Patents
Literature
84 results about "Dysprosium nitrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dysprosium nitrate, Dy(NO 3) 3, is a strong oxidizing agent and will readily ignite on contact with organic substances. Soluble dysprosium salts, such as dysprosium chloride and dysprosium nitrate, are mildly toxic when ingested.
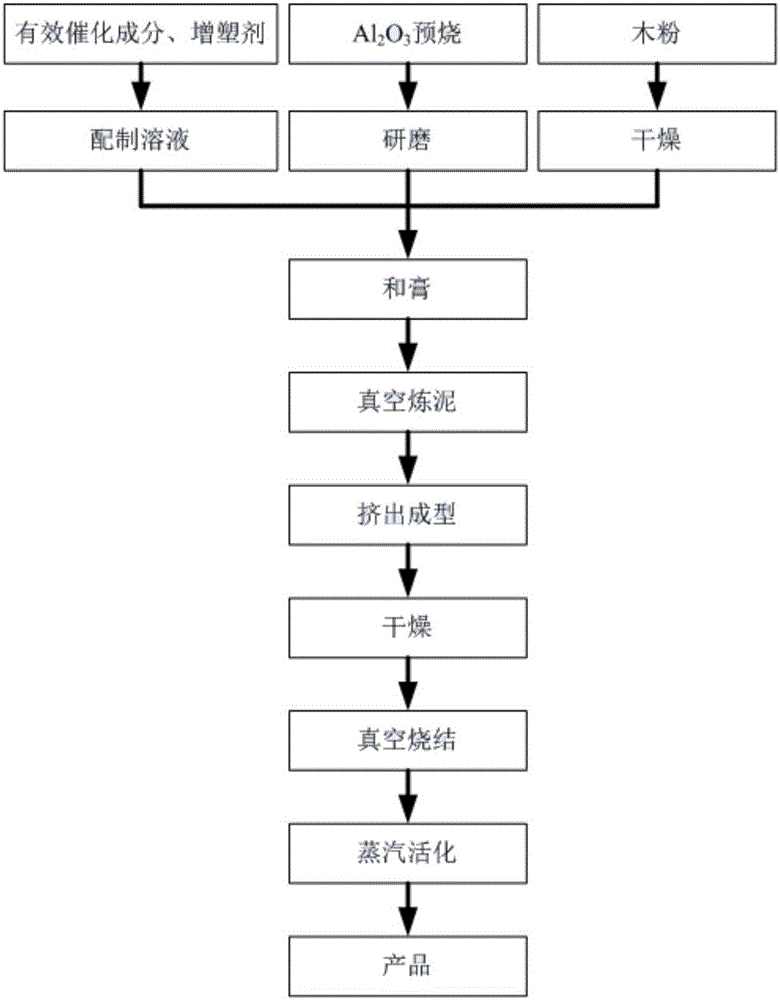
Microporous overcurrent ozone catalytic ceramic membrane for waste water deep treatment as well as preparation method and application method thereof
ActiveCN106745673AGuaranteed deep processing effectImprove mass transfer efficiencyWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsPolyethylene glycolDysprosium nitrate
The invention discloses a microporous overcurrent ozone catalytic ceramic membrane for waste water deep treatment as well as a preparation method and an application method thereof and belongs to the technical field of catalysts for waste water deep treatment. The catalytic ceramic membrane disclosed by the invention is prepared by the following steps: mixing pre-roasted and ground 400-600-mesh Al2O3 power with a catalytic component solution of dysprosium nitrate, molybdenum nitrate and manganous nitrate; and by taking hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, polyethylene glycol and an aqueous solution of dysprosium nitrate, molybdenum nitrate and manganous nitrate as a forming assistant, pasting, mixing, extruding and forming, drying and vacuum-sintering the mixture to obtain the microporous overcurrent ozone catalytic ceramic membrane. The microporous overcurrent ozone catalytic ceramic membrane prepared by the invention creatively couples a microporous overcurrent with a catalytic ozonation technology, so that waste water passes through micron order ducts of the ceramic membrane at a relatively high flow rate by means of an external pressure different action, and therefore, the mass transfer efficiency of ozone and organic matter pollutants and the surface of the catalyst is effectively accelerated and meanwhile, the micron order ducts developing in the catalyst hugely increase the effective catalytic area of a catalytic module in a unit volume.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Rare earth doped hydroxyfluorapatite monocrystal nanometer wire and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102249205ALow costThe synthesis process is simpleMaterial nanotechnologyCoatingsNanowirePhosphate
The invention provides a rare earth doped hydroxyfluorapatite monocrystal nanometer wire and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: under an alkaline condition, enabling calcium nitrate, phosphate, sodium fluoride and rare earth nitrate to react with one another, thereby acquiring a hydroxyfluorapatite monocrystal nanometer wire, wherein the rare earthnitrate is at least one of lanthanum nitrate, cerous nitrate, praseodymium nitrate, neodymium nitrate, promethium nitrate, samarium nitrate, europium nitrate, gadolinium nitrate, terbium nitrate, dysprosium nitrate, holmium nitrate, erbium nitrate, thulium nitrate, ytterbium nitrate and lutecium nitrate. A monocrystal nanometer wire prepared by using the method can be further processed into a repairing material for biologic sclerous tissues, such as artificial bone, bone cement, and the like, and can be used for the basic research and clinical practice in the fields related to biological materials, organizational engineering, and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
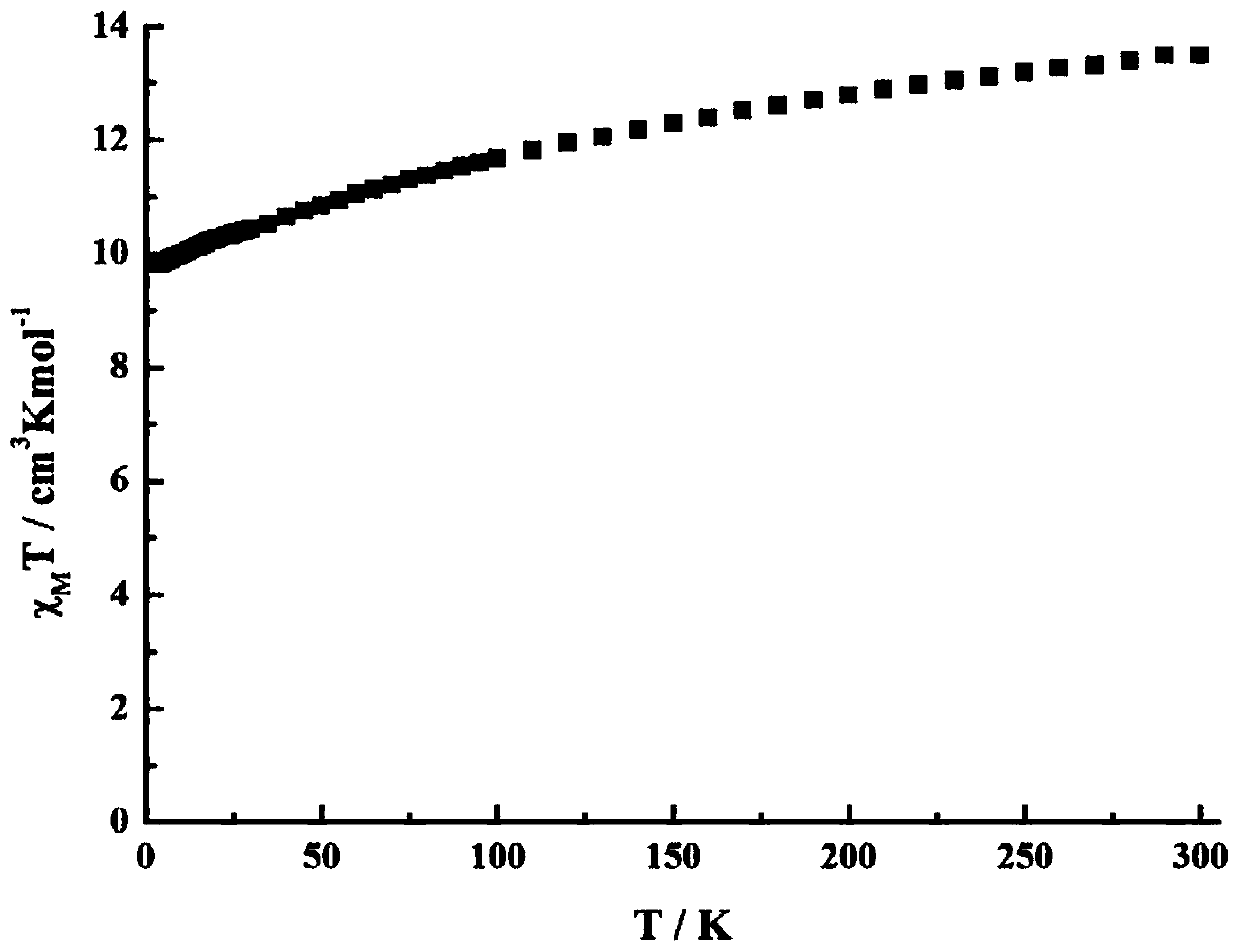
Dysprosium monomer magnet with dual functions of ferromagnetic and ferroelectric and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102136339AHave spontaneous polarizationImprove ferroelectric propertiesMagnetsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsSurface acoustic waveDysprosium nitrate
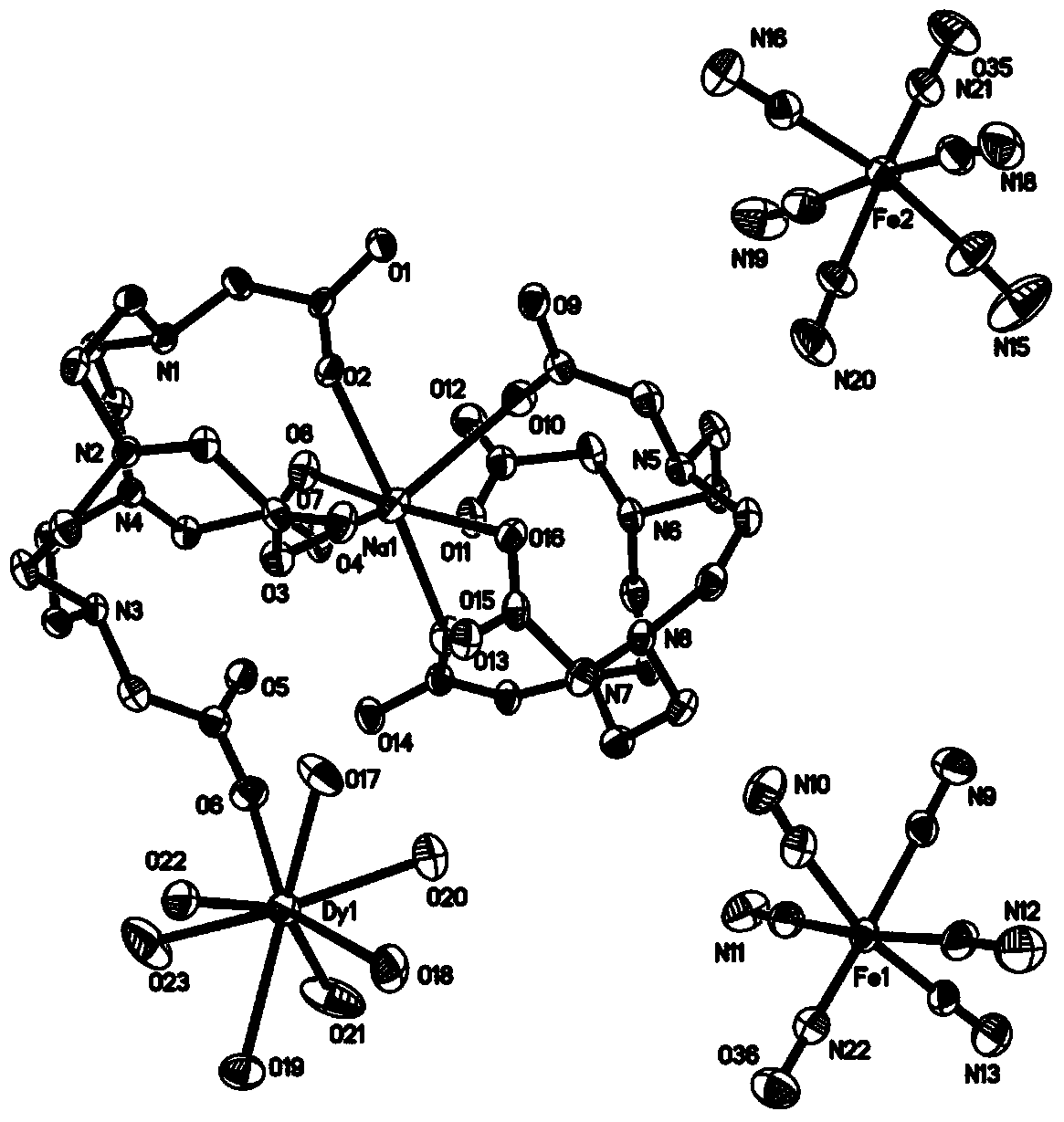
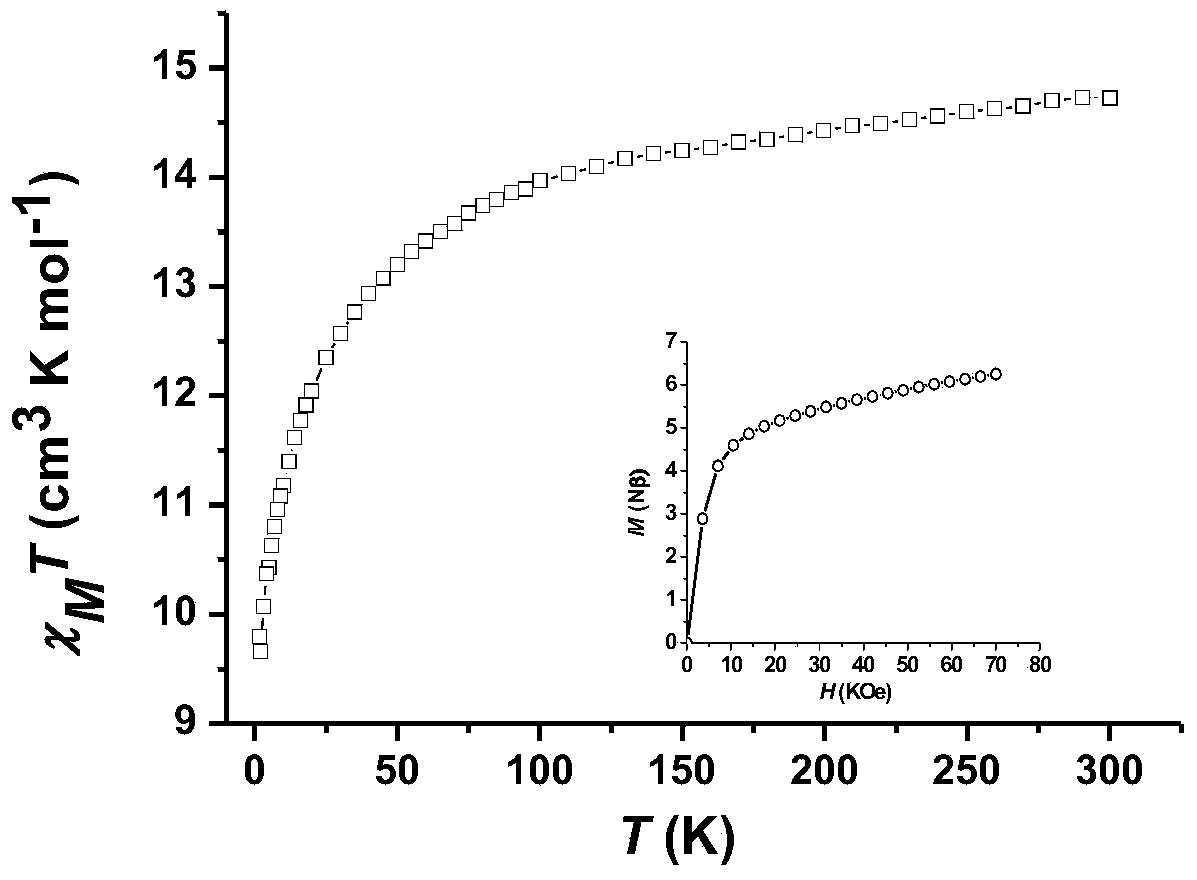
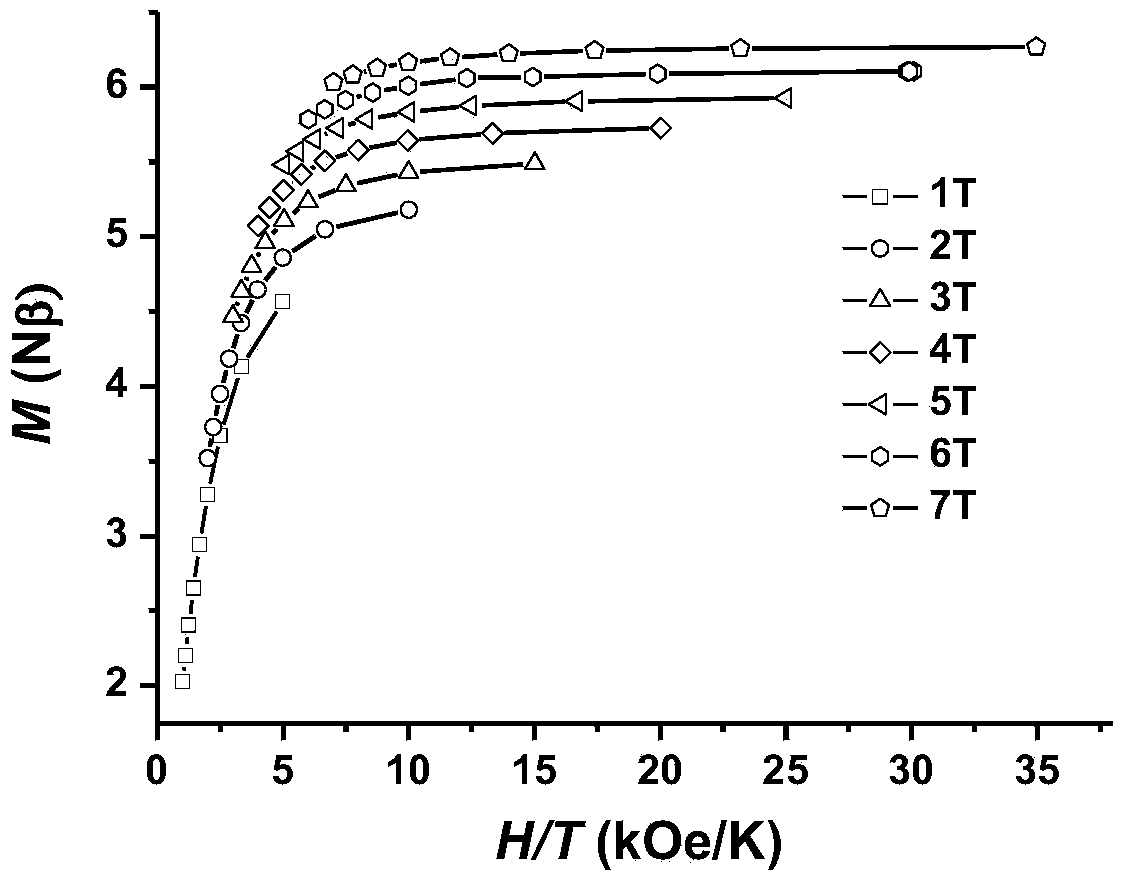
The invention discloses a dysprosium monomer magnet with the dual functions of ferromagnetic and ferroelectric, the chemical formula of which is represented as [Dy3(L)2(NO3)4].EtOH, wherein L is N, N, N', N'-tetrahydroxyethyl-ethylene diamine; and EtOH is ethanol. Three Dy atoms of different coordination environments exist in the dysprosium monomer magnet and form an unclosed triangle three-core Dy structure; a preparation method of the dysprosium monomer magnet is as follows: dysprosium nitrate hexahydrate is used as metal salt; L is used as a ligand, and LiOH is used as an alkaline substance to adjust the pH value to 7; and a mixed liquid is prepared by stirring, baking, separating and washing solids. The invention has the advantages that: the dysprosium monomer magnet not only shows rare dual relaxation monomer magnet behaviors, but also shows excellent ferroelectric properties; therefore, the material has high potential using values in solid devices like nanometer devices, low-temperature high-density storage devices, ferroelectric memorizers, infrared detectors, surface acoustic waves, and integrated ferroelectric devices, etc.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Nanometer dysprosium oxide preparation method
InactiveCN105502467AUniform particlesUniform particle sizeMaterial nanotechnologyRare earth metal compoundsDispersityThermal insulation
The present invention relates to a nanometer dysprosium oxide preparation method, which comprises: adding dysprosium nitrate with a concentration of 0.1-0.6 mol / L and prepared by using pure water to a reaction kettle, and weighing analytical pure sodium carbonate with a concentration of 0.1-0.6 mol / L and prepared by using pure water, wherein a mass ratio of the dysprosium nitrate to the analytical pure sodium carbonate is 1:1-1:1.2; weighing a polyethylene glycol 20000 surfactant with a mass ratio of 5-15% to the dysprosium nitrate, stirring for 15-30 min, uniformly adding a precipitating agent in a dropwise manner, carrying out stirring aging, carrying out suction filtration water washing, draining, adding a surfactant n-butanol, and uniformly stirring, wherein a molar ratio of the obtained substance to the n-butanol is 1:200-1:400; and calcining for 3-5 h at a temperature of 800 DEG C, and carrying out thermal insulation for 1 h so as to obtain the nanometer dysprosium oxide with a particle size of 40-60 nm and a specific surface area of greater than 25. With the preparation method of the present invention, the problems of non-uniform particles and insufficient dispersity are solved, and the characteristics of uniform particle and good dispersity are provided.
