Patents
Literature
139 results about "Dickite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dickite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4) is a phyllosilicate clay mineral named after the metallurgical chemist Allan Brugh Dick, who first described it. It is chemically composed of 20.90% aluminium, 21.76% silicon, 1.56% hydrogen and 55.78% oxygen. It has the same composition as kaolinite, nacrite, and halloysite, but with a different crystal structure (polymorph). Dickite sometimes contains impurities such as titanium, iron, magnesium, calcium, sodium and potassium.
Method of leaching copper in copper containing pyrite using bacteria
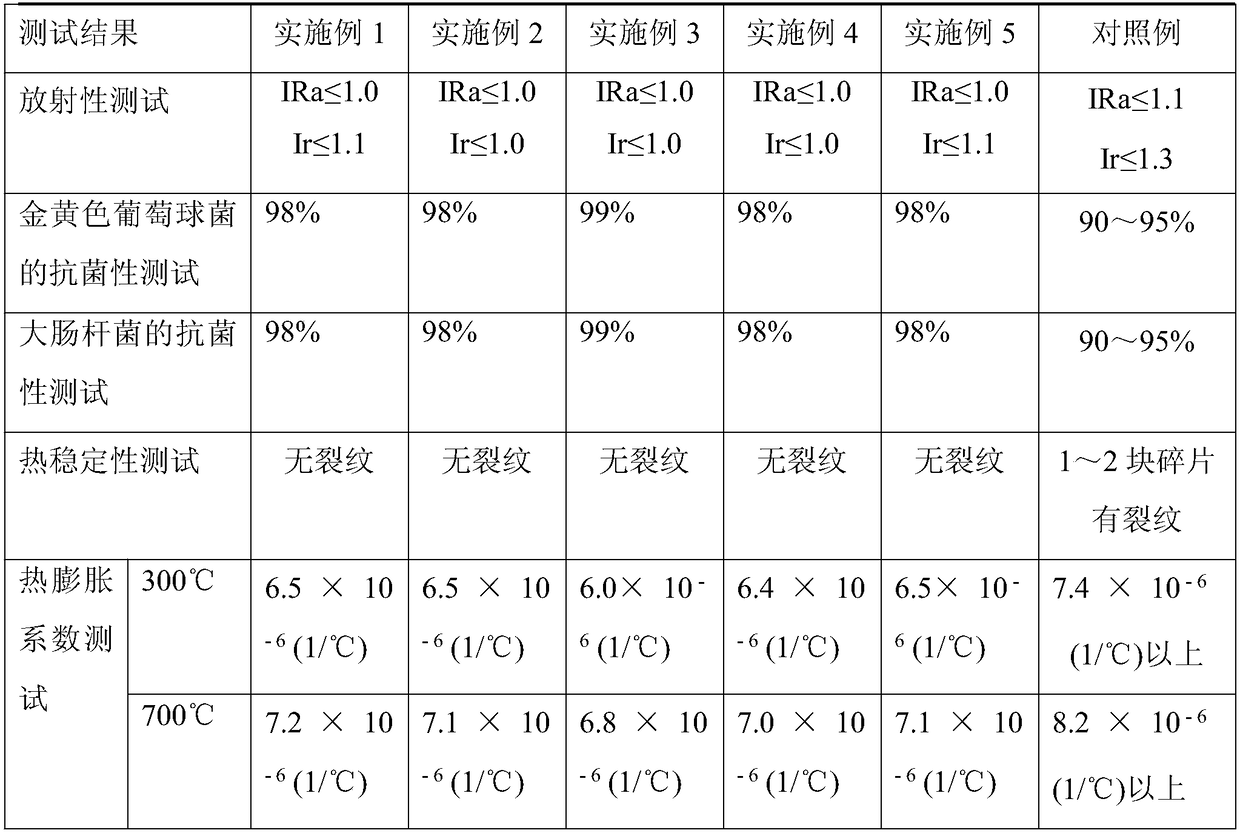
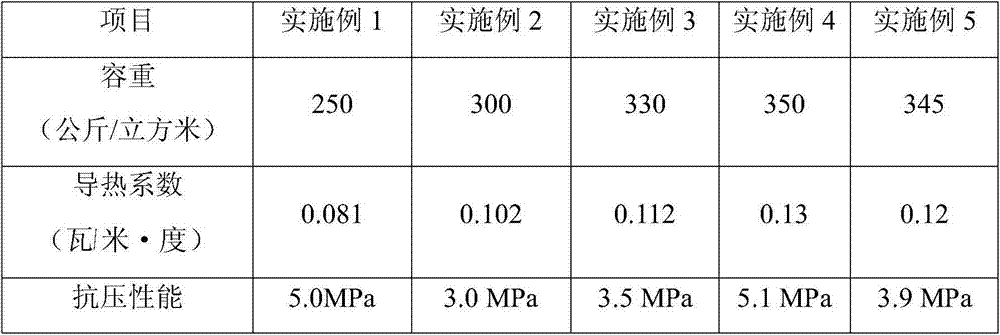
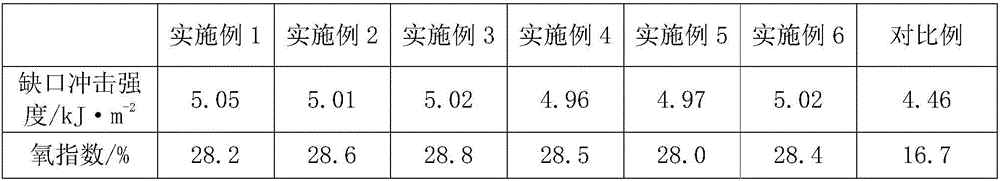
InactiveCN1556230ASulfur content risesImprove qualityProcess efficiency improvementSulfideCopper sulfide
A process for extracting Cu from the Cu-contained pyrite by bacteria features that the electrochemical catalyzing action of bacteria to different sulfide ores is used sufficiently, that is, the low-potential copper sulfide is used as corrosion anode, the high-potential pyrite or gold-silver ore is used as cathode, the bacteria are used to promote the Galvanic ell effect between them, and for the residual pyrite, the special microspirobacteria are used to suppress its oxidization. Its extraction-out rate can reach more than 75% within 4 months.
Owner:湖南世纪垠天鑫业科技有限公司
Modified phosphogypsum and its preparation
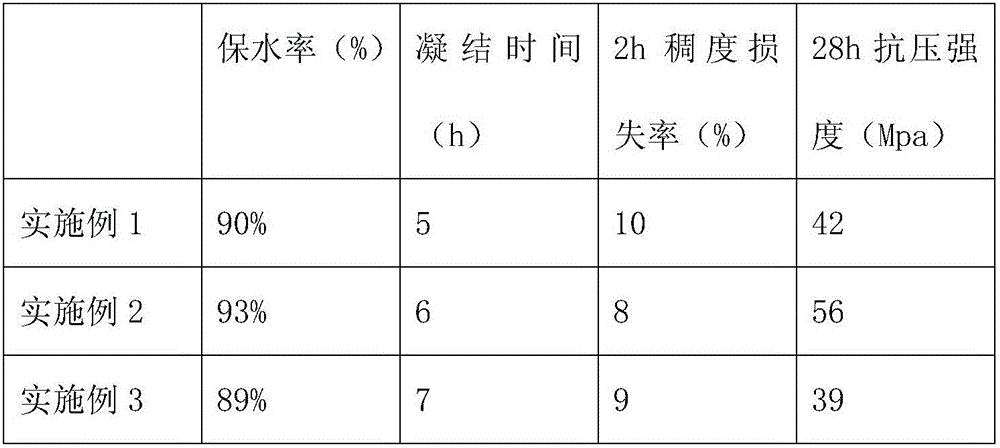
The present invention discloses a modified phosphogypsum and its preparation process. Its main weight composition is formed from 10-30% of additive (one, two or three kinds of aluminium sulfate slag, alum stone, plant ash, bentonite, slag, dickite, waste liquor and waste residue of paper mill and soda plant, white mud and sepiolite) and 70-90% of phosphogypsum. The phosphogypsum and additive are mixed together, and stacked at a certain temp. so as to obtain the modified phosphogypsum. If said modified phosphogypsum is closed-heated at 30-100 deg.C for 8-48 hr., and formed, dried and can be made into the cement retarded, and if the modified phosphogypsum closed-heated for 8-24 hr, is calcined at 600-900 deg.C, and can be made into cement reinforcing agent.
