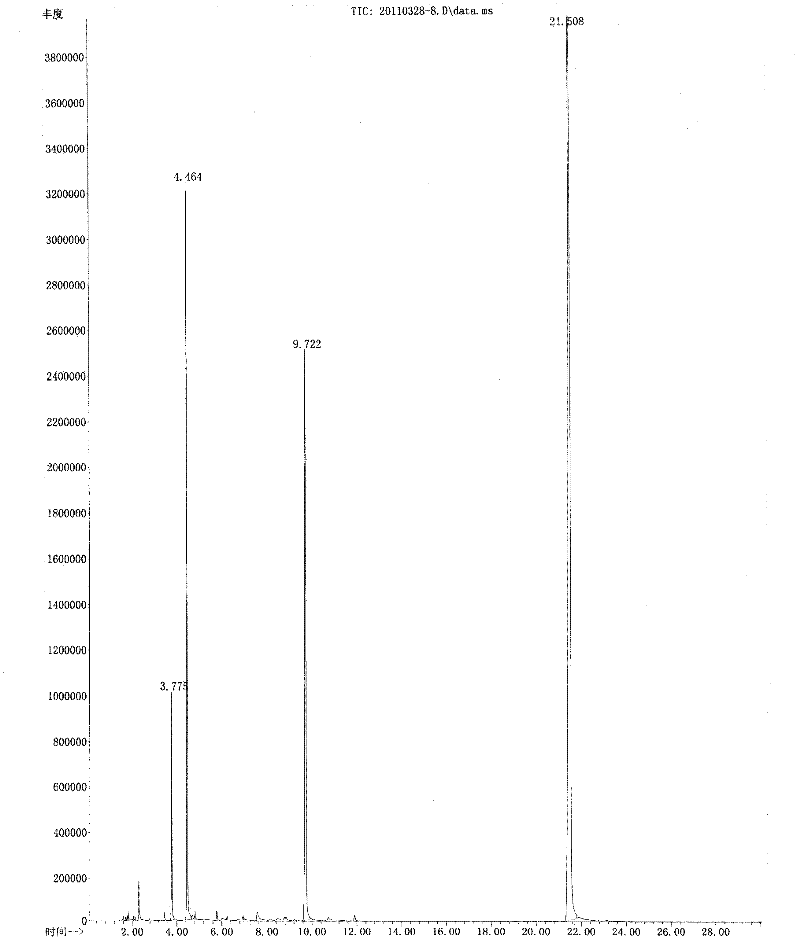
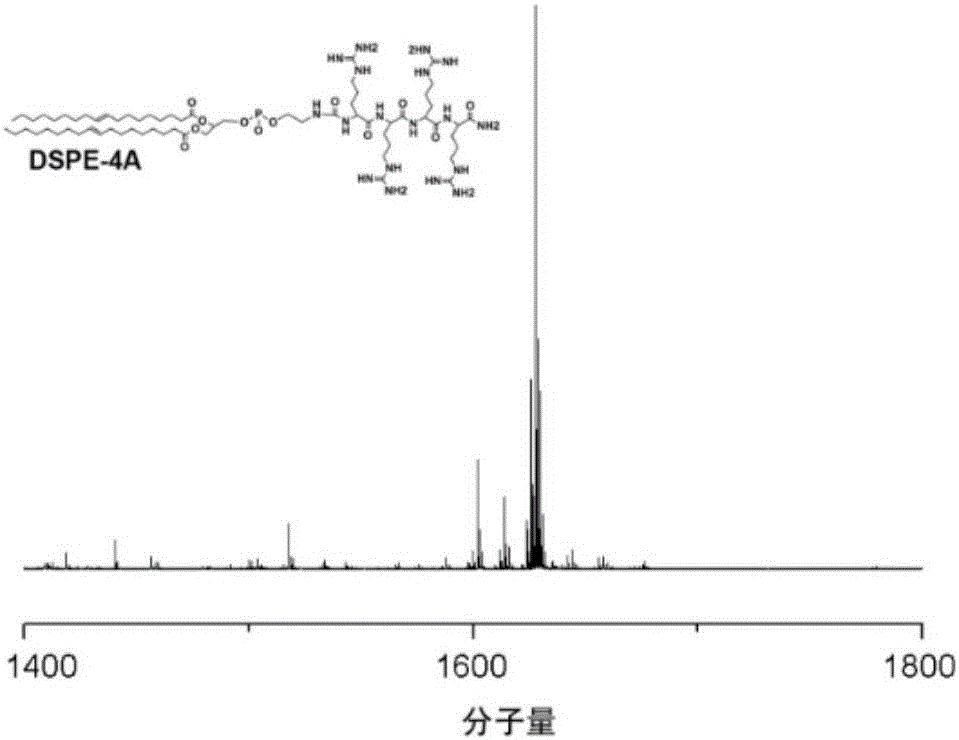
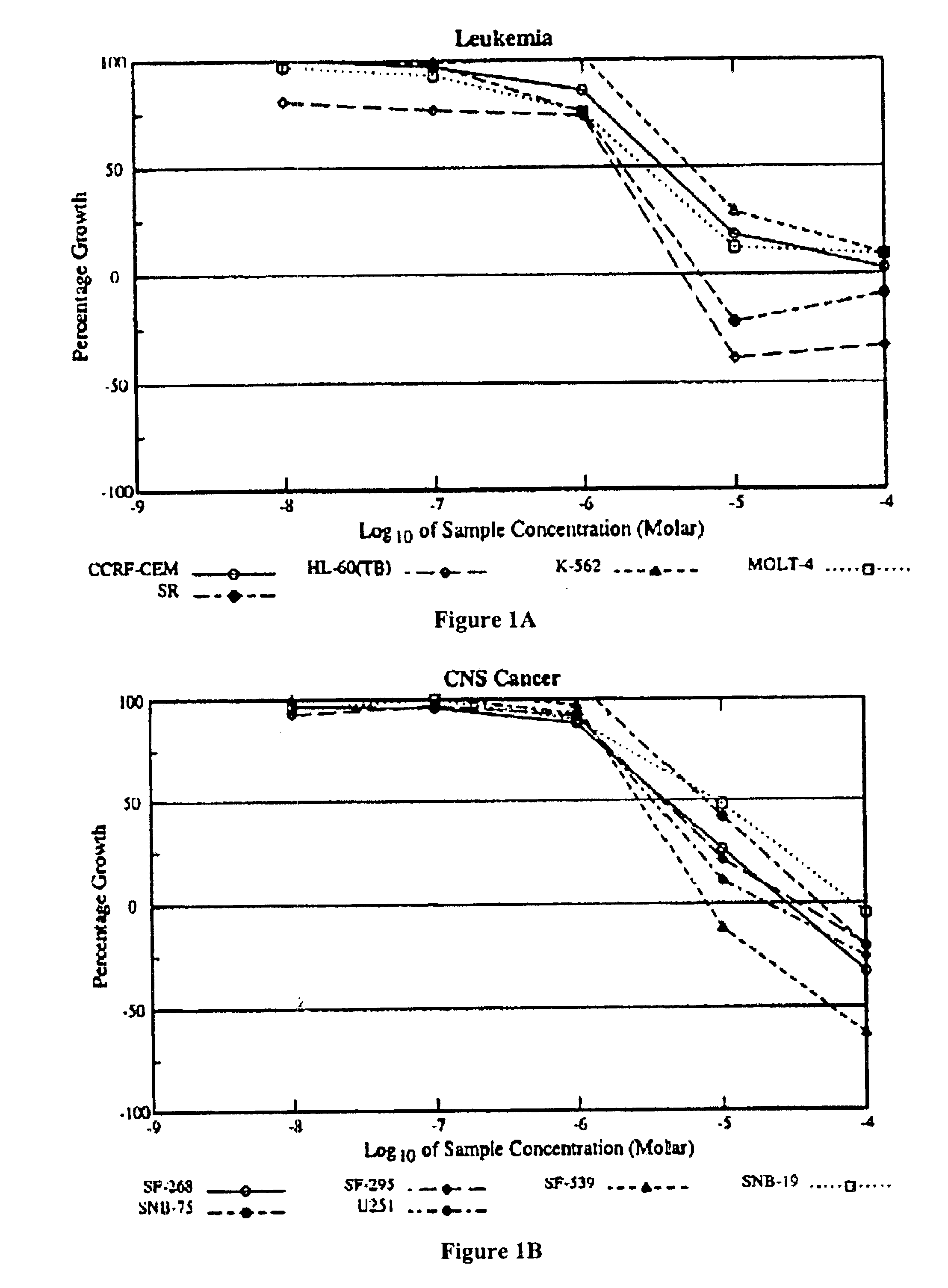
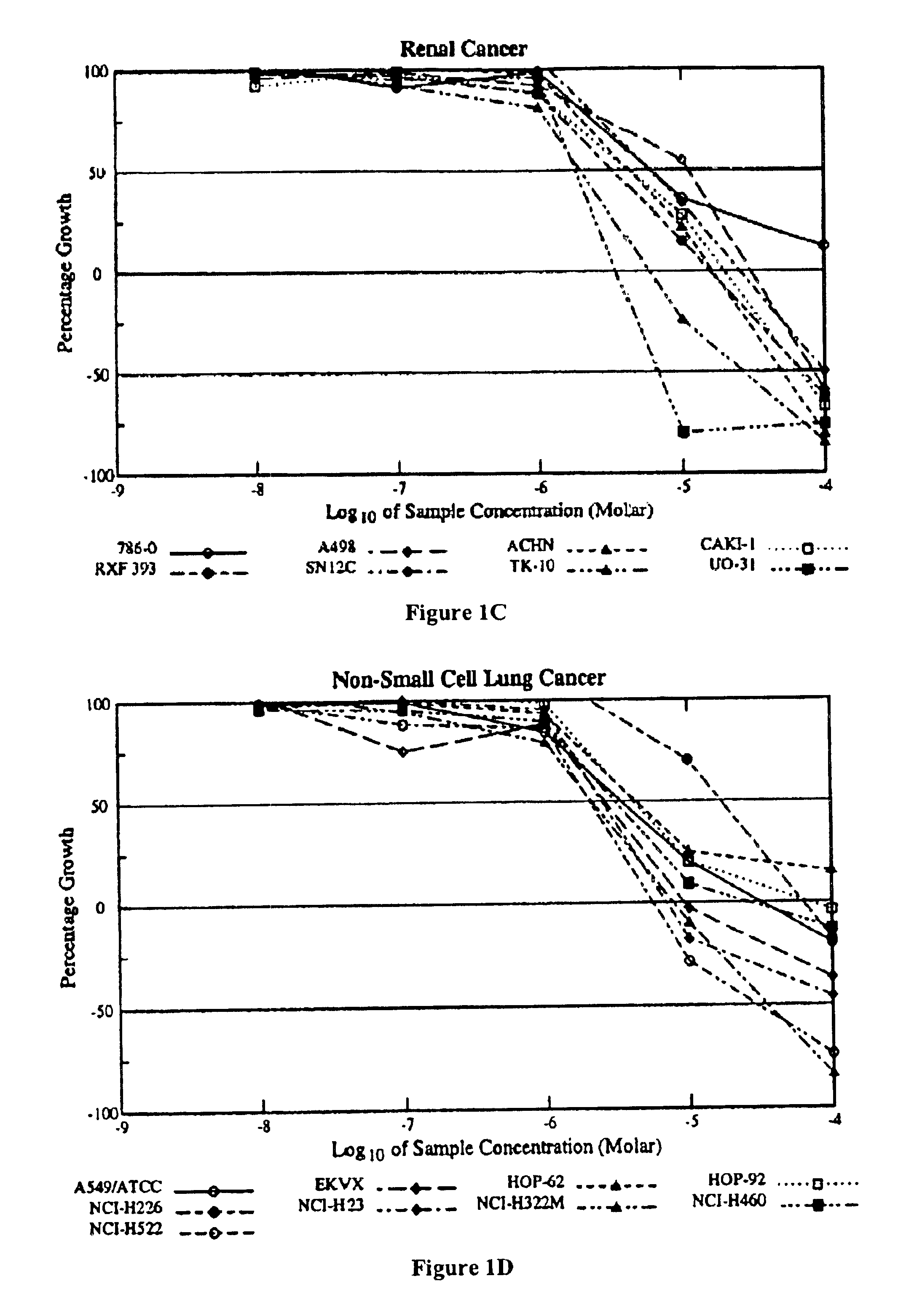
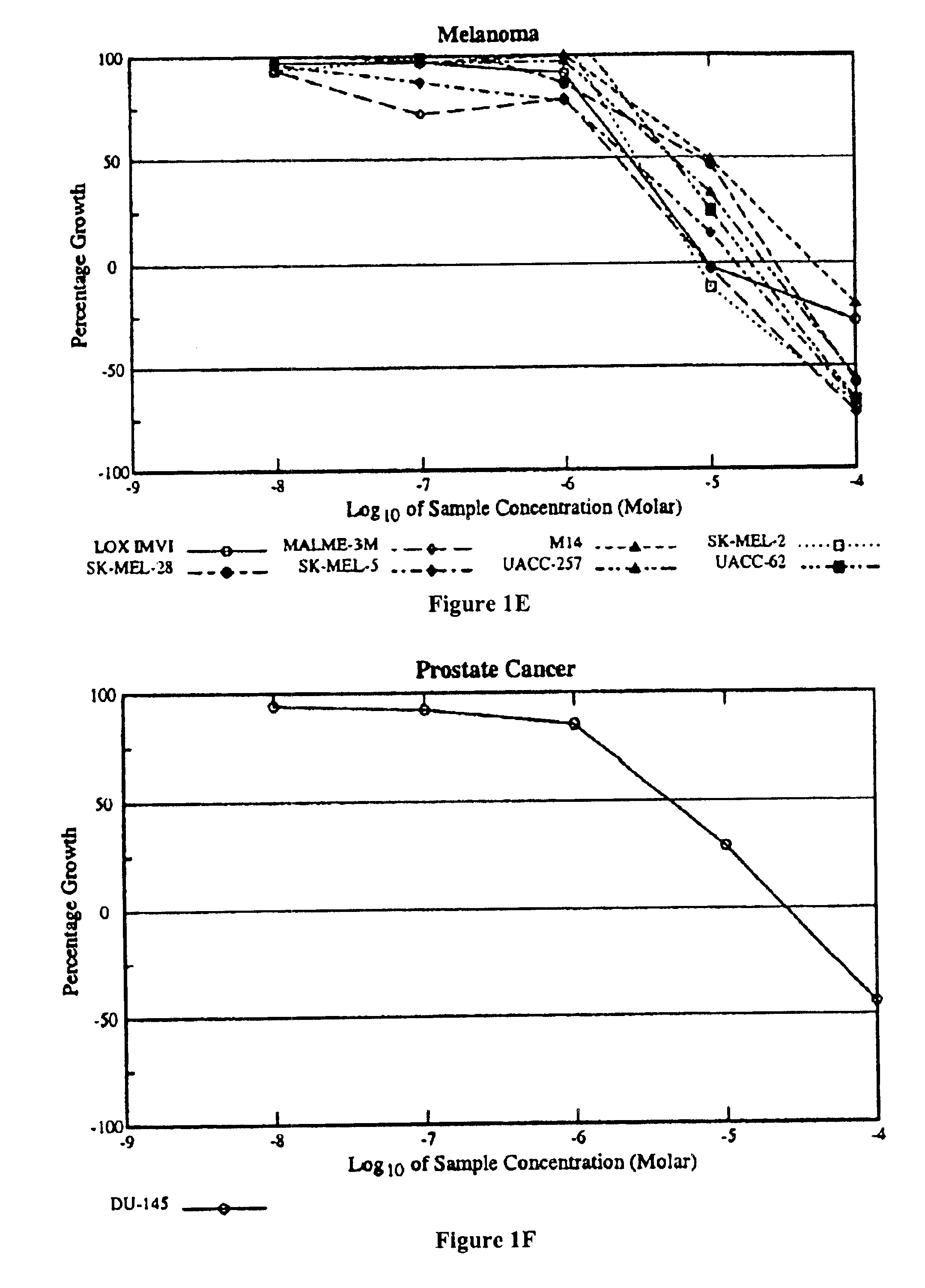
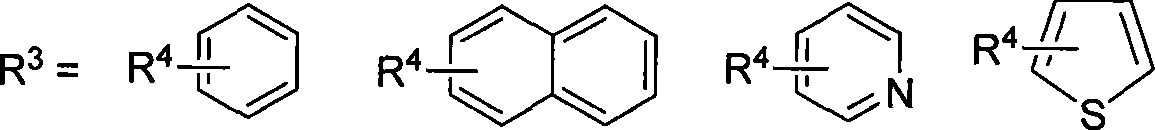
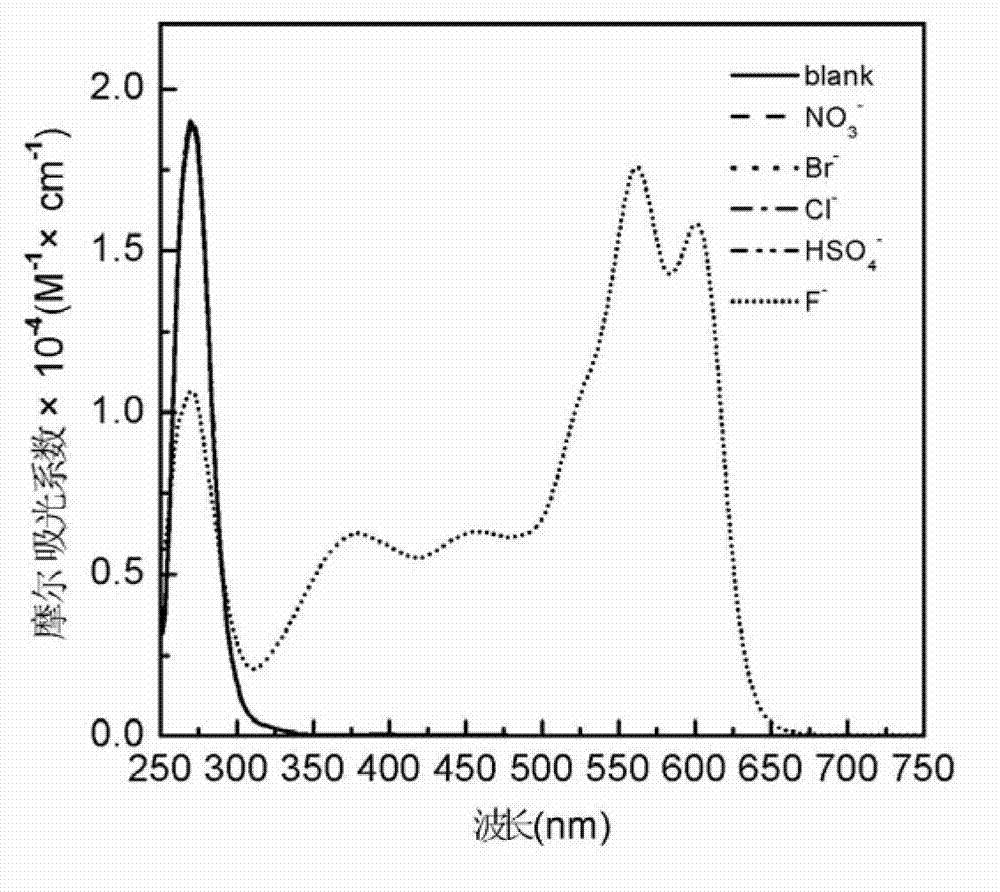
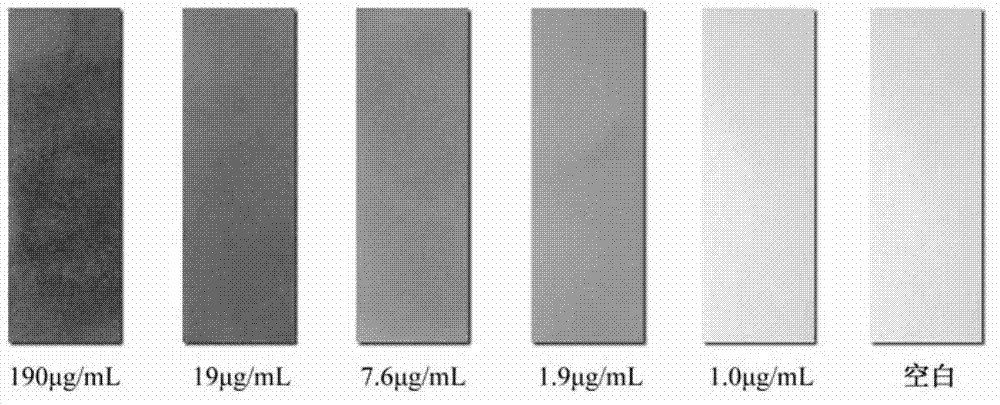
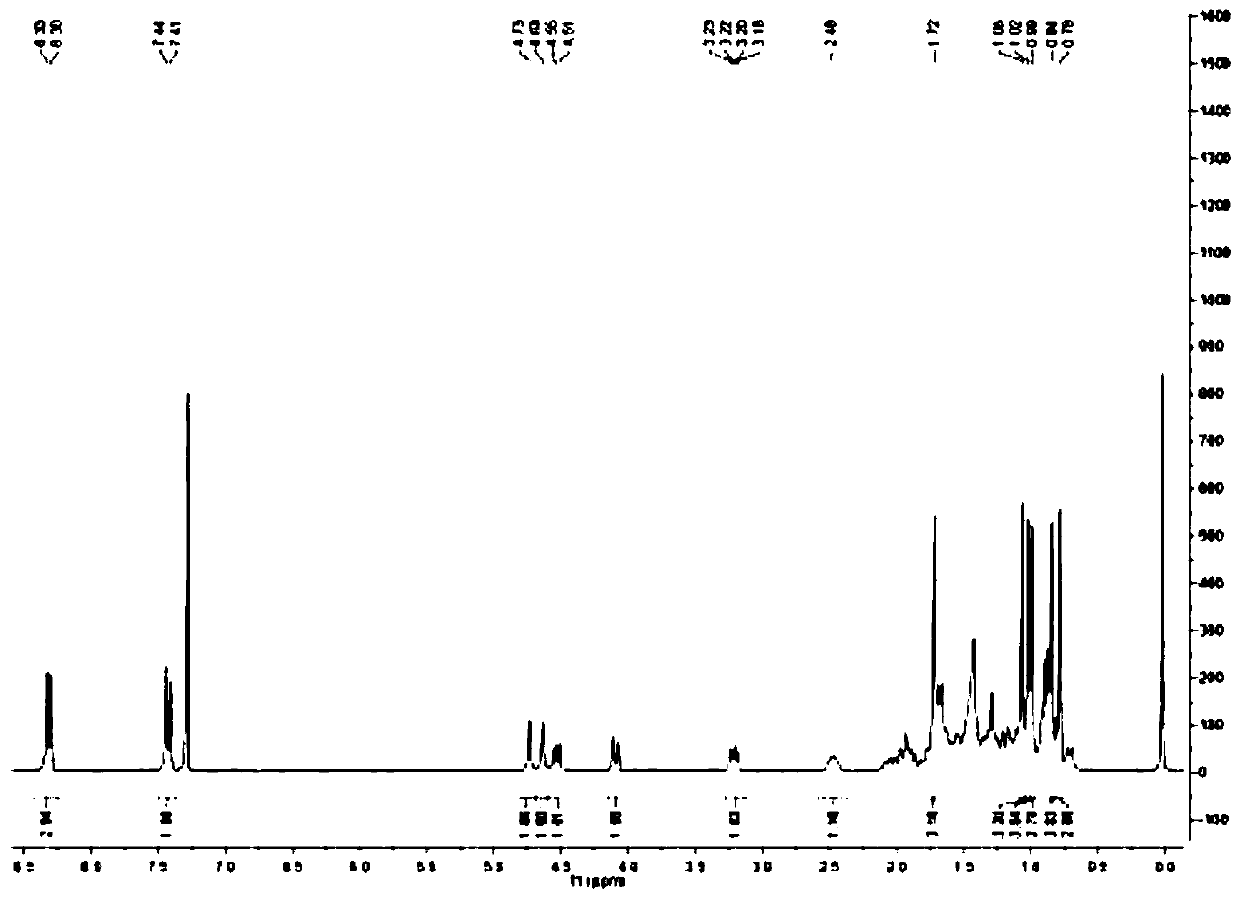
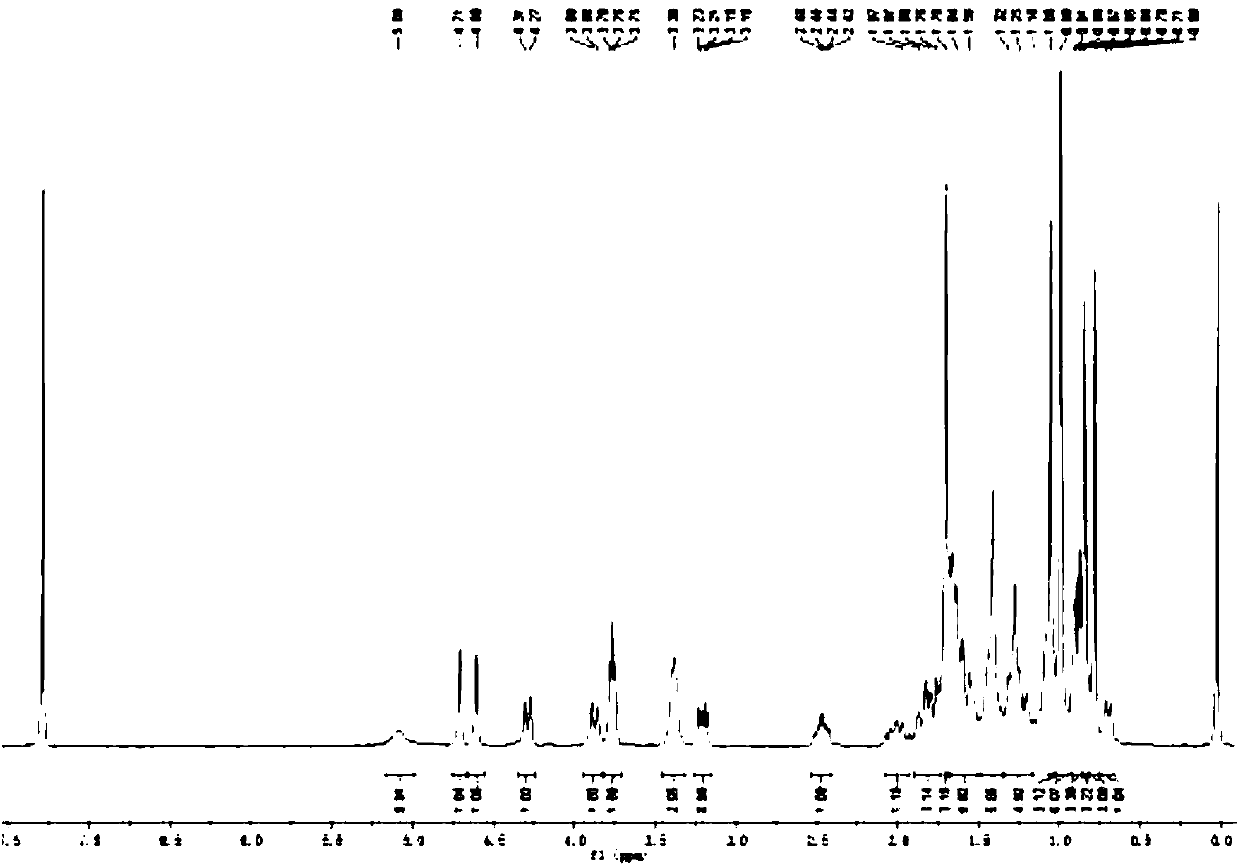
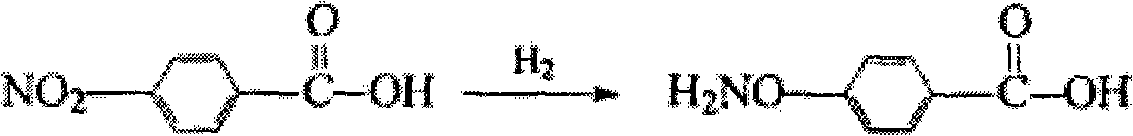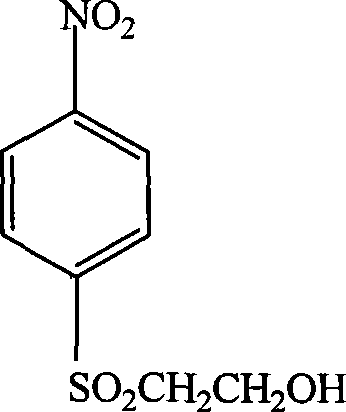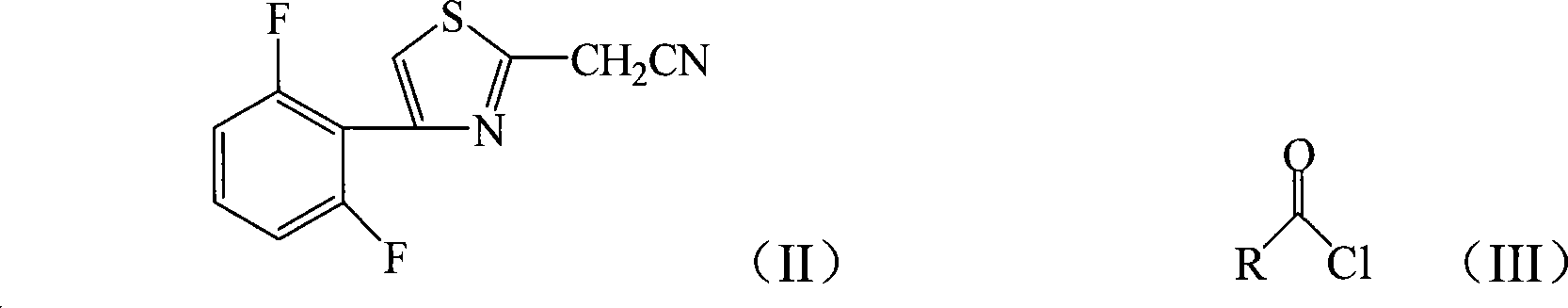Patents
Literature
132 results about "Para-nitrophenyl" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
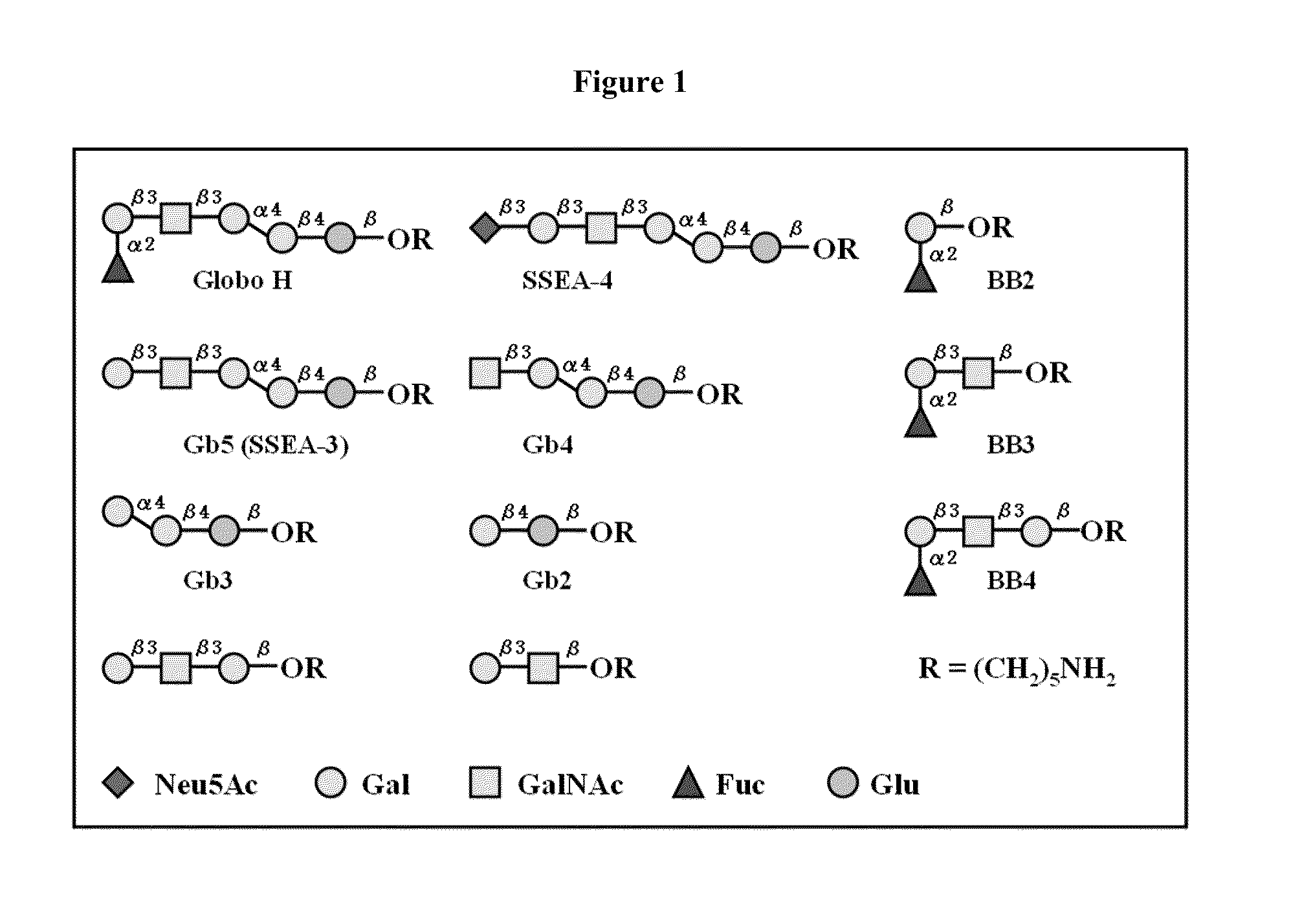
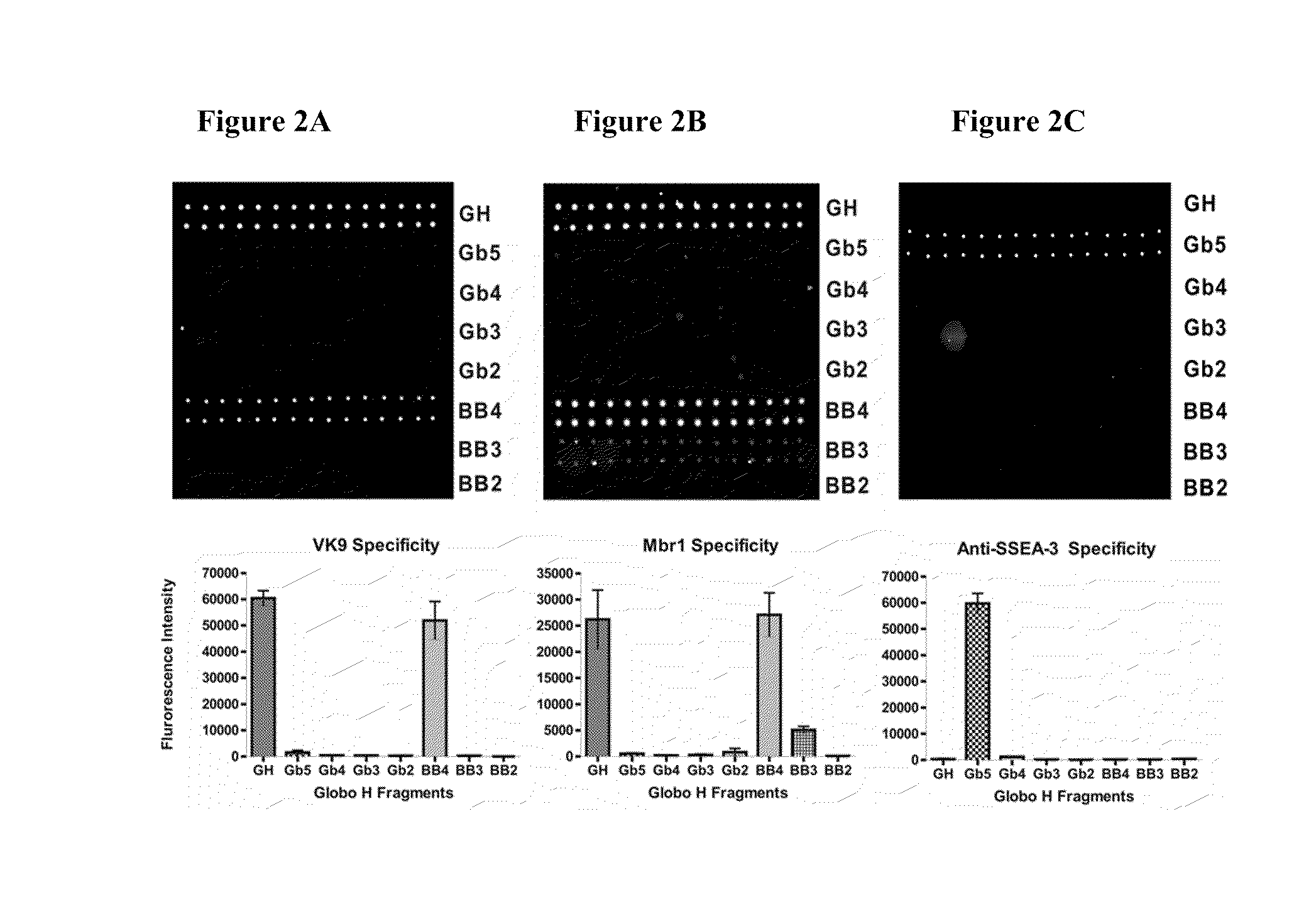
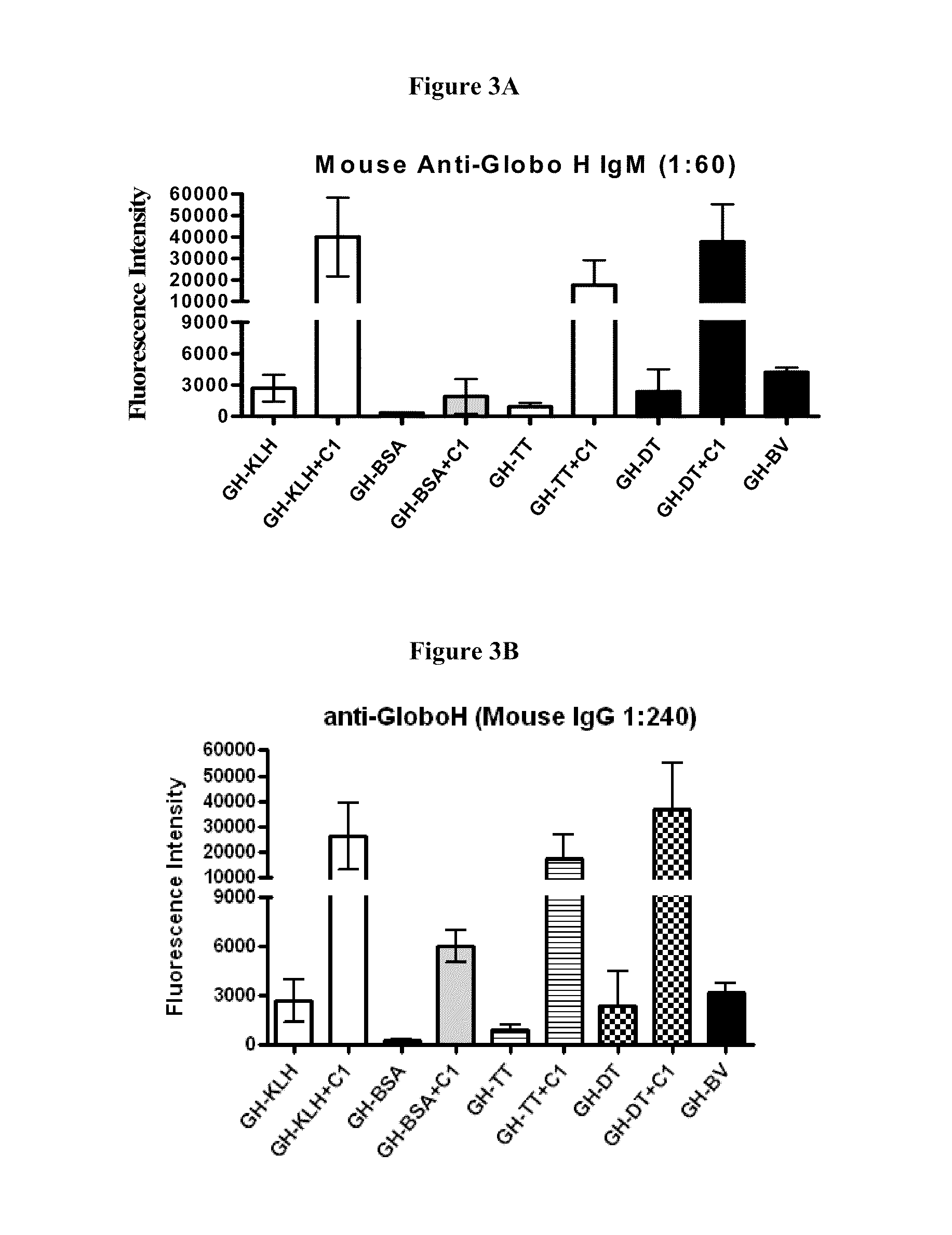
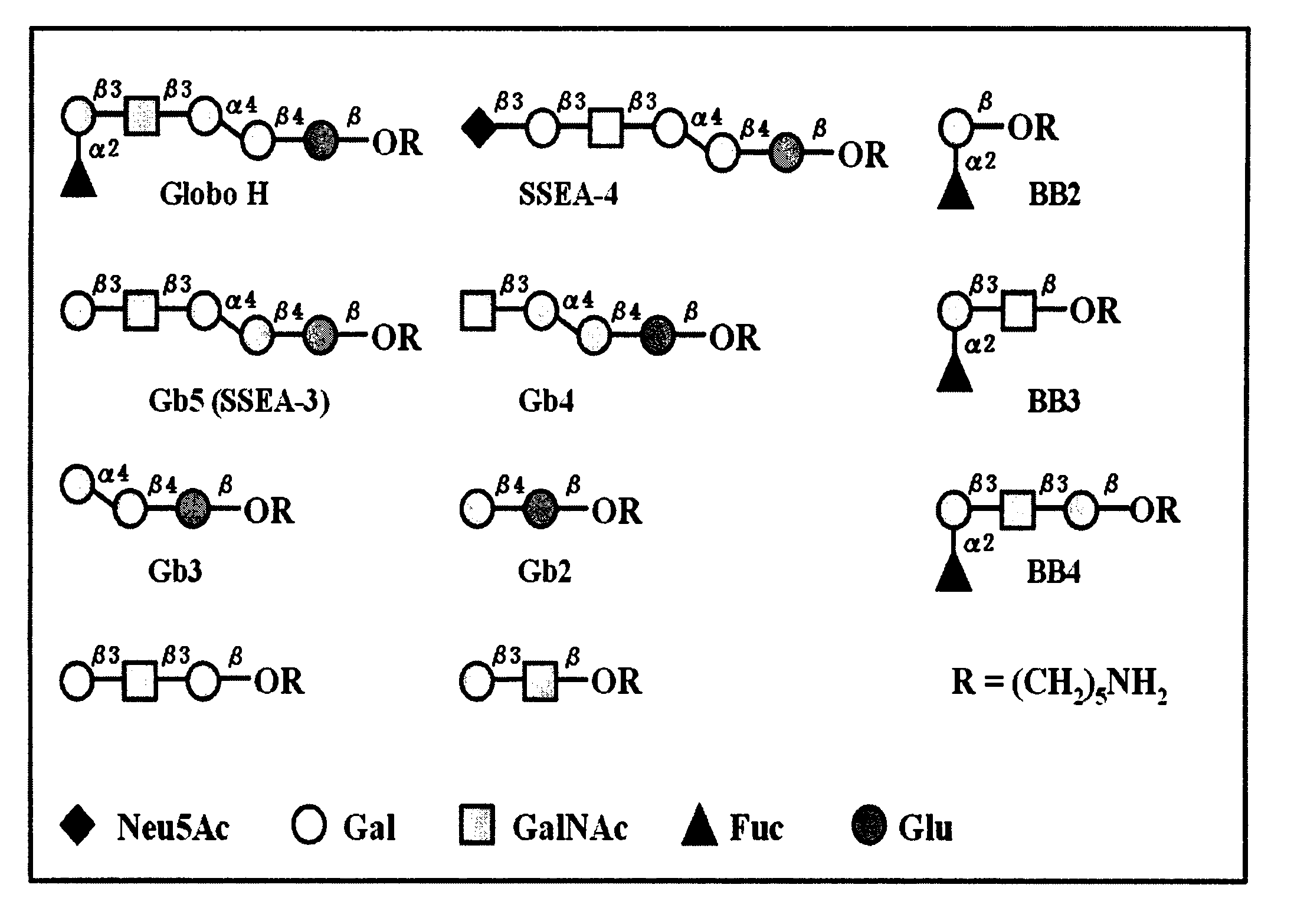
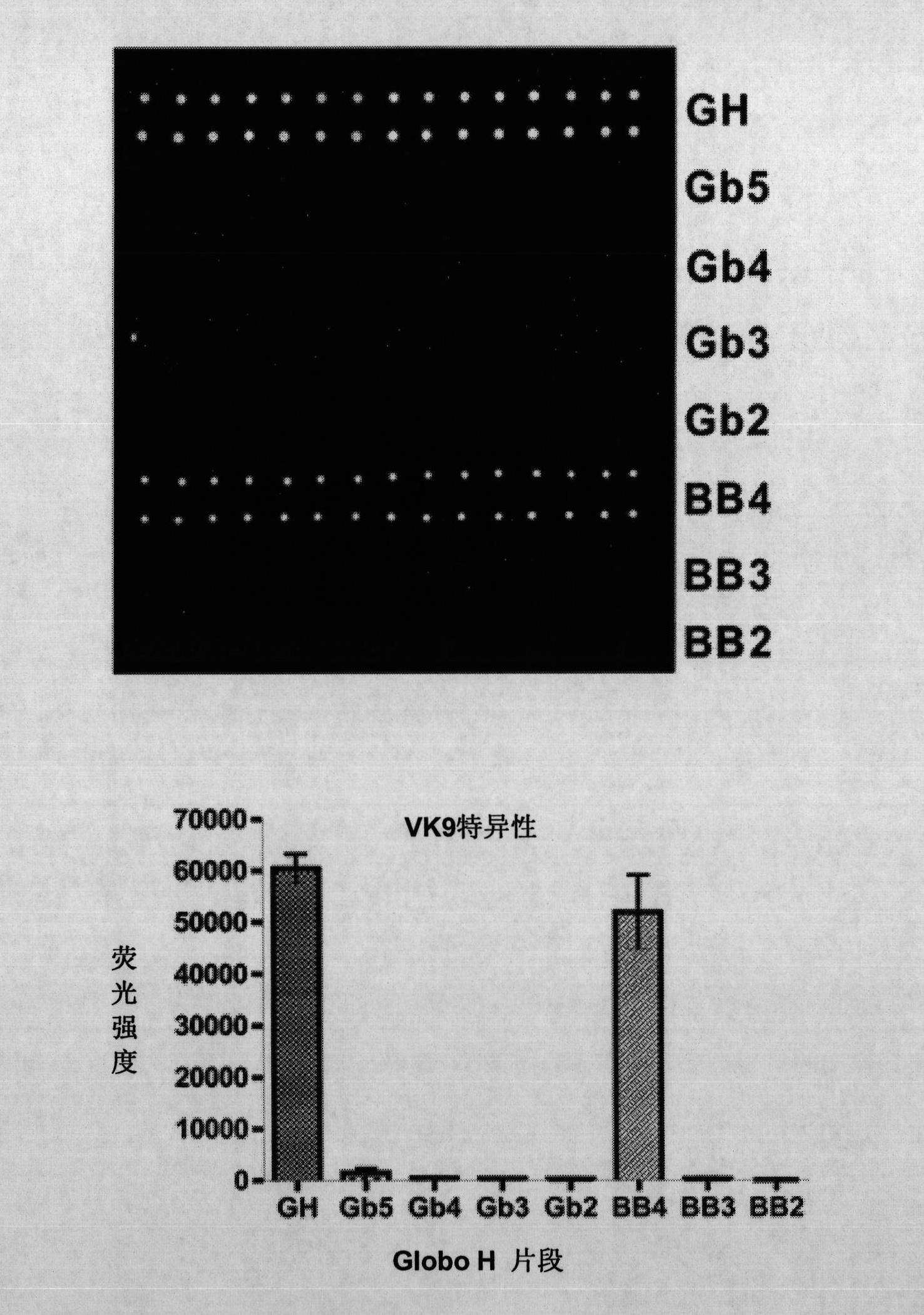
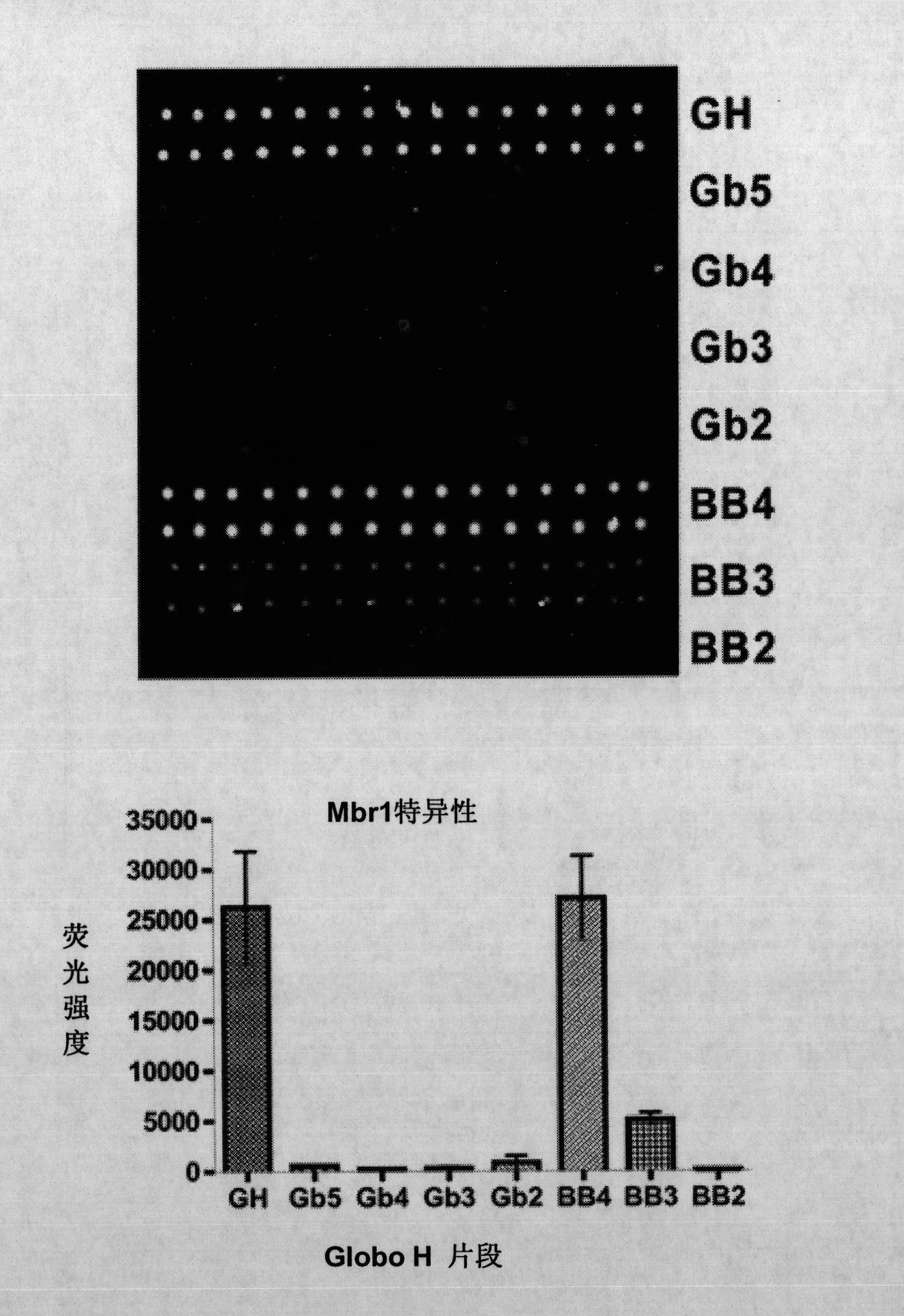
Globo h and related Anti-cancer vaccines with novel glycolipid adjuvants
ActiveUS20100136042A1Shrink tumorInhibit tumor growthOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDendritic cellAdjuvant
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Preparation method and application of acid sensitive doxorubicin prodrug based on polyethylene glycol
InactiveCN103834002ASimple purification technologyEasy to getOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBiocompatibility TestingPolyethylene glycol
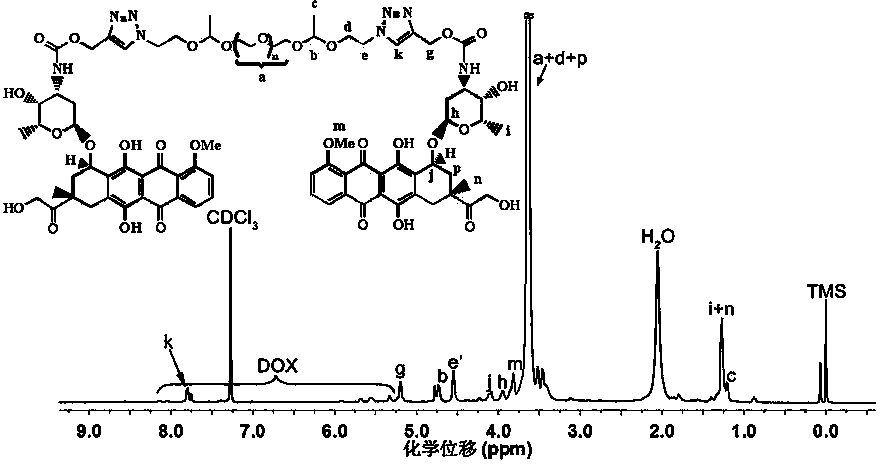
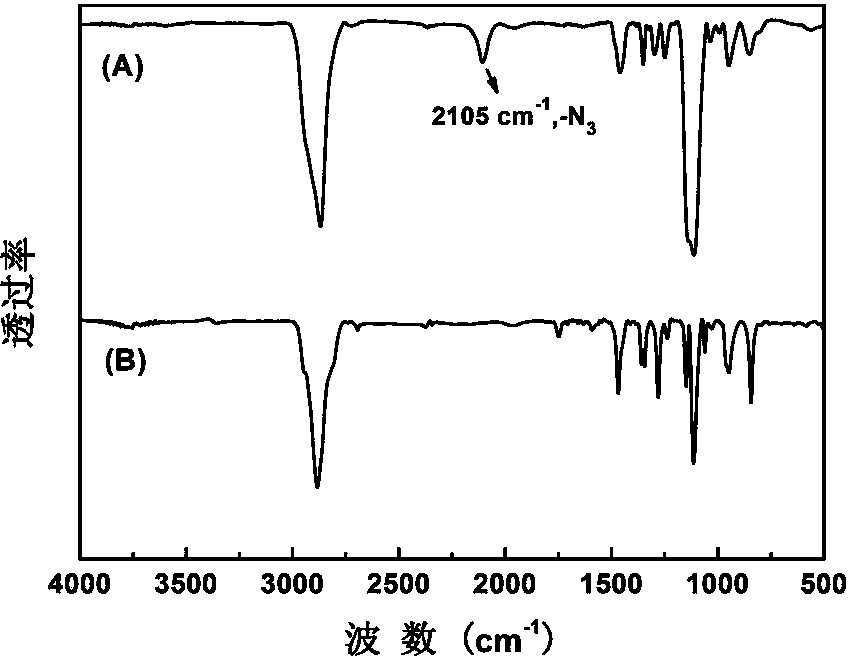
The present invention provides an acid sensitive doxorubicin prodrug based on polyethylene glycol, and a method and an application of the acid sensitive doxorubicin prodrug based on polyethylene glycol. The preparation method comprises: preparing a polyethylene glycol whose end contains an acid sensitive acetal group and a p-nitrophenyl ester azide group by a reaction of a polyethylene glycol whose double ends contain diazido ethyl diacetal groups with a p-nitro phenyl propargyl carbonate; preparing the acid sensitive doxorubicin prodrug based on the polyethylene glycol by the reaction of the prepared polyethylene glycol with doxorubicin hydrochloride. The acid sensitive and water soluble doxorubicin prodrug has good biocompatibility and acid sensitivity, thereby being used as a stimulation sensitive antineoplastic prodrug.