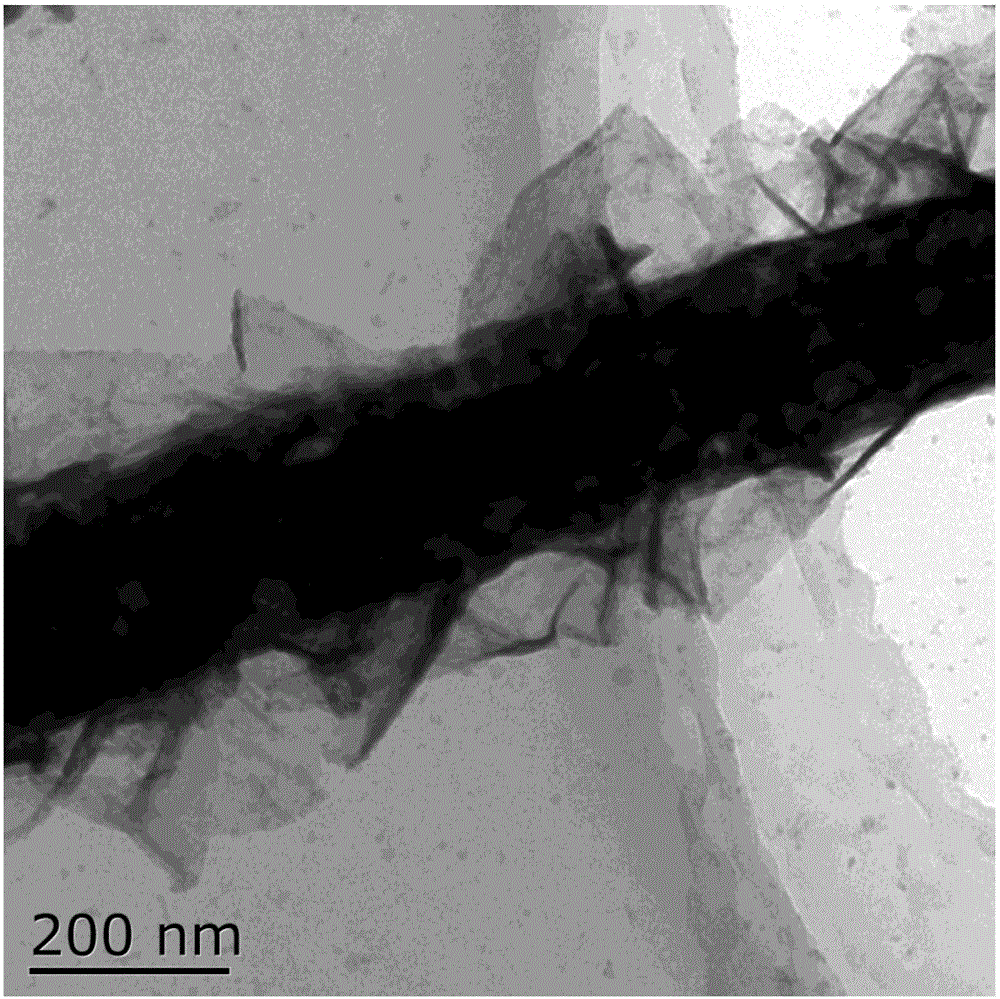
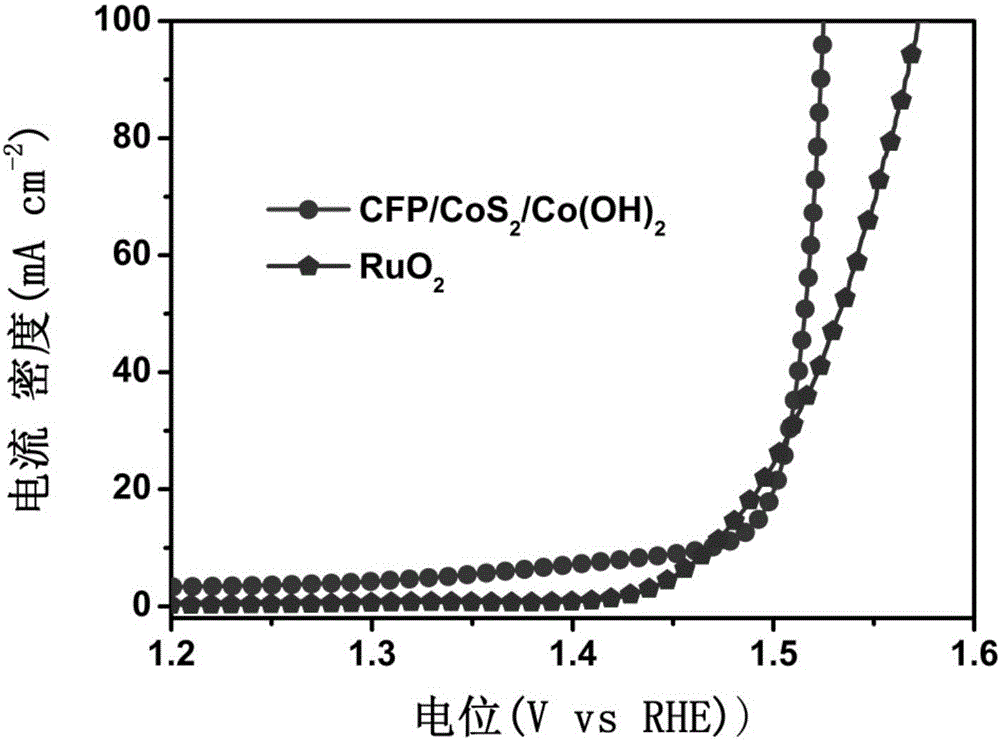
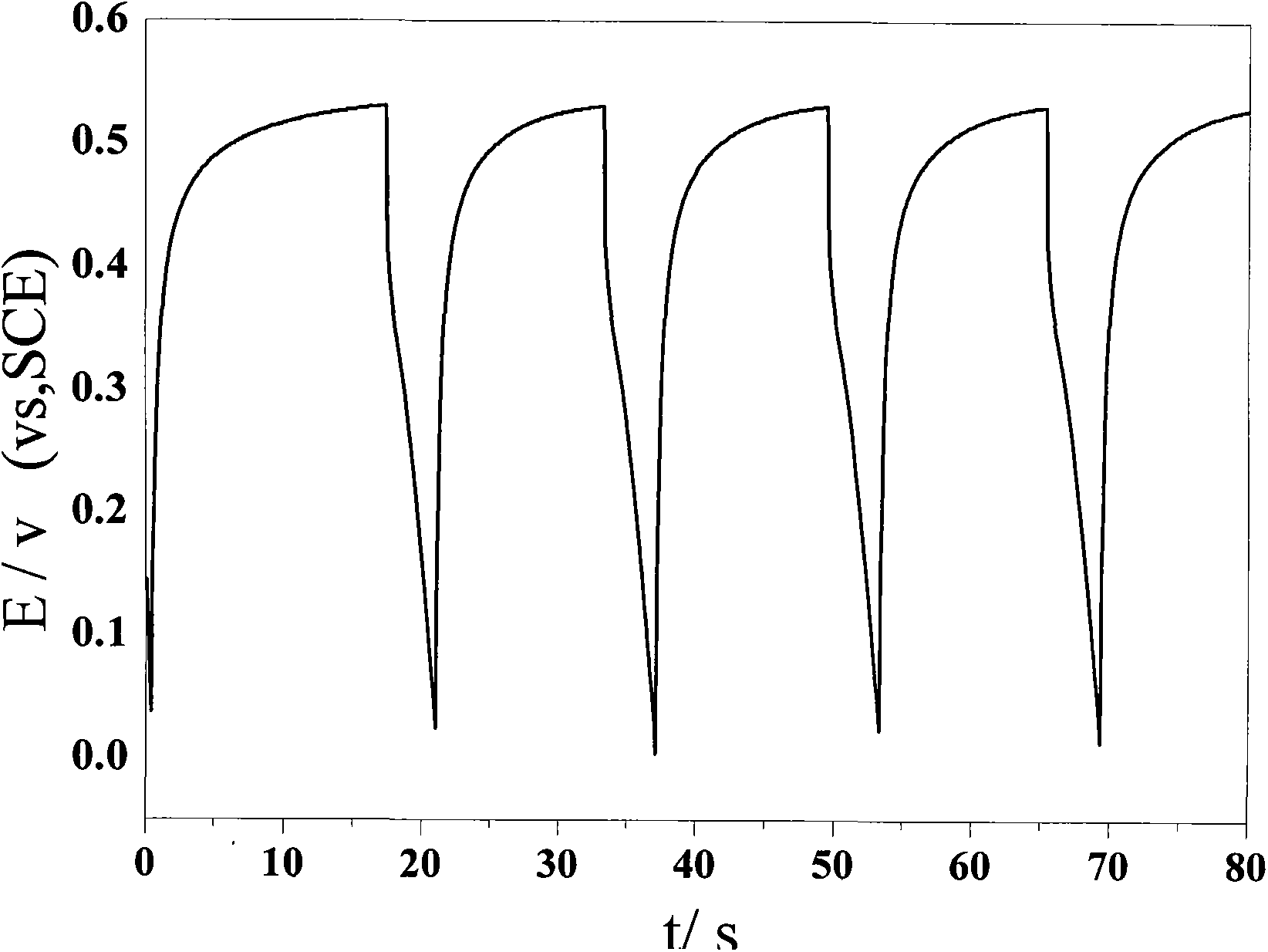
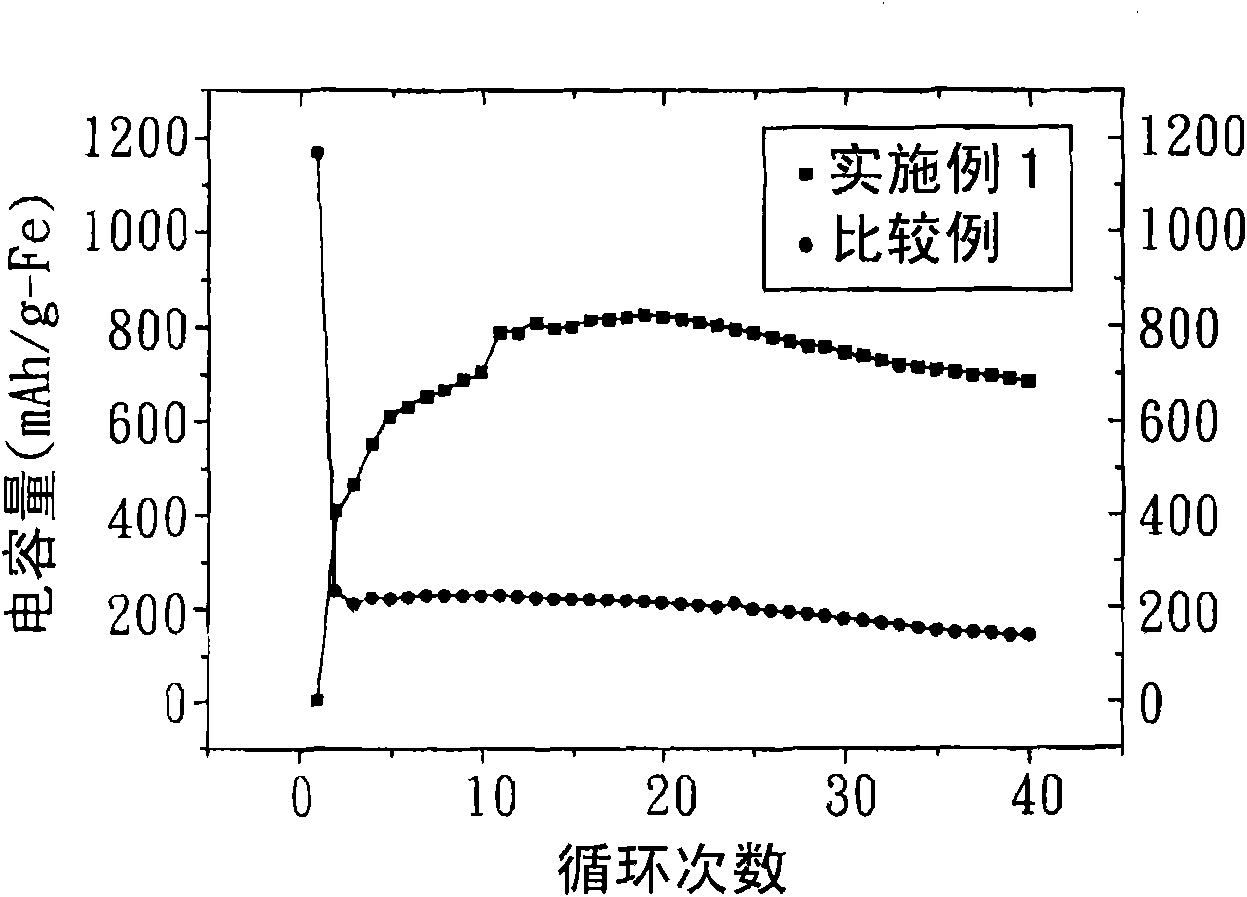
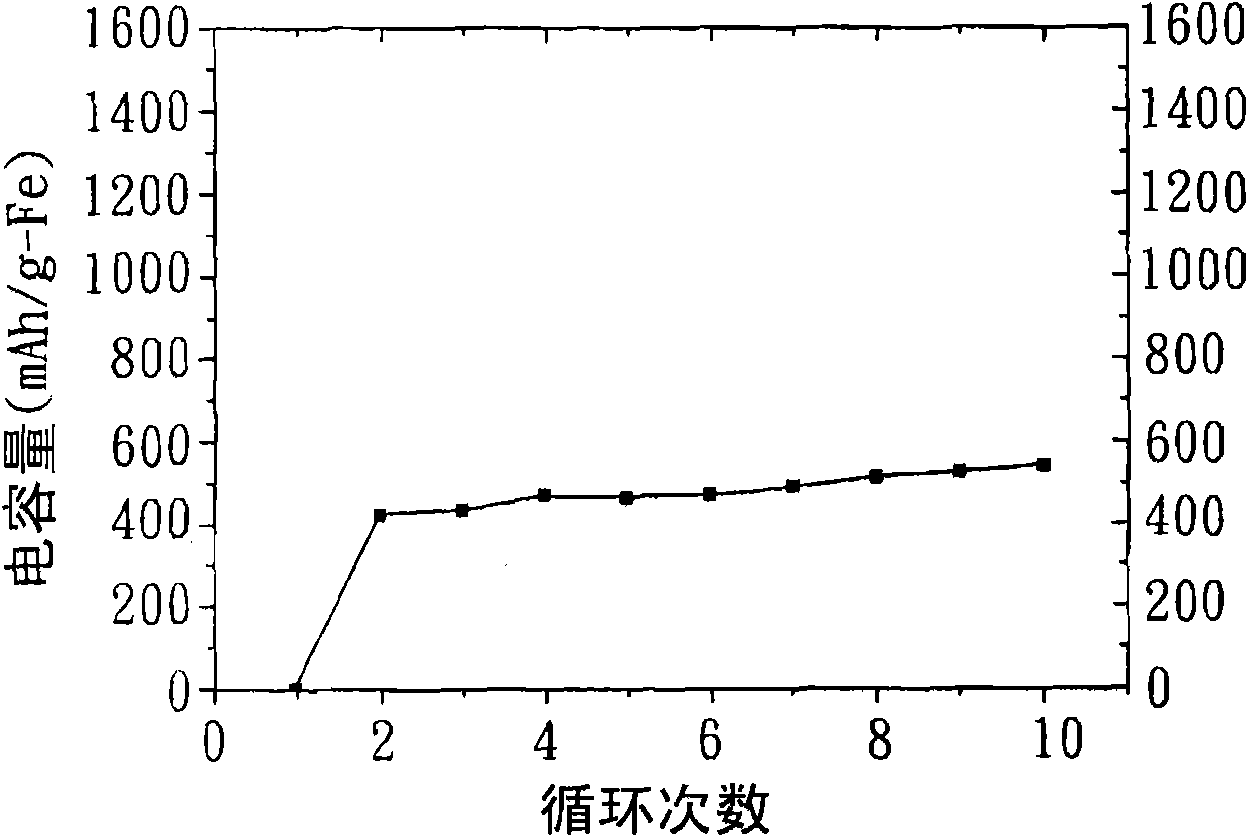
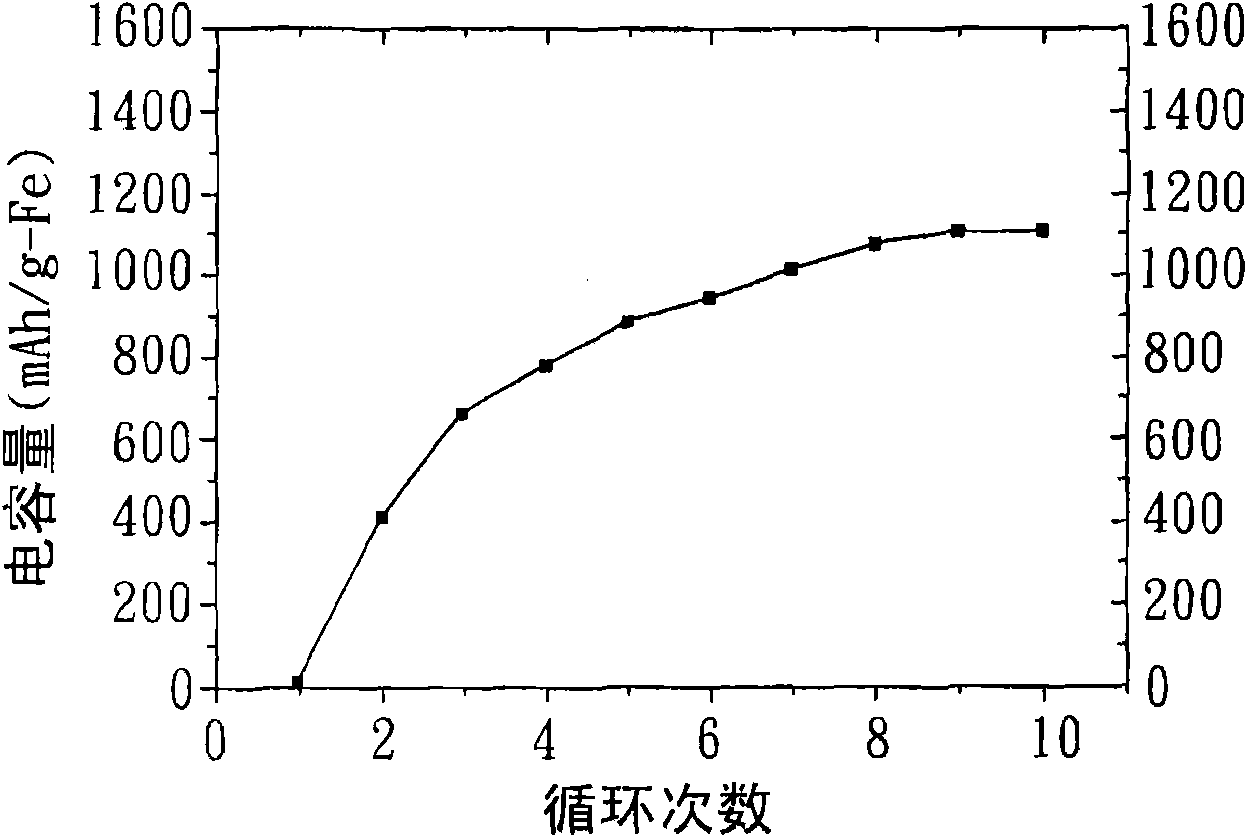
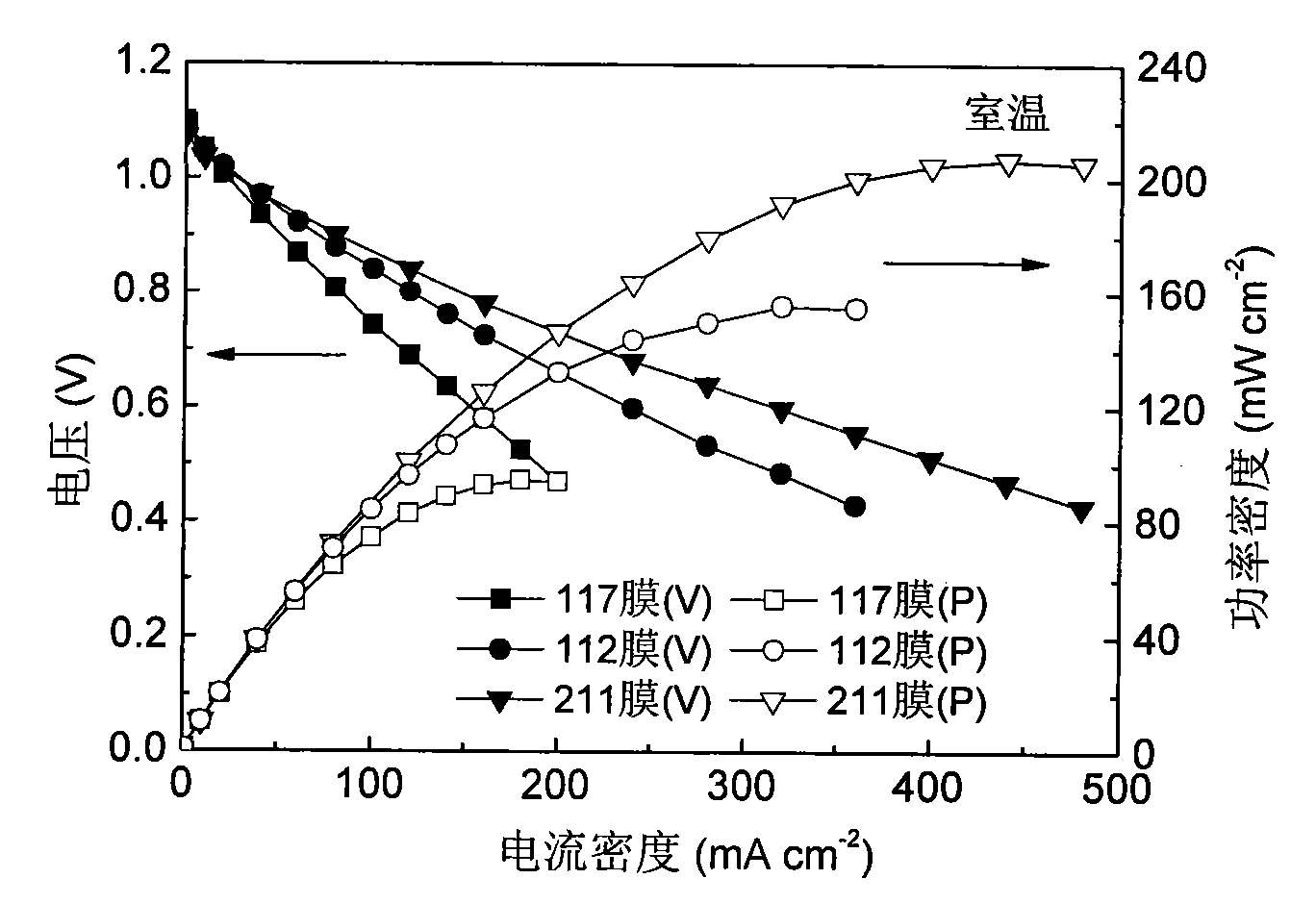
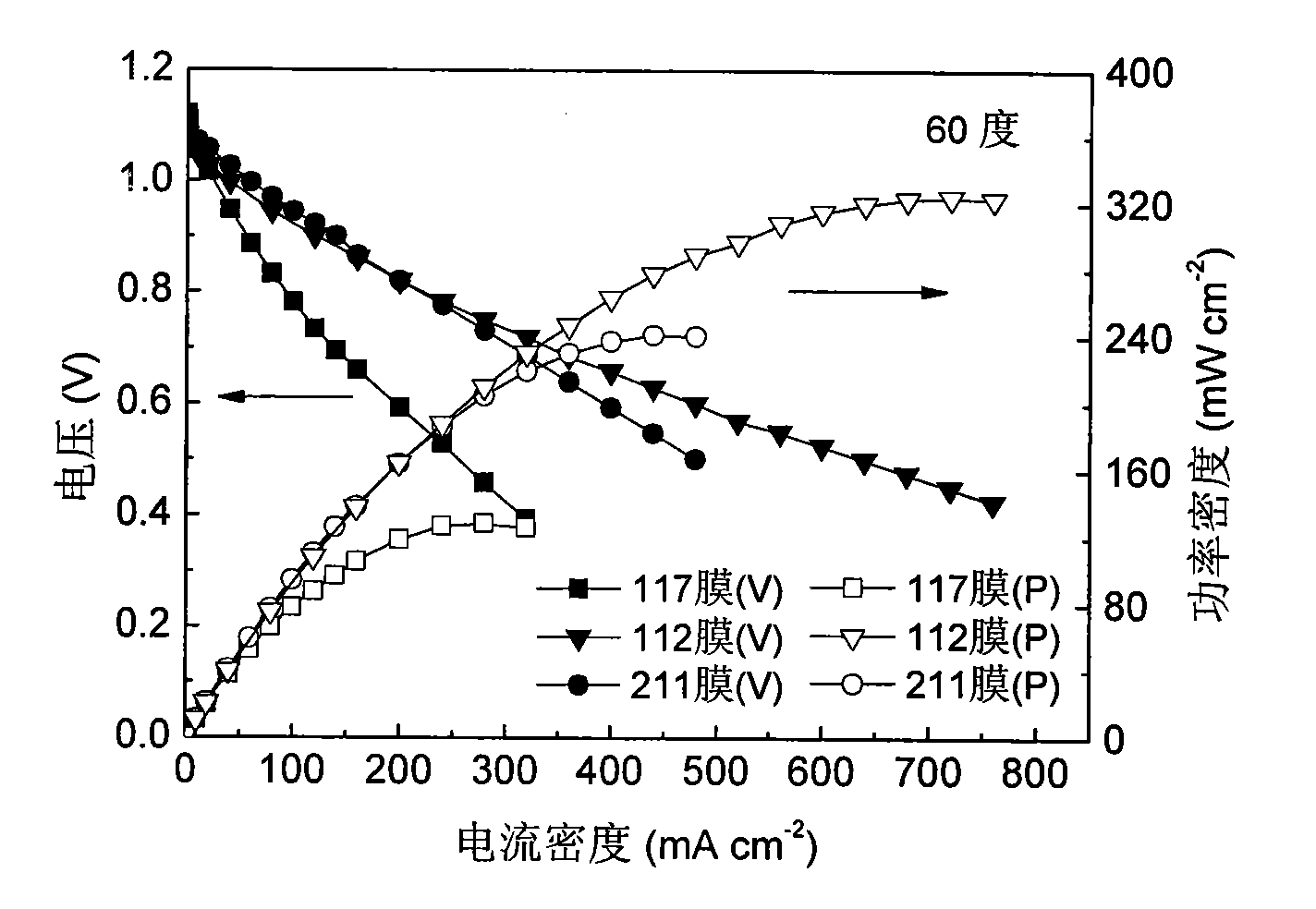
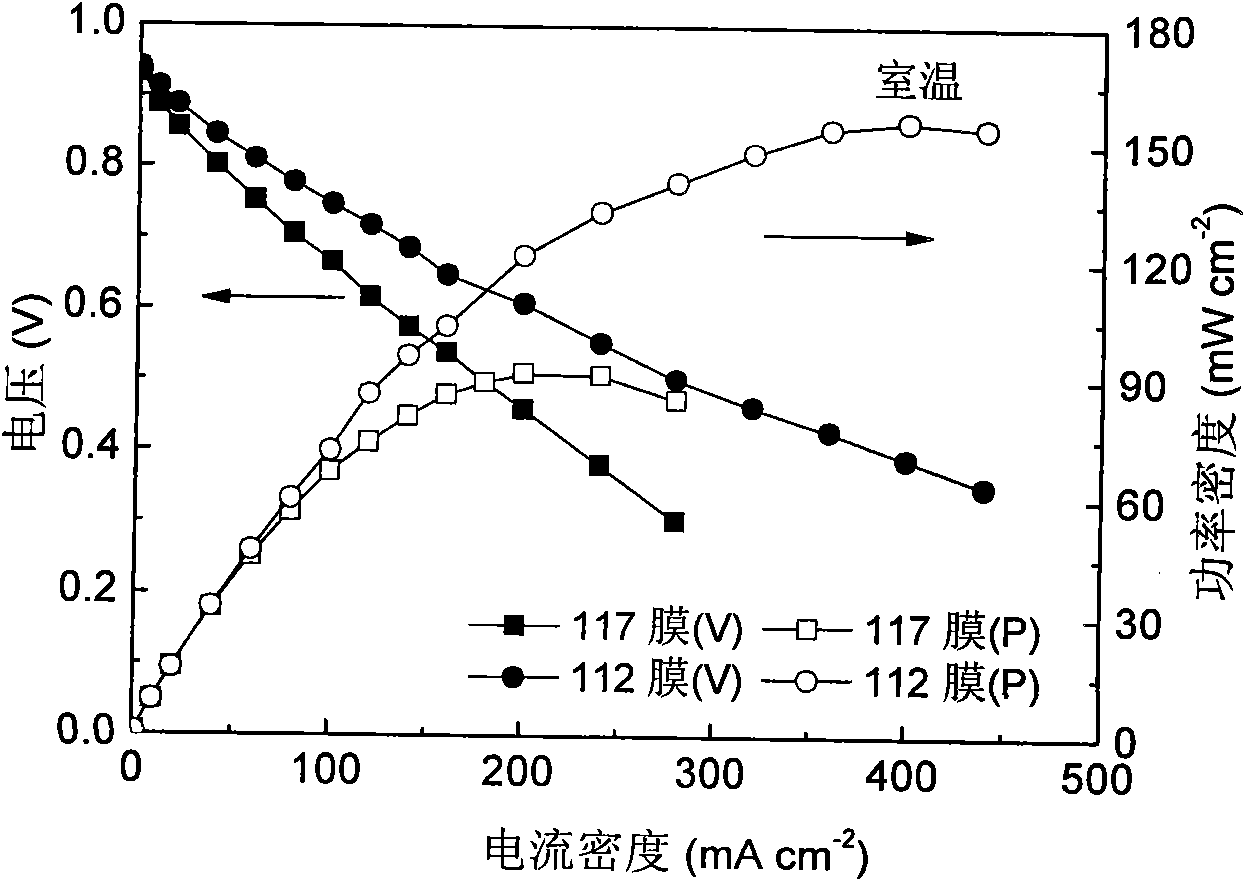
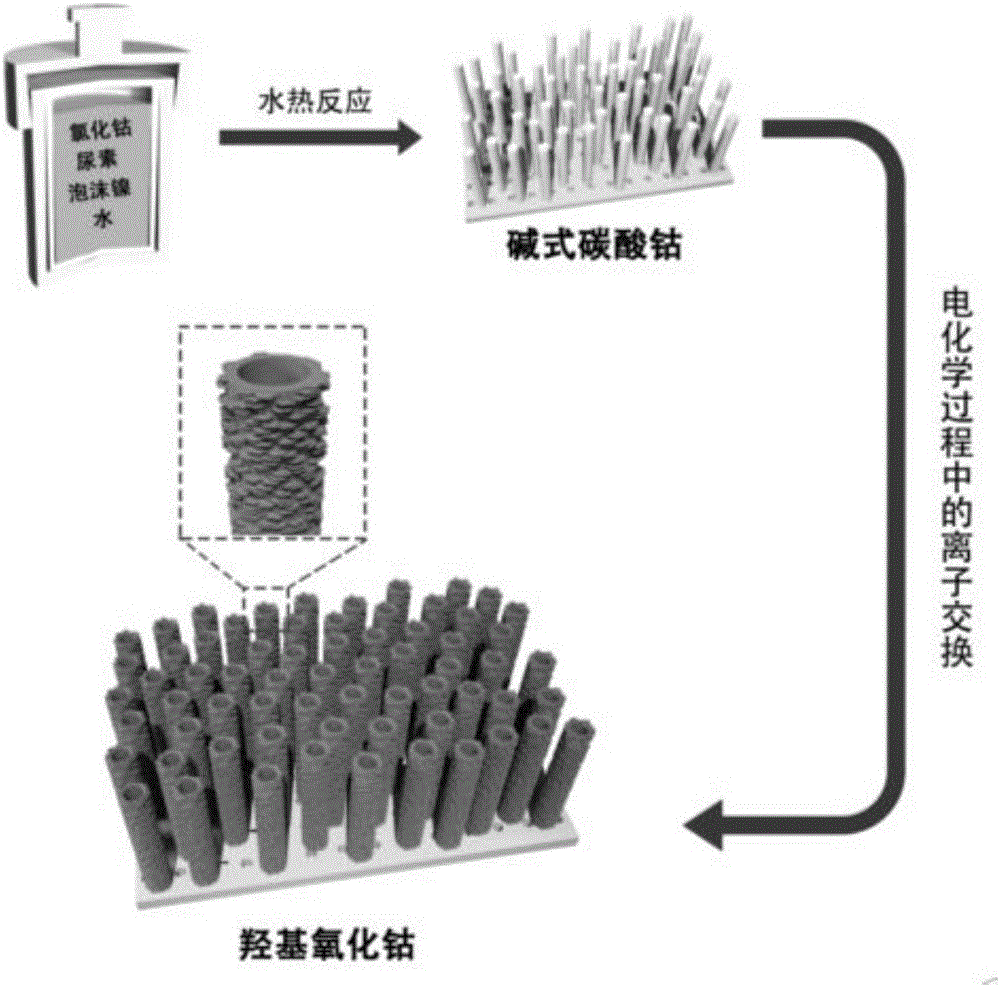
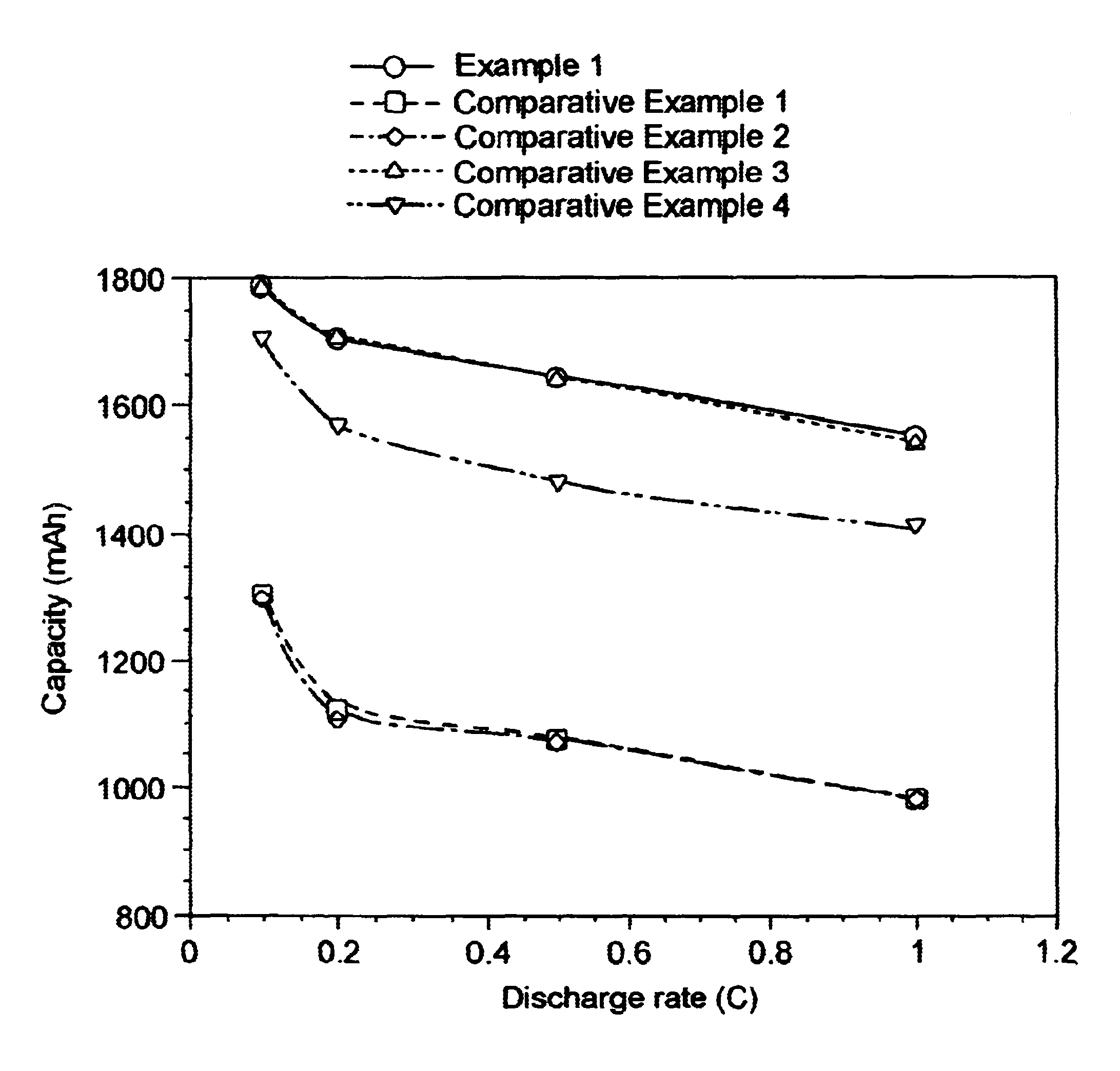
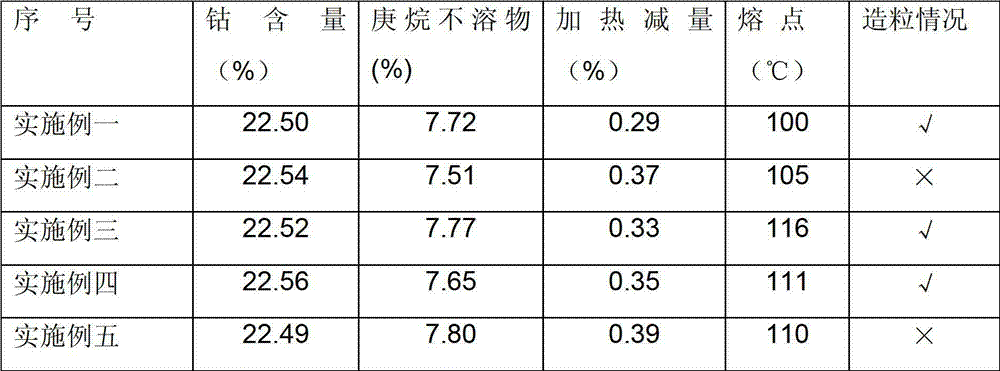
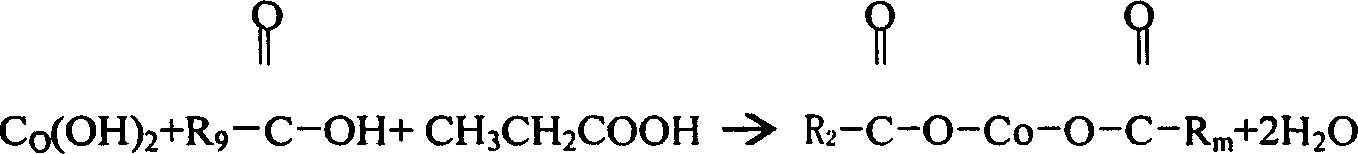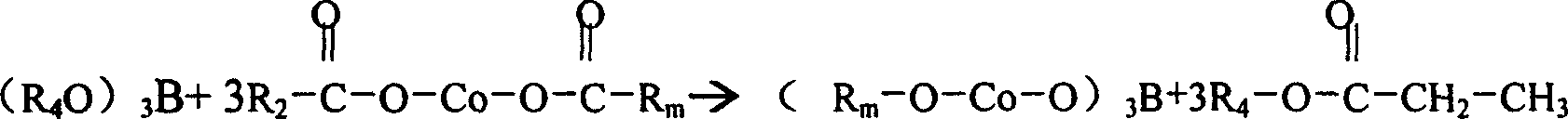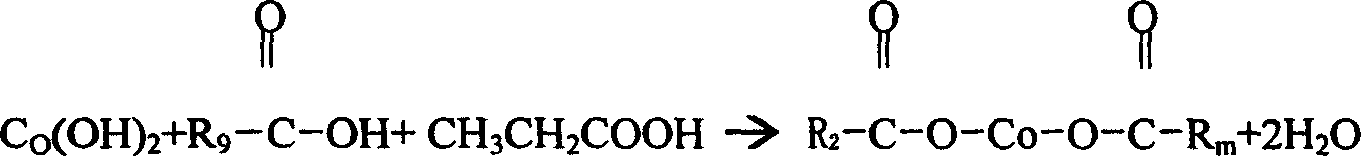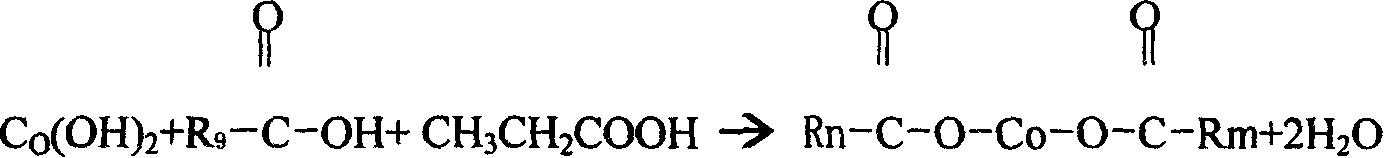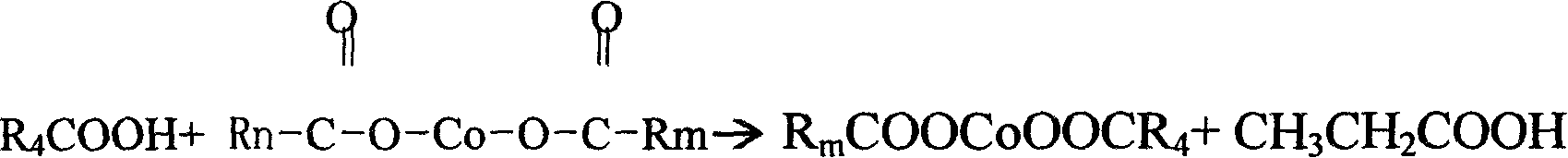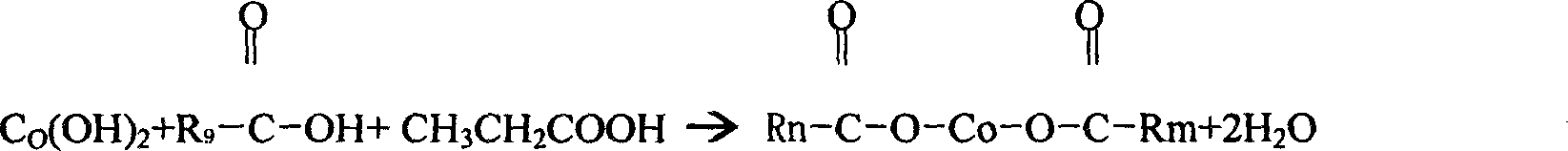Patents
Literature
92 results about "Cobalt(II) hydroxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
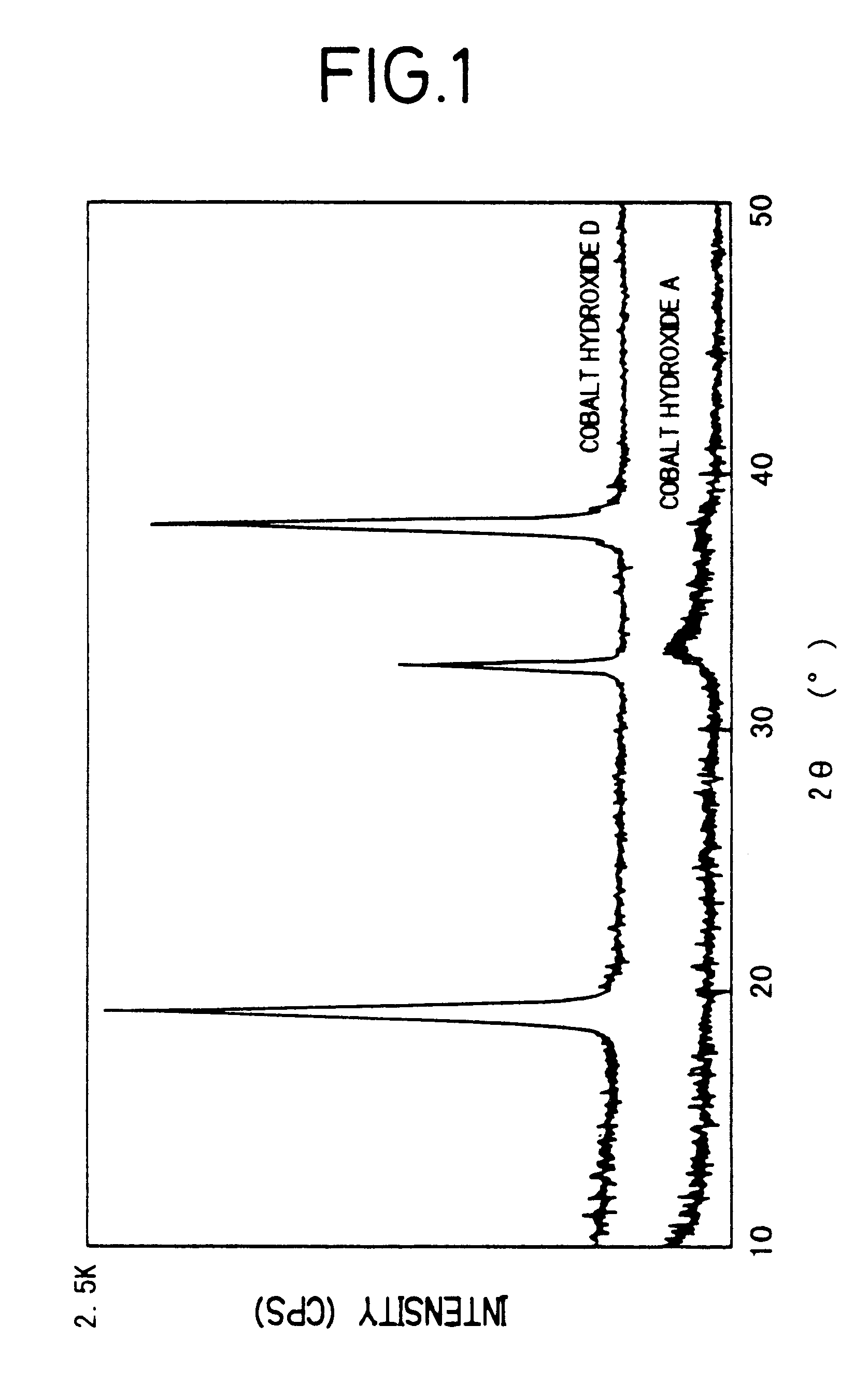
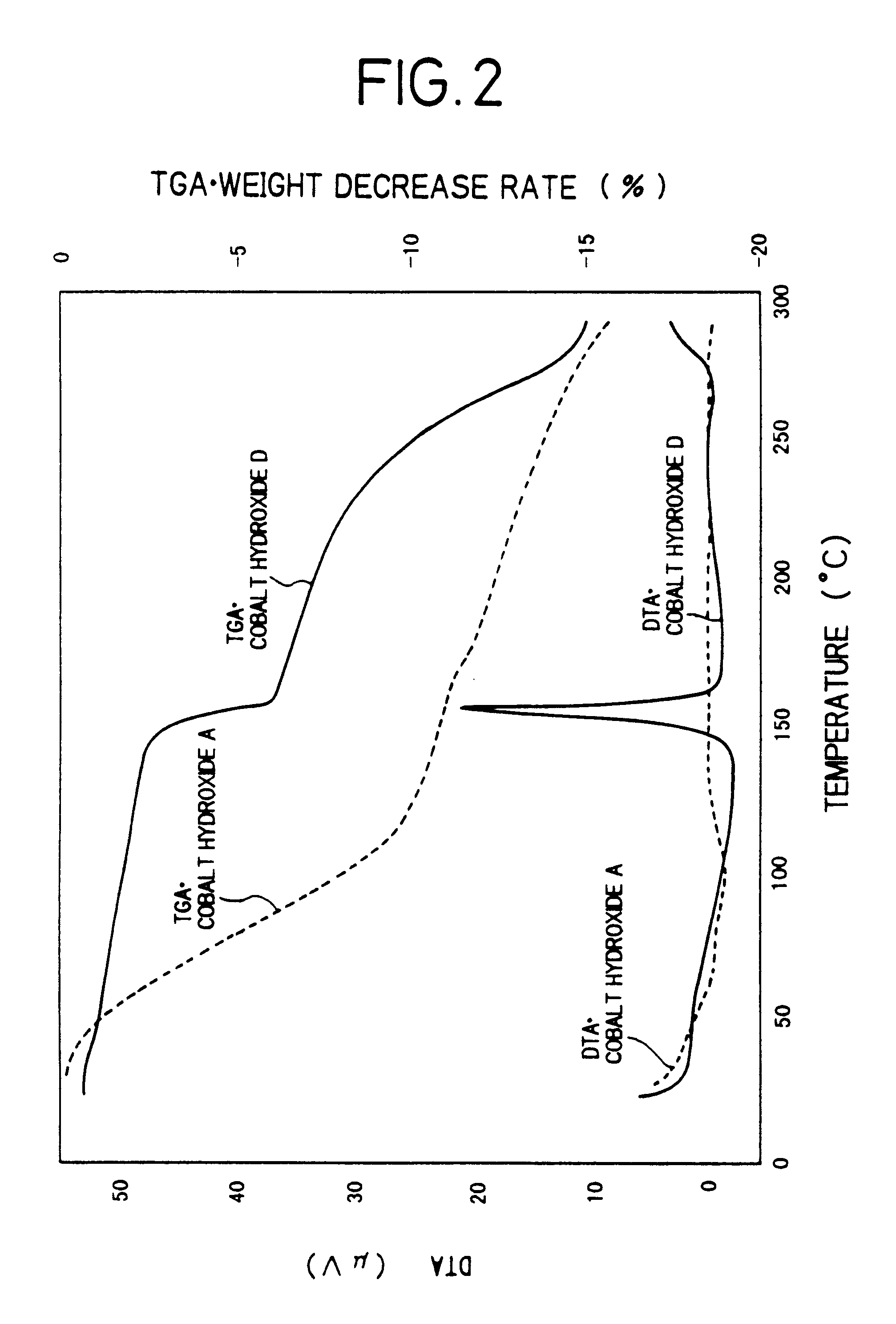
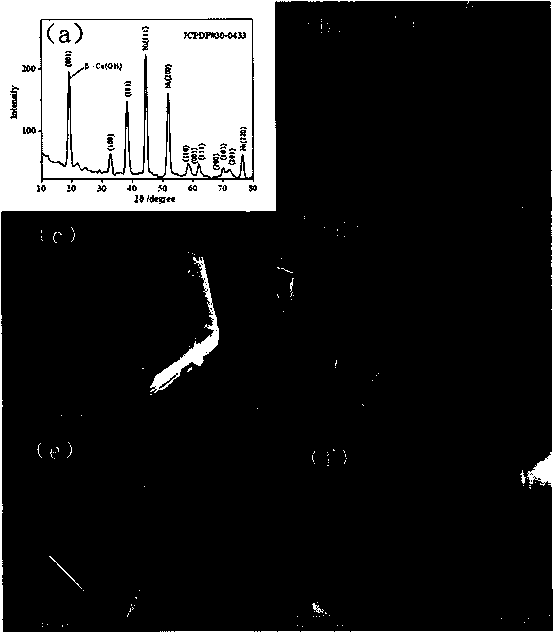
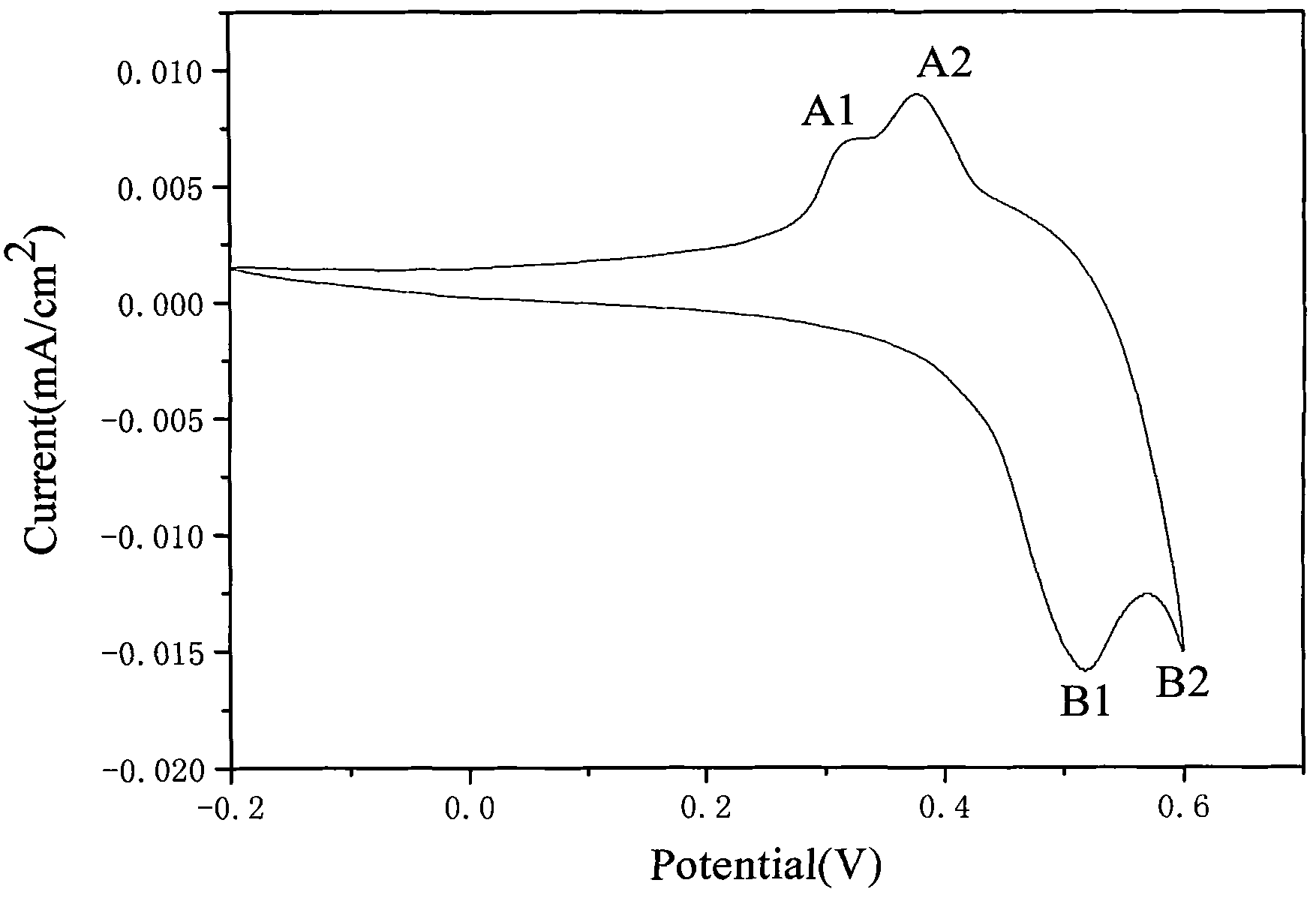
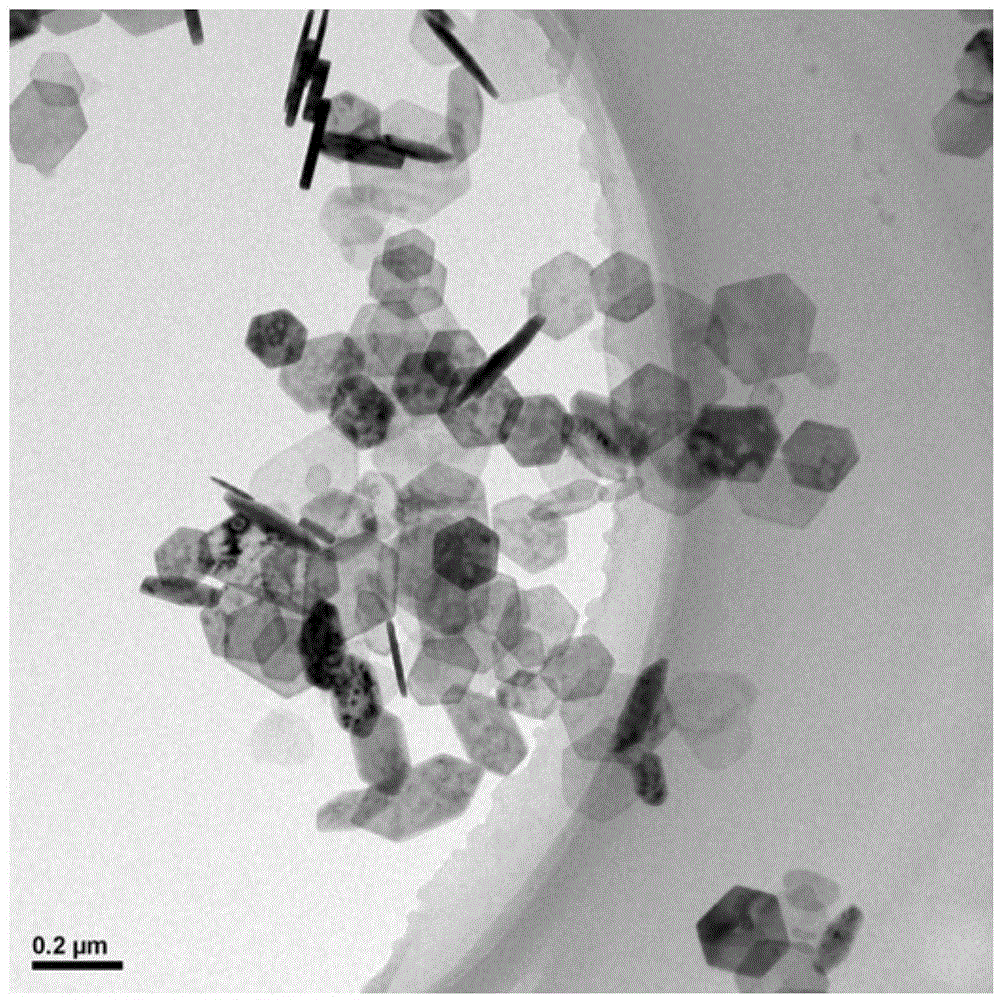
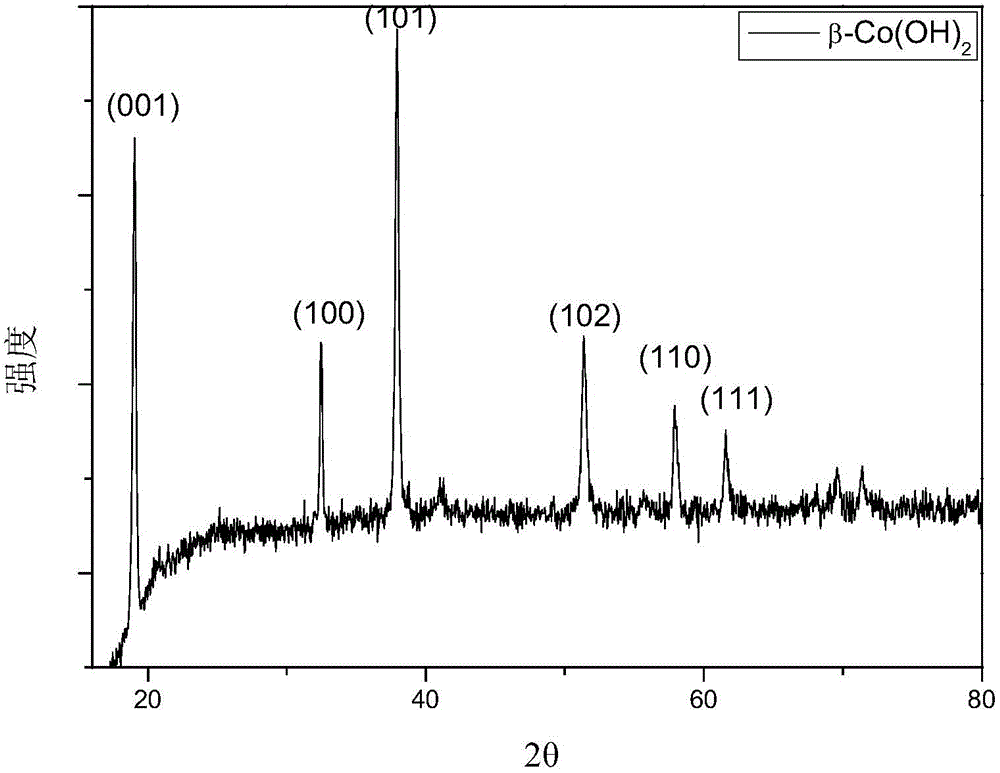
Cobalt(II) hydroxide or cobaltous hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Co(OH)₂, consisting of divalent cobalt cations Co²⁺ and hydroxide anions HO⁻. The pure compound, often called the "beta form" (β-Co(OH)₂) is a pink solid insoluble in water.
Electrocatalyst with cobalt-based multi-stage nano-composite structure for oxygen production by electrolysis of water and preparation method of electrocatalyst
InactiveCN106011926ALow costEasy to operateCobalt sulfidesElectrolytic inorganic material coatingFiberCarbon fibers
The invention provides an electrocatalyst with a cobalt-based multi-stage nano-composite structure for oxygen production by electrolysis of water and a preparation method of the electrocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving cobalt nitrate hexahydrate, urea and ammonium fluoride in deionized water to obtain a precursor solution; transferring the precursor solution into a hydrothermal reactor; adding carbon fiber paper; enabling basic cobalt carbonate nanowires to grow on the carbon fiber paper through solvothermal reaction; after finish of reaction, naturally cooling; then taking out a product; washing and drying to obtain a carbon fiver paper loaded basic cobalt carbonate nanowire composite structure; by taking powdered sulfur as the raw material, preparing a carbon fiber paper loaded cobalt sulfide nanowire composite structure through low-temperature sulfuration reaction under the condition of an inert gas; and finally, electroplating the surface of the carbon fiber paper loaded cobalt sulfide nanowire composite structure with a layer of cobalt hydroxide nanosheets by use of the electrochemical deposition method so as to obtain the electrocatalyst with the cobalt-based multi-stage nano-composite structure for oxygen production by electrolysis of water. As the sulfide and the hydroxide of transition metal cobalt are adopted as the catalyst, in comparison with noble metals, the cost of the catalyst is lowered.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
