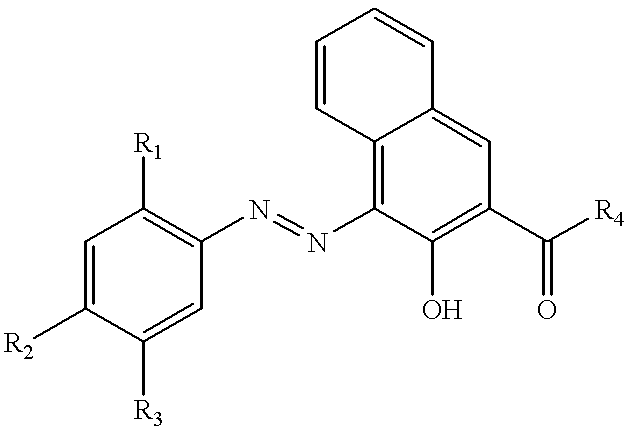
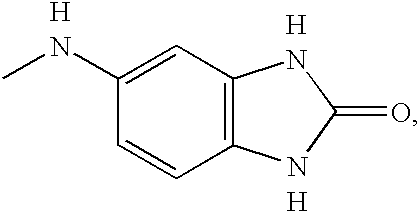
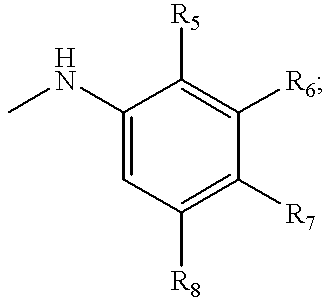
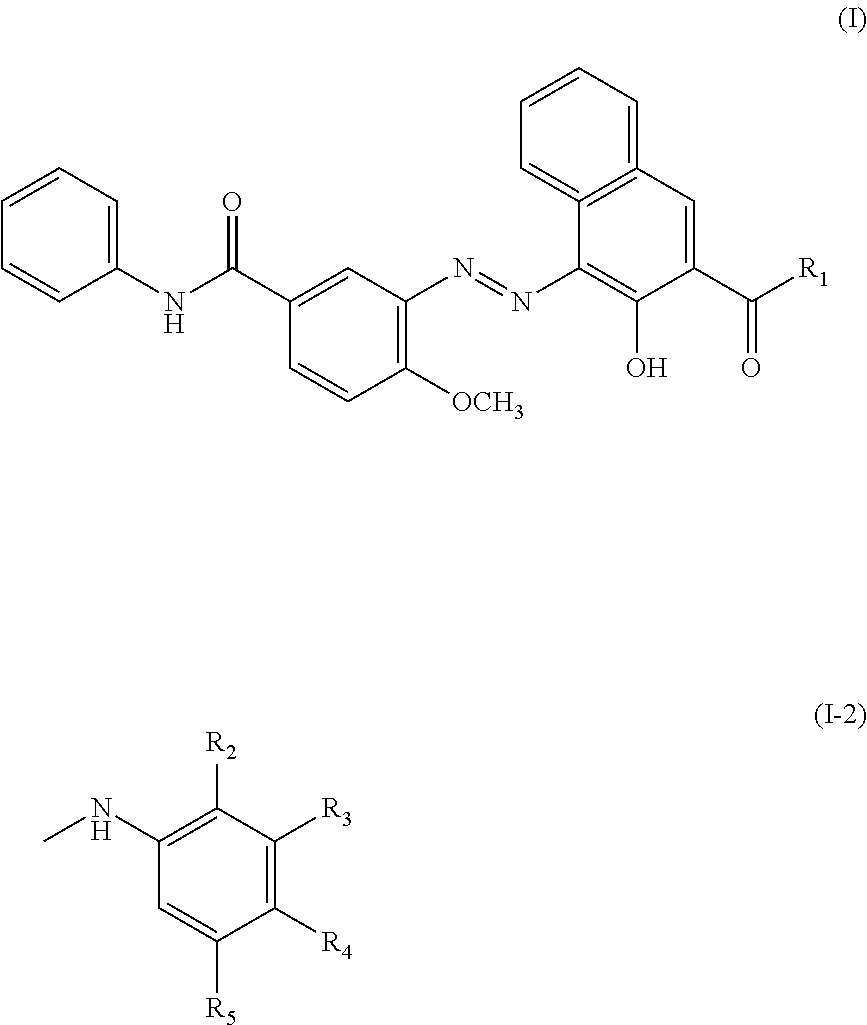
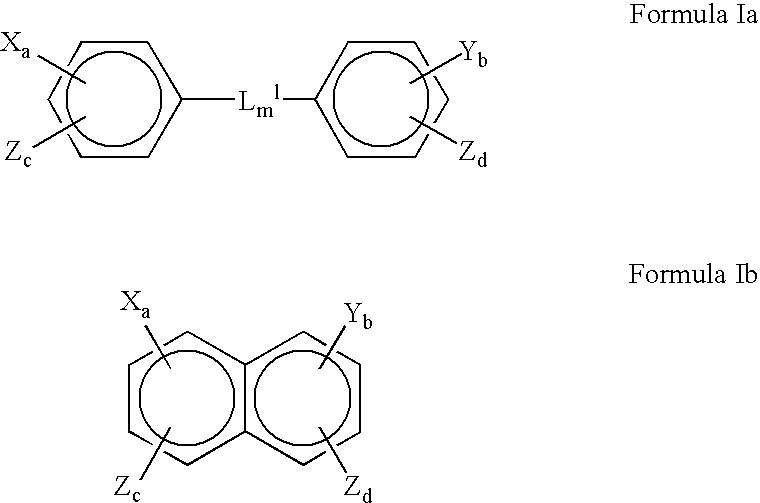
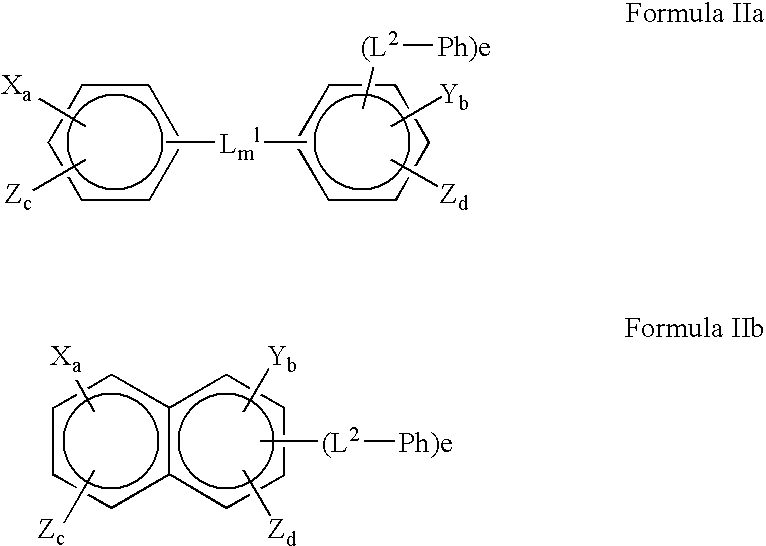
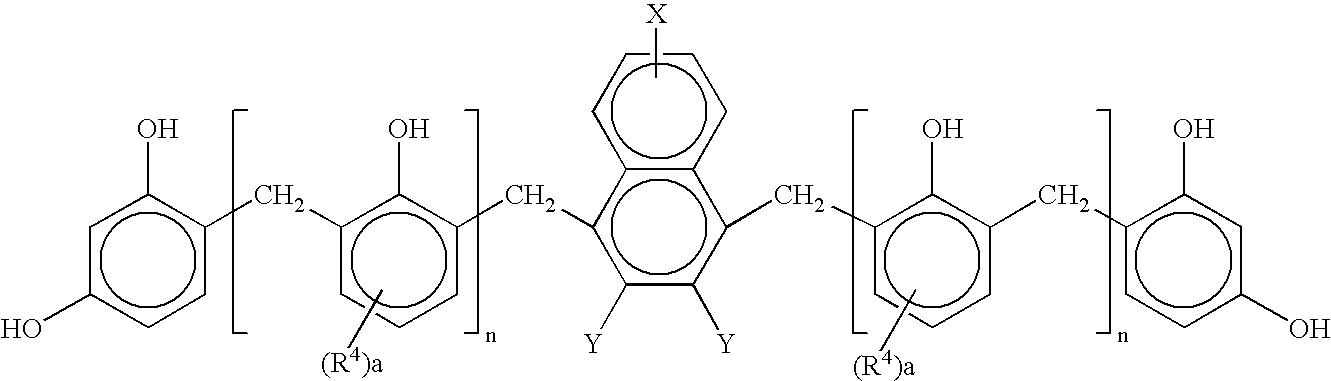
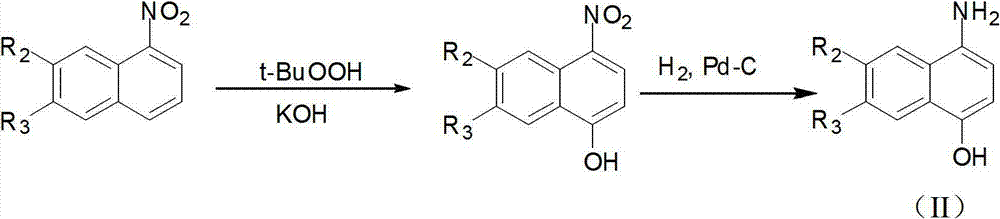
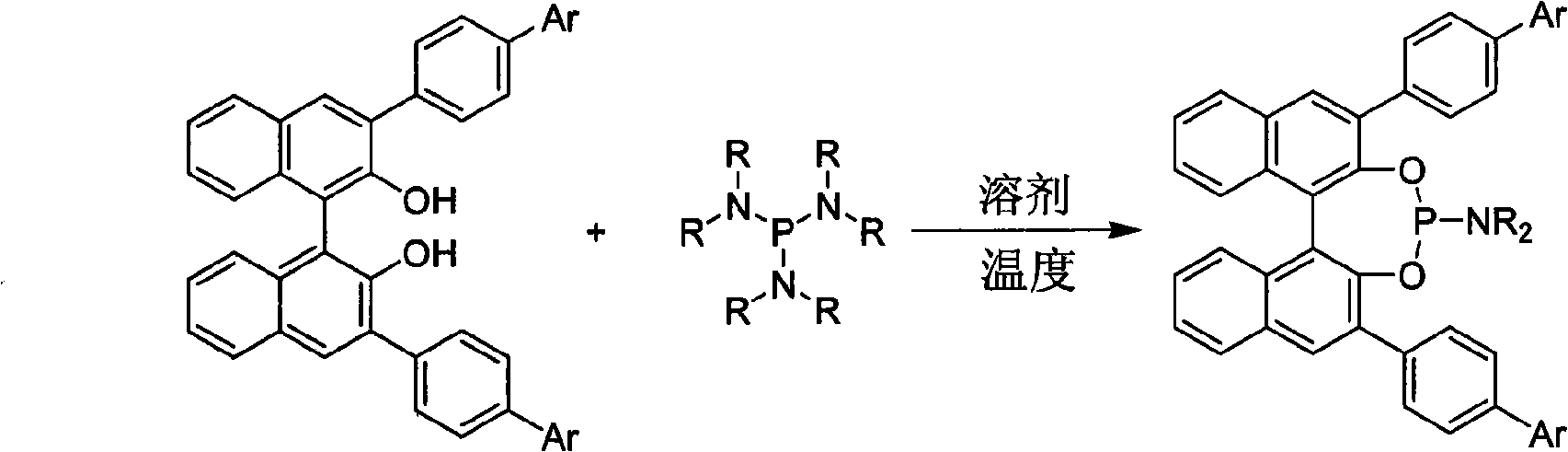
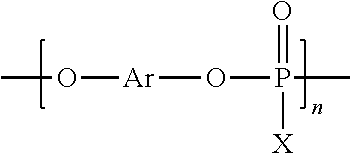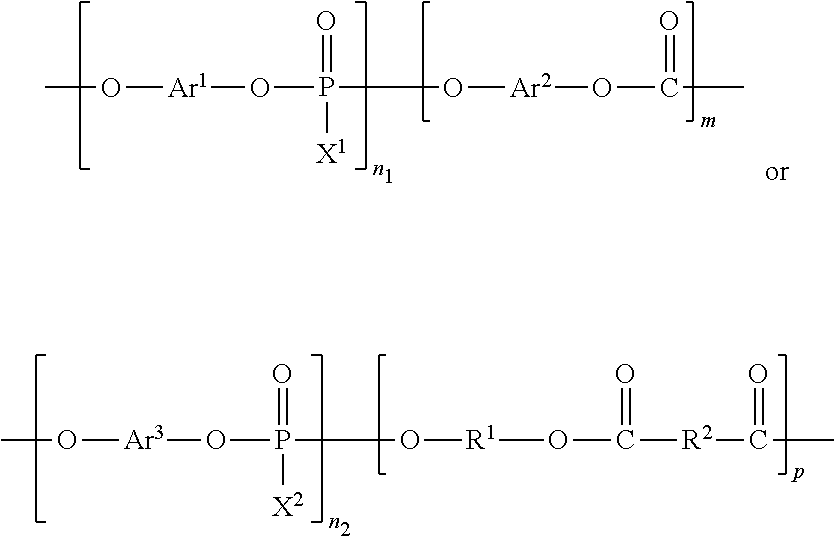Patents
Literature
559 results about "Alpha-naphthol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Environment-friendly type alkali lignin modified phenolic resin adhesive and preparation method thereof
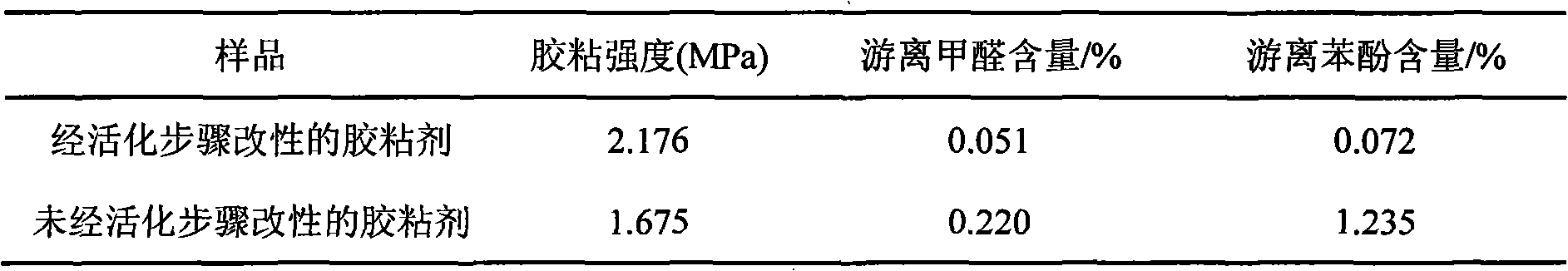
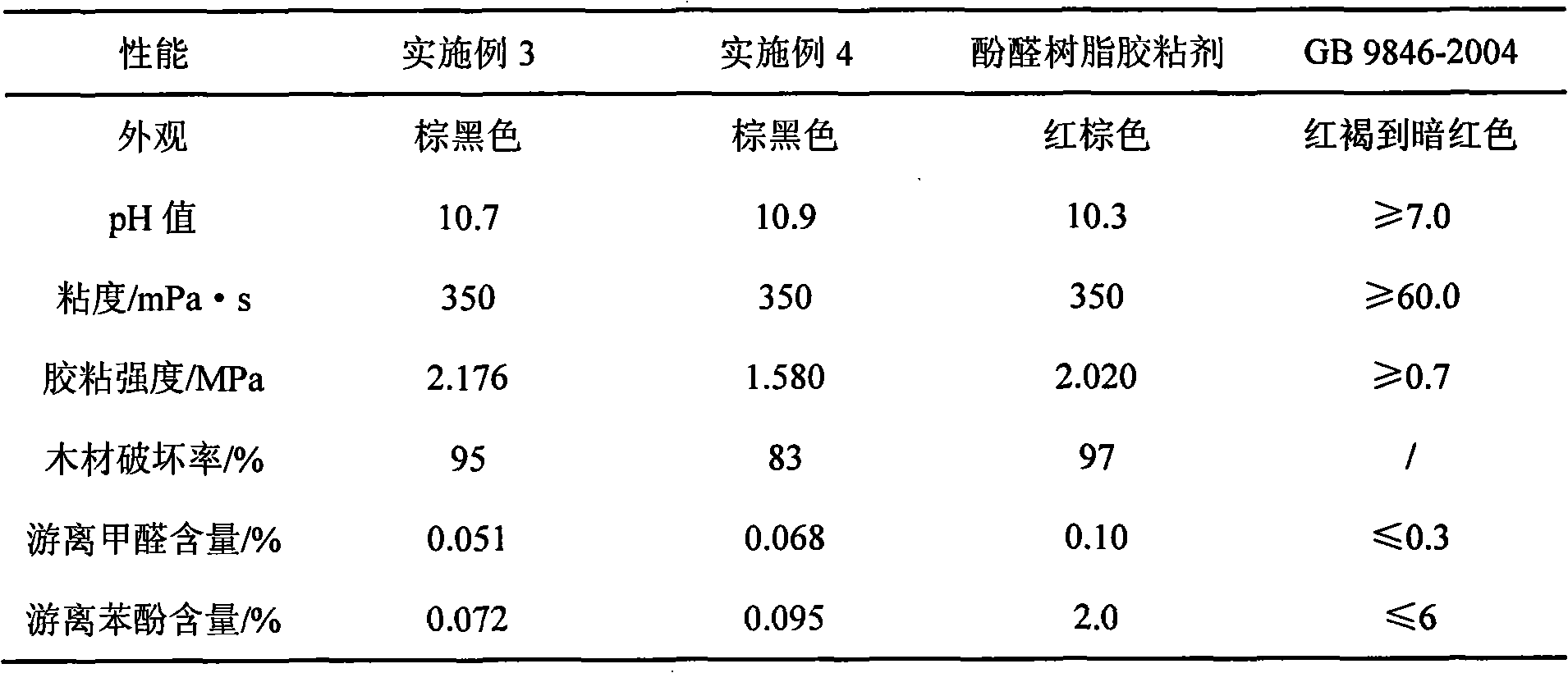
InactiveCN101358120AGood water resistanceLess phenolAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesProduct propertyPhenols
The present invention relates to an environment-friendly alkali-lignin-modified phenolic resin adhesive and a preparation method thereof. The method includes the following steps: water is added into alkali lignin powder, acid is then added, and under a temperature between 100 DEG C and 120 DEG C, acidolysis lasts for one to three hours; desugarized alkali lignin is obtained; the desugarized alkali lignin powder, sodium hydroxide and water are uniformly mixed, oxidant and 2-naphthol are added for reaction, the temperature is reduced to 45 DEG C to 50 DEG C, formaldehyde and phenol are added so that polycondensation reaction occurs, and the environment-friendly alkali-lignin-modified phenolic resin adhesive is prepared. The method adopts acidolysis desugarization to reduce a great deal of alcoholic hydroxyl content in the alkali lignin and modifies the alkali lignin by alkaline hydrolysis, degradation and nucleophilic addition reaction, thus greatly increasing the chemical reaction activity of the alkali lignin, the amount of toxic phenol required in the technique of preparing modified phenolic resin is little, and the residual phenol and formaldehyde are less, so the environment-friendly alkali-lignin-modified phenolic resin adhesive has the advantages of green production technique and product properties.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
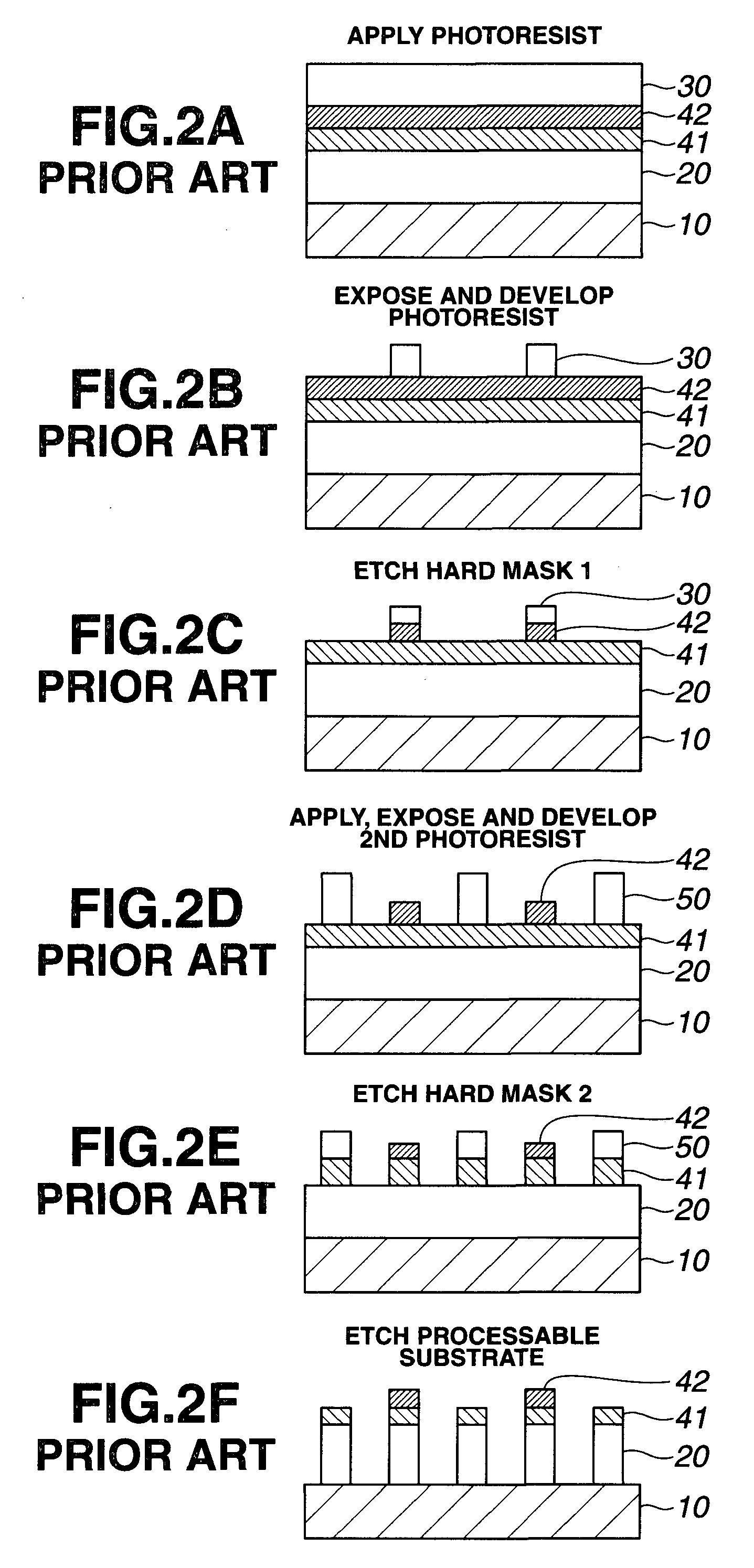
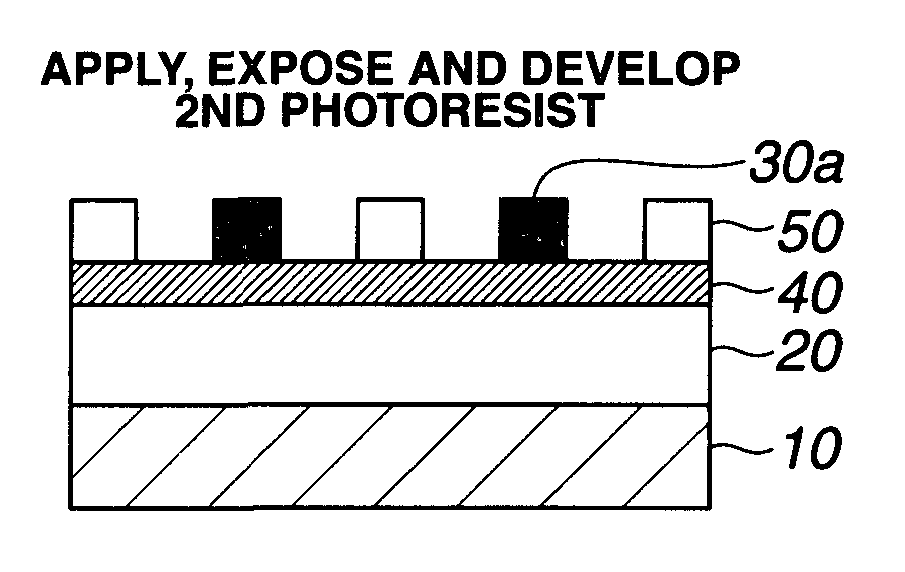
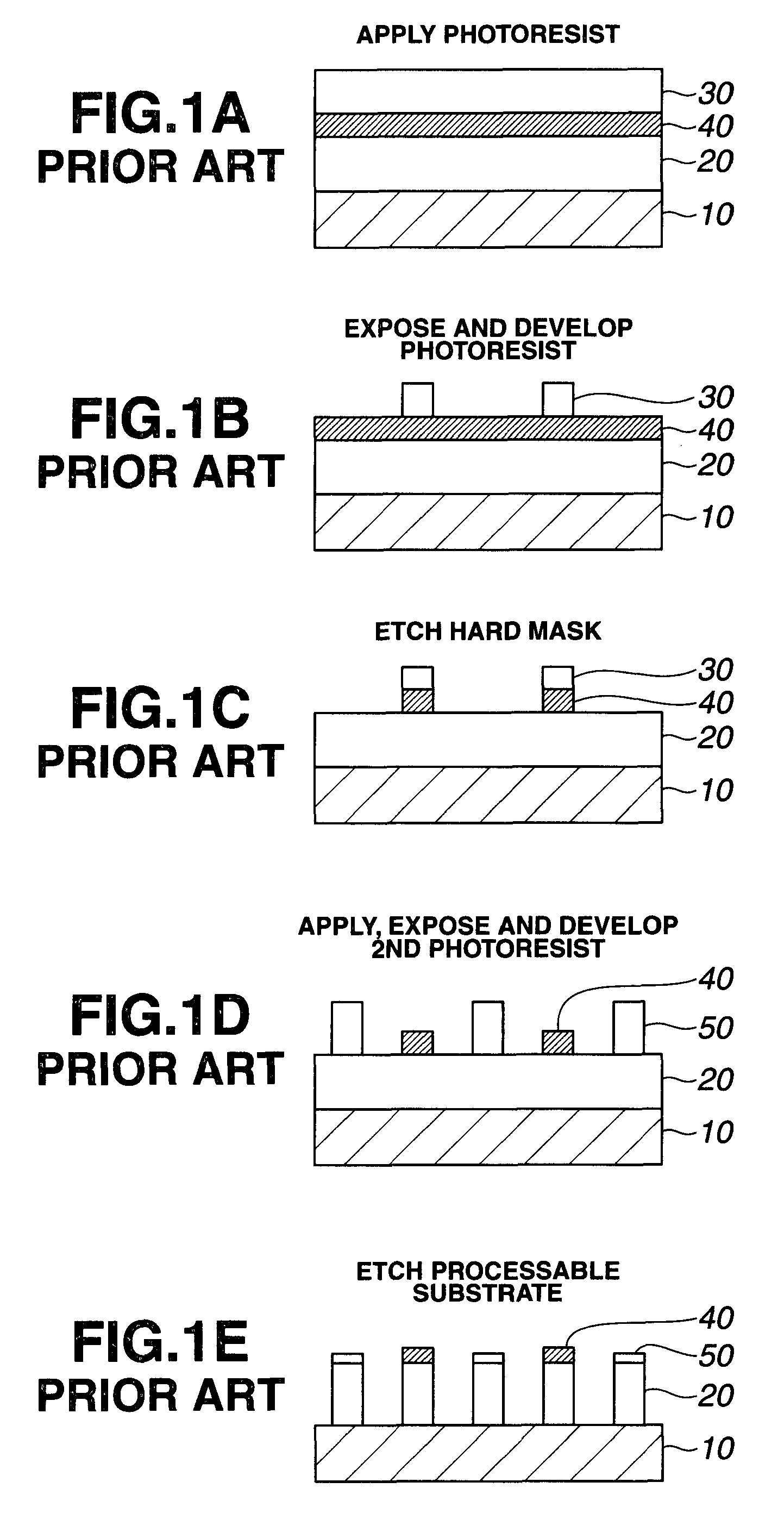