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Globo h and related anti-cancer vaccines with novel glycolipid adjuvants
Immunogenic compositions, cancer vaccines and methods for treating cancer are provided. Compositions comprising: (a) a glycan such as Globo H or an immunogenic fragment thereof, wherein the glycan is conjugated with a carrier protein by a linker such as para-nitrophenyl; and (b) an adjuvant comprising glycolipid capable of binding CDId on a dendritic cell, such as an a-galactosyl-ceramide derivative, wherein the immunogenic composition induces an immune response that induces a higher relative level of IgG isotype antibodies as compared to IgM isotype antibodies, are provided. Immunogenic compositions comprising the carrier protein diphtheria toxin cross-reacting material 197 (DT-CRM 197) and the adjuvant C34 are provided. Antibodies generated by immunogenic compositions disclosed herein further neutralize at least one of the antigens Globo H, stage-specific embryonic antigen-3 (SSEA-3) and stage-specific embryonic antigen-4 (SSEA-4). Therapeutics against breast cancer stem cells comprising immunogenic compositions comprising Globo H, SSEA-3 or SSEA-4 conjugated with DT-CRM 197.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Anti-tumor macromolecule bonding drug with multidrug synergistic effect and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106177979AGrowth inhibitionGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectLactide
The invention discloses an anti-tumor macromolecule bonding drug with a multidrug synergistic effect and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of sequentially triggering the polymerization of lactide containing norbornene and alpha bromination caprolactone through methoxy polyethylene glycol so as to obtain a triblock copolymer; modifying a