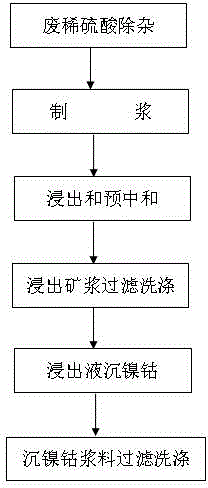
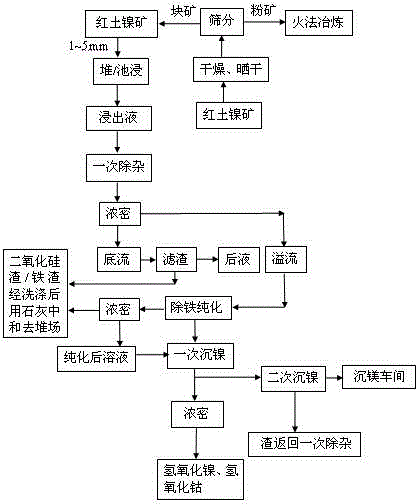
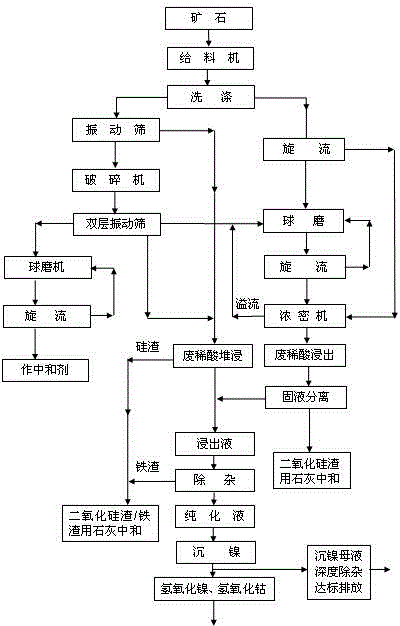
Method for leaching nickel and cobalt form low-iron and high-magnesium and high-iron and low-magnesium laterite-nickel ore by using waste dilute sulphuric acid
The invention provides a method for leaching nickel and cobalt from low-iron and high-magnesium and high-iron and low-magnesium laterite-nickel ore by using waste dilute sulphuric acid. Nickelous hydroxide, cobaltous hydroxide and the like are directly extracted by leaching the laterite-nickel ore with non-concentrated decolored and desalinated waste dilute sulphuric acid. The method specially comprises the steps of: removing impurities out of the waste dilute sulphuric acid, slurrying, leaching and pre-neutralizing, filtering and washing leached ore pulp, settling nickel and cobalt from leachate, filtering and washing nickel and cobalt settled slurry, electrically depositing nickel, and post-treating and recycling iron, magnesium, manganese and the like. The method provided by the invention overcomes the technical difficulty, ensures that a technology of a direct dilute sulphuric acid atmospheric pressure leaching process route operates stably, is greatly lowered in cost, is high in production efficiency, and is high in recycling rate of nickel, cobalt, iron, magnesium, manganese and other metals. The waste dilute sulphuric acid which is an byproduct in industries such as dye industry and is difficult to treat is effectively recycled, the method is environmental-friendly, any harmful gas is not emitted, waste slag is solid materials, trees can be planted on the waste slag for greening, the waste slag can be recycled, and waste water can completely reach the standard for emission.
Owner:杭州蓝普水务有限公司
Cobaltosic oxide hierarchical structure nano array materials and preparation method thereof, and application of cobaltosic oxide hierarchical structure nano array materials
ActiveCN108346522AHigh purityGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesNanowireDecomposition
The present invention provides cobaltosic oxide hierarchical structure nano array materials and a preparation method thereof, and an application of cobaltosic oxide hierarchical structure nano array materials. In a closed high temperature and high pressure reactor, redistilled water is taken as reaction solvent, cobalt salt, ammonium fluoride and urea are added into the reaction solvent for uniform mixing, and a reaction system is heated to generate a high-pressure environment to prepare cobaltous hydroxide precursor nanowire materials; then redistilled water is taken as reaction solvent, 