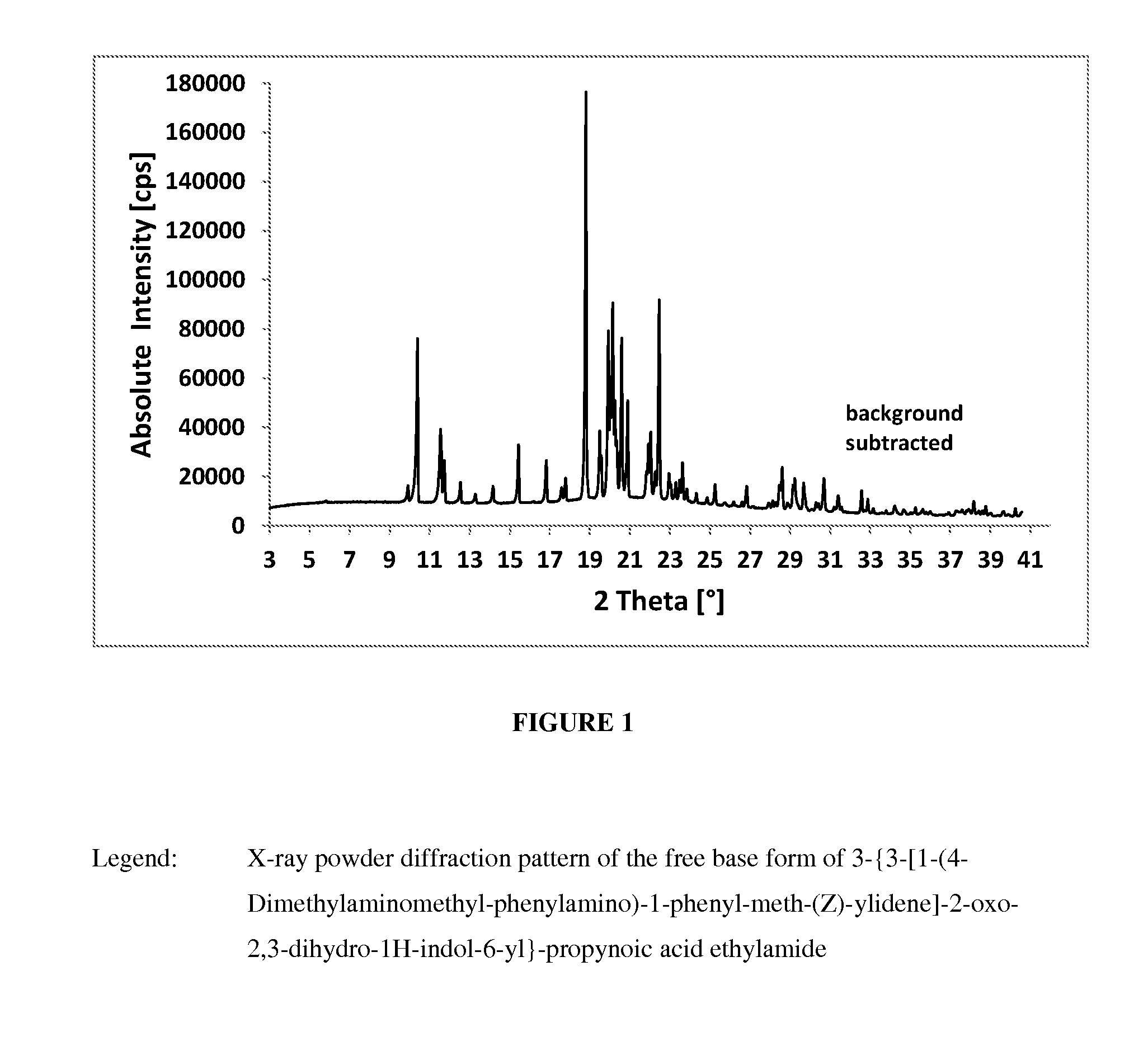
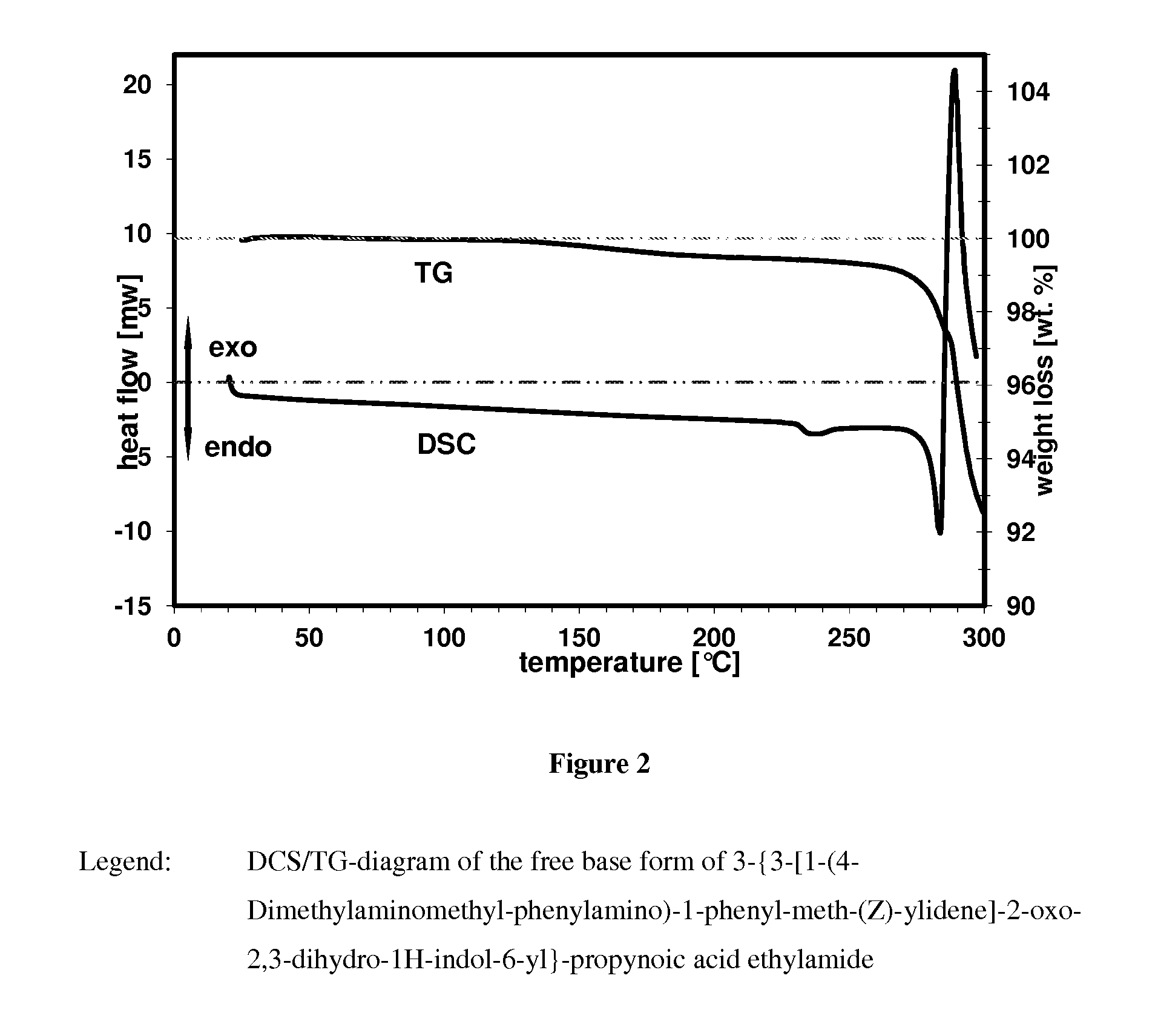
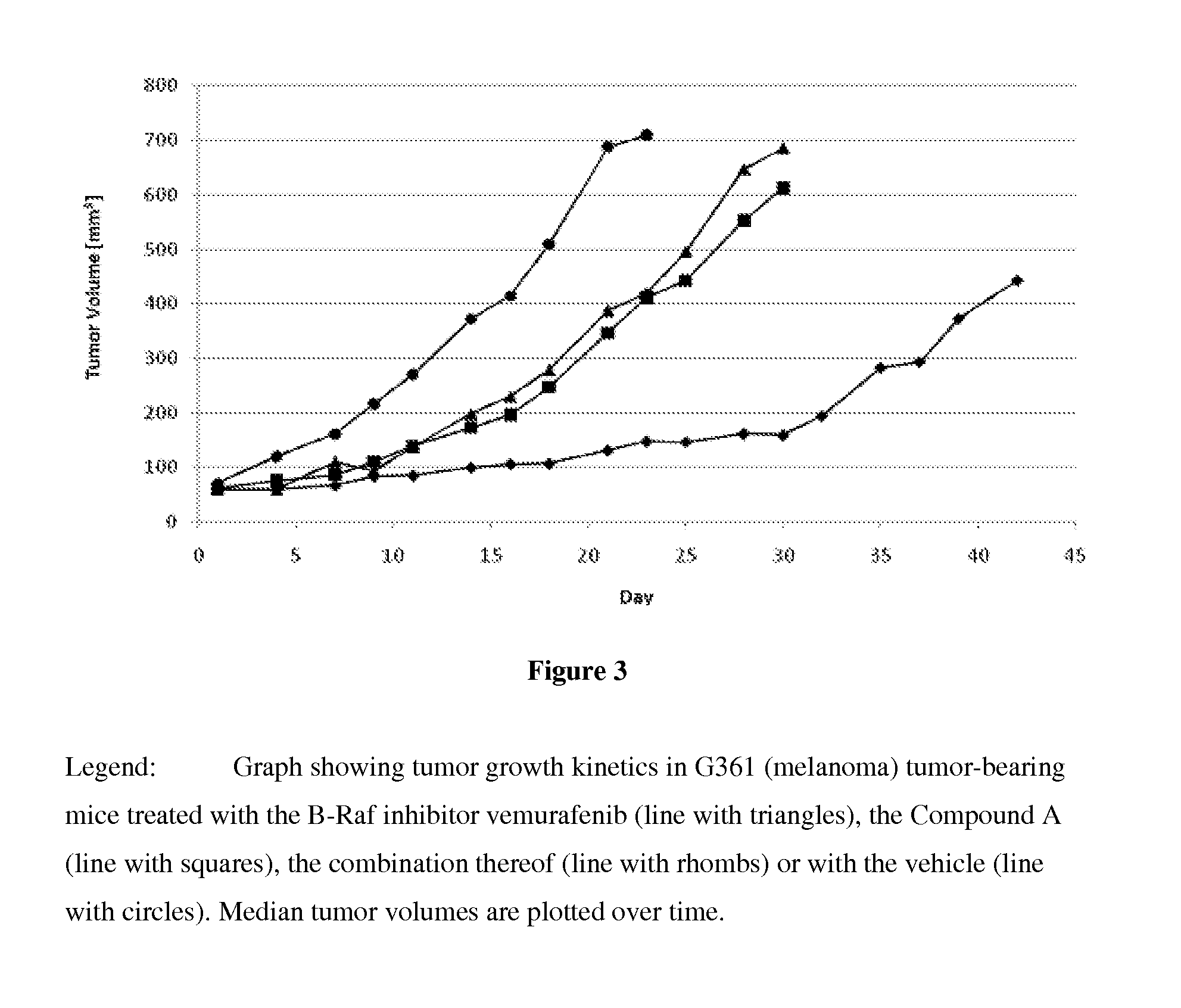
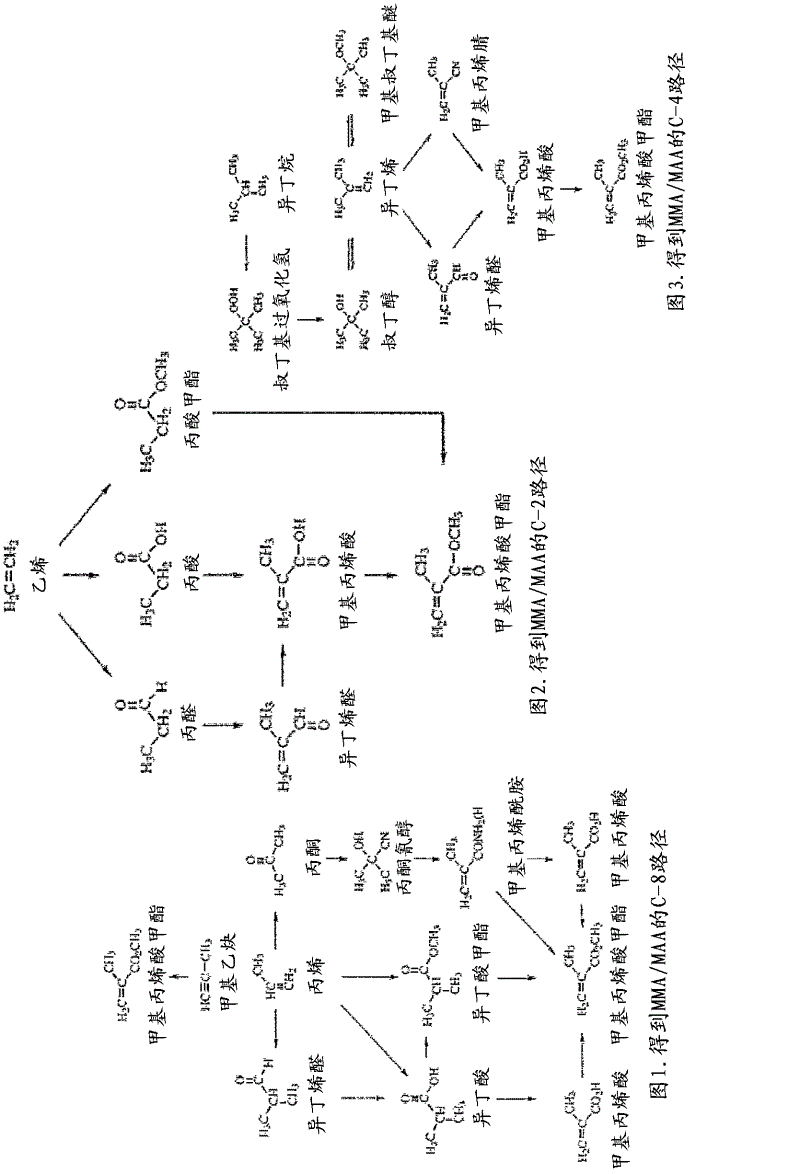
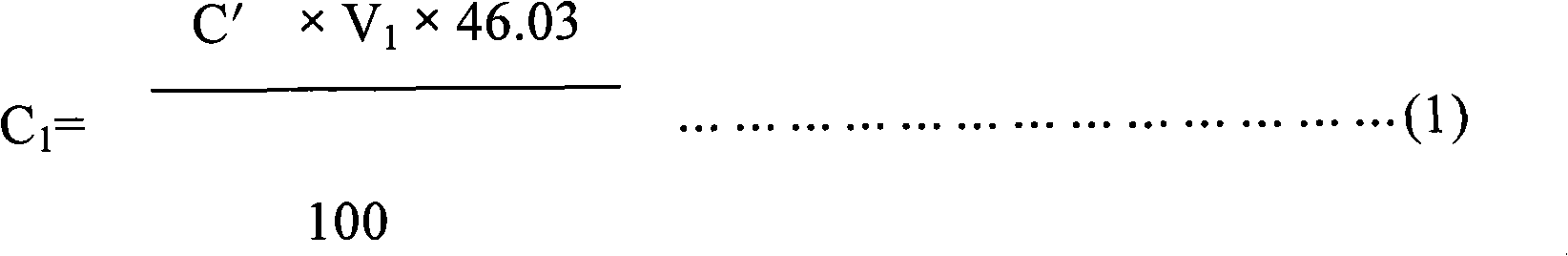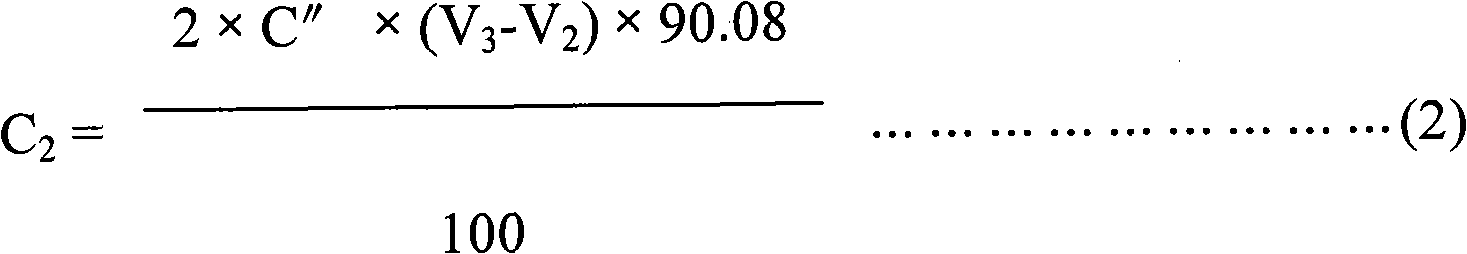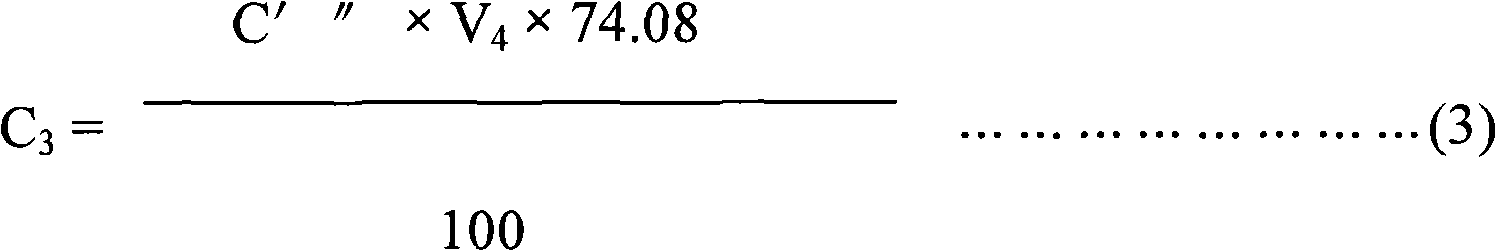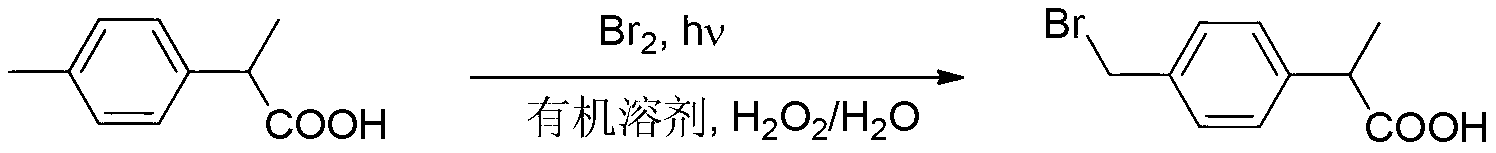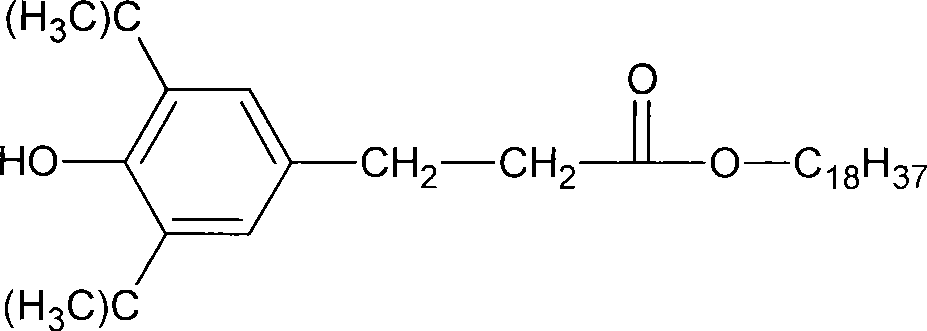Patents
Literature
172 results about "Propynoic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Propionic acid (from the Greek words protos, meaning "first", and pion, meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula C2H5COOH. It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor.
Method of reducing the sucrose ester concentration of a tobacco mixture
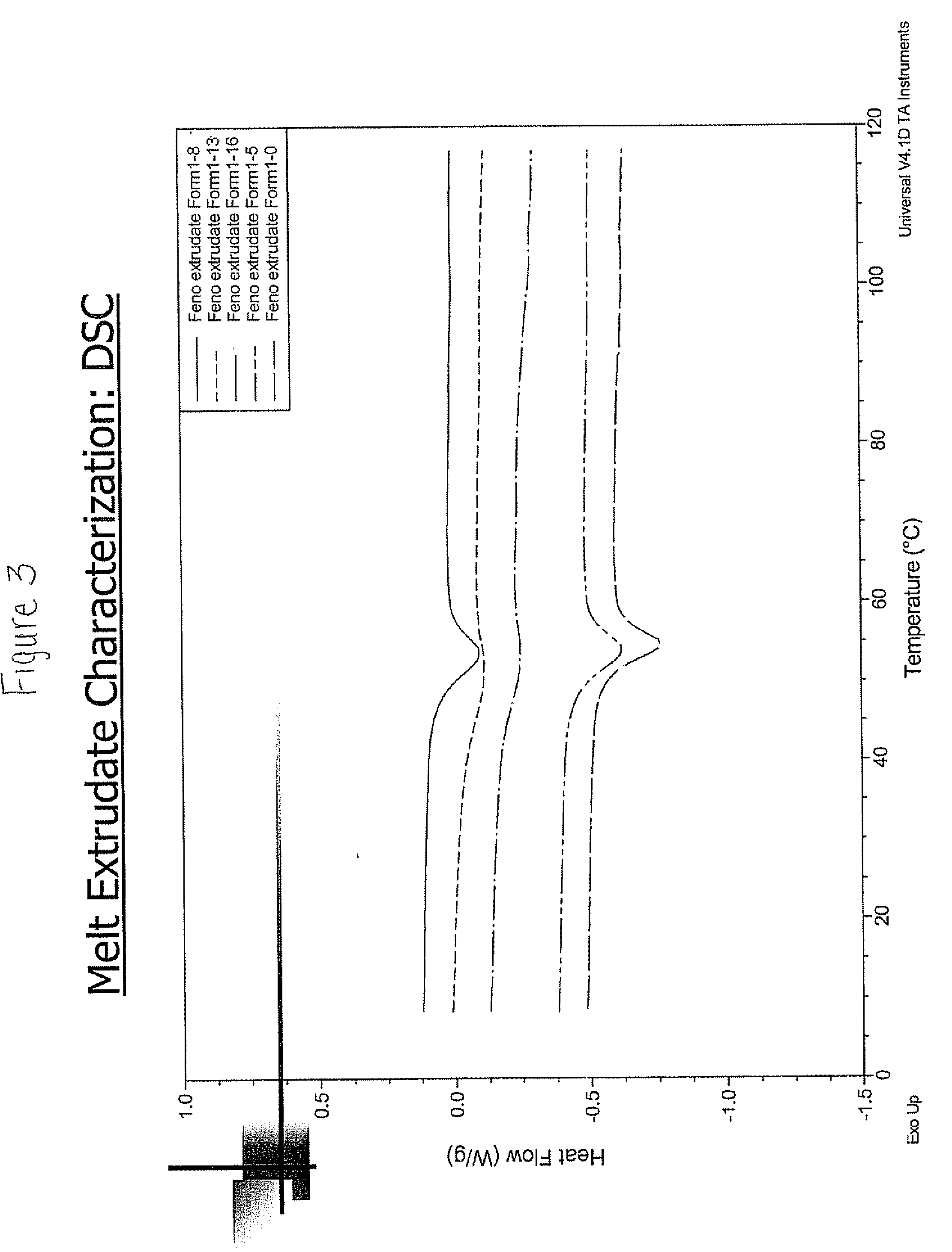
InactiveUS7025066B2Altering flavorAltering aroma characteristicTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentFlavor3-methylbutyric acid
The flavor and aroma characteristics of the smoke of a tobacco blend incorporating Oriental tobacco are improved by subjecting that blend to heat treatment. Oriental tobacco having a relatively high sucrose ester content is combined with a second dissimilar Oriental tobacco material and / or a non-Oriental tobacco material to form a tobacco mixture, and that mixture is heated for a time and under conditions sufficient to reduce the concentration of sucrose esters in the Oriental tobacco. Tobacco blends having reduced levels of sucrose esters yield smoke that does not possess undesirable off-notes provided by pyrolysis products of those sucrose esters; namely, 2-methylpropionic acid, 3-methylbutyric acid and 3-methylpentanoic acid.
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Propanoic acid polyhexamethylene guanide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101037503AOvercome strong hygroscopicityImprove the bactericidal effectBiocideFungicidesPolyhexamethylene guanidinePropynoic acid
The invention discloses polyhexamethylene guanidine propionic acid and preparing method thereof. The preparing method employs stepwise synthesis, which includes steps of: sufficiently mixing dicyandiamide and alanine under high temperature to synthesize aminoguanidine propionic acid, mixing the aminoguanidine propionic acid, triethylidenepropyldiamine and initiator under high temperature to synthesize the polyhexamethylene guanidine propionic acid. Advantages of the invention are: sterilization effect is excellent, toxity is actually nontoxic level, effect of sterilization is better than existent technique, due to overcoming strong hygroscopicity in existence, the polyhexamethylene guanidine propionic acid can be produced to stable powder, thereby being widely used in fields such as weave, plastic, daily chemicals and water treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIPOLY IND
Pharmaceutical compositions
InactiveUS20070048384A1Improve bioavailabilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsMedicinePropynoic acid
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising primarily amorphous 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid, 1-methylethyl ester.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Pharmaceutical compositions
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising primarily amorphous 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid, 1-methylethyl ester.