Owner:CHANGZHOU GEOQUIN NANO NEW MATERIALS
Dissimilar metal organic framework material of 2,2'-dipyridyl-3,3'-dicarboxylic acid and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN105669729ALow temperature requirementEasy temperature controlOrganic compound preparationGroup 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesN dimethylformamideSynthesis methods
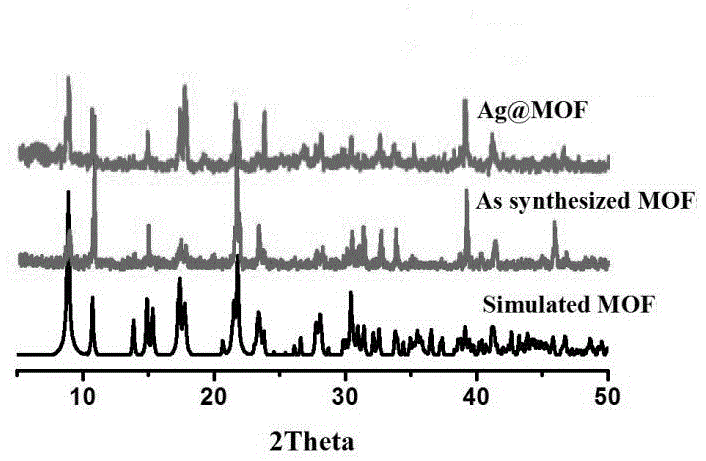
The invention provides a dissimilar metal organic framework material of 2,2'-dipyridyl-3,3'-dicarboxylic acid and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of crystalline materials. The chemical molecular formula is [Dy(cpa)2(H2O)2].[Me2NH2], wherein Me2NH2 is dimethylamine cation, and cpa represents 5-(4-carboxylphenyl)pyridyl formic acid. Under sealed conditions, an organic ligand pyridine carboxylic acid and dysprosium nitrate are subjected to solvothermal reaction in an N,N-dimethylformamide-water mixed solution by regulating the pH value with nitric acid, thereby obtaining the crystal of the metal organic framework material. The silver-supported metal organic framework material has favorable catalytic properties in p-nitrophenol reduction.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
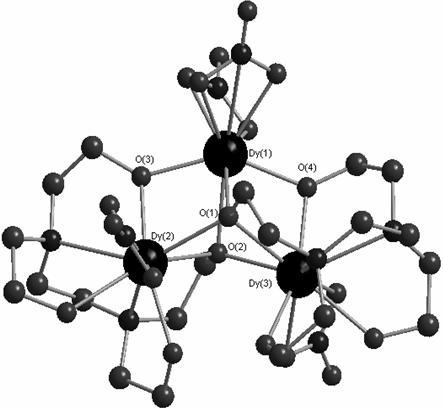
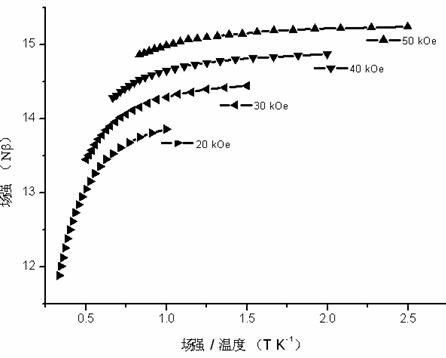
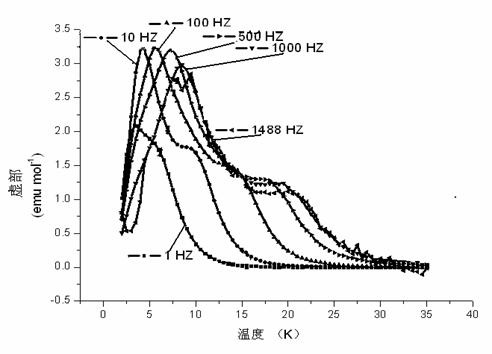
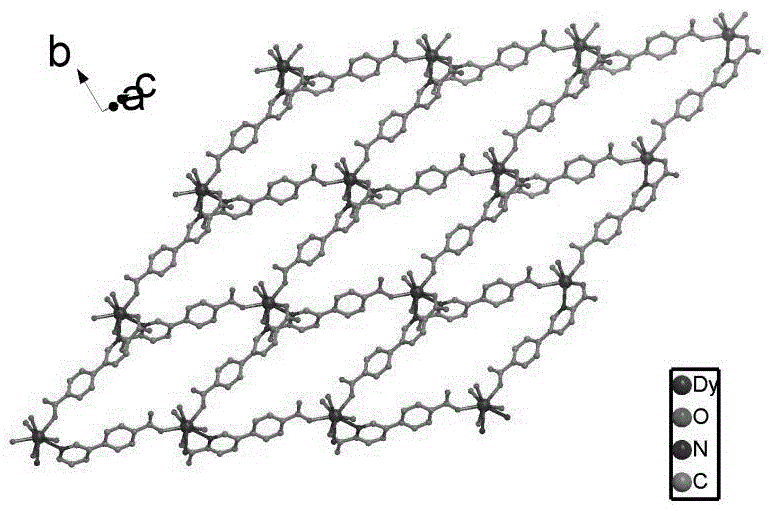
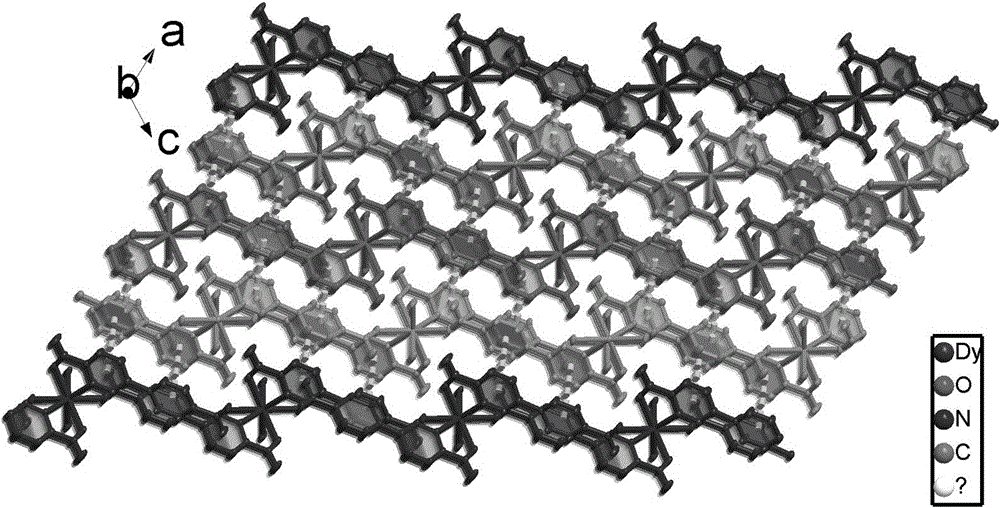
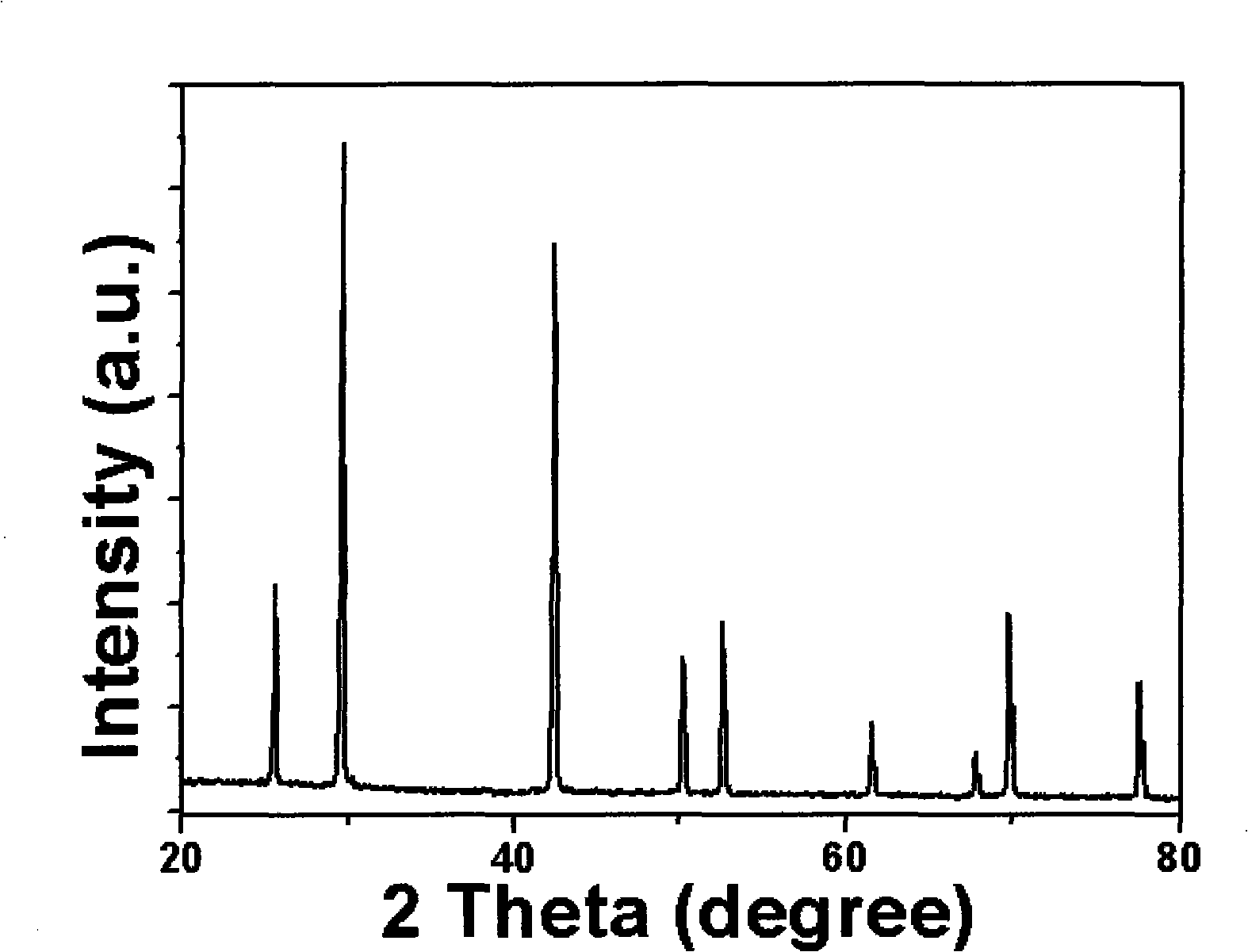
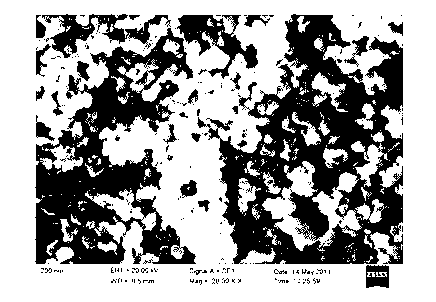
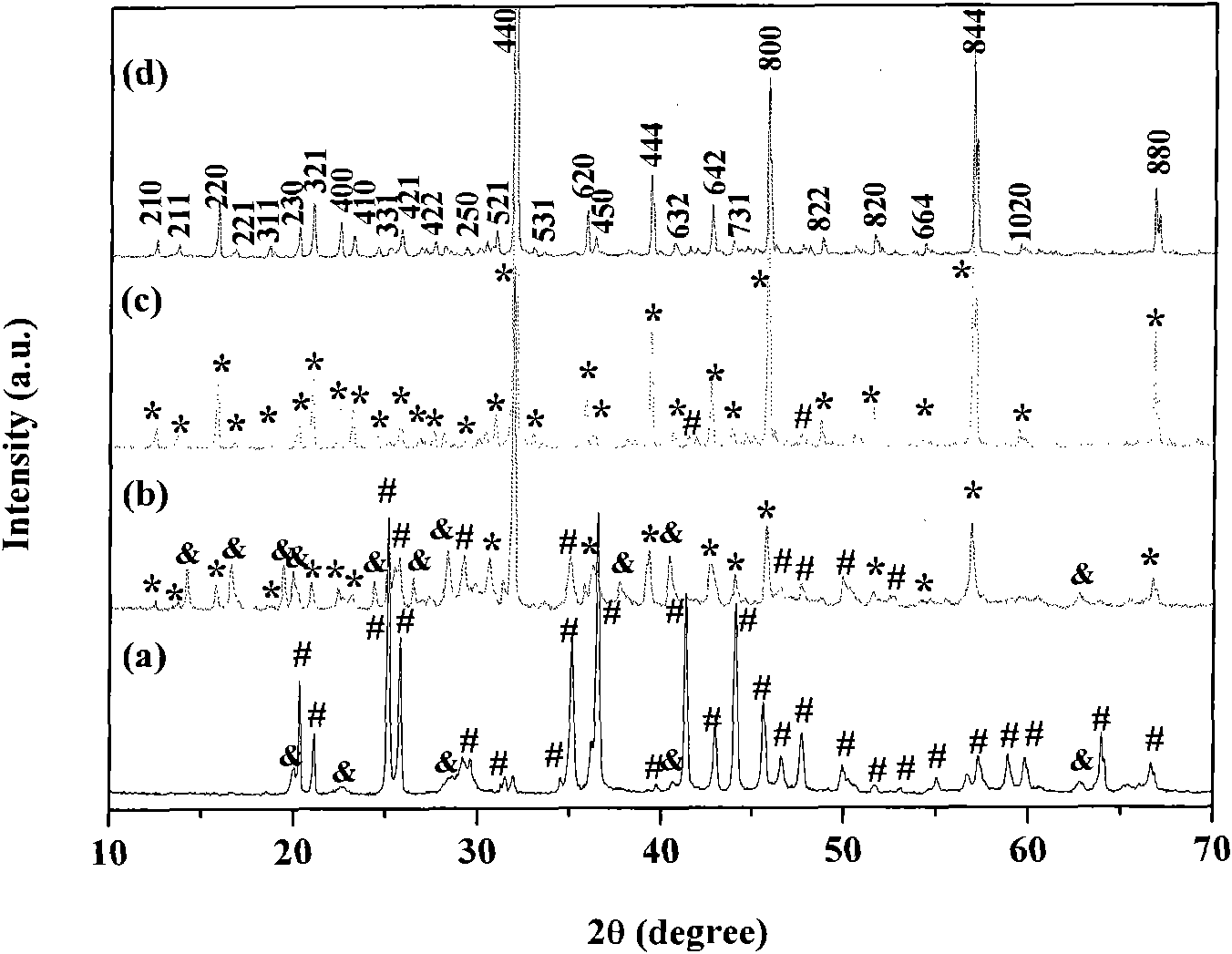
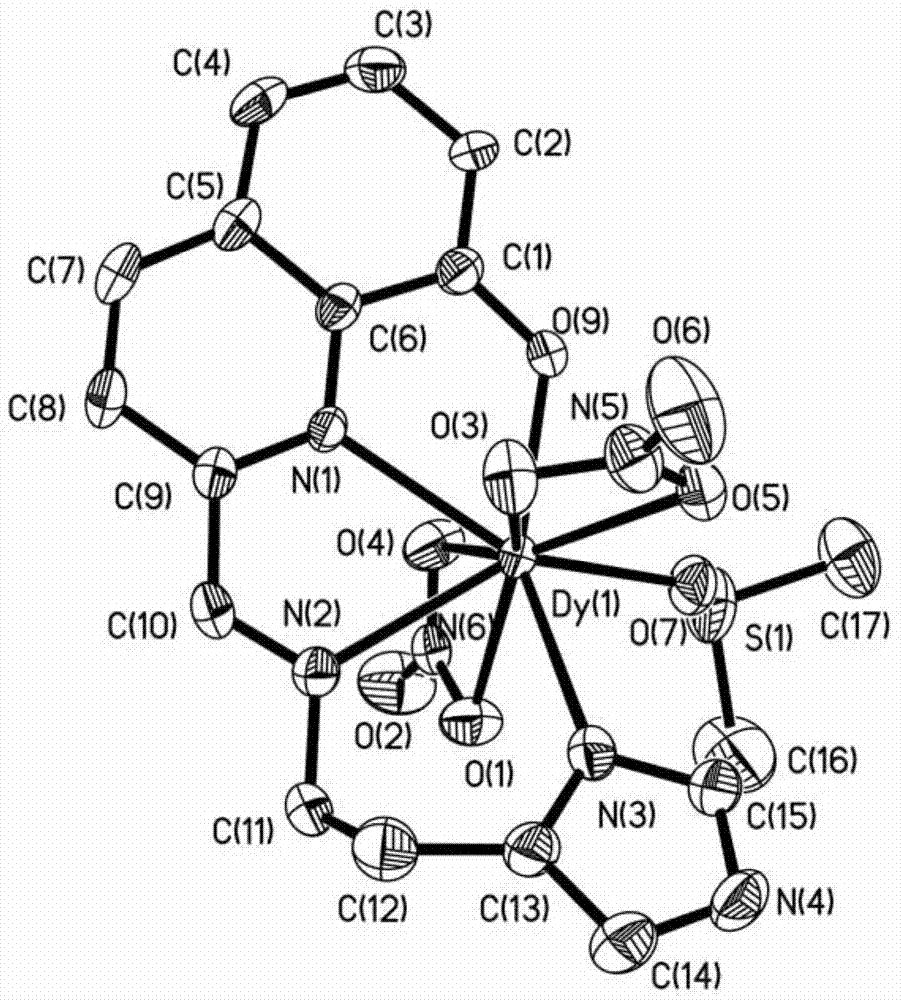
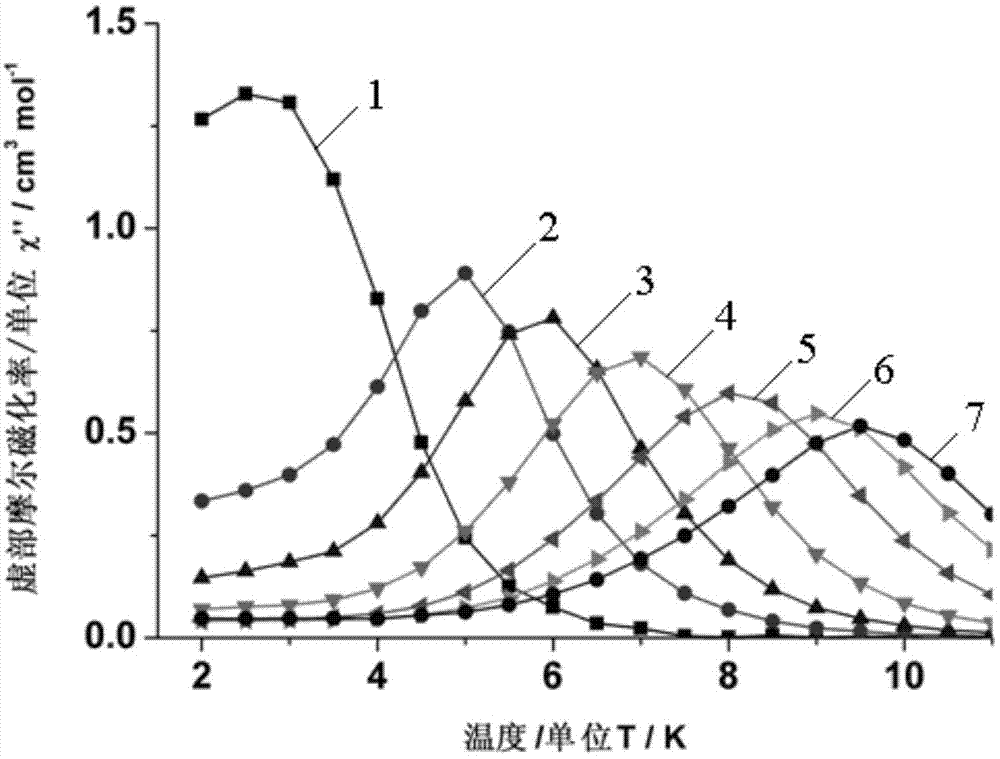
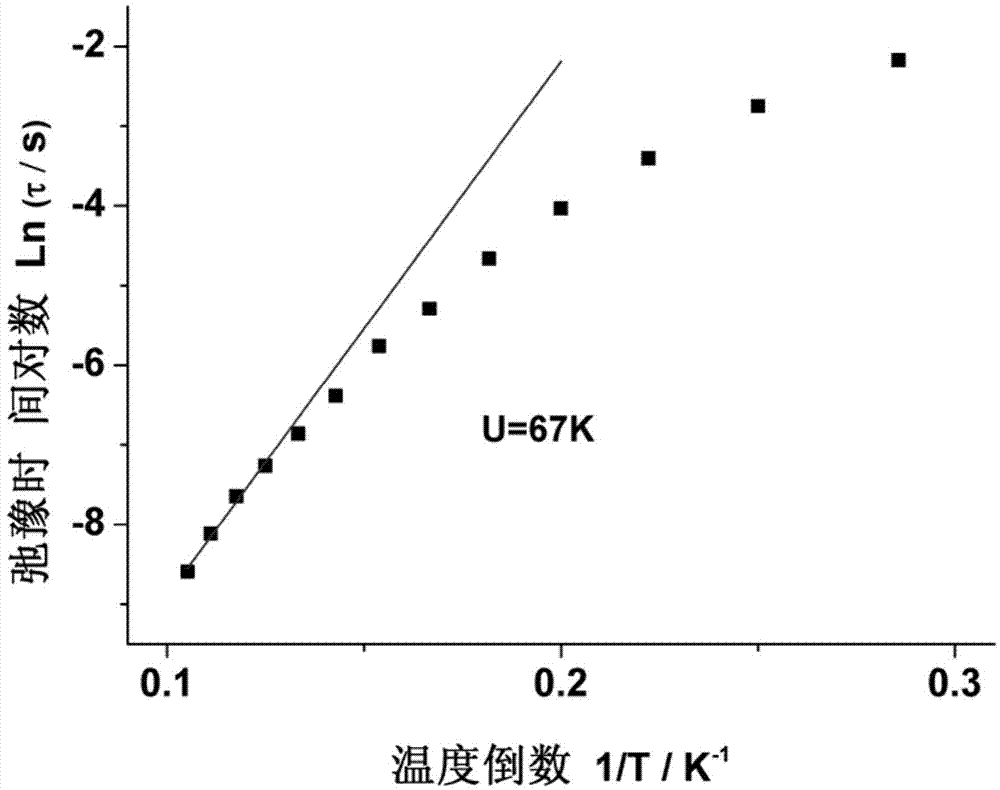
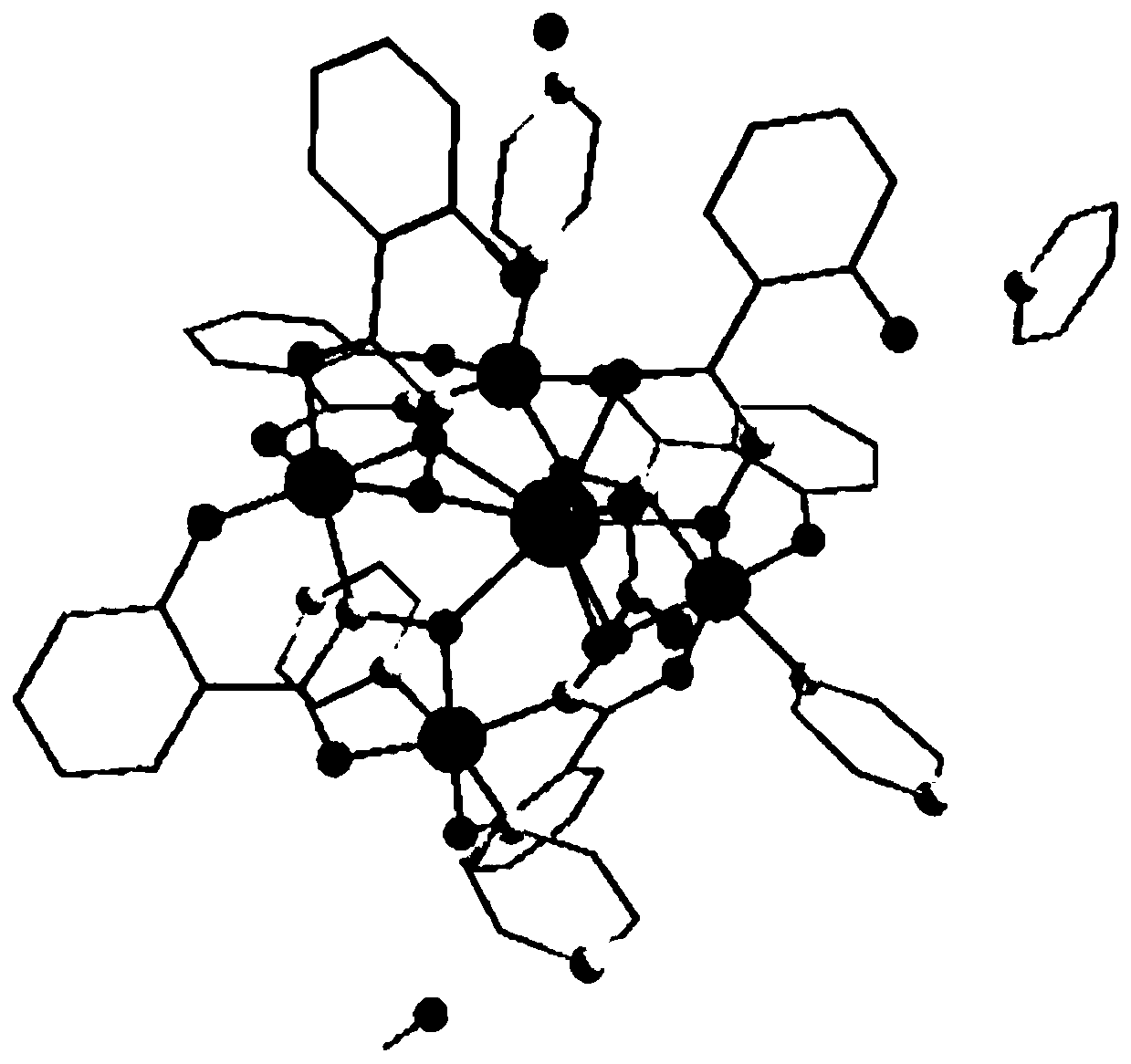
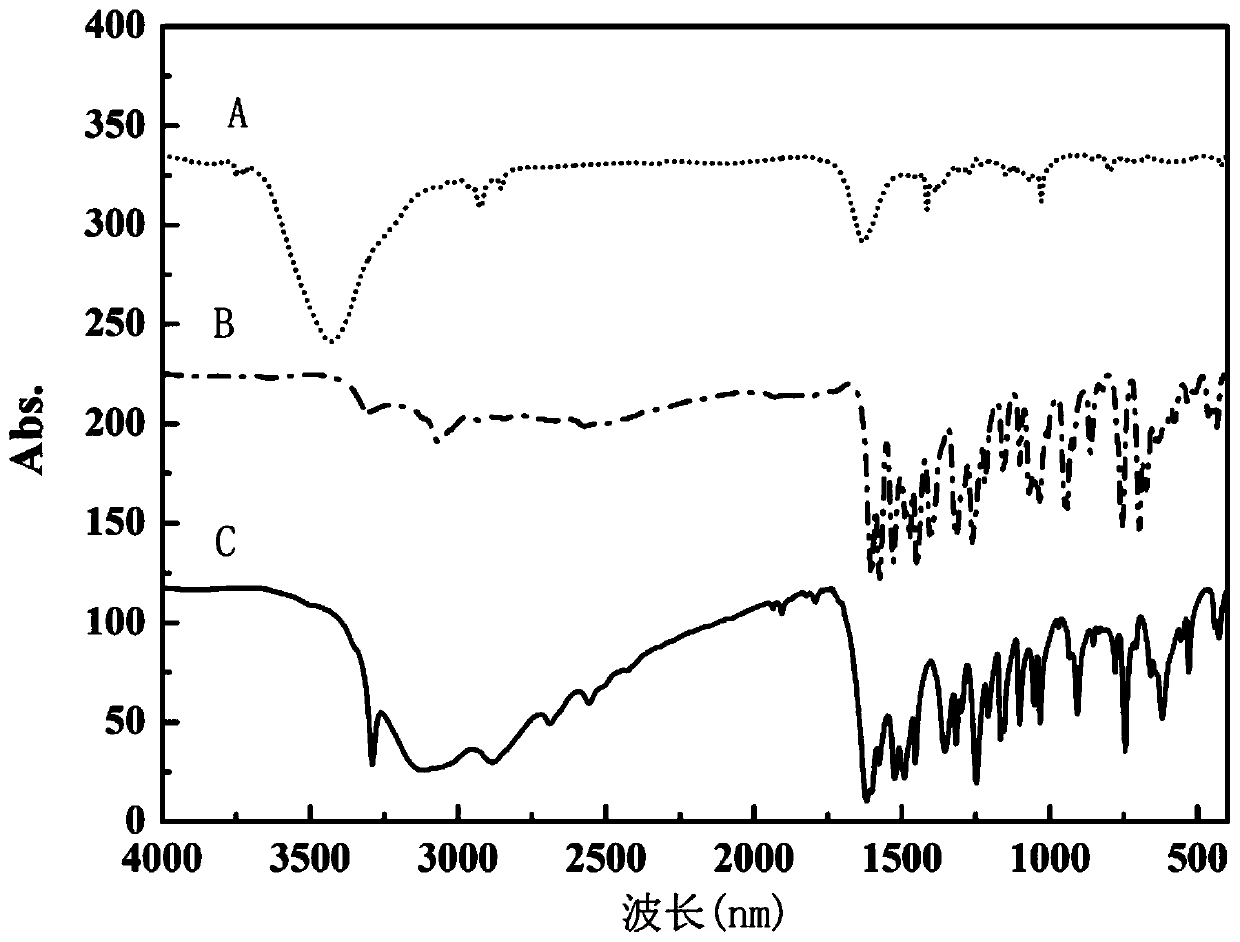
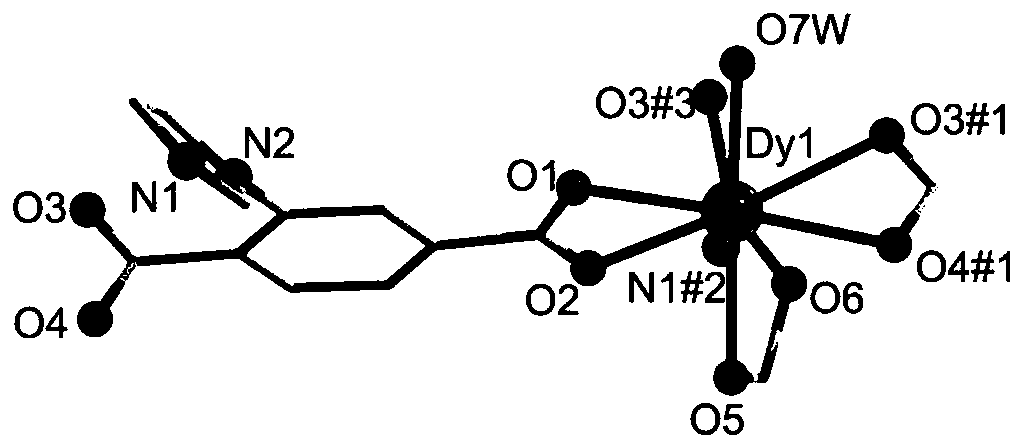
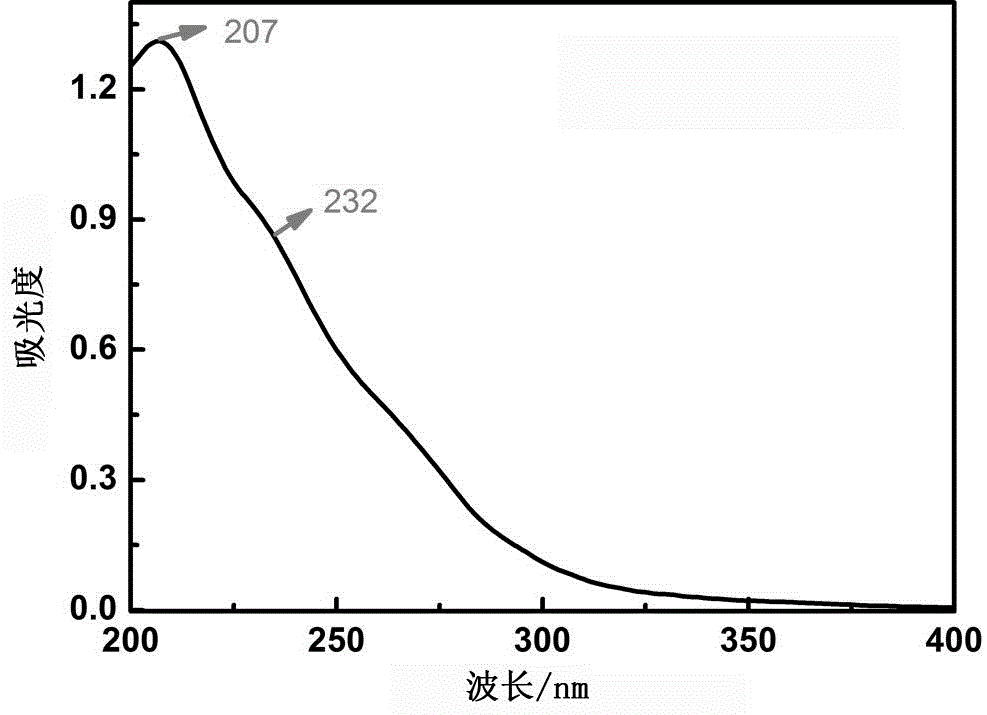
Method for preparing single-molecular magnet [Dy2(saph)2(NO3)2(CH3OH)4]
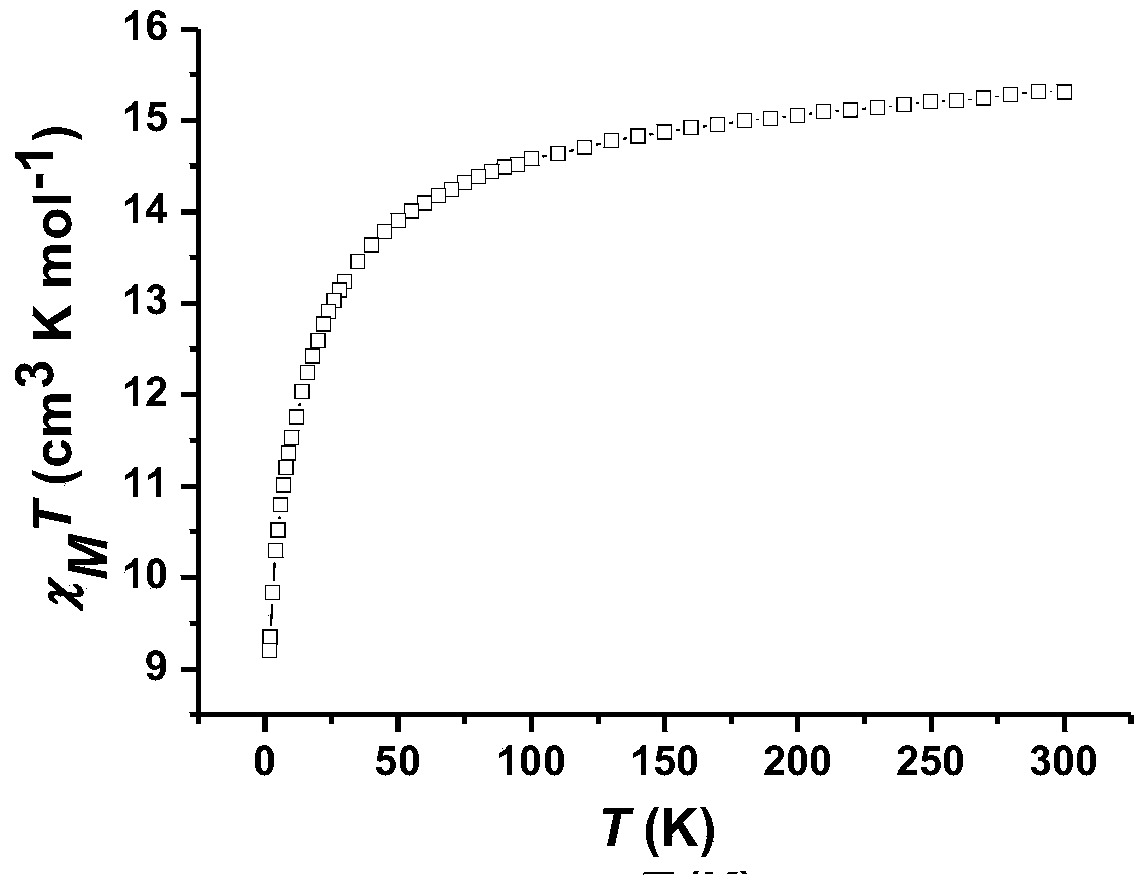
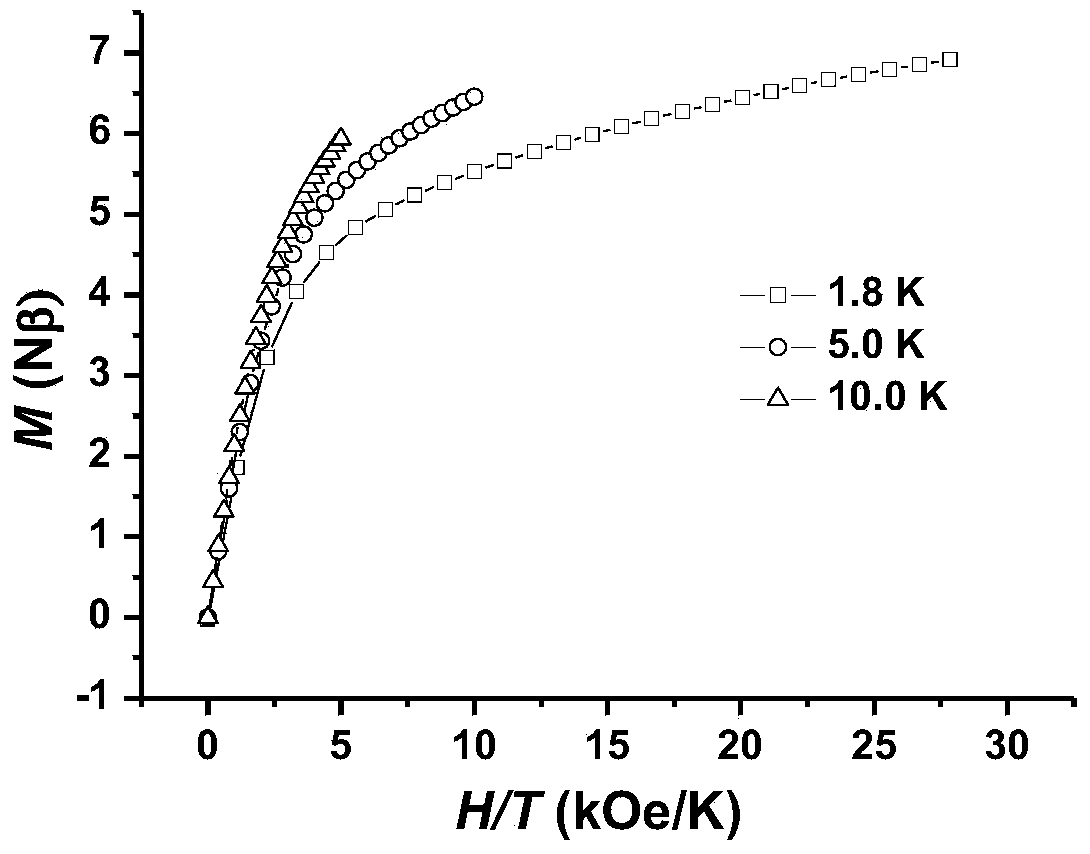
InactiveCN104557994AStrong ferromagnetismThe synthesis method is simpleGroup 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismSalicylaldehydeRare earth
The invention discloses a method for preparing a single-molecular magnet [Dy2(saph)2(NO3)2(CH3OH)4] and relates to a method for preparing a single-molecular magnet. The invention aims at solving the problems that the synthetic method of the conventional rare earth complex single-molecular magnet is low in yield and the synthetic method of the complex is complicated. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving o-aminophenol salicylaldehyde in acetonitrile, thereby obtaining a solution A; dissolving dysprosium nitrate in methanol, thereby obtaining a solution B; mixing the solution A and the solution B, adding a triethylamine solution into the mixed solution, stirring under room temperature condition, thereby obtaining a preform; and volatilizing a solvent out of the preform, thereby obtaining the complex. The [Dy2(saph)2(NO3)2(CH3OH)4] prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is a single-molecular magnet with good ferromagnetic properties, the yield of the preparation method disclosed by the invention is high and is over 52.84 percent, and the synthetic method of the single-molecular magnet is simple and high in repeatability. The invention belongs to the field of preparation of single-molecular magnets.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Preparation of red strontium sulphide long afterglow material
InactiveCN101328405AEasy to controlWell mixedLuminescent compositionsSolubilitySurface-active agents
The invention discloses a method for preparing a red strontium sulphide long afterglow material, comprising a hydrothermal coprecipitation method which comprises the following steps that: (a) water-solubility strontium salt, water-solubility europium salt, water-solubility dysprosium salt, carbamide and water are weight according to the mol ratio of 1: between 0.01 and 0.05: between 0.01 and 0.05: between 4 and 6: between 28 and 32 and are put inside a container to be stirred and dissolved, the mixture is insulated in a sealing state at a temperature of between 80 and 160 DEG C for 5 to 24 hours so that a precursor is obtained; (b) the precursor is subject to filtering and annealing at a temperature of between 900 and 1200 DEG C in the reaction environment for 0. 