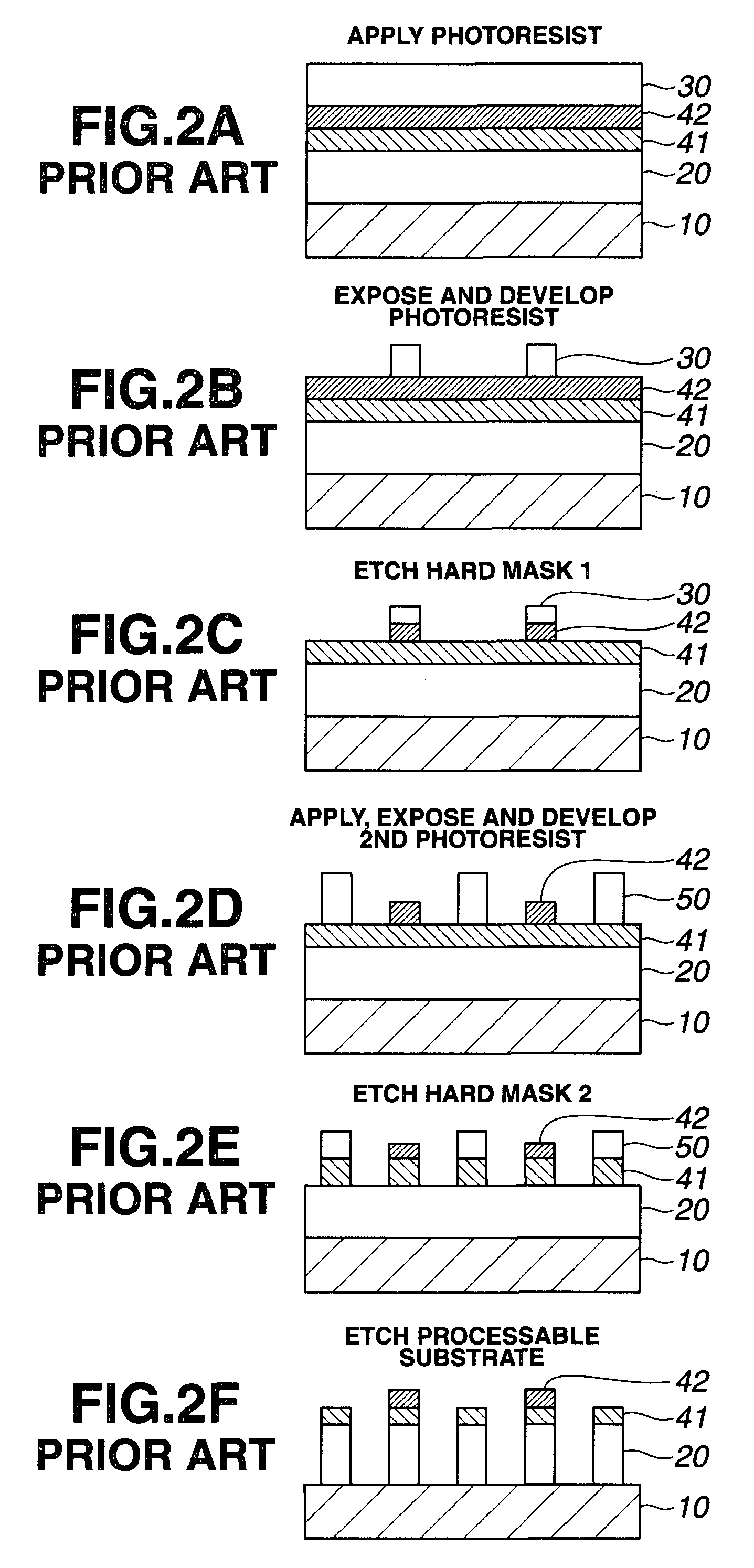
Patterning process and resist composition used therein
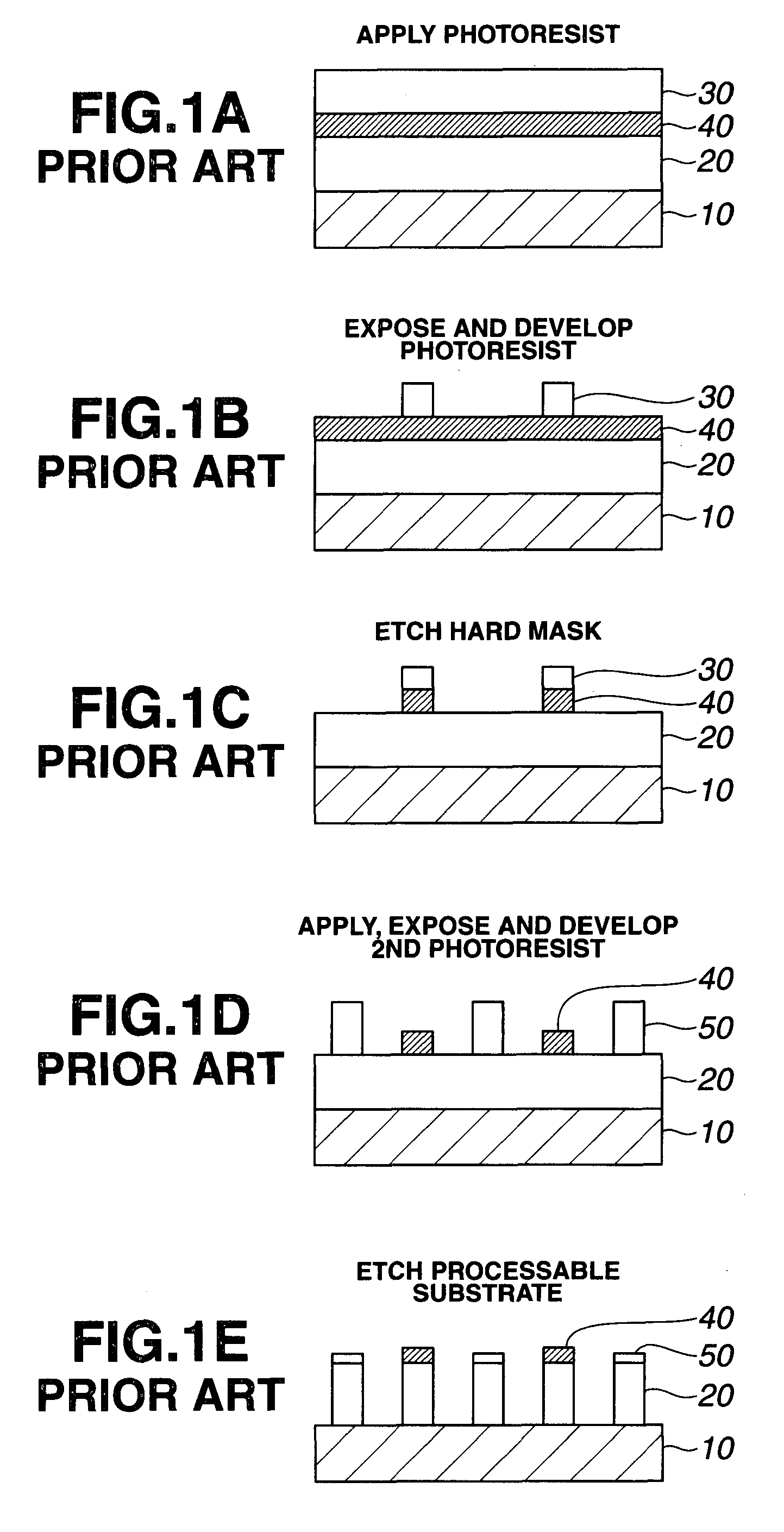
A pattern is formed by applying a first positive resist composition onto a substrate, heat treatment, exposure, heat treatment and development to form a first resist pattern, the first positive resist composition comprising a polymer having copolymerized recurring units having naphthol and recurring units with an alkaline solubility that increases under the action of acid; causing the first resist coating to crosslink and cure by irradiation of high-energy radiation of sub-200 nm wavelength; further applying a second positive resist composition onto the substrate, heat treatment, exposure, heat treatment and development to form a second resist pattern. The double patterning process reduces the pitch between patterns to one half.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
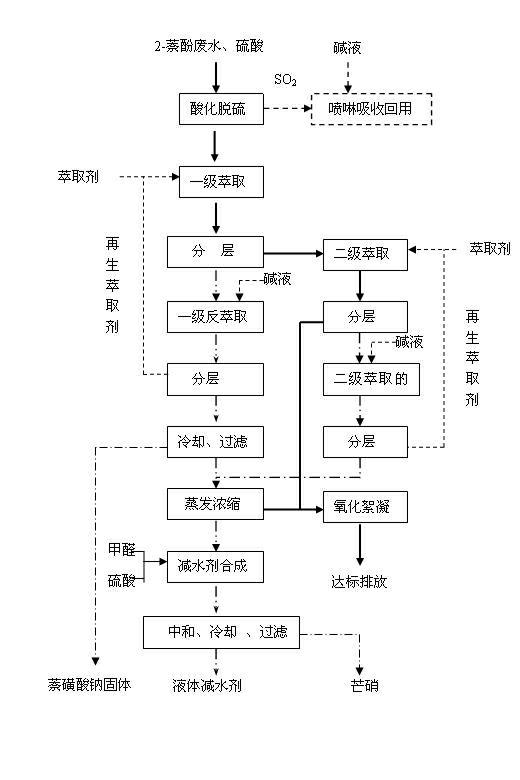
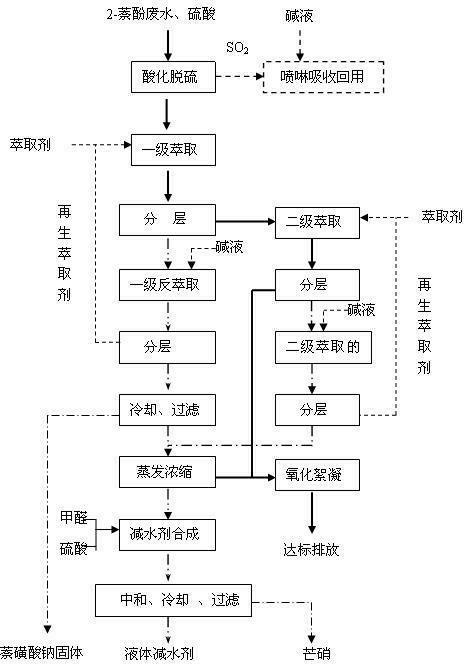
Comprehensive treatment and resource utilization technology of 2-naphthol production wastewater
ActiveCN102633399AAchieve governanceImplement resourcesMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterSulfonateAlpha-naphthol
The invention discloses a comprehensive treatment and resource utilization technology of 2-naphthol production wastewater. In the technology, the 2-naphthol production wastewater is directly acidified, and the discharged SO2 gas is absorbed and recycled by alkaline liquid; after the desulfurization wastewater is filtered to remove insoluble substance, two-level extraction is performed by use of acomplexing extracting agent; the extract phase is subjected to stripping by alkaline liquid, and the regenerated extracting agent is circularly utilized; the first-level strip liquor is cooled and filtered to obtain naphthalene sulfonate solid which is reused in a 2-naphthol hydrolysis naphthalene blowing process; the filtrate and the strip liquor of the second-level extraction are transferred toan evaporation system for evaporation concentration and then fed to a water reducing agent synthesis process; and the evaporation condensate water and the raffinate phase of the second-level extraction are subjected to oxidation flocculation treatment to reach the standard. The technology disclosed by the invention has reasonable design and treats the 2-naphthol production wastewater while realizing resource utilization of the wastewater.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
