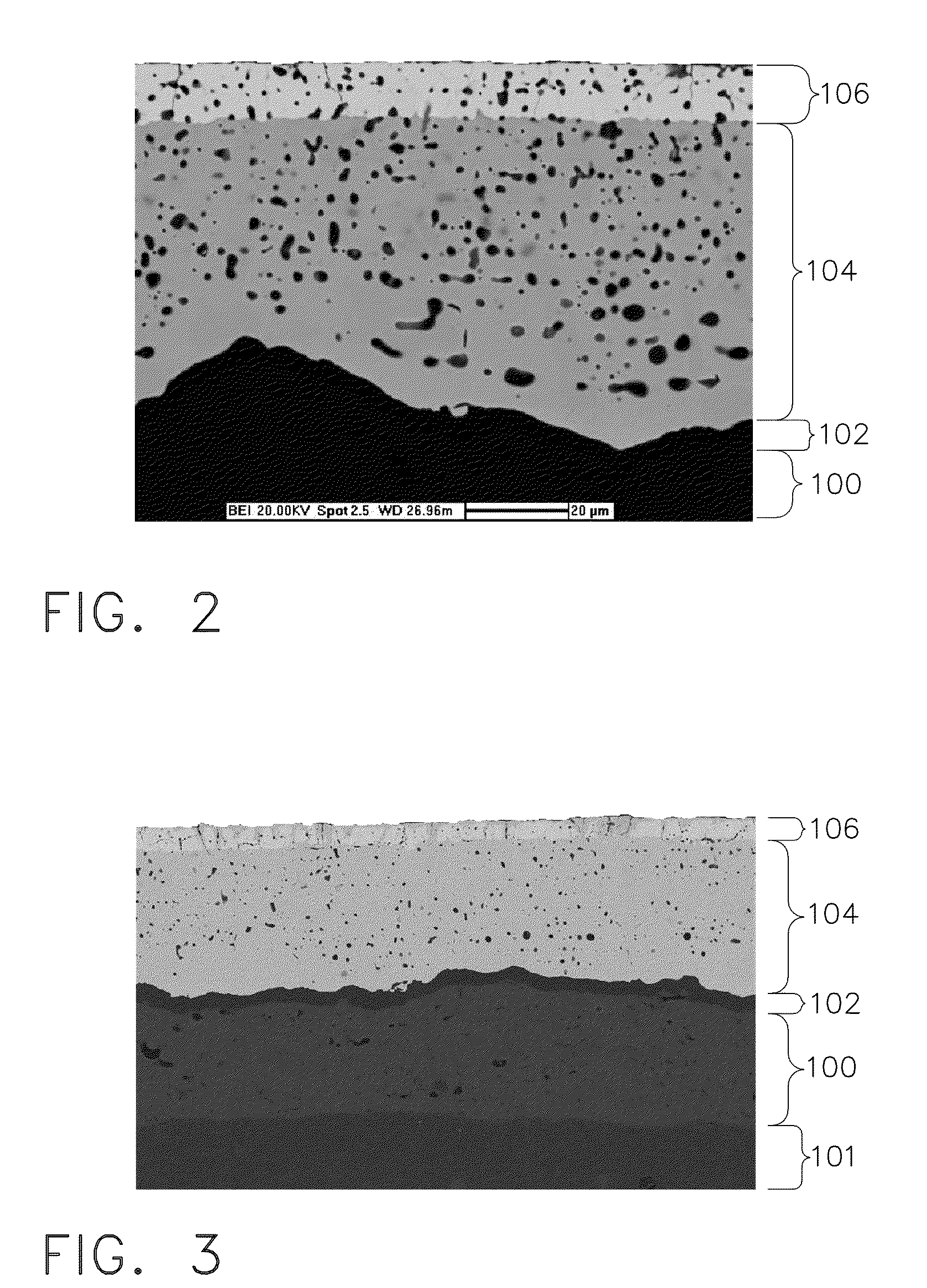
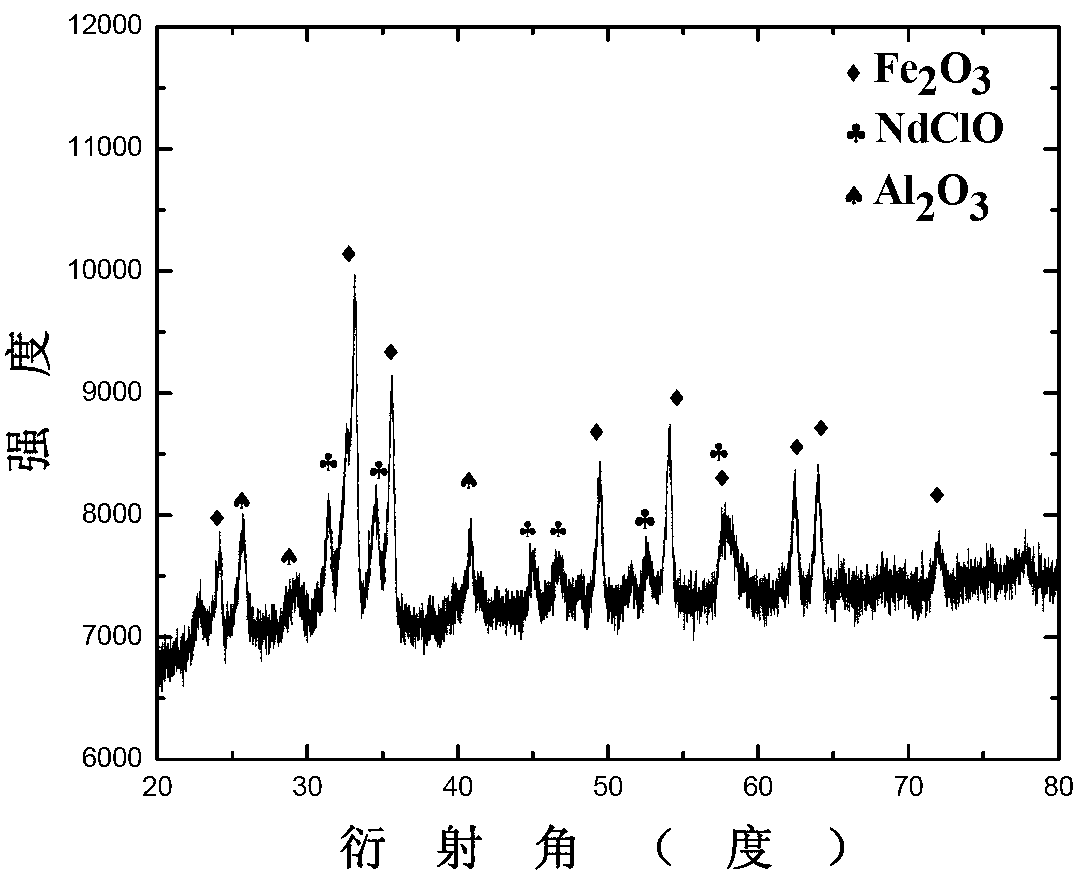
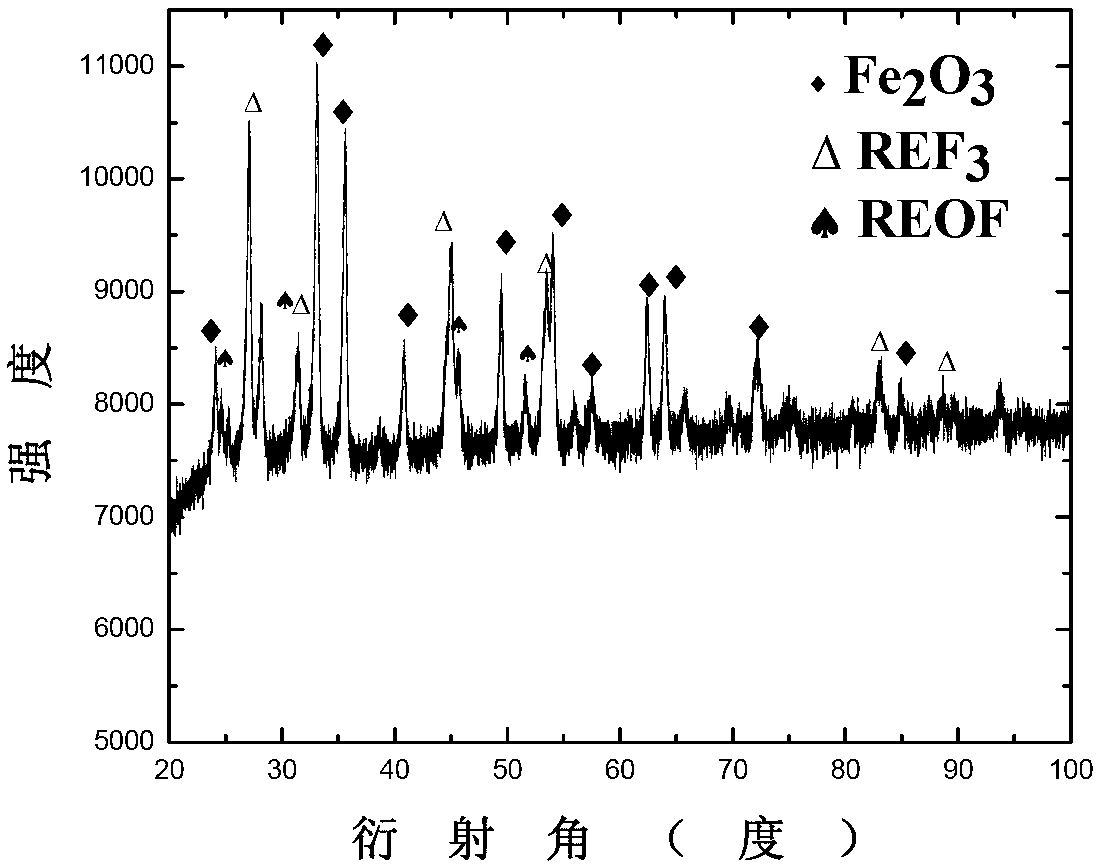
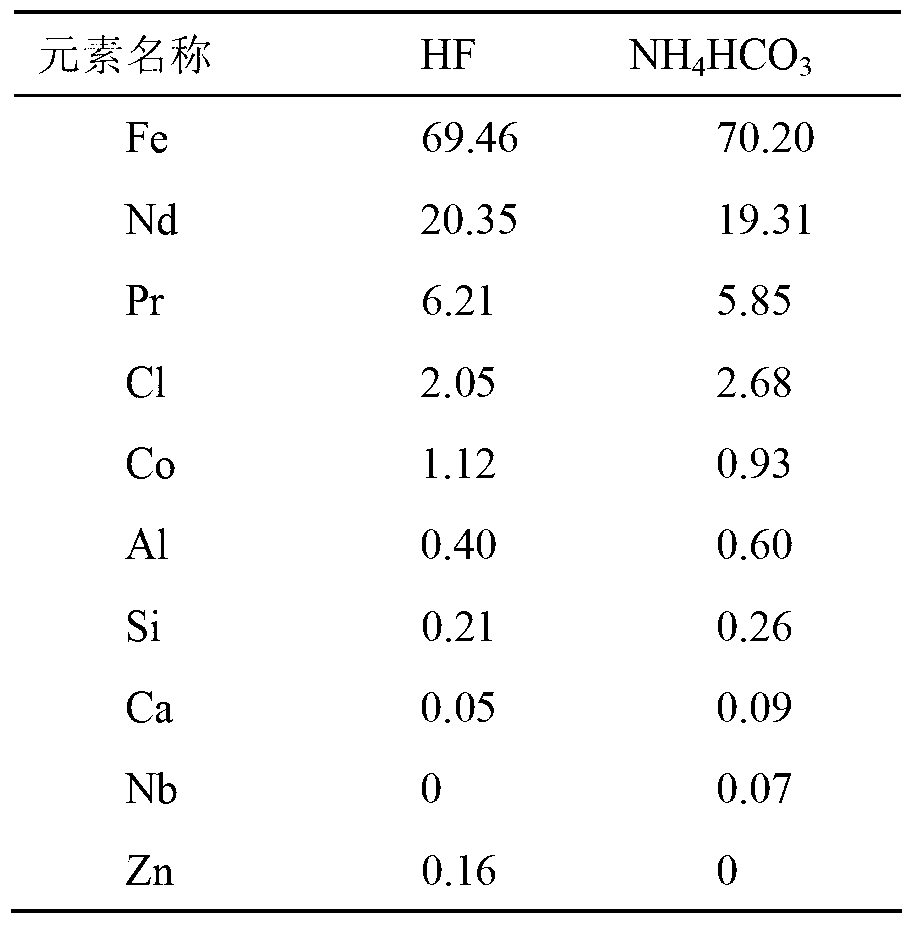
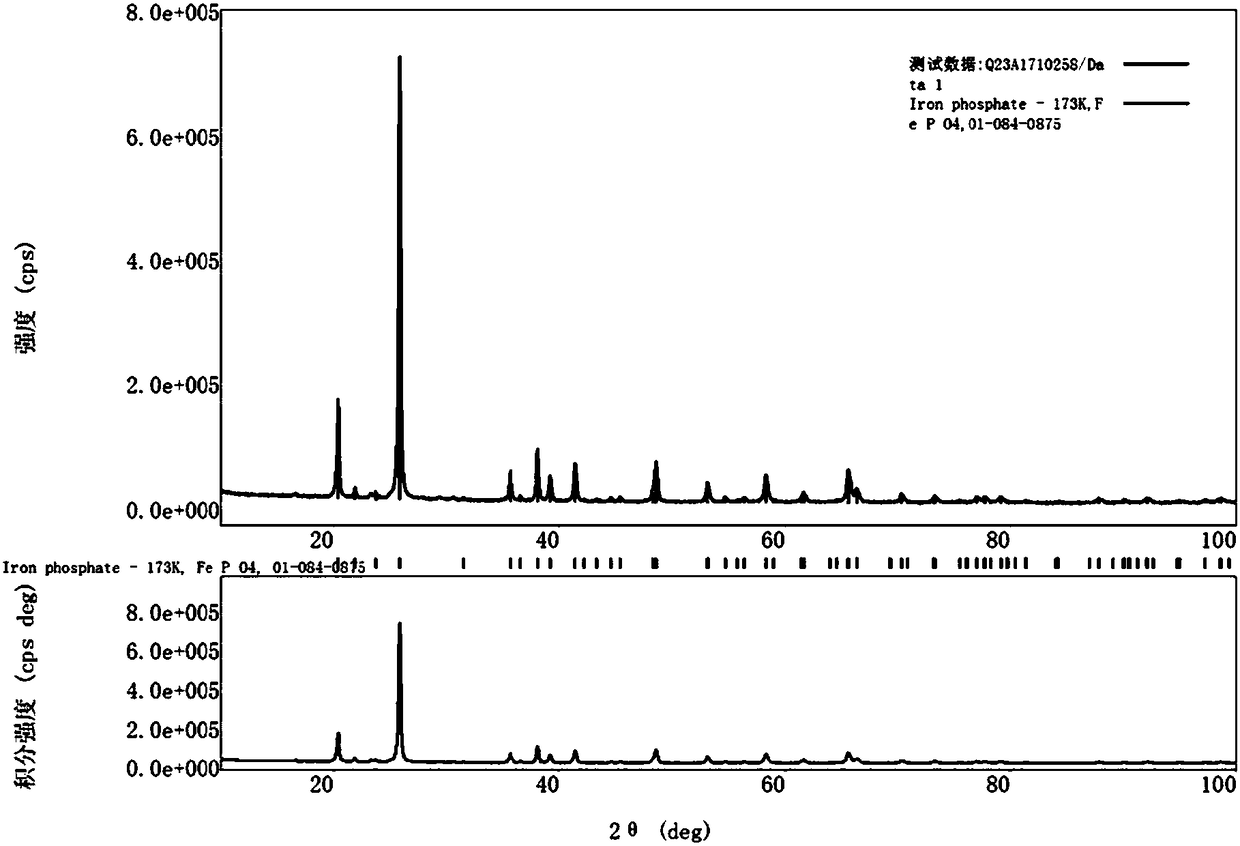
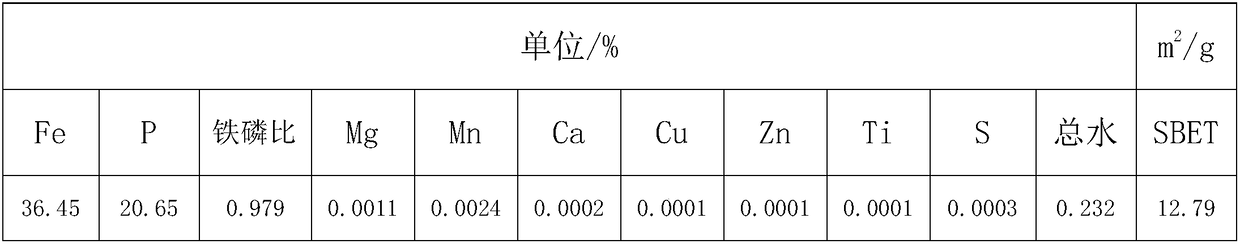
Patents
Literature
138 results about "Iron(III) oxide-hydroxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
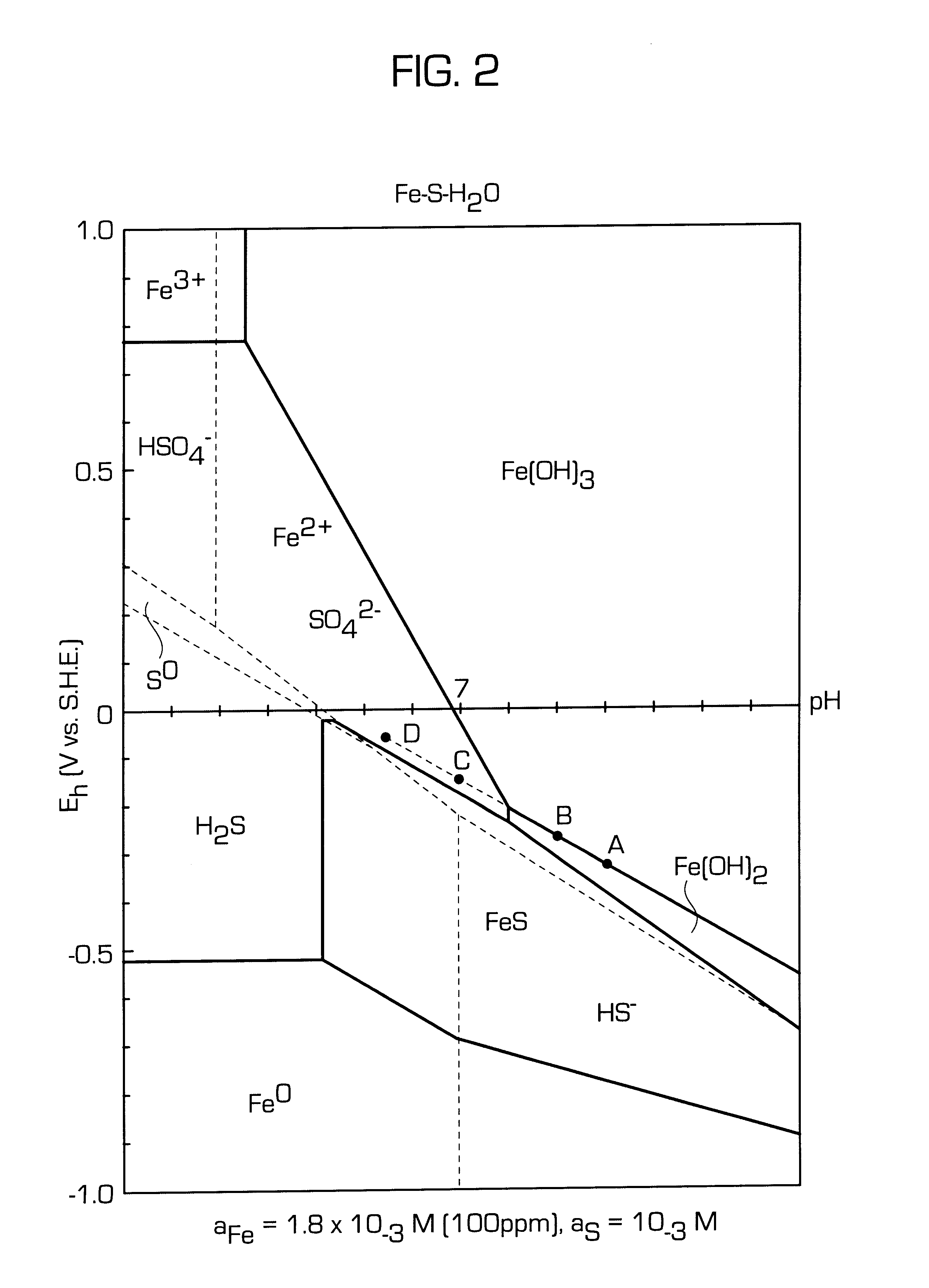
Iron(III) oxide-hydroxide or ferric oxyhydroxide is the chemical compound of iron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula FeO(OH). The compound is often encountered as one of its hydrates, FeO(OH)·nH₂O [Rust]. The monohydrate FeO(OH)·H₂O (CAS 51274-00-1, C.I. 77492) is often referred as iron(III) hydroxide Fe(OH)₃, hydrated iron oxide, yellow iron oxide, or Pigment Yellow 42.
Iron-based catalyst and method for preparing the same and use thereof
ActiveUS20160045901A1Superior productivity and selectivityGood effectOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionProduction rateSyngas
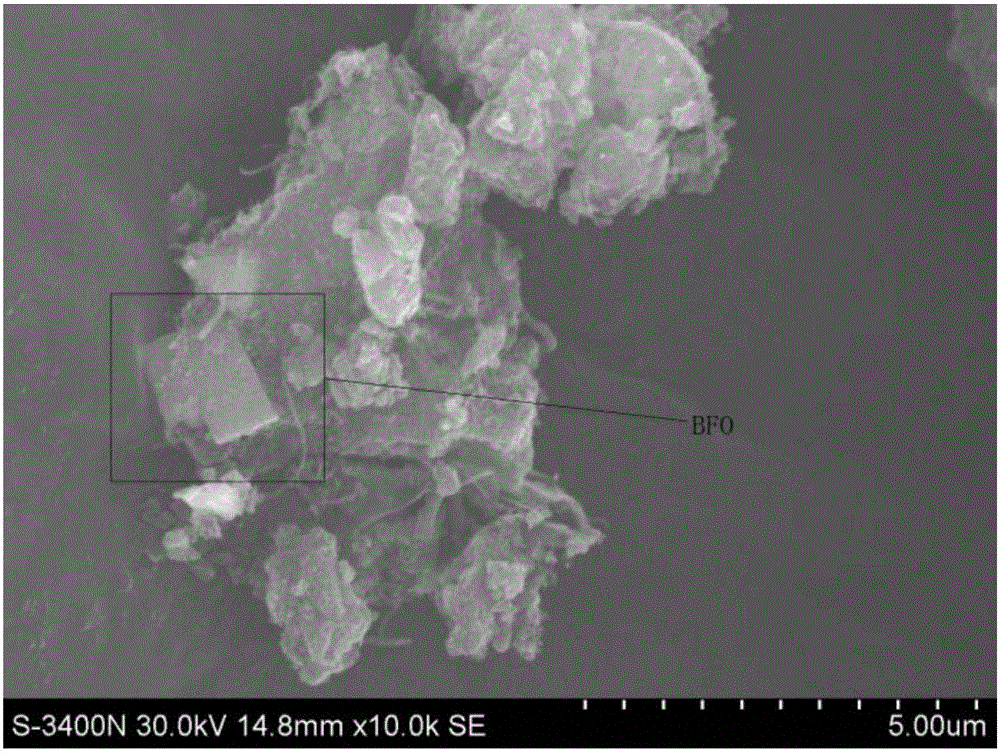
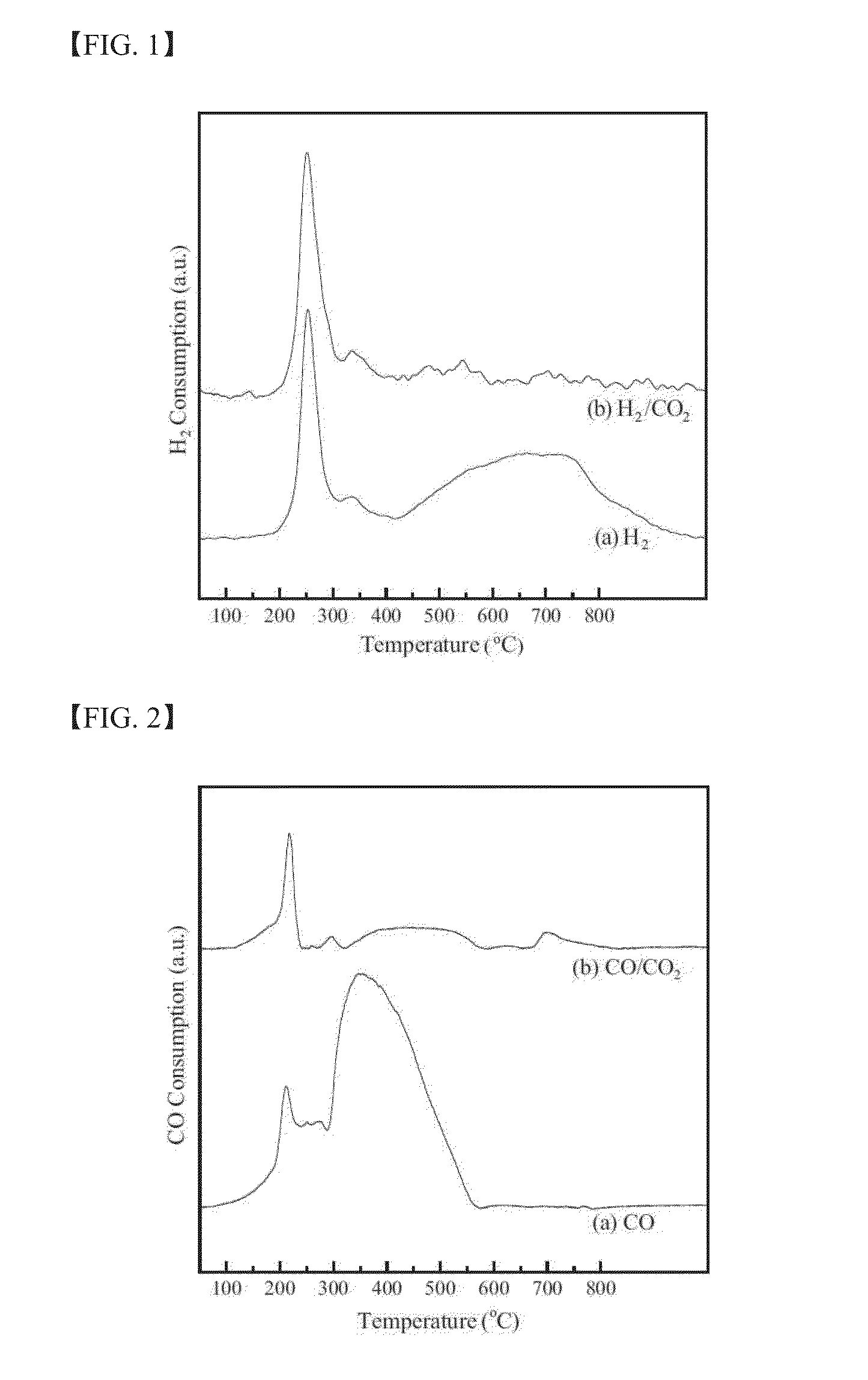
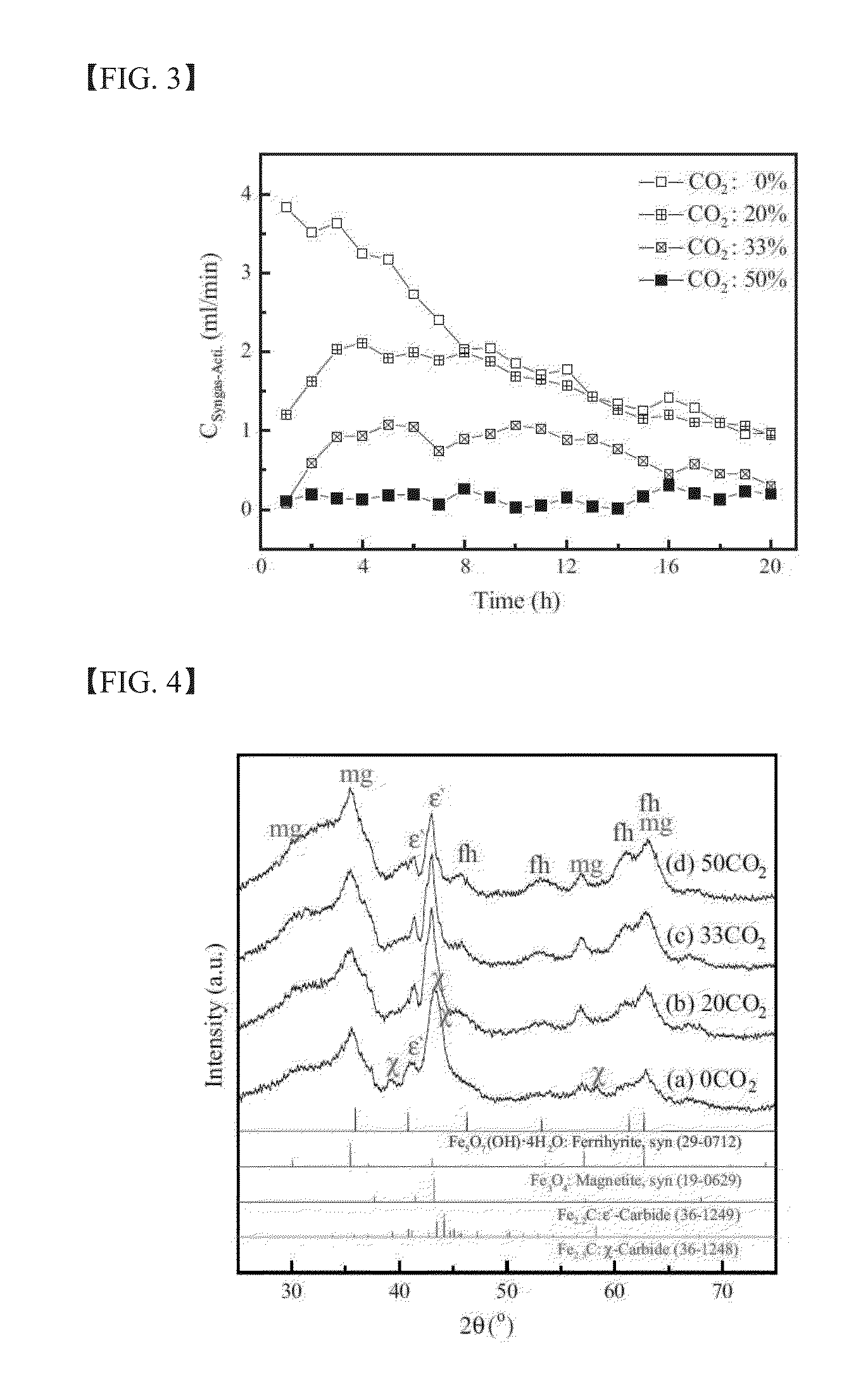
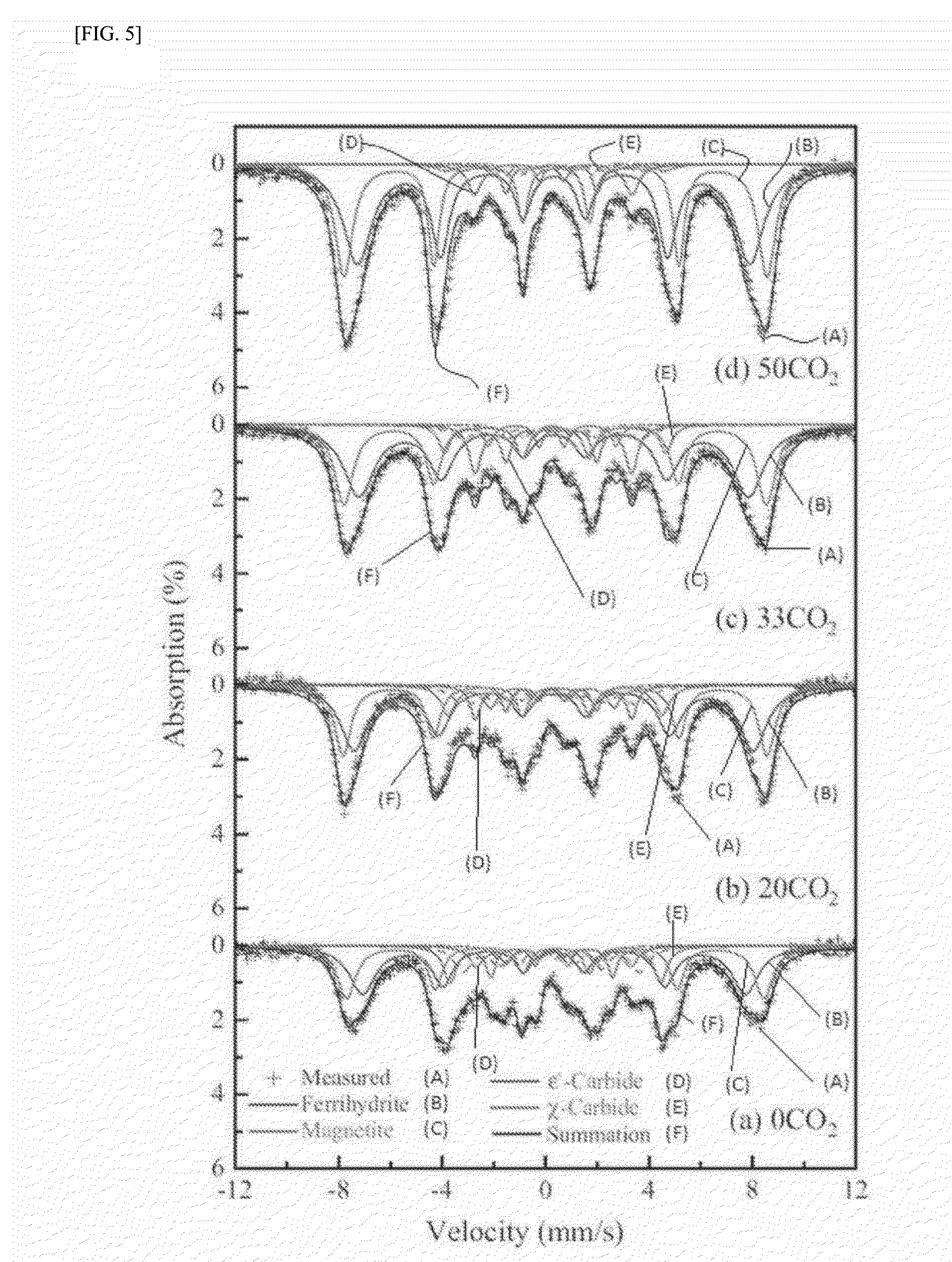
The present invention relates to a method for preparing liquid or solid hydrocarbons from syngas via the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis in the presence of iron-based catalysts, the iron-based catalysts for the use thereof, and a method for preparing the iron-based catalysts; more specifically, in the Fischer-Tropsch reaction, liquid or solid hydrocarbons may be prepared specifically with superior productivity and selectivity for C5+ hydrocarbons using the iron-based catalysts comprising iron hydroxide, iron oxide, and iron carbide wherein the number of iron atoms contained in the iron hydroxide is 30% or higher, and the number of iron atoms contained in the iron carbide is 50% or lower, relative to 100% of the number of iron atoms contained in the iron-based catalysts.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
Cathode active material for a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery and manufacturing method thereof, and a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery that uses cathode active material
ActiveUS20080311473A1Improve discharge capacityExcellent cycle characteristicsFinal product manufacturePositive electrodesManganeseSlurry
The present invention provides a cathode active material that makes possible a high capacity nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery that has excellent discharge load characteristics that provide both good cycle characteristics and thermal stability. The cathode active material comprises a lithium nickel composite oxide having the compositional formula LiNi1−aMaO2 (where, M is at least one kind of element that is selected from among a transitional metal other than Ni, a group 2 element, and group 13 element, and 0.01≦a≦0.5) to which fine lithium manganese composite oxide particle adhere to the surface thereof. This lithium nickel composite oxide is obtained by adding manganese salt solution to a lithium nickel composite oxide slurry, causing manganese hydroxide that contains lithium to adhere to the surface of the lithium nickel composite oxide particles, and then baking that lithium nickel composite oxide.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD +1