Owner:ROSENBERG JOERG +5
Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-polyurethane-polypeptide block-graft copolymer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102336913AEasy to preparePrecise control of relative contentPolypropylene glycolN isopropyl acrylamide
The invention relates to a poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-polyurethane-polypeptide block-graft copolymer and a preparation method thereof. In the copolymer, the molecular weight of polyurethane is 10000-60000; the molecular weight of poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) is 3000-10000; and the molecular weight of polypeptide is 500-4000. The preparation method comprises the steps: 1) synthesis of polyurethane containing side carboxyl group and terminal double-bond group: adding diisocyanate, polypropylene glycol, polyethylene glycol, a catalyst and a solvent to a reaction bottle and reacting, then sequentially adding bis(hydroxymethyl) propanoic acid, butylene glycol and hydroxypropyl acrylate and reacting; 2) synthesis of poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-polyurethane block copolymer: adding polyurethane containing side carboxyl group and terminal double-bond group, a solvent and an initiator, and isopropyl acrylamide to a reactor and reacting; and 3) adding poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-polyurethane block copolymer, a solvent, a condensing agent, and a polypeptide homopolymer to a reactor and reacting to obtain a target product with temperature and pH dual responsibility.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Controlled Drug Delivery Using a Zein Layer Modified with Levulinic Acid
The disclosure relates to medical devices coated with zein admixed with levulinic acid. The medical device may further include a therapeutic agent in contact with zein admixed with levulinic acid. Zein admixed with levulinic acid allows the therapeutic agent to be retained on the device during delivery and also controls the elution rate of the therapeutic agent following implantation. The disclosure further relates to methods of delivering a therapeutic agent on said medical devices as well as their use especially in the form of stents for prevention of restenosis.
Owner:MED INST INC +1
High-hardness micrometer grinding fluid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102311717AEasy to useMeet the requirements of thinning grinding processOther chemical processesPolyethylene glycolMechanical property
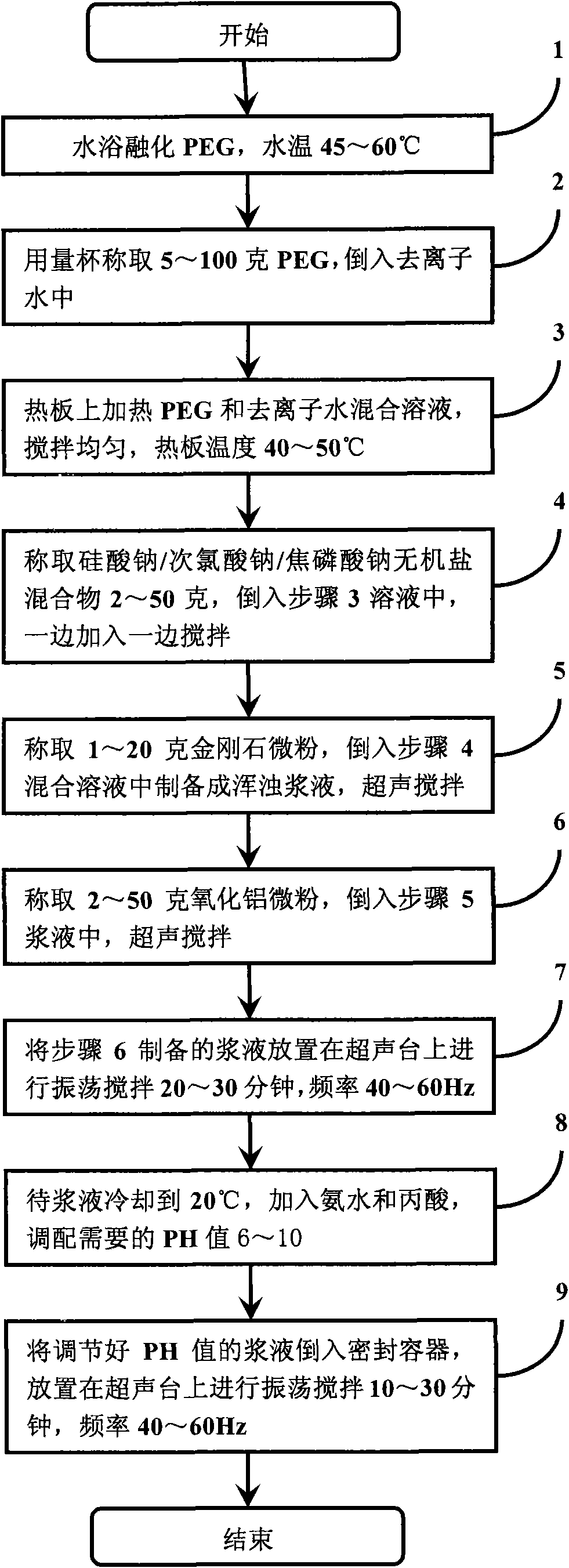
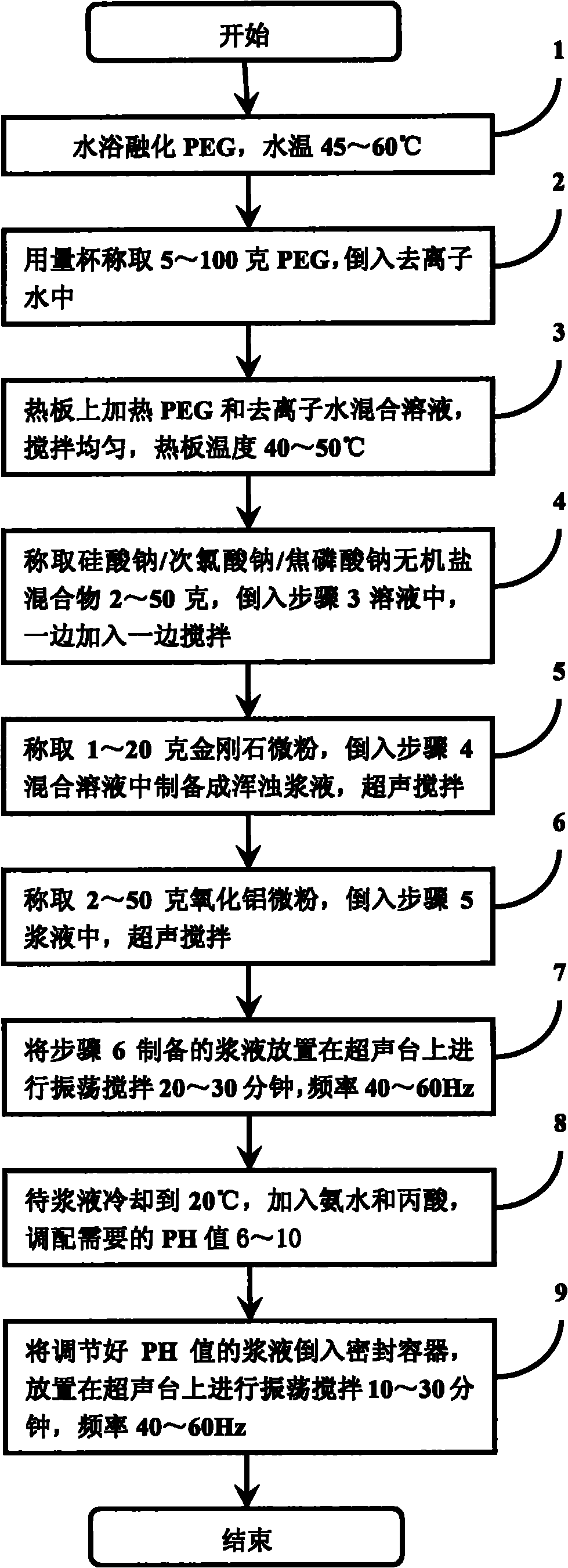
The invention discloses high-hardness micrometer grinding fluid and a preparation method thereof. The grinding fluid is prepared from the following materials in percentage by mass: 0.1 to 2.0 percent of monocrystal artificial diamond micro powder, 0.2 to 5.0 percent of aluminum oxide micro powder, 0.2 to 5.0 percent of inorganic salt mixture, 0.5 to 10 percent of organic matter polyethylene glycol (PEG) 200, 0.01 to 1 percent of ammonia water, 0.01 to 1 percent of propanoic acid and 78 to 98.5 percent of deionized water. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the grinding fluid. When the high-hardness micrometer grinding fluid and the preparation method thereof, which are provided by the invention, are used, high-hardness micrometer grinding material is adopted for blending the grinding fluid, the using effect is ideal, the mechanical properties are balanced, and the requirements of a GaN epitaxy substrate (silicon carbide, sapphire) thinning grinding process are met.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process For Production Of Acrylic Acid Or Its Derivatives
InactiveUS20130274517A1Organic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAcetic acidAcid derivative
Processes for the catalytic dehydration of hydroxypropionic acid, hydroxypropionic acid derivatives, or mixtures thereof to acrylic acid, acrylic acid derivatives, or mixtures thereof with high yield and selectivity and without significant conversion to undesired side products, such as, acetaldehyde, propanoic acid, and acetic acid, are provided. The processes can be carried out either in a gas phase or in a liquid phase.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method for simultaneously measuring contents of multiple organic acids in feeder acidulant
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously measuring contents of multiple organic acids in feeder acidulant. The method comprises the following steps: (1) respectively preparing standard storage stock solutions of formic acid, lactic acid, citric acid, fumaric acid and propanoic acid, and preparing a mixed standard solution by mixing and volume determination; (2) diluting the feeder acidulant specimen to be measured for 500-2,000 times; (3) filtering the diluted specimen solution, injecting 5-20 microlitres of specimen solution into a liquid chromatograph, and recording a chromatomapat the wave length of 210 nm under the condition that the flowing speed of the flowing phase is 0.6-1.0 mL / min; taking the same amount of mixed standard solution to measure by the method, and calculating the contents of the organic acids in the specimen by the peak area through an outer calibration method. The invention can simultaneously obtain content analyzing results of the formic acid, the lactic acid, the citric acid, the fumaric acid and the propanoic acid by using the specimen once under the condition of same chromatogram, and has the advantages of simplicity, convenience and high accuracy.
Owner:安徽泰格生物技术股份有限公司
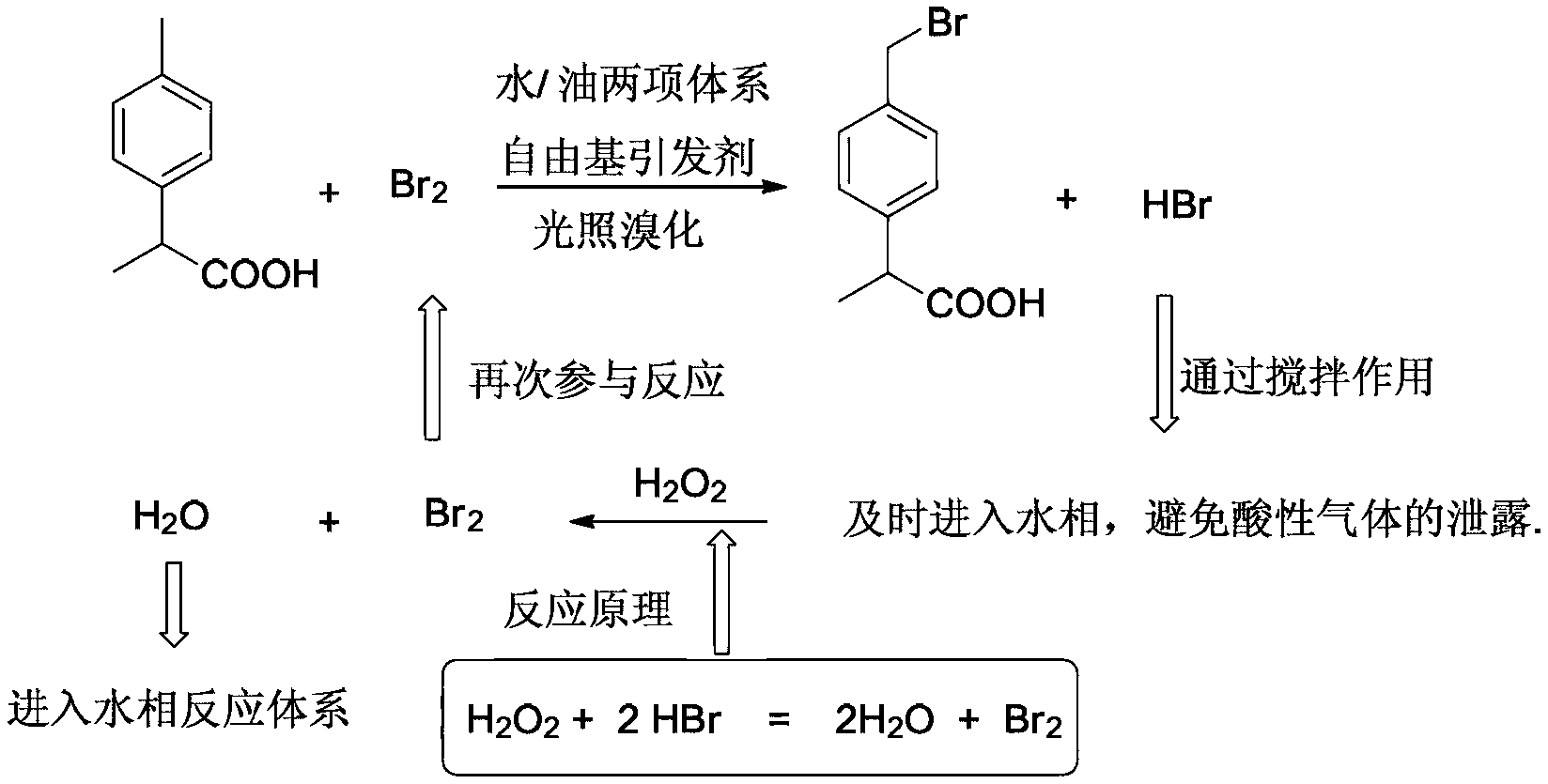
Environment-friendly preparation method of 2 - (4 - Bromomethylphenyl) propionic acid based on two-phase free radical reaction
InactiveCN103265426AHigh selectivityReduce dosageOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationPollutionPhotochemistry
The invention discloses an environment-friendly preparation method of 2 - (4 - Bromomethylphenyl) propionic acid based on two-phase free radical reaction, wherein 2 -(4-Bromomethylphenyl) propanoic acid is taken as starting material, and elemental bromine is adopted, and a two phrase mixture reaction system that mixes aqueous phase with organic solvent replaces other reaction systems of single organic solvent; the reaction is initiated by free radical in the two-phase system, or by light or radical initiator; then hydrobromic acid is oxidized with the aid of clean oxidation of hydrogen peroxide so as to get bromine, and the obtained bromine could involve in bromination reaction further, which could obtain 2-(4-bromomethylphenyl) propanoic acid with a better yield and bromide utilization. The product provided by the invention overcomes lots of shortcomings of the existing bromination method, and has the advantages of low cost and environment friendly, and realizes zero pollution in the process of production. Consequently, synthetic process and yield of 2-(4-bromomethylphenyl) propanoic acid are promoted remarkably, and it is very suitable for large scale industrial green production.
