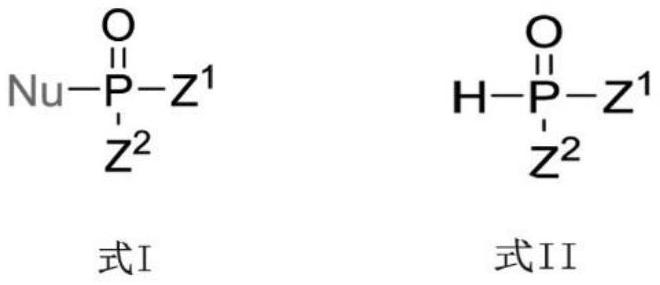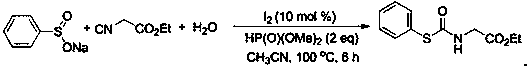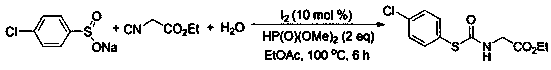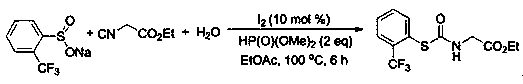Patents
Literature
56 results about "Iodine catalysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
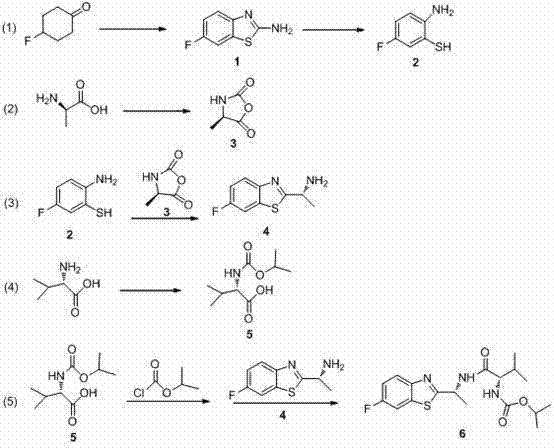
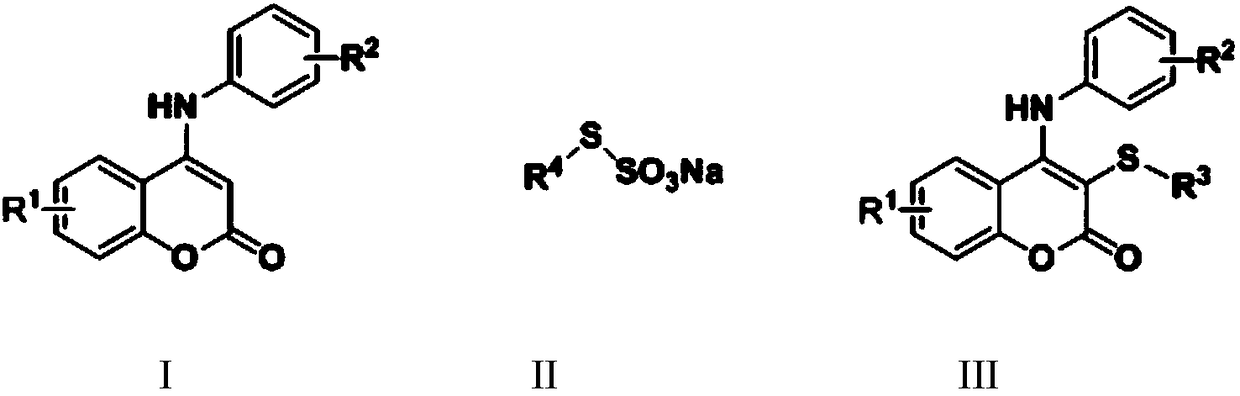
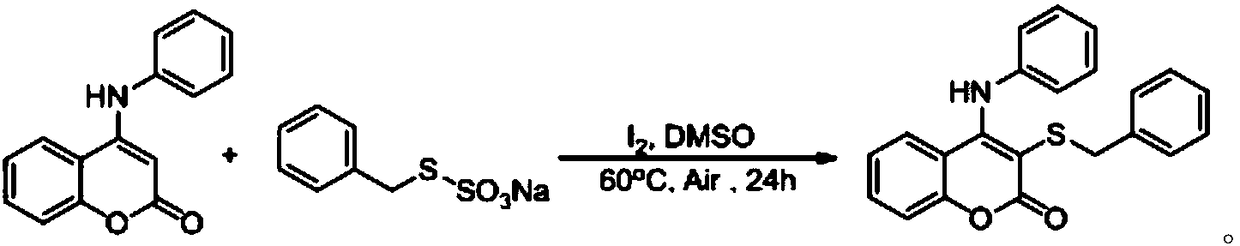
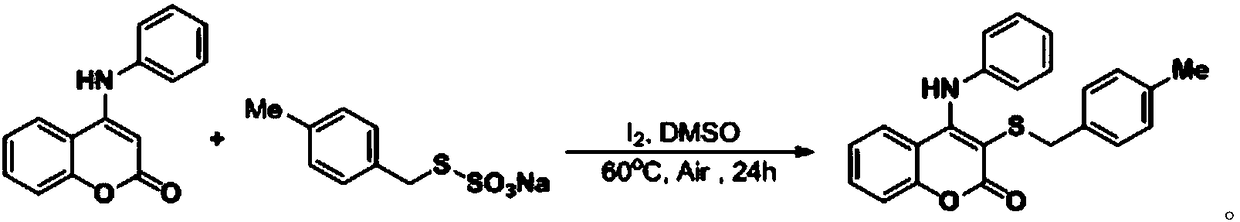
Synthetic method for thiocoumarin
The invention discloses a synthetic method for thiocoumarin, and relates to the field of organic synthesis. The synthetic method for thiocoumarin comprises the following steps: taking C-4-positioni amino substituted coumarin and organic thiosulfate as raw materials; and reacting for (18-30) h at the temperature of (40-100) DEG C through iodine catalysis to obtain a C-3-position sulfur substitutedcoumarin compound. The invention provides a novel method for synthesizing an amino coumarins derivative with potential anti-cancer activity. Raw materials are economical and easily obtained, reactionconditions are green, low-toxicity and odorless, and the synthetic method for thiocoumarin has the advantages of gentle reaction conditions, low cost, small environmental pollution, high yield and thelike.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
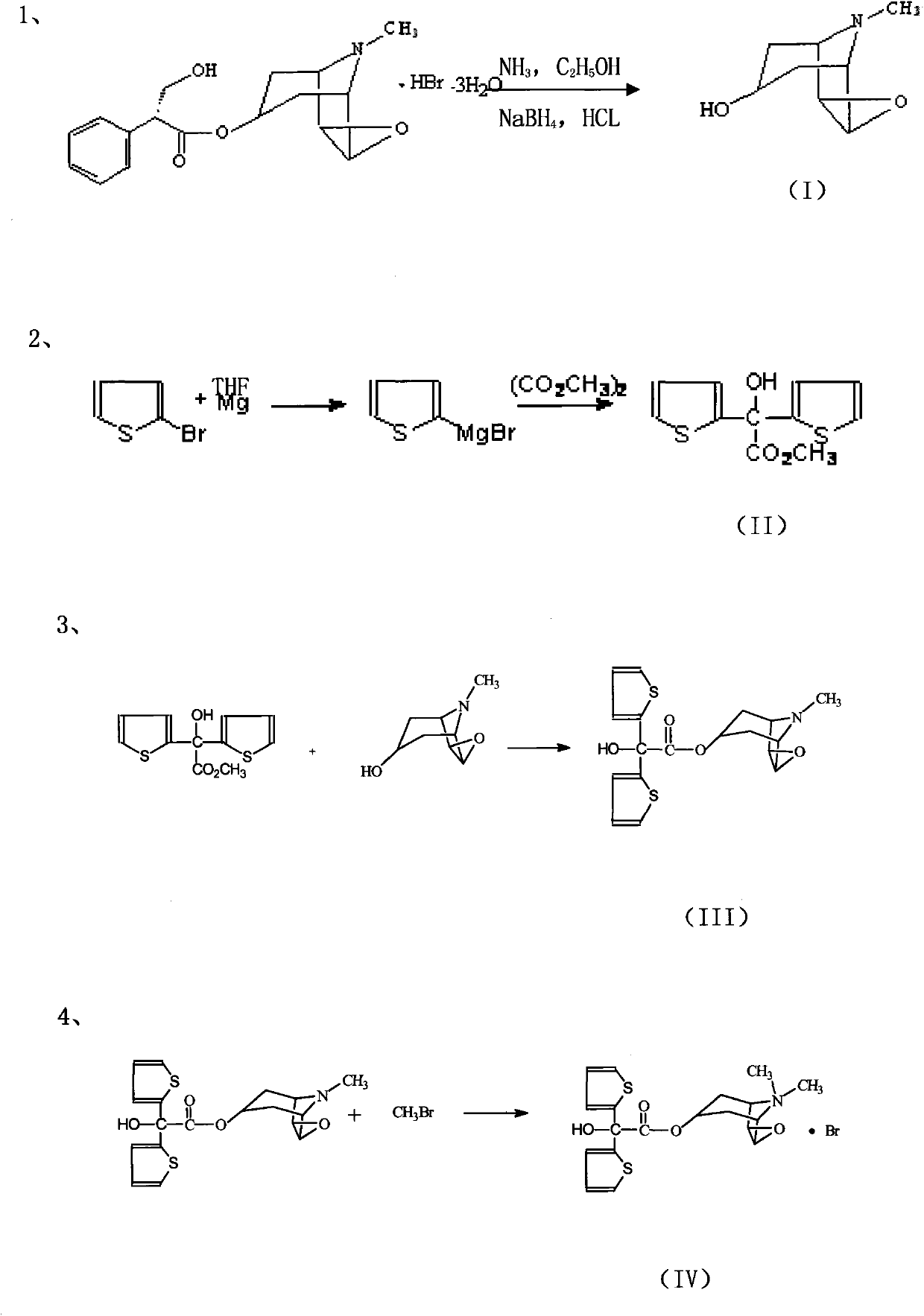
Tiotropium bromide anhydride and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101768158AQuality improvementHigh yieldOrganic chemistryFiltration separationGrignard reagentDimethyl oxalate
The invention discloses a method for preparing tiotropium bromide anhydride, which comprises the steps of: under the anhydrous and anaerobic condition, preparing an intermediate I by taking a special kettle bottom valve and a multi-functional reaction kettle as a reactor, taking a special filter as refining equipment and taking hydrobromic scopolamine as an initial raw material through reduction hydrogenation reaction; preparing an intermediate II by performing addition reaction of Grignard reagent and dimethyl oxalate in tetrahydrofuran, wherein the Grignard reagent is prepared from bromothiophene by taking tetrahydrofuran as a medium through iodine catalysis; preparing an intermediate III by performing ester exchange condensation reaction of the intermediate I and the intermediate II under the action of sodium; preparing an intermediate IV from the intermediate III through methylation bromination reaction; and preparing the tiotropium bromide anhydride by performing the activated carbon decoloration and recrystallization on the intermediate IV by using aqueous solution and acetonitrile methanol isopropyl ether solution. Compared with those in the prior art, reaction products of the method have the advantages of good quality, high yield, controlled reaction process, safe production and good environmental protection effect.
Owner:HONGYI SCI & TECH CO LTD NANCHANG
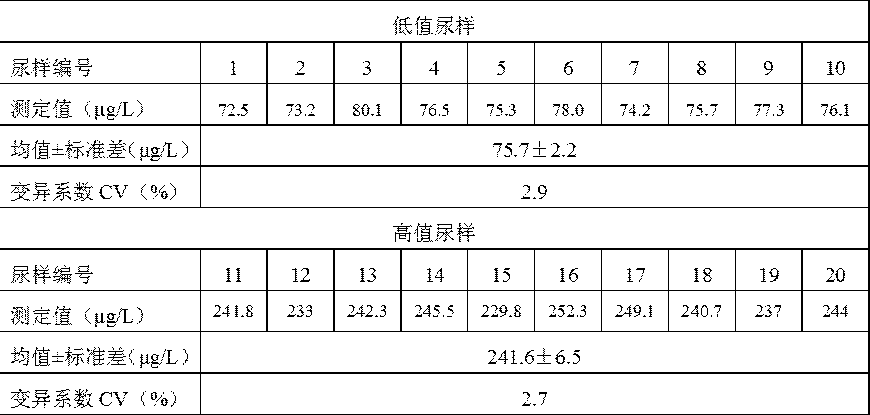
Iodide ion detection reagent based on iodide catalyzed hydrazine-[oxidant-Ferroin reagent] and iodide ion detection method
ActiveCN108776134ASensitive catalysisRapid responseMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsIodine testMedical testing
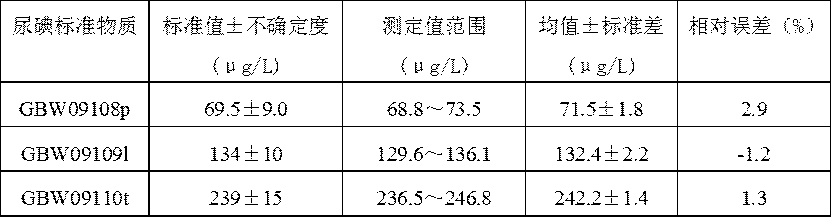
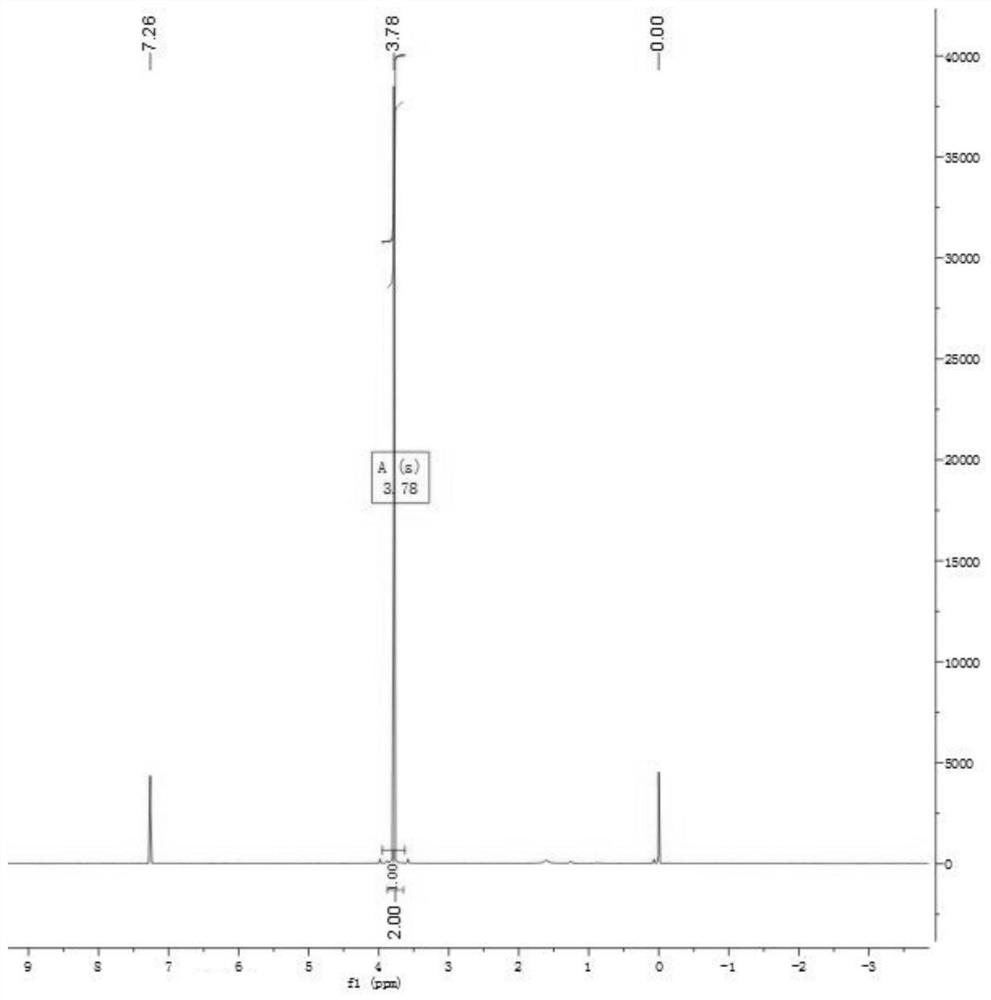
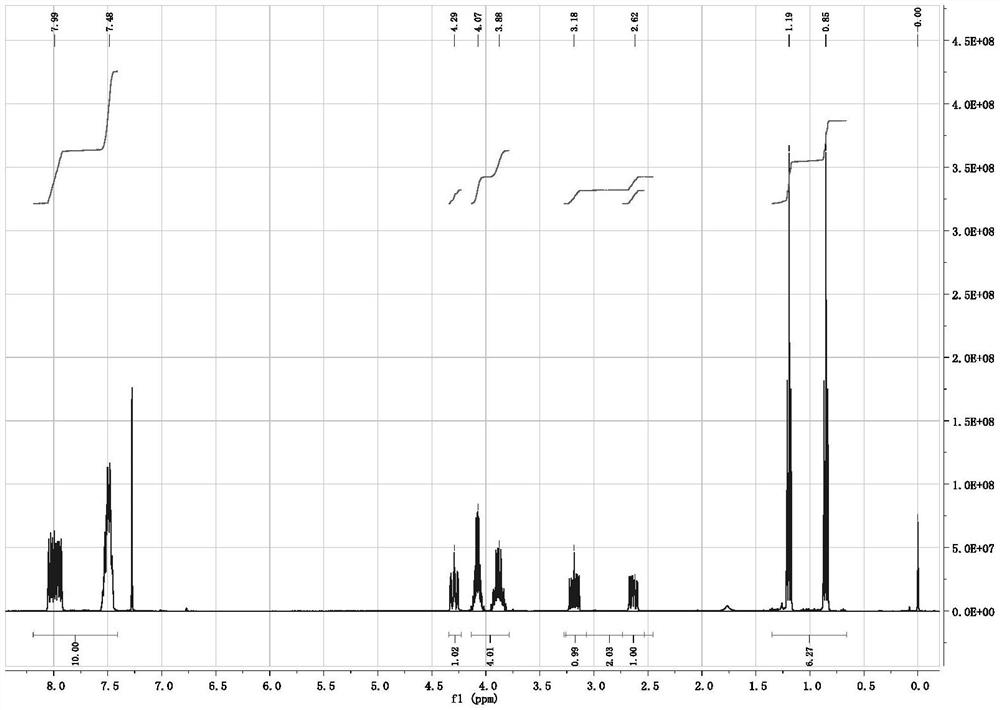
The invention discloses an iodide ion detection reagent based on iodide catalyzed hydrazine-[oxidant-Ferroin reagent] and an iodide ion detection method. In an acid medium, a tetravalent cerium solution or potassium permanganate solution is used for oxidizing an orange red Ferroin reagent solution into a blue solution in an acid medium, and a hydrazine saline solution is added to enable the blue solution to generate a reaction that blue is slowly faded to be turned into orange red; iodine has a sensitive oxidizing effect for the reaction, the higher the iodine concentration is, the higher thereaction speed is, a proportional relation is formed between the iodine concentration and the luminance value, and the iodine content of a sample can be calculated by an iodine standard curve. The detection result can be consistent to the result of the iodine tested by adopting a classical arsenic-cerium catalytic photometric method, and the use of a virulent hard-to-purchase arsenic trioxide reagent in the classical arsenic-cerium catalytic photometric method is avoided. The detection method has the advantages of being simple and convenient, rapid, specific, sensitive, accurate and the like,is expected to be widely applied to related fields needing to detect the iodine content of the sample, and especially is applied to urine iodine and water iodine detection in the fields of sanitary inspection and medical technology.