2-methylimidazole is added into the reaction solvent, the cobaltous hydroxide precursor loaded on carbon cloth is immersed in the solution, the cobaltous hydroxide is taken as a cobalt source, the reaction system is heated and the reaction time is controlled to control a ZIF67 nucleation rate so as to prepare a cobalt-based metal organic framework (ZIF67) array; and finally, calcining decomposition ofthe cobalt-based metal organic framework (ZIF67) array is performed to obtain a cobaltosic oxide hierarchical structure. The product purity is high, the dispersibility is good, the controllability isgood, the production cost is low, the reproducibility is good, the cobaltosic oxide hierarchical structure nano array materials have cycling stability and large active surface area, and have a potential application value at the aspect of supercapacitors.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
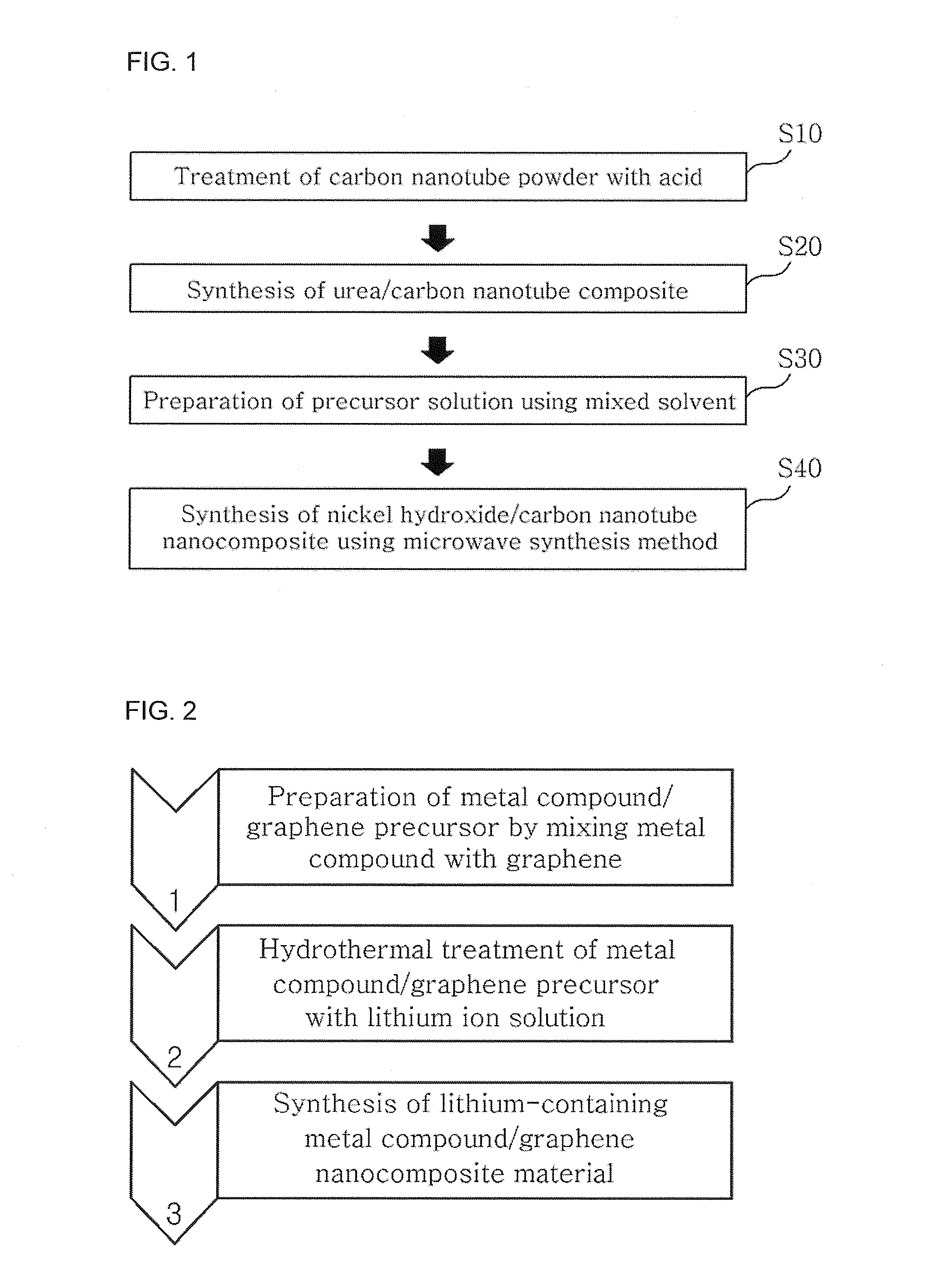
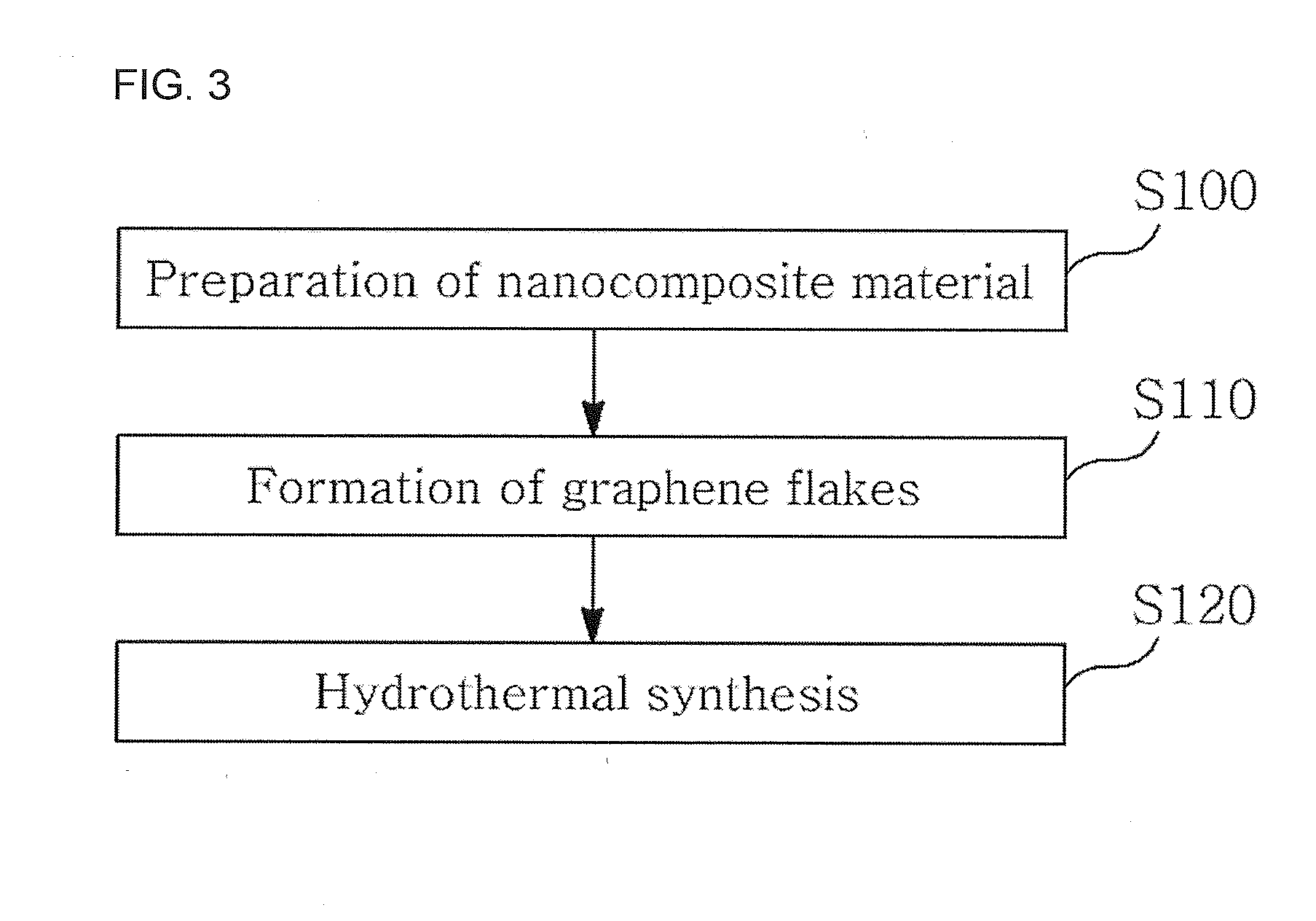
Method for preparing metal oxide-graphene nanocomposite and method for preparing electrode using metal oxide-graphene nanocomposite
InactiveUS20160218353A1Reduce processing stepsReduce processing costsSpecific nanostructure formationHybrid capacitor electrodesGraphene nanocompositesGraphene flake
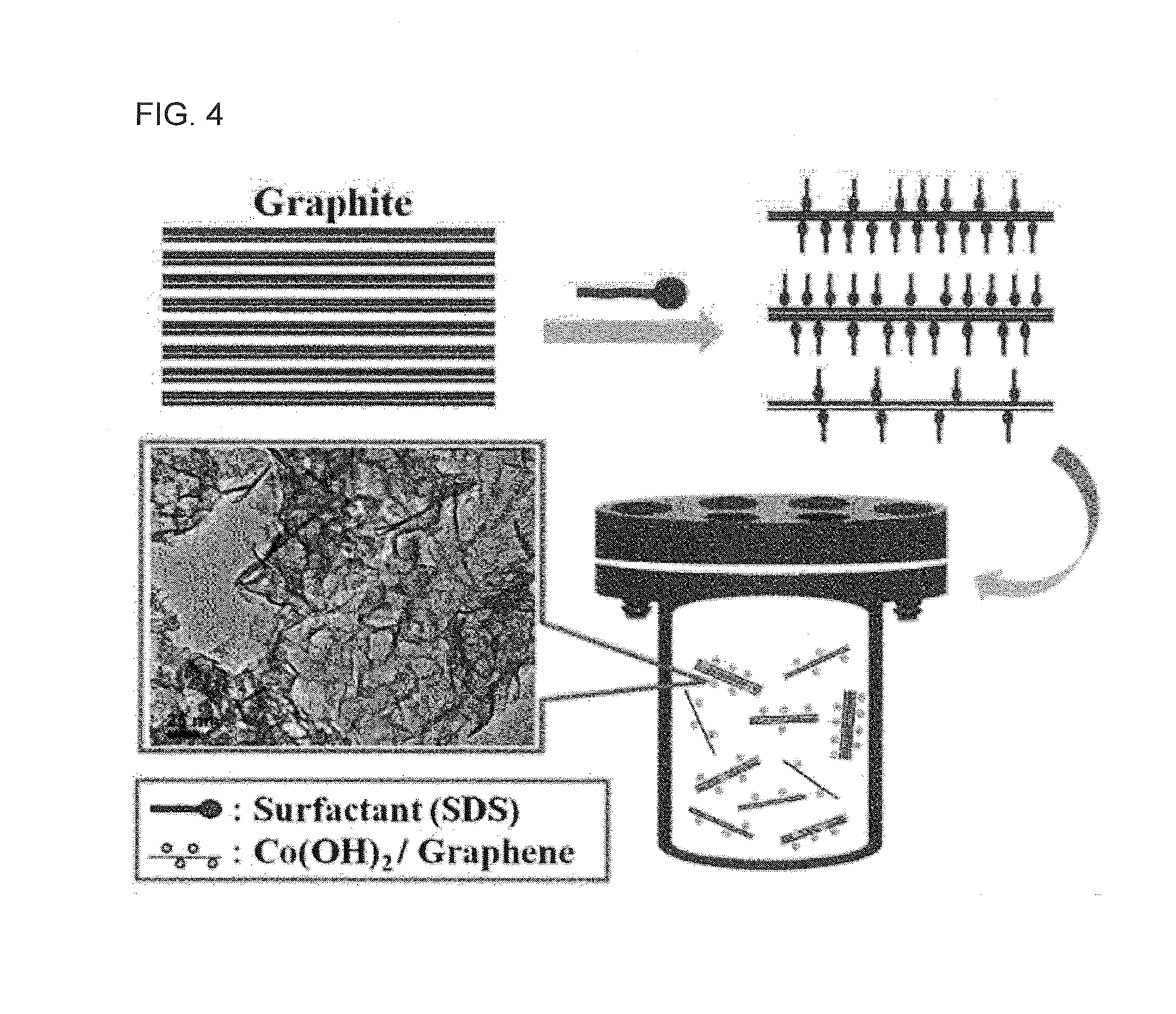
Disclosed is a method of preparing a metal oxide-graphene nanocomposite, including preparing a nanocomposite material, forming graphene flakes by pretreating the nanocomposite material, and hydrothermally synthesizing the pretreated nanocomposite material. A method of manufacturing an electrode using the metal oxide-graphene nanocomposite is also provided. According to this invention, the metal oxide-graphene nanocomposite is synthesized from inexpensive graphite through one-step processing using only a surfactant, in place of conventional methods using oxidants, reductants and high-temperature heat, thereby lowering the number of processing steps and processing costs. Also, in the fabrication of the electrode, low electrical resistance characteristic of graphene is applied as it is, in place of the conventional use of active material, conductive material and binder, thereby exhibiting desired processing efficiency without the addition of the conductive material. Furthermore, highly pure graphene is prepared in a short time and various metal oxide active materials suitable for use in energy storage devices, for example, unary, binary, and multicomponent metal oxides, is formed through one-step processing, and necessary oxides having desired weight ratios {cobalt oxide (CoO), tricobalt tetraoxide (Co3O4), and cobalt hydroxide [Co(OH)2]} can be easily prepared, and thus very wide application ranges (secondary batteries, gas sensors, etc.) are expected.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Preparation method of alpha phase cobaltous hydroxide nanosheet for oxygen evolution reaction
