Patents
Literature
74 results about "SU-8 photoresist" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
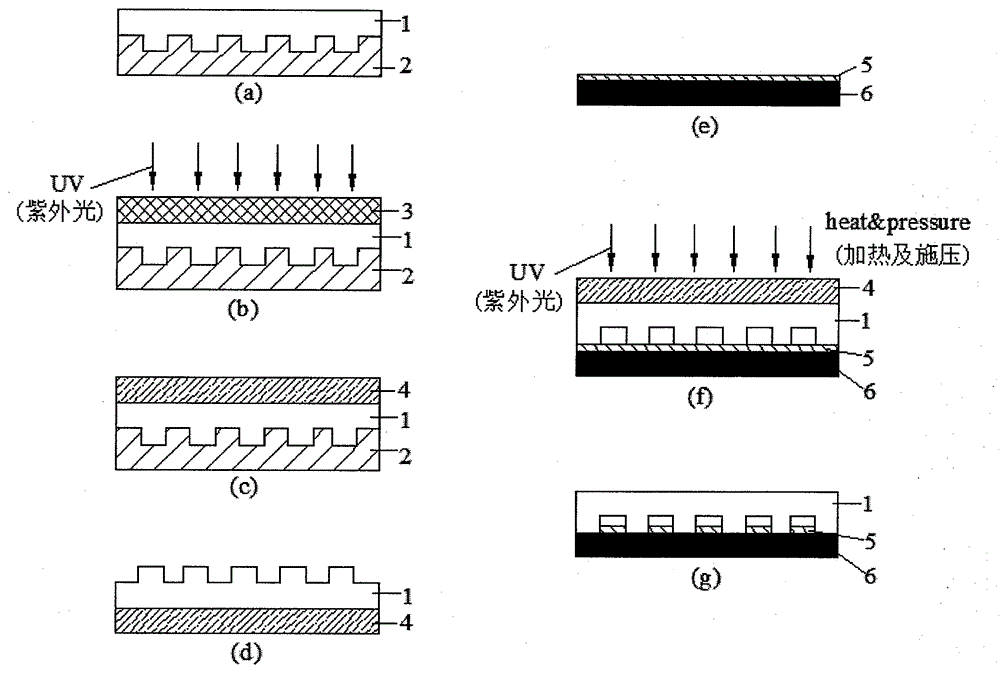
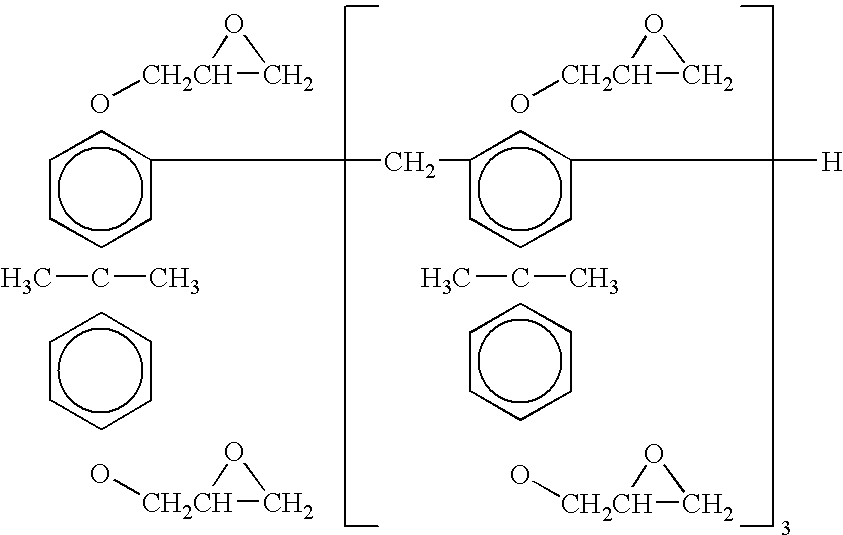
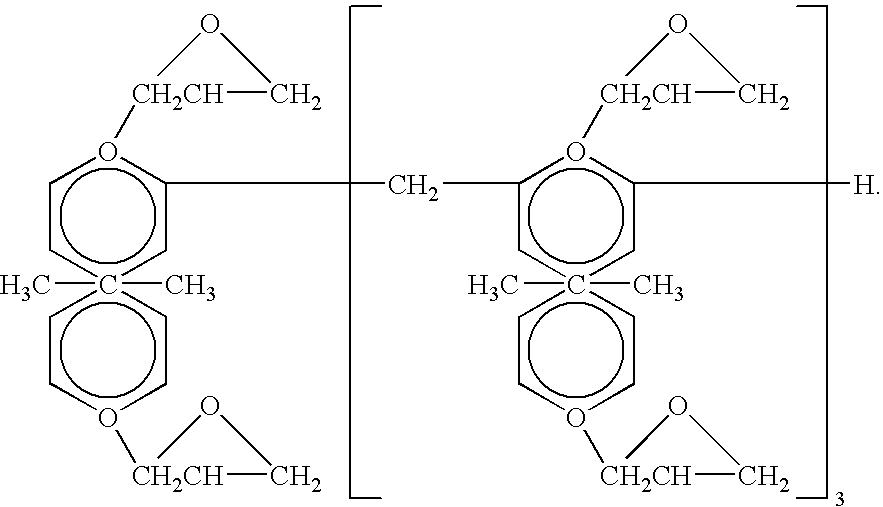
SU-8 is a commonly used epoxy-based negative photoresist. Negative refers to a photoresist whereby the parts exposed to UV become cross-linked, while the remainder of the film remains soluble and can be washed away during development.
Method of manufacturing magnetic micro-structure
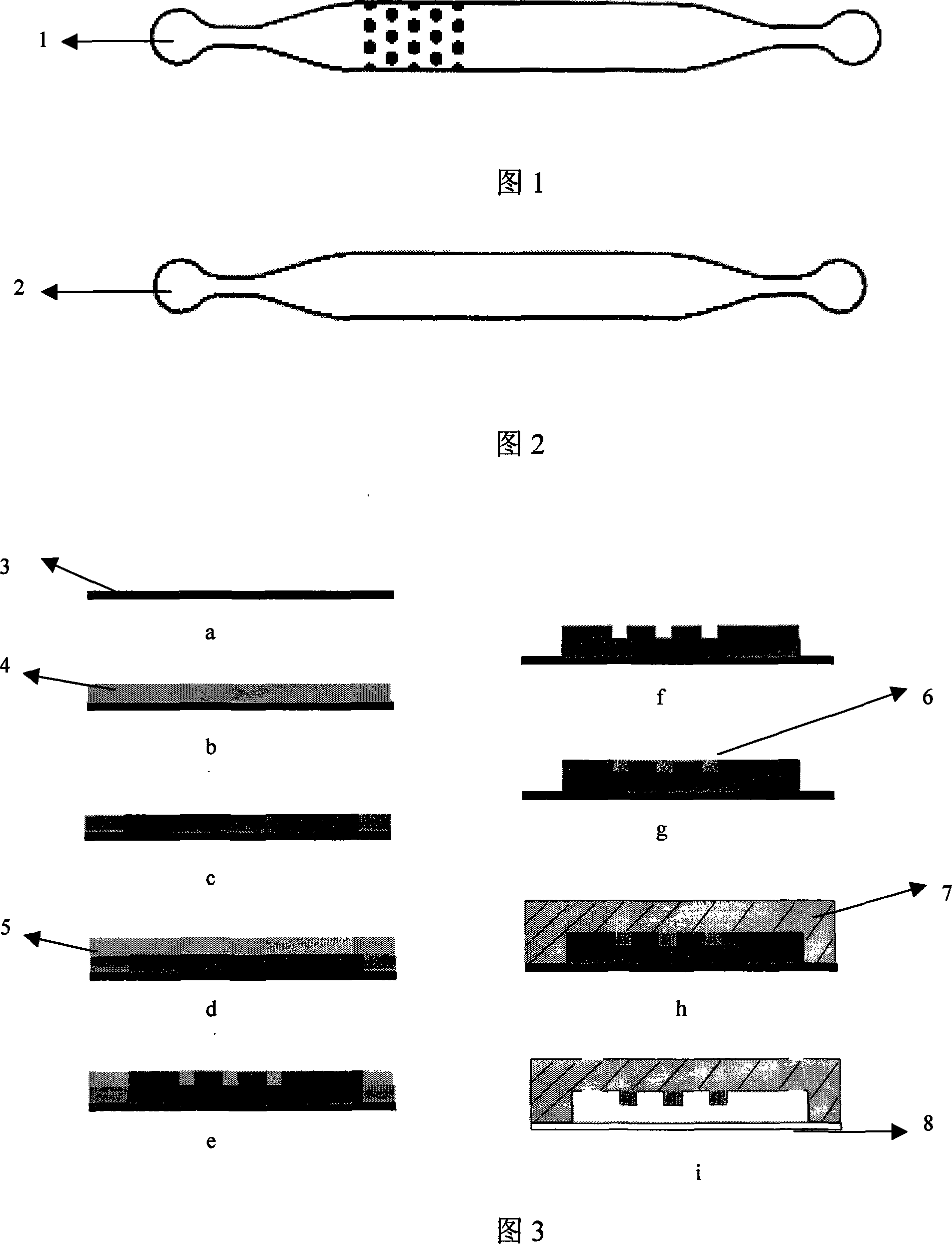
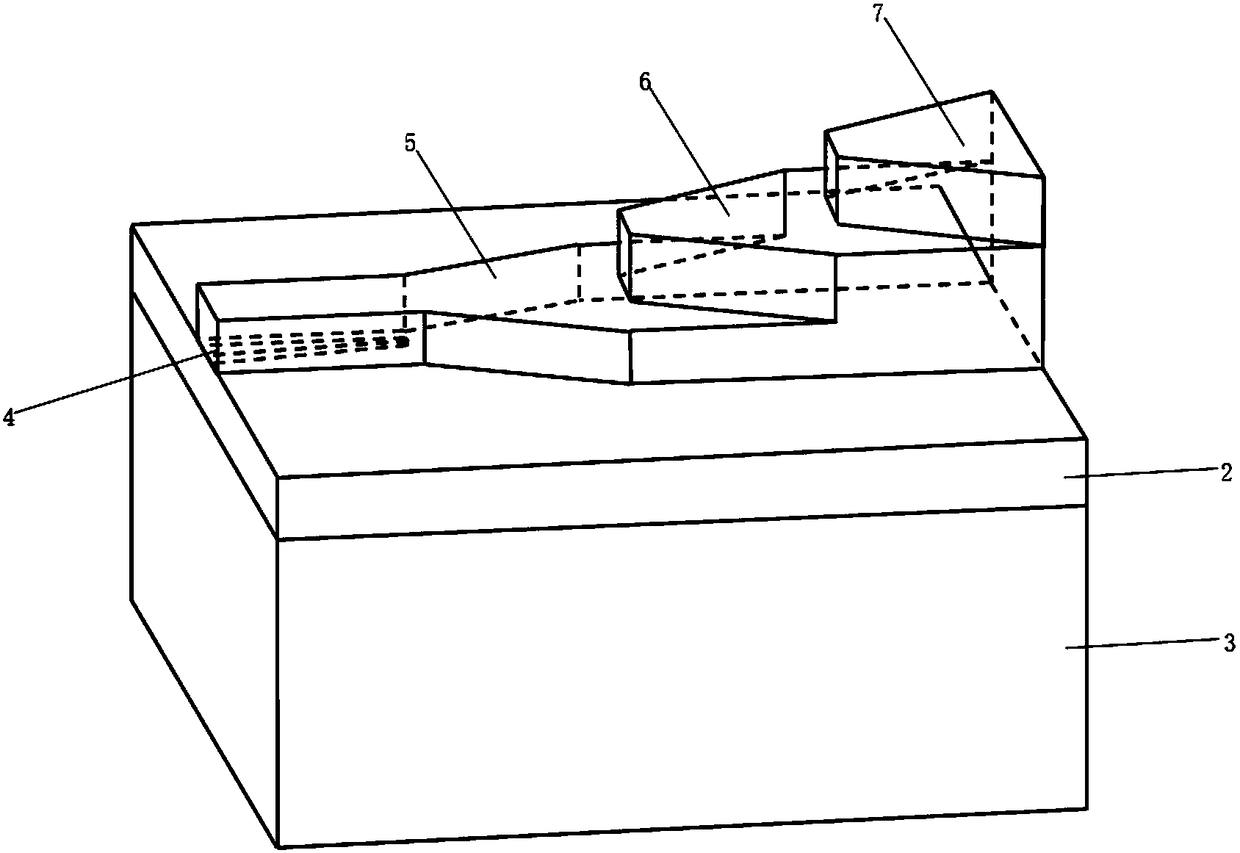
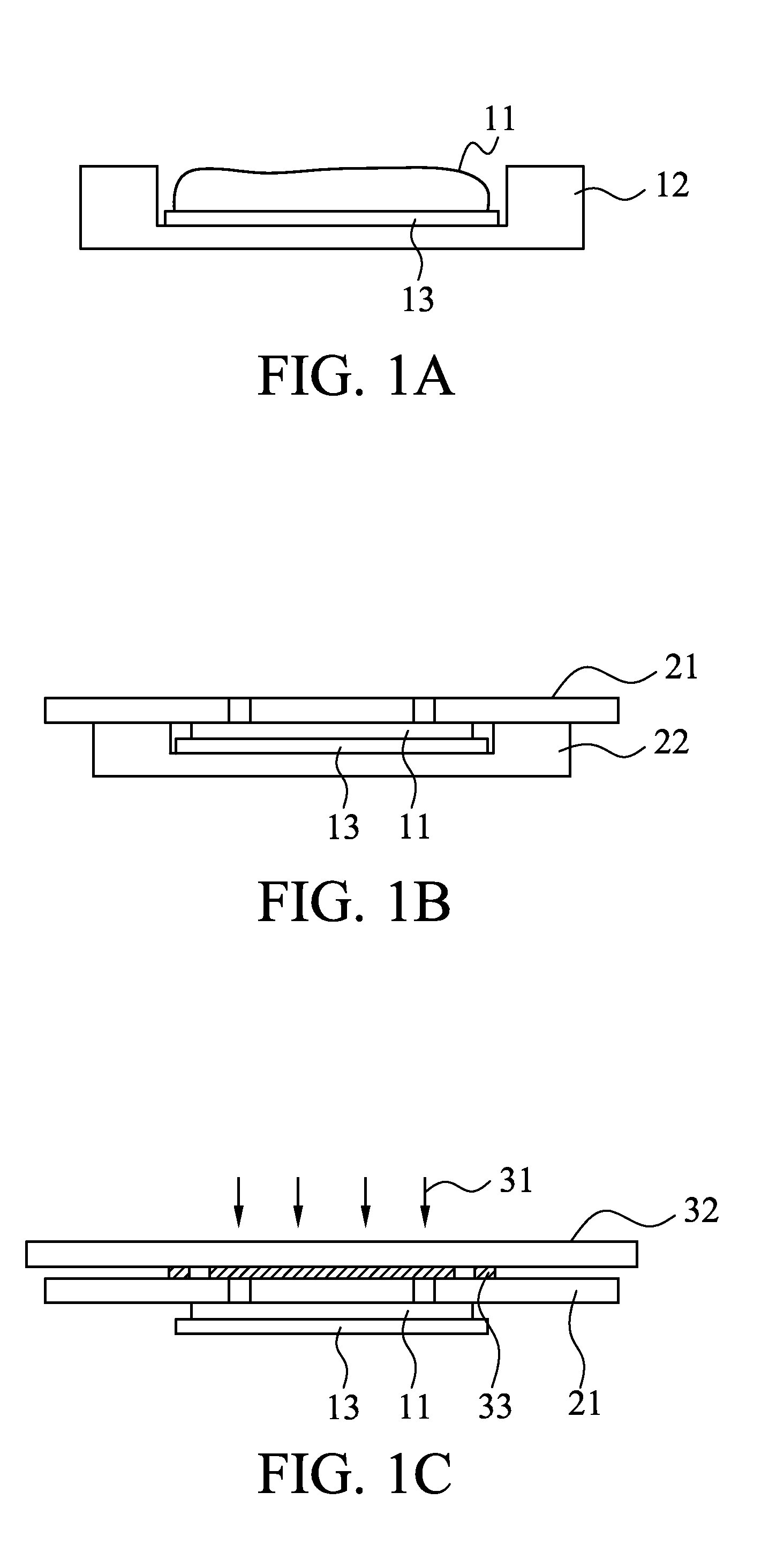
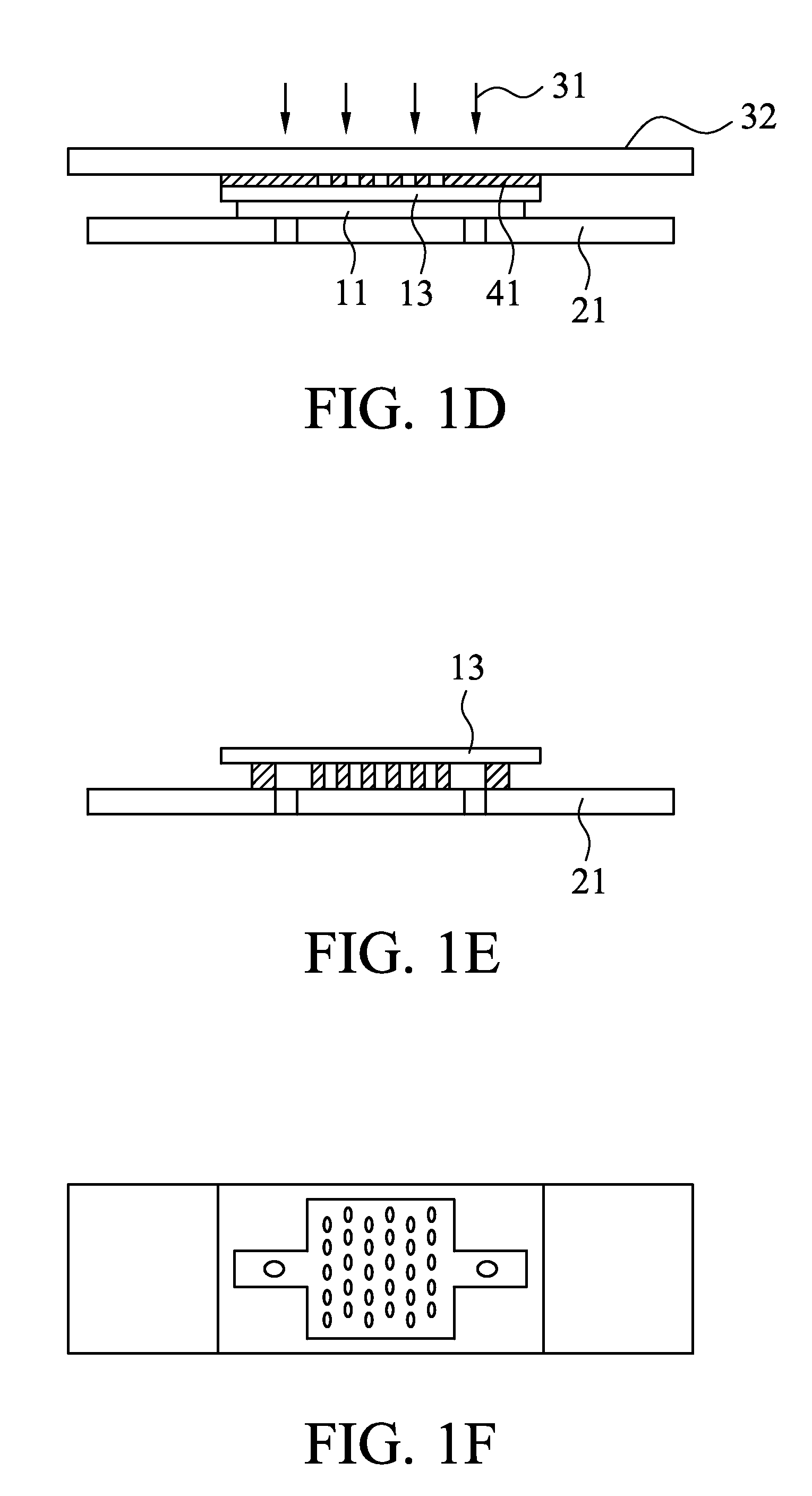
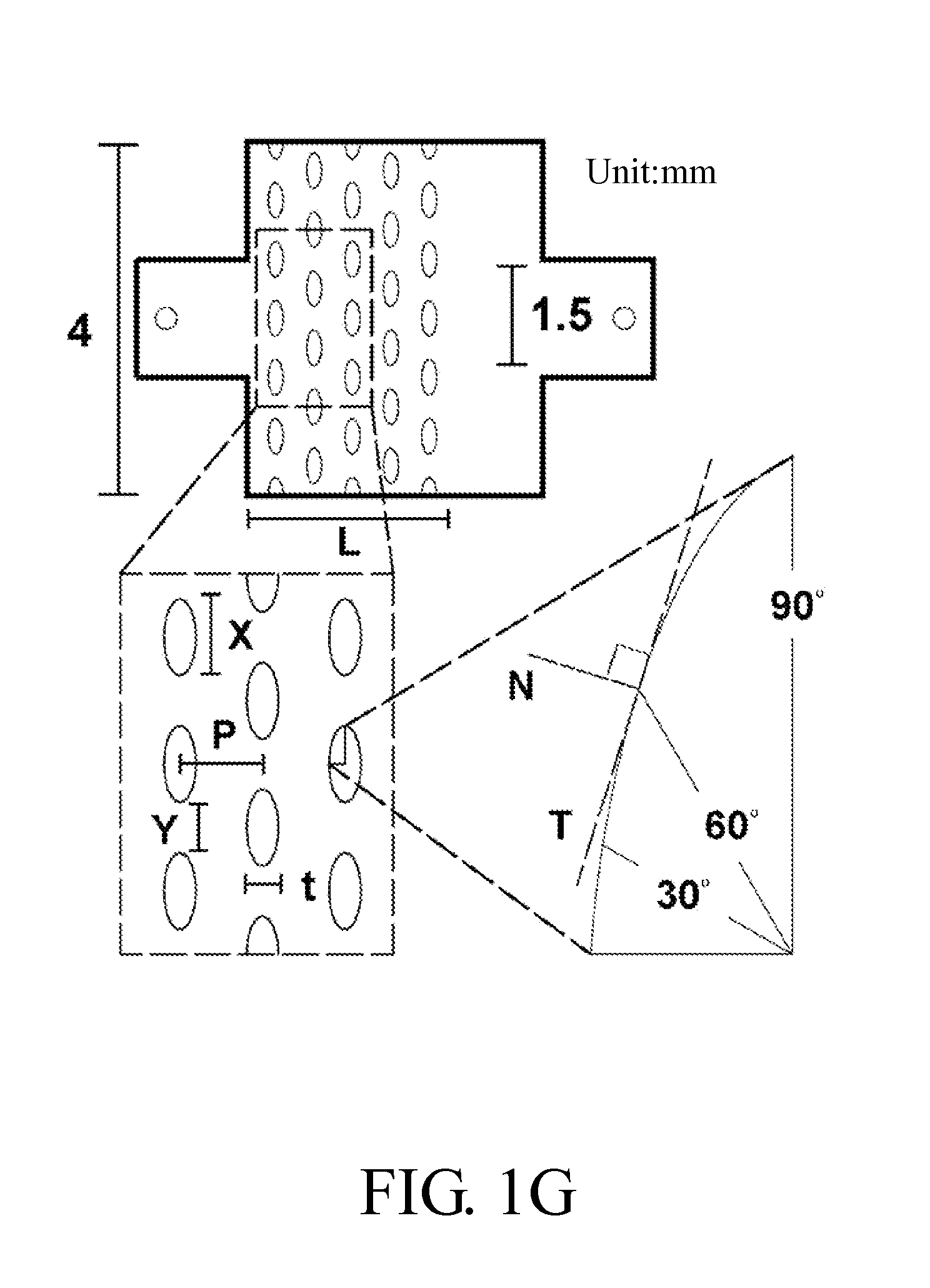
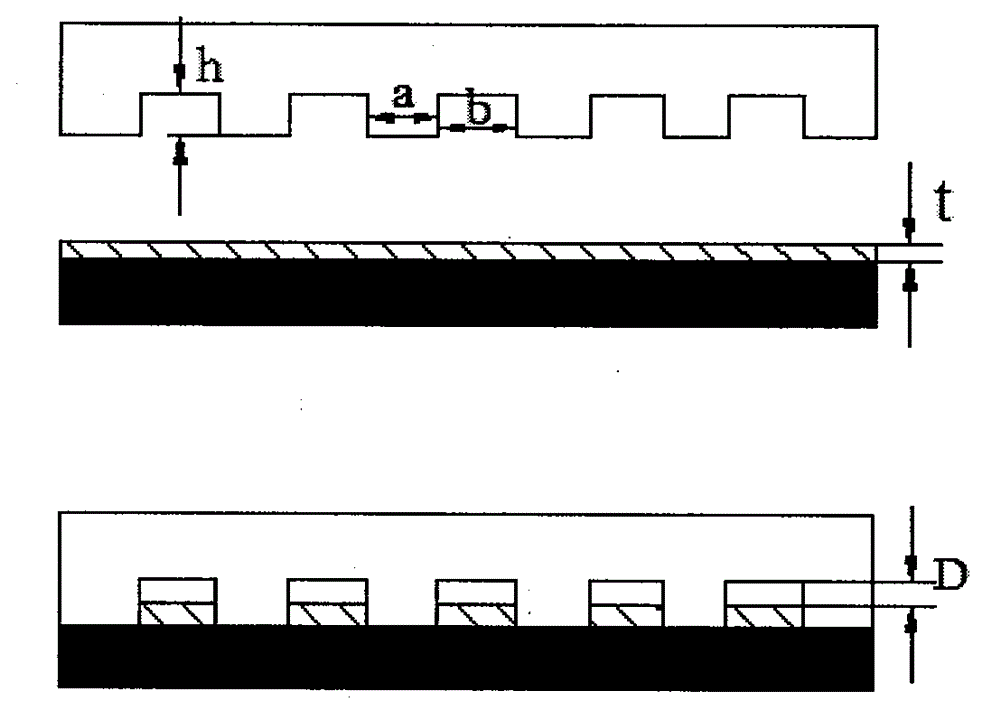
InactiveCN101108721AReduce manufacturing costEasy and quick to makeSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsMicro structureMicrometer
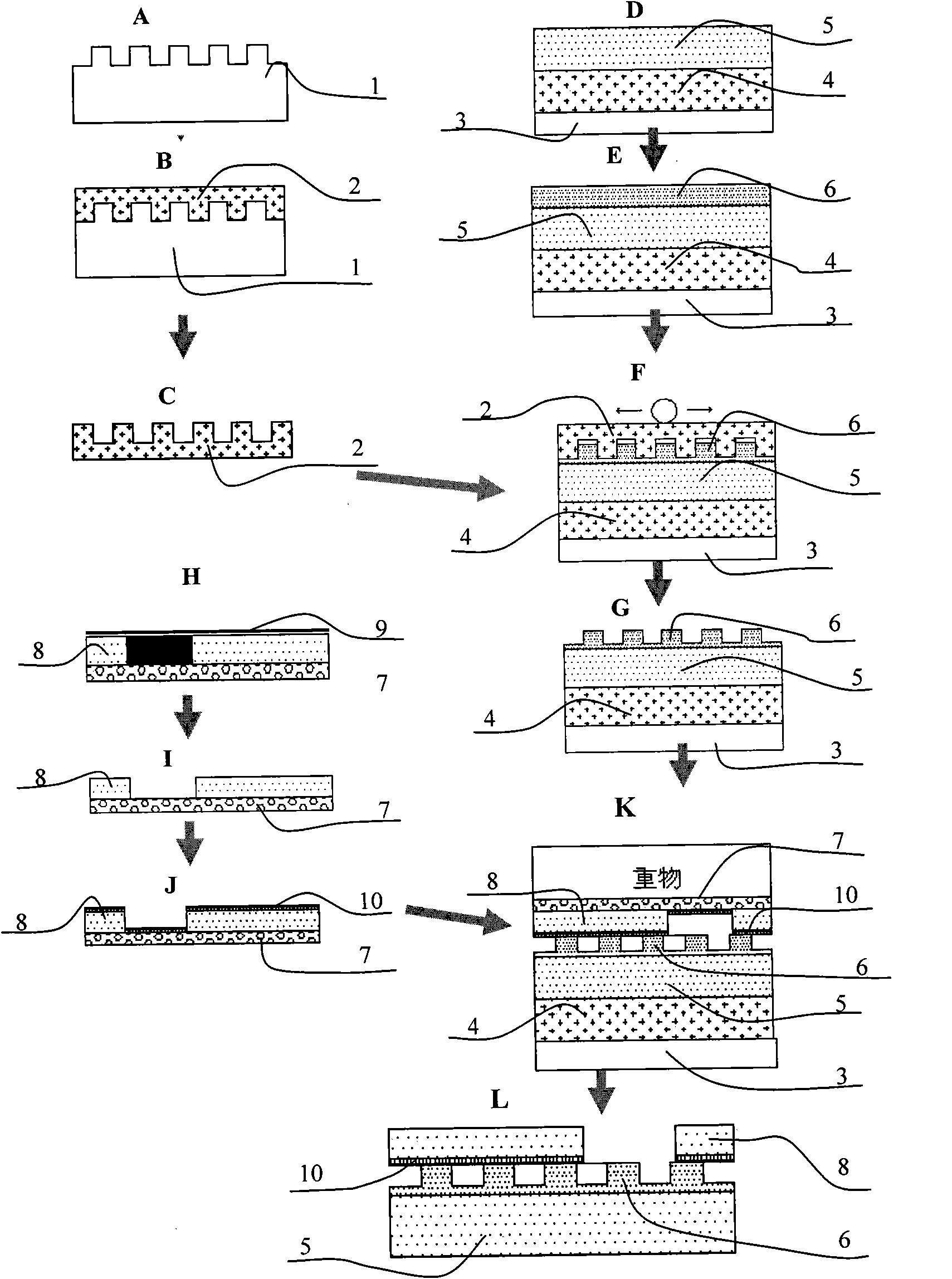
The invention relates to a fabrication method of the magnetic microstructure, which is characterized in that the invention comprises the fabrication of multilayer mould and the fabrication of the magnetic microstructure. The former is that the standard RCA cleaning process is used to clean silicon chips; multi layers of SU-8 photoresist are coated by rotating on the silicon chip surfaces and the multi layers of SU-8 mould are gotten after prebaking, photoetching, post baking and developing, and then the invention forms the magnetic microcolumn structure in the chip while molding dying the PDMS chip through directly filling the magnetic powders in the multilayer mould. Adopting the provided fabrication method can dispense with the electroplating process and fabricate the magnetic microstructure in the microfluid chip rapidly. The microstructure height is fabricated between micrometers less than ten and hundred of micrometers, which is determined by the photoresist layers of the rotating coating SU-8 and the magnetic microstructure is any one of the microcolumn, microline, microring or microcoil.