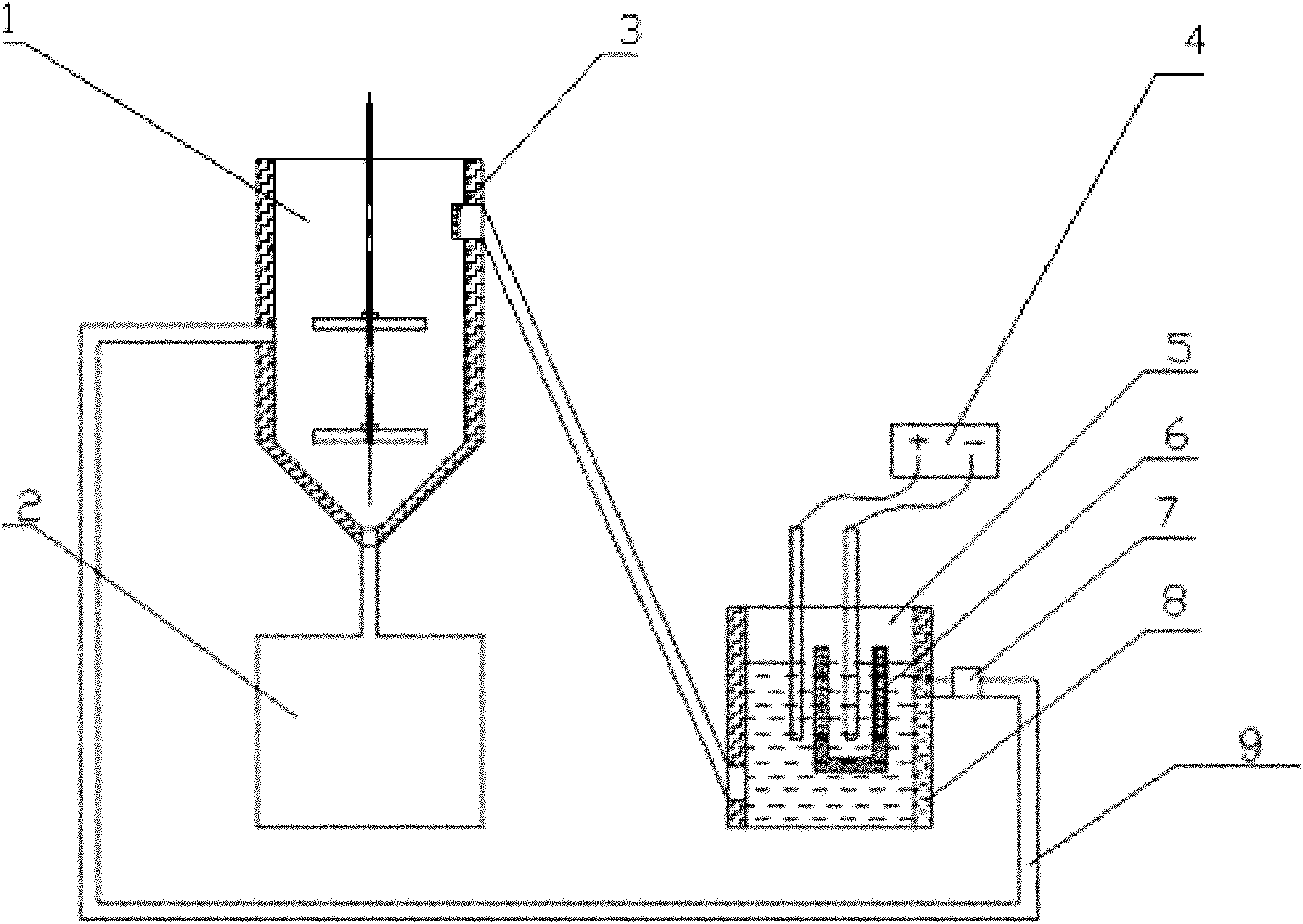
Method and device for recovering metallic lead from lead plaster of waste lead-acid storage battery
ActiveCN102031380AHigh concentrationConcentration unchangedPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementLead dioxideSlag
The invention belongs to recovery treatment on lead plaster of a waste lead-acid storage battery. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing the lead plaster of the waste lead-acid storage battery with waste sulfuric acid in the waste lead-acid storage battery according to the design requirement and roasting; adding roasting sand in a stirring kettle; adding tap water to a water level line of the device and stirring the roasting sand; adding a proper amount of calcium acetate, acetic acid and nitric acid; starting a solution circulating system pump, leaching out the roasting sand and maintaining the concentration of lead acetate to be saturated; adding a proper amount of bone glue and beta-naphthol, electrolyzing immersion liquid, recovering the metallic lead at the cathode and recovering lead dioxide at the anode; press filtering residues to obtain lead-off slag and filtrate; and adding calcium carbonate in the filtrate and recycling. The device mainly comprises a leaching part, a press filtration part, a circulating part and an electrolysis part, and concretely includes eight key components of the stirring kettle, a press filter, an overflow port, an electrolysis direct current power supply, an electrolytic cell, a cathode titanium basket, a corrosion resistant pump and a heating element.
Owner:北京绿色引领环保科技研究院有限公司
Patterning process and resist composition used therein
A pattern is formed by applying a first positive resist composition onto a substrate, heat treatment, exposure, heat treatment and development to form a first resist pattern, the first positive resist composition comprising a polymer having copolymerized recurring units having naphthol and recurring units with an alkaline solubility that increases under the action of acid; causing the first resist coating to crosslink and cure by irradiation of high-energy radiation of sub-200 nm wavelength; further applying a second positive resist composition onto the substrate, heat treatment, exposure, heat treatment and development to form a second resist pattern. The double patterning process reduces the pitch between patterns to one half.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Toner and image forming method