InactiveCN106563450AUniform size and shapeGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyCobalt oxides/hydroxidesOxygenOxygen evolution
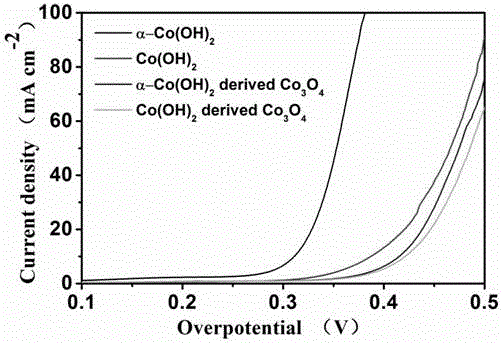
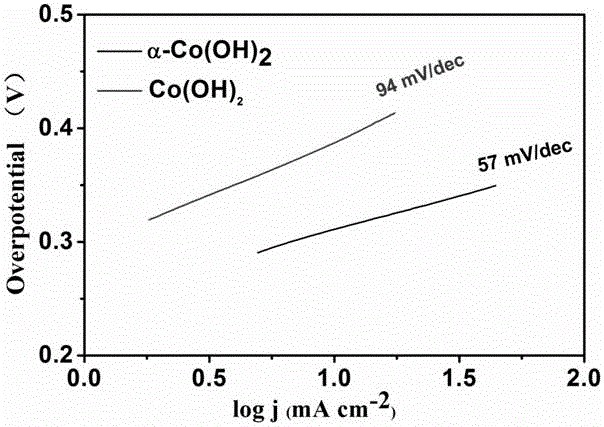
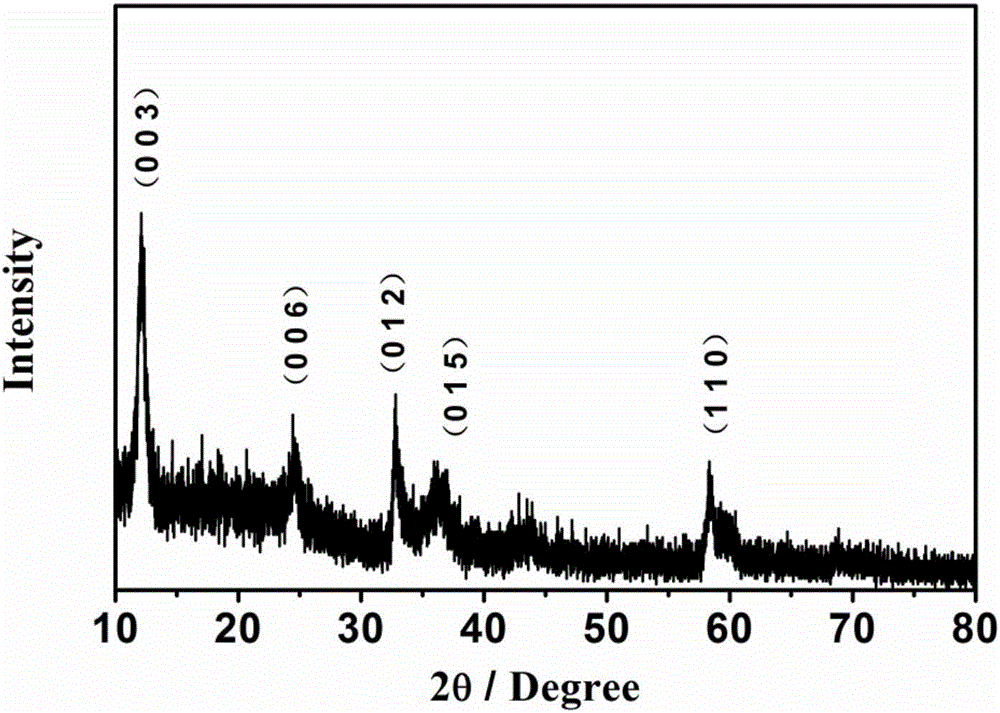
The invention discloses a preparation method of an alpha phase cobaltous hydroxide nanosheet for an oxygen evolution reaction. A cobalt source compound and an alkaline reagent are dissolved into hydrophilic solutions, reflux condensation under microwave heating is carried out after even mixing, natural cooling to the room temperature is carried out, separation is carried out after centrifugal washing, and the alpha phase cobaltous hydroxide nanosheet is obtained after vacuum drying. According to a preparation method, the microwave heating reflux condensation manner is adopted, the preparation method is simple, easy to operate, low in cost and environment-friendly, no special equipment is needed in the overall reaction process, industrial production is facilitated, and finally the obtained product is higher in quality. The alpha phase cobaltous hydroxide nanosheet prepared through the method can have the beneficial effects of being high in material electrical conductivity, many in active site, high in electrocatalytic activity and the like. The material prepared through the method is an ideal oxygen evolution reaction catalytic material with wide commercialization application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Composite anode material of graphene nanoflakes and cobalt hydroxide for lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101867046AImprove conductivityIncrease profitCell electrodesSodium-ion batteryLithium-ion battery
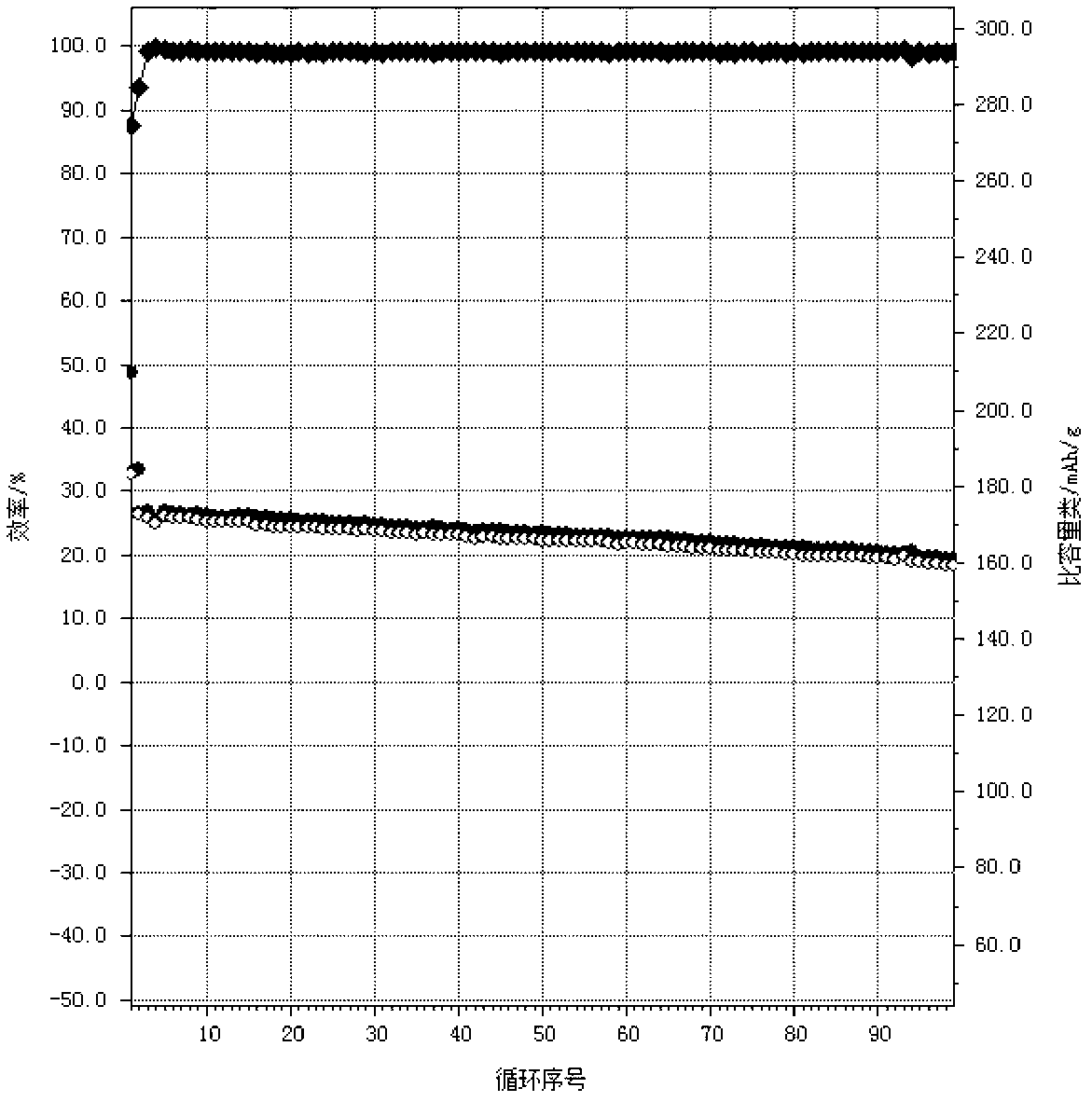
The invention provides a composite anode material of graphene nanoflakes and cobalt hydroxide for a lithium ion battery and a preparation method thereof. The anode material is composed of graphene nanoflakes and cobalt hydroxide, wherein the graphene nanoflakes are in interlaced distribution on the cobalt hydroxide particles; the mass fraction of the graphene nanoflakes is 10-90% and the thickness thereof is 1-50 nanometers; the particle diameter of the cobalt hydroxide is 0.5-30 micrometers. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out ultrasound or stirring on graphite oxide firstly to disperse in alcohol-water solution or water solution; adding cobalt salt, alkali and reductive agent to the solution; pouring the solution into a hydrothermal reactor after being stirred; and then sealing, reacting, filtering, washing and stoving the solution. As the anode material charges or discharges in 200 mA / g electric current, the reversible specific capacity of the composite material can be stabilized to be above 900 mAh / g.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Surface cladding cobaltous hydroxide for anode active material of alkaline cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN1635649AImprove conductivityIncrease profitAlkaline accumulator electrodesInternal resistanceNickel oxide hydroxide