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Silicon waveguide spot size converter based on multilayer polymer structure and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108132499AImprove coupling efficiencyEasy to integrateOptical waveguide light guideLithographic artistSilicon nanowires
The present invention discloses a silicon waveguide spot size converter based on a multilayer polymer structure and a preparation method thereof. The silicon waveguide spot size converter based on themultilayer polymer structure and the preparation method thereof are applied to coupling of silicon nanowire optical waveguides and common single-mode fibers. The structure is made by employing an integrated photoelectron process method, on a silicon substrate on an insulator layer, a taper-type silicon waveguide is made, a lithography technology is employed to continuously nest three layers of combined taper-type optical waveguides with materials of SU-8 photoresist on the insulator layer, and a silicon dioxide upper cladding is deposited to achieve making of a spot size converter. The taper-type portions of the three layers of combined taper-type optical waveguides with materials of SU-8 photoresist are employed to reduce the sizes of spot sizes entering the single-mode fibers in a horizontal direction and a vertical direction, perform cascade with a reverse taper-type silicon waveguide and finally allow a light field to couple into the silicon nanowire optical waveguides. The directend face connection between the silicon nanowire optical waveguides and the common single-mode fibers can be achieved, the matching with the single-mode fiber spot size is improved, the optical coupling efficiency is improved, and it is convenient to perform large-scale optical path integration.