Owner:孙国庆 +1
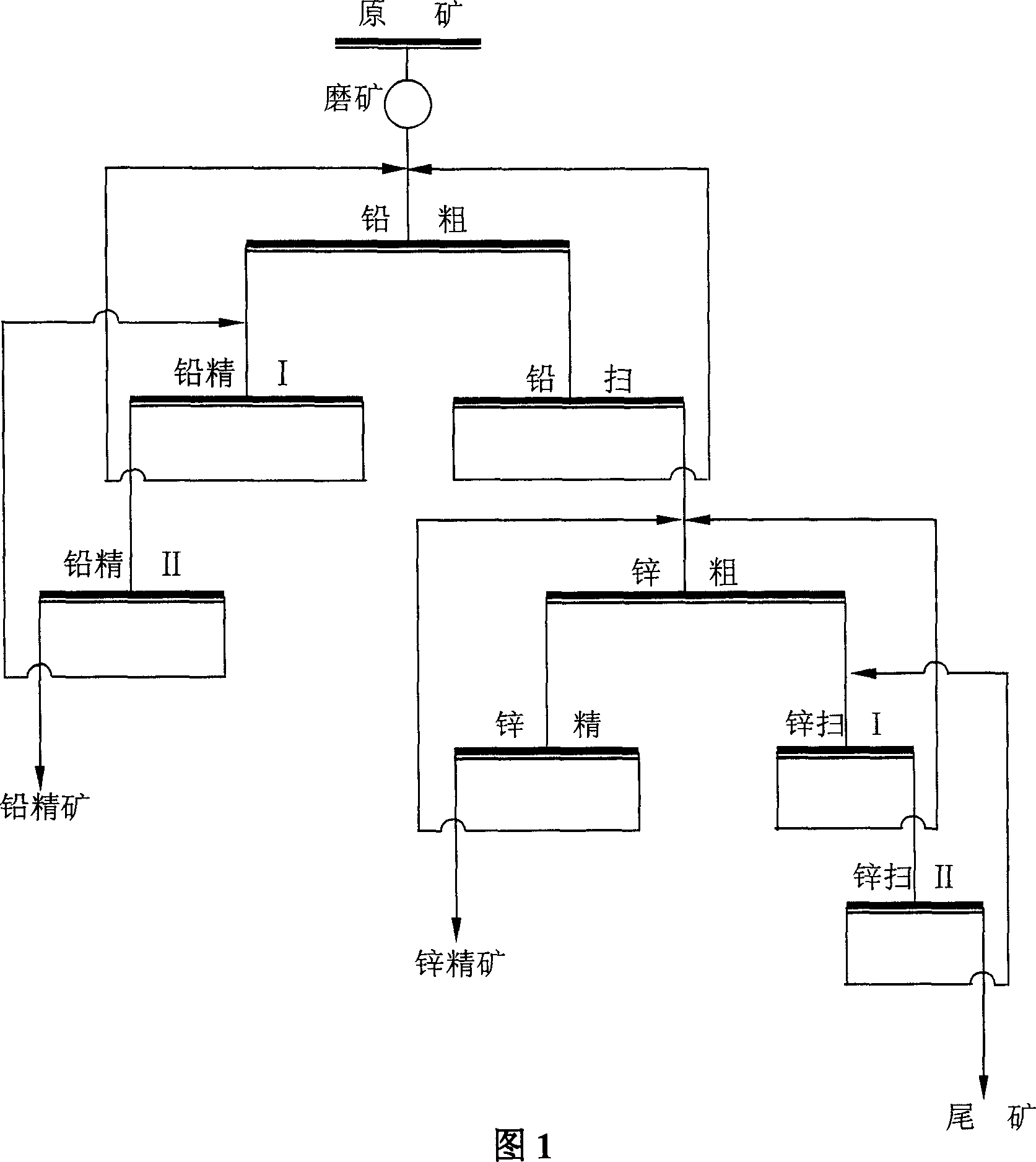
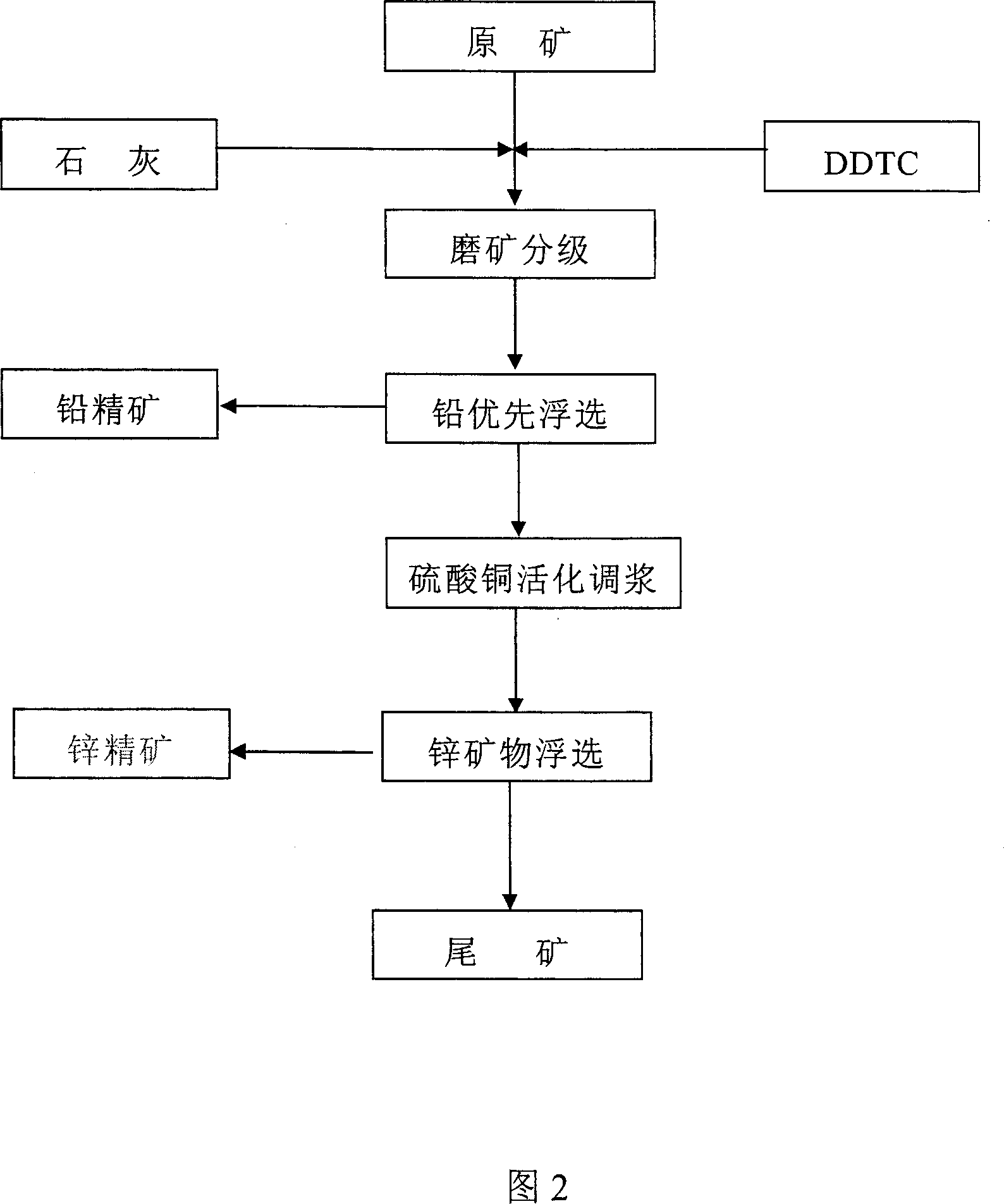
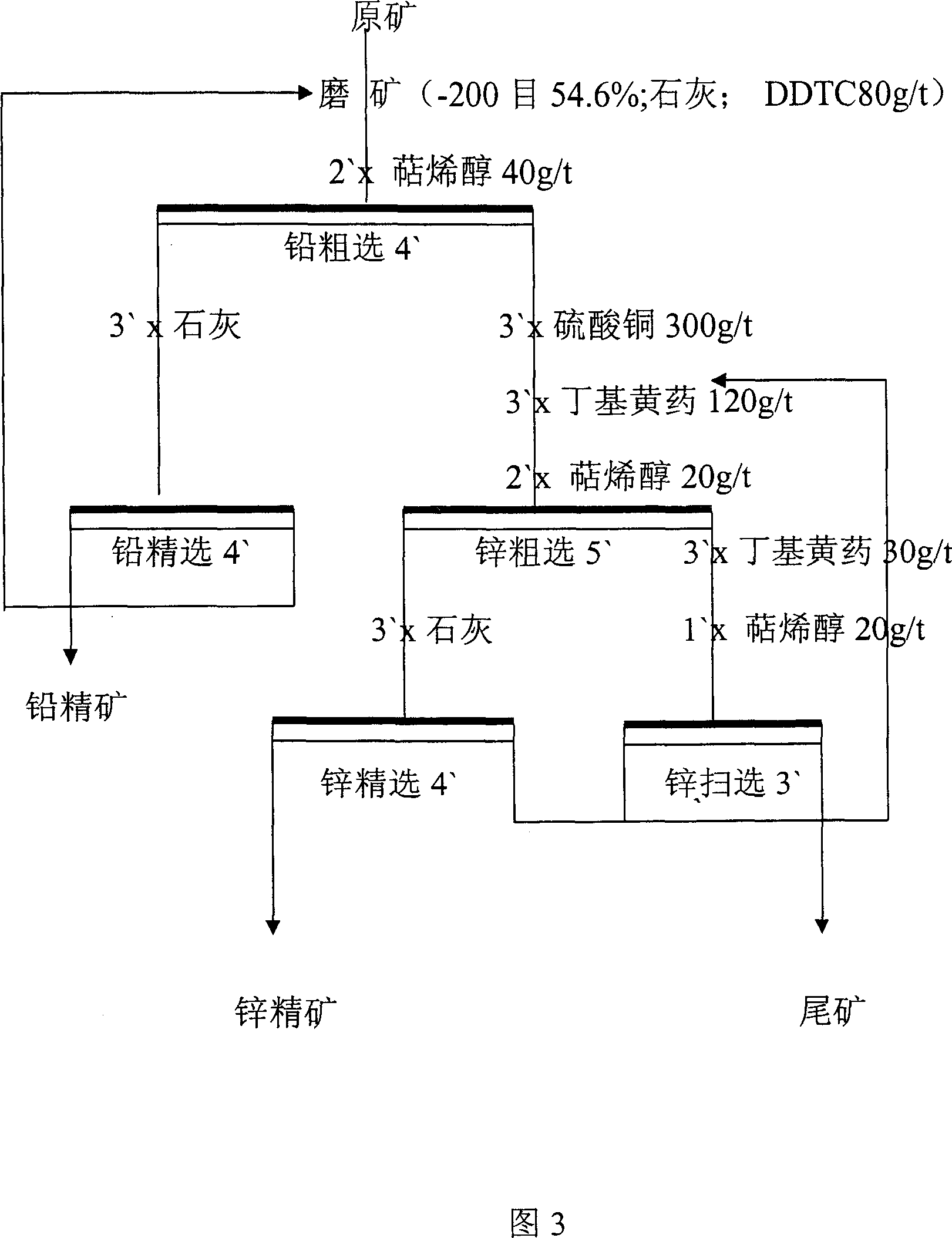
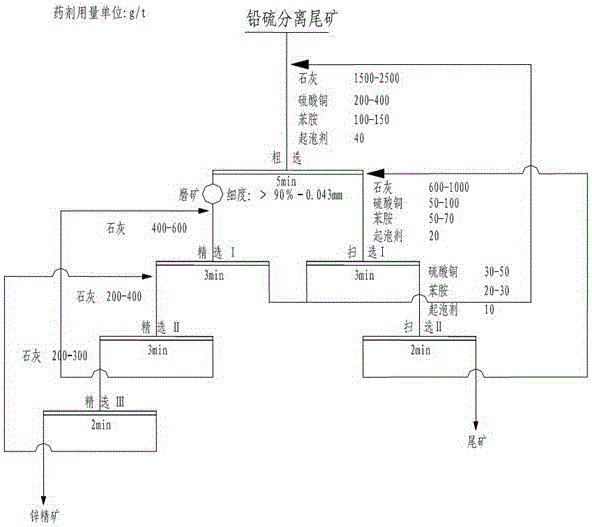
Process for increasing complicated sulfurized-lead-zinc ore dressing recovery rate
The present invention is green process of recovering complicated lead-zinc sulfide ore in high recovering rate. The technological process adopts lime to form high alkalinity and maintain the original potential of lead-zinc sulfide slurry during ore grinding floatation, sodium diethyl dithioamino formate as the selective lead mineral collecting agent, copper sulfate as the sphalerite activating agent and butyl xanthate as the zinc mineral collecting agent for optimized successive fast floatation. The present invention has raised recovering rate, low chemical consumption, simple technological process and low production cost.
Owner:青海西部矿业科技有限公司
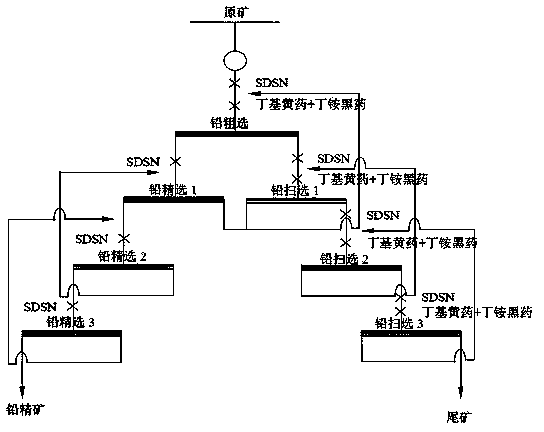
Flotation separation inhibitor and separation method of galena, pyrite and sphalerite
InactiveCN103909020AEfficient separationPlay a synergistic roleFlotationEcological environmentSeparation technology
The invention discloses a flotation separation inhibitor and separation method of galena, pyrite and sphalerite, and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing. The method includes adopting raw ores of sulfide lead-zinc mine as raw material, and adding SDSN (dimethyl dithiocarbamate : 2-(methylthio)ethylamine = 1-3:1)to serve as inhibitor of the pyrite and the sphalerite so as to perform lead and zinc sulphur flotation separation after the raw ores are grinded. Compared with an existing lead and zinc