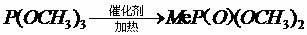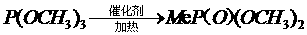Patents
Literature
38 results about "Methylphosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
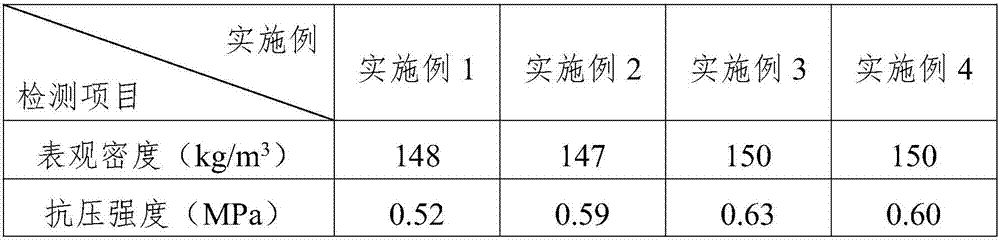
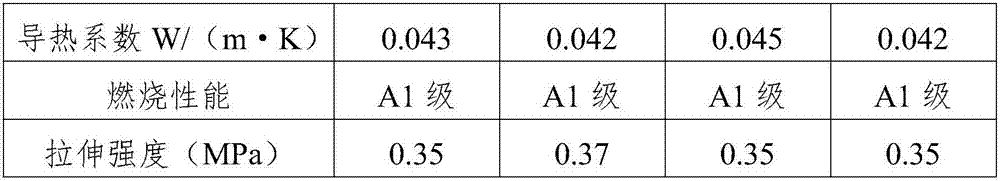
Antibacterial flame retardant coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104927491AImprove surface antimicrobial propertiesSimple processFireproof paintsAntifouling/underwater paintsFiberMeth-
The invention relates to an antibacterial flame retardant coating. The antibacterial flame retardant coating comprises the following components in parts by weight: 6-10 parts of zinc pyrithione, 15-30 parts of chitosan biguanidine hydrochloride, 8-16 parts of methylphenyl silicone resins, 10-25 parts of nanometer silver powder, 8-10 parts of a phosphate flame retardant, 4-10 parts of dihexadecyl peroxodicarbonate, 12-20 parts of benzyl butyl phthalate, 0.5-1 part of superfine acrylate rubber powder, 0.1-0.5 part of dimethyl methylphosphate, 5-15 parts of aluminium silicate fibers, and 1-3 parts of zinc oxide. The antibacterial flame retardant coating disclosed by the invention is prepared under normal temperature and normal pressure, and extra equipment is not needed; the technology is simple, and the production cost is low. After the antibacterial flame retardant coating disclosed by the invention is used, the antibacterial performance of surfaces of materials can be effectively improved, and the materials have good flame retardance; the antibacterial flame retardant coating integrally has favorable antibacterial flame retardance, and can be used according to needs.
Owner:龚灿锋
Heat-resistant and anti-corrosion 3D printing material for electronic engineering and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107141797AImprove heat resistanceImprove anti-corrosion performanceAdditive manufacturing apparatusHydrobromideAntioxidant
The invention discloses a heat-resistant and anti-corrosion 3D printing material for electronic engineering. The heat-resistant and anti-corrosion 3D printing material for electronic engineering comprises the following raw materials: modified polyphenylene sulfide, ethylene-propylene-diene monomer rubber, butadiene styrene rubber, epoxy resin, polyurethane acrylate, tripolycyanamide hydrobromide, ethylene-propylene-diene monomer rubber, ammonium polyphosphate, aluminum hydroxide, talcum powder, mica iron oxide, zinc oxide, magnesium oxide, asbestos fiber, glass fiber, nano-sized titanium dioxide, ethyl orthosilicate, a silane coupling agent KH-560, trioctyl trimellitate, sodium stearate, dioctyl phthalate, dicumyl peroxide, m-xylylenediamine, phenylpropyl triazole, ammonium polyphosphate, dimethyl methylphosphate, liquid paraffin, a phase solvent, an antioxidant, a defoaming agent and a modified filler. The invention further provides a preparation method of the heat-resistant and anti-corrosion 3D printing material for electronic engineering. The 3D printing material prepared according to the preparation method provided by the invention has excellent heat resistance and corrosion resistance and high in mechanical properties.
Owner:HEFEI SKE INTELLIGENT TECH
Preparation method for zinc oxide ore collecting agent
The invention discloses a preparation method for a zinc oxide ore collecting agent, and belongs to the field of ore processing. The preparation method particularly comprises the steps that a mixed solution of octadecylamine and lauryl amine is prepared to be contained into a water bath to be heated; NaOH is added into an obtained solution to adjust the pH, methyl alcohol, propyl alcohol and methylphosphate are sequentially added, a mixture is placed into the water bath to be heated; and thermostatic water bath stirring is carried out, ultrasonication is adopted, and the zinc oxide ore collecting agent is finally obtained. According to the method, in order to solve the problems that an existing amine collecting agent is poor in agent solubleness in zinc oxide floatation, the using condition is limited, and the action effect is poor, organic interaction dissolving, ultrasonic dissolving assisting, heating stirring and other methods are adopted, on the premise that the original collecting character is not influenced, the agent dissolving performance is strengthened, the using convenience is improved, and the finally the aim of improving the flotation effect is achieved.
Owner:CHIHONG TECH & ENG +1
Flame-retardant aging-failure-resistant polyurethane composite wave-absorbing material
The invention provides a flame-retardant aging-failure-resistant polyurethane composite wave-absorbing material, which is prepared by carrying out a polymerization reaction on the following componentsin parts by mass: 100 parts of polyether polyol, 30-60 parts of toluene diisocynate, 0.05-0.4 part of nanometer carbon sol, 0.2-0.5 part of nano white carbon black, 10-20 parts of deionized water, 5-20 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate, 2-8 parts of graphene oxide, 10-20 parts of ferrite, 2-10 parts of zirconium oxide, 2-8 parts of zinc borate, 0.02-0.4 part of stannous octoate, 0.03-0.6 part oftriethylene diamine, 0.2-3 parts of an organosilicon surfactant and 2-8 parts of sodium bicarbonate. The flame-retardant aging-failure-resistant polyurethane composite wave-absorbing material providedby the invention has the characteristics of low smoke, low toxicity, flame retardancy, wide absorption frequency distribution of absorbed waves and the like. The invention also provides a preparationmethod of the flame-retardant aging-failure-resistant polyurethane composite wave-absorbing material.
