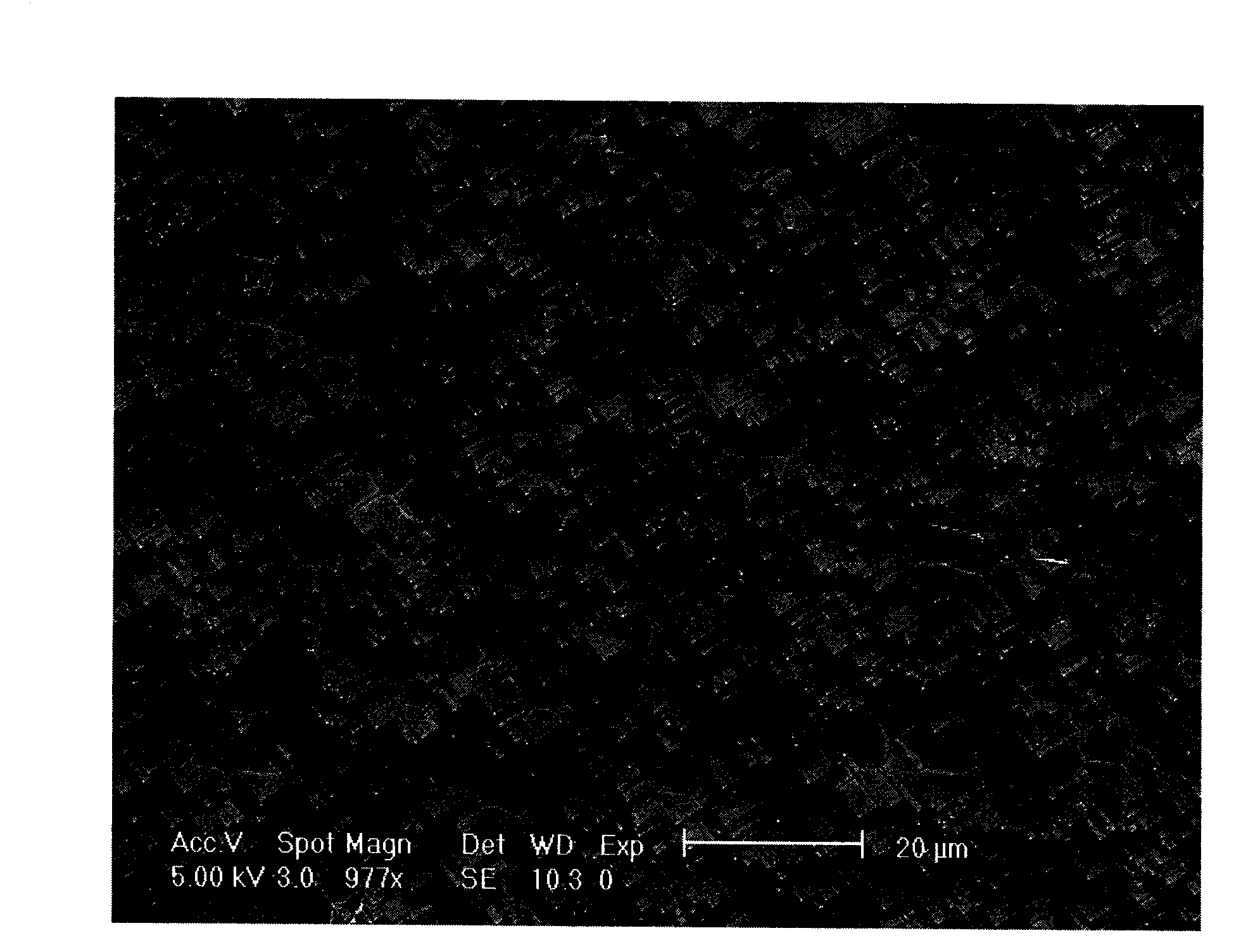
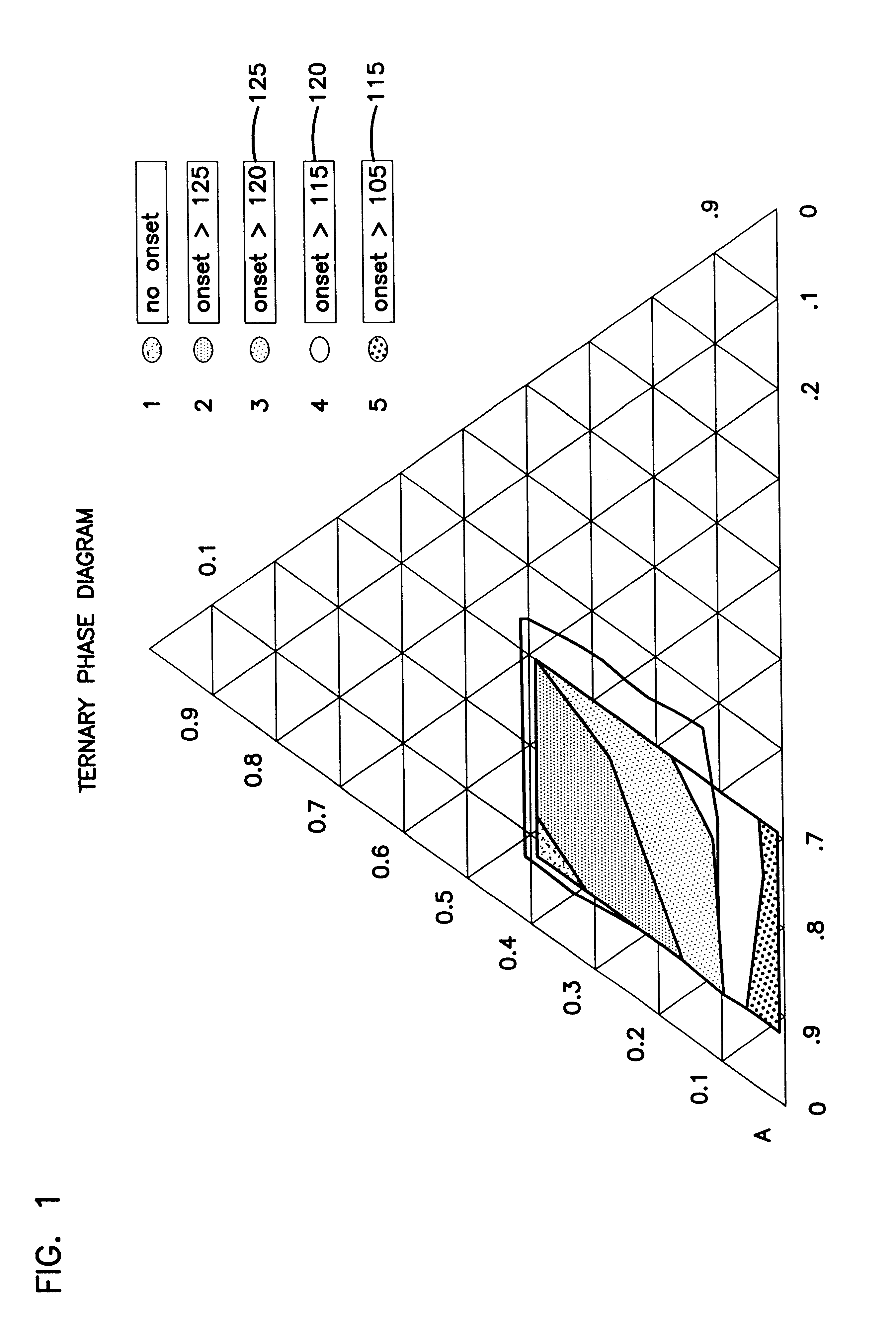
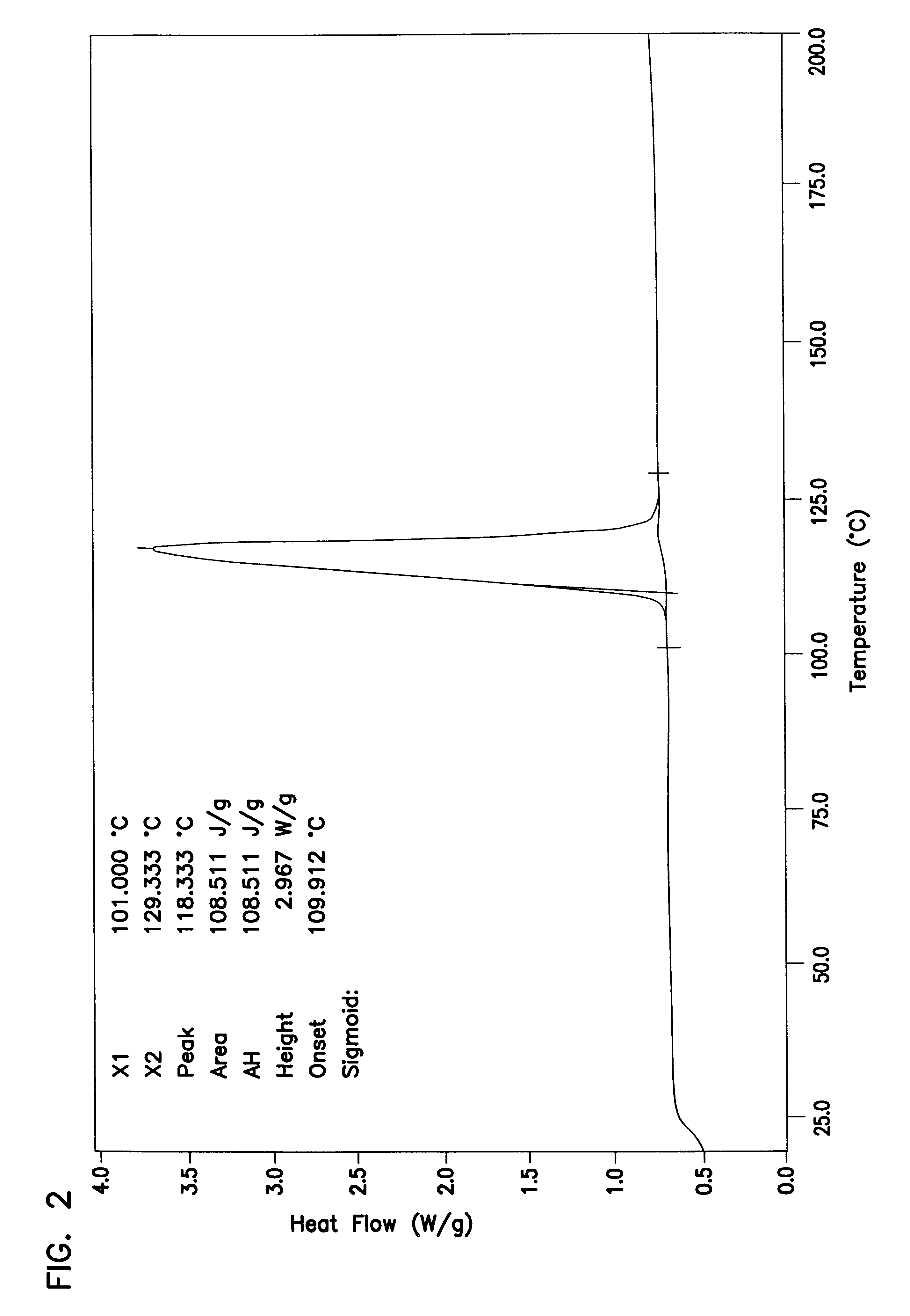
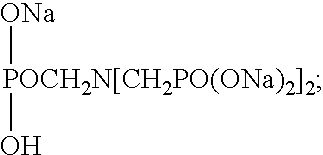Patents
Literature
3061 results about "Carbonate sodium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stable solid block detergent composition
InactiveUS6583094B1Easy to cleanImprove decontamination abilityInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAlkalinityIndustrial setting
The dimensionally stable alkaline solid block warewashing detergent uses an E-form binder forming a solid comprising a sodium carbonate source of alkalinity, a sequestrant, a surfactant package and other optional material. The solid block is dimensionally stable and highly effective in removing soil from the surfaces of dishware in the institutional and industrial environment. The E-form hydrate comprises an organic phosphonate and a hydrated carbonate.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Preparation method of hydrophilic block polyether aminosilicone
InactiveCN102617863AThe reaction steps are simpleThe reaction conditions are mild and simpleFibre treatmentEpoxyAcetic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of hydrophilic block polyether aminosilicone. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing terminal hydrogen-containing silicone oil: mixing hydrogen-containing double end enclosures, polysiloxane and acid, reacting, adding sodium carbonate under a vacuumizing condition, adjusting the pH, filtering a solid out, and extracting a low-boiling-point substance under reduced pressure to obtain low hydrogen-containing silicone oil; preparing epoxy silicone oil: mixing the obtained terminal hydrogen-containing silicone oil with allyl epoxy polyether and a catalyst, and reacting to obtain epoxy silicone oil; and preparing block polyether aminosilicone: and mixing the obtained epoxy silicone oil, polyetheramine, a catalyst and a solvent, reacting, cooling, adding an emulsifier for emulsifying, and adding glacial acetic acid for adjusting the pH to obtain the block polyether aminosilicone. According to the hydrophilic block polyether aminosilicone prepared with the method, the handfeel of a treated fabric can reach the handfeel of ordinary aminosilicone, and the treated fabric can keep a hydrophilic function permanently, is prevented from yellowing, and has high antistatic property.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Technology for recovering water resources and salt from coking wastewater in coal chemical industry
ActiveCN105502782ANo secondary hazardous waste generatedLow running costMultistage water/sewage treatmentAlkali metal chloridesChemical treatmentAdvanced oxidation process
A technology for recovering water resources and salt from coking wastewater in the coal chemical industry comprises the following steps: the wastewater is subjected to defluorination chemical treatment and subjected to sodium carbonate softening and precipitating treatment simultaneously, an advanced oxidation process is used for TOC (total organic carbon) degradation, a multi-medium and activated carbon filter is used for filtering separation, ultrafiltration is performed, nanofiltration membrane separation is performed, calcium and magnesium ions are separated, the calcium and magnesium ions in water produced through nanofiltration are lower than 2 mg / L, CaF2 crystallization scaling is hard to form, and nanofiltration passing liquid and nanofiltration strong brine are obtained; the nanofiltration passing liquid and the nanofiltration strong brine are treated respectively. Fluoride ions, hardness and organic carbon in the wastewater are removed, separation of multivalent salt and monovalent salt as well as concentration and evaporative crystallization of the salt is realized, more than 98% of the water resources is recovered, more than 95% of the salt resources are recovered, secondary hazardous waste is not produced, the system operation cost is reduced, and the problem about resource recovery and the environmental problem are solved finally.
