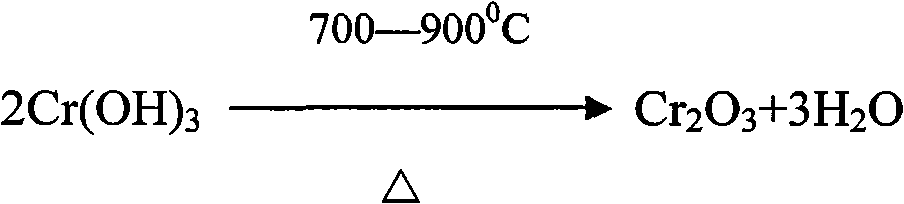Patents
Literature
657 results about "Chromium(III) oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chromium(III) oxide (or chromia) is an inorganic compound with the formula Cr₂O₃. It is one of the principal oxides of chromium and is used as a pigment. In nature, it occurs as the rare mineral eskolaite.
Nanometer grade low carbon paraffin dehydrogen catalyst
InactiveCN1911502ALarge specific surface areaHigh catalytic activityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlkaneCarbon nanotube
The present invention relates to one kind of nanometer level low carbon alkane dehydrogenating catalyst, and features that the C3-C5 low carbon alkane dehydrogenating catalyst comprises carrier of single wall or multiple wall carbon nanotube and two active components selected from chromic oxide in 2-30 wt%, alumina in 2-25 weight and nickel oxide in 2-30 wt%. The catalyst has high catalysis activity, increased active structures, long service life, low catalytic dehydrogenation reaction temperature, high conversion rate, high selectivity and other advantages.
Owner:DAQING PETROLEUM ADMINISTRATION
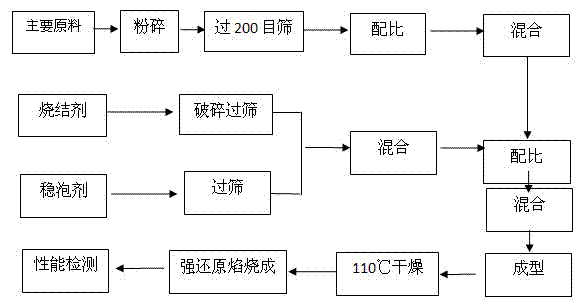
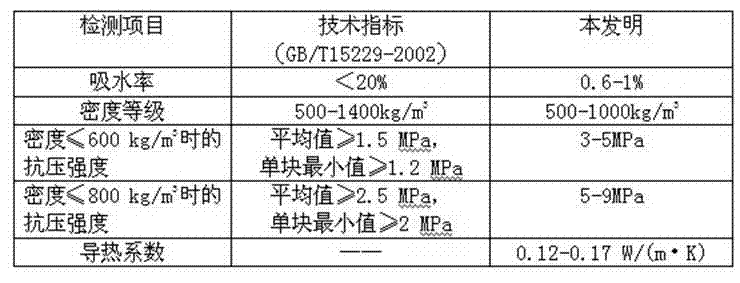
Method for preparing foam ceramic self-insulation wall material by utilizing solid wastes
InactiveCN103396150AReduce manufacturing costRealize comprehensive utilizationSolid waste disposalCeramicwareChromium sesquioxideInsulation layer
The invention relates to a method for preparing a foam ceramic self-insulation wall material by utilizing solid wastes. The wall material comprises a main material and an admixture. The main material is prepared from the following components in proportion: 25% to 35% of chromium slags, 19% to 27% of coal gangue, 20% to 26% of waste ceramic polishing residues, 17% to 25% of albite and 1% to 6% of bentonite. The method comprises the following steps of: adding 16 to 20g of the admixture into every 200g of the main material; evenly mixing and screening the mixture; putting the mixture into a die; molding the mixture in a pressing manner and drying; sintering the mixture under a strong reducing atmosphere at the temperature of 1120-1180 DEG C, thereby obtaining the foam ceramic self-insulation wall material. The carbon in the coal gangue can serve as a foaming agent or a reducing agent, so that hexavalent chromium is reduced into chromium sesquioxide at the high temperature and under the strong reducing atmosphere. Thus, the toxicity of the chromium slags is eliminated. The prepared foam ceramic self-insulation wall material is low in pyroconductivity, small in density and low in water absorption rate; the usage temperature can reach 900 DEG C. In addition, the foam ceramic self-insulation wall material is complete in fire resistance, high in strength and long in service life, and can be used for replacing the existing wall materials and flammable insulation materials. The wall material integrates protection and thermal insulation functions; an exterior wall insulating layer is not required. Thus, the construction cost is lowered.
Owner:HENAN COAL CHEM IND GROUP INST +1
Permanent ferrite magnetic tile and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101202138AIncrease solid solutionImprove performancePermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismFiberSilicon oxide
The invention relates to a permanent ferrite magnetic arc and the manufacturing method thereof, belonging to a manufacturing field of a motor permanent ferrite. Weight proportions of main material components and additive components are as the following: main materials: 8.7 to 9.0 percent of strontium oxide; 86 to 87 percent of iron oxide red; additives: 0.6 to 1.0 percent of calcium carbonate; 0.6 to 1.0 percent of aluminum oxide; 0.4 to 0.8 percent of chrome oxide; 0.3 to 0.6 percent of boric acid; 0.3 to 0.5 percent of silicon oxide; 0.2 to 0.4 percent of cobalt oxide; 0.2 to 0.4 percent of lanthanum oxide and 0.1 to 0.3 percent of silicate fiber. The invention is provided with high surplus magnetic induction strength and high intrinsic coercivity so as to enhance a mechanical strength of the magnetic arc.
Owner:CHANGZHOU DIER MAGIC MATERIALS
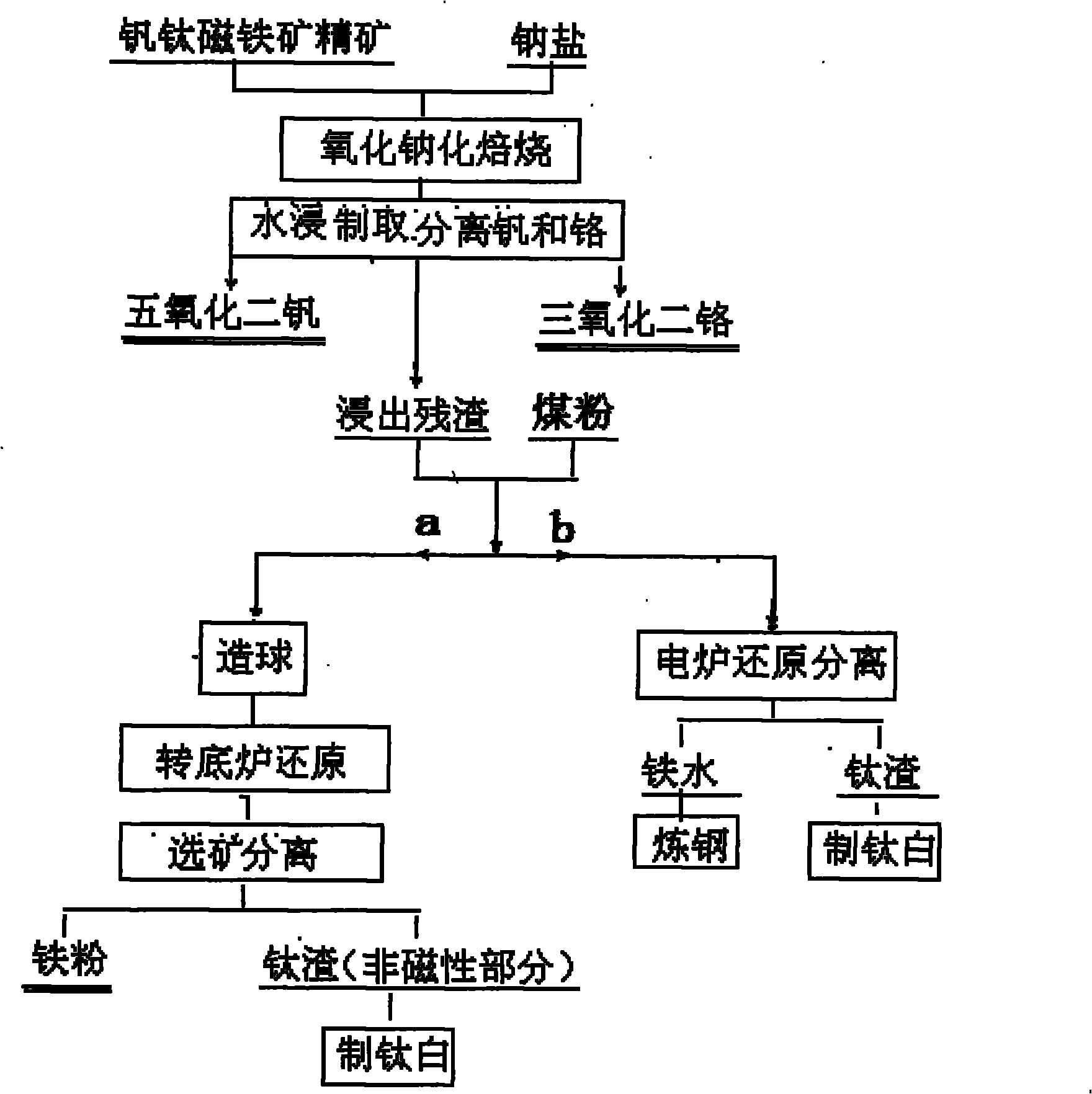
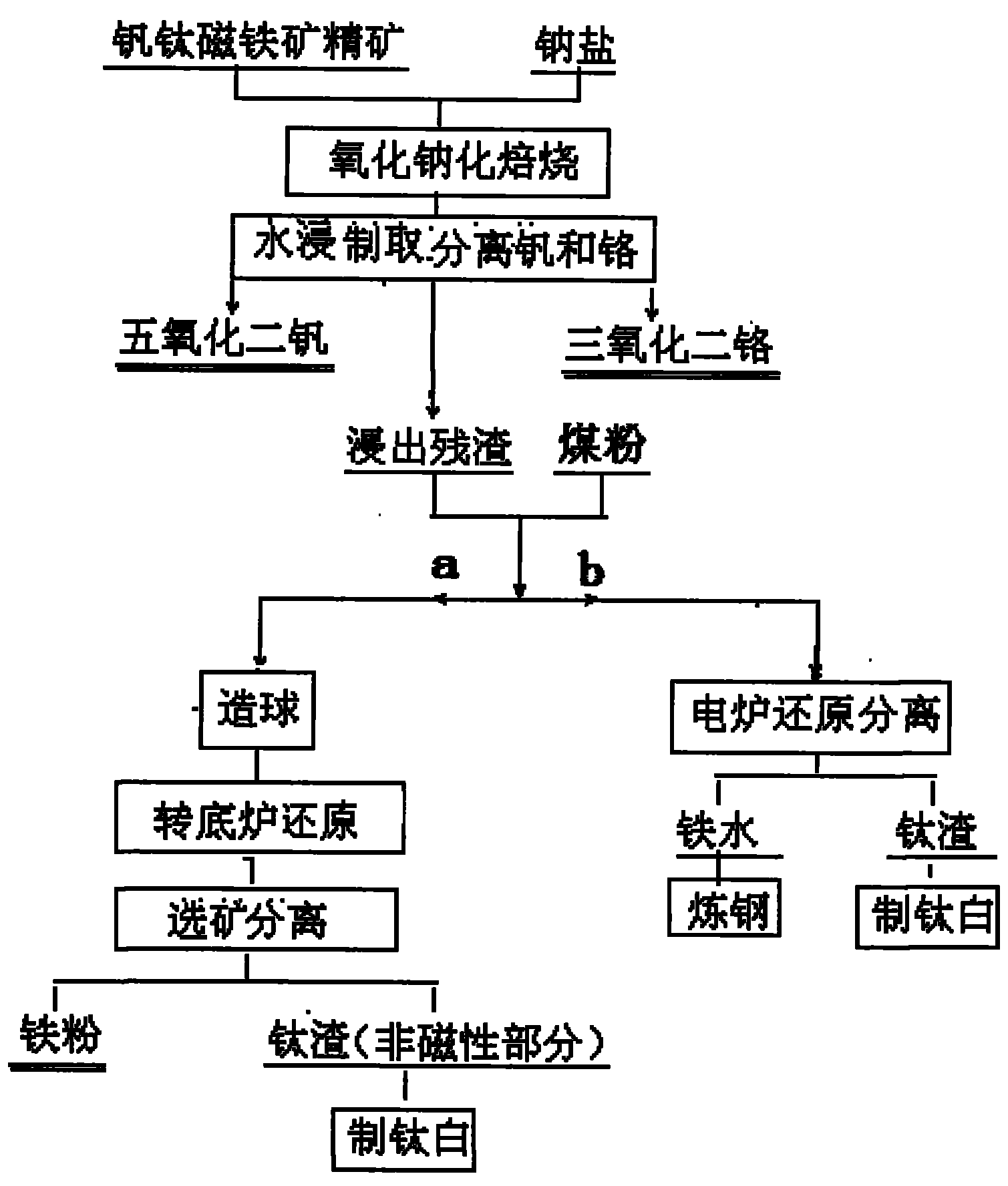
Method for recycling vanadium, chromium, titanium and iron from vanadium-titanium magnetite ore
ActiveCN102061397AHigh recovery rateSimple processProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingMagnetite
