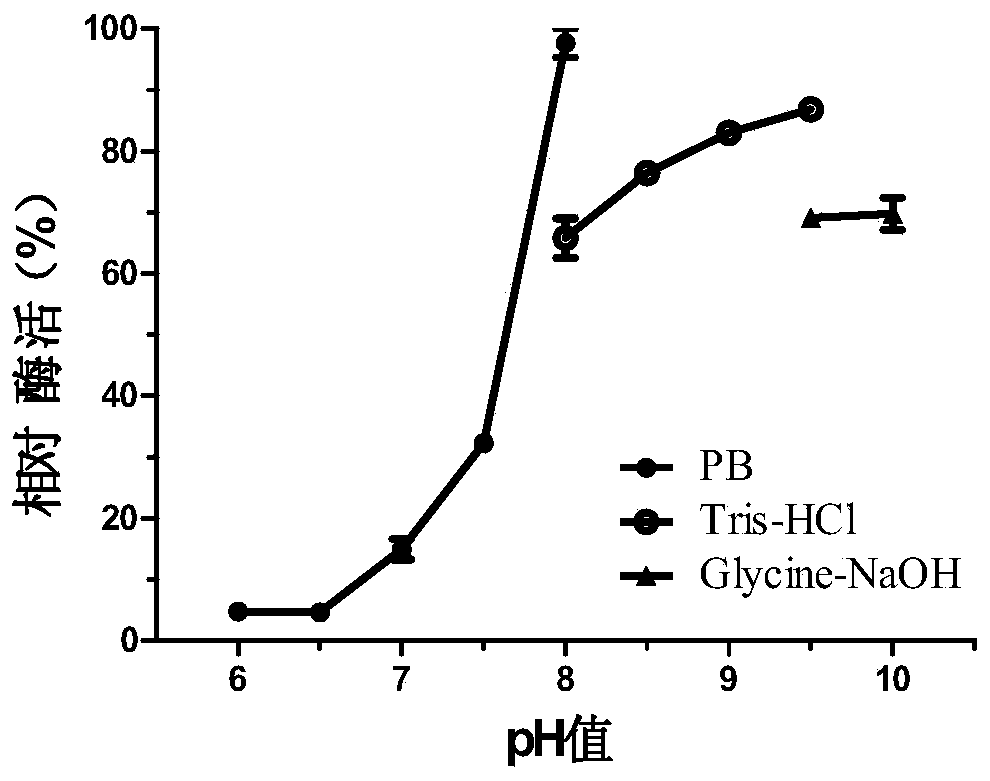
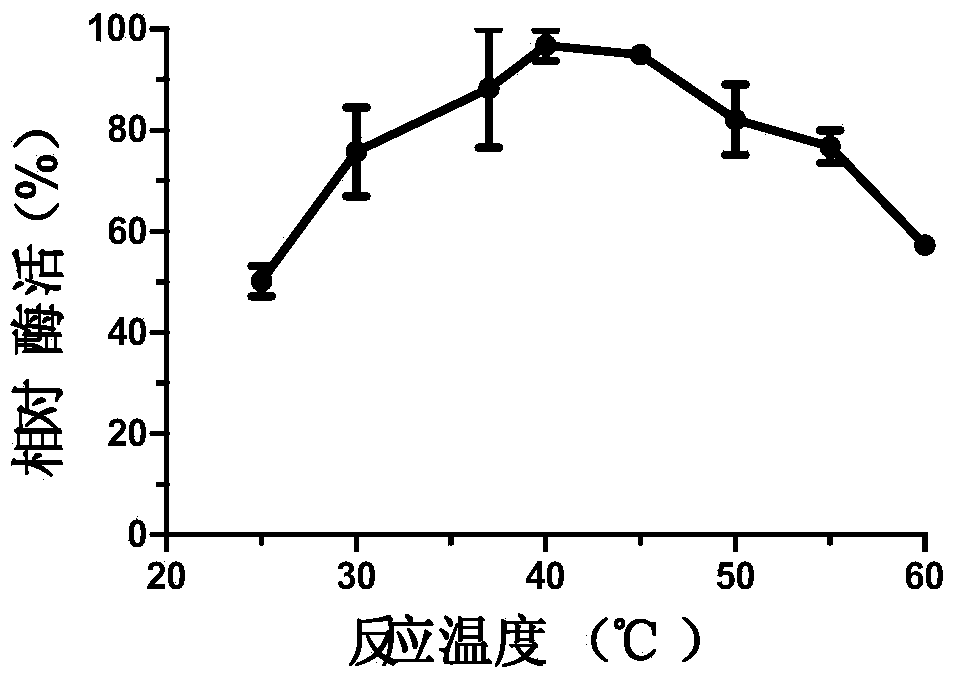
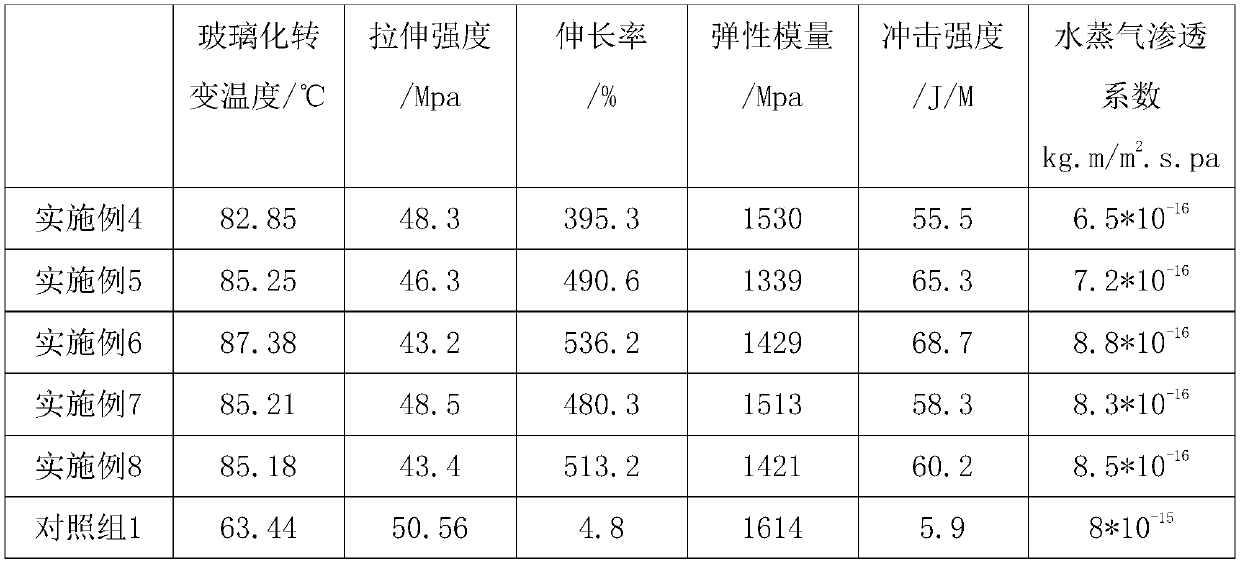
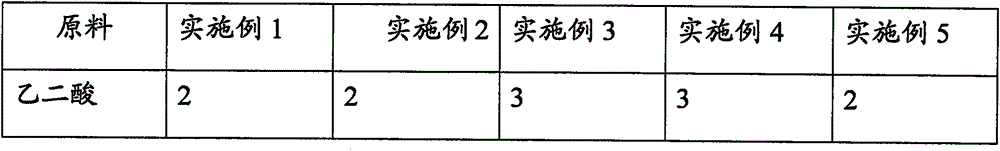
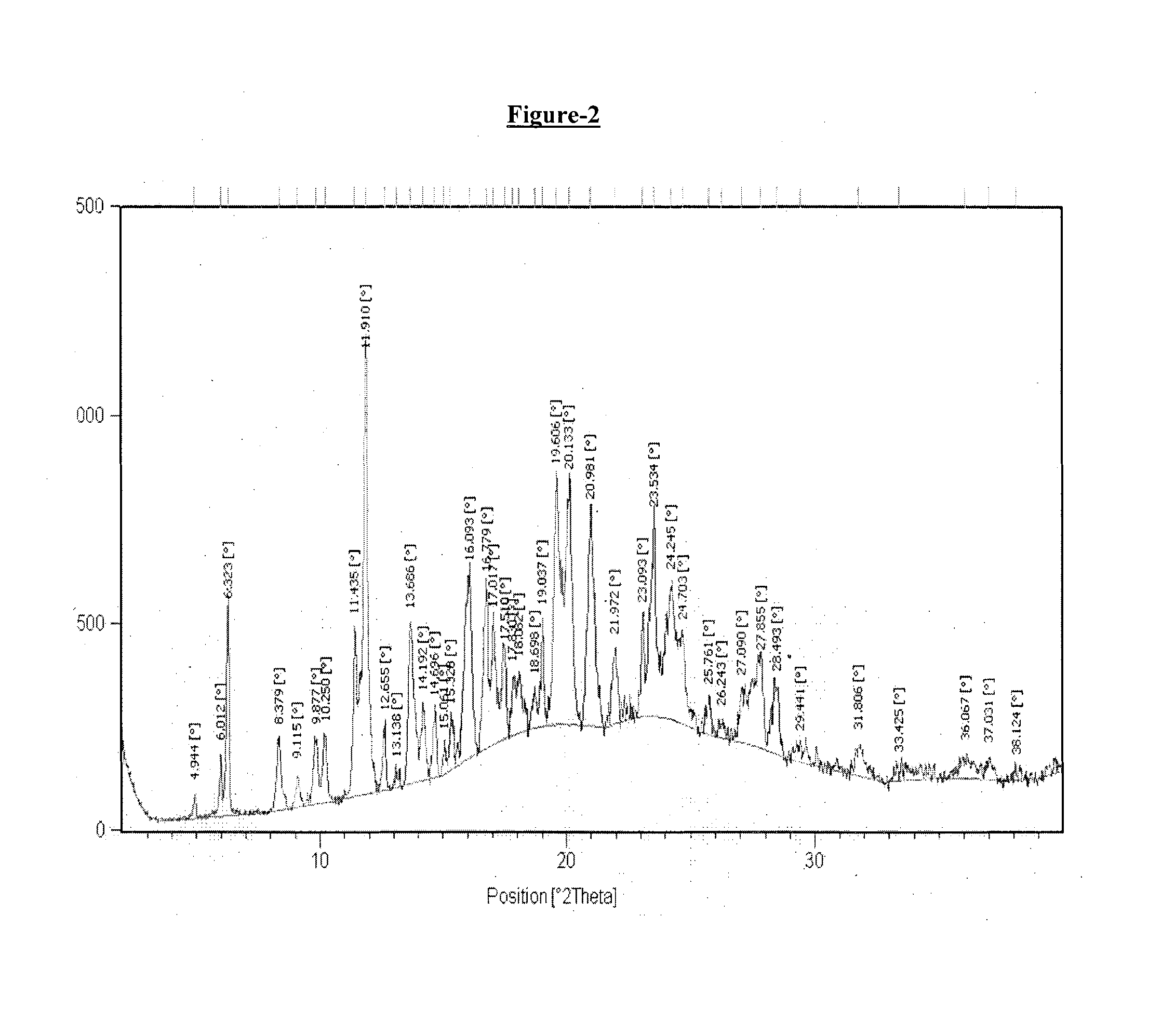
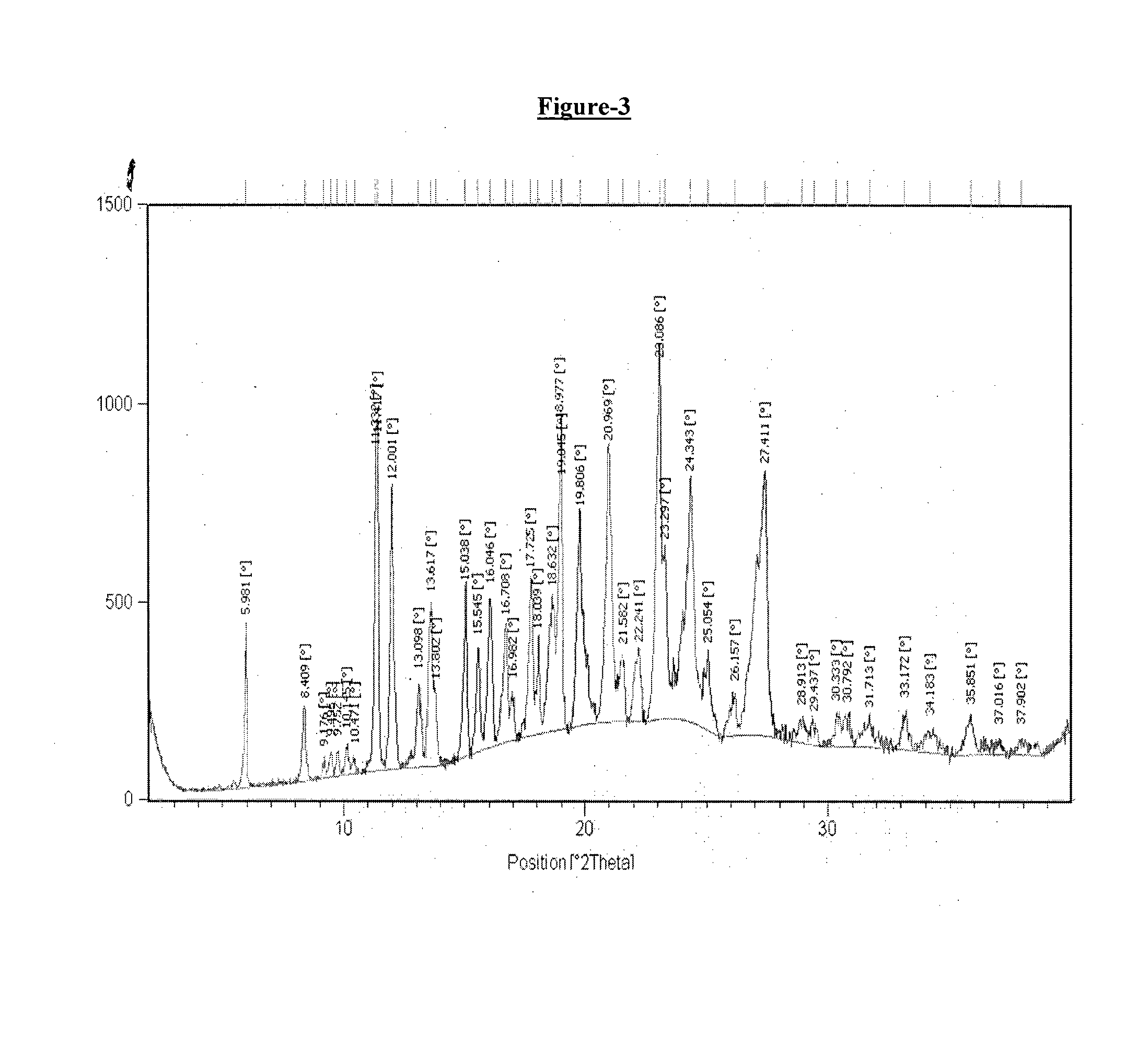
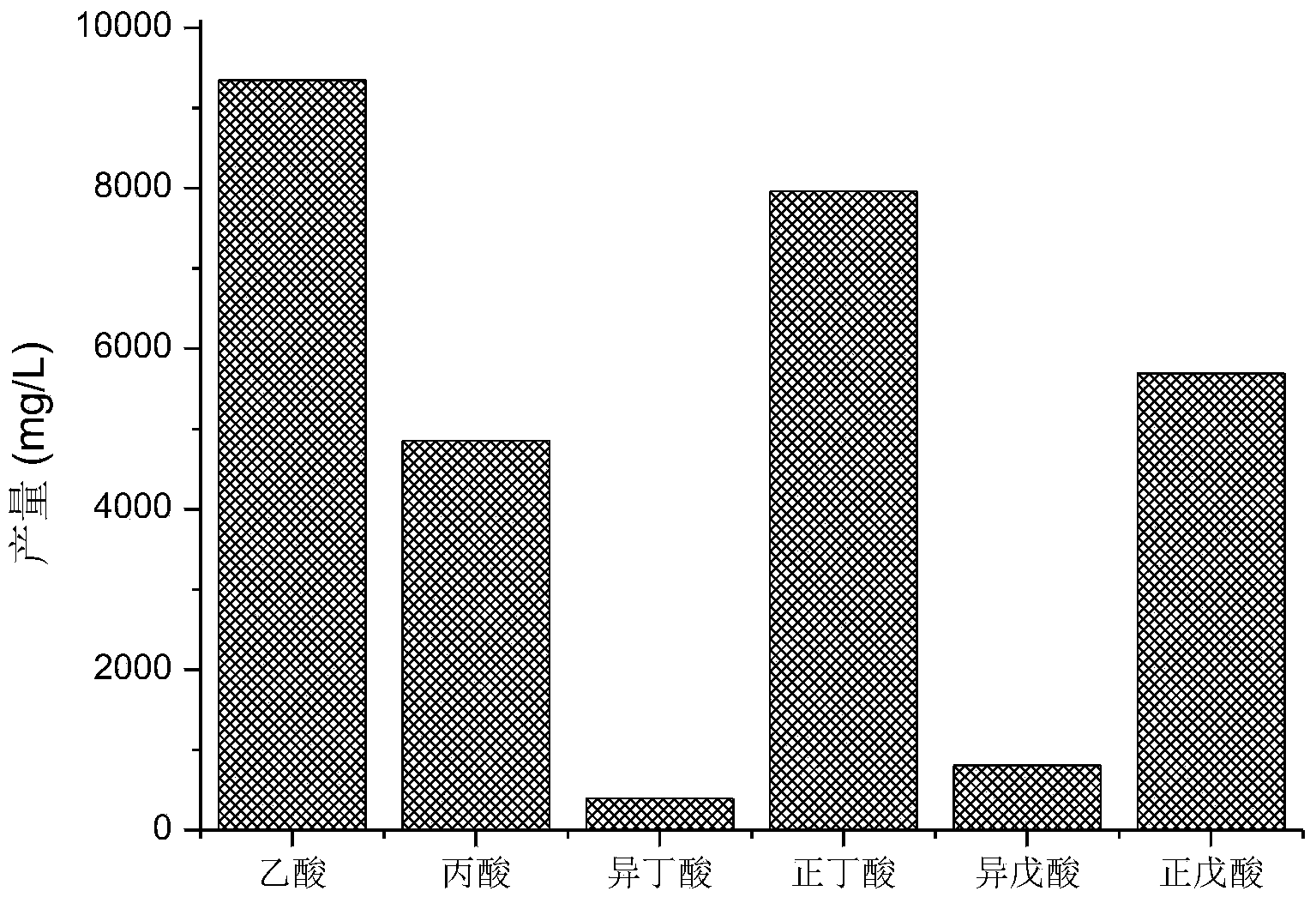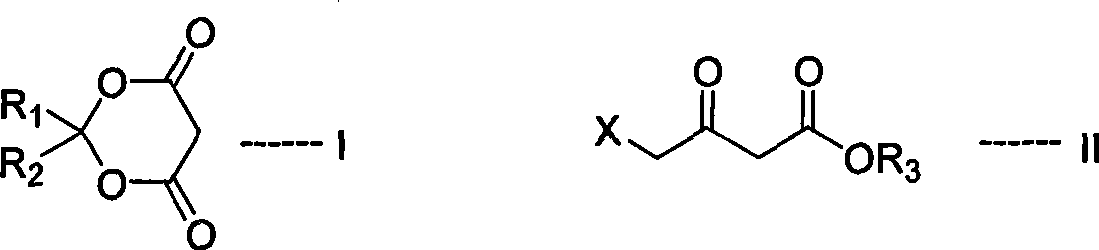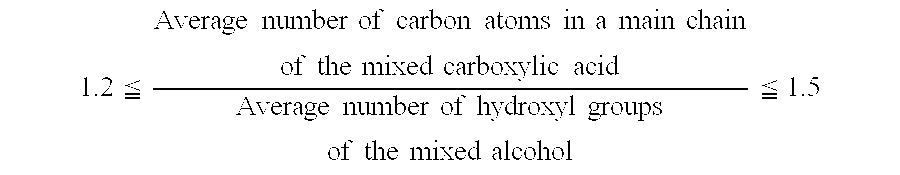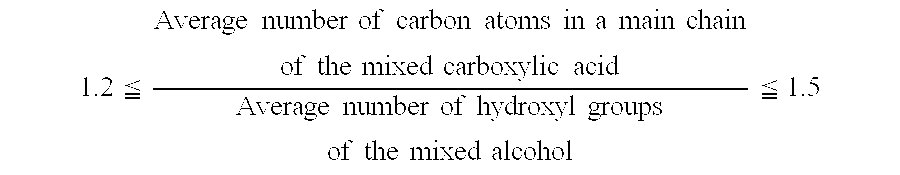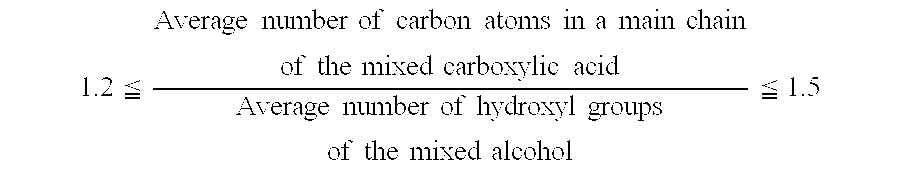