Owner:湖南湘牛环保实业有限公司
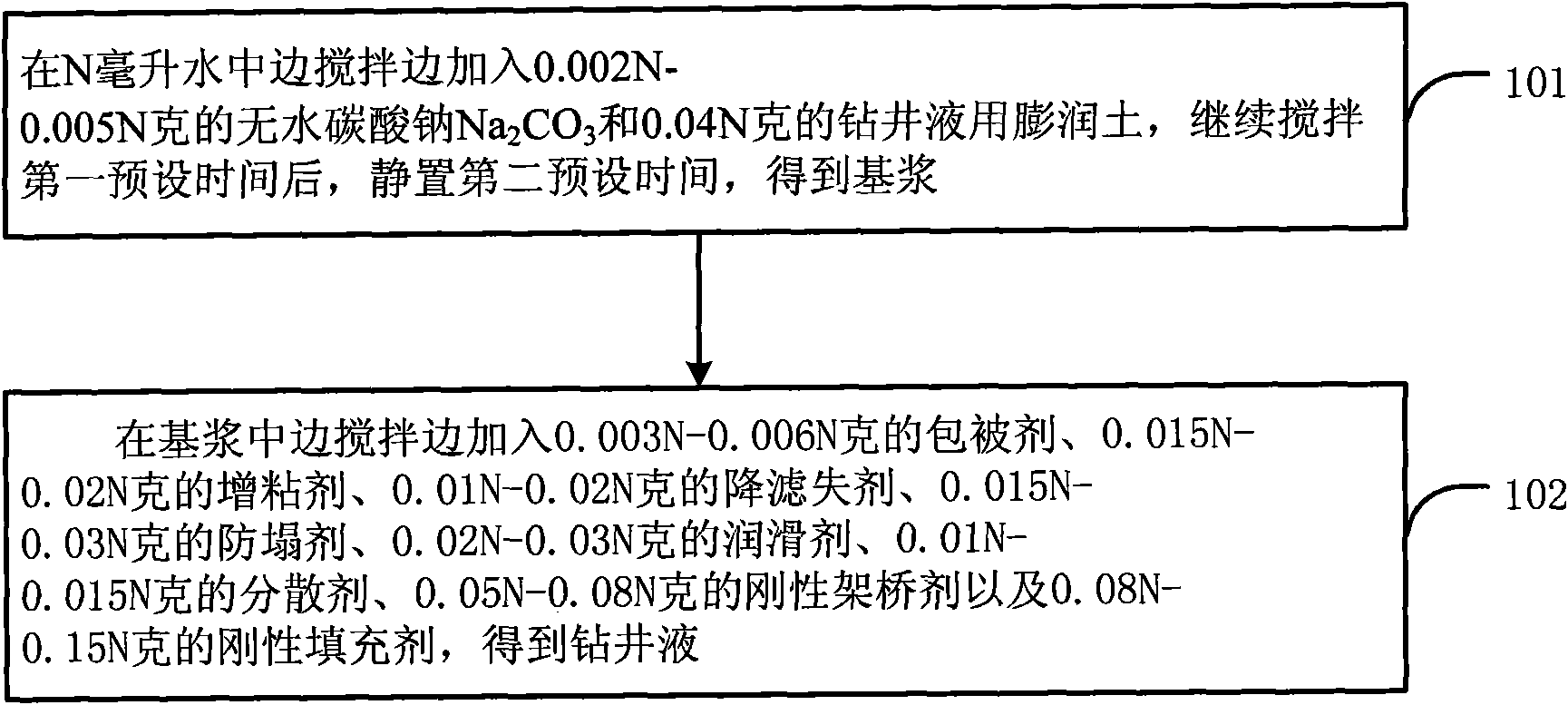
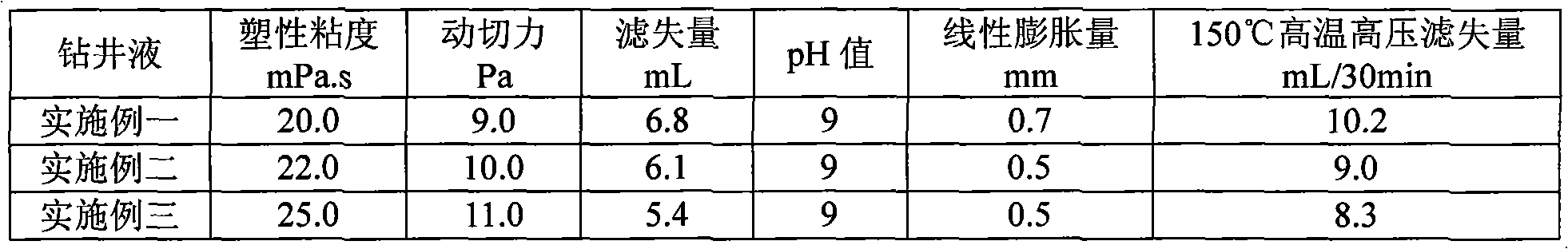
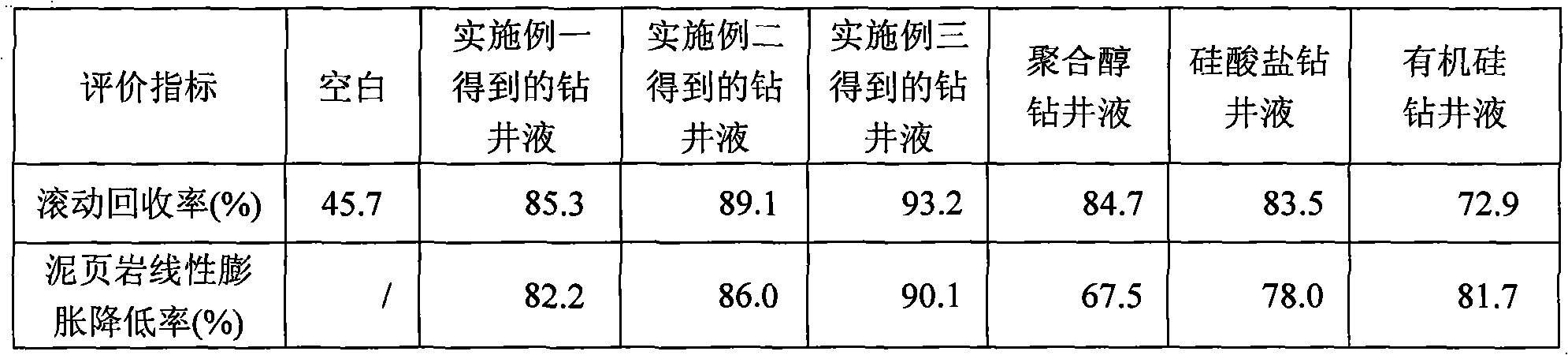
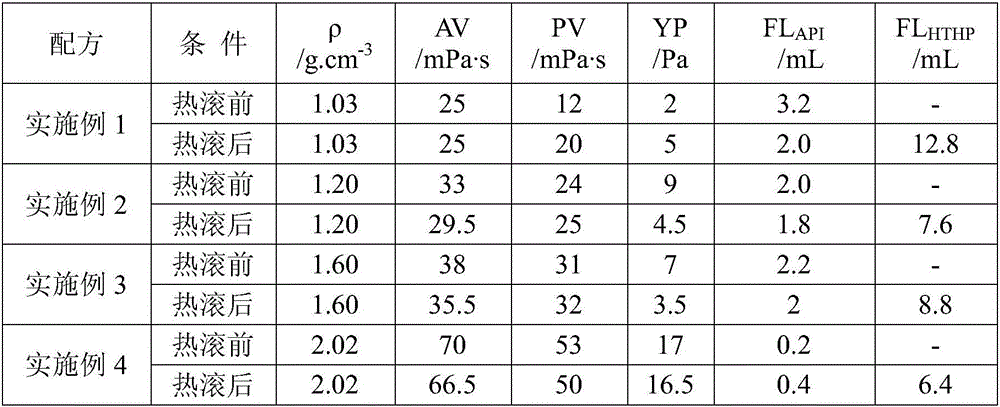
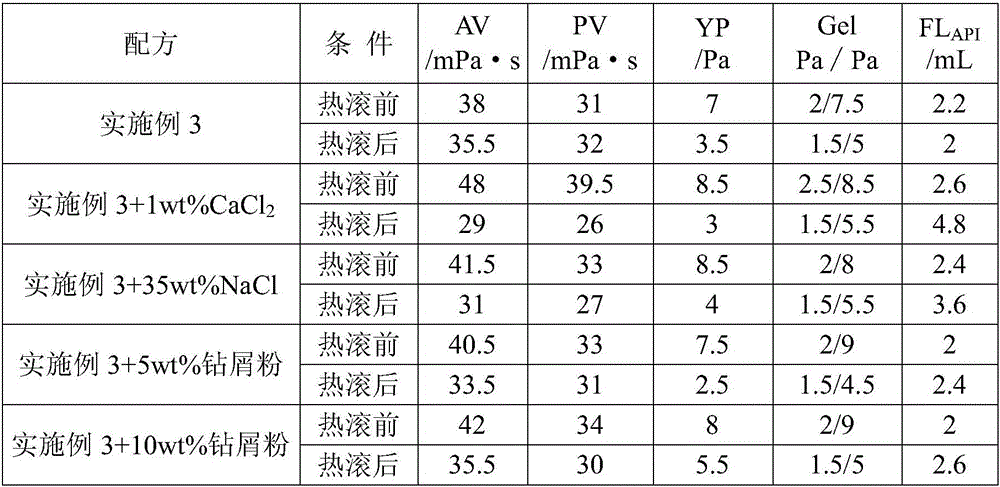
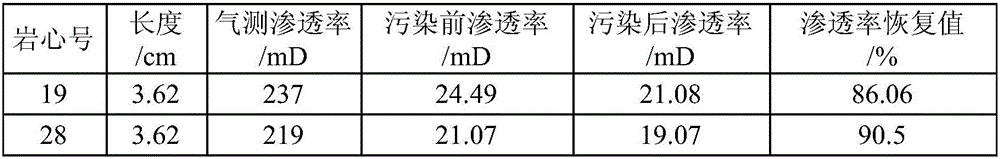
Drilling fluid and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a drilling fluid and a preparation method thereof. The drilling fluid comprises Nml of water, wherein N is a positive number, 0.002N-0.005N gram of anhydrous sodium carbonate Na2CO3, 0.04N gram of bentonite for the drilling fluid, 0.003N-0.006N gram of coating agent, 0.015N-0.02N gram of tackifier, 0.01N-0.02N gram of filtrate reducer, 0.015N-0.03N gram of anti-collapse agent, 0.02N-0.03N gram of lubricant, 0.01N-0.015N gram of dispersing agent, 0.05N-0.08N gram of rigid bridging agent and 0.08N-0.15N gram of rigid filler. The drilling fluid of the invention is applicable to a loss formation and has obvious leakage stoppage effect, a leak-proof function at the same time and obvious inhibiting effect on a formation which is easy to disperse and collapse.
Owner:CHINA UNITED COALBED METHANE NAT ENGRES CENT +1
Reactive dyestuff dyeing and fixing technique and printing and dyeing auxiliary agent used for the same
The invention relates to a dyeing and fixation process technical method of an activated dye and a textile auxiliary used in the method. The textile auxiliary or the substance or additive having the similar function like the textile auxiliary includes inorganic substance, organic substance, additive and adjusting ingredient; the raw materials are packed directly or packed after being smashed after the measurement, or heated to above 110 DEG C in water to be prepared into different products; in conventional equipment and without the modification of the fiber to be dyed, firstly, through only adding one of the products no more than the quantity of sodium carbonate to realize completely abandoning or no longer mainly relying on the sodium carbonate for fixing; secondly, meanwhile the normal contents of various salts are substantially reduced by 15 to 100 percent; therefore, thirdly, after getting rid of the restriction of relying on the sodium carbonate and the salt in the traditional process, the invention can substantially reduce the resources irrationally wasted in each process of dyeing such as water, power and vapor, etc. More particularly, the process operation is simplified, the processing cycle is shortened, and the effects of substantial energy saving and exhaust reducing, and effect strengthening and consumption reducing can be realized.
