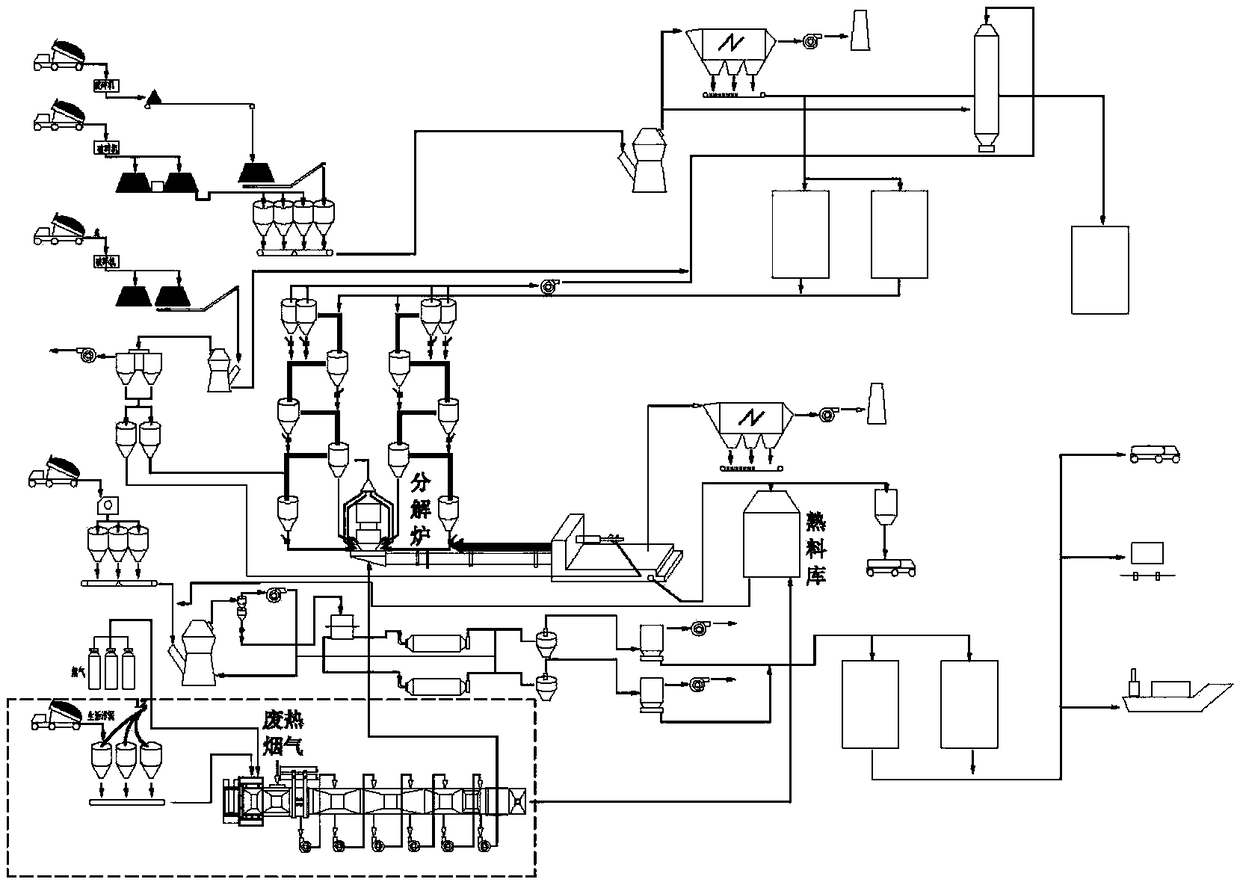
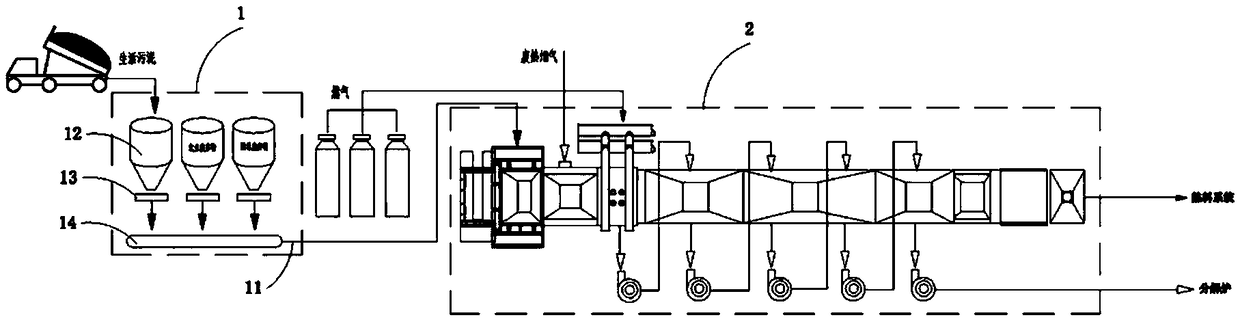
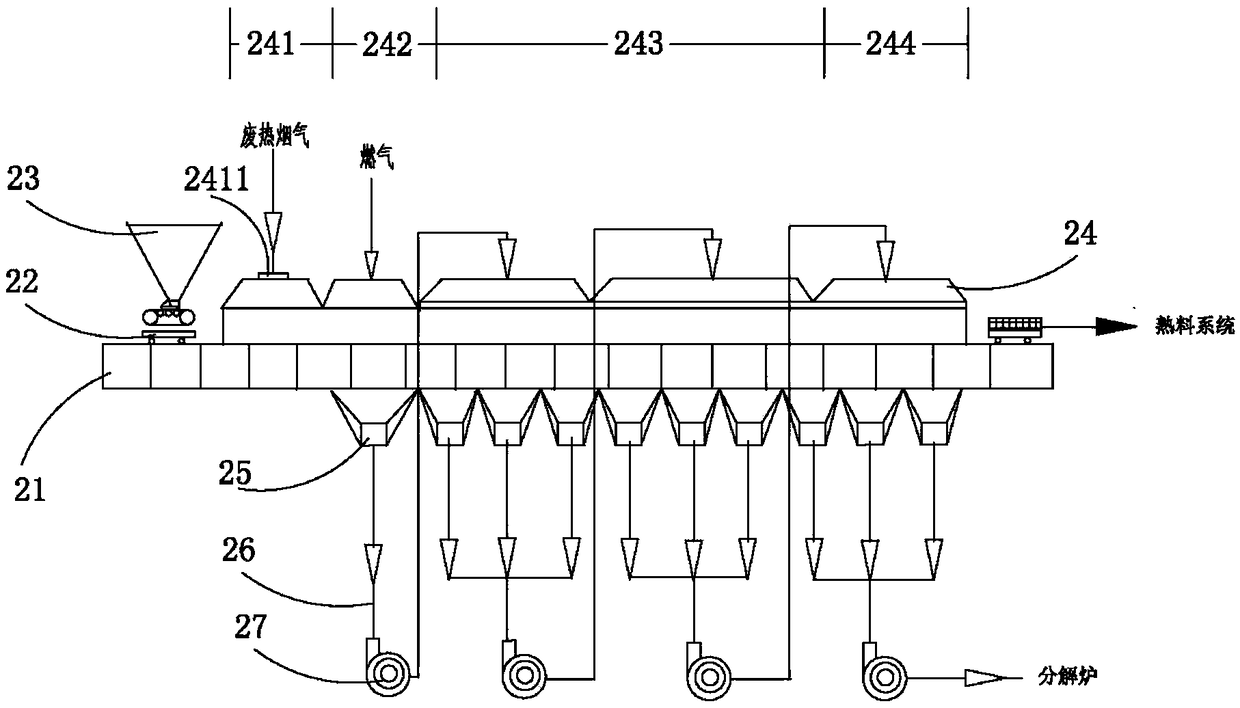
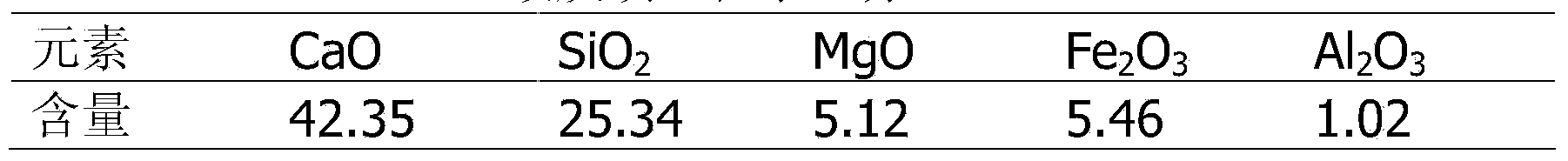Patents
Literature
47results about How to "No secondary waste" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for making coal fine into form coke by microwave energy
InactiveCN101497835AReduce manufacturing costIncrease productivitySolid fuelsMicrowave heatingMicrowaveWork in process
The invention relates to a method for producing formed coke, in particular to a method for preparing coal powder into the formed coke by microwave. The method adopts coal powder as raw material and comprises the following steps: sieving the coal powder for preparing fine coal powder, sending the fine coal powder into a first microwave heating device for dehydration until the water content of the heated fine coal powder is below 1 percent, and sending the heated fine coal powder into a second microwave heating device by a conveying device for dry distillation; performing the dry distillation to the fine coal powder by the second microwave heating device to analyze other materials in the coal powder, preparing carbocoal after the dry distillation, sending the carbocoal into a mixer by the conveying device to prepare the mixture after adding bonding material; sending the mixture to a forming machine by a conveyer for forming so as to prepare a formed coke semi-finished product; sending the reformed coke semi-finished product into a third microwave heating device for being heated and carbonized to prepare red coke, and sending the carbonized red coke into a coke car to prepare a formed coke product. The invention has low production cost, high production efficiency, cleanness and environment protection because coke powder and waste are not produced during the production.
Owner:唐山金强恒业压力型焦有限公司
Efficient biochemical nitrogen and phosphorus removal method for waste water
ActiveCN104556572AImprove mud life and recycling rateReduce stepsTreatment using aerobic processesWater contaminantsChemistryIon adsorption
The invention discloses an efficient biochemical nitrogen and phosphorus removal method for waste water. Ammonia nitrogen and phosphorus in waste water are efficiently removed by combining a modified A2 / O biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal technology and a chemical method, namely, zeolite adsorbing ammonia nitrogen method; the denitrification liquid flowing out from an anoxic denitrification tank enters an aerobic nitration tank to form internal circulation; the residual denitrification liquid directly enters a sedimentation tank for solid-liquid separation; phosphorus-accumulating bacteria directly flows back to an anaerobic tank from the sludge of a sedimentation tank, and then enters the anoxic nitration tank. Ion adsorption and biological regeneration treatment are combined; water outlet total nitrogen is less than or equal to 5 mg / L; the removal ratio of total nitrogen and total phosphorus is more than 90%; requirements that water outlet total nitrogen in Taihu basin chemical engineering zone is superior to the primary standard, namely, the A standard, of the urban sewage treatment plant pollutant discharge standard (GB18918-2002) are met stably.