Owner:XIAMEN CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
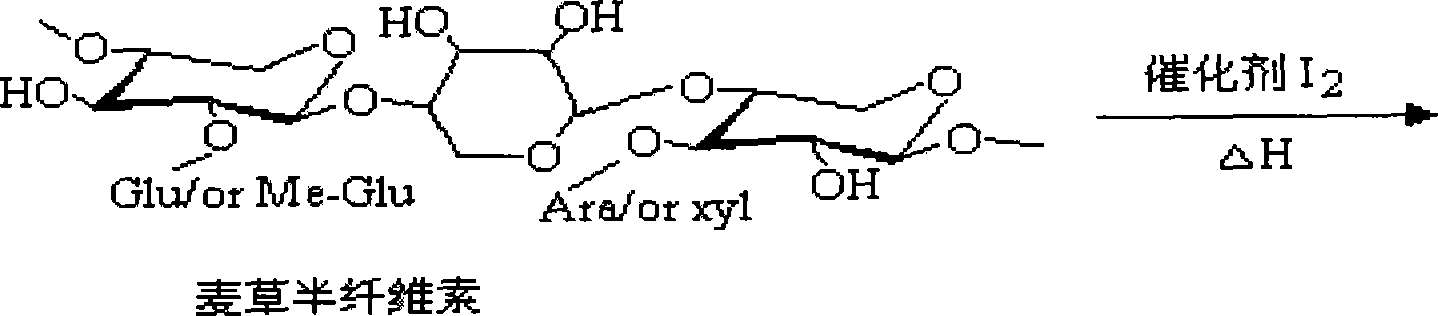
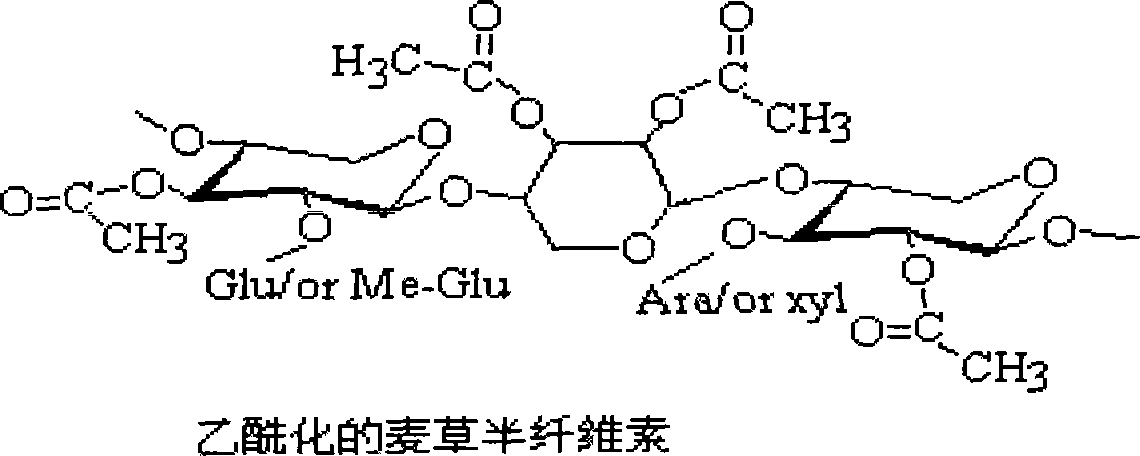
Method for preparing acetylated hemicellulose by employing catalysis of iodine
The invention discloses a method of applying iodine catalysis to prepare for acetylated hemicellulose. Firstly, KOH solution is used to dispose delignified wheat straw, then, dissolved alkali-soluble hemicellulose in filtrate is processed for purification and separation; subsequently, the hemicellulose after separation is added into 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazole chloride solution, the catalyst iodine with the weight of corresponding 10 percent to 15 percent of the hemicellulose is added, then the acetic anhydride which is 16 to 28 times of xylan hydroxyl in the compositions of the hemicellulose is added to react for 20 to 30 minutes under 90 DEG C to 110 DEG C and cooled, saturated sodium thiosulfate is added into a mixture, and ethanol is used for washing and drying to obtain the acetylated hemicellulose. The invention can obtain the acetylated hemicellulose with high substitution degree; compared with a heterogeneous system, the invention improved the reaction speed by five to ten times, increases the output and reduces the production cost, the hydrophobic nature of the hemicellulose after chemical modification is improved greatly, and the invention can be used for preparing for the degradable food-packing film.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
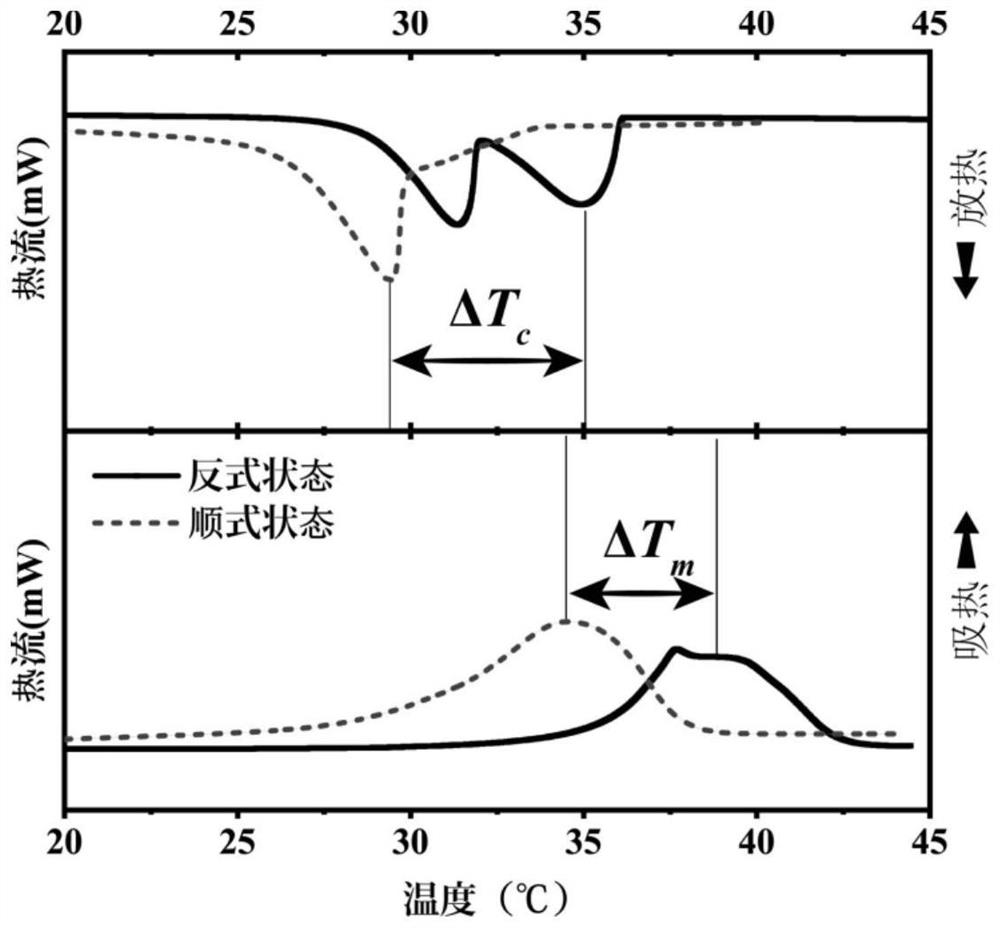
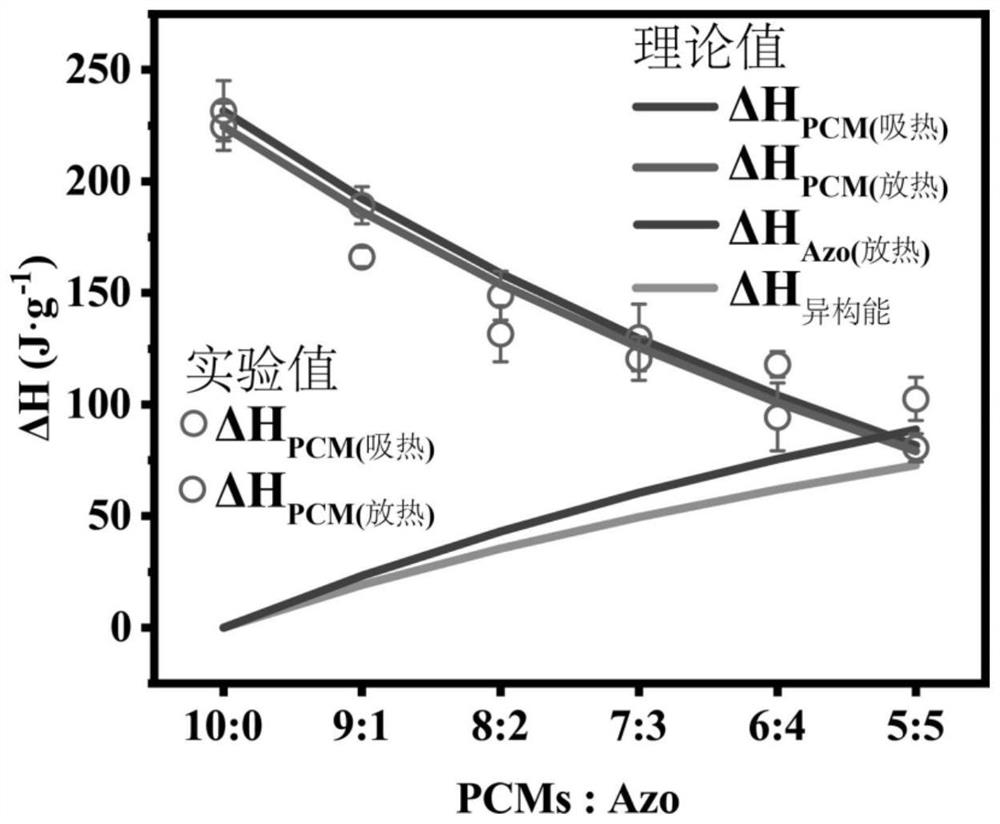
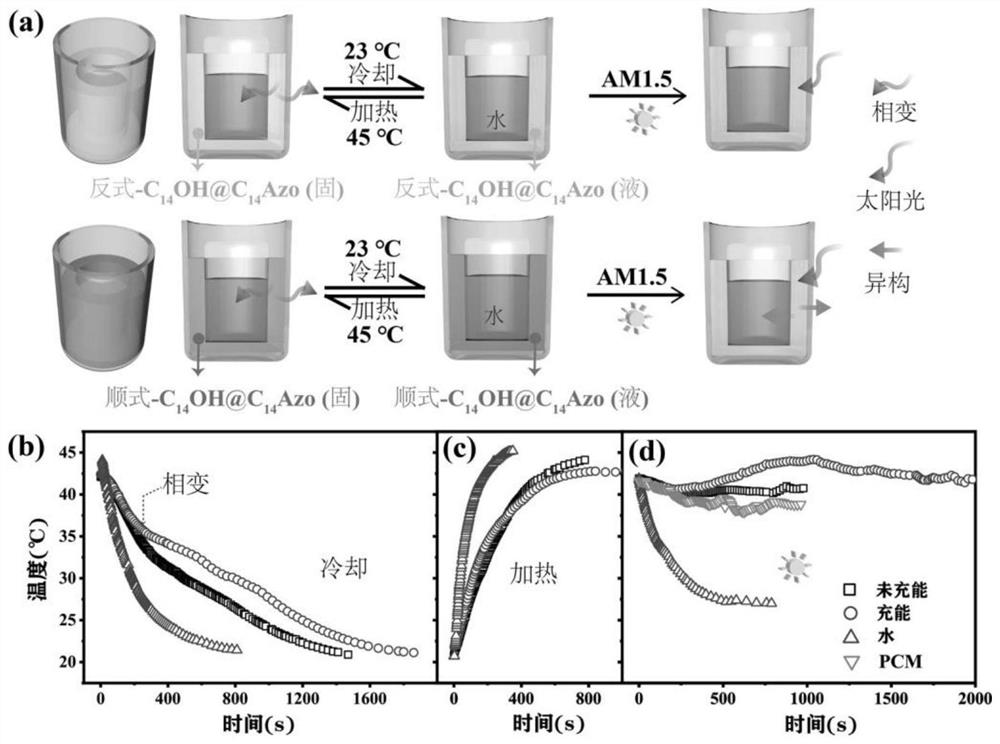
Preparation method and application of azobenzene-based light energy storage phase change material
PendingCN111748323AAchieve reversible releaseHigh speedOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAlkanePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of an azobenzene-based light energy storage phase change material. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) preparing photoresponse azobenzene molecules: carrying out a reaction on 4-hydroxyazobenzene and 1-bromoalkane by using N, N-dimethylformamide as a solvent under an alkali and iodine-containing catalyst condition to obtain 4-alkoxy azobenzene energy storage molecules; and (2) preparing the azobenzene light energy storage phase change material: carrying out melt blending on the 4-alkoxy azobenzene energy storage molecules prepared inthe step (1) and an organic phase change material, fully stirring the molecules and the organic phase change material to obtain the azobenzene light energy storage phase change material. The phase change point of the phase change material decreases under ultraviolet irradiation, the phase change point of the phase change material rises under visible light irradiation, light response phase change control exists. The azobenzene light energy storage molecules have photochromic performance; the change of the color can indicate the change of an isomerism degree; and based on the corresponding relation, an energy storage state can be monitored, and the utilization efficiency of energy is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
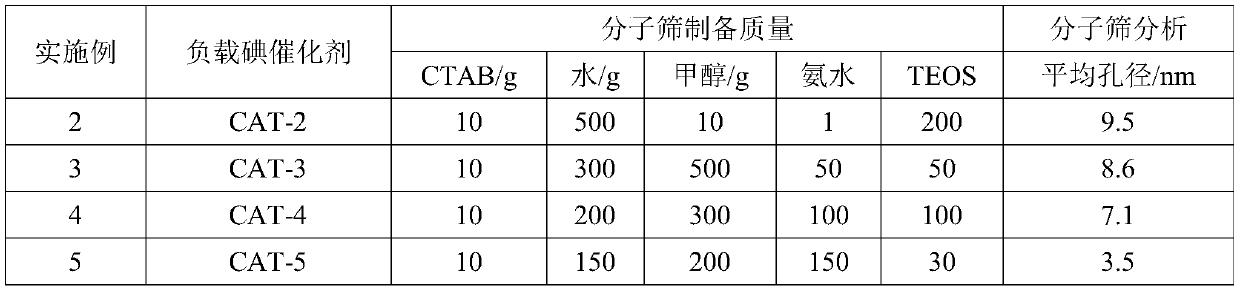
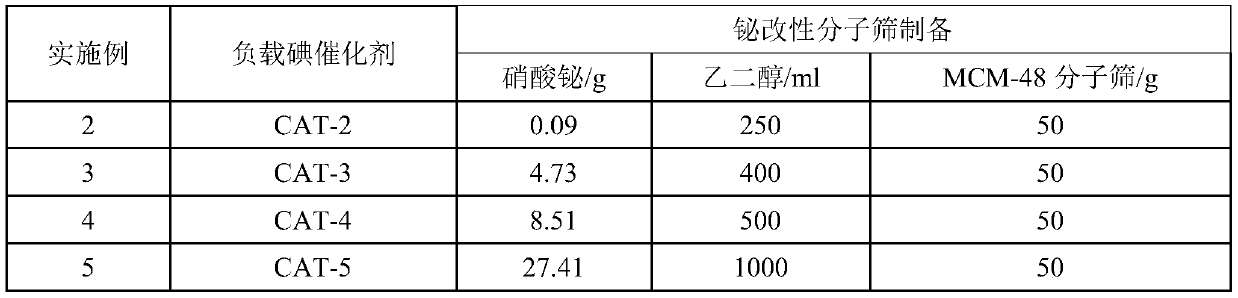
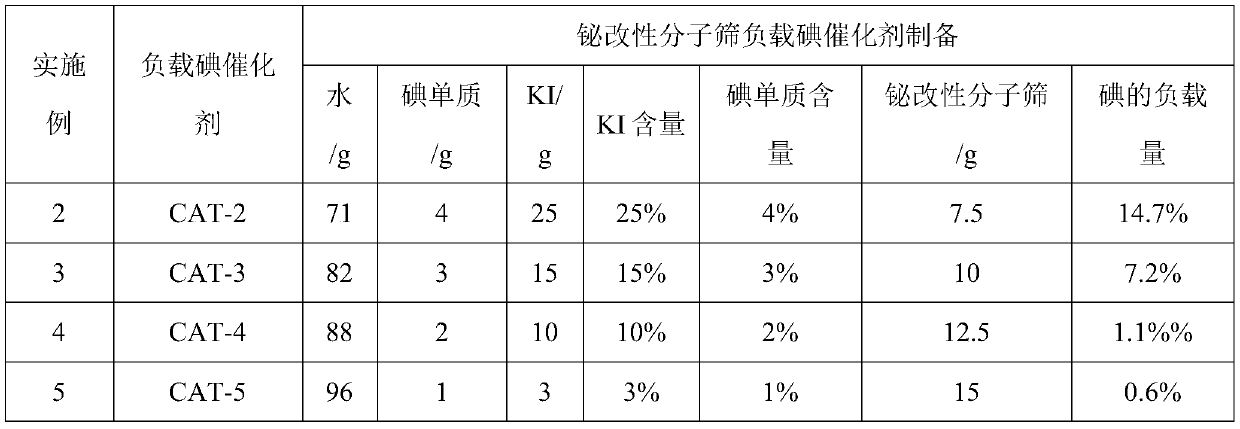
Method for preparing all-trans vitamin A acetate
ActiveCN111233726AEffectively adjust the distribution statusStrong interactionMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic chemistry methodsMolecular sieveIsomerization
The invention provides a method for preparing all-trans vitamin A acetate. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing raw materials; the method comprises the following steps: isomerizing VA crude oil containing 11-cis-vitamin A acetate and 9-cis-vitamin A acetate under the action of an iodine catalyst to generate all-trans-vitamin A acetate; the iodine catalyst comprises an active component iodine and a carrier bismuth modified molecular sieve, cis-vitamin A acetate, especially 9-cis-vitamin A acetate, can be efficiently isomerized into all-trans-vitamin A acetate by using the iodine-loaded catalyst, and the total conversion rate is up to 90% or above. The method has the advantages of low reaction cost, safe and convenient process operation, high isomerization efficiency and the like.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD
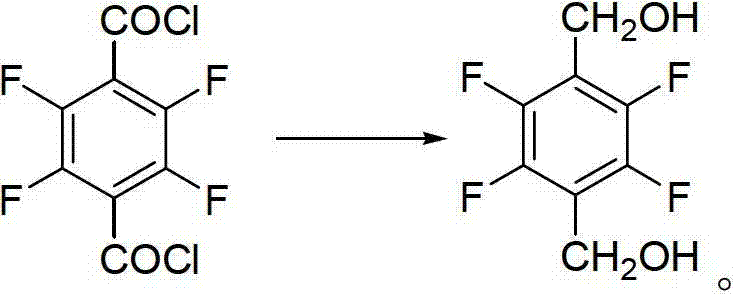
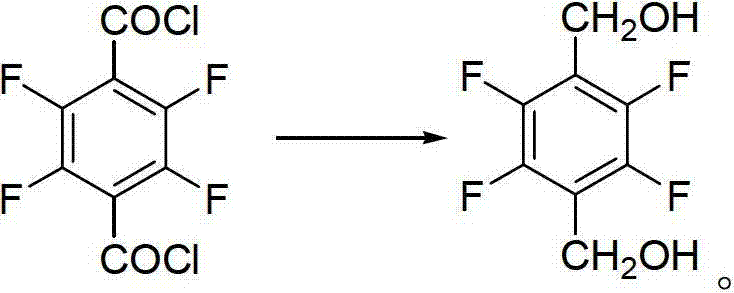
