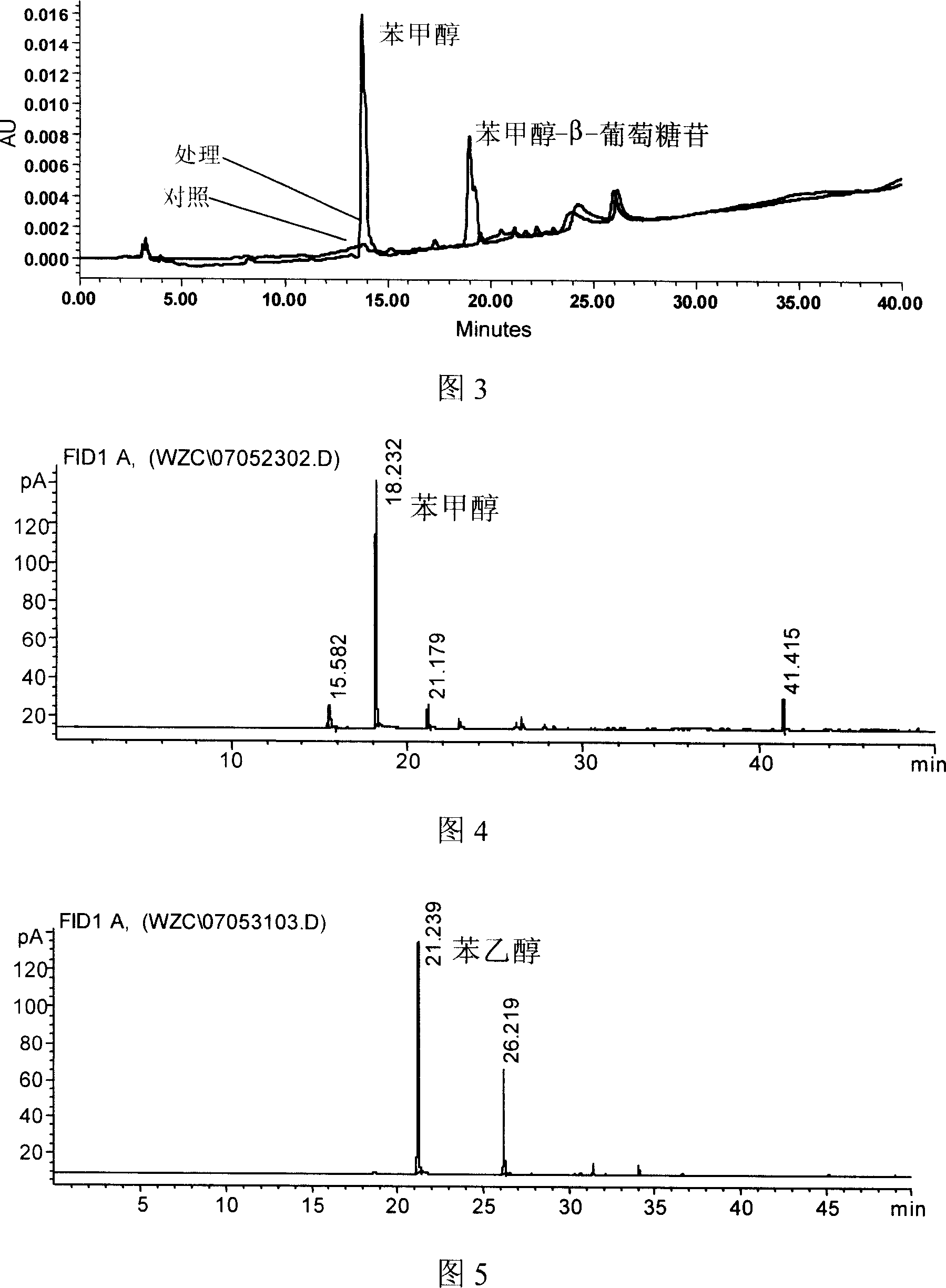
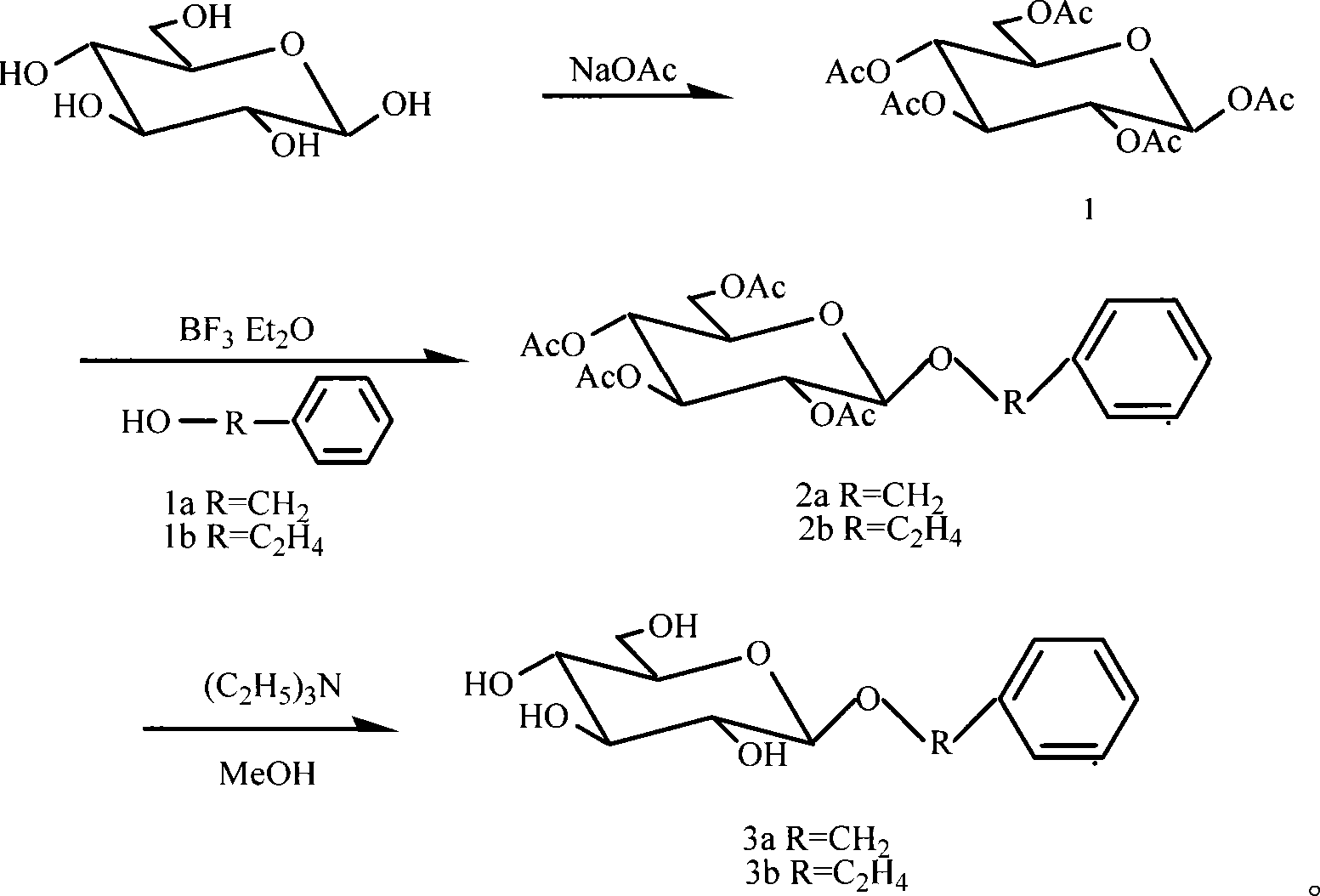
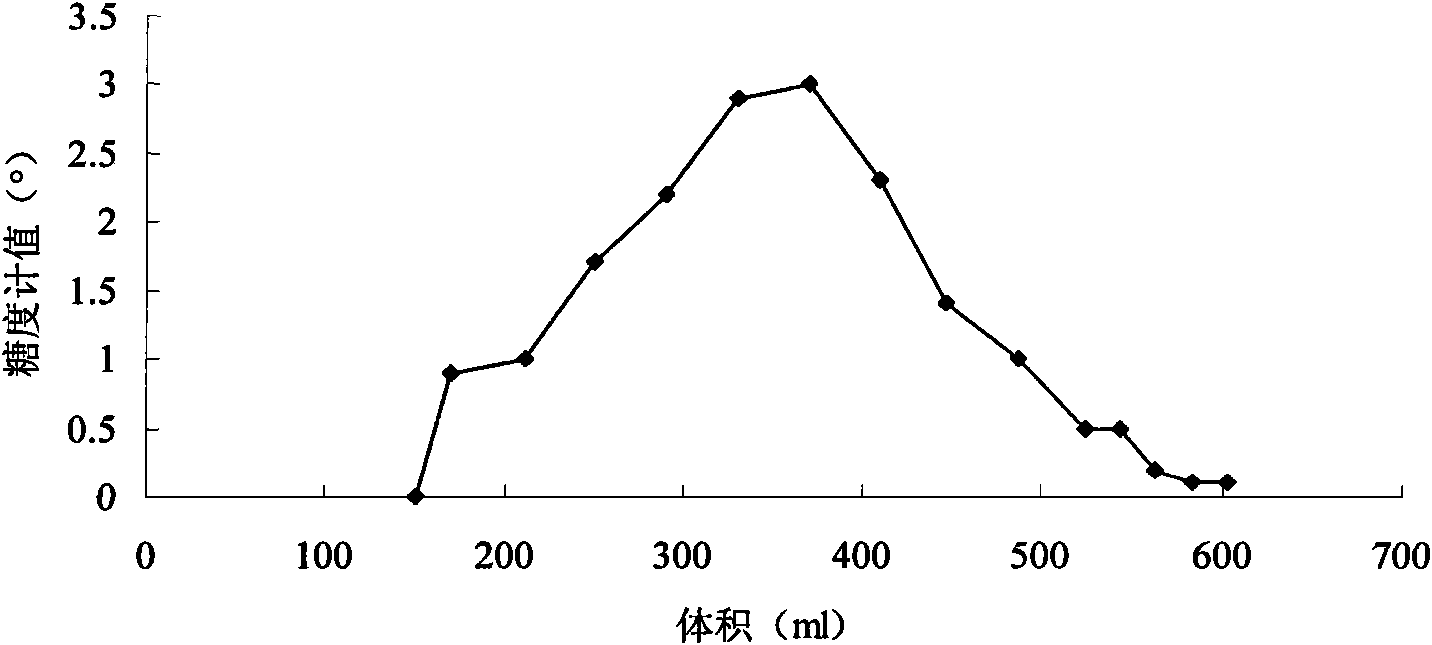
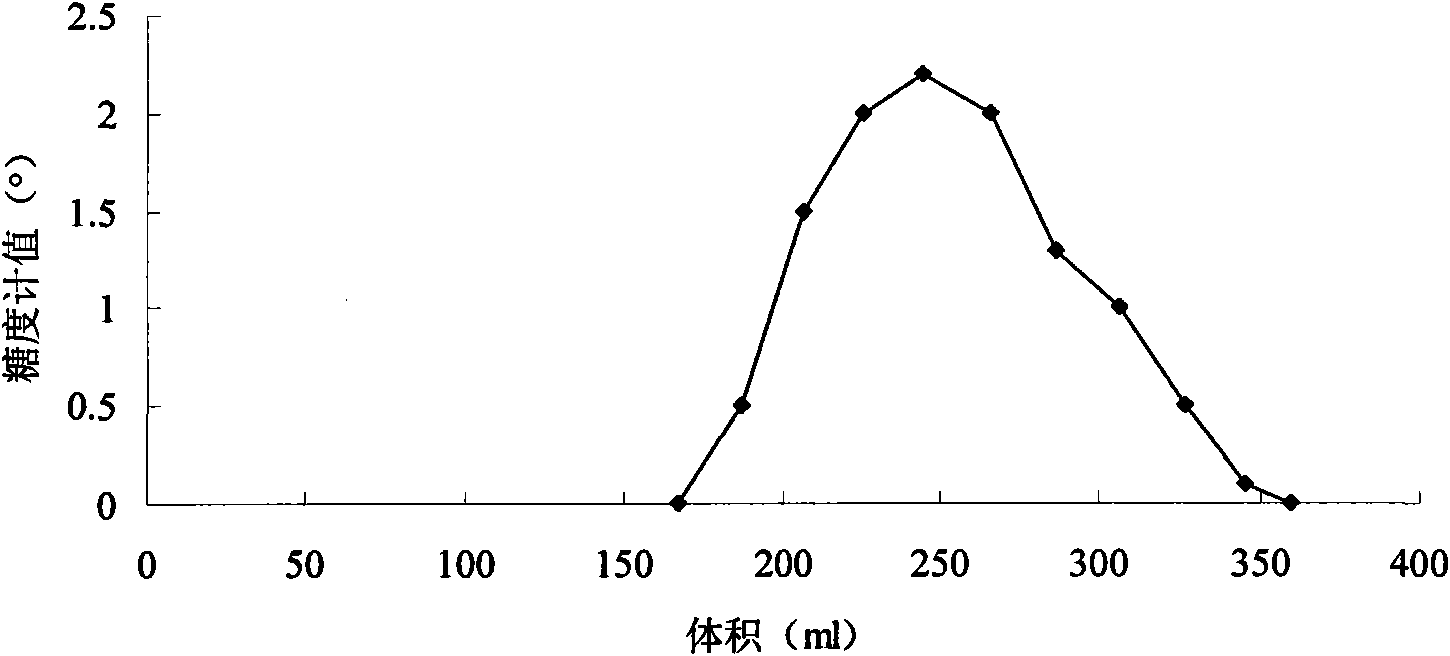
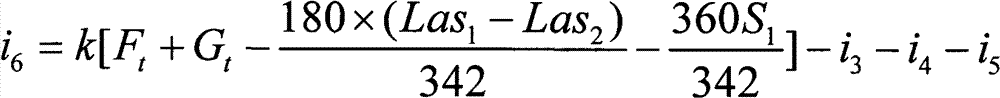Patents
Literature
169 results about "Glucin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glucin is the name of an artificial sweetening agent similar to saccharin that was used in the early 20th century. The substance is a sodium salt derived from coal tar. It is composed of a mixture of mono- and di-sulfonic acids with a chemical formula of C₁₉H₁₆N₄. It typically appears as a light brown powder, easily soluble in water. It is insoluble in ether and chloroform. Glucin is about three hundred times sweeter than cane sugar.
Method for preparing 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by solid acid catalysis
InactiveCN102399201AAccelerated precipitationEasy to separateCatalyst carriersOrganic chemistrySolid acidCarbonization
The invention discloses a method for preparing 5-hydroxymethylfurfural by solid acid catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of taking lignin residue hydrolyzed by biomass as carrier raw material of solid acid; synthesizing the raw material into solid acid through a two-step way of carbonization and sulfonation, so that the waste material is recycled and the problem of disposal of pollutants is solved. In the dehydration reaction of lignin-based solid acid catalyzed fructose and glucose, the yield of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural can be respectively 84% and 68%; after the dehydration reaction, the lignin-based solid acid is easy to separate and reusable, the acid density of the solid acid can be reduced after being reused five times, and the yield of the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural is still higher than 75%. The method provided by the invention can be used for realizing emission without pollution, and is helpful for realizing environment-friendly producing process of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural.