Owner:江苏艾特克环境工程设计研究院有限公司 +1
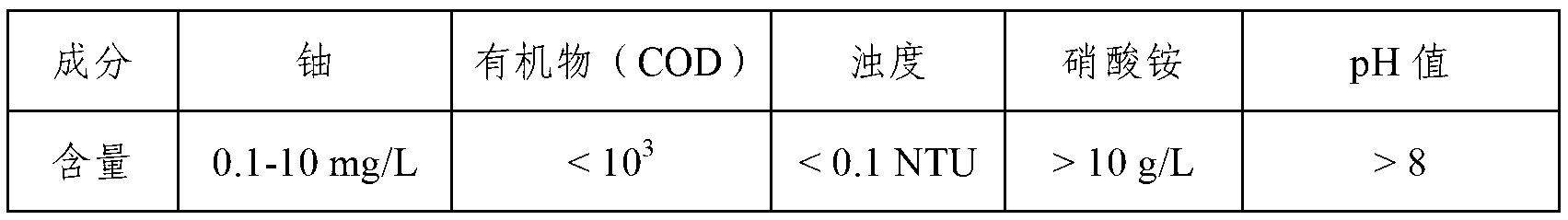
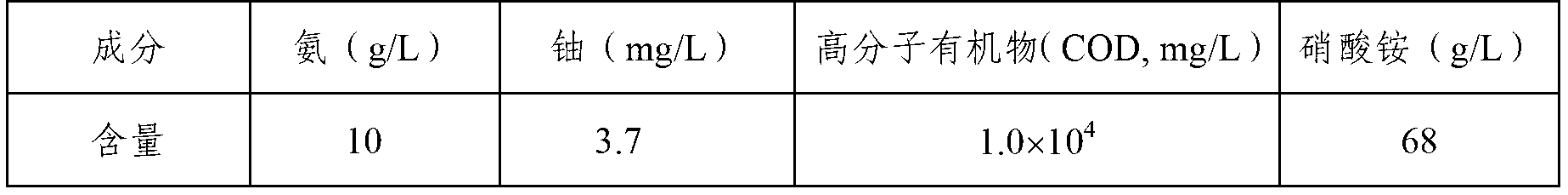
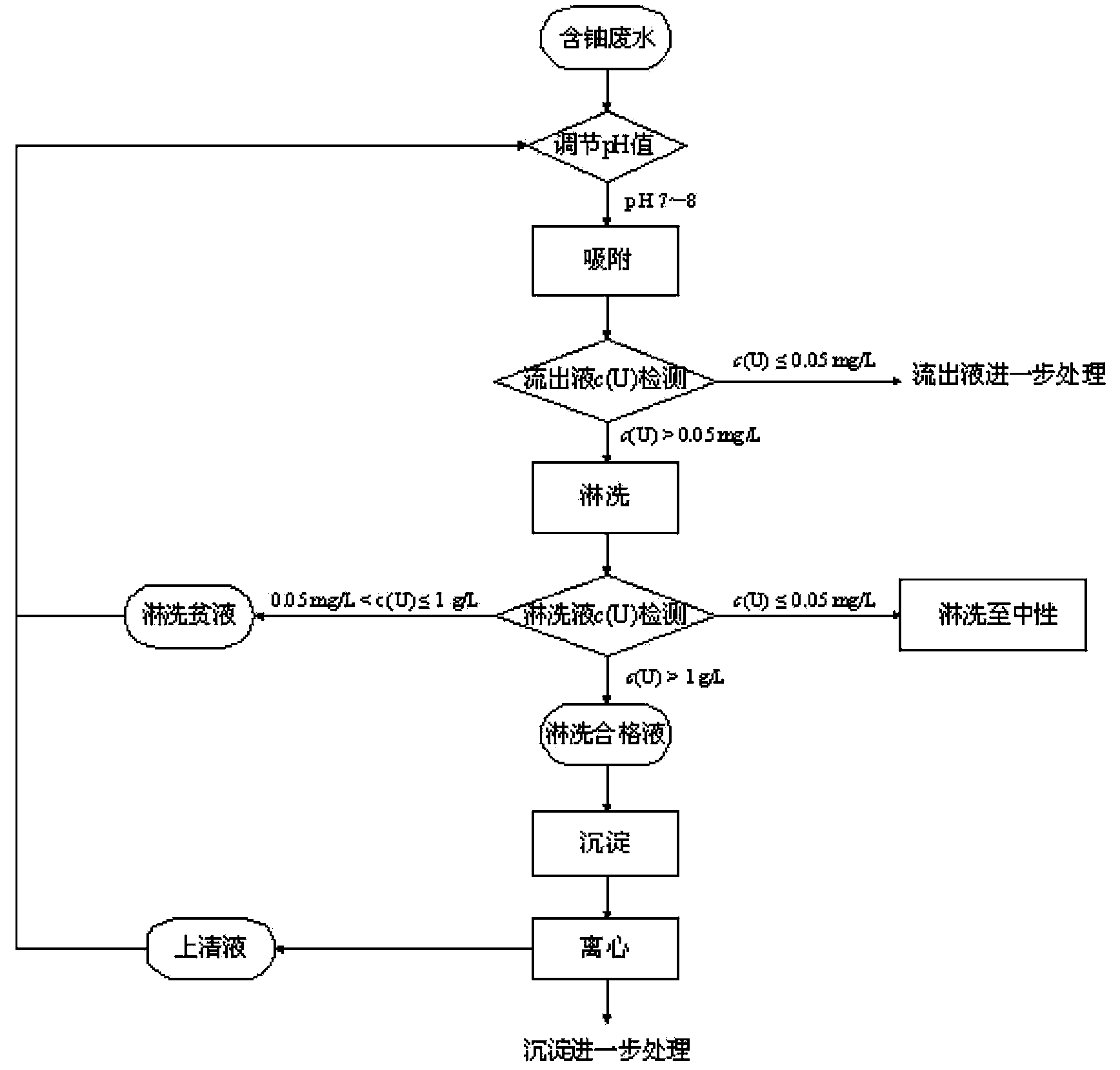
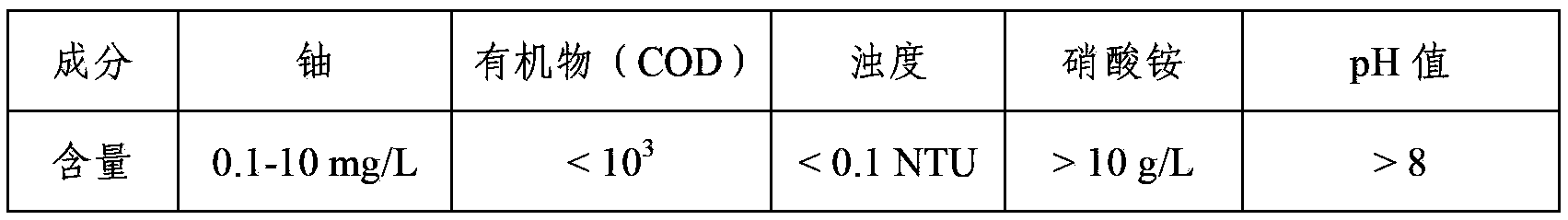
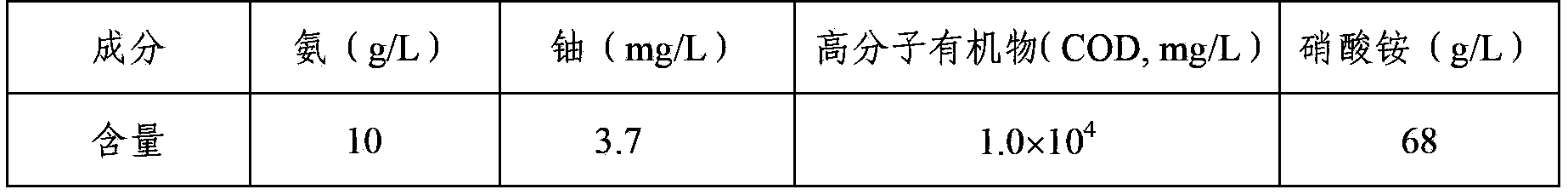
Method for recycling uranium in uranium-contained waste water
ActiveCN103193289ALow costNo secondary wasteMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by sorptionLiquid wasteWastewater
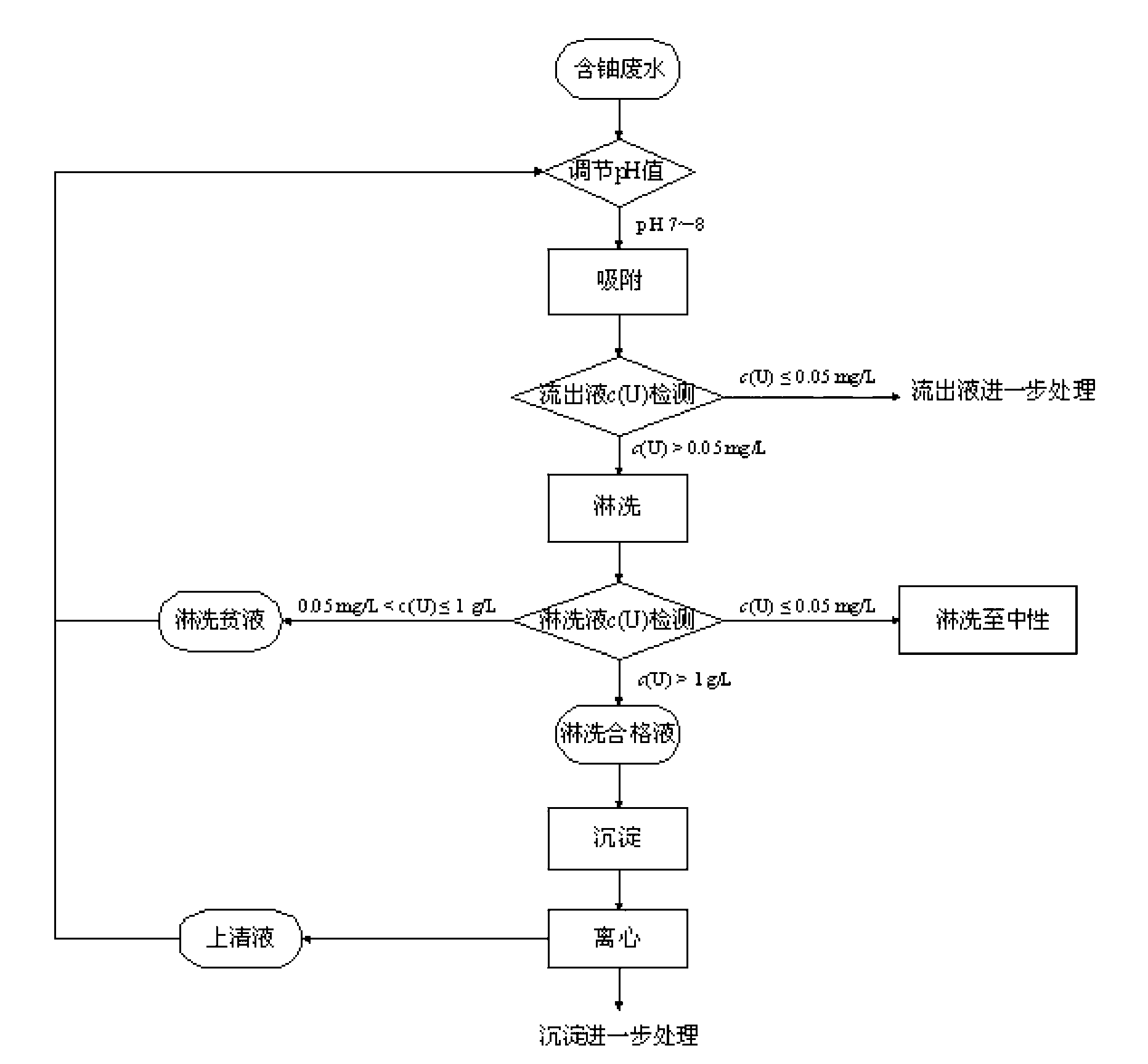
The invention provides a method for recycling uranium in uranium-contained waste water. The method is characterized by recycling and enriching the uranium in the waste water through the steps of ammonia removal of the waste water as well as pretreatment of organisms, uranium adsorption by chromatographic columns, scouring by acid solution and deposition. The method is high in recycling efficiency, low in cost, free from producing secondary waste liquid, compact in technological flow, applicable to the treatment of different uranium-contained waste liquid and high in practicability.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
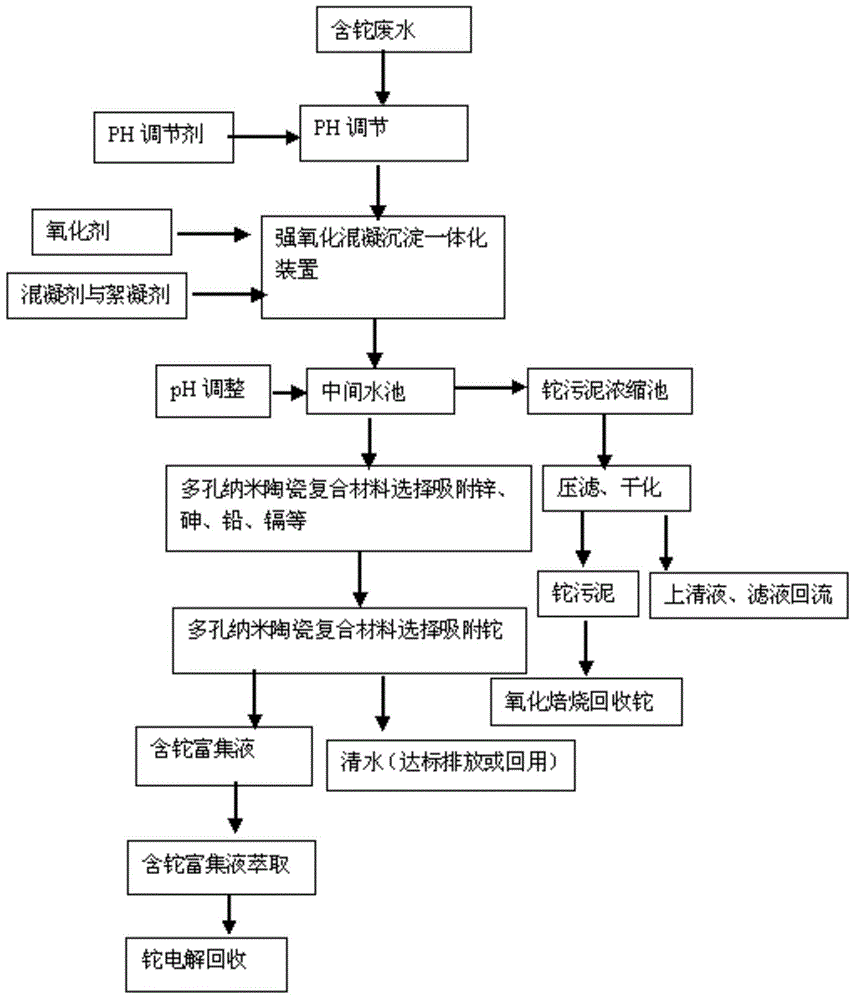
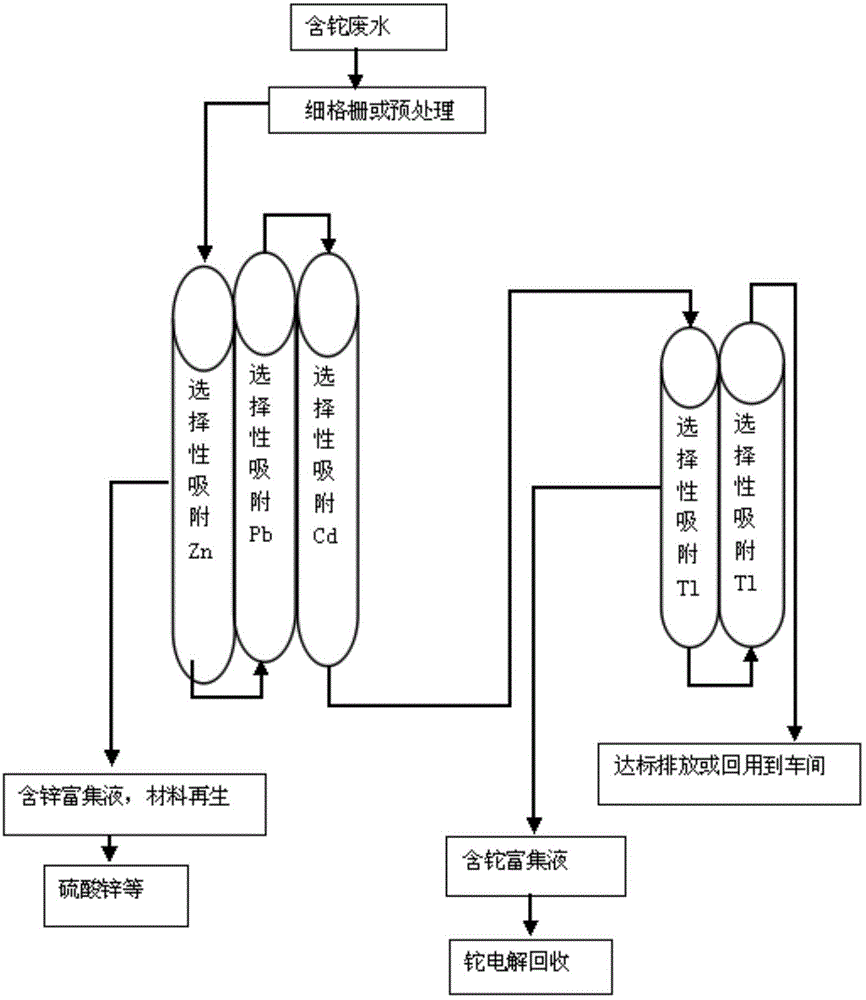
Thallium-containing wastewater strongly oxidizing, coagulating, adsorbing and recovering process
ActiveCN104310672AHighly selective adsorptionLarge specific surface areaWater treatment parameter controlSludge treatmentFiltrationSludge
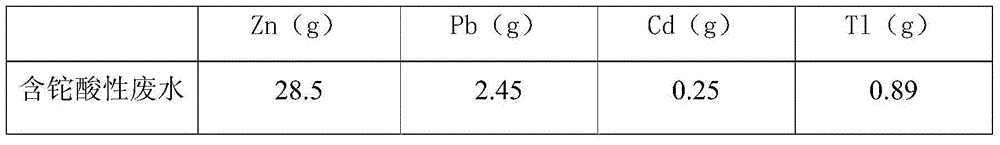
The invention provides a thallium-containing wastewater strongly oxidizing, coagulating, adsorbing and recovering process. The process includes the following procedures: thallium-containing wastewater concentration, pH regulation, strong oxidization, coagulation, flocculation, precipitated sludge treatment, pH regulation, solid impurity filtration, removal of Zn, Pb, Cd and Tl, and the like. The process has the beneficial effects that the process has the advantages of advanced technology, maturity, good effluent quality, stability in operation, conciseness in process, strong practicability, easiness in start and stop, convenience in maintenance and management, small investment, low operating cost, small floor area for construction, short construction period and large application ranges of projects; treatment of heavy metal ion polluted sewage is not limited by temperatures; the limitation that a biological method can not be used in cold regions in the north can be overcome.