sulphur separation technology, the composite inhibitor SDSN has the advantages that selectivities of the pyrite and the sphalerite are high, inhibiting capability is high, usage is fewer, and adding is facilitated. The the pyrite and the sphalerite can be inhibited well, efficient separation of the galena and the zinc sulphur is implemented, the problems that according to the traditional lime or cyanide method, the recovery rate of associated gold, silver and other precious metals in the lead-zinc sulfide mine is low and ecological environment is seriously damaged are overcome, and an efficient and environment-friendly flotation separation method is provided for complex sulfide lead-zinc mine separation.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS
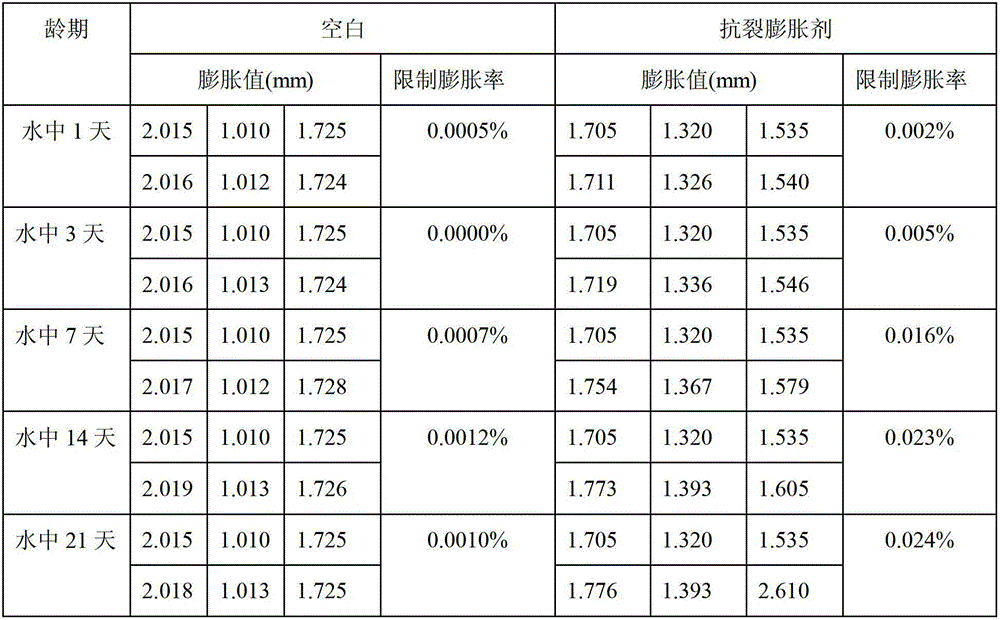
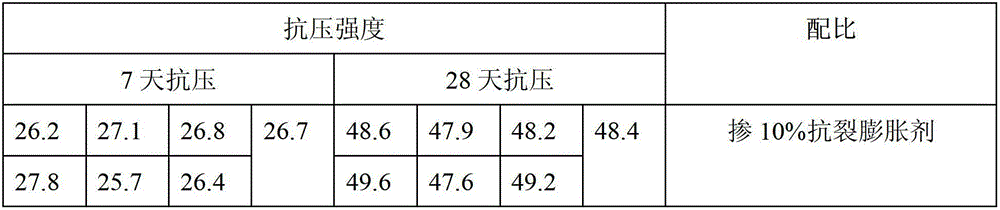
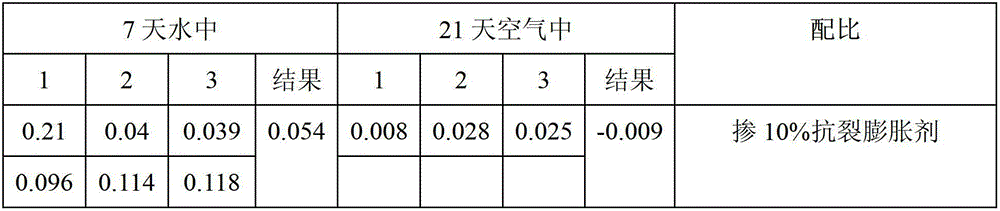
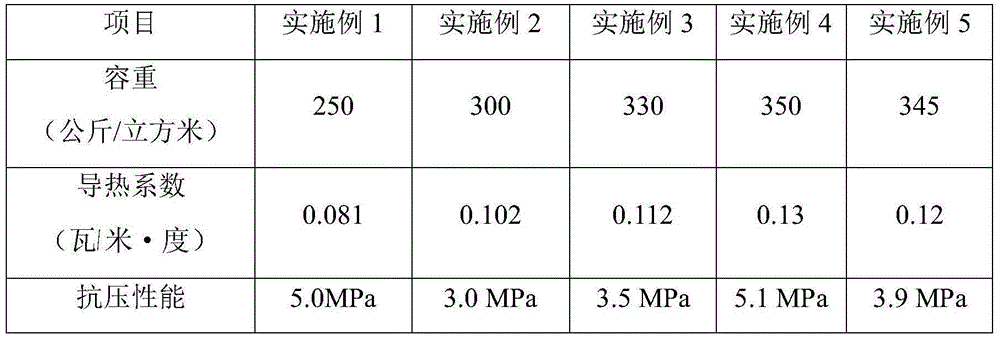
Anti-crack expanding agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102745933AImprove densification performanceImprove waterproof performanceWollastoniteDickite
The invention discloses an anti-crack expanding agent which comprises the following ingredients by weight: 35%-40% of calcium oxide clinker, 15%-20% of gypsum, 30%-35% of dickite, 5%-10% of coal ash and 2%-5% of wollastonite powder, wherein the sum of the weight ratios is 100%. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the anti-crack expanding agent. Compared with the prior art, the anti-crack expanding agent disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being capable of effectively preventing concrete from cracking so as to improve compactness.