p-nitrophenyl formic ether lateral group and a carboxyl lateral group on the triblock copolymer so as to obtain a polymeric carrier; bonding the polymeric carrier, an anti-tumor drug containing hydroxyl and an anti-tumor drug containing amino so as to obtain the anti-tumor macromolecule bonding drug. The preparation method is simple to operate, moderate in reaction conditions, less in side reaction, high in yield, large in drug loading capacity, controllable, and high in product purity; according to the prepared anti-tumor macromolecule bonding drug, the anti-tumor activity is improved through a various signal channel effect (the synergistic effect), and meanwhile, due to the joint action of various drugs, the dosage of each drug can be reduced, so that a toxic and side effect of chemotherapy is reduced.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Novel method for preparing aromatic amine through halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon
InactiveCN102134176AEfficient constructionEasy to useOrganic compound preparationAmino group formation/introductionN dimethylformamidePotassium carbonate
The invention provides a novel method for preparing an aromatic amine compound through halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon and an organic amine zinc chloride complex compound. A reaction general formula is as shown in a figure in the specification, wherein Ar is aryl and can be selected from 2,4-dinitrophenyl, p-nitrophenyl, 2-nitro-4-chlorphenyl, p-trifluoromethylphenyl, 4-formaldehyde phenyl, 2-pyrimidyl, and the like; X can be selected from F, Cl, Br, I, and the like; R1 and R2 are H, alkyl, aryl or heteroaryl, or R1 and R2 form a ternary to heptatomic naphthenic base together with carbon atoms connected with R1 and R2; reaction media are methylbenzene, dimethyl sulfoxide, N,N-dimethylformamide, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, acetone and water; reacted alkalis are cesium carbonate, potassium phosphate, triethylamine, potassium carbonate, sodium (potassium) hydroxide and sodium (potassium) alkoxide; reaction can be implemented through both conventional heating and microwave promotion; and the means of recrystallization or column chromatography is adopted for purification. The invention provides a low-cost non-toxic efficient green method (without ligands) for establishing an aromatic C-N bond.