Owner:HUNAN JINGYUAN ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
Dry cutting method for dry ice cooling
InactiveCN103801979ANo secondary wasteInhibitionMaintainance and safety accessoriesEconomic benefitsDry ice
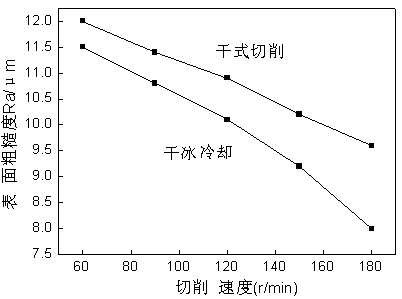
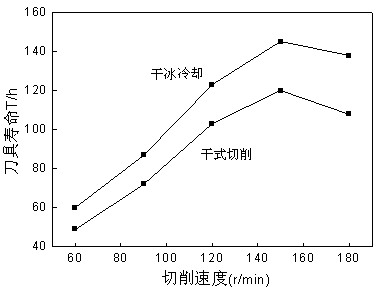
The invention relates to the technical field of turning, in particular to a dry cutting method for dry ice cooling. The dry cutting method is characterized in that dry ice is smashed into powder, the powder and compressed air are mixed, and the powder is sprayed on a cutting machining portion of a cutting tool at the same time in the machining process. According to the dry cutting method, the problems of waste of cutting liquid and environmental pollution caused by the cutting liquid in the existing turning process are solved, the temperature of a cutting area is obviously reduced, precision of a machining surface is improved, the service life of a tool is prolonged, and economic benefits in the cutting machining process are improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for treating production waste of phosphorus industry and products produced by same
The invention relates to a method for treating production waste of phosphorus industry and recycling phosphorus from the treated production waste, which includes performing high-temperature oxidation of the waste at the temperature of from 250 DEG C to 1200 DEG C by enabling the production waste of phosphorus industry to contact with oxygen-containing gases, and recycling the obtained solid products. By using the method, use of expensive drugs can be avoided, and secondary waste which is hard to deal with cannot be produced. Production waste liquid of phosphorous pesticides can be converted into matters such as pyrophosphate, polyphosphates, metaphosphate, orthophosphate and the like. The matters can be applied to other chemical industrial productions, so that phosphorus elements can be recycled and utilized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINAN CHEM INDAL GROUP
Preparation method of aluminum calcium carbonate composite cementing material and product thereof
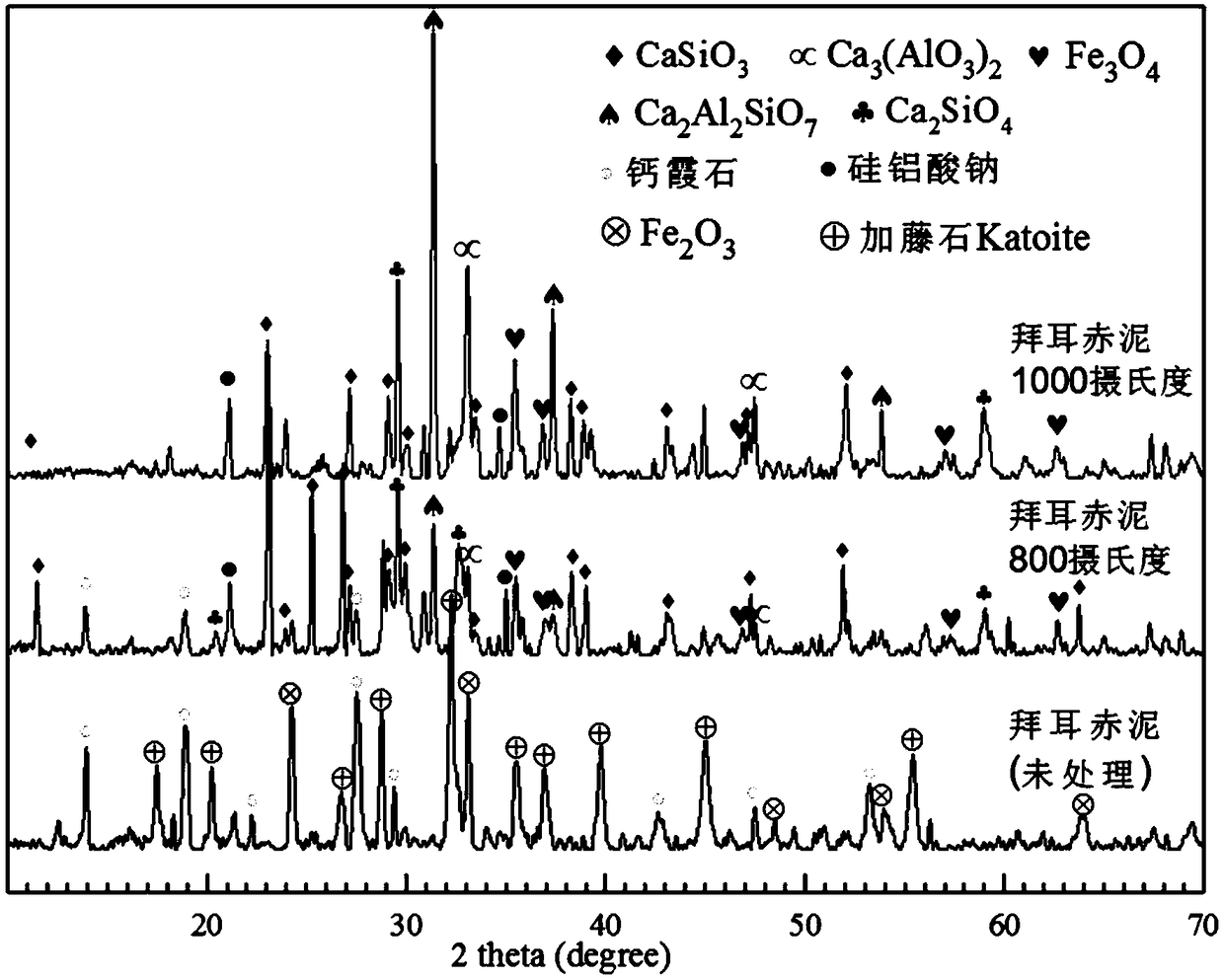
The invention relates to a preparation method of an aluminum calcium carbonate composite cementing material and a product thereof. The preparation method comprises following steps: (1) adjusting the calcium and silicon contents of red mud, and carrying out heat activation, cooling, water washing, and drying to obtain thermally activated red mud; and (2) mixing thermally activated red mud, cement,and an auxiliary cementing material, adding water, curing molding, and then performing CO2 mineralization enhancement to obtain the aluminum calcium carbonate composite cementing material. The methodhas the advantages that red mud can adapt to the technical characteristics of CO2 mineralization enhancement; low value red mud with a high alkali content is utilized, and the low carbon benefits of building materials are maximized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for treating materiel of containing arsenic
InactiveCN1540005AReduce processing costsNo secondary wasteProcess efficiency improvementAmmoniaSodium salt
A process for treating the As-contained alkaline waste dregs includes such steps as immersing in water to remove ash and obtain dregs and As alkali contained solution, returning the dregs back to production line for recovering valuable metals, adding ammonium salt to said solution for neutralizing alkali, heating to volatilize ammonia and CO2, absorbing them by a mother for preparing ammonium hydrogen carbonate or sodium carbonate, adding As precipitant to deposit As, and using the residual solution to prepare sodium salt. Its advantage is no secondary pollution.
Owner:锡矿山闪星锑业有限责任公司
Underground oil tank lining structure of gas station and construction method
ActiveCN107284887AComplete Double StructureNo site excavation requiredLarge containersGlass fiberFirming agent
The invention discloses a underground oil tank lining structure of a gas station and a construction method, and solves the problem of influence on environmental protection by the corrosion leakage of a traditional underground oil steel tank. The structure comprises a double-layer lining structure design; according to the load borne by an oil tank, the stress strength of the double-layer lining structure independent from the traditional underground oil steel tank is calculated, and the thicknesses of an outer layer, a middle gap layer and an inner-layer glass fiber reinforced composite material are determined; the dry ice derusting cleaning and the resin bottom brushing are performed on the inner surface of the oil tank; the outer layer, the middle gap layer and the inner-layer glass fiber reinforced composite material are constructed in sequence; photocuring unsaturated resins and a photocuring agent are uniformly mixed according to 100: (0.2-0.6); a ultraviolet curing lamp is used for curing; and anti-thunder and anti-static grouding leakage detecting signal outgoing lines are leaded out from an inlet hole of the oil tank by the middle gap layer. The structure has such advantages as no need of field excavation, short construction period and low comprehensive cost; and the improved oil tank has complete double-layer structure to accord with national standards.
Owner:HUACHANG POLYMER EAST CHINA UNIV OFSCI & TECH