Owner:FUJIAN SANTAI BIO PHARM +1
Solid forms of (s)-2-amino-3-(4-(2-amino-6-((r)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(3'-methoxybiphenyl-4-yl)ethoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)phenyl)propanoic acid and methods of their use
Solid forms of (S)-2-amino-3-(4-(2-amino-6-((R)-2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(3′-methoxybiphenyl-4-yl)ethoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl)phenyl)propanoic acid and salts thereof are disclosed.
Owner:LEXICON PHARM INC
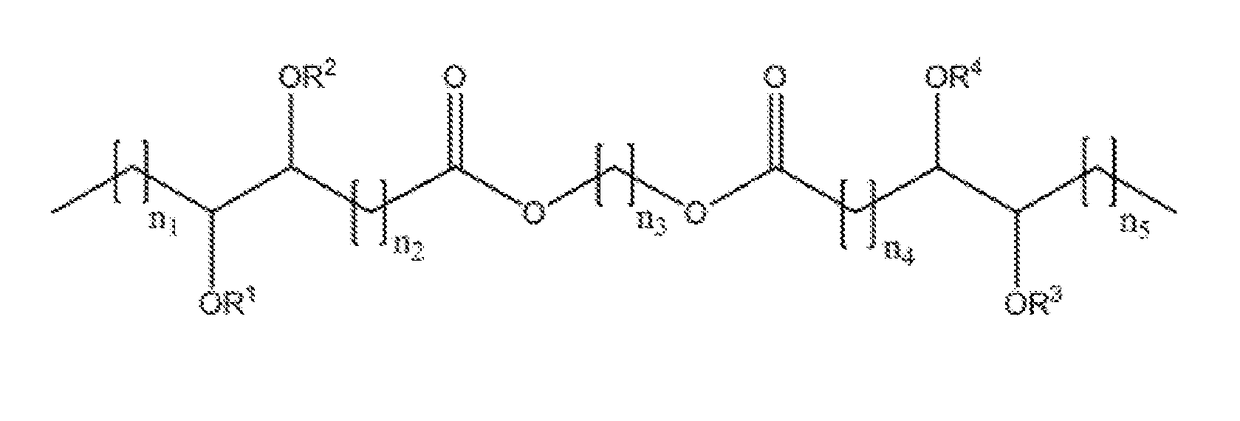
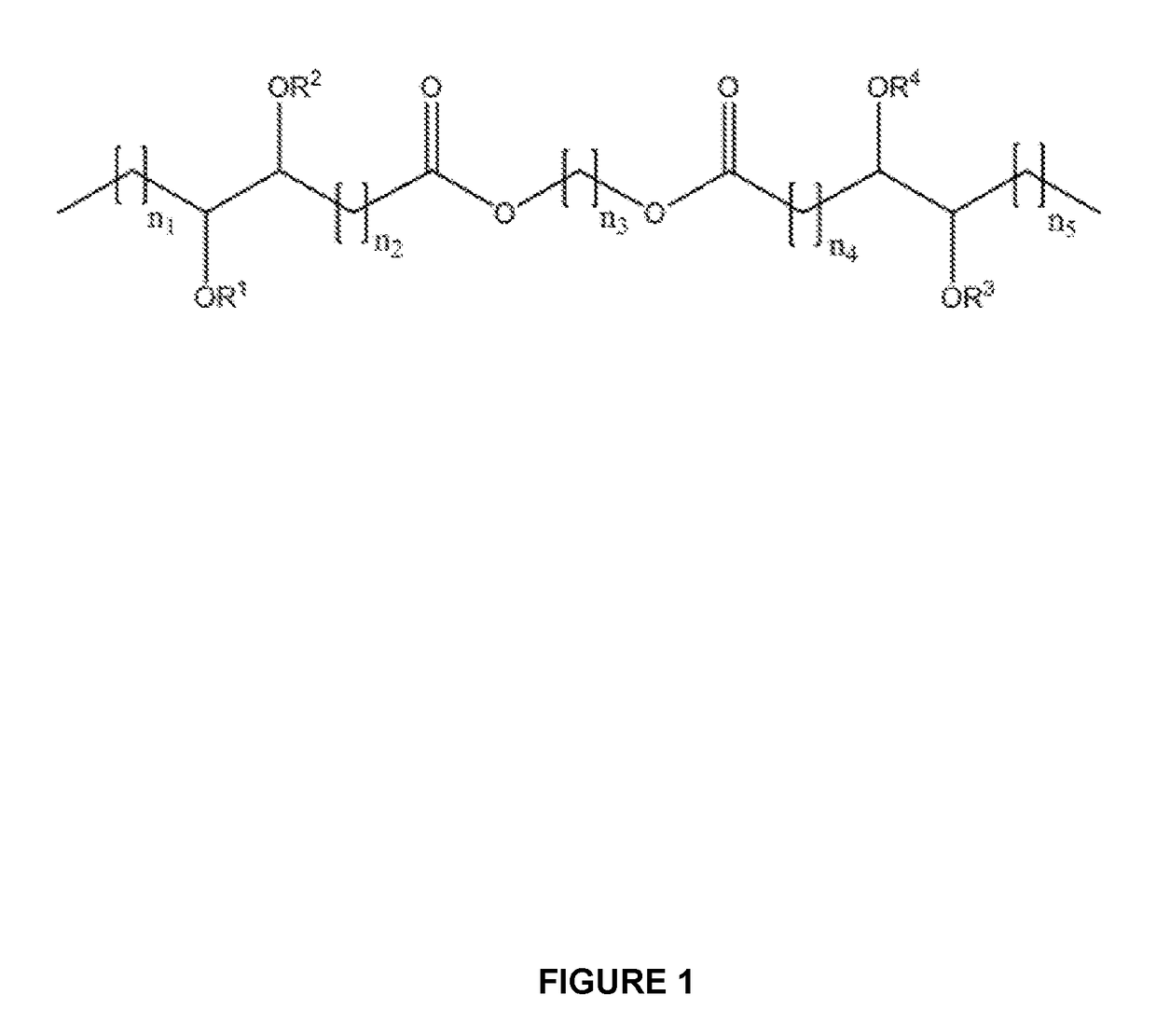
Branched diesters and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20170137739A1High viscosityImprove low temperature performanceOrganic chemistryLiquid carbonaceous fuelsVegetable oilSolvent free
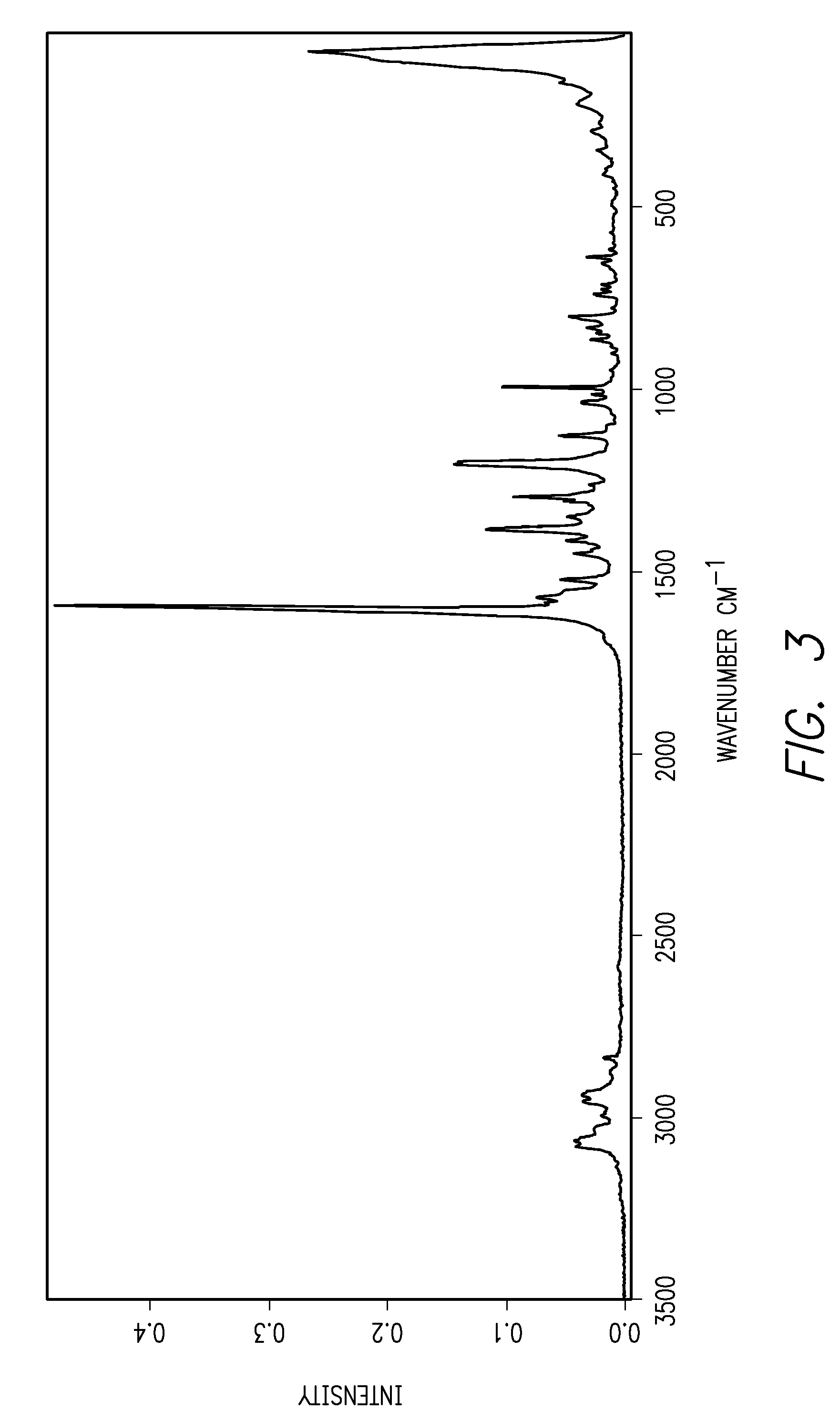
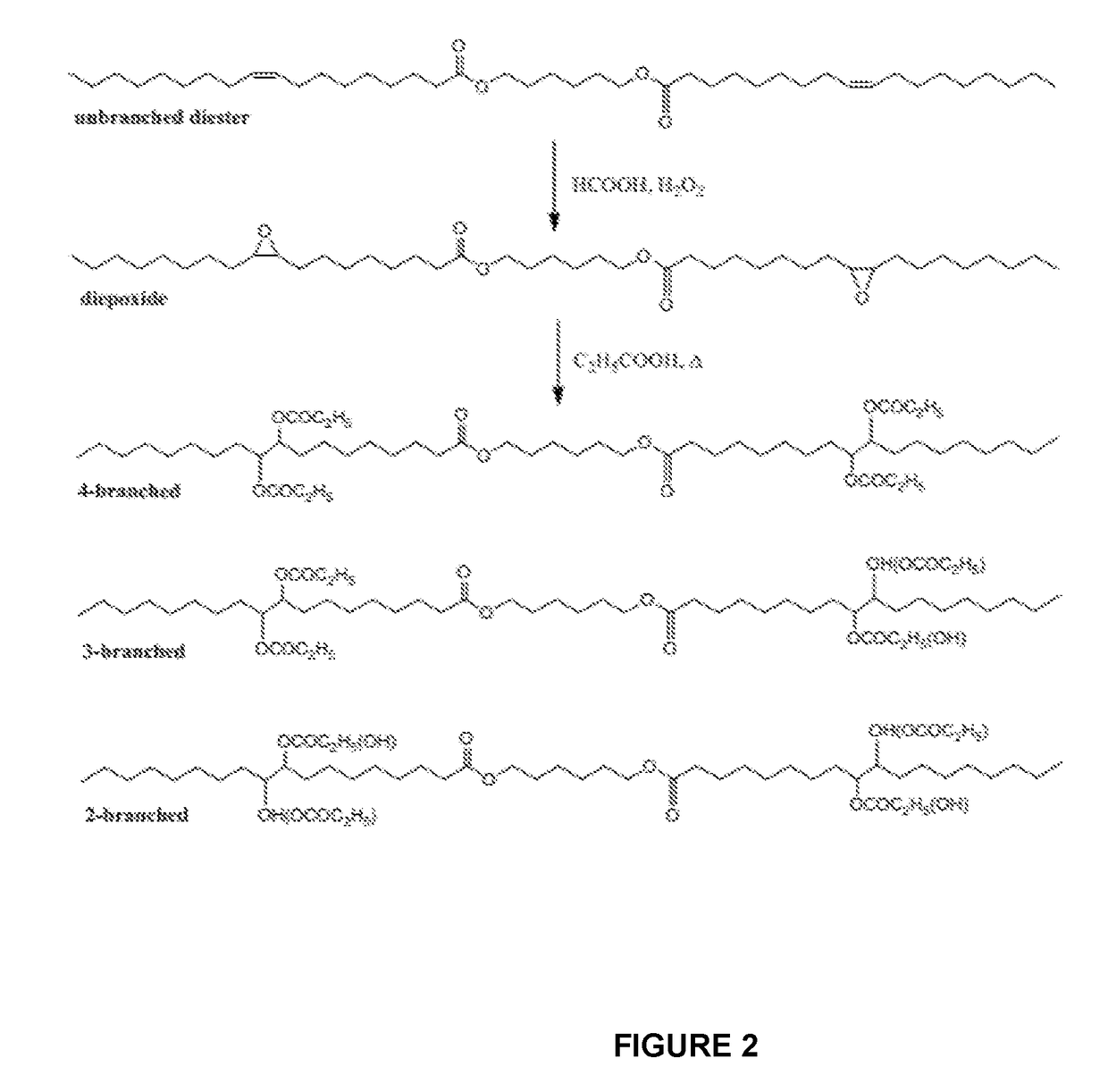
The disclosure generally provides branched diester compounds having exceptional low-temperature and flow properties. The disclosure also provides uses of the branched diester compounds in lubricant compositions, for example, as a base oil, and in other applications where their low-temperature and flow properties can be employed beneficially. The disclosure also provides efficient and green methods for making the branched diester compounds.In certain embodiments, a vegetable oil-based diester (1,6-hexyldioleate) was branched with propanoic acid (C3) using a green synthetic approach involving solvent-free and catalyst-free epoxide ring opening followed by in situ normal esterification. A total of three branched ester derivatives possessing varied numbers of internal protruding branched ester groups and hydroxyl groups were obtained. All of the pure branched derivatives were comprised of mixtures of positional isomers and / or stereoisomers. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) showed that regardless of the composition inhomogeneity of each branched derivative, crystallization was suppressed completely in all of the branched compounds, and they all demonstrated glass transitions below −65° C.Without being bound by any theory, it is believed that this unique thermal behavior is attributed to the internal protruding branched moieties and hydroxyl groups, which dramatically slowed down mass transfer starting with the least branched compound (2-branched derivative). The viscosity of the branched compounds was one order of magnitude larger than that of the starting di ester due to the increased branching and increased resistance to flow associated with hydrogen bonding introduced by the OH groups. Overall, these branched diesters demonstrated superior low temperature and flow properties comparable to existing non-sustainable commercial lubricants and analogous biobased materials which makes them suitable alternatives for use in lubricant formulations particularly in high performance industrial gear and bearing lubricants.
Owner:TRENT UNIVERSITY
Crystalline form of a indolinone derivative and its use
InactiveUS20140018372A1Treating and preventing disorderAvoid adjustmentBiocideOrganic chemistryMeth-Propynoic acid
A crystalline form of 3-{3-[1-(4-Dimethylaminomethyl-phenylamino)-1-phenyl-meth-(Z)-ylidene]-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-6-yl}-propynoic acid ethylamide.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
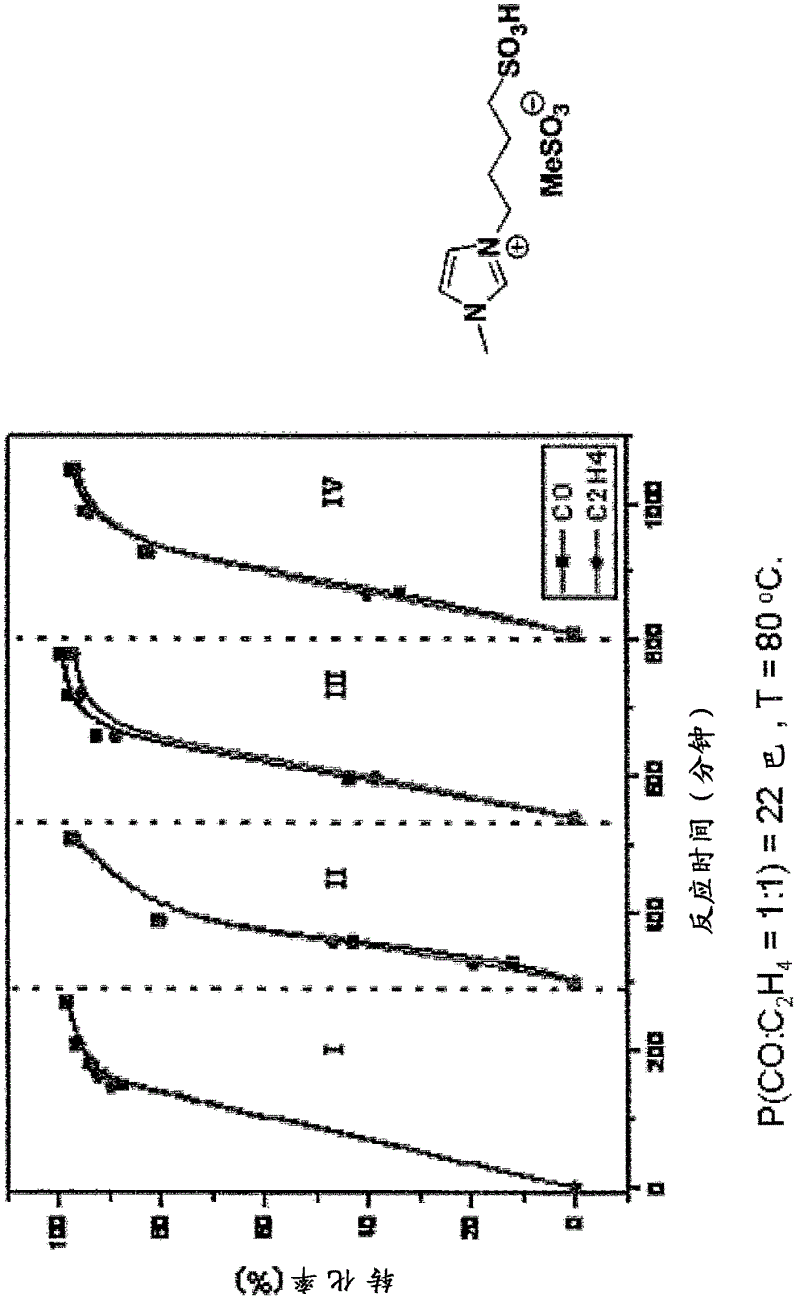
Palladium catalyst system comprising zwitterion and/or acid-functionalized ionic liquid
InactiveCN102625731AOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPalladium catalystIonic liquid
The present invention concerns a catalyst system in particular a catalyst system comprising Palladium (Pd), a zwitterion and / or an acid-functionalized ionic liquid, and one or more phosphine ligands, wherein the Pd catalyst can be provided by a complex precursor, such as Pd(CH3COO)2, PdCI2, Pd(CH3COCHCOCH3), Pd (CF3COO)2, Pd(PPh3)4 or Pd2(dibenzylideneacetone)3. Such catalyst systems can be used for e.g. alkoxycarbonylation reactions, carboxylation reactions, and / or in a co-polymerization reaction, e.g. in the production of methyl propionate and / or propanoic acid, optionally in processes forming methyl methacrylate and / or methacrylic acid. Catalyst systems according to the invention are suitable for reactions forming separable product and catalyst phases and supported ionic liquid phase SILP applications.