Owner:张猛
Waterproof and high temperature resistant sealant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104830256AImprove flame retardant performanceImprove water resistanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesStarch adhesivesPotato starchGas phase
The invention discloses a waterproof and high temperature resistant sealant and a preparation method thereof. The waterproof and high temperature resistant sealant includes the following raw materials by weight: 50-80 parts of an acrylate emulsion, 5-10 parts of nitrile rubber, 10-20 parts of potato waste residue powder, 12-18 parts of talcum powder, 10-13 parts of expandable graphite, 1-3 parts of glass bead, 5-6 parts of gas phase white carbon black, 5-8 parts of nano calcium carbonate, 10-12 parts of epoxidized soybean oil, 0.5-1.5 parts of dibutyl tin diacetate, 3-5 parts of dibutyl phthalate, 5-10 parts of zinc borate, and 2-3 parts of pentaerythritol. The preparation method consists of: (1) subjecting potato waste residue to natural air dying and crushing, conducting soaking in dimethyl methylphosphate for 5-10h, carrying out separation and natural drying to obtain potato waste residue powder; and (2) mixing the raw materials according to the ratio in certain sequence to prepared the sealant. According to the invention, the potato starch waste, expandable graphite and talcum powder are mixed to obtain the biomass charring agent with flame retardant effect. And by applying the biomass charring agent into the sealant, the high temperature resistance, flame retardation and waterproofness of the sealant can be significantly improved, and at the same time the waste treatment cost of starch production enterprises can be reduced, thereby being beneficial to environmental protection.
Owner:TONGLING XIANGYUN FIRE FIGHTING TECH
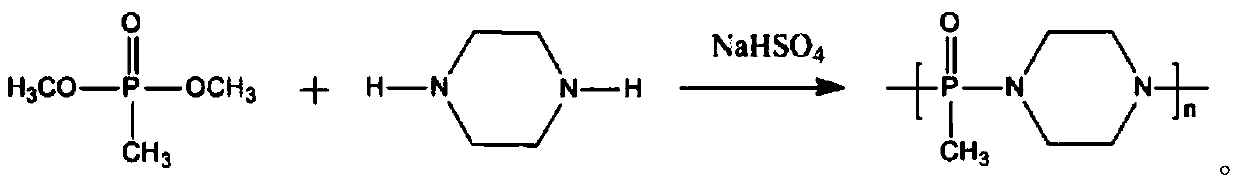
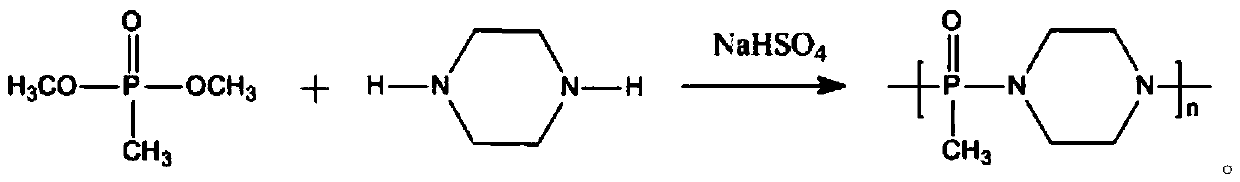
Flame retardant with nitrogen-containing phosphonate and synthesis method of flame retardant
The invention discloses a flame retardant with nitrogen-containing phosphonate and a synthesis method of the flame retardant, belongs to the field of flame retardant synthesis and particularly relatesto a flame retardant and a synthesis method thereof. The problems of large addition amount, deep color, poor durability and low flame-retarded efficiency are solved. The chemical name of the flame retardant with the nitrogen-containing phosphonate is polymethyl phosphonic acid piperazine ester; the preparation method comprises the steps that dimethyl methylphosphate is taken in a reaction container, piperazine and a catalyst are added, sufficient stirring is conducted until the mixture is dissolved, and after heating and a reaction for several hours, fraction methyl alcohol is collected; after the reaction is ended, cooling is conducted, and the product polymethyl phosphonic acid piperazine ester can be obtained. A synergistic effect exists between a nitrogen element and a phosphorus element in the flame retardant, the two ends of each flame retardant molecule contain amidogen, in the curing process, the amidogen can react with epoxy groups of epoxy resin, so that the epoxy resin obtain permanent flame retardance, and the char yield of the epoxy resin is obviously increased. The flame retardant is applied to preparation of the flame retardant with the nitrogen-containing phosphonate.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Flame-retardant rubber composition and preparation method of flame-retardant rubber
InactiveCN106188700AImprove flame retardant performanceHigh mechanical strengthPolymer scienceCombustion
The invention discloses a flame-retardant rubber composition and a preparation method of flame-retardant rubber. The preparation method comprises the steps that styrene butadiene rubber, natural rubber, dimethyl methylphosphate, diethyl ethylphosphonate, a scorch retarder and an accelerant are blended and then mixed, and the flame-retardant rubber is obtained. The problem that common rubber products are low in flame retardation and prone to combustion, and consequently the application range of the common rubber products is greatly narrowed is solved.
Owner:WUHU FENGXUE RUBBER
Preparation method of flame-retardant aging-failure-resistant polyurethane composite wave-absorbing material
The invention provides a flame-retardant aging-failure-resistant polyurethane composite wave-absorbing material, which is prepared by carrying out a polymerization reaction on the following componentsin parts by mass: 100 parts of polyether polyol, 30-60 parts of toluene diisocynate, 0.05-0.4 part of nanometer carbon sol, 0.2-0.5 part of nano white carbon black, 10-20 parts of deionized water, 5-20 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate, 2-8 parts of graphene oxide, 10-20 parts of ferrite, 2-10 parts of zirconium oxide, 2-8 parts of zinc borate, 0.02-0.4 part of stannous octoate, 0.03-0.6 part oftriethylene diamine, 0.2-3 parts of an organosilicon surfactant and 2-8 parts of sodium bicarbonate. The flame-retardant aging-failure-resistant polyurethane composite wave-absorbing material providedby the invention has the characteristics of low smoke, low toxicity, flame retardancy, wide absorption frequency distribution of absorbed waves and the like. The invention also provides a preparationmethod of the flame-retardant aging-failure-resistant polyurethane composite wave-absorbing material.