Preparation method of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,4-benzenedimethanol
ActiveCN103113192AEasy to recycleEasy to handleOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationWastewaterChloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,4-benzenedimethanol. The preparation method of 2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,4-benzenedimethanol comprises the following step: in a solvent, under the condition of iodine catalysis, carrying out reduction reaction on 2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,4-benzenedicarbonyl chloride and a hydroboron reducing agent so as to obtain 2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,4-benzenedimethanol. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is mild in reaction conditions, high in yield, safe in operation and simple in post-treatment process; the solvent is easy to recycle; the cost is low; wastewater does not contain metal ions, therefore, the method is easy to handle and environment-friendly; and the method is high in product purity, and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU LIANHE CHEM TECH +4
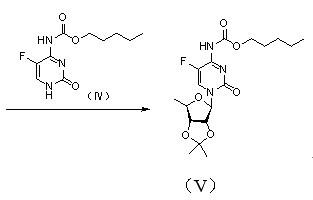
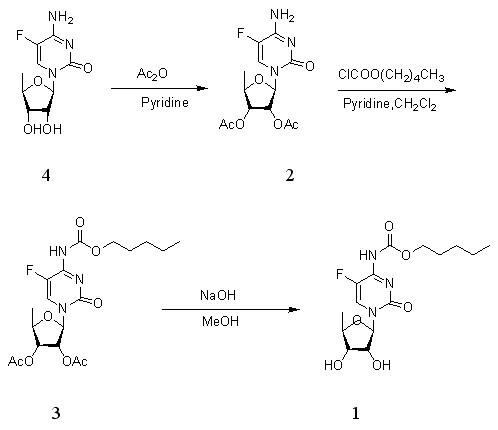
Novel synthesis process of capecitabine
ActiveCN102140124ASimple post-processingAvoid pollutionSugar derivativesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCytosineBiochemical engineering
The invention discloses a novel synthesis process of capecitabine and discloses a preparation method of 2',3'-O-isopropylidene-5'-deoxy-5-fluoro-N4-(carbopentyloxy)cytimidine (compound V) serving as an intermediate. Meanwhile, the invention discloses a preparation method for obtaining capecitabine by removing a protective group from the compound serving as a raw material under the catalytic action of iodine. The method has the advantages of readily available raw materials, environmental friendliness, high yield and no heavy metal pollution, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:湖南欧亚药业有限公司
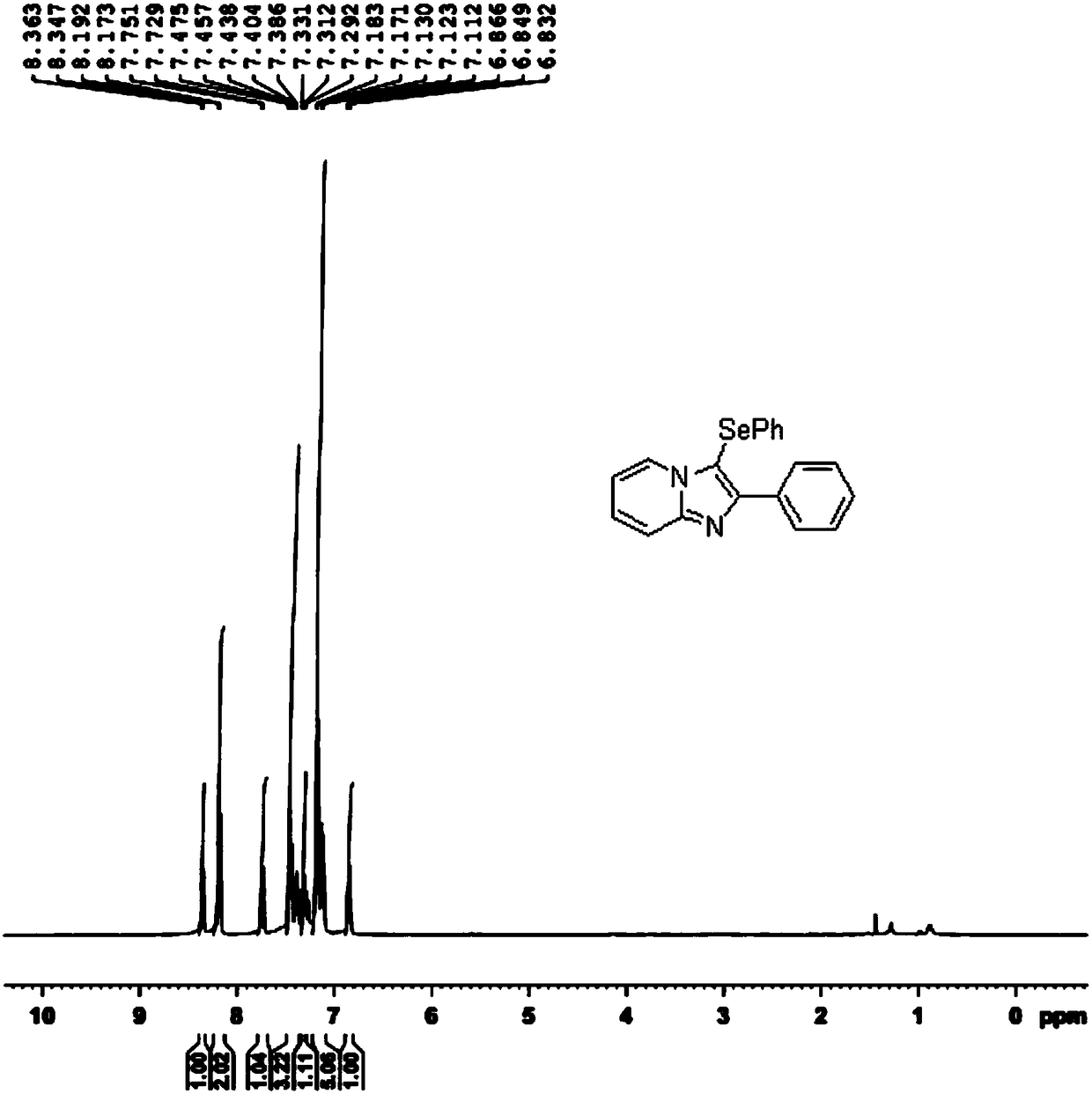
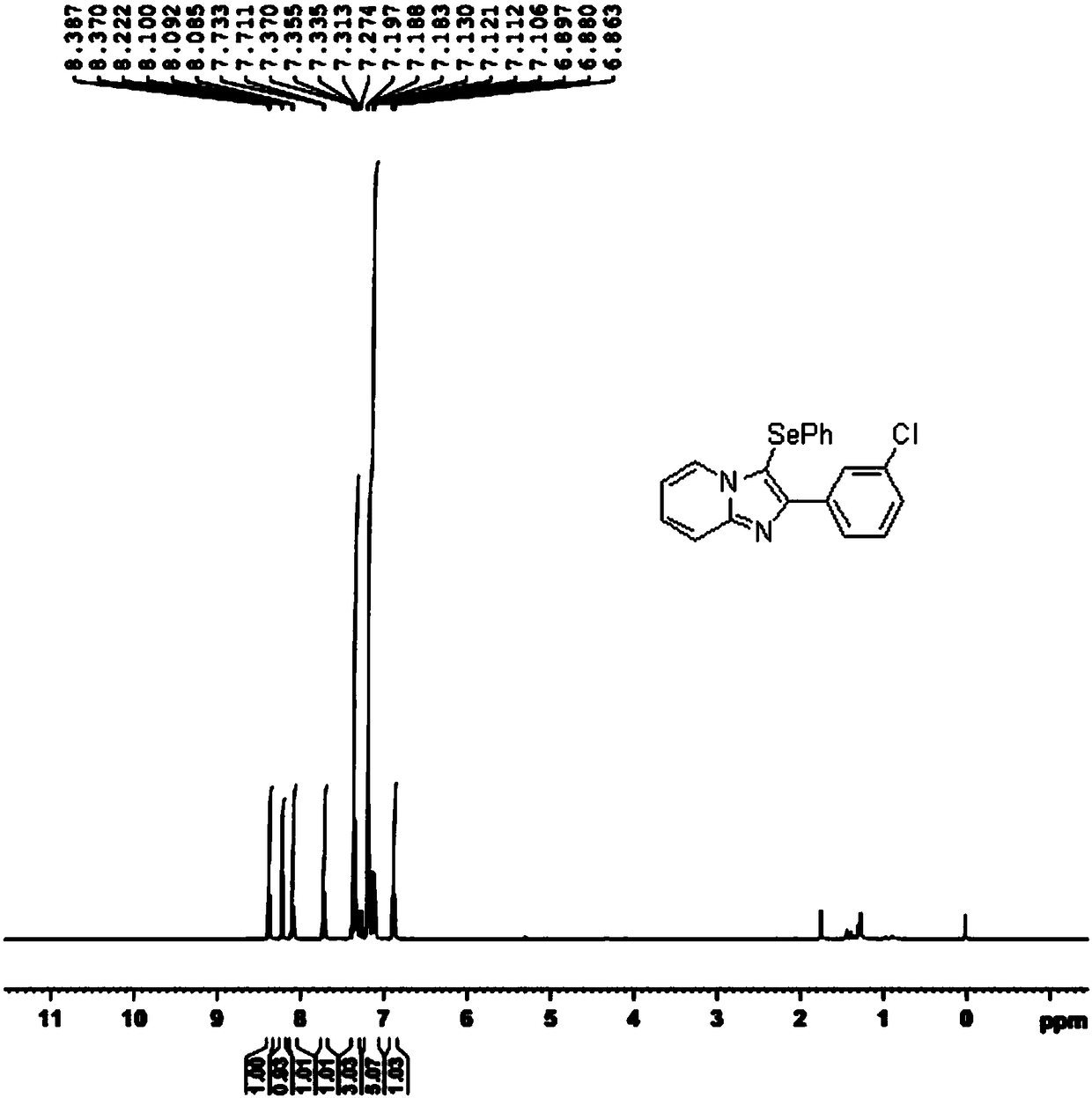
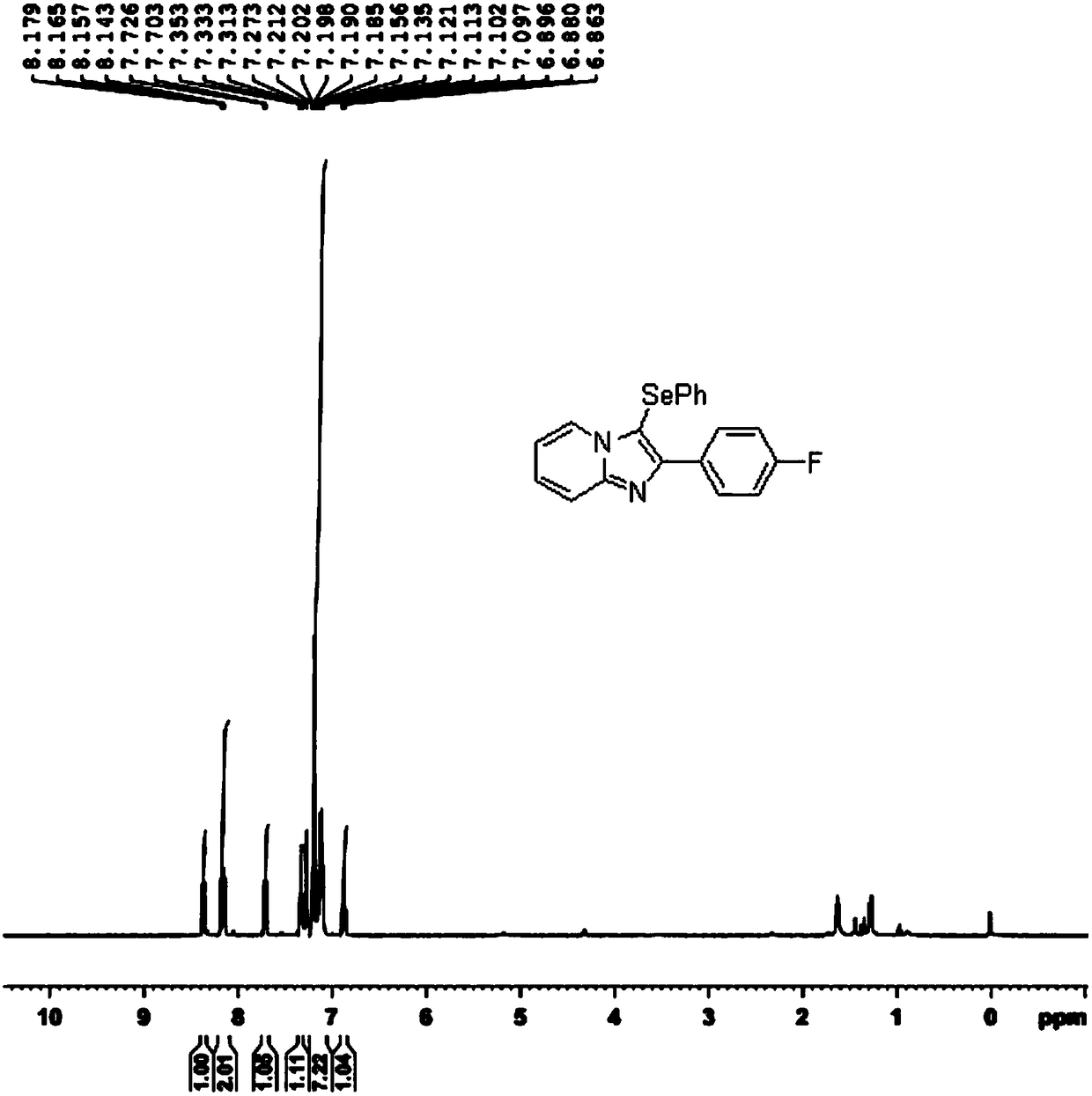
Novel selenization method for imidazopyridine derivative C3 position
InactiveCN108191856AIncrease choiceImprove compatibilityFunctional group formation/introductionOrganic synthesisPyridine
The invention discloses a novel selenization method for an imidazopyridine derivative C3 position under the condition of elementary substance iodine catalysis, and belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis. The novel selenization method adopts elementary substance iodine as a catalyst to construct a catalytic system, and greatly expands selection of a selenium reagent in the selenizationreaction of a pyridine compound C3 position; catalysis of noble metal salt and assistance of protonic acid are not needed, the selenization reaction of the imidazopyridine derivative C3 position canbe smoothly realized under the condition of the elementary substance iodine catalysis. The novel selenization method has the characteristics that the raw material is easy to obtain, the steps are simple and easy to operate, the functional group compatibility is good, the yield is high, and the like, the novel selenization method is suitable for the selenization reaction at a C3 position of synthesizing various imidazopyridine derivatives and suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:ANYANG NORMAL UNIV
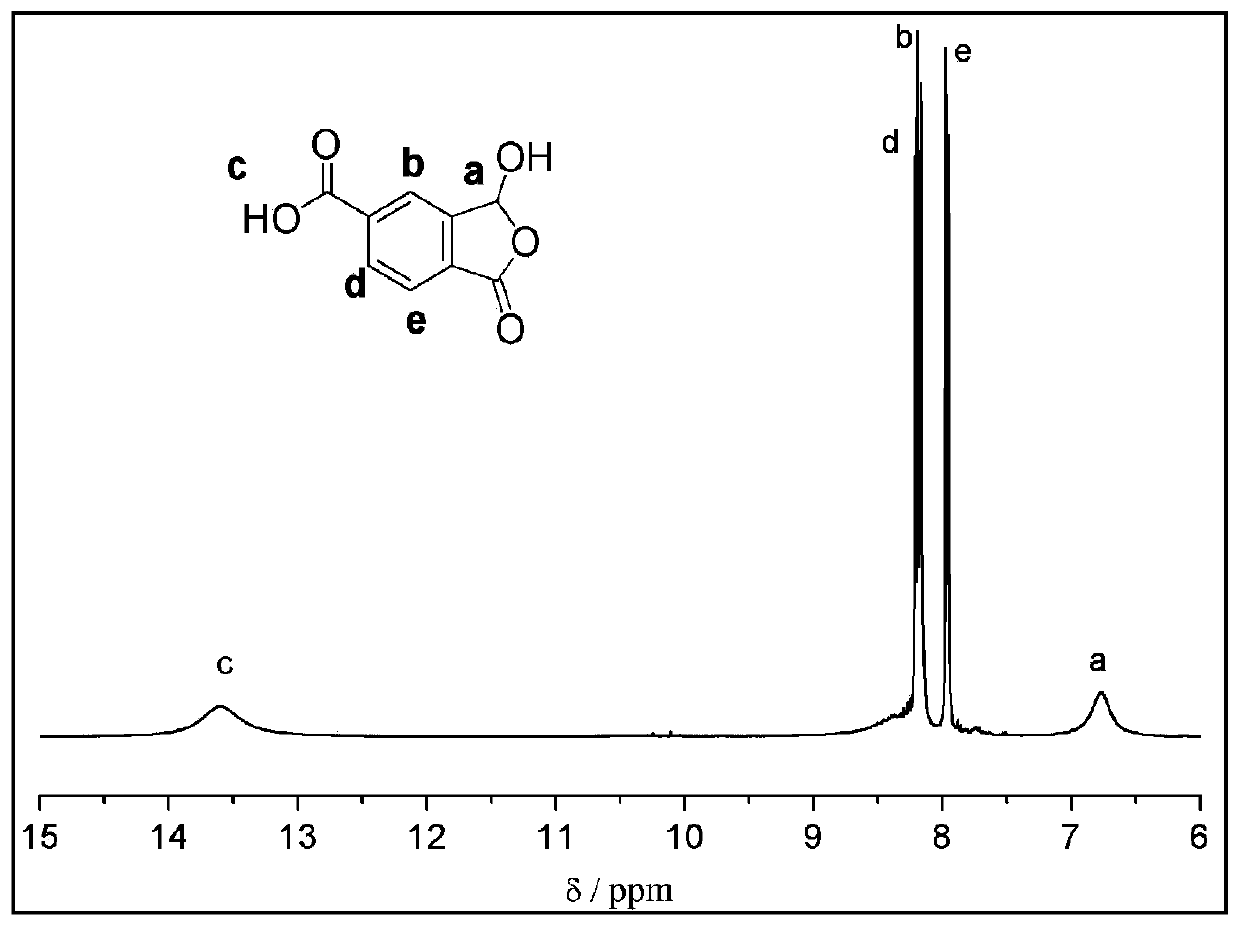
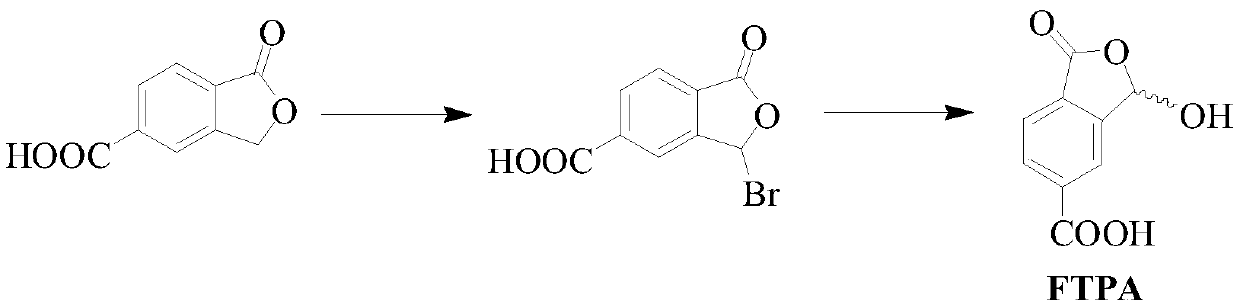
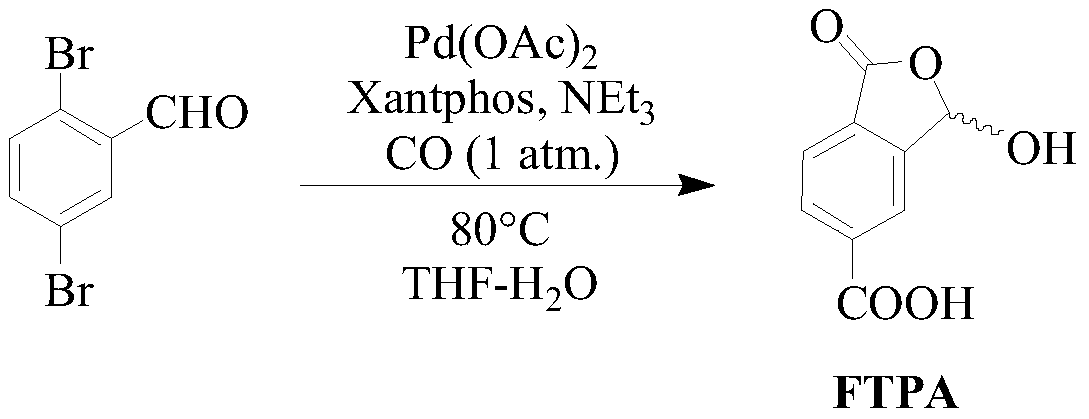
Method for preparing 1-oxo-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxybenzofuran-5-formic acid
ActiveCN110452203ASimple requirementsReaction handling is simpleOrganic chemistryChromium trioxideAcetic anhydride
The invention discloses a method for preparing 1-oxo-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxybenzofuran-5-formic acid. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: dissolving 2,5-toluene dihalideinto a tetrahydrofuran solution, carrying out a reaction with magnesium metal under iodine catalysis so as to obtain a corresponding Grignard reagent, and introducing carbon dioxide so as to obtain 2-methylterephthalic acid; performing chromium trioxide oxidation and diluted hydrochloric acid hydrolysis on the 2-methylterephthalic acid in the presence of glacial acetic acid, acetic anhydride andconcentrated sulfuric acid so as to prepare the 1-oxo-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxybenzofuran-5-formic acid. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple in synthesis, cheap and readily available in raw material and convenient for large-scale preparation, reaction treatment in the invention is simple, and a pure target product can be obtained by virtue of washing, extracting and filtering only. Moreover, requirements on reaction instruments and equipment are simple, and since the raw materials are cheap and readily available, the method has great advantages on reaction cost, improves economic benefits and has excellent industrial prospects.