Owner:XISHUANGBANNA TROPICAL BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dehydrated polysaccharide gel containing microorganisms, a sugar and a polyol for producing fermented drinks
Improved fermentation activity of microorganisms in a polysaccharide gel such as an alginate gel is obtained after dehydration, staorage and rehydration by soaking the gel containing the microorganisms prior to dehydration in a sugar solution to provide in the gel an amount of sugar of at least 100 g / kg and less than 500 g / kg of gel, preferably less than 300 g / k of gel. The dehydration may be carried out in a fluidized bed or by lyophilization. The gel may be in the form of beads or fibers having a double layer structure formed by an internal layer or core of gel containing the microorganisms and an external lay er or envelope of gel essentially devoid of the microoraganisms. The sugar is preferably xylose, glucose, fructose, lactose or sucrose, and the sugar solution may contain a polyol such as sorbitol, inositol or glycerol to provide in the gel an amount of polyol of at least 30 g / kg of gel. The sugar solution may also contain a non-ionic surfactant such as sorbitan monostearate as a protecting substance to fur ther improve fermentation activity. The microorganisms in the gel are preferably yeast, and after rehydration the yeast containing gel is used in producing a fermented drink such as in secondary fermentaion of wine to produce sparkling wine or champagne.
Owner:MOET & CHANDON
Pharmaceutical dental formulation for topical application of metronidazole benzoate and chlorhexidine gluconate
InactiveUS6017516ACosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWater dispersibleDental plaque induced gingivitis
A pharmaceutical dental formulation of therapeutically effective amounts of metronidazole benzoate and chlorhexidine gluconate is described. The formulation also includes a gelled hydrophilic and water-dipersible polymer having free carboxylic groups, an aqueous base, a penetration enhancer and a chelating agent. The formulation is for topical application in the form of an aqueous gel in the treatment of periodontal diseases including gingivitis, stomatitis, Apthous ulcers and post-extraction infection.