The invention discloses a method for recycling valuable elements from vanadium-titanium magnetite ore, which comprises the following steps of: crushing the ore or concentrate, adding sodium salt, performing oxidizing roasting, converting vanadium and chromium into water-soluble sodium vanadate and sodium chromate, performing water leaching in solution, and separating the vanadium and chromium from the solution to obtain vanadium pentoxide and chromium sesquioxide products; and adding coal dust into the leached residue for pelletizing, reducing in a rotary hearth furnace, magnetically separating iron and titanium, using the obtained magnetic iron powder as a raw material for powder metallurgy or steelmaking, and using a nonmagnetic product containing more than 50 percent of TiO2 as a raw material for extracting the titanium; or reducing iron from the leached residue in an electric furnace, using the obtained molten iron as a raw material for steelmaking and using electric furnace slag containing more than 50 percent of TiO2 as a raw material for extracting the titanium. The method is short in process flow and economical; and the recovery rate of the vanadium, chromium, titanium and iron is high.
Owner:SICHUAN LOMON MINING & METALLURGY +1
Inorganic heat-insulating material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101973750AImprove isolation abilityStrong anti-radiation heat conduction abilitySolid waste managementSodium BentoniteCarbon fibers
The invention relates to an inorganic heat-insulating material and a preparation method thereof. The inorganic heat-insulating material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 15-37 parts of basic material, 45-70 percent of pigment and filler and 9-26 parts of auxiliary agent, wherein the basic material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10-20 partsof phosphoric acid, 3-8 parts of aluminium hydroxide, 2-8 parts of aluminum-silver slurry auxiliary agent, 0.5-5 parts of silicate and 1-5 parts of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose; the pigment and filler is one or a combination of potassium titanate whiskers, expanded perlite, ceramic microspheres, nano-silicon dioxide aerogel, heat-insulating powder, carbon fibers, meerschaum, needle-shaped wollastonite powder and magnesium hydrate; and the auxiliary agent is one or a combination of boron nitride, dichromium trioxide, glass powder, boric acid, nano-zirconia, calcium oxide and calcium-based bentonite. The invention inorganic heat-insulating material has strong insulating capability for solid conductive heat at high temperature (150-500 DEG C) and simultaneously also has strong insulating capability for radiation and flow conductive heat.
Owner:童金荣
Non-carbon residue feather edge brick for refining steel ladle and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a refractory and mainly provides a non-carbon residue feather edge brick for a refining steel ladle and a preparation method thereof. The non-carbon residue feather edge brick is formed by taking corundum grains, electrofused spinel grains and electrofused magnesia grains as aggregate, taking corundum fine powder, high-temperature alumina micropowder, electrofused magnesia, chromium sesquioxide, aluminum metal powder and other powders as base components and adopting a mode of compounding and adding inorganic and organic bonding agents and a mode of machine pressing. The obtained non-carbon residue feather edge brick has the advantages of high strength of generated blanks, no firing, favorable thermal shock stability, strong capability of resisting acid and alkali molten slag, no pollution on molten steel and the like and can be applied to residue line parts of the steel ladle under the conditions of RH and specified LF / VD refining.
Owner:SINOSTEEL LUOYANG INST OF REFRACTORIES RES
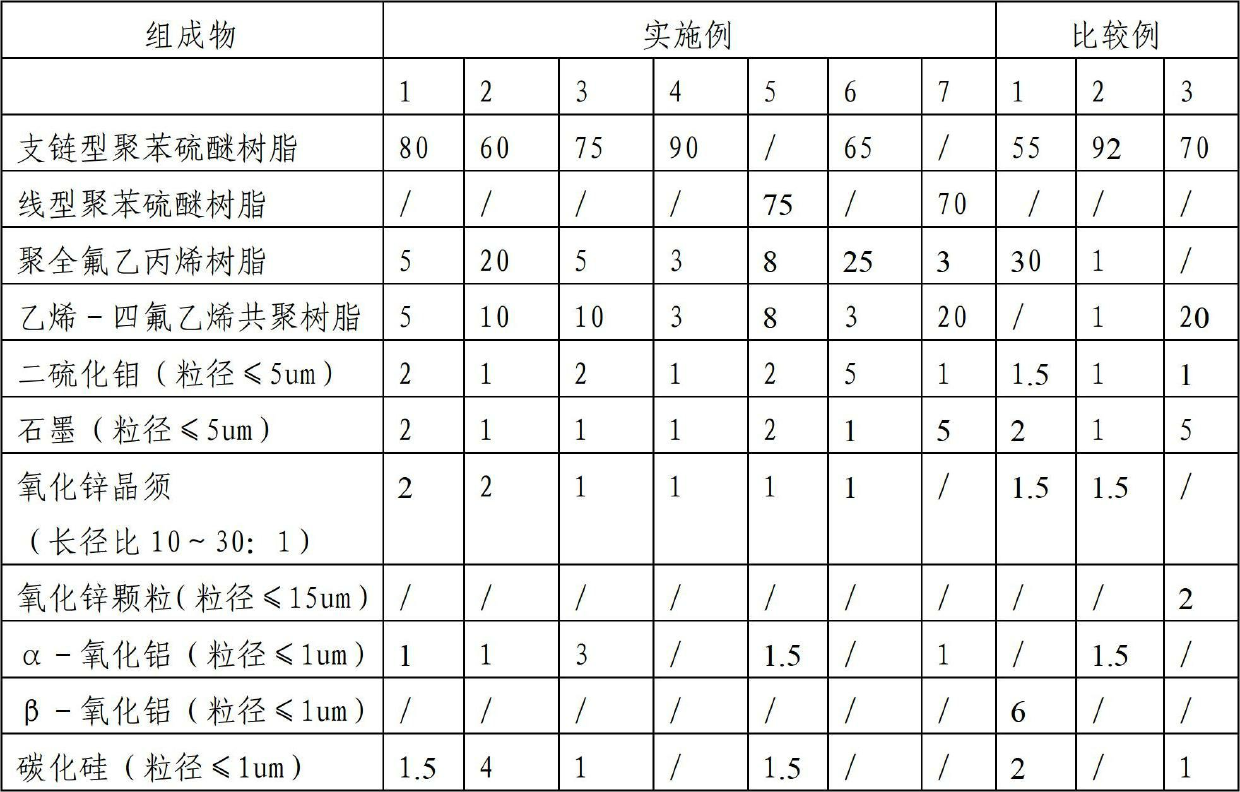
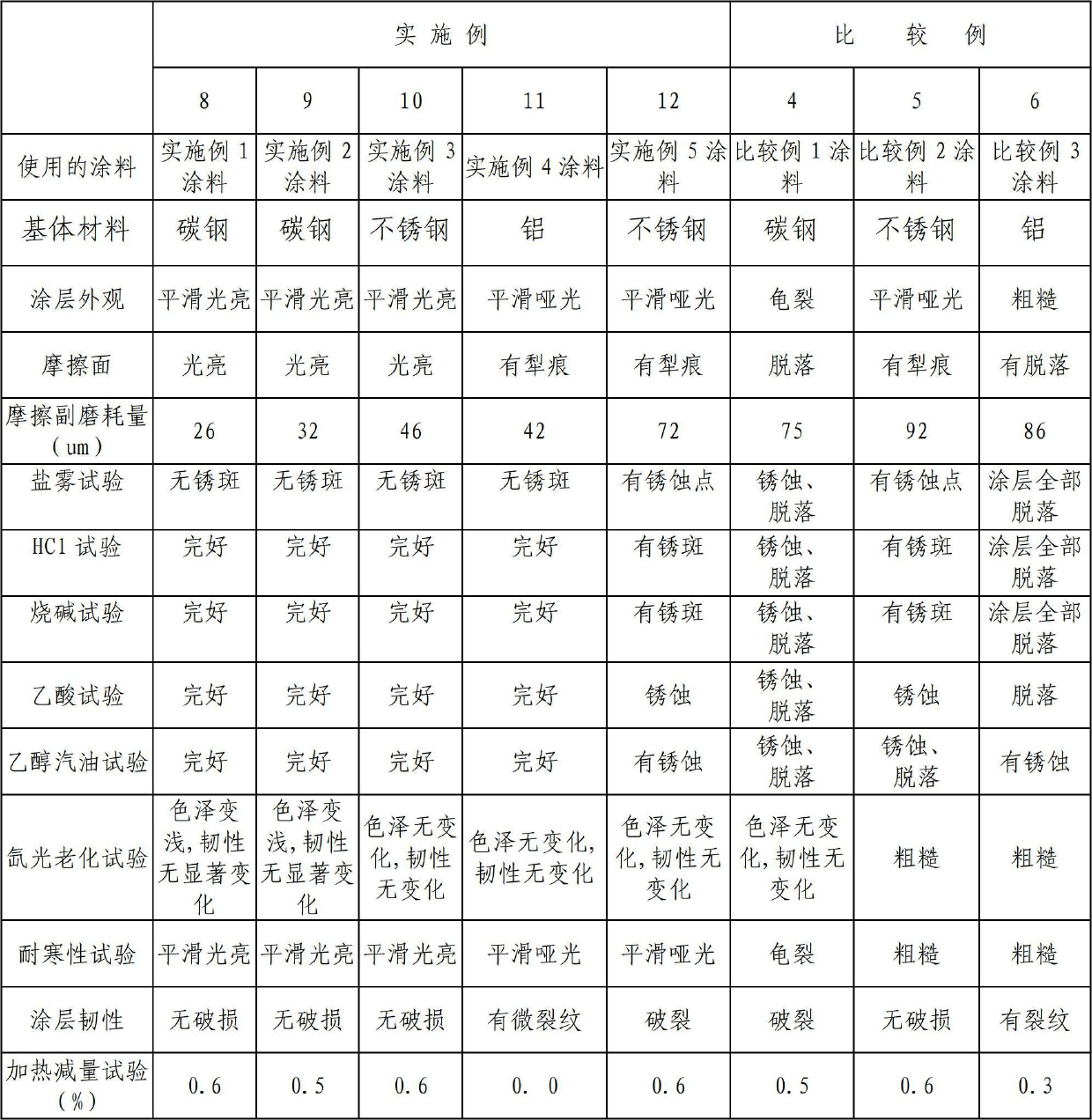
Modified polyphenylene sulfide coating and application thereof
ActiveCN102676048AImprove corrosion resistanceSelf-lubricatingAnti-corrosive paintsWear resistantCorrosion