Owner:苏州易缆微光电技术有限公司
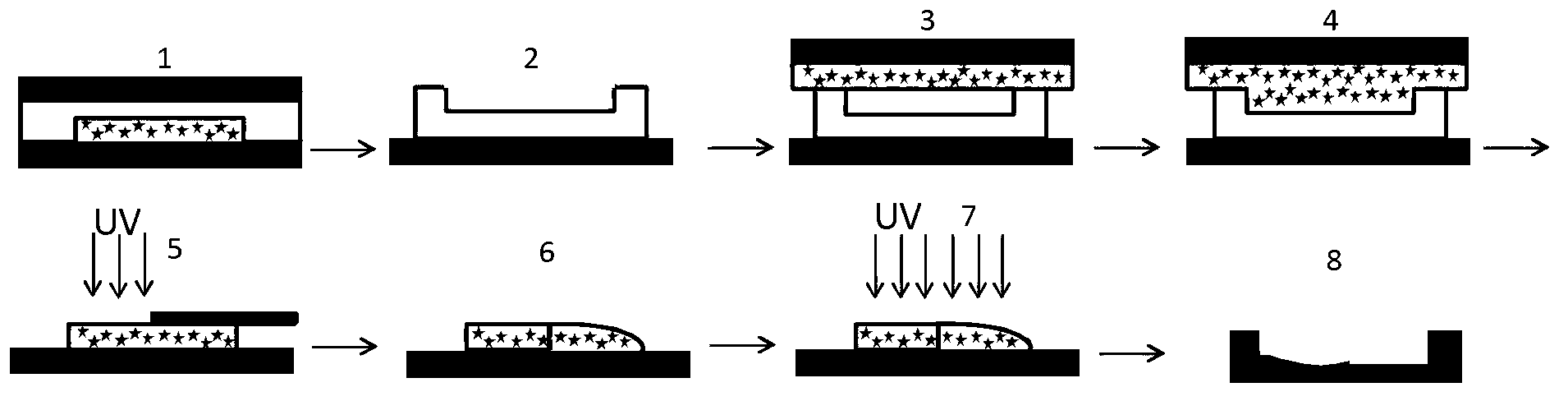
Method for making self-supporting structure of nano fluid system based on SU-8 photoresist
InactiveCN102012633AIncrease the areaLow production weekDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusBond interfacePolyethylene terephthalate
The invention discloses a method for making a self-supporting structure of a nano fluid system based on a SU-8 photoresist, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly processing and making a PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) flexible template, making a SU-8 nano channel substrate by utilizing the PDMS flexible template, simultaneously making a SU-8 bonding layer comprising a sample pond by utilizing ultraviolet exposure development, realizing the bonding sealing of the SU-8 nano channel substrate and the bonding layer by utilizing a bonding technique, and finally removing PDNS and PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) flexible substrates to obtain the self-supporting structure of the nano fluid system. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low making cost and low equipment requirement. The making result shows that the system has no delamination and blockage, the bonded interface can be hardly seen, and the outline of a channel is clear and visible so that the self-supporting structure of the nano fluid system has good quality.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Polypyrrole microelectrode with three-dimensional structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101950685AIncrease storage capacityImprove featuresElectrolytic capacitorsCooking & bakingResist
The invention discloses a polypyrrole microelectrode with three-dimensional structure which belongs to the technical field of the micro-electro-mechanical preparation and is used in the miniature supercapacitor, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the microelectrode comprises the following steps: adopting the MEMS technology to coat a SU-8 epoxy group negative chemically amplified resist on the surface of a copper substrate, performing spin-coating, pre-baking, lithographic process treatment, exposure, post-baking, development, rinsing and heat setting to form a columnar structure which is prepared from SU-8 photoresist and is in an array arrangement, on the surface of the copper substrate, and covering a functional film composed of polypyrrole and conductive material on the surfaces of the copper substrate and the microcolumn array microelectrode. The invention solves the problems that the common polypyrrole electrode with a two-dimensional structure can not store a large quantity of charges, have high internal resistance and the like, thus improving the energy storage characteristic and large current discharge performance of the miniature supercapacitor. The miniature supercapacitor of the invention has wide application prospect in the fields of sensor network node power supply, micro-robot driving power and fuze power.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for producing microelectromoulding metal mould
InactiveCN1715455AReduce internal stressGood side wall verticalityElectroforming processesMicro structureHigh surface
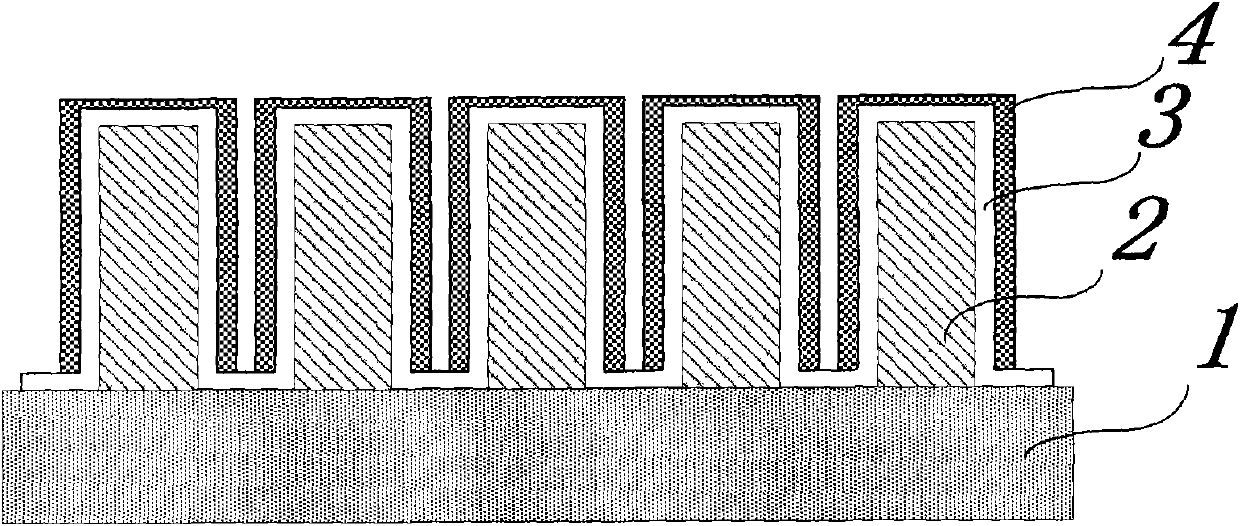
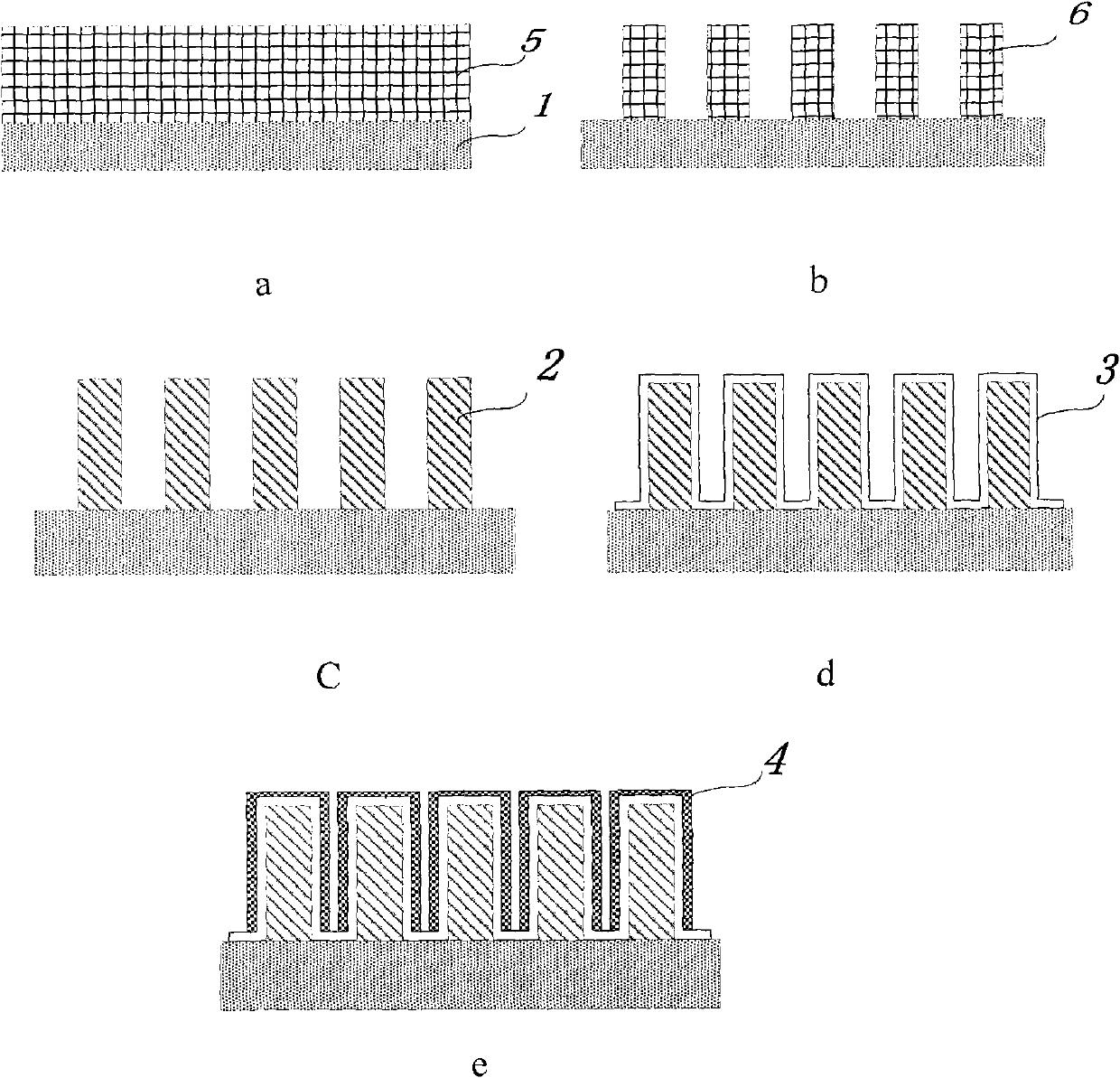
The microelectromolding metal mold making process belongs to the field of micro machine building technology. The microelectromolding metal mold making process includes the steps of: pre-treatment of mold base, making microelectromolding mother mold, microelectromolding, post-treatment and detection. The present invention adopts so-called 'no-back board growth process', in which micro structure pattern is electromolded directly on nickel substrate via ultraviolet irradiation on photoetching mask. During making microelectromolding mother mold, one seed layer is added between the SU-8 photoresist and the substrate; and in the post-treatment, vacuum annealing is adopted. The microelectromolding metal mold made in the method of the present invention has the merits of high side wall verticality and high surface smoothness. The present invention is suitable for fine machining of organic polymer, including plastic.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Blended self-assembly membrane based micro ampere immunity sensor and preparation thereof
InactiveCN1908665AReduce volumeHigh sensitivitySolid-state devicesMaterial electrochemical variablesInsulation layerAmpere
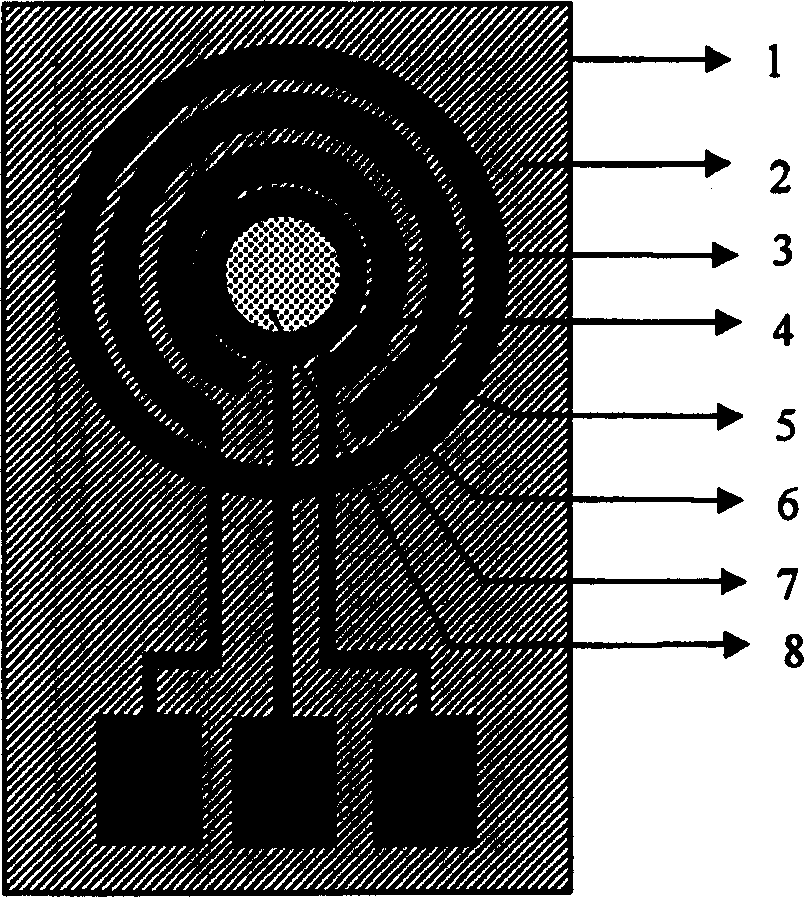
The micro-amp immunity sensor based on mixed self-assembly film comprises: a silicon substrate, a SiO2 and Si3N4 insulation layer, and the concentric circular gold film electrode, SU-8 photoresist ring sensitive film pond, a ring Pt-film counter electrode / reference electrode, a Su-8 photoresist ring reaction pond, and a bio-molecular sensitive film fixed on the electrode. With nano technology and mixed self-assembly film, this invention has well consistence, correlativity and compatibility with IC, and shows a new path for immunity analysis and detection.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing high aspect ratio metal microgratings on metal substrate
InactiveCN103913789ASolution depthSolve the fragile baseDiffraction gratingsElectroforming processesBinding forceWidth ratio
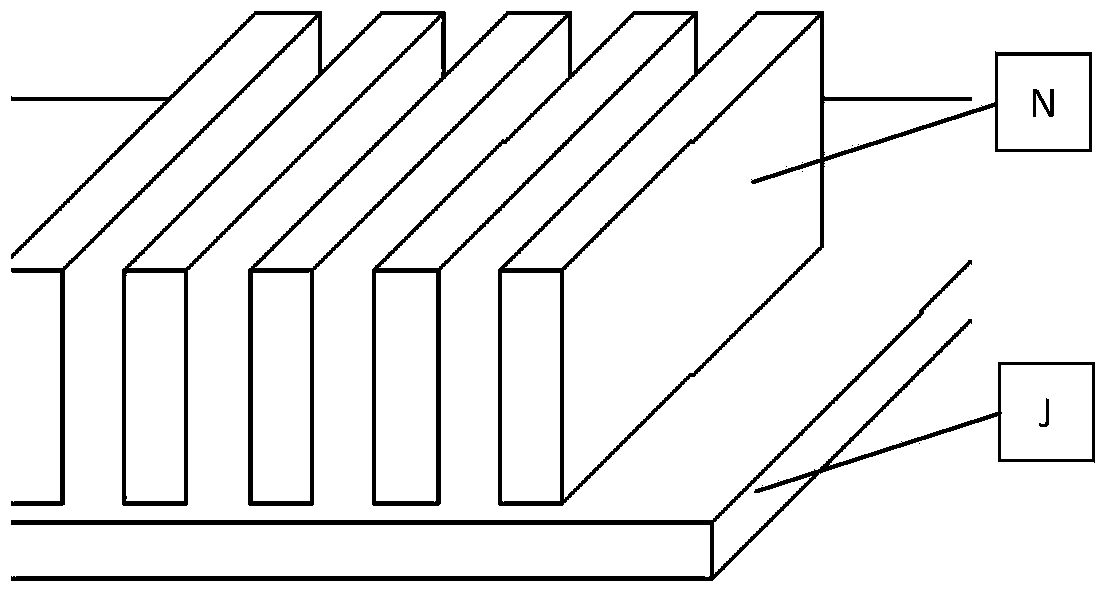
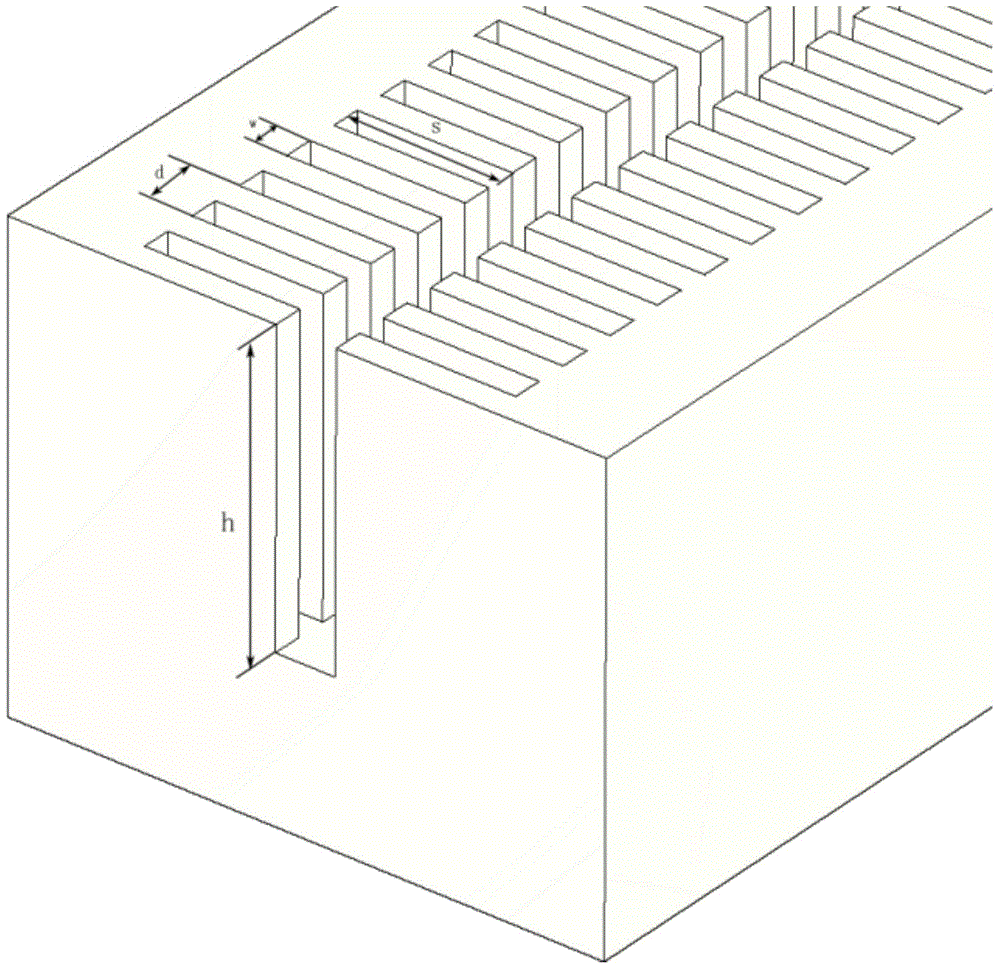
The invention discloses a method for preparing high aspect ratio metal microgratings on a metal substrate, and belongs to the micro-manufacturing technical field. A UV-LIGA technology is adopted, the photolithography technological processes such as two-time photoresist homogenizing, layered exposure and one-time developing are executed on a high-purity nickel plate substrate J to obtain an SU-8 photoresist film, and then the metal microgratings can be manufactured through micro electroforming nickel N after micro electroforming treatment; a line width compensating method is used for solving the problem that line width is decreased due to swelling; in the photoresist removing process, a 'ultrasound-soaking-ultrasound-soaking' circulating method is used for removing photoresist; in annealing operation, vacuum annealing is adopted to remove residual stress, and the binding force between the substrate and the metal gratings is improved. The method for preparing high aspect ratio metal microgratings on the metal substrate has the advantages that when the method is used for preparing the metal microgratings on the metal substrate J, the depth-to-width ratio is large, dimensional precision is high, mechanical strength is high, the preparation technology is simple, and cost is low.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
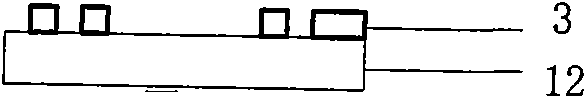
Micro-well based gas sensor array and its making method
ActiveCN102735712AAvoid cross contaminationHigh selectivityDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesSensor arrayMultilayer membrane
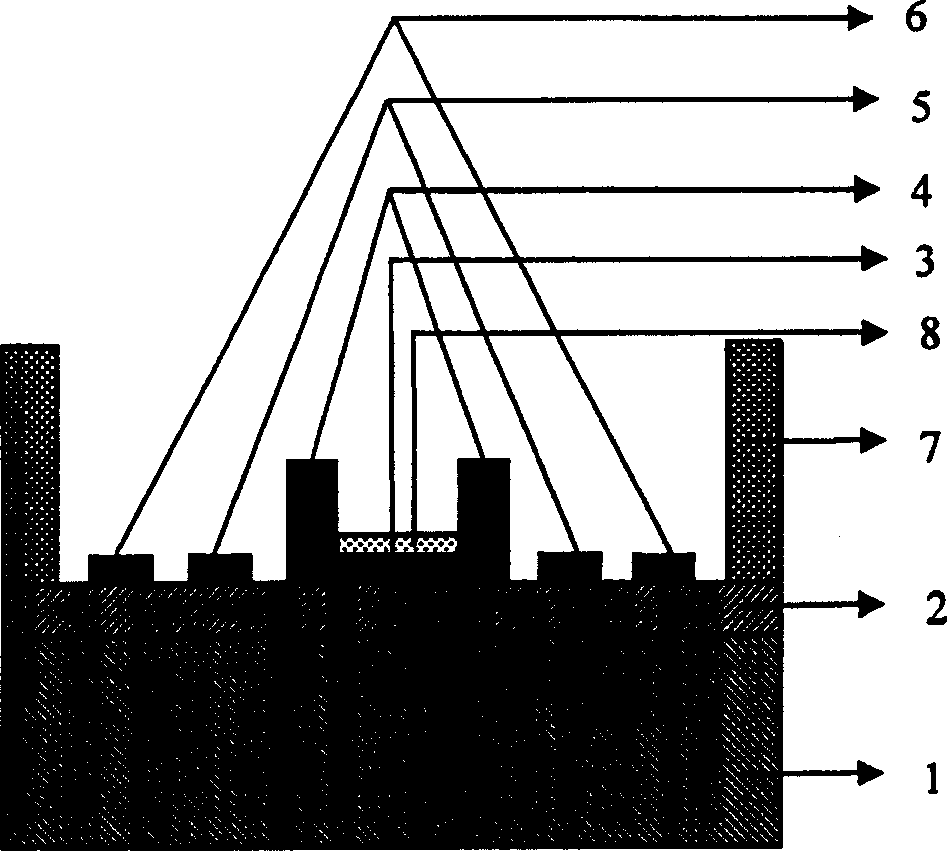
The invention discloses a micro-well based gas sensor array and its making method. According to the invention, (1) the gas sensor array adopts an MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology, an interdigital electrode is prepared on an SOI wafer surface, an SU-8 photoresist is used to make a micro-well isolation layer for preventing cross contamination of sensitive materials among different interdigital electrodes during sensitive membrane preparation, and each sensor array at least includes 4 interdigital electrode units; (2) an independent heating unit is located under each interdigital electrode, thus greatly improving the sensitivity and response recovery time of the sensor; (3) an organic membrane, an organic / inorganic composite membrane or an organic-inorganic multilayer membrane is taken as the sensitive membrane, and by determining the resistance change during gas adsorption of the sensitive membrane, qualitative and quantitative detection of a gas can be realized; and (4) using a droplet coating, gas jet or electronic injection technique to prepare the sensitive membrane. The gas sensor array has broad application prospects in the fields of atmospheric environment monitoring, aerospace sealed cabin air quality testing and food security, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Microfluidic device
InactiveUS20110301058A1Improve sealingIncrease success rateChemical library matterLibrary screeningCancer cellSpecific antibody