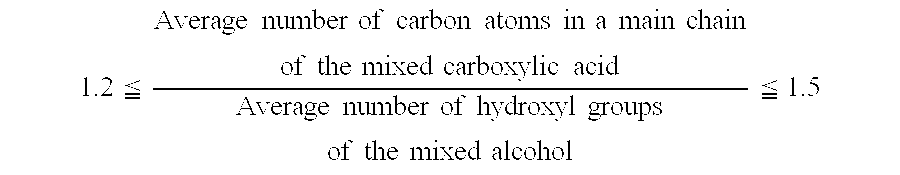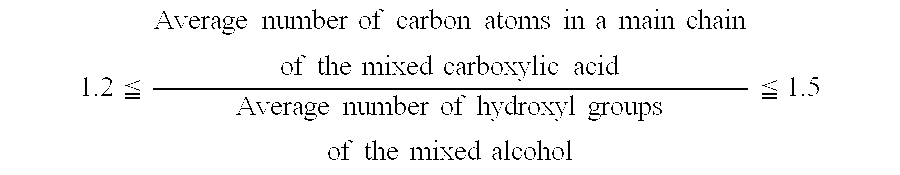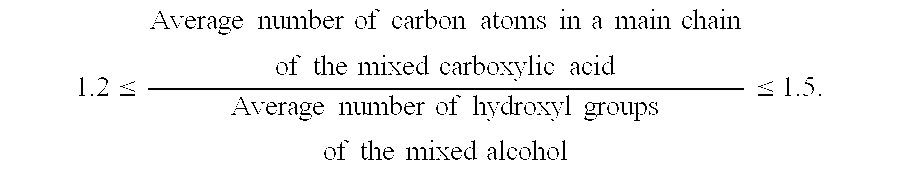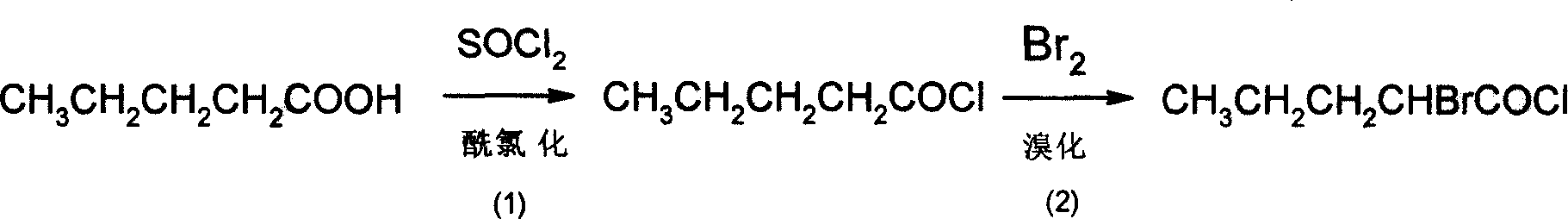Patents
Literature
220 results about "N-pentanoic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Valeric acid, or pentanoic acid, is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH. 3(CH. 2) 3COOH. Like other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids, it has a very unpleasant odor.