The invention discloses a modified polyphenylene sulfide coating and the application thereof. The modified polyphenylene sulfide coating consists of the following components by weight percentage: 60-90 percent of polyphenylene sulfide resin, 3-25 percent of poly-perfluorinated ethylene propylene resin, 3-20 percent of ethylene-tetrafluoroethylene copolymer resin, 1-5 percent of molybdenum disulfide, 1-5 percent of graphite and the balance of filler, wherein the filler is any one of or a mixture of zinc oxide, aluminum oxide, silicon carbide and chromium sesquioxide. The modified polyphenylene sulfide coating disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the compatibility among the components is good; a prepared coating layer has higher corrosion resistance, higher self-lubricity and strong wear-resistant ability, is resistant to high temperature, is highly insulated, has good toughness, can bear impact force capable of being borne by a metal surface, has excellent bond performance with a metal material and is particularly suitable for the using and working condition of cold / hot sudden changes which cannot be borne by glass lining equipment; and through spraying the coating disclosed by the invention on the surface of the metal matrix material, a manufactured work piece has excellent physical-chemical performance, a long service life and a wide application range.
Owner:CHENGDU LETIAN PLASTICS
Compound polishing powder for polishing optical elements, preparation method and polishing technology
ActiveCN101362925BImprove effectivenessImprove machining accuracyOptical surface grinding machinesOther chemical processesSurface finishGranularity
The invention provides a compound polishing powder of a polishing optical element, a preparation method and a polishing process, belonging to expendable material used for polishing the optical element, the preparation method and the polishing process of the polishing powder; wherein, the polishing powder comprises 0.5-3 of Cr2O3 powder and 1 of Al2O3 according to the weight proportion; the granularity of the Cr2O3 powder is ranging from 0.05 microns to 0.10 microns and the granularity of the Al2O3 powder is ranging from 0.05 microns and 0.10 microns; the polishing process comprises the steps as follows: 1) installing polishing formworks for the optical element; 2) filling the polishing powder; 3) arranging a lens disc; 4) fixing the lens disc; 5) rubbing and polishing. The polishing formwork comprises 500 of polishing asphalt and 20-200 of Al2O3 according to the weight parts; in the polishing process, the polishing powder and the polishing formwork can be used for polishing the optical element which is made of zinc selenide, with the surface smoothness of more than 20-10.
Owner:CHENGDU Z & Z OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
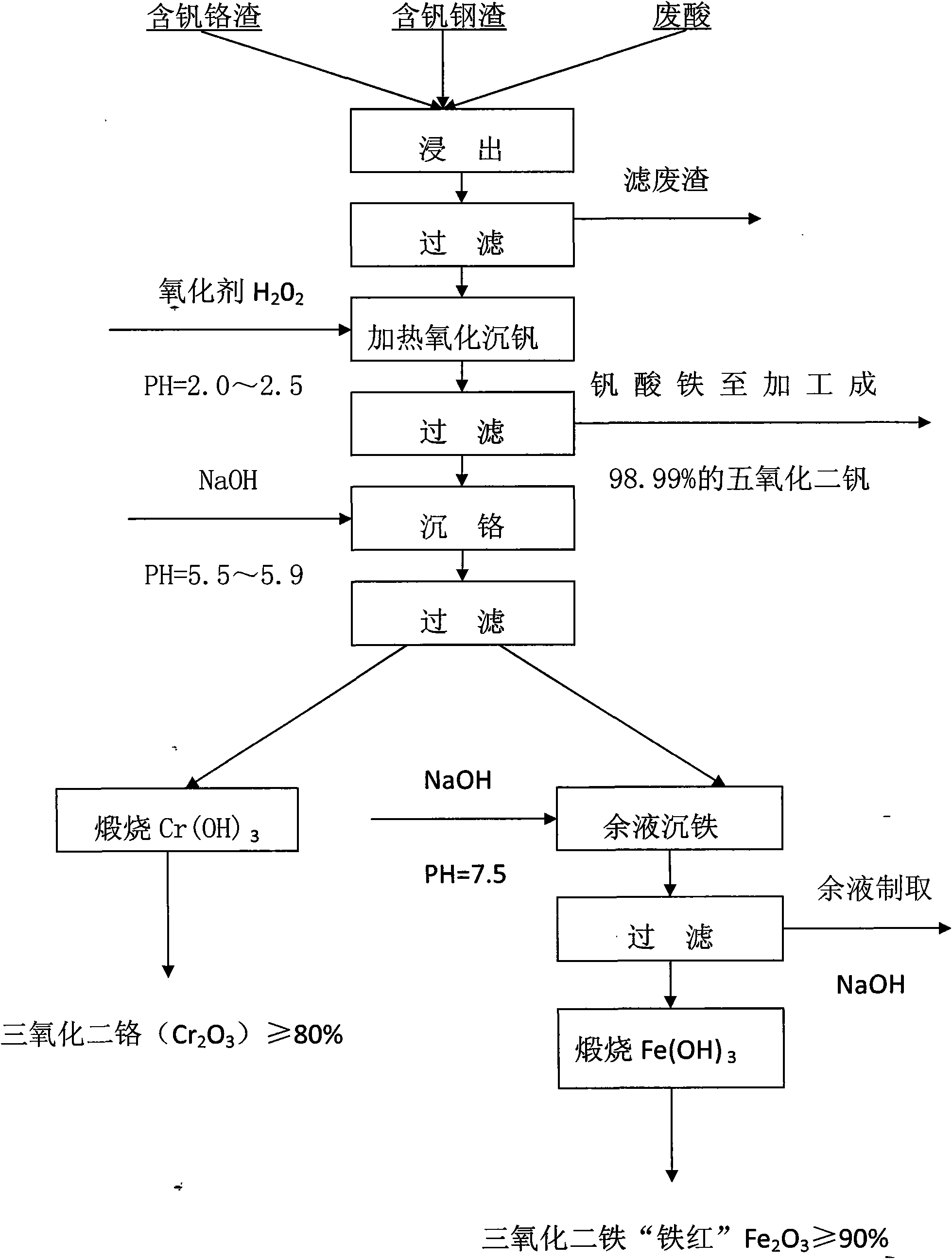
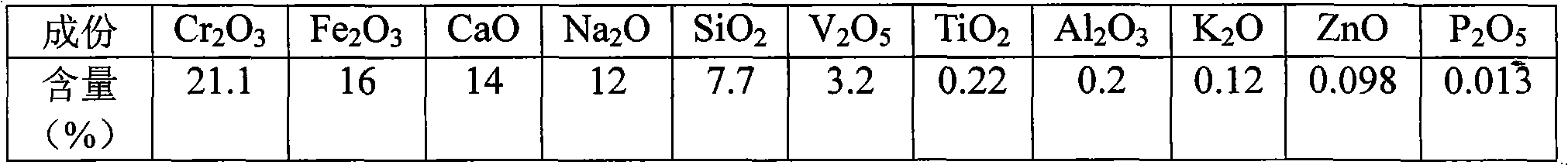
Process for extracting vanadium and chromium from chromic slag by using waste acid of titanium powder plant
InactiveCN101979683AFiltration process goes wellAchieve the purpose of separationProcess efficiency improvementChromium(III) hydroxideSlag
The invention discloses a method for separating and extracting vanadium and chromium. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) producing chromium fine sand (Cr2O3) of which the content is over 80 percent and ferric vandate of which the content is over 20 percent from two waste materials by taking waste acid of a titanium powder plant as a leaching agent and vanadium-chromium slag (containing 2.5 to 4.5 percent of vanadium and 14 to 25 percent of chromium) as a raw material; (2) putting the vanadium-chromium slag into the waste acid to allow the chromium and the vanadium in the slag to form chromium sulfate and vanadyl sulfate which can be dissolved in water very easily, wherein the leaching time is about 6 hours; (3) adding a certain amount of steel making steel slag during leaching to fulfill the aim of generating a great deal of calcium sulfate when a great deal of calcium oxide meets the acid during filtration, and wrapping, adsorbing or and stopping 'silica gel' formed by silicon dioxide in the chromium slag by the calcium sulfate which is used as a filter medium to ensure that the filtration is performed smoothly; (4) adjusting the pH value of the filtrate to be 2.5 by using sodium hydroxide, and then adding an oxidant and oxydol to ensure that the chromium in the solution is oxidized to be hexavalent, the iron is oxidized to be trivalent, and the vanadium is oxidized to be pentavalent; (5) heating the leaching solution to the temperature of between 70 and 90 DEG C to ensure that the vanadium and the iron is combined together to generate water-fast 'ferric vandate', wherein the time for thermal precipitation is about one hour, and the vanadium residual in the solution is not more than 0.4 g / L; (6) adding sodium hydroxide into the solution of which the ferric vandate is filtered out, and fully stirring the mixture until the pH value of the solution is between 5.5 and 5.9 to ensure that the chromium in the solution is completely converted into chromium.