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Polymer hydrogel based on Fe3+-dopamine modification and preparing method thereof
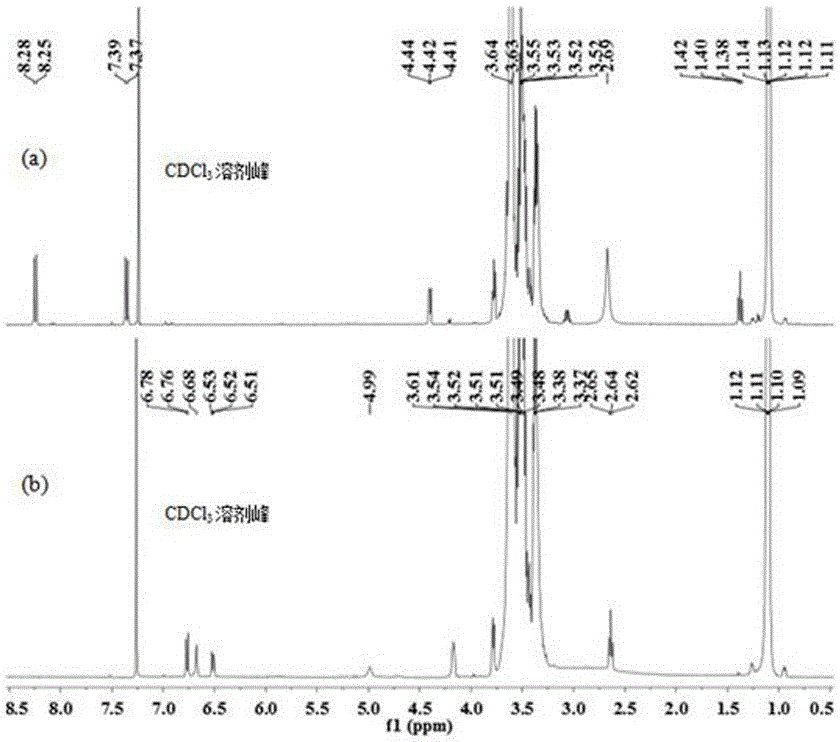
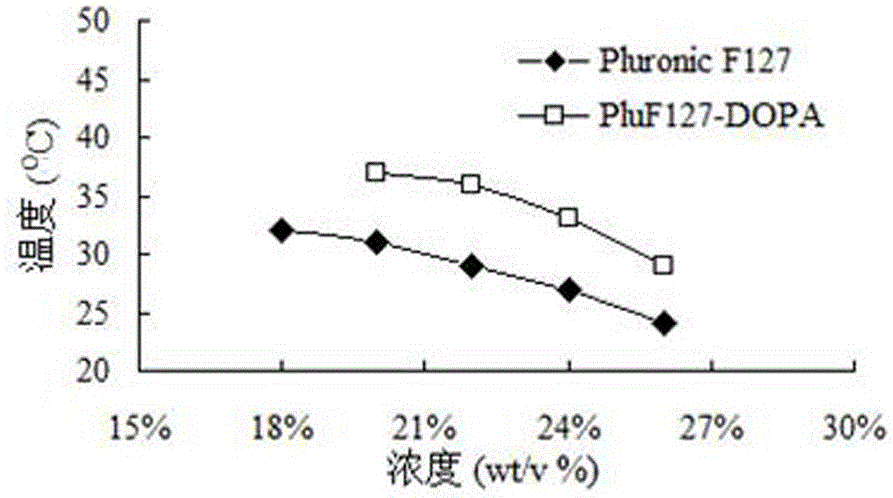
The invention discloses polymer hydrogel based on Fe3+-dopamine modification and a preparing method thereof. Polymer containing a hydroxyl group is used as a main raw material, dopamine is selected as a functional group, and p-nitrophenyl chlorate is used as an activating agent and directly reacts with dopamine hydrochloride to prepare the polymer with the terminal modified by dopamine; coordination of the polymer with the terminal modified by dopamine and Fe3+ through pH adjustment is achieved. The hydrogel has adhesiveness, thermosensitivity, pH responsiveness, self-healing and other multifunctional characteristics and has potential application value in biomedical engineering and underwater mechanical coatings.
Owner:SANMING UNIV
Method for preparing acetosyringone and vanillyl ethyl ketone by oxidizing lignin
InactiveCN102295547AEfficient use ofHarm reductionCarbonyl compound preparation by oxidationGas liquid chromatographicNitrobenzene
The invention discloses a method for preparing acetovanillone and acetosyringone (AS) through oxidation of lignin by using an oxidizing agent. According to the method, an oxidizing agent reacts with the lignin in an alkaline solution; the resulting reaction solution is subjected to acidification, extraction and concentration to obtain the crude product after completing the reaction; the treatments of recrystallization and rectification are performed to obtain the acetovanillone and the AS. The oxidizing agent is the one selected from p-nitrobenzoic acid, 3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid, 