This invention refers to cobalt hydroxide and preparation thereof, which is used to be coated on the surface of spherical nickel hydroxide of alkaline cell, wherein the cobalt is 1.0-10 % of total weight, the spherical nickel hydroxide contains 0-10 % of co-sinks of Co, Zn or hydroxide of Co and Zd. The preparation contains surface covering, filtering, washing, dewatering and drying. The spherical nickel hydroxide is oxidized to cobalt hydroxide with high conductivity in charge process, which effectively improves the conductivity of active substance, raises the availability of active substance, increases cell capacity, discharge capacity, reduces cell internal resistance, increases cycle service life and greatly raises the quality of cell positive active substance.
Owner:NINGBO RONBAY LITHIUM BATTERY MATERIAL CO LTD
Method for manufacturing positive pole active material for alkaline secondary battery, paste nickel pole, and alkaline secondary battery and method for manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS6258483B1Convenience to workGuaranteed to workFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsElectrical batteryNickel oxide hydroxide
There is provided a method of producing an active material of a positive electrode used for an alkaline secondary battery which is difficult to be oxidized, and high in its reactivity with an alkaline electrolyte to form a cobalt electric conductive matrix improved in electric conductivity. The method of producing thereof is characterized in that nickel hydroxide powder is dispersed in an aqueous solution of a strongly acidic cobalt salt and the dispersed solution thereof is, while being stirred, added gradually with an aqueous alkali solution to made to react one with another to precipitate a cobalt hydroxide while maintaining the reaction solution in the region of acidity to neutrality, and a solid part in which the cobalt hydroxide is mixed in the nickel hydroxide is separated from the reaction solution which is in the region of acidity to neutrality after the completion of the reaction, and is then washed with water. By this method of producing, there is obtained an active material of a positive electrode used for an alkaline secondary battery in which the amorphous to microcrystal cobalt hydroxide is mixed in the nickel hydroxide. Thus, using this active material of the positive electrode, a paste-type nickel electrode improved in utilization rate is obtained, and using the nickel electrode, an alkaline storage battery which has a high capacity and is excellent in the battery characteristics such as discharging characteristics, etc. is obtained.