Owner:TIANJIN JINSHENGYUAN SPECIAL BUILDING MATERIALS
Method for recycling sphalerite from separated tailings of lead-sulfur bulk concentrate
InactiveCN106552715AImprove the level of comprehensive utilizationRelieve stressFlotationSulfur productFoaming agent
The invention discloses a method for recycling sphalerite from separated tailings of lead-sulfur bulk concentrate. The method for recycling the sphalerite from the separated tailings of the lead-sulfur bulk concentrate comprises the steps that firstly, water is added to the separated tailings of the lead-sulfur bulk concentrate, and the mass percent concentration of a pulp is adjusted to be 25%-32%; secondly, an appropriate amount of lime is added so that the pH value of the pulp can be adjusted, and pyrite is inhibited at the same time; thirdly, copper sulfate is added as an activating agent to activate the sphalerite; and finally, a collecting agent, aniline, and a foaming agent are added for flotation of the sphalerite, the flotation procedure comprises one-time rough flotation, two-time scavenging and three-time concentration (after the concentrate obtained through rough flotation is ground to the extent that the ores reaching the grain level of >-0.043 mm account for 90%, concentration is conducted ), and effective concentration of the sphalerite is achieved. According to the sphalerite obtained through the method, the zinc grade is higher than 40%, and the recovery rate of zinc is higher than 80%. By the adoption of the method for recycling the sphalerite from the separated tailings of the lead-sulfur bulk concentrate, the zinc lost in the lead-sulfur separated tailings, namely sulfur products, can be well recycled, the comprehensive recovery rate of zinc is improved, and the economic benefits of a concentrating plant are increased.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for reinforcing microbiological leaching effect of zinc blende
InactiveCN105734285APromote oxidative decompositionImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementChemical factorHigh pressure
The invention discloses a method for reinforcing the microbiological leaching effect of zinc blende. The method comprises the steps of 1, smashing zinc blende sample ore into particles and smashing iron pyrite sample ore and / or copper pyrite sample ore to be added into particles; 2, sterilizing a culture medium, the zinc blende and iron pyrites and / or copper pyrites to be added at high temperature and high pressure; 3, adding the sterilized zinc blende into a shake flask containing the culture medium, then adding the iron pyrites or the copper pyrites into the shake flask and carrying out inoculation of mineral leaching microorganisms; 4, placing the shake flask in the step 3 on a constant-temperature shaker for cultivation; 5, measuring the leaching efficiency of zinc in the leaching process. According to the method, by adding the iron pyrites in a microbiological leaching system of the zinc blende, the pH value in solutions is low, the concentration of iron ions is high, the redox potential is high, oxygenolysis of the zinc blende is reinforced under the synergistic effect of the microorganisms and physical and chemical factors, and the leaching efficiency of the zinc can be improved obviously. The method provides technological guidance for efficient leaching of the zinc blende.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method of admixture taking kieselguhr as main raw material
The invention discloses a preparation method of an admixture taking kieselguhr as a main raw material. The admixture taking kieselguhr as a main raw material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 25-30 parts of kieselguhr, 25-30 parts of dickite, 15-20 parts of montmorillonite, 10-15 parts of allophane, 15-25 parts of vermiculite, 15-20 parts of mirabilite, 3-4 parts of polyvinyl alcohol, 3-4 parts of iron chloride, 1-3 parts of borax, 2-4 parts of gypsum, 2-3 parts of sodium silicate, 1-2 parts of ferrous sulfate, 2-3 parts of methyl cellulose and 1-2 parts of sodium carbonate. In the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the raw materials of the admixture taking kieselguhr as a main raw material are easily available, and the production process is simple and easy for producing products; when in use, the preparation method is convenient and can be uniformly used and meets the production stability; moreover, the production efficiency is improved, and the cost is saved.
Owner:武汉澳格瑞节能环保技术有限公司
Anti-static ceramic tile and production method thereof