3-nitrosalicylic acid, 5-nitrosalicylic acid or 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid. According to the present invention, the oxidizing agent has low toxicity, such that the harm to the environment can be reduced; the post-treatment steps are simplified, and the uses of the organic solvents are reduced, such that the secondary pollution to the environment is reduced; the yield is relatively high, the purities of the products are respectively 97.3% and 98.2% through the gas chromatography analysis; the two important chemical raw materials of guaiacol and lilac alcohol can be synchronously obtained when preparing the acetovanillone and the AS.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Electrolyte for chip aluminum electrolytic capacitor and preparation method thereof
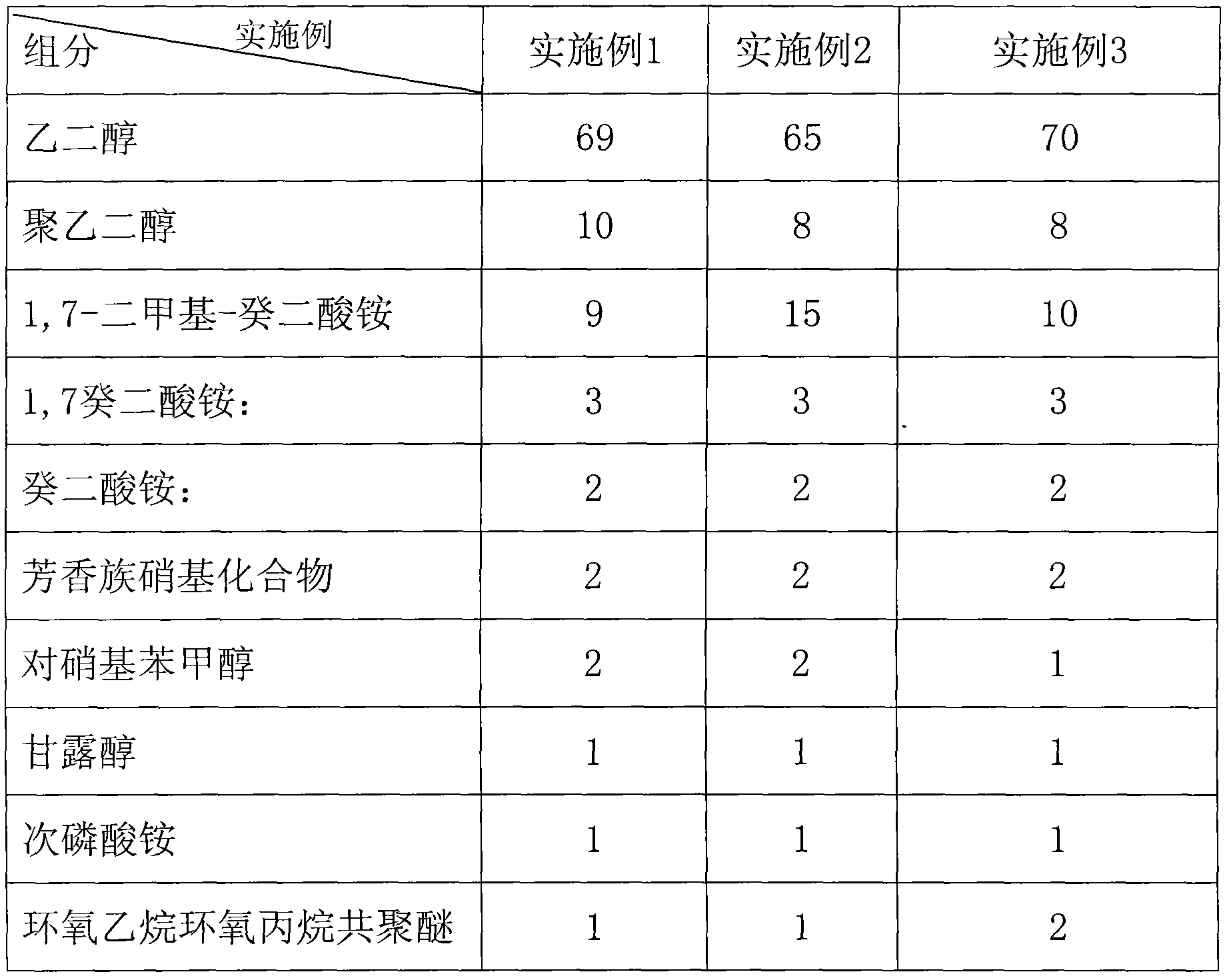
InactiveCN102074364AGood electrochemical propertiesHigh temperature resistantElectrolytic capacitorsPolyethylene glycolTemperature resistance
The invention provides a method for preparing an electrolyte for a chip aluminum electrolytic capacitor. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) weighing: weighing raw materials; (2) dissolving: adding ethylene glycol into a container with a stirrer and a thermometer, raising the temperature to 60 DEG C by using a closed electric heater, sequentially adding polyethylene glycol, 1,7-ammonium-sebacate, ammonium sebacate, 1,7-dimethyl-ammonium-sebacate, mannitol, ammonium hypophosphite, paranitrobenzoic acid or para-nitrophenyl methanol, and oxirane and epoxypropane copolyether, heating to 130 DEG C, and stirring to totally dissolve the components; and (3) cooling: standing and cooling to room temperature to obtain the electrolyte. The technology is simple, the condition is easy to control, and the preparation method is suitable for scale production. The invention also provides an electrolyte which has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, high spark voltage and long service life, and is applicable for making the chip aluminum electrolytic capacitor.