Owner:罗海航 +1
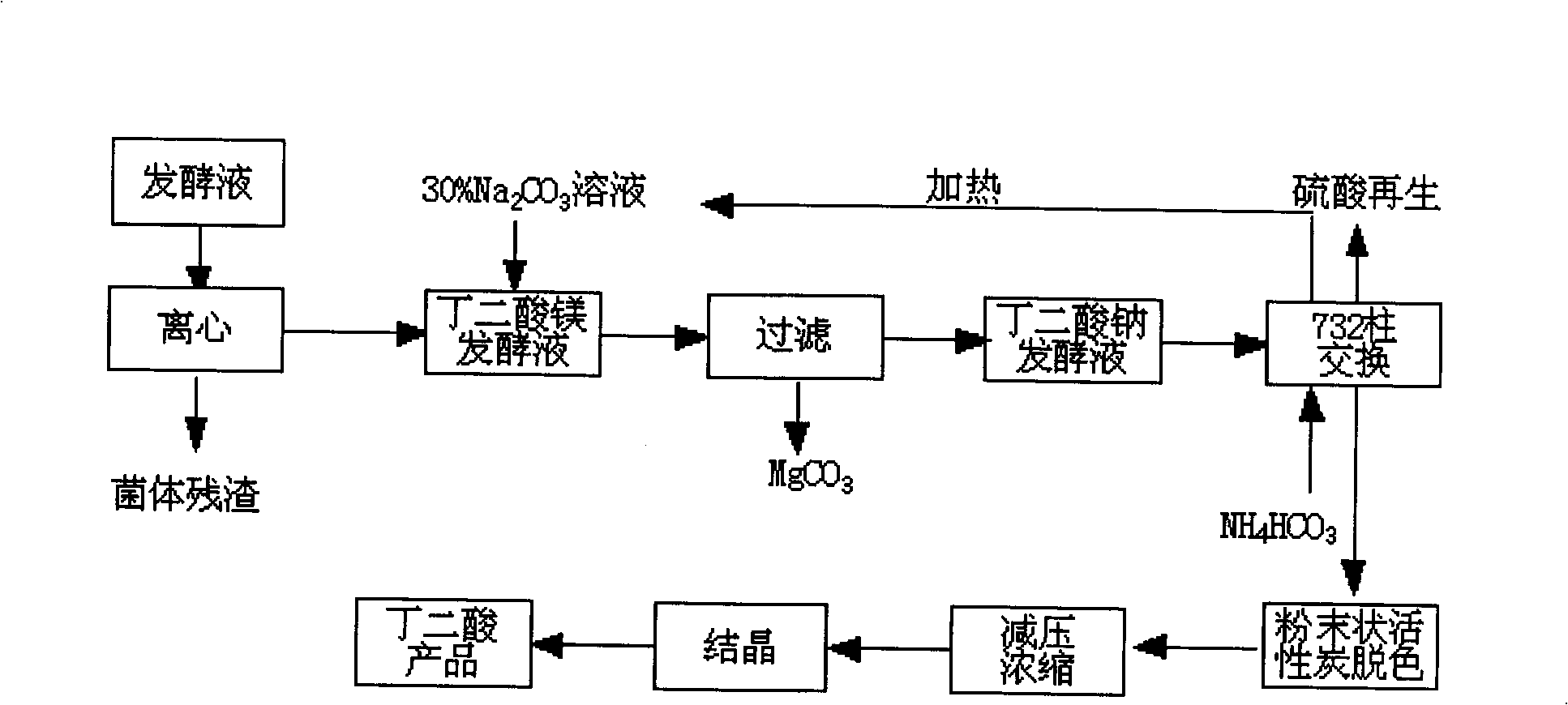
Method for extracting amber acid in fermentation liquor by cationic resin exchange
InactiveCN101348429AAchieving a circular economyShort process routeAmmonium sulfatesFermentationSodium bicarbonateSuccinic acid
A method for extracting succinic acid from fermentation broth through cation resin exchange belongs to the biochemical technical field. The method comprises the following steps that fermentation broth undergoes heated centrifugal filtration or membrane filtration so as to eliminate thalli; sodium carbonate is added in the clear solution to generate magnesium carbonate precipitation; a filter cake is reclaimed after filtration; then, the filtrate flows through a cation resin column, and the effluent is succinic acid solution; a succinic acid product is obtained after decoloring, concentration and crystallization; the cation resin column is eluted by ammonium carbonate after exchange so as to obtain sodium bicarbonate effluent; sodium salt is reclaimed and reused in fermentation broth treatment after ammonia is eliminated by heating; furthermore, resin regeneration can be realized by sulphuric acid through a conventional method, and the generated (NH4)2 SO4 can be used as a fertilizer. The method does not need to carry out acidification for the filtrate, and has the advantages of short technological line and high yield, thereby realizing element cycle economy. The invention provides a method for extracting succinic acid from microorganism fermentation broth with simple operation and economical efficiency.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Boiler coal combustion-improving desulfurizing and denitrifying agent composition and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a boiler coal combustion-improving desulfurizing and denitrifying agent composition. The composition comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-7 parts of sodium carbonate, 1-3 parts of alumina, 2-8 parts of aluminium hydroxide, 2-5 parts of ferric trichloride, 2-6 parts of ferric oxide, 3-10 parts of potassium permanganate, 3-10 parts of potassium chlorate, 10-35 parts of activated attapulgite clay, 15-30 parts of urea, 2-4 parts of ammonium formate, 2-4 parts of ammonium chloride, 6-23 parts of ammonium acetate, 3-9 parts of manganese oxide, 9-12 parts of copper chloride, 1-3 parts of copper oxide, 2-4 parts of zinc sulfate, 1-3 parts of zinc nitrate, 7-18 parts of potassium dichromate, 1.0-1.5 parts of titanium dioxide, 0.5-1.0 part of barium molybdate, 0.5-1.5 parts of cobalt sulfate, 0.5-1.5 parts of vanadium pentoxide, 0.3-0.7 part of cerium oxide, 0.1-0.2 part of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and 0.1-0.2 part of alkyl glyceryl ether. The composition is convenient to use, has stable properties, plays roles of combustion improving, desulfurization and denitrification, has coal saving rate of 8-25% and can remove fixed sulfur by 50-70%.
Owner:兰州熙瑞化工科技有限公司
Method for recycling vanadium and molybdenum from waste petroleum catalyst
InactiveCN105274344AReduce pollutionAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementPtru catalystPorphyrin
The invention relates to a method for recycling vanadium and molybdenum from a waste petroleum catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of petrochemical industry. The method comprises air-burning and ball-removing, ball-milling, soda roasting-water leaching, aluminum removing, molybdenum precipitating and enriching molybdenum by ion exchange. The method specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, igniting sticky oil in the waste catalyst in air to burn carbon and oils in the waste catalyst; then, oxidizing the vanadium and nickel in the forms of porphyrin compounds in the waste catalyst into vanadium oxide and nickel oxide, converting most of the molybdenum into molybdenum oxide, wherein the waste catalyst subjected to air-burning and oil-removing is more beneficial for crushing, and the crushed waste catalyst and a certain proportion of sodium carbonate are mixed, and are roasted at a high temperature; leaching roasted materials by hot water, dissolving sodium salts of the vanadium and the molybdenum into water to obtain a solution, filtering the solution, introducing the filtered solution into a leaching solution, introducing a little aluminum into the leaching solution, regulating the pH value of the solution to remove aluminum; regulating the pH value of the solution to 8-9, adding ammonium chloride, precipitating and separating out the vanadium in the form of ammonium vanadate; and concentrating vanadium-precipitated solution by adopting an ion exchange process and enriching an ammonium molybdate solution.
Owner:刘楚玲
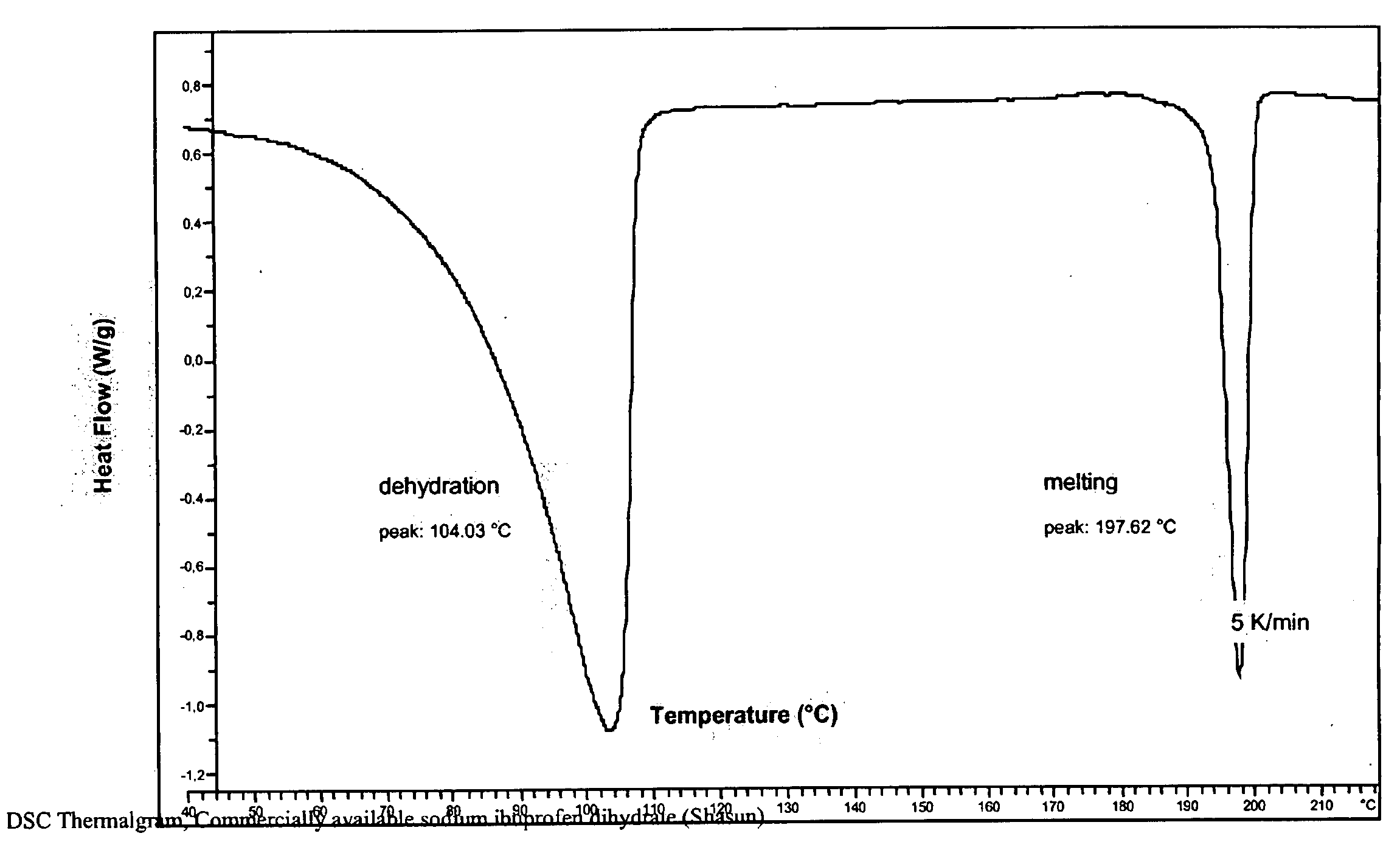
Solubilized ibuprofen
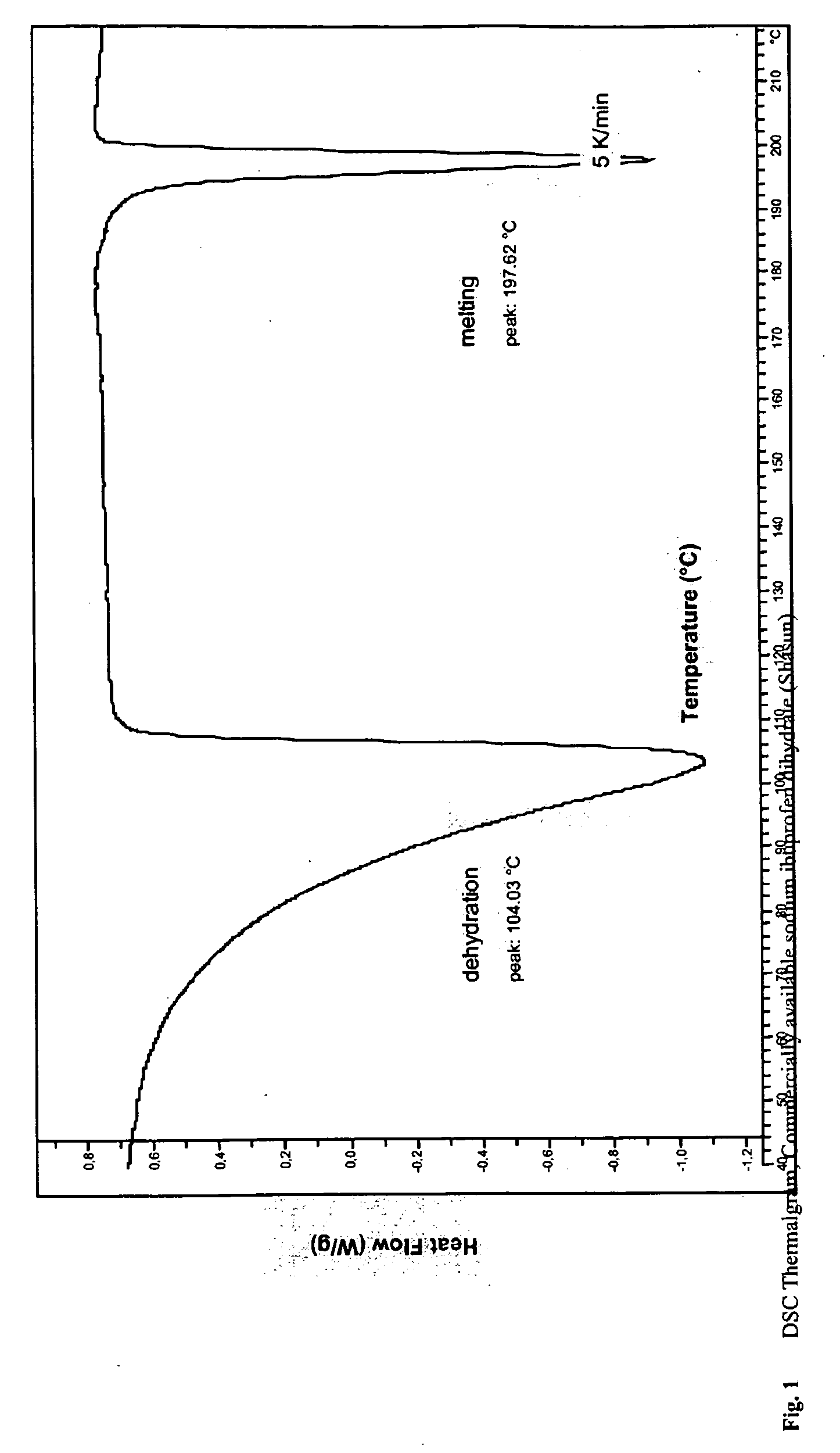
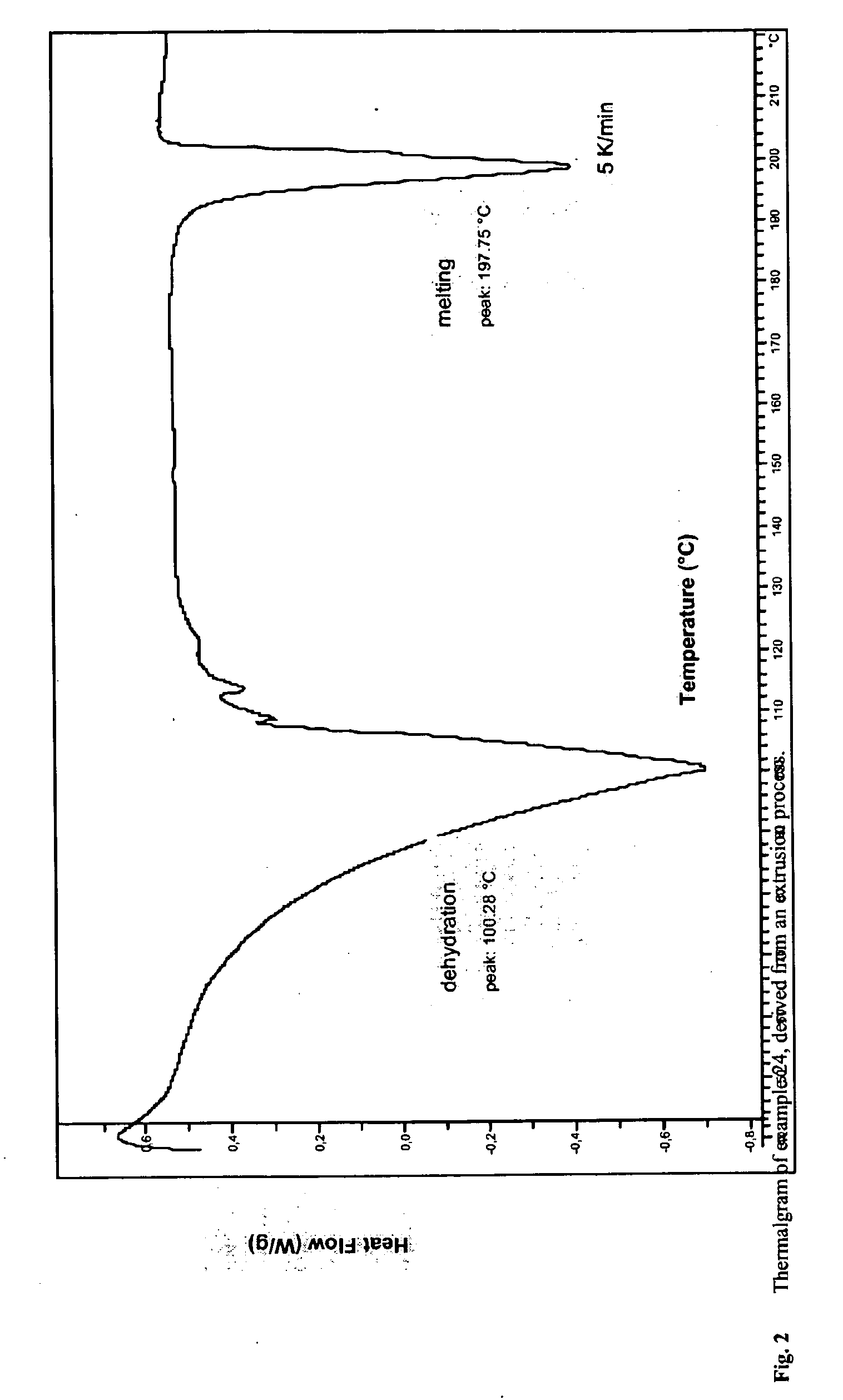
ActiveUS20090175940A1Easy to produceIncreased blood levelsBiocideOrganic compound preparationSolubilityPotassium hydroxide
A process for producing a solubilized ibuprofen, preferably in the form of a granulate, the process comprising the steps of: providing a mixture comprising solid ibuprofen and a first base selected from the group consisting of sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, sodium glycinate, potassium glycinate and tribasic sodium and potassium phosphates and mixtures thereof, and reacting the ibuprofen and the first base in essentially dry state. The obtainable granulate and the pharmaceutical compositions and dosage forms that may be produced therefrom are distinguished by their high solubility and rapid disintegration and dissolution in aqueous media, by their good flow properties and compressibility, by rapidly achieving onset of analgesic effect.