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Expanding flame-retardant silicone rubber and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to expanding flame-retardant silicone rubber and a preparation method thereof. The expanding flame-retardant silicone rubber consists of the following components in parts by weight: 90 to 95 parts of vinyl-terminated polysiloxane, 5 to 10 parts of hydrogen-containing polysiloxane, 0.3 to 0.5 part of a catalyst and 20 to 30 parts of an expanding flame retardant, wherein the expanding flame retardant consists of ammonium polyphosphate, tetra[beta-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid]pentaerythritol ester and a melamine-polyimide supermolecular network composite material. A supermolecular technology is adopted to modify the flame retardant and prepare the flame-retardant silicone rubber, so that the combustion performance of the obtained silicone rubber is obviously reduced, the mechanical performance, the heat stability and the flame retardance can be remarkably improved, and the application fields are broadened.
Owner:北京勇搏科技有限公司
Quantitative quality control method of herbal tea product
InactiveCN103808829AEffective quality controlAccurate quality controlComponent separationFlos chrysanthemiGLYCYRRHIZA EXTRACT
The invention discloses a quantitative quality control method of a herbal tea product, the herbal tea is the product prepared by using mesona chinensis, plumeria rubra, microcos paniculata, flos chrysanthemi, honeysuckle, selfheal and liquorice as raw materials, and the aim of effectively controlling the product quality is achieved by quantitatively determining three feature components in the product: tanshinol, (alpha)-3-carboxy-alpha-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid and rosmarinic acid. The method can be used for performing content determination and quantitative quality control on the herbal tea product and a raw material extract so as to effectively guarantee the quality and stability of the produced herbal tea, thereby well guaranteeing the safety of vast consumer. The quantitative quality control on three components of the herbal tea product adopts the high performance liquid chromatography, the content ranges of the three feature components including tanshinol, (alpha)-3-carboxy-alpha-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid and rosmarinic acid in qualified raw material extract are respectively 0.01wt-45wt%, the content range of each component in the quality herbal tea beverage product is respectively 0.1-5000microgram / mL.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Extraction method of benzothiophene
ActiveCN103361107AImprove extraction efficiencyHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryHydrocarbon oils refiningTetra-n-butylammonium chlorideN octane
The invention relates to an extraction method of benzothiophene, belonging to the field of extraction and separation. The extraction method of the benzothiophene comprises the step of enabling an extraction agent to be in contact with a mixture, wherein the extraction agent is a deep-eutectic solvent constituted by tetra-n-butylammonium chloride and propanoic acid according to the molar ratio of (1: 1)-(1: 5); and the mixture is constituted by the benzothiophene and n-octane. The extraction method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high extraction efficiency, strong selectivity, capability of deeply removing the benzothiophene to below 10ppm, mild operation conditions and environmental friendliness.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
Electrochemical polishing electrolytic solution of zirconium alloy and electrochemical polishing method of electrochemical polishing electrolytic solution
The invention discloses an electrochemical polishing electrolytic solution of zirconium alloy and an electrochemical polishing method of the electrochemical polishing electrolytic solution. The formula is composed of perchloric acid, anhydrous acetic acid and propanoic acid, and is an anhydrous formula; the formula can effectively remove small scratches on the surface of the zirconium alloy and impurities generated in a sand papering polishing process and the like at room temperature, thereby obtaining a good polishing surface and having the advantages of strong practicability, high efficiency, long service life of the solution and the like; and the formula also can be used for zirconium alloy with different components and different shapes. The electrochemical polishing method of the formula can be used for surface pretreatment during operations such as sputtering, electroplating and the like of zirconium alloy, and also can be used for final treatment of devices made of zirconium alloy, thus the application range is wide..
