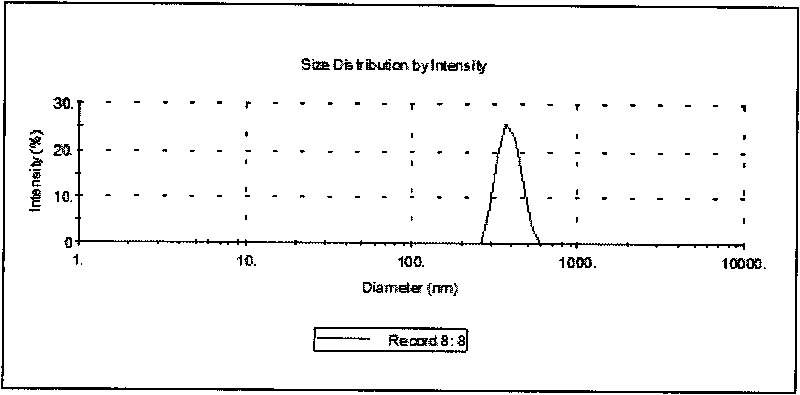
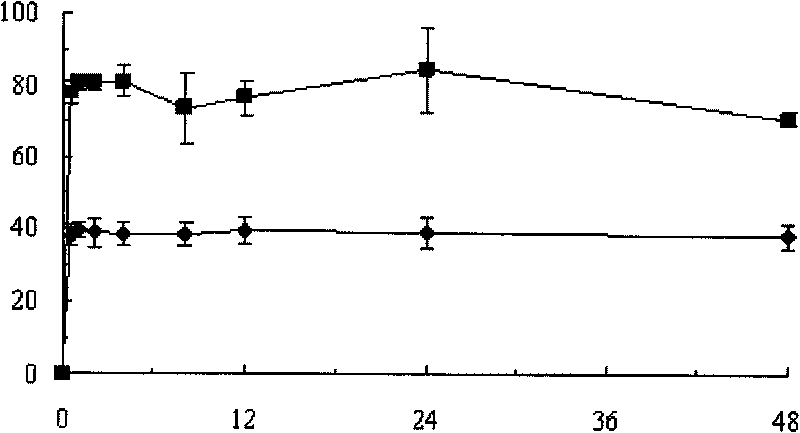
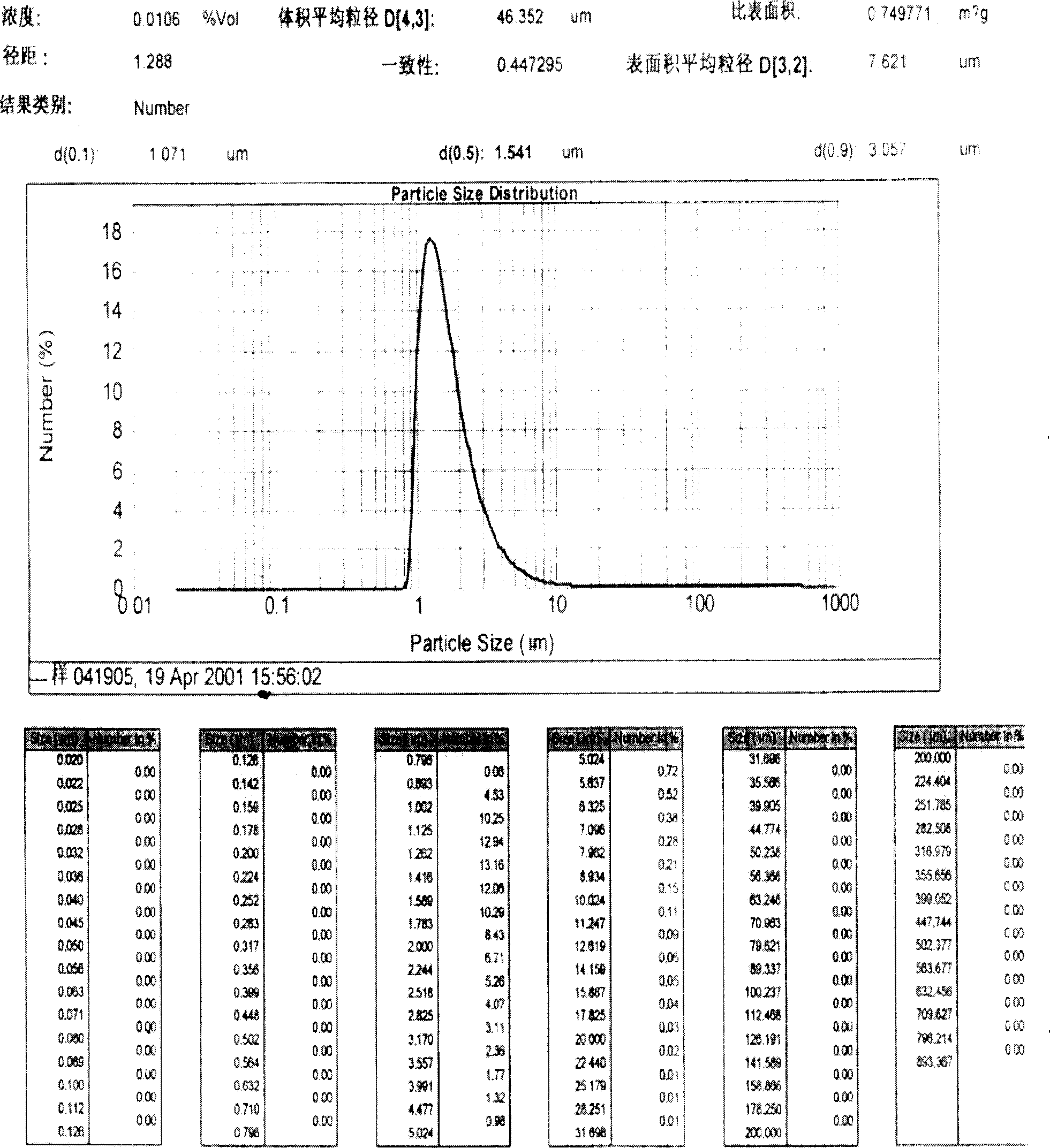
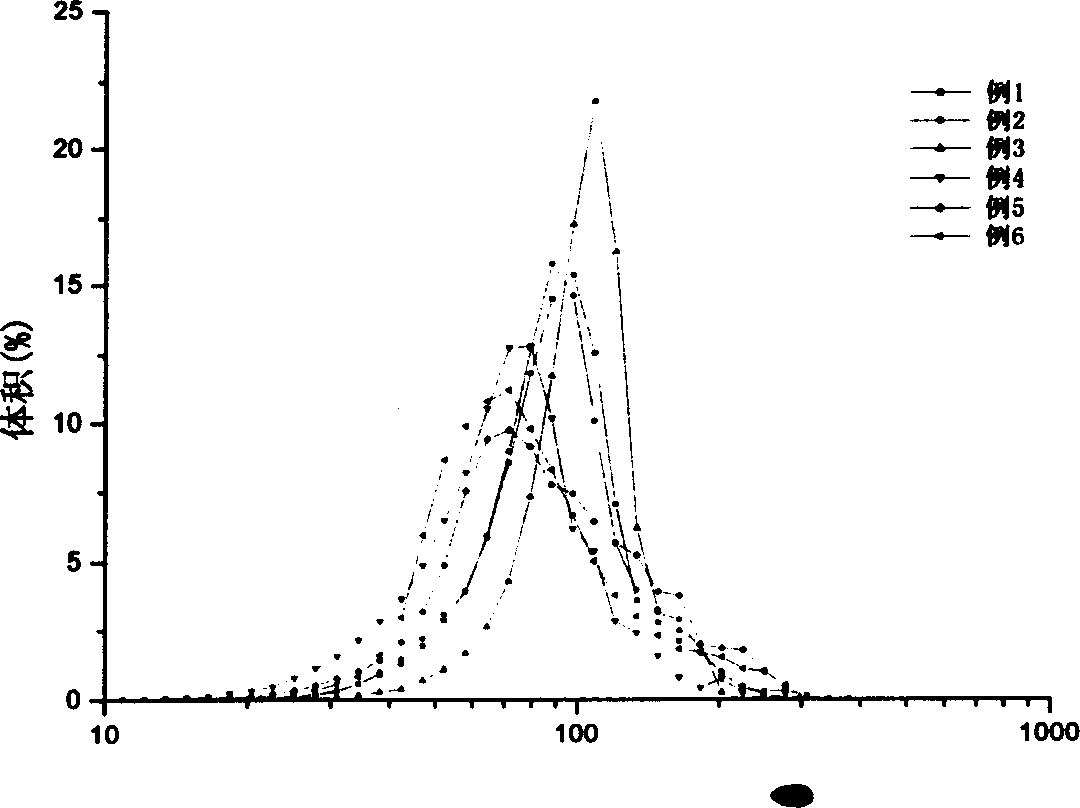
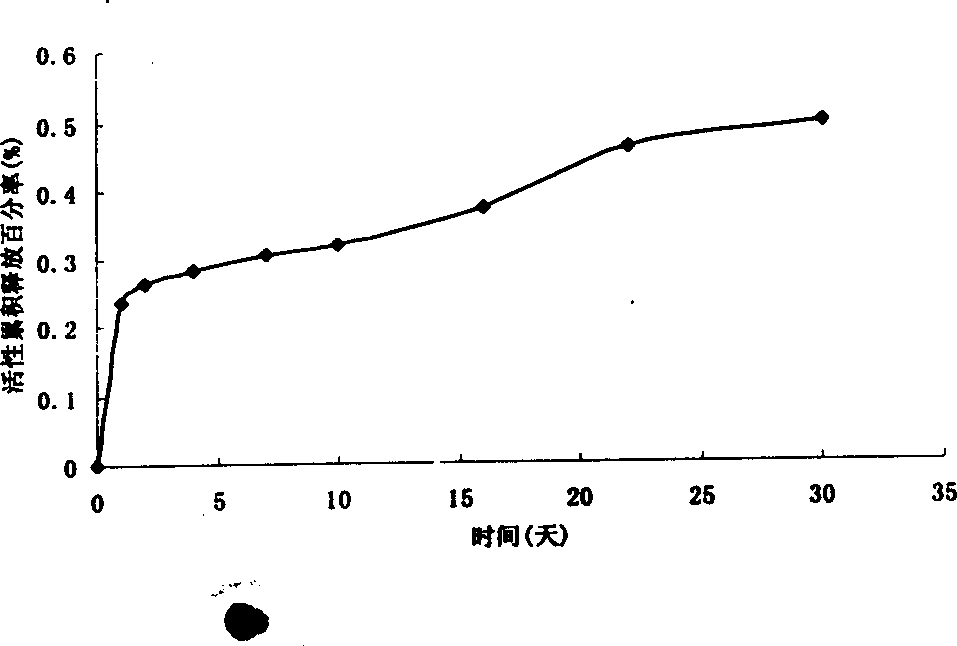
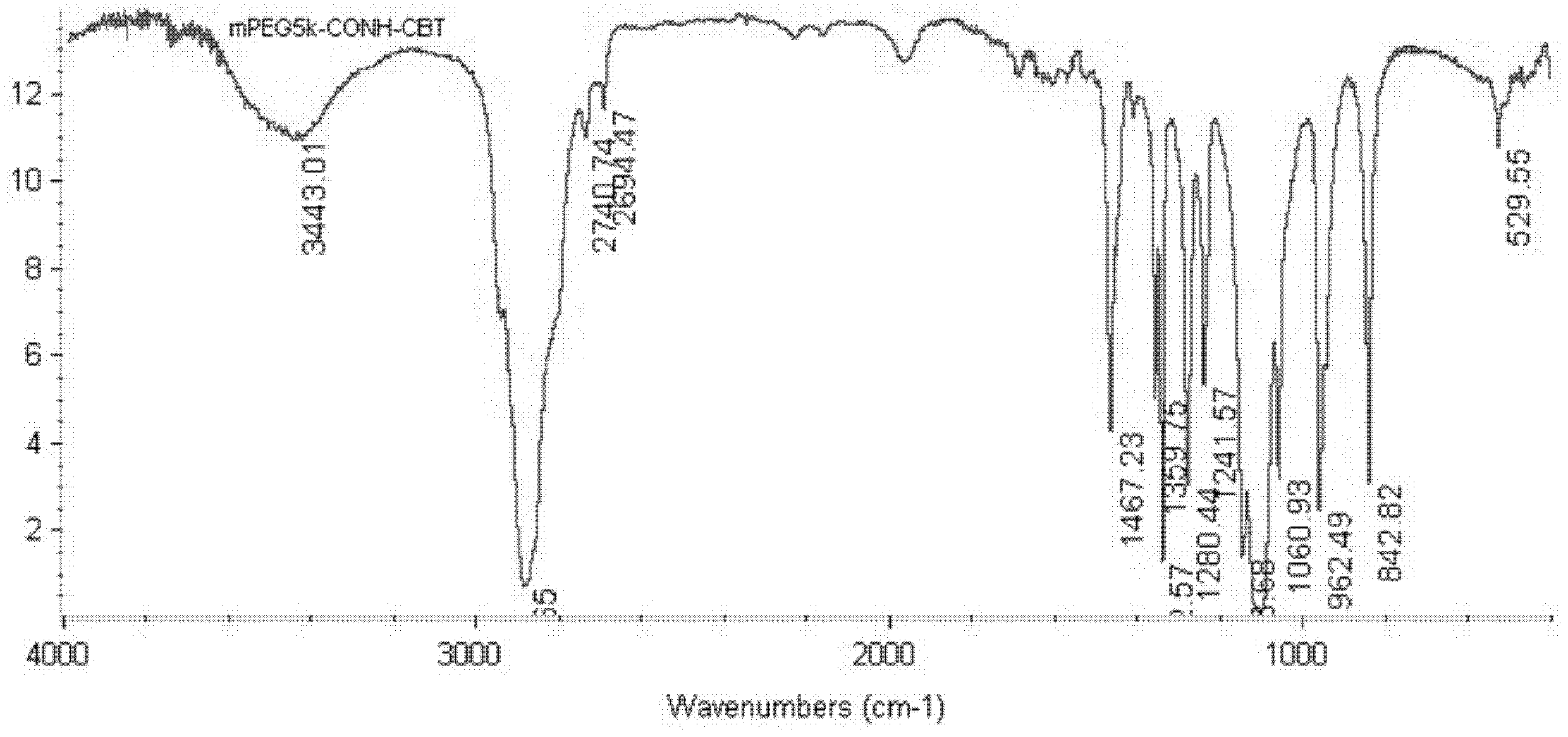
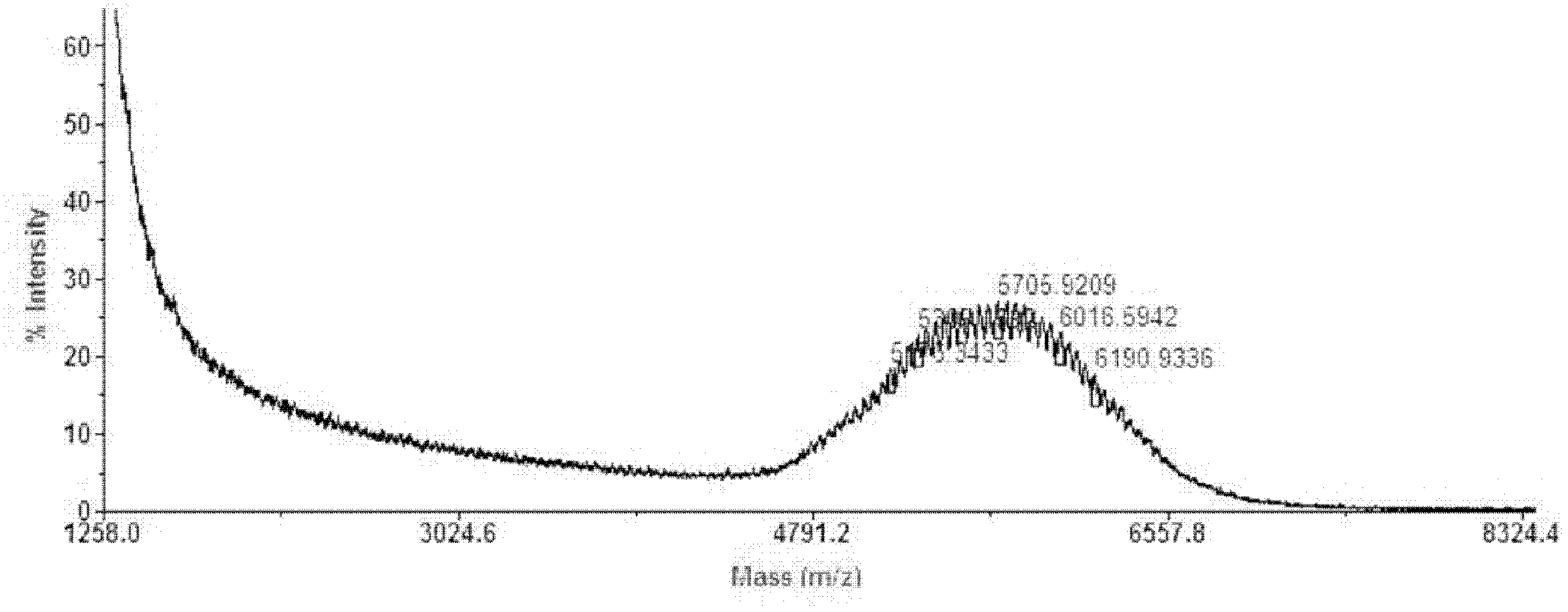
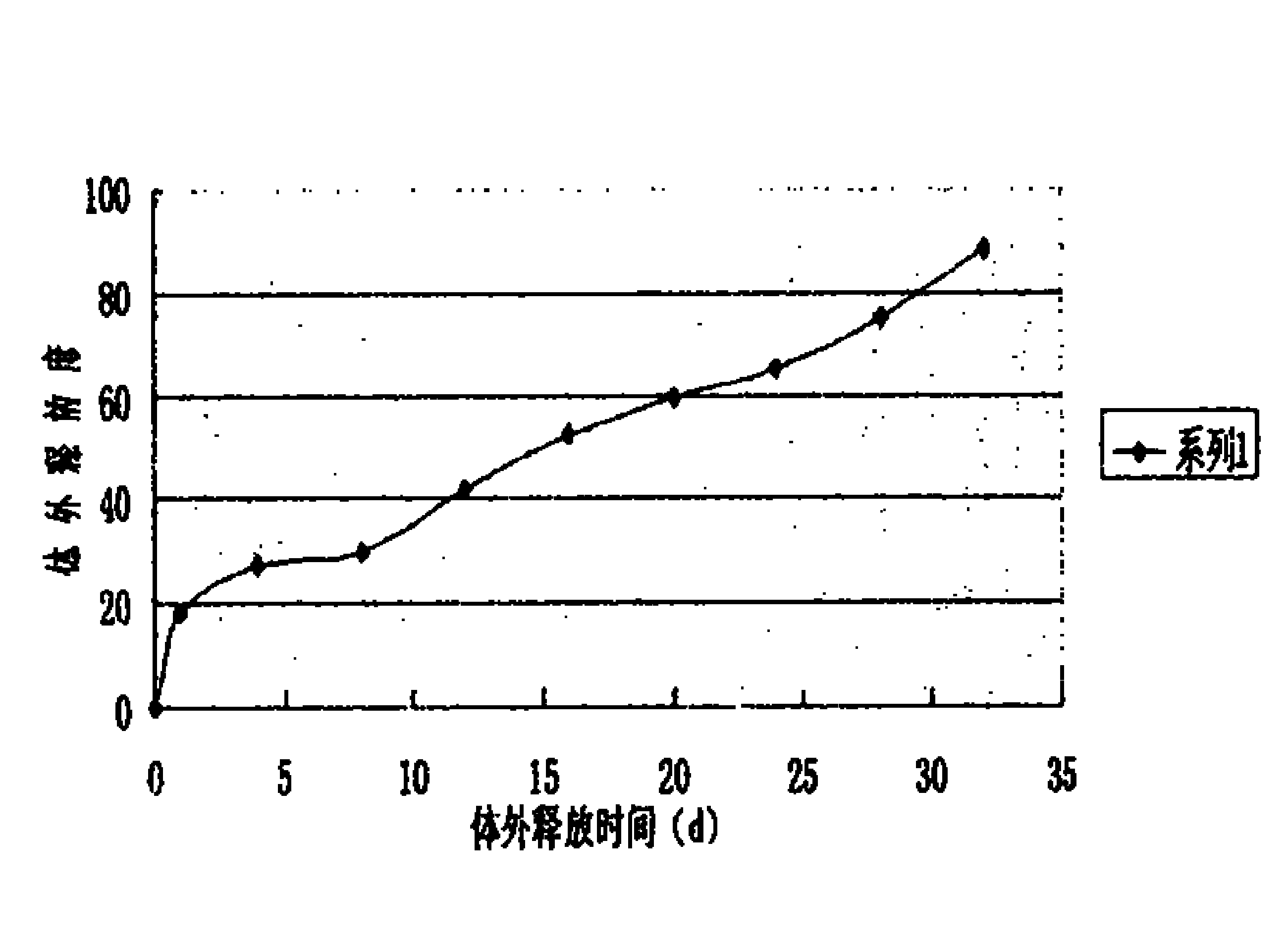
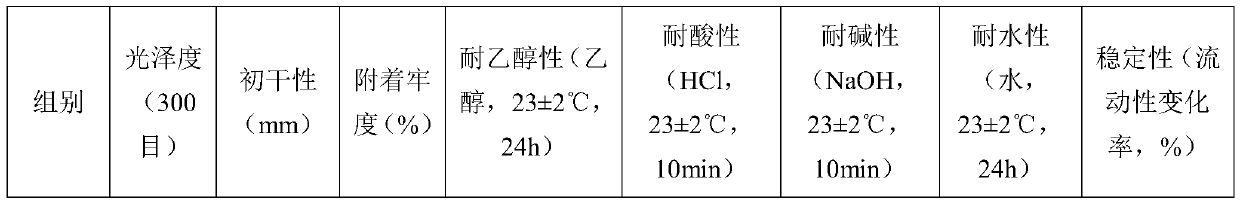
Patents
Literature
148 results about "Polylactide co glycolide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
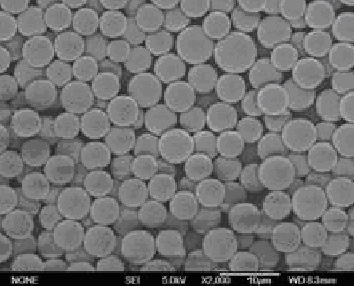
Polyester poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) is a copolymer of poly lactic acid (PLA) and poly glycolic acid (PGA). Poly lactic acid contains an asymmetric α-carbon which is typically described as the D or L form in classical stereochemical terms and sometimes as R and S form, respectively.
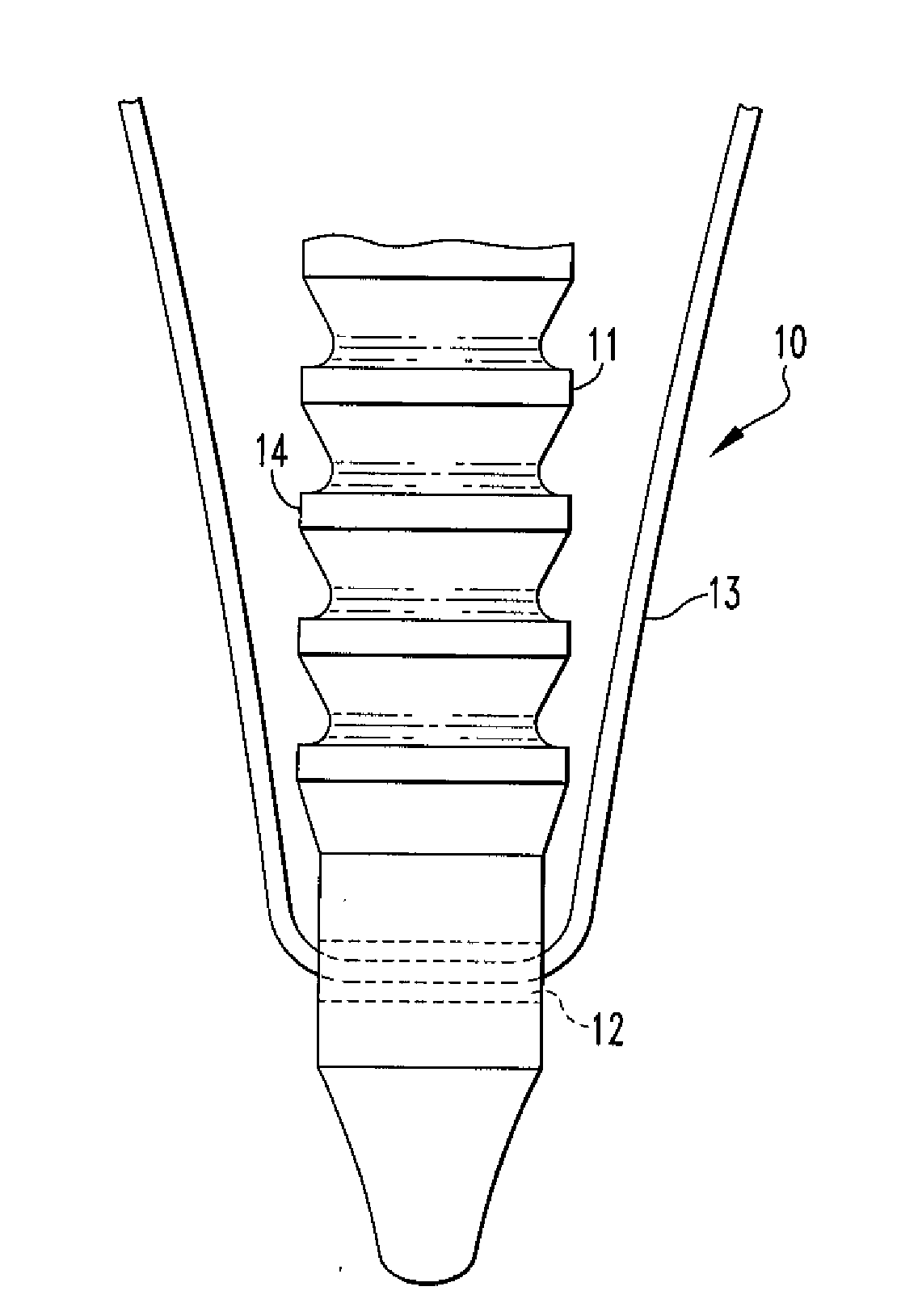
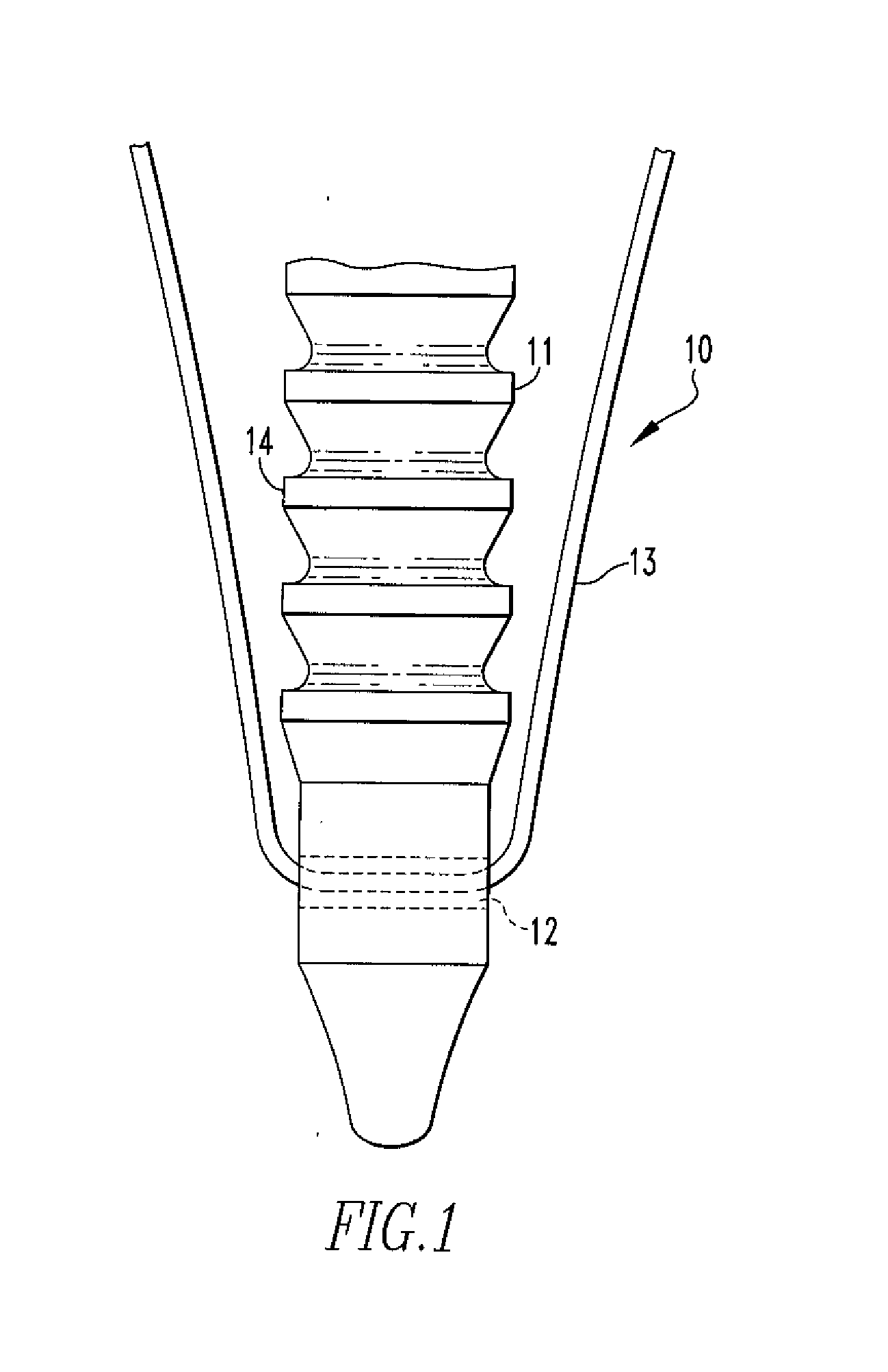
Fixation Devices and Method of Repair
InactiveUS20080234730A1Easy to fixShorten the lengthSuture equipmentsLigamentsRepair methodSurgical device
In one aspect, the present disclosure relates to a surgical device including an anchor body having an opening, the anchor body having a copolymer composition including polylactide-co-glycolide and calcium carbonate, wherein the calcium carbonate comprises more than 30% but less than 40% of the weight of the composition; and a flexible member passing through the opening, wherein deformation of the device occurs at body temperature. The present disclosure also relates to an oriented polymer material having a copolymer composition including a polylactide-co-glycolide and calcium carbonate, the calcium carbonate comprising more than 30% but less than 40% of the weight of the composition, wherein the material changes shape upon introduction to an environment having a temperature that is lower than a relaxation temperature of the material. A method of repairing soft tissue and other surgical devices are also disclosed.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Biodegradable fluorourcacil polyester medicine-carried nanospheres and its preparation method
InactiveCN101053553AHigh drug loadingSmall particle sizeOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPolyesterPolymer science
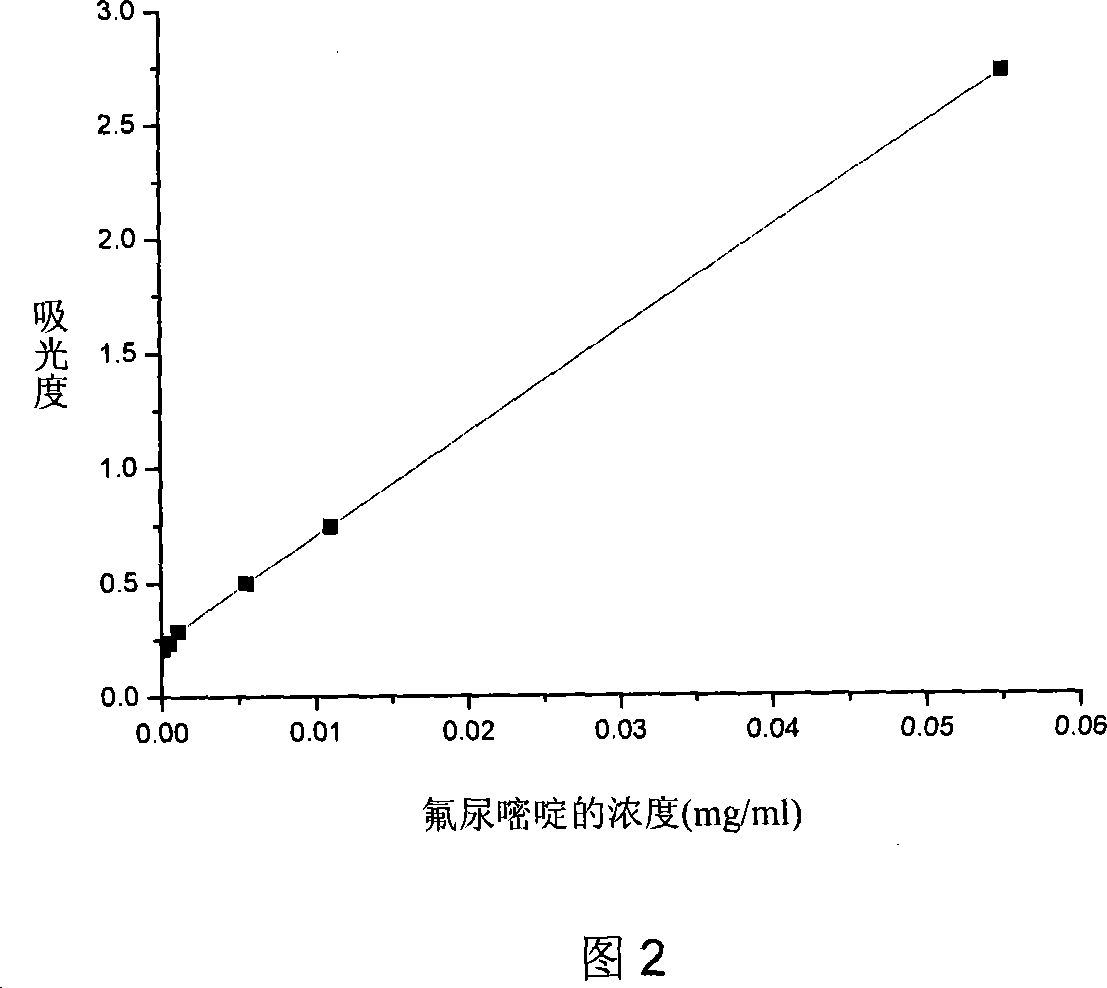
The invention relates to biodegradable fluorouracil(Fu) polyester drug-bearing manoparticles with a coating material of polylactic acid, polylactic acid-glycolic acid, polylactic acid-polyethylene glycol block copolymer or polylactic acid-glycolic acid-polyethylene glycol block copolymer and the producing method including: firstly, fully dissolving the copolymer in the dichloromethane, under the ultrasonic shock, injecting the fluorouracil NaOH solution in the dichloromethane solution, dispersing uniformly, forming W / O primary latex, and beating up the primary latex and injecting into the fluorouracil saturated water solution containing 5 wt% of polyvinylalcohol (PVA), and storing in the refrigeratory after freeze-dry. The drug-bearing manoparticle has a drug content which is 10-25% of the microparticle mass, and has a smooth surface, an even diameter distribution, a remarkable slow release function and not adhesive. The micropartical size is 100-1000nm.