5 to 2 hours so that the red strontium sulphide long afterglow material is prepared; the water-solubility strontium salt is strontium nitrate or strontium chloride or strontium acetate, the water-solubility europium salt is europium nitrate, europium chloride or polyimide, the water-solubility dysprosium salt is dysprosium nitrate or dysprosium chloride or dysprosium acetate, and a surface active agent is added according to the mol ratio of the water-solubility strontium salt to the surface active agent of 1: between 0.0001 and 0.0003. The method is widely applied to the fields such as building decoration, traffic transportation, military facilities, fire emergency service and goods for everyday consumption.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
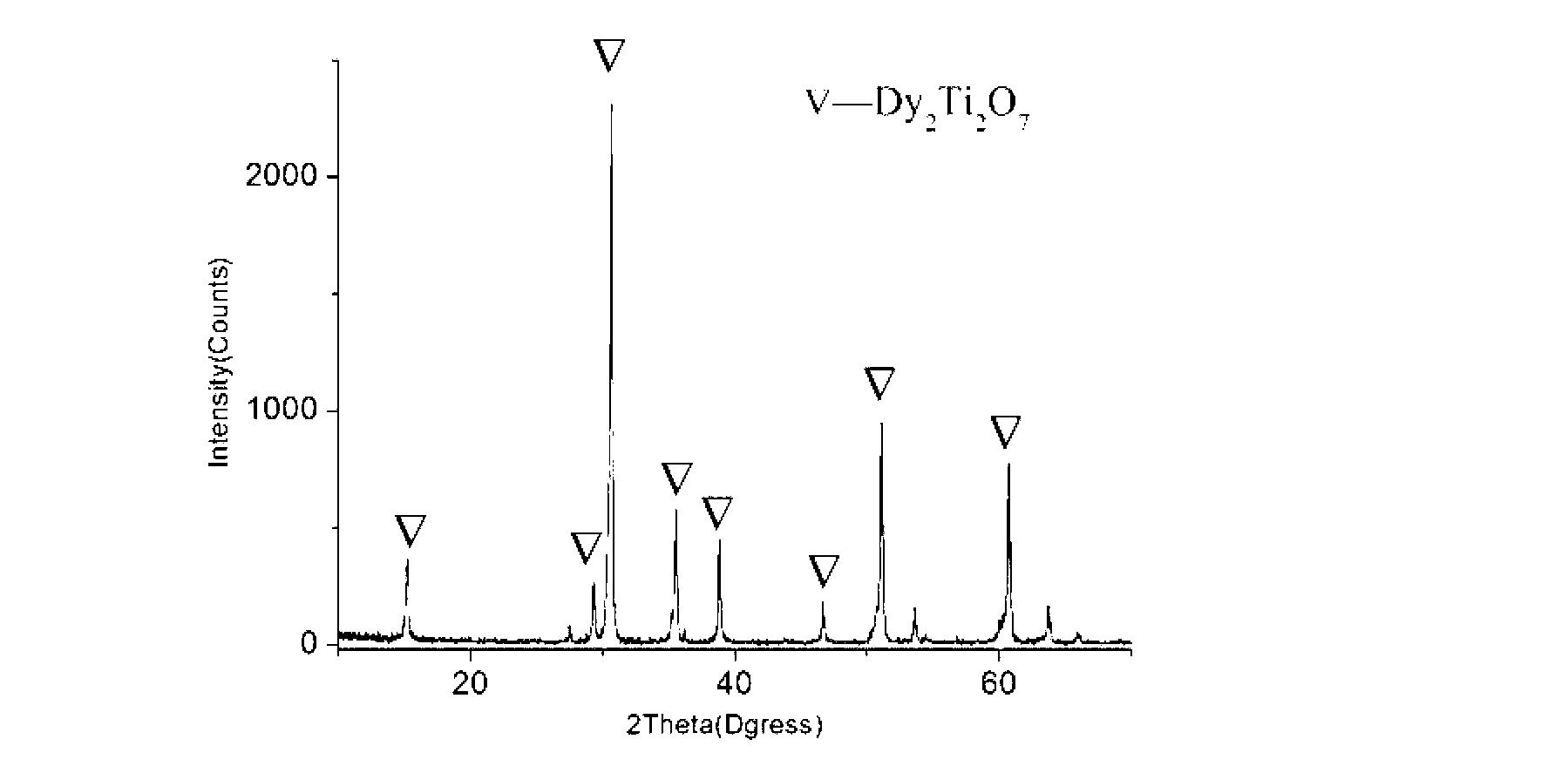
Preparation method of nano dysprosium titanate powder
InactiveCN102701273AReduce hydrolysisSlow down aggregationNanotechnologyTitanium compoundsAcetic acidAlcohol
The invention relates to a preparation method of nano dysprosium titanate powder. The method comprises the steps of dropping alcohol / water / glacial acetic acid mixed solution containing dysprosium nitrate into titanium acid butyl ester alcohol solution according to the molar ratio of Dy:Ti=(1-2:1); ageing obtained colloidal sol at the room temperature so as to obtain gel; drying and crushing the gel, arranging the gel into an aluminum oxide crucible, sintering the gel at 8001100 DEG C so as to obtain the nano dysprosium titanate powder. The nano dysprosium titanate powder preparation process is simple, the grain size of the powder is even and small, and the purity is high; and the powder can be used as neutron absorbing materials.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Regular honeycomb ceramic carbon carrier based doped ozone catalyst for advanced treatment of industrial wastewater and preparation method of regular honeycomb ceramic carbon carrier based doped ozone catalyst
ActiveCN106390988AHarmonized mechanical strengthCoordinating Contradictions in Enrichment and Mass TransferCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSteam activationPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a regular honeycomb ceramic carbon carrier based doped ozone catalyst for advanced treatment of industrial wastewater and a preparation method of the regular honeycomb ceramic carbon carrier based doped ozone catalyst. The regular ozone catalyst is prepared by steps: mixing pre-calcined and ground 150-500-mesh Al2O3 powder with 150-500-mesh wood meal according to a specific proportion; taking hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, polyethylene glycol and dysprosium nitrate and molybdenum nitrate aqueous solution as auxiliary forming agents, and performing paste mixing, refining, extrusion molding, drying, vacuum sintering, steam activation and the like to obtain the catalyst. The catalyst is capable of promoting enrichment and mass transfer of ozone and organic pollutants in water in an ozone catalytic oxidation process, and catalysis efficiency is improved; by adoption of aluminum oxide ceramics as skeletons, problems of damages and losses caused by reduction in material strength in the catalytic oxidation process of activated carbon are solved. The regular ozone catalyst is high in treatment efficiency, low in operating cost, convenient to fill and maintain and suitable for advanced treatment of wastewater, ozone oxidation effects are strengthened, and the decoloring rate and the COD removal rate are increased.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Strontium aluminate luminous material and controllable synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN101831292ACalcination temperature is lowReduce energy consumptionLuminescent compositionsAir atmosphereAluminate