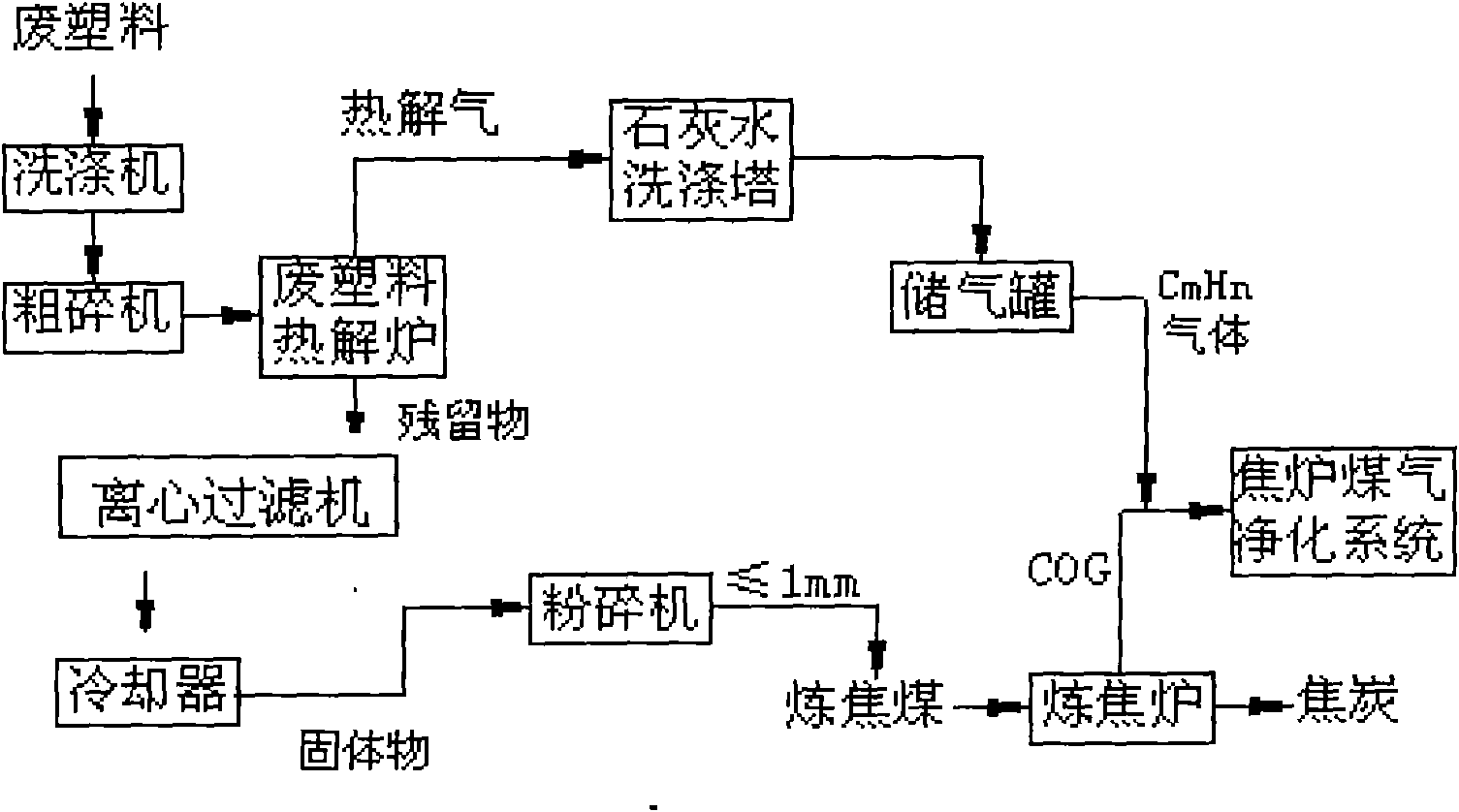
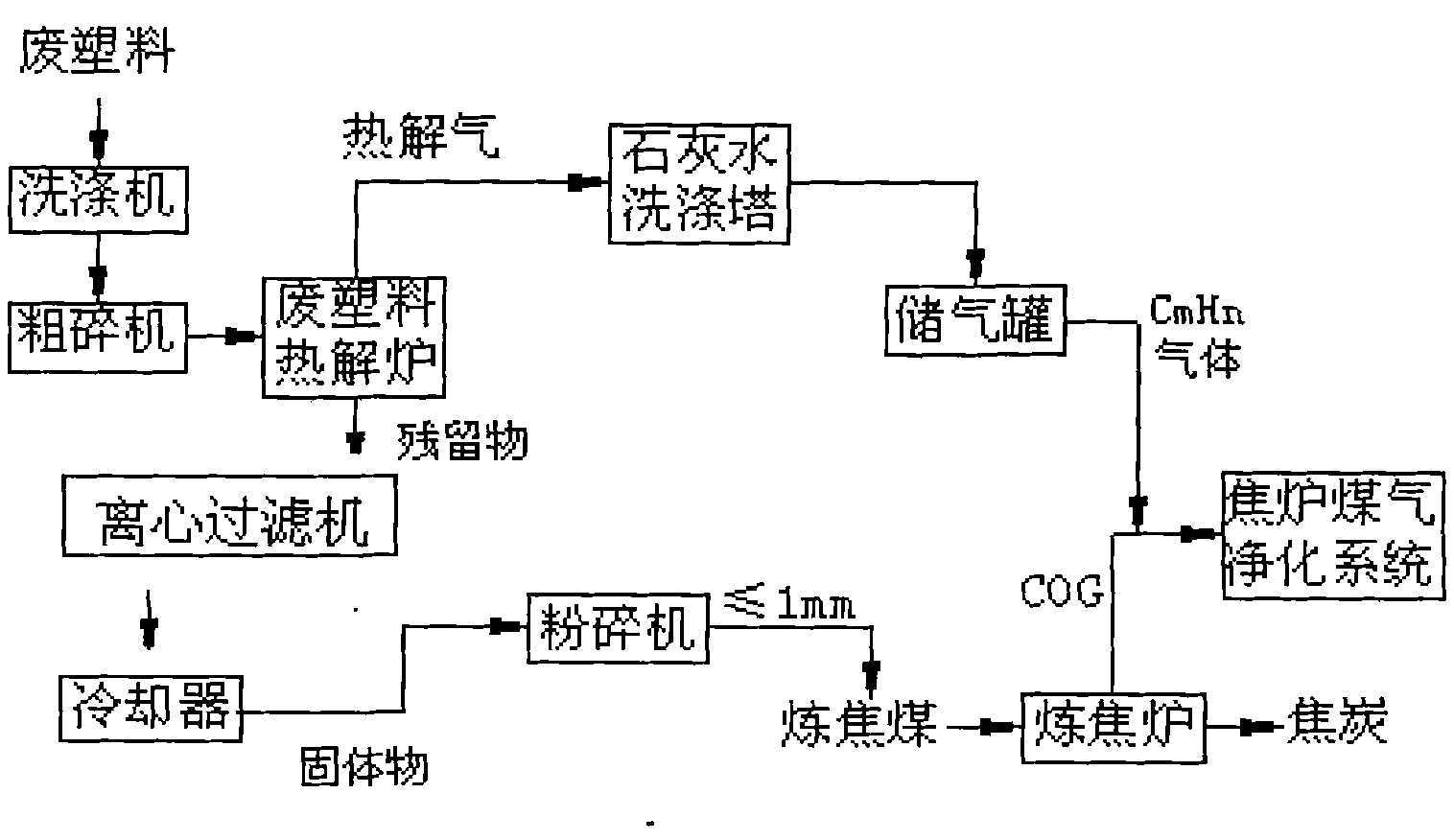
Waste plastics pretreatment process based on coking by coke oven
InactiveCN101831313AAvoid corrosionAvoid uneven dispersionProductsReagentsEnvironmental effectEnvironmental engineering
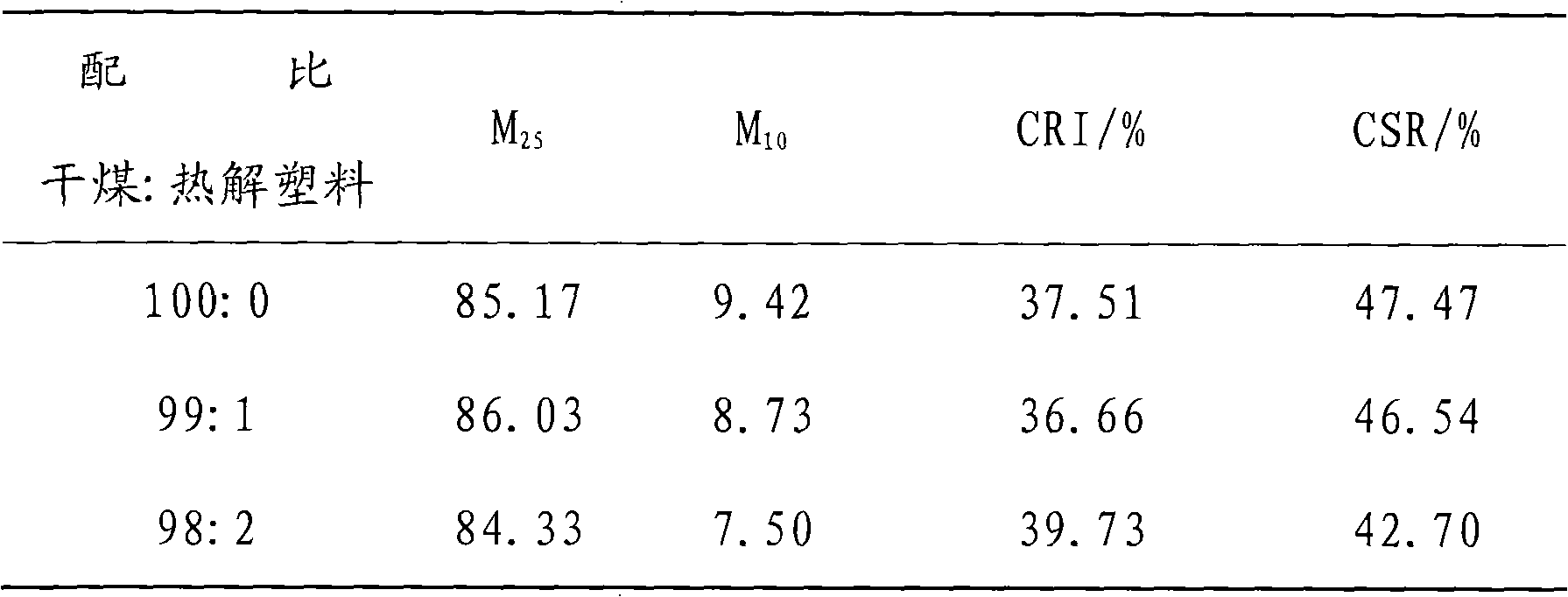
The invention discloses a waste plastics pretreatment process based on coking by a coke oven, which solves the problems of low equipment life, large environmental influence and influenced coke quality after coal blending in the process of treating waste plastics by using the coking process in the prior art. The technical scheme adopted by the invention is as follows: (1) performing coarse crushing on the waste plastics by a crusher until the grain size is 8-12mm; (2) feeding the waste plastics with the grain size of 8-12mm after coarse crushing in a pyrolysis oven, heating to 225-275 DEG C under the condition of air isolation, pyrolyzing for 30-90min at a constant temperature and dissolving out pyrolysis gas; (3) cooling the fluid residue of the waste plastics after pyrolysis to form solid-state solids, and feeding the solid-state solids in the crusher again for crushing until the grain size is no more than 1mm; and (4) blending the solid-state solids in coking coal according to the proportioning of 1% by weight. The invention has the advantages of simple process, no environment pollution and no influence on coke quality.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司 +2
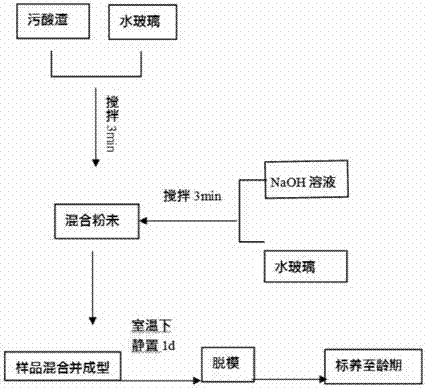
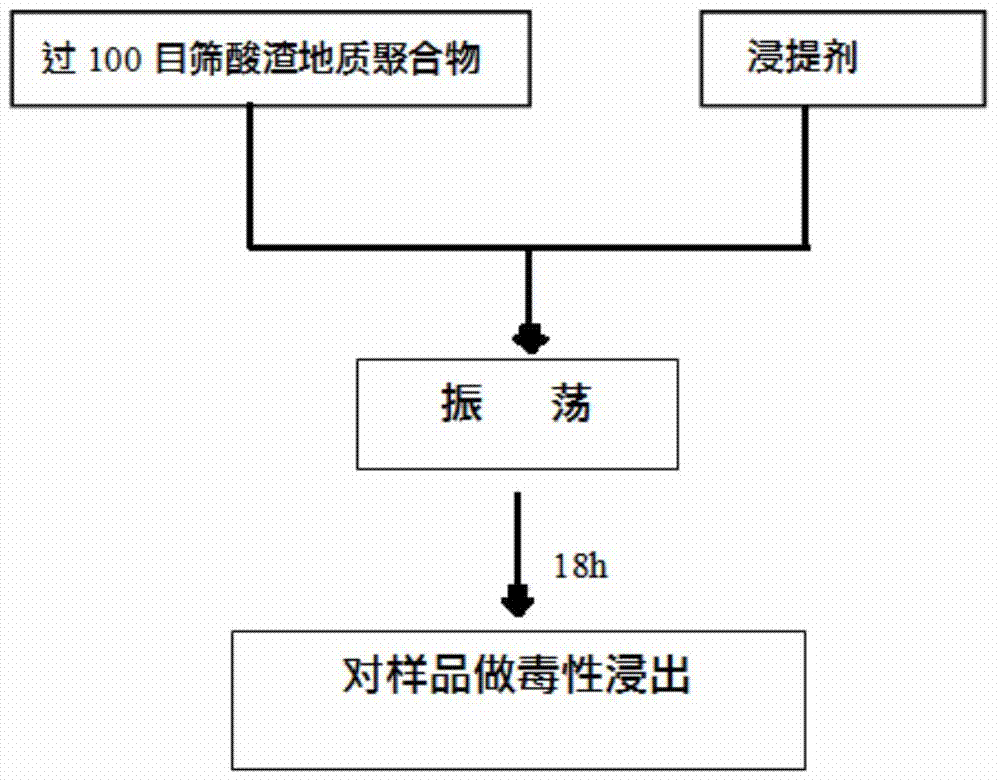
Method for preparing geopolymer by utilizing waste acid sludge
The invention relates to a method for preparing geopolymer by utilizing waste acid sludge. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: mixing waste acid sludge powder, modified magnesium slag powder and bauxitic clay powder, wherein the weight ratio of the waste acid sludge to the modified magnesium slag is 1:1-3, and the addition amount of bauxitic clay accounts for 20%-60% by weight of the total mixed powder; then mixing a NaOH solution with the mass concentration of 20-50% and a water glass solution with the mass concentration of 5-50% according to the volume ratio of 3:1-3, then pouring into the above mixed powder, uniformly stirring, and then pouring a die for molding; and finally demolding and maintaining. The provided processing method is clean and environment-friendly, is applicable to solidify heavy metal Cd in the waste acid sludge, and is low in cost. The preparation technology is simple, does not need high-temperature sintering, does not employ expensive materials, is easy to construct, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:BEIFANG UNIV OF NATITIES
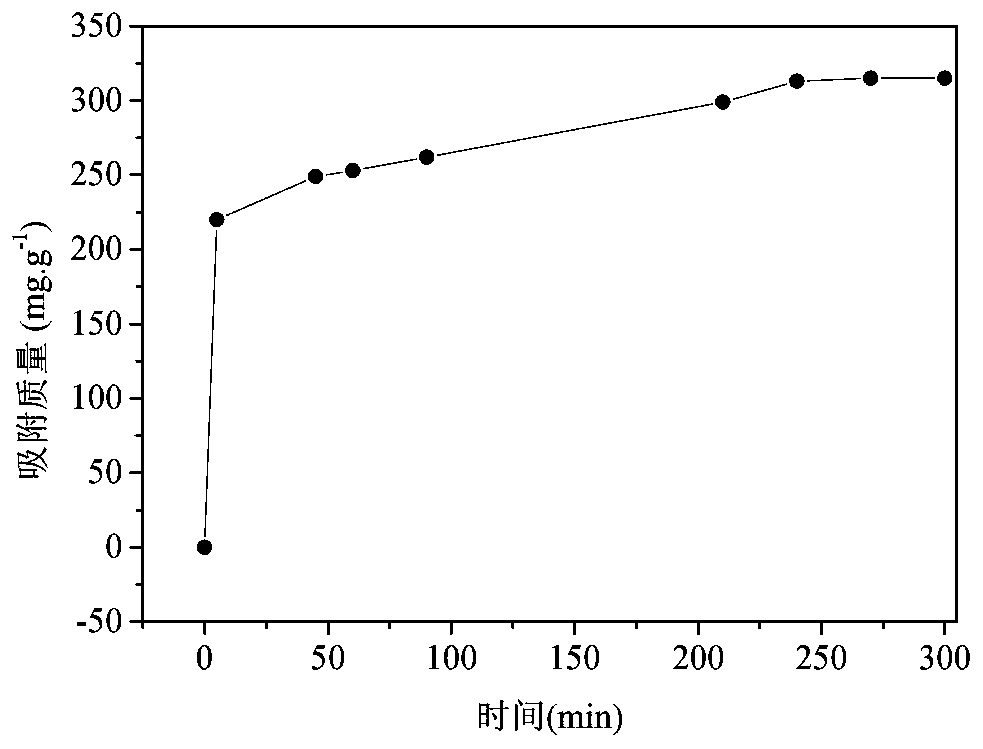
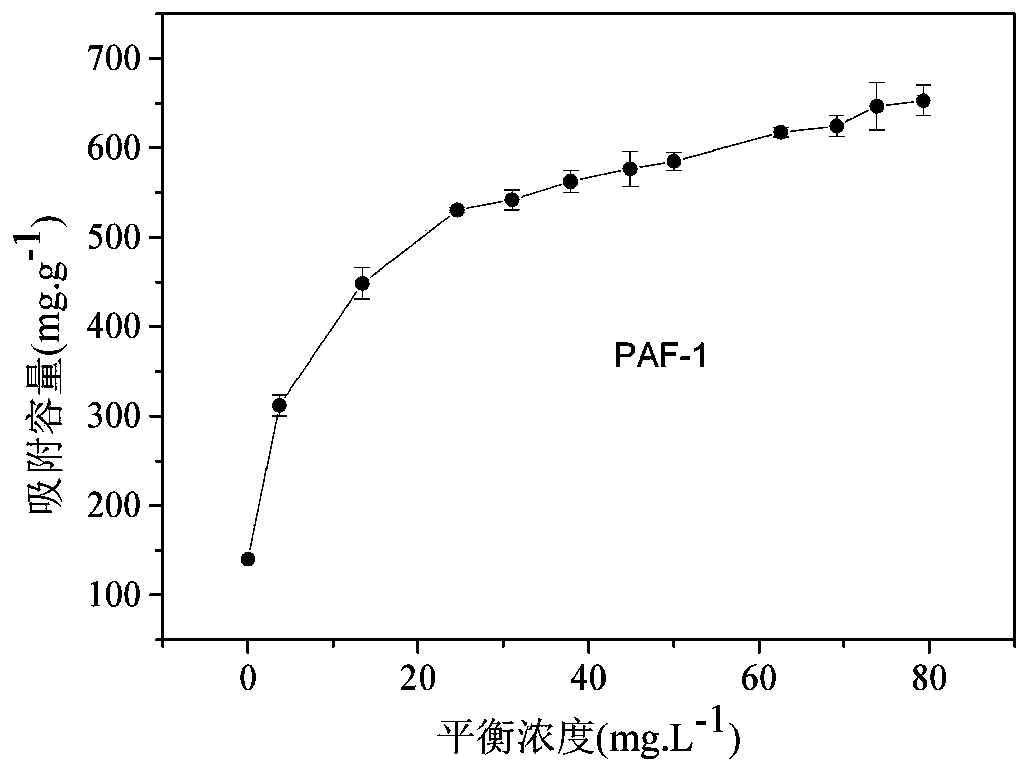
Material for adsorbing uranium from basic nuclear waste liquid and preparation method
ActiveCN109908873AImprove adsorption capacityHigh adsorption selectivityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesPhosphonium saltCarbon Chloride
The invention discloses a material for adsorbing uranium from a basic nuclear waste liquid and a preparation method of the material. The material for adsorbing uranium from the basic nuclear waste liquid is prepared from a polymer PPN-6 as a matrix by connecting short-chain quaternary phosphonium salt with the chlorinated carbon atom number being 1-4 onto a benzene ring of PPN-6. The material hasquite high adsorption capacity on uranyl tricarbonate, and has quite high adsorption selectivity and faster adsorption kinetics, a back extraction agent of the material is diluted hydrochloric acid, and besides, a back extraction method is very simple and convenient and has good recyclability; the material can be incinerated after being repeatedly used, and no secondary waste is produced.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for recycling fluorine-containing sulfuric acid
PendingCN112645287AMild hydrolysis conditionsMild conditionsHydrogen fluorideSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidHydrogen SulfateFluorosulfuric acid
The invention relates to a method for recycling fluorine-containing sulfuric acid. The method comprises the steps of under normal pressure, adding a certain amount of deionized water into a reaction kettle filled with fluorine-containing sulfuric acid, with the addition amount of the deionized water being 90 to 120% of the theoretical water amount required for hydrolyzing fluorosulfonic acid in fluorine-containing sulfuric acid; introducing inert gas which does not react with sulfuric acid, hydrofluoric acid and water, heating, collecting tail gas, and absorbing with deionized water to obtain hydrofluoric acid; and fluorine-free sulfuric acid being left in the reaction kettle. After treatment, fluorine-free sulfuric acid is finally left in the reaction kettle, and the concentration of the sulfuric acid is 80 to 98%; the content of hydrofluoric acid is below 10ppm; after the tail gas is absorbed by the deionized water, hydrofluoric acid with the concentration of 30 to 48% is obtained, and the content of sulfuric acid is 20 ppm or below. Therefore, after the fluorine-containing sulfuric acid is treated by adopting the method disclosed by the invention, high-concentration and high-purity sulfuric acid and hydrofluoric acid which are directly commercialized or produced and applied can be obtained.