Owner:JILIN UNIV +1
Sustained intraocular delivery of drugs from biodegradable polymeric microparticles
ActiveUS20100261646A1Lower eye pressureSustained releaseHormone peptidesBiocideMicrosphereActive agent
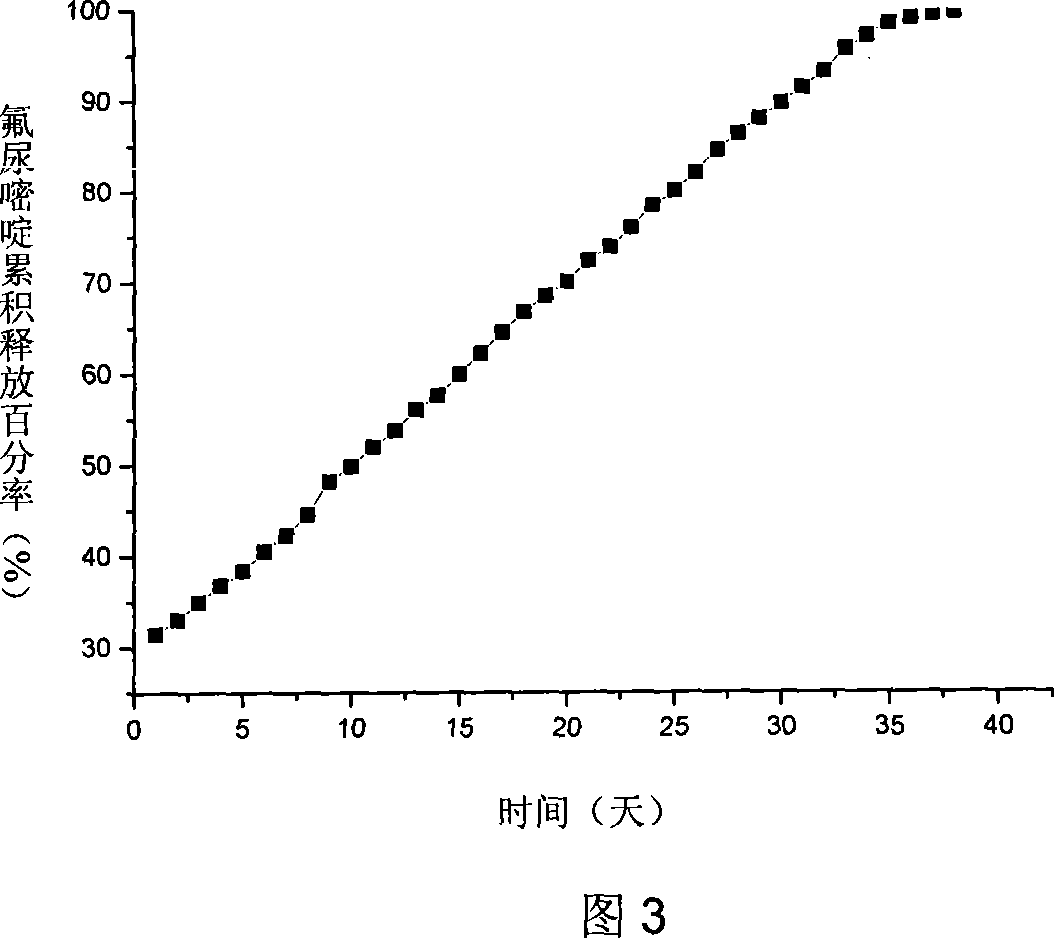
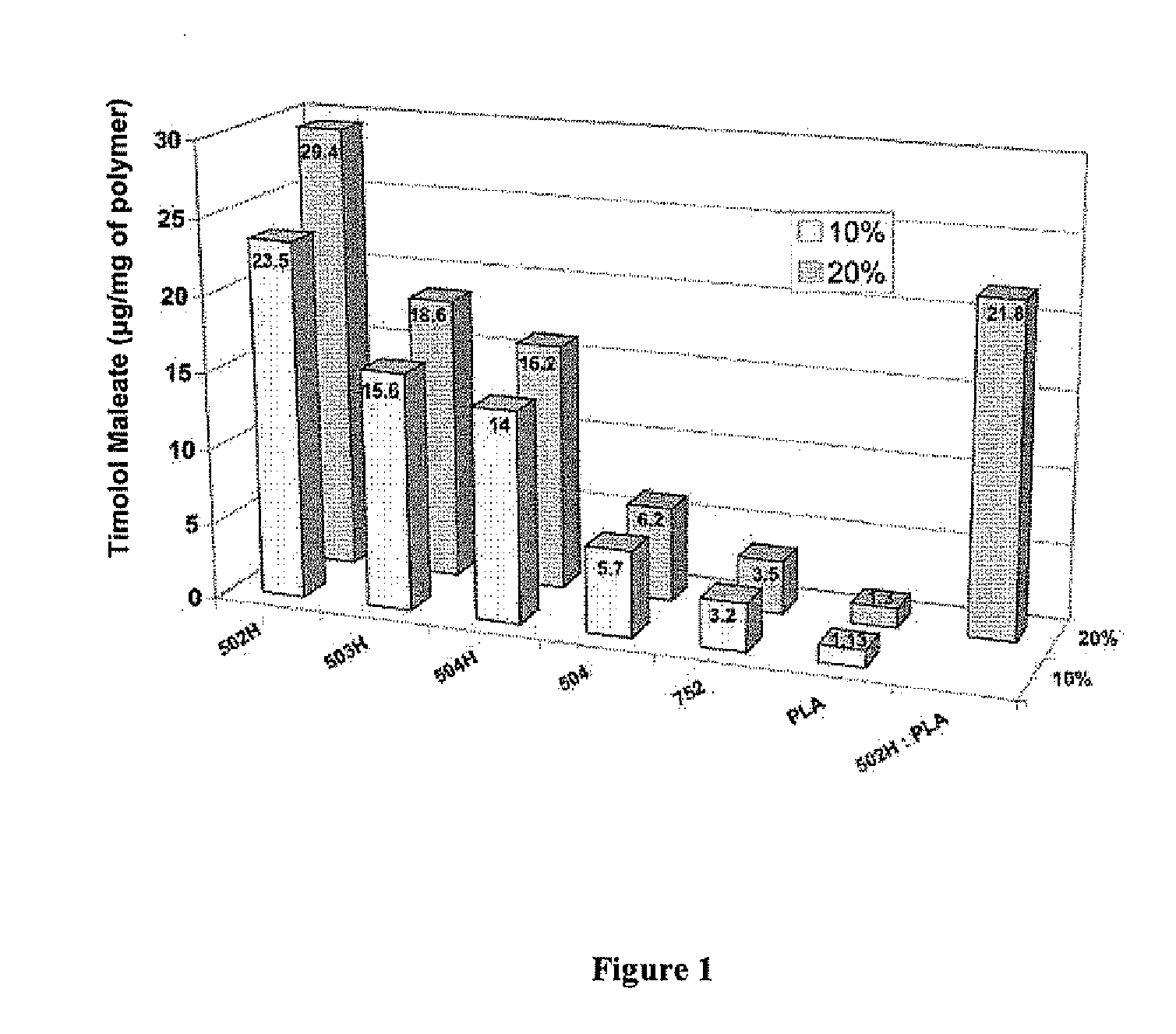
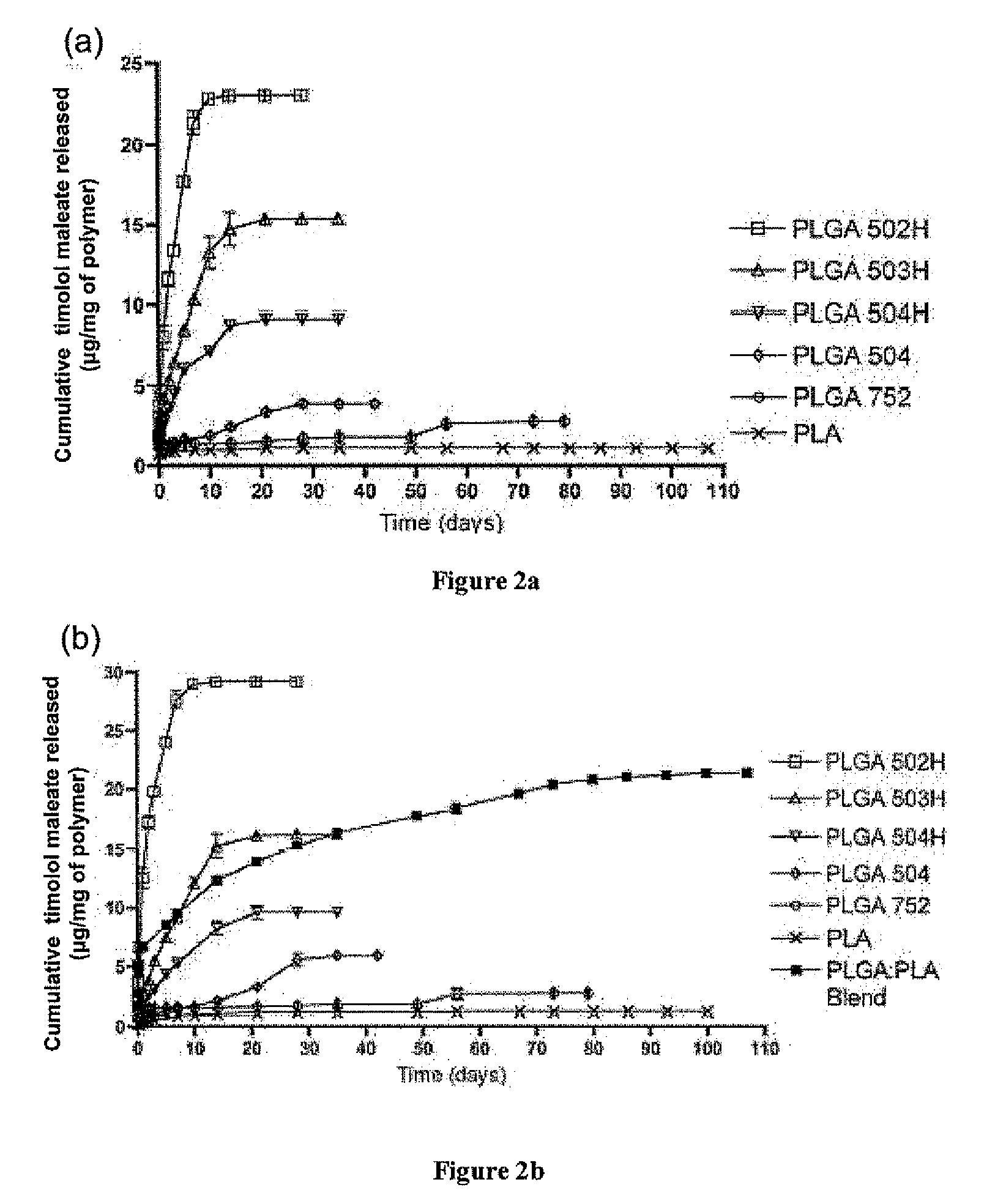
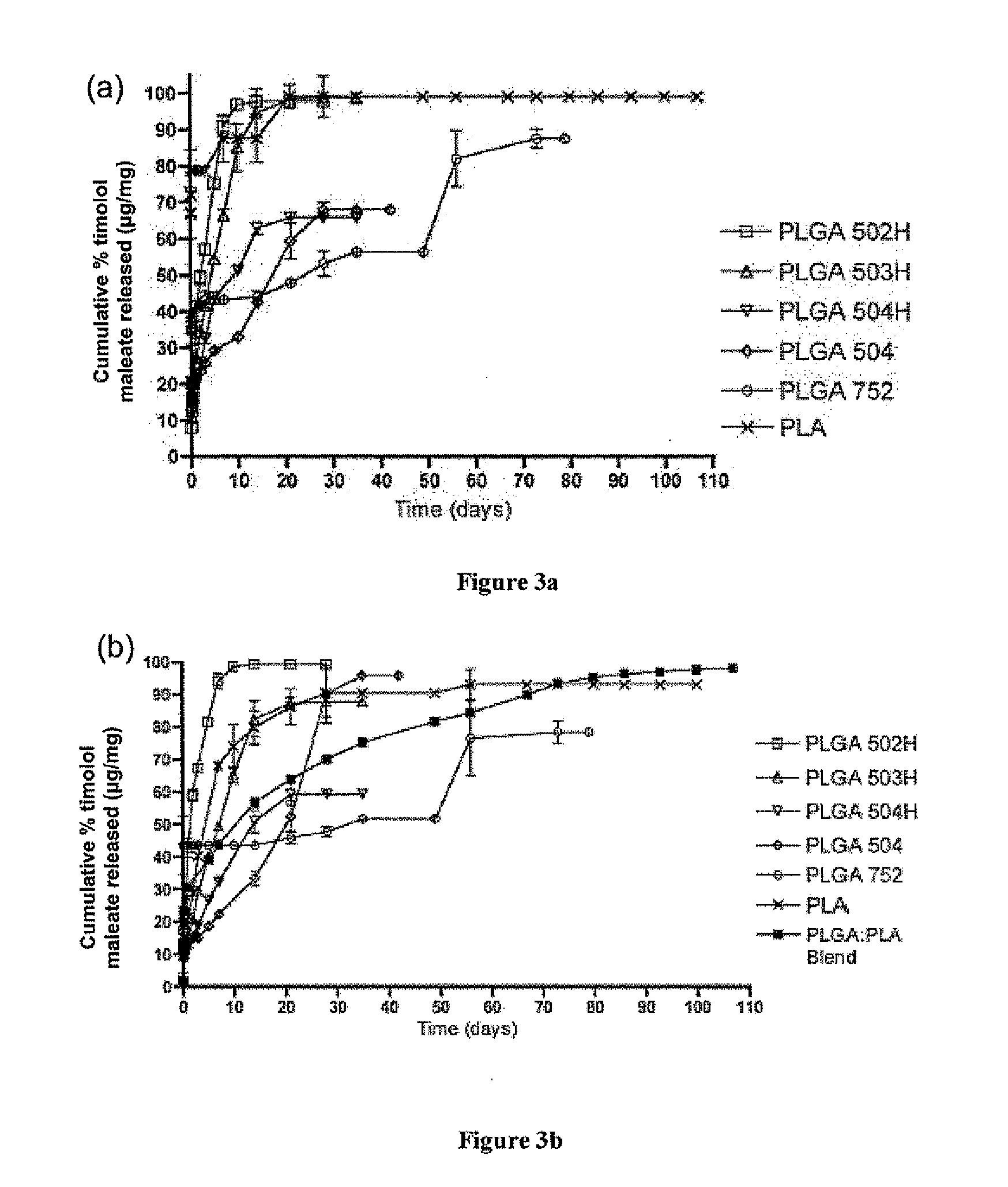
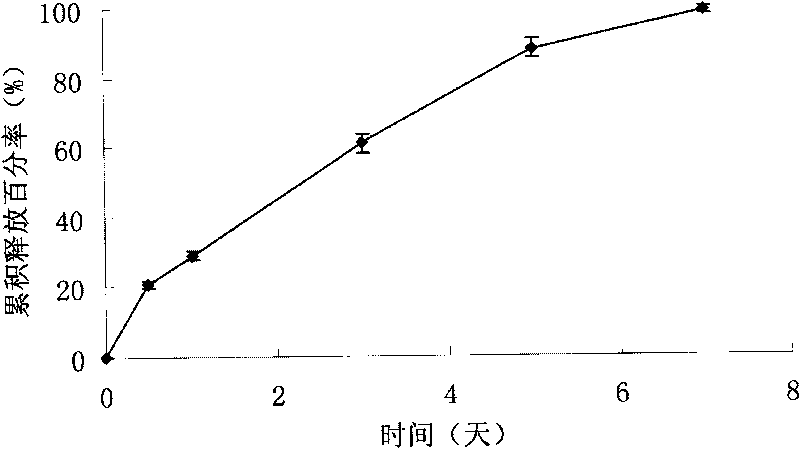
Biodegradable polymeric microparticle compositions containing one or more active agents, especially those useful for treating or preventing or one or more diseases or disorders of the eye, and methods of making and using thereof, are described. The microsphere compositions release an effective amount of the one or more active agents for a period greater than 14 days in vivo, preferably greater than 60 days in vivo, more preferably up to 73 days in vivo, more preferably greater than 90 days in vivo, even more preferably over 100 days in vivo, and most preferably greater than 107 days in vivo. In a preferred embodiment, the microparticle compositions contain one or more active agents useful for managing elevated intraocular pressure (TOP) in the eye. In one embodiment, the microspheres are formed from polylactide-co-glycolide (“PLGA”); in another embodiment, the microspheres are formed from a blend PLGA and poly lactic acid (“PLA”). Relatively hydrophilic, and preferably carboxylated, polymeric materials such as PLGA are used for a drug such as timolol maleate, which is relatively water soluble, to increase drug loading. Higher molecular weight polymers, as well as the ratio of LA (which has a longer degradation time, up to one to two years) to GA (which has a short degradation time, as short as a few days to a week), are used to provide release over a longer period of time. The combination of drug loading and release rate, as well as the minimization of initial burst release, result in prolonged release of a higher amount of drug.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Rivastigmine slow-release microspheres and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101708164AHigh drug loadingHigh encapsulation efficiencyNervous disorderPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMicrosphereRivastigmine
The invention discloses slow-release microspheres coated with rivastigmine tartrate / rivastigmine for PLGA / PLA injection and a preparation method thereof. The slow-release microspheres mainly comprise rivastigmine tartrate / rivastigmine and PLGA and PLA serving as biodegradable polymer medicinal materials, and can be prepared by adopting a W1 / O / W2 composite emulsified solvent volatilization method, an O / W emulsified solvent volatilization method, an O1 / O2 emulsion drying method and a spray drying method. The grain diameter of the microspheres is less than 100 microns. The slow-release microspheres have high medicament loading amount, have no obvious burst release effect, can be continuously released for one week, one mouth or three mouths, are used for treating senile diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson disease and the like, and can prolong the acting time of the medicament, reduce the application times and greatly improve the administration compliance of patients.