Owner:汉瑞药业(荆门)有限公司
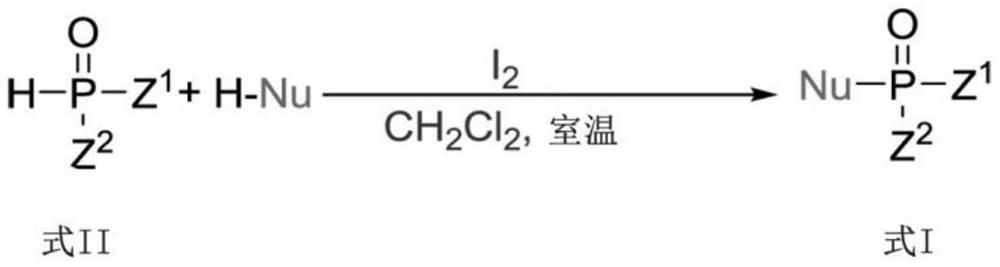
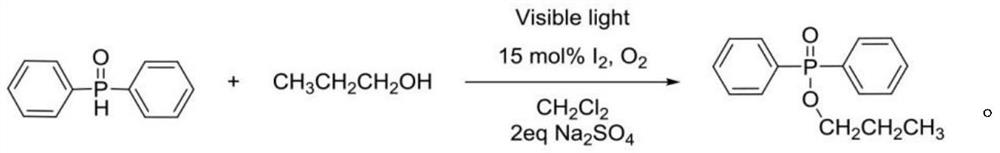
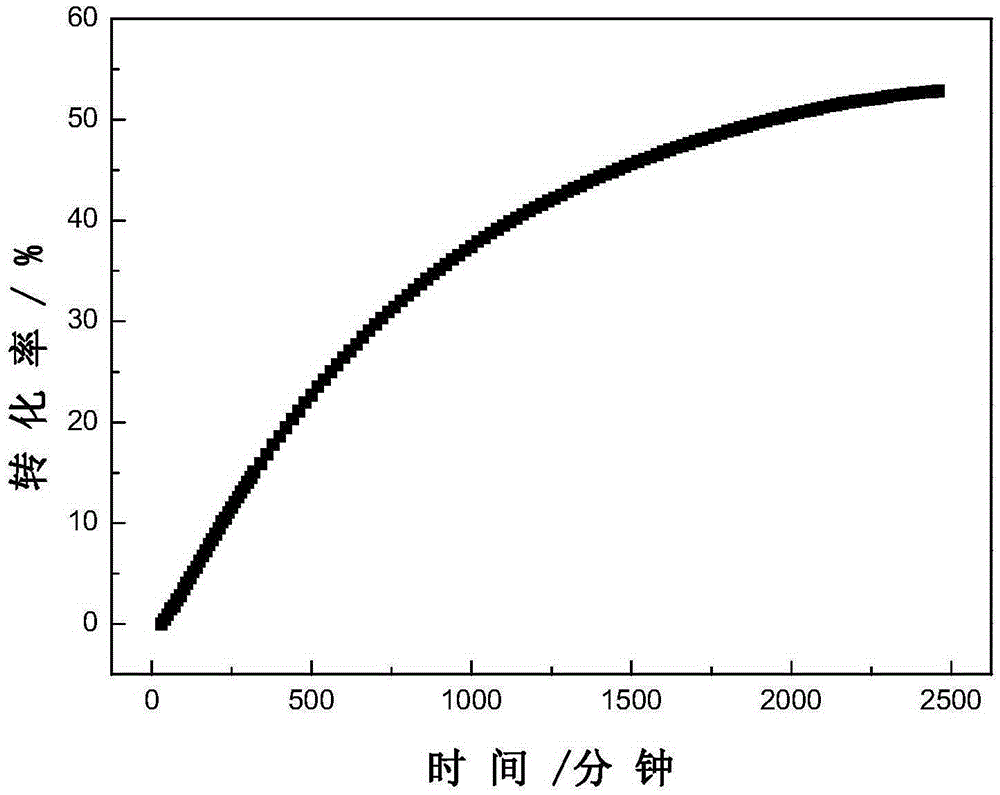
Photoinduced Iodine Catalyzed Atherton-Todd Reaction Synthesis of Organophosphorus Compounds
ActiveCN108864183BHigh yieldImprove universalityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic synthesisCombinatorial chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis, discloses a method for synthesis of organophosphorus compound by photo-induced iodine catalyzed Atherton-Todd reaction. The method comprises the following steps: a compound shown as formula II and a nucleophilic reagent are subjected to reaction for 24 hours in a dichloromethane solvent, an oxygen atmosphere, under irradiation condition of room temperature and the action of a halogenated reagent I2, then the organophosphorus compound shown as the formula II is obtained through washing, drying, separating and purifying. According to the the method provided by the invention, compared with traditional Atherton-Todd reaction, no catalysis of metal is needed,no addition of alkali is needed, reaction environment such as metal, high temperature and strong base is replaced, a series of organophosphorus compounds can be synthesized by catalyzing a variety of substrates under the irradiation condition of room temperature, and hasthe advantages of good universality, short reaction time and higher yield.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Dithiocarboxylic acid pentafluorobenzyl ester, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105294524AEasy to operateImprove hydrophobicityOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionThiocarboxylic acidGrignard reagent
The invention discloses a dithiocarboxylic acid pentafluorobenzyl ester, a preparation method and an application thereof. A structural formula of the dithiocarboxylic acid pentafluorobenzyl ester is shown in a specification, the preparation method comprises the following steps: taking pentafluoride bromo-carbons as a substrate, under iodine catalysis, reacting the substrate and magnesium powder or reacting the substrate and brominated ethyl magnesium for synthesizing a grignard reagent having a pentafiuorophenyl end group, reacting the reagent with carbon disulfide for synthesizing to obtain dithiocarboxylate, then performing an esterification reaction with alpha-bromine-2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorotoluene to prepare the dithiocarboxylic acid pentafluorobenzyl ester. According to the invention, the dithiocarboxylic acid pentafluorobenzyl ester can be taken as a high fluorine-containing RAFT reagent, can be used for a supercritical carbon dioxide system to realize RAFT polymerization of a (methyl) fluoroalkyl acrylate fluorine-containing monomer under mild condition, and the prepared fluorine-containing polymer having a highly stable pentafiuorophenyl end group. The polymer has good hydrophobicity, weatherability and soiling resistance, the high fluorine-containing end group can enhance heat stability and transmittance of the polymer, so that application requirement under special condition can be satisfied.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
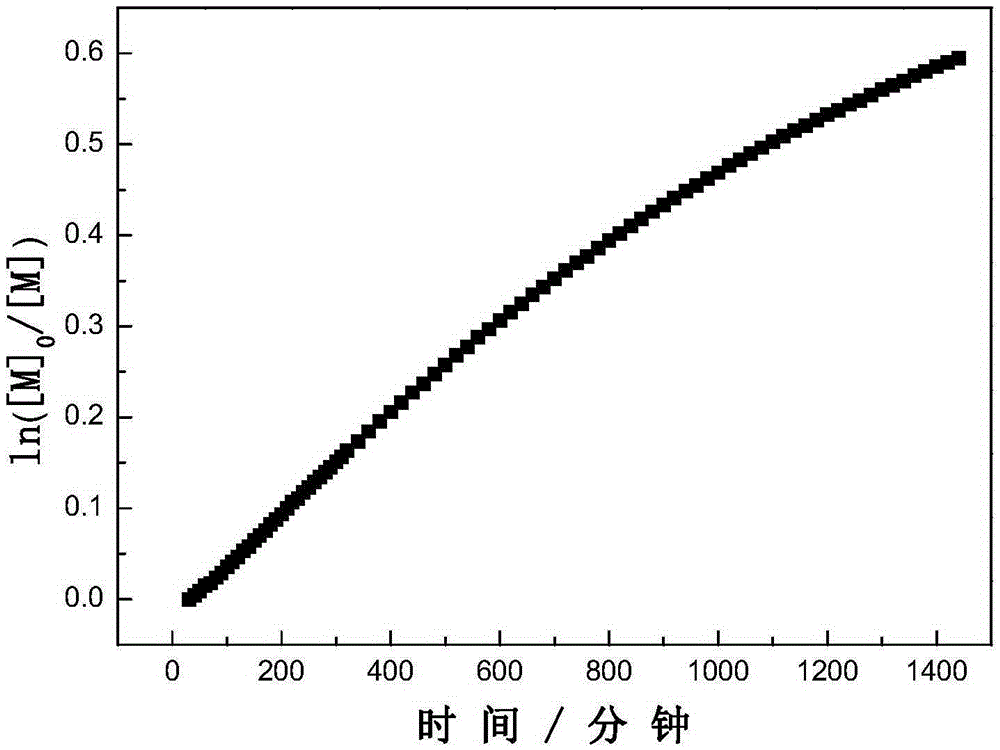
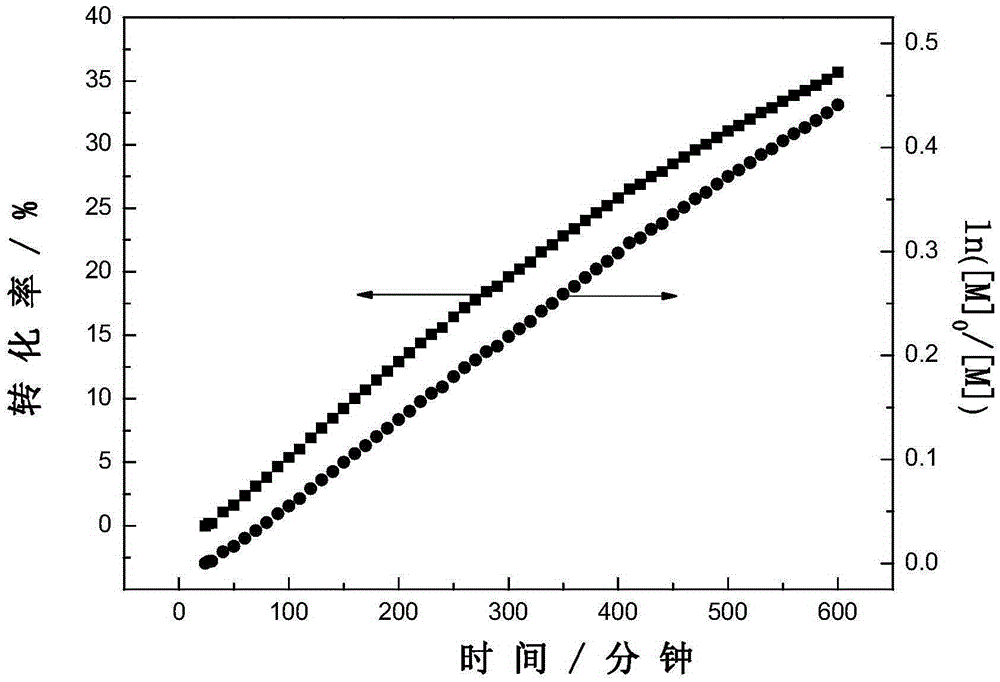
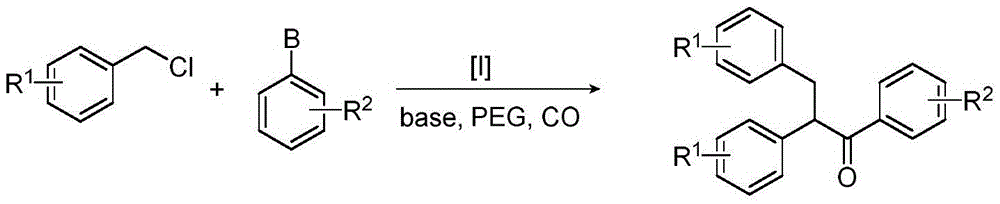
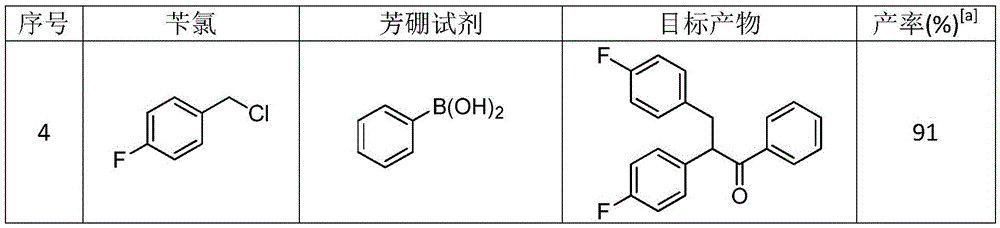
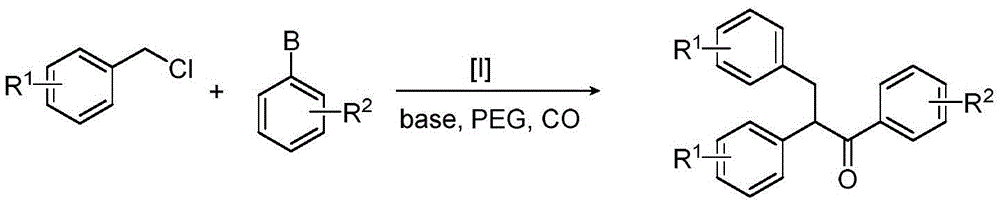
Method for synthesizing 1,2,3-triaryl-1-acetone compound from benzyl chloride through non-metal-catalyzed carbonylation
InactiveCN105669400AWide range of substrate sourcesGenerate less wasteOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsCarbonyl groupBenzyl chloride