InactiveUS6667140B2Excellent characteristicsGood reproducibilityDevelopersElectrographic processes using charge patternColor imageWax
A color toner (magenta toner) showing not only color image forming performances such as color reproducibility, gradation characteristic, light-fastness, full-color image forming characteristic and a chargeability but also excellent in matching with various members of an electrophotographic apparatus is produced from a binder resin, a wax component and a specific monoazo pigment composition. The monoazo pigment composition is characterized by a principal monoazo pigment of a specific structure and specified amounts of a beta-naphthol derivative and an aromatic amine, usable as materials for synthesizing the monoazo pigment.
Owner:CANON KK
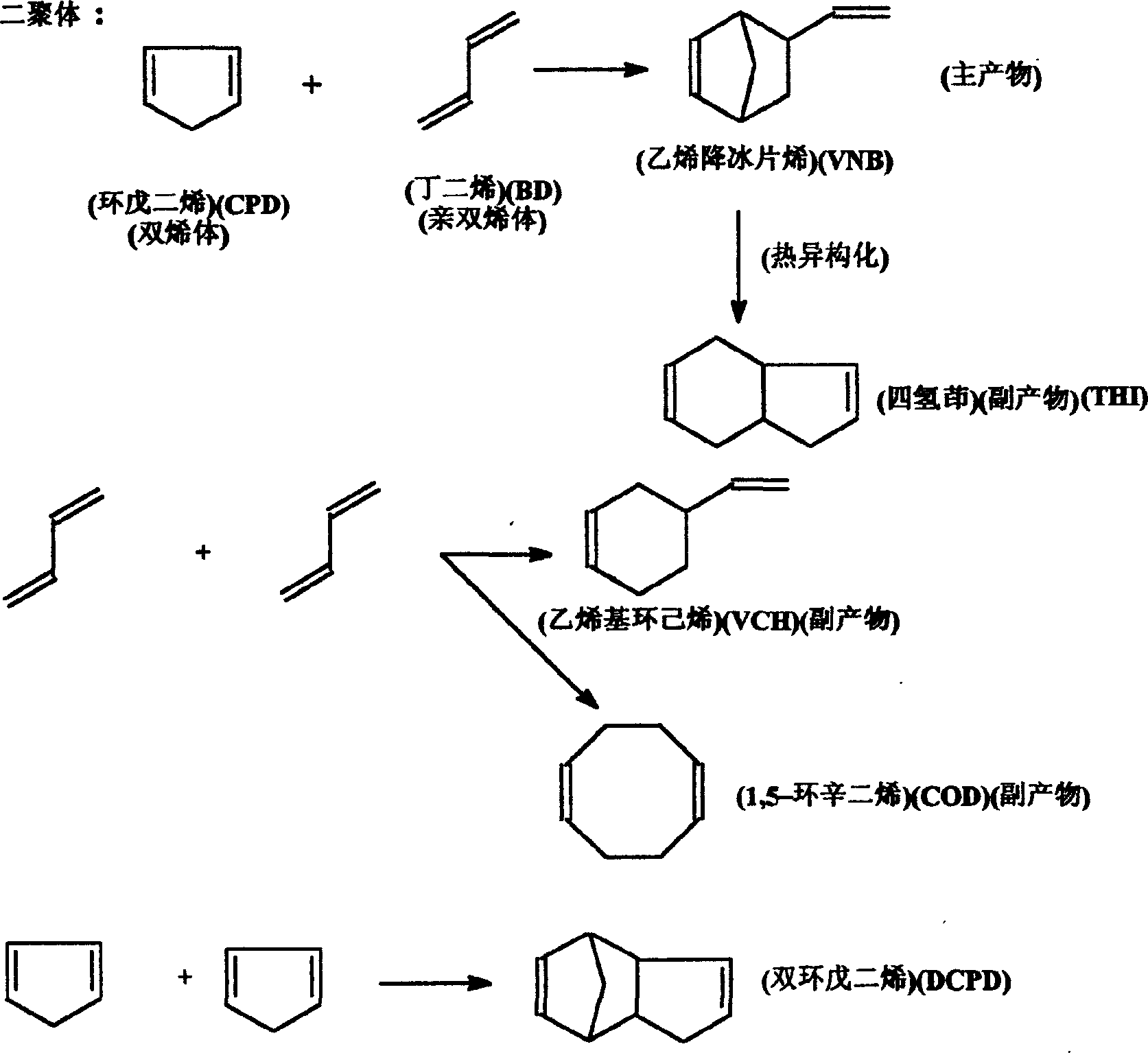
Method for synthesizing 5-vinyl-2-norbornaene
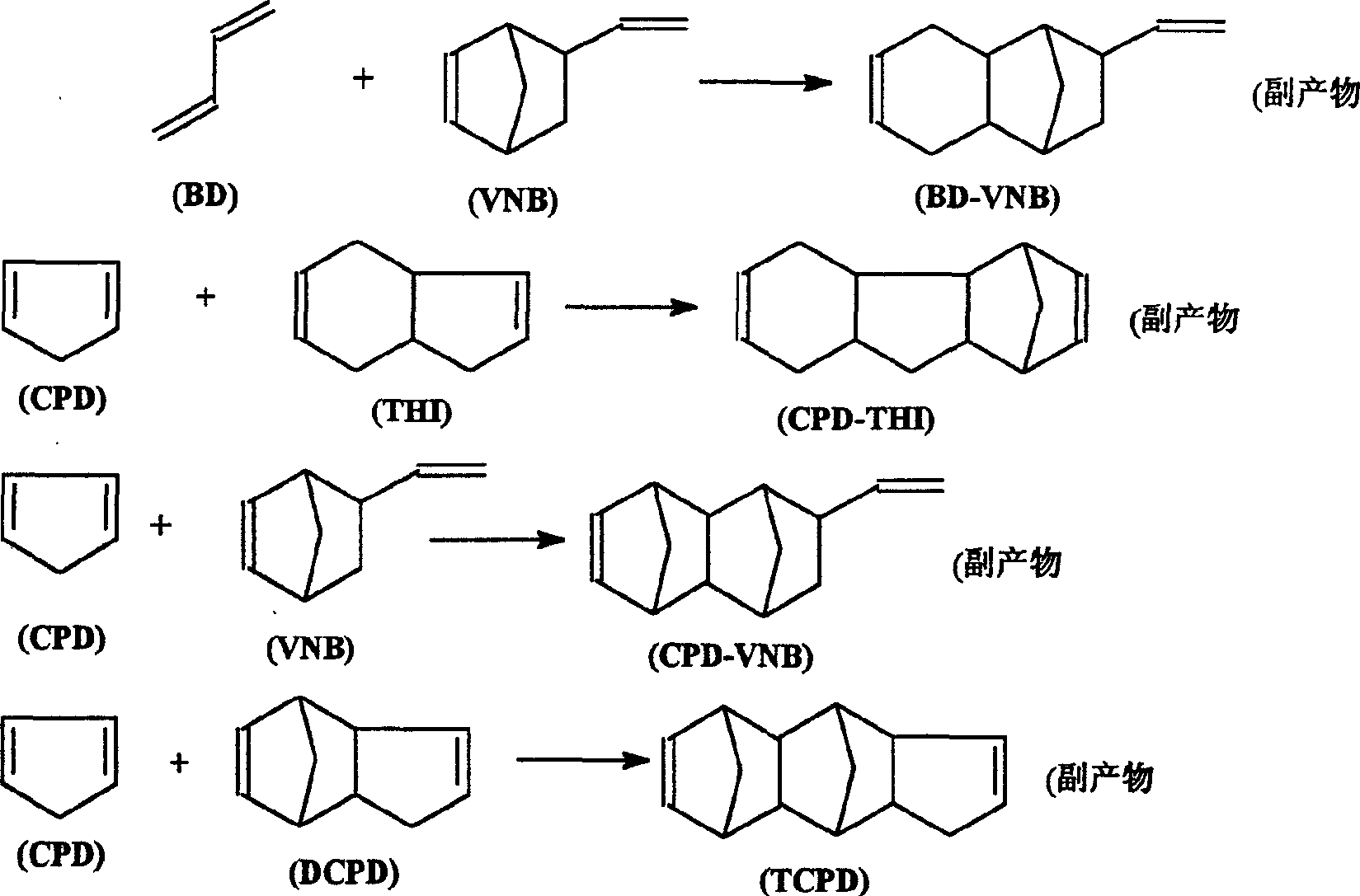
InactiveCN1580015AFlexible operationIncrease elasticityHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionAlpha-naphtholToluene
The invention refers to the synthesizing method of 5-ethylene-2-norborene. The mol ratio of the butadiene and cyclopentadiene is 1-2:1. The invention chooses toluene or normal hexane as the solvent and the weight ratio of the reactants added to the solvent is between 20% and 30%. It chooses alpha-naphthol as the inhibitor and its dosage is between 50ppm and 3000ppm of the reactants. We put the material into the reaction kettle, increase the temperature when or after whisking and make them reacting for between 0.25 hour and 4 hours at the temperature of between 130deg.C and 160deg.C and at the pressure of between 1MPa and 8MPa. Or after being mixed we put the material into the reaction kettle or the tubular reactor and stay for between 0.25 hour and 1.0 hour at the temperature of between 130deg.C and 160deg.C and at the pressure of 1.8MPa. The weight ration of the dicyclopentadiene in the material of cyclopentadiene is less than between 5% and 8%. The invention obviously increases the yield of the turnoff by over 5mol%.