Method for directly producing high-purity electronic level cobaltous sulfate by using cobalt-containing waste
ActiveCN102061390AMeet high purity requirementsImprove overall recoveryProcess efficiency improvementTotal recoveryGoethite
The invention provides a method for directly producing high-purity electronic level cobaltous sulfate by using cobalt-containing waste, in particular a process for producing cobaltous sulfate by using cobalt-containing waste. The method comprises the steps of: checking and classifying raw materials, wet-milling and size-mixing, acid-decomposing, filtering, washing, separating, and extracting copper sponge. The method is characterized by also comprising the steps of: removing iron with a goethite process, extracting P2O4 and removing impurities, separating nickel from cobalt, extracting N235, purifying, concentrating and crystallizing. The high purity electron level cobaltous sulfate is directly regenerated by using various kinds of cobalt wastes, the requirement of the modern high-technology industry on high purity of the cobaltous sulfate is met; the total recovery of the cobalt is higher than or equal to 98 percent; various usable elements can be comprehensively recycled, and coppersponge, tungsten carbide, iron hydroxide and nickel carbonate can be regenerated while the electronic level cobaltous sulfate as a main product is regenerated. The invention has the advantages of comprehensively utilizing waste cobalt resources, recycling the wastes, improving the enterprise benefit, and being beneficial to the development of energy conservation, emission reduction, environment protection and circular economy.
Owner:HUNAN JINYUAN NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Methods of improving surface roughness of an environmental barrier coating and components comprising environmental barrier coatings having improved surface roughness
Methods for improving surface roughness of an environmental barrier coating including providing a component having a plasma sprayed environmental barrier coating; applying a slurry to the environmental barrier coating of the component, the slurry being a transition layer slurry or an outer layer slurry; drying the environmental barrier coating having the applied slurry; and sintering the component to produce a component having an improved surface roughness where the slurry includes a solvent; a primary transition material, or a primary outer material; and a slurry sintering aid selected from iron oxide, gallium oxide, aluminum oxide, nickel oxide, titanium oxide, boron oxide, alkaline earth oxides, carbonyl iron, iron metal, aluminum metal, boron, nickel metal, iron hydroxide, gallium hydroxide, aluminum hydroxide, nickel hydroxide, titanium hydroxide, alkaline earth hydroxides, iron carbonate, gallium carbonate, aluminum carbonate, nickel carbonate, boron carbonate, alkaline earth carbonates, iron oxalate, gallium oxalate, aluminum oxalate, nickel oxalate, titanium oxalate, solvent soluble iron salts, solvent soluble gallium salts, solvent soluble aluminum salts, solvent soluble nickel salts, solvent titanium salts, solvent soluble boron salts, and solvent soluble alkaline earth salts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for recovering neodymium and iron from neodymium iron boron oil sludge