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a 1,2,3-triaryl-1-acetone compound from benzyl chloride through non-metal-catalyzed carbonylation. According to the method, carbon monoxide is taken as a carbonyl source, and an iodine catalyst is utilized for catalyzing carbonylation-alkylation domino reaction of benzyl chloride and an aryl boron reagent in medium polyethylene glycol in the presence of the iodine catalyst and alkali so as to directly prepare the 1,2,3-triaryl-1-acetone compound. In the method, noble metal catalysts and ligands are not used, and the reaction can be carried out under the normal pressure; and the method has the advantages that a substrate is wide in source, stable and low in cost, the catalyst is low in cost and easily available, little waste is produced, the application range is wide, the reaction selectivity is high, and the yield of the target product is high.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing cyanophenyl compound
InactiveCN102659624AReduce manufacturing costEasy to separate and purifyCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationCyanide compoundBenzene
The invention relates to a method for preparing a cyanophenyl compound, which comprises the following steps: adding an alkoxy benzene compound, iodine, catalyst copper nitrate, cyanide and an acetonitrile solvent into a reaction vessel in sequence, wherein the weigh ratio of the alkoxy benzene compound to the cyanide, the catalyst copper nitrate and the iodine is 1:(0.1-5):(0.8-1.2):(0.4-0.5), then sealing the reaction container, agitating and reacting for 5-45 hours at a temperature of 150-200 DEG C, cooling to a room temperature after reaction and purifying a reacted mixture through a column chromatography to obtain the cyanophenyl compound. The preparation method has the beneficial effects that the relatively-cheap the alkoxy benzene compound is taken as a raw material, acid and high-pressure gas are not used, the production cost is remarkably reduced, and as low-boiling point solvent acetonitrile is used, a product is easy to separate and purify.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
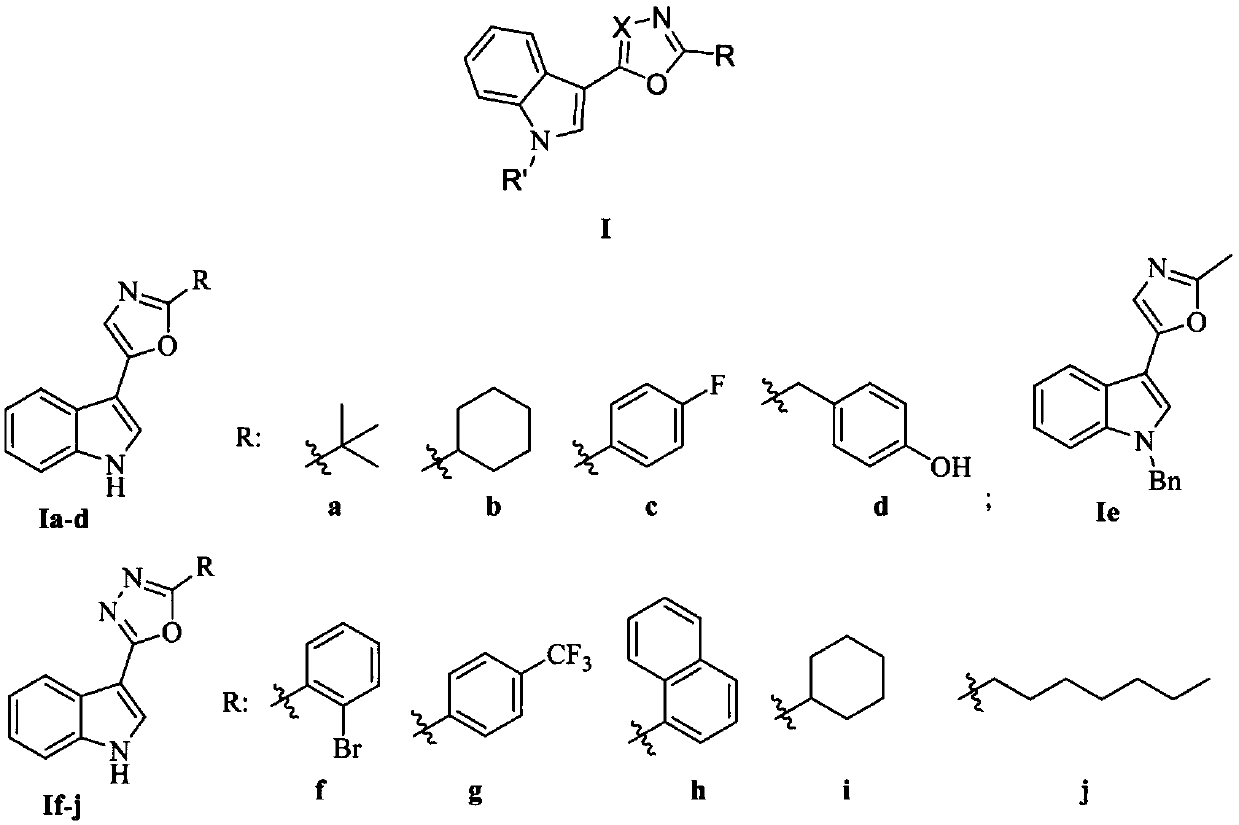
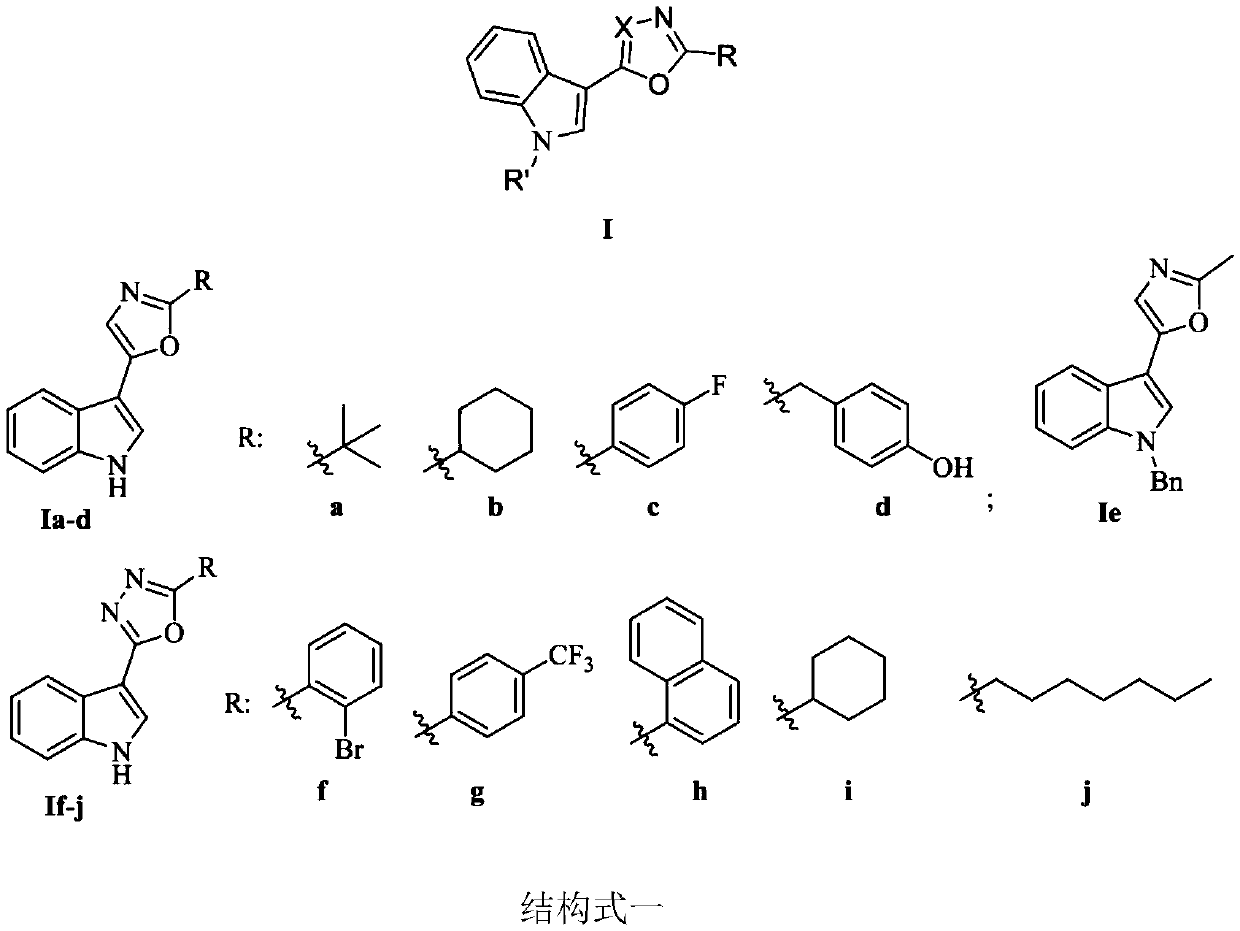
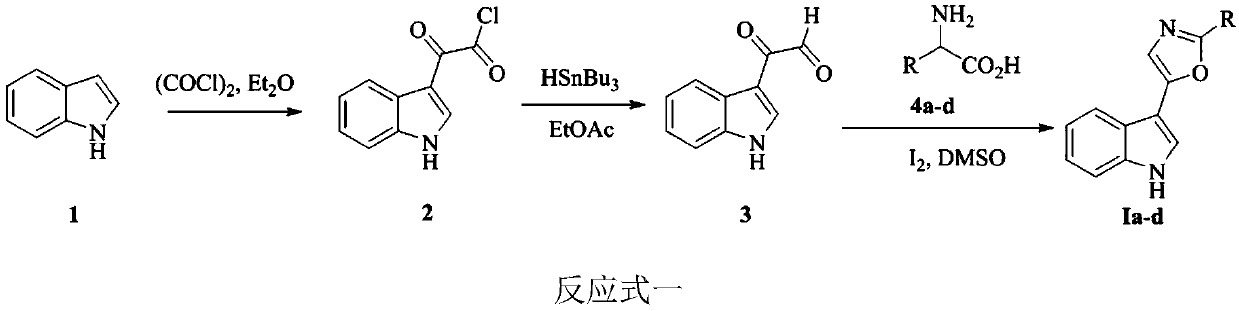
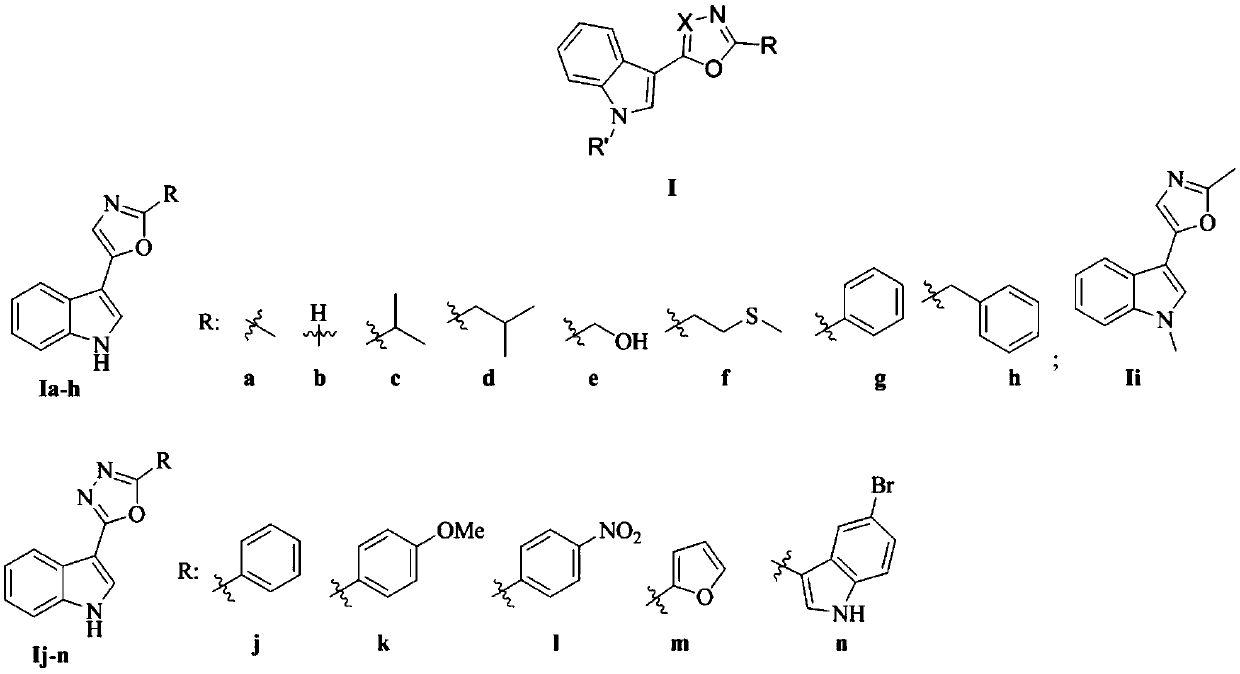
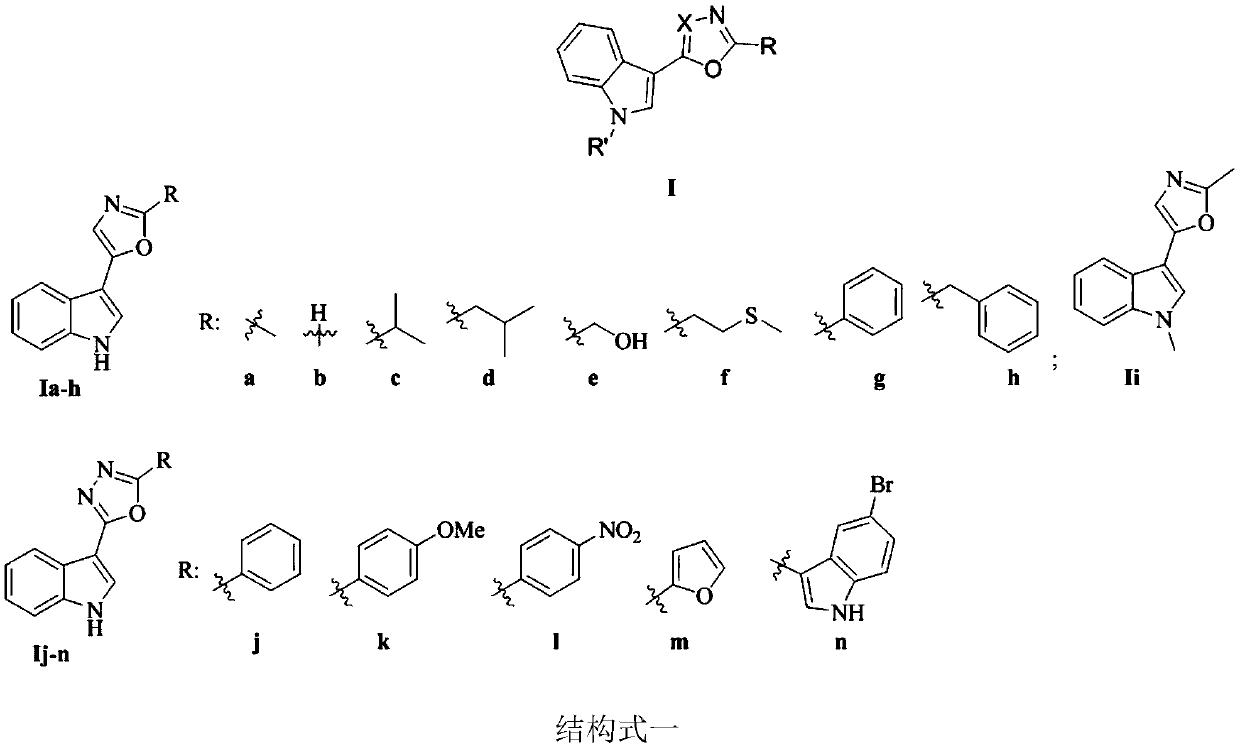
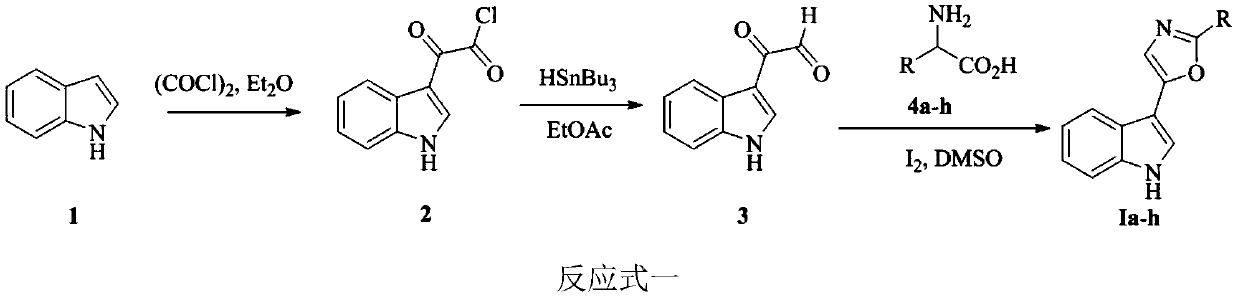
Indole-based heterocyclic compound as well as preparation method and application thereof in prevention and treatment of plant diseases
ActiveCN111349088ASuppress witheringHigh activityOrganic chemistryFungicidesTobacco mosaic virusEthylic acid
The invention discloses an indole-based heterocyclic compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof in prevention and treatment of plant diseases. According to the method, indole isreacted with oxalyl chloride to obtain indole oxalyl chloride, then indole oxalyl chloride is reduced by tributylstannane to obtain indole carbonyl acetaldehyde, and finally indole carbonyl acetaldehyde is reacted with a corresponding amino acid under the catalysis of iodine to obtain a compound; or indole hydrazide is reacted with an aldehyde, and oxidizing with iodobenzene acetate is carried outto obtain the compound. The indole heterocyclic compound provided by the invention shows especially excellent plant virus resisting activity, can well inhibit the tobacco mosaic virus, and also showsbroad-spectrum plant pathogenic bacteria resisting activity.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
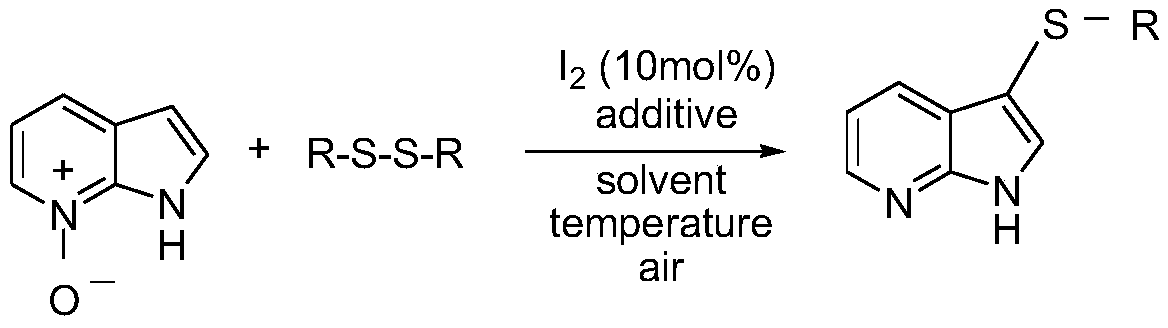
Regioselective deoxidation thionation reaction for 7-azaindole-nitrogen oxide
InactiveCN110759907AEasy to operateRegioselective regulationOrganic chemistryPtru catalystOrganic synthesis
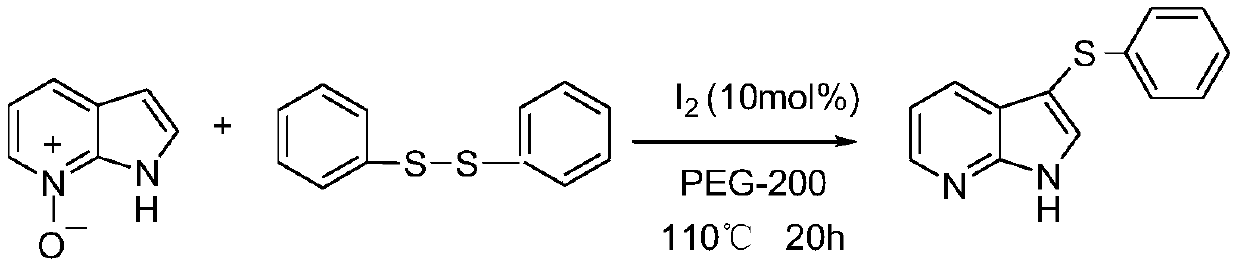
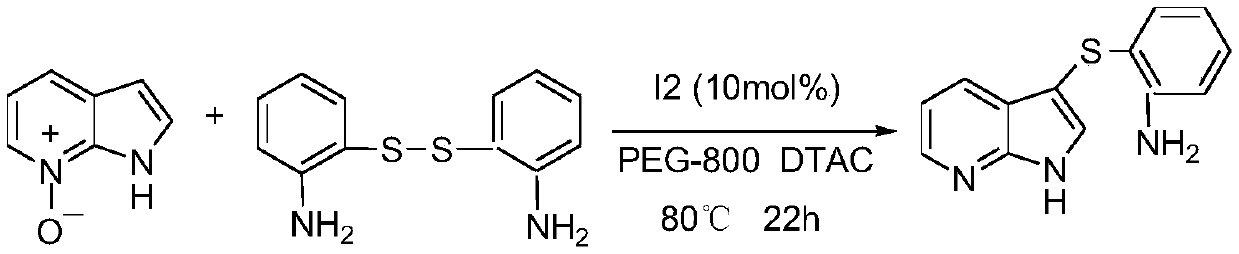
The invention relates to the fields of organic synthesis and medicine and chemical industry, in particular relates to an iodine-catalyzed regioselective deoxidation thionation reaction method for 7-azaindole-nitrogen oxide, and aims to overcome the problems of high toxicity, low efficiency and poor adaptability existing in the prior art. The technical solution adopted in the invention is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: by using the 7-azaindole-nitrogen oxide as a substrate and an internal oxidant, and a disulfide as a thioetherification reagent, under the condition of the molar ratio of the 7-azaindole-nitrogen oxide to the disulfide of 1:(0.5-2), adding molecular iodine as a catalyst, and performing a deoxidation thioetherification reaction in a solvent, wherein the use amount of the solvent is 2-10 mL, and the molar concentration of the 7-azaindole-nitrogen oxide is 0.1-0.5 mol / L; and sequentially adding the measured reactants into a pressure-resistanttube with a magneton, sealing the pressure-resistant tube, performing stirring on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature, performing a reaction at pressure of 0.1 MPa and temperature of 80-120 DEG Cfor 12-36 h, performing cooling to room temperature, performing extraction for several times, combining organic phases, removing the solvent, and performing purification to obtain 7-azaindole sulfide.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Indole heterocyclic compound, preparation method thereof and application of indole heterocyclic compound in prevention and treatment of plant diseases