Owner:THE FURUKAWA BATTERY CO LTD
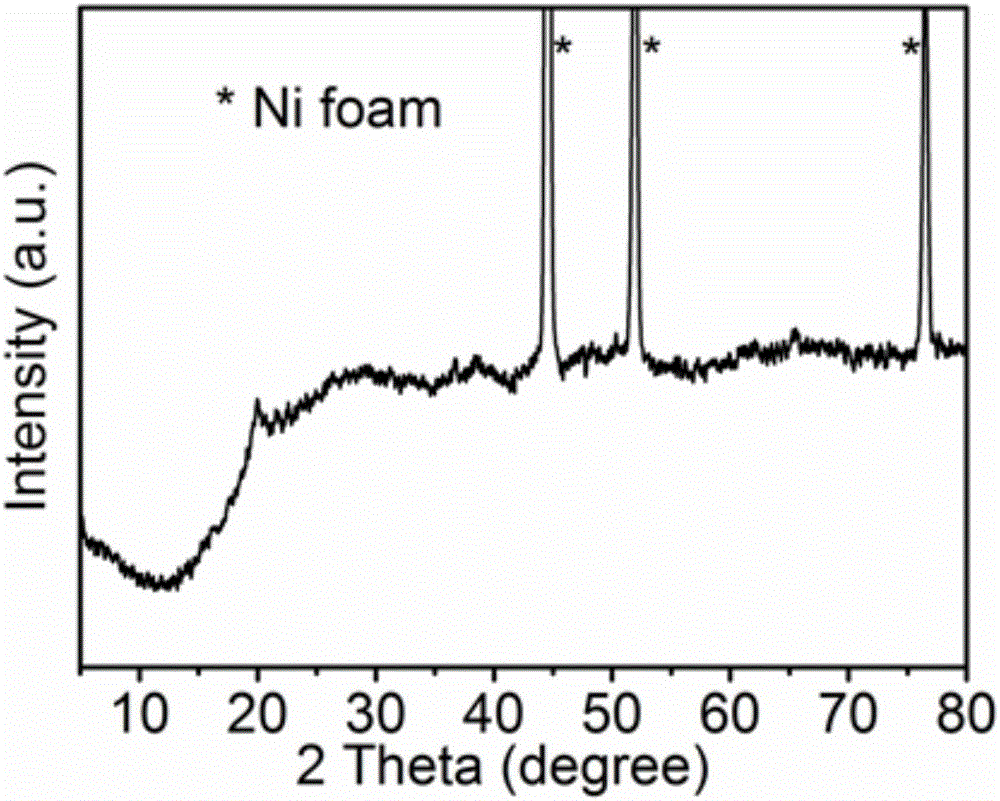
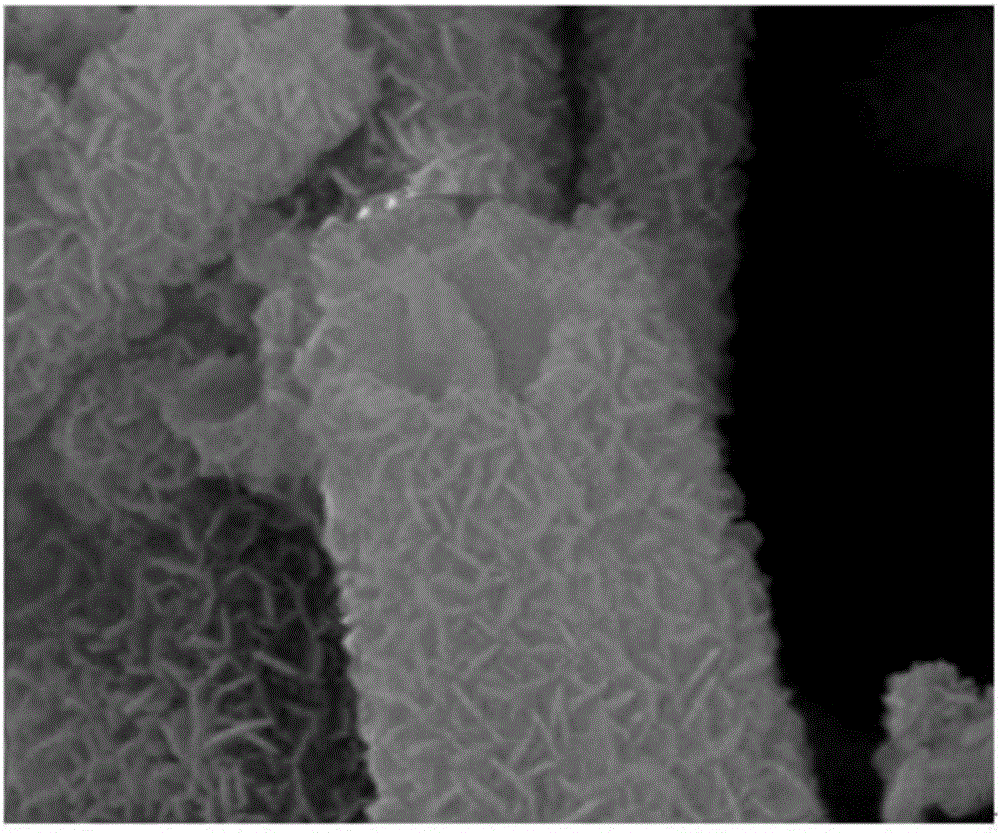
Method for growing hexagonal Co(OH)2 on surface of metal foamed nickel
InactiveCN103887082AReaction conditions are easy to controlReduce manufacturing costHybrid capacitor electrodesMetal foamCobalt(II) hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for growing hexagonal Co(OH)2 on the surface of metal foamed nickel. The method comprises the steps of firstly, preparing a cobalt source mother solution through soluble cobalt salt and ammonium fluoride, and then adjusting the pH value of the mother solution to range from 9 to 12; transferring the solution with the adjusted pH value into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, adding the metal foamed nickel used as a matrix, conducting a hydrothermal reaction at the temperature ranging from 110 DEG C to 180 DEG C for 1 h to 24 h, repeatedly conducting washing with deionized water and ethyl alcohol, conducting drying for 1 h to 4 h, and obtaining a hexagonal Co(OH)2 piece growing on the surface of the metal foamed nickel, wherein the thickness of the hexagonal Co(OH)2 piece ranges from 3 microns to 10 microns, and the side length of the hexagonal Co(OH)2 piece ranges from 10 microns to 20 microns. According to the method for growing the hexagonal Co(OH)2 on the surface of the metal foamed nickel, the structural advantage of the foamed nickel and the conductivity of metal nickel are fully utilized, the hexagonal Co(OH)2 is grown on the surface of the metal foamed nickel, the structure has the rapid ion and charge transfer capacity, and the charging and discharging properties are improved. Meanwhile, all hexagonal Co(OH)2 crystals are grown on the metal nickel, the effect of fixing the Co(OH)2 is achieved, and the obtained material can be directly used as an electrode material of a super capacitor.
Owner:HUZHOU TEACHERS COLLEGE
Cathode electrode composite material and preparation method thereof and electrochemical device applying same
InactiveCN102214822ASimple processReduce manufacturing costAlkaline accumulator electrodesNickel accumulatorsIndiumNickel salt
The invention discloses a cathode electrode composite material, which comprises a plurality of ferriferous oxide particles and a conductive aid which is selected from copper, cobalt, nickel, tin, antimony, bismuth, indium, silver, gold, lead, cadmium, carbon black, graphite, cupric salt, cobalt salt, nickel salt, tin salt, antimonic salt, bismuth salt, indium salt, silver salt, gold salt, lead salt, cadmium salt, cupric hydroxide, cobalt hydroxide, nickel hydroxide, tin hydroxide, stibine hydroxide, bismuth hydroxide, indium hydroxide, silver hydroxide, gold hydroxide, lead hydroxide, cadmium hydroxide and a group consisting of the combinations. When applied to an electrochemical device, the cathode electrode composite material can show high charging and discharging characteristics and high electric capacity. Moreover, the invention provides a preparation method of the cathode electrode composite material and an electrochemical device applying the same.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Fuel cell using conductive polymer modified carbon based cobaltous hydroxide composite catalyst
InactiveCN101552345ALow costImprove conductivityCell electrodesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsModified carbonConductive polymer
The invention relates to the fuel cell field, aims to provide a direct liquid fuel cell using conductive polymer modified carbon based cobaltous hydroxide composite catalyst. The cell comprises a negative pole using foam nickel as matrix and a positive pole using hydrophobic processed carbon paper or carbon cloth as matrix; The negative pole is made by mixing the conductive polymer modified carbon based cobaltous hydroxide composite catalyst, water, perfluoro sulfonic group resin solution with concentration of 5wt% and anhydrous ethanol, blending into slurry, coating on foam nickel and drying in air naturally. The beneficial effects of the invention is: conductive polymer can increase electrode electrical conductivity, reduce electrode impedance, improve electrode activity, and improve the electricity generation performance of cell; the synthesized conductive polymer modified carbon based cobaltous hydroxide composite catalyst is non-Pt catalyst, has a low cost, is favorable to the popularization of fuel cell technology.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing hydroxyl cobaltous oxide nanotube electrode
InactiveCN105869916AImprove conductivityLow conductivityHybrid capacitor electrodesNanotechnologyReaction temperatureIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for preparing a hydroxyl cobaltous oxide nanotube electrode. The method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing soluble cobalt salt, urea and foamed nickel in water, enabling the components to react sufficiently by using a hydrothermal method, washing, and drying so as to obtain a basic carbonate precursor; and (2) by taking the basic carbonate precursor as a supercapacitor electrode piece, performing cyclic voltammetry tests on the electrode piece, wherein ion exchange is generated in the test process so as to generate cobaltous hydroxide nanotubes, thereby obtaining hydroxyl cobaltous oxide nanotubes along with circulation. The method for preparing the hydroxyl cobaltous oxide nanotube electrode, which is disclosed by the invention, is simple in preparation process, and materials for ion exchange can be generated while the precursor is subjected to electrochemical testes, so that regulation and control on solution concentration, reaction time and reaction temperature are avoided, repeatability of the preparation process is improved, and prepared hydroxyl cobaltous oxide is good in stability and excellent in property.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for extracting ferric oxide, aluminum oxide and scandium oxide through neutralization of cobaltous hydroxide nickel smelting slag and waste titanium dioxide acid
The invention relates to a method for extracting ferric oxide, aluminum oxide and scandium oxide through neutralization of cobaltous hydroxide nickel smelting slag and waste titanium dioxide acid. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing neutralization on cobaltous hydroxide nickel smelting slag with the waste titanium dioxide acid and water in a certain ratio, adding a flocculant to remove silicon, filtering so as to obtain filtrate, performing reextraction of Al, Fe and Sc in the obtained filtrate by using an extraction agent respectively so as to obtain aluminum salt, ferric salt and Sc(OH)3, performing high-temperature roasting on the ferric salt and the aluminum salt, thereby obtaining oxides with relatively high purity, and roasting the Sc(OH)3, thereby obtaining the scandium oxide. The method has the beneficial effects that valuable metals such as iron and aluminum are extracted by using the cobaltous hydroxide nickel smelting slag, and the rare earth metal scandium is recycled, so that the comprehensive utilization rate of metals in ore can be increased, environment pollution can be reduced, and high economic benefits and environment benefits can be created.
Owner:万华化学(烟台)电池材料科技有限公司
Method for preparing finished products of salt mixture of organic cobalt class of giving priority to cobalt boroacidate
InactiveCN101003544AHigh reactivityBalance pHNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesCobalt organic compoundsPropionatePropanoic acid
This invention relates to a method for preparing organic cobalt mixed salt product mainly composed of cobalt boroacylate. The method comprises: (1) reacting cobalt hydroxide and mixed acids of propionic acid and octocapric acid in a normal pressure sealed container at 150-190 deg.C for more than 2 h; (2) adding butyl borate, and reacting at 190-200 deg.C for more than 1 h to form cobalt boroacylate and butyl propionate byproduct; (3) adding calcium metaborate at 180-190 deg.C to obtain the organic cobalt mixed salt product. The raw materials comprise: cobalt hydroxide 31-22 parts, octocapric acid 60-62 parts, propionic acid 25-27 parts, butyl borate 26-28 parts, and calcium metaborate 7-8 parts. The method has such advantages as high cobalt content, high reaction activity, and appropriate melting point.
Owner:徐美华
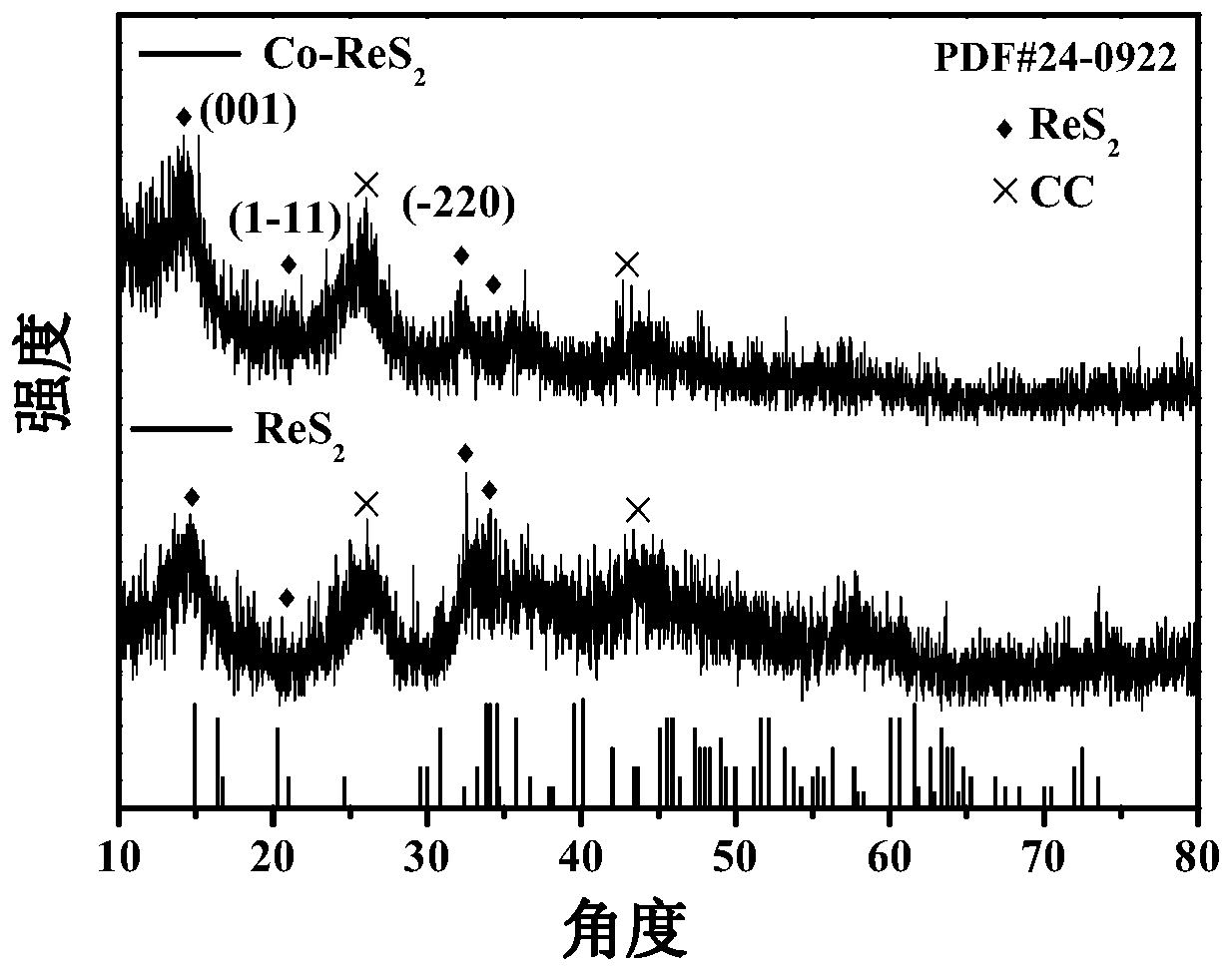
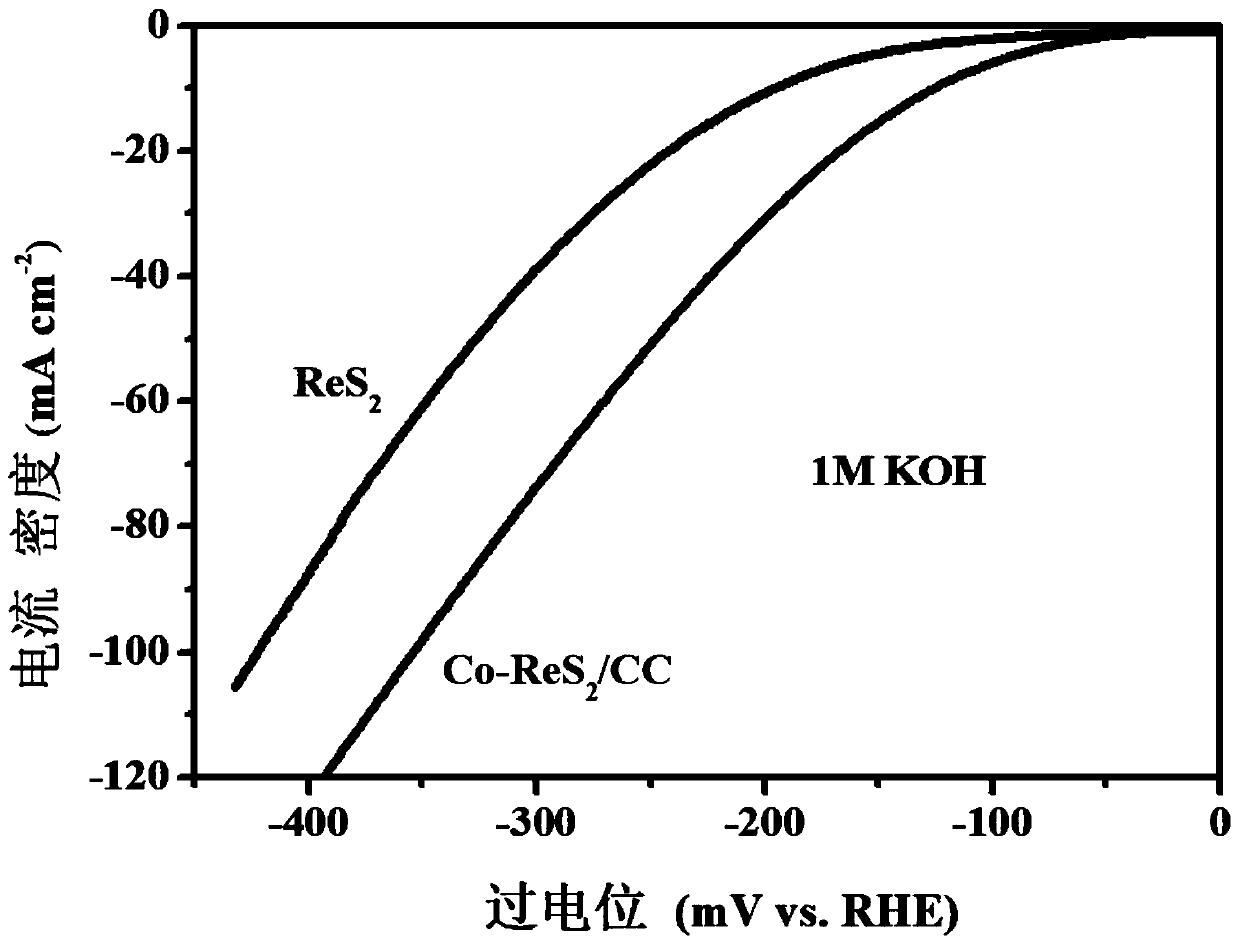
Preparation method of cobalt-doped rhenium disulfide nanosheet array for electro-catalytic hydrogen evolution
InactiveCN110538662AExcellent electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution performanceImprove hydrogen evolution reaction activityMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationRheniumHydrolysis
The invention relates to a preparation method of a cobalt-doped rhenium disulfide nanosheet array for electro-catalytic hydrogen evolution. The preparation method comprises the following steps: addingan aqueous 2-methylimidazole solution into an aqueous solution of cobalt nitrate hexahydrate, and immersing a piece of acid-treated carbon cloth into the formed mixed solution; after a reaction for aperiod of time, taking a sample, and cleaning the sample with deionized water; carrying out growing in the same solution for a period of time so as to obtain a ZIF-67 nanoarray sample which is namedas ZIF-67 / CC; cleaning and drying the sample; dissolving the cobalt nitrate hexahydrate into a mixed solution of ultrapure water and ethanol, and putting the prepared ZIF-67 / CC into the mixed solutionfor hydrolysis to obtain the product cobalt hydroxide nanoarray Co(OH)2 / CC; and preparing the product Co-ReS2 / CC. The Co-ReS2 / CC prepared by using the preparation method disclosed by the invention isapplied to an HER electrocatalyst.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Process for preparing organic cobalts mixed salt finished product with cobalt neodecanoate as main raw material
The invention relates to a method for preparation of finished goods of organic cobalt composite salts, of which the cobalt neocaprate is the main substance. The method is characterized in that it selects cobalt hydroxide and organic acid as raw materials and performs acid-base salt reaction and acid replacement reaction to obtain the product. The method includes: selecting cobalt hydroxide, ethylformic acid and neocaprate as raw materials and reacting to prepare composite salts of cobalt propionate and cobalt neocaprate at a temperature of 150 DEG C-190 DEG C for more than 2 hours in an atmosphere airtight container; adding neopentanoic acid to react for replacement of propanoic acid at a temperature of 190 DEG C-200 DEG C for more than one hour; controlling the temperature between 180 DEG C and 190 DEG C; then adding calcium metaborate to prepare finished goods of organic cobalt composite salts, of which the cobalt neocaprate is the main substance. The product obtained by this invention has a higher cobalt content and fusing point.