Owner:JIUJIANG TINCI ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
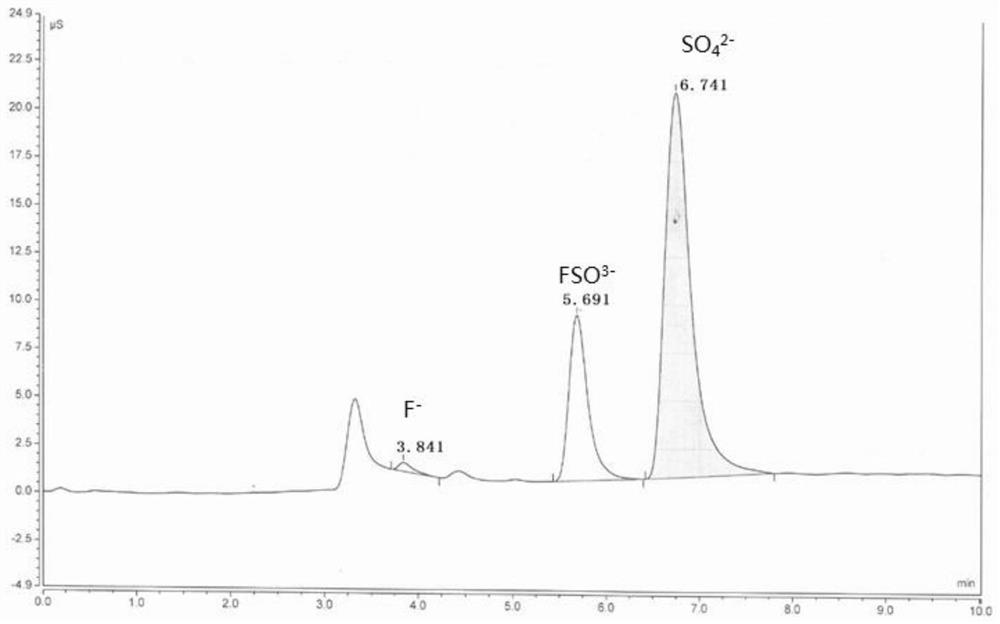
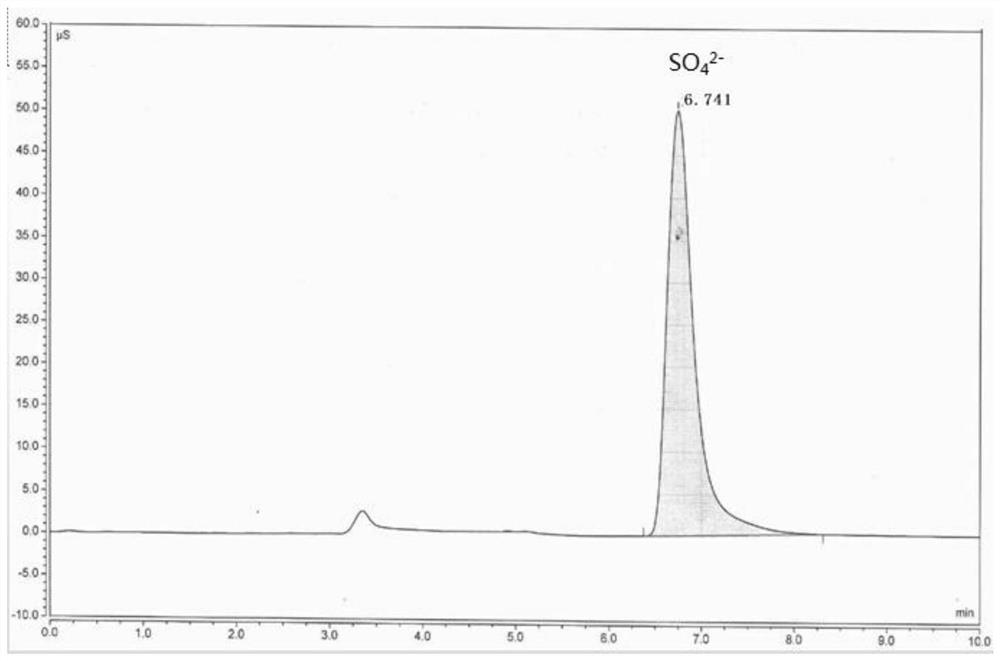
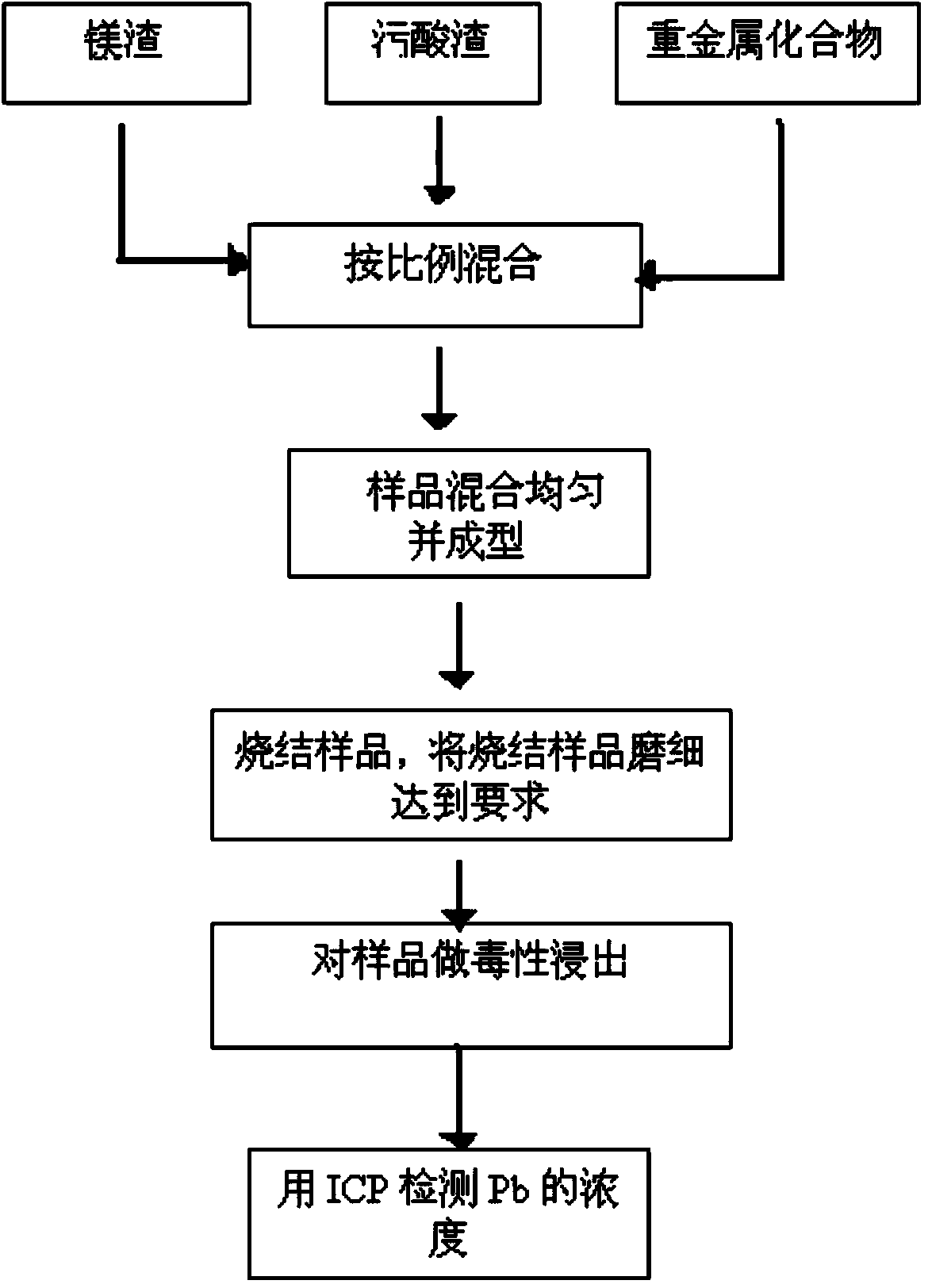
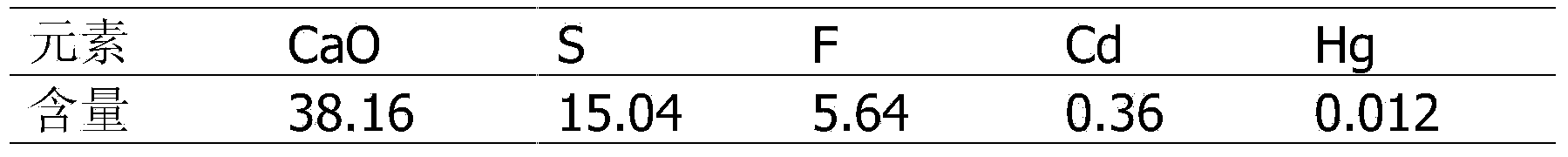
Method for curing lead in fouling acid slag
The method relates to a method for curing lead in fouling acid slag. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that modified magnesium metal slag is added to the fouling acid slag after drying and grinding first, the modified magnesium metal slag and the fouling acid slag are mixed uniformly and then briquetted, and the obtained briquettes are placed in a sintering furnace for heat preservation under the temperature of 500-900 DEG C for 0.5-6 hours and are cooled and taken out. The method is a clean environmental protection treatment method for curing heavy metal Pb in the fouling acid slag, the modified magnesium slag of curing agents is magnesium metal smelting reducing slag, the purpose of waste control by waste is achieved, and therefore cost is low. The curing process for the fouling acid slag is simple, expensive materials are not used, and a project is easy to implement, so that industrialized operation is achieved; secondary waste slag, waste water and waste gas are not generated in the curing process, and the method can be implemented under safe and environment-friendly conditions.
Owner:BEIFANG UNIV OF NATITIES
Method for recycling uranium in uranium-contained waste water
ActiveCN103193289BLow costNo secondary wasteMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by sorptionRecovery methodWastewater
The invention provides a method for recycling uranium in uranium-contained waste water. The method is characterized by recycling and enriching the uranium in the waste water through the steps of ammonia removal of the waste water as well as pretreatment of organisms, uranium adsorption by chromatographic columns, scouring by acid solution and deposition. The method is high in recycling efficiency, low in cost, free from producing secondary waste liquid, compact in technological flow, applicable to the treatment of different uranium-contained waste liquid and high in practicability.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing high-strength permeable concrete by high-iron low-quality coal ash
InactiveCN108585751AImprove utilization efficiencyRapid development of strengthPre treatmentBuilding material
The invention belongs to the field of building materials, and particularly relates to a method for preparing high-strength permeable concrete by high-iron low-quality coal ash serving as a main raw material. Compared with traditional cement-based permeable concrete, the method has the advantages that the activity of the low-quality coal ash is improved by pretreating the coal ash, the use ratio ofthe coal ash is 100%, the adding amount of the coal ash in a product is not lower than 80%, mineral consumption and CO2 emission are reduced, secondary products are avoided, waste is used, environments are protected, the potential destructive effect of iron on the concrete is reduced by pretreatment, the pigment effect of iron in the coal ash is sufficiently achieved, red permeable concrete can be prepared without adding pigments, the early strength of a product mainly prepared from the low-quality coal ash is improved, the compressive strength of standard curing 1d can reach 20MPa, the strength of standard curing 3d can reach 30-40MPa, permeable rate is not lower than 2mm / s, special curing is omitted, strength development is rapid, production cycle is shot, and production cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
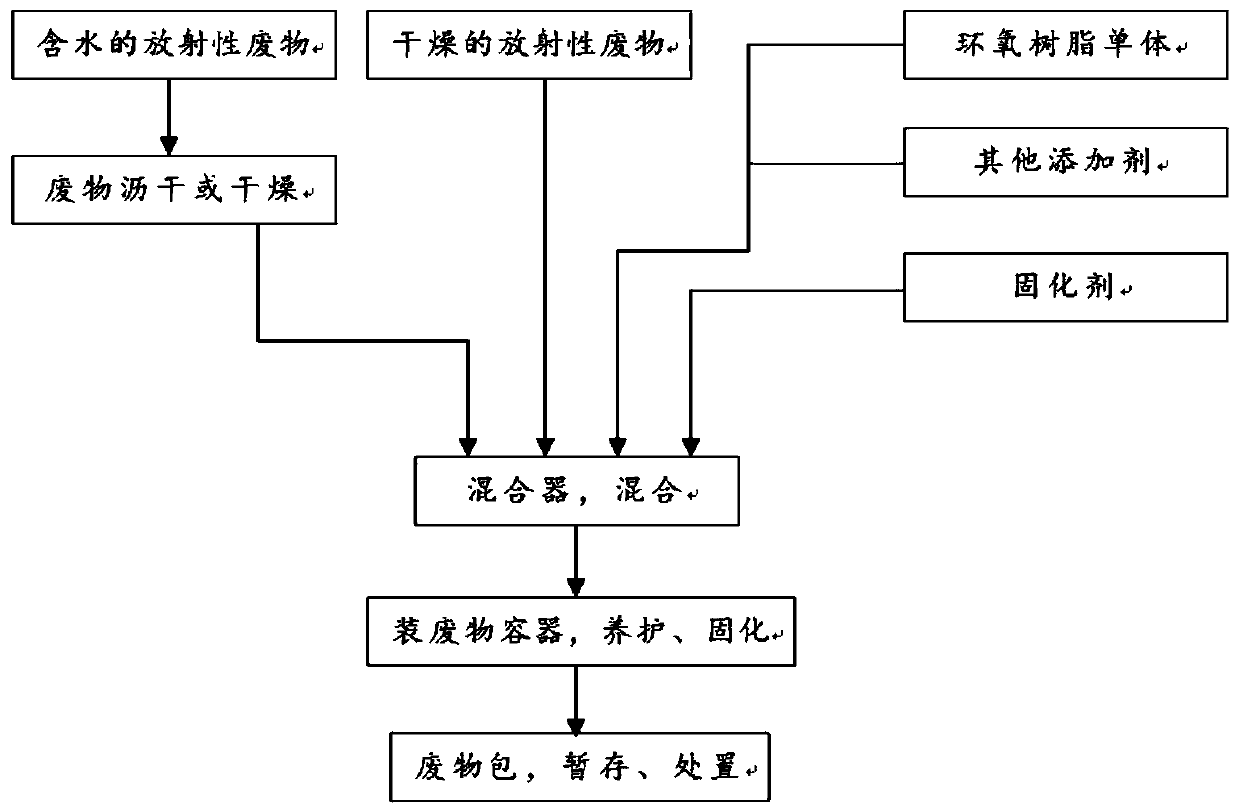
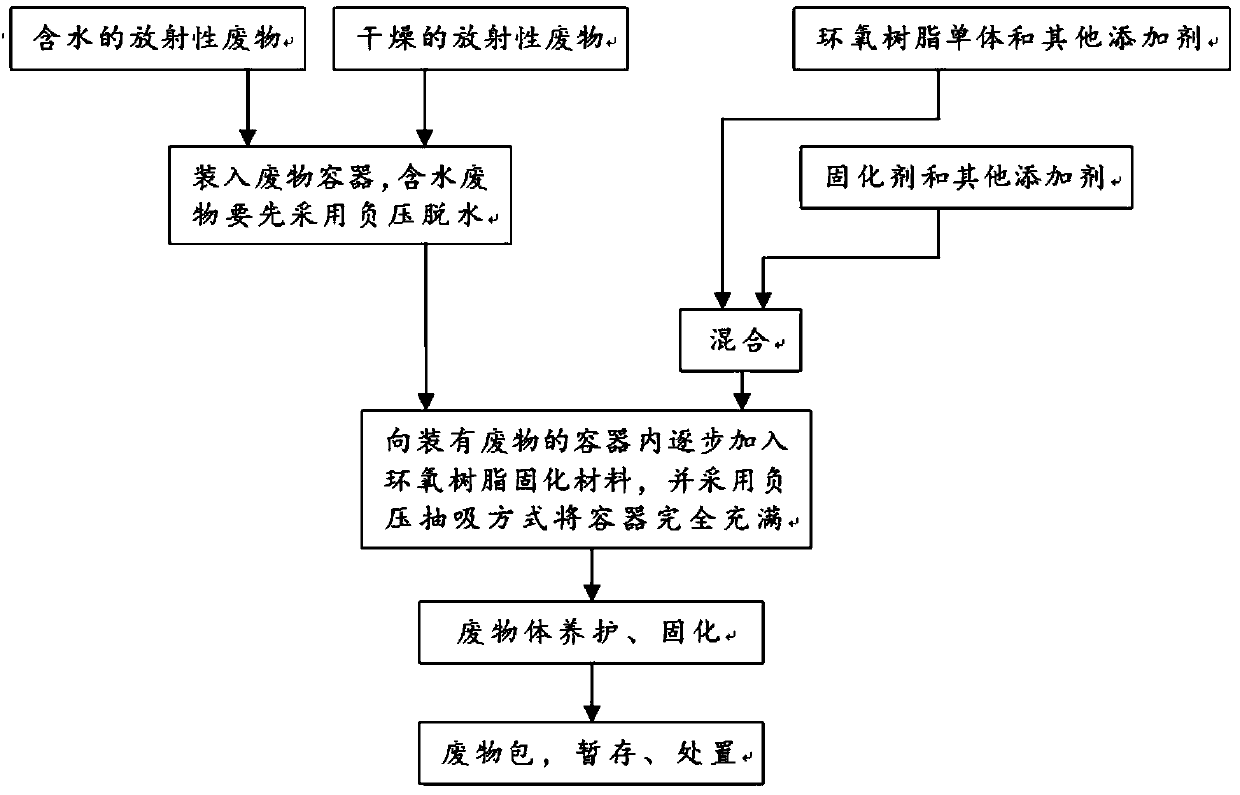
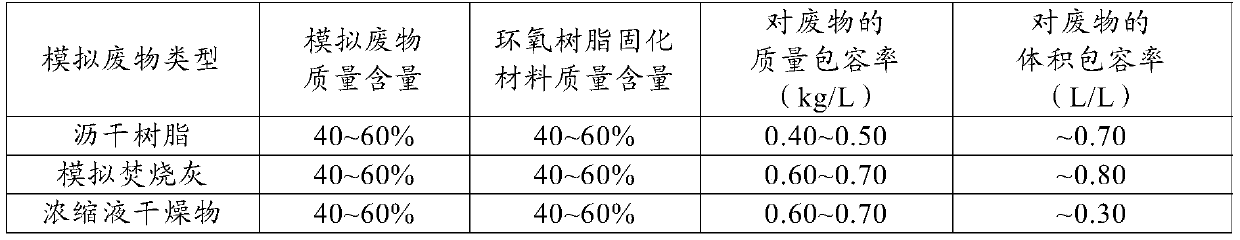
Radioactive waste curing method and application thereof
InactiveCN110648776AMeet disposal requirementsLarge inclusive rateRadioactive decontaminationEpoxyEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a radioactive waste curing method and application thereof. The radioactive waste curing method includes the following steps: (1) mixing an epoxy resin curing material and radioactive waste so as to obtain a mixture; and (2) performing maintenance curing on the mixture so as to obtain an epoxy resin waste cured body. According to the curing method, curing treatment is performed on low-and-medium level radioactive waste through the epoxy resin curing material, the curing method with high adaptability to the to-be-treated waste, a large tolerance rate of waste and excellent cured body performance is provided for treatment of the low-and-medium level radioactive waste, disposal requirements of the radioactive waste in China can be met, and no secondary waste is generated through the curing method.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Comprehensive processing method for waste through production of phthalic anhydride
InactiveCN107381896ANo secondary wasteSimple processSolid waste disposalPreparation from carboxylic acid anhydridesGas phaseEngineering
The invention discloses a comprehensive processing method for waste through production of phthalic anhydride. The phthalic anhydride is produced by employing an air gas phase oxidation process, the waste comprises waste silica-gel spheres generated from a dehydration sublimation process of a production system, industrial exhaust gas discharged from a trap at an end of a production system, and organic waste water generated during hydrolysis of phthalic anhydride; and the processing method comprises the following steps: 1) waste silica-gel sphere processing; 2) tail gas recovery; 3) organic waste water processing; and 4) waste liquid processing. The comprehensive processing method for waste through production of phthalic anhydride can process and recover all wastes in a solid state, a liquid state or a gas state generated during production of phthalic anhydride, and the wastes enable reasonable recovery and utilization, no secondary refuse is generated, and the comprehensive processing method has the advantages of simple process, high enforceability, low energy consumption, and excellent comprehensive properties.