Owner:吉林市大宇化工有限公司
Non-cyanide silvering brightener and plating solution thereof
The invention relates to a non-cyanide silvering brightener and a plating solution thereof. The non-cyanide silvering brightener uses water as solvent and comprises the following main components: 10-20g / L of sodium dodecyldibenzenesulphonate, 15-30g / L of beta-naphthol ethoxylate, 0.8-2g / L of hydroxyethyl ethylenediamine triacetic acid (HEDTA), 0.5-3g / L of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 5-15g / L of urea, 3-18g / L of polyethylene glycol, 40-80g / L of sulfur-containing heterocyclic compound and 5-15g / L of nitrogen-containing carboxylic acid. The brightener of the invention does not contain cyanide, the mirror surface of the coating is bright, the same effect of cyanide-containing silvering can be realized; the performance tests of the coating show that the color of the coating obtained by using the non-cyanide bright silvering plating solution of the invention is difficult to change, and the coating has low brittleness and good adhesive force and can meet the requirements on coating in different application aspects.
Owner:济南德锡科技有限公司
Magenta toner
Provided is a magenta toner having a toner particle containing a binder resin, a wax and a colorant, wherein the colorant contains a specific amount of a compound (1), the colorant also contains one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of a naphthol compound, a quinacridone compound and a lake compound thereof in addition to the compound (1), and the binder resin contains a specific amount of a polyester resin.
Owner:CANON KK
Reduced graphene oxide @ZIF-8 composite-modified electrode and preparing method and detection application thereof
ActiveCN110412096AUniform particle sizeEasy to prepareMaterial electrochemical variablesDispersityComposite film
The invention discloses a reduced graphene oxide @ZIF-8 composite-film-modified electrode, a preparing method thereof and application of the electrode in simultaneously detecting naphthol isomers. According to the preparing method, a 2-methylimidazole solution is added into a reaction tube containing a graphene oxide agar gel matrix, a natural diffusion and penetration method is adopted for preparing a graphene oxide @ZIF-8 nano-compound, then a sample is divided into three layers according to the diffusion depth, afterwards, thermal reduction is conducted to prepare a reduced graphene oxide @ZIF-8 nano-compound, and then the corresponding modified electrode is prepared. The obtained modified electrode has the advantages of large effective area, many active sites, good dispersity and the like. Reduced graphene oxide and ZIF-8 overcome mutual defects, the synergistic effects of the reduced graphene oxide and ZIF-8 in the aspect of improving direct electrochemistry and electro-catalyticperformance are achieved, and the conductivity and catalytic performance of the modified electrode are improved. The obtained modified electrode simultaneously detects the high sensitivity of the naphthol isomers and has the advantages of being low in detection limit, wide in detection range, high in response speed and the like.
Owner:青岛鸿硅高沃新材料科技有限公司
Method for preparing stable tin methanesulfonate solution
InactiveCN103952718AImprove direct yieldQuality improvementElectrolysis componentsOrganic chemistryMeth-Ascorbic acid
The invention belongs to the field of tin chemical engineering and in particular relates to a method for preparing a stable tin methanesulfonate solution. The method comprises the steps of preparing anode and cathode sheets from refined tin, adding stabilizers into methanesulfonic acid to prepare an anolyte, adding electroplating additives into methanesulfonic acid to prepare the catholyte, shade, separating the anolyte from the catholyte by an anion separator, preparing a crude tin methanesulfonate solution by a direct current electric melting method, and concentrating the crude tin methanesulfonate solution in vacuum under the protection of inert gas to obtain the stable tin methanesulfonate solution, wherein the stabilizers are phenol, ascorbic acid or tartaric acid and the electroplating additives are phenol sulphonic acid, latex, gelatin, cresol, aloin, cresylic acid or beta-naphthol. The stable tin methanesulfonate solution prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of stable quality and no precipitation, is difficult to oxidize and discolor, and has the advantages of simple preparation process, low cost, environment friendliness and the like, and good popularization and application value are achieved.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN
Method for measuring content of magnesium oxide in iron ores
ActiveCN102636617ASimple methodLow costAnalysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using titrationSodium hydroxideMagnesium ion
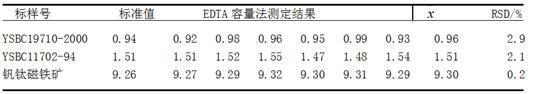
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of magnesium oxide in iron ores, relates to a detection method, and particularly relates to a method for measuring the content of magnesium oxide in depositing iron rocks and ores. The method includes adopting sodium hydroxide as a fusing agent to melt an iron ore sample in a high-temperature furnace and leading magnesium ions to enter solution after acidification by aid of nitric acid; and adding benzilic acid, ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA) solution and triethanolamine to mask metal ions of titanium, iron, aluminum, alkaline earth and the like, generating magnesium hydroxide deposit in alkaline solution with the pH (potential of hydrogen) larger than 12, depositing to generate hydrochloric acid solute after filtering, using acid chrome blue K and naphthol green B as indicators in solution with the pH of 10, adopting ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) standard solution for titration, and obtaining the content of the magnesium oxide. The method has the advantages of simplicity, convenience, speediness, low cost, fine reproducibility and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN PHOSPHATE CHEM GROUP CORP
Novel aromatic prenyltransferases, nucleic acids encoding same and uses therefor
ActiveUS20060183211A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrenyltransferase activityIsoprene
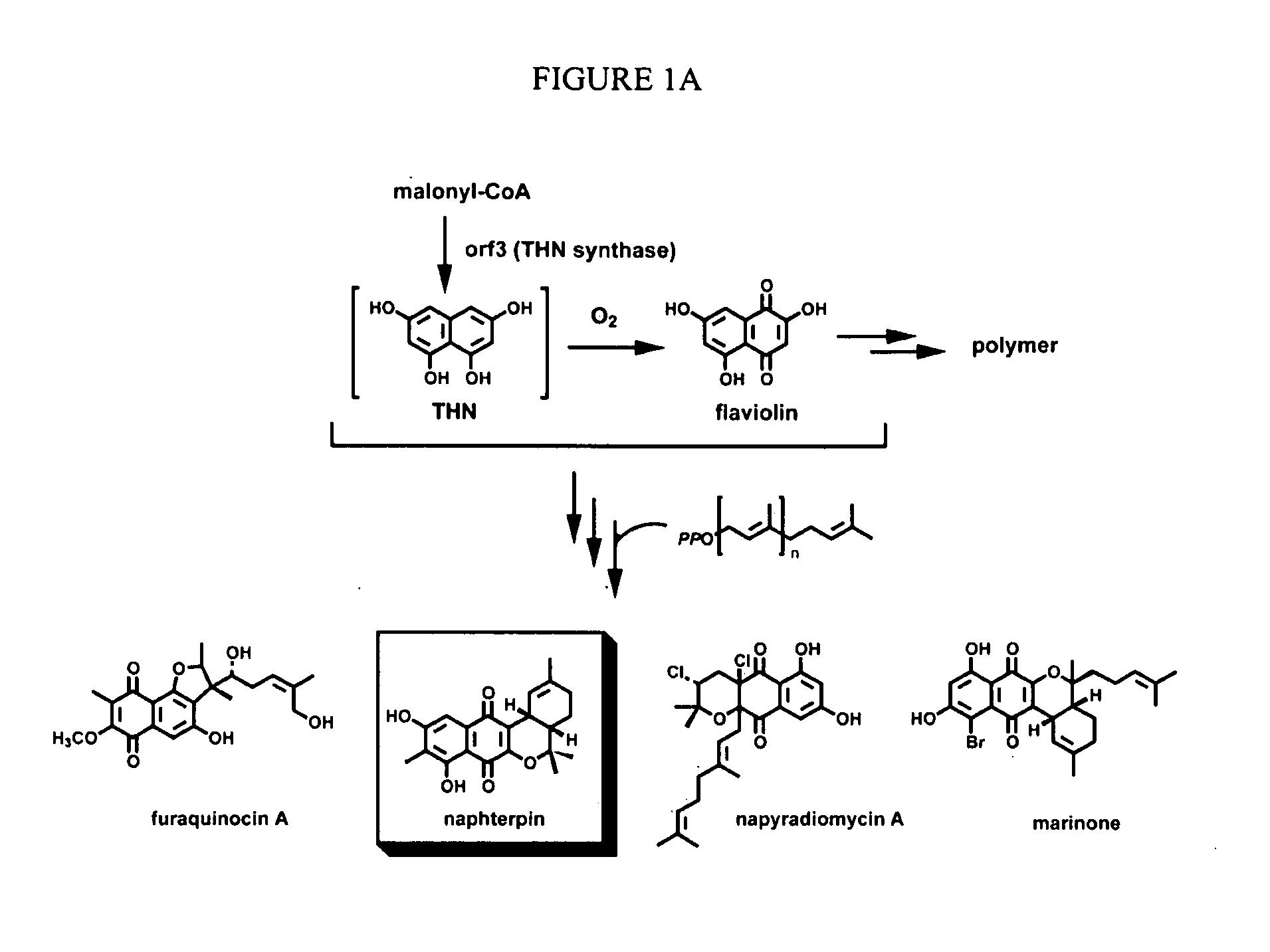
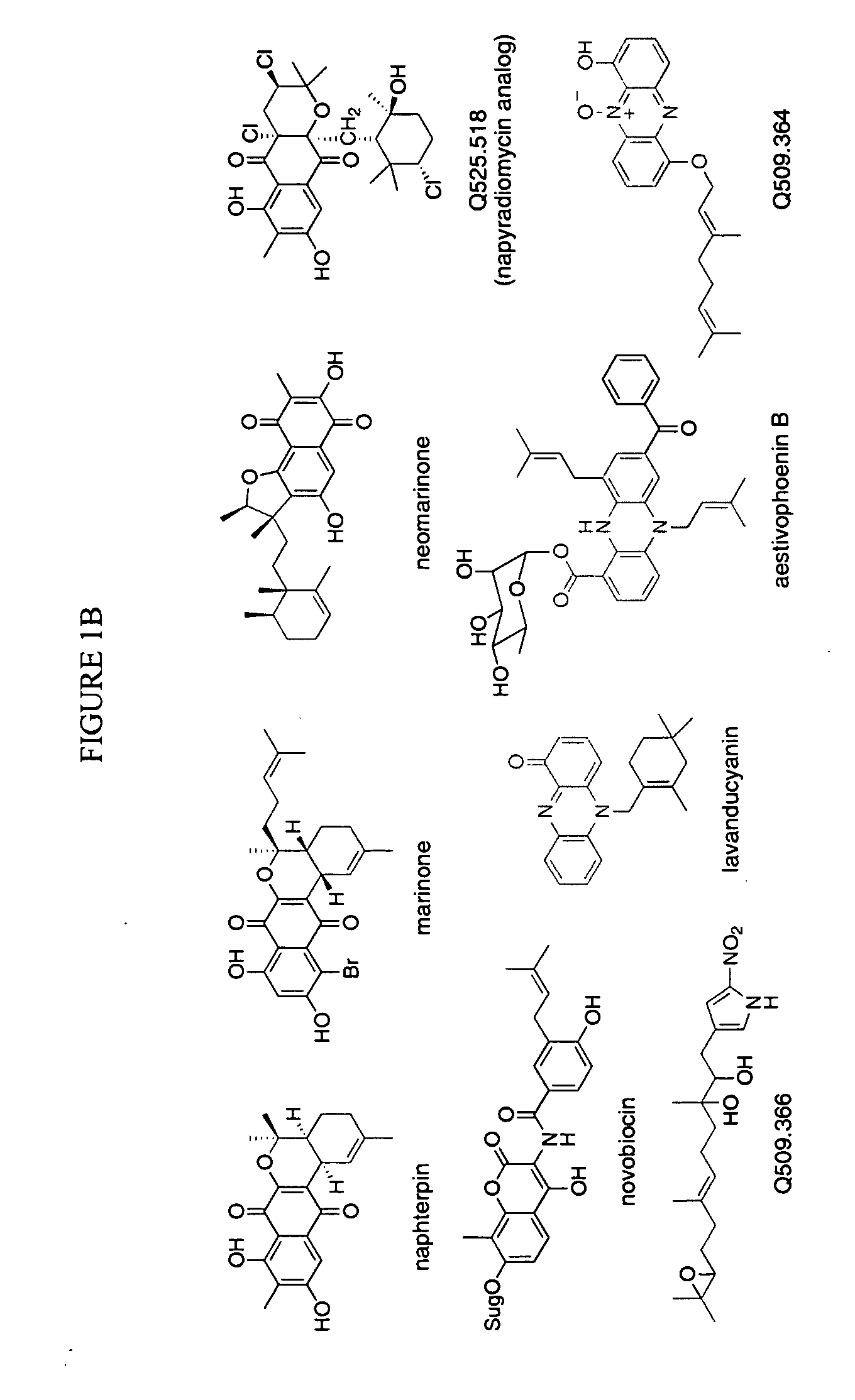
In accordance with the present invention, a novel aromatic prenyltransferase, Orf2 from Streptomyces sp. strain CL190, involved in naphterpin biosynthesis has been identified and the structure thereof elucidated. This prenyltransferase catalyzes the formation of a C—C bond between a prenyl group and a compound containing an aromatic nucleus, and also displays C—O bond formation activity. Numerous crystallographic structures of the prenyltransferase have been solved and refined, e.g., (1) prenyltransferase complexed with a buffer molecule (TAPS), (2) prenyltransferase as a binary complex with geranyl diphosphate (GPP) and Mg2+, and prenyltransferase as ternary complexes with a non-hydrolyzable substrate analogue, geranyl S-thiolodiphosphate (GSPP) and either (3) 1,6-dihydroxynaphthalene (1,6-DHN), or (4) flaviolin (i.e., 2,5,7-trihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, which is the oxidized product of 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene (THN)). These structures have been solved and refined to 1.5 Å, 2.25 Å, 1.95 Å and 2.02 Å, respectively. This first structure of an aromatic prenyltransferase displays an unexpected and non-canonical (β / α)-barrel architecture. The complexes with both aromatic substrates and prenyl containing substrates and analogs delineate the active site and are consistent with a proposed electrophilic mechanism of prenyl group transfer. These structures also provide a mechanistic basis for understanding prenyl chain length determination and aromatic co-substrate recognition in this structurally unique family of aromatic prenyltransferases. This structural information is useful for predicting the aromatic prenyltransferase activity of proteins.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Two-part aqueous metal protection treatment
InactiveUS6902766B1Avoids and reduces blister formationOvercome disadvantagesAdhesive processes with surface pretreatmentAbrasion apparatusOrganic filmElastomer
A two-part metal protection composition includes: an aqueous metal treatment conversion coating component that includes an admixture of an acid and a coating forming component; and an aqueous protective coating component that is applied over metal treated with the aqueous metal treatment conversion coating component and includes an admixture of a blister suppressing agent and an organic film forming protective component. The aqueous metal treatment conversion coating component may contain an accelerator, such as hydroxylamine. In a preferred embodiment, the blister suppressing agent is an organic oxidizing agent that includes one or more of nitroguanidine; aromatic nitrosulfonates, Naphthol Yellow S; and picric acid (trinitrophenol). A method for treating a metallic surface includes: (a) applying an aqueous metal treatment conversion coating component described above; and (b) applying an aqueous protective coating component, described above, to the surface that has at least been partially treated with the aqueous metal treatment conversion coating component. A method for bonding an elastomeric substrate surface to a metallic substrate surface includes: (a) applying an aqueous metal treatment conversion coating component, described above, to the surface; (b) applying an aqueous coating or primer composition, described above, to the surface that has at least been partially treated with the aqueous metal treatment conversion coating component; and (c) applying an adhesive overcoat to effect bonding of the metallic substrate to the elastomeric substrate.