A novel approach for fabricating Monolithic Internal micro Pillars (MIPi) made of SU-8 photoresist is described. A microfluidic chip with the internal pillars (a MIPi chip) was used for cell capturing study. The surface of MIPi was coated with specific antibody and then used for capturing cells by affinity binding. An antibody, anti-EGFR, which has high affinity to lung cancer cells, CL1-5, was coated on the micro pillars. The coated MIPi chip specifically captured the cancer cells that were pumped through the MIPi chip. Simulation and experiment was carried out to compare the effect of different geometry of the micro pillars on the cell capturing rate.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Reverse thermal bonding technology for making micro and nano fluid system with controllable size
InactiveCN103145089ASmall sizeIncrease contactDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingGratingThin layer
The invention discloses a reverse thermal bonding technology for making micro and nano fluid system with controllable size. The technology comprises steps of: coating a pretreated grating template with a layer of SU 8 photoresist; copying a graph to the SU-8 photoresist through a reverse embossing technology; then tearing off the cured SU-8 photoresist by using an adhesive UV tape according to different adhesion among interfaces, so as to successfully transfer the graph to a flexible UV adhesive tape; spinning a thin layer of SU-8 photoresist on another Si sheet to form a sealing layer Si substrate; covering the prepared SU-8 adhesive graphic structure layer on the Si substrate; and preparing the micro and nano fluid system through the reverse bonding technology. The invention combines an embossing technology and a bonding technology together, and has advantages of simple operation, no requirement on high temperature and high pressure, controllable channel size and no clogging; and a low manufacturing cost is conducive to mass production.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing PDMS chip including both square and arc-shaped channel
A method for preparing a PDMS chip including both square and arc-shaped channels comprises the following steps: clamping an SU-8 male mold of a cross-linked state prepared by standard photolithography with liquid PDMS to obtain a PDMS female mold with an inverted male mold pattern after the PDMS is cured; clamping the female mold PDMS with the solid uncross-linked SU-8 photoresist, heating the photoresist by a vacuum oven to make the photoresist be in a fluid state to fill the PDMS channels to obtain the uncrosslinked SU-8 male mold; selectively exposing the uncrosslinked SU-8 male mold to make the SU-8 male mold partially crosslink to form square protrusion portions; heating the male mold for some time to make the uncrosslinked portions be arc-shaped; performing a fully exposed crosslinking reaction, post-baking, solidifying the mold to get the stereotyped SU-8 square and arc-shaped male mold; and pouring with PDMS, curing, demolding to get the PDMS chip including both square and arc-shaped channels. The chip produced by the present invention is applied to preparation of a micro-fluidic chip liquid channel layer integrated with pneumatic micro-valves. The SU-8 male mold prepared by the invention is not easy to peel off from substrates. The radian of the PDMS chip arc-shaped channel is controllable. The simple and stable method is provided for the preparation of complex chips.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
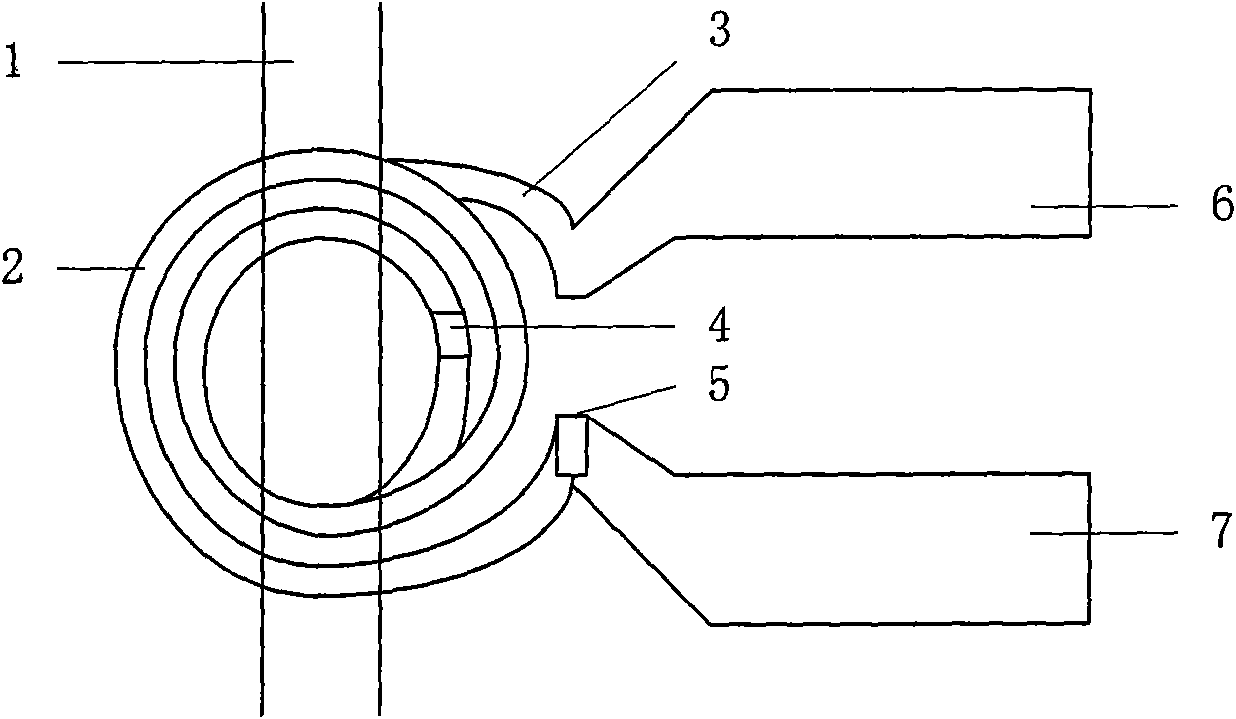
Nuclear magnetic resonance radio-frequency micro-coil and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101650412AHigh Q valueHigh magnetic field distribution uniformityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMicro coil
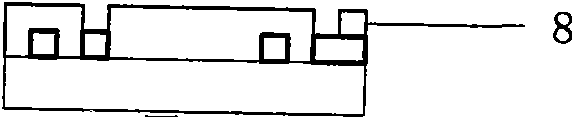
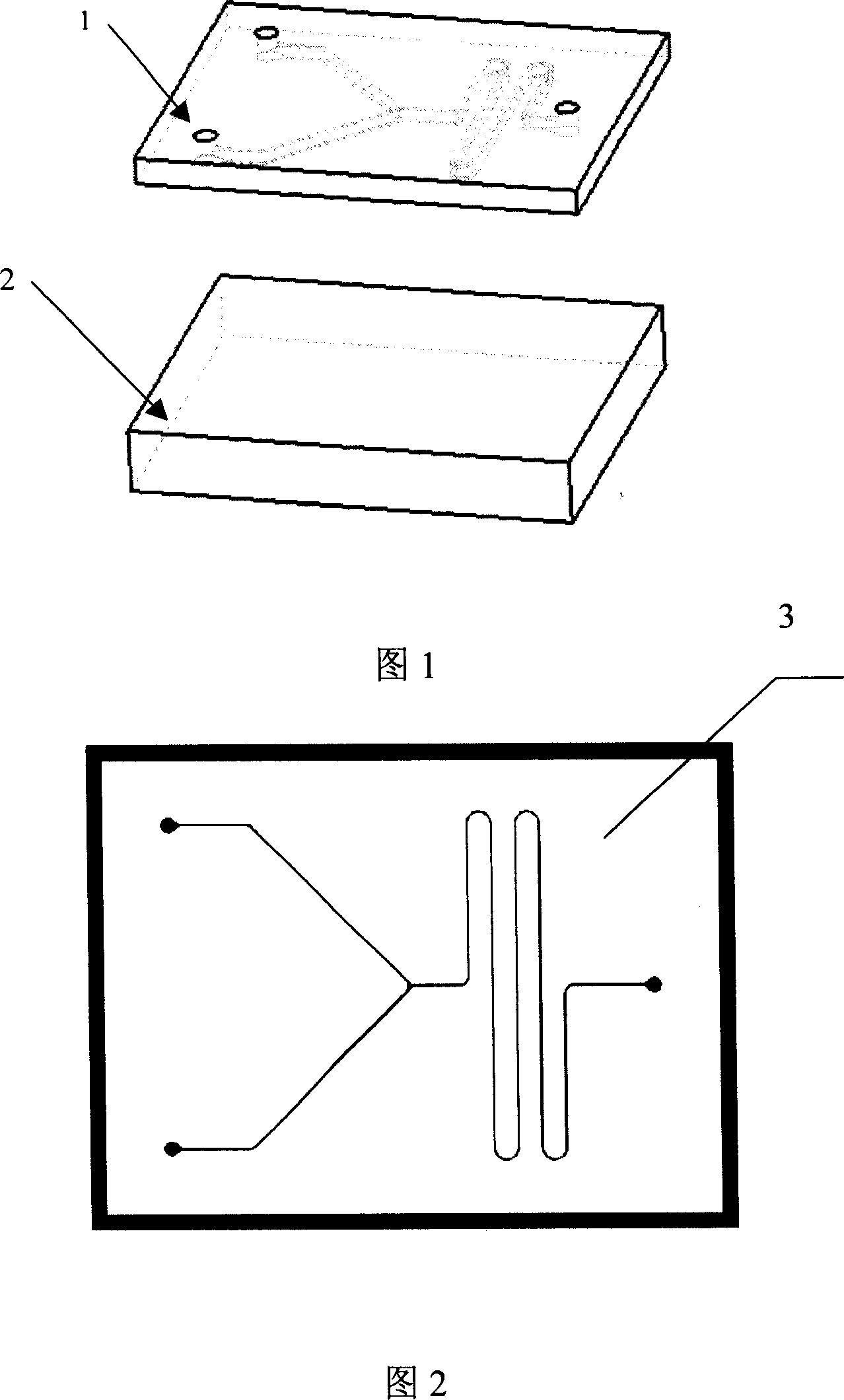
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance radio-frequency micro-coil, comprising an upper flat subcoil and a lower flat subcoil which are mutually parallel, i.e. a top layer subcoil (2) and a bottom layer subcoil (3). The two flat subcoils have the same shape, and the distance between the subcoils is larger than or equal to the inside radius of the subcoils; the two flat subcoils are connected through a wire; a micro channel (1) used for containing a sample is positioned between and parallel with the top layer subcoil (2) and the bottom layer subcoil (3). An inner through hole (4)is positioned at the joint between the bottom layer subcoil (3) and the top layer subcoil (2); and an outer through hole (5) is positioned at the joint between the top layer subcoil (2) an a second bonding pad (7). The invention can emit radio-frequency pulse signal and (or) receive free induction decay echo signals coming from a tested object. The micro-coil is manufactured based on SU-8 photoresist by utilizing a micro-electro-mechanical system process on a Pyrex substrate (12). The invention can be used for nuclear magnetic resonance test of a nano-liter bio-chemical sample.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing micro-flowing injection type chemical luminous chip
InactiveCN1928534AIncrease productivityLow costChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceChemical microanalysisEtchingShell molding
The manufacture method for micro-flow injector chemical luminous chip comprises: with silicon piece, PDMS and SU-8 photoresist as material, manufacturing micro-channel and interfaces by standard micro-manufacturing technique; manufacturing mold structure by standard photo-etching technique, using molding cast and solidification technology to prepare the micro-chip structure; finally, irreversible packing the channel. This invention is simple and reliable, and is high sensitive with a little sample.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Processing method of all metal channel microstructure with great thickness and high depth-to-width ratio
InactiveCN103818873ALower the altitudeDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingUltravioletBottle neck
The invention discloses a processing method of an all metal channel microstructure with great thickness and a high depth-to-width ratio. The processing method comprises the particular technical steps of spin-coating a copper substrate in a set size with a layer of SU-8 photoresist, performing technical procedures such as prebaking, exposing, postbaking, developing, and film upright to form a micro-electroforming female mold, obtaining 1 / 2 structures by a micro-electroforming and striping technology, and finally, combining the two 1 / 2 structures into a whole by a pin connection technology. According to the method, the all metal channel microstructure with the great thickness and the high depth-to-width ratio can be obtained by a once gluing technology together with the pin connection technology; the problem in verticality of a side wall caused by exposure and the problem of photoresist residual in a channel caused by incomplete striping when a great thickness glue film is obtained by using the gluing technology for many times are avoided; and a processing bottle neck in the structural thickness and the depth-to-width ratio when the all metal microstructure is prepared by the conventional UV-LIGA (Ultraviolet-Lithographie, Galanoformung and Abformung) technology and the deep reactive ion etching technology are broken through.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
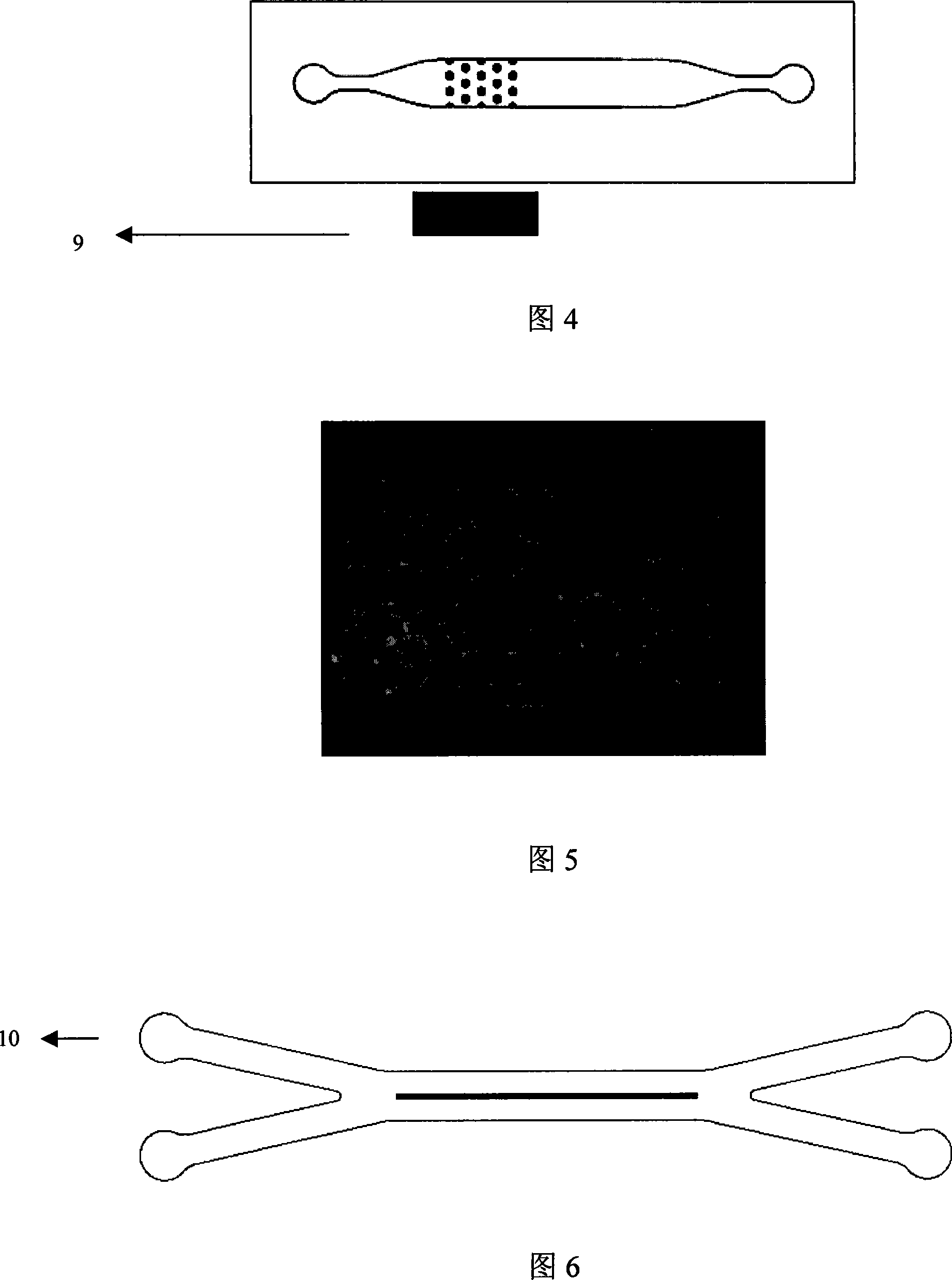
Processing method of micro-component in multi-layer structure and solidified SU-8 photoresist sheet
InactiveCN102147569AAvoid destructionUnlimited sizeDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicro structureSputtering
The invention discloses a processing method of a micro-component in a multi-layer structure and a solidified SU-8 photoresist sheet. The method comprises the following steps of: a, homogenizing and drying a photoresist on a substrate of a metal seed layer; b, carrying out ultraviolet exposure on the dried photoresist; c, post-drying and developing the exposed photoresist; d, adhering the solidified SU-8 photoresist sheet; e, exposing the solidified SU-8 photoresist sheet in the step d; f, post-drying and developing the solidified SU-8 photoresist sheet in the step e; g, sputtering the metal seed layer; h, adhering the solidified SU-8 photoresist sheet; i, exposing the solidified SU-8 photoresist sheet in the step h; j, post-drying and developing the solidified SU-8 photoresist sheet in the step i; and k, carrying out electroforming. The method has the advantages that: because the solidified SU-8 photoresist sheet is used, damage to a pattern on a previous layer is avoided, the size of the pattern between two adjacent layers is not limited, and a micro-structure can provide much more convenience for subsequent assembly process.