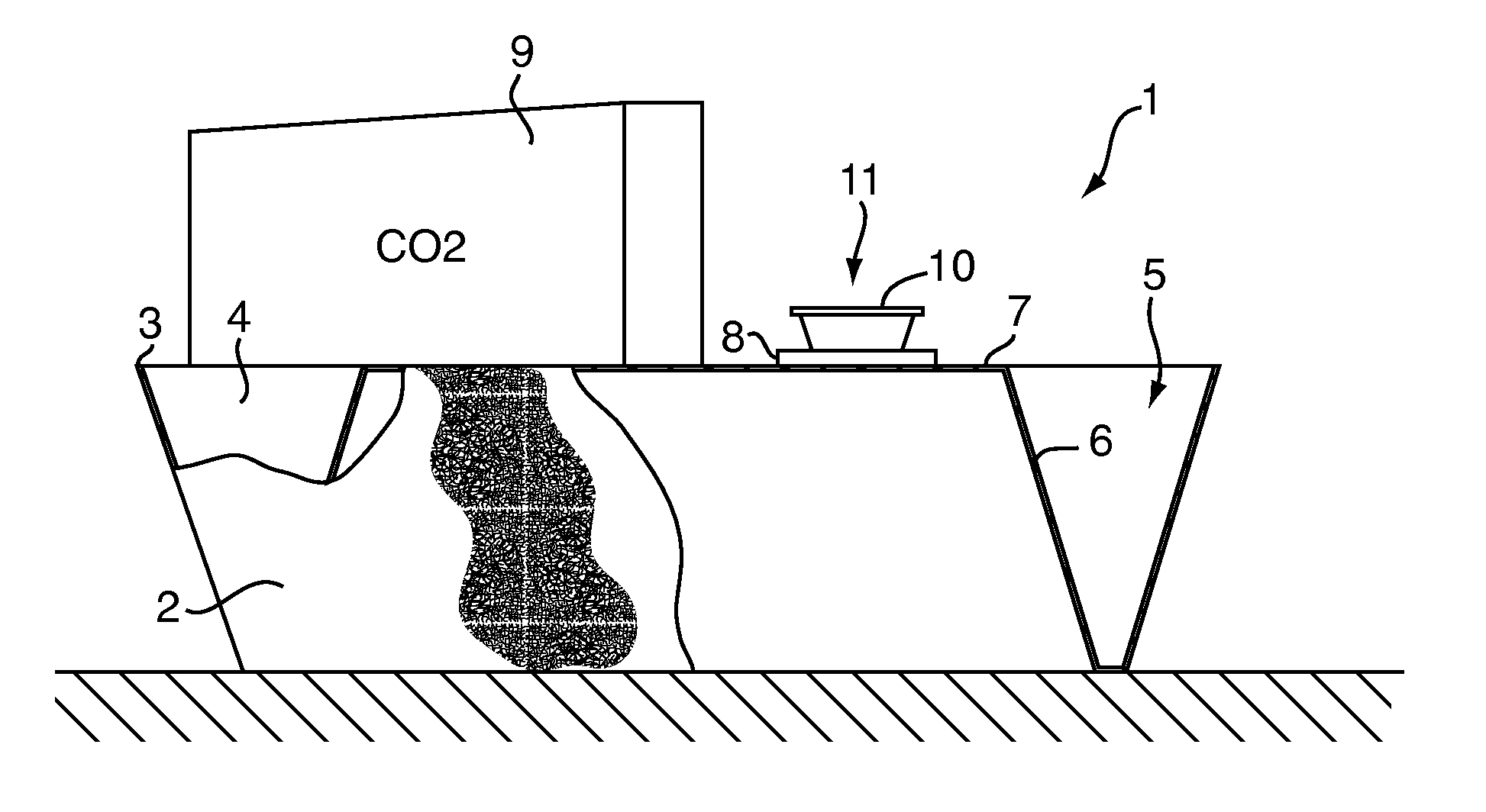
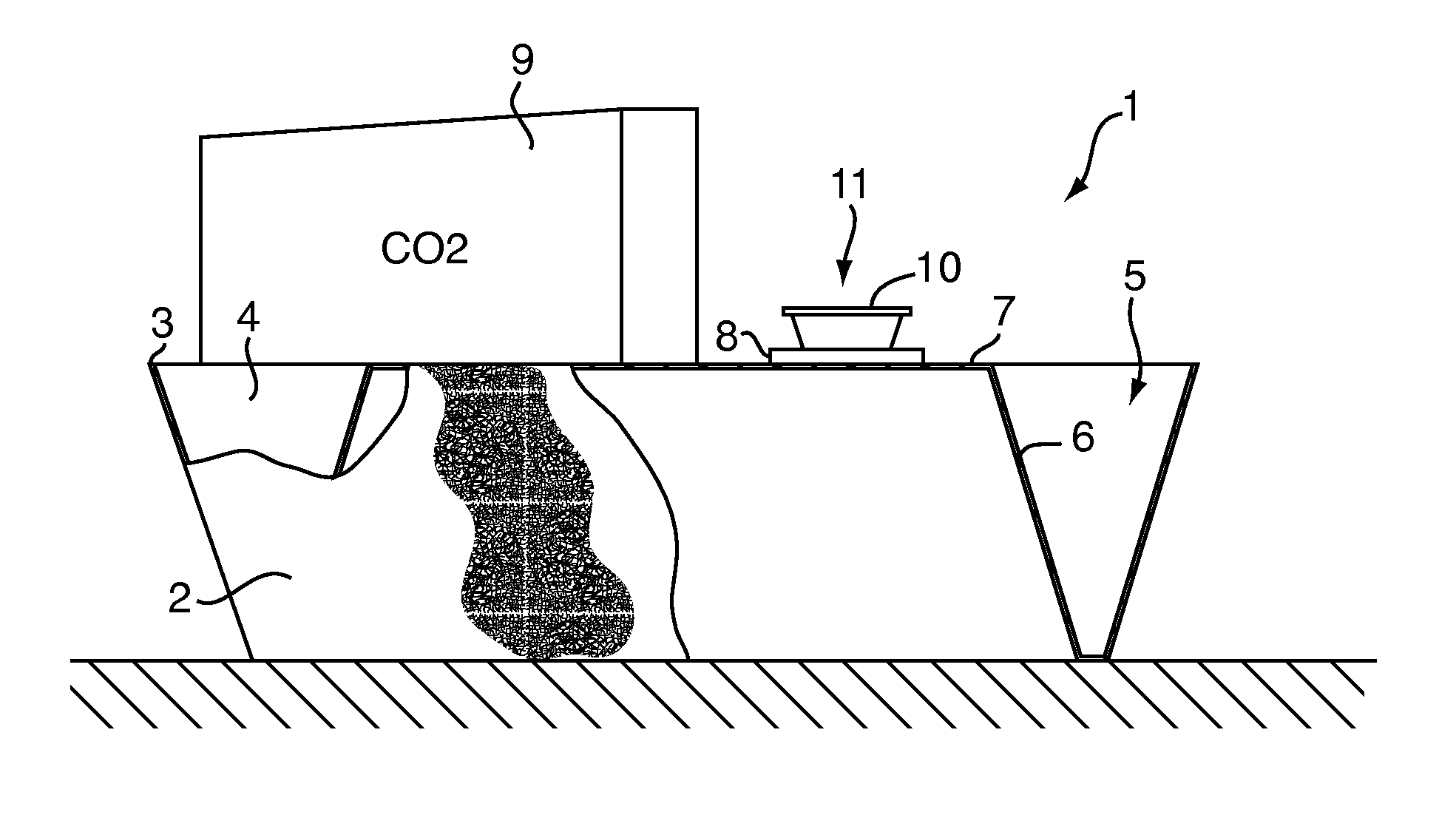
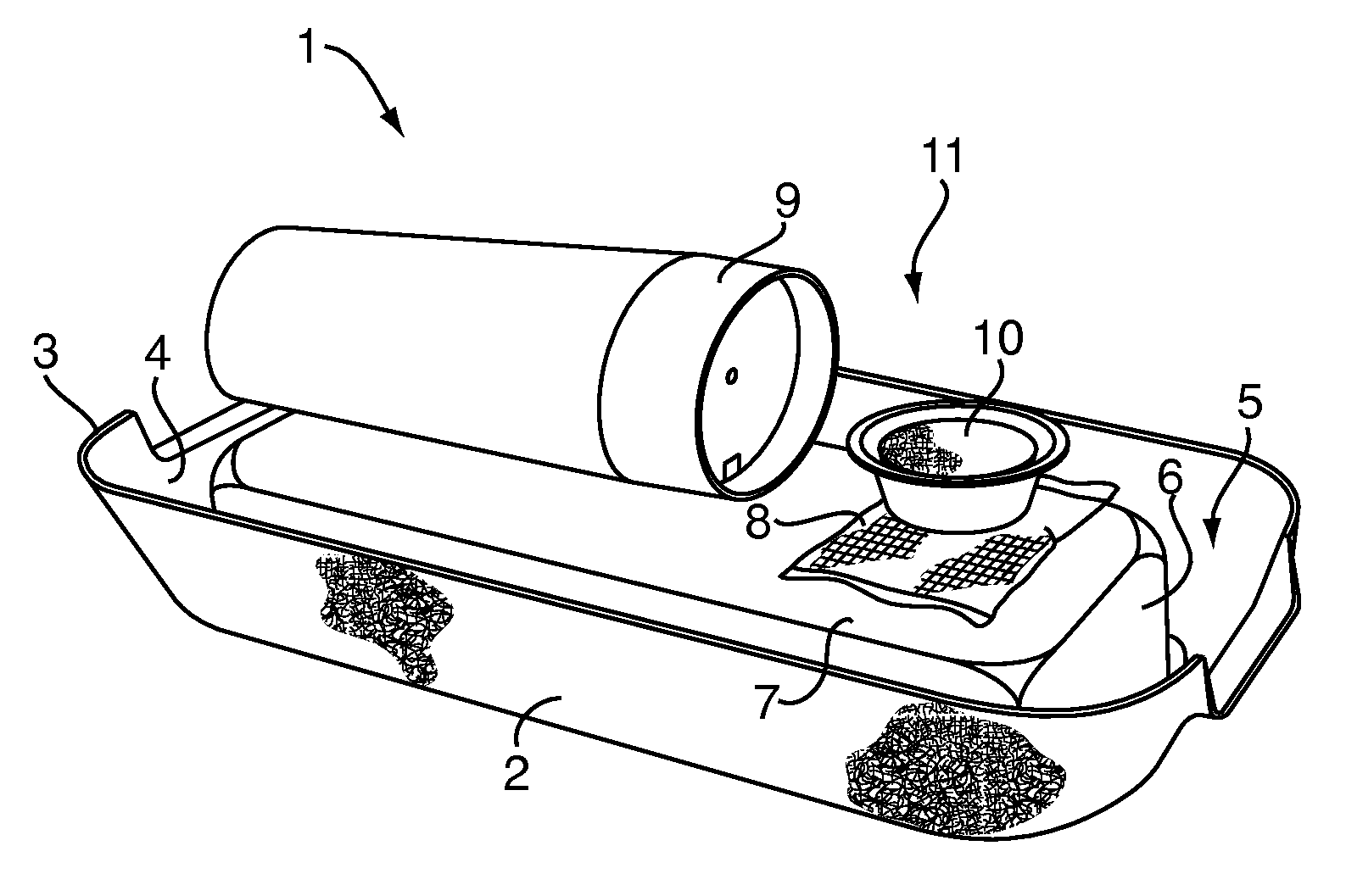
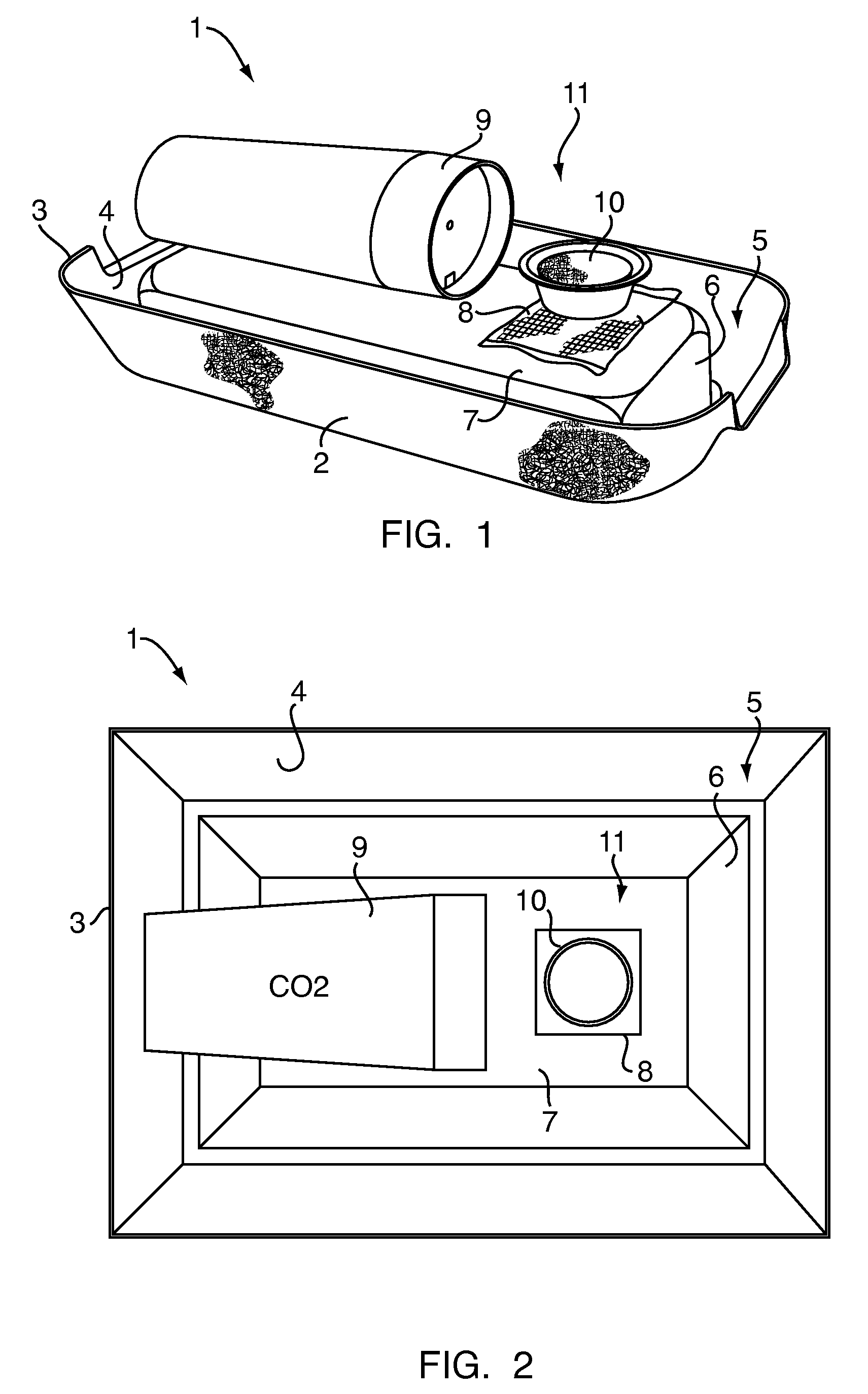
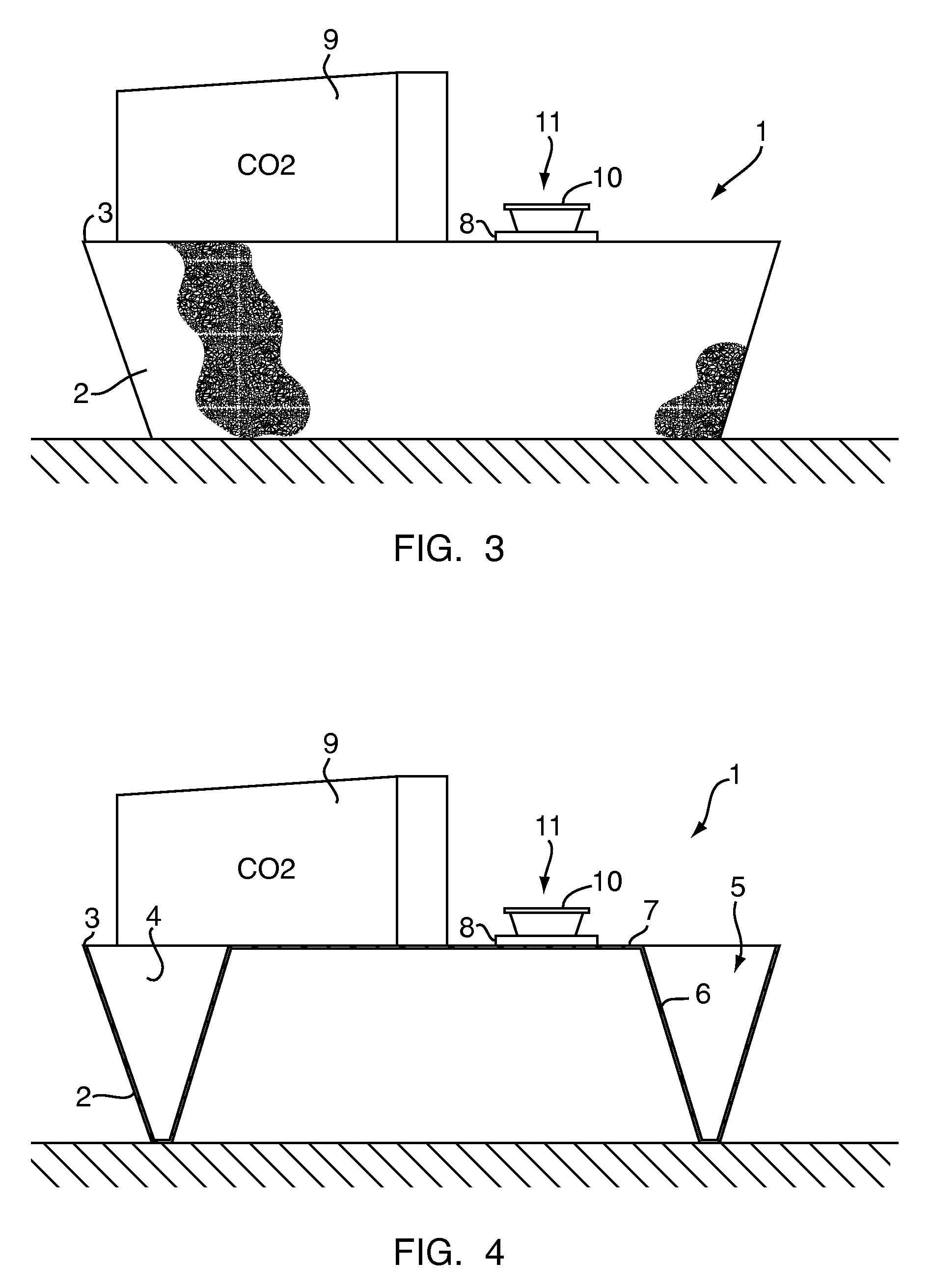
Chemical lure composition, apparatus, and method for trapping bed bugs
A method for attracting bed bugs includes placing a climb-up pitfall trap apparatus that includes a chemical lure composition. The lure composition includes a combination of (a) L-lactic acid, and (b) at least one fatty acid or salt selected from the group consisting of (1) propionic acid, (2) butyric acid, and (3) valeric acid, and (c) 1-octen-3-ol, and (d) a suitable ketone, and (e) a suitable aliphatic sulfide. The trap may also include in conjunction with the lure composition a carbon dioxide source and / or a heat source to compose a lure arrangement.