Owner:J B CHEM & PHARMA
Preparation method of biomass-based colloidal carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method of biomass-based colloidal carbon and in particular relates to a colloidal carbon ball using xylose or glucose as a precursor. The colloidal carbon ball is prepared by hydrolyzing biomass by using dilute acid or concentrated acid respectively to obtain saccharic acid solution of xylose and glucose and performing in-situ polycondensation and carbonization on the saccharic acid solution. The preparation method particular comprises the following steps of: hydrolyzing the biomass by using dilute acid at a certain concentration; filtering to obtain xylosic acid solution and filter residues; adjusting the concentration of the saccharic acid solution and performing polycondensation and carbonization to prepare the colloidal carbon ball with grain size of 160 to 1,800 nm; performing alkali boiling on the residues to remove lignin; performing hydrolysis reaction on the residues and the concentrated sulfuric acid; filtering to obtain acid solution of the glucose; and performing in-situ polycondensation and carbonization to prepare the colloidal carbon ball with grain size of 180 to 2,000 nm. The method for preparing the colloidal carbon from the biomass is a green production route of sustainable development.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Liquid chelated calcium as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN103626790AHigh in calciumGood water solubilityCalcareous fertilisersCalcium organic compoundsSolubilityGlycerol
The invention relates to liquid chelated calcium as well as a preparation method and use thereof and belongs to the chemical fertilizer filed in agricultural science and farming techniques. The invention provides the liquid chelated calcium and the preparation method thereof. Active ingredients of the liquid chelated calcium disclosed by the invention are prepared by chelating 45-70 parts by weight of calcium nitrate and 10-25 parts by weight of polyhydroxy compounds in water, wherein the polyhydroxy compounds are ethylene glycol, glycerol, mannitol, xylitol, sorbitol or glucose. The liquid chelated calcium disclosed by the invention is high in calcium content which is greater than 120 g / L, safe and non-toxic, free from harmful effect on crops, can be mixed with other pesticides, weakly-acidic and neutral fertilizers for use, good in water solubility for being conveniently mixed with water for using and metering, good in stability, and can be stored by resisting a low temperature; besides, the liquid chelated calcium is produced by adopting a chelating process, so that crops can be absorbed better and quicker.
Owner:CHENGDU NEWSUN CROPSCI
Method of preparing sugar by utilizing sweet potato residues
ActiveCN102559811AIncrease synergistic enzymolysisPromote digestionFermentationLiquid productAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to filed of biology and in particular relates to a method of preparing sugar by utilizing biomass sweet potato residues, used for microbial fermentation, as a sugar source. The method comprises the following steps of: adjusting the pH of sweet potato residue powder or wet residue to be 5.5-8.0, and carrying out heat preservation by adding alpha-amylase; adjusting the pH to be 3.0-5.5, carrying out enzyme removal after carrying out heat preservation at 40-65 DEG C by adding saccharifying enzyme, acid protease and cellulose; and carrying out solid-liquid separation on a feed liquid, and concentrating the liquid to obtain a sugar liquid product, wherein the ingredient of the sugar liquid product is basically the glucose. The preparation method is simple in process, highin specificity, high in product quality, and high in yield, can be used for solving the problem that the environment is severely polluted by the sweet potato residues, and is good in industrial application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG BIO SUNKEEN
Fasudil hydrochloride injection and its preparation process
InactiveCN1729985AEasy to useAvoid pollutionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGlucose polymersAqueous solution
The invention provides a Fasudil hydrochloride injection, which comprises Fasudil hydrochloride, sodium chloride, glucose, amino acid, and the aqueous solution of other pharmaceutically acceptable thinning agent, wherein the content of Fasudil hydrochloride is 0.01-0.2 wt%, the content of the aqueous solution of other pharmaceutically acceptable thinning agent is 0.5-50 wt%, the content of sodium chloride is 0.9-5 wt%, the content of glucose is 5-20%, the content of amino acid is 0.5-30 wt%.
Owner:吴良信
Pollen filling agent for plant pollination and preparing technology and using method of pollen filling agent
ActiveCN104137771AImprove germination rateQuality improvementPlant genotype modificationFiller ExcipientPollen
The invention belongs to the technical field of filling agents and discloses a pollen filling agent for plant pollination and a preparing technology and a using method of the pollen filling agent. The pollen filling agent is mainly characterized in that the pollen filling agent for plant pollination comprises water, white carbon black, saccharose or fructose or glucose or sorbitol, vitamin B1, an equivalent mixture of vitamin B6 and niacin or niacinaminde, borax or boric acid, gibberellin GA3 or GA4 + 7, cytokinin 6-BA or forchlorfenuron, ethyl alcohol with the concentration of at least 95%, phosphoric acid or citric acid. The pollen filling agent for plant pollination is prepared by common raw materials and can be suitable for various plants, cost is low, raw materials are sufficient, environment pollution is avoided from production to application, residue problems are avoided for agricultural products, through added nutrition, growth promotion matter and proper moisture, the germination rate and the germination quality of pollen are improved, the using effect under a dry weather environment is improved, and the quality and the efficiency of hand pollination are greatly improved.
Owner:岑建卫
Burdock inulin and its preparing method
Burdock synanthrin and its preparation method. the matter is extracted from root of burdock, white or weak yellow amorphous loose solid powder, freely soluble in water, slightly sweet, stable thermally. The left of optical rotation in water is -29.8í
Owner:THE FIRST INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY SOA
Multi-functional sugar alcohol calcium leaf fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104496653AFast absorptionAddress physical barriersFertilizer mixturesSolubilityAlcohol sugars
The invention relates to a multi-functional sugar alcohol calcium leaf fertilizer which comprises 20-30 parts by weight of polyol, 15-20 parts by weight of calcium nitrate, molybdate, a boron type compound and the balance of water, wherein the weight of the molybdate is 0.1-2 percent of the weight of the polyol; the weight of the boron type compound is 0.1-2 percent of that of the polyol. A preparation method of the multi-functional sugar alcohol calcium leaf fertilizer comprises the following steps: transforming a glucose solution into mannose by means of partial epimerization; performing hydrogenation reaction to prepare mixed alcohol of mannitol and sorbitol; subsequently allowing the mixed alcohol to react with the calcium nitrate to prepare the multi-functional sugar alcohol calcium leaf fertilizer. The leaf fertilizer disclosed by the invention is good in water solubility, capable of enabling a leaf to absorb abundant calcium elements coexisting in a sugar alcohol complexed state and beneficial for solving physiological barriers caused by the fact that the calcium elements can not reach tender positions easily.
Owner:QINGDAO BRIGHT MOON SEAWEED GROUP
Prepn of aminoglucose sulfate
The method for preparing aminoglucose sulfate includes the following steps: using sulfuric acid whose mass concentration is 20-80% as hydralytic reagent, under the reaction condition of 80-150 deg.C hydrolyzing chitin, decolouring hydrolysate, extracting with organic solvent, recrystallizing or using alkali to make precipitation and separation to obtain the refined aminoglucose sulfate containingno chlorine ion. Its method is simple and yield rate is high.
Owner:HUBEI PUAI BIOENG
Method for preparing sweet orange essence microcapsule
InactiveCN101240224AOvercome defectsUniform particlesEssential-oils/perfumesMicroballoon preparationAcetic acidEmulsion
A preparation method for sweet orange essence microcapsule relates to a preparation technology of essence microcapsule. A preparation method for sweet orange essence microcapsule is provided with simple technology, safe and controlled operation, collapse and excellent releasing performance microcapsule wall film. The preparation steps comprise bean separation albumen aqueous solution and Arabic gum aqueous solution is prepared, an emulsion is obtainer by putting sweet orange essence into bean separation albumen aqueous solution and homogenizing, a wet microcapsule is obtained by putting and mixing Arabic gum aqueous solution into emulsion and putting alcaine or acetic acid to adjust PH to 4.0. The reinforced wet microcapsule is obtained by cooling the wet microcapsule down to 0 to 15 DEG C and dextrose being putting into the solution concomitant mixing. The powder-shaped sweet orange essence microcapsule can be obtained by putting the reinforced wet microcapsule into ultra low temperature ice box and drying the reinforced wet microcapsule in vacuum freeze drier.
Owner:SHENZHEN POLYTECHNIC
Method for detecting anhydrous dextrose bacteria endotoxin content by spectrophotometry
InactiveCN101387647AExplain carefullyInterference test fastMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLuminous intensityTurbidity
The invention relates to a method for using luminous intensity to test the bacterial endotoxin content of glucosum anhydricum, belonging to the analytical chemistry technical field. The technical scheme is that: using luminous intensity to test the reaction time from the reaction of limulus polyphemus agent and the endotoxin to the turbidity of the mixture reaching a preset absorbency; finding the endotoxin content of the object glucosum anhydricum sample. According to the scheme, the method dilutes an endotoxin operation standard sample of known content into operation standard sample series of different contents, tests the times of different endotoxin content standards reaching the preset absorbency, and draws a standard curve; and tests the time of the object glucosum anhydricum sample reaching the preset value, to find the content of the endotoxin of the glucosum anhydricum sample.