Owner:JIANGYIN SANLIANG CHEM
Method for preparing compound fatty acid cobalt salt
ActiveCN102336925AGood compatibilityImprove anti-agingCarboxylic acid salt preparationHydrogenCobalt salt
The invention relates to a method for preparing compound aliphatic acid cobalt salt, which is characterized in that stearic acid, tallol fatty acid and hydrogen cobalt oxide are taken as raw materials to generate the compound fatty acid cobalt salt which takes stearic acid and turic acid cobalt as main components, the proportion of stearic acid and tallol fatty acid are and calculated according to the actual acid value measurement of 1-4 parts of stearic acid which is required to be consumed by Co(OH)2 and 1 part of tallol fatty acid which is required to be consumed by Co(OH)2. The prepared compound fatty acid cobalt salt has good dissolvability while mixing with rubber, large active cobalt release amount, strong rubber and steel wire adhesion promoting function, good anti-aging properties, low cost, less pollution and the like.
Owner:JIANGYIN SANLIANG CHEM
Coated nickel lithium cobalt oxide positive material with high capacity, low residual alkali and low pH value, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103296274AThe process is simple and easy to controlHigh tap densityCell electrodesGradient materialCobalt(II) hydroxide
The invention relates to a coated lithium cobalt oxide positive material with high capacity, low residual alkali and low pH value, and a preparation method thereof. The method is mainly characterized in that cobaltous hydroxide is coated on the surface of nickelous hydroxide by utilizing a coprecipitation method, so as to form a precursor of a gradient material [Co(OH)2]x.[Ni(OH)2][1-x], wherein x is smaller than or equal to 0.35 and greater than 0; the precursor is mixed with a lithium source, then high-temperature sintering is carried out at oxygen atmosphere so as to obtain the lithium cobalt oxide positive material [LiCoO2]x.[LiNiO2][1-x] with a gradient structure. The prepared lithium cobalt oxide positive material with the gradient structure disclosed by the invention is low in pH value, excellent in cycle performance, simple in product process, easy to control, low in cost and suitable for volume production.
Owner:北京盟固利新材料科技有限公司
Preparing method for oxide dispersion strengthening iron-cobalt-nickel medium-entropy alloy
The invention provides a preparing method for an oxide dispersion strengthening iron-cobalt-nickel medium-entropy alloy. A dispersion strengthening phase is yttrium oxide. Ferric trichloride hexahydrate serves as an iron source, cobalt chloride hexahydrate serves as a cobalt source, nickel chloride hexahydrate serves as a nickel source, yttrium nitrate hexahydrate serves as a yttrium source, a sodium hydroxide solution serves as a precipitator, and iron, cobalt, nickel and yttrium ions generate corresponding hydroxide coprecipitation. Then, obtained precipitation is washed, dried and roasted,and ferric hydroxide, cobaltous hydroxide, nickelous hydroxide and yttrium hydroxide in the precipitation are decomposed into corresponding oxide. The roasted oxide powder is subjected to high-temperature reducing in the hydrogen atmosphere, and since yttrium oxide cannot be reduced, the mixture powder of iron, cobalt, nickel and yttrium oxide is finally obtained. The obtained powder is sintered,and the oxide dispersion strengthening iron-cobalt-nickel medium-entropy alloy is obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Pseudo capacitor electrode based on nickel/cobalt sulfide three-dimensional hierarchical nanostructure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106128783AImproved magnification performanceImprove cycle stabilityHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceEtching
The invention relates to a pseudo capacitor electrode based on a nickel / cobalt sulfide three-dimensional hierarchical nanostructure and a preparation method thereof. The electrode comprises a nickel foam substrate and multiple nickel / cobalt sulfide nanosheets located on the nickel foam substrate. The nickel / cobalt sulfide nanosheets are mutually connected and are honeycomb. Multiple nanoscale holes are distributed on each nickel / cobalt sulfide nanosheet. The preparation method comprises the steps of 1), preparing the foam nickel containing cobalt / nickel hydroxide nanosheets through a hydrothermal method, wherein the cobalt / nickel hydroxide nanosheets are located on the foam nickel, are mutually connected and are honeycomb; 2), processing the foam nickel containing cobalt / nickel hydroxide nanosheets obtained in the step 1) through a sulfidization method, thereby transforming the cobalt / nickel hydroxide nanosheets into cobalt / nickel sulfide nanosheets; and 3), constructing evenly distributed nanoscale holes on the nickel / cobalt sulfide nanosheets through an alkali solution etching method. The method is simple in technology and low in cost. The prepared electrode has the three-dimensional hierarchical nanostructure, very high specific capacitance, good rate capability and excellent cyclic stability.
Owner:重庆中科超容科技有限公司
Moly-sulfide/cobaltosic oxide composite material and preparation method thereof, and application thereof
ActiveCN106504907AIncrease the areaImprove conductivityHybrid capacitor electrodesNano structuringReaction temperature
The invention relates to a moly-sulfide / cobaltosic oxide composite material, a preparation method thereof, and an application thereof. According to the structure of the composite material, cobaltosic oxide nano lines grow on a moly-sulfide nano sheet. The method comprises steps that peeling of moly-sulfide ore is carried out through a solution method to acquire the moly-sulfide nano sheet, ultrasonic dispersion of the moly-sulfide nano sheet is carried out through a solvent transfer method to acquire moly-sulfide nano sheet aqueous dispersion; a cobaltous hydroxide nano structure grows on the moly-sulfide nano sheet through a chemical bath sedimentation method, after high temperature treatment, the moly-sulfide / cobaltosic oxide composite material is acquired. The method is advantaged in that the process is simple, operation is easy, reaction temperature is low, a safety coefficient is high, and the prepared moly-sulfide / cobaltosic oxide composite material can be taken as an electrode material of new energy devices such as excellent high-performance super capacitors and lithium cells.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
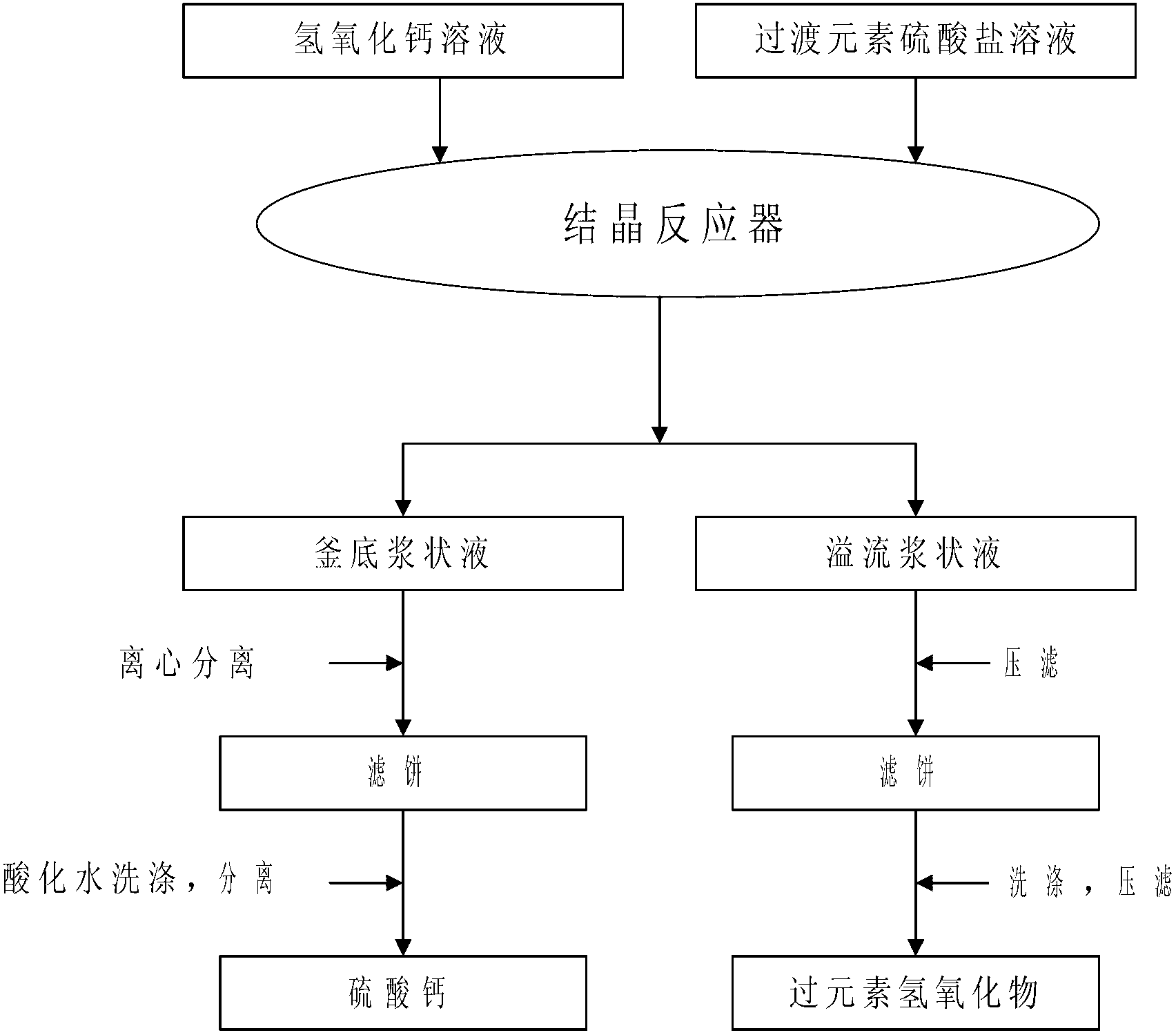
Method for preparing transition element hydroxide by using calcium hydroxide
InactiveCN103011229AReduce supersaturationInhibition of spontaneous nucleationZinc oxides/hydroxidesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesZinc hydroxideCalcium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing a transition element hydroxide by using calcium hydroxide. According to the method, two solutions are continuously mixed to react in a crystallization reactor, and in the process of hybrid reaction, through controlling the flows of a transition element sulfate solution and a circulating solution of a circulating lifting device in the reactor, sulfate ions and calcium ions form calcium sulphate crystals with large particle sizes and the crystals subside to the kettle bottom of the crystallization reactor; transition element ions are combined with hydroxy radicals so as to generate transition element hydroxides with small particle sizes, and the transition element hydroxides overflow through an upper overflow tank by using the circulating lifting device, thereby separating the transition element hydroxides from calcium sulfate. The prepared transition element hydroxides comprise cobalt hydroxide, nickel hydroxide, copper hydroxide and zinc hydroxide. The method for preparing transition element hydroxides has the advantages of low cost, simpleness in process, and high conversion rate of transition element ions, and the like, therefore, the method has a broad application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN SEA WATER DESALINATION & COMPLEX UTILIZATION INST STATE OCEANOGRAPHI
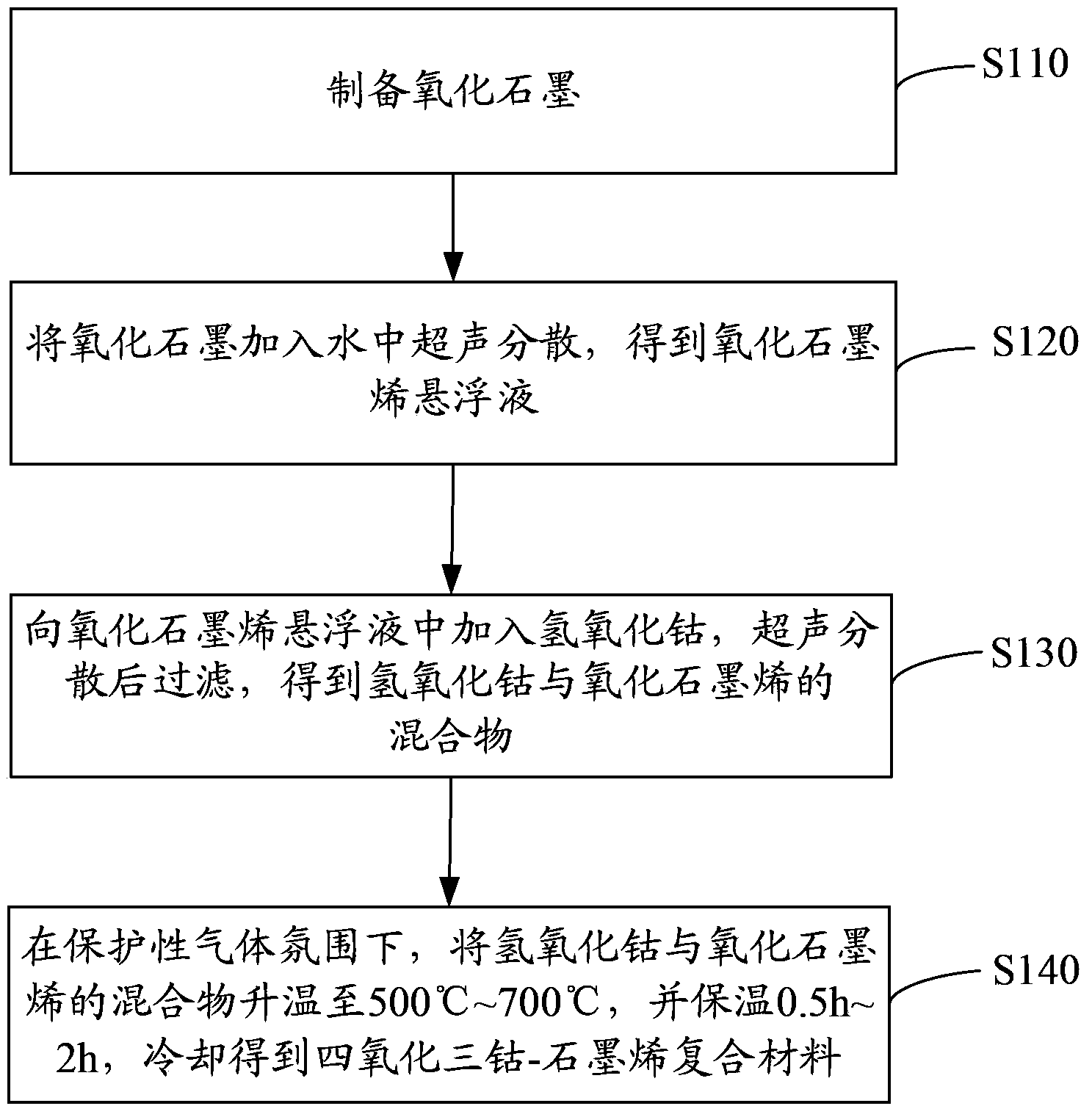
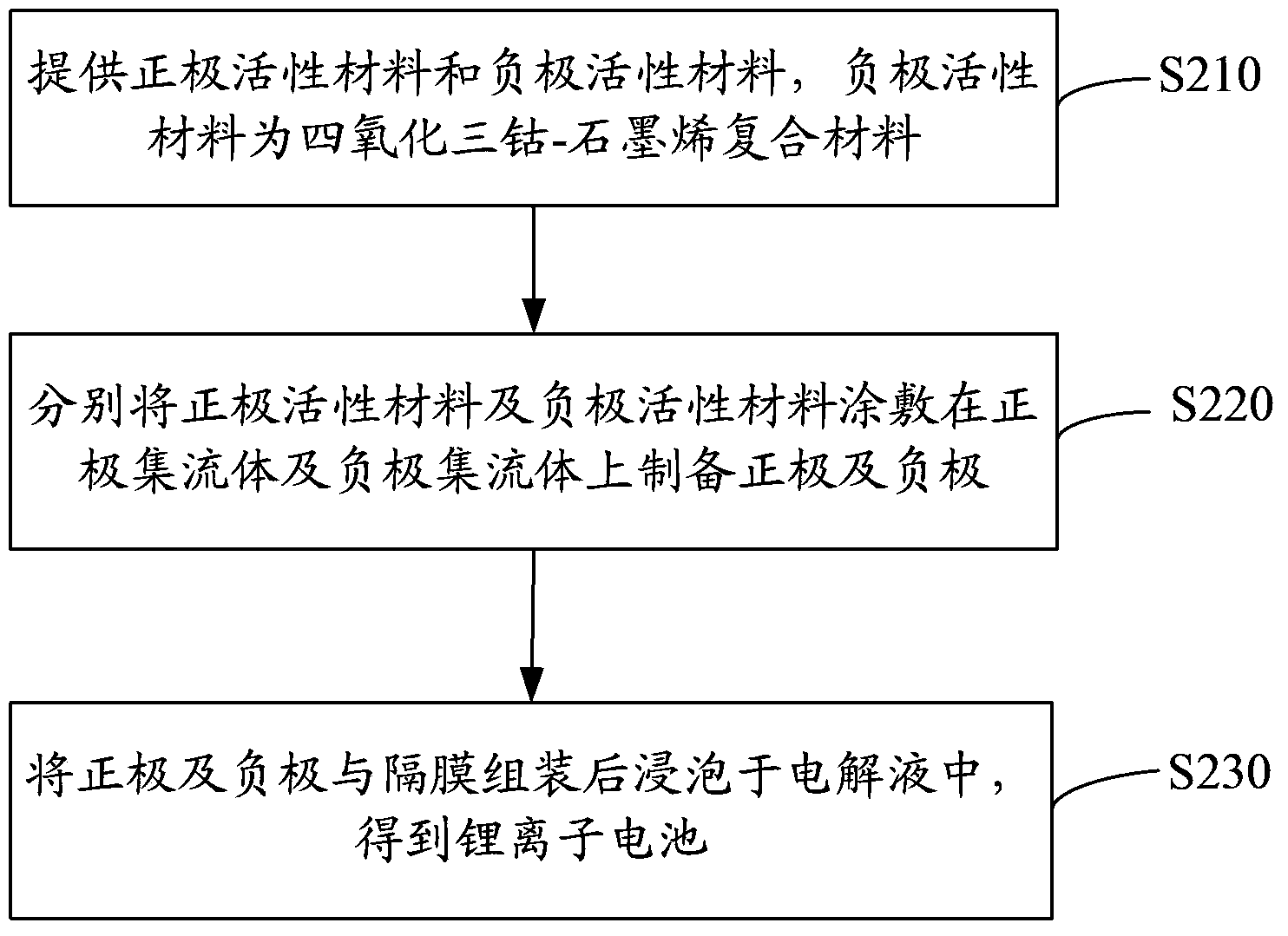
Preparation method for cobaltosic oxide-graphene composite material and preparation method for lithium ion battery
InactiveCN103633318AEvenly dispersedHigh performance featuresCell electrodesFinal product manufactureCobalt(II,III) oxideUltrasonic dispersion
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cobaltosic oxide-graphene composite material. The preparation method of the composite material comprises steps of adding graphite oxide into water and performing ultrasonic dispersion to obtain a graphene oxide suspension; adding cobaltous hydroxide into the graphene oxide suspension and filtering after ultrasonic dispersion to obtain a mixture of the cobaltous hydroxide and the graphene oxide; under an atmosphere of a protective gas, raising the temperature of the mixture of the cobaltous hydroxide and the graphene oxide to 500-700 DEGC, maintaining the temperature for 0.5-2 h and cooling to obtain the cobaltosic oxide-graphene composite material. The cobaltosic oxide-graphene composite material prepared can enhance the multiplying power and cycling performance of a lithium ion battery using the composite material. The invention also provides a preparation method of the lithium ion battery.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