ActiveCN103343233AReduce adsorptionHigh purityProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for recovering neodymium and iron from neodymium iron boron oil sludge, belonging to the technical field of recycling of neodymium iron boron oil sludge. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving the neodymium iron boron oil sludge by using hydrochloric acid and filtering undissolved substances, and then, controlling a certain pH value and reaction temperature after oxidizing through adding hydrogen peroxide; sequentially adding ammonium bicarbonate and ammonium hydroxide or hydrofluoric acid and ammonium hydroxide; co-precipitating a neodymium and iron sediment mixture through adsorption among rare earth carbonate, rare earth fluoride and iron hydroxide colloid according to the physical properties of the rare earth carbonate and the rare earth fluoride; and respectively roasting a filtered product at the proper decomposition temperature to obtain a neodymium and iron compound. A complex wet-method process for obtaining single high-purity rare earth in recovery is avoided, and advantageous conditions are provided for subsequently preparing neodymium iron boron regeneration magnetic powder.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for simultaneous removal of cadmium and thallium in raw water
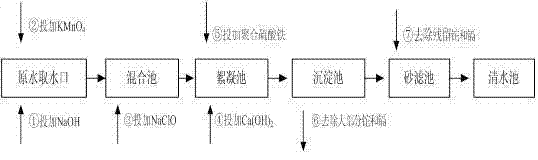
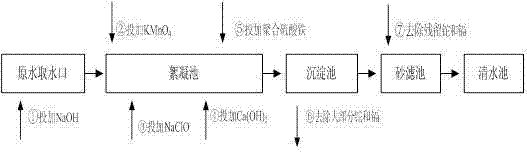
ActiveCN103693774ASimple processEasy to implementWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentCadmium CationTreated water
The invention provides a method for simultaneous removal of cadmium and thallium in raw water. The method comprises the following steps: step A, adding sodium hydroxide into raw water, adjusting a pH value to alkalescence and then adding potassium permanganate with a concentration of 0.3 to 0.8 mg / L; step B, adding sodium hypochlorite or liquid chlorine, wherein the concentration of added sodium hypochlorite or liquid chlorine is 0.5 to 2.5 mg / L in term of effective chlorine; step C, adding limewash into raw water having undergone a full oxidation reaction and adjusting a pH value to 8.5 to 9.0; step D, adding a flocculating agent, carrying out a flocculation reaction for 10 to 20 min and then carrying out deposition for at least 0.5 h so as to remove cadmium, thallium and colloids of manganese hydroxide and iron hydroxide through coprecipitation, wherein the pH value of water after precipitation drops to 7.0 to 8.5; and step E, filtering raw water obtained after precipitation by using quartz sand. The invention has the following beneficial effects: cadmium concentration of treated water is as small as the limit of a detection method, i.e., 0.02 mu g / L, or less than 0.02 mu g / L; thallium concentration of treated water is as small as the limit of a detection method, i.e., 0.01 mu g / L, or less than 0.01 mu g / L; and the pH value, manganese ions and iron ions of the treated water all meet requirements prescribed in drinking water quality standards.