Owner:XIWANG GROUP
Preparation method of organic titanium cross-linking agent for polyhydroxy alcohol fracturing fluid
ActiveCN102108294AReduce typesSimple preparation processDrilling compositionEthylenediamineCross-link
The invention relates to a preparation method of an organic titanium cross-linking agent for polyhydroxy alcohol fracturing fluid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding alkali, sugar, divalent alcohol and tetrabutyl titanate into a reactor, uniformly mixing, raising temperature to 110-150 DEG C, keeping the temperature unchanged, performing reaction for 1-5 hours under continuous stirring, and getting golden yellow liquid which is the organic titanium cross-linking agent for the polyhydroxy alcohol fracturing fluid, wherein the alkali is sodium hydroxide, ethylenediamine, trimethylamine or triethanolamine; the sugar is monosaccharose or disaccharide, the monosaccharose is fructose or glucose, the disaccharide is sucrose, maltose or lactose; the divalent alcohol is ethylene glycol or propylene glycol; the weight ratio of the alkali to the sugar to the divalent alcohol is 0.01-0.2: 0.1-0.4: 1; and the weight ratio of the tetrabutyl titanate to the divalent alcoholis 0.1-0.2: 1. The cross-linking agent has the characteristics of strong sand carrying capability, good temperature resistance, low friction, adjustable delay time, low harm, excellent compatibility with the polyhydroxy alcohol fracturing fluid and the like.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
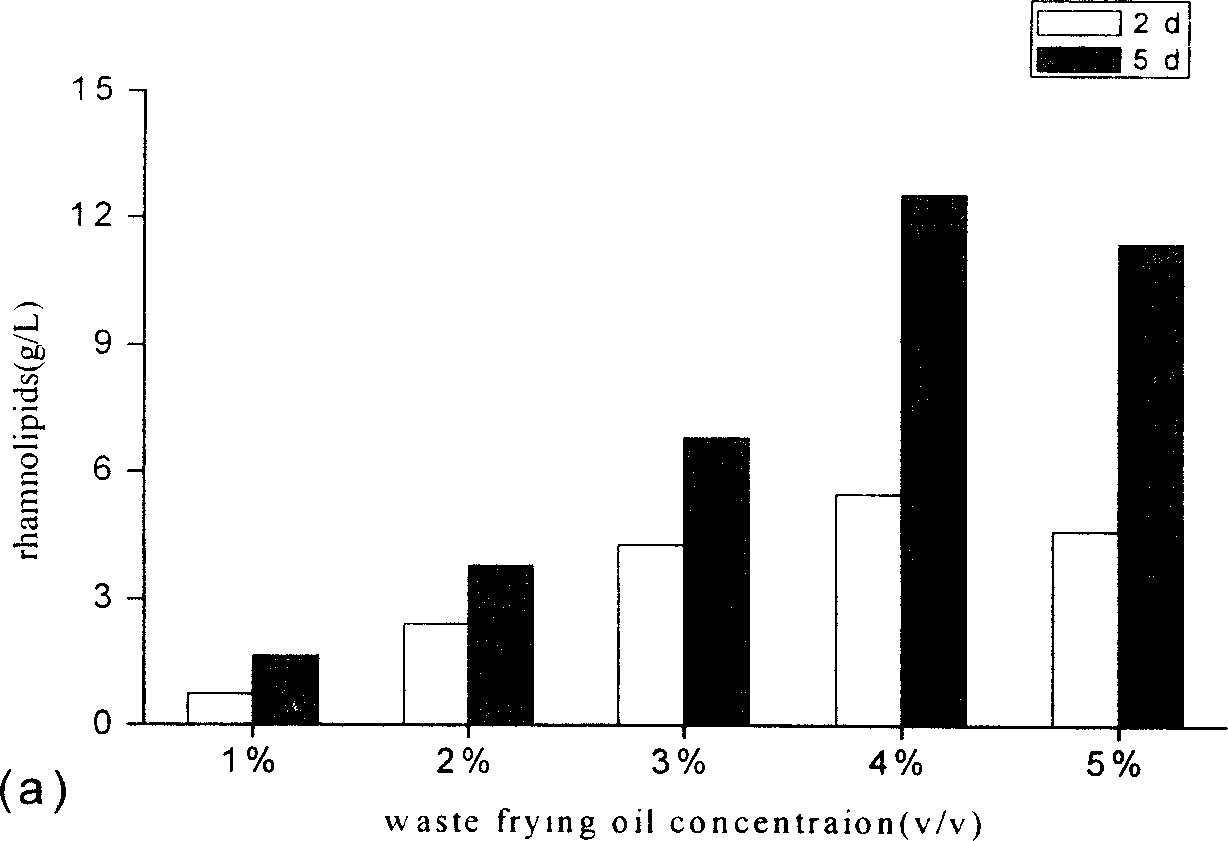
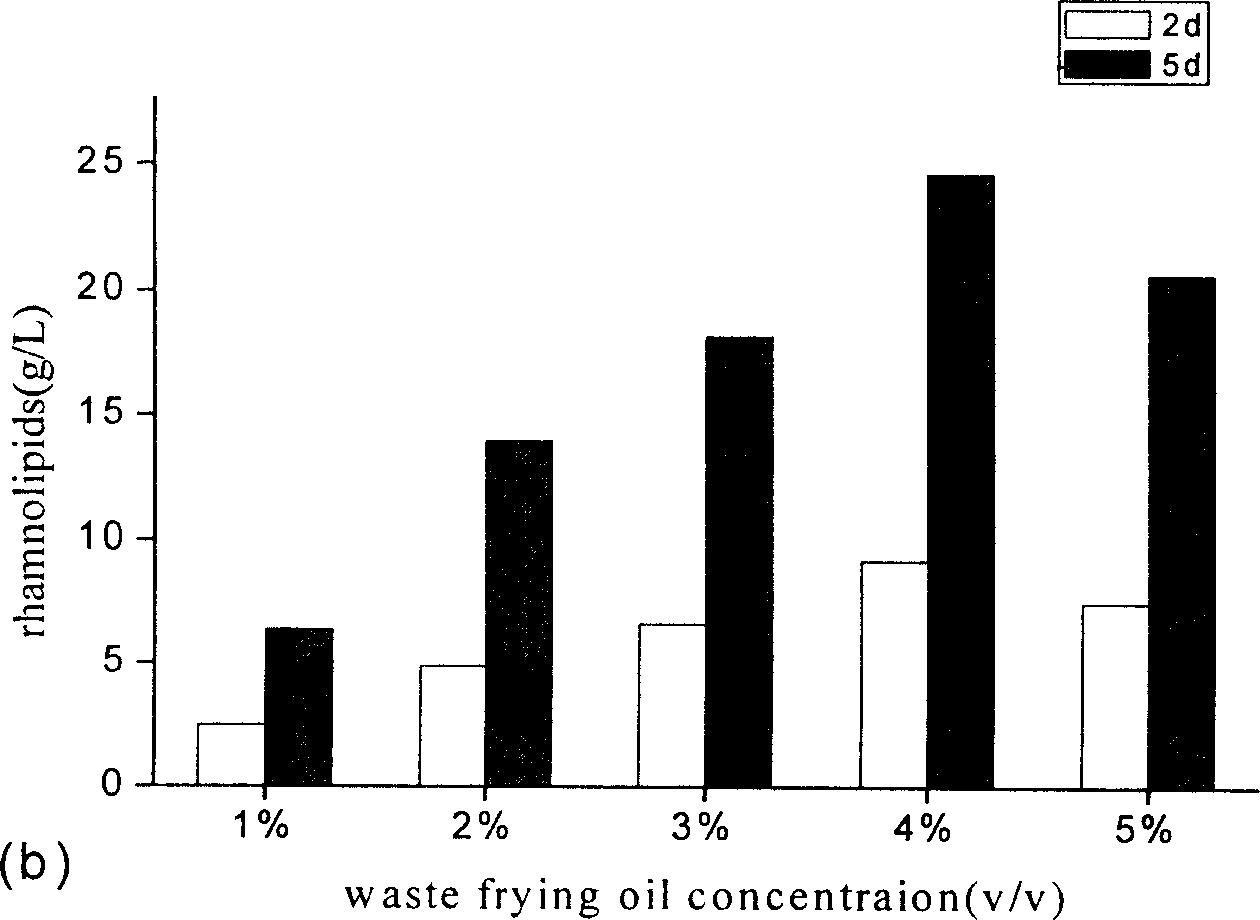
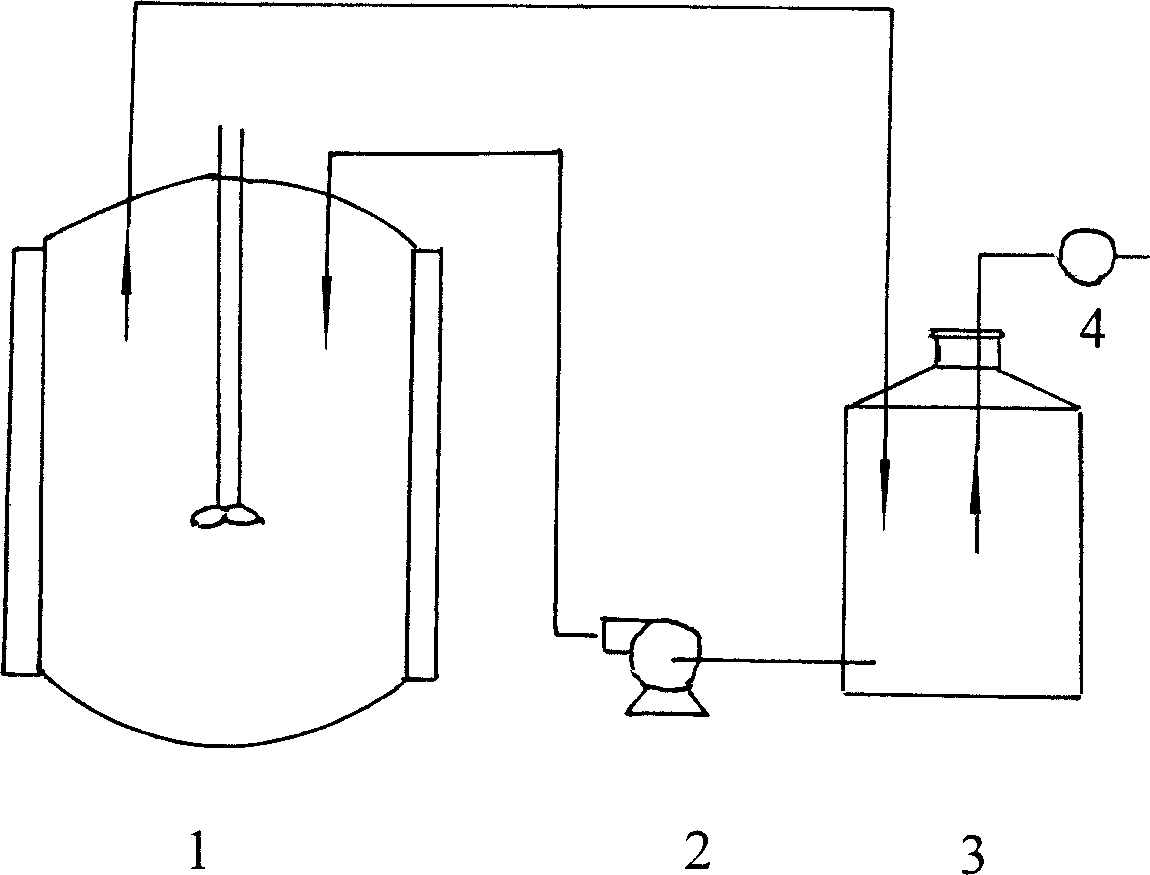
Rhamnolipid crude extract prepared by fermenting food and rink waste oil and application thereof
InactiveCN1908180AImprove processing efficiencyReduce processing timeOther chemical processesFermentationVegetable oilUltrafiltration
the invention discloses a manufacturing method of rough rhamnolipid extract and application fermented by waste food and drink oil, which is characterized by the following: proceeding ultraviolet mutagenesis for natural sieved pseudomonas; picking fitful bacteria; adopting waste food and drink oil as ferment carbon source; making the density of rhamnolipid reach 35-45g / L; ultrafiltrating the ferment liquid to remove bacteria to obtain the powder-shaped rough extract through spraying and drying method; adding 0.01-3% rough extract in the biochemical dirty water to improve disposing efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
External-use medicinal dressing preparation of composition containing garlic glycoside and garlic bioactive components and use thereof
InactiveCN101474422AImprove the effect of adjuvant therapyImprove absorption rateDevices for heating/cooling reflex pointsAbsorbent padsDiseaseAllium sativum
The invention relates to a topical medicine dressing preparation containing combination of garlic glycosides and bioactivity compositions and the application thereof. The preparation is made of the following materials by weight portions: 30-80 portions of the sticky combination of the garlic glycosides and the bioactivity compositions, 30-70 portions of ginger and 0.1-30 portions of Chinese herb. The three materials are smashed and mixed into paste. The topical medicine dressing preparation containing the combination of the garlic glycosides and the bioactivity compositions can improve the adjuvant therapy effects on various diseases accordingly, and the absorption rate of human body to bioactivity components, glucose molecules and drugs and has the functions of dredging blood vessels, especially capillaries, inhibiting the generation of vascular distensible zymose, softening capillary walls and preventing the excessive condensation of platelets. The capillaries are expanded and channels and collaterals at acupuncture points are dredged. The effect of moxibustion is strengthened. The moxibustion treatment course is shortened, and the cure effect is improved.