Owner:LOSAN PHARMA GMBH
High-manganese high-nitrogen low-nickel stainless steel plate blank continuous casting crystallizer covering slag and preparation method thereof
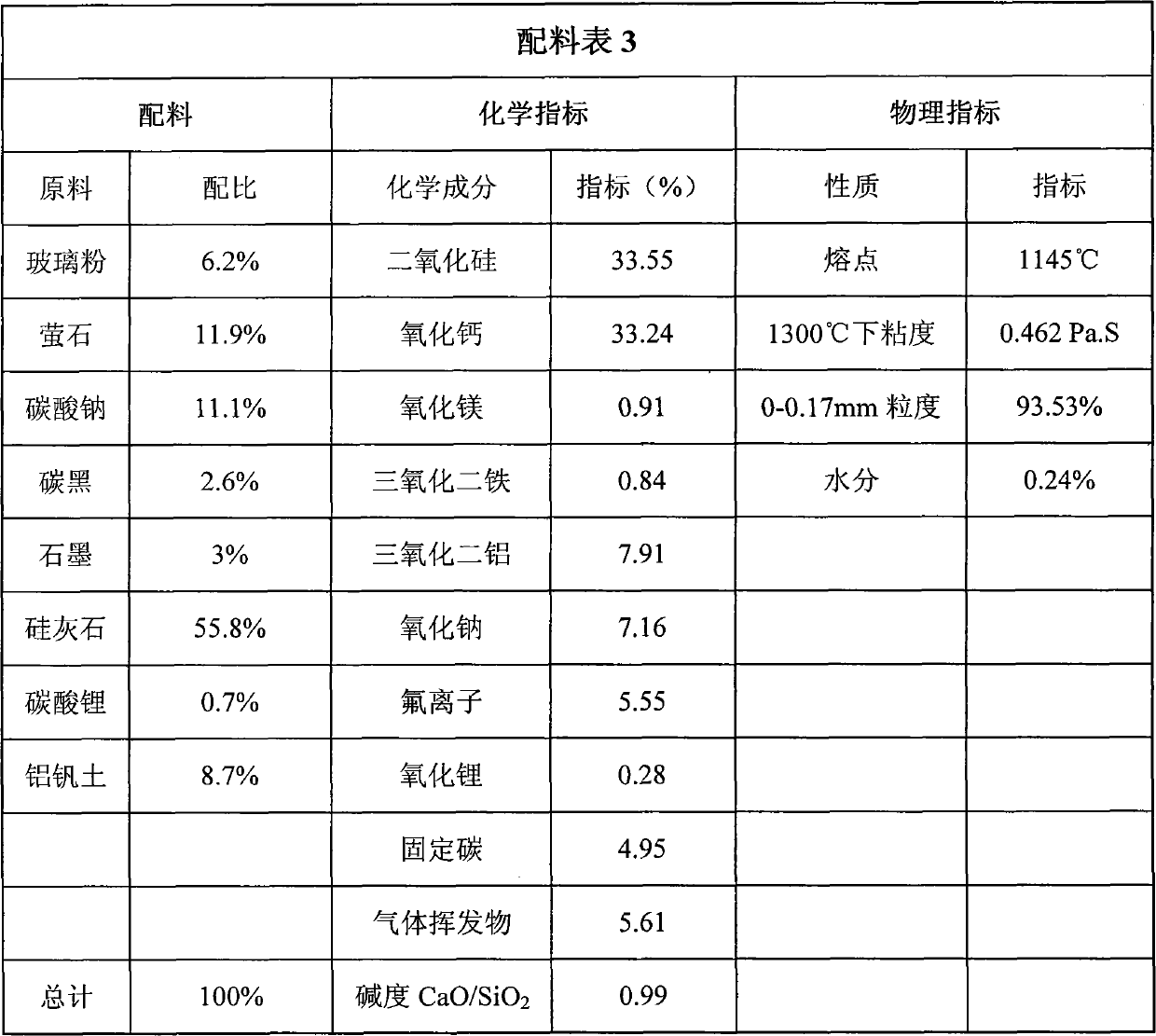
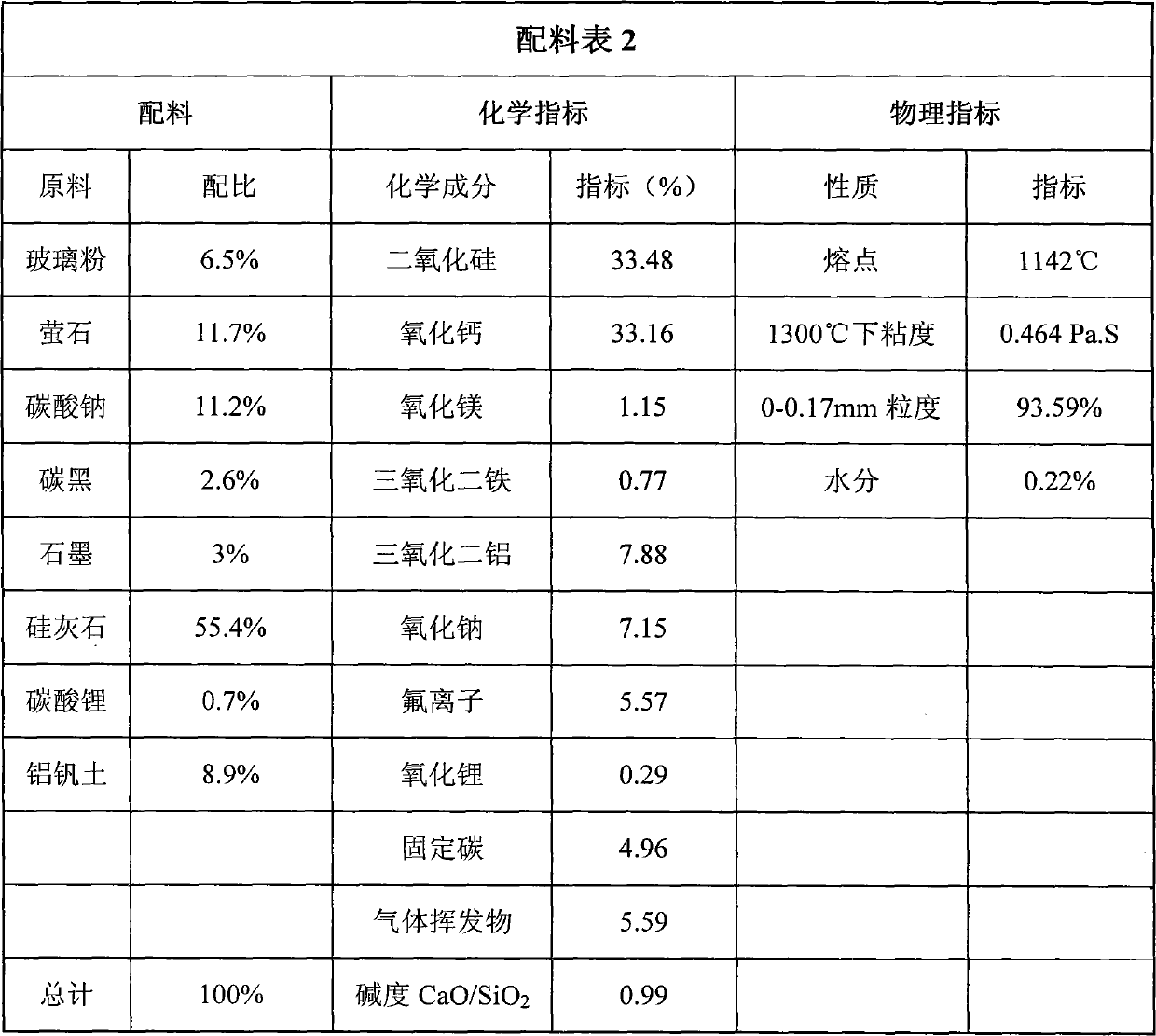
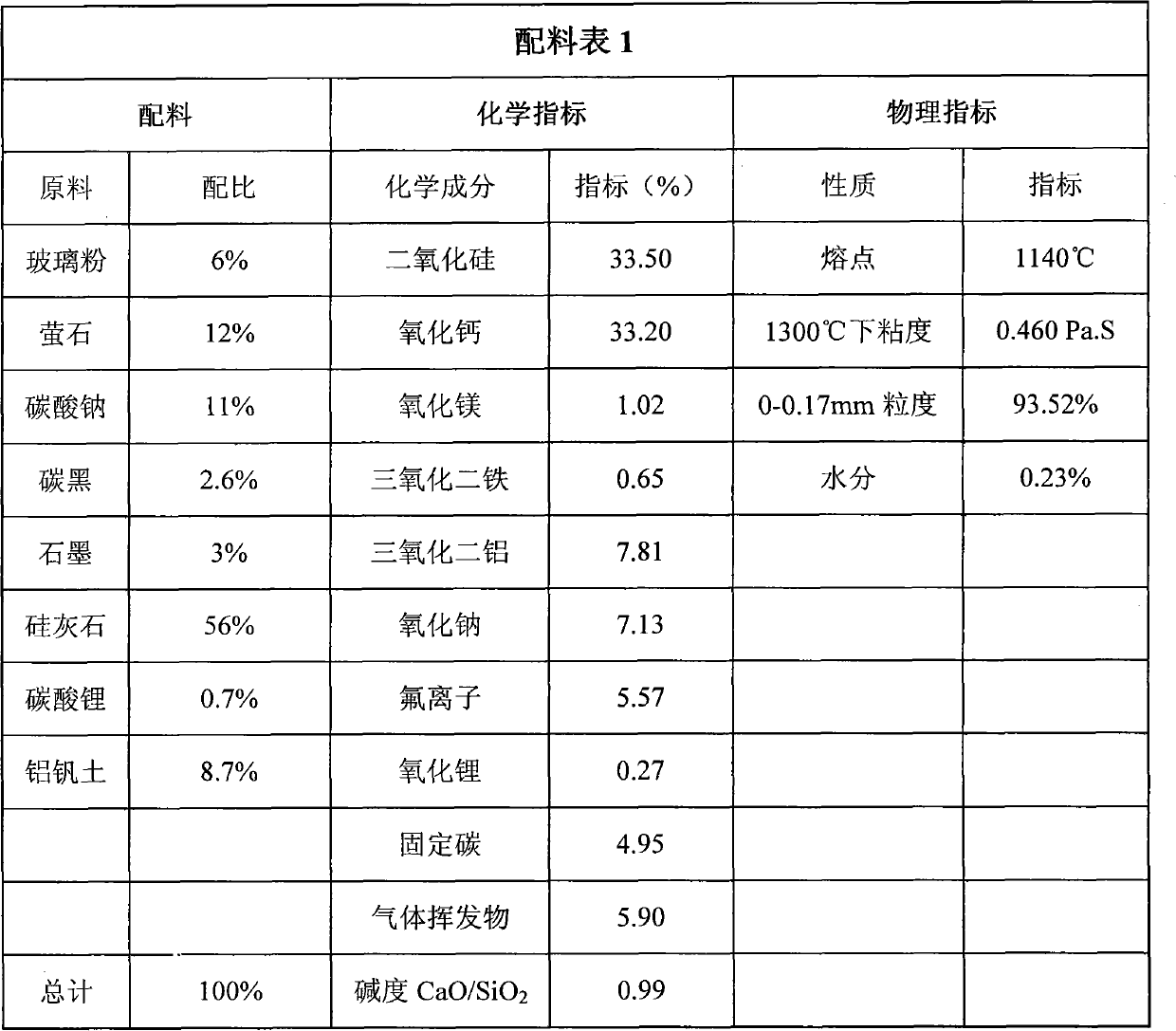
The invention discloses high-manganese high-nitrogen low-nickel stainless steel plate blank continuous casting crystallizer covering slag which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 54-57% of wollastonite, 9-13% of fluorite, 9-13% of sodium carbonate, 0-1% of lithium carbonate, 5-7% of glass dust, 8-12% of vanadine soil, 2.5-2.7% of soot carbon and 3-3.5% of graphite, and comprises the chemical components in percentage by weight: 31.9-34.9% of calcium oxide, 32.1-35.1% of silicon dioxide, 7.3-8.3% of aluminium oxide, 0.5-1.5% of magnesium oxide, 0.5-1.4% of iron sesquioxide, 4.4-6.4% of fluorion, 6.5-7.5% of sodium oxide, 0-0.39% of lithium oxide, 4.5-6.0% of fixed carbon and 4-7% of gas volatile matters. The alkalinity of the covering slag, namely the ratio of CaO to SiO2, is 0.91 to 1.00, the melting point of the covering slag is 1100 DEG C to 1160 DEG C, and the viscosity of the covering slag is 0.3 to 0.6 Pa.s at 1300 DEG C. The invention can solve the problems of easy crusting, slag entrainment, slag inclusion, slag sticking on casting blank surfaces, bubbles under skins, cracks, deep chatter mark, felting, bleed-out, and the like of the covering slag in the crystallizer during high-manganese high-nitrogen low-nickel stainless steel plate blank continuous casting, and has the advantages of uniform and stable slagging in the crystallizer, good casting blank quality, difficult felting and bleed-out, and the like.