Owner:常熟联邦化工股份有限公司
Urine sample detection and post-detection treatment system
InactiveCN114609401ANo need to worry about the risk of leakageClean up thoroughlyLavatory sanitoryMedical waste disposalLiquid wasteHazardous substance
The invention relates to a urine sample detection and post-detection treatment system which comprises a urine detection system and a post-detection treatment system, the urine detection system comprises test strip sorting equipment, sample pretreatment equipment and urine sample detection equipment which are connected in sequence; the after-test treatment system comprises a liquid waste treatment system and a solid waste treatment system, the liquid waste treatment system comprises urine sample after-test treatment equipment, and the solid waste treatment system comprises test strip after-test treatment equipment and test tube after-test treatment equipment; the automatic urine monitoring system and the after-detection treatment system are organically combined together, so that various solid and liquid wastes generated in urine detection can be treated in time while urine sample detection can be efficiently treated in batches, and the leakage risk caused by untimely treatment or improper treatment of harmful substances is avoided; and the detection environment and detection personnel are protected.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
A kind of preparation method of electrochromic double-layer fabric
ActiveCN103496233BEasy to operateGood flexibilityPhysical treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsFiberPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention relates to the field of electrochromic materials, in particular to a method for preparing a novel electrochromic double-layer fabric. The polyaniline / polyvinyl alcohol electrochromic fiber is made by spinning method; then the polyaniline / polyvinyl alcohol electrochromic fiber and the conductive fiber are woven into an electrochromic double-layer fabric, in which the surface layer is polyaniline / polyethylene Alcohol electrochromic layer, the inner layer is a conductive base cloth; finally, the electrochromic double-layer fabric is pretreated, and then the polyaniline / polyvinyl alcohol emulsion is evenly applied to the surface of the conductive base cloth layer of the double-layer fabric, and dried ; Continue to apply polyaniline / polyvinyl alcohol emulsion on the surface of the conductive base cloth layer, seal and dry. The preparation method provided by the invention has strong operability and simple process, and the reversible color change and color change sensitivity of the double-layer fabric are high, the chemical stability is good, the softness is good, and the conductivity is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
Method of treating sludge by adopting self-propagating pyrolyzation device coordinated with cement plant
PendingCN109502941AReduce pollutantsSmall footprintSludge treatment by pyrolysisWater contaminantsSlagPre treatment
The invention relates to the field of solid waste treatment, in particular to a method of treating sludge by adopting a self-propagating pyrolyzation device coordinated with a cement plant. The methodcomprises the following steps: by pyrolyzing sludge by means of the self-propagating pyrolyzation device, distributing the pre-treated sludge as a material on a chain belt / trolley below a distributorof the self-propagating pyrolyzation device to form a material bed; preheating the material bed by waste heat flue gas of the cement plant; then pyrolyzing the material bed by heat generated by combustion of fuel gas, wherein organic matters in the material bed form a gas compound; introducing the gas compound along with pyrolyzed flue gas into a decomposing furnace of the cement plant; then feeding the same into a flue gas purification system of the cement plant; and feeding the sludge ash residues formed by the pyrolyzed material bed as cement clinker into a cement clinker system. The method has the obvious advantages that a cement kiln is high in treatment temperature, large in incineration space, long in incineration standing time, large in treatment scale, free of secondary slag emission and the like. Meanwhile, the method also solves the problem of reconstruction cost and influence on production as a result of high water content of household sludge.
Owner:CHONGQING ANGRUIYUE SCI & TECH
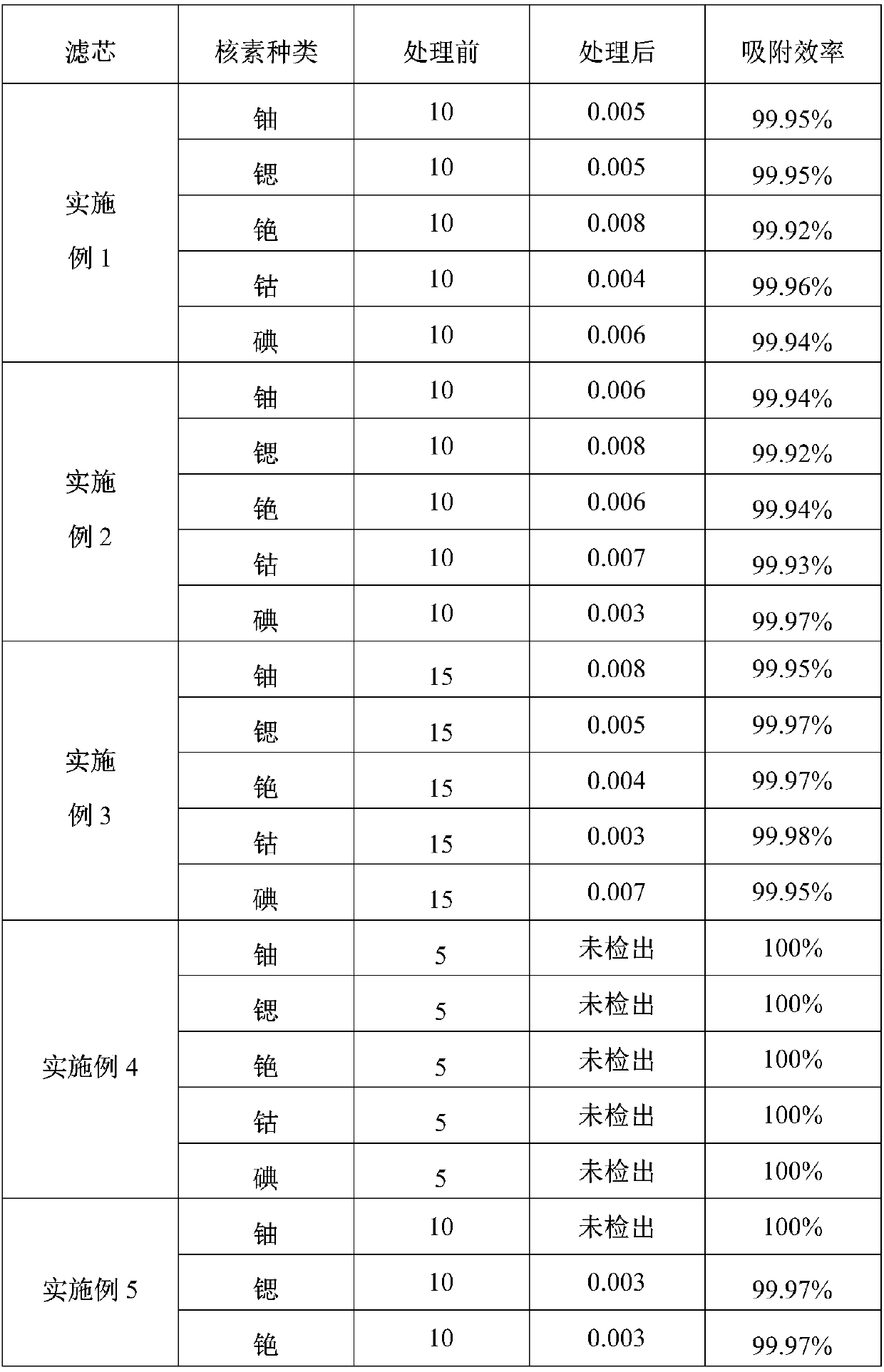
Preparation method of adsorption filter element used for treating radioactive waste liquid and adsorption filter element
ActiveCN109603313AHigh mechanical strengthImprove adsorption capacityMembrane filtersFiltration separationLiquid wasteSodium Bentonite
The invention discloses a preparation method of an adsorption filter element used for treating a radioactive waste liquid and the adsorption filter element. According to the high-density extrusion process molding provided by the invention, the filter element has a compact structure and high mechanical strength, and conditions of damage and leakage of micro-particles do not occur during use; and the filter element is formed by high-density extrusion molding of microporous materials such as zeolite powder, bentonite, kaolin, graphene, aluminum oxide and the like, the filter element has a compactstructure and the characteristics of a large adsorption surface area, high adsorption capacity and high adsorption efficiency.