The invention discloses an anti-static ceramic tile and a production method thereof. The anti-static ceramic tile is formed by the following raw materials of, by weight, 27 to 41 parts of river sand, 19 to 33 parts of lithium China stone, 16 to 28 parts of dickite, 15 to 25 parts of pebble chips, 12 to 24 parts of steel slags, 14 to 22 parts of composite clay, 10 to 15 parts of colloidal graphite powder, 8 to 14 parts of molybdenum disilicide, 3 to 6 parts of tin antimony oxide, 5 to 7 parts of liquid phenolic resin, 2 to 3 parts of sodium lauryl sulfate and 3 to 4 parts of chitosan. According to the anti-static ceramic tile and the production method thereof, the colloidal graphite powder, the molybdenum disilicide, the tin antimony oxide and the other components are added and accordingly the high anti-static function is achieved through the produced ceramic tile, the national anti-static ceramic tile standard GB26539-2011 requirements for the anti-static property are met, the strength is high, the heat stability is good, the abrasion resistance is good, the corrosion resistance is good, the service life of the anti-static ceramic tile is extended, and the use range of the anti-static ceramic tile is expanded.
Owner:安徽省亚欧陶瓷有限责任公司
Method for preparing cement reinforcer
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cement reinforcer. The cement reinforcer is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-40 parts of dickite, 30-40 parts of montmorillonite, 20-30 parts of shale, 10-20 parts of calcite, 10-20 parts of kieselguhr, 5-10 parts of calcium fluoride, 5-10 parts of mirabilite, 3-4 parts of polyving alcohol, 3-4 parts of sodium acetate, 1-3 parts of sodium carbonate, 2-4 parts of gypsum, 2-3 parts of sodium silicate, 1-2 parts of aluminum powder and 1-2 parts of calcium nitrate. The cement reinforcer disclosed by the invention is uncomplicated in production technology, and simple and easy to produce, and can be conveniently and evenly used in the use procedure, the raw materials are easy to purchase, the stability of production is met, the production efficiency is improved, and the cost is saved.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV +2
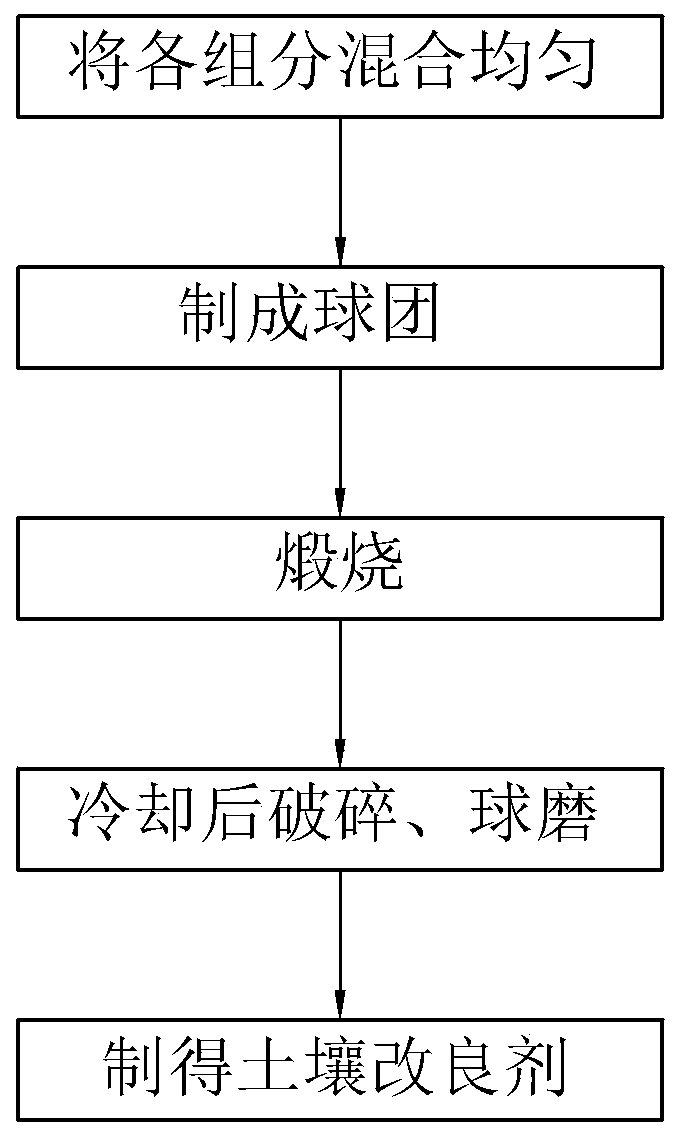
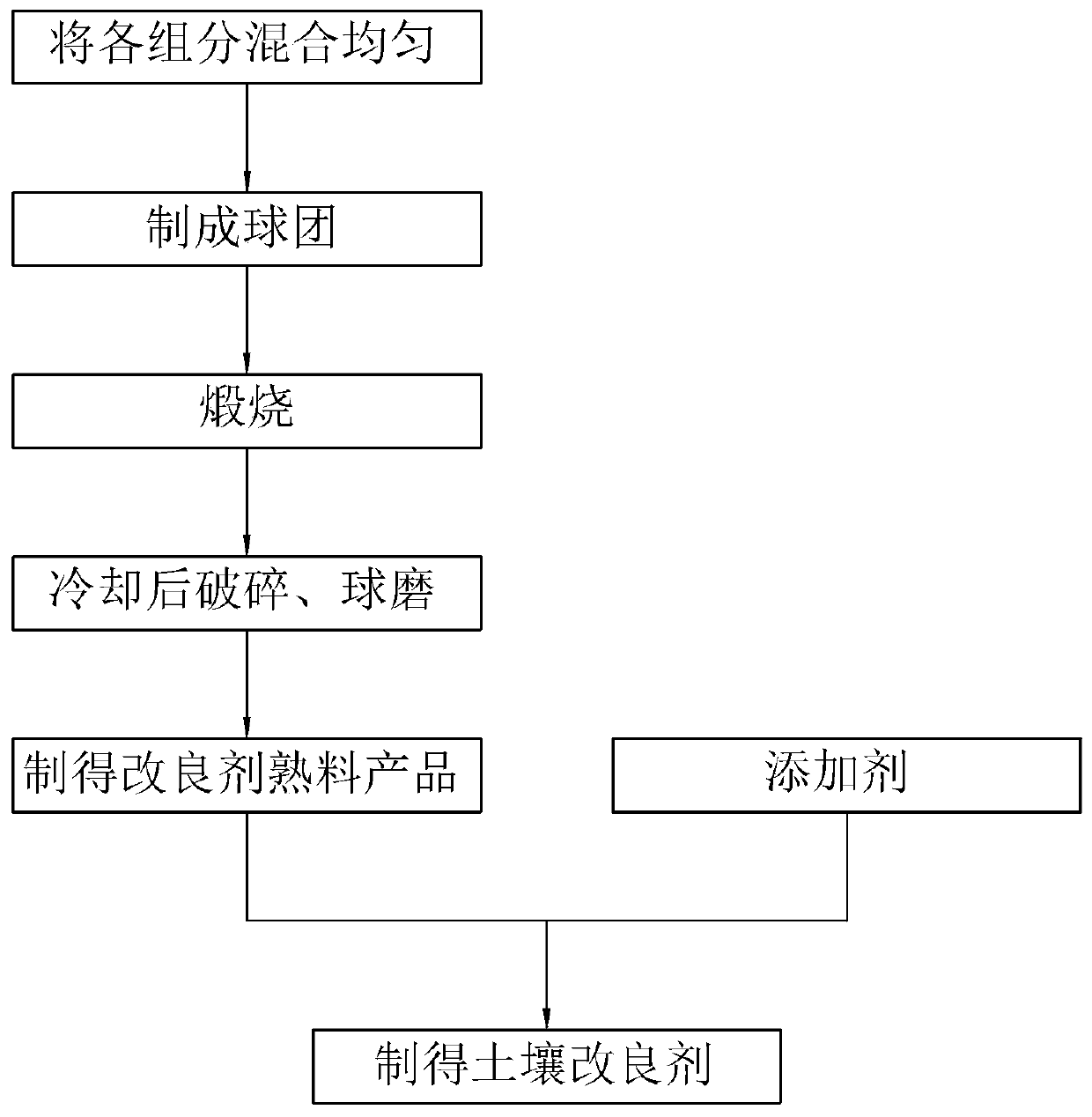
Soil conditioner as well as preparation method and use method thereof
ActiveCN110079332AWide variety of sourcesReduce typesCalcareous fertilisersAgriculture tools and machinesDickiteAlunite
The invention relates to the technical field of soil remediation, in particular to a soil conditioner as well as a preparation method and use method thereof. The soil conditioner comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 40-60% of copper tailings, 20-40% of fluorite tailings or limestone, 6-20% of talc, serpentine or dolomite, and 2-5% of a pellet curing agent, wherein the totalweight is 100%; and the copper tailings include quartz, alunite and dickite. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, weighing the components and mixing the components uniformly;sep 2, preparing the mixture obtained in the step 1 into pellets; step 3, calcining the pellets at a temperature of at least 1000 DEG C for at least 1.5 hours; and step 4, cooling activated pellets and performing ball milling to obtain the soil conditioner. The soil container contains non-ferrous metal and non-metallic ores, various major, medium and trace elements necessary for the growth of crops, fruit trees and seedlings, and basically no additional major, medium and trace elements need to be added.
Owner:SHENZHEN MPD HITECH CO LTD
Sewage purifying agent for improving sewage purifying effect
InactiveCN105692735AImprove purification effectEfficient degradationWater/sewage treatmentCarboxymethyl celluloseSewage
The invention discloses a sewage purifying agent for improving sewage purification effect, which comprises the following components in parts by weight: diatomite, 45-55 parts; light calcium carbonate, 30-40 parts; vermiculite powder, 35-45 parts powder; dickite, 25-35 parts; sericite powder, 10-20 parts; quartz sand, 15-25 parts; natural gypsum, 15-25 parts; zinc stearate, 4-8 parts; carboxymethyl fiber A mixture of cellulose and sodium alginate, 5-7 parts; the weight ratio of the carboxymethyl cellulose and sodium alginate is 4-6:1. The sewage purifying agent provided by the invention can efficiently degrade organic matter in sewage, significantly reduce COD value and total nitrogen content, and improve sewage purification effect. The preparation method of the sewage purifying agent of the present invention is simple, does not need large-scale equipment, can be produced on a large scale, and has low cost.
Owner:叶君芝
Preparation method of cement enhancer capable of improving strength of cement product
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cement enhancer capable of improving the strength of a cement product. The preparation method is characterized in that the cement enhancer is prepared from the following raw materials: dickite, montmorillonite, shale, calcite, diatomaceous earth, calcium fluoride, mirabilite, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium acetate, sodium carbonate, gypsum, sodium silicate, aluminum powder and calcium nitrate. The raw materials of the enhancer are easy to buy, the production process is uncomplicated, simple and easy for product production, and the cement enhancer is convenient and uniform to use, and the stability in production can be satisfied; moreover, the production efficiency can be improved, and the cost can be saved.