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing yttrium barium copper oxide high-temperature superconducting film
InactiveCN104446434ALow costEase of industrial productionSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesSolventVacuum evaporation
The invention relates to a method for preparing a yttrium barium copper oxide high-temperature superconducting film. The method comprises the following steps: firstly weighing yttrium acetate Y(CH3COO)3, barium acetate Ba(CH3COO)2 and cupric acetate Cu (CH3COO)2 according to the mole ratio of Y to Ba to Cu of 1:2:3; mixing the yttrium acetate and the cupric acetate, dissolving into a deionized water solution with 10-20mol% propanoic acid, uniformly stirring, and then carrying out vacuum evaporation on a solvent to obtain a gel 1; dissolving the barium acetate into a mixed solution of trifluoroacetic acid, the propanoic acid and deionized water, uniformly stirring, and then carrying out the vacuum evaporation on the solvent to obtain the gel 2, wherein the mole ratio of the trifluoroacetic acid to the barium acetate is 1:3; mixing the gel 1 and the gel 2, then adding methanol, uniformly stirring, then adding ammonia water, and regulating the pH of a solution to 5-7; carrying out the vacuum evaporation on the solvent of the solution to obtain a gel, and adding the methanol and terpilenol to prepare a precursor solution with total concentration of three metal ions, namely Y, Ba and Cu, at 1.0-2.0 mol / L; then coating the precursor solution on a substrate; firstly carrying out a fast low-temperature heat treatment process at 300-500 DEG C for 1 hour on a completely coated film, and then carrying out high-temperature heat treatment at 750-850 DEG C and an annealing process at 450-550 DEG C on the completely coated film to form the YBCO superconducting film.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pharmaceutical formulations
InactiveUS20100310607A1Modulate hydrophilicityModulate hydrophobicityBiocideSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsActive agentPropynoic acid
The present invention relates to oral formulations comprising an active agent comprising at least one of 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid, salts of 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid or buffered 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoic acid.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
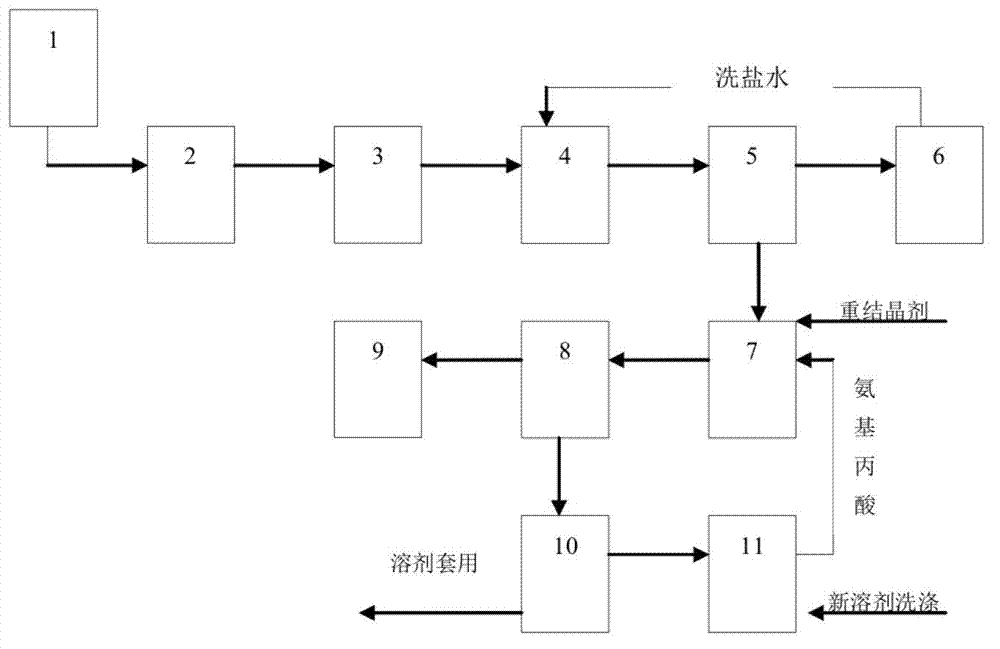
Novel beta-aminopropanoic acid synthesis technology
ActiveCN102827010AImprove efficiencyConcentration cycle is shortOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationSalting outFiltration
The invention discloses a novel beta-aminopropanoic acid synthesis technology, which comprises the following steps: hydrolyzing beta-aminopropionitrile under an alkali solution condition, neutralizing, concentrating for a while and adding a salting-out agent for direct hot filtration, cooling a filtrate and filtering to obtain the aminopropanoic acid crude product, returning the filtrate for concentrating, filtering and performing a cycle operation, dissolving the beta-aminopropanoic acid crude product, adding a novel recrystallization solvent for recrystallization, filtering a recrystallization mixture to obtain the beta-aminopropanoic acid refine product, drying to obtain the finished product, rectifying a crystallization mother liquor, recovering the solvent for application, performing spray drying on rectification raffinate to obtain the aminopropanoic acid, and recovering the aminopropanoic acid and washing through the novel solvent and dissolving for a recrystallization cycle operation. The synthesis technology has the advantages of high efficiency, short concentration period and high yield, and the refined yield can reach 95% by refining process.
Owner:江苏兄弟维生素有限公司
Organo-iodine complex
InactiveCN1834087AComprehensive ecological nutritional medicineGood for healthOrganic chemistryPeptide/protein ingredientsCoccidiosisDisease
This invention relates to an organic iodine complex, in which iodine serves as coordination center and functional group-containing organics serve as chelating reagent. The functional groups can be amino and / or hydroxyl and / or carboxyl, and the representatives of hydroxyl- and carboxyl-containing organics are 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutanoic acid and 2-hydroxypropanoic acid, respectively. This invention also relates to a combination of organic iodine complex and its application in pharmacy. The combination comprises 0.3~40% organic iodine complex as active ingredient and one or more ingredients chosen from the following ones: natural aminoacyl iodine, solvent, surfactant, food additives, food and synthesized drugs. This combination can be used in preparation of drug against AIDS, white spot syndrome virus in penaeid shrimp, Taura syndrome virus; grass carp hemorrhage virus, stomatitis, pharyngitis, colpitis, tumor, digestive tract diseases in poultry, histomoniasis, coccidiosis, human digestive tract diseases and iodine deficiency diseases.
Owner:曾雄飞
Antioxidant for thermoplastic butylbenzene segmented copolymer
The invention relates to an antioxidant for a thermoplastic butylbenzene segmented copolymer. The antioxidant comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1.0 part of 4-hydroxy-3,5-di-tert-butyl propanoic acid C7-C9 mixed alcohol ester, 1.8-2.2 parts of 2-methyl-4,6-di(methyl octyl sulfide) phenol and 0.8-1.2 parts of reaction products of N-aminobiphenyl and 2,4,4-trimethylpentene. The compound antioxidant system disclosed by the invention is added in a production process of SBS (Styrene Butadiene Styrene), and the addition amount of the compound antioxidant system accounts for 0.2%-0.6% of the weight of SBS crude rubber. The antioxidant disclosed by the invention is a liquid product, has 100% oxidation resisting function, can be dissolved into a cyclohexane solvent at high concentration, can not be precipitated at usage temperature, can not block a conveying pipeline, and achieves the convenience for use.
Owner:RIANLON
Epoxy resin encapsulation adhesive and use thereof
InactiveCN101372608AGood anti-light decay performanceImprove anti-agingOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhosphoniumAntioxidant
The invention relates to an encapsulation adhesive used for an electronic device, in particular to an epoxy resin encapsulation material for encapsulating a light emitting diode. The encapsulation adhesive has the advantages of good anti-optical weaken performance, short curing time, not getting yellow of the color of cured resin, good aging resistance, long operative time, etc. The encapsulation adhesive comprises two parts of component A and component B which are mixed to be used. The component A is A-typed bisphenol epoxy resin. The component B comprises methyl hexahydrophthalic anhydride, ethyl triphenyl iodo phosphonium, triphenylphosphine and beta-(3, 5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propanoic acid n-octadecanol antioxidant. The mass ratio of A to B is 1 to 0.8-1.