Owner:张猛
Improved polyurethane foamed heat-preservation plate and preparation method thereof
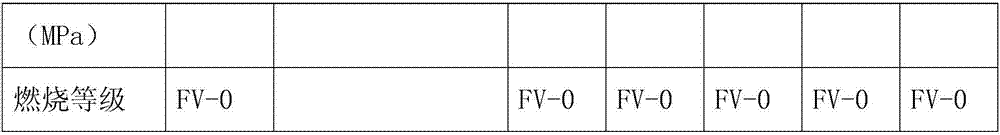
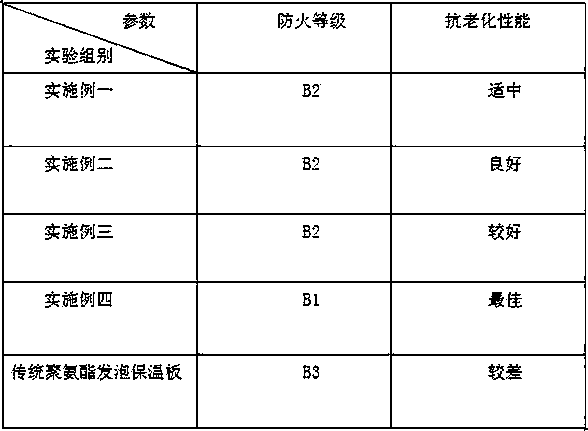
The invention discloses an improved polyurethane foamed heat-preservation plate of which the formulae comprise the following components: 25-35% of polyurethane, 26-34% of polystyrene, 8-12% of dimethyl methylphosphate, 2-6% of magnesium powder, 1-5% of mica powder, 2-6% of a film formation agent and the balance of a solvent. The invention further discloses the improved polyurethane foamed heat-preservation plate and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, performing quantitative weighing; S2, performing polymerization treatment; S3, molding plates; S4, performing trimming treatment; and S5, performing coating treatment. The formulae used in the plate are all raw materials provided by national standards, in addition, the performance of the polyurethane foamed plate disclosed by the invention is greatly improved, the fireproof grade of the plate can be increased, the aging resistance of the plate is improved, articles made of the plate areapplicable to more situations, the cost of the polyurethane foamed plate disclosed by the invention is lowered, company benefits can be increased, and the plate is applicable to popularization.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Polyurethane-barium titanate composite wave-absorbing porous material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107868221ALow smokeLow toxicityOther chemical processesSodium bicarbonateToluene diisocyanate
The invention provides a polyurethane-barium titanate composite wave-absorbing porous material. The material is prepared from 100 parts by mass of polyether polyol, 30 to 60 parts by mass of toluene diisocyanate, 0.05 to 0.4 parts by mass of nanometer carbon sol, 0.2 to 0.5 parts by mass of nanometer white carbon black, 10 to 20 parts by mass of deionized water, 5 to 25 parts by mass of dimethyl methylphosphate, 2 to 8 parts by mass of graphene oxide, 10 to 20 parts by mass of barium titanate, 1 to 3 parts by mass of nano-zinc oxide, 0.5 to 2 parts by mass of nano-tungsten oxide, 2 to 8 partsby mass of zinc borate, 0.02 to 0.4 parts by mass of stannous octoate, 0.03 to 0.6 parts by mass of triethylenediamine, 0.2 to 3 parts by mass of an organosilicone surfactant and 2 to 8 parts by massof sodium bicarbonate through polymerization. The polyurethane-barium titanate composite wave-absorbing porous material has the characteristics of low smoke, low toxicity, flame retardancy and wide absorption frequency of absorbed waves. The invention also provides a preparation method of the polyurethane-barium titanate composite wave-absorbing porous material.
Owner:HENAN HAINADE NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Composite wave-absorbing porous polyurethane material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107857857ALow toxicityFlame retardantOther chemical processesSodium bicarbonateToluene diisocyanate
The invention provides a composite wave-absorbing porous polyurethane material. The composite wave-absorbing porous polyurethane material is obtained through a polymerization reaction of the followingcomponents, by mass, 100 parts of polyether polyol, 30-60 parts of toluene diisocyanate, 0.05-0.4 part of nano-carbon sol, 0.2-0.5 part of nanometer white carbon black, 10-20 parts of deionized water, 5-20 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate, 2-8 parts of graphene oxide, 10-20 parts of ferrite, 2-10 parts of zirconium oxide, 2-8 parts of zinc borate, 0.02-0.4 part of stannous octoate, 0.03-0.6 partof triethylenediamine, 0.2-3 parts of an organosilicone surfactant and 2-8 parts of sodium bicarbonate. The composite wave-absorbing porous polyurethane material has the characteristics of low smoke,low toxicity, flame retardancy, and wide absorption frequency distribution of absorbed waves. The invention also provides a preparation method of the composite wave-absorbing porous polyurethane material.
Owner:HENAN HAINADE NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Waterproof sealant for bathroom
InactiveCN104232003AImprove sealingNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesOther chemical processesAdipateSealant
The invention discloses a waterproof sealant for a bathroom. The waterproof sealant comprises the following components in parts by weight: 23 to 32 parts of polypropylene carbonate type polyurethane elastomer, 15 to 23 parts of polyglycol propylene glycol diol adipate, 2 to 4 parts of an initiator, 3 to 5 parts of beta-cyclodextrin, 1 to 3 parts of a crosslinking agent, 11 to 18 parts of 1,4-phenylene diisocyanate, 5 to 8 parts of inorganic filler and 8 to 12 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate. The waterproof sealant is resistant to medium erosion, and the long-term stability of a sealing effect can be ensured.