Owner:SHENZHEN WATER GRP CO LTD
Method for treating sewage through catalytic oxidation
InactiveCN102030432AReduce generationReduce productionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationOrganic acidCatalytic oxidation
The invention relates to a method for treating sewage through catalytic oxidation, which comprises the following steps of: introducing sewage to be treated into an oxidation reactor, controlling the pH value of the sewage to be less than 7, adding an oxidant, a catalyst and a complexant for performing a catalytic oxidation reaction, and separating sewage and waste residues obtained after the reaction. The complexant is an organic acid metal complexant. The addition of the complexant in the invention enables iron ions and the complexant to produce a complex compound so as to reduce the generation of iron hydroxide precipitates, and thus, more iron ions can participate in the catalytic oxidation process. The utilization efficiency of the catalyst is increased, the consumption of the catalyst can be reduced, and simultaneously, the generation of waste residues can be reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Separation of minerals
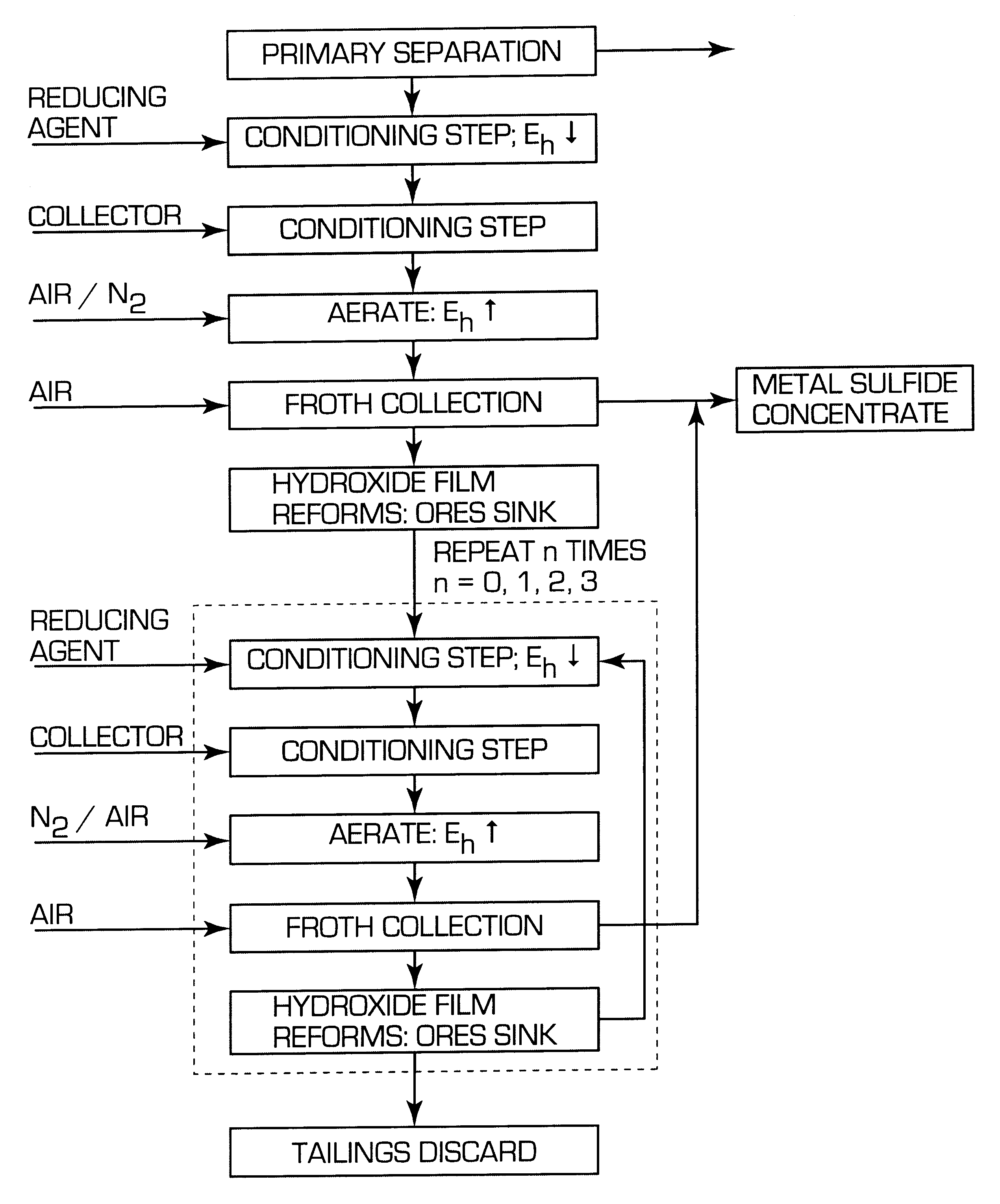
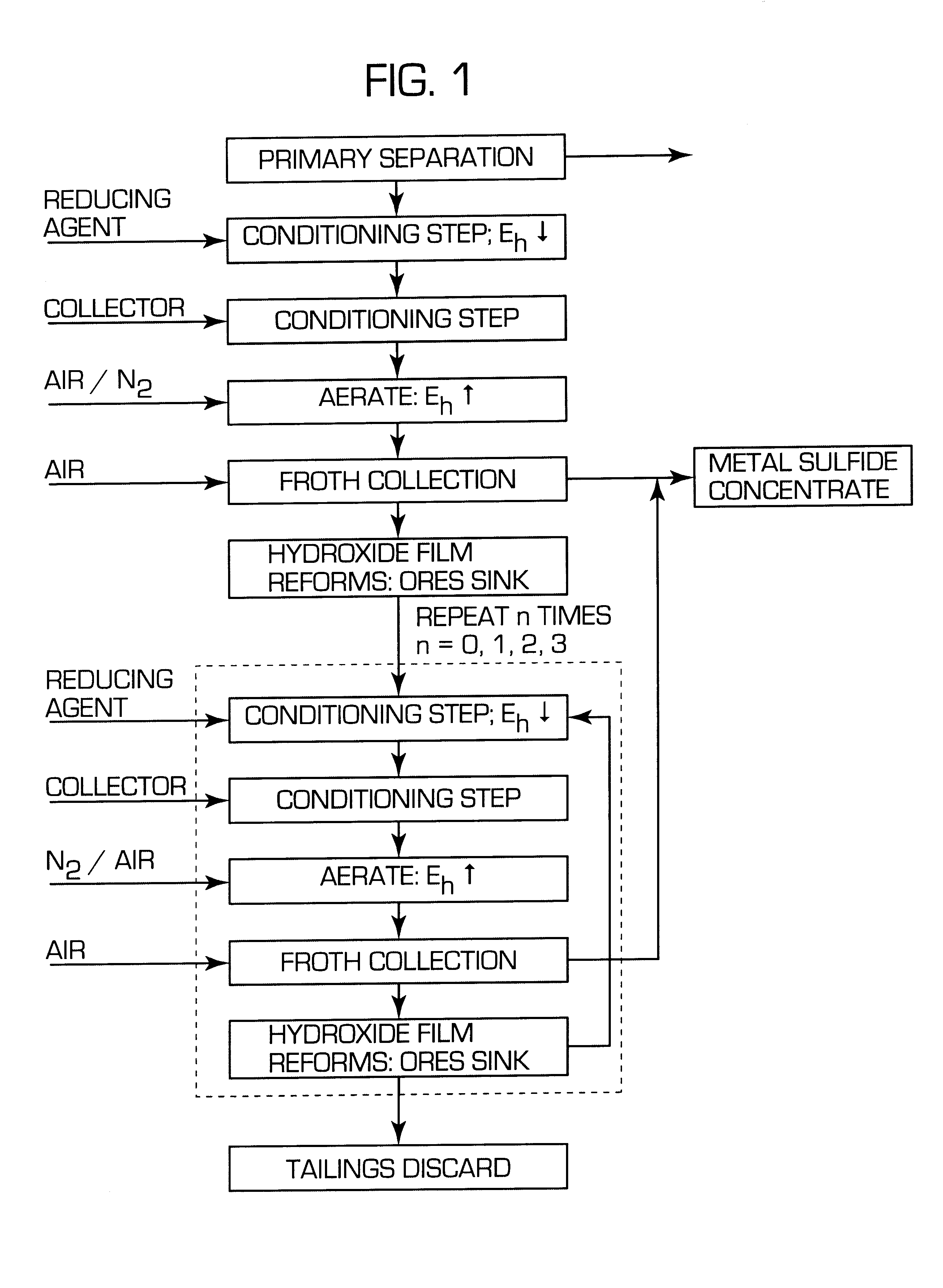
A process for floating fine particles containing metal values of an iron-bearing sulphide mineral ore including the steps of conditioning the aqueous pulp of ore at a pH of between about 7 and about 10 with a reducing agent which is preferably oxy-sulphur compound which dissociates to form oxy-sulphur ions having the general formula:where n is greater than 1; y is greater than 2; and z is the valance of the ion.A suitable collector is then added to the conditioned aqueous pulp to further condition the pulp and the pulp potential of the pulp raised to a sufficient level for the collector to adsorb onto the sulphide mineral ore. Gas is then bubbled through the aqueous pulp to subject the pulp to froth flotation. The froth from the flotation process is recovered to produce a concentrate of fine sulphide mineral and other metal values.By conditioning the aqueous pulp at a pulp potential which dissolves the iron hydroxide film from the surface of the metal sulphide inclusions in the ore and subjecting the ore to froth flotation at a suitable pulp potential before the iron hydroxide can reform, the recovery of metal values in the fine ores can be greatly enhanced.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Preparation method of graphene supported ferriferrous oxide nanocomposite
InactiveCN102660220ASimple structureGood crystallizationMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesCarbon nanotubeNanocomposite
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene supported ferriferrous oxide nanocomposite, comprising the following steps: preparing a precursor by deposition precipitation method, depositing ferric nitrate ninehydrate or ferric chloride hexahydrate on graphene in the form of iron hydroxide by using sodium hydroxide or ammonia to obtain black powder, washing and drying the obtained black powder, grinding the dried black powder, then calcining under the protection of argon, and then cooling, and reducing under the protection of a mixed gas of argon and hydrogen or argon and ammonia gas to obtain the graphene supported ferriferrous oxide nanocomposite. The preparation method is simple and stable. In the obtained composite, ferriferrous oxide is uniformly distributed on graphene and has good interface combination of the substrate graphene, thus the absorbing properties and the like of the composite as a functional material can be improved. The method also can be used for preparing carbon material supported ferriferrous oxide nanocomposites with different substrates by using carbon nanotube, graphite oxide and other carbon materials as the substrate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Ferronickel hydroxide/reduction-oxidation graphene electrochemical oxygen evolution catalyst with nickel foam as carrier and preparation method of ferronickel hydroxide/reduction-oxidation graphene electrochemical oxygen evolution catalyst
InactiveCN108707923AHigh activityImprove stabilityLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectrode shape/formsIron saltsNickel salt
The invention relates to a ferronickel hydroxide / reduction-oxidation graphene electrochemical oxygen evolution catalyst with nickel foam as a carrier and a preparation method of the ferronickel hydroxide / reduction-oxidation graphene electrochemical oxygen evolution catalyst. The nickel foam is used as the carrier of the catalyst, ferric hydroxide, nickel hydroxide or a compound of the ferric hydroxide and the nickel hydroxide is used as the active component of the catalyst, and reduction-oxidation graphene is used as the conductive material of the catalyst. The catalyst is prepared through a water heating and impregnation method. Firstly, the nickel foam is subjected to ultrasonic cleaning and drying; then, a certain amount of nickel salt and a certain amount of urea are weighed, dissolvedin deionized water and stirred to be evenly mixed at the room temperature; then, oxidized graphene is added, ultrasonic treatment is conducted, and evenly-dispersed mixed liquor is obtained; the nickel foam and the mixed liquor are transferred into a water heating kettle and react for 12 h to 24 h at the temperature being 120-200 DEG C; the nickel foam subjected to reaction is cleaned and dried;and finally, after the nickel foam is soaked in an iron salt solution with the concentration ranging from 5 mmol / L to 30 mmol / L for 0 h to 48 h, cleaning and drying are conducted, and the ferronickelhydroxide / reduction-oxidation graphene electrochemical oxygen evolution catalyst with the nickel foam as the carrier is obtained. The catalyst is good in catalysis activity and high in stability; andthe preparation method is simple and controllable, and industrial popularization is facilitated.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Atmospheric pressure leach process for lateritic nickel ore
An atmospheric leach process in the recovery of nickel and cobalt from lateritic ores, said processing including the steps of: a) separating the lateritic ore into a low magnesium containing ore fraction, and a high magnesium containing ore fraction by selective mining or post mining classification; b) separately slurrying the separated ore fractions; c) leaching the low magnesium containing ore fraction with concentrated sulphuric acid as a primary leach step; and d) introducing the high magnesium content ore slurry following substantial completion of the primary leach step and precipitating iron as goethite or another low sulphate containing form of iron oxide or iron hydroxide, wherein sulphuric acid released during iron precipitation is used to leach the high magnesium ore fraction as a secondary leach step.