Owner:大连芯拓光电有限公司
Preparation method of envelopes of phosphoric acid micropore acidulant granules
The invention relates to a preparation method of envelopes of phosphoric acid micropore acidulant granules. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps: (1) mixing 10-15 parts of chitosan, 10-15 parts of citric acid, and 10-15 parts of malic acid to obtain a mixture A, screening the mixture with a sieve of 300 meshes, adding lactic acid and polyethylene glycol, uniformly mixing the screened mixture A, the lactic acid and the polyethylene glycol to obtain a mixture B, spraying the mixture B, and pelleting the sprayed mixture B; (2) uniformly mixing 3-5 parts of phosphoric acid, 1-2 parts of formic acid, 8-10 parts of acetic acid, 3-5 parts of propanoic acid, 8-10 parts of butyric acid, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, gas phase silicon dioxide and the pelleted mixture B obtained in the step (1) to obtain a mixture C, pelleting the mixture C by using a screw extruder, and oppositely impacting the pelleted mixture C by using airflows during pelleting; (3) and uniformly mixing 1-3 parts of phosphoric acid, 1-3 parts of fumaric acid, 5-10 parts of ethanol, 1-3 parts of benzoic acid, and 20-25 parts of melted polyacrylic resins to obtain a liquid lagging cover for lagging covers. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the preparation technology is simple, the performance is stable, the storage is easy, the quality guarantee period is long, the preparation method has the notable effect of protecting the health of the alimentary canals of livestock, and the bioactivity of the livestock can be obviously improved.
Owner:无锡华诺威动物保健品有限公司
Epsilon-polylysine-p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid antibiotic hydrogel dressing and preparation method thereof
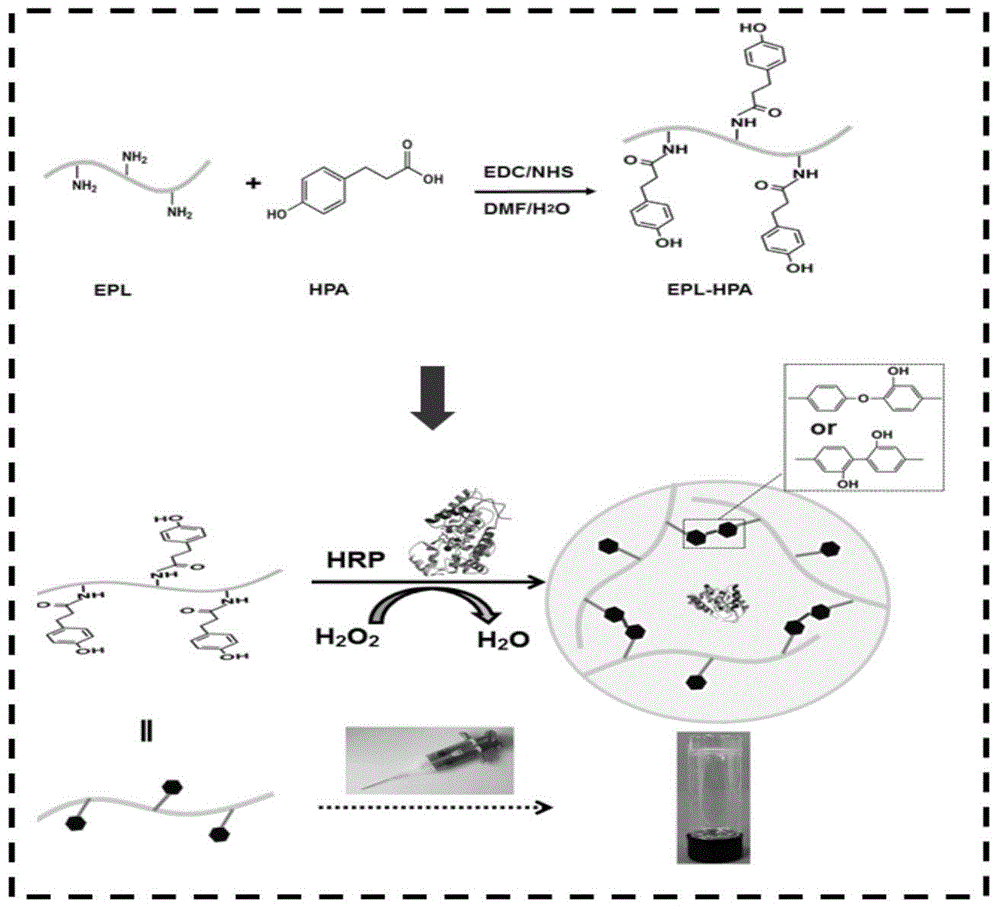
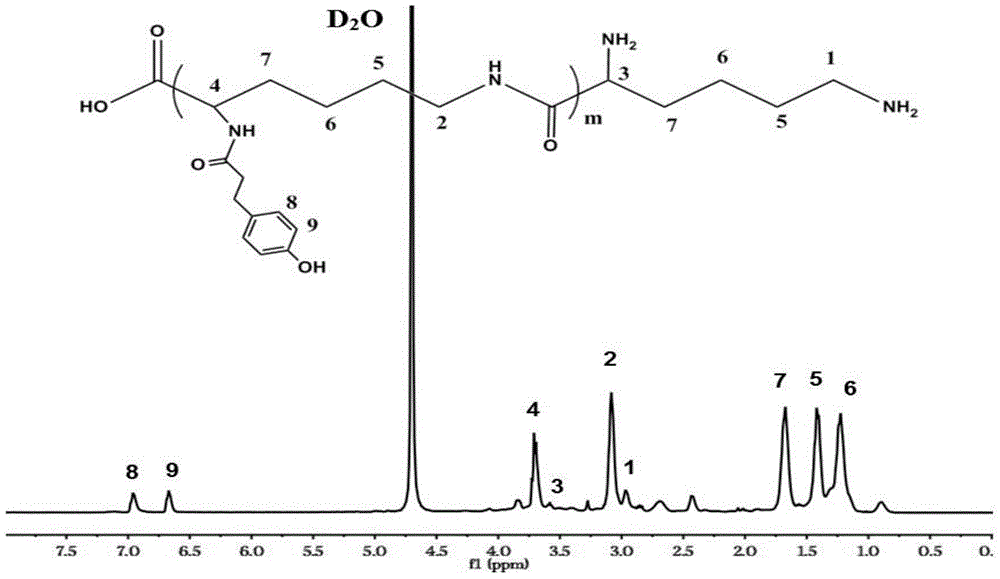
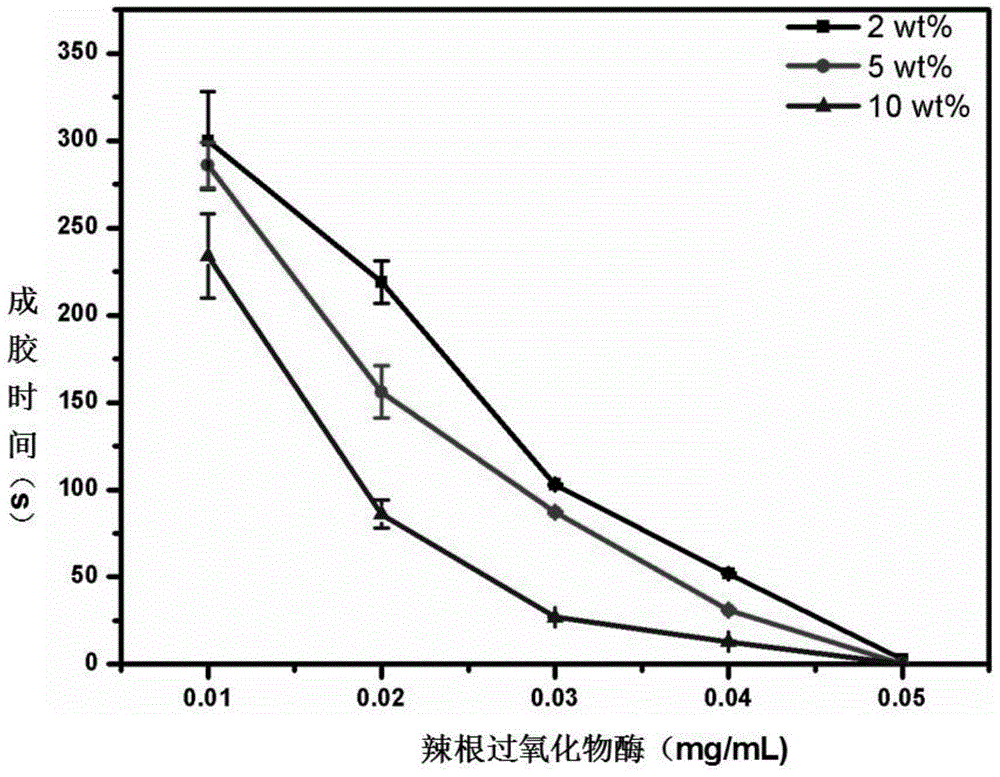
ActiveCN104857550AGood inhibitory effectGood biocompatibilityAbsorbent padsBandagesAntibiotic YBiological activation
The invention discloses a preparation method of epsilon-polylysine-p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid antibiotic hydrogel dressing. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid in a blended solvent of an organic solvent and deionized water, and stirring and uniformly mixing; adding 1-(3-dimethylamino propyl)-3-ethyl carbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide, and performing activation in an ice-bath condition; adding epsilon-polylysine dissolved by deionized water into an activated system, so as to enable the epsilon-polylysine to react with the activated system at the room temperature; transferring an obtained system into a dialysis bag, so as to dialyze the system; freezing and drying dialyze purified solution, so as to obtain epsilon-polylysine-p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid copolymer; respectively preparing a stock solution A and a stock solution B by taking PBS buffer solution as a solvent, respectively adding the stock solution A and the stock solution B into a tube A and a tube B of a double-end injector, and slowly pushing out the stock solution A and the stock solution B, so as to obtain the uniform and transparent epsilon-polylysine-p-hydroxybenzene propanoic acid antibiotic hydrogel dressing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
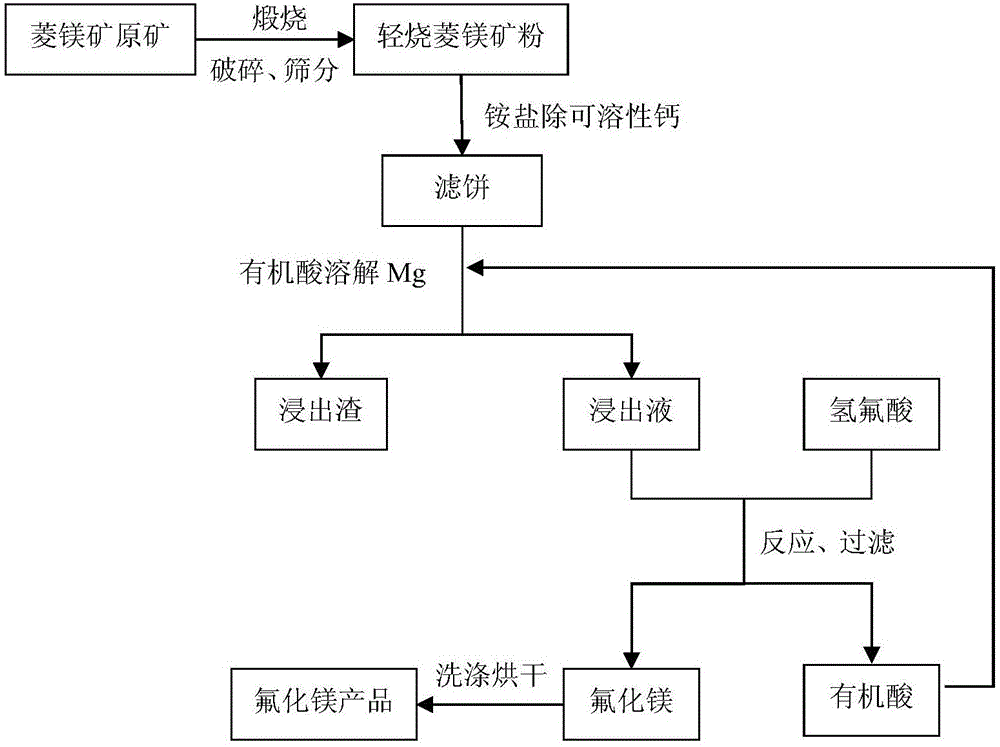
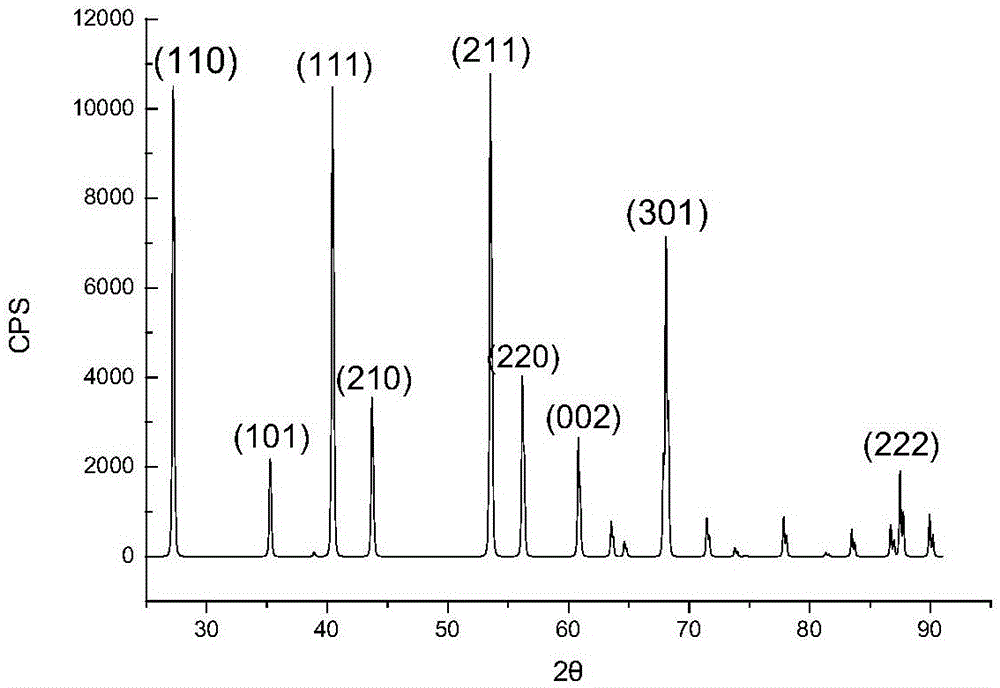
Method for preparing high-purity magnesium fluoride by using magnesite
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity magnesium fluoride by using magnesite. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) calcining the magnesite, thus obtaining light calcined magnesia mineral powder; (2) taking and adding the light calclined magnesia mineral powder in an ammonium salt solution to remove soluble calcium, and filtering, thus obtaining filter cake, wherein ammonium salt is one or several of ammonium chloride, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, ammonium oxalate or ammonium acetate; (3) adding the obtained filter cake in an organic acid solution for reacting, and filtering after reacting, thus obtaining leachate, wherein an organic acid is one or several of a formic acid, an acetic acid, a propanoic acid, a lactic acid, a citric acid, a glycolic acid, a malonic acid, a succinic acid or an adipic acid; (4) adding a hydrofluoric acid in the leachate, generating a precipitate, filtering, washing, and drying, thus obtaining the high-purity magnesium fluoride. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the source of raw materials is wide, the cost is low, the requirements of a device are low, the high-purity magnesium fluoride can be obtained by utilizing cheap magnesite, and the production cost of the high-purity magnesium fluoride is reduced to a large extent.
Owner:东营市东凯新材料技术研发有限责任公司
Coated sustained-release agent of small-molecular organic acid type acid preparation
InactiveCN107821788AAvoid reactionLower pHAccessory food factorsWorking-up animal fodderSilicon dioxideAntibiotic effect
The invention discloses a coated sustained-release agent of a small-molecular organic acid type acid preparation. The coated sustained-release agent of the small-molecular organic acid type acid preparation is characterized by being prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-30 parts of formic acid, 10-20 parts of ammonia water, 10-20 parts of lactic acid, 5-10 parts of acetic acid, 5-10 parts of citric acid, 1-5 parts of propanoic acid, 2-5 parts of fumaric acid, 20-30 parts of silicon dioxide, 10-30 parts of glyceryl monostearate and 5-20 parts of ethanol. The acid preparation component of the coated sustained-release agent is effectively separated from other materials, so the problems are avoided; the characteristic that the glyceryl monostearate is digested in theintestinal tracts is utilized, and the acid preparation component can pass through the stomach and be released in the intestinal tracts in a targeted mode, thereby effectively reducing the pH value in the intestinal tracts, enhancing the antibiotic effects of the intestinal tracts and bringing greater breeding benefit; and also the coated sustained-release agent of the small-molecular organic acid type acid preparation is a trend in the future.