Owner:XIXIA LONGCHENG METALLURGICAL MATERIALS CO LTD
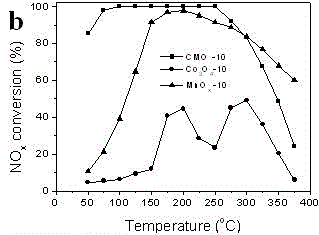
Method for recycling manganese and lithium from power type lithium manganate battery for electric automobile
InactiveCN102347521AReduce pollutionEasy to operateWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementElectrolytic agentManganate
The invention discloses a method for recycling manganese and lithium from a power type lithium manganate battery for an electric automobile, which comprises the following steps of: (1) after discharging a waste and old lithium ion battery, detaching a shell to obtain an anode part; (2) removing an organic adhesive of the anode part to obtain a power type lithium manganate anode material; (3) adding acid and a reducing agent into the inorganic material obtained in the step (2), dissolving the inorganic material and filtering to remove the undissolved substance acetylene black to obtain filter liquid; (4) carrying out electrochemical deposition for 5-8 hours by using the filter liquid obtained in the step (3) as electrolyte, using a titanium sheet as a working electrode, using a graphite rod as a counter electrode and controlling the constant current density of 300-800A / m<2> and the temperature of 60-80 DEG C to obtain a manganese dioxide solid; (5) adjusting the pH of the residual liquid in the step (4) to be 9 to 10 and filtering to obtain a sediment and filter liquid; (6) adding a sodium carbonate solution with the concentration of 30-40 percent into the filter liquid obtained in the step (5) till the filter liquid is completely deposited; and filtering, washing and drying to obtain a lithium carbonate solid. MnO2 is recycled by utilizing an electrochemical deposition method, and thereby the method has the advantage of environmental protection; and the high-purity lithium carbonate solid is recycled.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH
Water-based drilling fluid applicable to horizontal shale and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103937470AEnhanced inhibitory effectIncrease speedDrilling compositionComponents of crude oilTackifier
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Corrosive liquid for preparing monocrystal silicon textured surface and method thereof
InactiveCN101634026AHigh thermodynamic stabilityGood chemical stabilityAfter-treatment detailsSemiconductor devicesPotassium hydroxidePerfluorooctanoic acid
The invention relates to a corrosive liquid for preparing monocrystal silicon textured surfaces and a method thereof. The corrosive liquid comprises an alkali solution, sodium silicate and isopropanol, and is characterized by also comprising a perfluoro octoate aqueous solution, wherein the perfluoro octoate aqueous solution has the volume percent of 0.2-1 percent and the concentration within a range of 5*10<-5>-5*10<-3>mol / L; the alkali solution has the mass percent of 1-2.5 percent, the sodium silicate has the mass percent of 0.1-2 percent, and the isopropanol has the volume percent of 0.3-2 percent; and the alkali solution is sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. The corrosive liquid has low cost, pyramids formed on the prepared monocrystal silicon textured surfaces have small and uniform sizes, and the corrosive liquid is favorable for solar energy absorption and can be widely applied to the field of solar batteries.
Owner:BEIJING SOLAR ENERGY INST +1
Anion easy-cleaning functional ceramic additive and preparation method thereof, ceramic prepared by using additive and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramics, and particularly relates to an anion easy-cleaning functional ceramic additive and a preparation method thereof, a ceramic prepared by using the additive and a preparation method thereof. The additive is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 10-16% of Chongguang stones with a particle size of 5-20 microns, 16-25% of tourmaline with a particle size of 5-15 microns, 5-15% of copper pectolite with a particle size of 5-20 microns, 8-12% of nano titanium dioxide, 6-8% of nano zinc oxide, 5-10% of lead-free frits, 7-20% of rare earth materials, 8-10% of superfine alumina, 8-15% of superfine quartz powder and 5-10% of sodium carbonate. The preparation method of the additive comprises the following steps of carrying out mixed ball-milling on the lead-free frits, the rare earth materials, the superfine alumina, the superfine quartz powder and the sodium carbonate firstly; and then, adding the Chongguang stones, the tourmaline, the copper pectolite, the nano titanium dioxide and the nano zinc oxide into the obtained product, and ball-milling the obtained mixture, so that the additive with a particle size of 1-10 microns is obtained. The additive disclosed by the invention has a self-polarizing performance, and has strong adsorption and decomposition functions, so that negative ions are produced; and after the additive is added into a ceramic, the ceramic is extremely easy to clean and not stained, and has no hidden dirt, therefore, the ceramic has a strong affinity to water.
Owner:ZIBO BAIKANG ECONOMIC & TRADE
Trace elements
The invention discloses a trace element solution, which comprises at least one metal selected from the group comprising selenium, copper, zinc, manganese and chromium and which comprises a concentration of the metal(s) of at least 60 mg / ml. The solution further comprises at least one compound selected from the group comprising iodine, potassium iodide, sodium iodide, iron, iron chloride, zinc oxide, manganese sulphate, sodium selenite, copper carbonate, sodium carbonate, anhydrous disodium EDTA and sodium hydroxide. The trace element solution is prepared by a method consisting essentially of the steps of preparing a MnCO3 mixture in a container; adding an EDTA / NaOH mixture to the container and subsequently adding at least one metal compound; and adding Na2SeO3 to the container to obtain the trace element solution. The method also comprises the step of adding CrCl3.6H2O to the trace element solution.
Owner:WARBURTON TECH
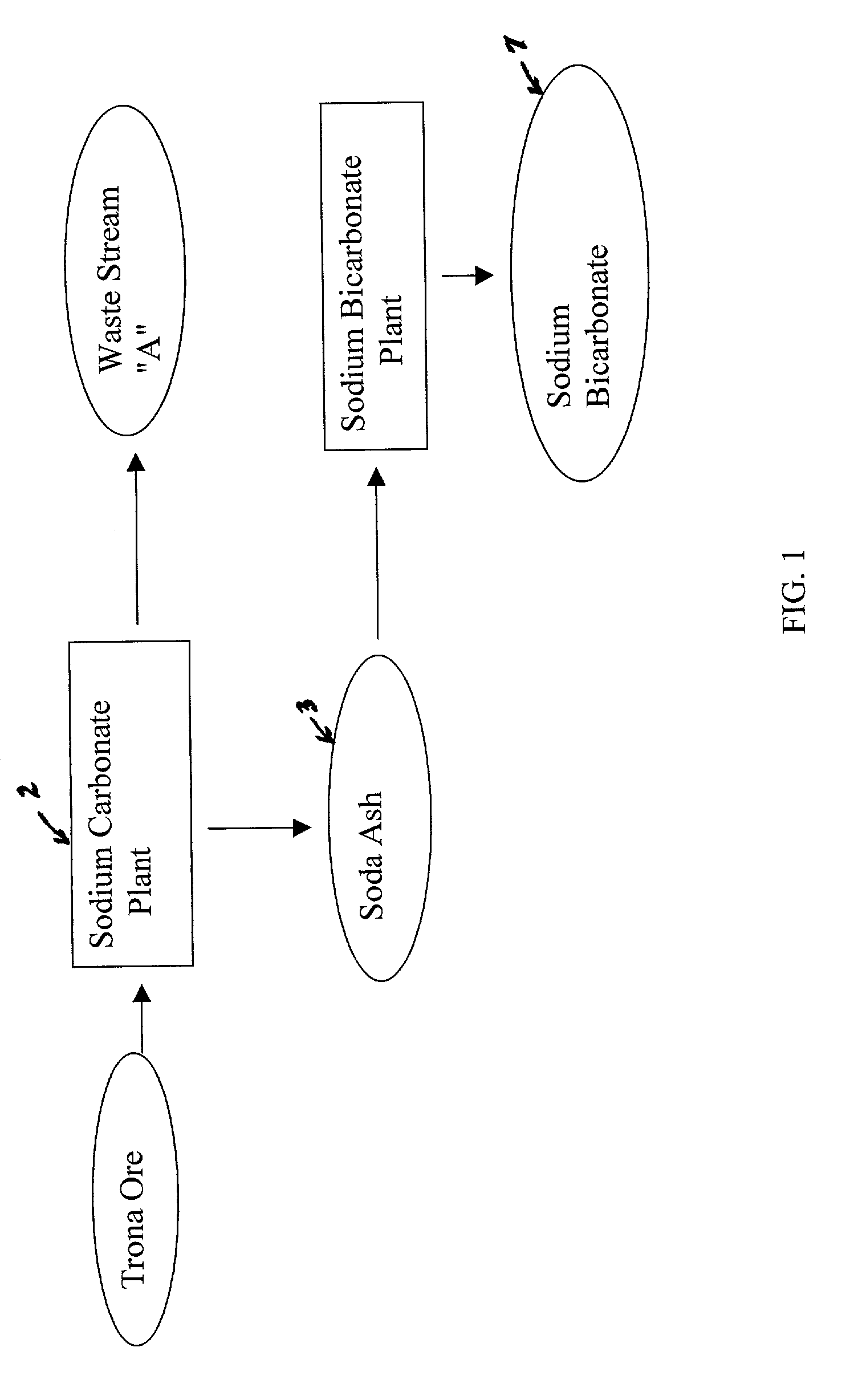
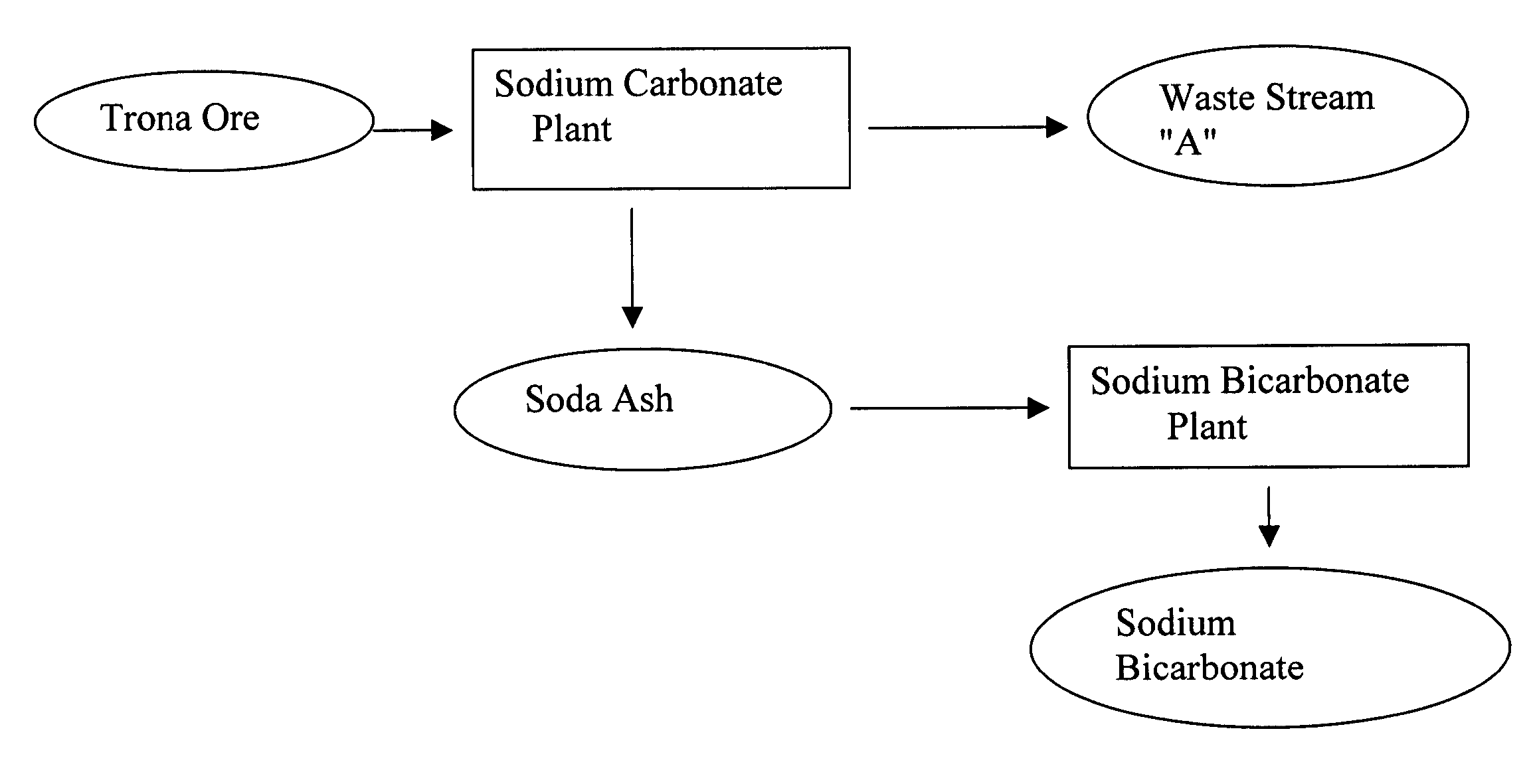
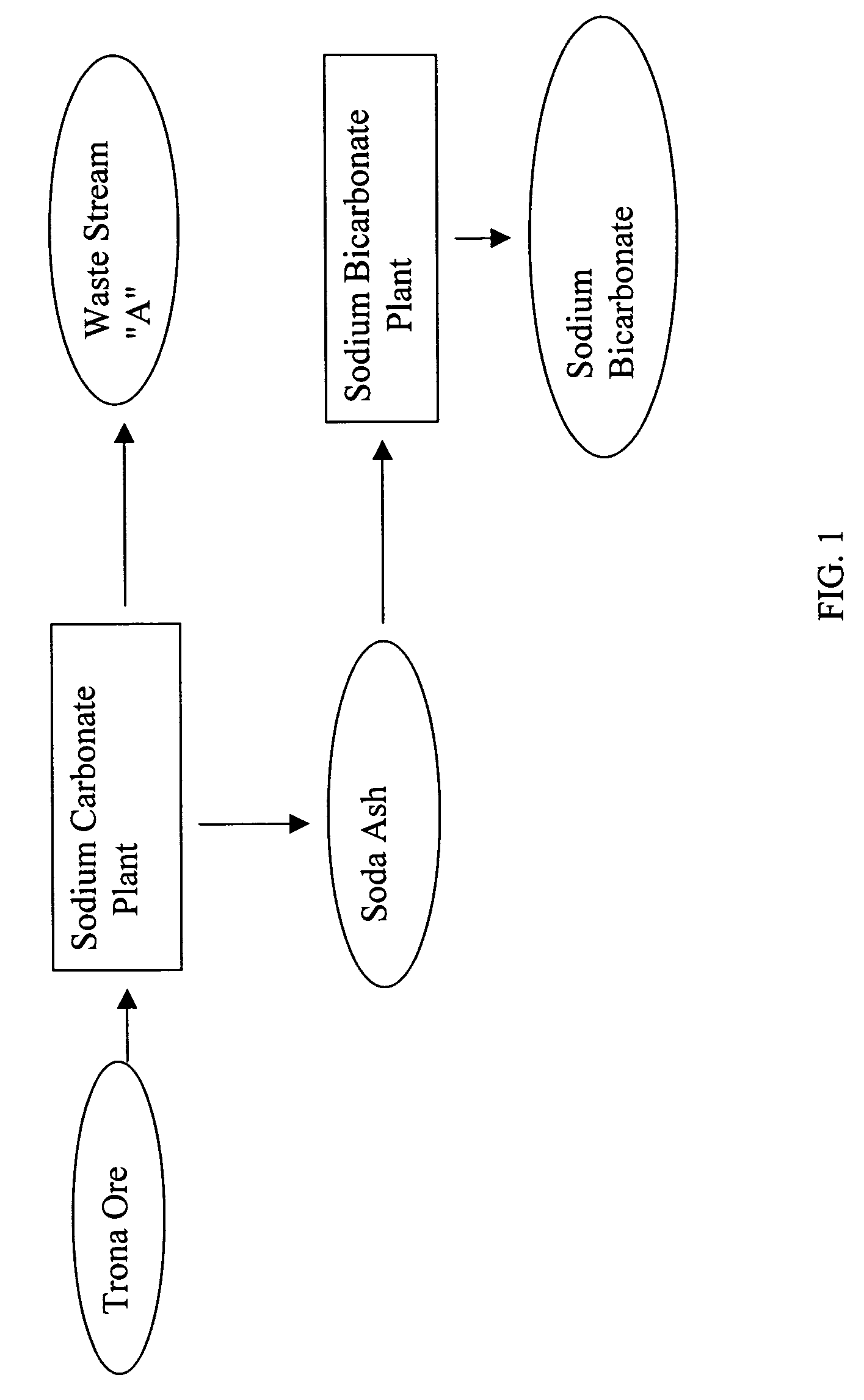
Sodium bicarbonate production method
InactiveUS20030017099A1Improvement in recovered sodium valuePromote recoveryBicarbonate preparationRubidium/caesium/francium compoundsEnvironmental engineeringSodium hydrogencarbonate
A method of producing additional sodium bicarbonate having a high degree of purity and obtaining a net reduction in effluent waste water, as compared to prior processes, when starting from trona ore is disclosed. The process entails utilizing the waste-water effluent stream from the conversion of trona ore to sodium carbonate as the feed for the conversion of sodium carbonate to sodium bicarbonate.
Owner:CHURCH & DWIGHT CO INC
Nano layered calcium carbonate base bionic composite material and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN101085880ACalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsEnvironmental geologyInorganic chemistry