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Liraglutide sustained-release microsphere preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102429876AHigh drug loadingHigh encapsulation efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderLactideMicrosphere
The invention relates to a formula of a liraglutide sustained-release microsphere preparation. The preparation mainly comprises 5 to 60 parts of liraglutide and 50 to 200 parts of biodegradable substrate material, wherein the biodegradable substrate material is polylactic acid (PLA), polylactic acid-glycollic acid (PLGA) block copolymer, glycolide-lactide (PLCG) copolymer, polyglycolic acid (PGA), polycaprolactone (PCL), polylactic acid-glycollic acid-polycaprolactone (PLGA-PCL) copolymer or PLCG-polycaprolactone (PLCG-PCL) or a mixture of any two or more than two of the compounds, preferably the PLGA-PCL copolymer. The sustained-release microspheres have a high encapsulating rate and a good sustained-release effect.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
Method for preparing targeted curcumin nanoparticles for treating ulcerative colitis
InactiveCN101711740AHigh drug loading rateGood freeze-drying and reconstitution propertiesAntibacterial agentsPowder deliverySucrosePolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a prescription of targeted curcumin-polylactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer (PLGA) nanoparticles for treating ulcerative colitis and a preparation process thereof. The prescription uses the targeting characteristic of the nanoparticles to an inflammatory part to reduce a medicament administration dosage and side effect and improve treatment effect. The preparation process comprises the following steps: taking a biodegradable material PLGA as a carrier material, polyvinyl alcohol as an emulsifier and 2 to 5 percent cane sugar as a freeze-drying protective agent, adding PEG 6000 into a water phase, and preparing the curcumin-PLGA nanoparticles by an emulsion-solvent volatilization method. The prescription process is optimized by taking the grain sizes of the nanoparticles and a medicament-loading rate as indexes. The prepared nanoparticles are round or elliptic and uniform in the size, have a mean grain size of 20 to 800nm and the medicament-loading rate of 10 to 20 percent, reduce dumping effect and have obviously better treatment effect on an animal pattern than a 5-aminosalicylic acid control group.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Slow-releasing bFGF-PLGA microball and its prepn and use