ActiveCN111349089ASuppress witheringGood against plant virusBiocideOrganic chemistryNicotiana tabacumTobacco mosaic virus
The invention discloses an indole heterocyclic compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof in prevention and treatment of plant diseases. According to the method, indole is reacted with oxalyl chloride to obtain indole oxalyl chloride, then indole oxalyl chloride is reduced by tributylstannane to obtain indole carbonyl acetaldehyde, and finally indole carbonyl acetaldehyde isreacted with a corresponding amino acid under the catalysis of iodine to obtain a compound. The indole heterocyclic compound provided by the invention shows especially excellent plant virus resistingactivity, can well inhibit the tobacco mosaic virus, and also shows broad-spectrum plant pathogenic bacteria resisting activity.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
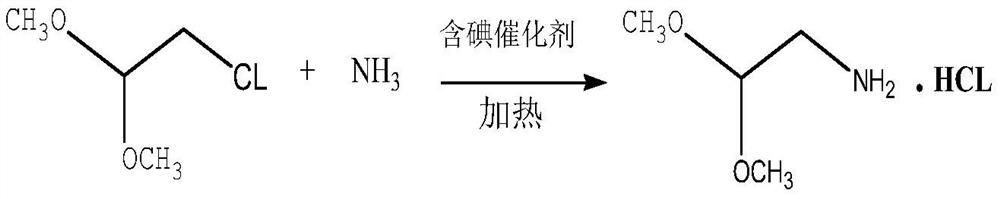
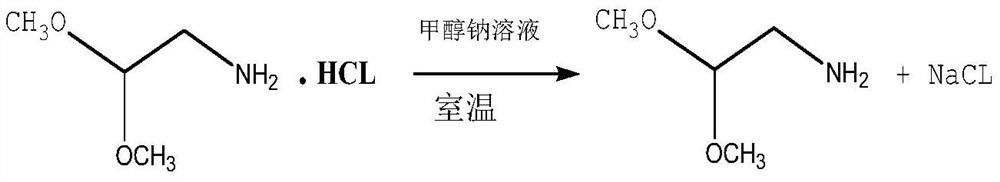
Production process of high-purity aminoacetaldehyde dimethyl acetal
PendingCN112375003AAvoid separation difficultiesHigh purityOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationPtru catalystDimethyl acetal
The invention discloses a production process of high-purity aminoacetaldehyde dimethyl acetal. The process comprises the following steps: proportionally mixing chloroacetaldehyde dimethyl acetal withanhydrous liquid ammonia to react, and carrying out ammoniation, deamination recovery, alkali neutralization desalination, distillation and rectification in the presence of an iodine-containing catalyst to obtain the high-purity aminoacetaldehyde dimethyl acetal. According to the method, chloroacetaldehyde dimethyl acetal is innovatively used as a main raw material, anhydrous liquid ammonia is used as a solvent and a reaction raw material, an iodine-containing catalyst is added, and the anhydrous high-purity aminoacetaldehyde dimethyl acetal is obtained through ammoniation, deamination, alkalineutralization desalination, distillation and rectification. In practice, the technical process can reduce the generation of by-product conjugates, can realize higher conversion rate than the traditional process under the condition of higher catalytic effect, and simultaneously reduces the requirements on organic solvents and energy sources; and under the condition of the same proportion, the single-batch feeding amount and the product yield of the novel process are improved by 50% or above, the yield is about 20% higher than that of a traditional process, and the effects of saving energy, improving quality, reducing cost and reducing consumption can be achieved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA SAINTCHEM CHEM
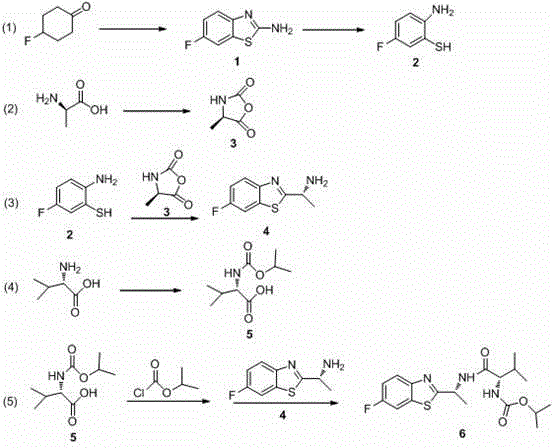
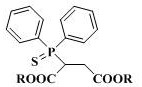
Synthesis technology of benthiavalicarb isopropyl
The invention discloses a new synthesis technology of benthiavalicarb isopropyl, and belongs to the field of pesticide chemistry. A method for implementing the synthesis technology comprises the steps as follows: fluorocyclohexanone is used as a raw material and catalyzed by iodine to generate 2-amino-6-fluorobenzothiazole through oxidative cyclization, and after hydrolysis and acidification, 2-amino-5-fluorothiophenol is prepared; meanwhile, D-alanine is used as a raw material and reacts with triphosgene to generate (R)-4-methyl-oxazolidine-2, 5-diketone, and an intermediate reacts with 2-amino-5-fluorothiophenol to prepare chiral (R)-1-(6-fluorine-benzothiazole-2-) ethylamine; and L-valine is used as a raw material and reacts with isopropyl chlorocarbonate to prepare N- Isopropoxy carbonyl-L-valine, carboxyl activation is performed simultaneously, and finally, the raw materials and (R)-1-(6-fluorine-benzothiazole-2-) ethylamine perform a one-pot reaction to directly generate benthiavalicarb isopropyl. The synthesis technology has short process route and high total yield, and purity degree is higher than 95%.