Owner:李甲怀
Low-substituted hydroxypropylcellulose powder and method for producing the same
Provided are a solid dosage form comprising an enteric solid dispersion that allows a drug in the preparation to be rapidly dissolved without compromising the solubility of the solid dispersion, and a method for producing the same. More specifically, provided is a solid dosage form comprising an enteric solid dispersion comprising a poorly soluble drug, an enteric polymer and a disintegrant, wherein the disintegrant is low-substituted hydroxypropylcellulose having an average particle size of 10 to 100 [mu]m and a specific surface area measured by BET method of at least 1.0 m 2 / g. Moreover, provided is a method for producing a solid dosage form comprising an enteric solid dispersion, the method comprising steps of: spraying an enteric polymer solution in which a poorly soluble drug has been dispersed or dissolved, on a powder of low-substituted hydroxypropylcellulose having an average particle size of 10 to 100 [mu] m and a specific surface area measured by BET method of at least 1.0 m 2 / g and serving as a disintegrant; and granulating the resultant; and drying.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for analyzing and detecting inulin in infant formula
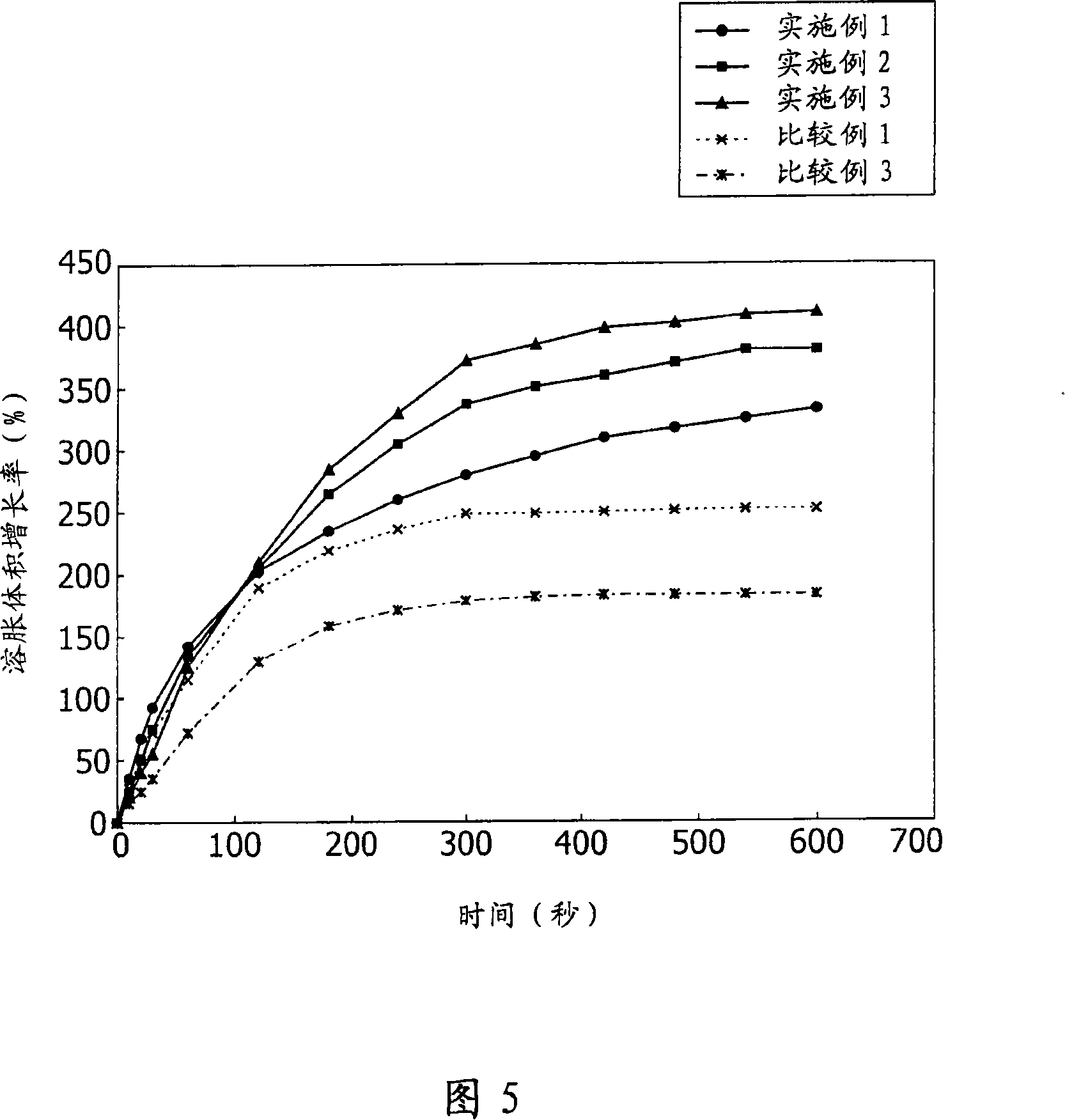
The invention provides a method for analyzing and detecting inulin in infant formula. The method includes: (1) removing biomacromolecules in infant formula by means of ultrafiltration; and (2) testing content of fructo-oligosaccharide and total levan in the infant formula: determining and calculating the kestose percentage composition i3, the nystose percentage composition i4, fructofuranosylnystose percentage composition i5, lactose percentage composition Las1 and sucrose percentage content S1 in the infant formula by means of efficient liquid chromatography; using inulase for enzymolysis of sample solution, performing centrifugal ultrafiltration, and determining and calculating fructose percentage composition Ft and glucose percentage composition Gt in the sample subjected to enzymolysis and the percentage composition Las2 of the residue lactose not subjected to enzymolysis by means of efficient liquid chromatography; and conversing the inulin percentage composition i6 according to a formula a, wherein the conversion coefficient k is 0.9. The method is extremely high in accuracy and is capable of successfully detecting the inulin content in the infant formula.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nano silver-group formaldehyde eradicating-liquid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN1907546AImprove eliminationNot corrosiveDispersed particle separationDeodrantsEscherichia coliComplexons
The invention relates to a nanometer silver formaldehyde eradicating-liquid, which is formed by triethanolamine, sodium sulfite, complexon, amchlor, amylaceum, water and water-soluble colloidal silver, wherein the average diameter of water-soluble colloidal silver is 1-100nm; said eradicating-liquid can quickly disinfect bacillus coli, etc, and reduce the free formaldehyde density under 0.08mg / m3, while the virus disinfection rate is above 90%. The invention also discloses a relative preparation.