The invention discloses a strontium aluminate luminous material and a controllable synthesis method thereof. According to the method, Al(NO3)3.9H2O, Sr(NO3)2, CO(NH2)2, C6H5Na3O7.2H2O, Eu2O3, Dy2O3 and HNO3 are used as raw materials. The method is a hydrothermal synthesis-calcining two-step method, and comprises the following steps of: (1) dissolving the Sr(NO3)2 and the Al(NO3)3.9H2O into distilled water respectively to form nitrate solution, taking the nitrate solution with metering, fully mixing the nitrate solution, then adding europium nitrate and dysprosium nitrate into the mixed nitrate solution, mixing the solution and CO(NH2)2 or surfactant in a certain ratio, placing the mixture into a closed reaction kettle, dissolving the mixture with stirring, and preserving the heat at certain temperature to obtain a precursor; and (2) filtering and drying the precursor, and annealing the precursor for several hours in an air atmosphere and a reducing atmosphere at different temperatures respectively to obtain the nano aluminate luminous material. The hydrothermal synthesis-calcining two-step method for preparing the strontium aluminate luminous material can effectively control the form and luminous color of the product; and the strontium aluminate luminous material has good dispersion property and expands the application field of luminous materials.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Dy monomolecular magnetic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104497027AStable mononuclear structureThe maximum flip energy barrier is excellentGroup 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismPotassium hydroxideEther
The invention discloses a Dy monomolecular magnetic material and a preparation method thereof, relating to a monomolecular magnetic material and a preparation method thereof and aiming at solving the problems that the existing monomolecular magnetic material has an unstable structure and the preparation method is complicated and low in yield. The expression of the Dy monomolecular magnetic material is [Dy(nma)(NO3)2(DMSO)].CH3OH, the structural formula is as shown in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing dichloromethane, methanol and dimethyl sulfoxide, to obtain a mixed solvent; then adding dysprosium nitrate, histamine dihydrochloride, potassium hydroxide and 2-formyl-8-hydroxyquinoline into the mixed solvent, stirring and reacting for 12h-24h, and then filtering to obtain a filtrate; and dropwise adding ether into the filtrate, and standing to obtain the Dy monomolecular magnetic material. The yield of the prepared Dy monomolecular magnetic material is 70%-72%. The invention provides a Dy monomolecular magnetic material and a preparation method thereof.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Whole color fluorescent material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101045861AUniform phaseGood chemical stabilityLuminescent compositionsDysprosium nitrateYttrium
This invention relates to a panchromatic luminescent material, formulae is LiYZrO:Eu3+, Dy3+, R3+. The R represents B3+ or mixture of any kinds of rare earth ion and B3+ ion. The process: dissolve lithium nitrate, yttrium nitrate, zirconium nitrate, europium nitrate, dysprosium nitrate and boric acid or mixture of any rare earth nitrate and boric acid in de-ionized water, then add urea and citric acid to above solution, heat and whip, then by agglutination to gain product. This luminescent material is panchromatic blazing, has high emissive power, uniformity phase, small granularity, belong to nanometer level, and has good chemical stability.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
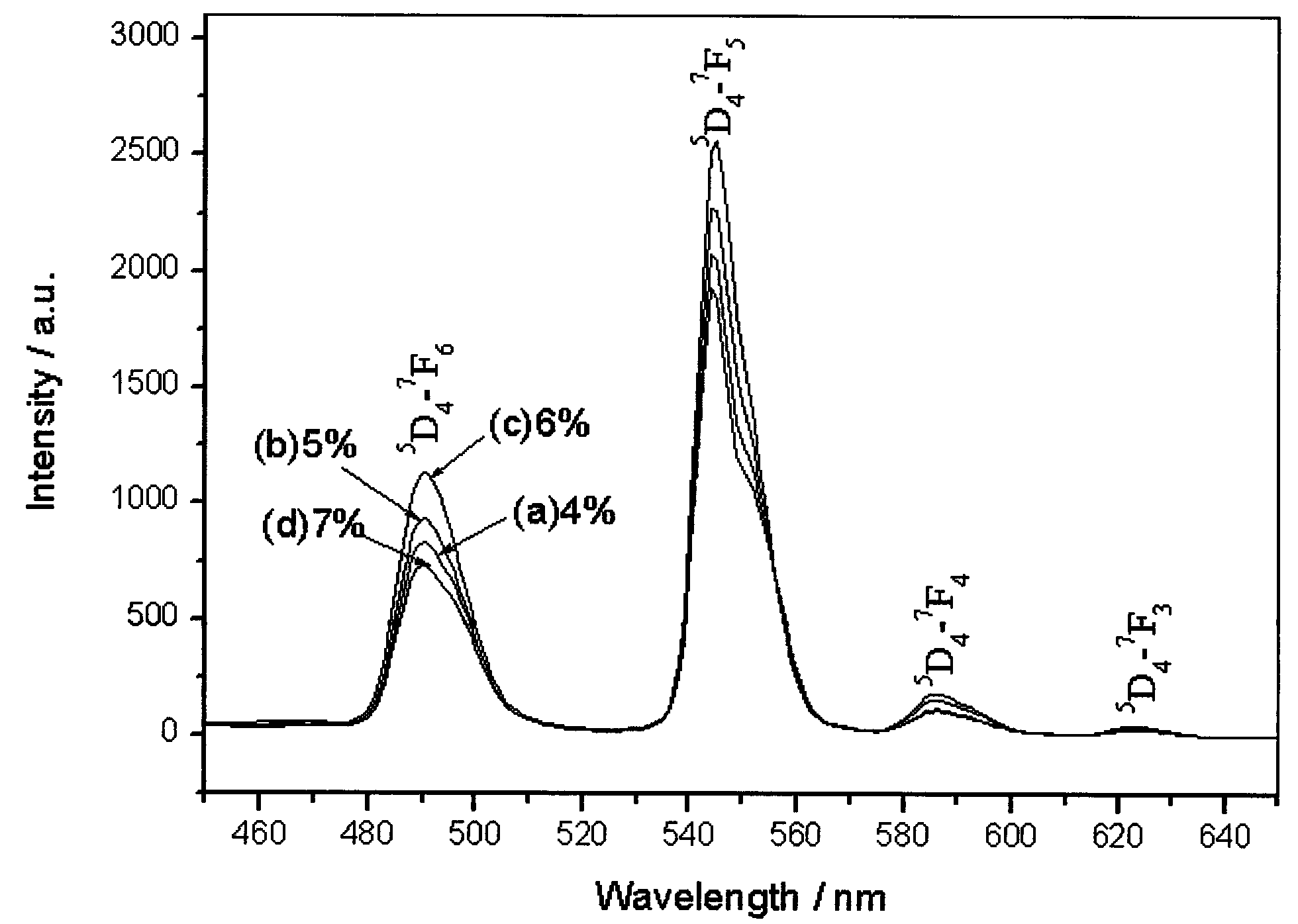
Synthesis of SrAl<2>O<4>:Dy<3+>/ Eu<2+> green steady persistence fluorescent material
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a SrAl<2>O<4>:Dy<3+> / Eu<2+> green steady persistence fluorescent material. The chemical formula of the SrAl<2>O<4>:Dy<3+> / Eu<2+> green steady persistence fluorescent material is SrAl<2>O<4>:Dy<3+> / Eu<2+>; the steady persistence fluorescent powder is prepared through following steps: a mother salt is prepared through mixing of strontium nitrate, dysprosium nitrate, gadolinium nitrate, europium nitrate, and aluminum nitrate at a certain ratio, the mother salt is added drop by drop into a ammonium bicarbonate solution of a certain concentration, after adding, reaction is carried out for 30min, and then centrifugation, washing, and drying are carried out to obtain a precursor powder, and at last, calcining is carried out at reducing atmosphere to obtain the SrAl<2>O<4>:Dy<3+> / Eu<2+> green steady persistence fluorescent material. The SrAl<2>O<4>:Dy<3+> / Eu<2+> green steady persistence fluorescent material is excellent in fluorescent performance, and it is promising to achieve important effect in the field of illumination and cell display.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