The invention relates to calcium carbonate based artificial material and the synthesizing method. It is characterized in that the method comprises following steps: adding low- molecular weight organic matter into system of calcium chloride and sodium carbonate according to a certain proportion, heating, organic molecule absorning selectively on crystal surface to nanocrystal growth along said crystal surface, so it is thin structure for crystal, assembling the crystal thin structure on three-dimensional orientation under interactive action of organic molecule and extension growth of crystal, getting staged layer structure crystal, and that is mentioned final product. The invention is of great importance for understanding biomineralization process and atificial synthesis for biological mineralising material.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Iodine doped bismuthyl carbonate nanosheet and molybdenum disulfide modified carbon nanofiber composites, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveUS20190127883A1Low costEasy to operateFullerenesArtificial filament washing/dryingFiberSodium iodide
Iodine doped bismuthyl carbonate nanosheet and molybdenum disulfide modified carbon nanofiber composites, preparation method and its application in wastewater treatment are disclosed. Bismuth citrate and sodium carbonate as precursors, sodium carbonate as a precipitating agent, dispersed in a mixed solution of water and ethylene glycol, sodium iodide as a iodine source, nano carbon fiber membrane act as the carrier, to synthesis carbon fiber membrane that modified by iodine-doped Bi2O2CO3 nanosheets; then sodium molybdate and thioacetamide as precursors, dispersed in water to react to obtain iodine doped bismuthyl carbonate nanosheet and molybdenum disulfide modified carbon nanofiber composites. The composite material synthesized through a series of steps exhibit excellent photocatalytic activity for the degradation of Rhodamine B and can be recycled for many times. And this invention has the advantages of simple preparation process, easy recovery and multiple use, etc., and has industrial application prospect in water pollution treatment.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Nano carbon material modified copper base catalyst and its preparing method
InactiveCN1586718AHigh activityHigh hydrogen selectivityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsHydrogen selectivityWater vapor
The present invention belongs to the field of chemical technology, and especially one kind of copper base catalyst with nanometer carbon material as co-catalyst for vapor reformation of methanol to prepare hydrogen and its preparation process. The catalyst is prepared through the process including the steps of: compounding 0.1 M solution of Cu / Zn / Al nitrate; compounding 0.1 M solution of sodium carbonate, dropping the 0.1 M solution of Cu / Zn / Al nitrate and 0.1 M solution of sodium carbonate in the same rate into reactor with nanometer carbon material for co-precipitation under strong stirring and 60 deg.c to obtain carbonate coprecipitate containing nanometer carbon material; washing, drying, roasting, etc. The prepared catalyst has unique porous structure of great specific surface area, high low temperature activity and high hydrogen selectivity, and may be used in preparing reformed product with hydrogen content up to 75 % and CO content lower than 0.1 %.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
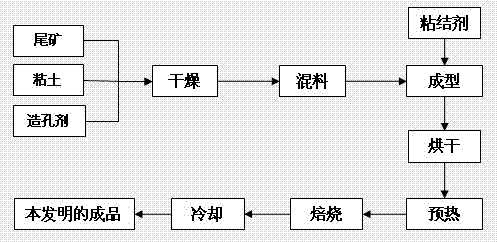
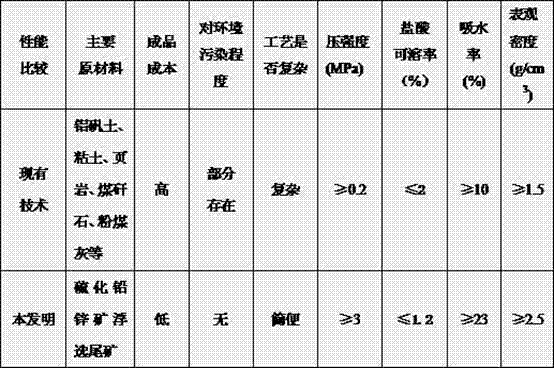
Biological ceramisite filter material made of vulcanized lead zinc ore flotation tailings, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103086741AImprove performance qualityLow costSolid waste disposalCeramicwareMining engineeringSulfidation
The invention relates to a biological ceramisite filter material made of vulcanized lead zinc ore flotation tailings. The material is characterized by being prepared from 80-90wt% of vulcanized lead zinc ore flotation tailings, 8-18wt% of clay, 1.5-2.5wt% of pore former and an additional bonder, wherein the pore former is sawdust, bamboo scraps or straws, the bonder is lignin calcium xanthate, sodium carbonate or sodium silicate liquid, and the solid-to-liquid ratio of materials used by the biological ceramisite filter material is (8-12):1. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: weighing based on proportion of main and auxiliary materials; drying; mixing; forming; drying; preheating; roasting; and cooling to prepare a biological ceramisite filter material product made of the vulcanized lead zinc ore flotation tailings. The preparation method is simple and convenient to implement, free from secondary pollution, practical and reliable. The biological ceramisite filter material made of the vulcanized lead zinc ore flotation tailings provided by the invention has the advantages of turning ore waste residue into wealth and greatly lowering the cost of materials, so that the biological ceramisite filter material is a high-quality water treatment agent.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
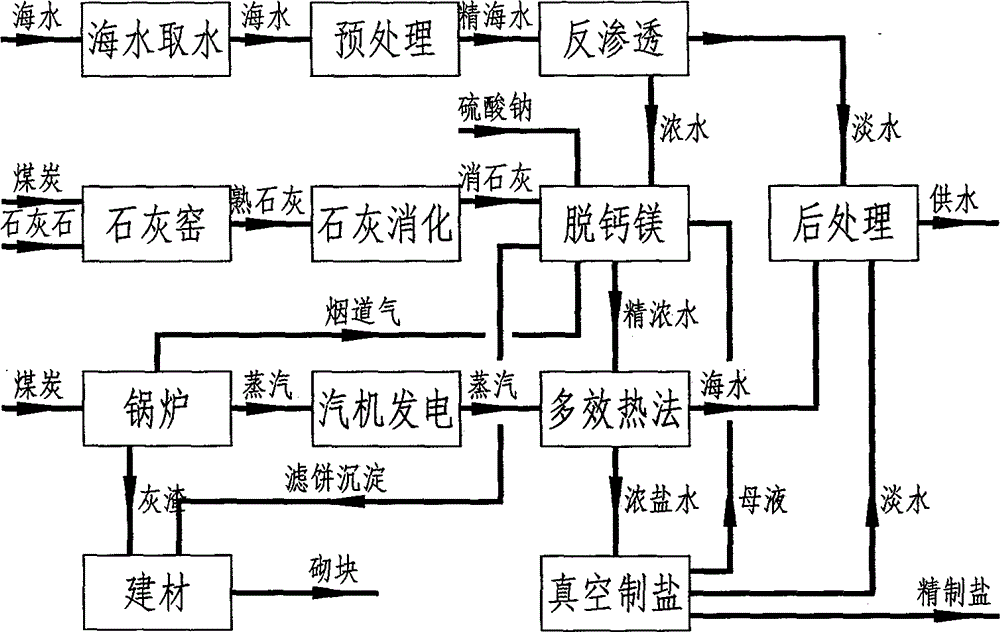
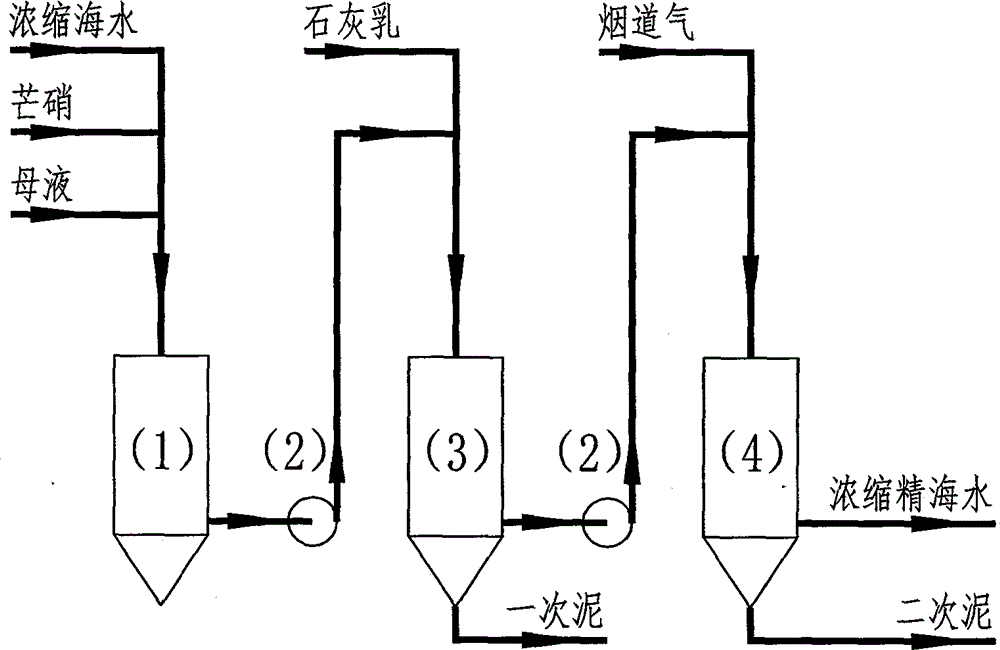
Methods for removing calcium and magnesium and co-producing water and salt by low-cost process during sea water desalination
InactiveCN102795719AScaling limitGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentWater desalinationMirabilite
The invention discloses methods for removing calcium and magnesium and co-producing water and salt by a low-cost process during sea water desalination. By the methods, on the basis of removing the calcium and magnesium in the sea water desalination industry, water and salt producing processes can be integrated, so that fresh water can be produced when the crude salt is produced; sea water is treated by a low-cost method for removing calcium and magnesium ions, so that the sea water cannot be scaled, and the sea water desalination and vacuum salt production are linked; the sea water is refined by a lime-mirabilite-carbon dioxide method, and the used raw materials are lime, mirabilite and carbon dioxide which are cheap and readily available; the process comprises the following steps of removing magnesium, namely adding a proper amount of mirabilite into the sea water, adding lime milk, and reacting the magnesium ions to form magnesium hydroxide precipitations so as to remove the magnesium; causticizing, namely causticizing superfluous calcium hydroxide and sodium sulfate to form calcium hydroxide and sodium sulfate precipitations, and separating the produced sodium sulfate precipitation; removing calcium, namely introducing flue gas into concentrated sea water subjected to magnesium removal and causticizing, reacting the calcium hydroxide and the carbon dioxide to form sodium carbonate, reacting the sodium carbonate and the calcium ions to form calcium carbonate so as to remove calcium.