Owner:SUSAN MCKNIGHT
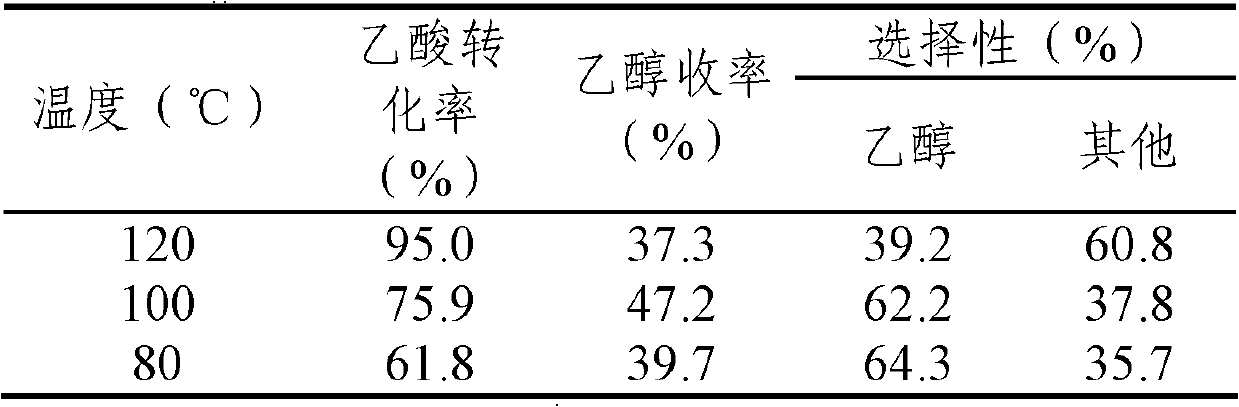
Method for preparing monohydric alcohol or dihydric alcohol through organic acid hydrogenation
ActiveCN103288596AOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparation3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing monohydric alcohol or dihydric alcohol through organic acid hydrogenation. According to the method, any one of acetic acid, propionic acid, valeric acid, stearic acid, oleic acid, palmitic acid, levulinic acid, lactic acid, succinic acid, 3-hydracrylic acid and other organic acids is taken as a reactant, and an A-B / X supported catalyst is adopted, wherein the component A is any one or more than two from Ir, Pt, Pd, Rh and Ru, the assistant B is any one or more than two from Mo, Re and W, the carrier X is any one in SiO2, activated carbon, titanium oxide, zirconium oxide, SiO2-Al2O3 (the mass content of Al2O3 accounts for 17 percent) and molecular sieves, the mass load amount of A in the catalyst is 0.5-10 percent, the molar ratio of the assistant B to A is 0.01-1.0, the reaction pressure is 2-20 MPa, and the reaction temperature is 40-180 DEG C. The catalyst has the characteristics of mild reaction conditions, high reaction activity and good selectivity, and a novel effective way for preparing monohydric alcohol or dihydric alcohol from biomass is provided.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for increasing sewage-reinforced biological phosphor-removing effect by resource utilizing mud organic substance
InactiveCN101070217AImprove phosphorus removal effectReduce volumeWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesEutrophicationOxygen
This invention belongs to new style green technology region, concretely relates to a method of using sludge organic matter to advance biologic dephosphorization effect of sewage. Excess sludge at basicity condition is carried out anaerobic fermentation to produce organic acid; adopt guano precipitation means to reclaim nitrogen and phosphorus of organic acid; add the treatment fluid after reclaiming nitrogen and phosphorus to municipal sewage, under anaerobic-aerobic condition aerobic conditito carry out biological sewage treatment,through solid-liquid separation, the out water reaches the mark and is discharged. This invention through the method of adding excess sludge broth to sewage, not only advance the ability of microbe of synthesizing poly- hydroxy valeric acid(PHV)under anaerobic condition, advance availability of poly- hydroxy eicosanoic acid, decrease glycogen metabolization quantity, in favor of maintaining higher dephosphorization effect at aerobic condition, reduce phosphorus concentration in the out water, prevent water substance eutrophication occurring, but also decrease sludge volume, thereby decrease sludge treatment cost and pollute to environmental.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Trap for bed bugs and the like
Owner:J T EATON
Resin Composition, Molded Product From Resin Composition and Method for Preparing Resin Composition
InactiveUS20070270527A1Eliminate the problemImprove flame retardant performanceConductive materialOrganic conductorsCellulosePolybutylene
Disclosed is a biodegradable resin composition containing at least one biodegradable organic high molecular compound, a flame retardant additive containing a phosphorus-containing compound, and a hydrolysis suppressing agent suppressing the hydrolysis of the at least one biodegradable organic high molecular compound. An aliphatic polyester resin is polylactic acid, polycaprolactone, polyhydroxy lactic acid, polyhydroxy valeric acid, polyethylene succinate, polybutylene succinate, polybutylene adipate, polymalic acid, polyesters synthesized by fermentation, or a copolymer containing at least one of them. A polysaccharide is cellulose, starch, chitin, chitosan, dextrane, a derivative of at least one of them, or a copolymer containing at least one of them.
Owner:LERNER DAVID LITTENBERG KRUMHOLZ & MENTLIK LLP
Method for producing volatile fatty acid through promoting anaerobic fermentation of kitchen wastes
InactiveCN103555775AReduce processing costsReduce investment and operating costsFermentationAcetic acidPropanoic acid
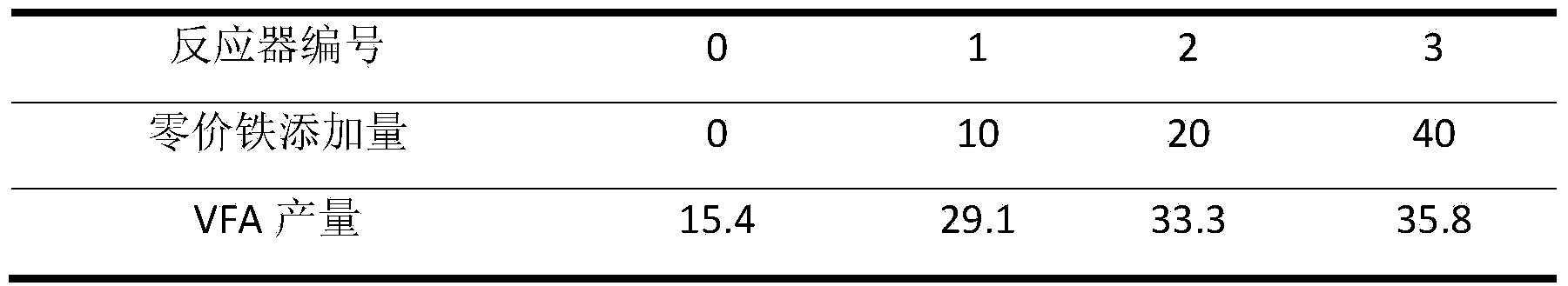
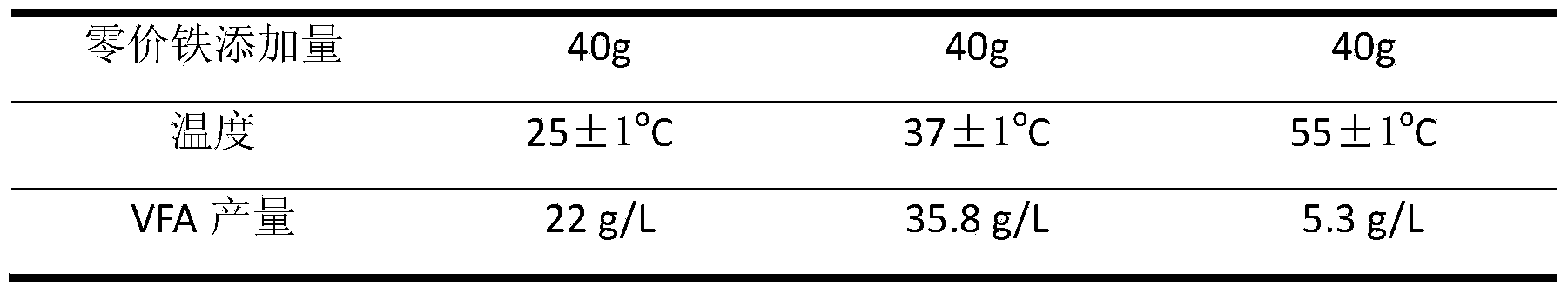
The invention relates to a method for producing volatile fatty acid through promoting the anaerobic fermentation of kitchen wastes. The method comprises the steps of firstly, crushing the kitchen wastes to be up to the particle size of 1-5mm; then, regulating the content of solids to 100mg / L; next, placing the crushed kitchen wastes into an anaerobic fermentation reactor, adding 10-40g / L of marketing zero-valent iron with the particle size of 800 meshes, fermenting at the temperature of 15-40 DEG C for 4-17 days while stirring at the rotating speed of 120r / min, centrifuging, recycling the zero-valent iron in filter residues, and taking out the residual organic components to be composted or used as a liquid fertilizer to obtain the volatile fatty acid with the yield of 29.1-35.8g / L in a supernatant liquid, wherein the volatile fatty acid is detected to contain 32% of acetic acid, 17% of propionic acid, 27% of n-butanoic acid and 20% of n-pentanoic acid when the yield of the volatile fatty acid in the supernatant liquid is 29.1g / L. Compared with the conventional anaerobic fermentation for the kitchen wastes, the method has the advantages that the content of the volatile fatty acid in the supernatant liquid is increased by 2.3-13 times, the recycling of the kitchen wastes is effectively realized, and the method is low in cost, high in speed and high in social, economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
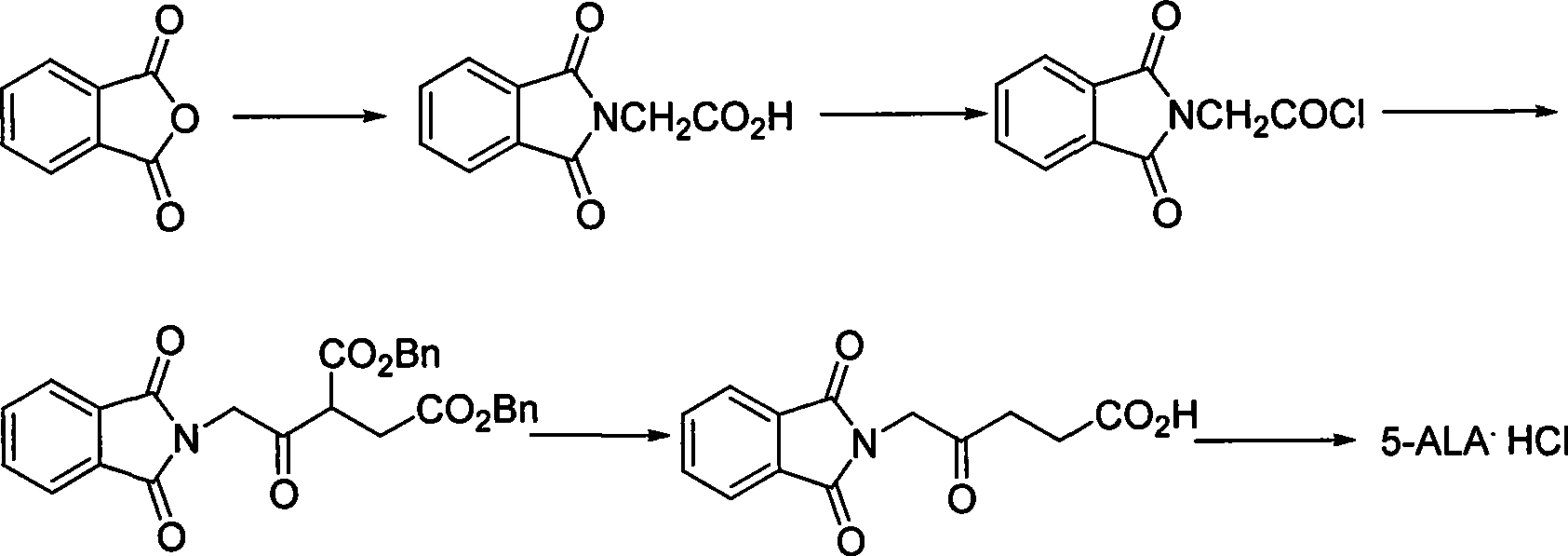
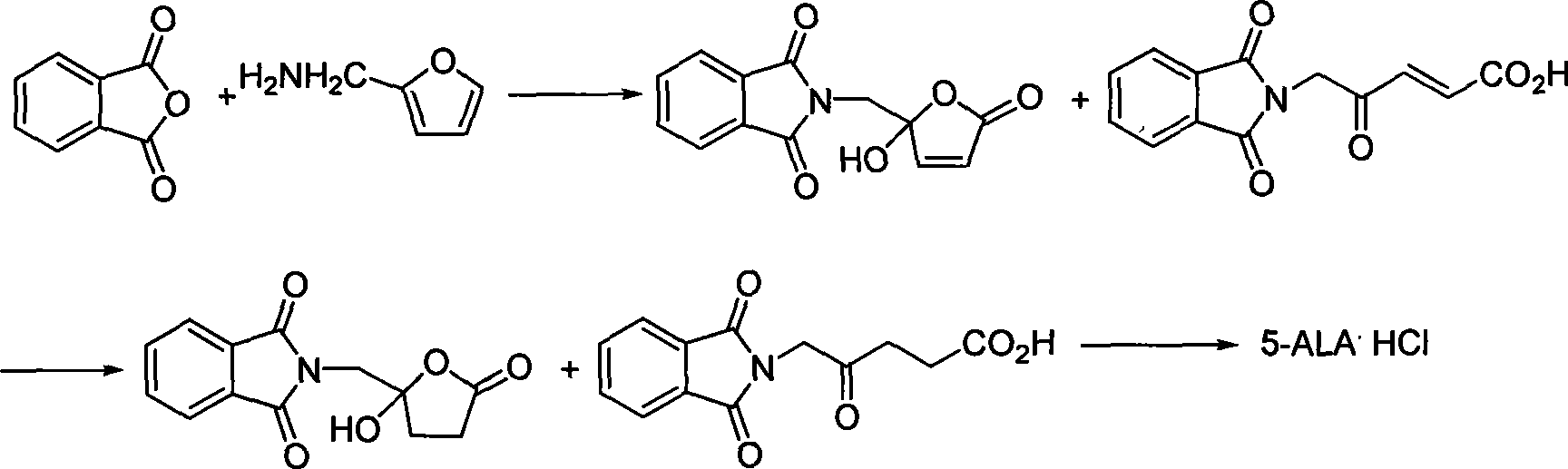
Process for synthesizing 5-aminovaleric acid hydrochloride
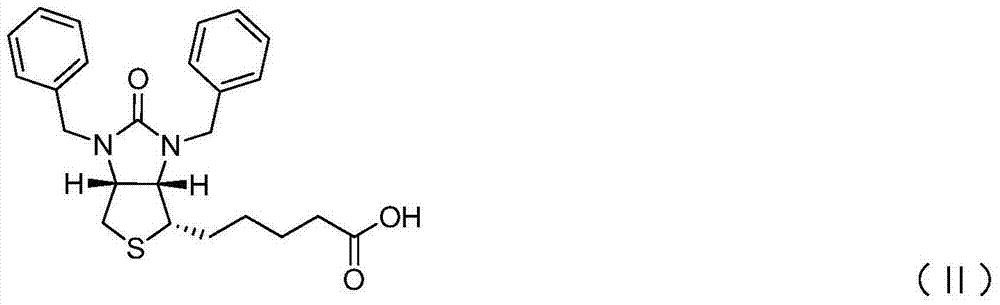
ActiveCN101462974AEasy to crystallize and purifyRaw materials are simpleOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationBenzyl groupAlkyl transfer
The invention relates to an efficient novel method for synthesizing photosensitizing agent 5-ketoamine valerate hydrochloride. The method uses compounds of formula (I) and formula (II). In the formulas, R1 and R2 represent hydrogen or C1-C4 alkyl or substituted benzyl; R3 represents the C1-C4 alkyl or the substituted benzyl; and X represents Cl, Br, OTs and OMs. High purity 5-ketoamine valerate hydrochloride is prepared after alkylation reaction, interesterification, hydroxylamination, reduction and hydrolysis decarboxylation finally.