Owner:SHANGQIU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
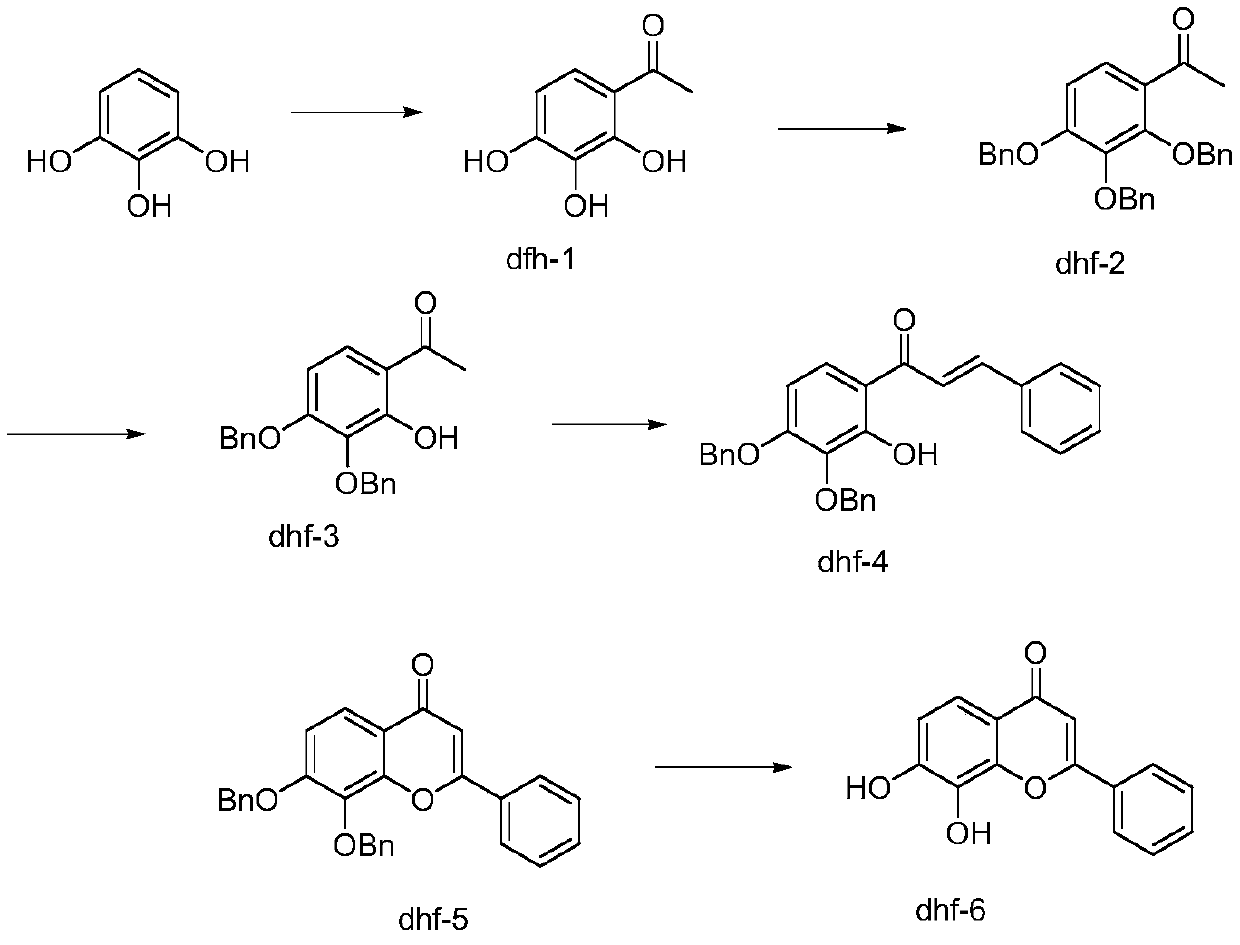
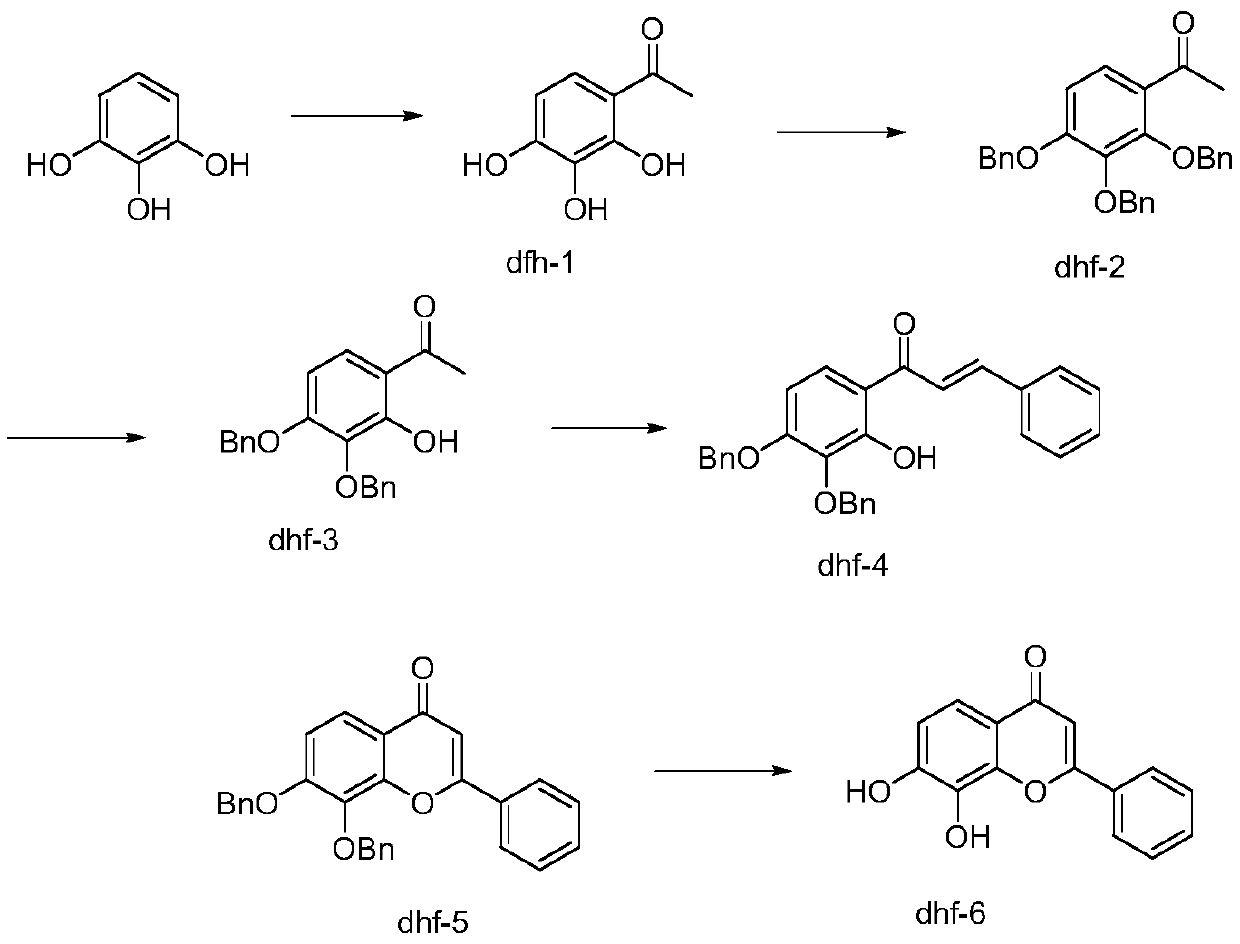
Preparation method of 7,8-dihydroxy flavone
PendingCN111303105AEase of industrial implementationLow priceOrganic chemistryBenzaldehydeOrtho position
The invention relates to a preparation method of 7,8-dihydroxy flavone, and belongs to the technical field of synthesis of medical intermediates. The preparation method comprises the following steps:by taking pyrogallol as a raw material, introducing an acetyl group to synthesize DHF1; protecting three phenolic hydroxyl groups to synthesize DHF2; selectively reducing the ortho-hydroxyl group of the acetyl group to synthesize DHF3; carrying out an aldol condensation reaction on DHF3 and benzaldehyde to prepare DHF4; carrying out a cyclization reaction under the condition of iodine catalysis toobtain DHF5; and finally carrying out a hydrolysis reaction to generate the final product. The method is simple and convenient to operate, reasonable in reaction process, low in production cost, goodin product quality, free of environmental pollution and suitable for industrial production, wherein the content of the product is higher than 98%.
Owner:湖北万知化工医药股份有限公司 +1
Reagent and method for detecting iodine through antimony-cerium reaction iodine catalysis method
PendingCN111537462AEasy to useImprove stabilityPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsNutritionCerium
A classic trace iodine detection method is an arsenic-cerium catalytic spectrophotometric method, such as a sanitary industry standard method WS / T 107-2016 for urine iodine detection, and is widely applied to iodine deficiency and iodine nutrition monitoring in China. However, a highly toxic arsenic trioxide (arsenic trioxide) reagent needs to be used in the method, and the application of the method is increasingly limited due to environmental protection. A non-toxic trace iodine detection reagent and a non-toxic trace iodine detection method are urgently needed in the field of health care. The invention discloses a reagent and a method for detecting iodide ions by adopting an iodine catalyzed antimony-cerium redox reaction principle. Iodine ions catalyze Sb < 3 + > to reduce yellow Ce < 4+ > into colorless Ce < 3 + >, and the reaction speed and the iodine content are in a positive correlation quantitative relation. And after a certain reaction time, the absorbance of the residual Ce< 4 + > in the solution is measured by using a spectrophotometric method, and the iodine content of the measured sample is calculated according to the quantitative relationship between the iodine content and the absorbance. According to the method, toxic-free antimony is adopted to replace highly-toxic arsenic in a classic method, the detection effect consistent with that of an arsenic-cerium catalytic spectrophotometry is achieved, the highly-toxic arsenic trioxide reagent is prevented from being used, and the method is applied to detection of urine iodine, blood iodine, water iodine, salt iodine, food iodine, soil iodine and the like and has important public health significance.
Owner:刘列钧
Method for preparing bromoacetonitrile from chloroacetonitrile
ActiveCN114507157AHigh reaction yieldSimple and fast operationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid nitrile purification/separationPtru catalystBromoacetonitrile
The invention discloses a method for preparing bromoacetonitrile from chloroacetonitrile, and belongs to the field of chemical engineering. The method comprises the following steps: heating and refluxing chloroacetonitrile, inorganic bromide and an iodine-containing catalyst in a solvent, and purifying after the reaction is completed to obtain bromoacetonitrile. The easily available inorganic bromide is used as the bromine source, the used solvent is environment-friendly and recyclable, the reaction yield is greatly improved, the post-treatment method is simple, and the whole reaction route is clean and environment-friendly.
Owner:沧州维智达美制药有限公司
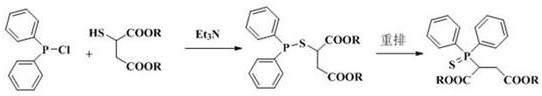
2-(diphenylthiophosphoryl) succinate as well as synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN114315896AHigh flame retardant efficiencyFast charcoal speedGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsButanedioic acidThio-
The invention relates to 2-(diphenylthiophosphoryl) succinate as well as a synthesis method and application thereof. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: by taking triethylamine as an acid-binding agent under the protection of nitrogen atmosphere, carrying out reaction on diphenylphosphonium chloride and 2-mercaptosuccinic acid diester to prepare a 2-((diphenylphosphono) thio) succinic acid diester intermediate; and then the 2-(diphenylthiophosphoryl) succinate is prepared through a rearrangement reaction catalyzed by iodine. The 2-(diphenylthiophosphoryl) succinic acid (ester) (DPS-MA) phosphorus-containing flame retardant provided by the invention has a higher char forming speed and better flame retardant efficiency than a 2-(diphenylphosphoryl) succinic acid (ester) (DPO-MA) phosphorus-containing flame retardant.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Synthesis technology of benthiavalicarb isopropyl
The invention discloses a new synthesis technology of benthiavalicarb isopropyl, and belongs to the field of pesticide chemistry. A method for implementing the synthesis technology comprises the steps as follows: fluorocyclohexanone is used as a raw material and catalyzed by iodine to generate 2-amino-6-fluorobenzothiazole through oxidative cyclization, and after hydrolysis and acidification, 2-amino-5-fluorothiophenol is prepared; meanwhile, D-alanine is used as a raw material and reacts with triphosgene to generate (R)-4-methyl-oxazolidine-2, 5-diketone, and an intermediate reacts with 2-amino-5-fluorothiophenol to prepare chiral (R)-1-(6-fluorine-benzothiazole-2-) ethylamine; and L-valine is used as a raw material and reacts with isopropyl chlorocarbonate to prepare N- Isopropoxy carbonyl-L-valine, carboxyl activation is performed simultaneously, and finally, the raw materials and (R)-1-(6-fluorine-benzothiazole-2-) ethylamine perform a one-pot reaction to directly generate benthiavalicarb isopropyl. The synthesis technology has short process route and high total yield, and purity degree is higher than 95%.