Owner:王凯勋
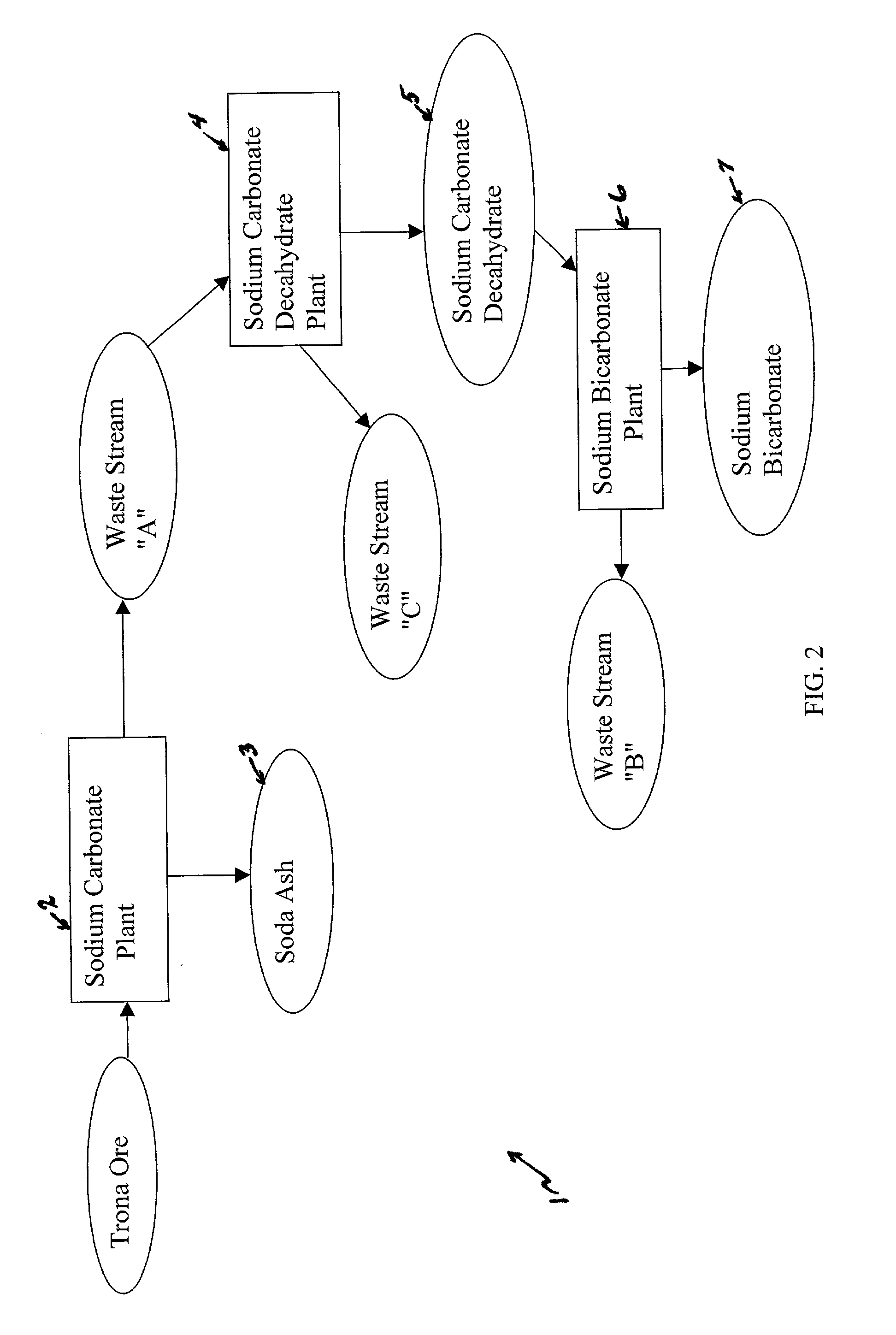
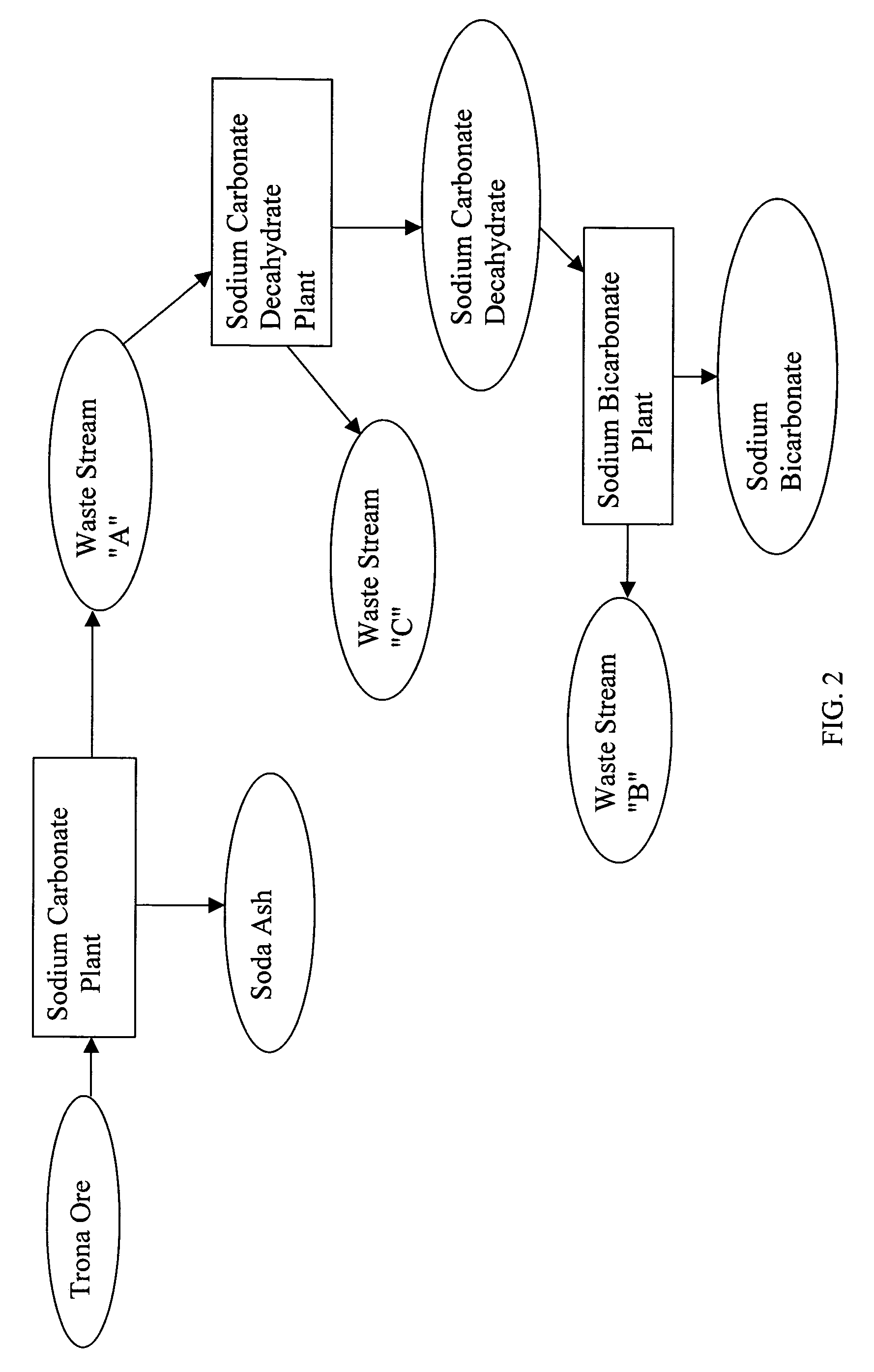
Sodium bicarbonate production method
InactiveUS20040057892A1Improvement in recovered sodium valuePromote recoveryBicarbonate preparationVarying alkali metal carbonate water contentWastewaterEngineering
A method of producing sodium bicarbonate having a high degree of purity and obtaining a net reduction in effluent waste water, as compared to prior processes, when starting from trona ore is disclosed. The process entails utilizing the waste-water effluent stream from the conversion of trona ore to sodium carbonate as the feed for the conversion of sodium carbonate to sodium bicarbonate.