Owner:上海沪正实业有限公司
Method for preparing 5-hydroxymethyl furfural
ActiveCN102850302AEfficient separationEasy to separateOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionSucroseNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a method for preparing 5-hydroxymethyl furfural. In the method, biomass sugar is taken as a raw material and a biomass transformation technology is adopted. The method comprises the steps of: putting 50-150ml of ionic liquid, 6-40g of biomass sugar and 0.5-6g of catalyst with the sulfonation degree of 8-100% into a 250mol of round-bottom flask together; replacing the air with nitrogen; heating up to 140-180 DEG C by oil bath under the stirring of magnetic force, reacting for 0.5-8 hours and then cooling; and then, extracting with ethyl acetate and separating out the 5-hydroxymethyl furfural, wherein the ionic liquid is N-methyl imidazole ionic liquid, pyridine ionic liquid, amino acid ionic liquid or morpholine ionic liquid, the biomass sugar is cellulose, starch, inulin, cane sugar, glucose or fructose, and the catalyst is collaborative hybrid organic material formed by polyphenylene sulfide, sulfonic acid and sulfur ether, or collaborative hybrid organic inorganic material formed by inorganic material, sulfonic acid and metal ions.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Water-soluble polysaccharide extracted from black fungus and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102585032AEnhance immune functionImprove defense functionImmunological disordersFood preparationFreeze-dryingWater soluble polysaccharides
The invention relates to a water-soluble polysaccharide extracted from black fungus and preparation method of the water-soluble polysaccharide. The main chain of the water-soluble polysaccharide is beta-(1->3)-D-glucan; 51-70% of main chain structure unit is connected with a (1->6) bonded glucose side group; the weight-average molecular weight is 400 thousand to 3 million; and the water-soluble polysaccharide is in expanded rigid single chain in water. The preparation method comprises the steps of: cutting dry black funguses; removing the fat; dipping in mixed solvent of ethanol / water, extracting the residue with normal saline at 70-100 DEG C, and centrifuging; decoloring the supernatant; removing the dissociative protein; dialyzing, concentrating, and carrying out freeze drying so as to obtain a crude polysaccharide of black fungus; redissolving the crude polysaccharide into water; precipitating and isolating with ethanol, and centrifuging; dissolving the precipitate in water; and dialyzing and carrying out freeze drying so as to obtain a water-soluble neutral polysaccharide. The prepared water-soluble polysaccharide has extremely high viscosity at a dilute solution state, is easy to gel and can be used for preparing efficient thickeners for foodstuff or health care products.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for preparing rose cut flower flavouring agent and use method of flavouring agent
InactiveCN101130560AThe effect of increasing fragrance is obviousMaintain and Extend the Vitality of Rose Cut PeanutsSugar derivativesWater basedCut flowers
The invention relates to a making method of flavouring agent of fresh-cut rose and usage of the flavouring agent based on the fresh-cut rose with beautiful color and slight scent, which is characterized by the following: using beta-glycosides as the flavouring agent to synthesize aromatic substance through chemical method to add in water-based according to a proper density; absorbing the beta-glucosidase accompanied by absorption of water and nutrient into the fresh-cut rose; releasing the natural scent of rose and fruit of the aromatic substance to make the fresh-cut rose with fragrant flavour after hydrolyzing the beta-glycosides partially under effect of fresh flower endogenous glucosidase. The invention extends the life of bottle flower by addition of amylaceum of the fresh flower because of producing a large amount amylaceum after hydrolytic decomposition of the beta-glycosides, which displays characters of holding and extending the vital force of the fresh-cut rose.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing high fructose corn syrup from crystallized sugar mother solution as raw material
InactiveCN103981241AIncrease added valueSimplify multiple separationsSugar derivativesFermentationChromatographic separationActivated carbon
The invention relates to a method for preparing high fructose corn syrup from a crystallized sugar mother solution as a raw material. The method comprises the steps of separating by simulated moving bed chromatography, carrying out isomerism by liquid isomerase, absorbing by activated carbon, carrying out ion exchange and concentrating to obtain the high fructose corn syrup, wherein the glucose mother solution is taken as a raw material. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the crystallized sugar mother solution with complex components is separated and purified by a simulated moving bed chromatographic separation device, then the glucose is converted to fructose by liquid isomerase, and then pigment components contained in the crude crystallized sugar mother solution are removed by activated carbon and ion exchange, so that the existing ion exchange and decolorizing steps for many times are greatly simplified, the investment on equipment is reduced and the yield of the product is increased.
Owner:SHANDONG LUZHOU FOOD GROUP
Technique for glycosylated degradation of white spirit waste lees to prepare fermentalbe sugar
InactiveCN101775446AIncrease sugar yieldReduce separation costsGlucose productionSaccharic acidSulfate radicals
The invention relates to a technique for glycosylated degradation of white spirit waste lees to prepare fermentalbe sugar, which includes the procedures of drying and grinding of the white spirit waste lees, glycosylated degradation, the separation of saccharic acid, and the like. The technique is as follows: mixing ground waste lees with hydrogen chloride with mass fraction of 2% according to mass per unit volume of 1:10 for glycosylated degradation and collecting the filtrate; letting the filtrate pass through a chromatographic column which is filled with anionic resin, eluting through distilled water and collecting the eluate by step; and combining the eluates with sugar content equal to or more than 0.5 to be recovered sugar liquid. The recovered sugar liquid can be used as material for alcohol fermentation or other fermentations after being concentrated, and the used anionic exchange resin can be regenerated through NaOH. The concentration of the reducing sugar in the recovered sugar liquid prepared through the technique is equal to or more than 1%, wherein the content of dextrose is 55%, the content of xylose is 35% and the content of others is 10%; and the separation and recovery rate of the saccharic acid is more than 75%. The saccharic acid separation process is low in cost and no harmful impurities such as sulfate radical and the like are left behind, so the fermentalbe sugar has little effect to the subsequent alcohol fermentation or other fermentations. Therefore, the fermentalbe sugar is ideal material for alcohol fermentation and other fermentations.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for preparing activated carbon from rice husks
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of activated carbon, and particularly relates to a method for preparing activated carbon from rice husks. According to the method, zinc chloride is used as an activator to treat substances, dissolved in zinc chloride, in raw material rice husks, saccharides such as glucose and the like are gradually decomposed and then further oxidized into uronic acid, uronic acid and aldose are condensed to form furfural, the furfural further has a polycyclic aromatization reaction to form condensed carbon, finally, an activated carbon structure is formed, the activated carbon structure is loose, the porous structure is more stable, and the specific surface area is larger. Alkali dissolution is performed with a sodium hydroxide solution, silicon dioxide in the rice husks is removed, and the porosity and activity of carbon are further increased. The more expensive zinc chloride can be recycled in the production process, raw materials are easy to obtain, the preparation process is pollution-free, and the product is low in impurity content, good in looseness, large in specific surface area and high in adsorption capacity.