Owner:WUXI HITXINCHENG POLYMER TECH
Environment-friendly heat-resistant flame-retardant aging-resistant modified natural rubber material
The invention discloses an environment-friendly heat-resistant flame-retardant aging-resistant modified natural rubber material. The environment-friendly heat-resistant flame-retardant aging-resistant modified natural rubber material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-50 parts of modified natural rubber, 15-35 parts of butyronitrile rubber, 1-3 parts of tetrabenzylthiuram disulfide, 2-4 parts of a fluorine-containing surfactant, 1-2 parts of 1,1-di-t-butylperoxy-3,3,5-trimethyl siloxane, 2-4 parts of an accelerator M, 1-3 parts of an accelerator TMTD, 25-35 parts of white carbon black, 30-40 parts of talc powder, 25-35 parts of nano kaolin, 30-40 parts of ultrafine magnesium hydroxide, 5-8 parts of manganese phosphate, 6-9 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate, 5-11 parts of calcium hydrogen phosphate, 4-6 parts of magnesium borate, 1-3 parts of an anti-aging agent MB, 2-3 parts of an anti-aging agent RD, 2-4 parts of aromatic oil and 2-3.5 parts of stearic acid. The environment-friendly heat-resistant flame-retardant aging-resistant modified natural rubber material disclosed by the invention has the advantages of environmental friendliness, good heat resistance, flame-retardant property and aging resistance.
Owner:QIAOJIAN NEW ENERGY TECH SUZHOU
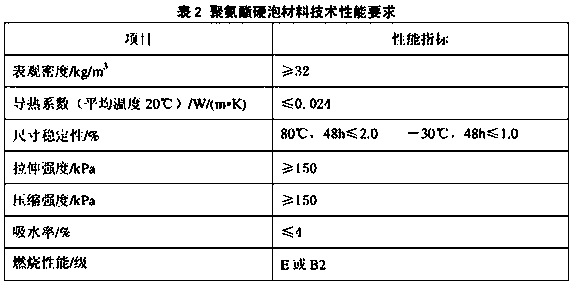
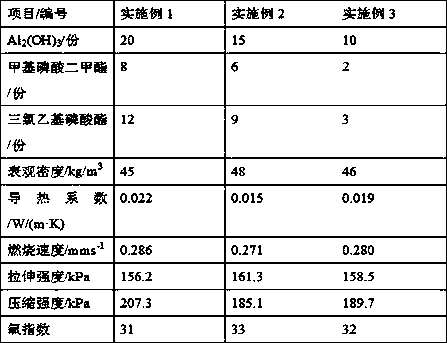
Flame retardant polyurethane hard foamed plastic
InactiveCN107778429AOvercoming the problem of rising thermal conductivityImprove OIPolymer scienceCombustion
The invention belongs to the technical field of a polyurethane material, and relates to flame retardant polyurethane hard foamed plastic. The flame retardant polyurethane hard foamed plastic is prepared from the following ingredients in parts by weight: 90 to 100 parts of mixed polyalcohol, 3 to 5 parts of foam stabilizers, 2 to 5 parts of antioxidants, 9 to 40 parts of flame retardants, 5 to 7 parts of chemical foaming agents, 5 to 7 parts of physical foaming agents, 1 to 2 parts of composite catalysts and 1.5 to 4.0 parts of isocyanate index, wherein the flame retardants include Al2(OH)3, dimethyl methylphosphate and 2-chloroethanol phosphate. The flame retardant polyurethane hard foamed plastic has the advantages that the flame retardant performance is obvious; through test, the OI (oxygen index) of the hard polyurethane foamed plastic reaches the standard that the OI is greater than B1 grade, specified in classification methods for combustion performance of building materials; theflame retardant polyurethane hard foamed plastic can be used at high temperature.
Owner:SHENYANG SHUNFENG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
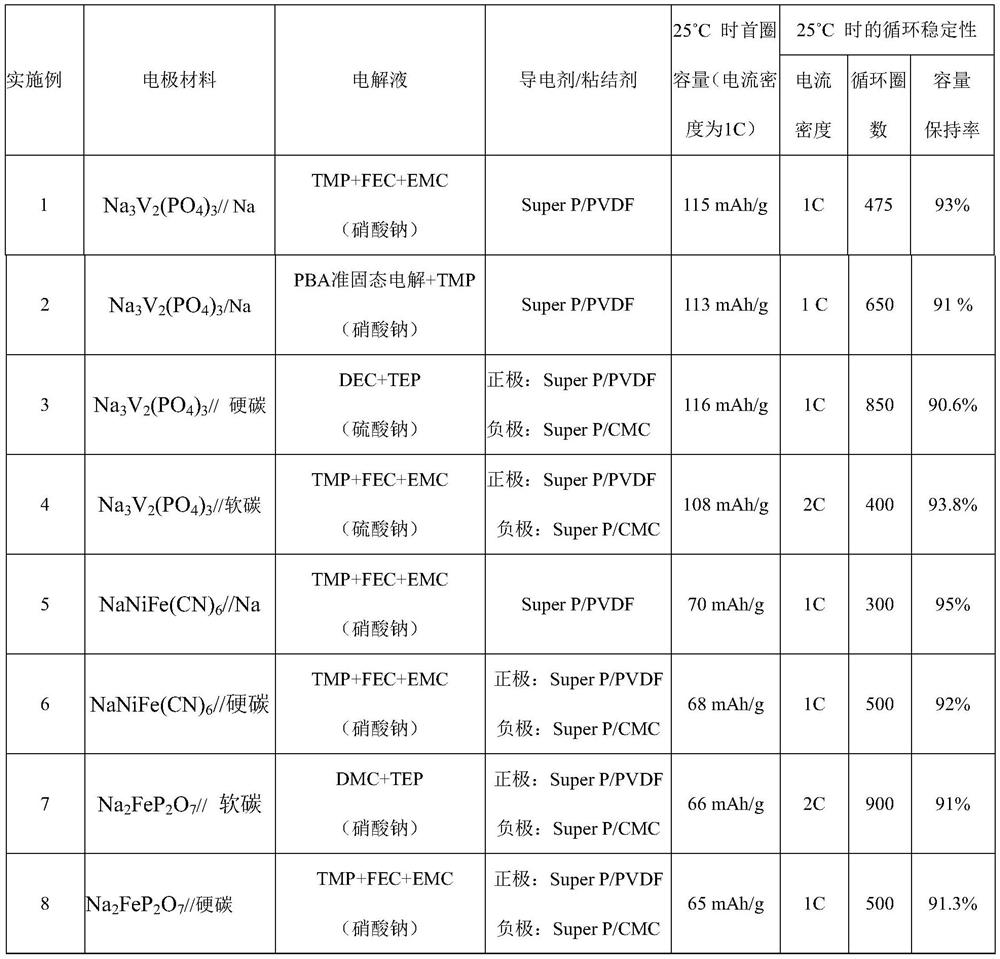
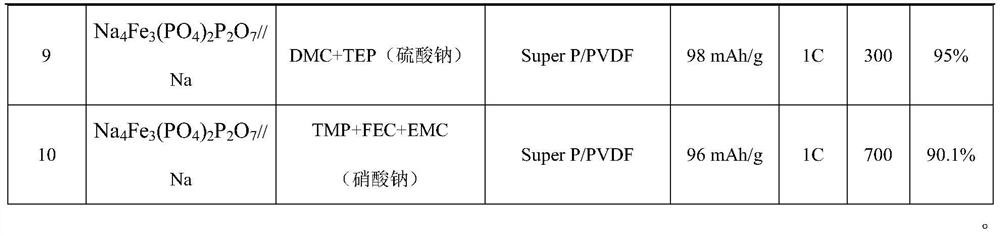
Non-combustible high-safety sodium ion battery
PendingCN114122516AReduce manufacturing costLow costFinal product manufactureFire rescueDiethyl phosphateElectrolytic agent
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrochemistry, and particularly relates to a non-combustible high-safety sodium ion battery. The lithium ion battery comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode and an electrolyte, wherein the electrolyte comprises a sodium salt, an ester solvent and a flame retardant; wherein the sodium salt is selected from one or more of NaNO3, Na2SO4, Na3PO4, NaI, NaPF6, NaTFSI, NaFSI or NaTFMS, and the flame retardant is selected from one or more of trimethyl phosphate, triethyl phosphate, tributyl phosphate, dimethyl methylphosphate, diethyl ethylphosphate, diphenyl isopropylphenyl phosphate or hexamethylphosphoramide. Electrolyte used by a traditional sodium ion battery is combustible, and the safety of the battery is damaged. The sodium-ion battery electrolyte provided by the invention is non-combustible, so that the sodium-ion battery electrolyte shows a safer characteristic compared with a traditional sodium-ion battery, and has a certain application prospect in the aspects of large energy storage and power batteries.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
4-{6-[5-(2-chlorinde-6- methylaniline formyl)-thiazole-2-amido]-2-methyl pyrimidine-4}-piperazine-1- diethyl methylphosphate
ActiveCN101323629AImprove bioavailabilityLimited surface expressionOrganic active ingredientsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMethylanilineProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The invention relates to a chemical compound of 4-(6-(5-(2-chlorine-6-methylaniline formoxyl)-thiazole-2-amido)-2-methylpyrimidine-4)-piperazine-1-methyl triethyl phosphate shown in general formula I, salts thereof for medical purposes, hydrates and solvates thereof, polycrystals and eutectic crystals thereof, precursors or derivatives thereof with the same biological function, a preparation method thereof, a composition containing one or more chemical compounds and the application of the chemical compound in the treatment of diseases relating to protein tyrosine kinase, such as immune disorder and oncology diseases.
Owner:CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA GRP CO LTD +1
Lithium ion battery
InactiveCN106972194AEnsure safetyEasy to useSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceEngineeringCharge discharge