Owner:CHURCH & DWIGHT CO INC
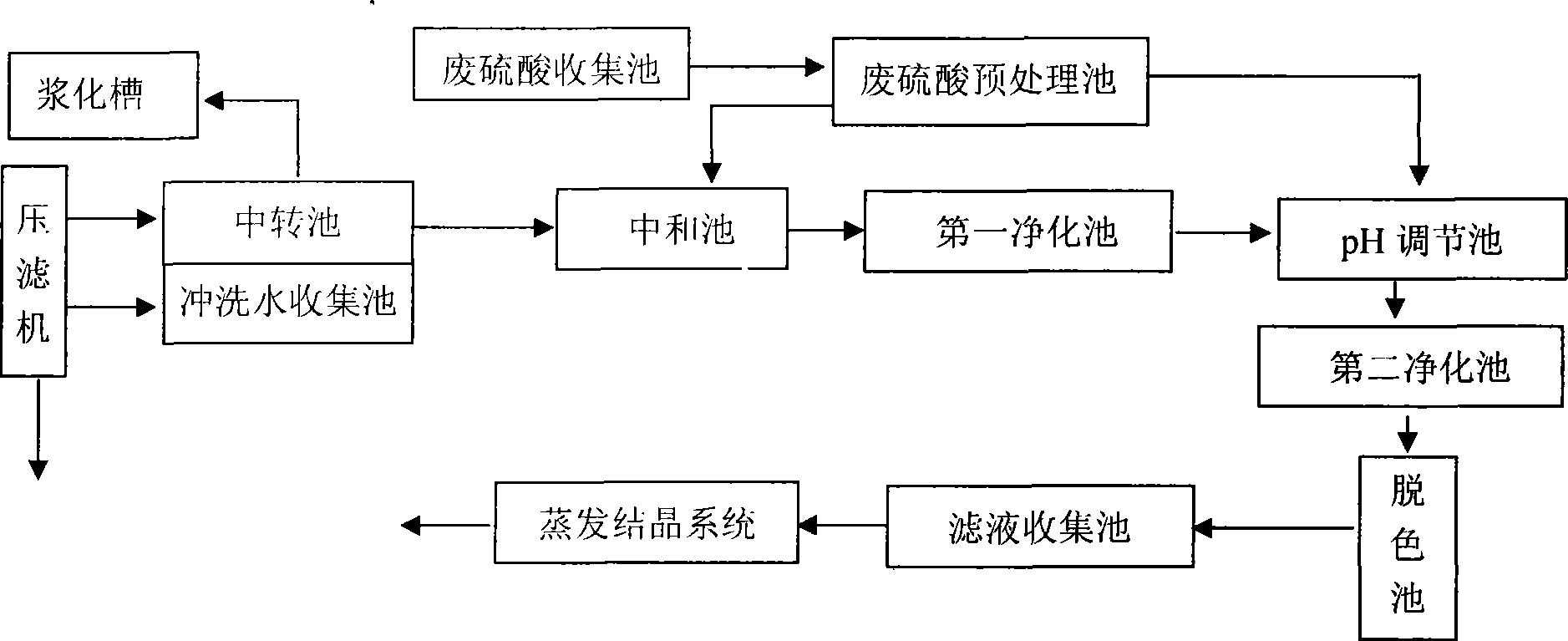
Method and device for recycling anhydrous sodium sulfate from desulfurization lead plaster filter liquor
ActiveCN101244831AEvaporative crystallizationGuaranteed Concentration RequirementsSulfate/bisulfate preparationAlkali metal sulfite/sulfate purificationFiltrationResource recovery
The invention relates to a method of recycling anhydrous sulfate sodium from de-sulfurized lead paste filtration, belonging to a resource recovery and utilization process, which avoids the disadvantages that waste sulfate is used and low concentration sulfate sodium is emitted into the environment. The method of the invention comprises: desulfurized lead paste filtration collection, sodium carbonate neutralization, first time heavy metal removal, filtration PH value adjustment, second-time heavy metal removal, decolorizing step, and vaporization and crystallization step; the device comprises a transfer tank, a neutralization tank, a first-stage purifying tank, a PH adjusting tank, a second-stage purifying tank, a decolorization tank, a filtration collection tank and a vaporization crystallization system; the waste sulfate collection tank is connected with a waste sulfate pre-processing tank, the waste sulfate pre-processing tank is respectively connected with the neutralization tank and the PH adjusting tank. The invention can directly recycle anhydrous sulfate sodium, the waste sulfate is used to neutralize the carbonate sodium remained in the filtration; the heavy metal ions and other ions in the filtration are removed according to two steps, so that the grade of obtained anhydrous sulfate sodium is equal to or larger than industrial grade.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Environment-friendly water-based drilling fluid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106675535AImprove rheologyGood filter loss reduction effectDrilling compositionWater basedFiltration
The invention provides environment-friendly water-based drilling fluid and a preparation method thereof. The water-based drilling fluid is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of water, 1-5 parts of bentonite, 0.05-0.4 part of sodium carbonate, 0.5-3 parts of a filtrate reducer A, 0.2-3 parts of a filtrate reducer B, 0.1-1 part of a viscosity / yield boosting agent, 0.5-4 parts of an inhibitor, 1-5 parts of a lubricant, 2-6 parts of a micro / nano particle plugging agent and 0-200 parts of weighting materials. The preparation method of the drilling fluid comprises the steps of adding bentonite and sodium carbonate into water; sequentially adding the filtrate reducer A, the filtrate reducer B, the viscosity / yield boosting agent, the inhibitor, the lubricant and the micro / nano particle plugging agent; adjusting the pH value by using sodium carbonate; selectively adding the weighting materials until the density reaches the drilling requirements. The resisting temperature of the drilling fluid can reach 150 DEG C, EC50 is greater than 3.0*10<4>mg / L, and the drilling fluid is nontoxic and environmentally friendly and has good rheological property, filtration reducing property, rejection capability, lubricating property, pollution resistance and reservoir protection effect.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +3
Synthesis method for low-temperature manganese-based compound metal oxide denitration catalysts
InactiveCN104001520AInhibition of agglomerationGood resistance to low temperature freezingDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNickel saltPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of material preparation, and particularly relates to a synthesis method for low-temperature manganese-based compound metal oxide denitration catalysts. According to the method, a manganese salt and a salt from a cobalt salt, a ferric salt or a nickel salt are dissolved in ethylene glycol in a mixed manner; a sodium carbonate water solution is dripped at a low temperature, and coprecipitation is carried out; and coprecipitation products are washed by water, are dried, and are calcined in the air, and products can be obtained. The synthesis method provided by the invention adopts a low-temperature artificially induced crystal splitting technology, one kind of ions from cobalt ions, ferric ions and nickel ions are added, and manganese ion precipitate crystals are induced to split in the manganese ion precipitate crystal growth process. The split crystals do not agglomerate during the growing in low-temperature environment. After the crystals after splitting growth are calcined, manganese-based compound metal oxides with high specific surface area can be obtained, and the manganese-based compound metal oxides can show excellent low-temperature catalytic activity when being used for catalyzing a denitration reaction. The synthesis method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the control is easy, and raw materials can be easily obtained, so the synthesis method is suitable for large-scale production, and in addition, the environment pollution is little.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Deep-fry cereal instant noodles and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses deep-fry cereal instant noodles and a preparation method thereof. The deep-fry cereal instant noodles are prepared from wheat flour, solanum tuberdsm, tapioca starch, guar gum, sodium polyacrylate, composite phosphate and sodium carbonate in parts by weight. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: putting the materials into a dough mixer, adding water to prepare paste, and curing the paste; compositing the cured paste to be strips through a laminating machine, and cutting the strips and shaping; and cooking the shaped noodles, spraying condiments, frying, finally carrying out regular air cooling and then packaging. The deep-fry cereal instant noodles prepared according to the technical scheme are good in mouth feeling, rich in nutrition and few in oil content, and are beneficial to the health of people.
Owner:河南面之缘食品有限公司
Nano-selenium-containing amino acid foliar fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104387192ASolve the problem of resource reuseSolve pollutionCalcareous fertilisersAnimal corpse fertilisersBiotechnologyActive agent
The invention discloses a nano-selenium-containing amino acid foliar fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The nano-selenium-containing amino acid foliar fertilizer is prepared from such raw materials as molasses, animal hair, selenium dioxide, sulfuric acid, copper sulfate, manganese sulfate, zinc oxide, ferrous sulfate, ammonium carbonate, ammonium molybdate, urea, potassium chloride, boric acid, fulvic acid, a surfactant, ethylene glycol, sodium carbonate, quick lime or calcium hydroxide, phosphoric acid and water. The preparation comprises the steps of reducing selenium dioxide by use of the molasses to obtain nano-selenium, hydrolyzing the animal hair into an amino acid solution, and then performing the reactions of neutralization, complexing, emulsification and the like to obtain the nano-selenium-containing amino acid foliar fertilizer. According to the nano-selenium-containing amino acid foliar fertilizer, the problem of transforming inorganic selenium into nano-selenium and the problem of recycling waste both are solved; the fertilizer is capable of improving the water retention and drought resisting capability of plants and increasing the content of the organic selenium element content in crops; the preparation method of the fertilizer is mild in reaction conditions, simple in process, relatively low in production cost and prone to industrial production, and has excellent economic benefit, social benefit and ecologic benefit.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES
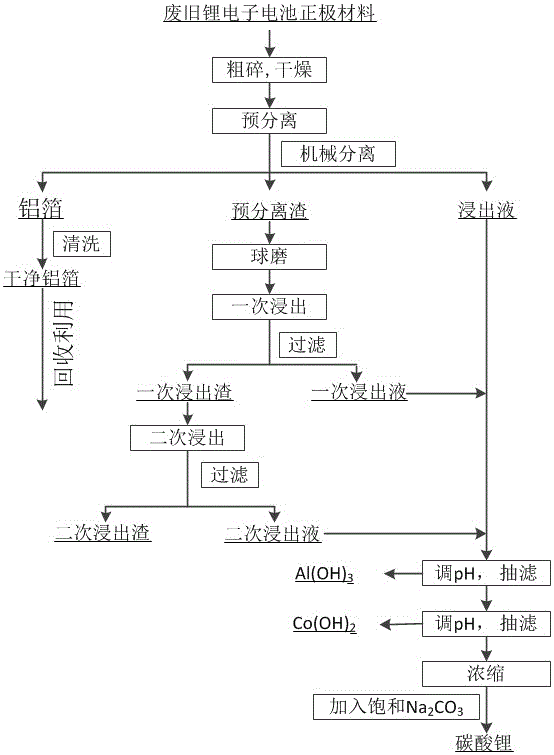
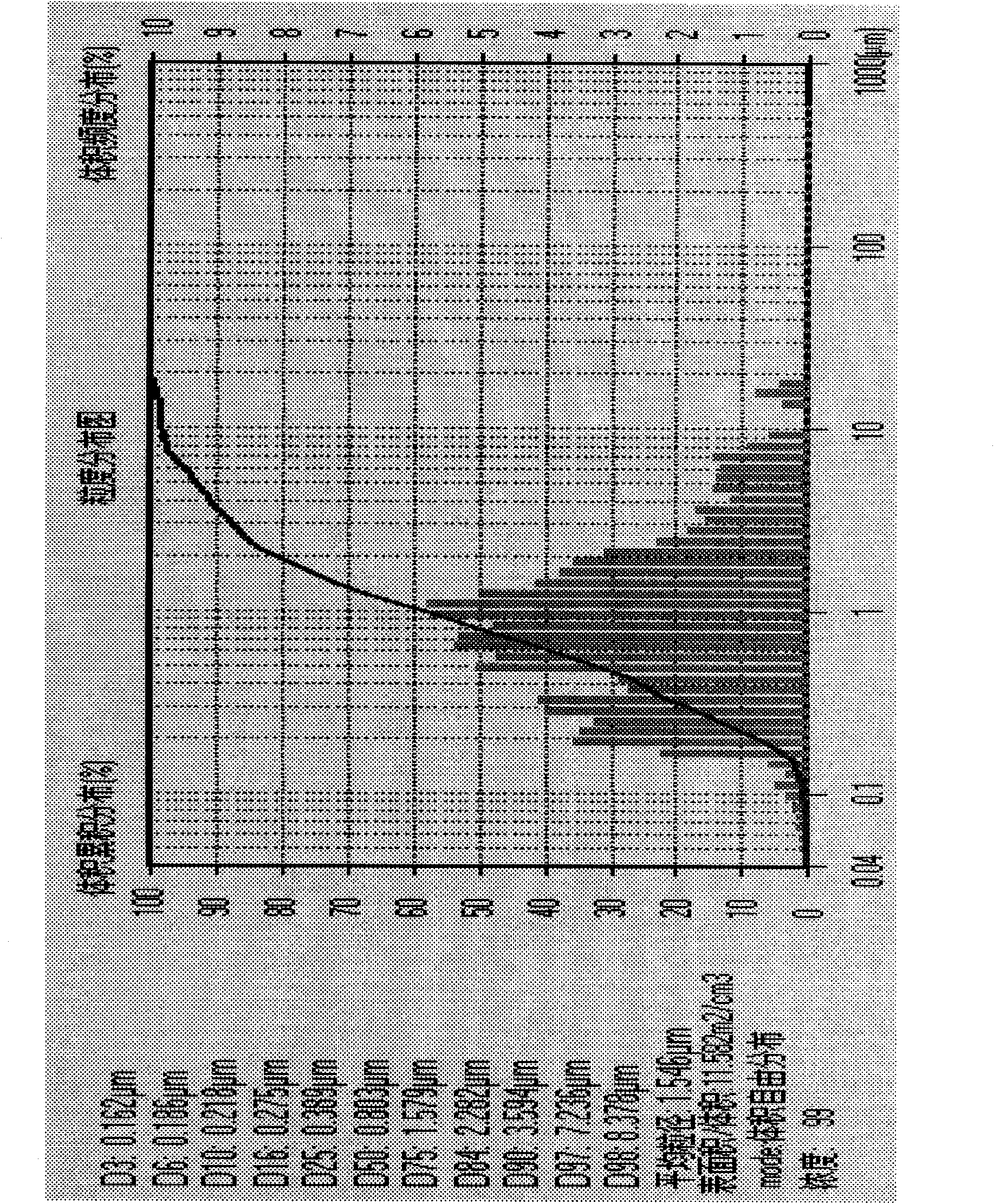
Method for mixed acid leaching and recovery of positive pole materials of waste and old lithium ion batteries
ActiveCN106848471AWide range of sourcesImprove leaching efficiencyWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingAluminium hydroxideFiltration
The invention provides a method for mixed acid leaching and recovery of metal components of positive pole materials of waste and old lithium ion batteries. The method comprises carrying out coarse crushing on wastes, drying the crushed wastes, pre-leaching the wastes through a mixed acid containing a reduction agent to obtain pre-separated residues, carrying out ball milling, carrying out primary and secondary leaching, mixing the primary and secondary leachates and the pre-leachate, adjusting pH of the mixture, carrying out suction filtration to obtain aluminum hydroxide and raffinate containing cobalt and lithium, adjusting pH of the raffinate containing cobalt and lithium at a high temperature, carrying out suction filtration to obtain cobalt hydroxide and raffinate containing lithium, carrying out concentration on the raffinate containing lithium at a high temperature, adding a saturated sodium carbonate solution into the concentrate to obtain high purity lithium carbonate, and recovering aluminum foil. The method utilizes a mixed acid leaching agent, has high leaching efficiency, can gradually acquire high purity aluminum, aluminum hydroxide, cobalt hydroxide and high purity lithium carbonate (having purity of 99.9%), realizes efficient recovery, overall recovery and collaborative recovery of high-value metals in the waste and old lithium-ion batteries and has a good application prospect.
Owner:BOTREE CYCLING SCI &TECH CO LTD
Iron base catalyzer through Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and preparation method
InactiveCN1245255CReduce manufacturing costReduce preparation energy consumptionHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsMicrosphereSlurry
A Fe-base catalyst with high antiwear performance, activity and stability for the Fischer-Tropsch synthesis contains Fe, Zn, Cu, K and SiO2. It is prepared through proportionally mixing sodium carbonate solution as precipitant with the mixed solution of iron nitrate, zinc nitrate and copper acetate, depositing to obtain deposit slurry, adding the mixed solution of potassium silicate and silicon sol, spray drying and calcining.
Owner:中科合成油淮南催化剂有限公司
New process for co-producing ultra-fine white carbon black and calcium carbonate
InactiveCN101898776AAddress effectivenessImprove qualityCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesSilicaPhysical chemistryCarbide
The invention provides a method for co-producing white carbon black and calcium carbonate. Carbide slag or lime and quartz sand are used as main raw materials. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing sodium silicate solution into carbon dioxide to obtain a mixture of white carbon black and sodium carbonate or sodium bicarbonate, filtering the solution, adding lime or carbide slag into the solution, preparing caustic soda and ultra-fine calcium carbonate by causticizing reaction, adding the quartz sand into the filtered dilute alkali liquor, and reacting the mixture under a heating band pressure to obtain sodium silicate solution so as to realize circulation and co-production.
Owner:BEIJING ZIGUANG YINGLI CHEM TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com