Owner:PANZHIHUA SHUOSHENG IND & TRADING
Fluorination catalyst, and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN104907065AIncrease the areaHigh pore volumePreparation by halogen replacementMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsChromium CompoundsChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a fluorination catalyst, and a preparation method and a use thereof, and belongs to the field of chemical synthesis. The precursor of the catalyst is formed by blending 40-95mass% of a trivalent chromium compound with 5-60mass% of tungstate, wherein the trivalent chromium compound can be chromic oxide or chromium hydroxide, and the tungstate can be zinc tungstate, nickel tungstate, magnesium tungstate, aluminum tungstate, silicotungstic acid, ammonium tungstate, ammonium paratungstate or ammonium metatungstate. The fluorination catalyst has the advantages of high use temperature, high catalysis activity and long service life, and can be mainly used in reactions for preparing fluorinated alkenes through gas phase catalysis of fluorination of alkenyl halides at a high temperature.
Owner:泉州宇极新材料科技有限公司
Anti-oxidation coating for heat treatment of iron and preparation method thereof
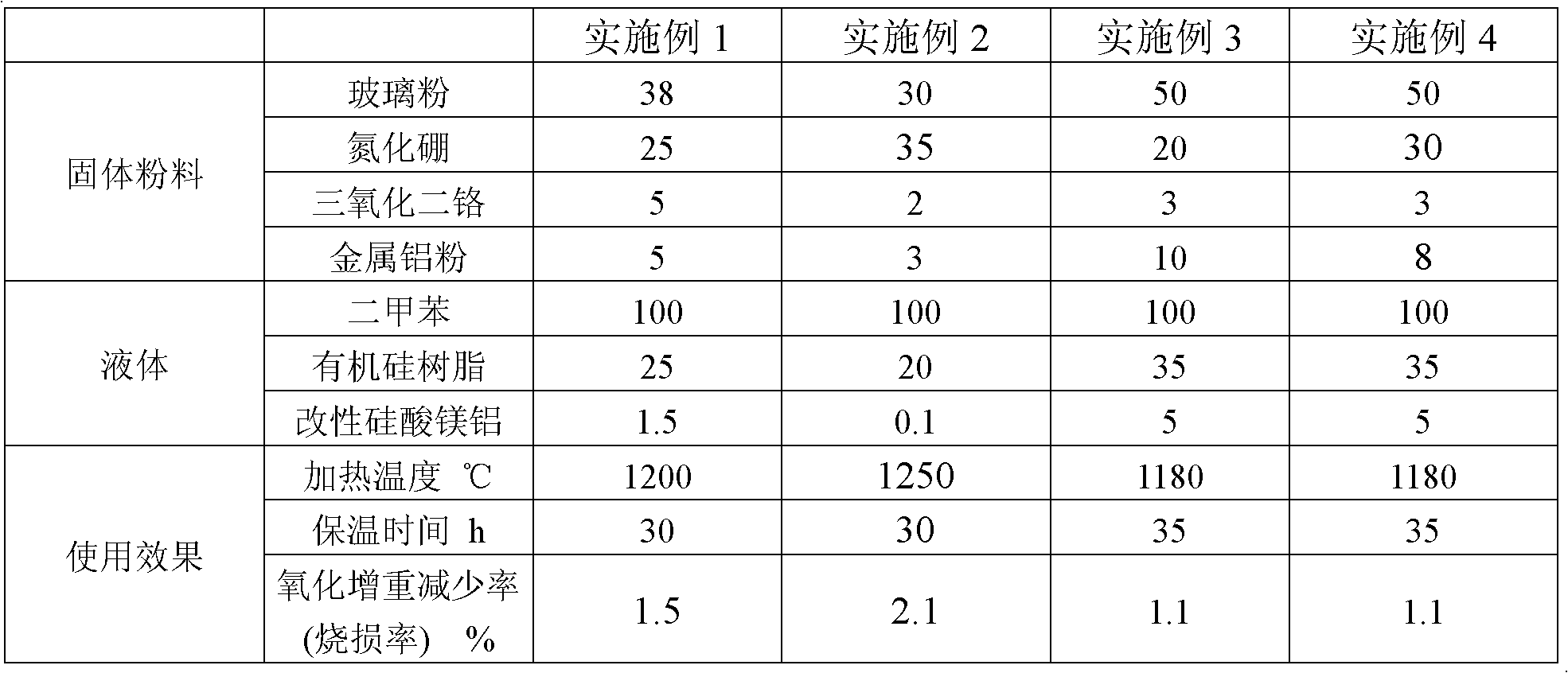
ActiveCN102585568AImprove performanceWide variety of sourcesSpecial surfacesCoatingsBoron nitrideOxidation resistant
The invention belongs to the technical field of the preparation of high-temperature anti-oxidation coatings, in particular to an anti-oxidation coating used in a long-time heat treatment process of iron, and the like at high temperature. The coating comprises solid powder and liquid, and is characterized in that the solid powder comprises following components by weight part: 30 to 50 parts of glass powder, 10 to 50 parts of boron nitride, 2 to 5 parts of chromic oxide and 3 to 10 parts of metal aluminum powder; and the liquid comprises following components by weight part: 0.1 to 5 parts of modified magnesium aluminosilicate, 20 to 35 parts of organic silicone resin and 100 parts of xylene. Through the adoption of the coating, oxydic weight gain of carbon steel or alloy steel can be guaranteed to be reduced by more than 80 percent in the heat treatment process for a long time (larger than 30 hours) at temperature of 1200 DEG C and above.
Owner:CHINA ERZHONG GRP DEYANG HEAVY IND
Process for roasting chromite resources in ring kiln through pure oxygen by using low-temperature method and harmlessly and deeply utilizing chromium residue
InactiveCN101824530AImprove resource conversion rateMagnesium carbonatesChromium trioxideSodium bicarbonateSlag
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy and chemical engineering. The process comprises the following steps of: firstly, crushing chromite, adding sodium hydroxide and a catalyst to be oxidized and roasted by using a low-temperature pure oxygen method; diluting, cooling, extracting and filtering to obtain a sodium chromate crystal and ferrum-magnesium slag; adding an alkali washing solution into a sodium hydroxide solution to back extract to obtain the sodium hydroxide solution for recycling; adding water into the sodium chromate crystal and ferrum-magnesium slag to be dissolved and feeding filtrate into a carbonizer to decompose to extract aluminum; carbonizing, evaporating, condensing and crystallizing the extracted solution to obtain sodium chromate; and carbonizing ferrum-magnesium filter slag to generate sodium bicarbonate, reacting to generate a magnesium hydrogen carbonate solution, heating and cracking to generate a magnesium carbonate product and drying a filter cake to obtain ore refined powder; and secondly, crushing chromium residue, adding sodium bicarbonate in the ration of 1:8, adding a catalyst for calcination, cooling and adding water to soak; adding an aluminum hydroxide crystal into supernatant liquid, carbonizing and decomposing to remove aluminum in a reaction tank; filtering and washing an aluminum hydroxide product; adding a reducing agent into the filtrate to reduce hexavalent chromium to generate anhydrous chromium hydroxide and drying and roasting to obtain chromium sesquioxide; and returning the filtrate to a system for mixing after pyrolyzing and extracting to remove magnesium.