Owner:LORD CORP
Thermosetting resin composition and usage thereof
InactiveUS20150183992A1Good processing characteristicHigh peel strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsPrepolymerDielectric loss
The present invention relates to a thermosetting resin composition, wherein the resin composition comprises: (A) an epoxy resin with main chain containing naphthol structure; (B) a cyanate ester compound or / and an isocyanate ester prepolymer; (C) a poly phosphonate ester or / and phosphonate-carbonate copolymer. The thermosetting resin provided by the present invention has low dielectric constant and dielectric loss angular tangent value. The prepreg and copper-clad laminate made from the thermosetting resin composition above has excellent dielectrical properties, wet-heat resistance, flame resistance of UL94 V-0 grade and good technical processing performance.
Owner:GUANGDONG SHENGYI SCI TECH
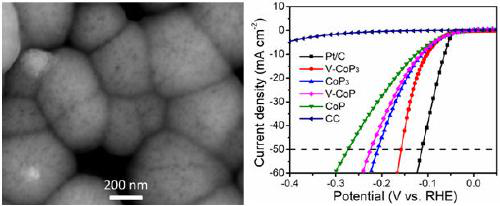
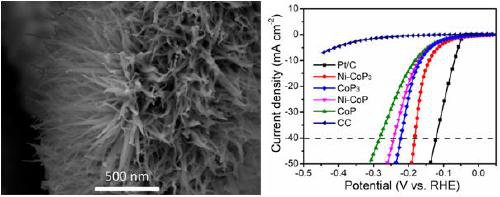
Metal-doped CoP3 and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109967100AAchieving shape-controllable devicesHigh activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesPolymer adhesiveIntrinsic activity
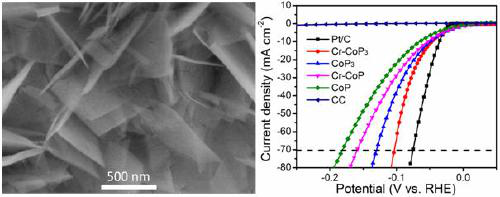
The invention discloses metal-doped CoP3 and a preparation method and application thereof. A cobalt-based precursor doped with different metals and red phosphorus are mixed in a cobalt-phosphorus atomic ratio of (1:3)-(1:4), reacted for 3-5 hours under the vacuum condition of 5*10<-5>-5*10<-4> Pa at the temperature of 625-700 DEG C, and taken out to be soaked into pure CS2 for treatment so as to remove excessive phosphorus, and then the metal-doped CoP3 is obtained. According to the preparation method, CoP3 is doped with the metal elements for the first time, on-site growth of the CoP3 on thesurface of carbon cloth or other flexible materials is achieved, the electrocatalytic intrinsic activity of the CoP3 is improved, the problem that electrocatalyst powder needs to be fixed with naphthol or other polymer adhesives is solved, and the metal-doped CoP3 is suitable for large-scale electrocatalytic industrial hydrogen production.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Citrobacter farmeri Citrobacter farmeriSC01 and application thereof
InactiveCN101240256AHigh average degradation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSludgeCitrobacter farmeri
The invention discloses a fashi citric acid rod Citrobacter farmeri SC01 and the application. The bacterium is obtained by artificial accumulation culture and separation cleansing from phenols cyanogen waste water treatment station one level aerobic pool sludge. The bacterium is preserved in china typical culture entreasure center of Wuhan University on January 7th 2008 year whose short form is CCTCC and preserving identification serial number is CCTCC NO: M208004. The fashi citric acid rod Citrobacter farmeri SC01 incorporating the invention can degrade phenyl hydrate, 2-methylphenol, m-cresol, 1-naphthyl hydroxide, 696mg / L m-cresol in 114 hours on aerobic condition, and the average degrading rate of speed ran up to 8.94mg / (L h) and the bacterium is sensitive to acheomycin, chloramphenicol, rifampicin and streptomycin, and the bacterium can be used safe and wide in harnessing and repairing wasted water and soil phenols pollution because the bacterium can not carryover drug-resistance factor spreading in aborigines bacterium when the bacterium is released into environment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for determining alumina content in iron ore
InactiveCN103105396ARapid determinationThe result is accurateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSodium acetatePotassium hydroxide
The invention relates to a detection method, in particular to a method for determining the alumina content in deposited iron briquette rock ore. The method includes: using potassium hydroxide as a fusing agent to fuse an iron ore sample in a high temperature furnace, conducting acidification by nitric acid, letting aluminum ions enter the solution, adding mandelic acid and excess ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA) standard solution to shelter titanium, iron, aluminum and other metal ions, and in an acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution with pH of 4, taking 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol as an indicator, carrying out titration on the residual ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA) standard solution by means of a copper sulfate standard solution, adding a sodium fluoride solution to replace the ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA) standard solution cooperating with the aluminum ions, and then carrying out titration by a copper sulfate standard solution, thus obtaining the alumina content. The method provided in the invention has the characteristics of simplicity, rapidity, low cost and good repeatability, etc.
Owner:YUNNAN PHOSPHATE CHEM GROUP CORP
Preparing method of mannich base
InactiveCN101717320ALow costImprove securityOrganic compound preparationAmino group formation/introductionRoom temperatureKetone
The invention provides a preparing method of mannich base. The method takes three components of aldehyde, amine, ketone or naphthol as a raw material, takes water as a solvent, and takes liquid superacid as a catalyst, the raw material, the solvent and the catalyst are reacted at normal pressure and room temperature, and then recrystallized and dried to obtain the product of mannich base. The method has the advantages of mild condition, convenient operation, environment protection, high efficiency, good selectivity, high productivity and easy realization.
Owner:ANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Novel synthesizing method of dapoxetine
InactiveCN103304434AHigh yieldHigh stereoselectivityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationHydroxylaminePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a novel synthesizing method of dapoxetine, wherein a series of reactions are carried out on trans-cinnamaldehyde and N-carbobenzoxy hydroxylamine which serve as initiative raw materials under the action of a self-prepared catalyst (s)-alpha-alpha-diisopropyl dimethyl tert-butyl silicon oxygroup prolinol, so that an important intermediate of the dapoxetine, namely an important chiral intermediate (S)-3-amino-3-phenyl propyl alcohol (compound 4), is obtained. The invention further discloses a preparation method of capecitabine, wherein the compound serving as a raw material is methylated and protected by hydroxyl and then reacts with 1-naphthol to form a salt, so that the capecitabine is obtained. The preparation method is easy in raw material obtainment, good in stereoselectivity and high in yield, thereby being suitable for industrial production.
Owner:湖南欧亚药业有限公司
Visual detection method of isothermal amplification products of nucleic acids
InactiveCN103725750ASolve pollutionRealize closed cover detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDimerPyrophosphate
The present invention relates to two visual detection reagents of isothermal amplification products of nucleic acids, the two visual detection reagents are that 1-(1-hydroxy-2-naphthalene azo)-6-nitro-2-naphthol-4-sodium sulfonate or derivatives thereof (hereinafter referred to as the reagent 1) and 4-(2-pyridine azo) resorcinol sodium salt or derivatives thereof (hereinafter referred to as the reagent 2), the two visual detection reagents are used alone, at the beginning of a reaction, the reagent 1 combines with magnesium ions to become red, and the reagent 2 combines with the magnesium ions to form an orange complex, with the reaction, by-product pyrophosphate groups combines the magnesium ions to form a precipitation, the reagent 1 or loses the magnesium ions to become blue from red, the reagent 2 becomes yellow from orange, amplification reaction results can be judged by color change, detection without opening of a cover can be realized by the method, the aerosol pollution can be overcome, and the false positive problem caused by primer dimmers can be solved.
Owner:HARBIN DEGE BIOTECH
2-sulfo-4-amino-1-naphthol derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102766103AImprove in vivo activityLow cytotoxicityOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsSolventLow toxicity
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemicals, and in particular relates to a 2-sulfo-4-amino-1-naphthol derivative and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a solvate of the derivative, and a solvate of the pharmaceutically acceptable salt. The invention also relates to a preparation method, a medical composition and application of the 2-sulfo-4-amino-1-naphthol derivative. The 2-sulfo-4-amino-1-naphthol derivative has a good tyrosine kinase inhibiting effect and low toxicity and has great significance for the clinical treatment of tumor.