Owner:CERRO MATOSO
Preparation method of bagasse active carbon/ferric oxide
InactiveCN101757892ASimple processReduce manufacturing costOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionOxide compositeChemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of bagasse active carbon / ferric oxide, which comprises the following steps of: adding 800ml of distilled water into a 2L beaker, adding 100ml of 0.01-0.1mol / L hexadecyl trimethylamine bromide into the 2L beaker, heating and boiling; slowly dropwise adding 100ml of 0.5-2.5mol / L ferric chloride solution in stirring to obtain a brownish red colloid; adding 20-60g of bagasse into the brownish red colloid, stirring and standing for 24 hours; slowly adding ammonia water with the volume ratio of 1.0-10.0 percent into the 2L beaker under stirring by using an automatic titrimeter and regulating pH to 7.4 to obtain water solution of a bagasse / iron hydroxide mixed suspended matter; filtering the water solution of the bagasse / iron hydroxide mixed suspended matter and drying 105-110 DEG C to obtain a bagasse / iron hydroxide mixture; respectively carbonizing the bagasse / iron hydroxide mixture at 400-600 DEG C to obtain an active carbon / ferric oxide composite; and grinding the active carbon / ferric oxide composite with over 60 meshes. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process and low cost, and the prepared product can be widely applied to dephosphorization production procedures in city town sewage treatment plants.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation of iron (II) acetate powder from a low grade magnetite
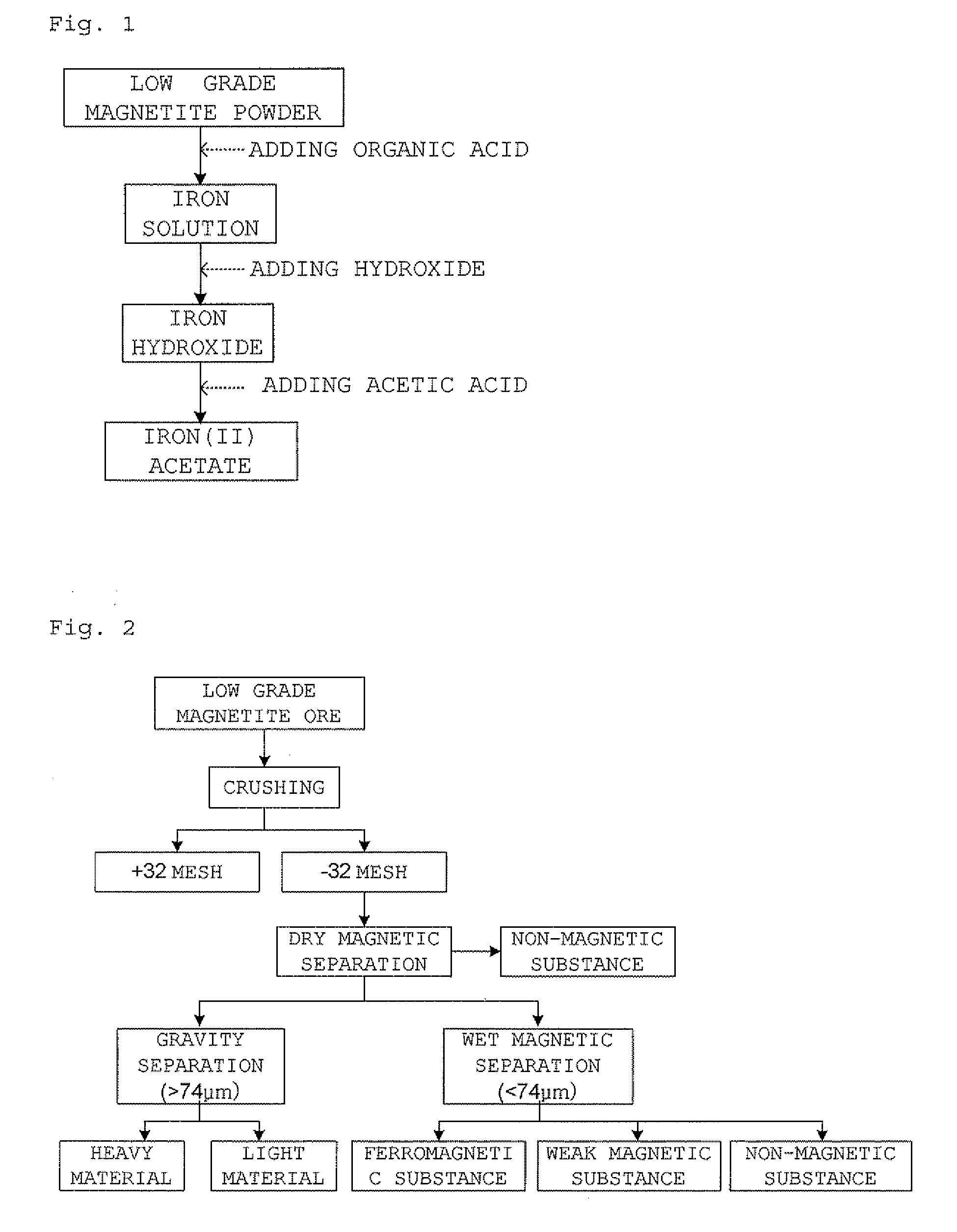
InactiveUS20090105493A1High yieldShort reaction timeOrganic compound preparationIron organic compoundsAcetic acidOrganic acid
The present invention relates to a preparation of iron(II) acetate powder from low grade magnetite and comprises the following steps: (a) adding organic acid to low grade magnetite powder to obtain iron solution; (b) adding hydroxide to the iron solution to obtain iron hydroxide; and (c) adding acetic acid to the iron hydroxide, thereby obtaining iron(II) acetate.According to the present invention, it is possible to obtain high purity iron(II) acetate using low grade magnetite and there are advantages of mass producible environmentally-friendly simple process and prevention of corrosion of facilities.
Owner:KOREA INST OF GEOSCI & MINERAL RESOURCES
Method of comprehensively recycling valuable metals in plating sludge
The invention belongs to the technical field of plating sludge treatment and discloses a method of comprehensively recycling valuable metals in plating sludge. The method comprises: extracting value metals from plating sludge by leaching, and isolating acid leaching residue and acid leaching liquid; adding iron powder, stirring, and filtering to isolate copper powder and a mother liquid; adding hydrogen peroxide and sodium carbonate solution, adding a composite flocculating agent so that iron ions in the solution form iron hydroxide precipitate and chromium ions form chromium hydroxide precipitate, wherein the precipitates settle fast, and isolating ferrochromium slag and a mother liquid containing zinc and nickel; using P507 extracting agent to extract zinc in the mother liquid containingzinc and nickel, back-extracting an organic phase via sulfuric acid to obtain zinc sulfate solution, and crystallizing to obtain zinc sulfate septahydrate; adding the sodium hydroxide solution into nickel raffinate, filtering to obtain nickel hydroxide precipitate, adjusting mother liquid pH to 7 for the filtrate through sulfuric acid, and crystallizing to isolate sodium sulfate decahydrate. Precipitate washing liquids herein are cyclically used, emission of wastewater is decreased, and significant economic and social benefits are created.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
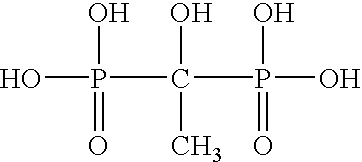
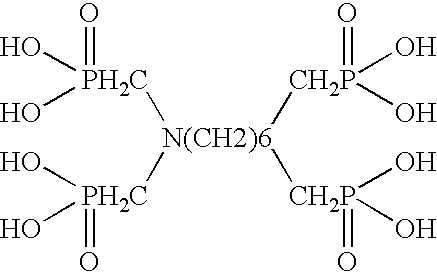
Ammonium polyphosphate solutions containing multi-functional phosphonate corrosion inhibitors
InactiveUS6846437B2Reduce corrosionOther chemical processesLiquid fertilisersSuspending AgentsFerrous Gluconate
A corrosion-inhibited fire retardant composition is provided that comprises at least one ammonium polyphosphate, at least one suspending agent, at least one phosphonate selected from a group consisting of aminotri(methylenephosphonic acid), 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid, hexamethylenediaminetetra(methylenephosphonic acid), diethylenetriaminepenta(methylenephosphonic acid), salts thereof, and mixtures thereof and a corrosion inhibiting system. The corrosion inhibiting system is comprised of at least one corrosion inhibiting compound selected from a group consisting of azoles, insoluble ferric pyrophosphate, soluble ferric pyrophosphate, ferrous oxalate, ferric citrate, ferrous sulfate, ferric ammonium citrate, insoluble ferric orthophosphate, soluble ferric orthophosphate, ferric ammonium oxalate, ferric ammonium sulfate, ferric bromide, ferric sodium oxalate, ferric stearate, ferric sulfate, ferrous acetate, ferrous ammonium sulfate, ferrous bromide, ferrous gluconate, ferrous iodide, ferric acetate, ferric fluoroborate, ferric hydroxide, ferric oleate, ferrous fumarate, ferrous oxalate, ferrous oxide, ferric lactate, ferric resinate, and any combination thereof. Methods of making and using the same are also described. In addition, agricultural plant nutrients comprising the same are provided.
Owner:PERIMETER SOLUTIONS LP
Method for manufacturing nanometer iron
The invention relates to an iron super-micro particle preparation technique, belongs to radiation chemical nanometer material production technique. The technique of the invention is that: nanometer material preparation: obtain iron hydroxide colloid solution by using iron sulfate as raw material and ammonia liquor as precipitant; control the crystal core accumulating speed and the particle size by hydrophilic surface-activator polyvinyl alcohol with isopropyl alcohol as free radical scavenger and in radiation chemistry principles; develop the radiation chemical reaction by the bunch of electrons generated by industrial electron accelerator; the radiated solution produces nanometer triple iron quadoxide which deoxidated with high purity hydrogen to obtain nanometer iron powder. The advantages of the invention are that: simple technical processes, short production cycle, non-pollution, the obtained particles are of uniform diameter and finely divided. The nanometer iron produced in above ways is of higher satiating hard magnetism and coercive force which is applicable on high intensity magnetic recording material..
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Fire retardant compositions with reduced aluminum corrosivity
InactiveUS6905639B2Reduced-tendency to corrode various metalBroaden applicationFireproof paintsAntifouling/underwater paintsBiopolymerFerrous Gluconate
Corrosion-inhibited fire retardant compositions and methods of making and using the same are provided. The corrosion-inhibited fire retardant compositions are comprised of at least one fire retardant component, at least one biopolymer having a particle size diameter of less than about 100 microns, and a corrosion inhibiting system. The corrosion inhibiting system is comprised of at least one corrosion inhibiting compound selected from a group of compounds including azoles, insoluble ferric pyrophosphate, soluble ferric pyrophosphate, ferrous oxalate, ferric citrate, ferrous sulfate, ferric ammonium citrate, soluble ferric orthophosphate, insoluble ferric orthophosphate, ferric ammonium oxalate, ferric ammonium sulfate, ferric bromide, ferric sodium oxalate, ferric stearate, ferric sulfate, ferrous acetate, ferrous ammonium sulfate, ferrous bromide, ferrous gluconate, ferrous iodide, ferric acetate, ferric fluoroborate, ferric hydroxide, ferric oleate, ferrous fumarate, ferrous oxide, ferric lactate, ferric resinate and any combination thereof. In a specific embodiment, the corrosion-inhibited fire retardant composition includes a xanthan biopolymer.