Owner:WEIFANG JIAYIJIA BIO TECH
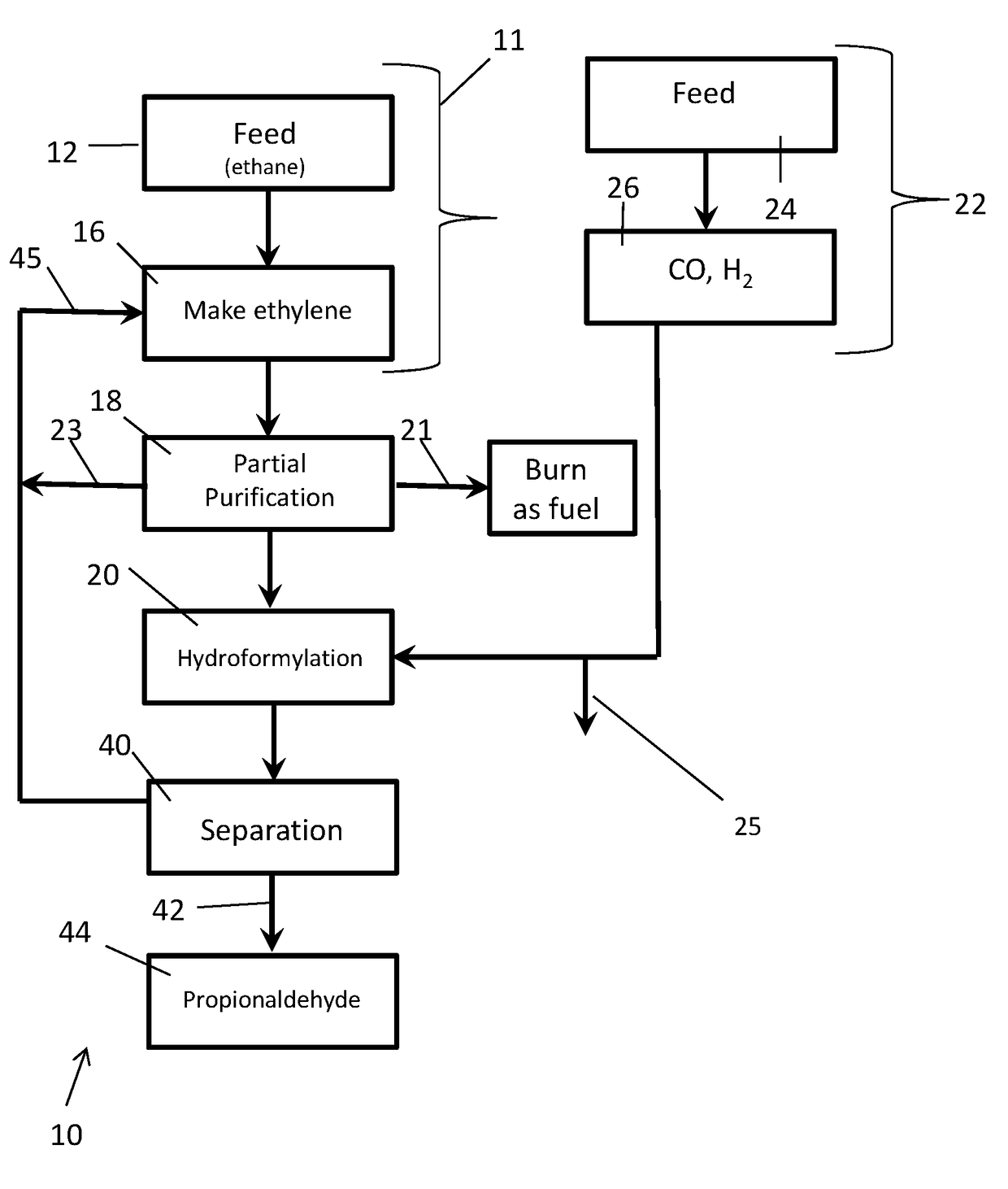
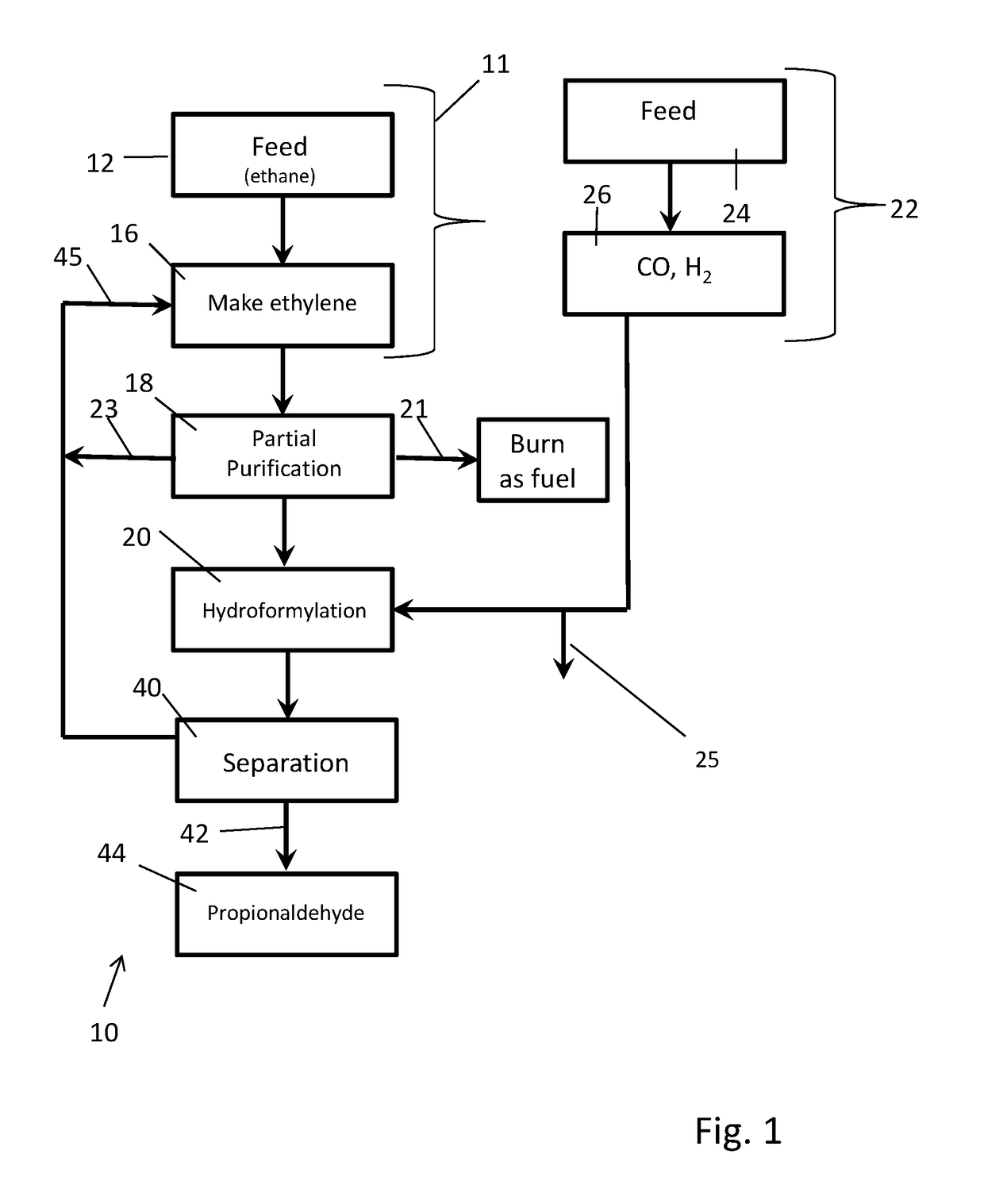
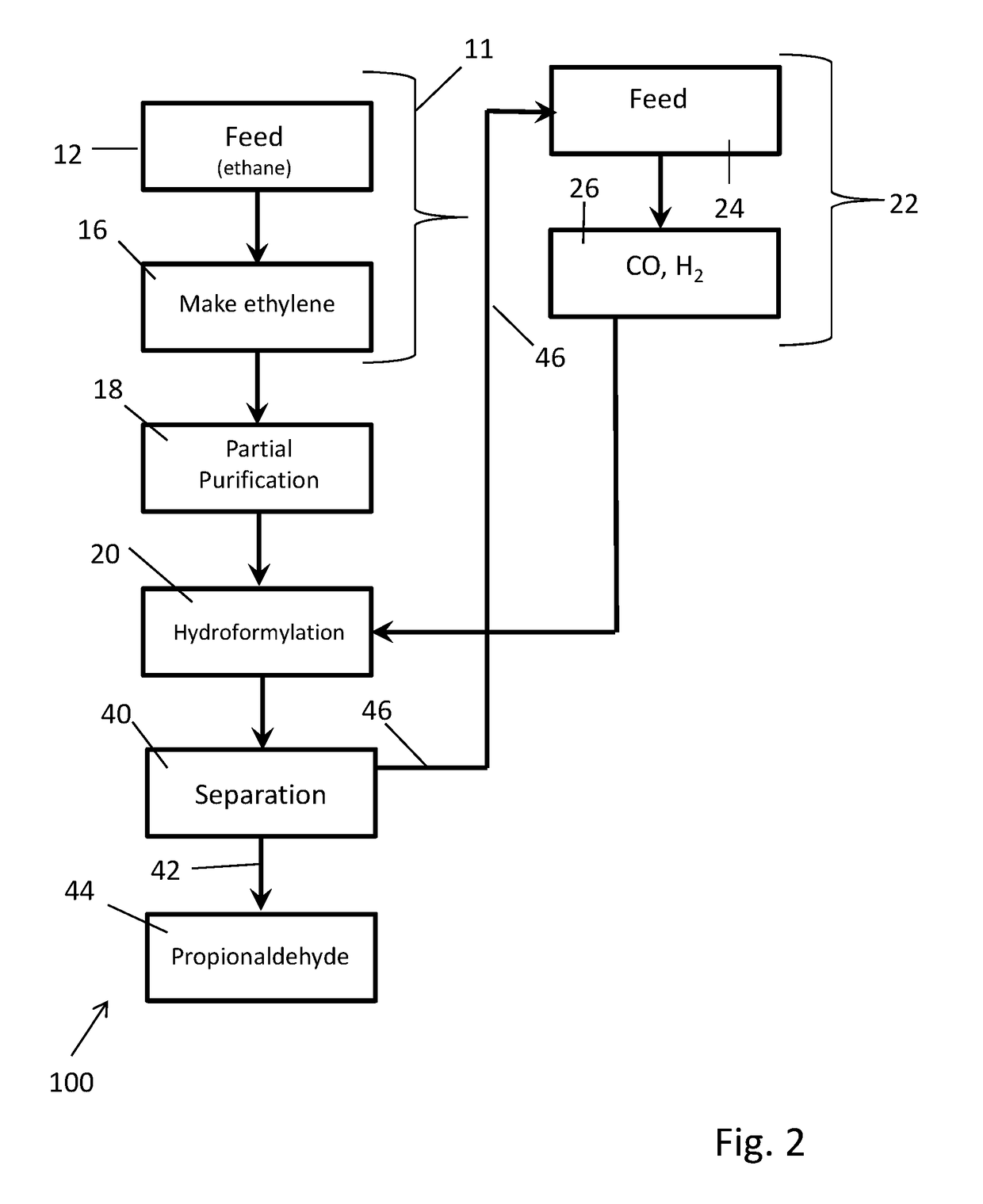
Processes for making C3 products from ethylene and syngas using hydroformylation strategies
The present invention relates to integrated processes for using hydroformylation reaction strategies to efficiently convert ethylene in ethylene feed mixtures into C3 products (i.e., products comprising 3 carbon atoms) such as propionaldehyde, 1-propanol, propylene, propanoic acid, and the like. An aspect of the present invention is to partially purify a feed comprising an ethane / ethylene mixture rather than to attempt more complete purification. In contrast to substantially complete purification of ethylene, partial purification is technically and economically feasible at lower cost and allows hydroformylation to be practiced at high productivity and with a lower hydrogen and CO requirement. The lower volumes of such syngas used in the hydroformylation reaction, as well as a more favorable profile of leftover reactants in following hydroformylation makes recycle strategies much easier to practice.
Owner:DP&PL LLC SERIES B
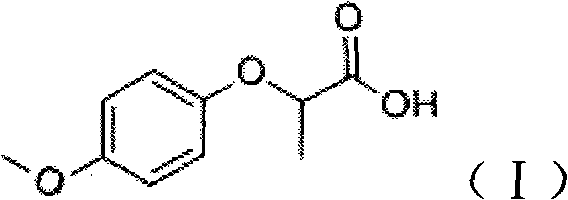
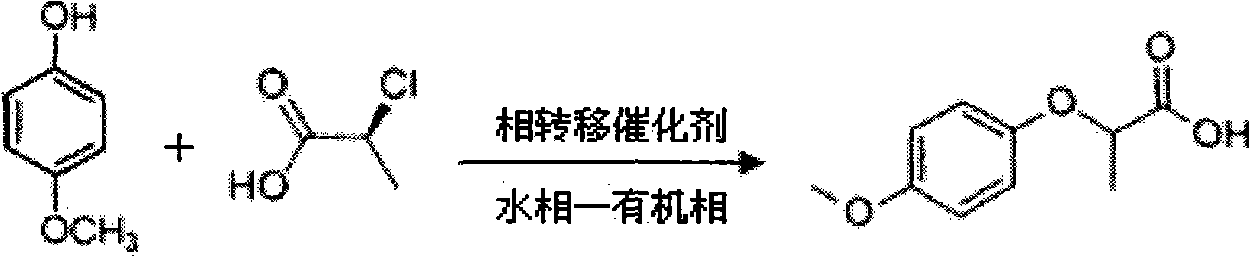
Industrial method for synthesizing 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-propionic acid through phase transfer
ActiveCN102010326AImprove conversion efficiencyGuaranteed conversion efficiencyOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparation4-MethoxyphenolHydroxybenzoate Ethers
The invention discloses an industrial method for synthesizing 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-propionic acid through phase transfer, which comprises the following steps of: stirring and mixing 4-Methoxyphenol, sodium hydroxide, a phase transfer catalyst and water, and reacting at normal temperature and normal pressure for 10 to 20 minutes to obtain mixed feed liquid; adding 2-chloro-propanoic acid and an organic phase into the mixed feed liquid, and reacting for 0.5 to 1.5 hours to obtain a product of 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-propionic acid; regulating the reaction liquid subjected to reaction to be acid byusing HCl or sulfuric acid solution, and standing to separate a water phase and the organic phase; and evaporating organic phase separation liquid to remove a solvent, and performing acid-base recrystallization to obtain the 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-propionic acid. When the reaction is finished, the yield of the 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-propionic acid is over 90 percent, the reaction temperature is reduced to 40-60 DEG C, the reaction time is only 0.5 to 1.5 hours, and the content of 2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-propionic acid in the final product is 99.5 percent.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com