Owner:白向南 +2
Hot-spraying nano composite ceramic coating plastic mold and production method thereof
InactiveCN101249698AEasy releaseRealize easy demouldingMolten spray coatingCeramic layered productsThermal sprayingComposite ceramic
A plastic mold for hot-spray nanometer composite ceramic coating and a production method thereof are provided. The plastic mold is composed of a plastic mold steel basal body, a bottom bonding layer and a nanometer composite ceramic working layer produced by hot-spray technology. The bottom bonding layer adopts any of the Ni / AI, AI / NI or NiCrAl materials. The nanometer composite ceramic working layer adopts the material of granular ball-shaped nanometer composite hot-spray coating powder which is a compound of chromium oxide chromium sesquioxide, titanium dioxide and silicon dioxide. The production method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing hot-spray coating on mold steel workpieces to be processed according to standard and optimized hot-spray process; secondly, conducting surface grinding and polishing to meet the technical requirements for the size, precision, surface toughness, etc. of the plastic mold. The production method is simple, low in production cost and easy to industrialize, and realizes the high-quality characteristics of the plastic mold such as high rigidity, high wear resistance, high corrosion resistance, long service life, and easiness to de-mould, so that the method has good market application prospect and high commercial value.
Owner:WUHAN YOUKE SURFACE ENG
Method for separating vanadium and chromium solution and recycling vanadium and chromium
ActiveCN105861829AAchieve restorationAchieve reduction of vanadiumProcess efficiency improvementVanadium dioxideVanadyl sulfate
The invention discloses a method for separating a vanadium and chromium solution and recycling vanadium and chromium. A reducing agent is added to the vanadium and chromium solution under the condition that the pH value ranges from 8 to 14, and the temperature ranges from 20 DEG C to 100 DEG C, and pentavalent vanadium and hexavalent chromium are reduced into tetravalent vanadium and trivalent chromium; the trivalent chromium forms chromic hydroxide precipitate in situ, and a chromic hydroxide filter cake and vanadium-containing filtrate are obtained through filtering; the chromic hydroxide filter cake is used for preparing chromic oxide; and the vanadium-containing filtrate is used for preparing hydration vanadium dioxide or vanadyl sulfate or vanadium pentoxide. By means of the method, efficient separation and recovery of vanadium and chromium are achieved, the vanadium recovery rate reaches 96% or higher, the chromium recovery rate reaches 98% or higher, and the purity of vanadium and chromium products reaches 98% or higher. The method has the beneficial effects that the technological processes are short, the separation efficiency is high, the cost of raw materials and auxiliary materials is low, operation is easy and convenient, and the method can be used for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Ceramsite sand for casting and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107298584AImprove thermal conductivityHigh thermal expansionFoundry mouldsFoundry coresExpanded clay aggregateSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to a ceramsite sand for casting and a preparation method thereof. The ceramsite sand comprises the following chemical components in parts by weight: 35-65 parts of silicon dioxide, 30-50 parts of aluminum oxide, 1-10 parts of iron oxide, 1-4 parts of manganese dioxide and 2-8 parts of chromic oxide. The method comprises the following steps: performing grinding, and detecting the chemical composition and contents of the raw materials; and sequentially performing proportioning, ball making, screening, sintering and grading to obtain the finished product. The ceramsite sand prepared by the invention is high in thermal conductivity and refractoriness, conforms to the requirements for casting sand, can be used for casting and casting mold production instead of silica sand, chromite sand and the like, reduces the discharge amount of solid waste in the casting industry, and improves the quality of cast products.
Owner:NINGXIA KOCEL MOLD
Method for producing chromic oxide by using sludge of containing chrome
A process for preparing Cr2O3 from the Cr contained sludge includes water washing, press filtering for dewatering, drying, calcining to obtain coarse Cr2O3 product, removing the water-soluble impurities by use of hot water, centrifugal drying, baking, grinding and sieving.
Owner:高志远
Manufacturing method of electrothermal film
ActiveCN104080208AImprove stabilityImprove temperature resistanceHeating element materialsNickel sesquioxideManganese
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an electrothermal film. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of A, preparing an electrothermal film treatment solution which comprises tin tetrachloride, titanium trichloride, antimony trichloride, calcium chloride, chromic oxide, manganese dioxide, nickel sesquioxide, isopropanol, alcohol and water, B, masking a substrate, C, heating the substrate to be 400-700 DEG C and then spraying the electrothermal film treatment solution on the substrate by a spray gun to form a semifinished electrothermal film, D, annealing the semifinished electrothermal film, and E, coating silver oxide paste on the surfaces of the two ends of the annealed semifinished electrothermal film, loading the semifinished electrothermal film into an electrode oven, baking and fusing the semifinished electrothermal film to form a whole, and obtaining the finished electrothermal film. The manufacturing method has the advantages that the stability of the electrothermal film is improved by adding antimony; the temperature resistance of the electrothermal film is improved by adding titanium; the infrared emitting ability of the electrothermal film is improved by adding nickel and manganese; and an adhesive force between the electrothermal film treatment solution and the substrate is increased by adding isopropanol.
Owner:成都世纪经尧科技有限公司
Method for precipitation separation and recovery of chromium and vanadium in chromium-vanadium solution
ActiveCN103849765AHigh removal rateLow Chromium Loss RateProcess efficiency improvementTwo stepReducing agent
The invention relates to a method for the precipitation separation and the recovery of chromium and vanadium in a chromium-vanadium solution. The method comprises the following steps: regulating the pH (Power Of Hydrogen) of a solution until the solution is acidic; adding an ammonium salt so as to precipitate the majority of vanadium from the solution in a form of ammonium polyvanadate; filtering and adding a certain amount of reducing agent into a vanadium-precipitated supernatant so as to perform reduction and precipitation on the partial vanadium in the solution; stirring and filtering; then adding the certain amount of reducing agent so as to reduce the rest of the vanadium in the precipitation solution; filtering; collecting filter residues obtained by two steps of reduction and precipitation; dissolving out in an oxidization manner and returning to the vanadium precipitation step via the ammonium salt; collecting the supernatants obtained by the two steps of reduction and precipitation; adding the certain amount of reducing agent again and precipitating chromium hydroxide; and filtering and calcining a filter cake so as to prepare chromium sesquioxide, wherein the supernatant after the precipitation of the chromic hydroxide can be taken as a mother liquor of a leaching process to be recycled. The method is simple in process, low in cost, less in equipment and small in reagent adding amount, and realizes the recycling of wastewater.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalyst for selective oxidation of sulfureted hydrogen into elemental sulfur and reaction process thereof
InactiveCN101380582AGood activity at low temperatureImprove conversion rateSulfur preparation/purificationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSesquioxideReaction temperature
A selective oxidation catalyst and process which converts the hydrogen sulphide into the element sulphur, wherein, the catalyst comprising a catalyst carrier and active components which are selected from the trioxide iron and / or trioxide chromium is characterized in that the carrier is the mixed oxides of the titanium dioxide and aluminum sesquioxide, in which the content of the titanium dioxide is 60-95%. The catalyst is used in the reaction which selectively oxidizes the mixed gas containing the hydrogen sulphide into the element sulphur. Reaction conditions are as follows: reaction temperature is 160-280 DEG C, reaction pressure is 0.02-10.0MPa, gas space velocity is 400-2000h<-1>, H2S is less than or equal to 3.0% (Vol%), the molar ratio of O2 and H2S is 0.6-3.0. The catalyst shows excellent activity at low temperature and has selective oxidation activity at 160 DEG C. The yield of the sulfur is high and is more than or equal to 90%.
Owner:淄博海川精细化工有限公司 +1
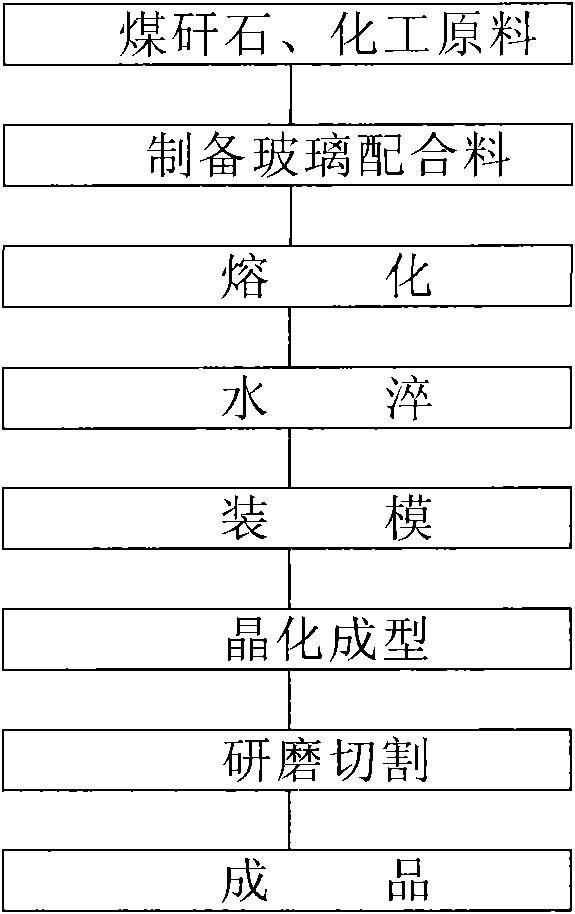
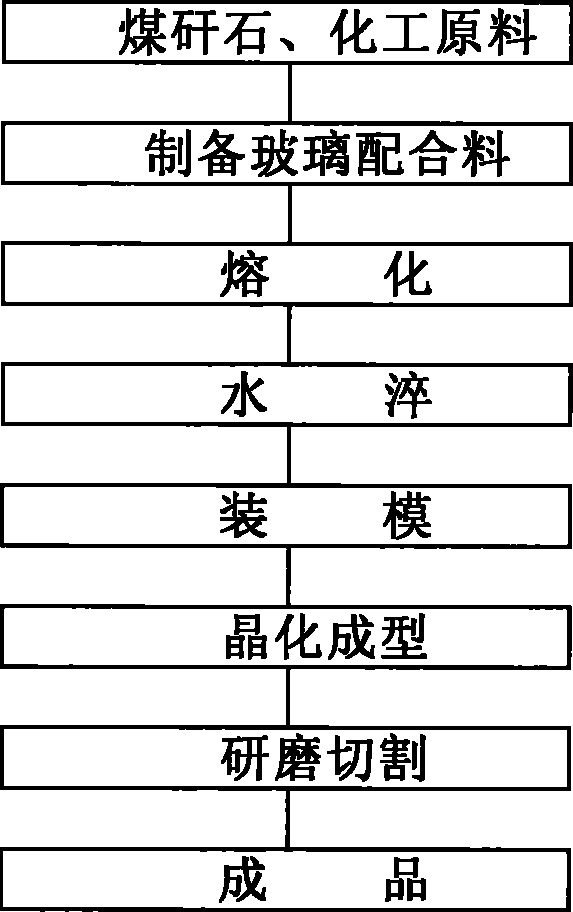
Method utilizing coal gangue to manufacture microcrystalline glass plate material
The invention discloses a method utilizing a coal gangue to manufacture a microcrystalline glass plate material. The method includes the following steps: the coal gangue, quartz sand, calcite, alumina, sodium carbonate, zinc oxide, barium carbonate, copper oxide, carbon powder, borax and chromic oxide are mixed together according to certain parts by weight so as to obtain a glass batch mixture; the glass batch mixture is molten into liquid glass; the liquid glass is poured into water to obtain glass particles; the glass particles are laid in a fireproof mould to carry out crystallization heat treatment; finally, the rough microcrystalline glass is ground and cut after the crystallization heat treatment so as to obtain the finished glass. The method in the invention utilizes wastes in the coal mining industry to manufacture the microcrystalline glass plate material, which not only reduces the stacking quantity of the coal gangue and lessens environmental pollution, but also improves the product performance and reduces the production cost. Therefore, the method in the invention has good social and economic benefits.