The invention discloses a lithium ion battery. The lithium ion battery comprises a battery main body, wherein the battery main body comprises a plurality of battery pole groups, at least one protection plate is arranged at a middle part of each battery pole group, the protection plate is of a hollow structure, and the hollow structure of each protection plate is filled with a protection functional material such as a liquid containing halogenated carbonate ester, a phosphonitrile compound, trimethyl phosphate, triethyl phosphate, triphenyl phosphate, tributyl phosphate, trichloroethyl phosphate or dimethyl methylphosphate, a phase change material, a heat conductive graphite material or a composite material of any one material combined. In the lithium ion battery disclosed by the invention, the thermal runway of the battery can be effectively prevented when an accident occurs due to inappropriate charging, short circuit, acupuncture, extrusion or the battery exposed in a severe environment such as high temperature, the safety performance of the battery is ensured, and meanwhile, the high-temperature charge-discharge performance of the battery is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN LISHEN BATTERY
High-toughness antistatic foamed polypropylene and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses high-toughness antistatic foamed polypropylene and a preparation method of the high-toughness antistatic foamed polypropylene. The high-toughness antistatic foamed polypropylene comprises the following components in parts by weight: 20-25 parts of colorless polypropylene particles, 10-15 parts of colored polypropylene particles, 2-4 parts of carbon black, 5-10 parts of an antistatic agent, 2-3 parts of a bacteriostatic agent, 3-5 parts of an anti-aging agent, 2-5 parts of a lubricant, 8-10 parts of cyclic fatty acid methyl ester, 4-8 parts of methyl phosphate and 3-5 parts of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate. The preparation method has the advantages of light weight and heat insulation, twice screening is carried out in the preparation process, particles with uniform sizes can be screened out each time, and uniform sizes of foamed polypropylene particles are guaranteed; added phenol can be mixed with trichlorotoluene and N-N '-diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine for use, the ageing resistance of the product is improved, bromine water is added in the preparation process, inert gas can be emitted in the combustion process, then the oxygen content is reduced, the certain flame retardant purpose is achieved, and the flame retardant property is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU HAOSHENG PLASTIC IND TECH CO LTD
Production process of inorganic modified polyphenyl granule incombustilble heat insulation plate
InactiveCN107188519AImprove fire and flame retardant performanceDelay the rate of thermal degradationHeat proofingFiberPhosphate
The invention provides a production process of an inorganic modified polyphenyl granule incombustilble heat insulation plate, and relates to the field of a building material. The production process comprises the following steps of adding magnesium oxide powder into a magnesium chloride solution; after the uniform stirring at the normal temperature, adding polyphenyl particles, expanded perlite, reinforced fiber, aluminum hydroxide and water glass; performing stirring at the normal temperature; then, adding polyvinyl acetate emulsion, dimethyl methylphosphate and tri(2-chloroethyl) phosphate; performing stirring at the normal temperature; pressing and forming the mixture by a roller; then, laying gridding cloth onto the surface of the bottom surface of a forming plate; obtaining a heat insulation plate semi-finished product; performing primary cutting on the heat insulation plate semi-finished product; after the natural curing, performing secondary cutting; obtaining a heat insulation plate finished product. The produced heat insulation plate has the advantages of good fireproof and flame retardant performance and high intensity toughness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUZHOU DEWANG BUILDING MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Polyester yarn with flame retardant property and preparation process thereof
PendingCN113122955AClosely arrangedPermanent Flame RetardancyFlame-proof filament manufactureYarnPolyesterYarn
The invention relates to the technical field of polyester yarn preparation processes, and provides a polyester yarn with flame retardance and a preparation process thereof. Flame retardants 2-carboxyethyl phenyl hypophosphorous acid and dimethyl methylphosphate are added in the process of esterifying PTA into PET; the flame retardant 2-carboxyethyl phenyl hypophosphorous acid and a dimethyl methylphosphate monomer can be embedded into the PTA macromolecular chain through the esterification reaction to form the PET, so that the 2-carboxyethyl phenyl hypophosphorous acid and the dimethyl methylphosphate can be closely arranged in the gaps of the PTA macromolecules so as to form the flame-retardant PET through copolymerization; at a high temperature, 2-carboxyethyl phenyl hypophosphorous acid and the dimethyl methylphosphate can exert the flame retardant property for flame retardance; and then flame-retardant PET is prepared into the flame-retardant polyester fiber, the flame-retardant polyester fiber is spun into the polyester yarn with the flame-retardant performance; and the polyester yarn prepared through the preparation process has no side reaction, does not affect the fiber performance and has permanent flame retardance.