Owner:TIANJIN SEAGULL WATCH CO LTD +1
Micromachining method for manufacturing polymer cylindrical microlens by electric field induction
InactiveCN102253435AEasy to processReduce processing costsPhotomechanical apparatusLensElectrical field strengthUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a micromachining method for manufacturing a polymer cylindrical microlens by electric field induction. The method comprises the following steps of: machining on a SiO2 substrate to form a transparent conductive grid structure, spinning an SU-8 photoresist, photoetching and developing a circle of bracket to form a cylindrical electric field contour surface, and evaporating a conductive indium tin oxide (ITO) layer at the bottom of the SiO2 substrate; spinning ultraviolet curing polymer, and pressing a transparent template on the ultraviolet curing polymer to make the bracket made of the SU-8 photoresist pressed into a polymer film; making the conductive grid structure of the plane generate the cylindrical electric field contour surface on the surface of the polymer film by using a direct current power supply, and forming a cylindrical microlens structure; keeping polymer rheology under an electric field with a stabilized voltage value to form the cylindrical microlens structure; and finally, exposing the curing polymer through ultraviolet light, and removing the template to obtain a needed polymer cylindrical microlens array. The method has the advantages of high production efficiency, simple process and low cost.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Preparation method of SU-8 photoresist-based three-dimensional microelectrode
InactiveCN104701020AImprove performanceHigh specific surface areaElectrolytic capacitorsCapacitanceElectrode array
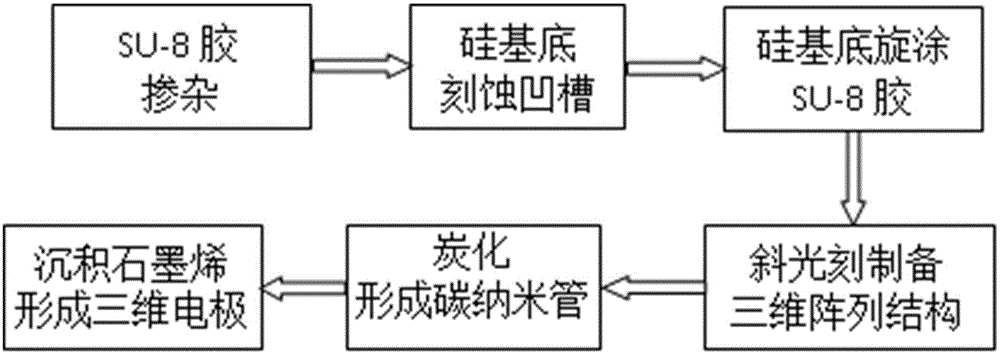
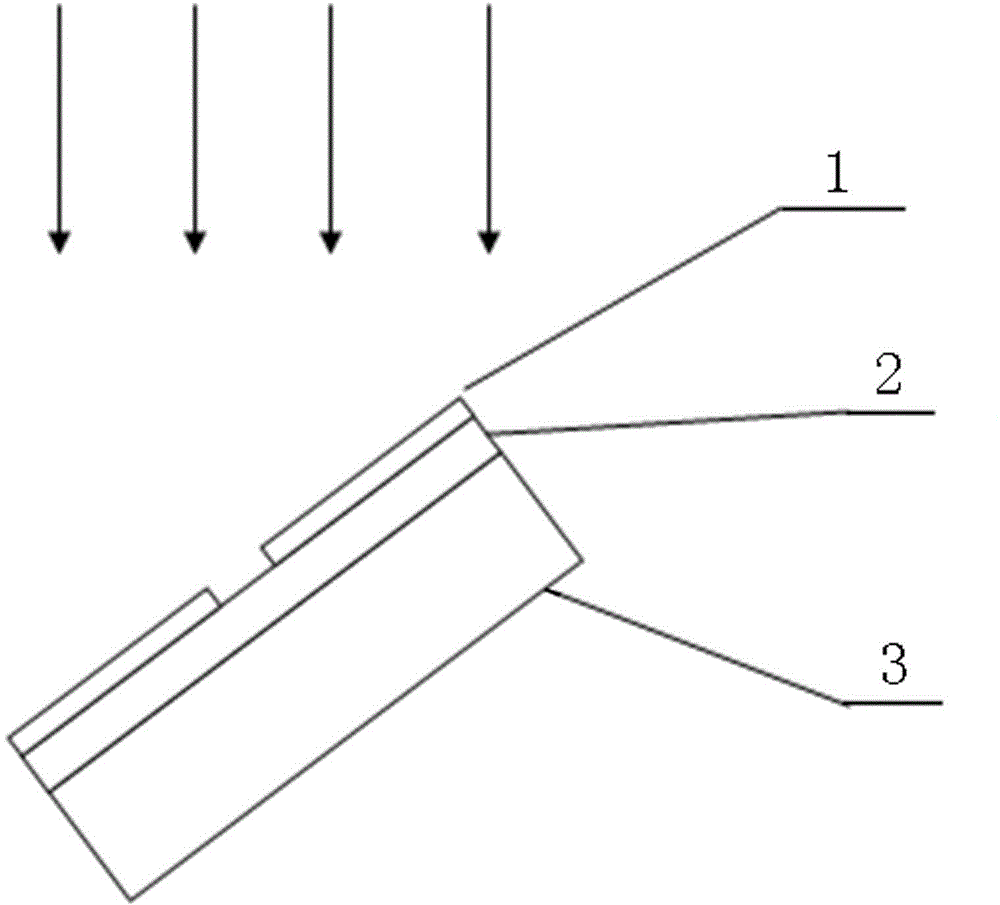
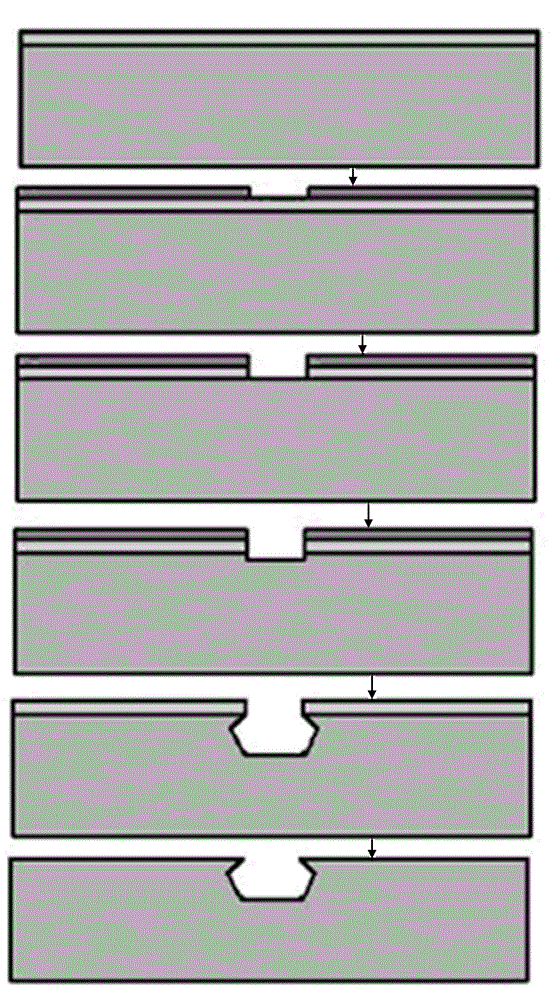
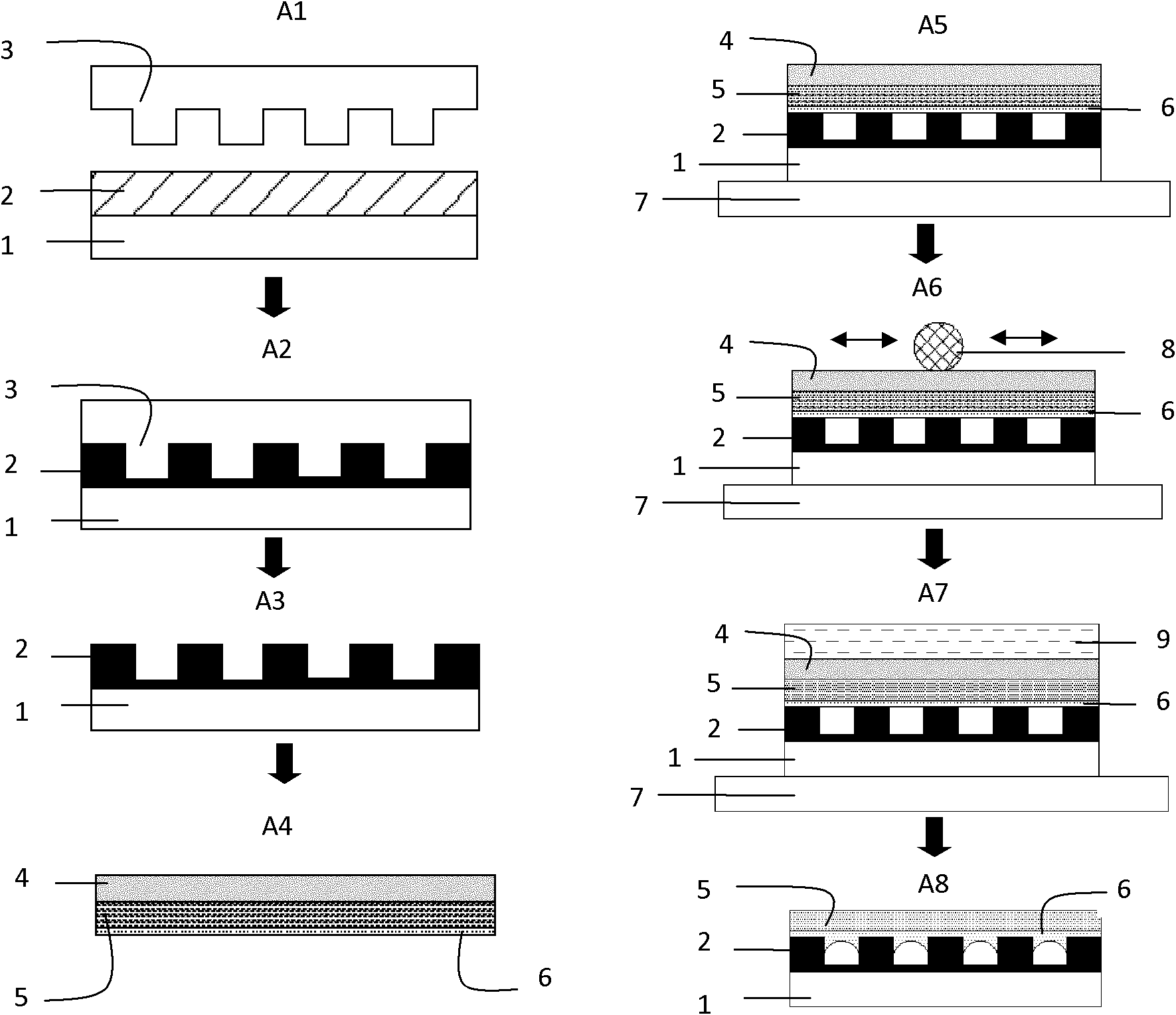
The invention relates to the technical field of MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System), particularly to a preparation method of an SU-8 photoresist-based three-dimensional microelectrode. The method specifically comprises doping nanoscale ferric chloride particles into SU-8 photoresist through a doping method; etching a groove structure with narrow mouth and wide inside in a silicon substrate; spinning the doped SU-8 photoresist onto the silicon substrate with the groove structure; preparing an SU-8 photoresist three-dimensional microelectrode array through the oblique photoetching micromachining technology; carbonizing the electrode array inside a carbonizing device to obtain an SU-8 carbon nanotube; depositing graphene onto the SU-8 carbon nanotube to form an SU-8 carbon nanotube electrode; filing liquid or colloidal electrolyte inside the prepared SU-8 carbon nanotube electrode. According to the preparation method of the SU-8 photoresist-based three-dimensional microelectrode, the aperture of the SU-8 nanotube is controlled and adjusted through the doping method; through combination of the oblique photoetching technology, the specific surface area of the three-dimensional carbon nanotube electrode can be effectively enlarged; compared with traditional capacitor electrode structures, the SU-8 photoresist-based three-dimensional microelectrode greatly improve the energy density and power density of super-capacitors.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for manufacturing micro-nano fluid control system by using low-pressure bonding technology
InactiveCN102060262ALow costGood flexibilityDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingSU-8 photoresistPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a micro-nano fluid control system by using a low-pressure bonding technology, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly taking a glass sheet as a substrate to manufacture a KMPR master mask with raster graphics and a PDMS soft stamp; using the PDMS soft stamp to manufacture a raster nano-sized structural Si substrate for manufacturing follow-up nano-channels; using a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) slice to manufacture a PET sheet with double layers of SU-8 photoresist; and manufacturing the micro-nano fluid control system by using the raster nano-sized structural Si substrate and the PET sheet with double layers of SU-8 photoresist. The channels manufactured by the method have the advantages of good uniformity, less possibility of blockage, high success rate, and low manufacturing cost, are flexible in operation and are suitable for large-area production.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Miniature electrochemical sensor based on direct forming mesoporous carbon technology and manufacturing method
InactiveCN104502428AImprove performanceRealize batch designMaterial electrochemical variablesInsulation layerGas phase
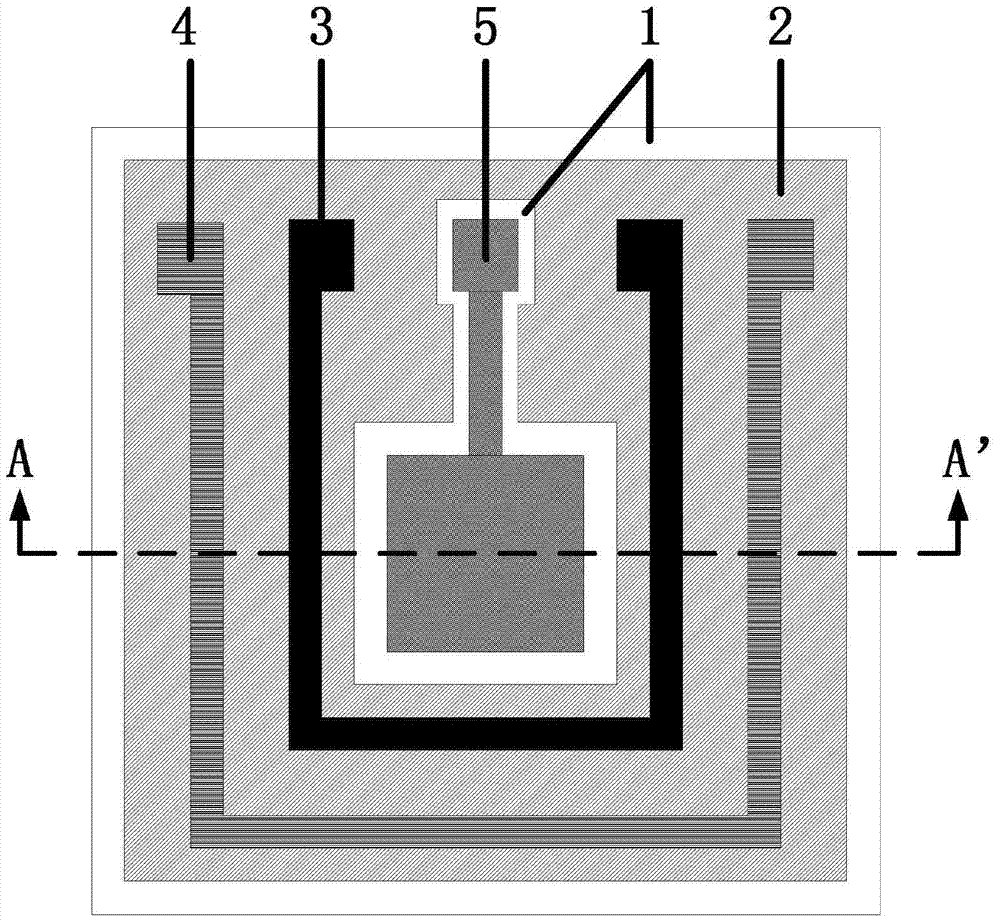
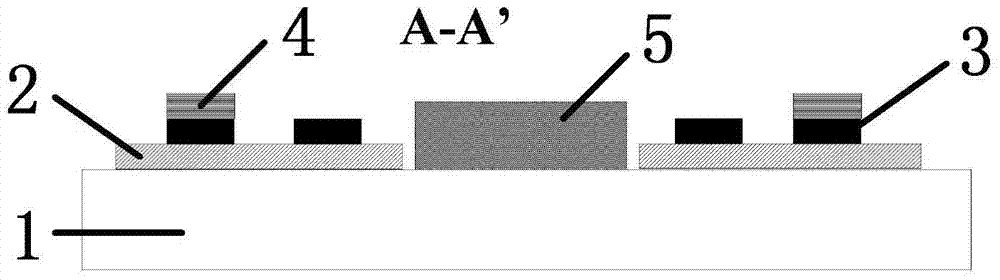
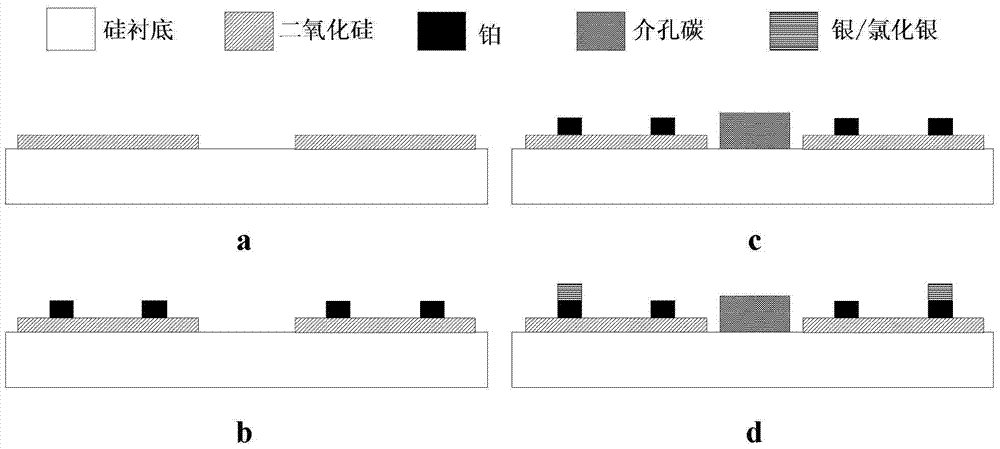