Owner:SHANDONG YONGYUAN CO LTD
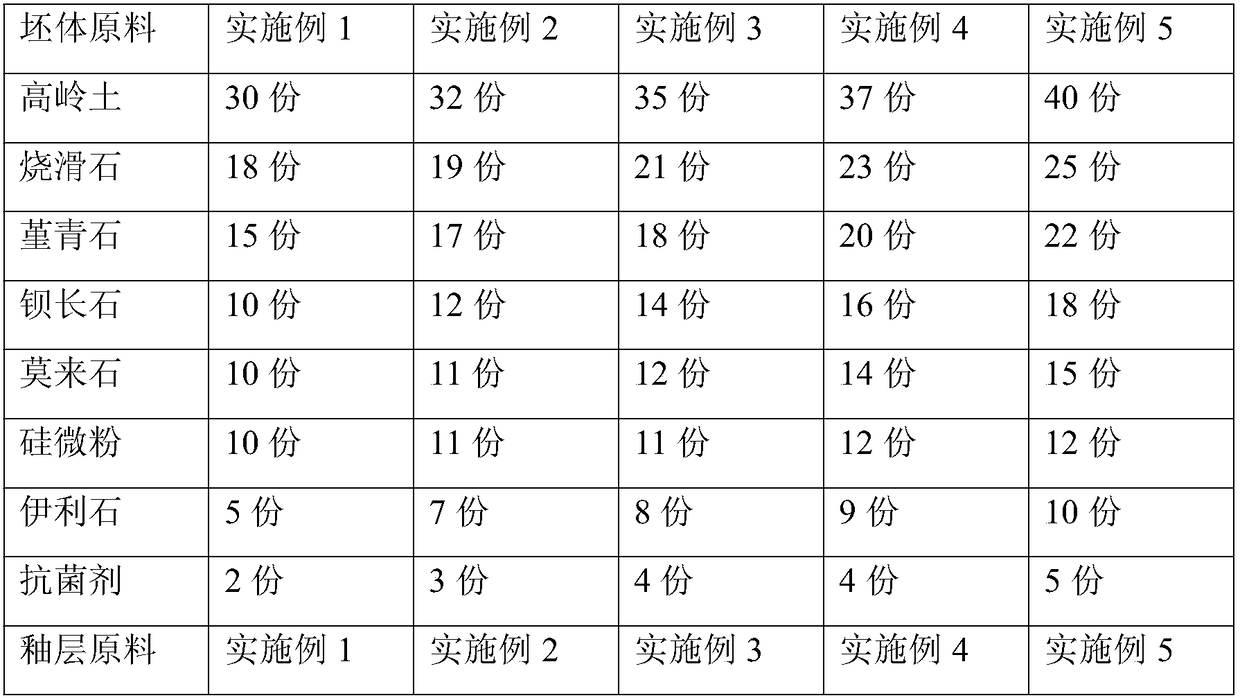
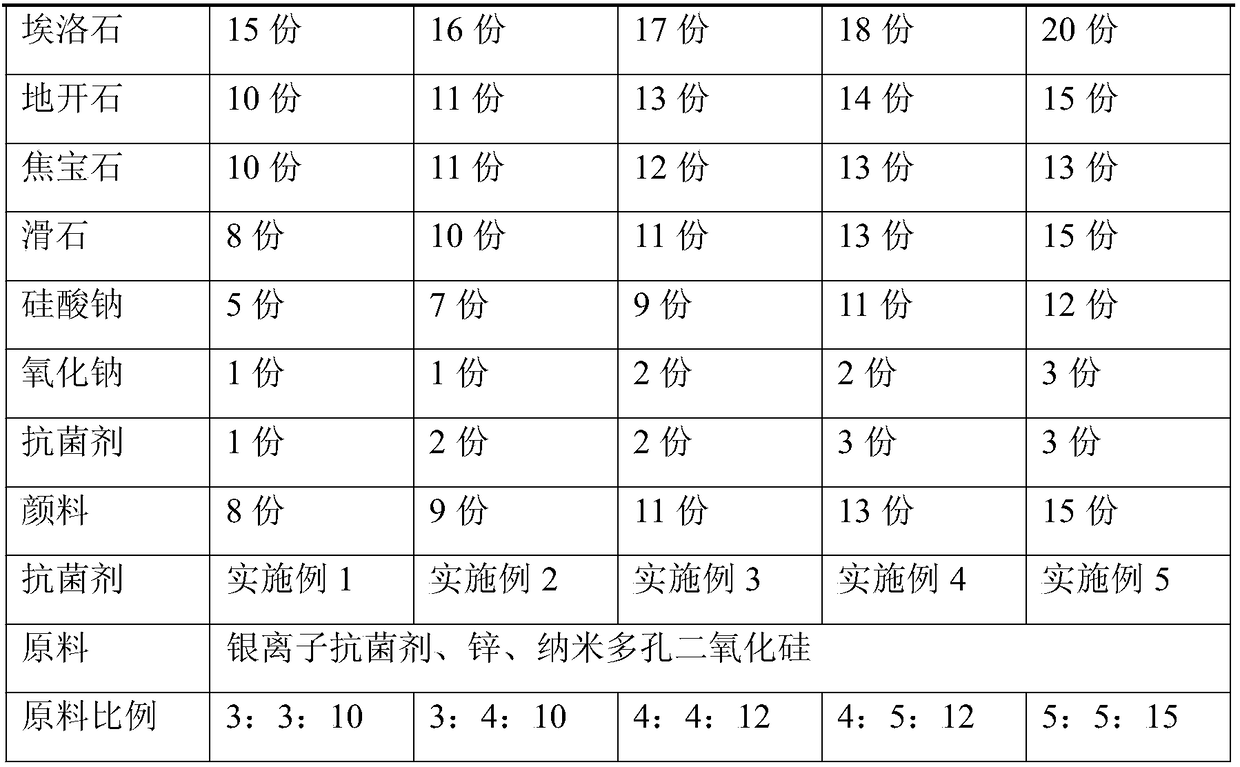
Low-expansion anti-sticking antibacterial ceramic pot and manufacturing process thereof
The invention provides a low-expansion anti-sticking antibacterial ceramic pot. The low-expansion anti-sticking antibacterial ceramic pot comprises a green body and an enamel layer, wherein the greenbody is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30 to 40 parts of kaolin, 18 to 25 parts of burned talcum, 15 to 22 parts of cordierite, 10 to 18 parts of barium feldspar, 10 to15 parts of mullite, 10 to 12 parts of silica powder, 5 to 10 parts of illite, and 2 to 5 parts of antibacterial agent; and the enamel layer is prepared from the raw materials in parts by weight: 15 to 20 parts of halloysite, 10 to 15 parts of dickite, 10 to 13 parts of flint clay, 8 to 15 parts of talcum, 5 to 12 parts of sodium silicate, 1 to 3 parts of sodium oxide, and 1 to 3 parts of antibacterial agent. The ceramic pot manufactured by adopting the raw materials and process provided by the invention is small in heat expansion coefficient, small in radioactivity, high in thermal stability,high in antibacterial performance, free from being fractured when in frequent use, free from breeding bacteria and free from damaging of the health of the human body.
Owner:福建省德化县福庆陶瓷有限公司
Wall building material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a wall building material, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 50-80 parts of ceramic polishing residue, 0-30 parts of feldspar, 2-10 parts of calcined soapstone, 10-20 parts of red mud, 0-10 parts of lithium feldspar, 0-15 parts of dickite, 0.5-2 parts of silicon carbide, 1.5-3 parts of stabilizer and 40-50 parts of water. The invention also provides a preparation method of the wall building material. The method comprises the following steps: ball-milling, drying, loading into a cellar, sintering and cutting. The wall building material disclosed by the invention is light in dead load, good in anti-seismic effect, high in thermal insulation properties and good in sound insulation.
Owner:河南中传装备有限公司
High-water-resistance two-component siloxane-acrylate copolymer cement-based waterproof coating and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high-water-resistance two-component siloxane-acrylate copolymer cement-based waterproof coating and a preparation method thereof. The coating is prepared from a liquid material A and a powdery material B in a mass ratio of 1: (1.5-2). The liquid material A is prepared from raw materials consisting of silicone acrylic emulsion, polyethylene glycol, trifluoroethyl methacrylate, octyldodecyl beeswax, polyribosome acrylate, disodium methylene dinaphthalene sulfonate, liquid paraffin, albolene, hydroxyethyl cellulose, Span-20, water and the like. The powdery material B is prepared from raw materials consisting of magnesium-slag Portland cement, river sand, silicon phosphorate, dickite, magnesium hexafluorosilicate hexahydrate, vanadium extraction tailings, halloysite slag, hydrophobic fumed silica, dolomite, converter slag, clastic rock, calcium rosinate, etc. The two-component siloxane-acrylate copolymer cement-based waterproof coating prepared in the invention is low in water absorption capacity and good in water resistance, does not swell in case of soaking in water and has excellent caking properties, corrosion resistance, temperature tolerance and ageing resistance.
Owner:ANHUI KUAILAI WATERPROOFING & ANTI CORROSION
Preparation method of high-performance glass fiber yarn
The invention relates to a preparation method of high-performance glass fiber yarn. The high-performance glass fiber yarn is prepared from, by weight, 0-40% of waste glass, 0-40% of silica sand, 3-7%of fluorite, 10-16% of pyrophyllite, 8-12% of kaoline, 4-8% of dickite, 4-8% of calciclase, 5-11% of sodium borate, 1-3% of limestone, 2-6% of marble, 5-9% of dolomite, 1-3% of fluorite and 2-4% of mirabilite. Crushing, smelting, wiredrawing, drying, yarn manufacturing and other technologies are adopted, and the high-quality glass fiber yarn is produced. According to the produced high-performanceglass fiber yarn, effective use of waste resources is enhanced, and environmental pollution is lowered; the produced glass fiber yarn has the advantages of being high in acid and alkali resistance, high in mechanical strength, good in rigidity and resistant to aging.
Owner:ANHUI TONGLI NEW MATERIALS
Method for preparing constructional composite mineral admixture
The invention discloses a method for preparing a constructional composite mineral admixture. The method is characterized by comprising the following raw materials in parts by weight: 45-50 parts of aluminum oxide clinker, 15-20 parts of calcined alunite, 5-10 parts of zinc sulfate, 25-30 parts of dickite, 25-30 parts of attapulgite clay, 20-25 parts of pulverized fuel gas, 1-5 parts of zeolite powder, 2-4 parts of diatomaceous earth, 2-5 parts of bentonite, 1-2 parts of methylcellulose, 0.5-1 part of sodium sulfite, 0.5-1 part of quicklime, 0.3-0.5 part of sodium carbonate, 0.5-1 part of gypsum and 0.2-1 part of sodium silicate. The constructional composite mineral admixture has the function of effectively resisting water, humidity, swelling, cracking, seepage and the like, and does not rust or corrode reinforcing steel bars.