Nickel tetrathiocobaltate/cobalt hydroxide nanosheet array structure composite material and preparation and application thereof
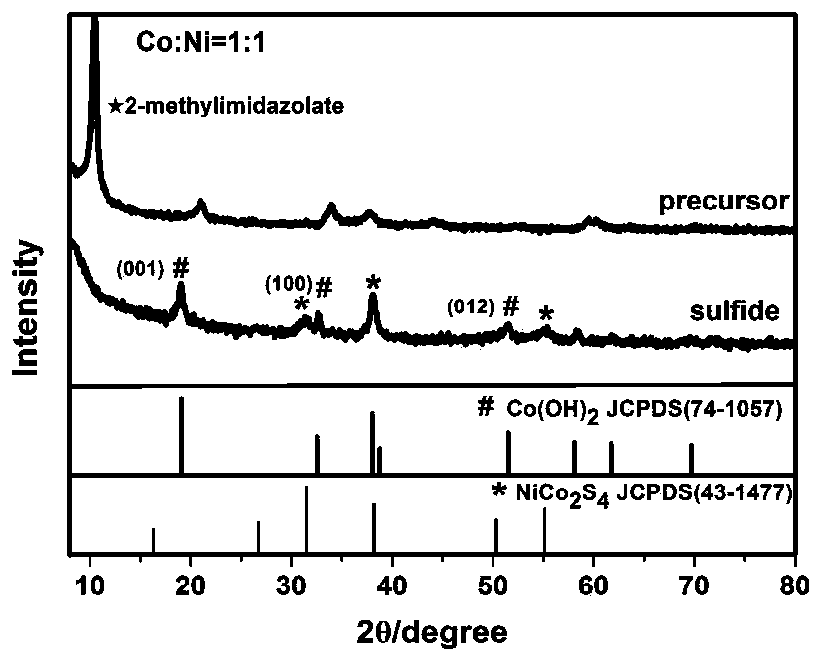
ActiveCN110526304AFacilitated DiffusionAtom utilization is highMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesCapacitanceCobalt metal
The invention provides a NiCo2S4 / Co(OH)2 nanosheet array structure composite material and a preparation method and application thereof. Firstly, by controlling a ratio of metal ions to dimethylimidazole, a cobalt nickel bimetallic organic ligand precursor is prepared by using a solvothermal method, the precursor has a two-dimensional nanosheet array structure, and the nanosheet structure and a pore size ensure relatively high atomic utilization rate and relatively good electrolyte diffusion. Secondly, by adjusting a concentration ratio of cobalt and nickel metal salts in the precursor, a controlled liquid phase hydrolysis-sulfurization process is utilized, namely the cobalt nickel bimetallic organic ligand precursor is vulcanized to a cobalt nickel bimetallic sulfide, and a part of cobaltis simultaneously hydrolyzed to cobalt hydroxide, that is to say, a NiCo2S4 / Co(OH)2 compound is obtained through one hydrothermal reaction, so that the pseudocapacitance behavior of the cobalt-nickelbimetals is synergistic with each other, the specific capacitance performance is greatly improved, the maximum specific capacitance is up to 3668 F / g, and the specific capacitance is higher than the theoretical specific capacity of cobalt metal.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of cobalt-wrapped nickelous hydroxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of cobalt-wrapped nickelous hydroxide. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: (1) preparing a cobaltous sulfate solution A, a potassium hydroxide solution B, an ammonia solution C, a sodium hydroxide solution D, an aqueous solution E of salts from rare earth metals, and an aqueous solution of complexing agent F; (2) preparing spherical nickel hydroxide and pure water in a reactor to obtain the mixture, and adjusting the pH (Potential Of Hydrogen) of the reactive liquid through the solution B; (3) synchronously and continuously adding the solution A, the solution B, the solution C, the solution E and the solution F into the reactor to carry out wrapping reaction; (4) separating the solid from the liquid of the product prepared in step (3), washing via the pure water, and parching to obtain the nickelous hydroxide wrapped with cobaltous hydroxide; (5) adding the nickelous hydroxide wrapped with cobaltous hydroxide into an oxidizing reactor to be oxidized; and (6) washing the oxidized material via pure water, and parching to obtain the product of nickelous hydroxide wrapped with cobalt oxide. The cobalt-wrapped nickelous hydroxide prepared by the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of uniform wrapping and oxidizing layer, high conductivity, uniform and complete conductive network, and high utilization of active materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI JINZHONG INFORMATION TECH
Preparation method of three-dimensional supported cobalt hydroxide and method of using three-dimensional supported cobalt hydroxide for catalytically treating phenol wastewater by persulfate
InactiveCN110420641ALarge specific surface areaAvoid secondary pollutionWater contaminantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrogen SulfatePersulfate
The invention relates to a preparation method of three-dimensional supported cobalt hydroxide and a method of using the three-dimensional supported cobalt hydroxide for catalytically treating phenol wastewater by persulfate. The invention solves the problems of complex preparation method and difficult recycling of an existing monoperoxide potassium hydrogen sulfate catalyst. The preparation of thethree-dimensional supported cobalt hydroxide is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) pretreating three-dimensional foam nickel; and (2) growing cobalt hydroxide nanosheets in situ onthe foamed nickel pretreated in the step (1) by an electrochemical deposition method to prepare the foamed nickel-based cobalt hydroxide. The method of using the three-dimensional supported cobalt hydroxide catalyst for catalyzing a method for catalytically treating phenol wastewater by persulfate comprises the following steps: adding the foamed nickel-based cobalt hydroxide catalyst into the phenol wastewater, then adding monoperoxide potassium hydrogen sulfate, and carrying out stirring to degrade the phenol wastewater. The three-dimensional supported cobalt hydroxide catalyst is simple in preparation method, can be used to realize high-efficiency degradation of phenol wastewater, and can be recycled.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
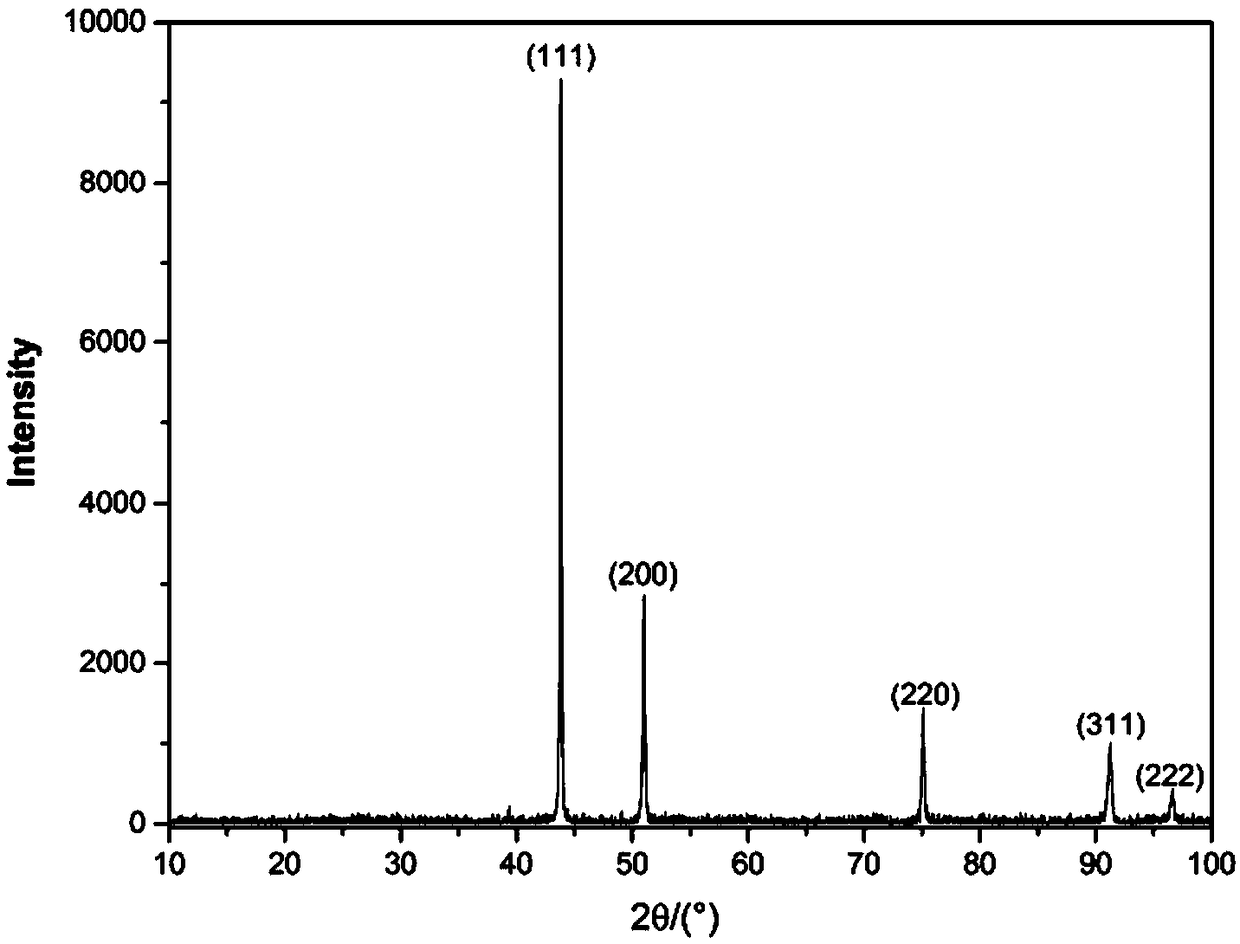
Hexagonal flaky cobalt hydroxide synthesis method
InactiveCN106186085AEasy alignmentEasy to separateMaterial nanotechnologyCobalt oxides/hydroxidesHigh concentrationSynthesis methods
The present invention relates to a hexagonal flaky cobalt hydroxide synthesis method, which comprises: dissolving a cobalt salt in deionized water to obtain a cobalt salt solution; dissolving caustic alkali and one or a plurality of small molecular nitrogen-containing ligands in deionized water so as to be adopted as a precipitant solution; and adding the precipitant solution into the cobalt salt solution to react with the cobalt ions so as to generate the cobalt hydroxide. According to the present invention, during the reaction precipitation process of the hydroxide ions and the cobalt ions, a certain amount of the one or the plurality of the small molecular nitrogen-containing ligands are added, and the nitrogen-containing ligands are strongly matched with the cobalt ions to make the cobalt hydroxide grow according to a certain direction, such that finally the hexagonal flaky structure having the edge length of 100-400 nm is formed; and the flaky structure can be obtained at the room temperature under the high concentration, the reaction time is short, and the mass production can be achieved.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
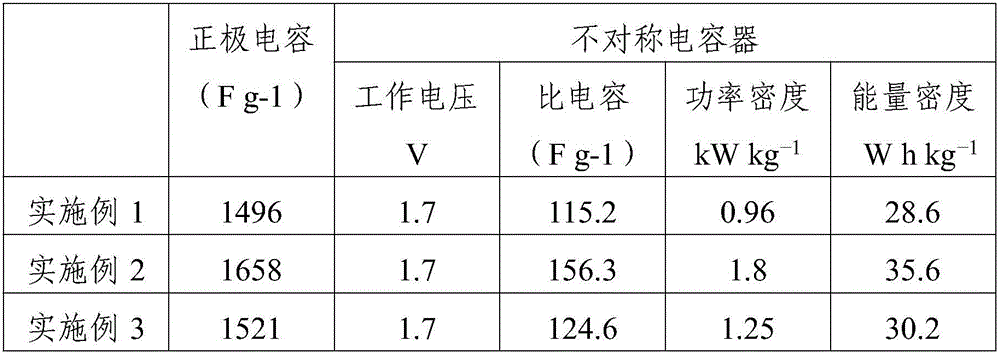
Preparation method of asymmetric supercapacitor
ActiveCN106683908AIncrease working voltageIncrease energy densityHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitancePorous carbon
The invention provides a preparation method of an asymmetric supercapacitor, wherein the preparation method relates to the technical field of supercapitors. According to the preparation method, cuprous oxide is used for preparing a sacrificial template; cobaltous hydroxide is obtained through normal-temperature mixing; and sulfuration is performed on the cobaltous hydroxide according to a hydrothermal method for obtaining hollow cobaltous sulfide powder. The hollow structure can reduce diffusion distance of ions and improves utilization rate of active substances, thereby improving specific capacitance of a material. The cobaltous sulfide powder is used as an anode and a porous carbon material is used as a cathode, and the asymmetric supercapacitor is obtained through assembling. The supercapacitor has a wide potential window. Furthermore energy density and power density of the supercapacitor are improved.
Owner:吴中区穹窿山倪源交通器材经营部
Alkaline storage battery
InactiveUS6620549B2Improve overall utilizationImprove discharge characteristicsPositive electrodesAlkaline accumulator electrodesNickel oxide hydroxideCobalt(II) hydroxide
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Preparation method for cobalt boroacylate with low melting point
ActiveCN103113416ALow melting pointSmall dispersionCobalt organic compoundsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsCalcium boratePropanoic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method for cobalt boroacylate with a low melting point. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out a neutralization reaction, namely, mixing neodecanoic acid, propionic acid, valeric acid, stearic acid, rosin, dimethylbenzene and cobalt hydroxide to carry out acid-base neutralization reaction so as to obtain an intermediate product after the neutralization reaction is completed; carrying out boro-acylation reaction, namely, adding tributyl borate to the obtained intermediate product to carry out boro-acylation reaction, adding the calcium borate as an additive, wherein the reaction product obtained by the boro-acylation reaction is cobalt boroacylate. The cobalt boroacylate prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention is low in melting point and good in dispersion; and moreover, high-concern substances mentioned by the REACH (REGULATION concerning the Registration, Evaluation,Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) are avoided, and a green passport is provided for the exportation of products.
Owner:大连爱柏斯化工股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com