Owner:RES INST OF PHYSICAL & CHEM ENG OF NUCLEAR IND
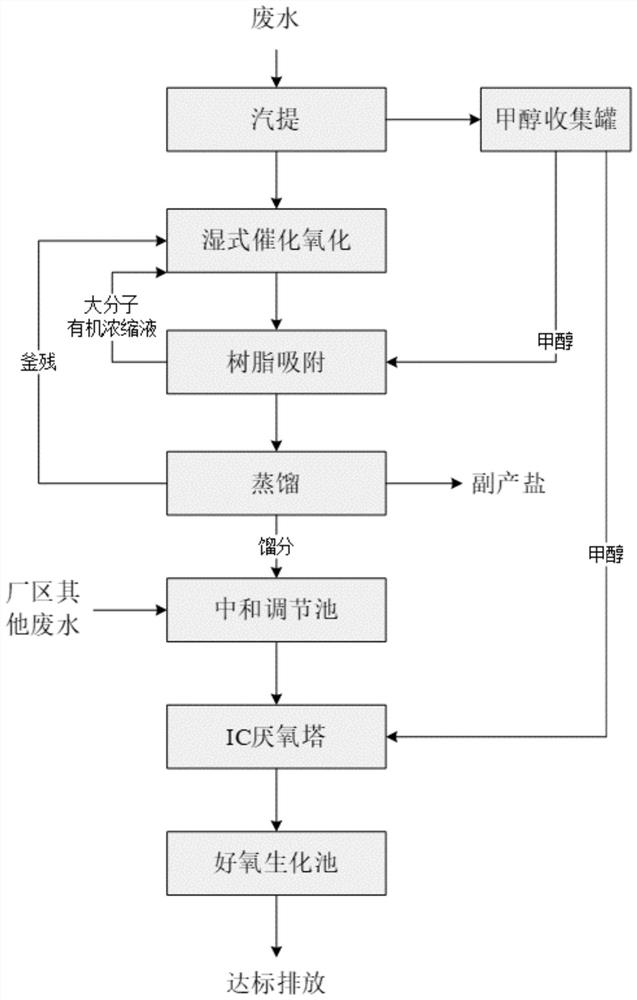
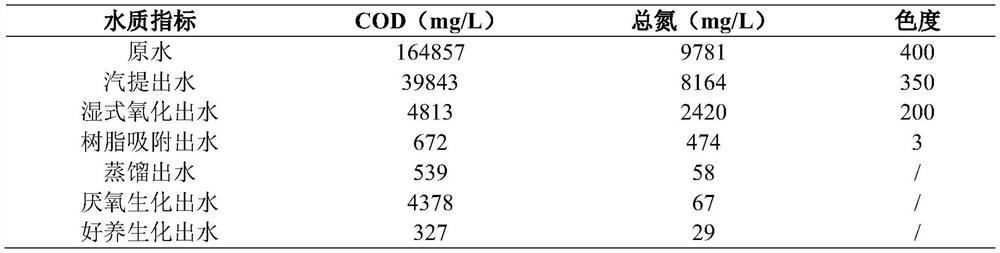
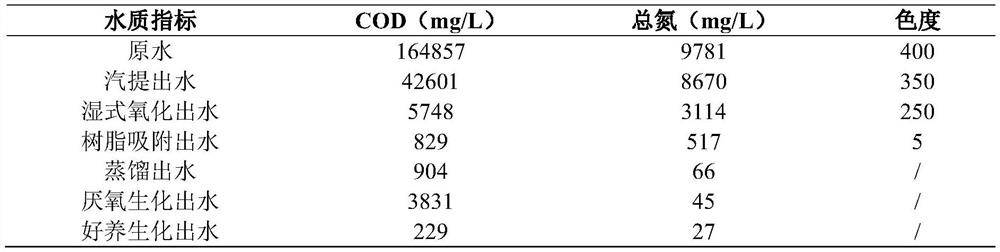
Treatment method of high-concentration high-salt methanol organic wastewater
ActiveCN113683261AReduce processing costsLow investment costWater treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesDistillationCatalytic oxidation
The invention belongs to the technical field of water treatment, and particularly relates to a treatment method of high-concentration high-salt methanol organic wastewater. The wastewater is sequentially subjected to steam stripping, wet catalytic oxidation, resin adsorption, distillation and biochemical treatment. Methanol recovery liquid generated in the wastewater treatment process can also be used as a resin regeneration liquid and / or a carbon source, a byproduct sodium chloride salt can be obtained by distilling the treated effluent, and meanwhile, the wet catalytic oxidation can also be used for oxidation treatment of the resin regeneration liquid and distillation still residues. According to the invention, organic matter in wastewater can be reasonably and effectively treated, the final effluent reaches the discharge standard of a park, the purpose of treating waste with waste is realized, and the problems of low treatment rate, poor treatment effect and large hazardous waste output in the prior art are solved.
Owner:江苏南大华兴环保科技股份公司
Treatment method for harmless solid waste
InactiveCN108326014ANo secondary wasteSolid waste disposalControl devices for furnacesPhosphoric acidScrap
A treatment method for harmless solid waste comprises the steps that firstly, inorganic oxide particles or hydroxide and a slow release agent are mixed to form a mixture; secondly, the prepared mixture and phosphoric acid are mixed to form an acid solution; thirdly, the acid solution and waste particles are mixed to generate a sizing agent; and fourthly, the sizing agent is solidified. The treatment method for the harmless solid waste is characterized in that oxide grains are fed into a plasma furnace through inorganic oxide to be roasted and then are cooled and pulverized, the temperature applied to the plasma furnace is raised every 10 minutes from the first temperature, in this way, roasting is carried out for 20 minutes, 40 minutes later, the second temperature is reached, and then constant roasting is carried out for 40 minutes at the second temperature to 120 minutes. The method is used for producing building materials, no secondary waste is generated, and the building materialswith low price and free of harmful gas emission can be generated.
Owner:安徽航天环境工程有限公司
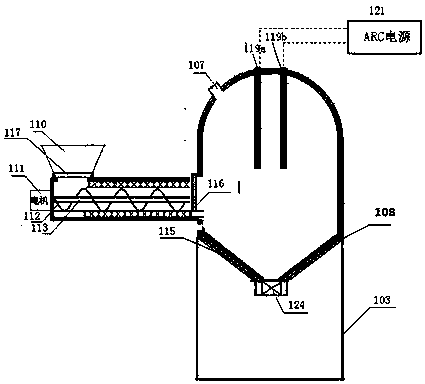
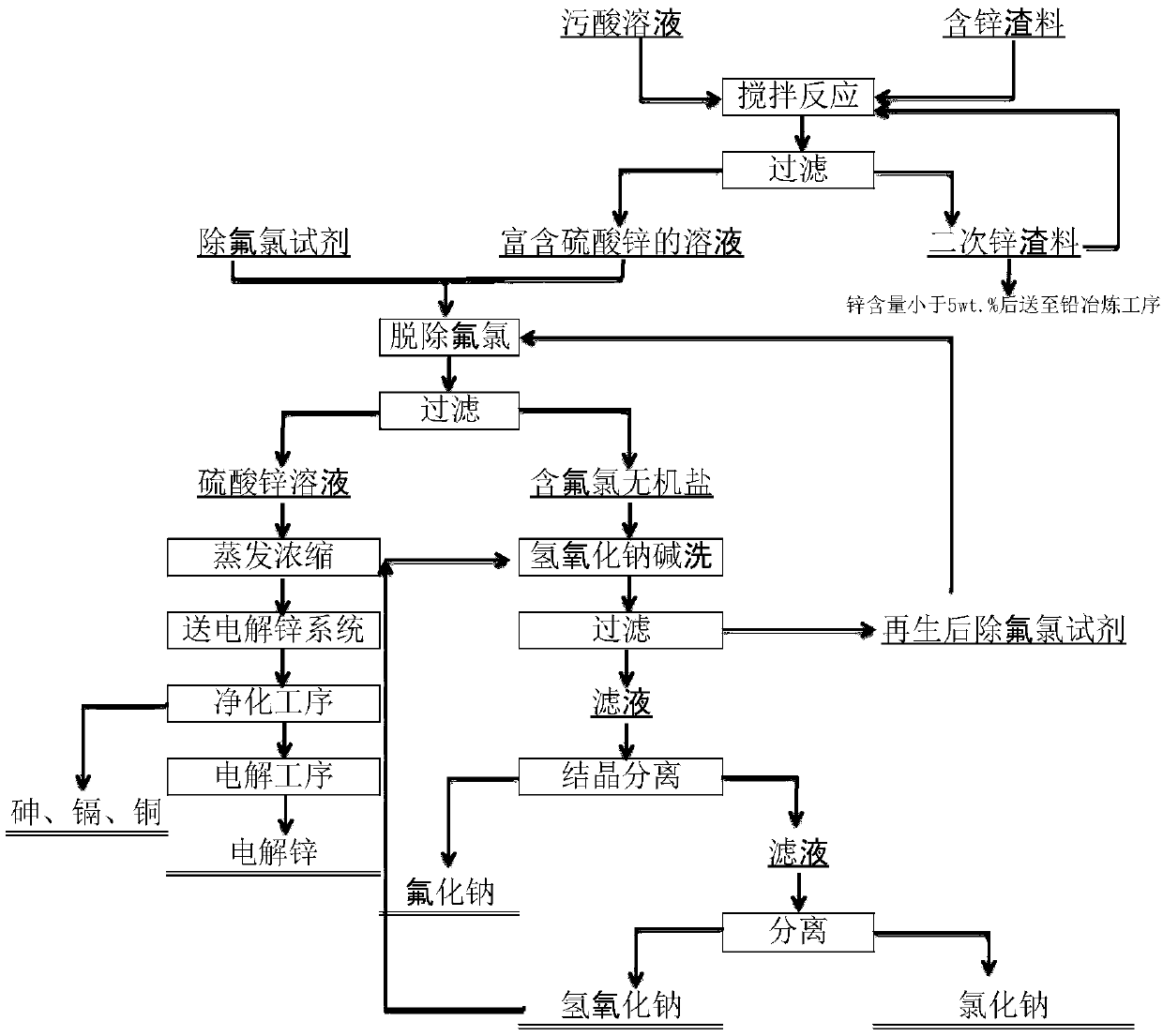
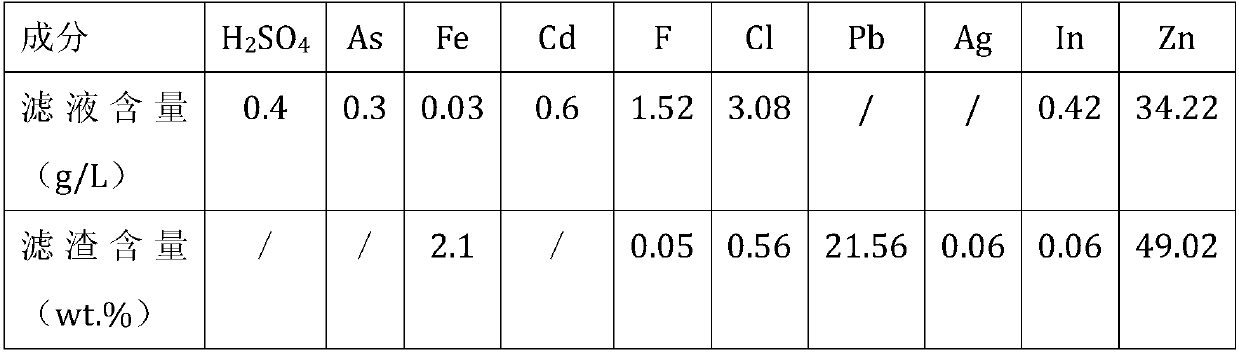
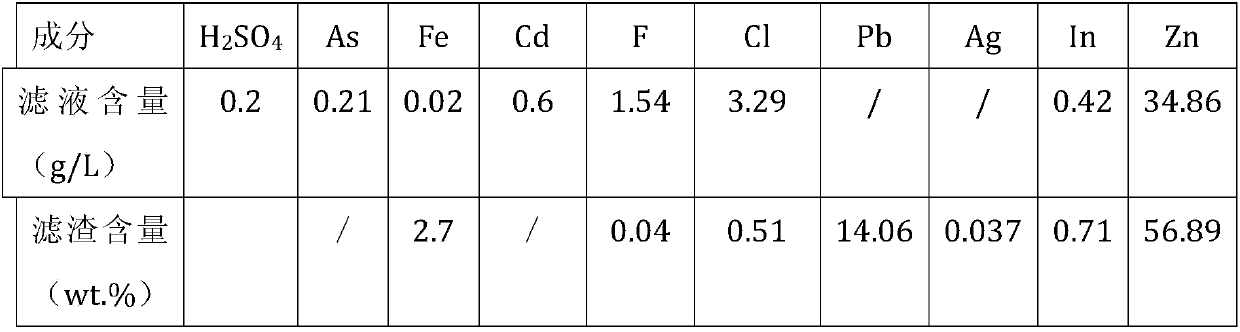
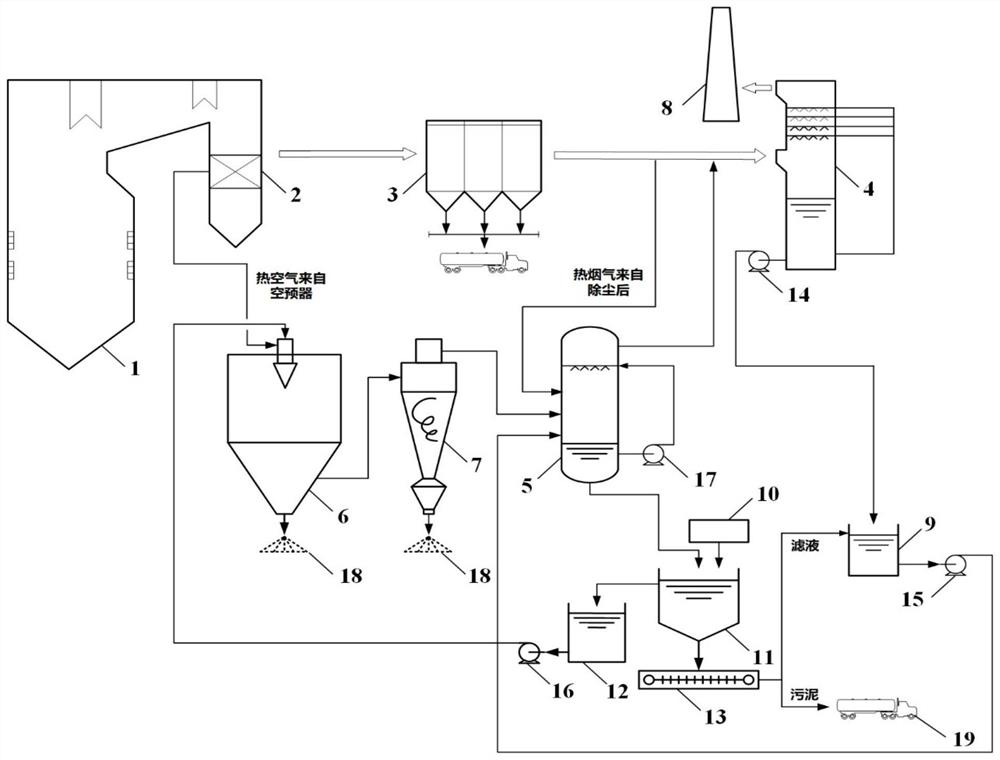
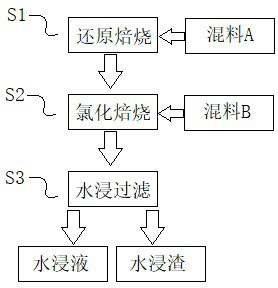
Comprehensive recovery and utilization method of non-ferrous metal smelting sewage acid and zinc-containing slag
ActiveCN105861844BHigh recovery rateNo secondary wasteProcess efficiency improvementHydrometallurgyNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
Disclosed is a comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues. The zinc-containing residues generated in the zinc smelting production process serve as an acidic wastewater neutralizer. Liquid obtained after neutralization is subjected to fluorine and chlorine removal and concentrated to meet the requirements for a zinc sulfate solution of a zinc system, and then directly enters the electrolytic zinc system. Valuable metal such as arsenic, cadmium and copper in the acidic wastewater is recycled through an impurity purification procedure of the zinc system. The zinc-containing residues are subjected to a neutralization step to be recycled and fed into a lead extraction procedure after being enriched with lead, silver and other metal. The filter residues with fluorine and chlorine removed are regenerated with a sodium hydroxide solution, the residues obtained after regeneration can be used for the fluorine and chlorine removal procedure repeatedly, and sodium fluoride, sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide in the liquid obtained after regeneration are separated and recycled through efficient evaporative crystallization. The comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues is based on an existing zinc hydrometallurgy system, the balance of original materials in the system is maintained, and an additional heavy metal impurity purification procedure is not added. The comprehensive recycling method for non-ferrous metal metallurgy acidic wastewater and zinc-containing residues is short in process, low in cost, high in valuable metal recycling rate, free of discharging of secondary waste residues and waste water and good in comprehensive economical benefit.