Owner:PERIMETER SOLUTIONS LP
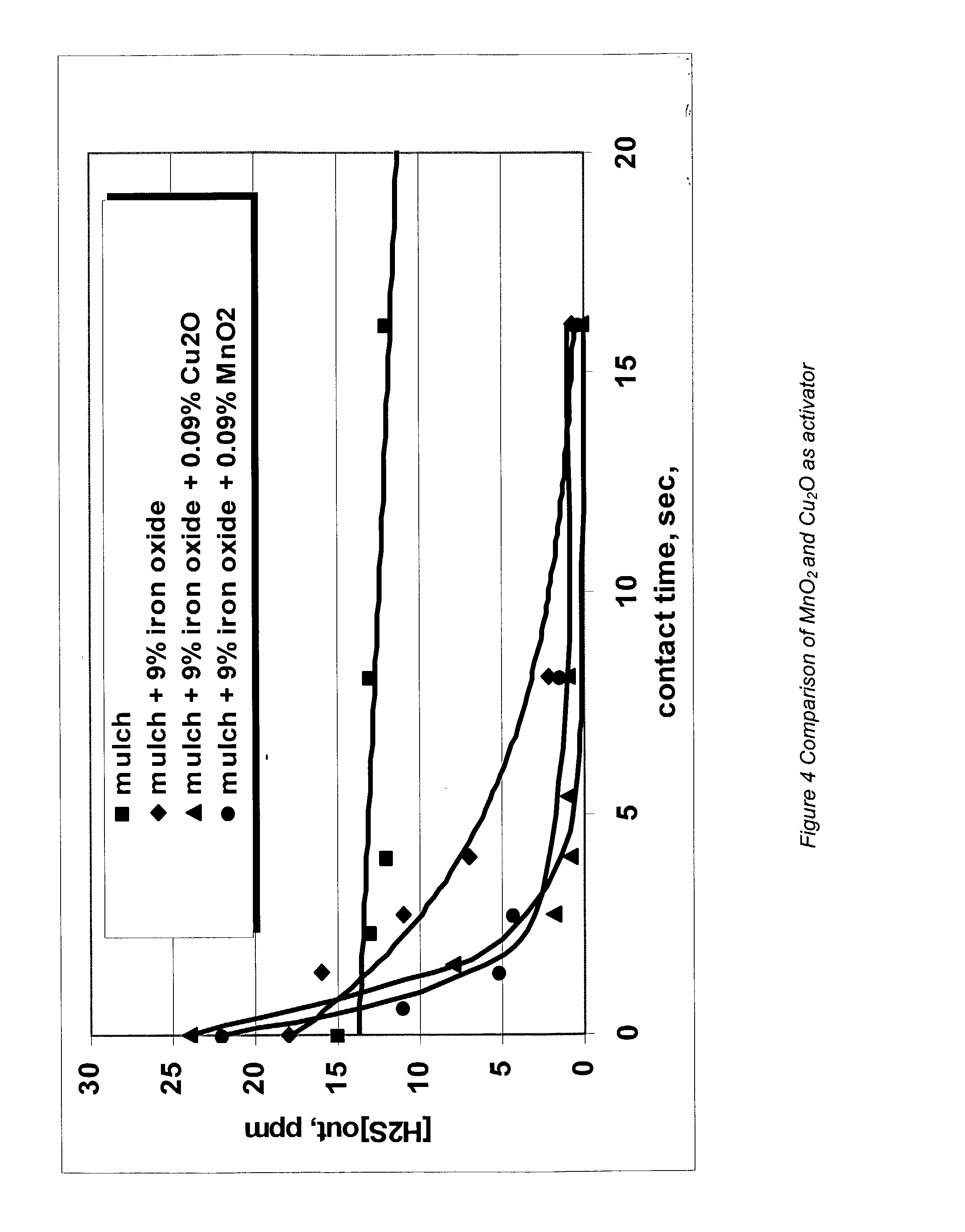
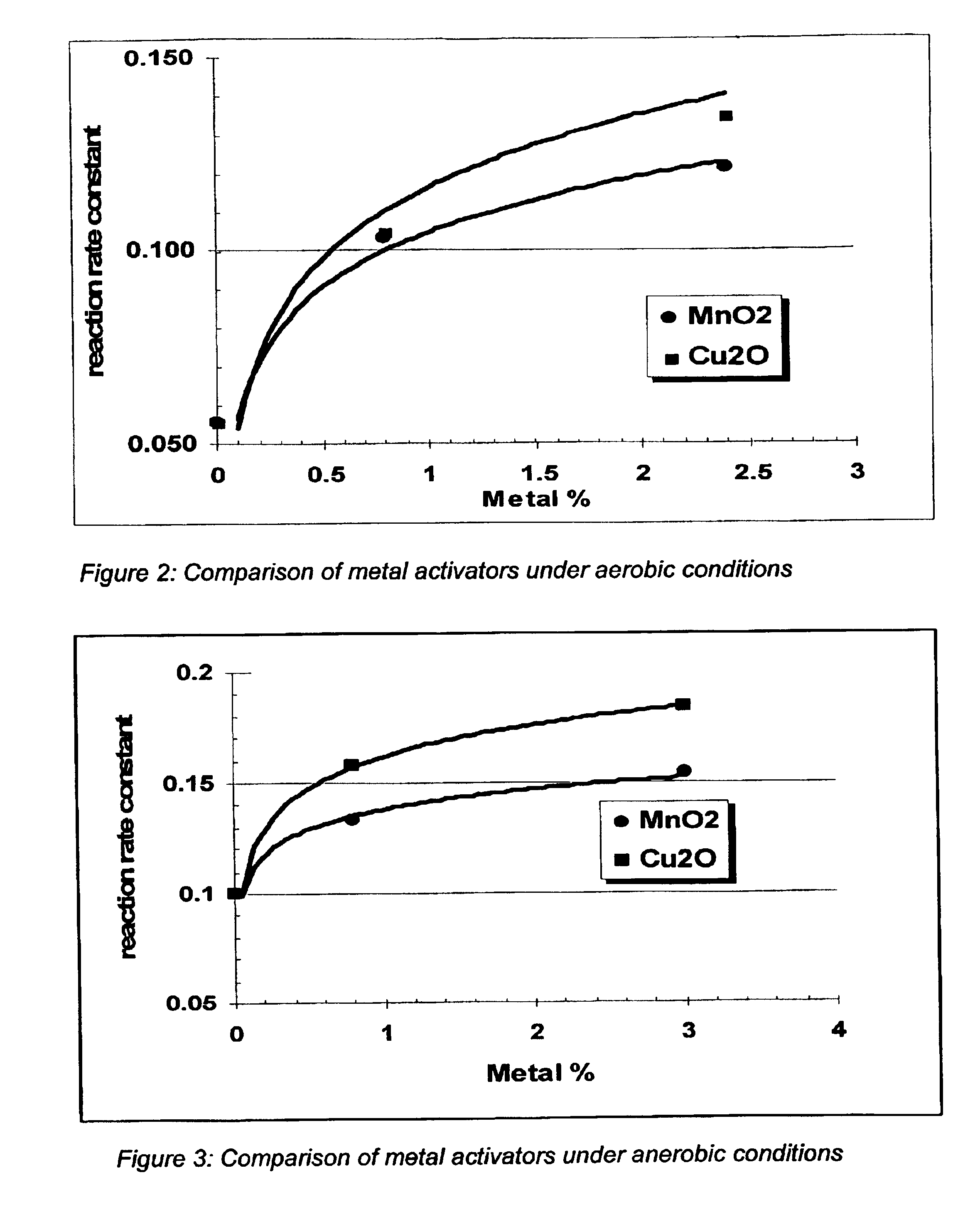
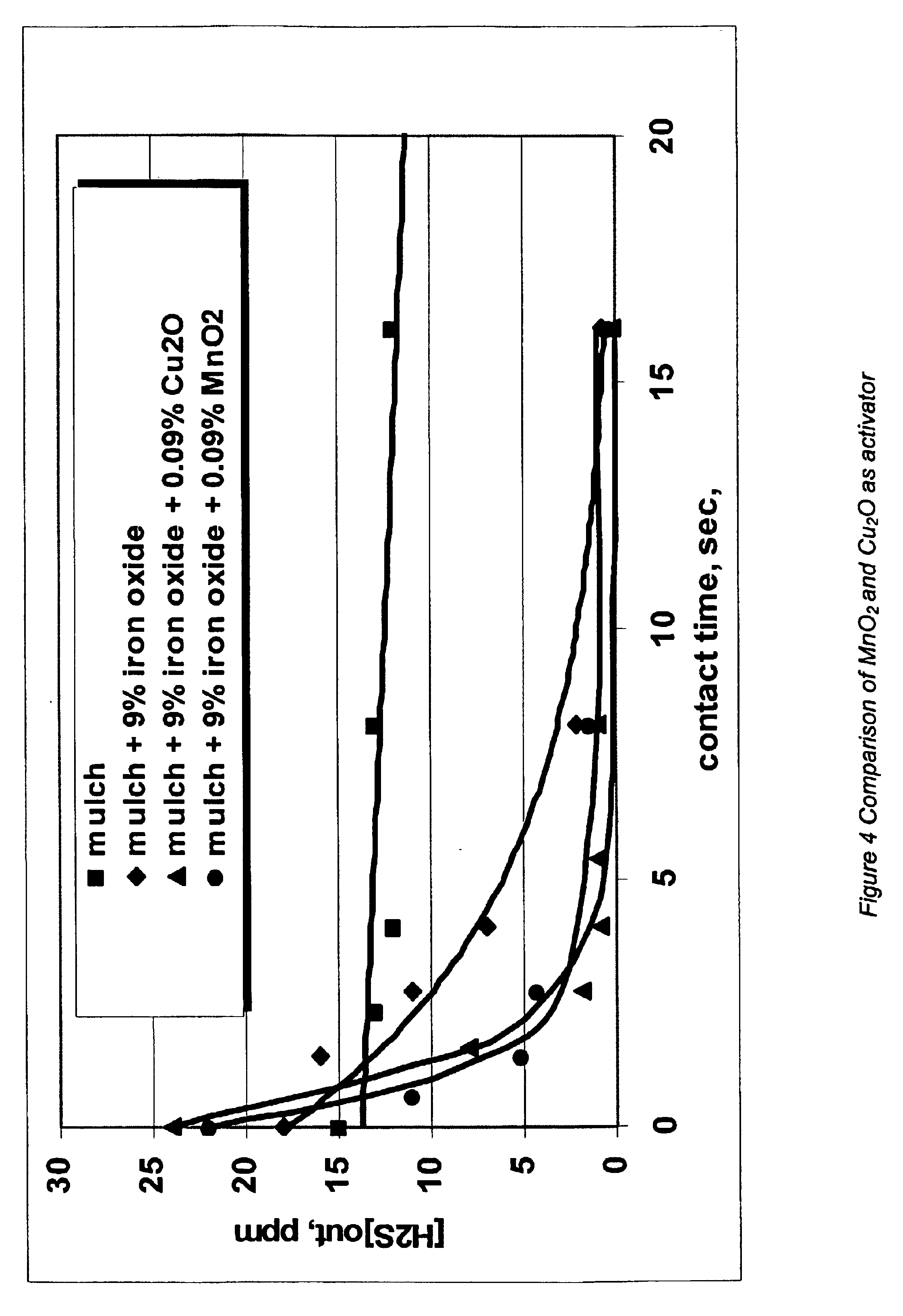
Process and composition for increasing the reactivity of sulfur scavenging oxides
InactiveUS20020182135A1Increase response rateRaise the potentialPhysical/chemical process catalystsOther chemical processesZinc hydroxideManganese oxide
In ridding fluids, including hydrocarbon fluids, both gaseous and liquid, of sulfur compounds including hydrogen sulfide, oxides of sulfur, and thiols, the present invention uses a small quantity of an activator, generally a noble metal oxide, preferably a copper species and / or a manganese species, along with a known oxide product, such as iron oxide, iron hydroxide, zinc oxide, zinc hydroxide, manganese oxide, manganese hydroxide, or combinations thereof, to thoroughly remove sulfur contaminants in a short amount of time. The activator allows for the use of smaller reactor vessels and the production of hydrocarbon fluids substantially free of sulfur products.