Owner:FUJIAN BOTE CHEM PROD
Method for synthesis of dronedarone
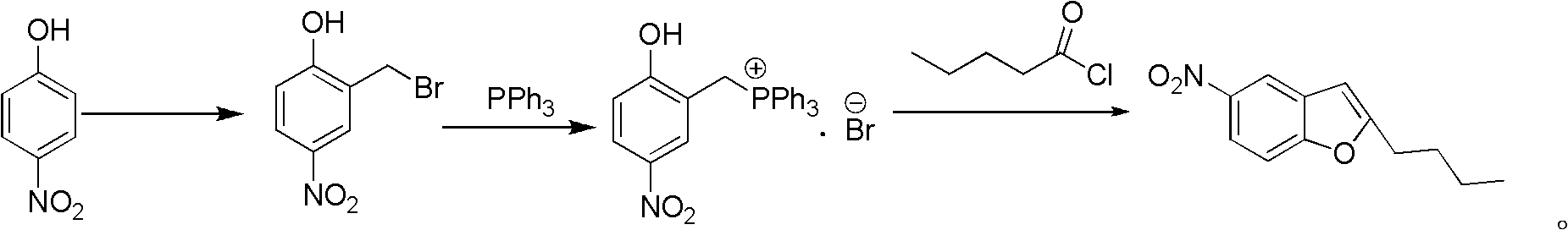
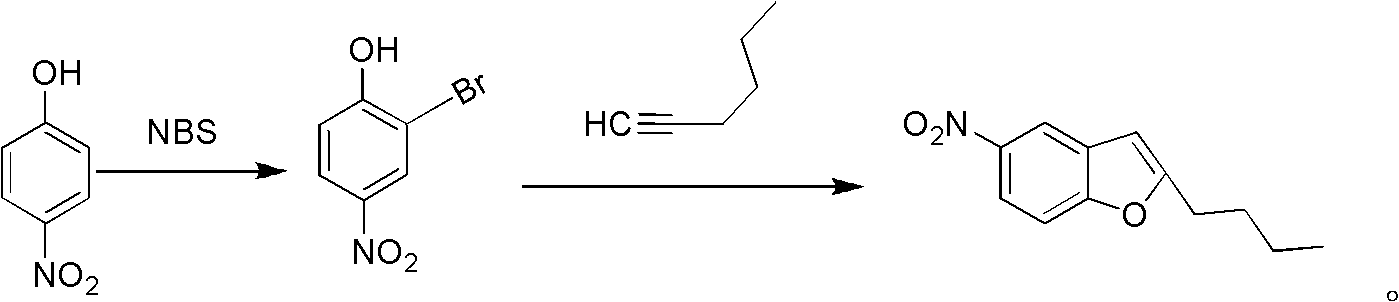
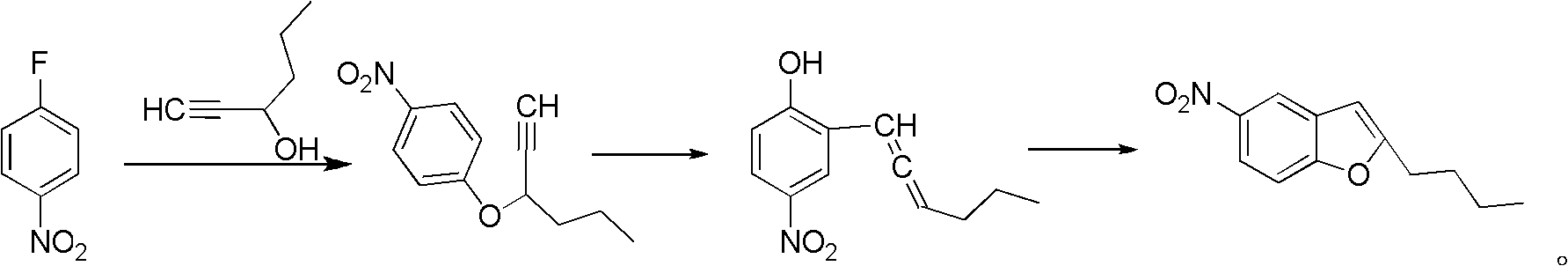
The invention relates to a method for synthesis of dronedarone. The method comprises the following steps that 1), p-nitrophenol, paraformaldehyde and concentrated hydrochloric acid as raw materials undergo a condensation reaction in the presence of concentrated hydrochloric acid or phosphoric acid as a catalyst to produce 2-chloromethyl-4-nitrophenol; 2), 2-chloromethyl-4-nitrophenol and triphenylphosphine undergo a reflux reaction in the presence of chloroform to produce 2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzyl-triphenyl-phosphonium chloride, and 3), 2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzyl-triphenyl-phosphonium chloride and n-valeryl chloride undergo a condensation reaction in a toluene solution in the presence of triethylamine and n-pentanoic acid as catalysts to produce 2-(n-butyl)-5-nitrobenzofuran.
Owner:FUJIAN COSUNTER PHARMA
Novel esterase as well as coding gene and application of esterase
InactiveCN104140959AImprove qualityMild reaction conditionsHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesPropanoic acidNucleotide
The invention discloses a novel esterase as well as a coding gene and an application of esterase. The esterase EST04211 has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The amino acid sequence of the gene of the esterase EST04211 is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The novel esterase disclosed by the invention is obtained by cloning Bacillus SCSIO15121 derived from deep sea of the Indian Ocean. The esterase has the largest characteristic that the esterification rate is 97% in catalytic synthesis of ethyl isobutyrate, and under similar conditions, the esterase can also catalyze propionic acid, butyric acid, valeric acid, caproic acid and ethanol, propanol, butanol, pentanol and hexanol to synthesize corresponding short-chain aromatic ester flavors, such as ethyl propionate, propyl propionate and butyl propionate, the esterification rate mostly reaches 85%-95%. The esterase can be applied in the industrial bio-manufacturing of the short-chain aromatic flavors, such as ethyl isobutyrate and the ester flavors are high in quality, belongs to natural products and can be applied in production industries, such as foods, cigarettes and daily chemical products.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-mechanical strength and biodegradable PLA-PHBV composite material, preparation method thereof and thin film
The invention discloses a high-mechanical strength and biodegradable PLA-PHBV composite material. The composite material contains the following components in parts by weight: 40-80 parts of polylacticacid and 5-30 parts of 3-hydroxybutyric acid-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid copolymer, 2-15 parts of an ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer grafted glycidyl methacrylate modified toughening agent, 2-8 parts of a solubilizer and 0.2-0.8 part of a nucleating agent. The composite material belongs to the field of high molecular materials and has the advantages that the mechanical property is improved, meanwhile, the glass transition temperature is high, the crystallization degree is low, and the melting temperature is low. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the composite material anda thin film prepared from the composite material. The thin film can present an excellent barrier property.
Owner:GUANGDONG JUHANG INST FOR ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
After-treatment method of crude tris-(2-isopropyl chloride) phosphate
ActiveCN102002068AEliminate odorEasy to removePhosphorus organic compoundsPhosphoric Acid EstersAlkaline water
The invention relates to an after-treatment method of crude tris-(2-isopropyl chloride) phosphate, in particular to a treatment method which can effectively remove the stinky 2-methyl-pentanal in the tris-(2-isopropyl chloride) phosphate. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of: introducing a certain amount of ozone in the crude tris-(2-isopropyl chloride) phosphate obtained by reaction; directly oxidizing the insoluble 2-methyl-pentanal generated by reaction into acidic materials such as 2- methyl-valeric acid and the like soluble in an alkaline solution; and conveniently removing the acidic materials in the subsequent washing process to ensure that the obtained tris-(2-isopropyl chloride) phosphate does not contain the 2-methyl-pentanal which stinks. The method of the invention reduces the content of the stinky 2-methyl-pentanal in the tris-(2-isopropyl chloride) phosphate from about 200-300ppm to less than 5ppm; and when the product is applied to the interior materials of automobiles or furniture and the like, the stink is eliminated, and therefore, the product is in the favor of consumers.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANSHENG
Process for making an egg shell ft catalyst
InactiveUS20080255257A1High activityLow methane selectivityOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionBenzoic acidPropanoic acid
A process for preparing a Fischer-Tropsch catalyst comprising the steps of a) providing a particle having a size of at least 1 mm and having a catalytically active metal homogenously distributed therein, wherein at least 50 wt % of the catalytically active metal is present as divalent oxide or divalent hydroxide; b) treating the particle with formic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, n-pentanoic acid, hexanoic acid, citric acid, and / or benzoic acid an organic acid for more than 5 minutes; c) washing the catalyst particle; and d) drying the catalyst particle and / or heating the particle to a temperature in the range of 200 to 400° C.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
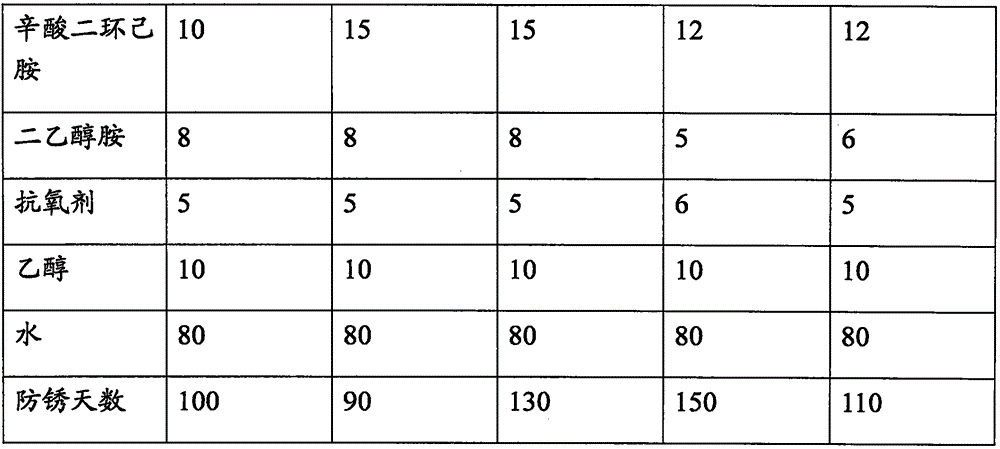
Water-soluble antirust agent
The invention provides a water-soluble antirust agent. The water-soluble antirust agent is prepared from fatty acid, specific amine, an additive, ethyl alcohol and water. The mass ratio of the fatty acid to the alcohol amine to the additive to the ethyl alcohol to the water is (2-3):(1-15):(5-10):(10-15):(80-100). The fatty acid is selected from one or more of oxalic acid, valeric acid, naphthenic acid, citric acid, benzoic acid, lauric acid, adipic acid, oleic acid and sebacic acid, the apecific amine is selected from one or more of octanoic acid dicyclohexylamine, triethanolamine, diethanol amine and ethanol amine, and the additive is an antioxidant. The antirust valid period of the water-soluble antirust agent is long and can reach 3-6 months; an antirust film is thin and is only tens of microns thick, a follow-up process cannot be influenced even though the antirust film is not removed, and the film can be removed with warm water due to the good film removability of the water-soluble antirust agent; and the water-soluble antirust agent is low in production cost, free of foreign smells and beneficial to environmental protection.