The invention belongs to the field of micro-sensors and micro-machining and particularly relates to a miniature electrochemical sensor based on a direct forming mesoporous carbon technology and a manufacturing method. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of using a silicon dioxide layer with 500 nm plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition thickness as an insulation layer on a silicon wafer and obtaining a working electrode region through photo-etching and etching; obtaining graphs of a counter electrode and a reference electrode substrate region through photo-etching, evaporating 80 nm platinum and then stripping a photoresist; spin-coating an SU-8 photoresist and silicon oxide mixture on a silicon substrate template in the working electrode region, obtaining the working electrode region through photo-etching imaging and using hydrofluoric acid to remove template material silicon dioxide so as to obtain working electrode mesoporous carbon after 900 DEG C high-temperature carbonization; coating silver / silver chloride slurry on reference electrode substrate platinum to obtain solid silver / silver chloride reference electrode.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing micro-nano-channels based on liquid-gas equilibrium polymer nano-channels self-building mechanism
InactiveCN102621805AImprove uniformityAvoid severe deformationDecorative surface effectsNanotechnologyPolymeric surfaceMicro nano
The invention discloses a method for preparing micro-nano-channels based on a liquid-gas equilibrium polymer nano-channels self-building mechanism. The method comprises the following steps of: first, preparing a nano grating structure of SU-8 photoresist by using a grating template and a nano-imprint lithography technology; then, spin-coating a layer of release agent on the grating structure of the SU-8 photoresist; and finally, coating a layer of SU-8 photoresist on the grating structure of the SU-8 photoresist coated with the release agent by a slit type extrusion gluing way, wherein the micro-nano-channels are formed by a coated SU-8 photoresist layer which is balanced with the air pressure trapped in a grating under the action of surface tension, and the preparation of a micro-nano flow control system is finished. According to the method, high pressure and high temperature are not needed, so that deformation and damage of a polymer grating structure are avoided; processing successrate is improved; and by the method, the sizes of the micro-nano-channels can be controlled by adjusting the surface tension of a polymer.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Three-dimensional asymmetric miniature resonant cavity polymer single-mode laser
ActiveCN104868352AAchieve the desired effectOptical resonator shape and constructionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicro nanoNon symmetric
The invention discloses a three-dimensional asymmetric miniature resonant cavity polymer single-mode laser, and belongs to the field of dye miniature resonant cavity lasers. A femtosecond laser micro-nano machining system is employed at first for the machining of SU-8 photoresist materials doped with dye Rhodamin B, thereby forming a polymer miniature resonant cavity laser. The shape of the miniature resonant cavity employs a no-pillar structure to be directly integrated on a substrate, and a double-layer stacked three-dimensional structure is designed, wherein the double-layer stacked three-dimensional structure is specifically a three-dimensional geometrical asymmetric structure where a spiral ring in a smaller size is internally tangent to a circular ring. The laser manufactured through the above method achieves the emission of laser with a single-longitudinal-mode wavelength under the room temperature, and the emitted laser is better in direction selectivity in a port direction of the spiral ring, thereby facilitating the further coupling and integration of a miniature optical element and the application in the field of light interconnection.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
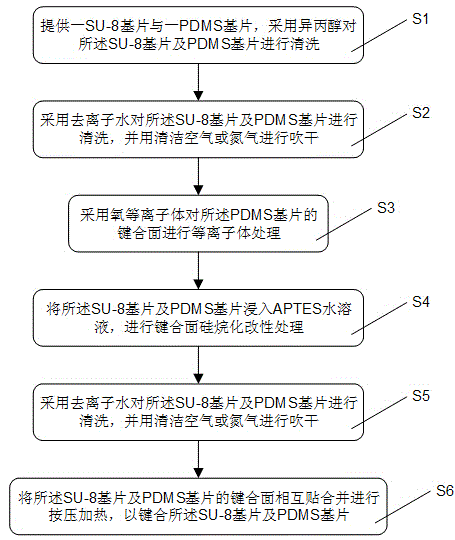
Microfluidic chip bonding method using SU-8 photoresist and PDMS as substrates
ActiveCN104627953ALess likely to leakImprove controllabilityDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingOxygen plasmaCorona discharge
The invention provides a microfluidic chip bonding method using an SU-8 photoresist and PDMS as substrates. The microfluidic chip bonding method comprises the following steps: firstly providing an SU-8 substrate and a PDMS substrate, cleaning the SU-8 substrate and the PDMS substrate by using isopropyl alcohol and deionized water, and then performing oxygen plasma treatment on the bonding surface of the PDMS substrate; performing silanization modification treatment on the bonding surfaces of the SU-8 substrate and the PDMS substrate by using an aqueous solution of APTES; and finally, enabling the bonding surfaces of the SU-8 substrate and the PDMS substrate to get close and carrying put press heating to bond the SU-8 substrate and the PDMS substrate to form a complete microfluidic chip. The microfluidic chip bonding method has the following beneficial effects that: 1) the bonding surface of the PDMS substrate can be modified by using an ordinary low-power plasma machine or a corona discharge instrument and other low-cost equipment; 2) the operation process is simple, the controllability, stability and repeatability of the process are high, the bonding strength and the yield are high, and the leakage does not easily occur; 3) the bonding of the SU-8 substrate and the PDMS substrate is helpful for realizing the precision multifunctional microfluidic chip with and complicated structure.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for manufacturing multi-layer metal mobile microstructure on metal base
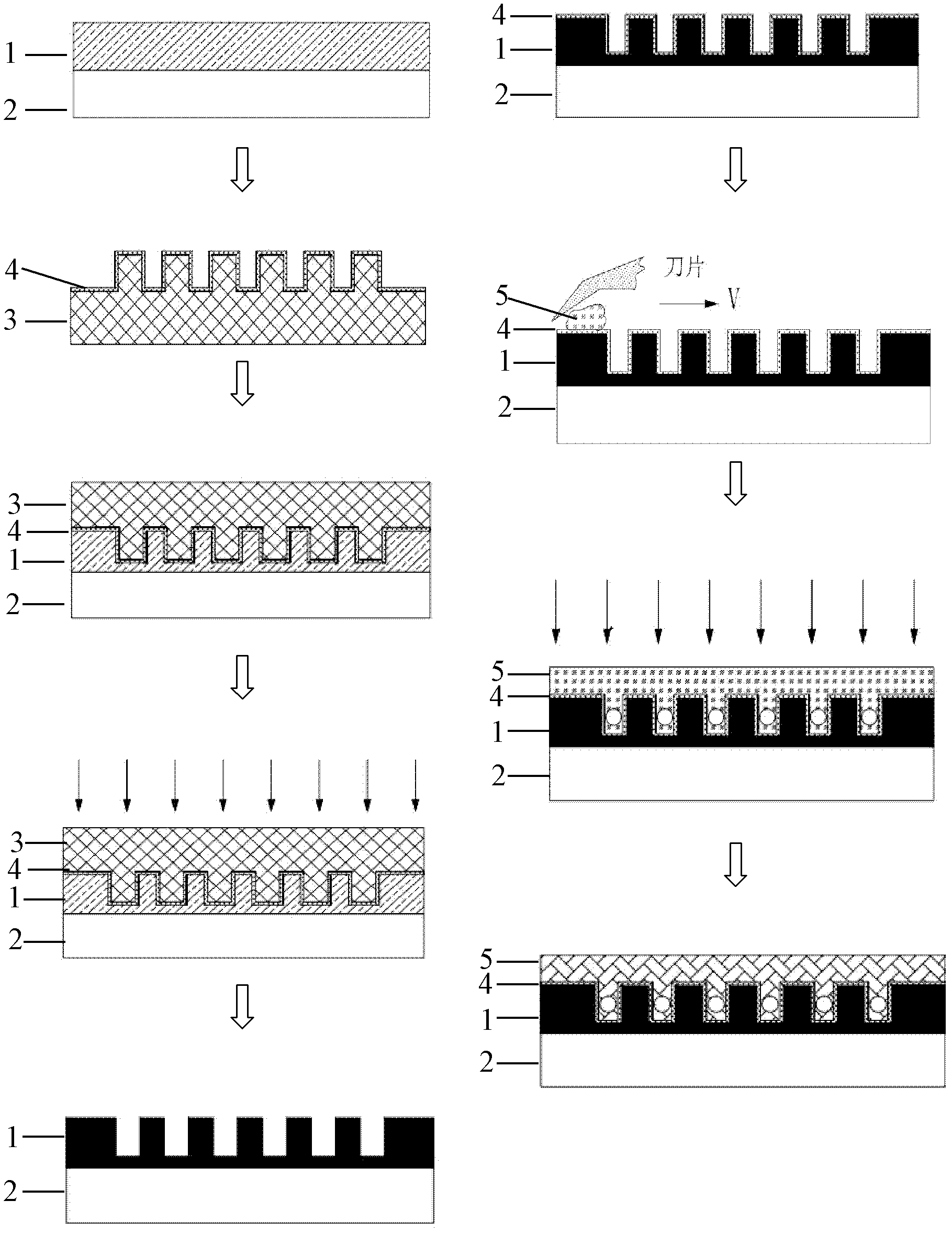
InactiveCN103103583AStrong impact resistanceStrong surface finishElectroforming processesShock resistanceBinding force