InactiveCN1398584AImproved particle size distributionGood conditionPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderDiseaseMicrosphere
The present invention provides one kind of slow-releasing basic fibroblast growdth factor (bFGF) microsphere and its preparation and use. The microsphere has coated bFGF as medicine, and matrix of polylactide-co-glycolide (PLGa). The slow-releasing bFGF microsphere is prepared by using PVA or mixed PVA-PEG liquid as dispersing medium and through w / o / wt% re-emulsion and drying process and mechanical stirring. Its freeze dried power has good dispersivity and low organic solvent residue. The present invention can be used for local administration or vein administration of treating fracture, bone defect and other diseases.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
High strength and tenacity degradable strontium calcium superphosphate composite bone cement and its preparation method
The invention discloses a high tensile degradable strontium phosphate calcium composite bone cement for repairing or intensifying fixation of human body holding bone defect and preparation method thereof. The solid material of bone cement is mixed powder of Ca4(PO4)2O ceramic with high crystallinity, SrHPO4, CaHPO4, curing liquid is thin phosphoric acid water solution, additive plasticizing unit is biocompatibility degradable macomolecule fiber with high tensile strength, selecting from lactic acid - hydroxyacetic acid copolymer fibre, polylatic acid fiber or polyglycolic acid fiber or other absorbable surgical suture, the enhancing unit is Ca4(PO4)2O residual ceramic particles after curing reaction. The preparation method coalesces kinds of techniques of ceramic particles in-situ reinforcing, initial plasticizing and later stage degradation of degradable fiber, Sr modification to get a novel high tensile degradable strontium phosphate calcium composite bone cement in like physiologic environment. The material has good biocompatibility, bioactivity, bone conductivity and degradation property.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
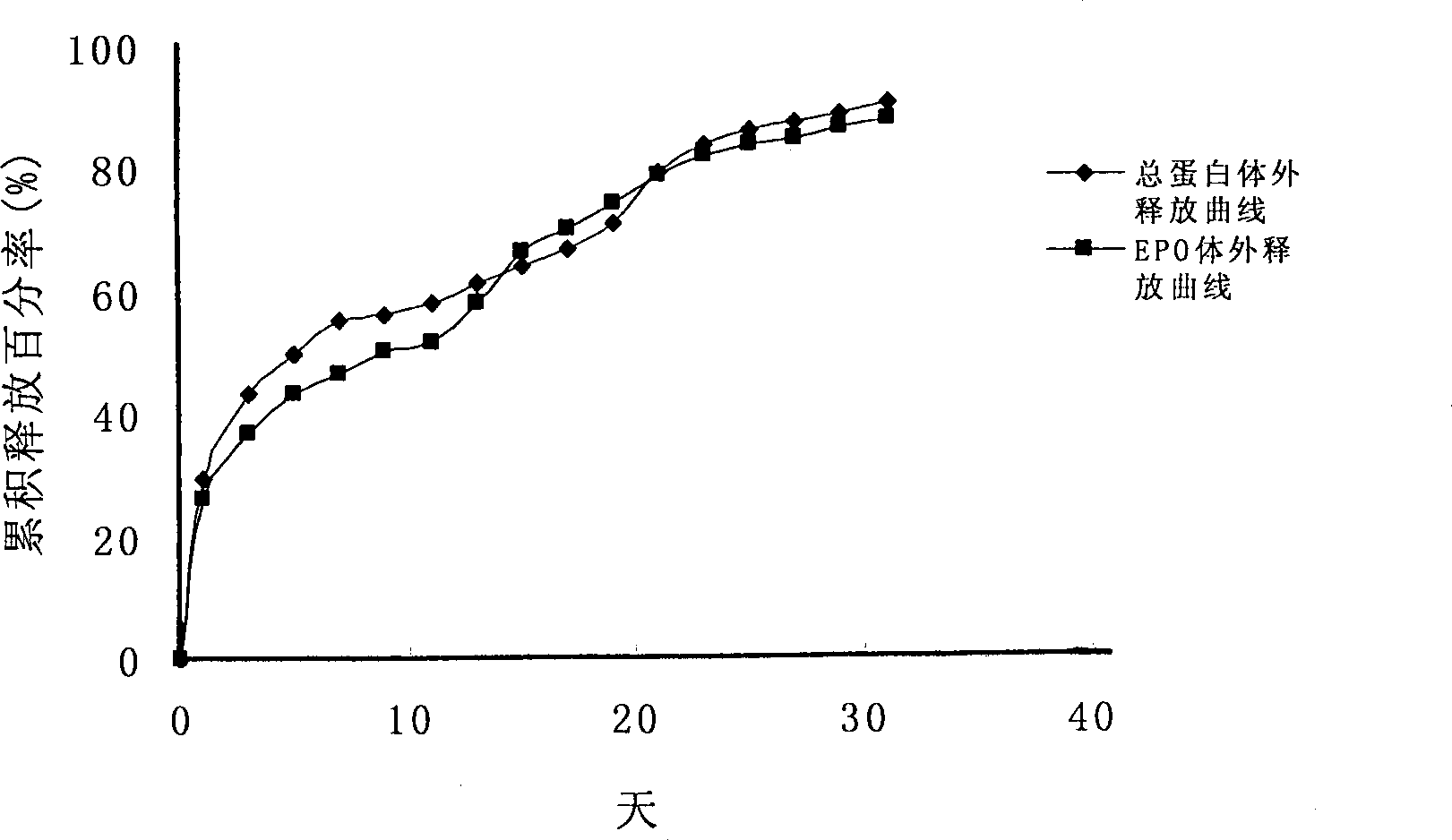
Sustained-release micro-spheres preparation containing recombined erythropoietin and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101507712AImprove stabilityFlat surfacePeptide/protein ingredientsGranular deliveryFreeze-dryingBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a slow-release microsphere preparation containing a recombined human haemopoietin. The slow-release microsphere preparation is prepared by the S / O / W compound emulsion solvent volatilization method. The preparation method comprises that: firstly, by the freeze-drying method, a micro particle containing the human serum albumin and the recombined human haemopoietin is prepared; secondly, by using a biodegradable high molecular material of lactic acid-glycollic acid block copolymer as a carrier material, the micro particle containing the human serum albumin and the recombined human haemopoietin is encapsulated; and thirdly, the lactic acid-glycollic acid block copolymer