Owner:彭国泉
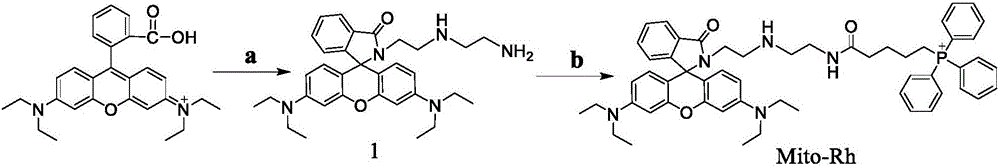
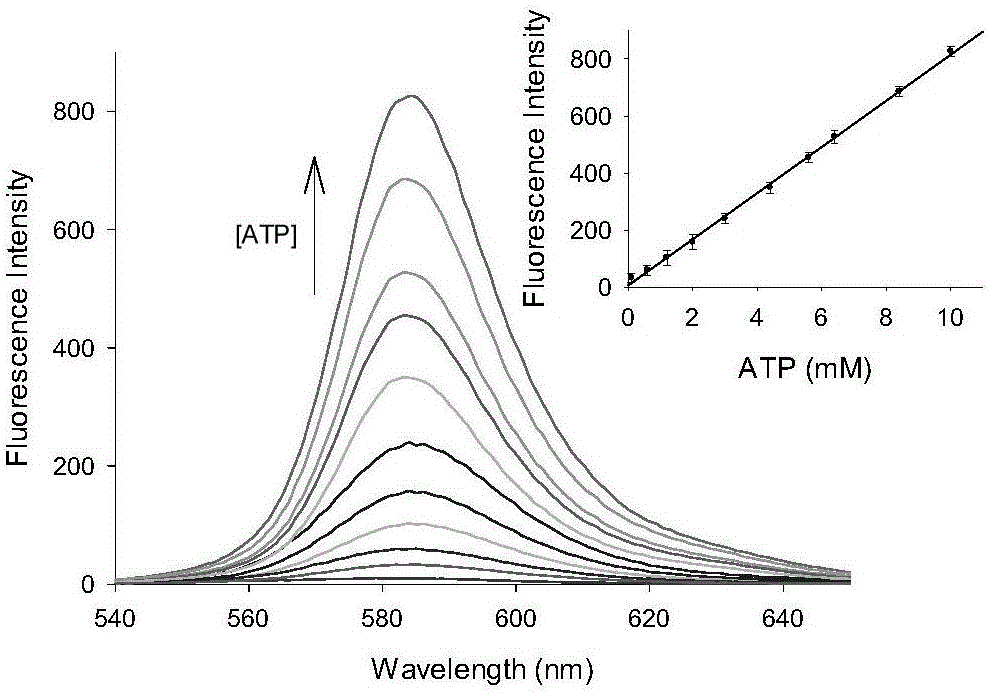
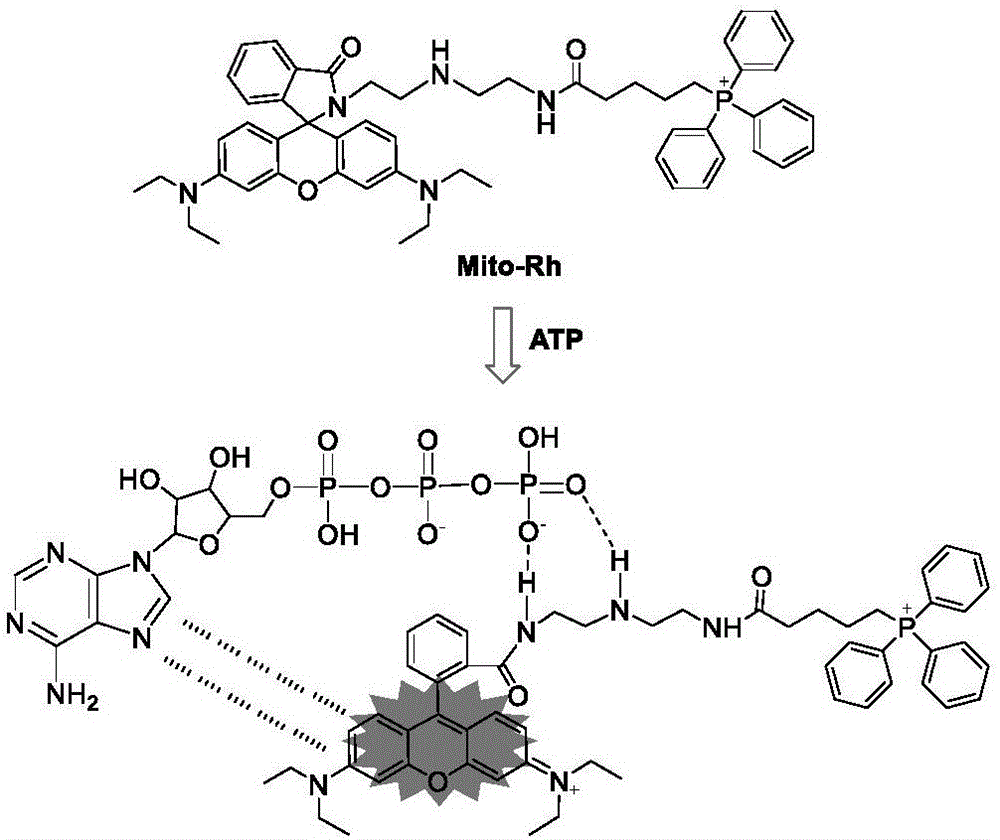
Preparation and application of ATP fluorescent probe for positioning mitochondria
InactiveCN106543226AReal-time monitoring of content changesDecreased fluorescence intensityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiethylenetriamineStructural formula
The invention discloses preparation and application of an ATP fluorescent probe for positioning mitochondria, wherein the probe has the structural formula defined in the specification and is synthesized by rhodamine B, diethylenetriamine, 5-bromo-valeric acid and triphenylphosphine as raw materials. In the system, ATP induces ring opening of a rhodamine lactam structure, strong fluorescence is produced, and high sensitivity is showed on ATP detection. At the same time, the probe shows good selectivity on the ATP, and is hardly interfered by other biological anions or inorganic anions. When the pH value is 6.0-8.0, ATP determination of the probe is not affected. In addition, the probe can be positioned in the mitochondria, and changes of the content of the ATP in the mitochondria are real-timely monitored.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Refrigeration lubricant composition
ActiveUS20060278845A1Improve the lubrication effectImprove stabilityLiquid carbonaceous fuelsHeat-exchange elementsCarboxylic acidN-pentanoic acid
The present invention provides a refrigeration lubricant composition that have necessary properties such as compatibility with a hydrofluorocarbon refrigerant, thermal stability, hydrolytic stability and low-temperature fluidity, and good lubricity, and has high stability under low temperature conditions so that crystals are prevented from being precipitated over a long term. The refrigeration lubricant includes an ester obtained from a mixed alcohol and a mixed carboxylic acid, wherein the mixed alcohol consists of 65 to 99.95 mol % of pentaerythritol and 0.05 to 35 mol % of dipentaerythritol, the mixed carboxylic acid consists of n-pentanoic acid, n-heptanoic acid, and isononanoic acid, the molar ratio of the n-pentanoic acid to the n-heptanoic acid is 0.3 or more and 10 or less, and the isononanoic acid is contained in the mixed carboxylic acid at a ratio of 10 mol % or more and 45 mol % or less.
Owner:NOF CORP
Degradable plastic material
The invention discloses a degradable plastic material. The degradable plastic material comprises the following raw materials in part by weight: 5-50 parts of hydroxybutyrate and valeric acid copolyester PHBV4, 50-55 parts of peanut protein prowder, 15-18 parts of nanometer cellulose whiskers, 12-15 parts of coconut fibers, 3-5 parts of amylase, 1.5-2.2 parts of silane coupling agents, 2-3 parts of potassium sorbate, 2-3 parts of dehydroacetic acids, 1.4-1.6 parts of dioctyl phthalate, 1.2-1.6 parts of zinc stearate, 10-12 parts of hard clay, 5-9 parts of kaolin, 7-11 parts of sepiolite and 1-1.4 parts of 2, 6- di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol BHT. The degradable plastic material can be completely decomposed into micromolecule substances under effects of microorganisms; the tensile strength, the breakage elongation and the light transmission of the degradable plastic material are close to those of the existing polypropylene; and the degradable plastic material can replace the polypropylene in some fields.
Owner:浙江创新旭隆新材料科技有限公司
Micropore polymethacrylimide foam with high thermal deformation temperature and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105037618AImprove heat resistanceHigh heat distortion temperatureCross-linkHeat deflection temperature
The invention relates to micropore polymethacrylimide foam with high thermal deformation temperature. The foam comprises, by mass, 35-60 parts of methacrylic acid (MAA), 65-40 parts of acrylonitrile, 0.10-4.0 parts of initiators, 1.0-20 parts of foaming agents, 1-5 parts of nucleating agents, 0.1-5 parts of cross-linking agents and 5-10 parts of heat-resisting additives; the initiators are azo-bis(4-cyano valeric acid) or mixtures of azo-bis(4-cyano valeric acid) and other azo compounds. The other azo compounds are azodiisobutyronitrile AIBN, azobisisovaleronitrile or azobisisoheptonitrile. According to the micropore polymethacrylimide foam high in thermal deformation temperature, the foam has the small pore diameter phi of 0.1-0.3 mm, thermal resistance is high, the thermal deformation temperature is high and is larger than 200 DEG C, and the mechanical property is excellent.
Owner:AEROSPACE RES INST OF MATERIAL & PROCESSING TECH +1
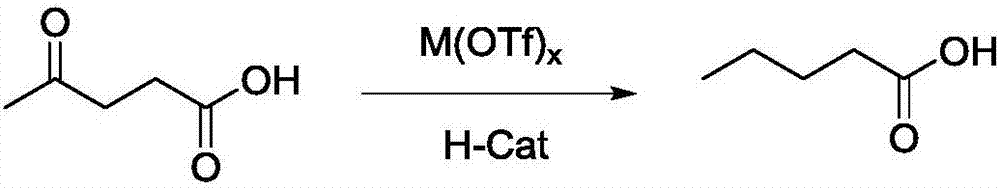
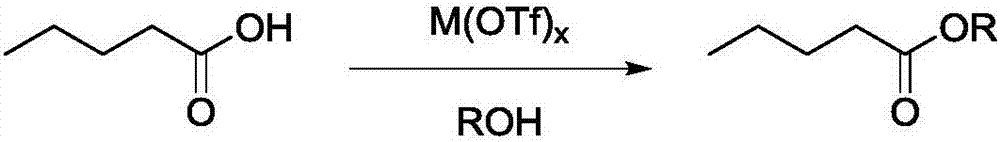
Method for preparing valeric acid and valerate from levulinic acid
ActiveCN106905137AHigh catalytic efficiencyIncrease profitOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationVernolic acidPropanoic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing valeric acid and valerate from levulinic acid. The method comprises the following steps: by taking levulinic acid as a raw material, hydrogenated catalyst and trifluoromethanesulfonic acid metal salt as a catalyst, performing catalytic hydrogenolytic cleavage reaction under hydrogen atmosphere, to obtain valeric acid; continuously by taking valeric acid as a raw material and trifluoromethanesulfonic acid metal salt as a catalyst, adding alcohol compound to perform esterification reaction, to obtain valerate. The method for preparing valeric acid and valerate from levulinic acid has the characteristics of being simple in technology, mild in reaction conditions, high in product yield, easily purified, environment-friendly and the like, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:合肥利夫生物科技有限公司
Refrigeration lubricant composition
ActiveUS7507348B2Maintain good propertiesImprove the level ofLiquid carbonaceous fuelsHeat-exchange elementsAlcoholPentaerythritol
The present invention provides a refrigeration lubricant composition that have necessary properties such as compatibility with a hydrofluorocarbon refrigerant, thermal stability, hydrolytic stability and low-temperature fluidity, and good lubricity, and has high stability under low temperature conditions so that crystals are prevented from being precipitated over a long term. The refrigeration lubricant includes an ester obtained from a mixed alcohol and a mixed carboxylic acid, wherein the mixed alcohol consists of 65 to 99.95 mol % of pentaerythritol and 0.05 to 35 mol % of dipentaerythritol, the mixed carboxylic acid consists of n-pentanoic acid, n-heptanoic acid, and isononanoic acid, the molar ratio of the n-pentanoic acid to the n-heptanoic acid is 0.3 or more and 10 or less, and the isononanoic acid is contained in the mixed carboxylic acid at a ratio of 10 mol % or more and 45 mol % or less.
Owner:NOF CORP
Method for preparing composition granules containing ibuprofen amino guanidyl valeric acid
ActiveCN1528278AOvercome the disadvantage of easy moisture absorptionMask pungent odorsOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticIbuprofen arginineAdhesive
The present invention provides a preparation method of granules containing ibuprofen arginine composite, and the described composite is formed from ibuprofen arginine, diluting agent and adhesive, and said preparation method includes two steps of granurating and coating, and uses the coating material containing silicon dioxide to make coating liquor, and uses the prepared coating liquor to coat the granules. Said granules can be tabletted, also cna be capsulized, and the conventional solid soage form prepared by using said method has good stability, quick disintegration speed and high biological utilization rate.