Owner:MI
Method for producing nano-magnetic FeO particle by iron extracted and utilized in tin tails
InactiveCN101029355AImprove utilizationReduce pollutionFerroso-ferric oxidesProcess efficiency improvementNanometreIron(III) oxide-hydroxide
Production of magnetic nano-Fe3O4 by iron in tin tails is carried out by extracting while separating out iron element by wetting metallurgical technology, reduction-chemical co-depositing to obtain magnetic nano-Fe3O4, extracting while controlling hydrolytic temperature, ageing, secondary depositing to obtain high-purity ironic hydroxide deposits and surface coating by surface activator to obtain Fe3O4 grain with grain size<10nm. It is efficient and can obtain fine and uniform grain size. It can be used for magnetization, catalytic and biological industries.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for establishing photo-Fenton system for tetracycline degradation based on composite bismuth ferrite material
InactiveCN106242015AIncrease profitImprove degradation efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsDissolutionControllability
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
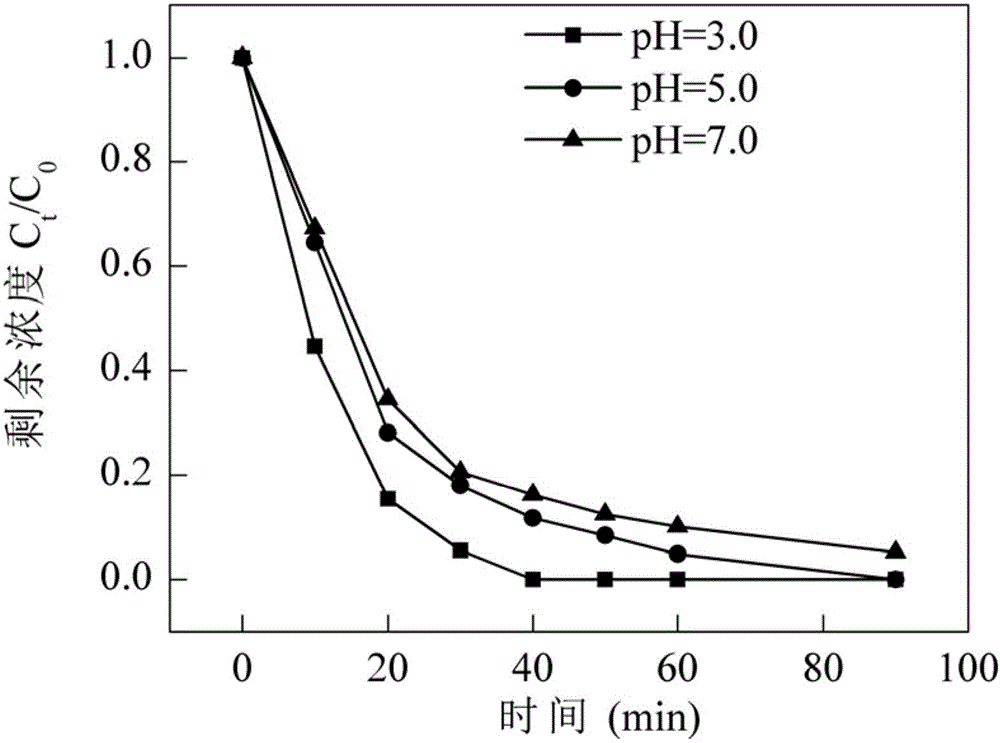
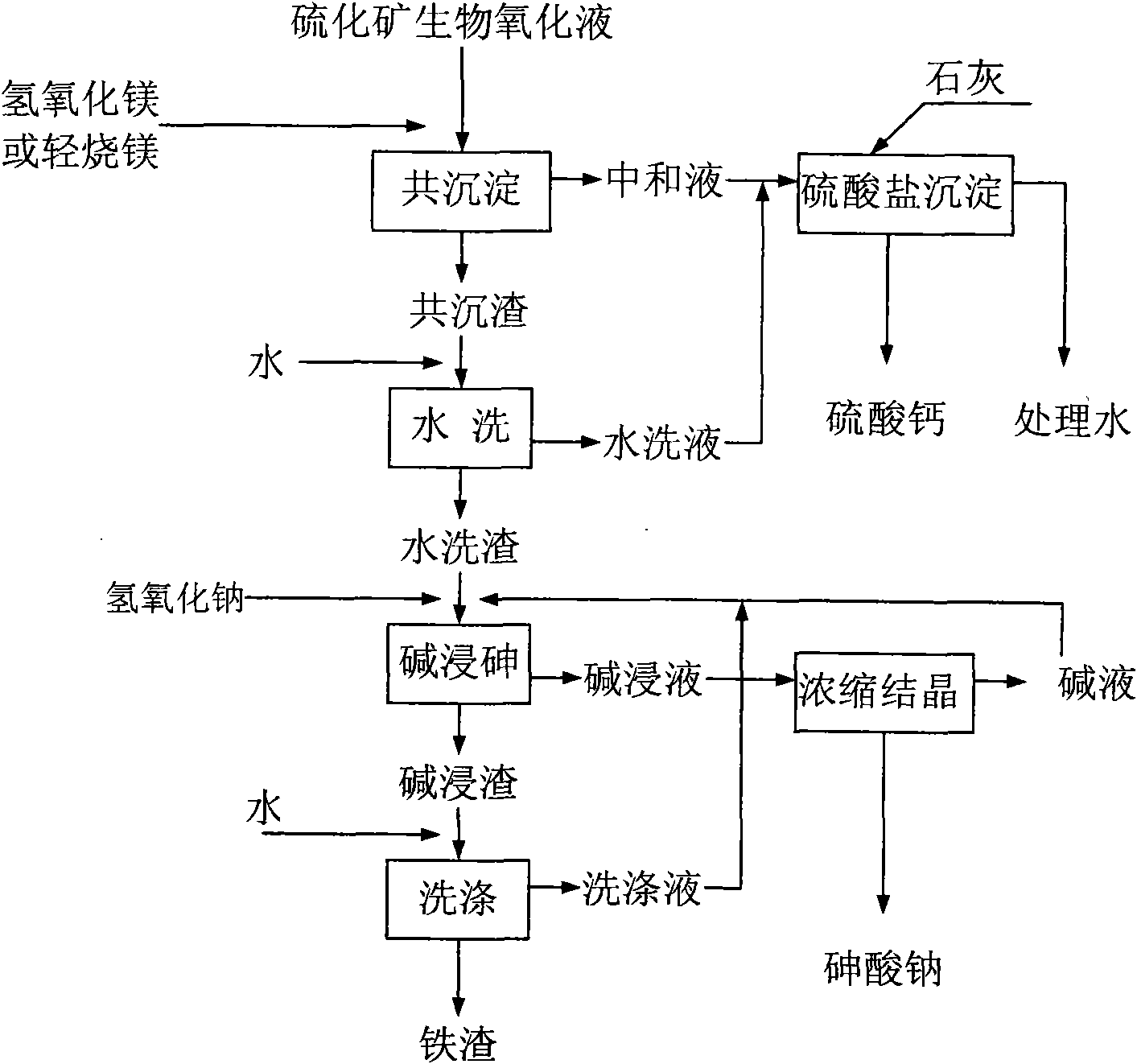
Method for separating and recycling arsenic and iron from biological oxidation solution of sulfide ore
ActiveCN101586185AReduce consumptionEasy to operateIron oxides/hydroxidesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesTreated waterSodium hydroxide
The present invention provides a method for separating and recycling arsenic and iron form the biological oxidation solution of sulfide ore and belongs to the technique. According to the method, firstly magnesium oxide is added into the biological oxidation solution of sulfide ore, then the pH value is adjusted to 5-6 so that the arsenic and iron in the biological oxidation solution generate coprecipitation, and the precipitate comprising iron and arsenic precipitate and the neutralizing agent are obtained through separating. Then the lime is added into the neutralizing solution so that the pH value obtains 8-10. The magnesium sulfate in the neutralizing agent and the lime generate calcium sulfate and magnesium hydroxide precipitate. The precipitate containing calcium sulfate and the treated water are separated. The separated water returns to the production system and the precipitate is recycled as the building material. After the coprecipitate is dried, water is added for leaching the magnesium sulfate in the coprecipitate. The precipitate after leaching and the water extract are separated. The water extract is combined with the neutralizing agent for entering the processing operation of the neutralizing agent. The arsenic in the precipitate after leaching is leached by the sodium hydroxide solution, and the arsenic leaching solution and the iron hydroxide precipitate are obtained after separation. The arsenic leaching solution is heated, evaporated and condensed to the arsenic content of 40g / L-60g / L. Then the solution is cooled for crystallizing. The sodium arsenate and the crystal mother liquor are obtained through separation. The mother liquor returns to the arsenic leaching system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST +1
Process for sulfur scavenging
InactiveUS6887445B2Increase response rateRaise the potentialOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationZinc hydroxideManganese oxide
Owner:MI
Method for removing multiple pollutants in copper smelting waste acid by using Bayer process red mud
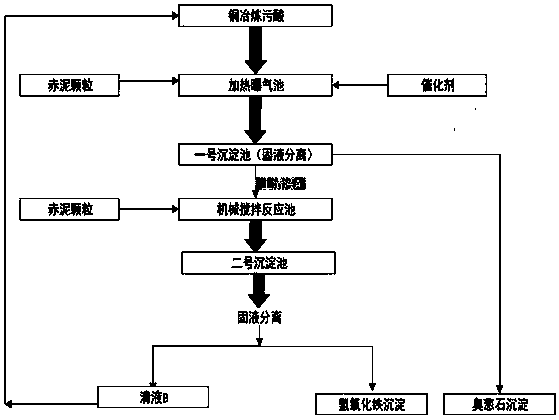
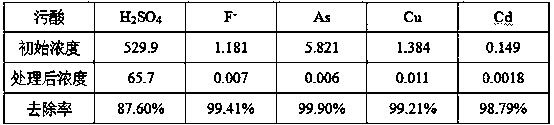
ActiveCN108128917AEnable co-processingReduce secondary pollutionWaste water treatment from metallurgical processMultistage water/sewage treatmentIron saltsRed mud
The invention relates to a method for removing multiple pollutants in copper smelting waste acid by using Bayer process red mud. The method comprises the steps of oxidizing trivalent arsenic into pentavalent arsenic in the waste acid by using a way of continuously aerating while heating; then, adding Bayer process red mud particles, controlling an arsenic-iron molar ratio and a pH value, forming amorphous iron arsenate by using iron in the Bayer process red mud and arsenic in the copper smelting waste acid, and then oxidizing to form stable iron arsenate so as to remove the arsenic in the waste acid and absorb the multiple pollutants in the waste acid. After the scheme is adopted, iron salt used for treating the arsenic does not need to be additionally added, so that the economic cost is reduced; the method realizes the co-disposal of the solid waste produced by the copper smelting industry and the Bayer process red mud produced by the alumina industry, and reduces the secondary pollution to the environment. The method also can obtain iron hydroxide with an economic value by controlling the pH value while changing the Bayer process red mud waste into valuable and treating the wasteacid; due to the increment and decrement of input cost, an enterprise can obtain considerable economic benefit.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing high-power lithium iron phosphate composite materials
InactiveCN101621121ASolving Diffusion ProblemsSolve essential problemsElectrode manufacturing processesChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesIron saltsHigh rate
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-power lithium iron phosphate composite materials, which belongs to the technical field of the preparation of lithium battery materials. The invention aims to provide the method for preparing the high-power lithium iron phosphate composite materials which can solve the problem that lithium iron phosphate has low electronic conductivity and difficult ion diffusion in high rate discharge. The invention is technically characterized by making carbon nanotubes reflux in concentrated nitric acid containing iron salt, adding ammonia water and hydroxide ions in a lithium source into the concentrated nitric acid to react to obtain iron hydroxide suspension solution embedded with the carbon nanotubes; then adding phosphate solution into the iron hydroxide suspension solution to obtain iron phosphate suspension solution embedded with the carbon nanotubes; and performing distillation on the iron phosphate suspension solution under reduced pressure to obtain a precursor of the lithium iron phosphate, and grinding the precursor and performing high-temperature sintering in a reductive and inert atmosphere to obtain the high-conductivity lithium iron phosphate composite materials. The lithium iron phosphate composite materials have good shapes with an average grain diameter of 10 to 100nm and excellent electrochemical performance, are particularly suitable for ultrahigh rate discharge requirement, and can meet the requirement of sustained 30C discharge and pulse 100C discharge.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Process for the preparation of iron-oxide-and/or iron-oxyhydroxide-containing ion exchangers