Owner:东莞宏强电子有限公司
Oligoarginine modified phospholipid, nanoparticles assembled by oligoarginine modified phospholipid, preparation method of oligoarginine modified phospholipid and application of nanoparticles
ActiveCN105801668ASpeed up entryImprove delivery efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsNanotechnologyChloroformateIn vivo
The invention relates to oligoarginine modified phospholipid, nanoparticles assembled by the oligoarginine modified phospholipid, a preparation method of the oligoarginine modified phospholipid and an application of the nanoparticles. After oligoarginine peptide chains are activated by DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide) / NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide), the oligoarginine peptide chains react with phosphatidyl ethanolamine, purification is performed, and oligoarginine modified phosphatidyl ethanolamine is obtained; or the oligoarginine peptide chains react with DCC / NHS activated phosphatidic acid, and oligoarginine modified phosphatidic acid is obtained through purification; or the oligoarginine peptide chains react with nitrophenyl chloroformate activated phosphatidylcholine, and oligoarginine modified phosphatidylcholine is obtained through purification. The nanoparticles assembled by the oligoarginine modified phospholipid is used for supporting genes, small-interfering RNA, polypeptides or proteinic drugs, antibodies and chemical drugs, and the formed aqueous dispersion of the drug-carrying nanoparticles is used for delivering drugs for in-vitro cells or in-vivo local intravenous injection. The nanoparticles are effectively promoted to enter the cells, and the intracellular drug delivery efficiency is improved.
Owner:天津渤化讯创科技有限公司
Harmine compound and applications of harmine compound in prevention and control of peronophthora litchi chen disease
ActiveCN105037350AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood control effectBiocideOrganic chemistryChemical structureHarmine
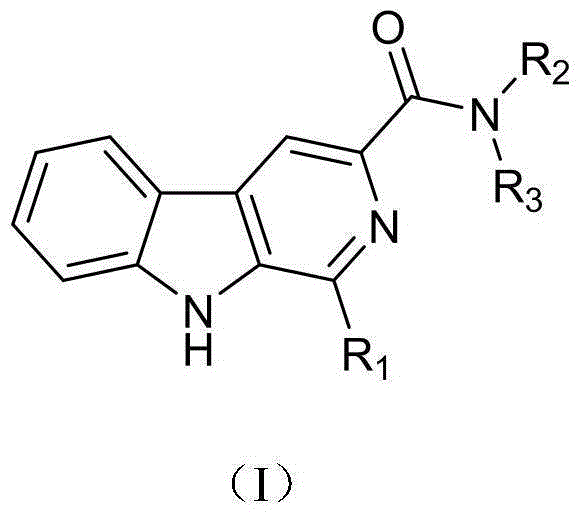
The present invention discloses a harmine compound, wherein the chemical structure formula is represented by a formula (I), R1 is selected from phenyl, p-nitrophenyl, p-methoxyphenyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, p-trifluoromethylphenyl and p-chlorophenyl, R2 is selected from ethyl, isopropyl, 2-pyridyl and 2-chlorophenyl, and R3 is selected from hydrogen and ethyl. According to the present invention, the compound provides good inhibition effects on multiple pathogenic bacteria, especially provides good inhibition and prevention and control effects on peronophthora litchi chen, has advantages of small molecular weight, simple structure, easy synthesis and the like, can effectively inhibit hypha growth, sporangium production and sporangium germination of peronophthora litchi chen, has good potential in prevention and control of peronophthora litchi chen disease, and is expected to become a new pesticide fungicide, such that the small molecule compound of the present invention can be used as the new pesticide for prevention and control of the peronophthora litchi chen disease so as to be developed and can provide the new way and means for prevention and control of the peronophthora litchi chen disease.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Photocatalytic coating
InactiveCN105602362AReduce surface temperatureImprove long-term weather resistanceAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesWater basedHeat conducting
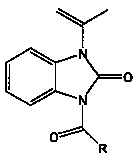
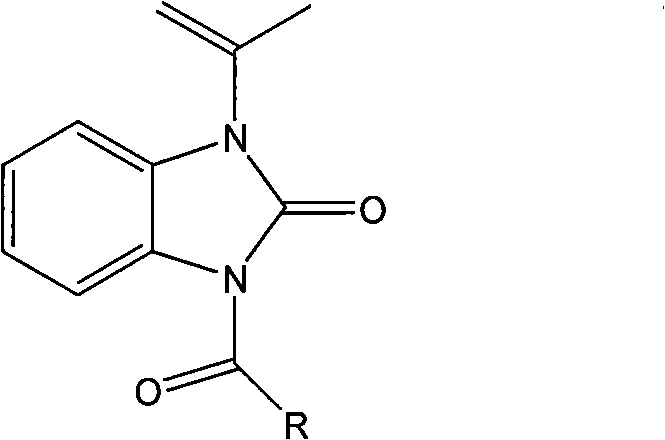
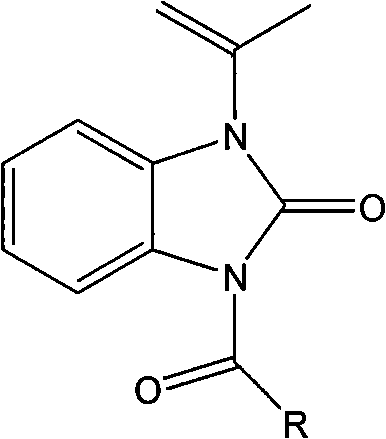
The invention discloses photocatalytic coating. The photocatalytic coating is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of water-based fluorocarbon resin emulsion, 15-59 parts of AS resin I, 1-10 parts of AS resin II, 0.1-0.2 part of nano carbon dioxide, 3-6 parts of anatase type lanthanum sulfide co-doped nano titanium dioxide, 5-25 parts of heat conducting filler, 0.25-2.5 parts of infrared reflection titanium dioxide, 0.1-0.5 part of a light stabilizer, 0.5-5 parts of a chemical resistant modifying agent, 0.5-1.5 parts of tea polyphenol, 2-4 parts of folium artemisiae argyi oil, 2-4 parts of vanillic aldehyde, 2-4 parts of thymol, 10-20 parts of acrylpimaric(2-p-nitrophenyl)thiadiazole, 1.5-2 parts of pigment and 0.5-2 parts of other auxiliaries. The photocatalytic coating can carry out good catalytic degradation and purification on gaseous pollutants in the air environment and also has good weather resistance, contamination resistance, corrosion resistance and antibacterial property.
Owner:SHENYANG NORMAL UNIV
Building method of pichia pastoris gene engineering strain for producing lipase
ActiveCN106047917AIncreased hydrolytic enzyme activityIncrease enzyme activityFungiHydrolasesLipid formationEnzymatic synthesis
The invention relates to a pichia pastoris gene engineering strain for producing lipase and a building method of the pichia pastoris gene engineering strain. During the enzymic catalytic reaction of the lipase, if the reaction promotes esterolysis in the oil-water interface, enzymatic synthesis and ester exchange can be achieved in the organic phase, and accordingly biodiesel can be synthesized by using waste edible oil, waste industrial oil and low-carbon alcohol as the raw materials. The lipase is massively fermented by transferring recombinant lipase Lip14 genes into pichia pastoris X33. P-nitrophenyl palmitate is used as the substrate to measure the long-chain lipid hydrolysis ability of the lipase, p-nitrophenyl laurate and p-nitrophenyl octoate are used to measure the medium-chain lipid hydrolysis ability of the lipase, p-nitrophenyl butyrate is used to measure the short-chain lipid hydrolysis ability of the lipase, and accordingly the long-chain, medium-chain and short-chain lipid hydrolysis activity of the lipase can be determined and a foundation is laid for the application of the lipase to the catalytic production of biodiesel.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
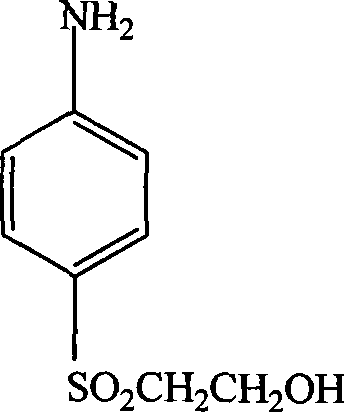
P-aminophenyl-beta-hydroxyethyl sulfone preparation method
InactiveCN101362712AShort reaction timeReduce energy consumptionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationNitro compoundDistillation
The invention relates to a method for preparing p-aminophenyl-beta-hydroxyethyl sulfone, in particular to a method for preparing beta-hydroxyethyl sulfone. The method solves the problems of high production cost, difficulty in catalyst recycling, low product yield and serious pollution to the environment existed in the prior art for preparing the p-aminophenyl-beta-hydroxyethyl sulfone. The method is as follows: p-aminophenyl-beta-hydroxyethyl sulfide and nickel aluminium alloy catalyst and solvent are added in a hydrogenation reactor; after nitrogen which removes off the air is introduced, hydrogen is introduced and the pressure of the hydrogen is controlled at 0.5MPa to 6MPa; meanwhile, stirring is carried out at the speed of 500r / min to 1000r / min and the temperature is raised to 40 DEG C to 100 DEG C for reaction for 4h to 12h; after filtration, distillation and drying, the p-aminophenyl-beta-hydroxyethyl sulfone is obtained. The method has the advantages of low production cost, easy-recycling catalyst, high product yield, high product pureness and less pollution to the environment. The pureness of the product is more than 97 percent and the yield is more than 95 percent (calculated by nitro compounds).
Owner:INST OF PETROCHEM HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
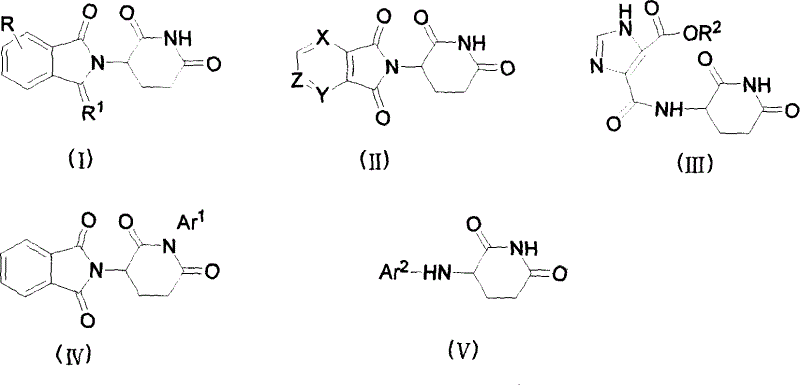
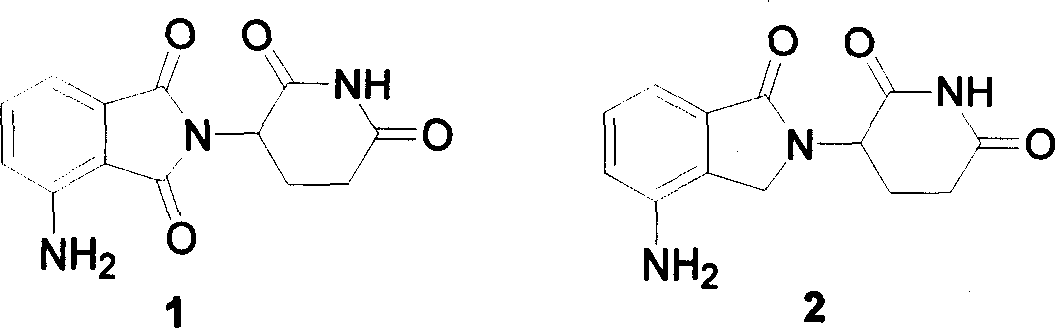
Analogue of thalidomide and preparation method
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Traditional Chinese medicine composition with antibacterial and anti-inflammation effects and preparation method of composition
InactiveCN105748764ASignificant anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effectEasy to useAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide effectAloe tomentosa
The invention discloses traditional Chinese medicine composition with antibacterial and anti-inflammation effects and a preparation method of the composition. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from 5-15 parts of Rumex crispus, 10-15 parts of dandelions, 5-10 parts of original aloe juice, 3-7 parts of lemon ferment powder, 6-10 parts of pine needle powder, 3-15 parts of common cnidium fruits, 3-17 parts of caulis lonicerae, 3-10 parts of an olive leaf extract, 5-10 parts of a red date leaf extract, 6-10 parts of a milk thistle extract, 4-10 parts of a cranberry extract and 10-15 parts of a rosin derivative which is acrylpimaric acid(2-p-nitrophenyl)thiadiazole. A special technology is adopted, multiple effective ingredients are obtained, and the scientific ratio is adopted, so that the obtained composition has significant antibacterial and anti-inflammation effects and is safe to use and free of side effects.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Mixed steroidal 1,2,4,5-tetraoxane compounds and methods of making and using thereof
Disclosed herein are mixed steroidal tetraoxanes having the following structural formula 1 wherein n is 0, 1, 2, or 3; R is H; ethanoyl, propanoyl, or benzoyl; R1 is H, methyl, ethyl, or isopropyl; R2 is H, methyl, or ethyl; R3 is H, methyl, or ethyl; R4 is H, methyl, ethyl, tert-butyl, phenyl, p-hydroxyphenyl, p-methoxyphenyl, or p-nitrophenyl, or wherein Y is a C1-C4 straight or branched-chain alkoxy, or wherein W is N, R5 is hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, or methyl ethanoate 2-yl, and R6 is hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, or n-propyl, or R5 and R6 are part of a pyrrolidine or piperidine ring; X is a C1-C4 straight or branched-chain alkoxy, a primary amino, a N-alkylamino wherein the alkyl is a straight-chain alkyl groups containing from 1 to 4 carbon atoms, methyl ethanoate-2-yl, N-phenylamino, p-nitrophenyl, N,N-dimethylamino, N,N-diethylamino, N,N-di(n-propyl)amino, N-pyrrolidino, or N-piperidino as single compounds, and any mixture of all possible stereoisomers at C(4″). n may be 0, 1, 2, or 3, and methods of making and using thereof. As disclosed herein, the mixed steroidal tetraoxanes of the present invention exhibit antimalarial, antibacterial, and antiproliferative activity. Thus, as disclosed herein, the mixed steroidal tetraoxanes of the present invention may be used to treat, prevent, or inhibit malaria, bacterial infections, and diseases and disorders associated with cell proliferation in a subject.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Animal husbandry and veterinary disinfection solution and preparation method of animal husbandry and veterinary disinfection solution
InactiveCN105748976ANon-toxicNo pollution in the processAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTurpentine OilWater quality
The invention discloses an animal husbandry and veterinary disinfection solution. The animal husbandry and veterinary disinfection solution is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 0.4 percent to 0.8 percent of bamboo vinegar powder, 0.05 percent to 0.25 percent of nano-silver mixed suspension, 0.3 percent to 0.6 percent of aloe powder, 10 percent to 20 percent of acrylpimaric(2-p-nitrophenyl)thiadiazole, 0.3 percent to 0.6 percent of calendula extract, 1 percent to 2 percent of fructooligosaccharide, 0.3 percent to 0.6 percent of jujube extract, 0.6 percent to 0.8 percent of turpentine oil, 1 percent to 3 percent of alkylphenol ethoxylate and the balance of de-ionized water. The animal husbandry and veterinary disinfection solution is high in sterilization efficiency and good in stability, has no toxin to human bodies and bred animals, has no pollution to environment and water quality, is high in safety performance and has a certain bacterium inhibition function.