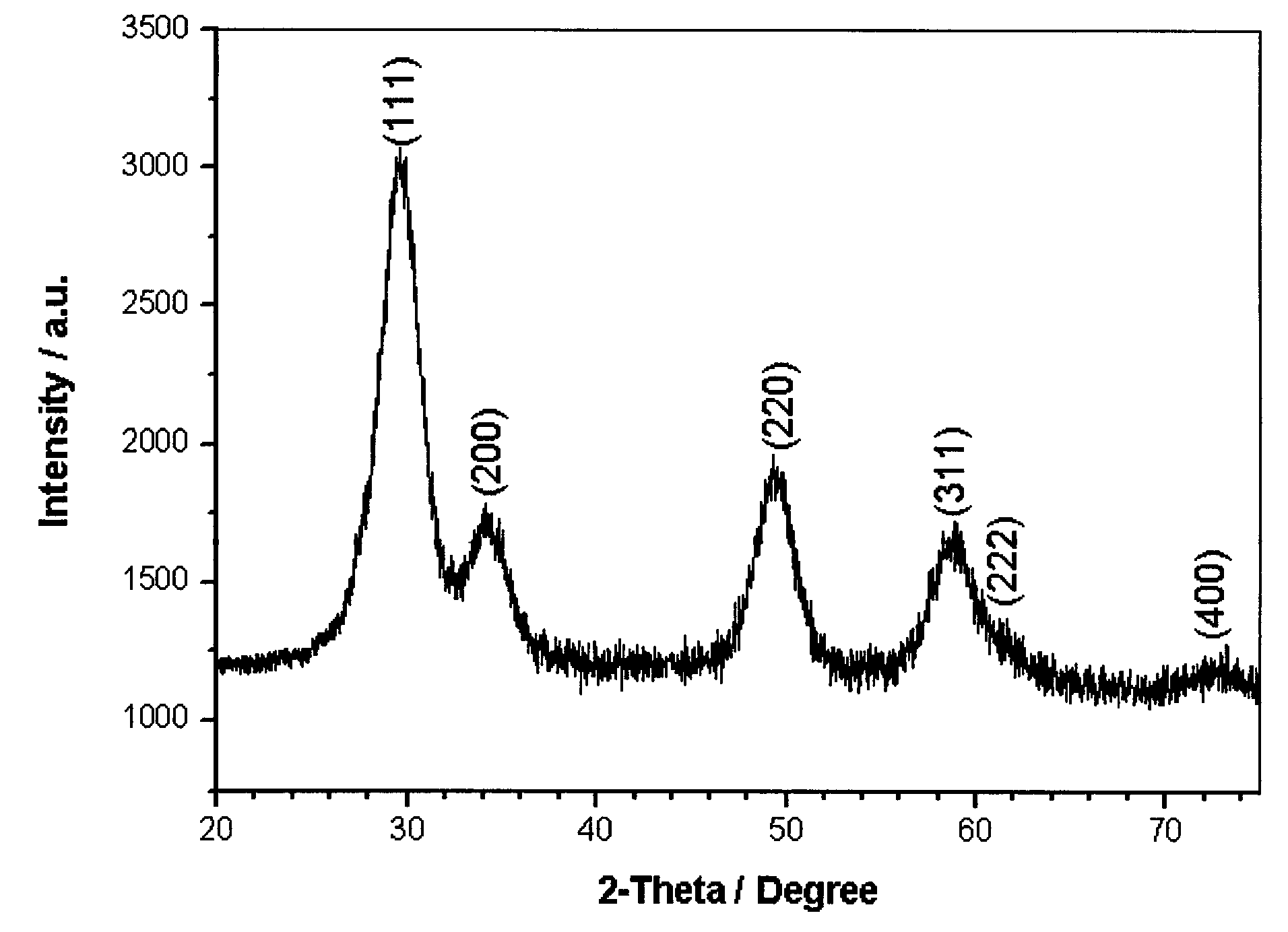
Method for preparing dysprosium oxide transparent ceramic
The invention discloses a method for preparing a dysprosium oxide transparent ceramic, the method is as follows: first, adding ammonia drop by drop into a dysprosium nitrate solution, and after the completion of the titration, aging to obtain a white precipitate; adding the filtered and washed white precipitate into a naphthol yellow sulphur solution for reaction to obtain a layered rare earth compound precursor containing naphthol yellow sulphur ion groups; in turn washing, drying, grinding, sieving and sintering the layered rare earth compound precursor containing the naphthol yellow sulphur ion groups to obtain dysprosium oxide nano powder; and finally, in turn performing pre pressing, cold isostatic compaction, high temperature pressureless sintering and machining on the dysprosium oxide nano powder to obtain the dysprosium oxide transparent ceramic. Advantages of method are that the obtained dysprosium oxide nano powder has high sintering activity, and is free of serious aggregation, the dysprosium oxide transparent ceramic can be prepared by the pressureless sintering technology, and the dysprosium oxide transparent ceramic with high transmittance also can be prepared by the pressureless sintering technology.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Preparation method of dysprosium zirconate terbium-doped green luminescent material
InactiveCN101671558AHigh crystallinitySimple preparation processLuminescent compositionsRare earthZirconate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a dysprosium zirconate terbium-doped green luminescent material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving dysprosium nitrate andterbium nitrate into deionized water according to mol ratio; dissolving zirconium oxychloride into deionized water, stirring, controlling the mol weight of the zirconium oxychloride to be equal to that of total rare earth kations, dipping the zirconium oxychloride drop by drop into the solution, and stirring; adding sodium hydroxide solution drop by drop to obtain white precipitate, and controlling the pH value of the solution to be 8 to 10; putting the solution into a high-pressure kettle with the filling degree of 80 percent, and treating for 5 to 20 hours at the temperature from 180 DEG Cto 220 DEG C; and finally centrifuging and drying the well-treated solution to obtain the dysprosium zirconate terbium-doped green luminescent material. The invention adopts a hydrothermal method to realize the synthesis of the dysprosium zirconate terbium-doped green luminescent material, and has good product crystallinity, simple process and mild conditions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
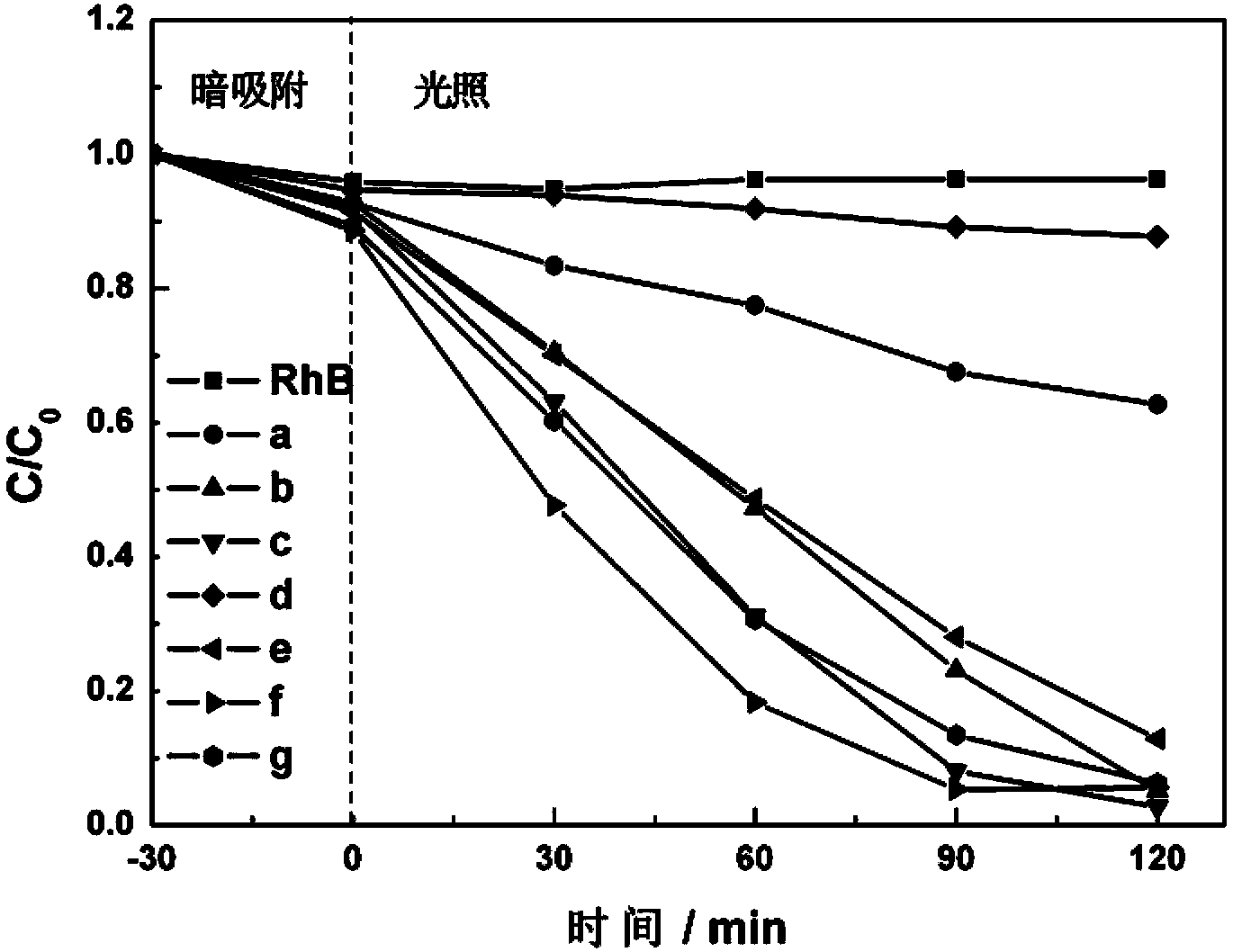
Dy/BiVO4 photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103447025AOvercome the disadvantage of uneven heatingIncreased efficiency in degrading organic pollutantsMaterial nanotechnologyMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsBismuthDysprosium nitrate
The invention relates to a Dy / BiVO4 photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The Dy / BiVO4 photocatalyst comprises a principal component of BiVO4, is in a square zircon-shaped structure and contains Dy<3+> in a BiVO4 lattice. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively dissolving bismuth nitrate pentahydrate and ammonium metavanadate in water to obtain a bismuth salt solution and a vanadium salt solution; adding the vanadium salt solution to the bismuth salt solution to obtain a mixed solution according to the mole ratio that Bi to V is equal to 1 to1; regulating the pH value of the mixed solution to 8; then adding dysprosium nitrate hexahydrate, wherein the mole ratio of Dy to Bi is (2.04-13.64) to 100; keeping temperature at the power of 300W and the temperature of 180 DEG C for 40 minutes by adopting a microwave hydrothermal method to prepare Dy / BiVO4. The preparation method disclosed by the invention combines the advantages of microwave heating and hydrothermal methods for synthesizing powder, is high in heating speed, uniform in heating, and capable of shortening the reaction time and improving the working efficiency; the synthesized Dy / BiVO4 photocatalyst is relatively high in photocatalysis activity and can be applied to environmental pollutant treatment.