slow-release microsphere preparation containing the recombined human haemopoietin is prepared. The microsphere of the invention has the advantages of smooth surface, uniform appearance, regular size and no adhesion, the average particle size is between 70 and 105mu m; moreover, the microsphere is high in drug-carrying quantity and encapsulating rate, and the in vitro slow release period is more than 30 days. The obtained slow-release microsphere preparation is good in biocompatibility and can be used for non-intravenous drug administration such as hypodermic drug administration and intramuscular drug administration, and when used as a drug preparation for treating renal anemia, the slow-release microsphere preparation can improve the hematocrit of a patient.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method of high-adsorbability cellulose diacetate composite electrostatic spinning nanofiber ordered porous film
ActiveCN105396563ACreate pollutionSmall fiber diameterOther chemical processesDispersed particle filtrationElectrospun nanofiberPolymer science
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-adsorbability cellulose diacetate composite electrostatic spinning nanofiber ordered porous film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving cellulose diacetate and polycaprolactone, or cellulose diacetate and a lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer, or cellulose diacetate and polyvinylpyrrolidone into an organic solvent so as to prepare a spinning solution, and preparing the cellulose diacetate composite electrostatic spinning nanofiber ordered porous film by adopting an electrostatic spinning method. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, and cannot pollute the environment in the preparation process. The prepared cellulose diacetate composite electrostatic spinning nanofiber ordered porous film has tiny fiber diameter, good pore diameter and order degree, is good in dry and wet state adsorption performances, is high in water absorption, can be applied to the flue gas and tobacco industry of the dry state and wet state adsorption and filtration separation industry, is wide in market application prospect, and has relatively high application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polyesters, method for producing same, and depot medicaments produced from these polyesters
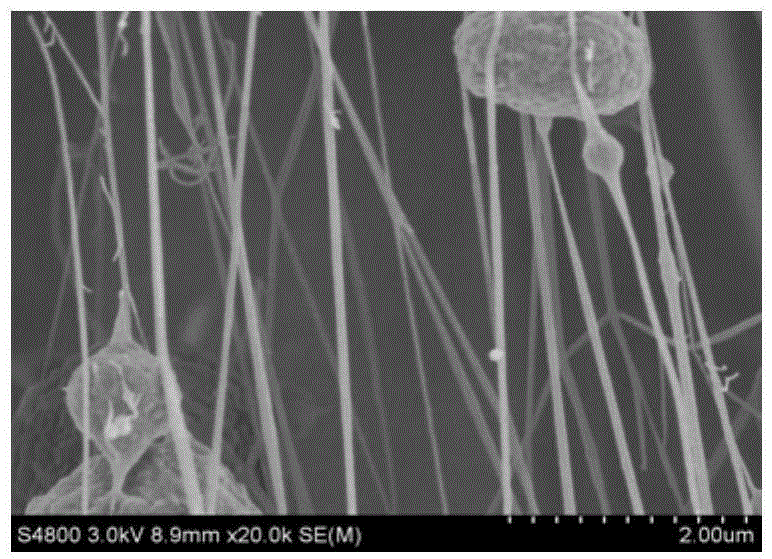
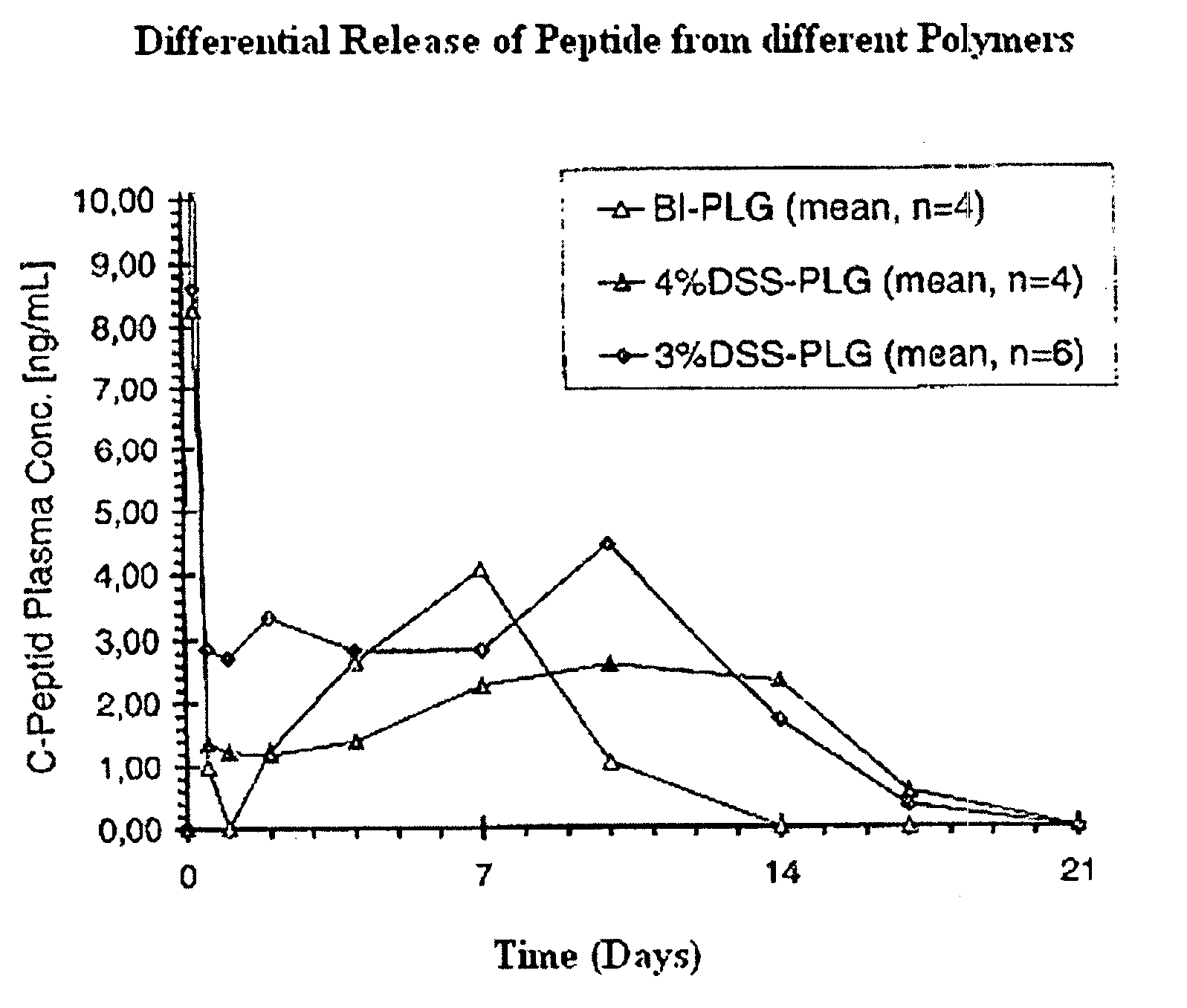
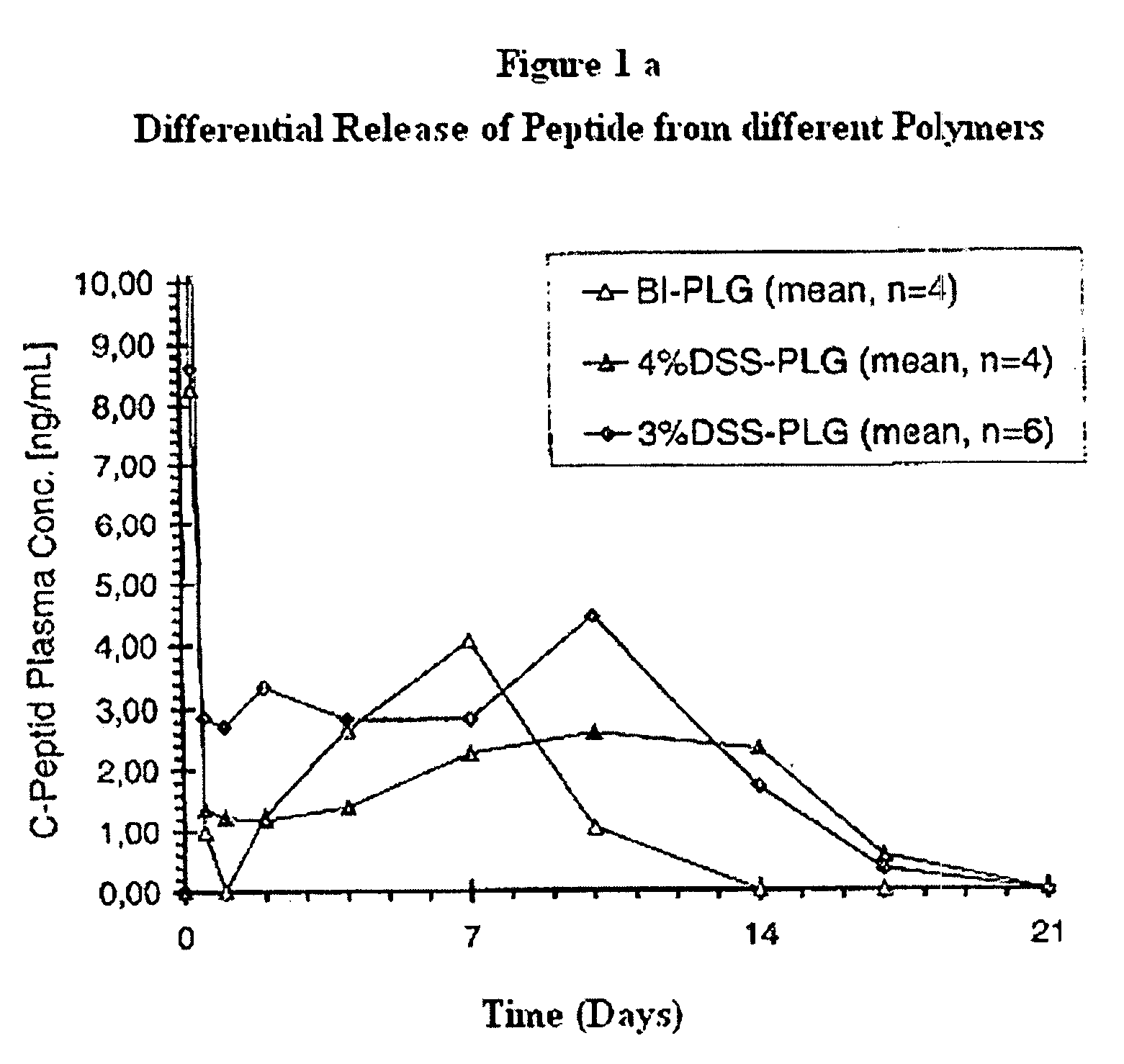
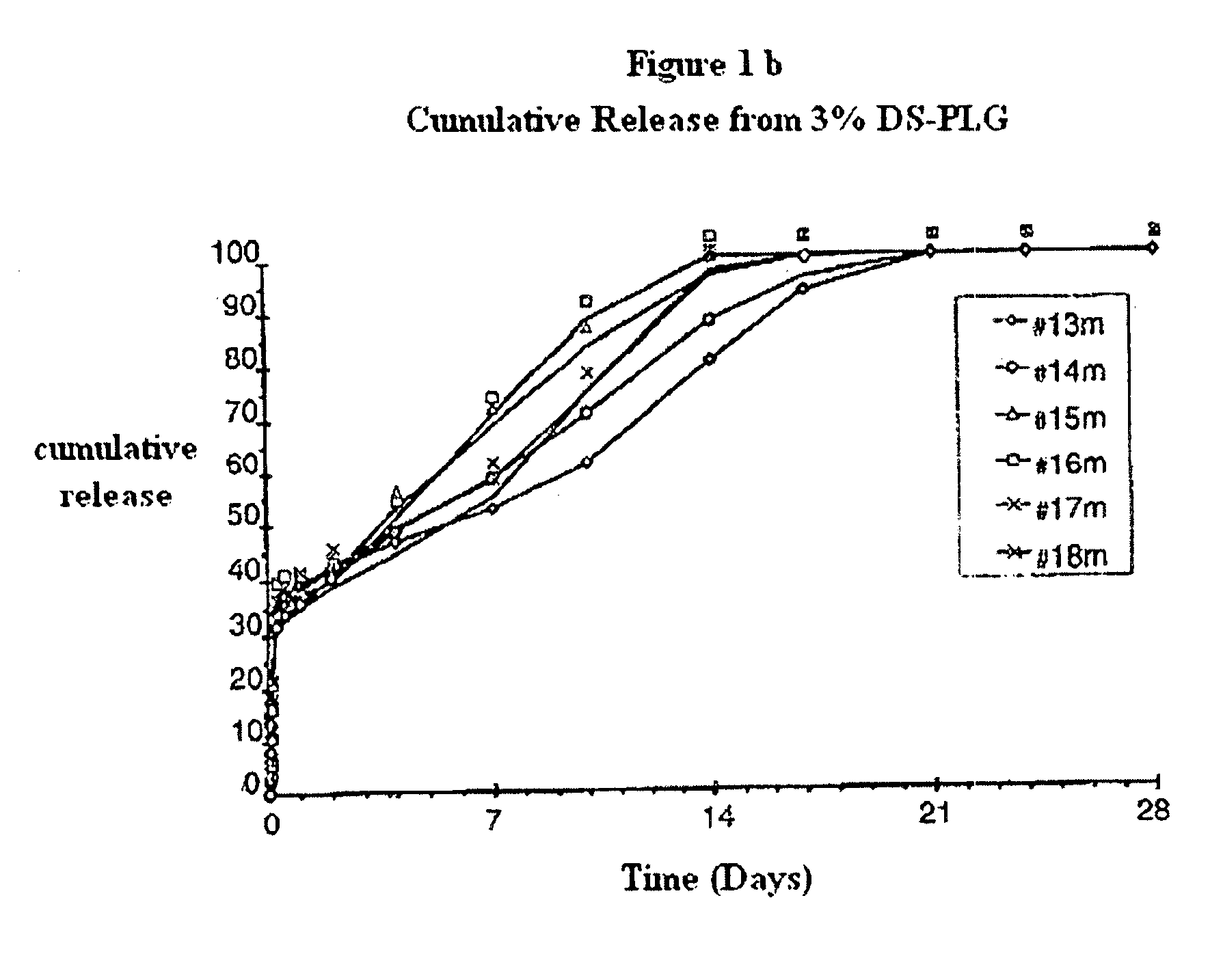
The invention relates to novel absorbable polyesters, produced by ring-opening polymerisation of hydroxycarboxylic acids in the presence of a polyol containing an electrolyte, in an extruder. In particular, the invention relates to novel polylactide glycolide polyesters which are essentially free of dextran sulphate and which are produced by ring-opening polymerisation of lactide and glycolide in the presence of dextran sulphate in the extruder; to the production of the same and to their use in depot medicaments.