Owner:杨淑珍
Biological agent prepared by Arthrobacter AS-1 strain and its application
InactiveCN1654632AImprove qualityShort fermentation cycleTobacco treatmentBacteriaBacteroidesBiotechnology
The present invention relates to biological preparation prepared with arthrobacter AS-1 strain and its application, and belongs to the field of microbial technology. The microbial strain is preserved in the preservation number of CGMCC No. 1281. The biological preparation is prepared through the process including the steps of: test seed culture, shaker culture, seeding tank culture and liquid fermentation in fermenting tank. The culture process has strain inoculating amount of 0.5-2 %, adopts the culture medium comprising beef paste, yeast extractum, peptone and glucose and of pH 6.8-7.2. The fermentation is controlled in 28-30 deg.c and pH 7.0-7.2, the fermentation time in the seeding tank is 16-20 hr, the fermentation time in the fermenting tank is 24-48 hr, and the biological preparation is obtained after the bacteria number in the fermentation liquid reaches 7.0 E8 / ml. The present invention has the advantages of short fermentation period, saving in power, low cost, no pollution, etc.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
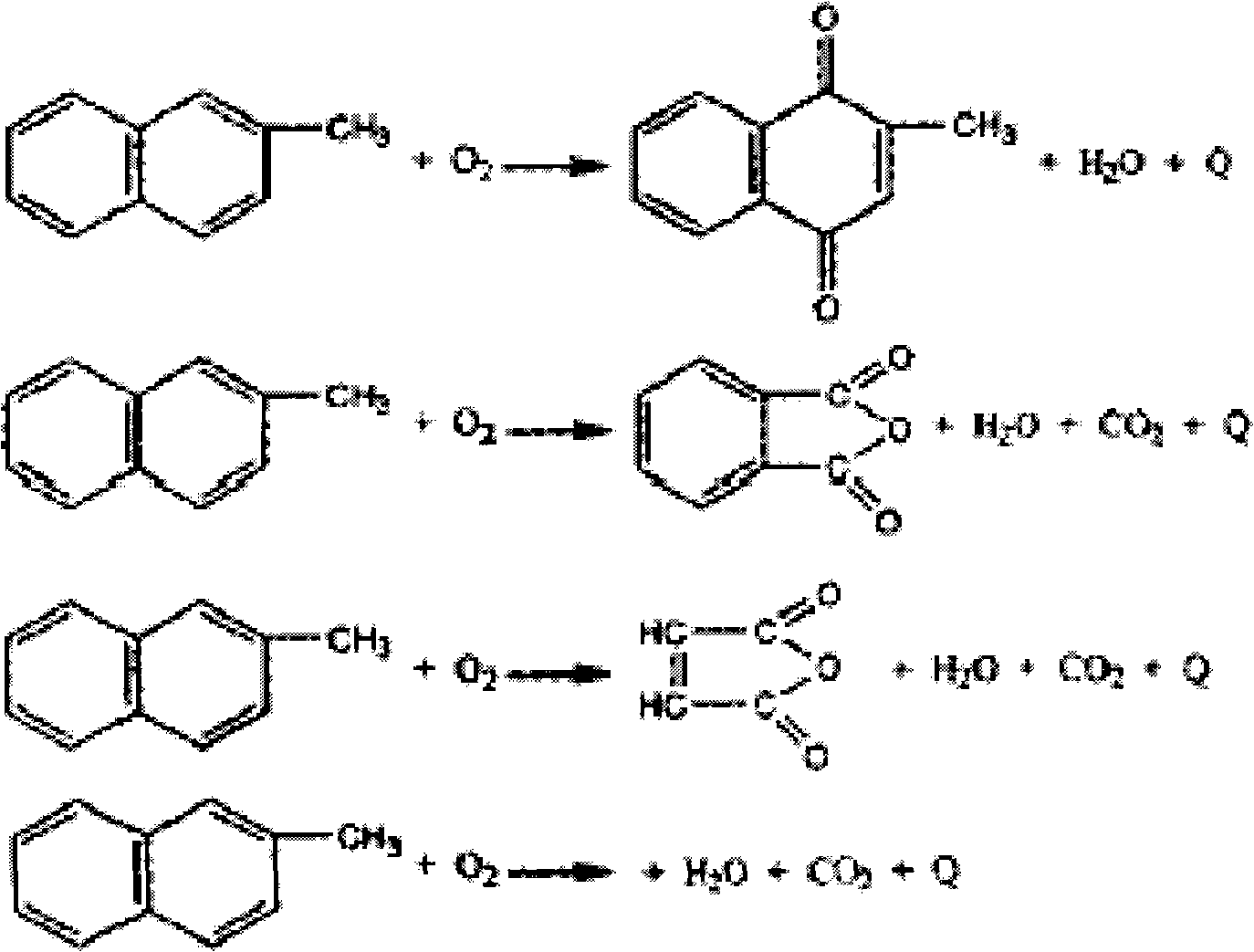
Method for coproduction of chrome tanning agent and menadione
InactiveCN101348425AEmission reductionHigh technical contentQuinone preparation by oxidationChromium sulfatesResource utilizationMenadione
The invention discloses the production of menadione, in particular disclosing a method for manufacturing menadione through combining with a chrome tanning agent. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the following (1) a step of preparing menadione, during which, methylnaphthalene, water and EL series emulsifying agents are added in a first reaction bulb; moreover, sodium bichromade and water are added in a second reaction bulb, and concentrated sulfuric acid is added slowly while stirring for cooling down; then prepared red liquor is slowly dripped into the first reaction bulb while stirring, and is filtered and dried so as to obtain bright yellow crystallized menadione powder; and (2) a step of preparing basic chrome sulphate, during which, the mother liquor obtained during preparing menadione is taken out, and sodium bichromade and dextrose solution are added in order; and chrome tanning agent basic chrome sulphate is obtained after spray drying. Through adopting a chrome tanning agent basic chrome sulphate production device to carry out joint production for menadione, the method realizes maximization of resource utilization; moreover, the method greatly reduces production cost for both sides and the release of waste liquids.