Owner:陕西乾盛环保建材工程有限公司
Method for separating and extracting vanadium and chromium from vanadium chromium leaching liquor
ActiveCN103276205AImprove oxidation capacityLess reducing doseProcess efficiency improvementChromium sesquioxideSulfite salt
The invention belongs to the field of wet metallurgy, and particularly relates to a method for separating and extracting vanadium and chromium from vanadium chromium leaching liquor. The method comprises the following steps of: adding sodium sulfite into the vanadium chromium leaching liquor, adjusting the pH value to 5 to 5.5; carrying out the precipitation reaction; filtering, calcining filtered solids and cooling; adding the calcination products into NaOH (sodium hydroxide) solution to obtain solid filter residue, i.e. chromium sesquioxide; adjusting the pH value of the liquid filtered after the precipitatio to 2.0 to 2.5, heating the filtered liquid to 90 to 95 DEG C, and adding ammonium sulfate to obtain precipitates, filtering the precipitates, wherein the solid filter residue is ammonium metavanadate. By adopting the moderate reduction, less reduction agent is added, the reduction action is carried out under a normal temperature condition, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
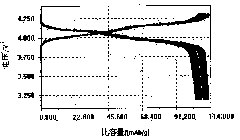
Cathode active substance for lithium ion secondary battery, preparation method and lithium ion secondary battery
InactiveCN102315427AThe first discharge specific capacity is highSimple production processCell electrodesSecondary cellsMolten saltSolvent
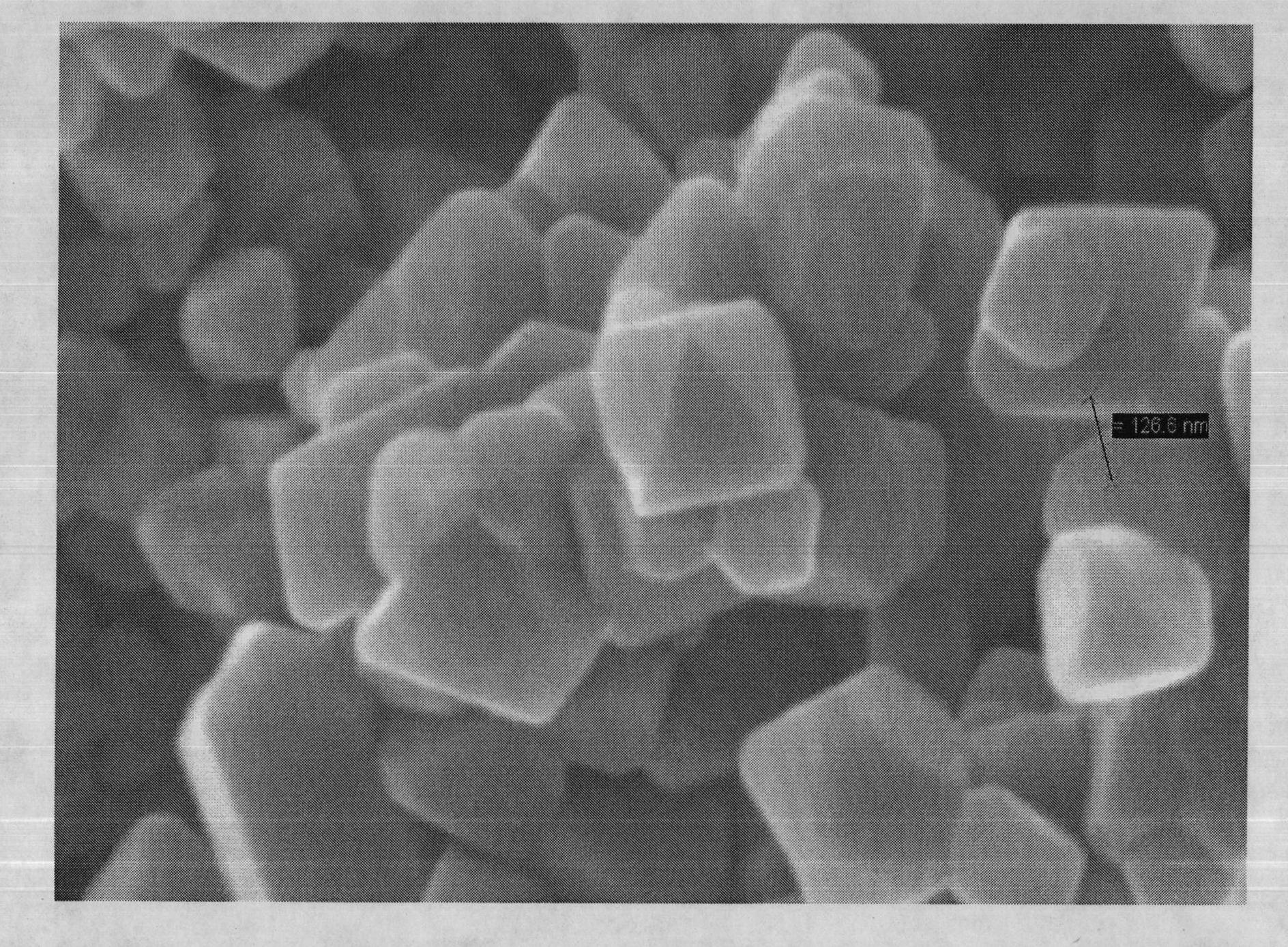
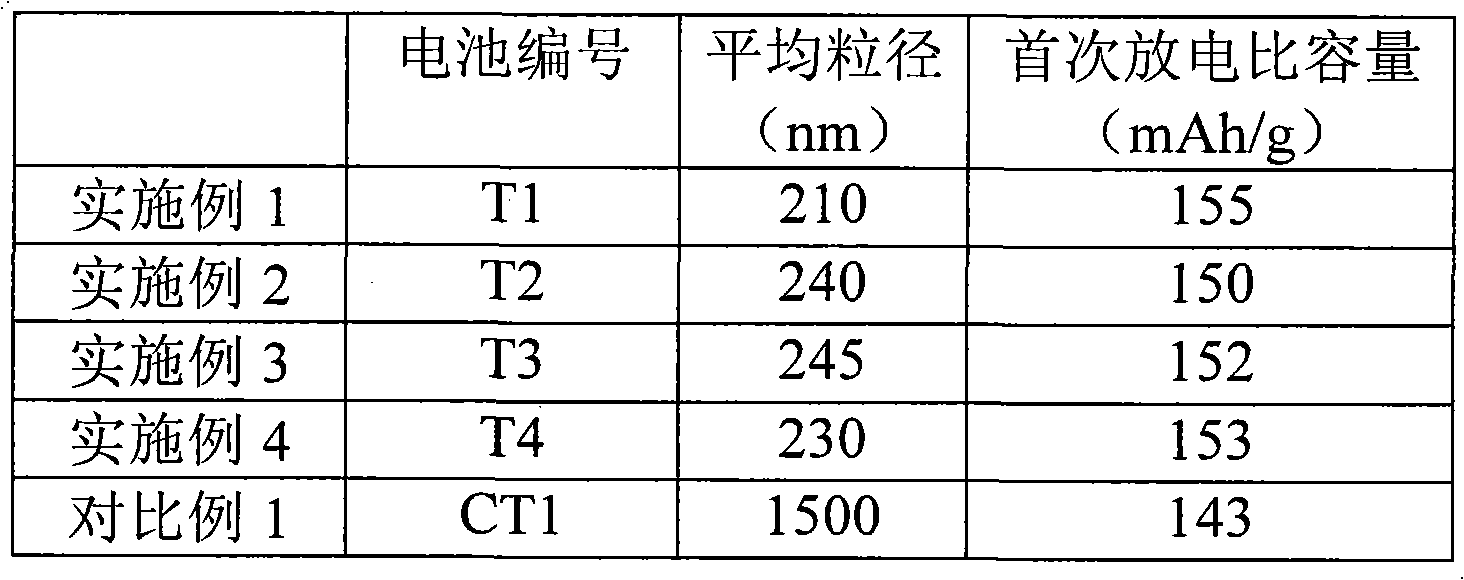
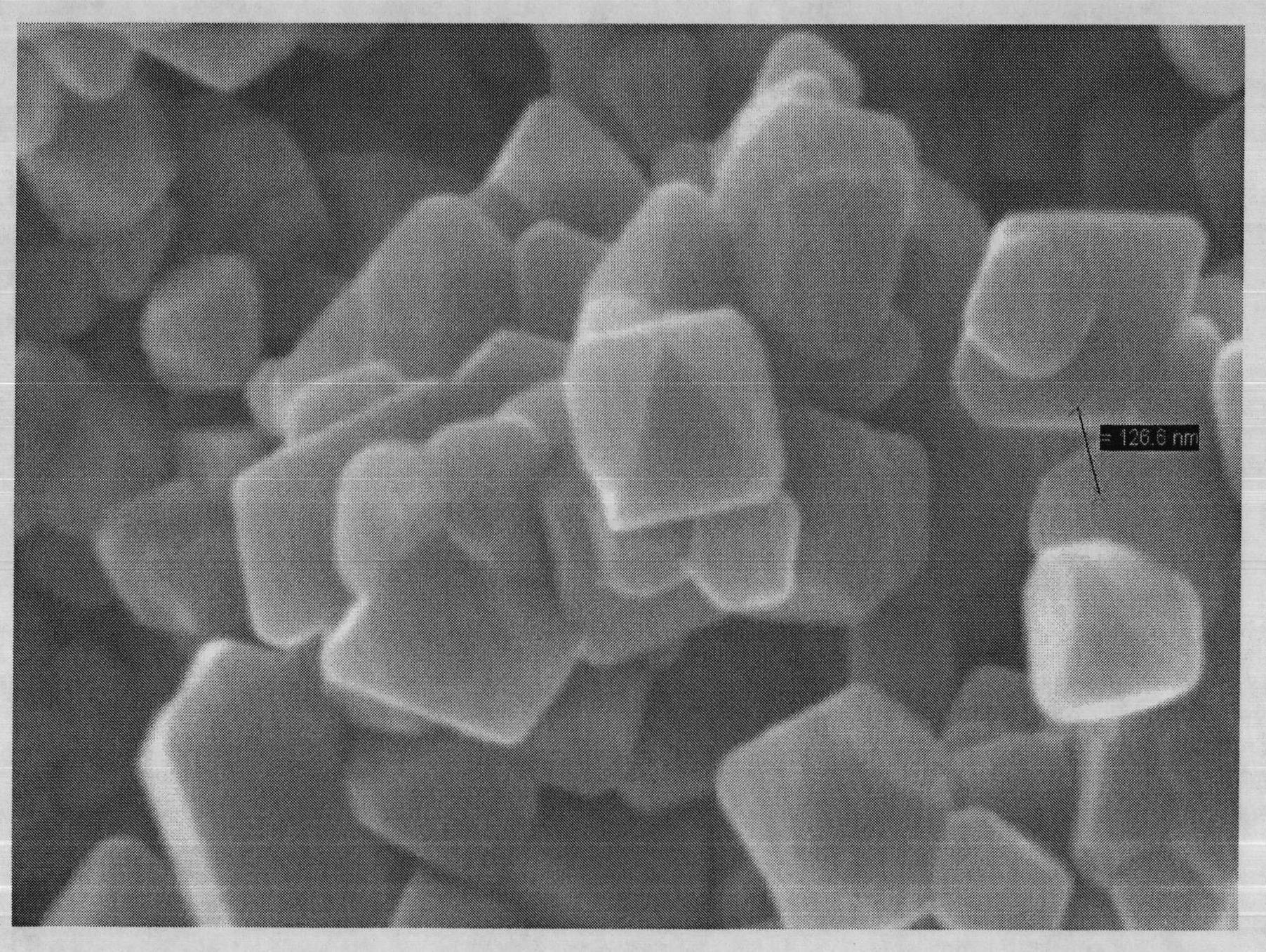
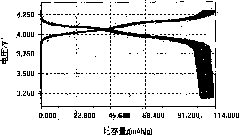
The invention provides a cathode active substance for lithium ion battery and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of 1) after titanium dioxide, chromic oxide, a lithium source and a solvent are mixed, conducting drying to remove the solvent to obtain first mixtures; 2) mixing the first mixtures obtained at the step 1 with the saturated solution of low-temperature fused salt and conducting drying to obtain second mixtures; and 3) calcining the second mixtures obtained at the step 2 and removing the low-temperature fused salt to obtain nanometer chromium lithium titanate, wherein the low-temperature fused salt is salt which can be fused under the condition of calcination and does not react with other components in the mixtures. The average grain size of the cathode active substance, i.e. the nanometer chromium lithium titanate prepared through the method provided by the invention is 200-250nm and the cathode active substance has an octahedral structure. The battery which is prepared by using the cathode active substance, i.e. the nanometer chromium lithium titanate provided by the invention has a good initial discharge specific capacity.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Method for producing high-purity metal chromium by using carbon reduction method
InactiveCN102965526AHigh speedIncrease productivityProcess efficiency improvementImpurityMaterials science