Owner:CREATIVE PEPTIDES SWEDEN
Double-layer sustained and controlled release nanoparticle and preparation method thereof and application
ActiveCN103381146AImprove hydrophilic abilityImprove flexibilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsControlled releaseMedicine
The invention discloses a double-layer sustained and controlled release nanoparticle and a preparation method thereof and application in preparation of antitumor medicines. The double-layer sustained and controlled release nanoparticle is formed by a lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer nanoparticle inner core and a polyethylene glycol questin grafting chitosan casing covering an outer layer of the lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer nanoparticle inner core and can simultaneously load hydrophilic and lipophilic medicines. The drug entrapment rate is high, time-ordered release of inner layer medicines and outer layer medicines can be achieved, the double-layer sustained and controlled release nanoparticle has the effects of sustained release and controlled release, and in addition, the double-layer sustained and controlled release nanoparticle further has the advantages of being controllable in grain size, uniform in particle size distribution, smooth and round in forma and good in stability and dispersibility and the like.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Non-spherical drug-loaded particles and controlled release preparation of lactyl polymer and preparation methods thereof
InactiveCN101953776AStable structureNo hemolyticPowder deliveryHydroxy compound active ingredientsSolventSustained-Release Preparations
The invention relates to non-spherical drug-loaded particles and a controlled release preparation of a lactyl polymer and preparation methods thereof. The non-spherical particles of polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) are prepared by using an emulsion-solvent volatilization method assisted by small molecule materials. The PLGA is used as raw material coated with at least one of the following hydrophobic drugs: all-trans retinoic acid, paclitaxel, epirubicin, camptothecin or roxithromycin, wherein the mass ratio of the hydrophobic drug to a lactyl polymer high polymer material is 1:4-40. The drug-loaded particles of the all-trans retinoic acid are prepared and subjected to in vitro drug release evaluation. The results show that the preparation method has the advantages of simple preparation process, good reproducibility, significantly increased drug loading amount and encapsulation efficiency relative to spherical particles, very good controlled-release effect, no hemolysis initiation and safety use. The novel carrier and preparation have a potential industrial production value in the field of long-circulating controlled release of the hydrophobic drugs.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
All-trans retinoic acid-camptothecin anticancer drug conjugate as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104478890AImprove solubilityExpand the scope of clinical applicationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPolyoxyethylene castor oilSolubility
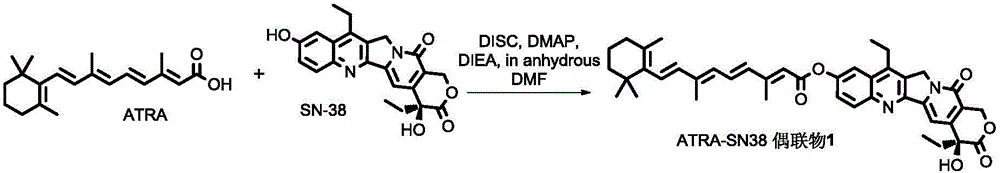
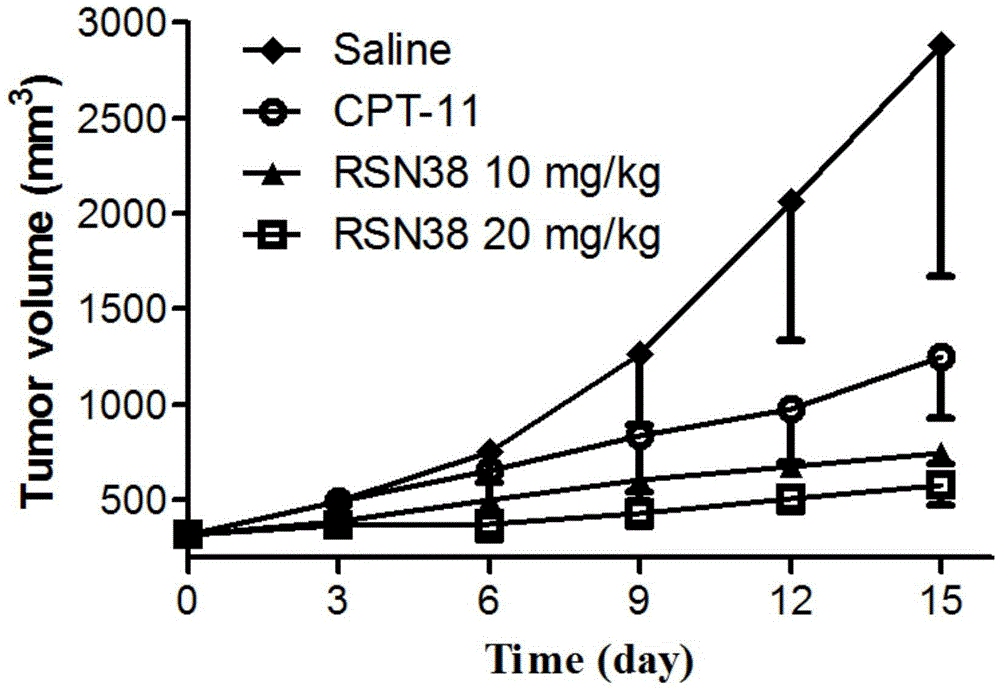
The invention discloses an all-trans retinoic acid-camptothecin anticancer drug conjugate as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the all-trans retinoic acid-camptothecin anticancer drug conjugate is shown in a formula (I), (II), (III), (IV), (V) or (VI). The all-trans retinoic acid-camptothecin anticancer drug conjugate has good solubility in Tween, polyoxyethylene castor oil, a Poly(ethylene adipate)-polylactic acid copolymer and a Poly(ethylene adipate)-poly (lactic acid-glycollic acid) copolymer, can be self assembled into nanometer grains in water, can be directly injected or taken orally or processed into other dosage forms. According to the all-trans retinoic acid-camptothecin anticancer drug conjugate disclosed by the invention, as all-trans retinoic acid and SN-38 or camptothecin take synergistic effect, compared with a conjugate only containing one of irinotecan, SN-38 and all-trans retinoic acid, the all-trans retinoic acid-camptothecin anticancer drug conjugate has good tumor suppression effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Local sustained release preparation for preventing and treating osteomyelitis, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101618209AImprove the bactericidal effectImprove release abilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrospherePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a local sustained release preparation for preventing and treating osteomyelitis, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.01 to 1 percent of staphylococcus lysozyme, 1 to 20 percent of polylactic acid (PLA), 0.5 to 10 percent of polylactide-co-glycolide (PLGA), and 70 to 90 percent of calcium phosphate cement (CPC). The preparation takes the staphylococcus lysozyme as a bactericidal active component to obtain PLA-PLGA polymer microspheres containing the staphylococcus lysozyme through supercritical fluid microparticle preparation technology, and the PLA-PLGA polymer microspheres are compounded with the calcium phosphate cement (CPC) to obtain a novel sustained release degradable antibacterial composite artificial bone carrying staphylococcus lysozyme microspheres. The preparation has good physical and chemical properties and strong sterilization effect, ensures that the in vitro medicament release process is long up to three months, has steady release rate, and can maintain steady and long-acting release at administration positions.
Owner:SHANGHAI HI TECH UNITED BIO TECHCAL RES
Method for preparing thermosensitive antimicrobial film and implant material from antibacterial composition
ActiveCN103623468ANo abuseNeed to ensure treatment of infectionSurgeryNon-woven fabricsPolymer scienceCyclodextrin
The invention discloses a method for preparing a thermosensitive antimicrobial film and an implant material from an antibacterial composition. The method comprises the following steps: injecting the antibacterial composition into an injector, and additionally arranging a stainless steel syringe needle; coating the implant material to be coated by adopting 10-30KV of high-voltage power supply, at 1-5mL / h of flow rate of a solution and 5-25cm of receiving distance; and finally drying the coated implant material in vacuum at room temperature for 24-48 hours, so as to obtain the thermosensitive antimicrobial film coated with the implant material, wherein the antibacterial composition comprises an organic polymer selected from polylactic acid, polycaprolactone, a polylactic acid-glycolic acid polymer and a polylactic acid-polyethylene glycol segmented copolymer, blending colloid of isopropylacrylamide and cyclodextrin or blending colloid of isopropylacrylamide and gelatin, and an antibacterial agent. The thermosensitive antimicrobial film prepared by the method can release antimicrobial medicines as long as the temperature of a human body ascends. Therefore, the method has strong pertinence.
Owner:WUXI ZHONGKE GUANGYUAN BIOMATERIALS
Absorbable intraosseous fixing device with biological activity and plasticity and forming method
InactiveCN104546103ARelieve painReduce sterile inflammationInternal osteosythesisFastenersBiocompatibility TestingDrug biological activity
The invention relates to the field of biological medical apparatus and instruments, and particularly relates to an absorbable intraosseous fixing device with biological activity and plasticity and a forming method. The absorbable intraosseous fixing device comprises a bone fracture plate and bone screws, wherein the bone fracture plate is provided with fixing holes and is made by a biologically absorbable high polymer material and biologically active ceramics or biologically active glass; the biologically absorbable high polymer material is 70-95% of the total weight of a composite material in parts by weight, and the biologically active ceramics or biologically active glass takes up 5-30% of the total weight of the composite material; the biologically absorbable high polymer material is selected from one or more of polylactic acid, polycaprolactone, polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer, polyglycolic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoate and polyhydroxybutyrate, and the molecular weight is 100,000 to 2,000,000. The absorbable intraosseous fixing device is good in biocompatibility, and can be degraded after the device is implanted in the body; meanwhile, aseptic inflammation caused in the course of material degradation can be reduced, and the pain of a patient can be alleviated; in addition, the personalized customization can be realized.
Owner:深圳市博立生物材料有限公司