Owner:XINYANG AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Forcipated diimidazoline palladium compound and its application in Suzuki reaction
ActiveCN101020701AReduce the impactEasy to manufactureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsLithium chlorideThin layer chromatographic
The present invention discloses one kind of forcipated diimidazoline palladium compound in the structure as shown and its application in Suzuki reaction. The forcipated diimidazoline palladium compound is synthesized through heating and refluxing diimidazoline benzene and palladium acetate in glacial acetic acid, the subsequent evaporating to dry, adding acetone / water solution of lithium chloride, stirring at room temperature to extract, drying, concentrating and thin-layer chromatographic separation. The compound is used in catalyzing coupling Suzuki reaction to synthesize biaryl compound.
Owner:PHARMARON BEIJING
Preparation method of functional biodegradable nano particle based on polyamino acid
ActiveCN105879048AIncrease the amount of enrichmentPromote degradationPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer dissolutionBenzyl chloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano particle based on polyamino acid. The preparation method of the nano particle based on the polyamino acid comprises the following steps of firstly adopting a hydrophobic hydroxy compound and p-nitro benzyl chloride acid ester as raw materials, and reacting to obtain a functional hydrophobic micromolecule activated by the p-nitro benzyl chloride acid ester; then adopting the functional hydrophobic micromolecule activated by the p-nitro benzyl chloride acid ester and a diamine compound as reactants, and reacting to preparing a hydrophobic amido compound; adopting the hydrophobic amido compound as an initiator, carrying out ring opening polymerization on alpha-amino acid-N-thiocarboxy anhydride compound to obtain a polymer based on the polyamino acid; finally dissolving the polymer based on the polyamino acid in water, then adding an acetone solution of the polymer, and stirring to obtain the functional biodegradable nano particle based on the polyamino acid. The obtained drug-loading targeting nano particle has higher stability, can be combined with targeting molecules so as to well gather to a tumor location, and has good therapeutical effect and low toxic and side effect on various solid tumors including human breast cancer.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG INST OF IND TECH SOOCHOW UNIV +1
2-thiazolylacrylonitrile compounds and its synthetic method and application
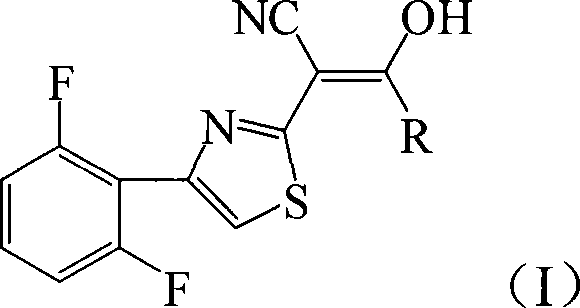
The invention discloses a 2-thiazolyl acrylonitriles coumpound, a synthesis process and an application. The structure of 2-thiazolyl acrylonitriles is showed as formula (I), wherein R is C1-C10 alkyl, C1-C5 halogenated alkyl, C3-C6 cycloalkyl, phenyl, benzyl or p-nitro phenyl. The synthesis process of the invention comprises conducting nucleophilic substitution towards2- cyanide-4-(2, 6-difluorophenyl) thiazole showed as formula (II) and acyl chloride showed in formula (III) in protonic solvent or nonprotonic solvent for 1-20h with 0-100 DEG C under the effect of acid binding agent to obtain reaction solution, and treating reaction solution to obtain 2-thiazolyl acrylonitriles compound. The 2-thiazolyl acrylonitriles compound can be used as herbicide, pesticide and pesticide, and adds new matters for the screening of herbicide, pesticide and pesticide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for the effective synthesis of optically active oxazoline-2-ketone derivative
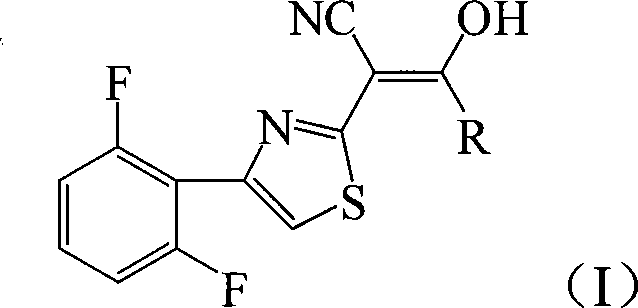
The invention discloses a method for the effective synthesis of optically active oxazoline-2-ketone derivative. The optically active oxazoline-2-ketone derivative has a structure represented by the formula (I), wherein, R is phenyl, para-methoxyphenyl, para-chlorophenyl, para-fluorophenyl, ortho-chlorophenyl, ortho-methoxyphenyl, meta-bromophenyl, 1-naphthyl, para-bromophenyl, para-nitrophenyl, para-methylphenyl or 3,4-difluorophenyl; R is phenyl, para-methylphenyl, para-methoxyphenyl, para-fluorophenyl, para-chlorophenyl, para-bromophenyl or 2-furyl. Such compounds can be obtained by means of high diastereoselectivity and high enantioselectivity of tandem reaction of organically catalytic C2 symmetrical chiral sulfur ylide and nitroolefin.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Regioselective fucosylation modification method of enzymatic nuclear glucoside class medicine
InactiveCN102965415AEasy to separateThe synthesis process is simpleFermentationFucosylationRegioselectivity
The invention discloses a regioselective fucosylation modification method of an enzymatic nuclear glucoside class medicine, and the method comprises the following specific steps of: (1) evenly mixing a buffer solution, nucleoside and p-nitro-phenyl-beta-fucoside together; (2) adding beta-galactosidase in an enzyme dosage of 1-30 U / gram of nucleoside, reacting for 5-100 hours under the conditions of 30-55 DEG C and 200 r / min, treating for 10 minutes at 100 DEG C, and performing quenching enzyme reaction; and (3) obtaining the modified product through column chromatography isolation. The method has the advantages of simple reaction process, high regioselectivity, no complex protection and deprotection steps, moderate reaction conditions, environmental friendliness, easiness for separation of products and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing antimer (R)or (S)-1,1'-bi-2-naphthol
InactiveCN1733673AHigh yieldHigh purityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationChloride2-Naphthol
The invention relates to a process for preparing chiral (R)- or (S)-1,1'-bi-2-naphthol, which comprises mixing racemic or non-racemic 1,1'-bi-2-naphthol and chiral inclusion agent by the mol ratio of 1.0:0.5-3.0 in organic polar solvent, heating, dissolving and cooling down for evolution of inclusion compound and crystallizing, decomposing the inclusion compound crystallization to obtain (S)-1,1'-bi-2-naphthol, evaporating the mother liquor, crystallizing the purifying the residue to obtain (R)-1,1'-bi-2-naphthol, the chiral inclusion agent is chloride (1S,2S)-1,3-dihydroxyl-1(nitrophenyl)-2-(N-benzyl-N,N-dimethyl) propanaminiumchloride.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Benzimidazole amide bactericide
The invention relates to a novel benzimidazole amide compound and an application thereof as an agricultural bactericide, belonging to the technical field of pesticides. The compound has the structural formula disclosed in the specification, wherein R represents an alkyl group with a carbon chain length of C1-C4, specifically a methyl, an ethyl, a propyl, a normal-butyl and an isobutyl; an alkenyl with a carbon chain length of C2-C4, specifically a vinyl, an allyl, an isopropenyl and an isobutenyl; a halogenated alkyl with a carbon chain length of C1-C2, specifically a chloromethyl group, a brooethyl, a 2-chloroethane and a 2-bromomethyl; and different substituted aryl groups specifically refer to a parachloro-penyl methyl, a p-bromophenyl methyl, a p-methoxybenzene methyl, a p-nitro phenyl; and a furfuryl.
Owner:PESTICIDE INST XIBEI AGRI & FORESTRY TECHUNIV
Foam aerosol for toilet
InactiveCN106590958AIntercept contactPrevent splashing waterInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsSodium hydroxideDiethanolamide
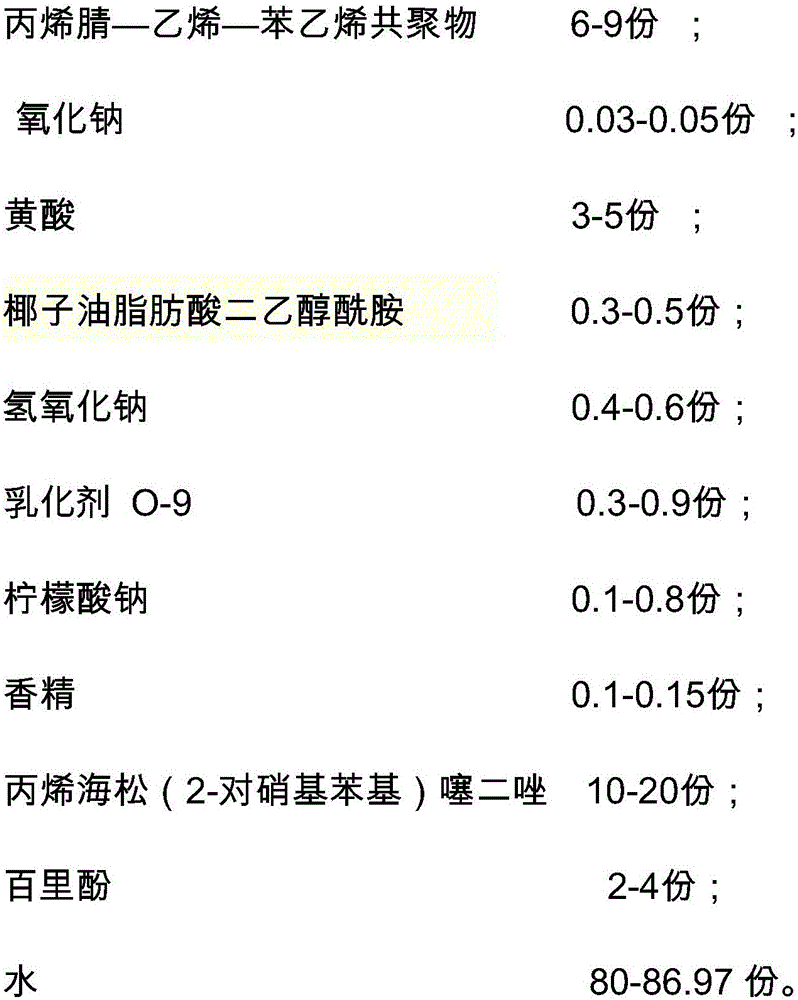
The invention discloses a foam aerosol for toilet, which is prepared from, by weight, 6-9 parts of an acrylonitrile-ethylene-styrene copolymer, 0.03-0.05 parts of sodium oxide, 3-5 parts of sulfonic acid, 0.3-0.5 parts of coconut fatty acid diethanolamide, 0.4-0.6 parts of sodium hydroxide, 0.3-0.9 parts of an emulsifier O-9, 0.1-0.8 parts of sodium citrate, 0.1-0.15 parts of essences, 10-20 parts of acrylpimaric(2-p-nitrophenyl)thiadiazole, 2-4 parts of thymol and 80-86.97 parts of water. The foam aerosol can avoid water splash and block virus contact, thus effectively achieving sanitary and healthy defense. Through isolation and coverage by the foams with combination of the fragrance of the essence, stink is effectively isolated. The foams contain cleaning factors, so that the foam aerosol can effectively clean the toilet. In addition, the foam can cover excrement, thereby avoiding visual sense.
Owner:彭良林
2-sulfohydantoin as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102924383AEasy to carryQuick checkOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical structurePhenylglycine methyl ester
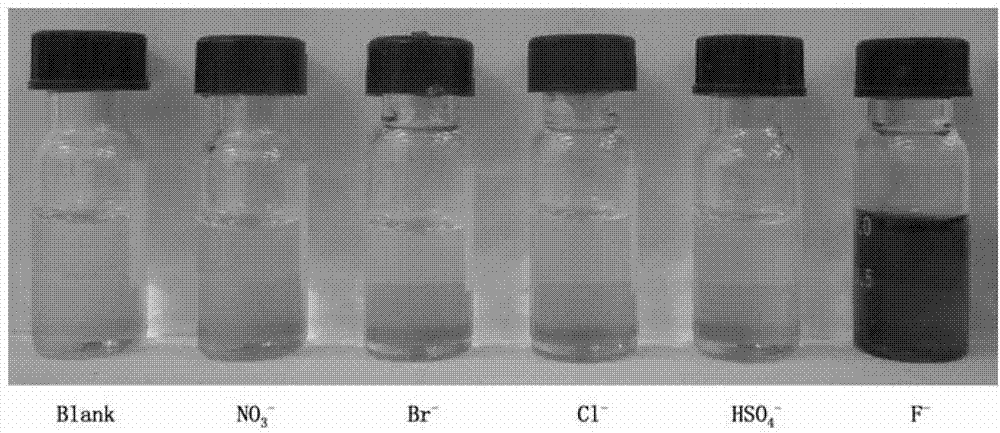
The invention relates to a sulfur-containing heterocyclic compound. The compound is 2-sulfohydantoin; a chemical structure of the 2-sulfohydantoin is shown in a formula (I) in the specification; and in the formula (I), R is one of C1-12 alkyl, p-nitrophenyl, p-cyano phenyl, p-methoxyphenyl, p-butyl phenyl, 3,5-di(trifluoromethyl)phenyl and phenyl. The 2-sulfohydantoin is obtained by reacting isothiocyanate with para hydroxy phenylglycine methyl ester, has an anion recognition performance, and can be used for detecting fluorinion.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
P-nitrophenoxy betulin (28) formyl ester and betulin derivatives synthesized therefrom, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107892709AMild reaction conditionsImprove bioavailabilityDigestive systemSteroidsSolubilityLysosome localization
The invention discloses p-nitrophenoxy betulin (28) formyl ester and betulin derivatives synthesized therefrom, and a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical fieldof pharmaceutical chemical. Four derivatives are synthesized with betulin as a matrix, that is to say, the tail end of a structure of the betulin is modified, a carbonacylation agent nitrophenyl chloroformate is introduced to a C-28 site, p-nitrophenoxy betulin (28) formyl ester is generated, and based on the p-nitrophenoxy betulin (28) formyl ester, four kinds of groups having biological activityand functionality are introduced. Specifically, with introduction of a structure of aminoethyl alcohol, the solubility is improved; with introduction of an N-amino morpholine group having a lysosomepositioning action and a triphenylphosphine active group having mitochondria targeted positioning, the product targetedly acts on cell organelles, the bioavailability is improved, and the higher biological activity is played; with introduction of a p-aminophenol structure, the synthesized compounds have certain antioxidant effects, and certain pharmacological activities are played by regulating the balance of redox in cells.