Owner:SHANDONG DAHUA GUANGJI BIOCHEM ENG
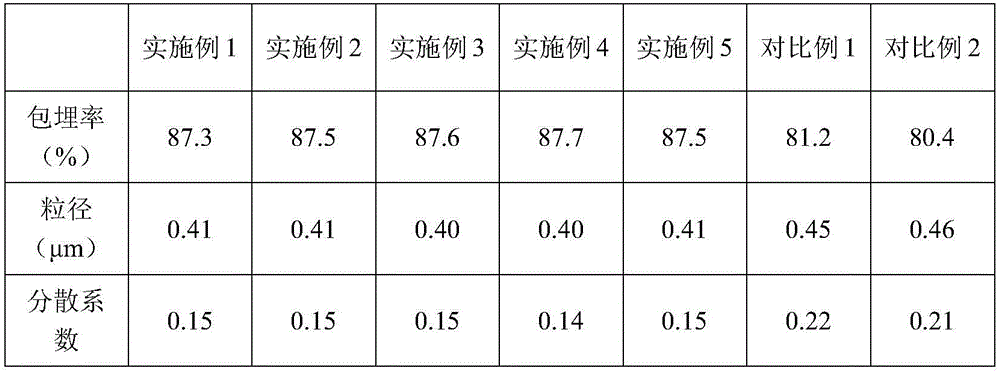
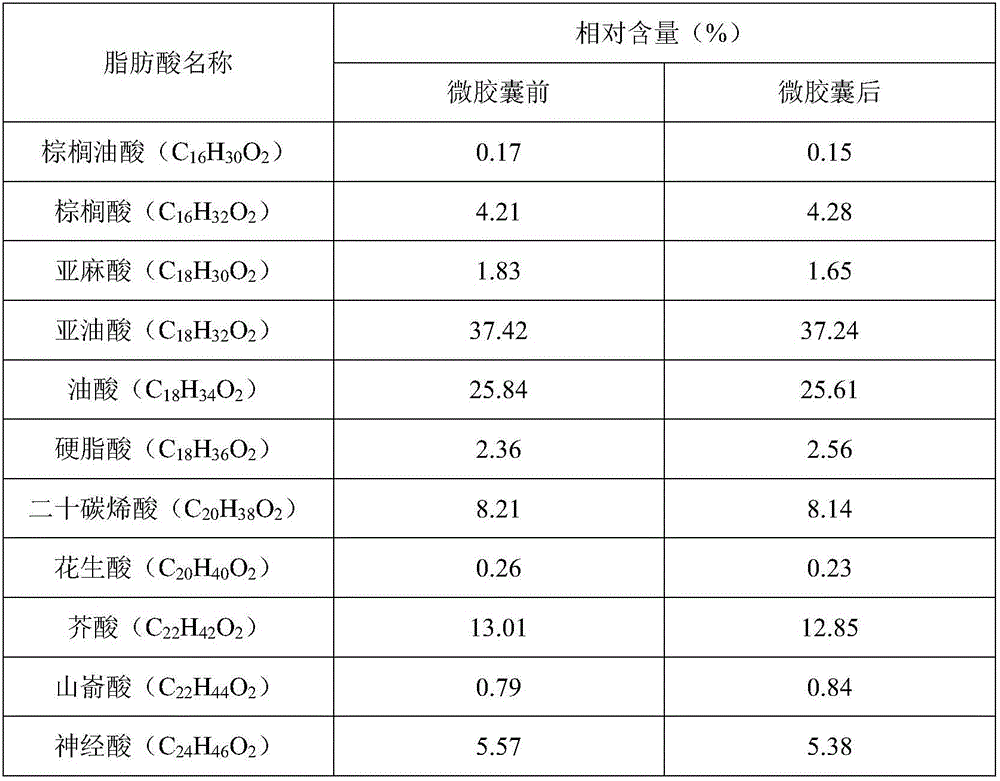
Acer truncatum oil microcapsule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106262927AFunction increaseHigh embedding rateSugar food ingredientsFood shapingMonoglyceridePhosphate
The invention discloses an acer truncatum oil microcapsule and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of oil. The acer truncatum oil microcapsule is prepared by the following steps: (1) mixing modified starch, maltodextrin and distilled water, heating to 60-70 DEG C and stirring for 20-40 minutes; (2) mixing and stirring acer truncatum oil, vitamin E, sodium starch octenyl succinate, molecular distilled monoglyceride, soyabean lecithin and gellan gum for 20-40 minutes; (3) mixing the mixed solution at room temperature and stirring the mixed solution for 2-5 minutes; (4) adding the mixed solution into a homogenizer for homogenizing; (5) adding d-sodium erythorbate, tert-butylhydroquinone, hydroxy propyl distarch phosphate and glucose, and continuing to homogenize for 2-5 minutes; and (6) adding the solution into a spray dryer for spray drying to obtain the acer truncatum oil microcapsule. The acer truncatum oil microcapsule is high in embedding rate, high in stability, rich in unsaturated fatty acid and slight in change of composition of fatty acid before and after microencapsulation, and can effectively retain the intrinsic good functions and properties of the acer truncatum oil.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and device for preparing 5-hydroxymethylfurfural through high fructose corn syrup
ActiveCN109879838ARaw materials are easy to getShort processOrganic chemistryOrganic solventHigh-fructose corn syrup
The invention discloses a method and device for preparing 5-hydroxymethylfurfural through high fructose corn syrup. The high fructose corn syrup is used as a raw material, acid is used as a catalyst,and in an aqueous solution, through a continuous process reaction, fructose and glucose in the high fructose corn syrup are converted to generate the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. According to the method and device for preparing the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from the high fructose corn syrup, for the difference of the conversion conditions of the fructose and the glucose in the high fructose corn syrup,a mode of double-reaction-kettle in series is adopted, in the aqueous solution, the fructose and the glucose are converted to generate the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural through the continuous process reaction, in the reaction process, a pure organic solvent is added, the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in a reaction system is transferred to an organic layer in real time to be extracted in real time, the yield of the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural is further increased, the continuously extracted organic solvent is recycled through reduced pressure distillation, a water phase can be recycled for many times after impurities of the water phase are removed through an adsorption tower, on the one hand, the production cost is effectively lowered, and on the other hand, emission of three wastes is reduced, and thus the pressure of environmental protection in the production process is decreased.
Owner:LUOYANG NORMAL UNIV
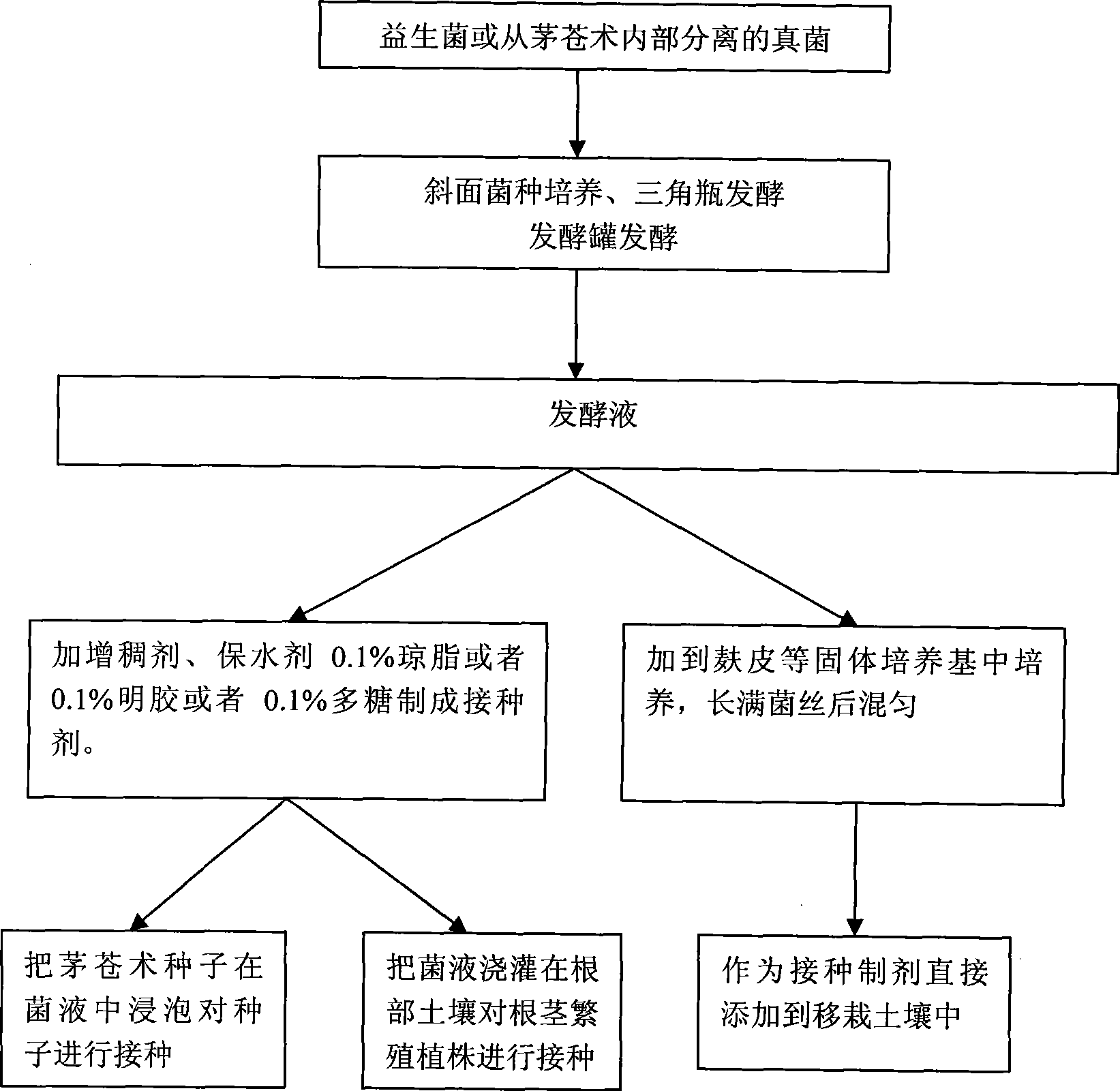
Method for producing novel lance atractylodes rhizome inoculation agent
InactiveCN101444230AShorten the production cycleSimple production processBiocideFungiPlant rootsGLUCOSE LIQUID
The invention relates to the field of agricultural seeds, in particular to a method for producing a lance atractylodes rhizome inoculation agent from lance atractylodes rhizome endophytic fungus or probiotic bacteria. The method specifically comprises the following steps: activating the lance atractylodes rhizome endophytic fungus or the probiotic bacteria; adding a small quantity of thickening agents or water retention agents after the lance atractylodes rhizome endophytic fungus or the probiotic bacteria are cultivated on a culture medium containing potato immersion liquid, lance atractylodes rhizome immersion liquid and glucose liquid or a solid medium containing lance atractylodes rhizome straws; and soaking lance atractylodes rhizome seeds and transplanting soaking roots or adding the seeds to rhizoplane soil directly. The inoculation agent is not easily influenced by the environment during the production and has short production period, simple production process, production time, easy control of output and remarkable action. The method adopting the soaking seeds, soaking plant roots or pouring and directly adding the seeds in soil ensures that the inoculation agent acts on plants and has the advantages of simple method, easy operation, less consumption, low cost and good effect.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com