Owner:盐城市鹤业实业投资有限公司
Method for preparing metal crown ether single-molecular magnets
InactiveCN109705151ANovel structureGood antiferromagneticGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismHydroxamic acidPyrazine
The invention discloses a method for preparing metal crown ether single-molecular magnets, and relates to a method for preparing single-molecular magnets. The invention aims to solve the problem of alow yield of a method for synthesizing metal crown ether rare earth complex single-molecular magnets in the prior art. The preparation method comprises the steps: dissolving salicyl hydroxamic acid, dysprosium nitrate and gallium nitrate in methanol so as to obtain a solution A, adding pyrazine to the solution A, performing stirring for a reaction so as to obtain a solution B, then adding pyridine, performing stirring at room temperature so as to obtain a preform, volatilizing the solvent of the preform so as to obtain the metal crown ether single-molecular magnets {Dy<3+>[Ga(III)MCshi]}. Themethod has the advantages that (1) the metal crown ether single-molecular magnets are single-molecular magnets with good antiferromagnetism, and (2) the preparation method is simple, and has high repeatability and a high yield which can reach 50% or above. The method is mainly applied to preparation of the metal crown ether single-molecular magnets {Dy<3+>[Ga(III)MCshi]}.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
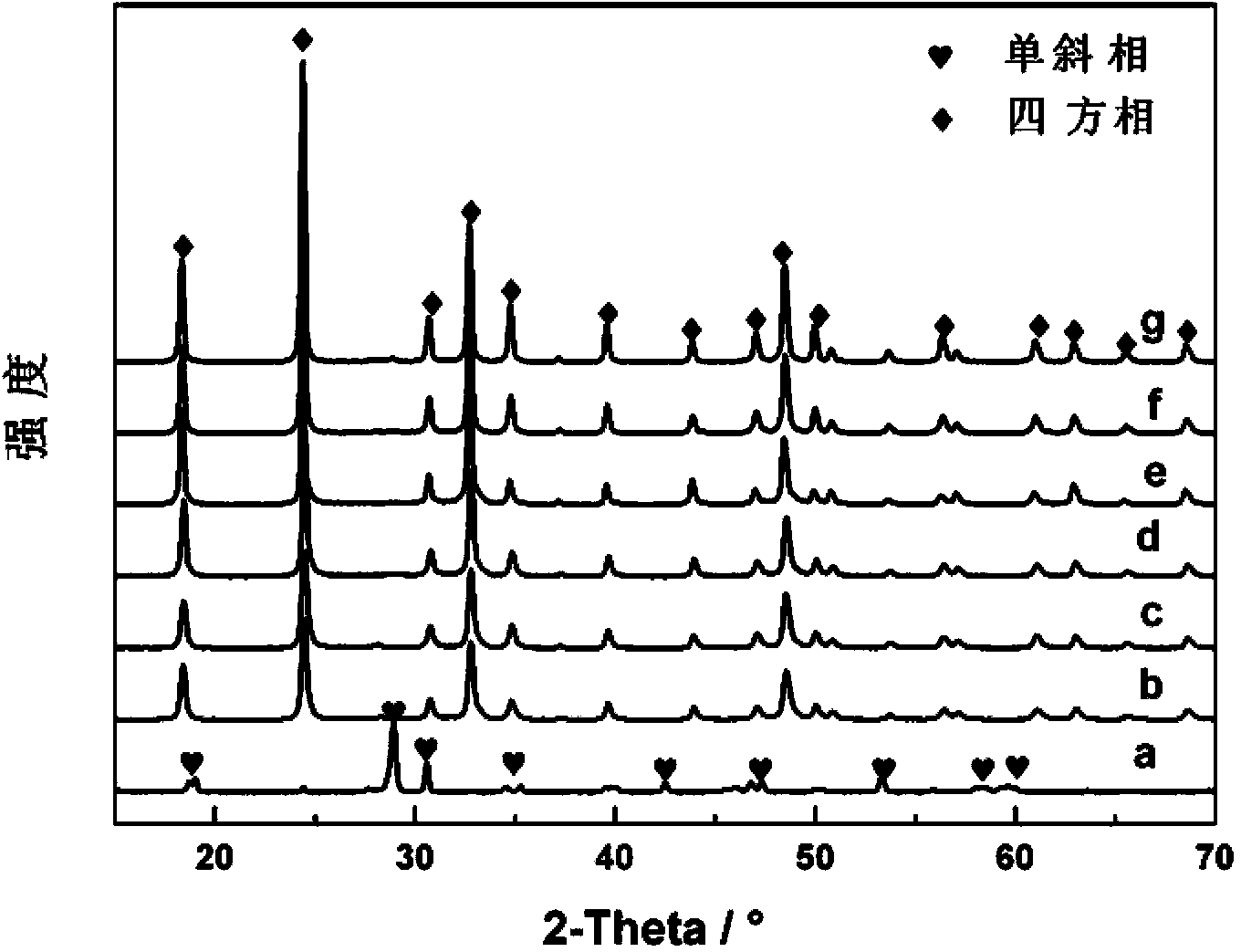
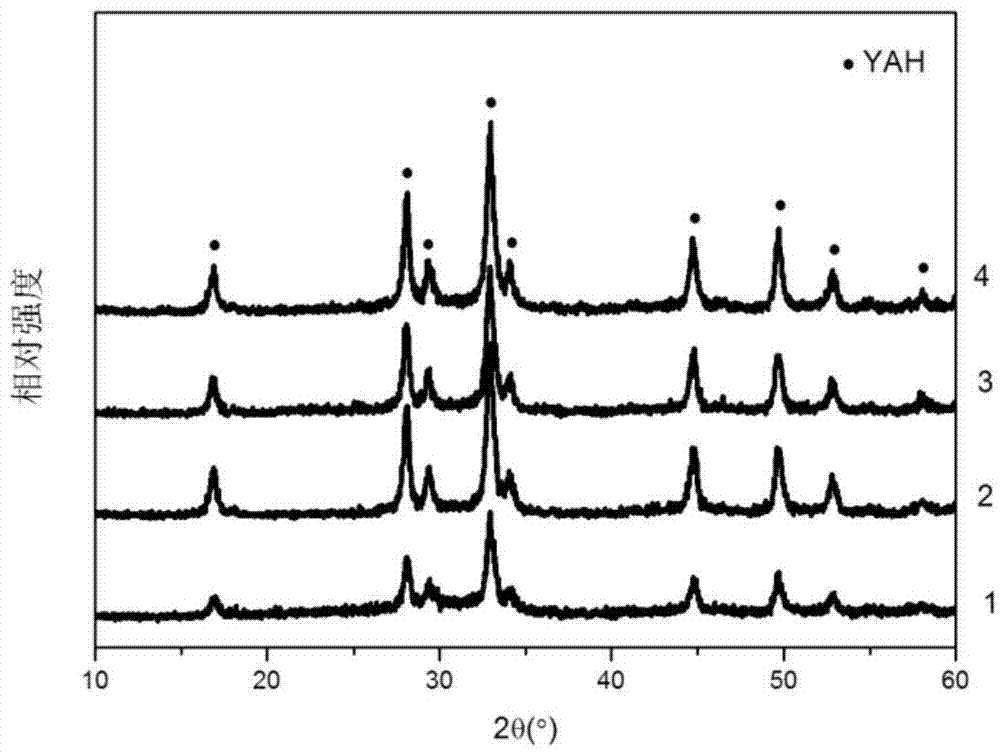
Dysprosium-doped hexagonal yttrium aluminate ceramic powder and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of ceramic materials, and particularly relates to a dysprosium-doped hexagonal yttrium aluminate ceramic powder and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing dysprosium nitrate pentahydrate, yttrium nitrate hexahydrate, aluminum nitrate nonahydrate and citric acid monohydrate, dissolving in deionized water, adding ammonia water to regulate the pH value to 1-2, sufficiently stirring, evaporating water, and drying to obtain xerogel; carrying out heat treatment, ball milling and drying on the xerogel to obtain a precursor powder; and (2) putting the precursor powder into a graphite reactor, sintering in a discharge plasma sintering unit, cooling to room temperature after finishing sintering, and grinding to obtain the dysprosium-doped hexagonal yttrium aluminate ceramic powder. The method can obtain the Dy:YAH powder with uniform and small particle size of which the crystalline phase is single-phase YAH. The Dy:YAH powder has favorable sintering activity, and can be used for preparing fine-crystalline Dy:YAH powder or Dy:YAH ceramic at low temperature.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
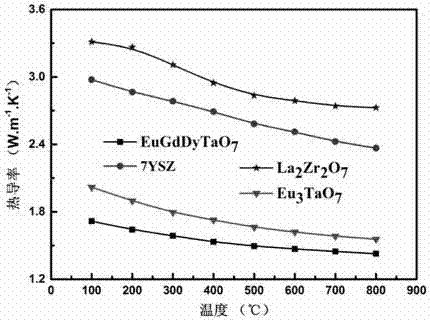
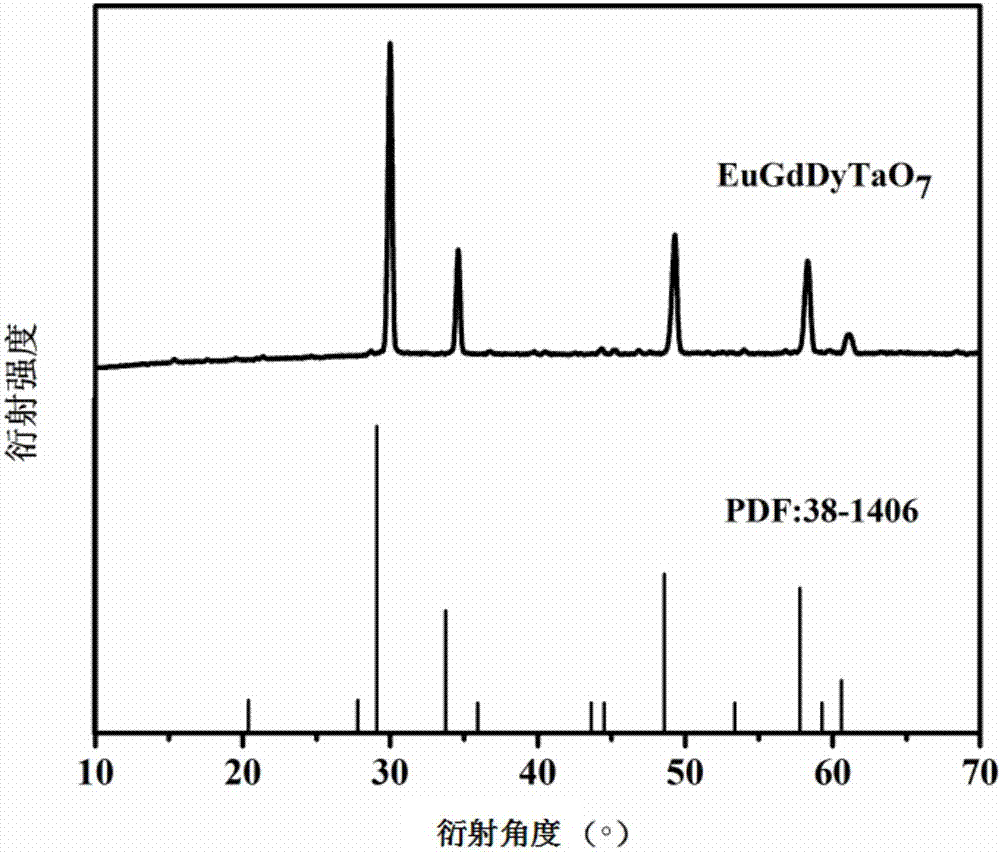
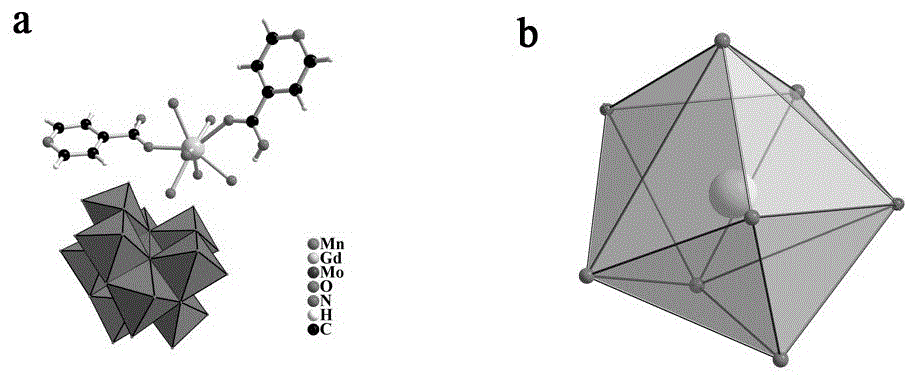
Eu-Gd-Dy trirare earth ion tantalate and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses Eu-Gd-Dy trirare earth ion tantalate and a preparation method and an application thereof, the Eu-Gd-Dy trirare earth ion tantalate has the chemical general formula of EuaGdbDycTaO7, wherein a+b+c=3, and a, b and c is 0.8-1.2. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) according to the stoichiometric ratio, weighing europium chloride, gadolinium nitrate, dysprosium nitrate and tantalum oxalate, mechanically mixing with citric acid with a set amount under a heat-retaining condition, adding strong aqua ammonia in the mixing process to neutralize the solution,and then mechanically mixing to promote the process of the reaction under a heat-retaining condition; and 2) drying the obtained solution, then calcining at high temperature to remove carbon impurities, and thus obtaining an Eu-Gd-Dy trirare earth ion tantalate powder. The Eu-Gd-Dy trirare earth ion tantalate has the advantages of good high temperature thermal stability and low thermal conductivity coefficient, and can be used as a thermal barrier coating material.
Owner:陕西天璇涂层科技有限公司
Preparation method for dysprosium oxide powder
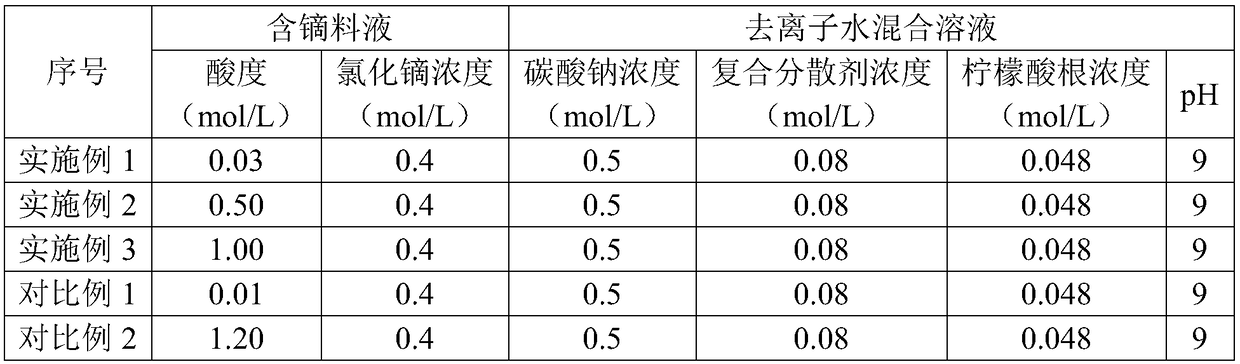
ActiveCN108975378ANarrow particle size distributionGood dispersionRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyApparent densityCITRATE ESTER
The invention discloses a preparation method for dysprosium oxide powder. The preparation method comprises the steps that 1) a dysprosium-containing stock solution with the acidity of 0.03-1 mol / L andthe concentration of dysprosium chloride and / or dysprosium nitrate of 0.3-1 mol / L is prepared; 2) a deionized water mixed solution with the concentration of carbonate ions of 0.3-0.6 mol / L and the concentration of a composite dispersing agent of 0.0045-0.08 mol / L is prepared, wherein the composite dispersing agent comprises citrate ions with the concentration of 0.002-0.048 mol / L; 3) the dysprosium-containing stock solution is dropwise added into the deionized water mixed solution while stirring is carried out, the temperature of the reaction process is controlled to be 40-50 DEG C so as to obtain a white precipitate; and 4) the white precipitate is filtered, washed, dried and fired so as to obtain the dysprosium oxide powder. The dysprosium oxide powder prepared through the preparation method has the advantages of being small in particle size, low in apparent density, high in dispersion and less in agglomeration.
Owner:FUJIAN CHANGJIANG GOLDEN DRAGON RARE EARTH CO LTD
Polyacid dysprosium single-molecular magnets and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103994792ASimple methodEasy to implementOrganic chemistryInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureDodecaneMagnetic storage
The invention discloses polyacid dysprosium single-molecular magnets and a preparation method of the polyacid dysprosium single-molecular magnets and belongs to the field of magnetic storage materials. The chemical formula of the single-molecular magnets is [NaDy(DOTA)2 7H2O] [Fe(CN)5NO]2 11H2O, wherein DOTA is 2,2',2'',2'''-(1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetra) quadrol. The preparation method of the polyacid dysprosium single-molecular magnets includes the following steps that dysprosium nitrate, DOTA and sodium nitroprusside are prepared into a solution according to the molar ratio 1:1:1, the solution is mixed at normal temperature for one hour and then filtered, filtrate stands still at normal temperature, crystals are separated out, and the crystals are the polyacid dysprosium single-molecular magnets. The polyacid dysprosium single-molecular magnets can be applied to new magnetic storage materials. The preparation method of the polyacid dysprosium single-molecular magnets is simple, easy to achieve and low in cost.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Bi0.90Dy0.10Fe1-XMnxO3 ferroelectric film with high dielectric constant, and preparation method for Bi0.90Dy0.10Fe1-XMnxO3 ferroelectric film with high dielectric constant
ActiveCN103663564AReduce volatilityImprove insulation performanceIron compoundsCooking & bakingDielectric
The invention provides a Bi0.90Dy0.10Fe1-XMnxO3 ferroelectric film with a high dielectric constant, and a preparation method for the Bi0.90Dy0.10Fe1-XMnxO3 ferroelectric film with the high dielectric constant. The film adopts a rhombohedral structure and has high homogeneity, the remanent polarization ranges from 59.3 [mu]C / cm<2> to 95.2 [mu]C / cm<2>, the coercive field ranges from 280 kV / cm to 368 kV / cm, and the high dielectric constant ranges from 239.2 to 348.57. The preparation method includes the following steps: bismuth nitrate, ferric nitrate, dysprosium nitrate and manganese acetate are dissolved in a mixed liquor of ethylene glycol monomethyl ether and acetic anhydride, so as to obtain a precursor; a substrate is spin-coated with the precursor; glue evening and baking are carried out in sequence to obtain a dry film; the dry film is annealed to obtain a Bi0.90Dy0.10Fe1-XMnxO3 film; the procedures of precursor spin-coating, baking and annealing are repeated until a required film thickness is reached, so that the film is obtained. The ferroelectric film has the advantages of simple equipment requirements and high controllability of the doping amount; the dielectric properties of a BiFeO3 (bismuth ferrite) film can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
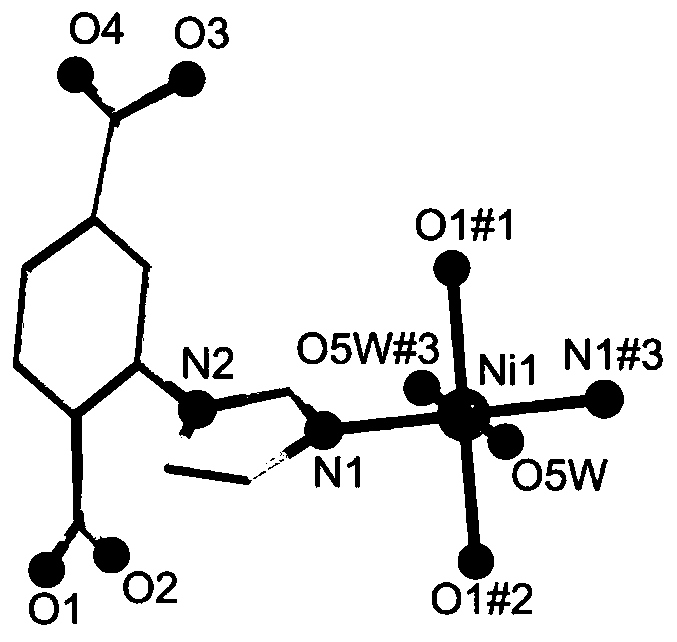
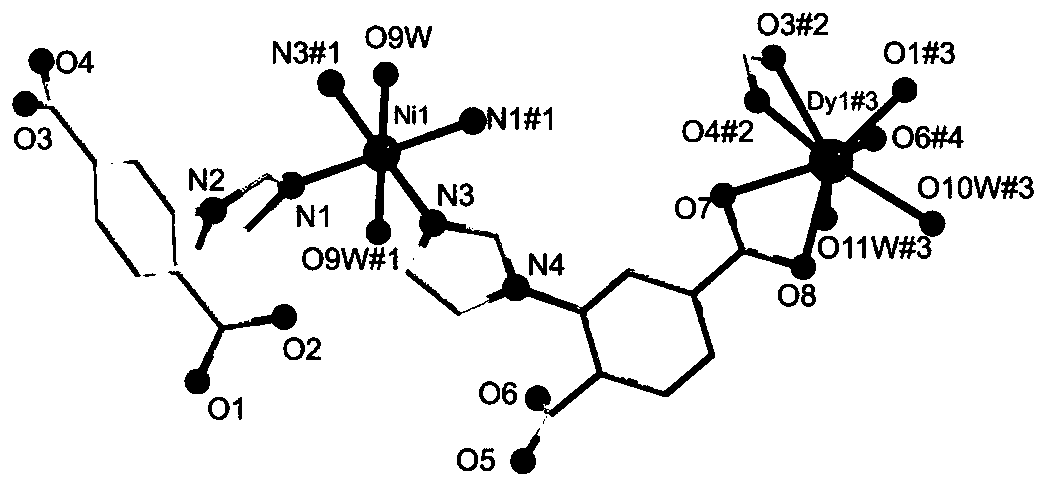
Preparation method of d-f heteronuclear bimetal organic framework material based on monometal coordination polymer
The invention provides a preparation method of a d-f heteronuclear bimetallic organic framework material based on a monometal coordination polymer. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing two cases of Ni-based and Dy-based monometal coordination polymers MOFs, namely MOF1 and MOF2, by using a hydrothermal method; and reacting MOF1 and MOF2 used as precursors with dysprosium nitrateand nickel nitrate respectively to successfully prepare the two d-f heteronuclear bimetallic organic frameworks HMOF3 and HMOF4. According to the method, a d-f heteronuclear bimetallic organic framework material HMOFs is prepared by taking monometal MOFs as a precursor. The HMOFs material prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has a coordination unsaturated bimetallic node and relatively large porosity, and is expected to be applied to the fields of gas adsorption and organic catalysis.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Waugh-type manganese molybdate included in dysprosium-isonicotinic acid, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106366102AImprove stabilityHigh reactivityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsMANGANESE ACETATEMolybdate
The invention relates to Waugh-type manganese molybdate included in dysprosium-isonicotinic acid. The Waugh-type manganese molybdate has a chemical formula of (NH4)3[Dy(Hina)2(H2O)6][MnIVMo9O32].7H2O. The Waugh-type manganese molybdate is prepared from manganese acetate, dysprosium nitrate, isonicotinic acid, hydrogen peroxide with a concentration of 30%, glacial acetate acid and ammonium heptamolybdate through a reaction in an aqueous solution. The preparation method is simple, easy to operate and low in cost; and crystals are fast in growth and high in yield. Experimental and research results show that the Waugh-type manganese molybdate exerts good photocatalytic degradation effect on azophloxine and provide experimental basis for application of polyoxomolybdate to photocatalytic degradation of organic dyestuffs.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
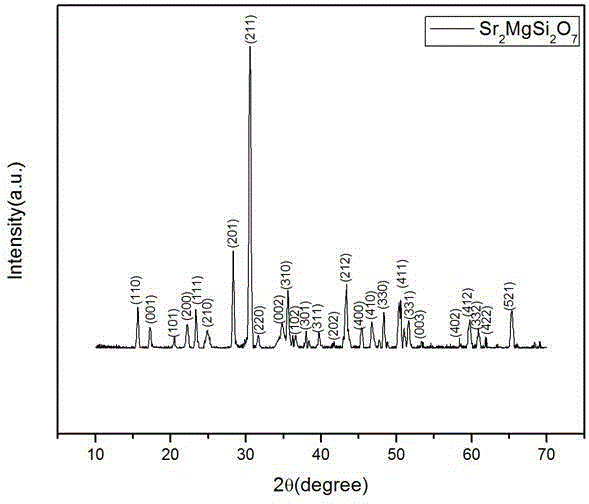
Preparation method of rare earth Eu and Dy doped strontium magnesium silicate powder
InactiveCN105219389AThere are no expensive raw materialsNo craftLuminescent compositionsEvaporationRare earth
The invention discloses a preparation method of rare earth Eu and Dy doped strontium magnesium silicate powder. The preparation method comprises the steps that strontium nitrate, magnesium nitrate, europium nitrate, dysprosium nitrate, sodium silicate and a reducing agent are weighed according to the mole ratio being 1.8-1.98:0.95-2:0.01-0.1:0.01-0.1:1-2:3-30; the sodium silicate is dissolved in water to form a sodium silicate water solution, then the strontium nitrate, the magnesium nitrate, the europium nitrate, the dysprosium nitrate and the reducing agent are completely dissolved in deionized water, then the sodium silicate water solution is poured into the mixture, a magnetic stirrer is used for heating to reach 90-100 DEG C, stirring continuously is carried out for 0.3-1 h, then the solution is directly shifted into a high-temperature sintering furnace preheated to reach 650-900 DEG C, fierce combustion is carried out along with moisture evaporation, and the fluffy foam product is obtained. The sodium silicate with the relatively low cost is adopted as a raw material, the cost is low, and the technology is simple.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Corrosion-resistant bathroom pendant and surface treatment method thereof
InactiveCN112375989AMeticulous structureImprove corrosion resistanceSuperimposed coating processPolymer scienceEthylic acid
The invention relates to the field of bathroom pendants, and particularly discloses a corrosion-resistant bathroom pendant and a surface treatment method thereof. The corrosion-resistant bathroom pendant comprises a bathroom pendant body made of a stainless steel material, and is characterized in that stainless steel comprises the following components: C, Cr, Ni, Mn, Si, P, S, Al, N, Sn, Fe and impurities. The surface treatment method of the corrosion-resistant bathroom pendant comprises the following steps: step 1, polishing the bathroom pendant body with abrasive paper, and soaking the polished bathroom pendant body in an acetic acid solution to obtain a pretreated bathroom pendant body; step 2, preparing an electroplating treatment solution; and step 3, carrying out electroplating treatment by taking the bathroom pendant body as a cathode and taking plating metal as an anode. The bathroom pendant has a compact electroplating layer, and the surface of the bathroom pendant is furthertreated by dysprosium nitrate, so that the bathroom pendant has relatively good hardness and corrosion resistance.