Owner:太仓市泽记新材料有限公司
Reactive flame retardant as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111116989AHigh oxygen indexPromote generationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsXylyleneEpoxy
The invention discloses a reactive flame retardant as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the reactive flame retardant is shown in the following formula (I), the preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing dimethyl methylphosphate, terephthalaldehyde, a catalyst and a solvent, carrying out a reaction in nitrogen or an inert atmosphere, and carrying out post-treatment to obtain the reactive flame retardant, wherein the catalyst is selected from at least one of xylene, 2, 3-dichlorotoluene and trimethylbenzene, and the solvent is selectedfrom tetrahydrofuran and / or acetonitrile. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, mild in condition, easy to control and high in product purity, and the prepared reactive flame retardant has the advantages of novel structure, high flame retardant efficiency, environmental protection and low toxicity; and especially, the prepared reactive flame retardant has excellent flame retardant property in an epoxy resin matrix.
Owner:SUZHOU HSM TECH CO LTD
Environment-friendly type solar thermal-insulation building material
The invention discloses an environment-friendly type solar thermal-insulation building material. The environment-friendly type solar thermal-insulation building material is characterized by being obtained by mixing, foaming and curing the following raw materials in parts by weight: 120-140 parts of a polyether foaming agent, 50-70 parts of polyether polyol I, 35-50 parts of polyether polyol II, 3-6 parts of expanded vermiculite, 5-8 parts of nano silicon dioxide, 10-20 parts of monochlorodifluoroethane, 5-6 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate, 1-5 parts of diethanol monoisopropanolamine and 1-5 parts of an organic silicon foam stabilizer, wherein the polyether polyol I is lignin polyether polyol, and the polyether polyol II is polyether polyol which is polymerized by taking modified peanut oil as an initiator and by taking epoxypropane as a polymerization monomer. Indexes such as a heat conduction efficient, compressive strength, tensile adhesive strength, dimension stable performance and porosity by closed pore of the environment-friendly type solar thermal-insulation building material are obviously improved in comparison with those of a current thermal-insulation building material; and the environment-friendly type solar thermal-insulation building material is a thermal-insulation building material which is free of phenomena such as shrinkage, deformation, expansion and cracking under a freezing or high-temperature condition, and is excellent in performance.
Owner:毛文辉
Cheap and environment-friendly lithium ion battery with high safety
PendingCN114122497ALow costImprove securitySecondary cellsElectrolytesDiethyl phosphateElectrolytic agent
The invention belongs to the field of an electrochemical technology, and particularly relates to a low-cost and environment-friendly lithium ion battery with high safety. The lithium ion battery comprises a positive electrode, a negative electrode and an electrolyte, wherein the electrolyte comprises inorganic lithium salt without fluorine element, an ester solvent and a flame retardant; the flame retardant is one or more of trimethyl phosphate, triethyl phosphate, tributyl phosphate, dimethyl methylphosphate, diethyl ethyl phosphate, diphenyl isopropylphenyl phosphate and hexamethylphosphoramide. The lithium ion battery provided by the invention does not involve fluorine-containing salt, and the electrolyte is non-combustible, so that compared with the traditional lithium ion battery, the lithium ion battery shows the characteristics of safety, low cost and environment friendliness, and has certain application prospects in the aspects of large energy storage and power batteries.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Flame-retardation and wave-absorption porous polyurethane material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107857854ALow smokeLow toxicityOther chemical processesSodium bicarbonateToluene diisocyanate
The invention provides a flame-retardation and wave-absorption porous polyurethane material. The flame-retardation and wave-absorption porous polyurethane material is obtained through a polymerizationreaction of the following components, by mass, 100 parts of polyether polyol, 20-70 parts of toluene diisocyanate, 0.05-0.4 part of nano-carbon sol, 0.2-0.5 part of nanometer white carbon black, 10-20 parts of deionized water, 5-25 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate, 2-10 parts of carboxyl multi-walled carbon nanotubes, 10-20 parts of ferroferric oxide, 2-8 parts of zinc borate, 0.02-0.4 part of stannous octoate, 0.03-0.6 part of triethylenediamine, 0.2-3 parts of an organosilicone surfactant and 2-8 parts of sodium bicarbonate. The flame-retardation and wave-absorption porous polyurethane material has the characteristics of low smoke, low toxicity, flame retardancy, and wide absorption frequency distribution of absorbed waves. The invention also provides a preparation method of the flame-retardation and wave-absorption porous polyurethane material.