Owner:SUNSTONE TANGSHAN PHARM CO LTD
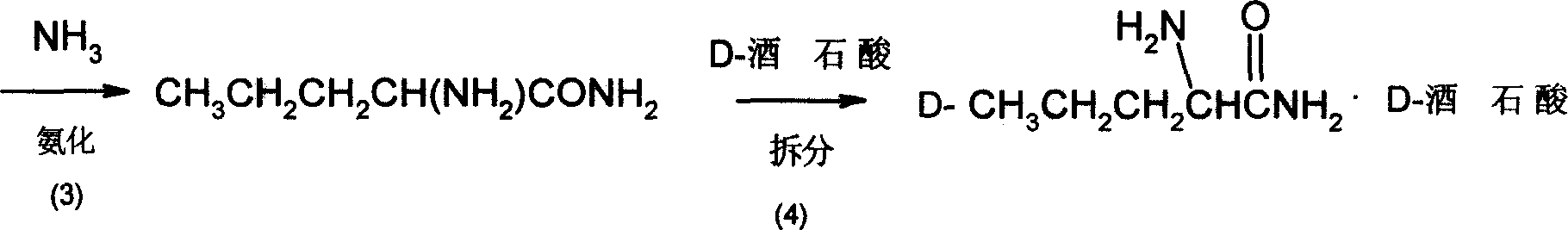
Method for synthesizing D-norvaline using n-pentanoic acid
InactiveCN101007774ASimple production processLow costOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationChemical synthesisAmino acid
The invention discloses a synthesizing method of D-norvaline, which comprises the following steps: adopting n-pentatonic acid as main original material; acylating and chlorinating; bromining; ammonifying; detaching; recrystallizing; hydrolyzing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Loading type composite metal-acid bifunctional catalyst
InactiveCN108187730AEasy to makeMild conditionsMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationHydrogen pressureCerium
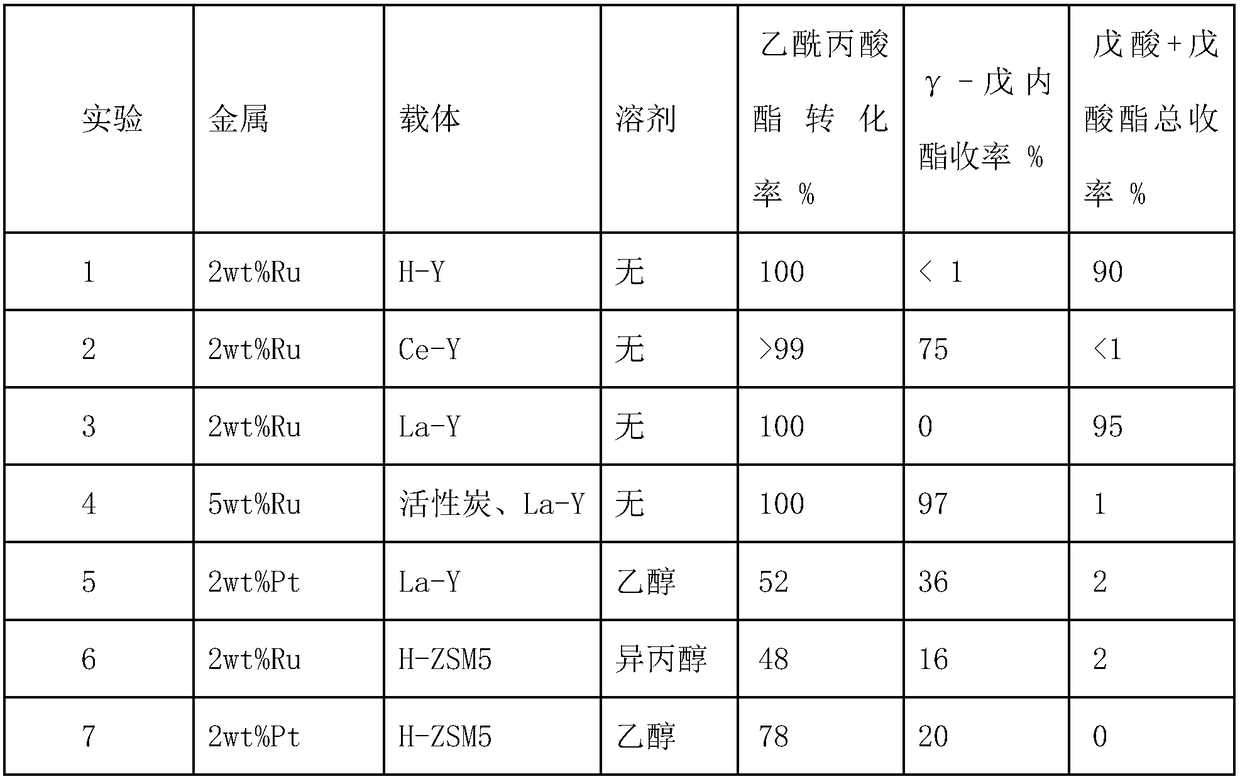
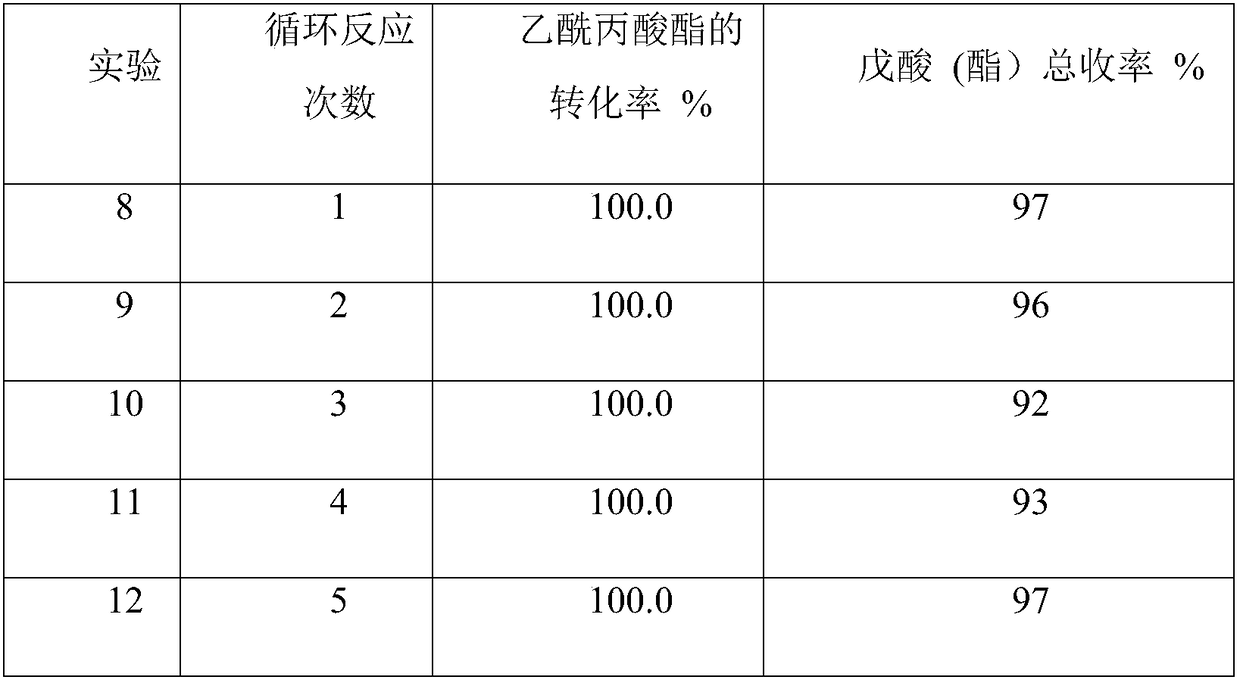
The invention discloses a loading type composite metal-acid bifunctional catalyst. The loading type composite metal-acid bifunctional catalyst is prepared from a catalytic activity component, a carrier and an rare earth element; the catalytic activity component is one or more of transition metal iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, platinum and gold; the carrier isone or more of active carbon, aluminum oxide, titanium dioxide, Y-shaped molecular sieve, ZSM-5 and beta-molecular sieve; and the rare earth element is one or more of oxides of lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium and neodymium. According to a method for preparing valeric acid (valerate) by adopting the loading type composite metal-acid bifunctional catalyst, levulinic acid platform molecules are takenas a reaction raw material to be subjected to a hydrogenation reaction in a sealed high pressure reaction still, wherein the reaction temperature is 50-400 DEG C, the hydrogen pressure is 1-20 MPa, and the reaction time is no less than 60 minutes. The composite metal-acid bifunctional catalyst disclosed by the invention presents the high activity, the high selectivity and the excellent stabilityunder a hydrothermal condition.
Owner:昆山普瑞凯纳米技术有限公司
Acid Addition Salt of Donepezil and Pharmaceutical Composition Thereof
Disclosed is an acid addition salt of donepezil, wherein acid counterion is selected from the group consisting of pamoic acid, cypionic acid, camphor sulfonic acid, enanthic acid, fusidic acid, gluceptic acid, gluconic acid, lactobionic acid, lauric acid, valeric acid, Dibenzoyl-D-Tartaric acid and terephthalic acid. Disclosed is a process for the preparation and pharmaceutical composition comprising the same. More specifically, disclosed is concerned with the pamoate acid addition salts of donepezil. Disclosed also is long acting formulation comprising the acid addition salt of donepezil and process for the preparation thereof.
Owner:TORRENT PHARMA LTD
Resin composition, molded product from resin composition and method for preparing resin composition
InactiveUS7645823B2Improve flame retardant performanceConductive materialOrganic conductorsCellulosePolybutylene
Owner:LERNER DAVID LITTENBERG KRUMHOLZ & MENTLIK LLP
Preparation process and application of novel foam ceramic material
ActiveCN102442833ASimple manufacturing processFew process stepsCeramicwarePolyvinyl alcoholPolyethylene glycol
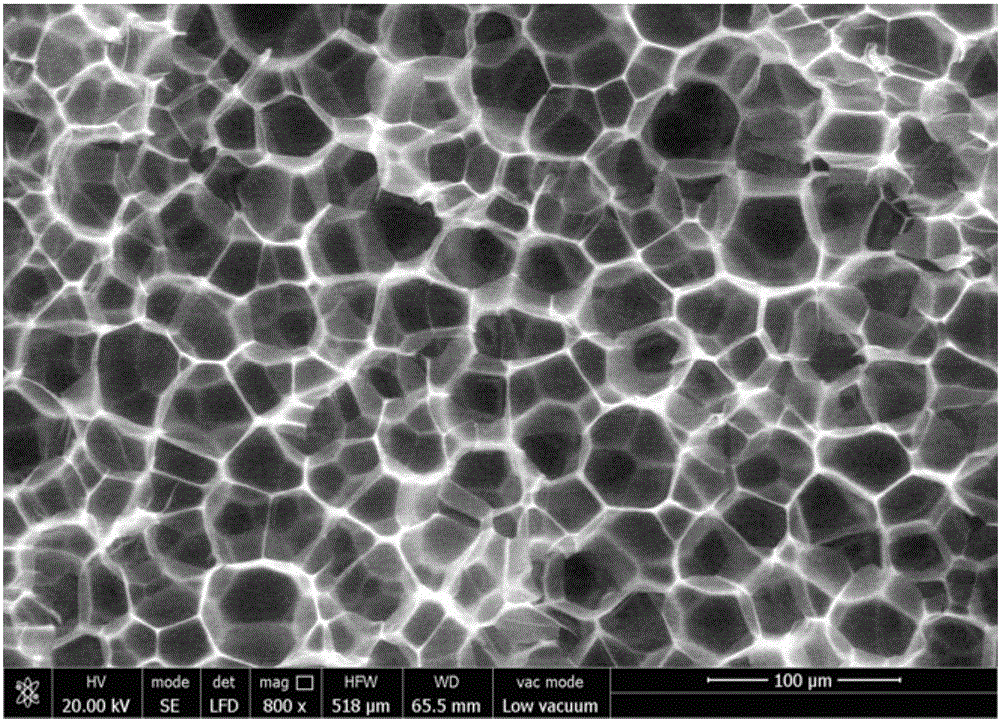
The invention relates to a foam ceramic material. The foam ceramic material is prepared from the following raw materials by weight fraction: silicon carbide powder: 90, de-ionized water: 20, zirconium diboride: 12, polycarbosilane: 10, carborundum: 8, calcium carbonate: 8, molybdenum disulfide: 6, graphite: 5, dolomite: 5, sodium tripolyphosphate: 3, polyethylene glycol: 2, polyvinyl alcohol: 1, ammonium chloride; 1 and valeric acid: 1. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the foam ceramic material. In the invention, the ceramic material prepared by using the preparation method has the advantages of strong compression strength and bending strength, uniform foams and smaller density, and the preparation process is simple and effective.
Owner:SHANDONG JINDE NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
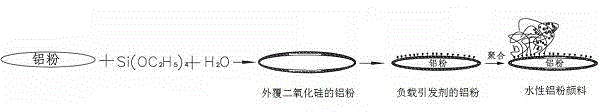
Coated modified aluminum powder pigment, and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN104893368AGood storage stabilityGood acid and alkali resistanceInksCoatingsAluminium powderPrinting ink
The invention relates to a coated modified aluminum powder pigment, and a preparation method and a use thereof; a surface coating layer of the coated modified aluminum powder pigment is silicon dioxide, the interior is an aluminum powder, the exterior of the surface coating layer is connected with a connection point through a chemical bond, and the connection point is 4,4'-azo(4-cyanovaleric acid(3'-dimethylchlorosilane)propyl ester), 4-azoisobutyl cyano 4-cyano(valeric acid(3'-dimethylchlorosilane)propyl ester) or azoisobutyl dicyano phenyl(3-ethyldimethylchlorosilane); the connection point is firmly fixed on the surface of silicon dioxide and has a quite good protective effect on the internal aluminum powder, and the coated modified aluminum powder pigment has quite good dispersibility in waterborne coatings and printing inks.