Owner:温州欧迪家居用品有限公司
Preparation method of white-light phosphor
ActiveCN102344806AImprove luminous efficiencyHigh yieldGas discharge lamp usageLuminescent compositionsCross-linkCerium nitrate
The invention relates to a preparation method of white-light phosphor, which adopts strontium nitrate, cerium nitrate, dysprosium nitrate, and europium nitrate as raw materials, adopts acrylamide as a monomer lattice reagent, adopts N-N' methylene diacrylamide as a cross-linking agent, adopts ammonium persulfate as an initiator, and adopts deionized water as a solvent medium; the raw materials are mixed, heated and stirred, gelated at a liquid phase, dried, calcined at a high temperature, cooled, grinded, sieved, and detected for analysis; finally white-light phosphor white powder is prepared; the product has excellent luminescent properties, a small particle size, and good dispersibility; the preparation method uses less equipment, has a short process flow, does not cause environment pollution, has a high product yield of up to 96%, and is a very ideal preparation method of white-light phosphor.
Owner:SHANXI FEIHONG MICRO NANO PHOTOELECTRONICS SCI & TECH
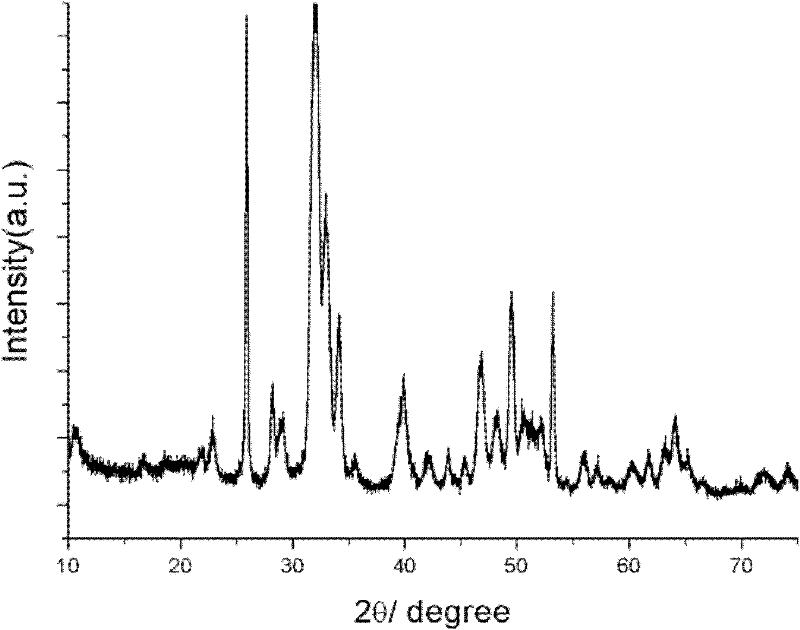
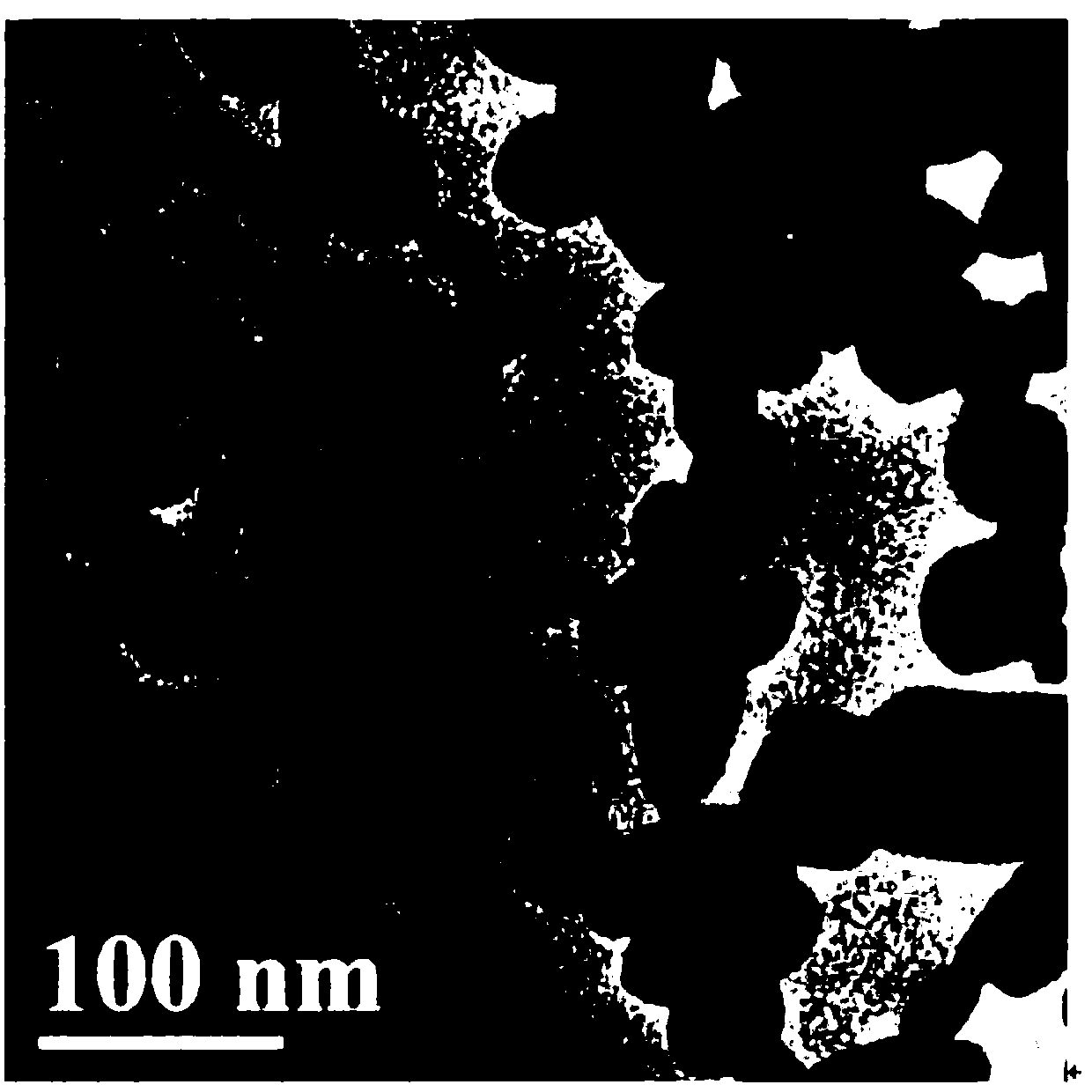
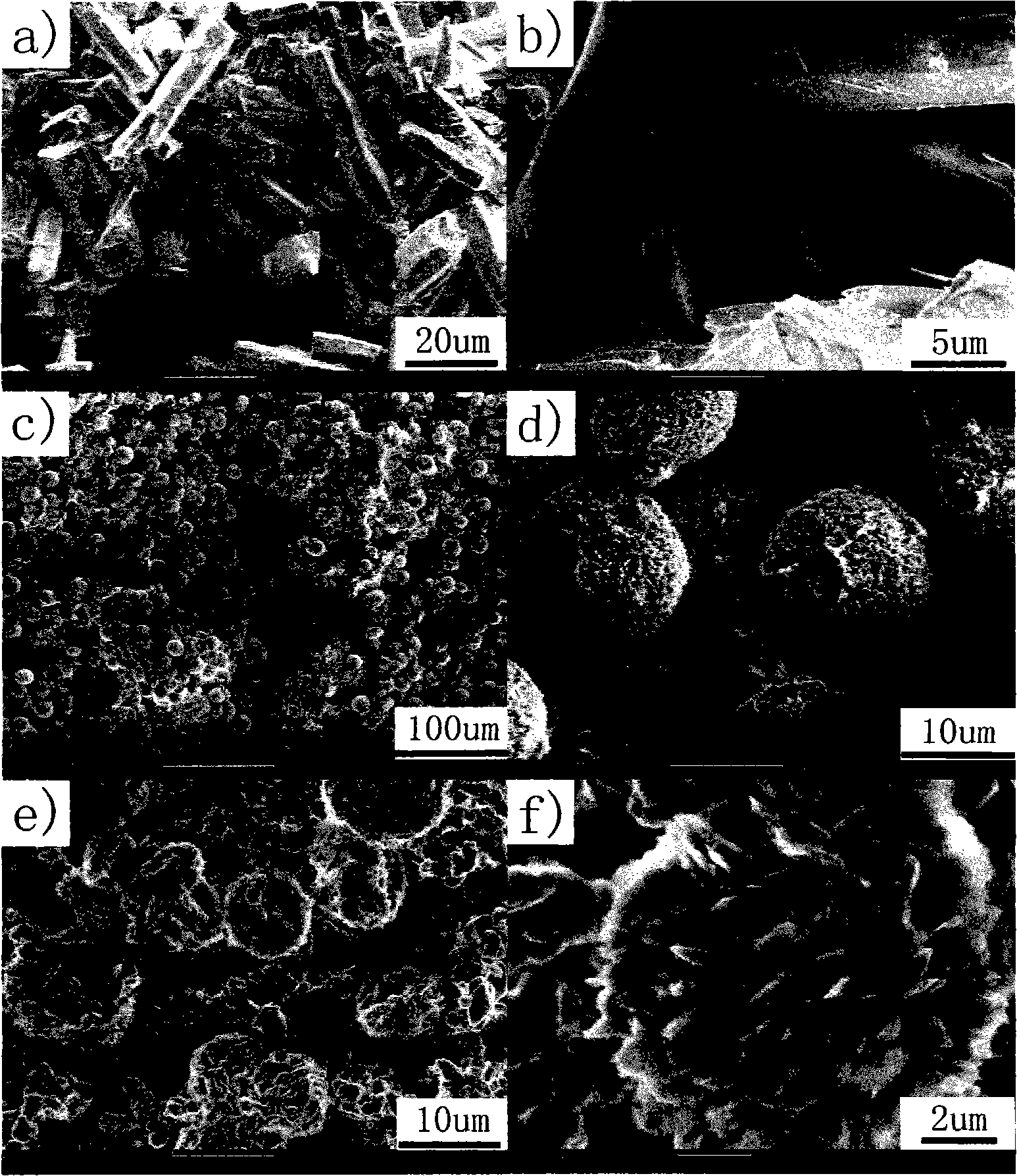
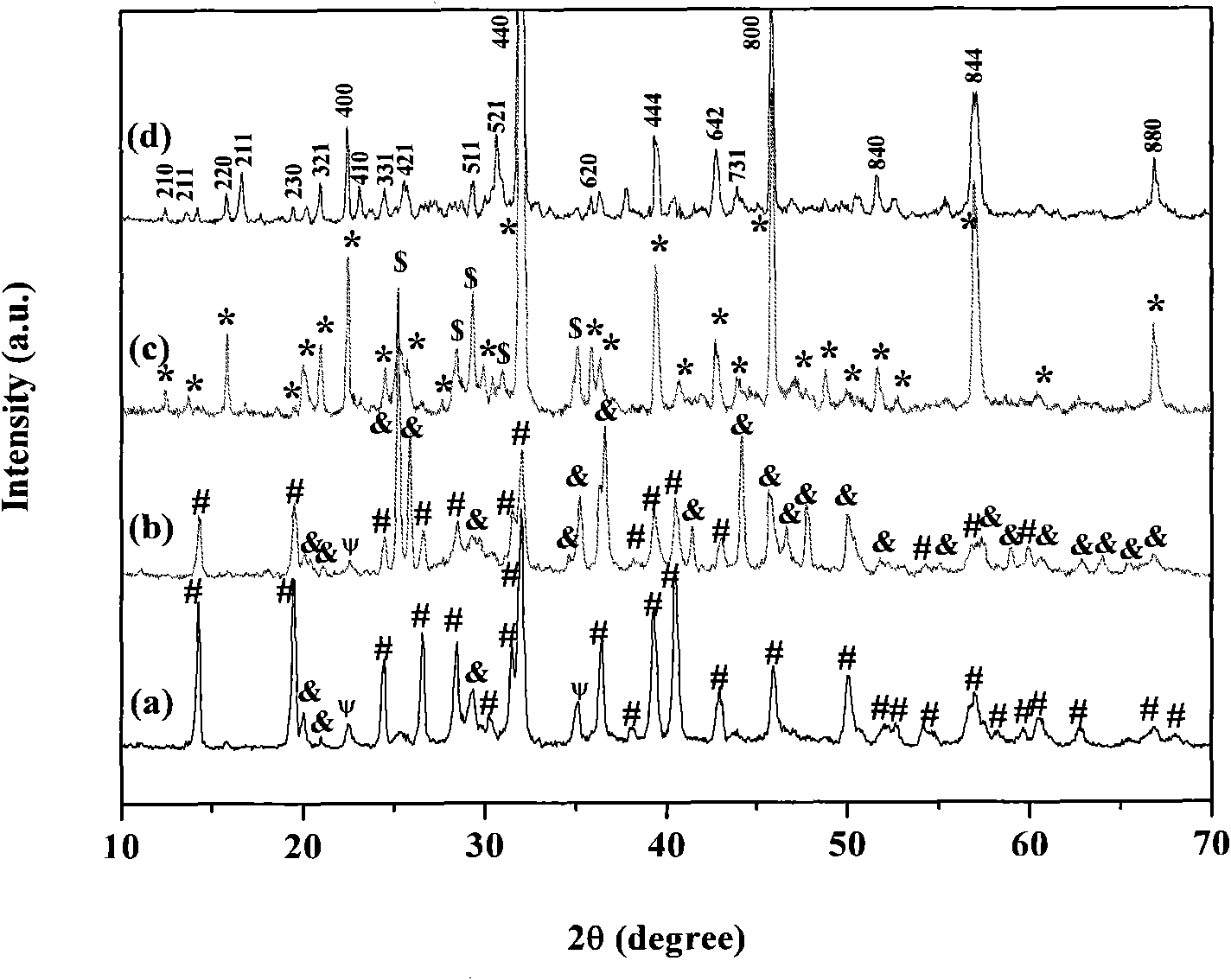
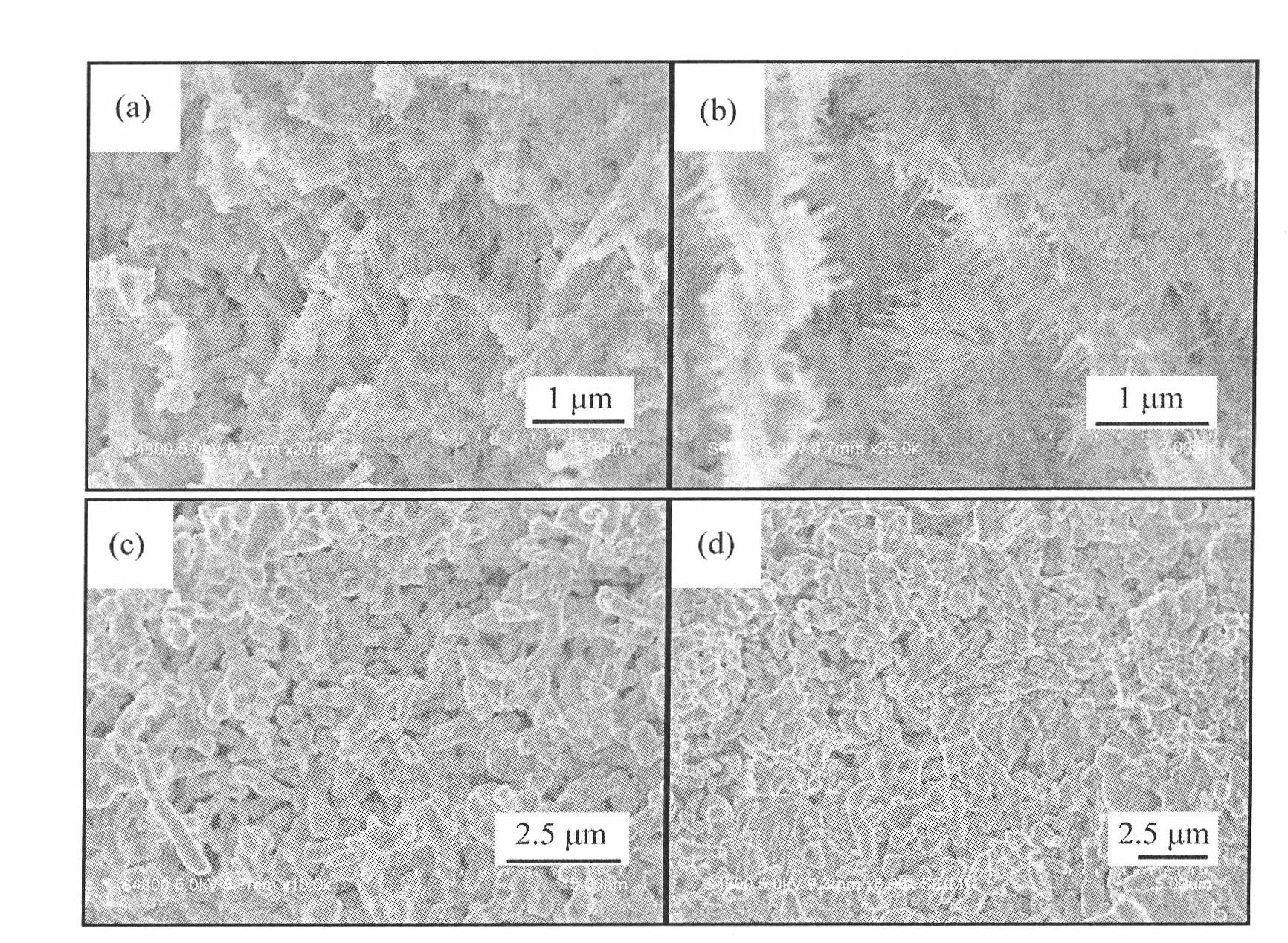
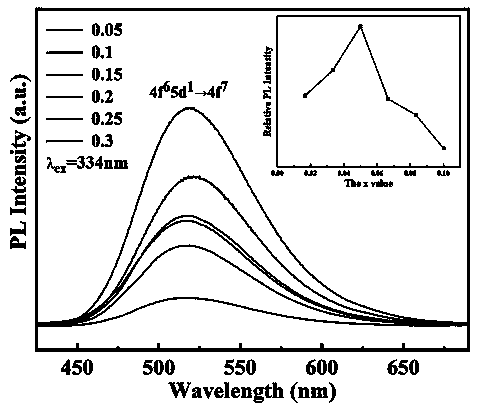
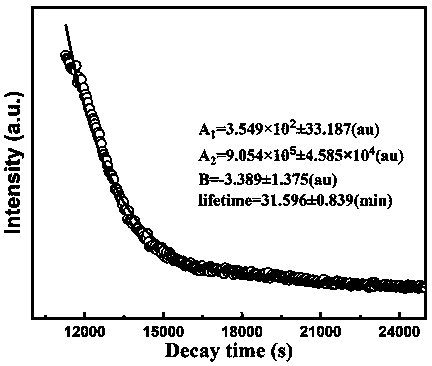
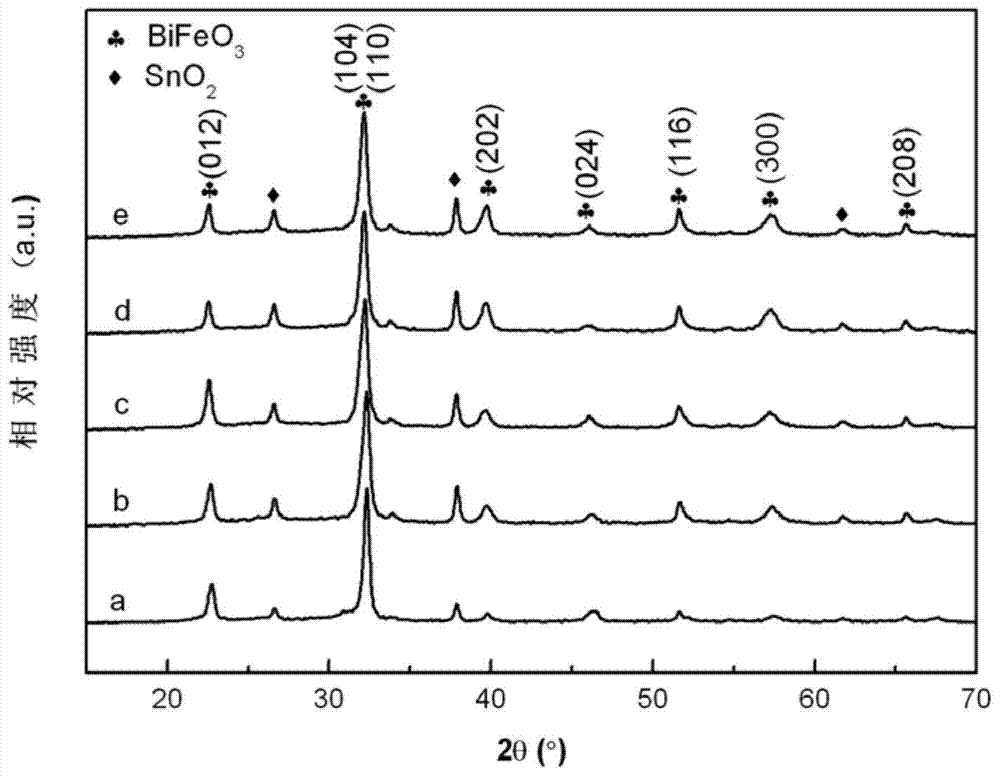
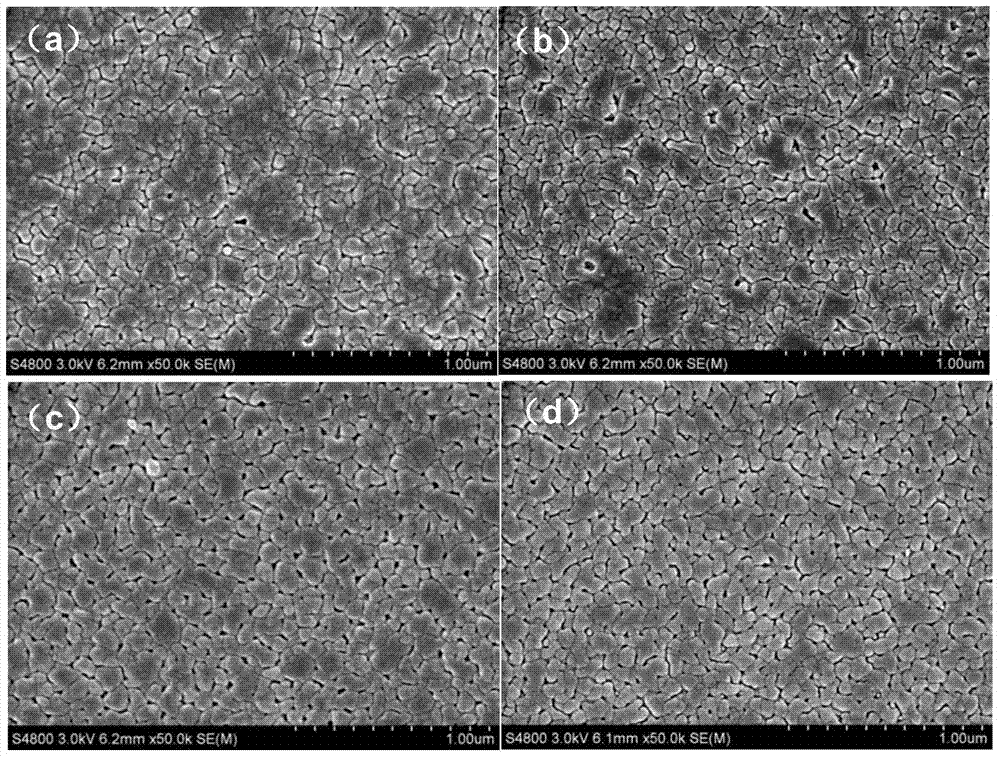
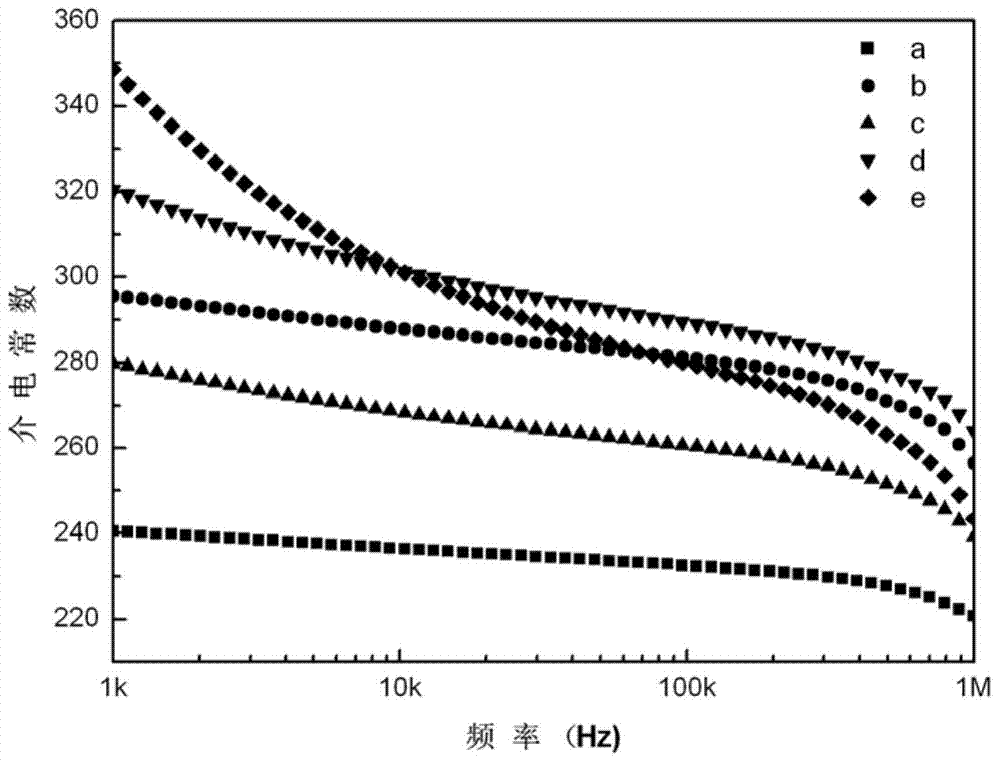
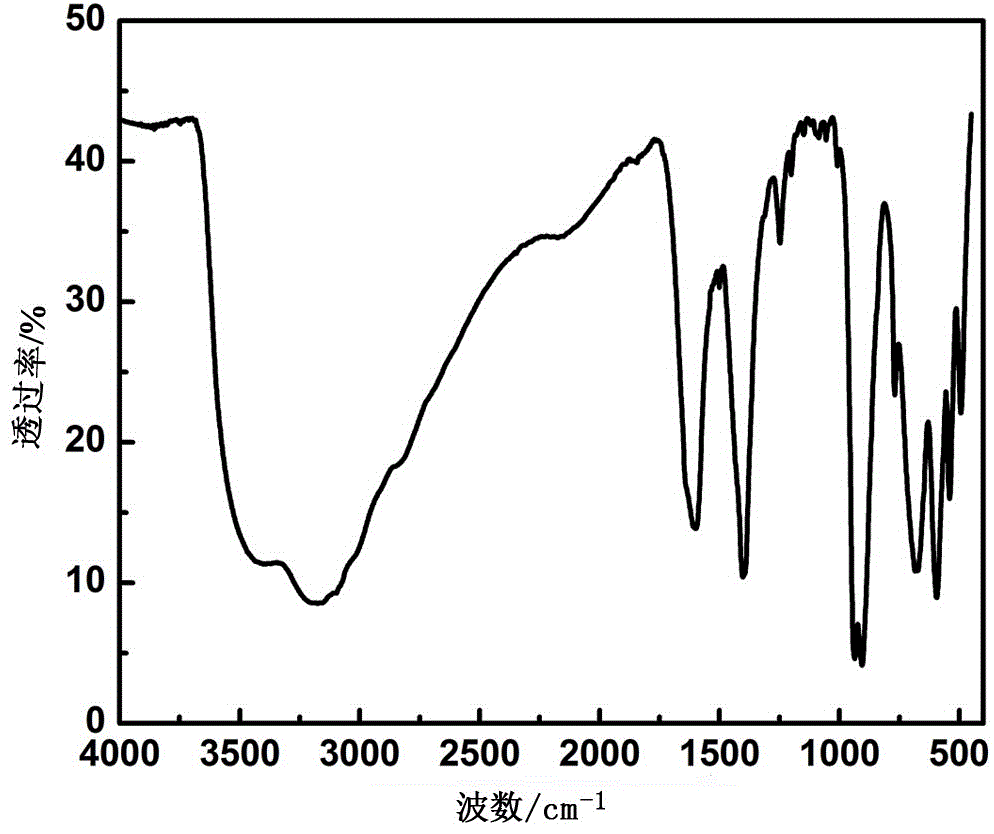
High-dielectric-constant Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103723771AImprove insulation performanceControl componentIron compoundsDielectricAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to a high-dielectric-constant Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film (x=0.06-0.08) and a preparation method thereof. The film is in a rhombohedral structure and has favorable uniformity; the space point group is R-3m(166); and under the frequency of 1kHz, the dielectric constant is 152.8-241.6. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving bismuth nitrate, iron nitrate and dysprosium nitrate in an ethylene glycol monomethyl ether-acetic anhydride mixed solution in a mole ratio of (1.05-x):1:x to obtain a precursor solution; evenly spin-coating the precursor solution on a substrate, baking to obtain a dry film, and annealing to obtain a Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film; and spin-coating the precursor solution again, baking and annealing to the required film thickness, thereby obtaining the high-dielectric-constant Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film. The method has the advantages of simple facility request and controllable doping amount, and can greatly enhance the dielectric properties of the BiFeO3 film.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
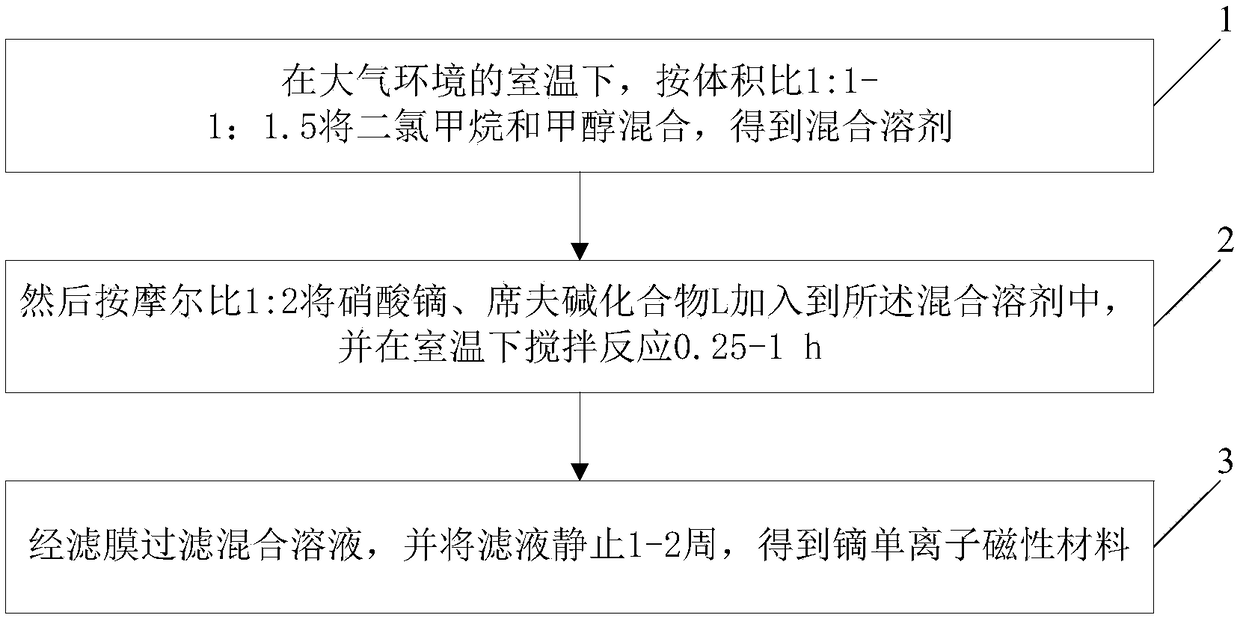
A preparation method of dysprosium single ion magnetic material
ActiveCN109243747ASimple methodEasy to operateOrganic/organic-metallic materials magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureHigh densityMagnetic storage