Owner:湖南麓云达环境科技有限公司
System and method for zero discharge of magnesium oxide method desulfurization wastewater
PendingCN112499652AIncrease added valueReduce system investmentDispersed particle separationMagnesium sulfitesAir preheaterFlue gas
The invention discloses a system and method for zero discharge of magnesium oxide method desulfurization wastewater, and belongs to the field of environmental protection. The system comprises a magnesium oxide method desulfurization absorption tower and a hot method decrement device, flue gas generated after boiler combustion is connected with the magnesium oxide method desulfurization absorptiontower sequentially through an air preheater and a dust remover, the output end of the bottom of the magnesium oxide method desulfurization absorption tower is connected with a waste water tank, and the output end of the bottom of the waste water tank is connected with the hot method decrement device. The output end of the bottom of the thermal decrement device is connected with a sedimentation tank, the output end of the top of the sedimentation tank is connected with a spray drying tower through a clear liquid tank, and the bottom end of the spray drying tower stores a target product. The system and method have the characteristics of low system investment, high additional value of byproducts, no secondary waste and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
A kind of manganese slag collaborative calcium chloride waste slag recycling treatment method
ActiveCN113387390BEasy to implementControls are responsiveCement productionManganese halidesCalcium silicateSulfate
The invention discloses a manganese slag and calcium chloride waste slag recycling treatment method. The manganese slag and calcium chloride waste slag are roasted in two stages to realize the synergistic recycling method. Calcium chloride, silicon dioxide and water vapor in the air are utilized. The reaction characteristics of calcium silicate and hydrogen chloride are formed at high temperature. The manganese slag containing the low-valent manganese phase formed by reduction roasting is mixed with the above materials to carry out high-temperature chlorination roasting, and the roasted product is separated by water leaching to obtain manganese chloride, and obtain The water leaching residue composed of calcium silicate, calcium sulfate and silica mixture realizes the synergistic utilization of manganese residue and calcium chloride waste residue, improves the resource value of the above solid waste, has high economic benefits, and reduces the For the environmental pollution caused by the separate treatment of the corresponding solid waste, the entire treatment process is simple and easy to implement, and the energy consumption is low, which can be widely used in the electrolytic manganese industry.
Owner:CHANGSHA SCI ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
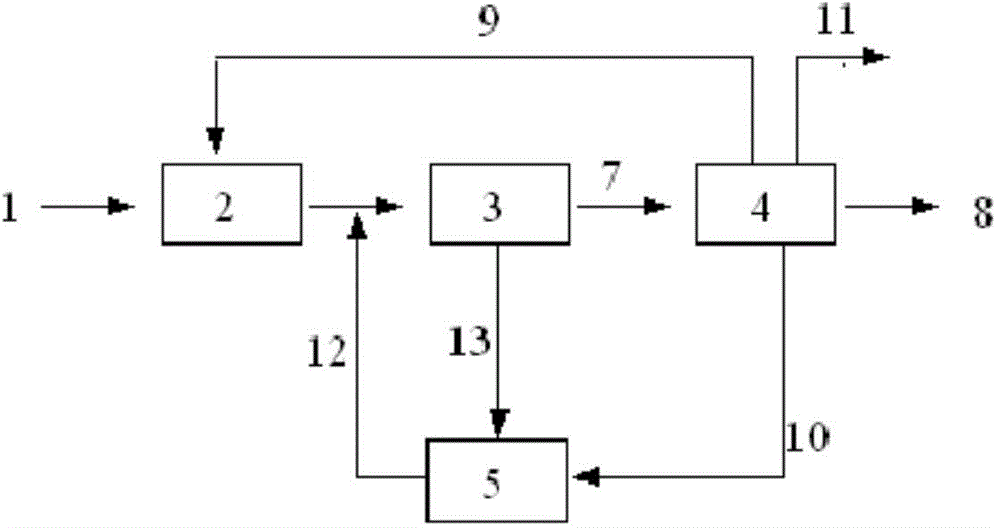
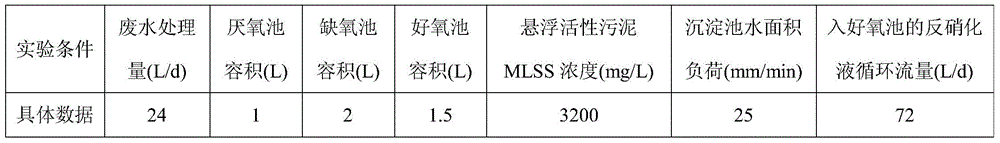
A method for efficient biochemical denitrification and dephosphorization of wastewater
ActiveCN104556572BImprove denitrification efficiencyImprove recycling rateTreatment using aerobic processesWater contaminantsTaihu basinNitration
Owner:江苏艾特克环境工程设计研究院有限公司 +1
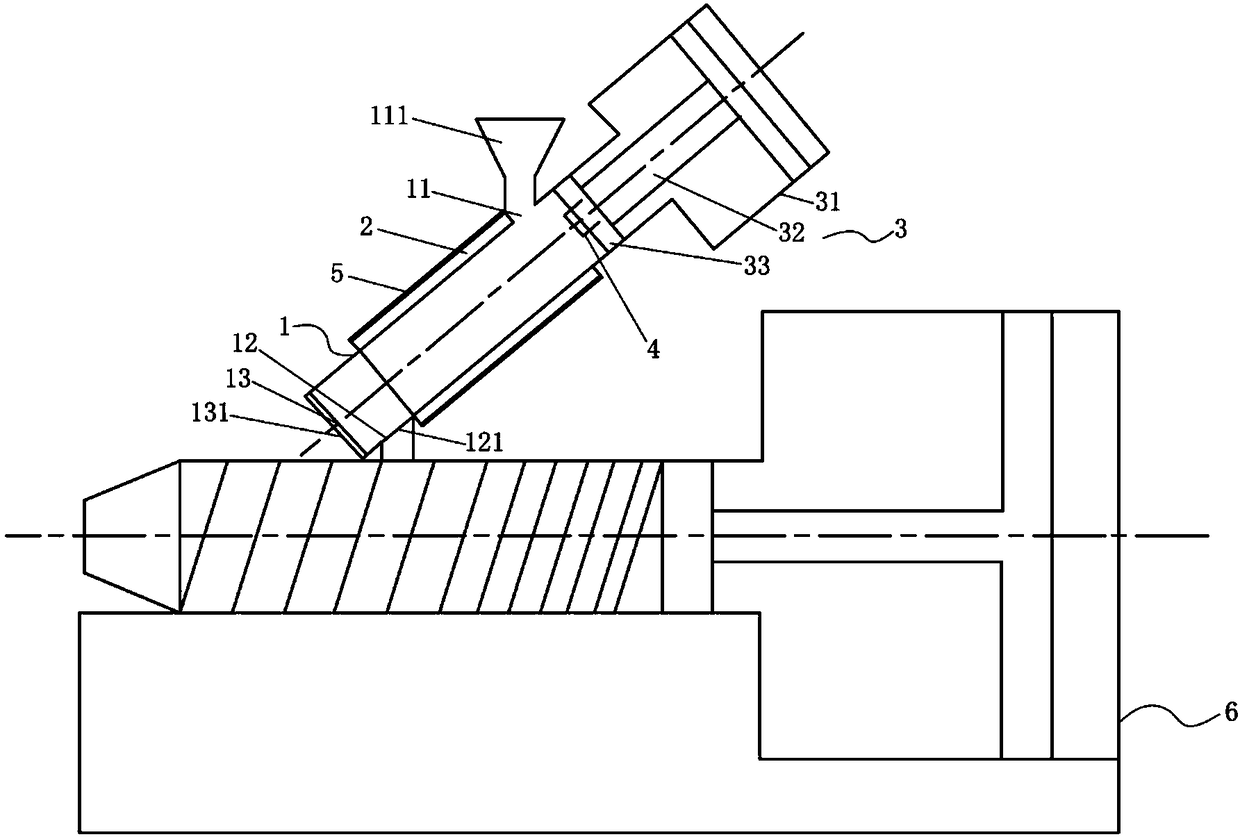
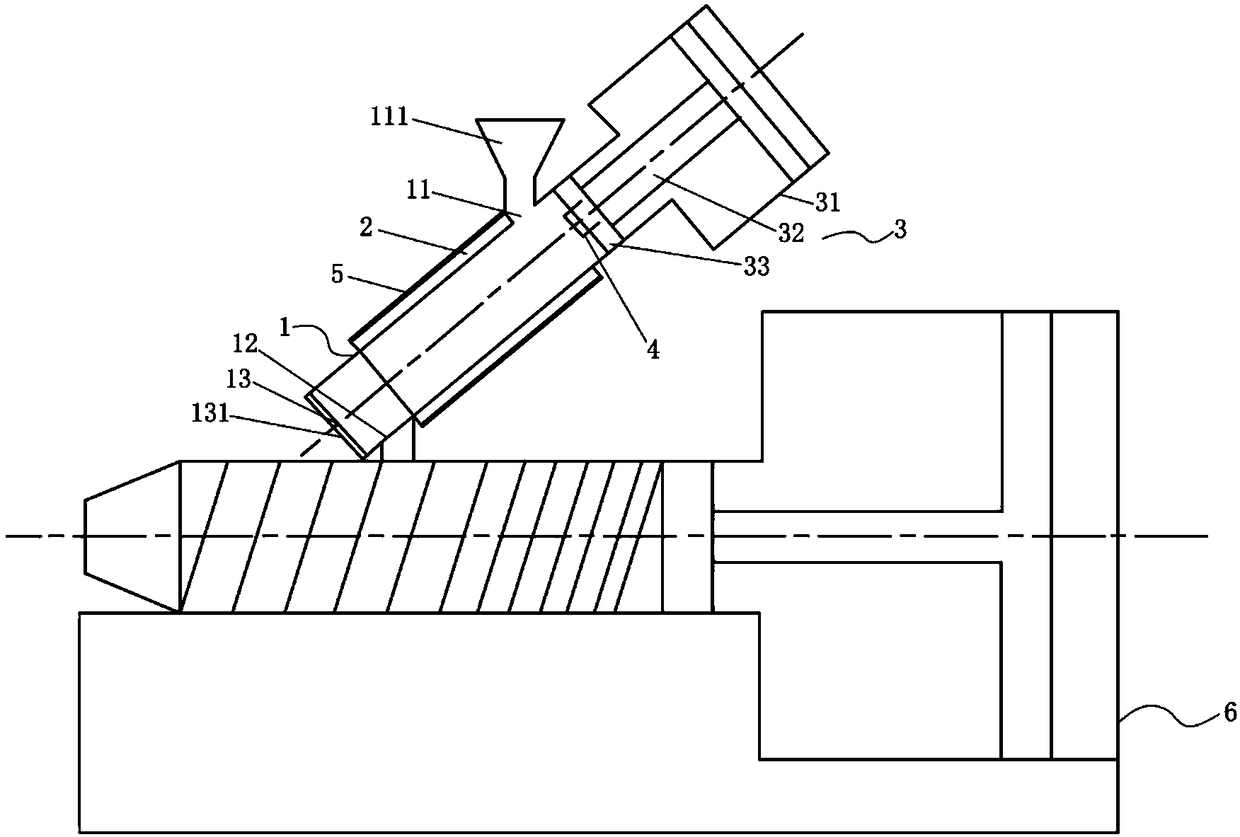
Electroplating product separation device and electroplating product separation method
The invention provides an electroplating product separation device. The device comprises a material cylinder, a heating mechanism, an extruding mechanism, a temperature sensor and a control unit; a feeding port and a discharging port are formed in the material cylinder, and the feeding port and the discharging port are oppositely arranged; the heating mechanism, the extruding mechanism and the temperature sensor are connected to the control unit correspondingly, the heating mechanism is arranged on the cylinder wall of the material cylinder, and the heating mechanism is used for heating materials to be separated in the material cylinder; the extruding mechanism is arranged at one end of the feeding port of the material cylinder, and the extruding mechanism is used for applying pressure tothe melted material to be separated and extruding melt from the discharging port; and the temperature sensor is arranged in the material cylinder, the control unit is used for receiving a signal of the temperature sensor, and the heating temperature of the heating mechanism and the movement of the extruding mechanism are controlled. According to the electroplating product separation device, plastic is recycled by adopting a mechanical method, so that the performance of the recycled plastic is improved, and secondary waste is not generated.
Owner:XIAMEN RUNNER IND CORP
Method for producing multielement nitro-compound fertilizer
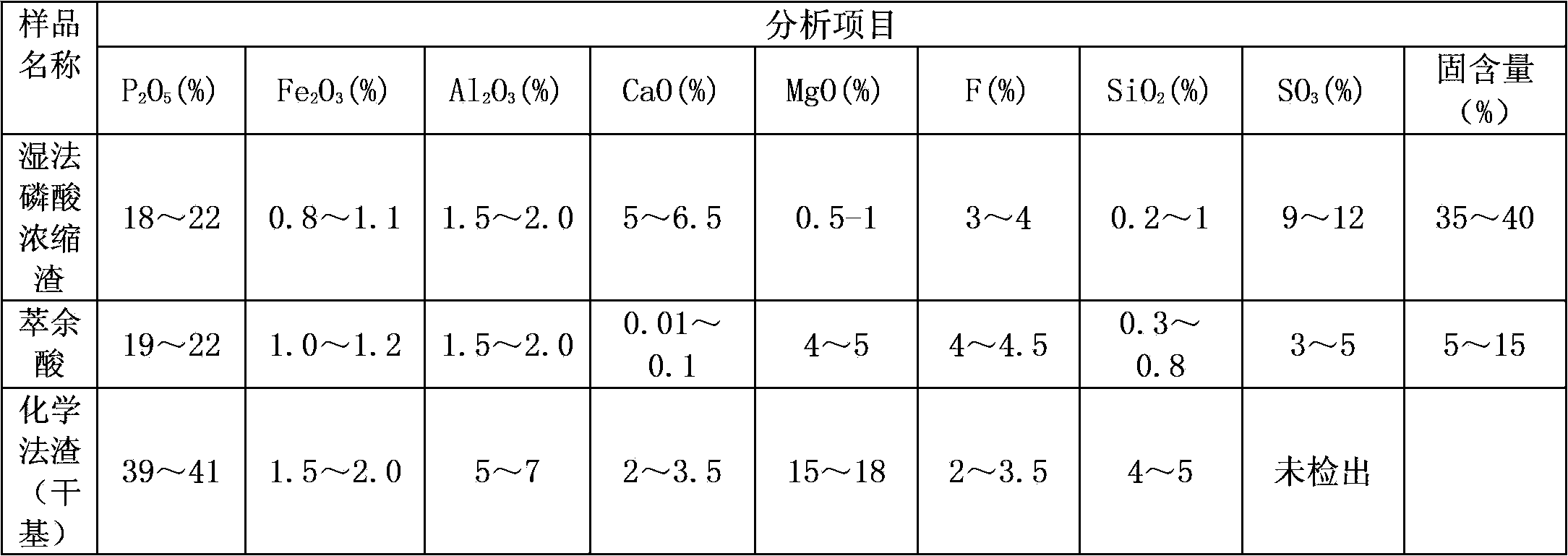
The invention discloses a method for producing multielement nitro-compound fertilizer. Wet-process phosphoric acid concentrated slag, chemical slag and extracted residual acid are mixed with potassium sulphate and microelements, nitric acid is then added for treatment, and the mixture is granulated and dried after the ammonia neutral reaction, so that the multielement nitro-compound fertilizer is produced. The multielement nitro-compound fertilizer has the characteristics of rich nutritional ingredients, easiness in absorption by plants, low cost, simplicity in technology, no generated waste and the like.
Owner:SINOCHEM AGRI LINYI R&D CENT CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com