Thymalfasin sustained-release microspheres and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103432570AReduce usageEasy to solvePeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemMicrosphereFreeze-drying
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines and discloses thymalfasin sustained-release microspheres and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: freeze-drying and sieving an aqueous solution of thymalfasin; collecting the thymalfasin powder; grinding and sieving polylactic acid or a polylactide-co-glycolide acid (PLGA); mixing the obtained polymer powder and the thymalfasin powder to obtain a mixture of raw and accessory materials; melting and extruding the mixture of raw and accessory materials to obtain a hot-melting extrudate; cooling to cure the hot-melting extrudate; cutting, grinding and sieving to obtain the thymalfasin sustained-release microspheres. According to the invention, the thymalfasin sustained-release microspheres are prepared by a hot-melting extrusion technology without needing an organic solvent, the problem of residual organic solvent is completely avoided, a few impurities are contained, and the drug release is steady; an advantage of continuously releasing the thymalfasin dose is realized, thus the administration time is reduced, the administration pain of a patient is eased, and the thymalfasin sustained-release microspheres are suitable to be popularized and applied to treatment.
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
Mesoporous bioactive glass/polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer composite microspheres and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111905151AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationTissue regenerationProsthesisTissue repairMicrosphere
The invention discloses mesoporous bioactive glass / poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) composite microspheres and a preparation method and application thereof. The mesoporous bioactive glass / poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) composite microspheres are prepared by the following method of: firstly, preparing mesoporous bioactive glass by using a microemulsion technology in combination with a sol-gel template method, then sequentially adding PLGA, span 80 and the mesoporous bioactive glass into dichloromethane, and carrying out uniform stirring and ultrasonic dispersing to form S / O emulsion;and sequentially adding the S / O emulsion into prepared polyethylene solution W1 and W2 with different concentration, stirring to evaporate a solvent, and carrying out washing, centrifugation, and freeze-drying to obtain the product. The preparation process flow of the composite microspheres is easy to control, and due to the addition of the mesoporous bioactive glass, the bone induction capabilityand the drug loading and slow release capability of the composite microspheres are improved; and the composite microspheres have good application prospect in the fields of bone and tooth tissue repair, tissue engineering and slow release carriers such as drugs, proteins and genes and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
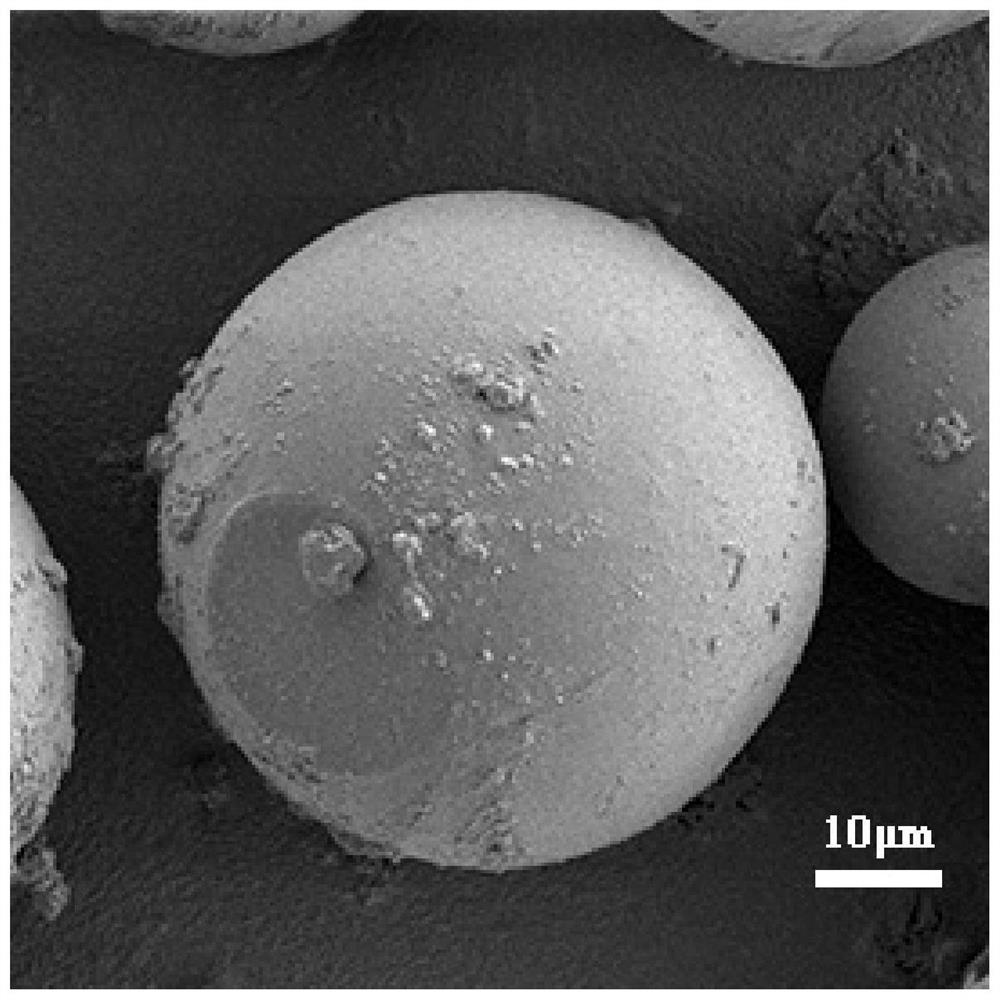
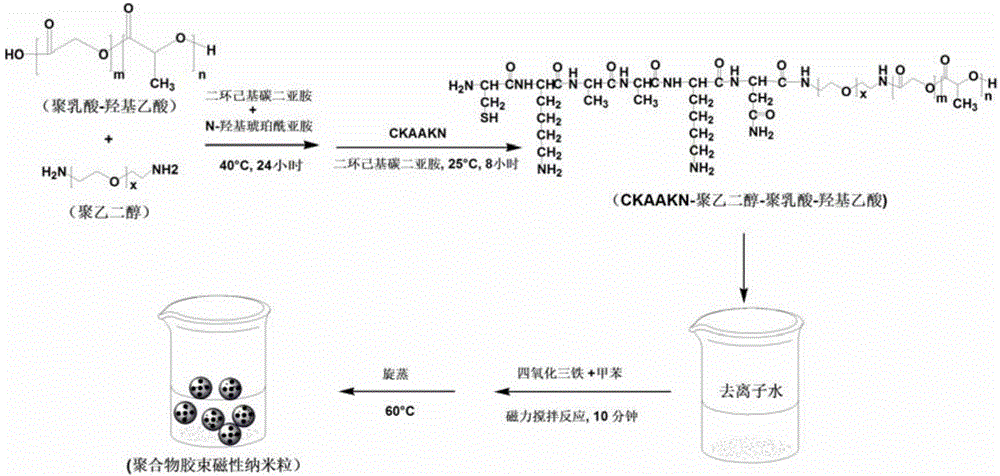
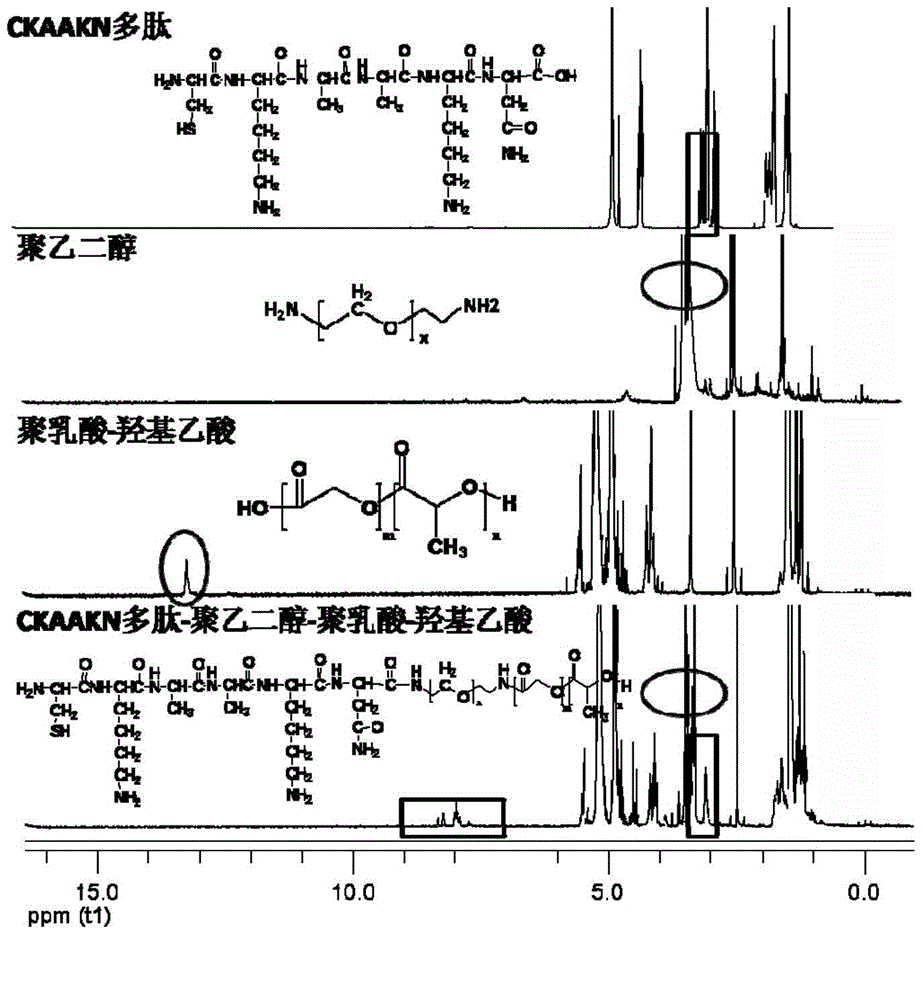
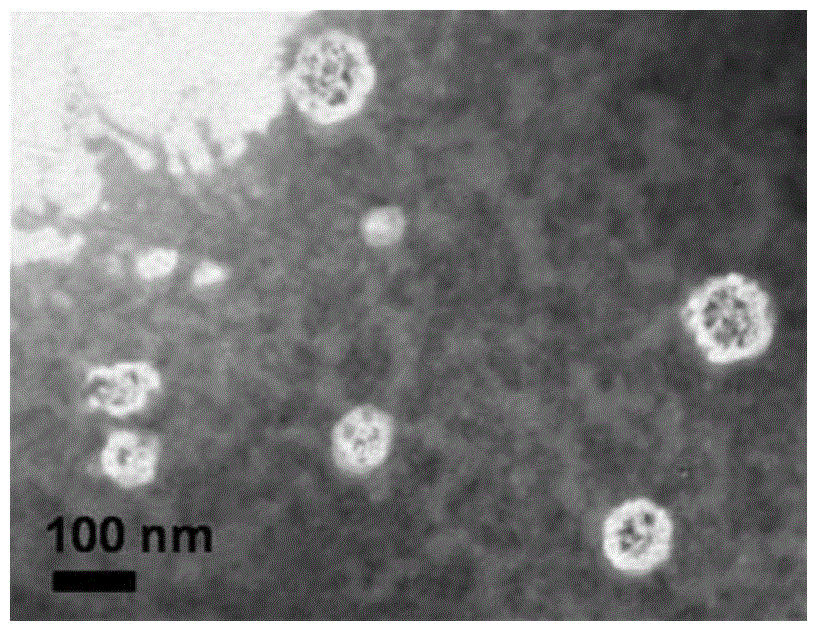
Targeted polymer micelle magnetic nanoparticle, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104815341AImprove independent innovation capabilitiesSecurity Image ImagingEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsPancreas CancersPolyethylene glycol
The invention provides a polymer micelle magnetic nanoparticle having a selective specific targeting function on pancreas cancer. A preparation method of the polymer micelle magnetic nanoparticle comprises the following steps: carrying out an amide reaction on a carboxyl group on a CKAAKN polypeptide and an amino group on the carboxyl group on polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid-glycolic acid, coupling the CKAAKN polypeptide to prepare a CKAAKN-PEG-PLGA graft product, and carrying out an aqueous solvent diffusion technology with a Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle as a targeting marker material to prepare the polymer micelle magnetic nanoparticle. The preparation method has the advantages of reasonable design, convenient operation and low cost. The polymer micelle magnetic nanoparticle provided by the invention has high magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle wrapping ability, has the advantages of good stability and dispersibility, small particle size and uniform dispersion, can enhance the targeted uptake ability of the pancreas cancer to improve the uptake rate, and can be used as a pancreas cancer targeted magnetic resonance specific contrast agent to realize safe and rapid pancreas cancer targeted molecule image imaging.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Neural restoration bracket and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110665054ASimple processEasy to operateTissue regenerationProsthesisBiocompatibilityDextran
The invention discloses a neural restoration bracket. The neural restoration bracket is characterized in that the neural restoration bracket is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 25-35 parts of a vinyl modified hydroxyl terminated poly (lactic acid-glycolic acid 75 / 25) copolymer, 0.2-0.5 part of pearl powder, 0.1-0.3 part of amino-modified dextran modified carboxylated fullerenes, 1-4 parts of amino-modified dextran modified oxidized graphene, 0.8-2 parts of a pore-foaming agent and 3-8 parts of a decellularized neural substrate. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the neural restoration bracket. The neural restoration bracket is large in porosity, uniform in pore diameter, good in biocompatibility, excellent in antisepsis and anti-inflammation performance, excellent in mechanical performance, capable in biodegradation and assisting the neural restoration function, high in reliability and high in clinical practicability.
Owner:张鹏 +1
Intrauterine adhesion prevention material
The invention discloses an intrauterine adhesion prevention material, and belongs to the field of medical materials. The intrauterine adhesion prevention material is characterized in that the intrauterine adhesion prevention material is a temperature-sensitive gel; the phase transition temperature of the temperature-sensitive gel is 25-40 degrees; the temperature-sensitive gel consists of a gel main body, a tissue affinity agent, a humectant, a gelling temperature regulation agent and pure water; the gel main body is one or several of poloxamer 407, a polylactide acid / glycolic acid / polyethylene glycol copolymer, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), chitosan, sodium beta-glycerophosphate, methoxy polyethylene glycol-(sebacic acid-D,L-lactic acid)polyester anhydride-methoxy polyethylene glycol triblock copolymer, cellulose, a cellulose derivative, and polyethylene glycol / polycaprolactone block copolymer; the tissue affinity agent is hyaluronic acid or sodium hyaluronate; the humectant is glycerol or sodium alginate; and the gelling temperature regulation agent is poloxamer 188 or polyethylene glycol. The intrauterine adhesion prevention material provided for people is good in liquidity and can be coated uniformly, and the surface of a wound can be covered quickly and completely.
Owner:广州市弘健生物医用制品科技有限公司
Sustained releasing microspheric preparation of glucokinase mutant and its making method
InactiveCN1679925AUniform appearanceHigh encapsulation efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolventMutant
A slow-releasing microsphere suitable for non-venous application is prepared from lactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid block copolymer (PLGA) as biodegradable high-molecular carrier and glucokinase mutant through ultrasonic or high-speed stirring for emulsifying and low-speed stirring for volatilizing solvent. Its advantages are high encapsulating rate and long release time (30 days).
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Polyethylene glycol benzothiazole derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103012770AComparative biological activityEfficient irreversible coupling reactionPeptide preparation methodsPolyethylene glycolStructural formula
The invention belongs to the technical field of polymer synthetic chemistry and relates to a polyethylene glycol benzothiazole derivative with the following structural formula shown in the specification and a preparation method and application thereof. In the polyethylene glycol benzothiazole derivative, one or two 2-cyanobenzothiazole groups are contained at the terminal of polyethylene glycol. According to the invention, the N-terminal cysteine protein and polypeptide medicine can be modified by the terminal cyanobenzothiazole polyethylene glycol, and the two can efficiently conduct an irreversible coupling reaction at normal temperature in physiological conditions. Through the invention, other high molecular benzothiazole derivatives such as polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer and polylysine can be prepared at the same time.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