The invention discloses a preparation method of dysprosium single ion magnetic material. dichloromethane and methanol are mixed according to the volume ratio of 1: 1.5 to obtain a mixed solvent; Dysprosium nitrate and Schiff base compound L were then added to that mixed solvent at a molar ratio of 1: 2 and stirring is performed at room temperature to react for 0.25-1h; The mixed solution is filtered through a filter membrane, and the filtrate is stationary for 1- 2 week, that dysprosium monoionic magnetic material was obtained. The method is simple and easy to operate. The obtained samples are stable in air and can be used in the fields of high density magnetic storage and quantum computer.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF PETROCHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Mixed metal ion single-molecular magnet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103980324ARaise the blocking temperatureHigh yieldOrganic chemistryMagnetsMagnetic storageSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a mixed metal ion single-molecular magnet and a synthesis method thereof, belonging to the field of magnetic storage materials. The chemical formula of the single-molecular magnet is D<y>(DMF)4(H2O)3Fe(CN)6.H2O, wherein DMF is N,N-dimethyl formamide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: evenly mixing dysprosium nitrate and a potassium ferricyanide solution, adding a DMF (dimethyl formamide) solution of quinoline-2-formic acid, stirring for one hour at normal temperature, filtering, standing a filtrate at the normal temperature, and separating out crystals, namely the mixed metal ion single-molecular magnet. The mixed metal ion single-molecular magnet can be applied to a novel magnetic storage material; the method is simple, easy to realize and low in cost.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com




![Method for preparing single-molecular magnet [Dy2(saph)2(NO3)2(CH3OH)4] Method for preparing single-molecular magnet [Dy2(saph)2(NO3)2(CH3OH)4]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/57537909-c307-494d-836f-821538d86323/HDA0000634118620000011.PNG)
![Method for preparing single-molecular magnet [Dy2(saph)2(NO3)2(CH3OH)4] Method for preparing single-molecular magnet [Dy2(saph)2(NO3)2(CH3OH)4]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/57537909-c307-494d-836f-821538d86323/HDA0000634118620000012.PNG)
![Method for preparing single-molecular magnet [Dy2(saph)2(NO3)2(CH3OH)4] Method for preparing single-molecular magnet [Dy2(saph)2(NO3)2(CH3OH)4]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/57537909-c307-494d-836f-821538d86323/HDA0000634118620000021.PNG)




![High-dielectric-constant Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film and preparation method thereof High-dielectric-constant Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/cd333db3-728b-41f3-b984-a73120cc2566/HDA0000443255000000011.png)
![High-dielectric-constant Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film and preparation method thereof High-dielectric-constant Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/cd333db3-728b-41f3-b984-a73120cc2566/HDA0000443255000000012.png)
![High-dielectric-constant Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film and preparation method thereof High-dielectric-constant Bi[1-x]DyxFeO3 film and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/cd333db3-728b-41f3-b984-a73120cc2566/HDA0000443255000000021.png)