Owner:HENAN HAINADE NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
A kind of method of synthesizing dimethyl methyl phosphate
ActiveCN107793449BDoes not destroy activityReusableGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphorous acidAluminium chloride
The invention provides a method for synthesizing dimethyl methylphosphate. The method comprises the following synthesizing steps: synthesizing lewis acid ionic liquid, namely, mixing quaternary ammonium salt and anhydrous aluminium chloride based on the molar ratio of 1:(1-4), and heating to obtain the ewis acid ionic liquid; mixing, heating and pressurizing trimethyl phosphite and the ionic liquid obtained in step 1; decreasing the temperature of the mixture after the reaction; allowing standing still for layering to obtain a lower ionic liquid mixing and dissolving layer and an upper dimethyl methylphosphate product layer. According to the method, little lewis acid ionic liquid is used; the activity of a catalyst remains in the reaction and separating process; the synthesized product ishigh in purity.
Owner:NANTONG JIANGSHAN AGROCHEM & CHEM LIMITED LIABILITY
Flame-retardant non-woven fabric and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112609457AImprove flame retardant performanceGood dispersionHeat resistant fibresPolymer scienceO-Phosphoric Acid
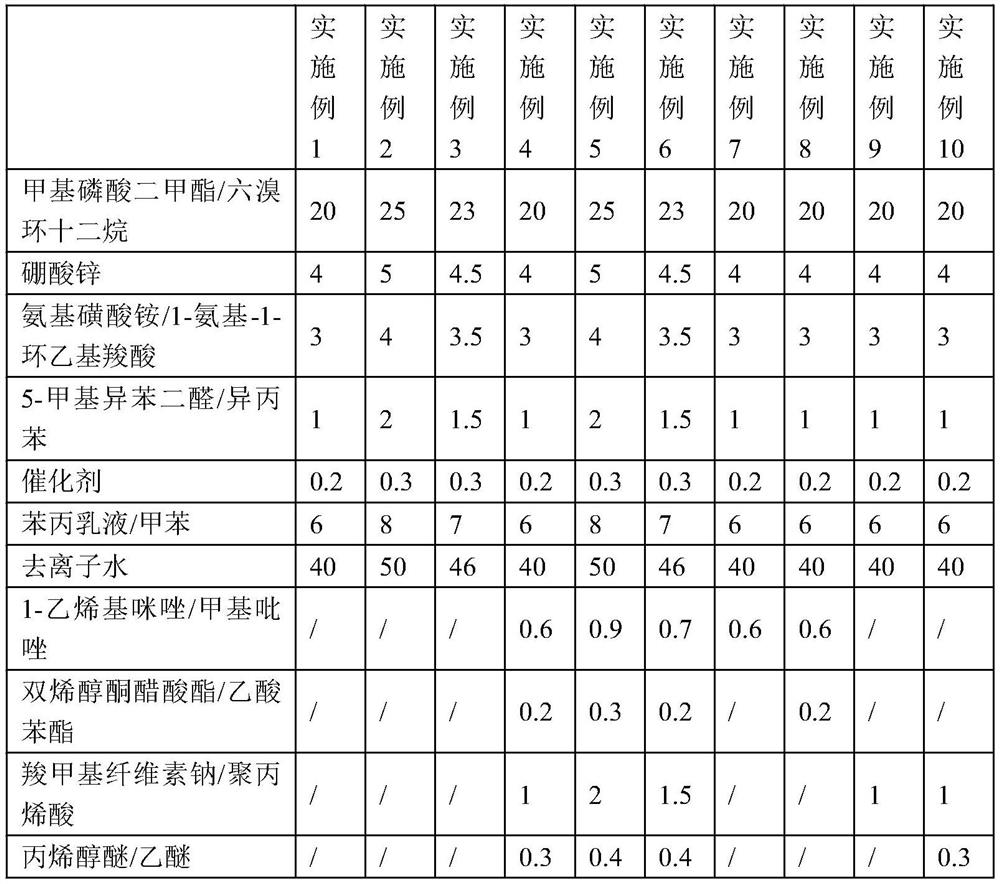
The invention relates to the field of non-woven fabrics, and discloses a flame-retardant non-woven fabric and a preparation method thereof. The non-woven fabric is treated by a flame-retardant treatment agent, and the flame-retardant treatment agent is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-25 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate, 4-5 parts of zinc borate, 3-4 parts of ammonium sulfamate, 1-2 parts of 5-methyl isophthalaldehyde, 0.2-0.3 part of a catalyst, 6-8 parts of a styrene-acrylic emulsion and 40-50 parts of deionized water; the preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing the flame-retardant finishing agent; and S2, flame-retardant finishing of the non-woven fabric. The non-woven fabric has the following advantages and effects: dimethyl methylphosphate and zinc borate with flame retardant effects are added together to play a synergistic flame retardant effect; the styrene-acrylic emulsion assists the components to form a homogeneous system; and the polymer obtained by the polymerization reaction of ammonium sulfamate and 5-methyl isophthalaldehyde can be carbonized under the dehydration action of phosphoric acid to form a carbonized layer, thereby being beneficial to isolating the non-woven fabric from oxygen and achieving the purpose of flame retardancy.
Owner:浙江雅宝无纺布制品有限公司
Heat preserving material of solar water heater water tank and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107778518AWide variety of sourcesLow costCollector thermal insulationSolar thermal energy generationPolymer sciencePolyol
The invention discloses a heat preserving material of a solar water heater water tank and a preparation method thereof. The material is prepared by mixing and foaming DMI and polyether polyol composition according to the ratio of 1-1.5: 1, wherein the polyether polyol composition comprises glycerin glucoside polyether polyol, water, chiton, dimethyl methylphosphate, HFC-356, N, N-dimethyl cyclohexyl amine and a foam stabilizer. According to the heat preserving material, the used raw materials are nontoxic and harmless, so that adverse effects on human body and environment are avoided; the shortage of high contracting after foaming and forming is overcome; the phenomena such as deforming, bulging, edging and even cracking of the water tank can be avoided; and moreover, the heat preserving performance and the heat insulation performance of the water heater water tank can be ensured.