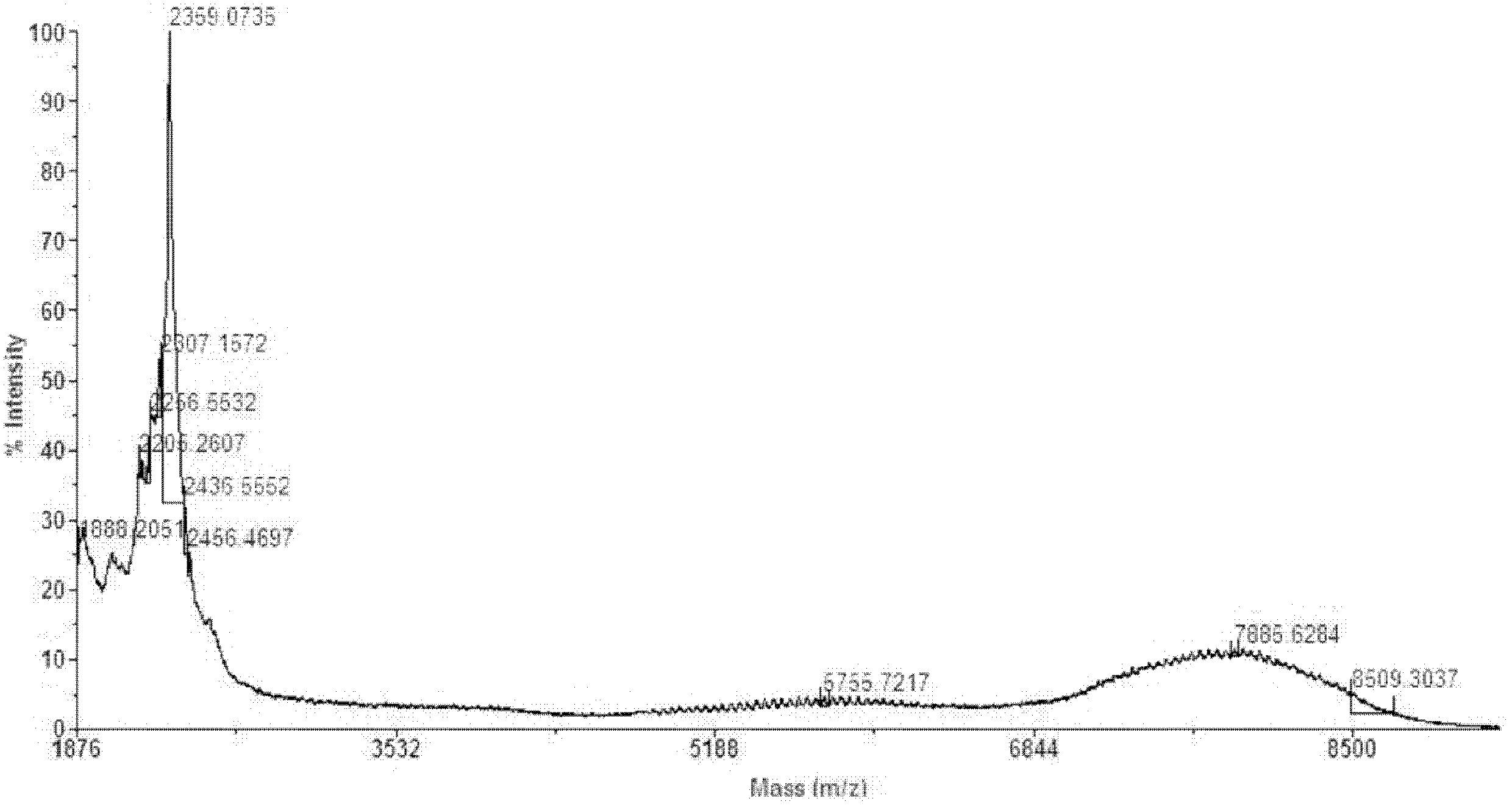
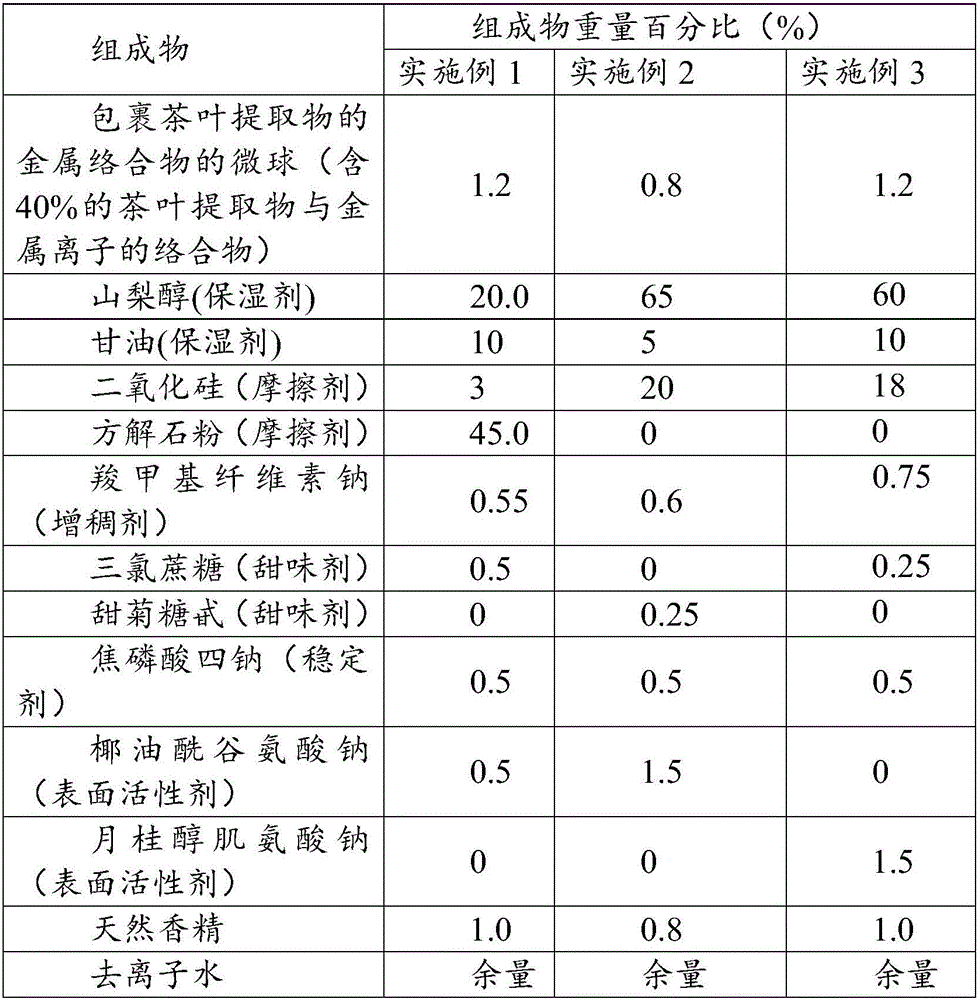
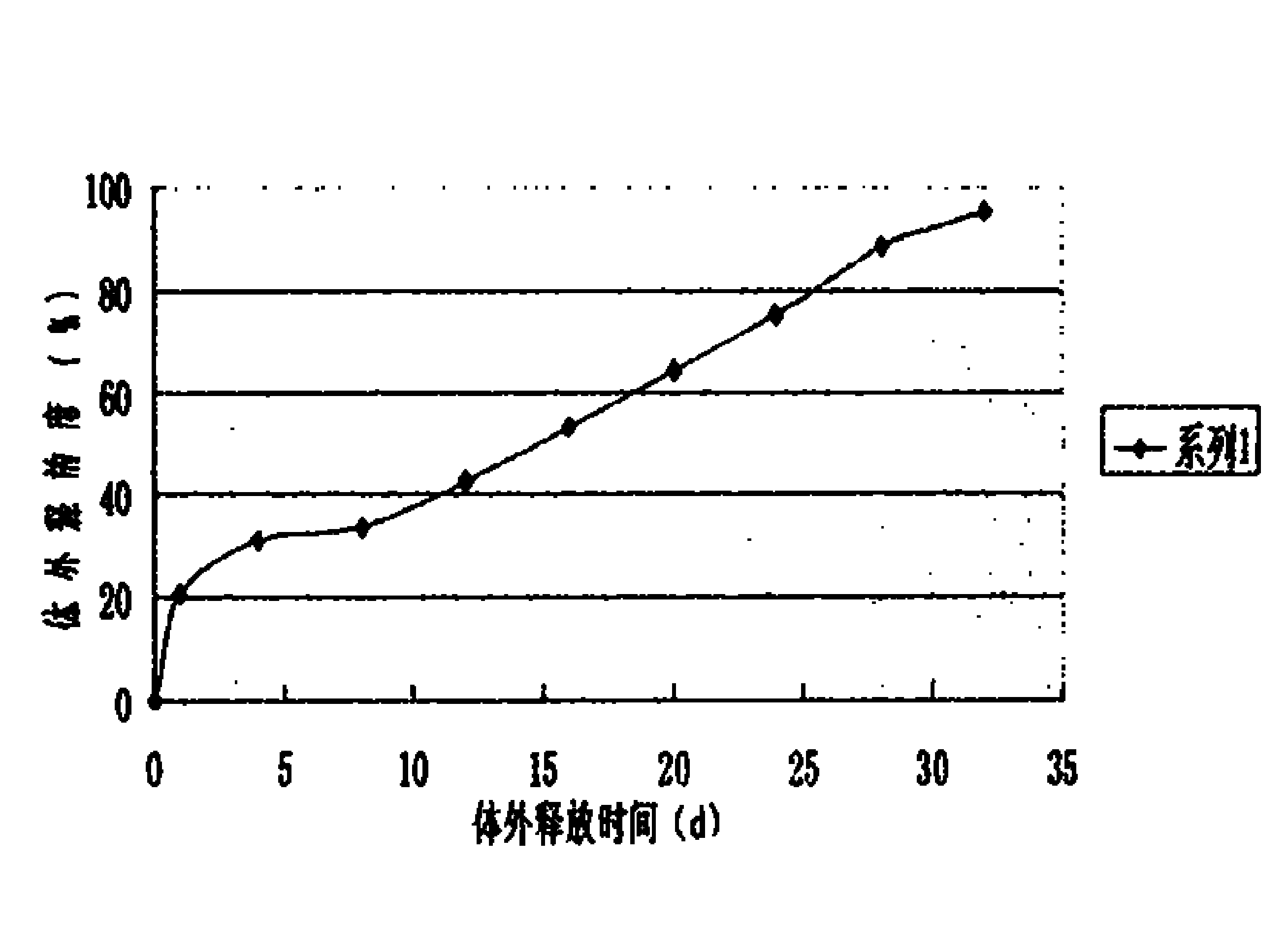
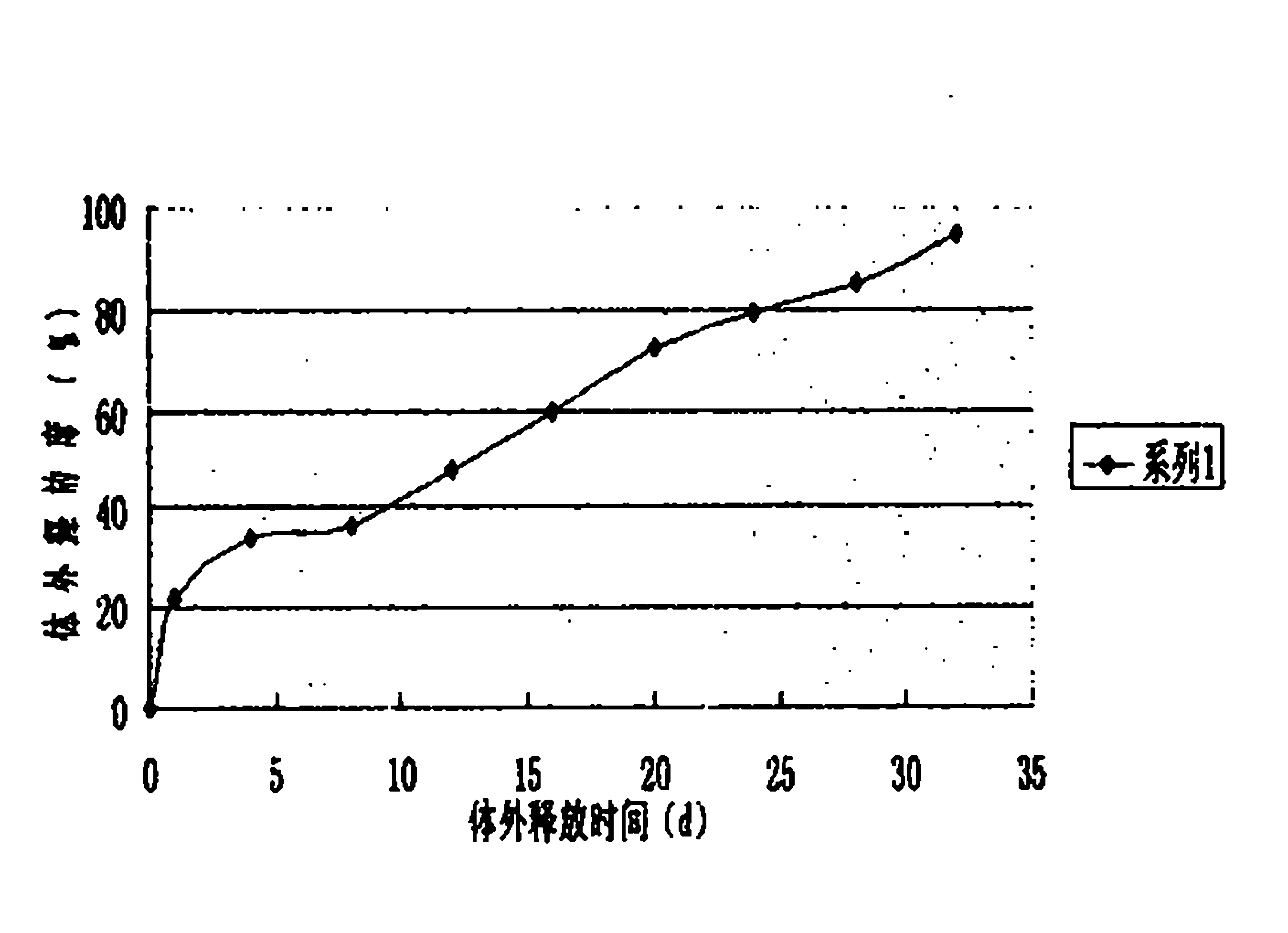
Microspheres with tea extract and complex wrapped and application thereof in natural edible toothpaste
ActiveCN106176376AGood antibacterialPrevent dental cariesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAcetic acidAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses microspheres with a tea extract and a complex wrapped and application of the microspheres in natural edible toothpaste. The microspheres with the tea extract and the complex wrapped is obtained by wrapping the tea extract and the metal ion complex with a lactic acid / glycolic acid copolymer. The invention further provides the natural edible toothpaste for children with the tea extract and the metal ion complex as main functional ingredients, the tea extract and the metal complex stably exist in the formula, and therefore the product has the quite effects of resisting bacteria, inhibiting dental plaque, preventing decayed teeth, making breath fresh, cleaning the oral cavity and making the gingiva healthy.
Owner:广州悦创实业有限公司
Organic polymer-based composite graphene electrode material and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN106328240AImprove conductivityHigh dielectric constantCarbon-silicon compound conductorsCable/conductor manufactureCyclohexanoneCharge discharge
The invention discloses an organic polymer-based composite graphene electrode material. The organic polymer-based composite graphene electrode material is prepared by the steps of taking graphene, rare earth, polyacrylamide, polypyrrole, polystyrene, a polylactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer, polytetramethylene glycol succinate, manganese trifluoride, dimethylacetamide, and magnesium hydrate as main components, adding N-methylbutyl piperdine bis(trifluoromethyl sulfonyl)imide), pentaethylene glycol, dimethyl carbonate, N, N-dimethyl formamide, silicon dioxide, cyclohexanone, starch aluminium octenylsuccinate, a dispersing agent, a silane coupling agent and an adhesive, and performing processes of ultrasonic dispersion, stirring and banburying, mixing in an inert gas environment, spraying and drying, electrode coating with a material, and the like in auxiliary manner. The prepared organic polymer-based composite graphene electrode material is excellent in electrical conductivity, high in dielectric constant, good in charge-discharge performance, capable of satisfying industrial requirements, and relatively high in application prospect.
Owner:广州顺倬能源科技有限公司
Phytoagglutinin modified lactic acid-hydroxacetic acid copolymer and its preparing method
InactiveCN1857734AEasy to degradeDegradation hasPowder deliveryMacromolecular non-active ingredientsRetention timeFreeze-drying
The present invention discloses phytoagglutinin modified lactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer with specific adhesion to prolong the retention time or preparation in gastrointestinal tract obviously and raise the bioavailability of orally taken medicine greatly. The polymer consists of biodegradable material lactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer and bioadhesive material phytoagglutinin. The phytoagglutinin modified lactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer is prepared through dissolving lactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer, 1-ethyl-3-carbodimide and N-hydroxy succinimide in non-proton type polar solvent, and reaction at room temperature via stirring for 2-12 hr; adding water, filtering and collecting precipitate to obtain PLGA-NHS; dissolving phytoagglutinin and PLGA-NHS in mixed solvent of water and non-proton type polar solvent, filtering the reacted mixture, taking the dialysate, and freeze drying to obtain the phytoagglutinin modified lactic acid-hydroxyacetic acid copolymer.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Controlled-release injection containing antidiuresis components and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a controlled-release injection containing antidiuresis components and a preparation method thereof. The controlled-release injection contains main drugs of desmopressin acetate, sustained release auxiliary materials, suspending agent and menstruum. The sustained release auxiliary materials are selected from polylactic acid, polylactic acid-co-glycolic acid, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, polifeprosan and the like, which can be used for slowly releasing medicine into disease local parts in a degrading and absorbing process, so that general toxicity reaction is obviously reduced, and simultaneously, the effective medicine concentration can be maintained on the disease local parts; the suspending agent is selected from sodium carboxymethylcellulose, mannitol and the like, which is used for suspending sustained-release granules or microspheres of biological active ingredients; and the menstruum is common menstruum or special menstruum containing the suspending agent, wherein the common menstruum is selected from distilled water, water for injection, physiological lotion, absolute ethyl alcohol or buffer solution prepared by various salts, and the like. According to the controlled-release injection, the action time of the medicine can be prolonged, the dosage times are reduced, the stability of blood drug concentration in vivo is maintained, and the drug toxic and side effects are reduced.
Owner:无锡市恒益健康科技有限公司
Porous calcium phosphate support loaded microsphere composite material, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109432020AReduce recurrenceAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryCalcium biphosphateAntituberculosis drug
The invention provides a porous calcium phosphate support loaded microsphere composite material, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The porous calcium phosphate support loaded microsphere composite material comprises a porous calcium phosphate support, wherein a polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microsphere is loaded in each hole of the porous calcium phosphate supportand the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microsphere coats one or more antituberculosis drugs. The experiment proves that the porous calcium phosphate support loaded microsphere composite material has a filling bone remodeling and bone inducing osteogenesis function, further has an effect of locally continuously and three-dimensionally slowly releasing the antituberculosis drugs, and achieves an effect of treating osteoarticular tuberculosis and reducing recurrence. The invention further provides the preparation method and the application of the porous calcium phosphate support loaded microsphere composite material.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Water-based ink for printing PVC decorative material and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of water-based ink, and provides water-based ink for printing a PVC decorative material and a preparation method of the water-based ink. The invention discloses water-based ink for printing a PVC decorative material. The water-based ink comprises the following components in parts by weight: 45-50 parts of water-based color paste, 15-20 parts of water-based acrylate emulsion, 20-25 parts of water-based acrylic acid modified polyurethane emulsion, 1-2 parts of water-based wax paste, 3-5 parts of a pH stabilizer, 0.9-1.5 parts of an antifoaming agent,0.5-1 part of a leveling agent, 1-2 parts of a drier and 2-5 parts of deionized water. Wherein the water-based color paste is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 40-60 parts ofwater and 1-5 parts of additive; 10 to 20 parts of water-based acrylic resin liquid; wherein the component A is prepared from, by mass, 33-35 parts of organic pigment, 2-4 parts of wetting dispersant,0.9-1.5 parts of organic silicon defoamer and 40-45 parts of deionized water, and the drier is a mixed solution of nano yttrium oxide, butadiene triethoxysilane, polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer and deionized water according to the mass ratio of 1: 0.2: 3: 7. By means of the technical scheme, the problems that in the prior art, water-based ink is slow in drying, low in adhesion fastness and poor in stability are solved.
Owner:石家庄市博思特油墨有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com