Owner:SHANGQIU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
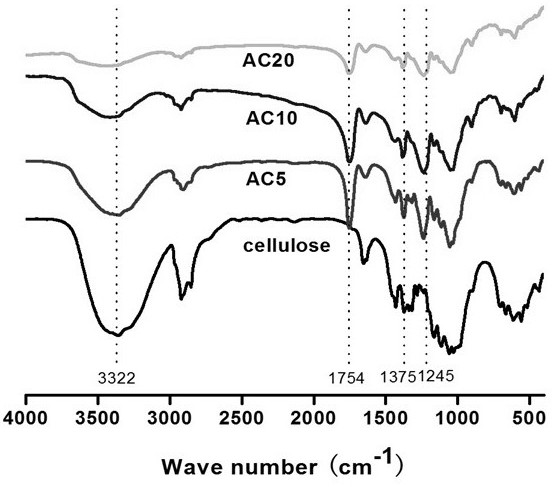
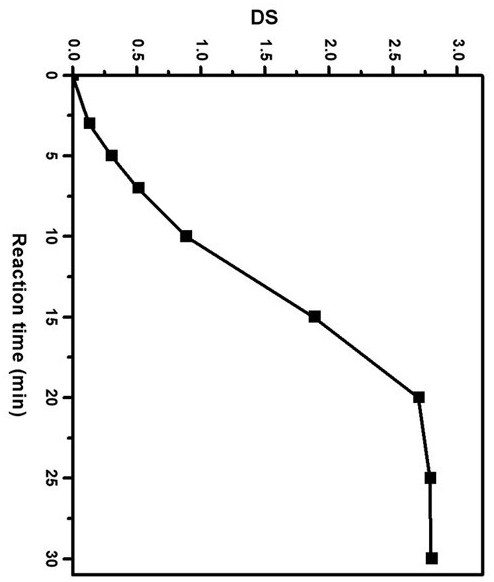
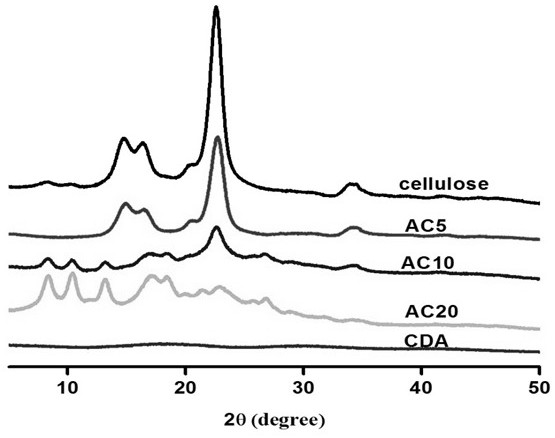
A kind of whole cellulose composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a holocellulose composite material and a preparation method thereof. Cellulose with the acetylated surface layer is prepared by adopting iodine catalysis and is adopted as a mechanical-enhancement filler fiber, and the surface of cellulosic fiber is gradually acetylated under iodine catalysis. Through the acetylation treatment of the cellulosic fiber, the compatibility ofthe cellulosic fiber and cellulose acetate is improved, but the crystallinity of the cellulose is also reduced, and the tensile strength of fiber is weakened, so that the substitution of acetyl on thefiber is controlled by the reaction time so as to balance two contrary functions, and thus the optimization is realized. The cellulose used as the mechanical-enhancement filler is partially acetylated and modified and is hot blended with plasticized CDA so as to prepare a full cellulose acetate composite material, and a matrix and a filler are provided with acetyl on the surfaces and have the similar chemical structures, so that by adding partially acetylated cellulose, the interfacial compatibility between the CDA matrix and the acetylated cellulosic fiber can be promoted to be improved, andfinally, the mechanical performance of the composite material is improved.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
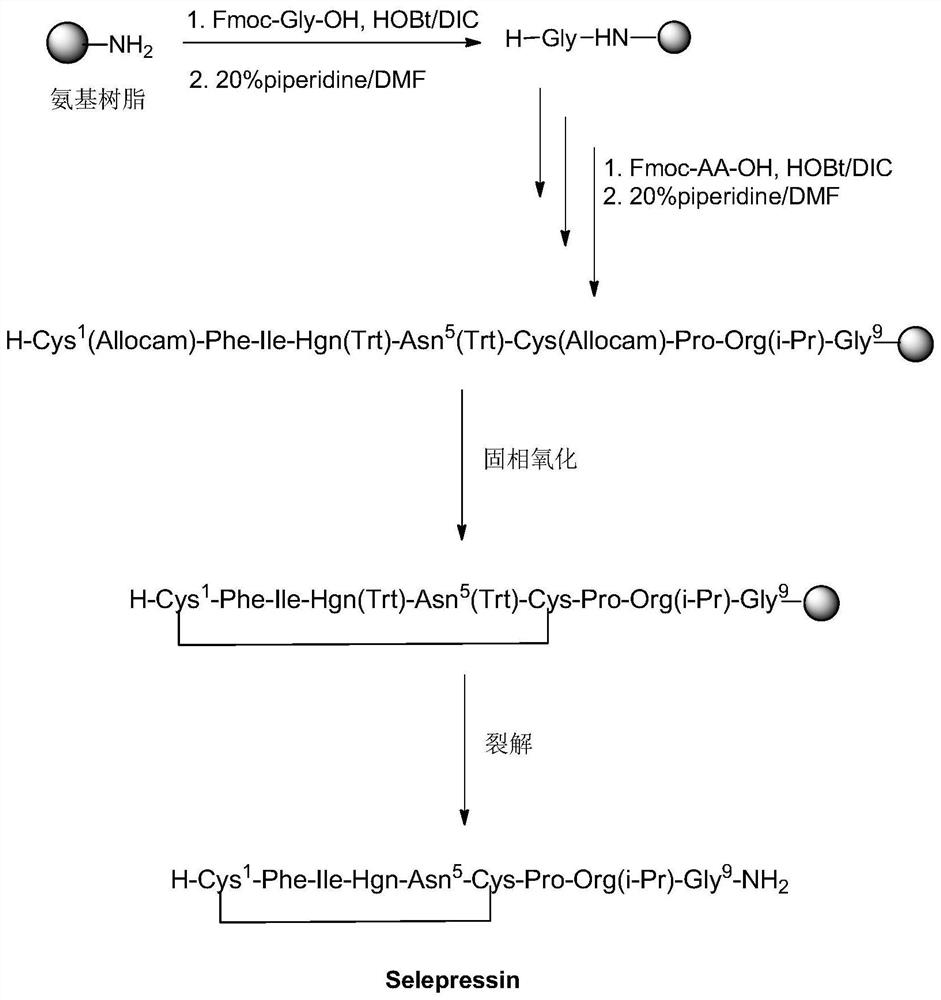
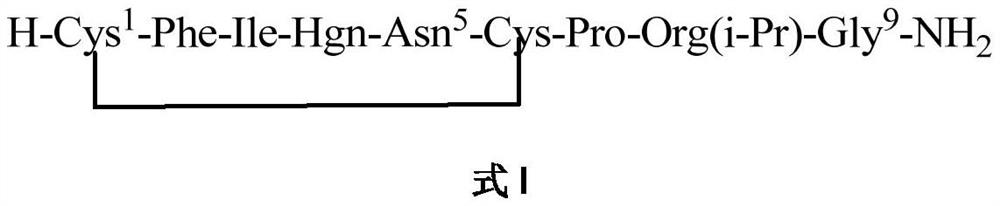
A method for solid-phase synthesis of vasopressin receptor peptide agonist selepressin
ActiveCN109748950BImprove reaction efficiencyEasy to operatePeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionAmino acid synthesisDisulfide bonding
Owner:HYBIO PHARMA
A kind of preparation method of thiocarbamate compound
ActiveCN109503442BReduce usageSimple and fast operationFunctional group formation/introductionThiocarbamatePhosphoric Acid Esters
The invention belongs to the field of synthesis of a compound, relates to a preparation method of a thiocarbamate compound, in particular to a method for synthesizing thiocarbamate through reacting ofcatalyzing three components of sodium sulfinate, isonitrile and water by iodine. The method comprises the following steps: adding the sodium sulfinate, the isonitrile and the water into ethyl acetate, then adding a molecular iodine catalyst and a phosphite reducing agent, heating, stirring and reacting for 6 to 10 hours under a condition that the temperature is 80 to 100 DEG C, and extracting, separating and purifying after finishing the reaction, thus obtaining the thiocarbamate. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the isonitrile is adopted as a carbon source, so that poisonous photogene and carbon monoxide are prevented from being used; odorless sodium sulfinate is adopted as a sulfur source, so that odorous thiophenol or thiol is prevented from being used; non-metalliciodine is adopted for catalyzing, so that a metal reagent is prevented from being used; the reaction has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient, the technology is safe, environmentfriendliness is realized, and the like.
Owner:QUFU NORMAL UNIV
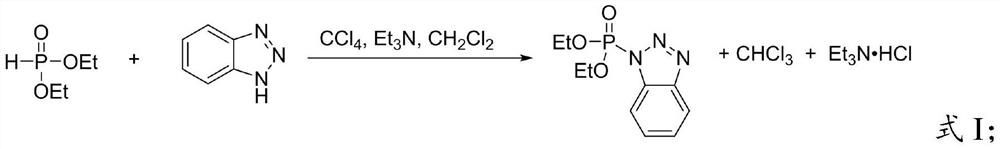
Preparation method of benzotriazole diethyl phosphate
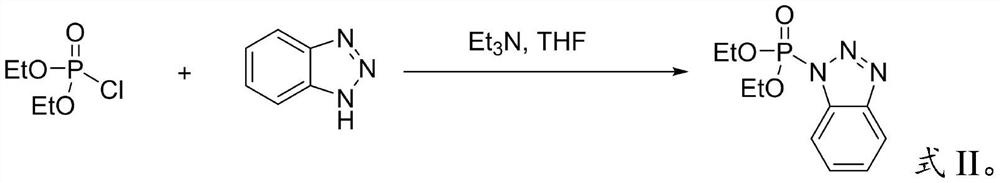
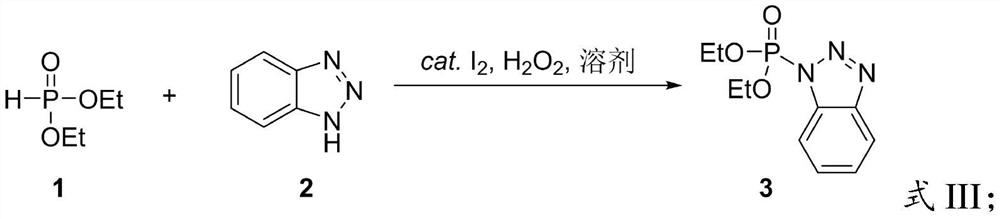
PendingCN113816995AEasy to separateHigh yieldGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDiethyl phosphatePhosphorous acid
The invention provides a preparation method of benzotriazole diethyl phosphate, which belongs to the field of organic synthesis. The method comprises the following steps of mixing diethyl phosphite, benzotriazole, an oxidant and an iodine catalyst, and carrying out oxidative coupling reaction to obtain benzotriazole diethyl phosphate. The oxidant is hydrogen peroxide or tert-butyl hydroperoxide, and the iodine catalyst is I2 or a compound containing iodide ions. According to the method, the benzotriazole diethyl phosphate is prepared through one-step reaction by using green oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide and hydrogen peroxide tert-butyl alcohol under the condition of an iodine catalyst, carbon tetrachloride with high toxicity or phosphoryl chloride with high corrosivity is not used, the reaction conditions are more green, toxic wastes are not generated, the reaction steps are simple, the conditions are mild, and the product is easy to separate and high in yield.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIV OF WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC POWER
Maleimide carbazole compound and synthesis method thereof
PendingCN114539266AOvercome people, wealthOvercoming the huge waste of goodsOrganic chemistryCyclohexanonePtru catalyst
The invention mainly relates to a synthesis method of maleimide carbazole and derivatives thereof, and adopts the technical scheme that maleimide carbazole and derivatives thereof are prepared from 2-(3-indolyl) cyclohexanone compounds and maleic imide compounds as raw materials in an oxygen atmosphere under the action of an iodine catalyst and acid. The synthesis method overcomes the defects that the existing synthesis method of the maleimide and carbazole compound has complex synthesis steps, can be completed by adopting a multi-step synthesis process, or needs to use a metal catalyst and an equivalent metal oxidant, and the like. The method has the advantages of simple and mild reaction conditions, no need of adding a transition metal catalyst or a reaction solvent, simplicity and convenience in operation, wide raw material source, wide substrate range, good atom economy, high yield and the like. The maleimide carbazole derivative and the synthesis method thereof can be used in a plurality of industrial production fields such as medicines, pesticides, dyes, organic functional materials and the like.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
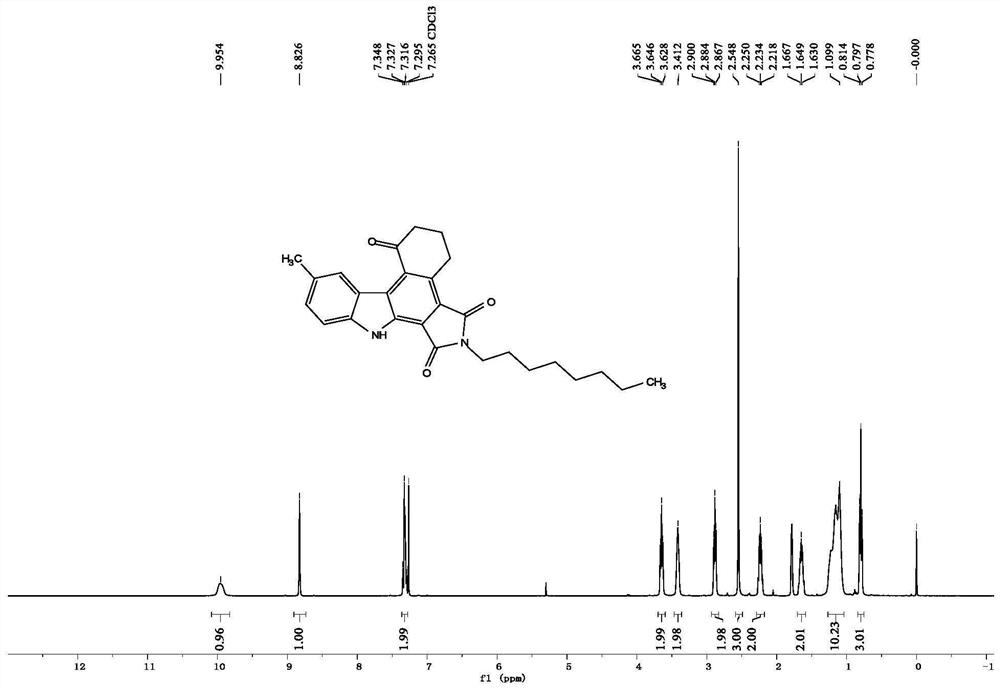
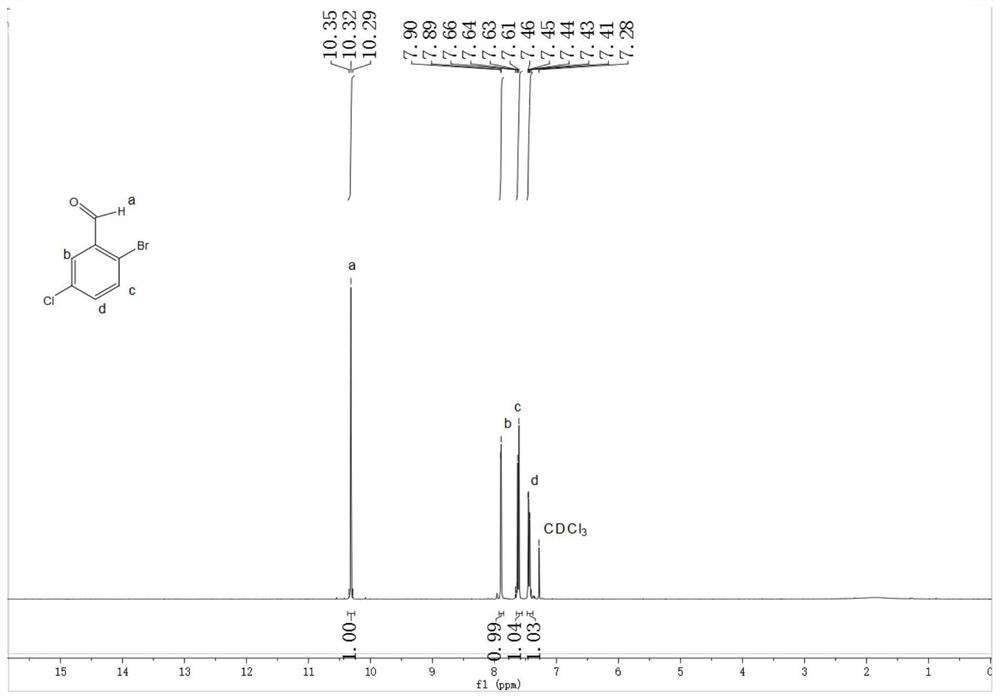
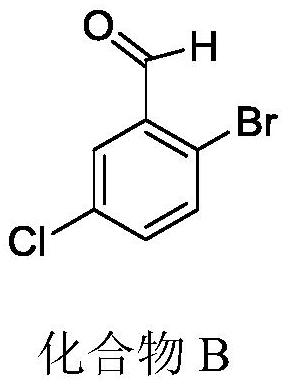
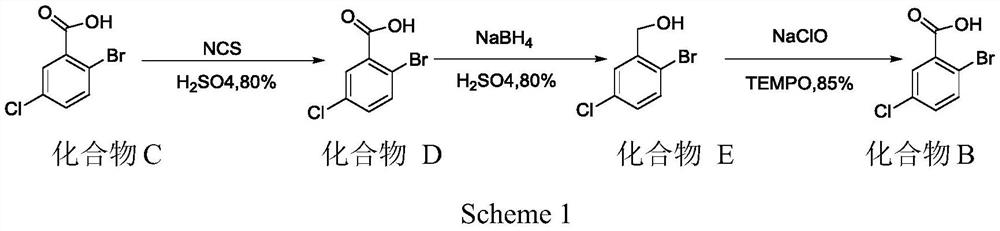
A kind of preparation method of 2-bromo-5-chlorobenzaldehyde
ActiveCN107879918BHigh yieldEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationChlorobenzenePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method of 2-bromo-5-chlorobenzaldehyde, which is characterized in that the steps are: a. In an inorganic strong acid solvent, control the temperature of the system to ≤10°C and slowly add 3-chlorobenzene successively dropwise Formaldehyde, iodine-containing catalyst; b. Control the temperature of the system to ≤15°C and add N-bromosuccinimide NBS several times in batches; c. After keeping the temperature for 2-10 hours, raise the temperature to 25-55°C to continue the reaction for 1- 6h; The solid product was obtained after post-processing. The present invention has one-step reaction, higher yield up to 90%, simpler operation, low cost, easy to obtain raw materials, less pollution to the environment, and only acid in the waste liquid, which can be neutralized with lye, more suitable The need for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Iodide ion detection reagent based on iodide catalyzed hydrazine-[oxidant-Ferroin reagent] and iodide ion detection method Iodide ion detection reagent based on iodide catalyzed hydrazine-[oxidant-Ferroin reagent] and iodide ion detection method](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/288e4589-063a-4305-bcd0-6ebd9831d031/HDA0001764659730000011.png)
![Iodide ion detection reagent based on iodide catalyzed hydrazine-[oxidant-Ferroin reagent] and iodide ion detection method Iodide ion detection reagent based on iodide catalyzed hydrazine-[oxidant-Ferroin reagent] and iodide ion detection method](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/288e4589-063a-4305-bcd0-6ebd9831d031/HDA0001764659730000012.png)
![Iodide ion detection reagent based on iodide catalyzed hydrazine-[oxidant-Ferroin reagent] and iodide ion detection method Iodide ion detection reagent based on iodide catalyzed hydrazine-[oxidant-Ferroin reagent] and iodide ion detection method](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/288e4589-063a-4305-bcd0-6ebd9831d031/HDA0001764659730000021.png)