The invention relates to a method for producing high-purity metal chromium by using a carbon reduction method. The method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing chromic oxide powder and carbon black powder, adding deionized water or alcohol to form a wet mixed material, carrying out press forming, and drying, thereby obtaining a mixed material block; putting the mixed material block in a vacuum furnace, and enabling chromic oxide to be reduced by carbon black under high-temperature vacuum conditions, thereby obtaining crude chromium; introducing gaseous carbon monoxide, and carrying out heat preservation for 3-8 hours at the temperature of 1,300-1,500 DEG C; introducing gaseous carbon dioxide, and carrying out heat preservation for 3-8 hours at the temperature of 800-1,000 DEG C; and cooling down, and discharging, thereby obtaining a high-purity metal chromium block. According to the method, a gas-solid reduction manner is adopted to remove residual raw materials and non-metallic impurities, so that the production cost is reduced, and the reduction time is shortened; and the produced high-purity metal chromium has the purity of 99.96-99.98%, the oxygen content less than 0.03%, the sulfur content less than 0.01% and the carbon content less than 0.01%, thereby meeting the standards of the high-purity metal chromium.
Owner:JINZHOU NEWROUTE HYPERPURE MATERIAL CO LTD
Method for separating and recycling vanadium and chromium
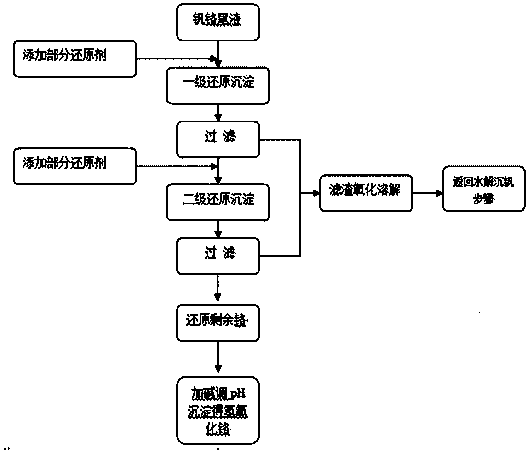
The invention relates to a method for separating and recycling vanadium and chromium in a vanadium and chromium contained solution or vanadium and chromium contained reducing and precipitating slag. The method for separating and recycling vanadium and chromium in a vanadium and chromium contained solution includes the following steps: reducing all vanadium and chromium in the vanadium and chromium contained solution through a certain quantity of a reducing agent, and then performing precipitation after alkali is added; calcining a filter cake at a high temperature for a certain time and cooling after precipitation and filtration; stirring the calcined product in an acid liquor and alkali liquor with a certain concentration or water and dissolving out vanadium and chromium, so as to enable vanadium to be dissolved in the aqueous phase mostly and chromium to be remained in the solid phase as chromic oxide mostly; filtering and separating the solid phase and the aqueous phase, hydrolyzing the filtered solution and precipitating vanadium or precipitating vanadium after ammonium addition, and obtaining the chromic oxide product after heating and drying the solid phase. The method for separating and recycling vanadium and chromium in vanadium and chromium contained reducing and precipitating slag is the same as the treatment manner for the precipitated filter cake in the step of separating and recycling vanadium and chromium in the vanadium and chromium contained solution; the method is simple in procedure and low in cost and enables waste water to be available to cyclic utilization.