Owner:CHANGDE JINPENG PRINTING
Method for synthesizing d-biotin
ActiveCN103772410AControl reaction depthAvoid it happening againOrganic chemistryCarbonate esterBiotin
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing d-biotin. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out cyclization on (2S, 3S, 4S)-5-(3,4-diamido-thiophane-2-yl) valeric acid and carbonic ester under the effect of an acid catalyst; carrying out post-treatment to obtain the d-biotin after the reaction is ended, wherein the structure of the carbonic ester is shown in the specification; R<1> and R<2> are independently selected from C1-C5 alkyls; the acid catalyst is one or combination of more of a protonic acid and a lewis acid. By adopting the synthetic method, the carbonic ester is adopted as a reagent to replace triphosgene or diphosgene to react, and generation of a virulent phosgene intermediate is avoided, so that the method is friendlier to the environment; meanwhile, the reaction efficiency is improved by selecting a specific catalyst, and the yield of the d-biotin is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NHU CO LTD +1
Method for recycling hexanediamine key intermediate reaction residues and co-producing carboxylic acid
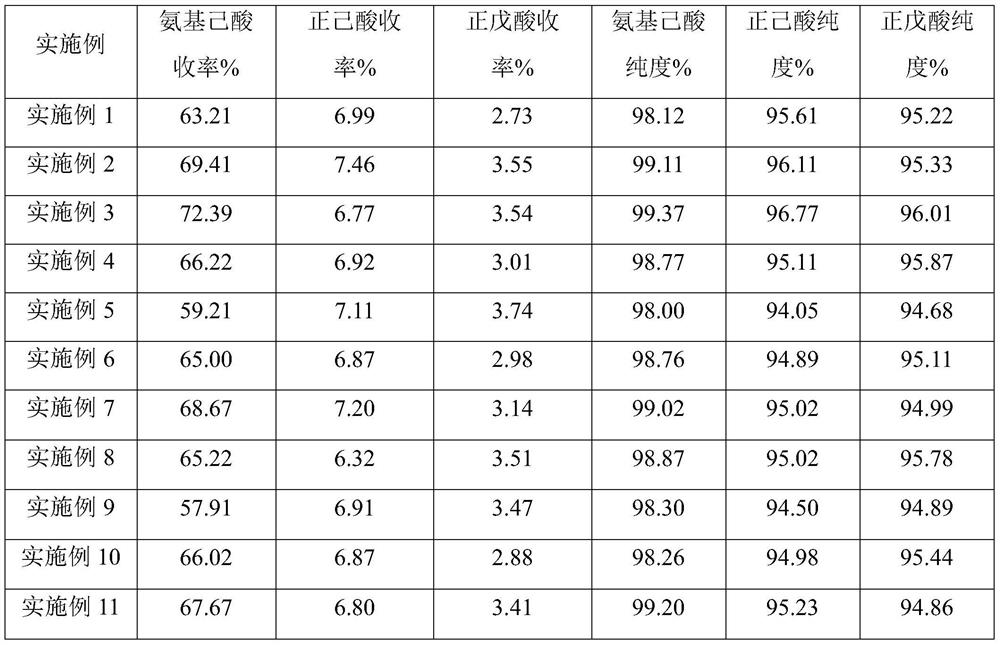
ActiveCN111635330ASolve pollutionProcess design innovationOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationDepolymerizationHexamethylenediamine
The invention relates to a method for recycling hexanediamine key intermediate reaction residues and co-producing carboxylic acid. The method comprises the following steps: introducing residues and water into a first fixed bed reactor, and carrying out a depolymerization reaction; carrying out heat exchange on the obtained depolymerization reaction liquid, then introducing into a second fixed bedreactor, and carrying out a hydrolysis reaction; carrying out a hydrogenation reaction on the obtained hydrolysis reaction solution, carrying out negative pressure distillation on the obtained hydrogenation reaction solution after the reaction is finished, and removing water to obtain a concentrated solution; and carrying out negative pressure rectification on the obtained concentrated solution, and collecting fractions at different gas phase temperatures to obtain corresponding products of aminocaproic acid, n-valeric acid and n-caproic acid. According to the invention, the method effectivelysolves the problem of key intermediate reaction residue pollution generally existing in existing hexanediamine production, realizes recovery and resource utilization of the key intermediate reactionresidue of hexanediamine, obtains a high-added-value product, reduces the production cost, increases the economic benefit, reduces the emission of three wastes, substantially reduces the pollution tothe environment and provides a guarantee for green and safe production.
Owner:JIANGSU YANGNONG CHEM GROUP +3
Method for preparing biomass fuel oil molecules from biomass platform compound through hydrogenation
ActiveCN110117266AHelps ease harsh conditionsExtend your lifeOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsVernolic acidPropanoic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing gamma-valerolactone, valeric acid and valerate from biomass platform molecules. According to the method, the gamma-valerolactone is prepared with levulinate as the reaction raw material, the valeric acid and valerate are prepared with the gamma-valerolactone or levulinate as the raw material, and the process of preparing the gamma-valerolactone from the levulinate, preparing the valeric acid and valerate from the gamma-valerolactone through hydrogenation or efficiently preparing the valeric acid and valerate from the levulinate at high selectivityand high yield through one step is realized. Valerate compounds can serve as biological fuel oil and have high compatibility with an existing fuel oil system; the valeric acid and valerate are prepared through the reaction, and the method has the remarkable advantages that the raw materials serve as the biomass resources and the atom economy is good. Meanwhile, compared with other technologies ofpreparing the valeric acid and valerate with levulinic acid as the raw material, the method has the advantages that the method is simple in reaction process, high in target product yield and mild in reaction condition and medium, and a catalyst is simple in preparing process and stable.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Functional oligomer used for non-viral gene vector material and application thereof
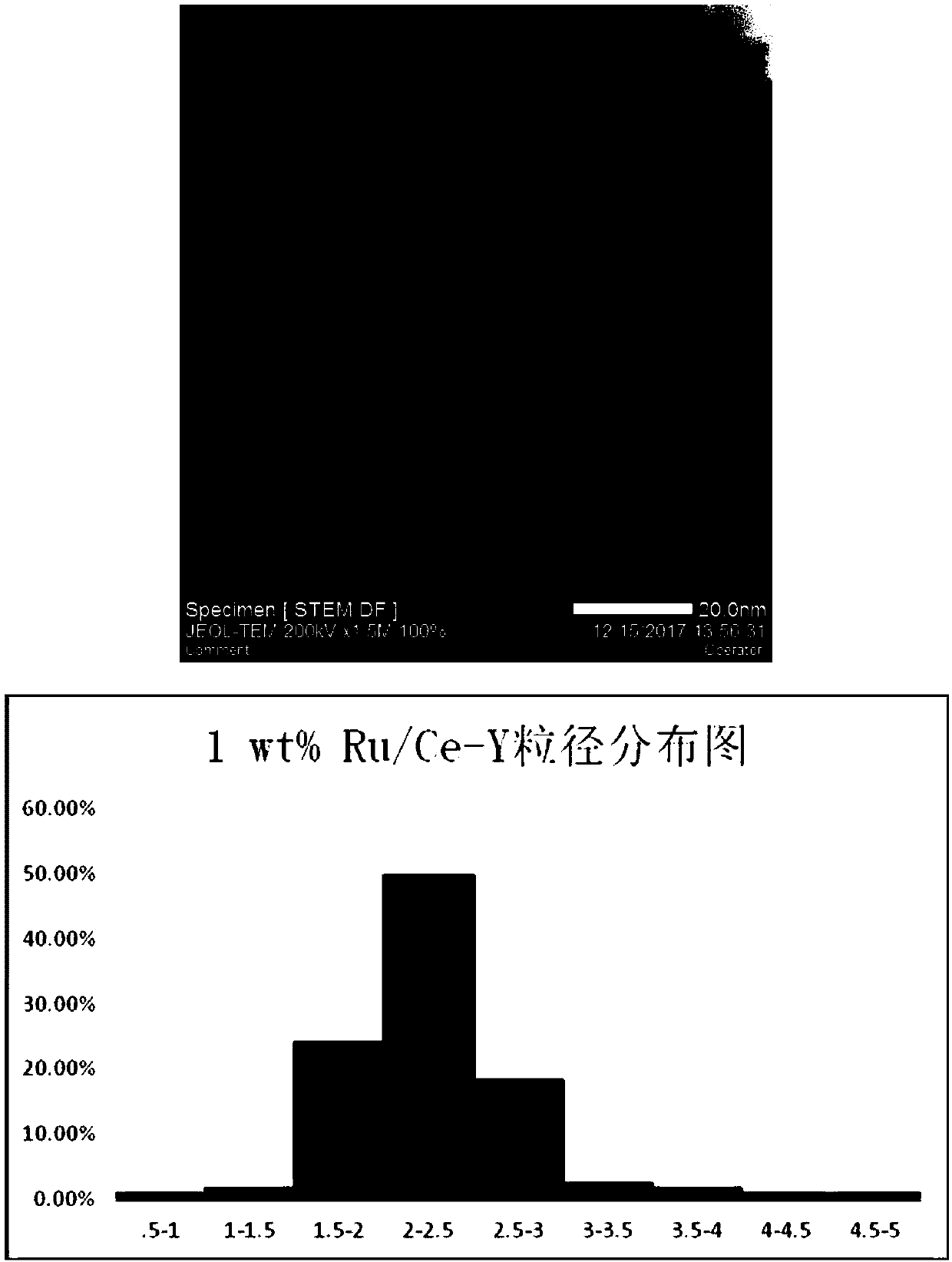
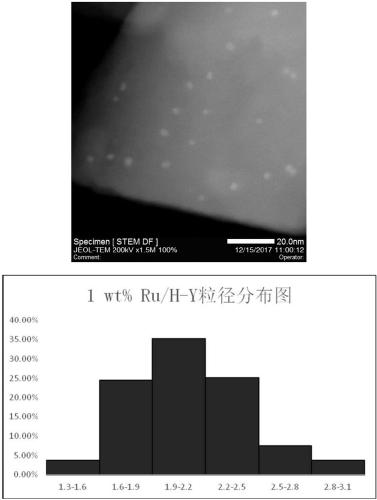
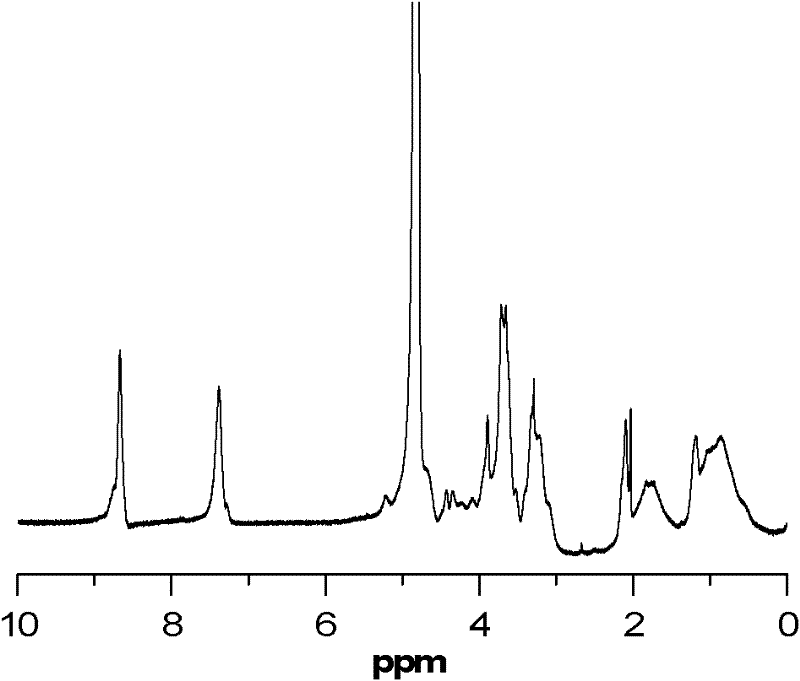
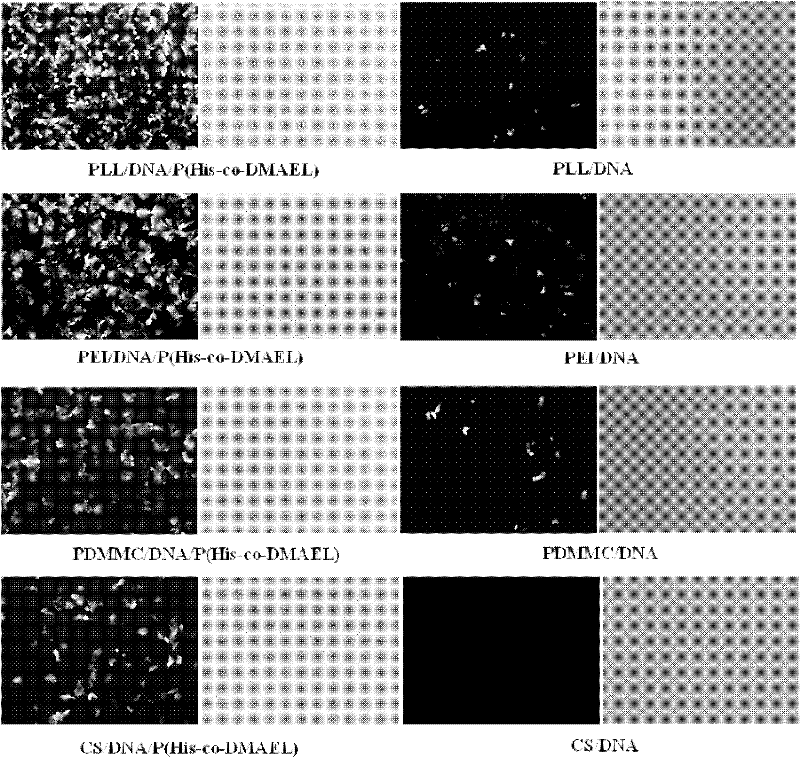
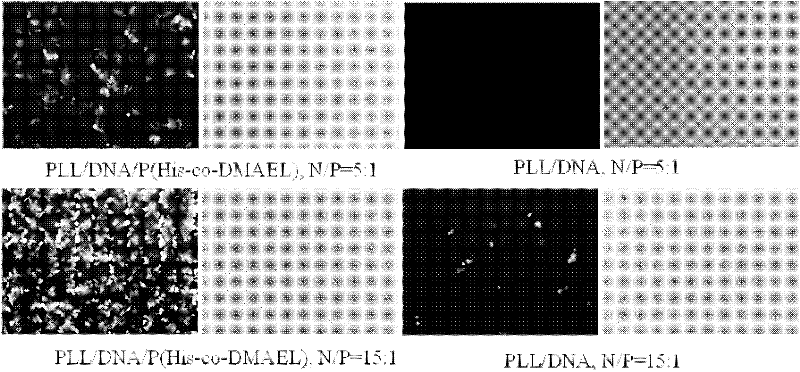
ActiveCN102532411AImprove escape efficiencyImprove protectionOther foreign material introduction processesLysosomeThio-
The invention provides a functional oligomer used for a non-viral gene vector material. The functional oligomer is prepared by free radical polymerization of MA-His-OMe and MAEL through taking water-soluble thio ester as a molecular weight regulating agent. In the preparation method, MA-His-OMe and MAEL are used as monomers, AIBN (2,2-azobisisbutyronitrile) or ACVA (4,4'-azobix(4-cyano valeric acid)) is used as an initiator, and CPADB (4-cyanopentanoic acid dithiobenzoate) is used as a chain transfer agent. According to the invention, the functional oligomer is mixed with a polycation material to prepare a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (ribonucleic acid) composite which is used as the non-viral gene vector material and a cell transfection experiment is carried out. The functional oligomer has the advantages that the functional oligomer has a good protection effect on plasma DNA and can be used for improving the binding action of a complex particle and a cell membrane surface and improving the escape efficiency of the plasma DNA from lysosme / endosome in a cell, thus the transfection efficiency of the complex particle on cells such as HeLa is greatly improved, and the toxicity of the functional oligomer is greatly reduced, therefore the functional oligomer is expected to reach a clinical application level.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com