The invention relates to a method for a manufacturing multi-layer metal mobile microstructure on a metal base, belonging to the technical field of micro-manufacture and relating to metal base micro electroforming metal devices. The method is characterized in that the multi-layer metal mobile microstructure can be manufactured on a high-purity nickel plate base through repeated SU-8 photoresist overlay, conducting layer preparation, repeated micro electroforming nickel and micro electroforming post treatment. In the manufacture process of conducting layer, copper is selected as a conducting material; residual stress is removed by vacuum annealing in an annealing process, and the binding force between layers is improved simultaneously; and in the glue film removing process, a concentrated sulfuric acid boiling manner is adopted. The method has the beneficial effects that the prepared multi-layer metal mobile microstructure has the advantages that the layers are combined firmly, the inner stress of the microelectroforming layer is small, the microstructure has strong shock resistance, the side wall is good in verticality, the surface smoothness is high, and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Photoresist formulation for high aspect ratio plating
InactiveUS7005233B2High aspect ratio lithographyImprove adhesionImpression capsPhotosensitive materialsResistPlasticizer
SU-8 photoresist compositions are modified to improve their adhesion properties by adding 1% to 6% of an adhesion promoter selected from the group consisting of glycidoxypropanetrimethoxysilane, mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane, and aminopropyltrimethoxysilane. SU-8 photoresist compositions are modified to improve their resistance to cracking and film stress by adding 0.5% to 3% of a plasticizer selected from the group consisting of dialkylphthalates, dialkylmalonates, dialkylsebacates, dialkyladipates, and diglycidyl hexahydrophthalates. The improvements can be obtained simultaneously by adding both the adhesion promoter and the plasticizer to SU-8 photoresist compositions.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Ultra-small-size optical fiber temperature sensing probe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106052903APrecisely control the three-dimensional movement trajectoryReduce volumeThermometers using physical/chemical changesSpectrometerTemperature sensitive
The invention relates to an ultra-small-size optical fiber temperature sensing probe and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of optical fiber sensing. The probe comprises a single-mode optical fiber and an ultra-small-size cuboid sealed liquid cavity. The cuboid sealed liquid cavity is internally provided with an SU-8 photoresist solution. The cuboid sealed liquid cavity is glued to the center of the tail end surface of the single-mode optical fiber, the diameter of an effective sensing area is smaller than 50 micrometers, and the length is smaller than a 30 micrometers. The optical fiber temperature sensing probe is connected with a wide-spectrum light source and a spectrometer through an optical fiber circulator. A Fabry-Perot interference spectrum can be observed on the spectrometer, the movement of an interference peak center wavelength on the spectrum is monitored so as to demodulate the environment temperature, and the temperature sensing sensitivity is higher than 800 pm / DEG C. The ultra-small-size optical fiber temperature sensing probe has the advantages that the structure is compact and simple, stability and reliability are realized, the temperature-sensitive liquid material is integrated into the optical fiber temperature sensing probe, and the temperature sensing sensitivity is greatly improved. The invention provides the ideal ultra-small-size optical fiber temperature sensing probe and the preparation method thereof which are applicable to the field of temperature sensing detection.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Manufacturing method of SU-8 photoresist micro-force sensor
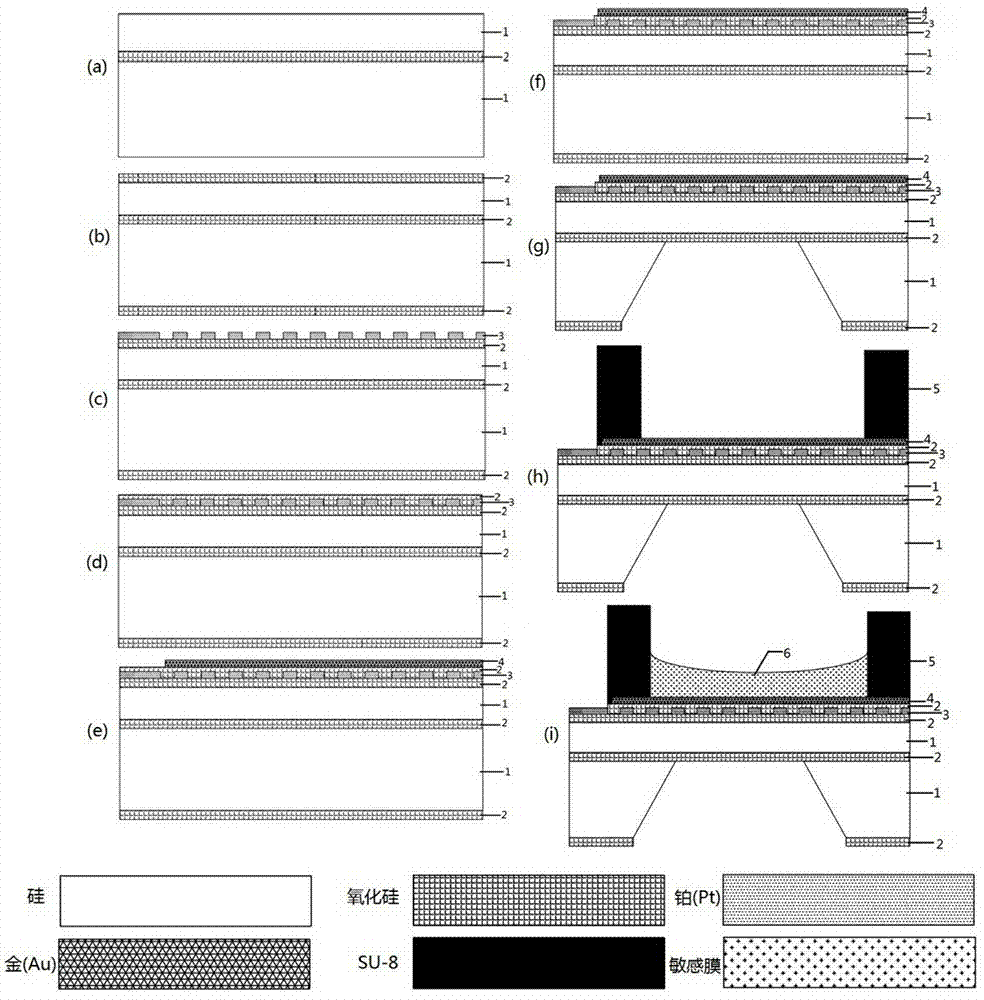
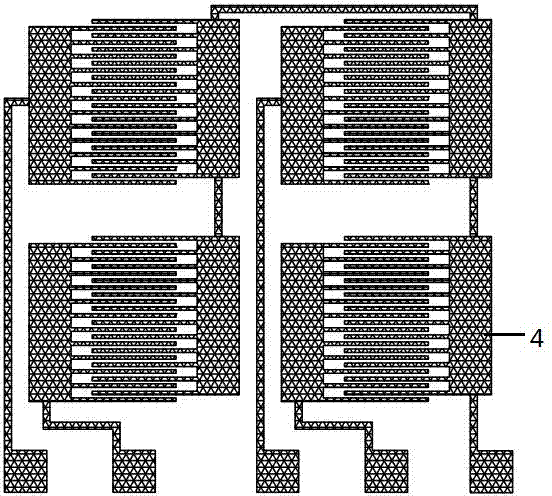
InactiveCN102249181AGood biocompatibilityLow elastic modulusDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMicroelectromechanical systemsMaterials science
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of a SU-8 photoresist micro-force sensor, wherein the SU-8 photoresist micro-force sensor is a microsensor belonging to the technical field of microelectromechanical systems. The manufacturing method is characterized by adopting silicon as a substrate material and omnicoat as a bonding layer material and a sacrificial layer material, and comprising the following steps of carrying out a first exposure and development process to obtain a SU-8 photoresist structure, carrying out a sputtering process, carrying out a second exposure and development process to obtain a positive photoresist mask, carrying out a metal layer corrosion process, and carrying out a releasing process. A sensor manufactured through the manufacturing method can be connected to a peripheral circuit through two electrodes to form a Wheatstone bridge and can convert resistance variations into voltage variations thereby measuring an acting force. A photoresist adopted by the manufacturing method is a SU-8 photoresist and the SU-8 photoresist has low modulus of elasticity, thus performances of a SU-8 photoresist micro-force sensor manufactured by the manufacturing method are similar to that of a semiconductor silicon micro-force sensor and the SU-8 photoresist micro-force sensor has good biological compatibility. The manufacturing method has the advantages of simple process, low cost, short processing cycle and good feasibility for volume production.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for manufacturing Pt resistor temperature sensor
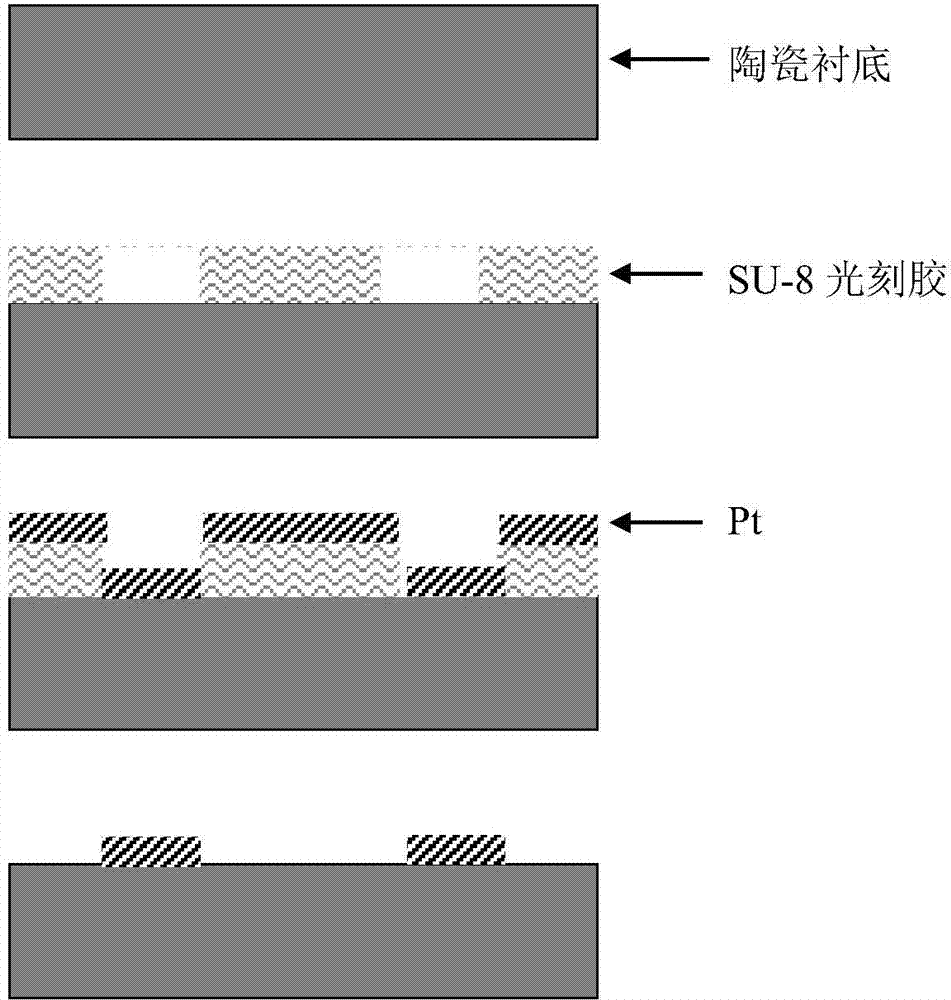