InactiveUS20060264521A1Cation exchanger materialsElectrolysis componentsIon exchangeIron oxyhydroxide
Owner:PODSZUN WOLFGANG +4
Method for preparing nanocrystalline lithium iron phosphate powder by adopting iron hydroxide colloid
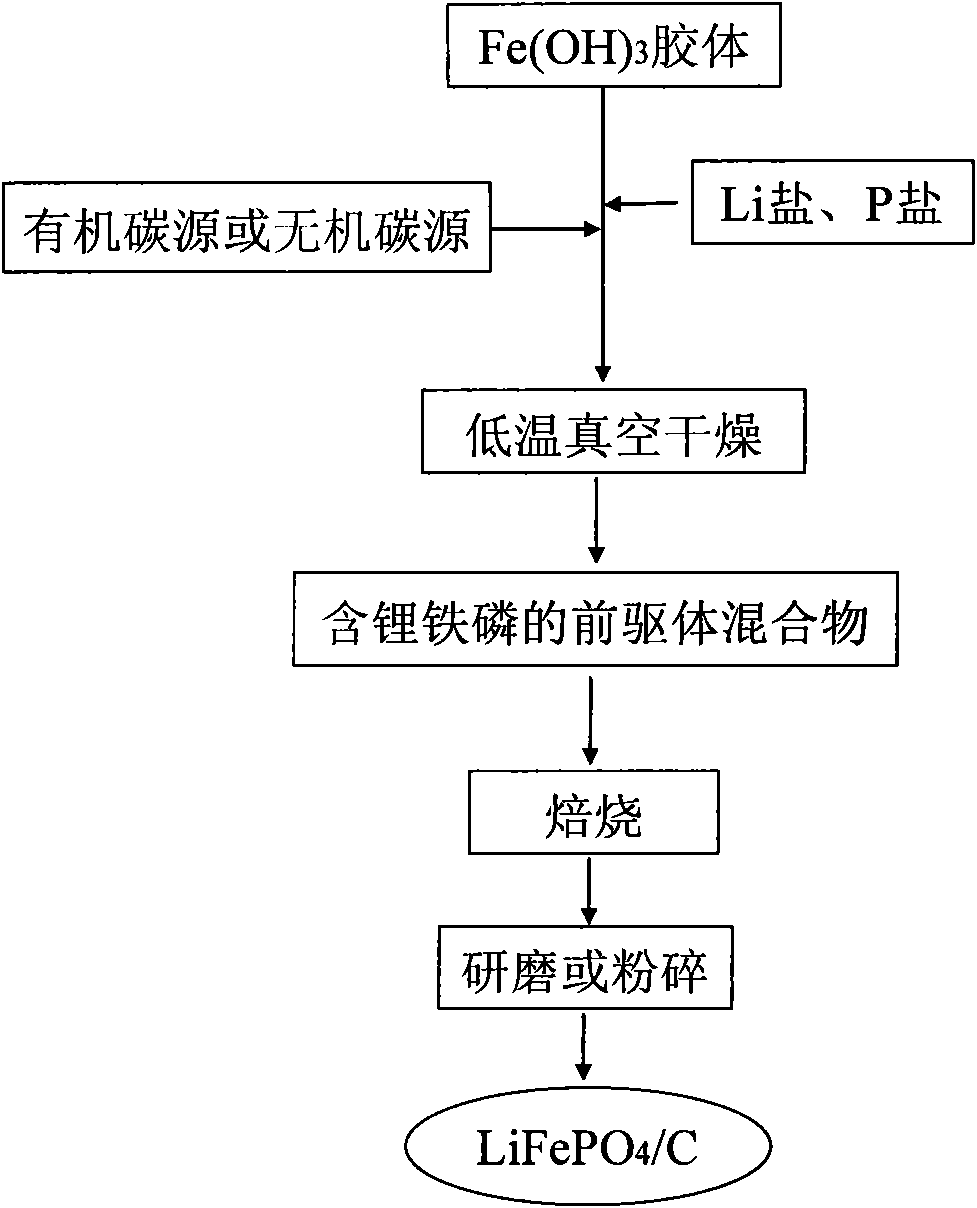
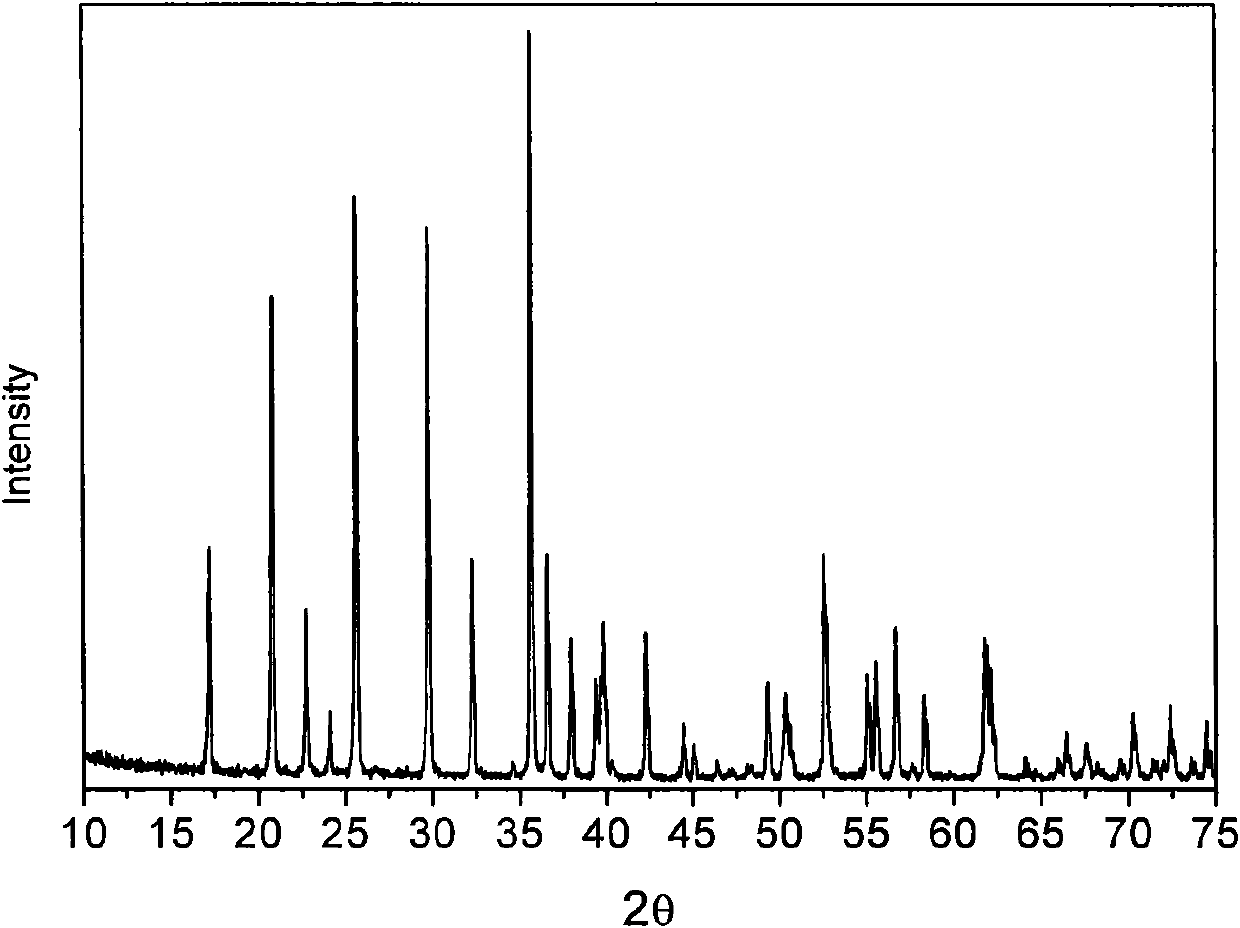
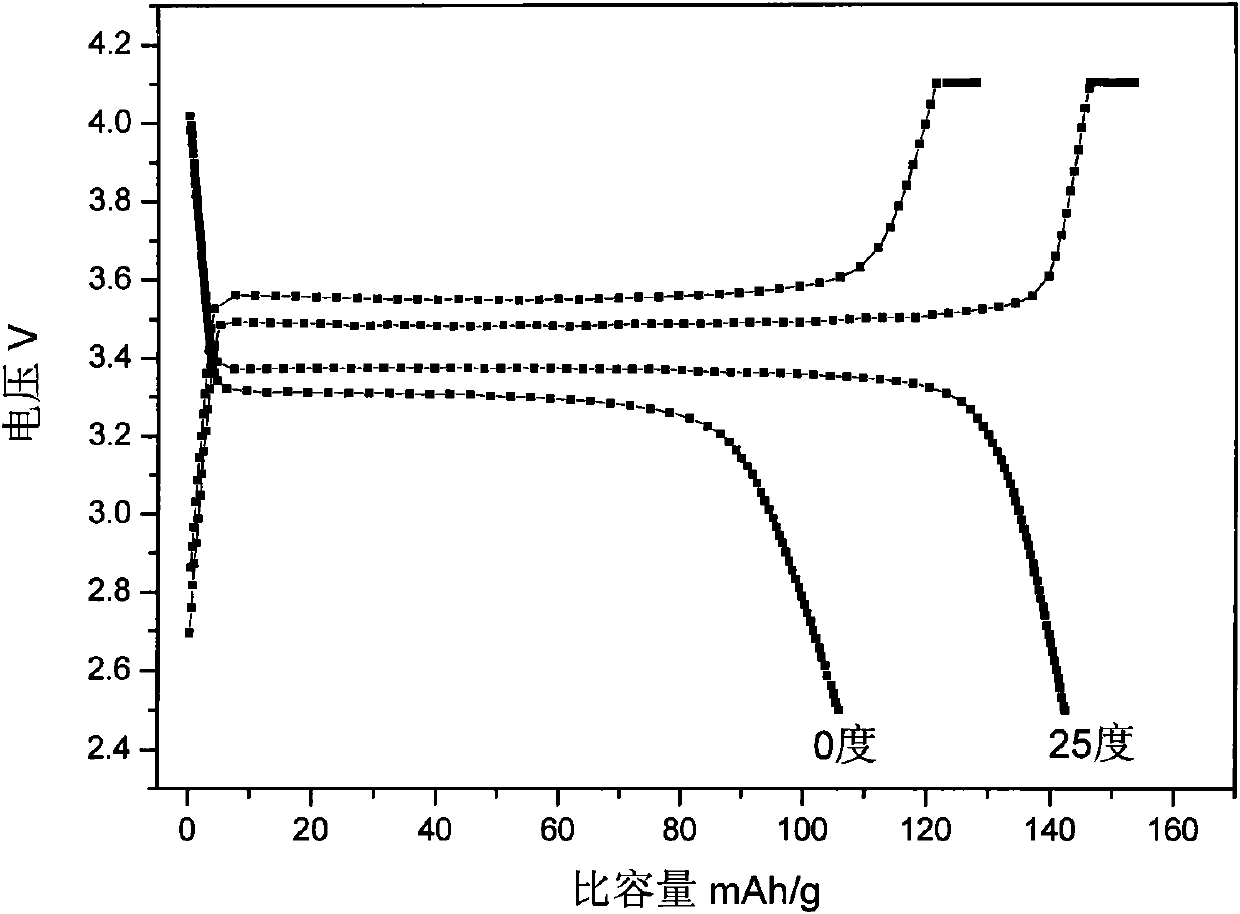
InactiveCN102005564AHigh specific capacityGood low temperatureCell electrodesNanotechnologyMuffle furnaceFERRIC IRON
The invention relates to a method for preparing nanocrystalline lithium iron phosphate powder by adopting iron hydroxide colloid, which comprises the steps of: with Fe(OH)3 colloid as a raw material, adding a lithium source, a phosphorus source and an organic carbon source in the colloid, powerfully and uniformly stirring and drying in vacuum at low temperature to form a uniform nano precursor containing lithium, iron, phosphorus and carbon; and placing in a crucible and raising the temperature to 500-800 DEG C in a muffle furnace protected by inert atmosphere, preserving the temperature for 2-24h, cracking the organic carbon source into carbon under the inert atmosphere, reducing ferric iron into ferrous iron by the carbon to form carbon wrapped lithium iron phosphate, naturally cooling to room temperature, and then grinding or crushing to obtain the nanocrystalline lithium iron phosphate powder. The colloid Fe(OH)3 is used as an iron source, the prepared lithium iron phosphate is of nano level, has excellent electrochemical property and low-temperature discharge property, is simple in process, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:杨志宽
Manufacturing method of catalyst for pentafluoroethane
ActiveCN1935360AAvoid the problem of insufficient activityHigh activityCatalyst activation/preparationHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationAluminium hydroxideNitrogen gas
Preparing a chromium oxide catalyst for preparing pentafluoroethane using chloroethane comprises heating chromium hydroxide powder at greater than 300 DEG C. to give chromium oxide powder; heating a metal hydroxide selected from magnesium hydroxide, iron hydroxide, molybdenum hydroxide, vanadium hydroxide or aluminum hydroxide at 300 DEG C. or less to give a metal oxide powder e.g. magnesium oxide, iron oxide, molybdenum oxide, vanadium oxide or aluminum oxide; mixing the chromium oxide powder (85-99.5 wt.%) with the metallic oxide powder (0.5-15 wt.%); granulating the obtained mixture; calcining the granules at 200-300 DEG C. under nitrogen gas medium; and calcining the obtained granules at 300-320 DEG C. under a gas mixture comprising nitrogen and hydrogen fluoride (HF) and then at 320-380 DEG C. using HF gas. According to the invention, the fluorinating catalyst can be efficietly to prepare HFC-125 using chloroethane as a material and high yield is achieved.
Owner:FOOSUNG
Method for producing complexation metal salt of ethylenediamine tetra acetic acid
InactiveCN1431193AHigh purityReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationComplexonsZinc hydroxide
A process for preparing a high-purity metal salt of complexon as trace-element fertilizer includes adding complexon and alkali (sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, or ammonia) to water, reaction while stirring to obtain complexon salt, adding metal salt (iron hydroxide, manganese hydroxide, etc.) at 150 deg.C for 0.5-5 hr, and filter to remove insoluble substance.
Owner:钟林 +2
Preparation method of battery grade iron phosphate with low impurity, high iron-phosphorus ratio and large specific surface
ActiveCN108455547ALow content of metal impurity ionsLow total water contentMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphorus compoundsSulfate radicalsManganese
The invention discloses a preparation method of a battery grade iron phosphate with low impurity, high iron-phosphorus ratio and large specific surface. The iron-phosphorus ratio in the current iron phosphate is 0.97 to 1.00, however a small amount of iron hydroxide is contained in the iron phosphate and absorbs a large amount of impurity ions, so that the contents of S, Mn and Mg impurity ions are high, and the requirement of battery grade iron phosphate is difficult to meet. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preliminarily purification and impurity removal: removing titanium,copper and aluminum impurity metal ions at high temperature; secondly, deep purification and impurity removal: removing manganese and magnesium metal ion impurities at low temperature; thirdly, performing ageing to remove sulfate radical in crude iron phosphate, adding alkali to control the endpoint pH value to be 5.5 to 6.5, and removing acidic salt; fourthly, washing and drying; fifthly, performing low-temperature calcinations to remove crystal water. Iron phosphate obtained through the method has the advantages that the iron-phosphorus ratio reaches greater than 0.975, the contents of mainimpurity elements Mn, Mg and S are smaller than 30ppm, the contents of other elements are smaller than 10ppm, the specific surface is adjustable between 8 to 12m2 / g, and the total water content is smaller than 0.3 percent.
Owner:취저우화여우코발트뉴머터리얼컴퍼니리미티드 +1
Hydroxide loading palladium catalyst and method for producing the same
InactiveCN101195089ASubstantiveHigh activityCatalyst carriersCatalyst activation/preparationAluminium hydroxideActive component
The invention relates to a hydroxide carried palladium catalyst and a process for preparation. A carrier of the catalyst is hydroxide, an active component is palladium, and the hydroxide is iron hydroxide or cobalt hydroxide or manganese hydroxide or nickel hydroxide or aluminum hydroxide. The invention adopts the method of co-precipitation. The catalyst has a comparatively high specific surface area and a comparatively high dispersing degree of the carrier. Steps of high-temperature drying, roasting and the like are not needed in the process for preparation, the invention saves energy consumption and doesn't discharge pollution gas, and the process for preparation is friendly to environment.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com