Owner:JIN GUANG DAO ENVIRONMENTAL CONSTR GRP
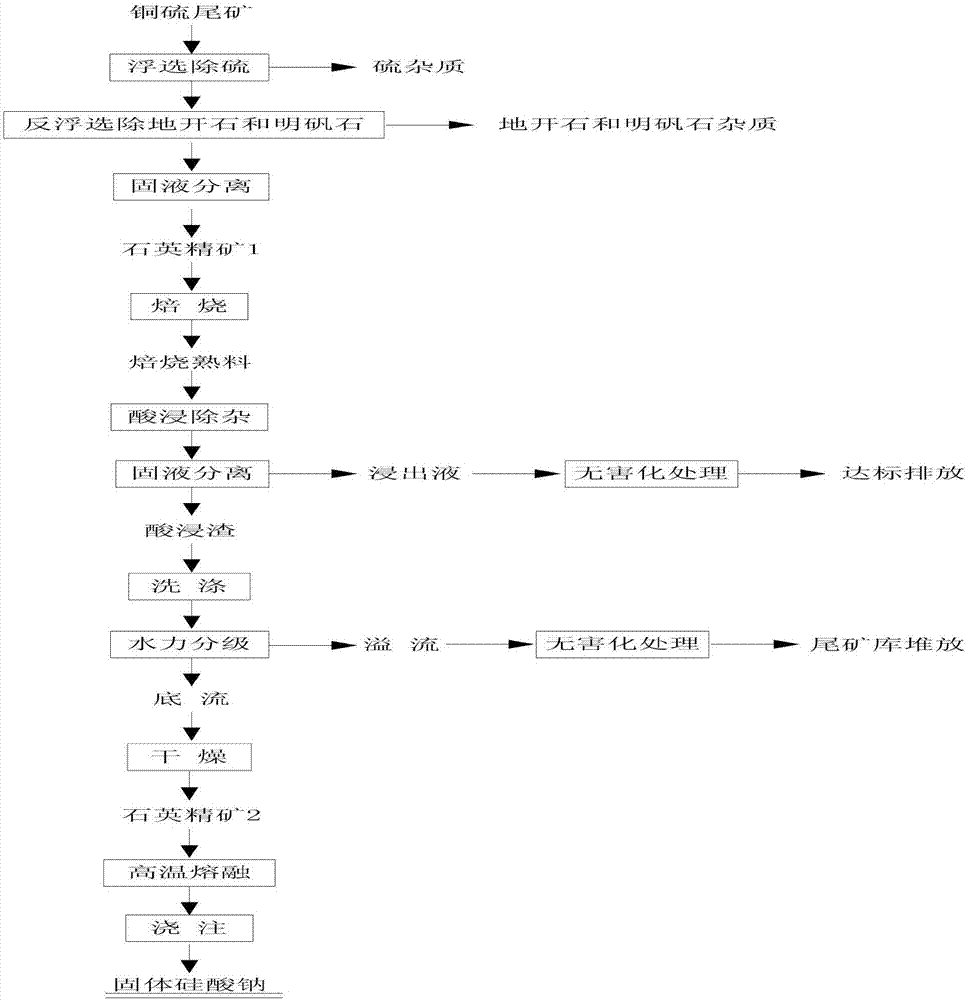
Method for preparing industrial sodium silicate by using waste copper sulfur tailings
The invention relates to a method for preparing industrial sodium silicate by using waste copper sulfur tailings. The method is conducted according to the following step procedures and conditions: performing flotation to remove impurities: adjusting the PH value of copper tailing slurry, adding ammonium dibutyl dithiophosphate, stirring, adding second oil, performing flotation to remove impurities to obtain tailing slurry 1, adding lauryl amine and sodium oleate, stirring, performing reverse flotation to remove impurities such as dickite and alunite to obtain tailing slurry 2, and performing solid liquid separation to obtain quartz concentrate 1; roasting: adding a carbon powder and sodium chloride, mixing uniformly and roasting to obtain roasting clinker; performing acid leaching to remove impurities: feeding the roasting clinker into an acid leaching system, enabling copper, iron and the like in the roasting clinker to leach out, performing solid liquid separation to obtain a leaching liquid and acid leach residue, grading the acid leaching residue to obtain overflow and underflow, and performing solid liquid separation and drying on the underflow to obtain quartz concentrate 2; melting at a high temperature: adding the quartz concentrate 2 into sodium carbonate, mixing uniformly, melting and pouring to obtain a solid sodium silicate product. The method has the advantages of simplicity in process operation, high in practicability, environmental friendliness, easiness in industrialization and the like, and is suitable for comprehensive utilization of mineral resources.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
High-toughness and halogen-free flame retardant polypropylene cable material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106633376AImprove fire resistanceLarge granularityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsPolymer scienceAntioxidant
The invention provides a high-toughness and halogen-free flame retardant polypropylene cable material. The high-toughness and halogen-free flame retardant polypropylene cable material is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of polypropylene, 0.5 to 1 part of an antioxidant, 1 to 1.5 parts of a lubricant, 0.2 to 0.7 part of an ultraviolet absorbent, 10 to 15 parts of a plasticizer, 4 to 4.5 parts of a compatilizer, 0.1 to 0.6 part of a nucleating agent, 6 to 11 parts of a flexible modifier, and 11 to 16 parts of modified dickite powder. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the high-toughness and halogen-free flame retardant polypropylene cable material. The high-toughness and halogen-free flame retardant polypropylene cable material disclosed by the invention is relatively high in toughness and relatively strong in flame retardancy.
Owner:FOSHAN FEISHIDA NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
High strength dry-mixed masonry mortar and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high strength dry-mixed masonry mortar and a preparation method thereof. The masonry mortar is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 to 150 parts of silicate cement, 20 to 30 parts of modified dickite powder, 10 to 20 parts of blast furnace slag, 10 to 20 parts of iron tailings, 3 to 6 parts of polyether sulfone, 3 to 7 parts of limestone, 5 to 10 parts of river sand, 2 to 8 parts of latex powder, 2 to 5 parts of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, 1 to 5 parts of water reducer, 1 to 3 parts of sodium abietate, and 2 to 5 parts of bonding auxiliary agent. The provided high strength dry-mixed masonry mortar has the advantages that the properties are stable; the workability, water retaining performance, and bonding strength are good; the bonding effect between the masonry mortar and building blocks is good; mortar joint is plump, the tightness is good, the strength is high, the cracking is difficult to happen, and the using performance of mortar is improved.
Owner:安庆市凯瑞建材有限公司
A kind of wall building material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a wall building material, comprising the following components in parts by weight: 50-80 parts of ceramic polishing residue, 0-30 parts of feldspar, 2-10 parts of calcined soapstone, 10-20 parts of red mud, 0-10 parts of lithium feldspar, 0-15 parts of dickite, 0.5-2 parts of silicon carbide, 1.5-3 parts of stabilizer and 40-50 parts of water. The invention also provides a preparation method of the wall building material. The method comprises the following steps: ball-milling, drying, loading into a cellar, sintering and cutting. The wall building material disclosed by the invention is light in dead load, good in anti-seismic effect, high in thermal insulation properties and good in sound insulation.
Owner:河南中传装备有限公司
Liquid fertilizer dedicated for flowers
InactiveCN105936614AIncrease profitEasy to viewAnimal corpse fertilisersExcrement fertilisersDiseaseDickite
The invention discloses a liquid fertilizer dedicated for flowers. The liquid fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials: cow dung, pigeon manure, earthworm manure, bean product leftover, leftover in slaughter house, fermentation leftover, gulfweed, sea tangle, feather powder, Angel yeast, natto strain, sulfur bacteria, rhizobium, bacillus subtilis, compound enzyme, protease, orthoclase, bryozoatum, and dickite. The provided liquid fertilizer has the advantages of scientific formula, comprehensive nutrients, easy absorption, safety, and no toxicity, and is suitable for many fertilizing and planting modes. Organic raw materials are decomposed and fermented by enzymes, macromolecular substances are decomposed, the fertilizing effect is quick and long-lasting, the soil hardening is relieved, the stress resistance is enhanced, the happening rate of diseases and insects is reduced by 12.7%, the blossom period is prolonged by 16 to 18 days; the organic raw materials are all wastes, the environment is protected, the technology is simple, the preparation efficiency is high, the cost is saved by 24.2%; and orthoclase, bryozoatum, and dickite can balance the nutrients, improve the soil structure, improve the fertilizer utilization rate, and enhance the ornamental value of flowers.