Owner:YANBIAN UNIV
PEGylated dendritic macromolecule drug carrier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109627449AOmit protectionGuaranteed efficient growthPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEthylenediamineIce water
The invention relates to a preparation method of a PEGylated dendritic macromolecule drug carrier, which comprises the following steps of: mixing trimethylolpropane triacrylate and ethylenediamine inan ice-water bath, reacting alternately in an organic solvent in a protective atmosphere at the reaction temperature of 25-60 DEG C, obtaining an amino-terminated dendritic macromolecule using ethylenediamine as a core or an acrylate-terminated dendritic macromolecule using trimethylolpropane triacrylate as a core; dissolving PEG, p-nitrophenyl chloroformate and triethylamine in an organic solvent, reacting at 20-30 DEG C, and obtaining PEGylated p-nitrophenyl carbonate after the reaction is complete; reacting the amino-terminated dendritic macromolecule using the ethylenediamine as the core or acrylate-terminated dendritic macromolecule using the trimethylolpropane triacrylate as the core with the PEGylated p-nitrophenyl carbonate in an organic solvent at a reaction temperature of 20-30 DEG C. The method is easy to operate, high in yield and low in cost; and the prepared drug carrier has excellent drug carrying performance on drugs which are difficult in dissolving in water.
Owner:惠州卫生职业技术学院
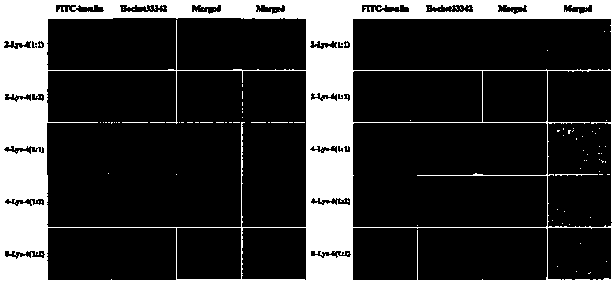
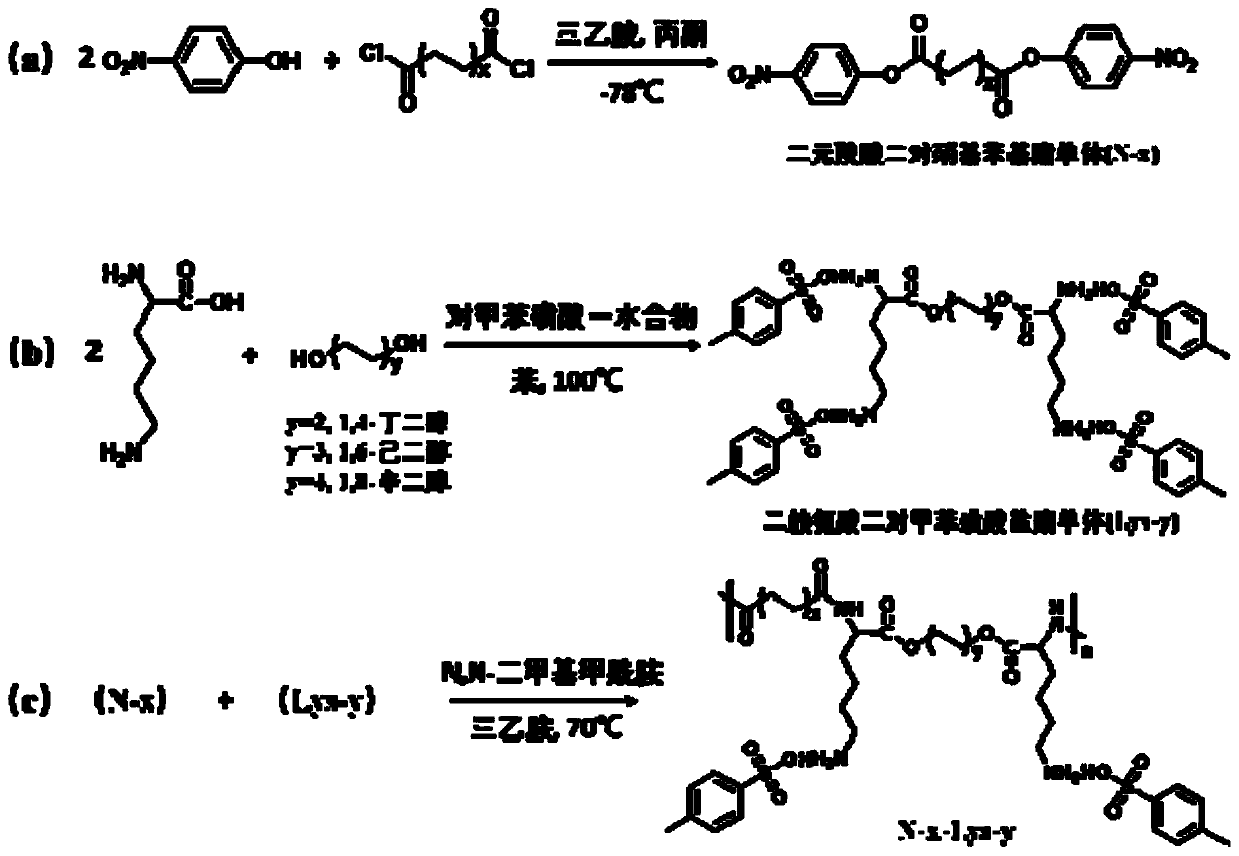
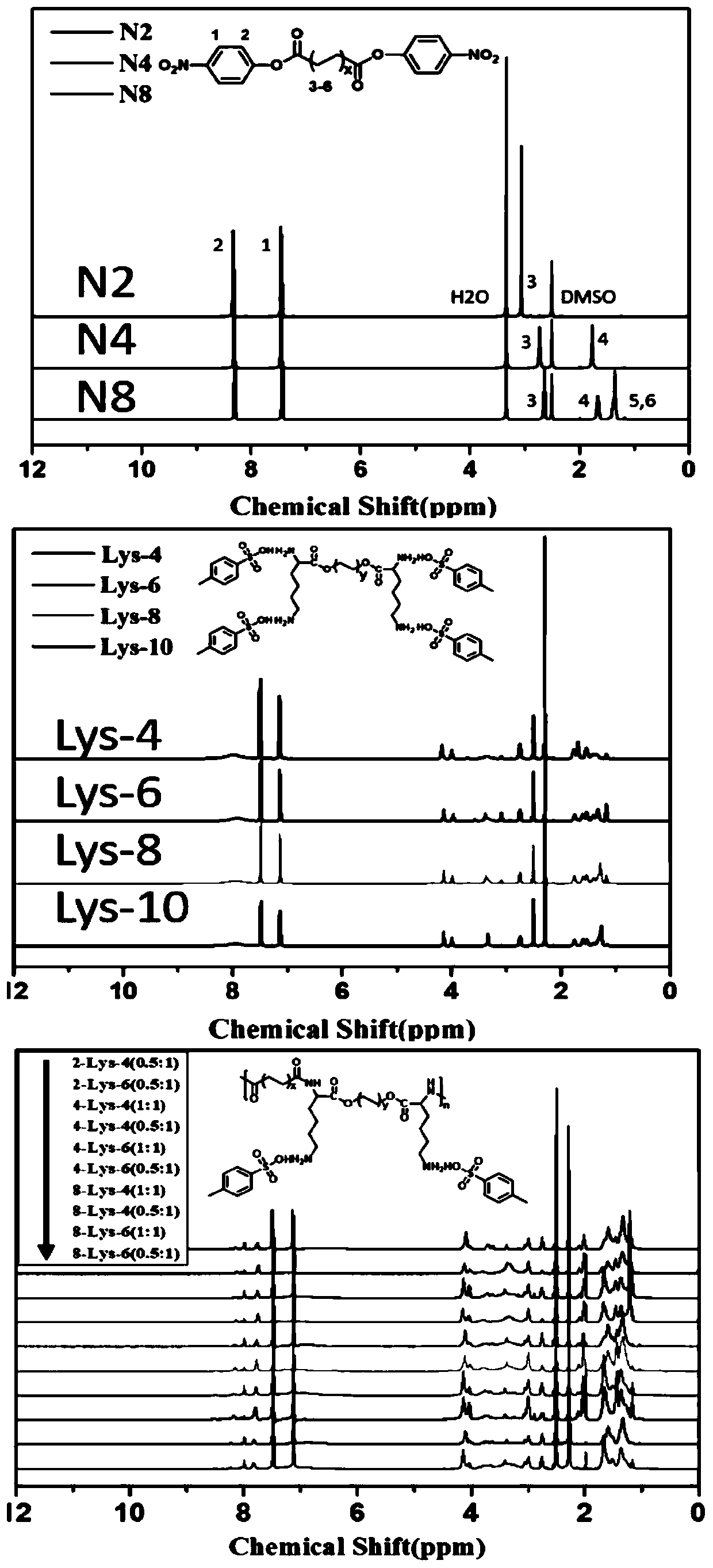
Lysine-based polyesteramide nano drug delivery system as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110804177AHigh biosecurityImprove biological activityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPolyesterPolymer science
The invention discloses a lysine-based polyesteramide nano drug delivery system as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the polyesteramide polymer includes the following steps: synthesizing a dicarboxylic acid di-p-nitrophenyl ester monomer; synthesizing a di-lysine di-p-toluenesulfonate ester monomer; and adding the dicarboxylic acid di-p-nitrophenyl ester monomer and the di-lysine di-p-toluenesulfonate ester monomer according to a mass ratio of equal to or less than 1:1 into a reaction solvent, adding triethylamine dropwise under stirring at 65-85 DEG C as a reaction catalyst, and performing a heating reaction at 60-80 DEG C for 24-96 h to obtain the polyesteramide polymer with good water solubility. The polyesteramide polymer can efficiently load and deliver and controllably release water-soluble protein drugs, has good biosecurity and drug release, and significantly improves the stability and bioavailability of the protein drugs in a systemic circulation.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
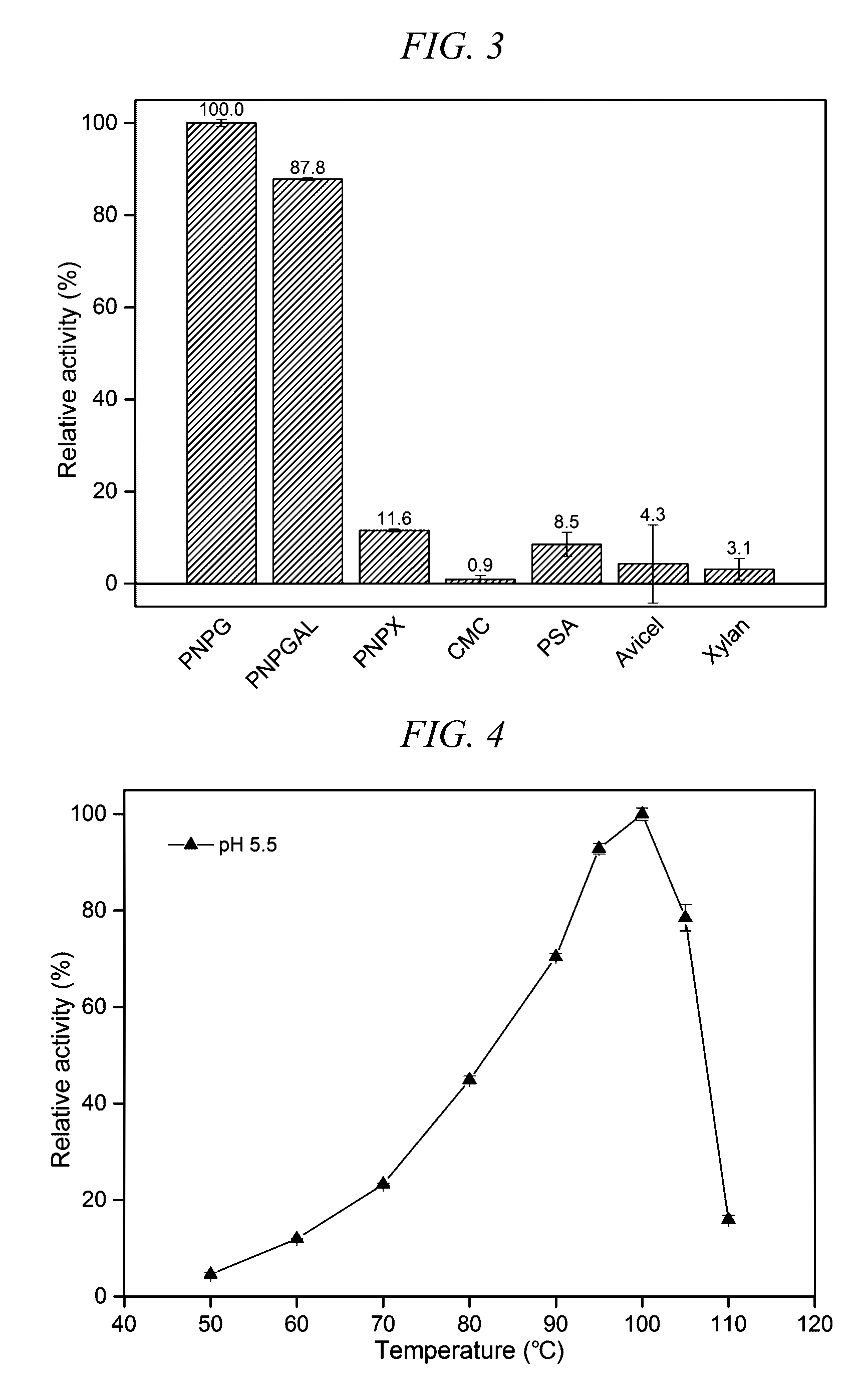
Thermostable beta-glucosidase
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com