Owner:QILU PHARMA +1
3, 3'-position biaryl group binaphthyl shaft chiral phosphoramidite ligand and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101565436AGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic solventPhosphorus trichloride
The invention relates to a 3, 3'-position binaphthyl shaft chiral phosphoramidite ligand containing biaryl group and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: leading 3, 3'-dual-biaryl group-2, 2'-dinaphthol to react with hexagon-alkyl group phosphoramidite in organic solvent at the temperature of 0-120 DEG C according to the mol rate of 1:1, or leading 3, 3'- dual-biaryl group-2, 2'-dinaphthol to react with phosphorus trichloride and dialkyl amine in steps, and after complete reaction, the object chiral phosphoramidite ligand can be obtained through washing, extraction and separation. After going through complexation with metallic copper salt, the chiral phosphoramidite ligand can be used for catalyzing the conjugate addition reaction of zinc alkyl with alpha, beta-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, and an additional product is prepared with high yield up to 78-98% and high enantioselectivity ee value up to 80-98%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Plating solution formula of lead tin plating process for electronic components and lead tin plating process
ActiveCN107099825AImprove antioxidant capacityGive full play to the strong reducibilitySuperimposed coating processTin platingPolyethylene glycol
The invention provides a plating solution formula of a lead tin plating process for electronic components and the lead tin plating process. The plating solution formula comprises the following components by mass-volume concentration: 70-120 g / L sulfuric acid (AR), 45-60 g / L stannous mono-sulphate, 0.2-0.8 g / L sodium hypophosphite, 0.5-1.5 g / L ascorbic acid, 2-6 g / L of polyethylene glycol, 1-1.5 g / L catechol, 1-1.5 g / L beta-naphthol, 3-6 g / L cerium sulfate, an 8-10 g / L OP-10 emulsifier, 10-30 g / L phenolsulfonic acid and pure water. According to the lead tin plating process, hot-melt drawing passivation treatment is adopted after tin plating. A tin plating layer of a product produced by adoption of both the formula and the production process is greatly improved in compactness, so that the tin whisker growth prevention performance, the high temperature resistance, the anti-tarnishing capability and the neutral salt spray resistance of the product are improved.
Owner:烟台东牧精密线材有限公司
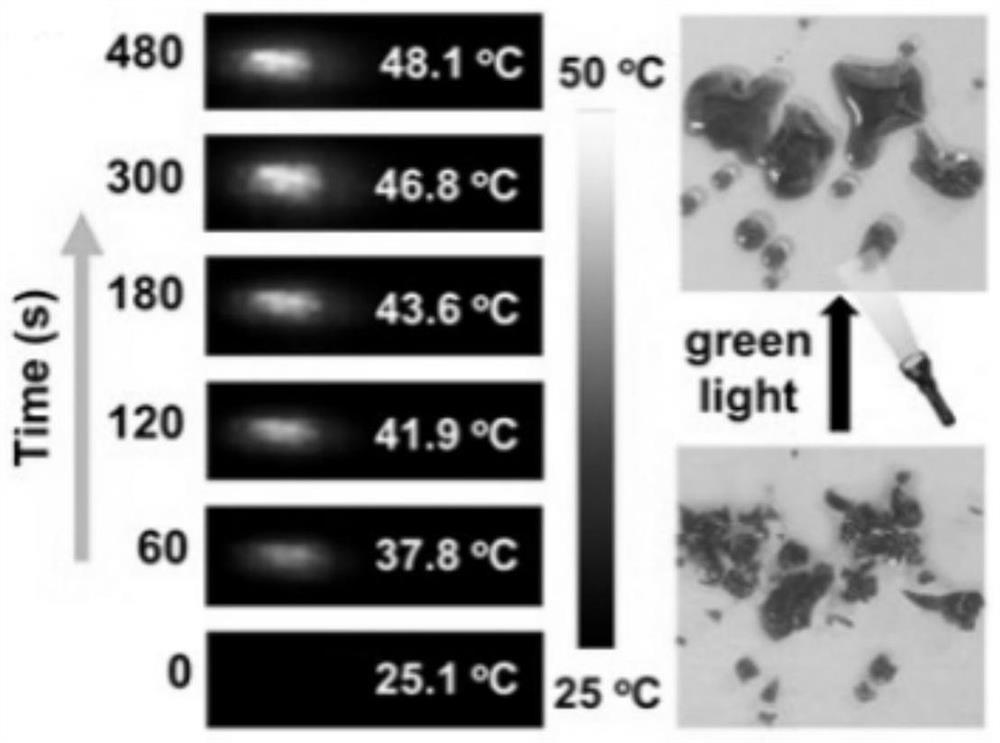
Azobenzene derivative, preparation method thereof, azobenzene-based light-operated reversible adhesive and use method thereof
InactiveCN112010775AImprove adhesionEasy to clean and recycleAdhesive processesOrganic chemistryBenzoic acidGreen-light
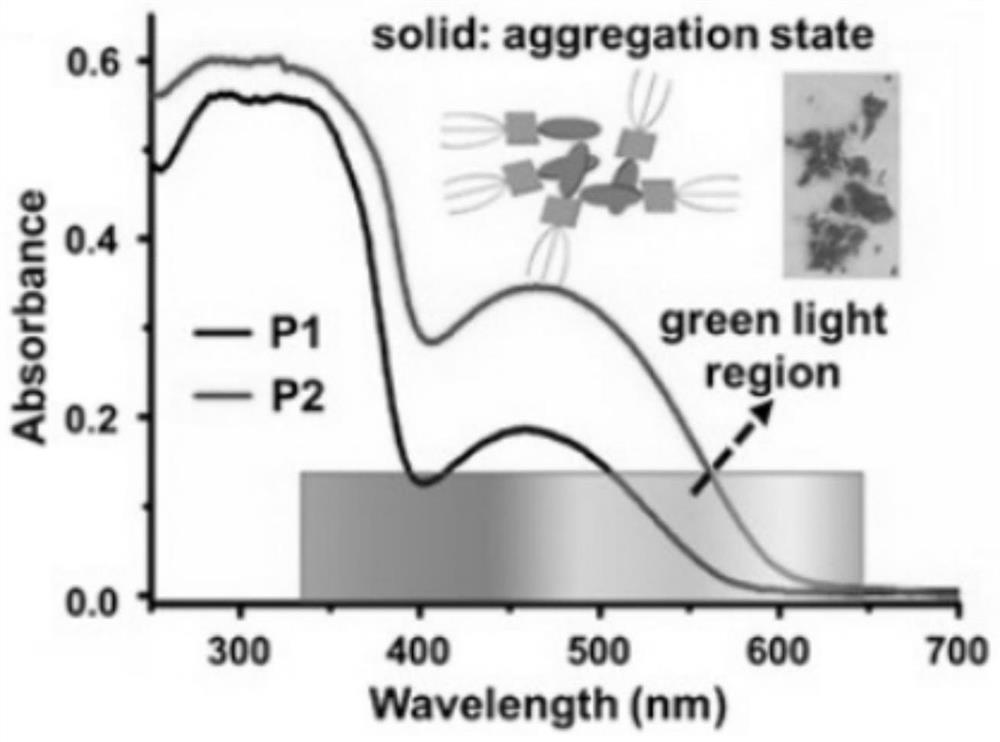
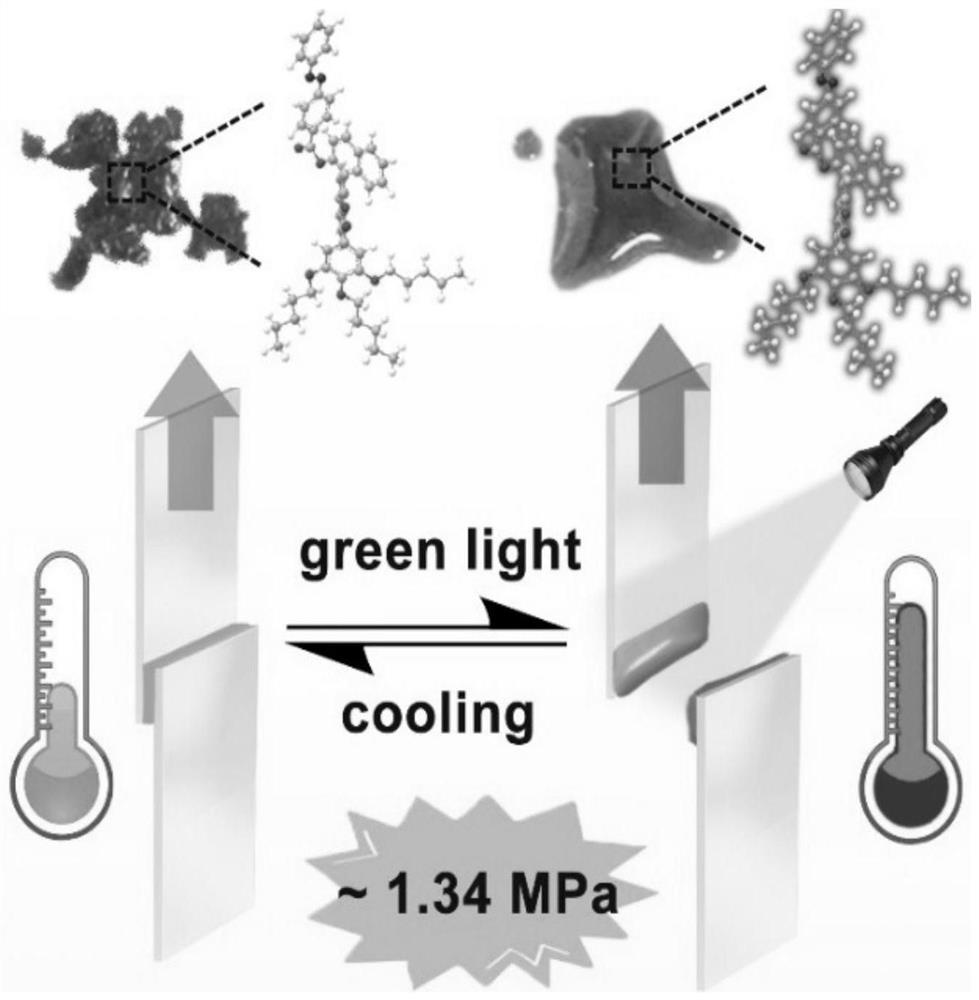
The invention discloses an azobenzene derivative, a preparation method of the azobenzene derivative, an azobenzene-based light-operated reversible adhesive and a use method of the azobenzene light-operated reversible adhesive. The molecular structure of the azobenzene derivative is shown as P1 and P2. According to the preparation method of the azobenzene derivative, an azobenzene group and 3, 4, 5-tripentoxyl benzoic acid or 3, 4, 5-tridodecyloxy benzoic acid undergo an esterification reaction with 2, 2'-dyhydroxy-1, 1'-binaphthol, so that P1 or P2 can be obtained. The azobenzene derivatives P1 and P2 are jointly adjusted to a melting point slightly higher than the room temperature by using alkyl chains and binaphthol, the liquid P1 and P2 can be spontaneously and quickly cured within 2 minutes, the cured azobenzene derivatives show excellent bonding performance, and the bonding strength can reach several MPa to meet the requirements of subsequent processes, under irradiation of greenlight, the photothermal effect of P1 and P2 causes conversion from solid to liquid, and after irradiation of green light, P1 and P2 are heated to be melted and lose the bonding performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
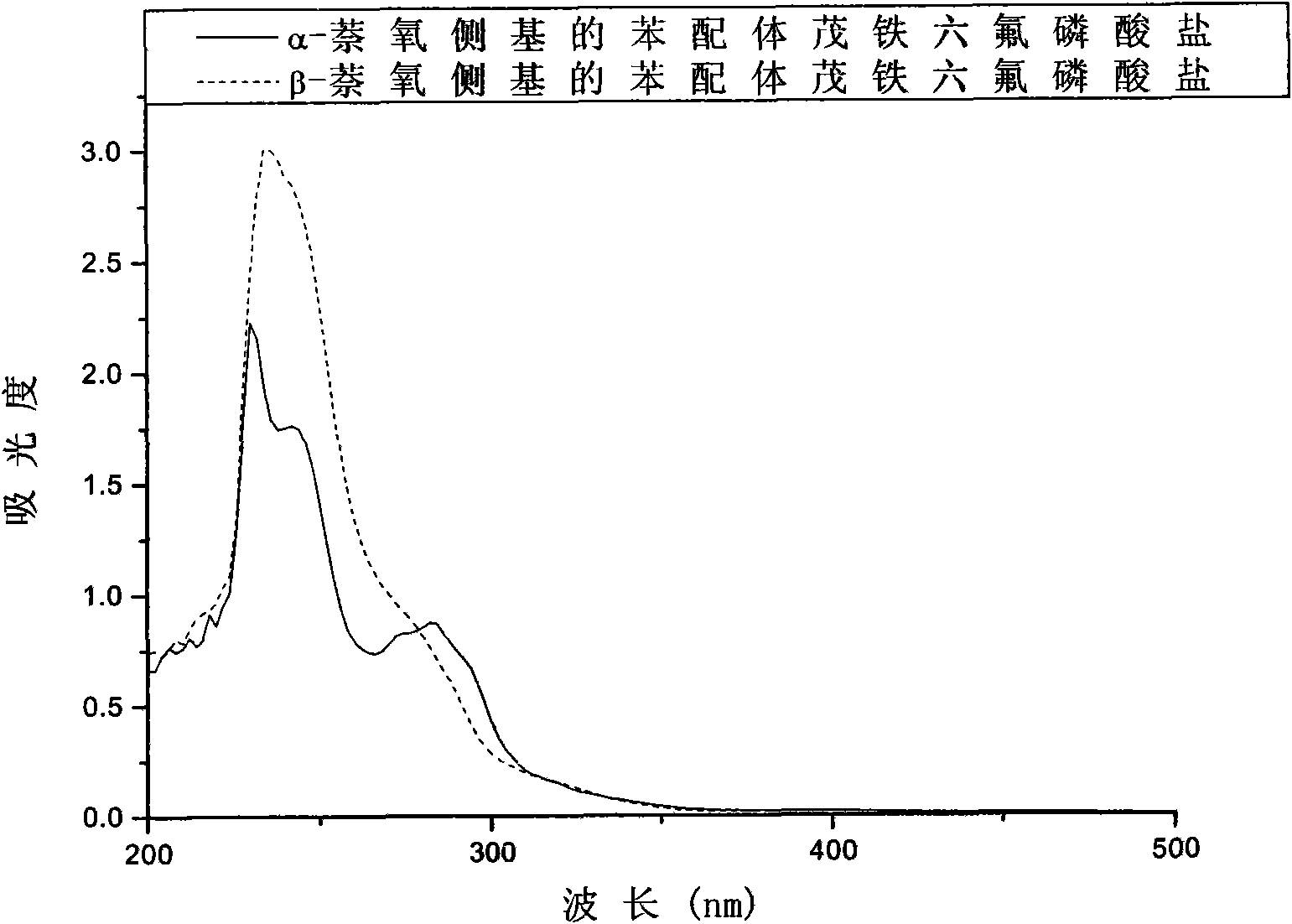
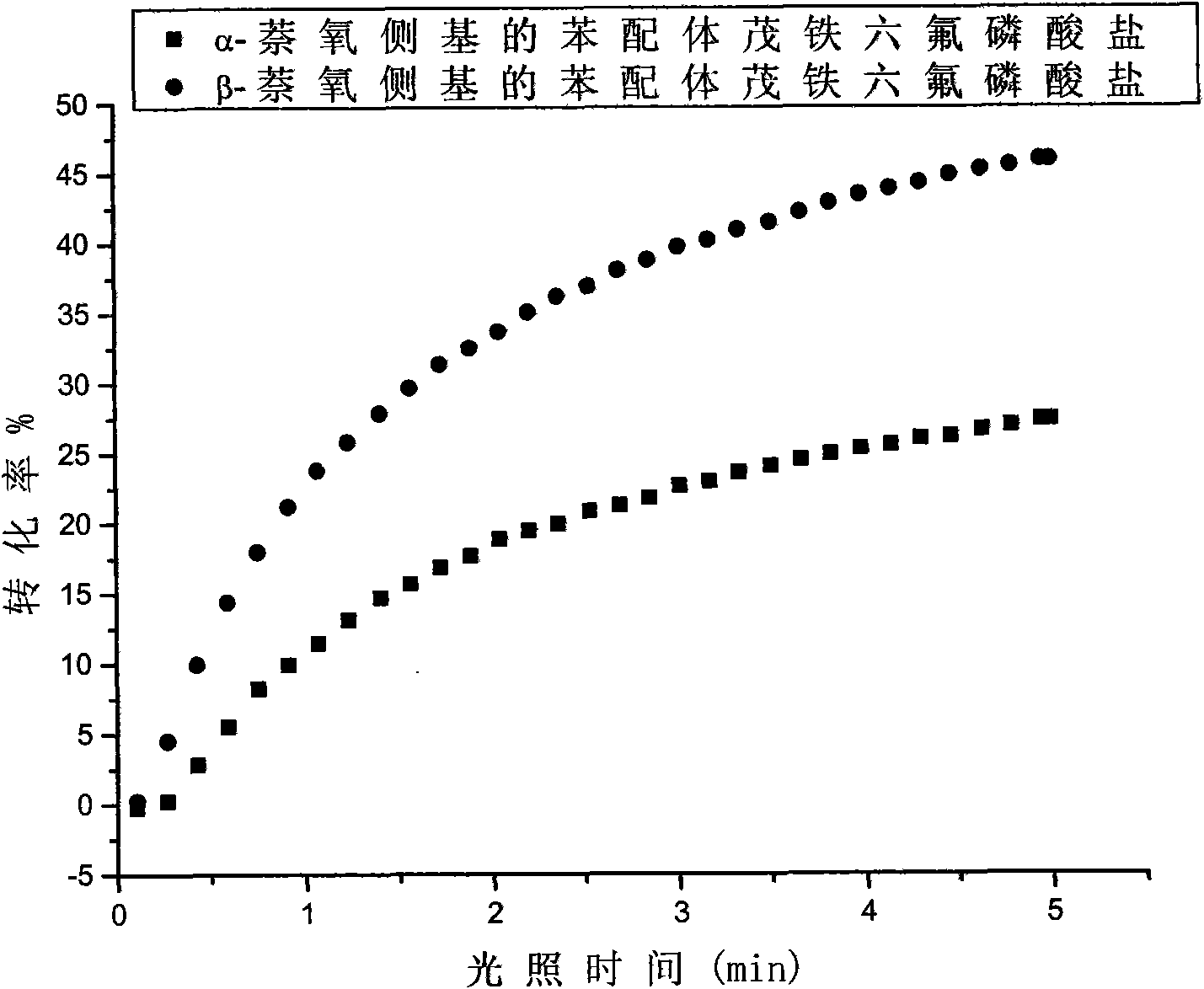
Pendant naphthalene group-containing benzene ligand ferrocenium salt cationic photoinitiators and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses pendant naphthalene group-containing cyclopentadienyl-iron-benzyl ferrocenium salt compounds used as photoinitiators for cationic photopolymerization, and belongs to the technical fields of organic synthesis and cationic photopolymerization. The preparation method of the compounds comprises two steps: 1, taking ferrocene and chlorobenzene as raw materials, and generating ligand exchange reaction to obtain cyclopentadienyl-iron-chlorobenzene salts under the catalysis of Lewis acid; and 2, generating nucleophilicsubstitutionreaction with corresponding naphthol compounds under alkaline environment, and introducing the pendant naphthalene group onto the benzene ligand. The compounds have good ultraviolet absorptivity and photo initiating activity, can initiate polymerization of epoxy compounds and vinyl ethers compounds, and have wide study potential and application prospect in the field of photocuring application.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Dinaphthalene azobenzene ring-type photosensitive chiral molecule and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109810129ARealize reversible regulationGood compatibilityMaterial analysis by optical meansGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsN dimethylformamideBoronic acid