Owner:GUANGXI JIKUAN SOLAR ENERGY EQUIP
Oil and rust removing agent for surface of copper material and preparation method of oil and rust removing agent
The invention discloses an oil and rust removing agent for the surface of a copper material and a preparation method of the oil and rust removing agent. The oil and rust removing agent is prepared from, by weight, 8-11 parts of polyving akohol, 10-13 parts of polyacrylamide, 11-14 parts of sebacic acid, 2-6 parts of alkylphenol ethoxylates, 8-11 parts of konjac glucomannan, 3-7 parts of benzotriazole, 3-6 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate, 3-6 parts of vinyltriethoxysilane, 3-7 parts of boric acid, 11-14 parts of sodium alga acid, 3-6 parts of tannic acid, and 2-5 parts of N-hydroxymethyl-3-(dimethoxyphosphoryl) propanamide. The oil and rust removing agent for the surface of the copper material is reasonable in formula, good in rust removing effect, high in rust removing efficiency and capable of removing oil dirt and rust spots on the metal surface rapidly, and corrosion to the copper material is avoided; and in addition, components in anti-rust liquid are environmentally friendly and non-poisonous, and the preparation method is simple and low in cost.
Owner:WUXI EPIC TECH
Method for synthesizing dimethyl methylphosphate
ActiveCN107793449ADoes not destroy activityReusableGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAluminium chlorideQuaternary ammonium cation
The invention provides a method for synthesizing dimethyl methylphosphate. The method comprises the following synthesizing steps: synthesizing lewis acid ionic liquid, namely, mixing quaternary ammonium salt and anhydrous aluminium chloride based on the molar ratio of 1:(1-4), and heating to obtain the ewis acid ionic liquid; mixing, heating and pressurizing trimethyl phosphite and the ionic liquid obtained in step 1; decreasing the temperature of the mixture after the reaction; allowing standing still for layering to obtain a lower ionic liquid mixing and dissolving layer and an upper dimethyl methylphosphate product layer. According to the method, little lewis acid ionic liquid is used; the activity of a catalyst remains in the reaction and separating process; the synthesized product ishigh in purity.
Owner:NANTONG JIANGSHAN AGROCHEM & CHEM LIMITED LIABILITY
Flame-retardant liquid silicone rubber for fabric reinforcement
InactiveCN106751912AImprove liquidityImprove flame retardant performanceCoatingsPolymer scienceAcetic anhydride
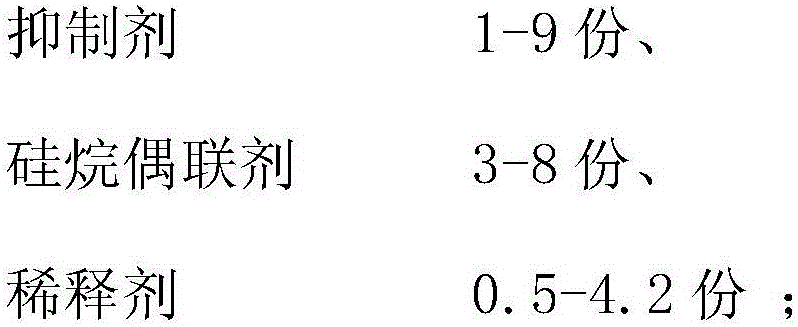
The invention relates to flame-retardant liquid silicone rubber for fabric reinforcement. The flame-retardant liquid silicone rubber for the fabric reinforcement comprises a component A, a component B and a component C, wherein the component A comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100-150 parts of base rubber I, 10-22 parts of a platinum complex and 5-12 parts of a tackifier; the component B comprises the following components in parts by weight: 60-80 parts of base rubber II, 1-9 parts of an inhibitor, 3-8 parts of a silane coupling agent and 0.5-4.2 parts of a diluent; the component C comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15-28 parts of dimethyl methylphosphate, 2-6 parts of magnesium hydroxide, 3-10 parts of sodium hydrogen carbonate, 1.3-2.4 parts of tea saponin, 2.8-4.6 parts of dicyandiamide, 0.2-0.4 part of ethylene glycol and 0.5-0.8 part of acetic anhydride. The flame-retardant liquid silicone rubber for the fabric reinforcement improves the softness and tolerance of fabric, and is environmentally friendly and free of toxic and side effects.
Owner:镇江高美新材料有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![4-{6-[5-(2-chlorinde-6- methylaniline formyl)-thiazole-2-amido]-2-methyl pyrimidine-4}-piperazine-1- diethyl methylphosphate 4-{6-[5-(2-chlorinde-6- methylaniline formyl)-thiazole-2-amido]-2-methyl pyrimidine-4}-piperazine-1- diethyl methylphosphate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/850fa9f0-3482-47a8-bb88-75ea0f42169d/a20081000819700171.PNG)
![4-{6-[5-(2-chlorinde-6- methylaniline formyl)-thiazole-2-amido]-2-methyl pyrimidine-4}-piperazine-1- diethyl methylphosphate 4-{6-[5-(2-chlorinde-6- methylaniline formyl)-thiazole-2-amido]-2-methyl pyrimidine-4}-piperazine-1- diethyl methylphosphate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/850fa9f0-3482-47a8-bb88-75ea0f42169d/a20081000819700181.PNG)
![4-{6-[5-(2-chlorinde-6- methylaniline formyl)-thiazole-2-amido]-2-methyl pyrimidine-4}-piperazine-1- diethyl methylphosphate 4-{6-[5-(2-chlorinde-6- methylaniline formyl)-thiazole-2-amido]-2-methyl pyrimidine-4}-piperazine-1- diethyl methylphosphate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/850fa9f0-3482-47a8-bb88-75ea0f42169d/a20081000819700191.PNG)