Owner:合肥市田然农业科技园有限公司
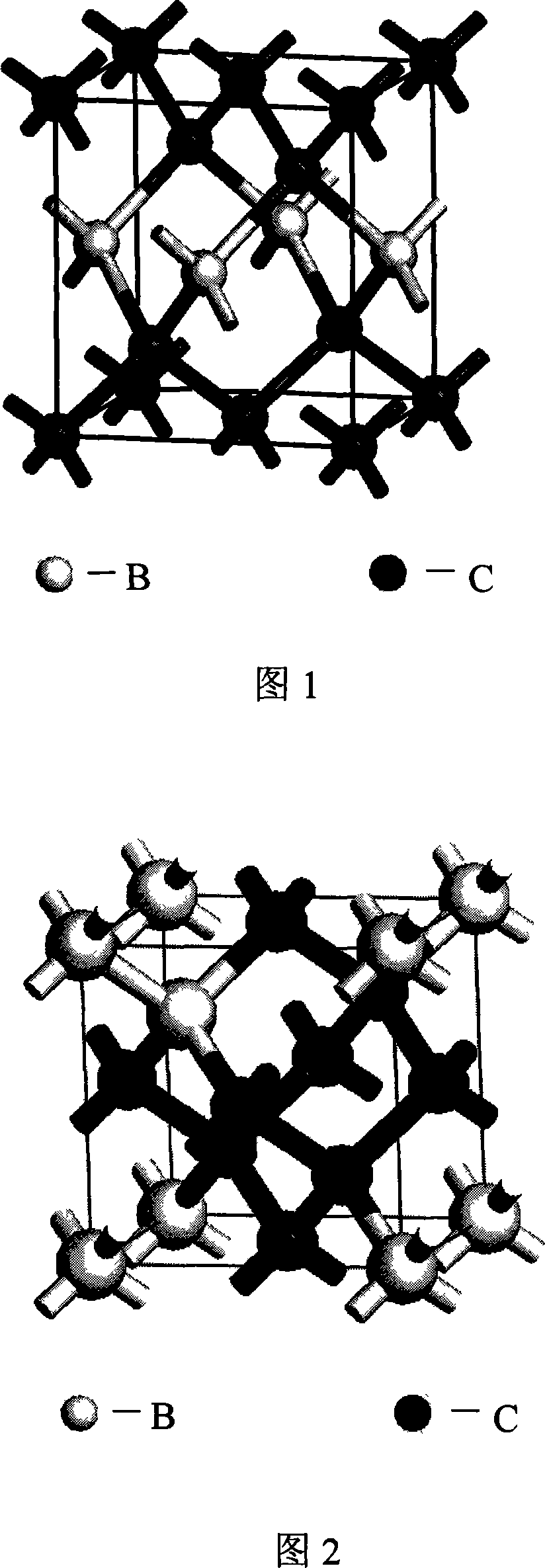
Conductive superhard material BxCy compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101121517AHas hybrid characteristicsConductive materialSuperhard materialChemical composition
The present invention relates to an electric superhard BxCy compound and the preparation method of the compound. The present invention is characterized in that the BxCy compound contains B of 5%-30%, C 70%-95% and a structure containing a sphalerite and a spiauterite; thereof the conductive B-C bond and C-C bond have the hybrid characteristic of sp3 and the rigidity is more than 40GPa. The preparation steps are as following: A precursor of the BxCy and a catalytic alloy of Mg-Ni are mixed and pressed to be a wafer or the precursor of the BxCy and the catalytic alloy of Mg-Ni are respectively pressed to be the wafer and then put into a pressure cavity of high pressure. The wafer is synthesized on a press at a high temperature between 1200 DEG C and 1800 DEG C and a high pressure between 3 GPa and 10 GPa. The catalyst of the obtained production is solubilized by a mixed liquor of a dilute sulfuric acid and a dilute nitric acid and then dried.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Quick-drying concrete
The invention relates to a quick-drying concrete, comprising hydrophobic perlite, crushed stone, mica powder, calcium fluoride, zinc sulfate, sodium silicate, montmorillonite, dickite and diatomite. By weight, 15-19 parts of the hydrophobic perlite, 30-47 parts of crushed stone, 20-24 parts of mica powder, 10-14 parts of calcium fluoride, 5-8 parts of zinc sulfate, 3-8 parts of sodium silicate , 15-19 parts of montmorillonite, 18-22 parts of dickite and 18-25 parts of diatomite. The invention can effectively realize the quick-drying of concrete, at the same time improve the flexural strength and toughness of concrete, limit the crack width, resist concrete surface cracking and anti-explosion fire resistance, and can be widely used in the fields of civil engineering, water conservancy, municipal transportation, marine military industry and the like concrete structure.
Owner:周淑华
Preparation method of cement composite additive
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cement composite additive. The preparation method is characterized in that the cement composite additive comprises the following materials in parts by weight: 30-35 parts of alumina clinker, 5-10 parts of calcined alunite, 1-5 parts of zinc sulfate, 10-20 parts of dickite, 10-20 parts of attapulgite clay, 10-15 parts of coal ashes, 1-5 parts of zeolite powder, 2-4 parts of diatomite, 2-5 parts of bentonite, 1-2 parts of methyl cellulose, 0.5-1 part of sodium sulfite, 0.5-1 part of quick lime and 0.2-0.5 part of calcium fluoride. The cement composite additive disclosed by the invention has functions of being efficient and waterproof, moisture-proof, inflation-proof, crack-resistant, impervious, and the like, and has no corrosion effect on a reinforcing steel bar.
Owner:郑州市公路工程公司
Craft porcelain with raised particle effect on glaze surface and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a craft porcelain with a raised particle effect on a glaze surface and a preparation method thereof. The craft porcelain with a raised particle effect on a glaze surface comprises a green body and overglaze arranged on the green body, the overglaze comprises a glaze slurry and frit dry particles, the glaze slurry comprises the following raw materials: Dehua quartz, halloysite, Dehua feldspar, montmorillonite, sepiolite, dickite, pyroxene, aluminum oxide and lanthanum oxide, during preparation of the craft porcelain, the overglaze is uniformly applied to the surface of the green body, then the green body is sent into a kiln for firing, the surface of the fired craft porcelain has the decoration effect of naturally fused convex bumped artistic patterns, and bump points are clear, vivid, full and rich in layering sense, thus further improving the aesthetic sense of the craft porcelain.
Owner:FUJIAN DEHUA JIASHUN CRAFTS
Heat-resistant ceramic pot and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a heat-resistant ceramic pot which is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 65-80 parts of spodumene, 13-20 parts of clay, 10-16 parts of kaolin, 8-13 parts of sandstorm soil, 6-11 parts of dickite, 5-9 parts of pyrauxite, 2-7 parts of obsidian and 0-0.5 part of zoisite. The preparation method of the heat-resistant ceramic pot comprises the following steps: S1. manufacturing of billet: mixing the raw materials according to parts by weight, pugging, carrying out injection forming, trimming the billet, sending the billet into a kiln, and carrying out bisque firing to prepare a biscuit; S2. treatment of biscuit internal surface: spraying a non-stick paint on the biscuit internal surface, and baking; and S3. treatment of biscuit external surface: spraying a ceramic paint on the biscuit external surface twice, spraying a metal coating, spraying silicone oil, and finally, spraying the non-stick paint. The heat-resistant ceramic pot product has greatly enhanced high-temperature capability, can directly contact the electromagnetic oven, has the advantages of high heat transfer rate and obvious energy saving effect, and can bear the high power of the electromagnetic oven of up to 2100W.
Owner:潮州市威成瓷艺有限公司
Production method of colored sintered alumina-silica refractory brick
The invention discloses a production method of a colored sintered alumina-silica refractory brick. The colored sintered alumina-silica refractory brick is formed by sintering kaolin, dickite, white mica, zircon, xenotime, ilmenite, a coloring substance, refractory fibers, a binder and a finishing agent. The method comprises the following steps: 1, forming a mixture; 2, forming a mixed slurry; 3, forming a brick to be finished; 4, forming a finished brick; 5, forming a brick to be sintered; and 6, carrying out sintering molding. The colored sintered alumina-silica refractory brick produced in the invention has the characteristics of bright color, diversified colors, long-time oxidation resistance, good erosion resistance, good permeation resistance, good anti-stripping performance and excellent thermal shock stability.
Owner:CHANGXING MENGYOU REFRACTORIES
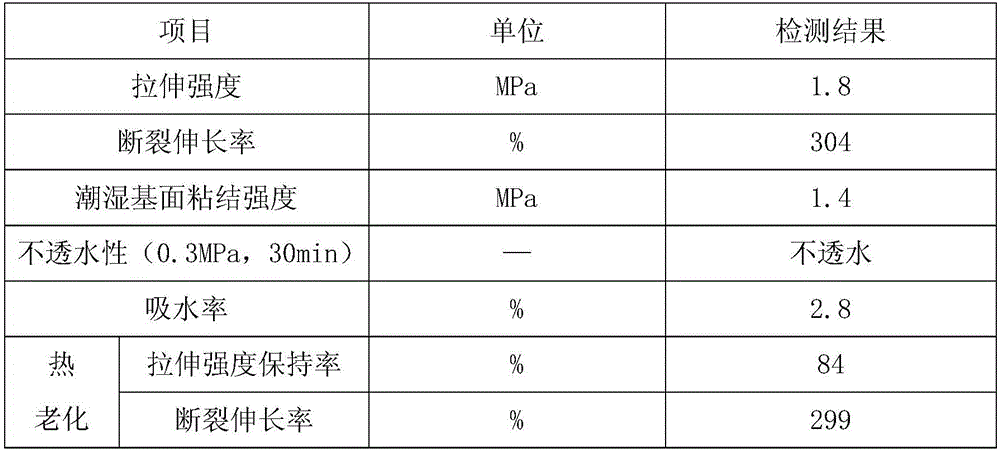
Method for restraining copper-activated sphalerite through whey proteins
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com