The invention discloses a dinaphthalene azobenzene ring-type photosensitive chiral molecule and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that 6,6'dibromo-1,1'-bi-2-naphthol, potassium carbonate, potassium iodide and 2-(2-chloroethoxy)ethanol are dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide, thus a midbody 1 is obtained, the midbody 1 and [4'-(pentyloxy)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]boronic acid are dissolved in 1,4-dioxane to react with a potassium carbonate aqueous solution and tetrakispalladium to obtain a midbody 2, the midbody 2 is dissolved through dichloromethane, and then triethylamine, 4-dimethylaminopyridine and paratoluensulfonyl chloride are added and react to obtain a midbody 3; and cesium carbonate is added into the midbody 3, 2,2'-dihydroxyazobenzene and dibenzo-18-crown ether-6 under the nitrogen atmosphere for reacting, and thus a target product T is obtained. The dinaphthalene azobenzene ring-type photosensitive chiral molecule is easy to synthesize and good in stability, the screw pitch of a cholesteric liquid crystal can be adjusted and controlled through photoinduced cis-trans isomerization, and good compatibility between the dinaphthalene azobenzene ring-type photosensitive chiral molecule and liquid crystal molecules is achieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
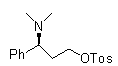
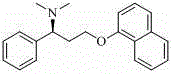
Method for preparing (S)-N, N-dimethyl-3-(naphthol-1-oxygroup)-1- phenyl propyl group-1-amine
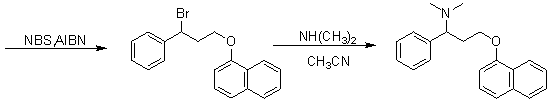
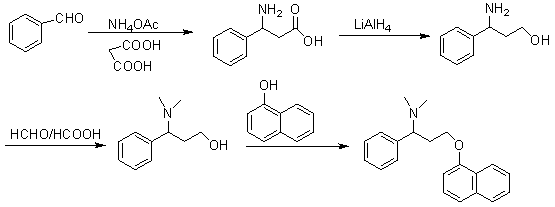
InactiveCN102942496ALow priceSimple and fast operationOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationAlpha-naphtholEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a method for preparing (S)-N, N-dimethyl-3-(naphthol-1-oxygroup)-1- phenyl propyl group-1-amine. (S)-3-(naphthol-1-oxygroup)-1- phenyl propyl group-1-amine serves as the raw materials, and dimethyl carbonate replaces formaldehyde in the prior art to serve as a methylation reagent to prepare the (S)-N, N-dimethyl-3-(naphthol-1-oxygroup)-1- phenyl propyl group-1-amine. On the basis, the (S)-N, N-dimethyl-3-(naphthol-1-oxygroup)-1- phenyl propyl group-1-amine is dissolved in ethyl acetate to further prepare (S)-N, N-dimethyl-3-(naphthol-1-oxygroup)-1- phenyl propyl group-1-amine hydrochloride. The method reduces environment pollution without increasing the cost, simplifies reaction operations, reduces requirements on equipment and can be used in industrial production easily.
Owner:YANGZHOU POLYTECHNIC INST
Sodium nitrite determination method
InactiveCN104777111ALow toxicityEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsEthyl groupVolumetric flask
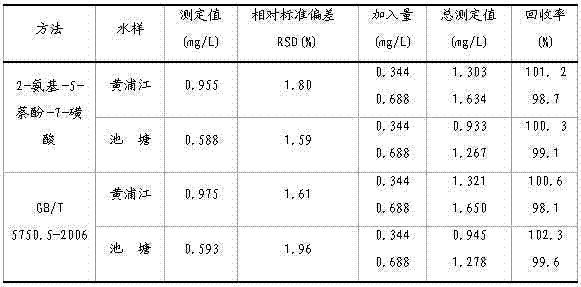
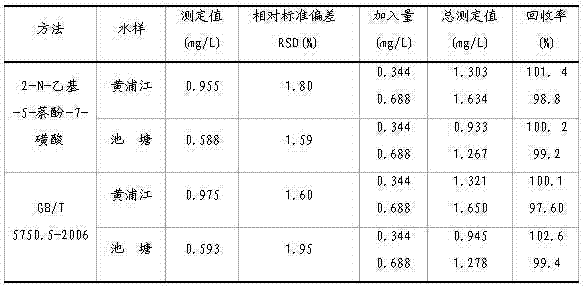
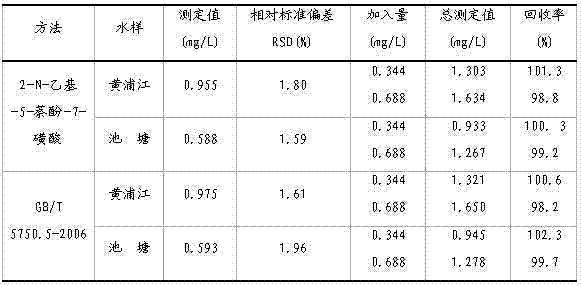
The invention discloses a sodium nitrite determination method. The method comprises the following steps: taking a water sample to be determined, standing the water sample to be determined for 30min, transferring 10.0mL of the above obtained supernatant into a 25mL colorimetric pipe through a pipet, sequentially adding 1.0mL of an aqueous potassium bromide solution, 1.0mL of an aqueous sulfanilic acid solution and 1.0mL of an aqueous hydrochloric acid solution, shaking up, and standing to obtain a solution of diazo salt of the sample to be determined; taking a 25mL volumetric flask, and adding 3mL of an aqueous sodium carbonate solution and 1.0mL of an aqueous 2-N-ethyl-5-naphthol-7-sulfonic acid solution; transferring the solution of diazo salt of the sample to be determined into the volumetric flask, adding deionized water to a certain volume, and determining the absorbance of the above obtained orange diazo compound solution at a wavelength of 480nm by using 1cm cuvette with a blank reagent as a reference; and calculating according to the curve regression equation of standard sodium nitrite to obtain the content of sodium nitrite in the sample to be determined. The determination method has the advantages of convenient operation, high sensitivity, accurate result, and small toxicity of used reagents.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Methyl naphthol wastewater treatment process
InactiveCN103086546AEasy to handleEliminate biochemical treatment processWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandFenton reagent
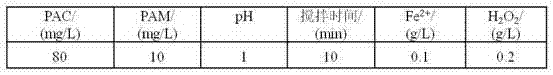
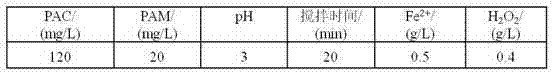
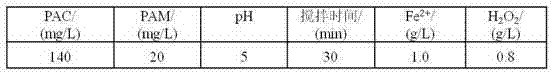
The invention discloses a methyl naphthol wastewater treatment method implemented by using a PAC / PAM composite coagulant and a Fenton reagent. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out pretreatment on methyl naphthol wastewater by using PAC / PAM, wherein the concentration of PAC is 80-160mg / L, the concentration of PAM is 10-40mg / L, the pH value of a solution is 1-9, the stirring speed is 60r / min, and the stirring time is 10-50min. When the concentration of PAC is 140mg / L, the concentration of PAM is 20mg / L, the pH value is 5, and the stirring time is 30min, the CODCr (chemical oxygen demand) of wastewater is reduced from 5665-4820mg / L to 2925-2688mg / L. When the concentration of Fe<2+> is 1.0g / L, the concentration of H2O2 is 0.8g / L, and the reaction time is 120min, the final removal rate of CODCr reaches to be 89.6-92.5%. According to the treatment method disclosed by the invention, simplicity is realized, the cost is low, and the treatment effect on wastewater which is high in organic pollutant content, deep in colority and poor in biodegradability is good.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com