InactiveCN103487160ANot easy to decomposeWill not deformThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansHeat resistancePhotolithography
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a Pt resistor temperature sensor. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, a ceramic substrate is coated with SU-8 photoresist, and a microstructural image is formed based on photolithography; secondly, by the adoption of the magnetron sputtering method, Pt metal is deposited on the ceramic substrate generated after photolithography is completed; thirdly, the ceramic substrate obtained in the second step is ablated in the oxygen atmosphere or placed into a salt bath so that the SU-8 photoresist can be removed; fourthly, a Pt metal microstructural image which is deposited on the ceramic substrate is obtained finally. According to the method for manufacturing the Pt resistor temperature sensor, the characteristic of good heat resistance of the SU-8 photoresist is utilized, the Pt resistor temperature sensor is manufactured by the adoption of the stripping technology, the technology is simple and easy to conduct, and cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Photoelasticity principle based flexile microprobe and application method thereof
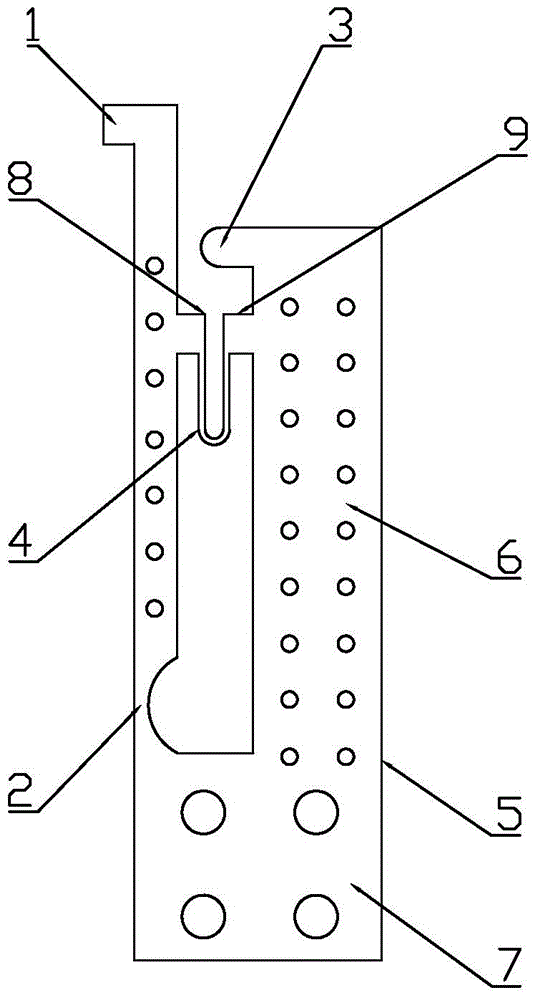
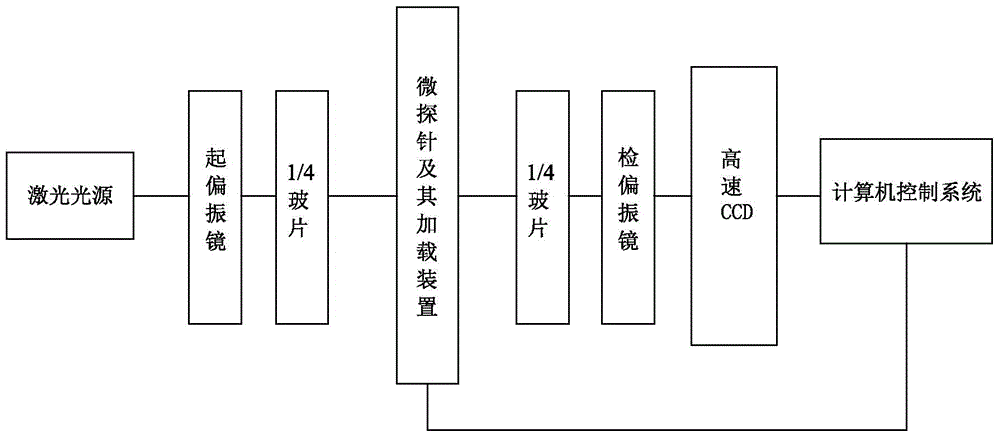
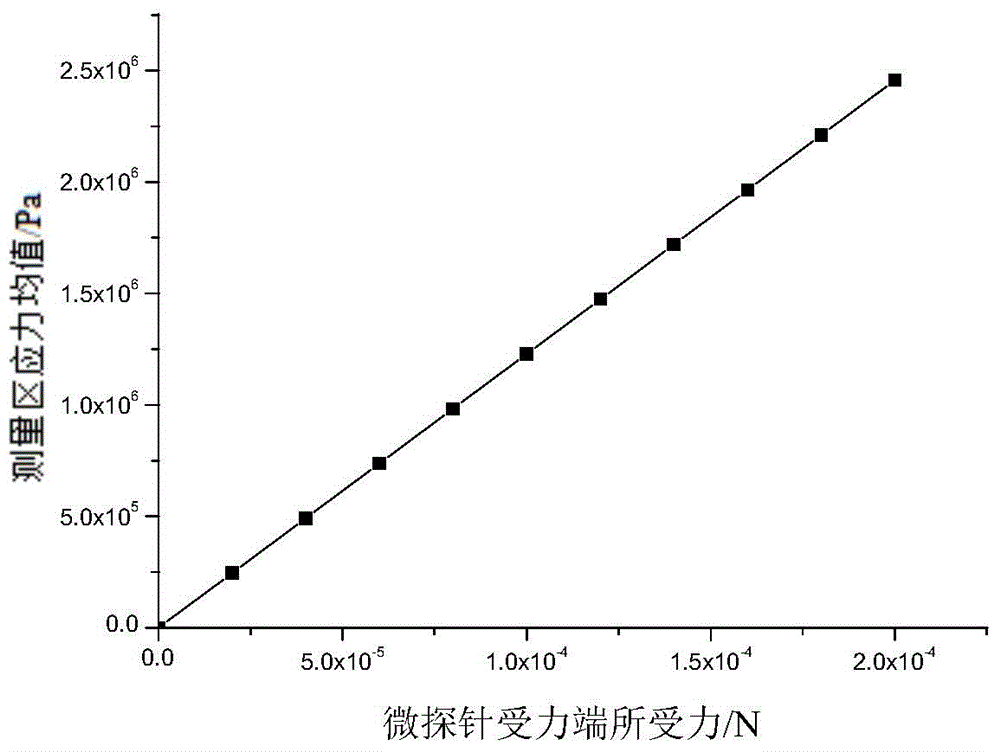
InactiveCN104807569AReduce processing costsShorten the production cycleForce measurement by measuring optical property variationStress measurementPhotoelasticity
The invention discloses a photoelasticity principle based flexile microprobe and an application method thereof. The photoelasticity principle based flexile microprobe, namely an integral structure made of SU-8 photoresist, comprises a microprobe stress end and a microprobe base body. The microprobe base body comprises a base body end and a base body tail. The base body end and the microprobe stress end are arranged on the same side of the base body tail to form a microprobe structure. The light intensity variation of polarized light transmitting a flexible hinge stress measurement area and a measurement light path is measured, a relationship between the light intensity variation and stress magnitude of the microprobe stress end is established, and accordingly, measurement of micro force can be achieved. The photoelasticity principle based flexile microprobe made of the SU-8 photoresist is low in processing technique cost and high in stability and has the advantages of chemical corrosion resistance, good mechanical property and biocompatibility, high light stress coefficient and the like; moreover, the photoelasticity principle based flexile microprobe of the integral structure is free from assembly, simple to produce and beneficial for functionalization of microoperation techniques in the fields of biomedicine, material chemistry and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of microchip for microprotein detection
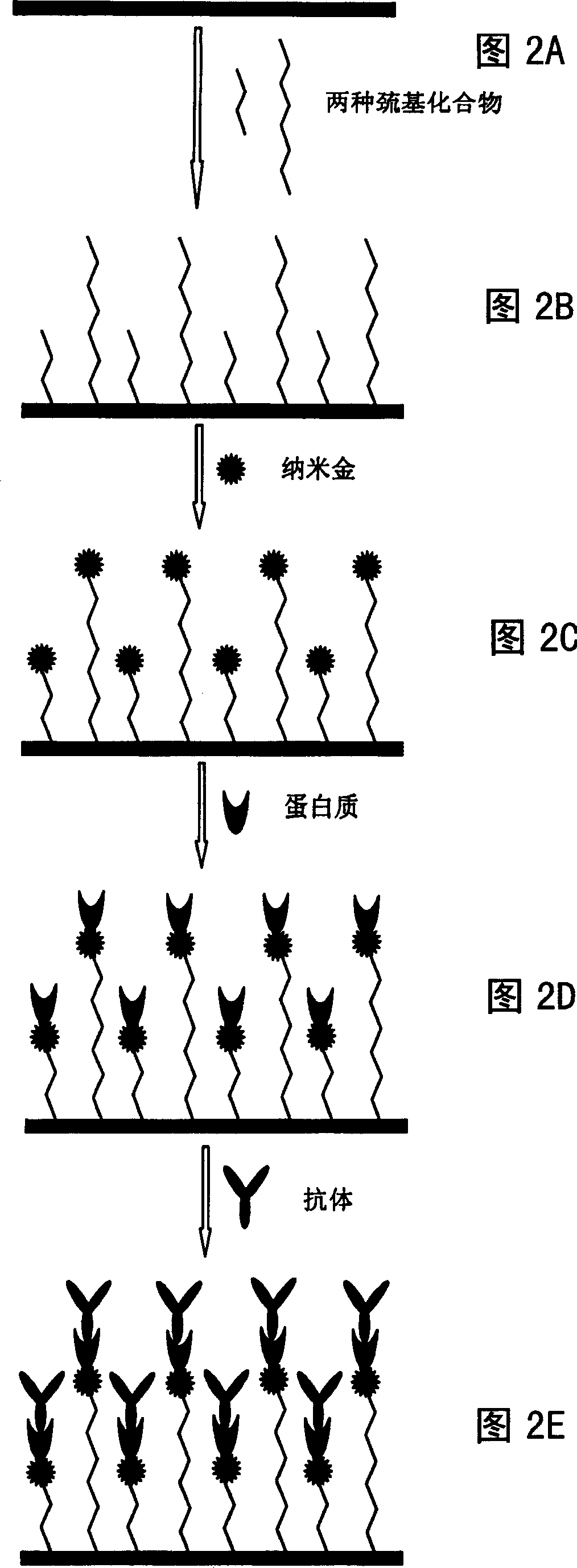
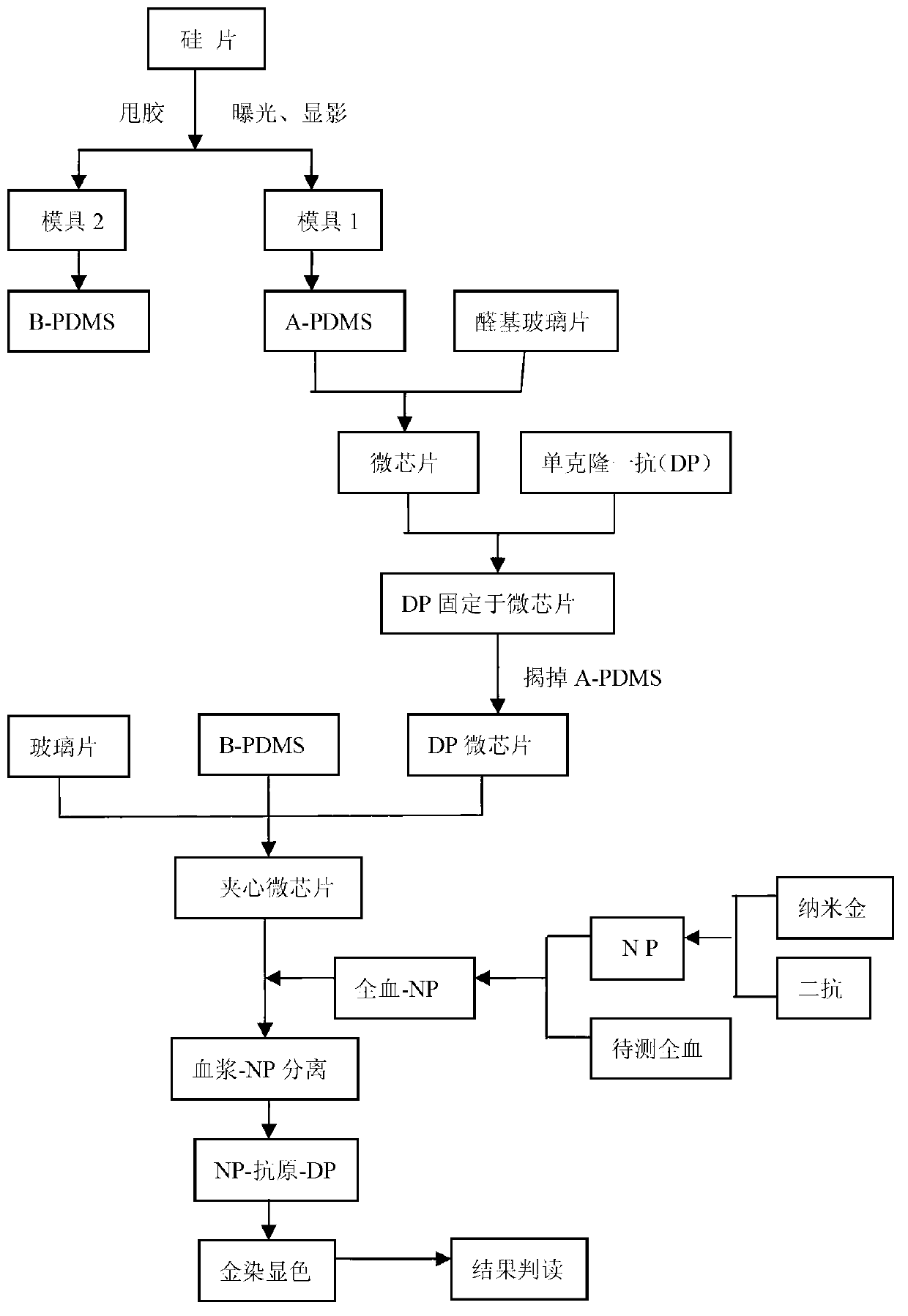
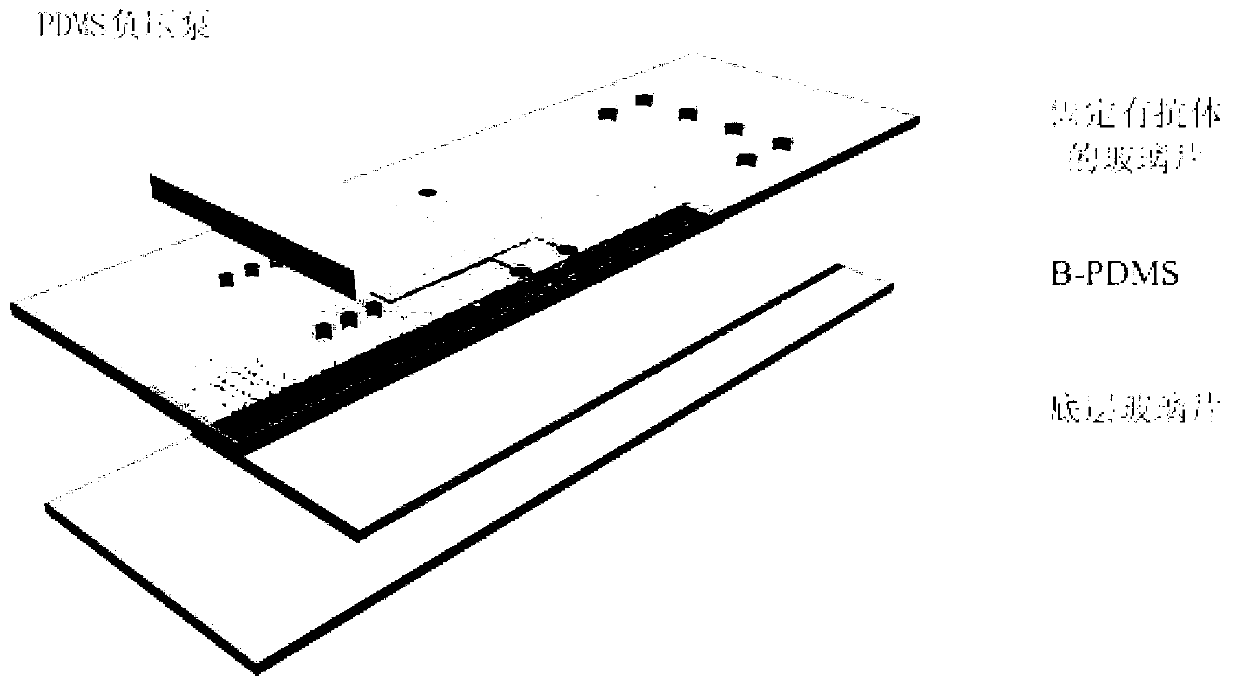
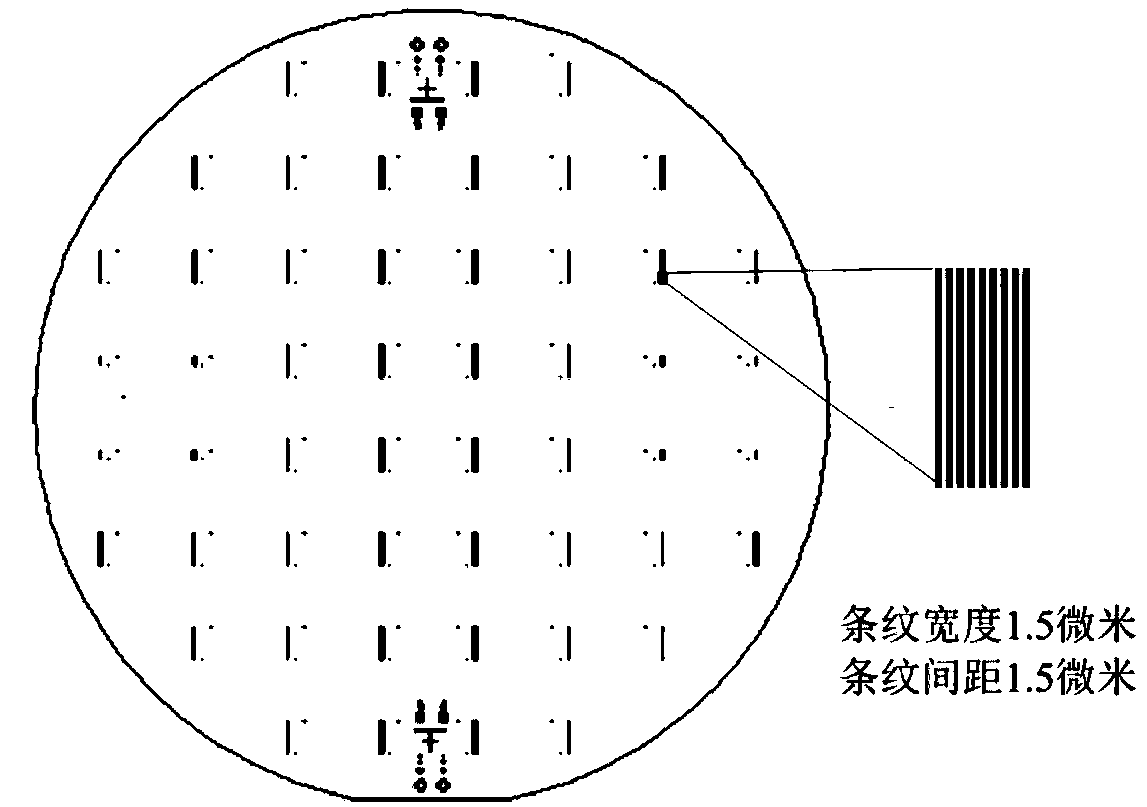
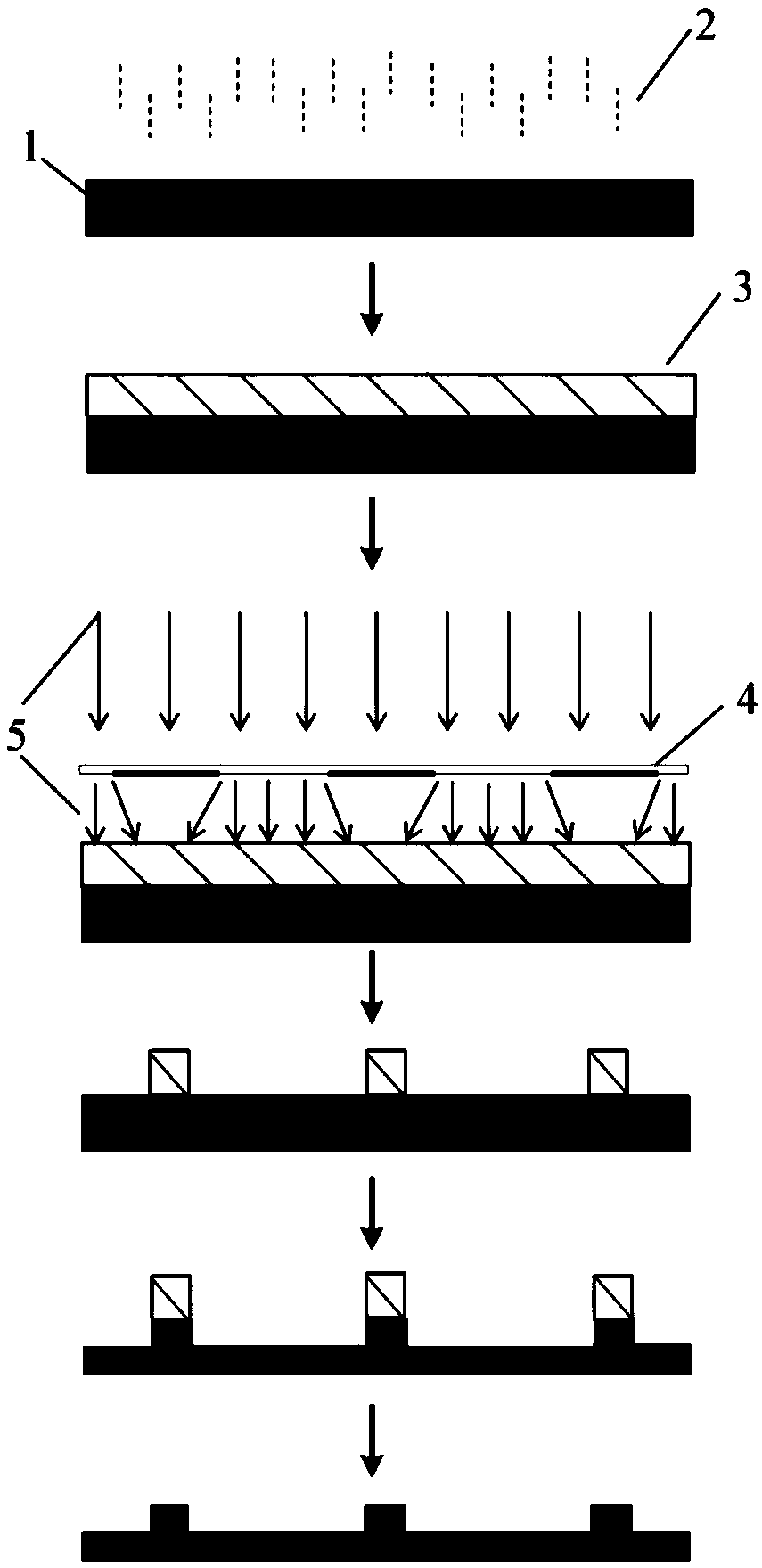
The invention relates to a preparation method of a microchip for microprotein detection. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: respectively exposing and developing a silicon wafer taken as a substrate material and SU-8 photoresist taken as a masking layer so as to manufacture a mold A and a mold B; mixing PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) with a curing agent, respectively pouring the mixture into a mold A and a mold B, heating and curing; respectively stripping A-PDMS and B-PDMS; punching the A-PDMS, gluing a processed glass sheet to the punched A-PDMS; and stripping away the A-PDMS, aligning and gluing the glass sheet on which an antibody is fixed with the B-PDMS, and gluing another punched glass sheet on the other surface of the B-PDMS, thus obtaining the microchip. The microchip can be used for integrating the separation and the detection of blood plasma in whole blood and detecting multiple targets, has the characteristics of specificity, rapidness and high sensitivity and can be expected to be applied to the clinical diagnosis and detection of multiple proteins in trace amounts of whole blood.
Owner:南京艾拓生命科技有限公司
Approximate ultraviolet exposure and thin film growth method-based method for preparing nanometer passage
ActiveCN108646520AImplement encapsulationEncapsulation is easy to implementNanotechnologyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusHot stampingSystems research
The invention belongs to the field of micro electromechanical system research, and relates to an approximate ultraviolet exposure and thin film growth method-based method for preparing a nanometer passage. An approximate ultraviolet exposure technology and a reaction ion etching technology are employed, a silicon nanometer die is fabricated, a pattern of the silicon nanometer die is transferred toa SU-8 photoresist die by hot stamping to form a nanometer channel, the channel size is reduced by growing a Parylene thin film to obtain a nanometer channel with a width smaller than 50 nanometers,the package of the nanometer channel is achieved through oxygen plasma auxiliary thermal bonding by a SU-8 photoresist cover plate, and a nanometer passage of which the height and the width both are smaller than 50 nanometers is finally obtained. The method has the characteristics of low cost and high production efficiency and is simple to operate.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com