Owner:孙刚
Microwave synthesis method for multi-element lithium manganate-doped positive electrode material of lithium ion battery
InactiveCN101800309AImprove the first discharge capacityGood charge and discharge cycle performanceCell electrodesElectrolysisSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a microwave synthesis method for a multi-element lithium manganate-doped positive electrode material of a lithium ion battery. The method comprises the following steps: adding deionized water into raw materials comprising lithium carbonate micropowder, industrial pure electrolytic manganese dioxide micropowder, analytical pure magnesium oxide micropowder, nickelic trioxide micropowder and chromic oxide micropowder to perform wet combination; mixing the raw materials with a ball mill; drying; mixing and sieving the dried products to serve as crude materials; shaping the crude materials into green bodies, and putting the green bodies into a microwave oven for sintering; and after the sintering is finished, taking the materials out, crushing and sieving the materials to obtain the lithium manganate-doped positive electrode material of the lithium ion battery. The material serving as a positive electrode active material can be used for preparing a positive plate of the lithium ion battery. The method has the characteristics of simpleness, energy saving and consumption reduction, low cost and contribution to industrial production; and the assembled lithium ion battery has the advantages of high initial discharge capacity and high charge and discharge cycling performance. The lithium manganate-doped positive electrode material of the lithium ion battery obtained by the method can be applied to electric automobiles, mobile phones, laptops and other equipment.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Corundum breathable seat brick with high thermal shock resistance and production method thereof
The invention discloses a corundum breathable seat brick with high thermal shock resistance. The brick consists of mixed corundum, a magnesium-containing material, a binding agent, chromium oxide, a water reducing agent and an explosion-proof agent. The production method of the corundum breathable seat brick comprises the following steps: dosing, and mixing to prepare mud; placing the mud in a mould, performing shake densification, demoulding, and drying to obtain a breathable seat green brick; and heating the breathable seat green brick, and roasting to obtain the corundum breathable seat brick with thermal shock resistance. The component ratio is reasonable, the production and preparation method is simple, the prepared breathable seat brick has good high-temperature strength and thermal shock resistance; and the service life of the breathable seat brick can be effectively prolonged, the use security of the breathable brick can be increased, the replacement times of the breathable brick can be reduced, the production cost of enterprises can be reduced and the production efficiency of ferrous metallurgy can be increased. The corundum breathable seat brick can replace the existing breathable seat brick and be suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
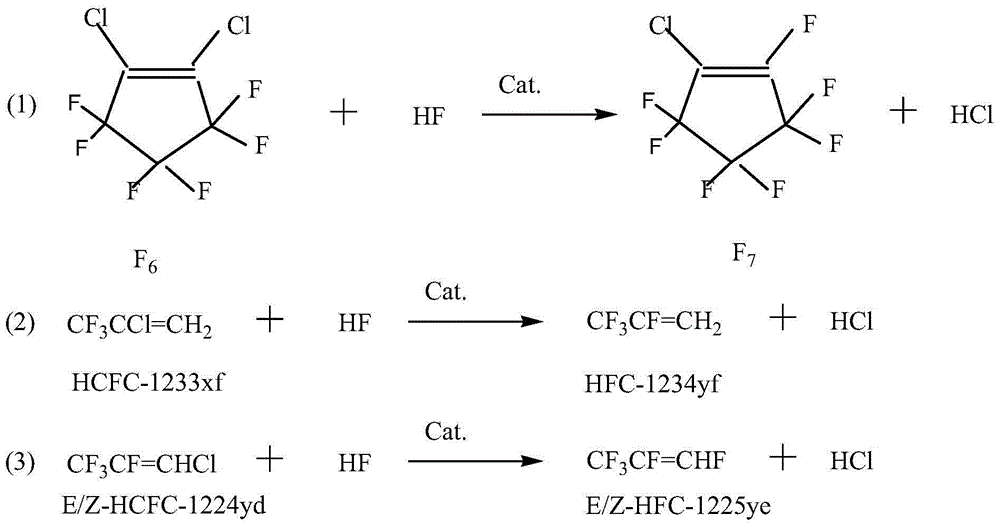
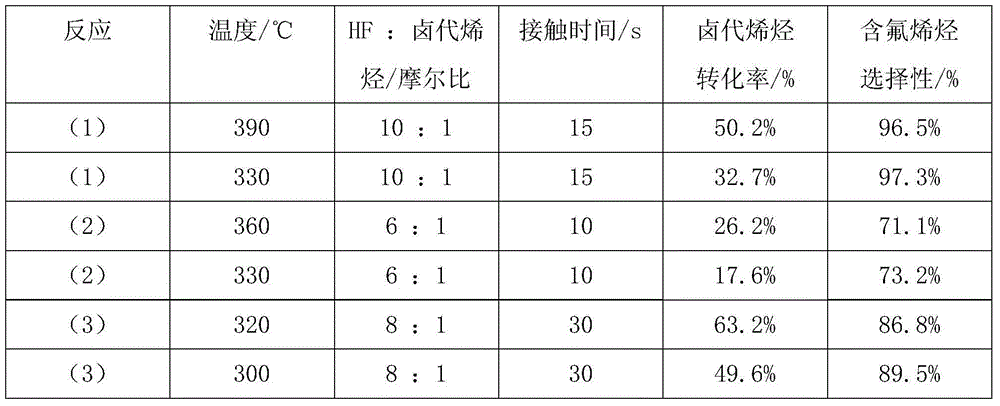
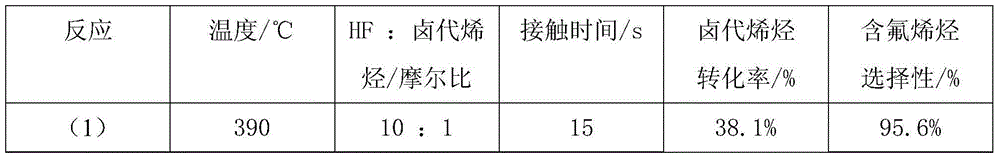
Method for producing 1-chlorine-3,3,3-triflupropylene
ActiveCN101028994AHigh yieldHigh selectivityPhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen replacementGas phaseChemistry
Owner:ZHEJIANG FLUORINE CHEM NEW MATERIAL
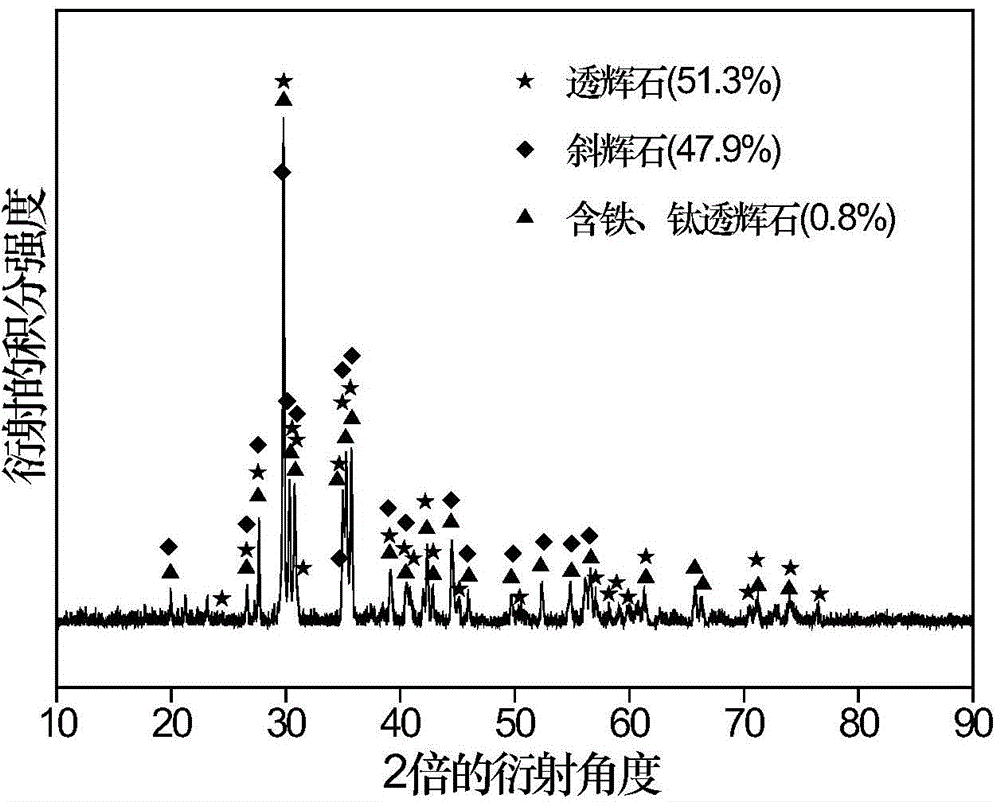
Vanadium titano-magnetite tailing glass-ceramic and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to vanadium titano-magnetite tailing glass-ceramic and a preparation method thereof. The vanadium titano-magnetite tailing glass-ceramic takes vanadium titano-magnetite tailings as a main raw material, and takes silica or silica sand (SiO2), limestone or calcite (CaCO3), sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), alumina (Al2O3), magnesium oxide (MgO), chromium sesquioxide (Cr2O3), calcium fluoride (CaF2) and sodium nitrate (NaNO3) as auxiliary raw materials, wherein the content of vanadium titano-magnetite tailings in all the raw materials of the glass-ceramic is 50.0 to 65.0 percent by weight. The preparation method comprises the following steps: smashing the vanadium titano-magnetite tailings; mixing the vanadium titano-magnetite tailing powder, the auxiliary raw materials and a flexible clarifying agent exactly according to a designed ingredient proportion to obtain a uniform mixture; putting the mixture into a smelter for melting; after homogenizing and clarification of glass melt, preparing a glass board or glass particles through formation or water quenching; conducting crystallization heat treatment on the formed glass board, or carrying out crystallization after a mold is filled with the glass particles; carrying out annealing to obtain a glass-ceramic board. The vanadium titano-magnetite tailing glass-ceramic and the preparation method have the advantages that the production cost of glass-ceramic is reduced; the problems of resource waste and environmental pollution are solved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ventilated brick and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a ventilated brick and a preparation method thereof. The ventilated brick is composed of the following raw materials: compact fused corundum, sintered tabular corundum, sintered spinel, fused magnesite, active alumina micro powder, industrial chromium trioxide, aluminium-enriched spinel micro powder, pure calcium aluminate cement, SM water reducing agent, SN-2 water reducing agent, sprayed aluminium powder and polypropylene fibre. The invention further relates to the preparation method of the ventilated brick. The ventilated brick prepared by the invention has the advantages of being strong in anti-pressure ability, long in service life, high in high-temperature resistant strength, good in anti-residue permeability and melting loss resistant peeling property, low in sintering temperature, low in energy consumption, clean, free from pollution, and simple and environment-friendly in preparation process; one ventilated brick can be used for above 90 times; and the sintering temperature is only 1200-1550 DEG C.
Owner:山东华强环保科技有限公司
Preparation method of LiAlO2-coated lithium manganese oxide spinel cathode material
InactiveCN102903904AIncrease capacityImprove cycle performanceCell electrodesMixed materialsAluminium isopropoxide
The invention relates to a preparation method of a LiAlO2-coated lithium manganese oxide spinel cathode material. The preparation method comprises the steps of: (a) blending electrolytic manganese dioxide, lithium carbonate and chromium oxide at a molar ratio of Li to Mn of 0.51, and a molar ratio of Cr to Mn of 0.026, crushing and mixing; (b) sintering the material mixture in an air sintering furnace, grinding, sieving, and mixing for the second time; (c) placing the mixed material in the air sintering furnace, and keeping temperature for 10 to 20 hours; (d) blending the product sintered for the second time with lithium fluoride, crushing, and mixing; (e) placing the mixture obtained in the step (d) in the air sintering furnace to obtain LiMn1.95Cr0.05O3.95F0.05; and (f) preparing a 0.2mol / L mixed solution containing lithium hydroxide monohydrate and aluminium isopropoxide, and coating to obtain the final product, namely LiAlO2-coated LiMn1.95Cr0.05O3.95F0.05. The capacity and the cycle performance of the cathode material can be improved effectively by modifying the lithium manganese oxide spinel cathode material by coating.
Owner:JIANGSU KING LITHIUM CELL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com